
User’s Guide
Publication Number 01660-97028
August 1998
For Safety information, Warranties, and Regulatory information, see
the pages behind the index.
©Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 1994-1998
All Rights Reserved
HP 1660E/ES/EP and 1670E
Series Logic Analyzers

HP 1660E/ES/EP-Series Logic Analyzers
The HP 1660E/ES/EP-Series are 100-MHz State/500-MHz Timing Logic
Analyzers with a VGA resolution color display. The HP 1660ES-Series
has a 2 GSa/s digitizing oscilloscope. The HP 1660EP-Series has a built
in 32 channel pattern generator.
Logic Analyzer Features
• 130 data channels and 6 clock/data channels in the HP 1660E
• 96 data channels and 6 clock/data channels in the HP 1661E
• 64 data channels and 4 clock/data channels in the HP 1662E
• 32 data channels and 2 clock/data channels in the HP 1663E
• 3.5-inch flexible disk drive and 2 GB hard disk drive
• HP-IB, RS-232-C, parallel printer, and LAN interfaces
• BNC and TP LAN ports
• Variable setup/hold time
• 4 K memory on all channels with 8 K in half-channel mode
•Marker measurements
• 12 levels of trigger sequencing for state and 10 levels of trigger sequencing
for timing
• Time tagging and number-of-states tagging
• Full programmability
• DIN mouse and keyboard support
2

Oscilloscope Features (HP 1660ES-Series only)
• 500 MHz bandwidth
• 2
Gigasample per second max sampling rate
• 32768 samples per channel
• Marker measurements
displays time between markers, acquires until specified time between
markers in captured, performs statistical analysis on time between markers
• Lightweight miniprobes
Pattern Generator Features (HP 1660EP-Series only)
• 16 output channels at 200 MHz
• 32 output channels at 100 MHz
• 258,048 vectors
Options
• Programmer's Guide
• Service Guide.
3

HP 1670E-Series Logic Analyzers
The HP 1670E-series logic analyzers are 100-MHz state/250-MHz timing logic
analyzers with VGA resolution color displays.
Features
• 132 data channels and 4 clock/data channels in the HP 1670E
• 98 data channels and 4 clock/data channels in the HP 1671E
• 64 data channels and 4 clock/data channels in the HP 1672E
• 3.5-inch flexible disk drive
• 2 GB hard disk drive
• HP-IB, RS-232-C, parallel printer, and LAN interfaces
• BNC and TP LAN ports
• Variable setup/hold time
• 1 M memory on all channels, 2 M in half-channel timing mode
• Marker measurements
• 12 levels of trigger sequencing for state and 10 levels of trigger sequencing
for timing
• Time tagging and state tagging
• Full programmability
• DIN mouse and keyboard support
Options
• Programmer's Guide
• Service Guide
4

In This Book
In This Book
This User’s Guide has three sections. Section 1 covers how to use the
HP 1660E/ES/EP and HP 1670E-series logic analyzers. Section 2
covers how to connect, use, and troubleshoot the HP logic analyzer via
a Local Area Network (LAN) connection. Section 3 covers the features
of the HP Symbol Utility software.
Section 1. Chapters 1 through 4 cover general product information
you need to use the logic analyzer. Chapter 5 covers how to use the
oscilloscope (1660ES-series only). Chapter 6 covers how to use the
pattern generator (1660EP-series only). Chapters 7 and 8 contains
detailed examples to help you use your analyzer in performing complex
measurements. Chapters 9 through 11 contains reference information
on the hardware and software, including the analyzer menus and how
they are used. Chapters 12 through 14 provides a basic service guide.
Section 2. Chapters 15 through 16 provides information about
connecting the logic analyzer to the network. Chapter 17 shows you
how to access the logic analyzer’s file system. Chapter 18 shows you
how to display the analyzer interface on an X Window server. Chapter
19 shows you how to retrieve measurement data, screen images, and
status information from you logic analyzer on the LAN, and how to
copy and restore configurations. Chapter 20 shows you methods for
programming the logic analyzer via the network connection. Chapter
21 contains additional information on the logic analyzer’s directory
structure and dynamic files. Chapter 22 describes what to do if you
have a problem using the logic analyzer on your network.
Section 3. Chapters 23 through 24 describe how to locate the menus
associated with the Symbol Utility. Chapter 25 describes how to use the
Symbol Utility to perform common tasks. Chapter 26 describes the
features and functions of the Symbol Utility.
5

In This Book
6

SECTION 1
Contents
In This Book 5
1 Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer 28
To make a measurement 31
2 Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals 38
To connect a mouse 39
To connect a keyboard 40
To connect to an HP-IB printer 41
To connect to an RS-232-C printer 43
To connect to a parallel printer 45
To connect to a controller 46
3 Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Logic Analyzer 48
Accessing the Menus 49
To access the System menus 50
To access the Analyzer menus 52
7

Contents
Using the Analyzer Menus 54
To label channel groups 54
To create a symbol 57
To examine an analyzer waveform 59
To examine an analyzer listing 62
To compare two listings 65
The Inverse Assembler 67
To use an inverse assembler 67
4 Using the Trigger Menu
Using the Trigger Menu 72
Specifying a Basic Trigger 73
To assign terms to an analyzer 74
To define a term 76
To change the trigger specification 77
Changing the Trigger Sequence 79
To add sequence levels 80
To change macros 82
Setting Up Time Correlation between Analyzers 83
To set up time correlation between two state analyzers 84
To set up time correlation between a timing and a state analyzer 85
Arming and Additional Instruments 86
To arm another instrument 86
To arm the oscilloscope with the analyzer (HP 1660ES-series only) 87
To receive an arm signal from another instrument 89
8

Contents
Managing Memory 91
To selectively store branch conditions (State only) 92
To set the memory length 94
To place the trigger in memory 96
To set the sampling rates (Timing only) 98
5Using the Oscilloscope
Using the Oscilloscope 100
Calibrating the oscilloscope 101
Calibration PROTECT/UNPROTECT switch 101
Set up the equipment 101
Load the default calibration factors 102
Self Cal menu calibrations 103
Protect the operational accuracy calibration factors 105
Oscilloscope Common Menus 106
Run/Stop options 106
Autoscale 108
Time base 110
The Scope Channel Menu 111
Offset field 111
Probe field 112
Coupling field 112
Preset field 113
9

Contents
The Scope Display Menu 114
Mode field 114
Connect Dots field 116
Grid field 116
Display Options field 117
The Scope Trigger Menu 118
Trigger marker 118
Mode/Arm menu 118
Level field 121
Source field 123
Slope field 123
Count field 124
Auto-Trig field 125
When field 126
Count field 129
The Scope Marker Menu 130
Manual time markers options 130
Automatic time markers options 133
Manual/Automatic Time Markers option 138
Voltage Markers options 139
Channel Label field 141
The Scope Auto Measure Menu 142
Input field 142
Automatic measurements display 143
Automatic measurement algorithms 145
6 Using the Pattern Generator
Using the Pattern Generator 150
10

Contents
Setting Up the Proper Configurations 151
To set up the configuration 151
To build a label 153
Building Test Vectors and Macros 154
To build a main vector sequence 155
To build an initialization sequence 156
To edit a main or initialization sequence 157
To include hardware instructions in a sequence 158
To include software instructions in a sequence 159
To include a user macro in a sequence 160
To build a user macro 161
To modify a macro name 162
To edit a macro 162
To add, delete, or rename parameters 163
To place parameters in a vector 164
To enter or modify parameters 165
To build a User Symbol Table 166
To include symbols in a sequence 167
To include symbols in a macro 168
To store a configuration 169
To load a configuration 170
To use Autoroll 171
The Format Menu 172
The Sequence Menu 176
The User Macros Menu 185
11

Contents
Loading ASCII Files 187
ASCII File Commands 188
ASCDown Command 188
LABel 189
VECTor 190
FORMat:xxx 193
Loading an ASCII file over a bus (example) 194
Pattern Generator Probing System 196
7 Triggering Examples
Triggering Examples 198
Single-Machine Trigger Examples 199
To store and time the execution of a subroutine 200
To trigger on the nth iteration of a loop 202
To trigger on the nth recursive call of a recursive function 204
To trigger on entry to a function 206
To capture a write of known bad data to a particular variable 208
To trigger on a loop that occasionally runs too long 209
To verify correct return from a function call 210
To trigger after all status bus lines finish transitioning 211
To find the nth assertion of a chip select line 212
To verify that the chip select line is strobed after the address is stable 213
To trigger when expected data does not appear when requested 214
To test minimum and maximum pulse limits 216
To detect a handshake violation 218
To detect bus contention 219
12

Contents
Cross-Arming Trigger Examples 220
To examine software execution when a timing violation occurs 221
To look at control and status signals during execution of a routine 223
To detect a glitch 224
To capture the waveform of a glitch using the oscilloscope (1660ES-series
only) 225
To view your target system processing an interrupt (1660ES-series only) 226
To trigger timing analysis of a count-down on a set of data lines 227
To monitor two coprocessors in a target system 228
Special Displays 230
To interleave trace lists 231
To view trace lists and waveforms on the same display 233
8 File Management
File Management 236
Transferring Files Using the Flexible Disk Drive 237
To save a configuration 238
To load a configuration 240
To save a trace list in ASCII format 242
To save a screen’s image 243
To load additional software 244
Transferring Files Using the LAN 245
To transfer files using ftp 246
13

Contents
9 Logic Analyzer Reference
HP 1660E/ES/EP-Series Logic Analyzer Description 248
HP 1660E/ES/EP-Series Configuration Capabilities 250
HP 1670E-Series Logic Analyzer Description 252
HP 1670E-Series Configuration Capabilities 253
Probing 256
General-purpose probing system description 259
Assembling the probing system 263
Oscilloscope probes 267
Connecting the pattern generator pods directly to a PC board 268
Pattern generator output pod characteristics 269
Keyboard Shortcuts 275
Moving the cursor 275
Entering data into a menu 276
Using the keyboard overlays 277
Common Menu Fields 278
Print field 279
Run/Stop field 281
Roll fields 282
Disk Drive Operations 283
Disk operations 283
Autoload 286
Format 286
Pack 287
Load and Store 288
14

Contents
The RS-232-C, HP-IB, and Centronics Interfaces 290
The HP-IB interface 291
The RS-232-C interface 292
The Centronics interface 293
The Ethernet LAN interface 294
System Utilities 297
Real Time Clock Adjustments field 297
Update FLASH ROM field 298
Display Color Selection 300
Setting the Color, Hue, Saturation, and Luminosity Fields 302
Returning to the Default Colors 302
The Analyzer Configuration Menu 303
Type field 303
Illegal configuration 304
The Analyzer Format Menu 305
Pod threshold field 305
State acquisition modes
(HP 1660E/ES/EP-series state only) 306
Timing acquisition modes
(HP 1660E/ES/EP-series timing only) 307
Acquisition modes (HP 1670E-series) 309
Clock Inputs Display 310
Pod clock field (State only) 311
Master and Slave Clock fields (State only) 314
Symbols field 317
Label fields 319
Label polarity fields 320
15

Contents
The Analyzer Trigger Menu 321
Trigger sequence levels 321
Modify Trigger field 322
Timing trigger macro library 323
State trigger macro library 325
Modifying the user macro 328
Resource terms 332
Arming Control field 336
Acquisition Control field 338
Count field (State only) 340
The Listing Menu 341
Markers 341
The Waveform Menu 343
sec/Div field 343
Accumulate field 343
Delay field 344
Waveform label field 344
Waveform display 346
The Mixed Display Menu 347
Interleaving state listings 347
Time-correlated displays 348
Markers 348
The Chart Menu 349
Min and Max scaling fields 350
Markers/Range field 350
Axis Control field (HP 1670E-series only) 351
Rescale field (HP 1670E-series only) 352
16

Contents
The Compare Menu 353
Reference Listing field 354
Difference Listing field 354
Copy Listing to Reference field 355
Find Error field 356
Compare Full/Compare Partial field 356
10 System Performance Analysis (SPA) Software
System Performance Analysis Software 360
What is System Performance Analysis? 362
Getting started 365
SPA measurement processes 367
Using State Overview, State Histogram, and Time Interval 383
Using SPA with other features 393
11 Logic Analyzer Concepts
Logic Analyzer Concepts 396
The File System 397
Directories 398
File types 399
Transitional Mode Theory (1660E/ES/EP-series only) 401
125-MHz Transitional mode 401
250-MHz Transitional mode 403
Other transitional timing considerations 406
17

Contents
The Trigger Sequence 407
Trigger sequence specification 408
Analyzer resources 411
Timing analyzer 416
State analyzer 416
Configuration Translation Between HP Logic Analyzers 417
The Analyzer Hardware 419
HP 1660E/ES/EP-series analyzer theory 420
Logic acquisition board theory 424
Oscilloscope board theory 428
Pattern Generator board theory 433
Self-tests description 436
12 Troubleshooting the Logic Analyzer
Troubleshooting the Logic Analyzer 438
Analyzer Problems 439
Intermittent data errors 439
Unwanted triggers 440
No activity on activity indicators 440
Capacitive loading 441
No trace list display 441
Analysis Probe Problems 442
Target system will not boot up 442
Slow clock 443
Erratic trace measurements 444
18

Contents
Inverse Assembler Problems 445
No inverse assembly or incorrect inverse assembly 445
Inverse assembler will not load or run 447
Error Messages 448
". . . Inverse Assembler Not Found" 448
"No Configuration File Loaded" 448
"Selected File is Incompatible" 449
"Slow or Missing Clock" 449
"Waiting for Trigger" 449
"Must have at least 1 edge specified" 450
"Time correlation of data is not possible" 450
"Maximum of 32 channels per label" 450
"Timer is off in sequence level n where it is used" 451
"Timer is specified in sequence, but never started" 451
"Inverse assembler not loaded - bad object code." 451
"Measurement Initialization Error" 452
"Warning: Run HALTED due to variable change" 452
13 Specifications
General Information 454
Accessories 454
Specifications (logic analyzer) 456
Specifications (oscilloscope) 457
Characteristics (logic analyzer) 458
Characteristics (oscilloscope) 459
Characteristics (pattern generator) 459
Supplemental characteristics (logic analyzer) 461
Supplemental characteristics (oscilloscope) 466
Operating environment 468
19

Contents
14 Operator’s Service
Operator’s Service 470
Preparing For Use 471
To inspect the logic analyzer 472
To apply power 472
To set the line voltage 473
To degauss the display 474
To clean the logic analyzer 474
To test the logic analyzer 474
Troubleshooting 475
To use the flowcharts 476
To check the power-up tests 478
To run the self-tests 479
To test the auxiliary power 488
SECTION 2
15 Introducing the LAN Interface
Introducing the LAN Interface 492
LAN section overview 494
16 Connecting and Configuring the LAN
Connecting and Configuring the LAN 496
To connect to your network 497
To configure the network addresses 498
To verify connectivity with the ping utility 501
To mount the logic analyzer 502
20

Contents
17 Accessing the Logic Analyzer File System Using the LAN
Accessing the Logic Analyzer File System Using the LAN 506
To mount the file system via NFS 507
To access the file system via ftp 512
18 Using the LAN’s X Window Interface
Using the LAN’s X Window Interface 514
To start the interface from the front panel 515
To start the interface from the computer 517
To close the interface 520
To load the custom fonts 521
Additional Information 524
19 Retrieving and Restoring Data Using the LAN
Retrieving and Restoring Data Using the LAN 526
To copy ASCII measurement data 527
To copy raw measurement data 528
To restore raw measurement data 529
To strip LIF structure from raw measurement data 530
To copy screen images from \system\graphics 532
To copy status information from \status 533
To copy configurations from setup.raw 535
To restore configurations 536
21

Contents
20 Programming the Logic Analyzer Using the LAN
Programming the Logic Analyzer Using the LAN 538
To set up for Ethernet LAN programming 539
To enter commands directly using telnet 540
To write programs that open the command parser socket 542
21 LAN Concepts
LAN Concepts 546
Directory structure of the logic analyzer’s file system 547
Dynamic files 550
LAN-related fields in the logic analyzer’s menus 551
22 Troubleshooting the LAN Connection
Troubleshooting the LAN Connection 554
Troubleshooting the Initial Connection 555
Assess the problem 555
Troubleshooting in a workstation environment 558
Troubleshooting in an MS-DOS environment 560
Troubleshooting in an MS Windows environment 562
Verify the logic analyzer performance 564
Status Number 566
Network Status Information 569
22

Contents
Solutions to Common Problems 571
If you cannot connect to the logic analyzer 571
If you cannot mount the logic analyzer file system 572
If you cannot access the file system via ftp 572
If you cannot start the XWindow interface 573
If your X Window looks odd 573
If you cannot copy files from the logic analyzer 574
If you cannot restore raw files 574
If you get an "operation timed-out" message 575
If the logic analyzer begins to operate slowly 575
If the logic analyzer does not respond 575
If all else fails 576
Getting Service Support 577
HP on-site service 577
Return to HP service 577
SECTION 3
23 Symbol Utility Introduction
Symbol Utility Introduction 582
Equipment Required 582
Supported Symbol File Formats 583
Symbol Utility section overview 585
24 Getting Started with the Symbol Utility
Getting Started with the Symbol Utility 588
To Access the Symbol File Load Menu 589
Method 1: Using the Module Field 589
Method 2: Using the Symbol Field in the Format Menu 591
To Access the Symbol Browser 593
23

Contents
25 Using the Symbol Utility
To generate a symbol file 596
To Load a Symbol File 597
To Display Symbols in the Trace List 600
To Trigger on a Symbol 602
To View a List of Symbol Files Currently Loaded into the System 605
To Remove a Symbol File From the System 606
26 Symbol Utility Features and Functions
Symbol Utility Features and Functions 608
The OMF Symbol File Load Menu 609
OMF File Field 610
Drive Field 610
Label Field 611
Module Field 611
Load Field 612
Current Loaded Files Field 613
Section Relocation Option 614
The OMF Symbol Browser Menu 616
Symbol Type Selection Field (User vs. OMF) 617
Find Field 618
Browse Results Display 620
Align to xx Byte Option 621
Offset Option 622
Context Display 623
Address Display 623
Symbol Mode Field 624
24

Contents
The General-Purpose ASCII File Format 625
Creating a GPA Symbol File 626
GPA File Format 627
Sections 629
Functions 631
Variables 632
Source Line Numbers 633
Start Address 634
Comments 634
25

Contents
26

Section 1
Logic Analyzer
27

28

1
Logic Analyzer Overview
29
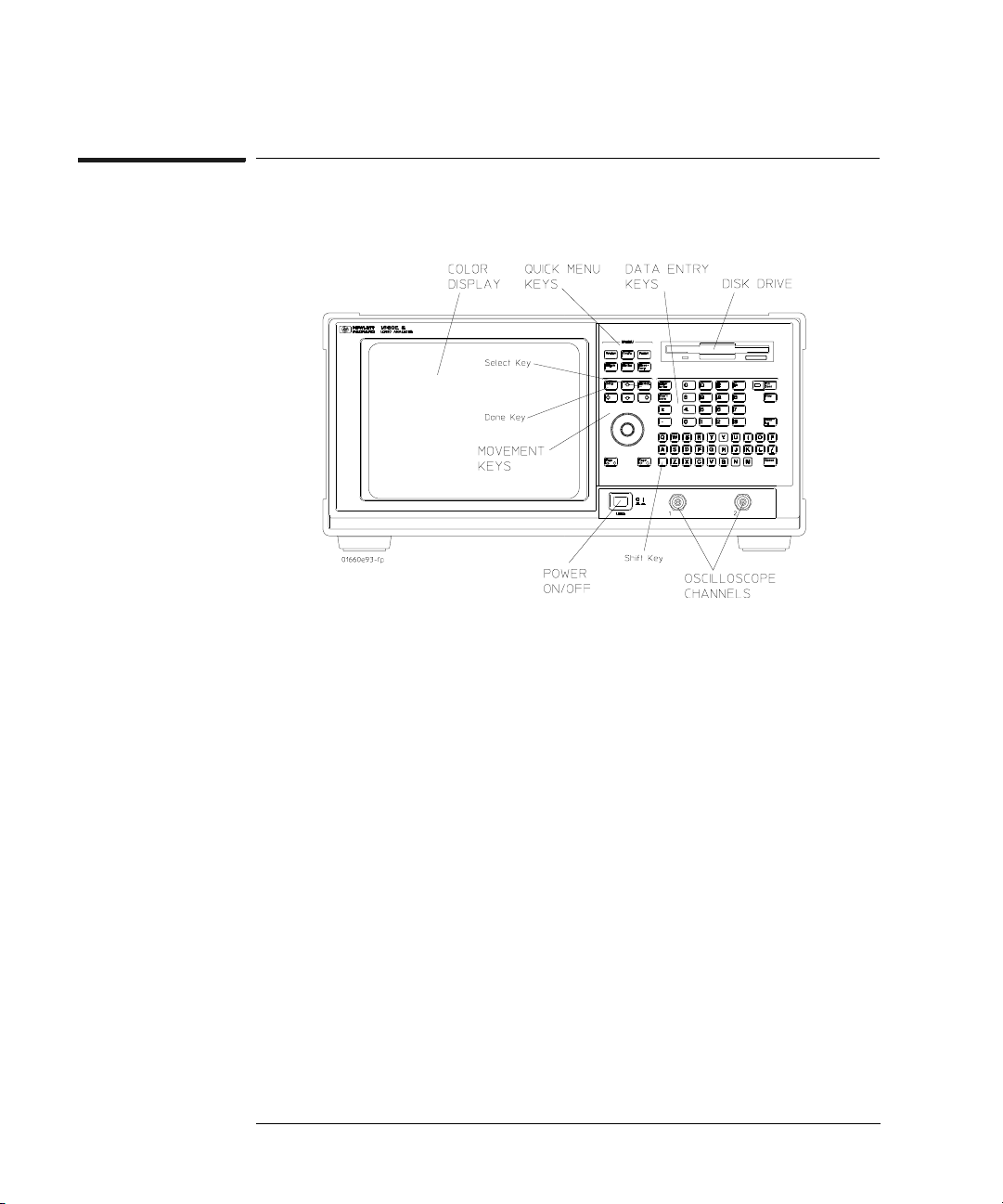
Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
HP 1660ES-Series Logic Analyzer Front Panel
Select Key
The Select key action depends on the type of field currently
highlighted. If the field is an option field, the Select key brings up an
option menu or, if there are only two possible values, toggles the value
in the field. If the highlighted field performs a function, the Select key
starts the function.
Done Key
The Done key saves assignments and closes pop-up menus. In some
fields, its action is the same as the Select key.
30

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
Shift Key
The Shift key, which is blue, provides lowercase letters and access to
the functions in blue on some of the keys. You do not need to hold the
shift key down while pressing the other key. Press the shift key first,
and then the function key.
Knob
The knob can be used in some fields to change values. These fields are
indicated by a side view of the knob placed on top of the field when it is
selected. The knob also scrolls the display and moves the cursor within
lists. If you are using a mouse, you can do the same actions by holding
down the right button of the mouse while dragging.
HP 1660EP-Series Logic Analyzer Back Panel
Line Power Module
Permits selection of 110-120 or 220-240 Vac and contains the fuses for
each of these voltage ranges.
31

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
External Trigger BNCs
The External Trigger BNCs provide the "Port In" and "Port Out"
connections for the Arm In and Arm Out of the Trigger Arming Control
menu.
RS-232-C Connector
Standard DB-25 type connector for connecting an RS-232-C printer or
controller.
HP-IB Connector
Standard HP-IB connector for connecting an HP-IB printer or
controller.
Parallel Printer Connector
Standard Centronics connector for connecting a parallel printer.
Oscilloscope Calibration Port
Provides signals for operational accuracy calibration for the
oscilloscope and the oscilloscope/probe together to optimize
performance.
LAN Connectors
Connects the logic analyzer to your local ethernet network. The BNC
connector on top accepts 10Base2 ("thinlan"). The UTP connector
below the BNC connector accepts 10Base-T ("ethertwist").
Calibration Memory Switch
Provides write protection for the calibration factors stored in memory.
Active Probe Power
Provides the power needed for active probes such as the HP 1144A.
32

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
To make a measurement
For more detail on any of the information below, see the referenced
chapters or the Logic Analyzer Training Kit. If you are using an analysis
probe with the logic analyzer, some of these steps may not apply.
Map to target
Connect probes
Connect probes from the target system to the logic analyzer to
physically map the target system to the channels in the logic analyzer.
Attach probes to a pod in a way that keeps logically-related channels
together. Remember to ground the pod.
See Also "Probing" on page 258 for more detail on constructing probes.
Set type*
When the logic analyzer is turned on, Analyzer 1 is named Machine 1
and is configured as a timing analyzer, and Analyzer 2 is off. To use
state analysis or software profiling, you must set the type of the
analyzer in the Analyzer Configuration menu. You can only use one
timing analyzer at a time.
33

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
Assign pods*
In the Analyzer Configuration menu, assign the connected pods to the
analyzer you want to use. The number of pods on your logic analyzer
depends on the model. Pods are paired and always assigned as a pair to
a particular analyzer.
* If you load a configuration file, this step is not necessary.
Set up analyzers*
Set modes and clocks
Set the state and timing analyzers using the Analyzer Format menu. In
general, these modes trade channel count for speed or storage. The
state analyzer also provides for complicated clocking. If your state
clock is set incorrectly, the data gathered by the logic analyzer might
indicate an error where none exists.
See Also "The Analyzer Format Menu" on page 307 for more information on
modes and clocks.
Group bits under labels
The Analyzer Format menu indicates active pod bits. You can create
groups of bits across pods or subgroups within pods and name the
groups or subgroups using labels.
34

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
Set up trigger
Define terms
In the Analyzer Trigger menu, define trigger variables called terms to
match specific conditions in your target system. Terms can match
patterns, ranges, or edges across multiple labels.
Configure Arming Control
Use Arming Control if:
• you want to correlate the triggers and data of both analyzers
• you want to use the logic analyzer to trigger an external instrument, or
• you want to use an external instrument to trigger the logic analyzer.
Set up trigger sequence
Create a sequence of steps that control when the logic analyzer starts
and stops storing data and filters which data it will store. For common
tasks, you can use a trigger macro to simplify the process or use the
user-defined macros to loop and jump in sequence.
See Also "Using the Trigger Menu" on page 74 and "Triggering Examples" on
page 200 for more information on setting up a trigger.
"The Trigger Sequence" on page 409 for more information about the
trigger sequence mechanism.
"To save a configuration" on page 240 and "To load a configuration" on
page 242 for instructions on saving and loading the setup so you don’t
have to repeat setting up the analyzer and trigger.
35

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
Run measurement
Select single or repetitive
From any Analyzer menu, select the field labeled Run in the upper
right corner to start measuring, or press the Run key. A single run will
run once, until memory is full; a repetitive run will go until you select
Stop or until a stop measurement condition that you set in the markers
menu is fulfilled.
If nothing happens, see Troubleshooting the Logic Analyzer.
When you start a run, your analyzer menu changes to one of the display
menus or a status message pops up. If nothing happens, press the Stop
key or select Cancel. If the analyzer still does not display any
measurements, see "Troubleshooting the Logic Analyzer" on page 440.
Gather data
You can gather statistics automatically by going to the Waveform or
Listing menu, turning on markers, and setting patterns for the X and O
markers. You can set the analyzer to stop if certain conditions are
exceeded, or just use the markers to count valid runs.
36

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
View data
Search for patterns
In both the Waveform and Listing menus you can use symbols and
markers to search for patterns in your data. In the Analyzer Waveform
or Analyzer Listing menu, toggle the Markers field to turn the pattern
markers on and then specify the pattern. When you switch views, the
markers keep their settings.
Correlate data
You can correlate data by setting Count Time in your state analyzer’s
Trigger menu and then using interleaving and mixed display.
Interleaving correlates the listings of two state analyzers. Mixed display
correlates a timing analyzer waveform and a state analyzer listing. The
System Performance Analysis (SPA) Software does not save a record of
actual activity, so it cannot be correlated with either timing or state
mode.
37

Logic Analyzer Overview
HP 1660/70-Series Logic Analyzer
Make measurements
The markers can count occurrences of events, measure durations, and
collect statistics, and SPA provides high-level summaries to help you
identify bottlenecks. To use the markers, select the appropriate marker
type in the display menu and specify the data patterns for the marker.
To use SPA, go to the SPA menu, select the most appropriate mode, fill
in the parameters, and press Run.
See Also "System Performance Analysis (SPA) Software" on page 362 for more
information on using SPA.
"The Waveform Menu" on page 345 and "The Listing Menu" on page 343
for additional information on the menu features.
38

2
Connecting Peripherals
39

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
The HP 1660E/ES/EP and HP 1670E-series logic analyzers comes with
a PS2 mouse. It also provides connectors for a keyboard, Centronics
(parallel) printer, and HP-IB and RS-232-C devices. This chapter tells
you how to connect peripheral equipment such as the mouse or a
printer to the logic analyzer.
Mouse and Keyboard
You can use either the supplied mouse and optional keyboard, or
another PS2 mouse and keyboard with standard DIN connector. The
DIN connector is the type commonly used by personal computer
accessories.
Printers
The logic analyzer communicates directly with HP PCL printers
supporting the printer control language or with other printers
supporting the Epson standard command set. Many non-Epson
printers have an Epson-emulation mode. HP PCL printers include the
following:
• HP ThinkJet
• HP LaserJet
• HP PaintJet
• HP DeskJet
• HP QuietJet
You can connect your printer to the logic analyzer using HP-IB, RS-232C, or the parallel printer port. The logic analyzer can only print to
printers directly connected to it. It cannot print to a networked printer.
40

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect a mouse
Hewlett-Packard supplies a mouse with the logic analyzer. If you prefer
a different style of mouse you can use any PS2 mouse with a standard
PS2 DIN interface.
1 Plug the mouse into the mouse connector on the back panel.
Make sure the plug shows the arrow on top.
2 To verify connection, check the System External I/O menu for a
mouse box.
The mouse box is on the right side above the Settings fields. If the logic
analyzer was displaying the System External I/O menu when you
plugged in the mouse, the menu won’t update until you exit and then
return to it.
The mouse pointer looks like a plus sign (+). To select a field, move the
pointer over it and press the left button. To duplicate the front-panel
knob, hold down the right button while moving the mouse. Moving the
mouse up or to the right duplicates turning the knob clockwise. Moving
the mouse down or to the left duplicates turning the knob
counterclockwise.
System External I/O Menu Showing Mouse Installed
41

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect a keyboard
You can use either the HP-recommended keyboard, HPE2427B, or any
other keyboard with a standard DIN connector.
1 Plug the keyboard into the keyboard connector on the back
panel.
2 To verify, check the System External I/O menu for a keyboard
box.
The keyboard box is on the right side, above the Settings fields. If the
logic analyzer was displaying the System External I/O menu while you
plugged the keyboard in, the menu won’t update until you exit and
then return to it.
The keyboard cursor is the location on the screen highlighted in
inverse video. To move the cursor, use the arrow keys. Pressing Enter
selects the highlighted field. The primary keyboard keys act like the
analyzer’s front-panel data entry keys.
See Also "Keyboard Shortcuts" on page 277 for complete key mappings.
System External I/O Menu Showing Keyboard Installed
42

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect to an HP-IB printer
Printers connected to the logic analyzer over HP-IB must support HPIB and Listen Always. When controlling a printer, the analyzer’s HP-IB
port does not respond to service requests (SRQ), so the SRQ enable
setting does not have any effect on printer operation.
1 Turn off the analyzer and the printer, and connect an HP-IB cable
from the printer to the HP-IB connector on the analyzer rear
panel.
2 Turn on the analyzer and printer.
3 Make sure the printer is set to Listen Always or Listen Only.
For example, the figure below shows the HP-IB configuration switches
for an HP-IB ThinkJet printer. For the Listen Always mode, move the
second switch from the left to the 1 position. Because the instrument
doesn’t respond to SRQ EN (Service Request Enable), the position of
the first switch doesn’t matter.
Listen AlwaysSwitchSetting
43

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
4 Go to the System External I/O menu and configure the analyzer’s
printer settings.
a If the analyzer is not already set to HP-IB, select the field
under Connected To: in the Printer box and choose HP-IB
from the menu.
b Select the Printer Settings field.
c In the top field of the pop-up, select the type of printer you
are using. If you are using an Epson graphics printer or an
Epson-compatible printer, select Alternate.
d If the default print width and page length are not what you
want, select the fields to toggle them.
If you select 132 characters per line when using a printer
other than QuietJet, the listings are printed in a compressed
mode. QuietJet printers can print 132 characters per line
without going to compressed mode, but require wider paper.
e Press Done.
44

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect to an RS-232-C printer
1 Turn off the analyzer and the printer, and connect a null-modem
RS-232-C cable from the printer to the RS-232-C connector on
the analyzer rear panel.
2 Before turning on the printer, locate the mode configuration
switches on the printer and set them as follows:
• For the HP QuietJet series printers, there are two banks of mode
function switches inside the front cover. Push all the switches down to
the 0 position.
• For the HP ThinkJet printer, the mode switches are on the rear panel of
the printer. Push all the switches down to the 0 position.
• For the HP LaserJet printer, the factory default switch settings are
okay.
3 Turn on the analyzer and printer.
4 Go to the System External I/O menu and configure the analyzer’s
printer settings.
a If the analyzer is not already set to RS232, select the field
under Connected To: in the Printer box and choose RS232
from the menu.
b Select the Printer Settings field.
c In the top field of the pop-up, select the type of printer you
are using. If you are using an Epson graphics printer or an
Epson-compatible printer, select Alternate.
45

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
d If the default print width and page length are not what you
want, select the fields to toggle them.
If you select 132 characters per line when using a printer
other than QuietJet, the listings are printed in a compressed
mode. QuietJet printers can print 132 characters per line
without going to compressed mode, but require wider paper.
e Press Done.
5 Select the RS232 Settings field and check that the current
settings are compatible with your printer.
See Also "The RS-232-C, HP-IB, and Centronics Interface" on page 292 for more
information on RS-232-C settings.
46

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect to a parallel printer
1 Turn off the analyzer and the printer, and connect a parallel
printer cable from the printer to the parallel printer connector on
the analyzer rear panel.
2 Before turning on the printer, configure the printer for parallel
operation.
The printer’s documentation will tell you what switches or menus need
to be configured.
3 Turn on the analyzer and printer.
4 Go to the System External I/O menu and configure the analyzer’s
printer settings.
a If the analyzer is not already set to Parallel, select the field
under Connected To: in the Printer box and choose Parallel
from the menu.
b Select the Printer Settings field.
c In the top field of the pop-up, select the type of printer you
are using. If you are using an Epson graphics printer or an
Epson-compatible printer, select Alternate.
d If the default print width and page length are not what you
want, select the fields to toggle them.
If you select 132 characters per line when using a printer
other than QuietJet, the listings are printed in a compressed
mode. QuietJet printers can print 132 characters per line
without going to compressed mode, but require wider paper.
e Press Done.
There are no settings specific to the parallel printer connector.
47

Connecting Peripherals
Connecting Peripherals
To connect to a controller
You can control the HP 1660E/ES/EP-series logic analyzer with another
instrument, such as a computer running a program with embedded
analyzer commands. The steps below outline the general procedure for
connecting to a controller using HP-IB or RS-232-C.
1 Turn off both instruments, and connect the cable.
If you are using RS-232-C, the cable must be a null-modem cable. If you
do not have a null-modem cable, you can purchase an adapter at any
electronics supply store.
2 Turn on the logic analyzer and then the controller.
3 In the System External I/O menu, select the field under
Connected To: in the Controller box and set it appropriately.
4 Select the appropriate Settings field and configure the values in
the pop-up menu to be compatible with the controller.
See Also HP 1660E/ES/EP or HP 1670E-Series Logic Analyzers Programmer’s
Guide and the LAN section of this book starting on page 494 for more
information on connecting controllers.
48

3
Using the Logic Analyzer
49

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Logic Analyzer
This chapter shows you how to perform the basic tasks necessary to
make a measurement. Each section uses an example to show how the
task fits into the overall goal of making a measurement.
50

Using the Logic Analyzer
Accessing the Menus
Accessing the Menus
When you power up the logic analyzer, the first screen after the system
tests is the Analyzer Configuration menu. Menus are identified by two
fields in the upper left corner.The leftmost field shows Analyzer. This
field is sometimes referred to as the "mode field" because it controls
which other set of menus you can access. The second field, just to the
right of the mode field, accesses menus within the mode and so is
called the "menu field." For example, if you are in Analyzer mode, the
menus for the analyzer are accessed from the menu field. Menus are
referred to by the titles that appear in the mode and menu fields, for
example, the Analyzer Configuration menu.
The figure below shows the top of the first screen. The mode field, item
1, displays "Analyzer." The menu field, item 2, displays "Configuration."
Because menus are identified by the titles in these two fields, this
menu is referred to as the Analyzer Configuration menu. When there is
no risk of confusion, the menu is sometimes referred to just by the title
showing in the second field, for example, the Configuration menu.
51

Using the Logic Analyzer
Accessing the Menus
To access the System menus
The System menus allow you to perform operations that affect the
entire logic analyzer, such as load configurations, change colors, and
perform system diagnostics.
1 Select the mode field.
Use the arrow keys to highlight the mode field, then press the Select
key. Or, if you are using the mouse, click on the field. This operation is
referred to as "select."
A pop-up menu appears with the choices System and Analyzer. (If you
have installed any optional software, there may be other choices as
well.)
2 Select System.
3 Select the menu field.
The pop-up lists five menus: Hard Disk, Flexible Disk, External I/O,
Utilities, and Test.
52

Using the Logic Analyzer
Accessing the Menus
• Hard Disk allows you to perform file operations on the hard disk.
• Flexible Disk allows you to perform file operations on the flexible disk.
• External I/O allows you to configure your HP-IB, RS-232-C, and LAN
interfaces and connect to a printer and controller.
See Also
• Utilities allows you to set the clock, update the operating system software,
and adjust the display.
• Test displays the installed software version number and loads the self tests.
For information on "File Management" see page 238, and for
information on "Disk Drive Operations" see page 285.
For information on the External I/O menu, "Connecting Peripherals",
see page 39, and "The RS-232-C, HP-IB, and Centronics Interfaces" see
page 292.
53

Using the Logic Analyzer
Accessing the Menus
To access the Analyzer menus
The Analyzer menus allow you to control the analyzer to make your
measurement, perform operations on the data, and view the results on
the display.
1 Select the mode field.
A pop-up menu appears with the choices System, Analyzer, and
Patt Gen or Scope. (If you have installed any optional software, there
may be other choices as well.)
2 Select Analyzer.
3 Select the menu field.
The figure on the next page does not show all of the possible menus
because certain menus are only accessible with the analyzer configured
in a particular mode. For instance, the Compare menu is only available
when you set an analyzer to state mode, and the SPA menu requires an
analyzer set to SPA.
• Configuration is always available in Analyzer mode. Use Configuration to
assign pods and set the analyzer type.
• Format is available whenever an analyzer is set to a type other than "Off."
Use Format to create data labels and symbols, adjust the pod threshold
level, and set modes and clocks.
• Trigger is available when an analyzer is set to State or Timing. Use Trigger
to specify a trigger sequence which will filter the raw information into the
measurement you want to see.
• Listing is available when an analyzer is set to State or Timing. Use Listing
to view your measurement as a list of states. Using an inverse assembler, a
state analyzer can display the measurement as though it were assembly
code.
• Compare is available only when an analyzer is set to State. Use Compare to
compare two listings and quickly scroll to the sections where they differ.
54

Using the Logic Analyzer
Accessing the Menus
• Mixed Display always appears in the menu list when an analyzer is set to
State or Timing, but it requires a State analyzer with time tags enabled.
• Waveform is available when an analyzer is set to State or Timing. Use
Waveform to view the data as logic levels on discrete lines.
• Chart is available only when an analyzer is set to State. Use Chart to view
your measurement as a graph of states versus time.
See Also
• SPA is available only when an analyzer is set to SPA. Use SPA to gather and
view overall statistics about your system performance.
"Logic Analyzer Reference" on page 249 for details on the State and
Timing menus and "System Performance Analysis (SPA) Software" on
page 361 for information on the SPA menu.
"Using the Analyzer Menus" in this chapter for how to use the menus.
55

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
Using the Analyzer Menus
The following examples show how to use some of the Analyzer menus
to configure the logic analyzer for measurements. These examples
assume that you have already determined which signals are of interest,
and have connected the logic analyzer to the target system. Some of
the examples use data from a Motorola 68360 target system, acquired
with an HP E2456A Analysis Probe.
To label channel groups
Hewlett-Packard logic analyzers give you the ability to separate or
group data channels and label the groups with a name that is
meaningful to your measurement. Labels also assist you in triggering
only on states of interest.
Labels can only be assigned in the Analyzer Format menu. Once
assigned, the labels are available in all display menus, where they can
be added to or deleted from the display. Use labels when you want to
group data channels by function with a name that has meaning to that
function.
The default label names are Lab1 through Lab126. However, you can
modify a name to any six-character string. If you are using an HP
analysis probe, the configuration file has predefined labels for your
specific processor.
56

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
To create or modify a label and assign channel groups, use the
following procedure.
1 Press the Format key to go to the Format menu.
2 Select a label under the Labels heading. In the pop-up menu,
select Modify Label.
3 Use the front panel to enter a name for the label and press Done.
In this example, the label is called CYCLE.
4 Select the pod containing the channels for the label. Use the
knob or the arrow keys to position the selector over a channel
you want to change.
An asterisk indicates the channel is selected; a dot indicates the
channel is not part of the current group.
57

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
5 Toggle the channel’s group status by pressing Select.
The indicator changes and the selector moves to the next channel.
In this example, the channels 3, 1, and 0 (Pod A1) are assigned to label
CYCLE
6 Press the Done key to complete selection.
58

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
To create a symbol
Symbols are alphanumeric mnemonics that represent specific data
patterns or ranges. When you define a symbol and set the base type to
Symbol in the Listing menu, the symbol is displayed in the data listing
where the bit pattern would normally be displayed. The symbols also
appear in the Waveform menu when you view a label in bus form.
Symbols allow you to quickly identify data of interest.
To create a symbol, use the following procedure.
1 In the Analyzer Format menu, select Symbols.
The symbol table menu appears. The symbol table is where all user
symbols are created and maintained. If you get a message, "No labels
specified," check that you have at least one label turned on with
channels assigned to it.
2 In the Symbol menu, select the Label field. In the pop-up menu,
select the label that contains the channel groups you want.
When you open the symbol table menu, the Label field displays the
name of the first active label.
If the label you want does not appear in the pop-up menu, the label is
probably off. Return to the Format menu, select the label you want,
and select Turn Label On. Another possibility is that the label is on the
other analyzer. The two analyzers manage resources separately.
3 Select the Base field. In the pop-up menu, select the base for the
pattern.
In this example, binary is used because CYCLE only contains three
channels.
4 Select the field below Symbol. Select Add a Symbol, type in the
symbol name, then press Done.
59

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
5 If additional Symbols are needed, repeat step 4 until you have
added all symbols.
In this example, three symbols are added: MEM RD, MEM WR, and
DATA RD.
6 Toggle the Type field to "range" or "pattern".
When Type is range, a third field appears under the Stop column. To
fully specify a range, you need to enter a value for it, too.
7 Select the Pattern/Start field and use the keypad to enter an
appropriate value in the selected base. Use X for "don’t care."
8 When the pattern is specified, press Done. If you created
additional Symbols, repeat steps 6 and 7 until all symbols are
specified.
9 To close the symbol table menu, select Done.
Symbol table Menu Showing Three Symbols
You can also download symbol tables created by your programming
environment using the Symbol Utility. The Symbol Utility is shipped
installed on all 1660/70-series logic analyzers.
See Also The Symbol Utility section of this book on page 583 for more
information on the Symbol Utility.
60

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
To examine an analyzer waveform
The Analyzer Waveform menu lets you view state or timing data in a
format similar to an oscilloscope display. The horizontal axis represents
states (in state mode) or time (in timing mode) and the vertical axis
represents logic highs and lows.
1 In Analyzer mode, press the Run key to acquire data.
In any mode other than Analyzer, Scope, or Patt Gen, pressing the Run
key has no effect. The menus which ignore Run lack the Run field
onscreen. In Analyzer mode with Run available, the menu changes to a
display menu.
2 Go to the Analyzer Waveform menu.
3 To adjust the horizontal axis (sec/Div or states/Div), use the
knob.
If nothing happens when you turn the knob, make sure the Div field has
a roll indicator above it, as in the figures on the next page. When you
first enter the Waveform menu, the knob adjusts the horizontal axis but
if you select another rollable field, the knob will control that field
instead.
4 To adjust the display relative to the trigger, select the Delay field
and enter a value or use the knob.
The portion of memory being displayed is indicated by a white bar
along the bottom of the display area. The position of the trigger in
memory is indicated by a red dot on the same line. When the bar
includes the dot, then the trigger is visible on the display as indicated
by a vertical line with a "t" underneath.
61

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
5 To scroll through waveforms, select the large rectangle below the
Div field and use the knob.
The roll indicator appears at the top of the rectangle and the name of
the first waveform is highlighted. The highlight moves as you turn the
knob.
6 To insert waveforms, select the large rectangle under the Div
field. In the pop-up, select Insert, and then select the labels and
channels.
The Sequential field inserts all the channels of the label as individual
waveforms; the Bus field groups the waveforms; the Bit N field inserts
just the Nth bit. Waveforms are inserted after the currently highlighted
one.
7 To take measurements, select the Markers field and choose the
appropriate marker type.
The markers available depend on the type of analyzer and whether or
not tagging is enabled. Use markers to locate patterns quickly.
62

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
Example The following example shows a state waveform from the Hewlett-
Packard analysis probe for the Motorola 68360. Notice how the bus
waveforms insert symbols or state data.
63

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
To examine an analyzer listing
The Analyzer Listing menu displays state or timing data as patterns
(states). The Listing menu uses any of several formats to display the
data such as binary, ASCII, or symbols. If you are using an inverse
assembler and select Invasm, the data is displayed in mnemonics that
closely resemble the microprocessor source code.
See Also "The Inverse Assembler" at the end of this chapter for additional
information on using an inverse assembler.
1 In Analyzer mode, press the Run key to acquire data.
In any mode other than Analyzer, Scope, or Patt Gen, pressing the Run
key has no effect. The menus which ignore Run lack the Run field
onscreen. In Analyzer mode with Run available, the menu changes to a
display menu.
2 Go to the Analyzer Listing menu.
All labels defined in the Analyzer Format menu appear in the listing. If
there are more labels than will fit on the screen, the Label/Base field is
shaded like a normal field.
3 To scroll the labels, select the Label/Base field and use the knob
or press the blue shift key and a page key.
If the Label/Base field is selectable, the roll indicator appears over the
field as in the example. To move the labels one full screen at a time,
press Shift and a Page key.
64

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
4 To scroll the data, use the Page keys or select the data roll field
and use the knob.
If you select the data roll field, the roll indicator moves to it. No matter
which field is currently controlled by the knob, however, the Page keys
page the data up or down.
The numbers in the data roll column indicate how many samples the
data is from the trigger. Negative numbers occurred before the trigger
and positive numbers occurred after.
5 If the labels have symbols associated with them, set the base to
Symbol.
The symbols you defined appear in the listing.
6 To insert a label, select one of the label fields, then select Insert
from the pop-up and the label you want to insert.
The last label cannot be deleted, so there is always at least one label.
You can insert the same label multiple times and display it in different
bases.
7 To take measurements, select the Markers field and choose the
appropriate marker type.
The markers available depend on the type of analyzer and whether or
not tagging is enabled. Use markers to locate states quickly.
65

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
Example The following illustration shows a listing from the Hewlett-Packard
analysis probe for the Motorola 68360. The ADDR label has the base set
to Hex to conserve space on the display. The DATA label has the base
set to Invasm for inverse assembly. The FC label has the base set to
Symbol. Additional labels are located to the right of FC, and can be
viewed by highlighting and selecting Label, then using the knob to
scroll the display horizontally.
66

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
To compare two listings
The Compare menu allows you to take two state analyzer acquisitions
and compare them to find the differences. You can use this function to
quickly find all the effects after changing the target system or to
quickly compare the results of quality tests with results from a working
system.
1 In Analyzer mode, press the Run key to acquire data.
In any mode other than Analyzer, Scope, or Patt Gen, pressing the Run
key has no effect. The menus which ignore Run lack the Run field
onscreen. In Analyzer mode with Run available, the menu changes to a
display menu.
2 Go to the Analyzer Compare menu, select Copy Listing to
Reference, and then select Execute.
The Compare menu initially is empty, but when you select Execute the
data appears.
3 Set up the other test that you want to compare to the first.
This can be a change to the hardware, or a different system. Do not
change the trigger, however, or all the states will be different.
4 Run the test again, then select the Reference listing field to
toggle to Difference listing.
The Difference listing is displayed on the next page.
67

Using the Logic Analyzer
Using the Analyzer Menus
The Difference listing displays the states that are identical in dark
typeface, and the states that are different in light typeface
(indistinguishable in the above illustration). The light typeface shows
the data from the compare file that is different from the data in the
reference file.
5 Select the Find Error field and use the knob to scroll through the
errors.
The display jumps past all states that are identical, and shows the
number of errors through the current state in the Find Error field. In
the above illustration, there are 37 errors through state 44 of the
listing.
68

Using the Logic Analyzer
The Inverse Assembler
The Inverse Assembler
When the analyzer captures a trace, it captures binary information. The
analyzer can then present this information in symbol, binary, octal,
decimal, hexadecimal, or ASCII. Or, if given information about the
meaning of the data captured, the analyzer can inverse assemble the
trace. The inverse assembler makes the trace list more readable by
presenting the trace results in terms of processor opcodes and data
transactions.
To use an inverse assembler
Most analysis probes include an inverse assembler in their software.
Loading the configuration file for the analysis probe sets up the logic
analyzer to provide certain types of information for the inverse
assembler. This section is provided in case you ever have to set up an
analyzer for inverse assembly yourself.
The inverse assembly software needs at least these five pieces of
information:
• Address bus. The inverse assembler expects to see the label ADDR, with
bits ordered in a particular sequence.
• Data bus. The inverse assembler expects to see the label DATA, with bits
ordered in a particular sequence.
• Status. The inverse assembler expects to see the label STAT, with bits
ordered in a particular sequence.
• Start state for disassembly. This is the first displayed state in the trace list,
not the cursor position. See the figure on the next page.
• Tables indicating the meaning of particular status and data combinations.
69

Using the Logic Analyzer
The Inverse Assembler
The particular sequences that each label requires depends on the type
of chip the inverse assembler was designed for. Because of this, inverse
assemblers cannot generally be transferred between platforms.
To run the inverse assembler, you must be sure the labels are spelled
correctly as shown here, or as directed in your inverse assembler
documentation. Even a minor difference such as not capitalizing each
letter will cause the inverse assembler to not work.
Inverse Assembly Synchronization
When you press the Invasm key to begin inverse assembly of a trace,
the inverse assembler begins with the first displayed state in the trace
list. This is called synchronization. It looks at the status bits (STAT)
and determines the type of processor operation, which is then
displayed under the STAT label. If the operation is an opcode fetch, the
inverse assembler uses the information on the data bus to look up the
corresponding opcode in a table, which is displayed under the DATA
label. If the operation is a data transfer, the data and corresponding
operation are displayed under the DATA label. This continues for all
subsequent states in the trace list.
70

Using the Logic Analyzer
The Inverse Assembler
If you roll the trace list to a new position and press Invasm again, the
inverse assembler repeats the above process. However, it does not
work backward in the trace list from the starting position. This may
cause differences in the trace list above and below the point where you
synchronized inverse assembly. The best way to ensure correct inverse
assembly is to synchronize using the first state you know to be the first
byte of an opcode fetch.
See Also The Analysis Probe User’s Guide for more information on controlling
inverse assembly. If you have problems using the inverse assembler, see
"Troubleshooting the Logic Analyzer" on page 439.
71

Using the Logic Analyzer
The Inverse Assembler
72

4
Using the Trigger Menu
73

Using the Trigger Menu
Using the Trigger Menu
Using the Trigger Menu
To use the logic analyzer efficiently, you need to be able to set up your
own triggers. This chapter provides examples of triggering. Those
examples assume you already know where to find fields in the trigger
menu.
This chapter shows you how to:
• Specify a basic trigger
• Change a trigger sequence
• Set up time correlation between analyzers
• Arm from another instrument, or arm another instrument
• Manage memory
74

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
Specifying a Basic Trigger
The default analyzer triggers are
While storing "anystate" TRIGGER on "a" 1 time
Store "anystate"
for state analyzers and
TRIGGER on "a" > 8 ns
for timing analyzers. If you want to simply record data, these will get
you started. They can quickly be tailored by specifying a particular
pattern to look for instead of the general case.
Customizing a trigger generally requires these steps:
• Assign terms.
• Define the terms.
• Change the trigger to use the new terms.
HP 1660ES-series
The oscilloscope can be used in complex triggering sequences
managed by the logic analyzer, but its inherent trigger mechanism is
much simpler. Using the oscilloscope in conjunction with one or both of
the analyzers is covered in “Arming and Additional Instruments” in this
chapter.
75

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
To assign terms to an analyzer
When you turn the logic analyzer on, Analyzer 1 is named Machine 1
and Analyzer 2 is off. Because trigger terms can only be used by one
analyzer at a time, all the terms are assigned to Analyzer 1. If you plan
to use both analyzers in your measurement, you need to assign some of
the terms to Analyzer 2.
1 Go to the Trigger Machine 1 menu.
If you have renamed Machine 1 in the Analyzer Configuration menu,
the name you changed it to will appear in the menu instead of Machine
1.
2 Select a term.
The terms are the fields below the roll field "Terms". See the figure
below.
3 Select Assign from the list that appears.
The Resource Term Assignment menu appears. It is divided into two
sections, one for each analyzer. All terms are listed.
76

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
4 To change a term assignment, select the term field.
The term fields toggle from one section to the other. You can get all
your terms assigned at once, or just change a few to meet immediate
needs.
5 To exit the term assignment menu, select Done.
77

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
To define a term
Both default triggers trigger on term "a". If you only need to look for the
occurrence of a certain state, such as a write to protected memory,
then you only need to define term "a" to make the measurement you
want.
1 In the Trigger menu, select the field at the intersection of the
term and the label whose value you want to trigger on.
You set labels in the Analyzer Format menu. If the channels you want
to monitor are not attached to a label, they will not appear in the
trigger menu.
2 Enter the value or pattern you want to trigger on.
If the label’s base is Symbol, a pop-up menu appears offering a choice
of symbols. For other bases, use the keypad. An "X" stands for "don’t
care".
If there are two conditions that need to be present at the same time, for
example a protected address on the address bus and a write on the
read/ write line, define both values on the same term. See the figure
below.
3 Press Done.
Term "a" Defined as a Data Write to Read-Only Memory
78

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
To change the trigger specification
Most triggers use terms other than "a." Even a simple trigger might use
additional terms to set conditions on the actual trigger. To use these
terms, you must include them in the trigger sequence specification.
1 In the Trigger menu, select the number beside the specific level
you want to modify.
A Sequence Level menu pops up. It shows the current specification for
that trigger level.
2 Select the field you want to change.
In the top row of the pop-up are three action fields: Insert Level, Select
New Macro, and Delete Level. The next section goes into detail on
them. The fields after "While storing", "TRIGGER on", and "Else on" are
completed with trigger terms. Selecting these fields pops up a menu of
terms.
3 Select the term you want to use from the pop-up, or enter a new
value, as appropriate to the field.
If you have renamed a term, that name is automatically used
everywhere the term would appear.
79

Using the Trigger Menu
Specifying a Basic Trigger
4 Select Done until you are back at the Trigger menu.
Term Selection Pop-up Menu
80

Using the Trigger Menu
Changing the Trigger Sequence
Changing the Trigger Sequence
Most measurements require more complicated triggers to better filter
information. From the basic trigger, you can:
• Add sequence levels
• Change macros
Your logic analyzer provides a macro library to make setting up the
trigger easier. There are 12 state macros and 13 timing macros. Most
macros take more than one level internally to implement, and can be
broken down into their separate levels. Once broken down, the levels
can be used to design your own trigger sequences.
81

Using the Trigger Menu
Changing the Trigger Sequence
To add sequence levels
You can add sequence levels anywhere except after the final one.
1 In the Trigger menu, select the number beside the sequence level
just after where you want to insert.
For example, if you want to insert a sequence level between levels 1
and 2, you would select level 2. To insert levels at the beginning, select
level 1.
A Sequence Level pop-up appears. Its exact contents depend on the
analyzer configuration and the level specification. However, all
Sequence Level pop-ups have an Insert Level field in the upper left
corner.
2 Select Insert Level.
Another pop-up offers the choices of Cancel, Before, or After. If the
level you started from was the last level, After will not appear.
3 Select Before.
The Trigger Macro pop-up replaces the Sequence Level pop-up. The
macros available depend on whether the analyzer is configured as state
or timing.
4 Use the knob to highlight a macro, and select Done.
A new Sequence level pop-up appears. Its contents reflect the macro
you just selected. The figure below shows a user macro for a state
analyzer.
82

5 Fill in the fields and select Done.
Sequence Level Pop-up Menu
Using the Trigger Menu
Changing the Trigger Sequence
83

Using the Trigger Menu
Changing the Trigger Sequence
To change macros
You do not need to add and delete levels just to change a level’s macro.
This can be done from within the Sequence Level pop-up.
1 From the Trigger menu, select the sequence level number of the
sequence level you want to modify.
A Sequence Level pop-up appears. Its contents reflect the current
macro.
2 Select Select New Macro.
The Trigger Macro pop-up replaces the Sequence Level pop-up. The
macros available depend on whether the analyzer is configured as state
or timing.
3 Use the knob to highlight the macro you want, and select Done.
A new Sequence Level pop-up appears. Its contents reflect the macro
you just selected. The wording of this screen is very similar to the
macro description, and the line drawing demonstrates what the macro
is measuring.
4 Select the appropriate assignment fields and insert the desired
pre-defined terms, numeric values, and other parameter fields
required by the macro. Select Done.
For state analyzers, a final "go to trigger" level is automatically placed
at the end of the trigger specification for you. This level must always be
a user level. Although you can change its fields, you cannot change the
macro. Timing analyzers do not have this restriction.
See Also "Timing Trigger Macro Library" and "State Trigger Macro Library" in
The Analyzer Trigger Menu on page 323 for a complete listing of
macros.
84

Using the Trigger Menu
Setting Up Time Correlation between Analyzers
Setting Up Time Correlation between Analyzers
There are two possible combinations of analyzers: state and state, and
state and timing. Timing and timing is not possible because the
Analyzer Configuration menu only permits one analyzer at a time to be
configured as a timing analyzer. For either combination, time
correlation is necessary for interleaving and mixed display.
Time correlation is useful when you want to store different sorts of
data for each trace, but see how they are related. For instance, you
could set up a timing and a correlated state analyzer and see if setup
and hold times are being met. Or, you could set up two state analyzers
and have one watch normal program execution and the other watch
the control and status lines.
Time correlation requires that state analyzers store time tags. You set
the state analyzer to store time tags by turning on Count Time in the
Analyzer Trigger menu. The timing analyzer already stores time tags
when it samples data.
See Also "Special displays" on page 232 for more information on interleaving and
mixed display.
85

Using the Trigger Menu
Setting Up Time Correlation between Analyzers
To set up time correlation between two state analyzers
To correlate the data between two state analyzers, both must have
Count Time turned on in their Trigger menus. Although both have
Count State available, it is not possible to correlate data based on
states even when they are identically defined.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Count.
Count may be Count Off, Count Time, or Count States. Selecting the
field causes a pop-up to appear.
2 Select the field after Count: and select Time.
A warning may appear about reduced memory. It will not prevent you
from changing Count to Count Time.
3 Select Done.
4 Repeat steps 1 through 3 for the other state analyzer.
Now when you acquire data you will be able to interleave the listings.
86

Using the Trigger Menu
Setting Up Time Correlation between Analyzers
To set up time correlation between a timing and a state analyzer
To set up time correlation between a timing and a state analyzer, only
the state analyzer needs to have Count Time turned on. The timing
analyzer automatically keeps track of time.
1 In the state Analyzer Trigger menu, select Count.
Count may be Count Off, Count Time, or Count States. Selecting the
field causes a pop-up to appear.
2 Select the field after Count: and select Time.
A warning may appear about reduced memory. It will not prevent you
from changing Count to Count Time.
3 Select Done.
Now when you acquire data you will be able to set up a mixed display.
87

Using the Trigger Menu
Arming and Additional Instruments
Arming and Additional Instruments
Occasionally you may need to start the analyzer acquiring data when
another instrument detects a problem. Or, you may want to have the
analyzer itself arm another measuring tool. This is accomplished from
the Arming Control field of the Analyzer Trigger menu.
To arm another instrument
1 Attach a BNC cable from the External Trigger Output port on the
back of the logic analyzer to the instrument you want to trigger.
The External Trigger Output port is also referred to as "Port Out." It
uses standard TTL logic signal levels, and will generate a rising edge
when trigger conditions are met.
2 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Arming Control.
Arming Control is below the Run button.
3 Select the field near Arm Out, and choose PORT OUT.
4 If you are using both analyzers, set the Arm Out Sent From field
in the upper right corner.
This field does not appear if only one analyzer is configured.
The selected analyzer will send the arm signal when it finds its trigger.
5 Select Done.
When you make a measurement, the analyzer will send an arm signal
through the External Trigger Output when the analyzer finds its
trigger.
88

Using the Trigger Menu
Arming and Additional Instruments
To arm the oscilloscope with the analyzer
(HP 1660ES-series only)
If both analyzer and the oscilloscope are turned on, you can configure
one analyzer to arm the other analyzer and the oscilloscope. An
example of this is when a state analyzer triggers on a bit pattern, then
arms a timing analyzer and the oscilloscope which capture and display
the waveform after they trigger.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Arming Control.
2 Select the Analyzer Arm Out Sent From field, and choose from
the list the Analyzer that will generate the arm.
3 Select the Analyzer Arm In field, and choose Group Run.
This allows you to time-correlate the data from the analyzers and the
scope. The Scope Trigger Mode must be Immediate for correlation.
4 Select the field of the instrument which will arm the others, and
in the pop-up set it to run from Group Run.
The Scope field is not selectable. To set how the scope is run, select the
field under Scope Arm In.
5 Select the other instrument fields and choose the mechanism
which will arm them.
The Analyzer Arm Out field determines which analyzer sends the
arming signal to Port Out and to the oscilloscope if the oscilloscope is
being armed by an analyzer.
As you set each machine, the arrows connecting the fields in the
Arming Control menu change. The arrows show the order in which the
instruments are armed.
See the example on the next page.
6 Select Done until you are back at the Trigger menu.
89

Using the Trigger Menu
Arming and Additional Instruments
Example In this example STATE MACH triggers from Group Run, then arms
TIME MACH and Scope.
To duplicate this, set STATE MACH to run from Group Run, TIME
MACH to run from STATE MACH, and Scope Arm In to Analyzer.
Arming with two analyzers and an oscilloscope
When the run starts, the state analyzer automatically begins evaluating
its trigger sequence instruction. When the trigger sequence is satisfied,
the state analyzer sends an “Arm” signal to the timing analyzer, the
oscilloscope, and the external trigger.
90

Arming and Additional Instruments
To receive an arm signal from another instrument
When you set the analyzer to wait for an arm signal, it does not react to
data that would normally trigger it until after it has received the arm
signal. The arm signal can be sent to any of the Trigger Sequence
levels, but will go to level 1 unless you change it. Setting up the
analyzer to receive an arm signal is more efficient when the sequence
levels are already in place.
1 Connect a BNC cable from the instrument which will be sending
the signal to the External Trigger Input port on the back of the
logic analyzer.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 5.5 volts on the External Trigger Input.
The External Trigger Input port is also referred to as "Port In." It uses
standard TTL logic signal levels, and expects a rising edge as input.
Using the Trigger Menu
2 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Arming Control.
Arming Control is below the Run button.
3 Select the leftmost field, and choose PORT IN.
The field is unlabeled and shows either Run or PORT IN. It has arrows
going from it to the analyzer(s).
91

Using the Trigger Menu
Arming and Additional Instruments
4 To change the default settings, select the analyzer field.
A small pop-up menu appears. To change which device the analyzer is
receiving its arm signal from, select the Run from field. To change
which sequence level is waiting for the arm signal, select the Arm
sequence level field.
5 Select Done until you are back at the Trigger menu.
Arming a logic analyzer versus OR’d trigger
If one analyzer is set to send the PORT OUT arm, and that analyzer is
also set to wait for an arm from the other analyzer, the dependent
analyzer does not begin to look for its trigger event until it receives the
arm signal. The first analyzer must arm the second analyzer, and then
the second analyzer must find its trigger event, before the Arm Out is
sent.
If OR’d trigger is on, the Arm Out will be sent as soon as the first
analyzer triggers.
92

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
Managing Memory
Sometimes you will need every last bit of memory you can get on the
logic analyzer. There are three simple ways to maximize memory when
specifying your trigger:
• Selectively store branch conditions (State only)
• To set the memory length
• Place the trigger relative to memory
• Set the sampling rates (Timing only)
93

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
To selectively store branch conditions
(State only)
Besides setting up your trigger levels to store anystate, no state, or
some subset of states, you can also choose whether or not to store
branch conditions. Branch conditions are always stored by default, and
can make tracing the analyzer’s path through a complicated trigger
easier. If you really need the extra memory, however, it is possible to
not store the branch conditions.
You cannot set the analyzer to store only some branches in a trigger
sequence specification.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Acquisition Control.
The Acquisition Control menu pops up. If the acquisition mode is set to
Automatic, the menu contains a single field and an explanation. If
Acquisition has been customized, it has 3 fields and a picture showing
where the trigger is currently placed in memory.
2 If the mode is Automatic, select the field and toggle it to Manual.
The menu now shows three fields and a picture.
3 Select the Branches Taken Stored field.
It toggles to Branches Taken Not Stored.
94

Using the Trigger Menu
4 Select Done.
Acquisition Control Menu with Branches Field Highlighted
Managing Memory
95

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
To set the memory length
The 1670E-series logic analyzer’s memory length can be adjusted. The
table on the following page shows the amount of memory available for
different modes of operation.
Typically you will want to use small amounts of memory at the
beginning of troubleshooting, when you are first looking for a problem,
and use deep memory when you are searching for the root cause.
Shallower memory provides faster acquisitions, but might not have
sufficient context. Deep memory provides more context, but takes
longer to fill, more time to display, and more time for you to analyze.
The Memory Length field allows you to configure the acquisition
memory to suit your needs.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Acquisition Control.
The Acquisition Control menu pops up. If the acquisition mode is set to
Automatic, the menu contains two fields and an explanation. If
Acquisition has been customized, it has four or five fields and a picture
showing the amount of memory and where the trigger is currently
placed in memory.
2 Select the Memory Length field.
Use the knob to select the memory length. Memory size can be set in
powers of 2 from 4096 to the maximum. The table below shows the
maximum memory for various modes of operation.
96

Using the Trigger Menu
3 Select Done to exit the Acquisition Control menu.
Mode Memory
Full-channel timing 1,040,384 (1 M)
Half-channel timing 2,088,960 (2 M)
Managing Memory
1
State
2
State
State Compare
State Compare
1
With tags turned off or non-interleaved tags. Tags are non-interleaved
1
2
1,040384 (1 M)
516,096 (504 K)
253,952 (248 K)
122,880 (120)
if there is an unassigned pod pair or a pod pair assigned to an analyzer
that is turned off.
2
With interleaved tags.
97

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
To place the trigger in memory
In Automatic Acquisition Mode, the exact location of the trigger
depends on the trigger specification but usually falls around the center.
You can manually place it at the beginning, end, or anywhere else.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Acquisition Control.
The Acquisition Control menu pops up. If the acquisition mode is set to
Automatic, the menu contains a single field and an explanation. If
Acquisition has been customized, it has 3 or 4 fields and a picture
showing where the trigger is currently placed in memory.
2 If the mode is Automatic, select the field to toggle it to Manual.
The menu now shows three fields and a picture.
3 Select the Trigger Position field.
4 Select the appropriate entry for your needs.
Start, Center, and End place the trigger respectively at the beginning,
middle, and end of the memory. Delay, available in timing analyzers
only, causes the analyzer to not save any data before the time delay has
elapsed. User Defined calls up a fourth field where you specify exactly
where you want the trigger.
98

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
5 Select Done.
Acquisition Control Menu with Trigger Position Pop-up for a Timing
Analyzer
99

Using the Trigger Menu
Managing Memory
To set the sampling rates (Timing only)
A timing analyzer samples the data based on its own internal clock. A
short sample period provides more detail about the device under test; a
long sample period allows more time before memory is full. However, if
the sample period is too large, some information may be missed.
1 In the Analyzer Trigger menu, select Acquisition Control.
The Acquisition Control menu pops up. If the acquisition mode is set to
Automatic, the menu contains a single field and an explanation. If
Acquisition has been customized, it has 3 or 4 fields and a picture
showing where the trigger is currently placed in memory.
2 If the mode is Automatic, select the field and toggle it to Manual.
The menu now shows three fields and a picture.
3 Set the Sample Period field using the knob, or select it to use the
keypad to enter the period.
4 Select Done.
Next time you take a measurement, the analyzer will sample at the rate
you entered.
Acquisition Control Menu with Sample Period Selected
100
 Loading...
Loading...