Page 1

V ERSION 1.8
Page 2

Technical Support: Phone: 800.492.2320
E-mail: support@aerocomm.com
Web: www.aerocomm.com/support
Sales: Phone: 800.492.2320
E-mail: sales@aerocomm.com
Web: www.aerocomm.com
Page 3

Document Information
Copyright © 2007 AeroComm, Inc. All rights reserved.
The information contained in this manual and the accompanying software programs are copyrighted and all rights are
reserved by AeroComm, Inc. AeroComm, Inc. reserves the right to make periodic modifications of this product without
obligation to notify any person or entity of such revision. Copying, duplicating, selling, or otherwise distributing any
part of this product or accompanying documentation/software without the prior consent of an authorized
representative of AeroComm, Inc. is strictly prohibited.
All brands and product names in this publication are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
This material is preliminary
Information furnished by AeroComm in this specification is believed to be accurate. Devices sold by AeroComm are
covered by the warranty and patent indemnification provisions appearing in its Terms of Sale only. AeroComm makes
no warranty, express, statutory, and implied or by description, regarding the information set forth herein. AeroComm
reserves the right to change specifications at any time and without notice.
AeroComm’s products are intended for use in normal commercial and industrial applications. Applications requiring
unusual environmental requirements such as military, medical life-support or life-sustaining equipment are specifically
not recommended without additional testing for such application.
Limited Warranty, Disclaimer, Limitation of Liability
For a period of one (1) year from the date of purchase by the OEM customer, AeroComm warrants the OEM
transceiver against defects in materials and workmanship. AeroComm will not honor this warranty (and this warranty
will be automatically void) if there has been any (1) tampering, signs of tampering; 2) repair or attempt to repair by
anyone other than an AeroComm authorized technician.
This warranty does not cover and AeroComm will not be liable for, any damage or failure caused by misuse, abuse,
acts of God, accidents, electrical irregularity, or other causes beyond AeroComm’s control, or claim by other than the
original purchaser.
In no event shall AeroComm be responsible or liable for any damages arising: From the use of product; From the loss
of use, revenue or profit of the product; or As a result of any event, circumstance, action, or abuse beyond the control
of AeroComm, whether such damages be direct, indirect, consequential, special or otherwise and whether such
damages are incurred by the person to whom this warranty extends or third party.
If, after inspection, AeroComm determines that there is a defect, AeroComm will repair or replace the OEM transceiver
at their discretion. If the product is replaced, it may be a new or refurbished product.
Page 4

Revision History
Revision Description
Version 1.0 7/21/06 - Initial Release Version
Version 1.1 7/25/06 - Updated Pin definitions, corrected status request
command to display 0x00 as firmware version, updated CC 08,
CC 21 and EEPROM byte write commands. Corrected PAN ID
EEPROM address to address 0x78. Updated Future
Enhancements section.
Version 1.2 9/15/06 - Changed Reset to active Low. Changed pin 20 to
Sleep pin and is active Low. Added second mechanical
drawing.
Version 1.3 1/18/07 - Corrected Read Temperature command.
Version 1.4 7/6/07 - Internal Release.
Version 1.5 7/17/07 - Added pinout for pluggable module.
Version 1.6 8/24/07 - Added API command set. Added Neighbor, Route, &
Radio Table commands. Added Energy scan command. Added
NV with soft reset command. Added static network parameters
information. Updated Broadcast section. Updated Serial
Interface section. Updated Channel Mask section. Added
power-down modes. Corrected status request response.
Added MAC retries to EEPROM parameter list.
Version 1.7 Corrected Read Channel Command (was CC 02 00; changed to
CC 02)
Version 1.8 12/17/07 - Updated Compliancy Information. Added approval for
ZB2430-D. Updated Approved Antenna List.
Page 5

Contents
ZB2430 TRANSCEIVER MODULE 1
ZB2430 Features 1
Overview 1
SPECIFICATIONS 2
Pin Definitions 4
HARDWARE INTERFACE 6
Pin Definitions 6
Generic I/O 6
RXD and TXD 6
Test/Sleep Int. 6
UP_Reset 6
Command/Data 6
In Range 6
RTS Handshaking* 6
CTS Handshaking 7
Sleep Ind. 7
AD In 7
TERMS & DEFINITIONS 8
THEORY OF OPERATION 11
IEEE 802.15.4 & ZigBee Overview 11
Creating a Network 12
Mesh 12
Parent/Child Relationship 12
Network Limitations 13
Maximum Network Depth 13
Maximum Number of Children per Parent 14
ZigBee Addressing 14
16-bit Network Address 14
64-bit MAC address 15
Mesh Routing (AODV) 15
Coordinator Addressing 17
Broadcast Transmissions 17
AT Commands 27
On-the-Fly Control Commands 27
Command Descriptions 29
EEPROM PARAMETERS 35
API OPERATION 38
API Transmit Packet 38
API Send Data Complete 38
API Receive Packet 39
ZB2430 ADDRESSING 40
ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS 42
Read Neighbor Table 42
Read Route Table 44
Perform Scan 45
Read Radio Table 47
DIMENSIONS 49
ZB2430 Mechanical 49
ORDERING INFORMATION 50
Product Part Numbers 50
COMPLIANCY INFORMATION 51
Agency Identification Numbers 51
Approved antenna List 51
FCC / IC Requirements for Modular Approval 51
OEM Equipment Labeling Requirements 52
Antenna Requirements 52
Warnings required in OEM Manuals 52
Channel Warning 52
SERIAL INTERFACE 19
Interface Modes 19
Transparent Mode 19
API Mode 19
Serial Interface Baud Rate 20
Interface Timeout / RF Packet Size 21
Flow Control 21
RXD Data Buffer and CTS 21
TXD Data Buffer and RTS 21
Networking 22
Power Down Modes 25
Cyclic Sleep 25
Deep Sleep 25
CONFIGURING THE ZB2430 26
Page 6

ZB2430 TRANSCEIVER MODULE
AeroComm’s new ZB2430 module is based on IEEE 802.15.4 wireless communication standard & the robust ZigBee
networking protocol and is one of the most powerful ZigBee compliant solutions on the market today. The ZB2430
provides OEMs with industry leading 2.4 GHz module performance in low power consumption, easy integration, long
range, and superior features and functionality. Requiring no additional FCC licensing in the Americas, OEMs can
easily make existing systems wireless with little or no RF expertise.
1
ZB2430 FEATURES
• Mesh architecture
• Retries and Acknowledgements
• Programmable Network Parameters
•Multiple generic I/O
• 250 kbps RF data stream
• Software selectable interface baud rates from 1200 bps to 115.2 kbps
• Non-standard baud rates supported
• Low cost, low power and small size ideal for high volume, portable and battery powered
applications
• All modules are qualified for Industrial temperatures (-40°C to 80°C)
• Advanced configuration available using AT commands
• Easy to use Configuration & Test Utility software
OVERVIEW
The ZB2430 is a member of AeroComm's FlexRF OEM transceiver family. The ZB2430 is a cost effective, high
performance, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) transceiver; designed for integration into OEM systems
operating under FCC part 15.247 regulations for the 2.4 GHz ISM band.
To boost data integrity and security, the ZB2430 uses DSSS technology featuring optional Advanced-Encryption
Standards (AES)
Communications include both system and configuration data via an asynchronous serial interface for OEM Host
communications. All association and RF system data transmission/reception is performed by the transceiver.
This document contains information about the hardware and software interface between an AeroComm ZB2430
transceiver and an OEM Host. Information includes the theory of operation, specifications, interface definitions,
configuration information and mechanical drawings.
Note: Unless mentioned specifically by name, the ZB2430 modules will be referred to as "radio" or "transceiver".
Individual naming is used to differentiate product specific features. The host (PC/Microcontroller/Any device to which
the ZB2430 module is connected) will be referred to as "OEM Host" or “Host.”
1.Feature not available at the time of this release.
1
. Fully transparent, these transceivers operate seamlessly in serial cable replacement applications.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 7

SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1: ZB2430 Specifications
General
Interface Connector SMT or Pluggable
Antenna Chip antenna (p/n Fractus FR05-S1-N-0-001) or U.FL connector
Serial Interface Data Rate Baud rates from 1200 bps to 115,200 bps. Non-standard baud rates are also supported.
Channels ZB2430-D: 15 Direct Sequence Channels
Security Channelization, Network Identification and optional 128-bit AES encryption
Frequency Band 2400 - 2483.5 MHz
Channel Bandwidth 3 MHz
Channel Spacing 5 MHz
RF Data Rate (Raw) 250 kbps
RF Technology Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
ZB2430-Q: 15 Direct Sequence Channels
1
Transceiver
2
Modulation 0-QPSK
Output Power EIRP (2dBi gain antenna) ZB2430-D: -12 dBm to +5 dBm
Supply Voltage 3.0 - 3.5V, ±50mV ripple
Current Draw (mA)
Note: Power down modes are not
Coordinator & Router devices.
Sensitivity (1% PER) ZB2430-D:-90 dBm typical
Range, Line of Site (based on 2dBi gain antenna) ZB2430-D: Up to 440 ft.
Temperature (Operating) -40°C to 85°C
Temperature (Storage) -50°C to +85°C
Dimensions 1.0” x 1.35” x 0.22” (25.4 x 34.3 x 5.5 mm)
supported on
ZB2430-Q : +2 dBm to +20 dBm
ZB2430-D: 25 mA 27 mA 0.5 uA 0.5 uA
ZB2430-Q: 140 mA 27 mA 15.5 uA 15.5 uA
ZB2430-Q:-100 dBm typical
ZB2430-Q: Up to 440 ft. at +2 dBm / Up to 3.5 miles at +20 dBm
100% TX 100% RX Cyclic Sleep Deep Sleep
Environmental
Physical
www.aerocomm.com
Page 8

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Table 1: ZB2430 Specifications
Certifications
SPECIFICATIONS
3
FCC Part 15.247 ZB2430-D: Pending
Industry Canada (IC) ZB2430-D: Pending
1. Feature not available at the time of this release.
ZB2430-Q:KQL-ZB2430-100
ZB2430-Q:2268C-ZB2430
www.aerocomm.com
Page 9

SPECIFICATIONS
4
PIN DEFINITIONS
The ZB2430 has a simple interface that allows OEM Host communications with the transceiver. Table 2 below shows
the connector pin numbers and associated functions.
Table 2: Pin Definitions for the ZB2430 transceiver
SMT Pin
1 4 O GIO_0 Generic Output Pin
2 6 O GIO_1 Generic Output Pin
3 8 Do not Connect Has internal connection, for Aerocomm use only.
4 7 I GI0_2 Generic Input pin
5 19 I GIO_3 / AD_0 Has Internal connection. Reserved for future GPIO.
6 3 I RXD Asynchronous serial data input to transceiver
7 2 O TXD Asynchronous serial data output from transceiver
8 10 GND GND Signal Ground
9 1 PWR VCC 3.0 - 3.5 V ±50mV ripple (must be connected)
10 - PWR VPA 3.0 - 3.5 V ±50mV ripple (must be connected)
11 - GND GND Signal Ground
12 9 I Test / Sleep Int. Test Mode – When pulled logic Low and then applying power or resetting, the
Pluggable
Pin
Type Signal Name Function
transceiver’s serial interface is forced to a 9600, 8-N-1 rate. To exit Test mode,
the transceiver must be reset or power-cycled with Test Mode pulled logic
High.
Note: Because this mode disables some modes of operation, it should not be
permanently pulled Low during normal operation.
Sleep mode interrupt - When logic Low, forces End Device to wake up from
sleep mode. When logic High, allows End Device to sleep and wake-up
according to specified poll rate. Sleep mode interrupt function available on
End Devices only.
1
13 18 I/O GIO_4 / AD_1 Has Internal connection. Reserved for future GPIO.
14 5 I UP_Reset RESET – Controlled by the ZB2430 for power-on reset if left unconnected.
15 11 I CMD/Data When logic Low, the transceiver interprets OEM Host data as command data.
16 20 O In Range When logic Low, the transceiver is associated with a parent and has been
17 16 I RTS Request to Send – When enabled in EEPROM, the OEM Host can take this
18 12 O CTS Clear to Send - Active Low when the transceiver is ready to accept data for
After a stable power-on reset, a logic Low pulse will reset the transceiver.
When logic High, the transceiver interprets OEM Host data as transmit data.
assigned a 16-bit Network Address. The Coordinator will report In Range after
selecting a clear channel to operate.
High when it is not ready to accept data from the transceiver. NOTE: Keeping
High for too long can cause data loss due to buffer overflow.
RTS
transmission.
2
Page 10
ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Table 2: Pin Definitions for the ZB2430 transceiver
SPECIFICATIONS
5
SMT Pin
19 14 I/O GIO_8 / AD_5 Has Internal connection. Reserved for future GPIO.
20 13 O Sleep Ind. Sleep mode indicator. When logic Low, transceiver is in sleep mode. When
21 17 I/O GIO_6 / AD_3 Has Internal connection. Reserved for future GPIO.
22 15 I GIO_7 / AD_4 Has Internal connection. Reserved for future GPIO.
1. May be left disconnected on ZB2430-D devices.
2. Feature not implemented at time of release.
Pluggable
Pin
Type Signal Name Function
logic High, transceiver is awake.
ENGINEER’S TIP
Design Notes:
• All I/O is 3.3V TTL.
• All inputs are weakly pulled High (20k) and may be left floating during normal operation.
When implemented, RTS
• Minimum Connections: VCC, VPA, GND, TXD, & RXD.
• Signal direction is with respect to the transceiver.
• Unused pins should be left disconnected.
will be weakly pulled Low.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 11

HARDWARE INTERFACE
3
PIN DEFINITIONS
Generic I/O
Both GIn and GOn pins serve as generic input/output pins. Reading and writing of these pins can be performed onthe-fly using CC Commands.
RXD and TXD
The ZB2430 accepts 3.3 VDC TTL level asynchronous serial data from the OEM Host via the RXD pin. Data is sent
from the transceiver, at 3.3V levels, to the OEM Host via the TXD pin.
Test/Sleep Int.
Test Mode - When pulled logic Low before applying power or resetting, the transceiver's serial interface is forced to
9600, 8-N-1 (8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit): regardless of actual EEPROM setting. The interface timeout is also set
to 3 ms and the RF packet size is set to the default size of 0x54 (84 bytes). To exit, the transceiver must be reset or
power-cycled with Test
Note: Because this pin disables some modes of operation, it should not
operation.
pin logic High or disconnected.
be permanently pulled Low during normal
Sleep Mode Interrupt - When logic Low, forces End Device to wake up from sleep mode. When logic High, allows End
Device to sleep and wake-up according to specified poll rate. Sleep Mode interrupt function available on End
Devices only.
UP_Reset
UP_Reset provides a direct connection to the reset pin on the ZB2430 microprocessor and is used to force a soft
reset. For a valid reset, reset must be asserted Low for an absolute minimum of 250 ns.
Command/Data
When logic High, the transceiver interprets incoming serial data as transmit data to be sent to other transceivers.
When logic Low, the transceiver interprets incoming serial data as command data. When logic Low, data packets
from the radio will not be transmitted over the RF interface however incoming packets from other radios will still be
received.
In Range
The In Range pin will be driven low when the radio is associated with a network. In Range will always be driven low on
a Coordinator.
RTS Handshaking*
With RTS mode disabled, the transceiver will send any received data to the OEM Host as soon as it is received.
However, some OEM Hosts are not able to accept data from the transceiver all of the time. With RTS enabled, the
OEM Host can prevent the transceiver from sending it data by de-asserting RTS
(Low), the transceiver will send packets to the OEM Host as they are received.
(High). Once RTS is re-asserted
www.aerocomm.com
Page 12

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Note: Leaving RTS de-asserted for too long can cause data loss once the transceiver's receive buffer reaches
capacity.
*Feature not implemented at time of release.
HARDWARE INTERFACE
CTS Handshaking
If the transceiver buffer fills up and more bytes are sent to it before the buffer can be emptied, data loss will occur. The
transceiver prevents this loss by deasserting CTS High as the buffer fills up and asserting CTS Low as the buffer is
emptied. CTS
High.
should be monitored by the Host device and data flow to the radio should be stopped when CTS is
Sleep Ind.
Sleep Indicator output. Sleep Ind. can be used to determine whether or not the transceiver is sleeping. When logic
Low, the transceiver is in sleep mode. When logic High, the transceiver is awake.
AD In
AD In can be used as a cost savings to replace Analog-to-Digital converter hardware with the onboard 12-bit ADC.
Reading of this pin can be performed locally using the Read ADC command found in the On-the-Fly Control
Command Reference.
7
www.aerocomm.com
Page 13

TERMS & DEFINITIONS
Ad-Hoc Network: A wireless network composed of communicating devices without preexisting infrastructure.
Typically created in a spontaneous manner and is self-organizing and self-maintaining.
Association: The process of joining a ZigBee PAN. A device joins the Network by joining a Coordinator or Router
which has previously associated with the Network. Upon joining, the Parent device issues a 16-bit Network Address
to the device.
Broadcast: Broadcast packets are sent to multiple radios. The ZB2430 allows several different broadcast types
including broadcast to all devices & broadcast to Coordinator & all Routers.
Broadcast jitter: The random delay which is automatically introduced by a device before relaying a broadcast packet
to prevent packet collisions.
Channel: The frequency selected for data communications within the PAN. The channel is selected by the Network
Coordinator on power-up.
Channel Mask: The Channel Mask is a 32-bit field which specifies the range of allowable channels that the radio has
to select from when choosing an RF channel. Valid only when Channel Select mode is enabled in EEPROM.
4
Clear Channel Assessment: An evaluation of the communication channel prior to a transmission to determine if the
channel is currently occupied.
Energy Scan: A sweep of the entire frequency band which reports noise readings on every channel & is also capable
of detecting Coordinators and reporting their Channel location.
FFD: Full Function Device. The Network Coordinator & Routers are examples of FFD’s.
IEEE 802.15.4: IEEE standard for Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN’s). Specifies the physical
interface between ZigBee devices.
MAC Address: A unique 64-bit address assigned to each radio. This address cannot be modified and never changes.
It is used by the network to identify the device when assigning 16-bit Network Addresses.
Maximum Network Depth: The maximum number or Routers (hops) that a device can be away from the Coordinator.
The current profile limit is 5.
Maximum Number of Routers: The total number of children that can serve as Routers for a Network device. The
current profile limit is 6.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 14

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
TERMS & DEFINITIONS
Maximum Number of Children: The total number of children that can be associated with a single Network device. The
current profile limit is 20; comprising of up to 6 Routers and 14 End Devices.
Neighbor Table: A table used by the Coordinator and Router(s) to keep track of other devices operating in the same
coverage area.
Network Address: The unique 16-bit address assigned to a device upon joining a PAN. This address is used for
routing messages between devices and can be different each time a device is powered on. The Network Coordinator
will always have a Network Address of 0x0000. Note that addresses are not assigned in numerical order.
Operating Channel: The specific frequency selected for data communications. The operating channel is determined
by the Coordinator on power-up.
Orphan Device: A device which has lost communication contact with or information about its Parent device.
PAN: Personal Area Network. Includes a Network Coordinator and one or more Routers/End Devices. The Network
formation is determined by the Maximum Network Depth, Maximum Number of Routers, and Maximum Number of
Children.
9
PAN ID: Similar to a Network ID. Devices which are operating with different PAN ID’s will not be associated to the
same network.
Parent/Child: When a device joins the Network, it becomes a child of the device with which it is associated. Similarly,
the device with which it associated becomes its parent device. Network devices can have multiple children, but only
one parent. End Devices cannot be parents and are always children of the Coordinator or a Router. The Coordinator
does not have a parent device.
POS: Personal Operating Space. The area within reception range of a specific device.
Profile: A collection of device descriptions, which together form a coorperative application. Devices utilizing different
profiles will only support very basic inter-communications. The ZB2430 uses a private profile as specified by
Aerocomm.
RFD: Reduced Function Device. The End Device is an example of an RFD.
Route Discovery: An operation using RREQ and RREP’s in which a ZigBee Coordinator or Router discovers a route to
a device outside its POS.
Route Reply (RREP): A ZigBee command used to reply to a Route Request command.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 15

TERMS & DEFINITIONS
10
Route Request (RREQ): A ZigBee command used to discover paths through the network over which messages may
be relayed.
Routing Table: A table in which the Coordinator or Router(s) store information required to participate in the routing of
data packets throughout the network. The entire route is not stored, only the first step in the route.
Star Network: A network employing a single, central device through which all communication between devices must
pass.
TX Cost: A counter of transmission successes/failures. TX Cost starts at 0x00, increments by one every time a packet
fails to be delivered, and decrements by one every time a packet is successfully delivered. TX Cost has a range
between 0x00 and 0x04.
Unicast: Unicast packets contain a destination address and are received by a single radio only. Unicast packets are
point-to-point and do not include Broadcast packets.
ZigBee Stack: A Network specification based on the IEEE 802.15.4 Standard for Wireless Personal Area Networks
(WPANs). The ZB2430 uses the Z-Stack (designed by TI) v.1.4.2 and complies to the ZigBee 2006 specification.
ZigBee Alliance: An association of companies working together to create a low-cost, low power consumption, twoway wireless communications standard (http://www.zigbee.org).
Page 16

THEORY OF OPERATION
5
IEEE 802.15.4 & ZIGBEE OVERVIEW
The ZB2430 uses the ZigBee protocol stack, a network layer protocol which uses small, low power digital transceivers
based on the IEEE 802.15.4 hardware standard. The 802.15.4 standard is a specification for a cost-effective, low data
rate (<250 kbps), 2.4 GHz or 868/928 MHz wireless technology designed for personal-area and device-to-device
wireless networking.
The IEEE 802.15.4 standard specifies the hardware requirements, including frequency bands, receiver sensitivity,
modulation and spreading requirements. The ZigBee layer is the software layer that sits atop the 802.15.4 PHY/MAC
layer and performs all packet routing and mesh networking.
There a three device types allowed in a ZigBee network: Coordinator, Router, and End Device. Each network consists
of a single Coordinator, optional Router(s), and optional Reduced Function End Device(s).
Coordinator
The Coordinator is responsible for establishing the
operating channel and PAN ID for the entire Network.
Once the Coordinator has established a Network, it allows
Routers and End Devices to join the Network; assigning
each device a unique 16-bit Network Address.
The Coordinator is intended to be mains powered (always
on).
Router
Routers are responsible for creating and maintaining
Network information and determining the optimal route for
a data packet. Routers must first associate with the
Network before other devices can join through them.
Routers are intended to be mains powered (always on).
End Device
While Coordinators and Routers can communicate with
any device type, End Devices can communicate only with
their parent device. Ideally the End Devices will be in
sleep mode all the time. When they have data to send,
they wake up, send the data and then go back to sleep.
The Parent (Coordinator/Router) of an End Device should
be mains powered to allow it to store data to be sent to
the End Device while it sleeps.
• One Coordinator per Network
• Establishes Channel and PAN ID
• Responsible for Network formation and
maintenance
• Full Function Device
• Packet routing capabilities
• Mains powered (always on)
• Power down modes are not supported
• Multiple Routers can be used
• Allows other Routers/End Devices to join
the Network
• Full Function Device
• Packet routing capabilities
• Mains powered (always on)
• Power down modes are not supported
• Multiple End Devices can be used
• No packet routing capabilities
• Can communicate with other devices in
the Network through its Parent Device
• Reduced Function Device
• Mains or battery powered
• Power down modes are supported
www.aerocomm.com
Page 17
THEORY OF OPERATION
12
CREATING A NETWORK
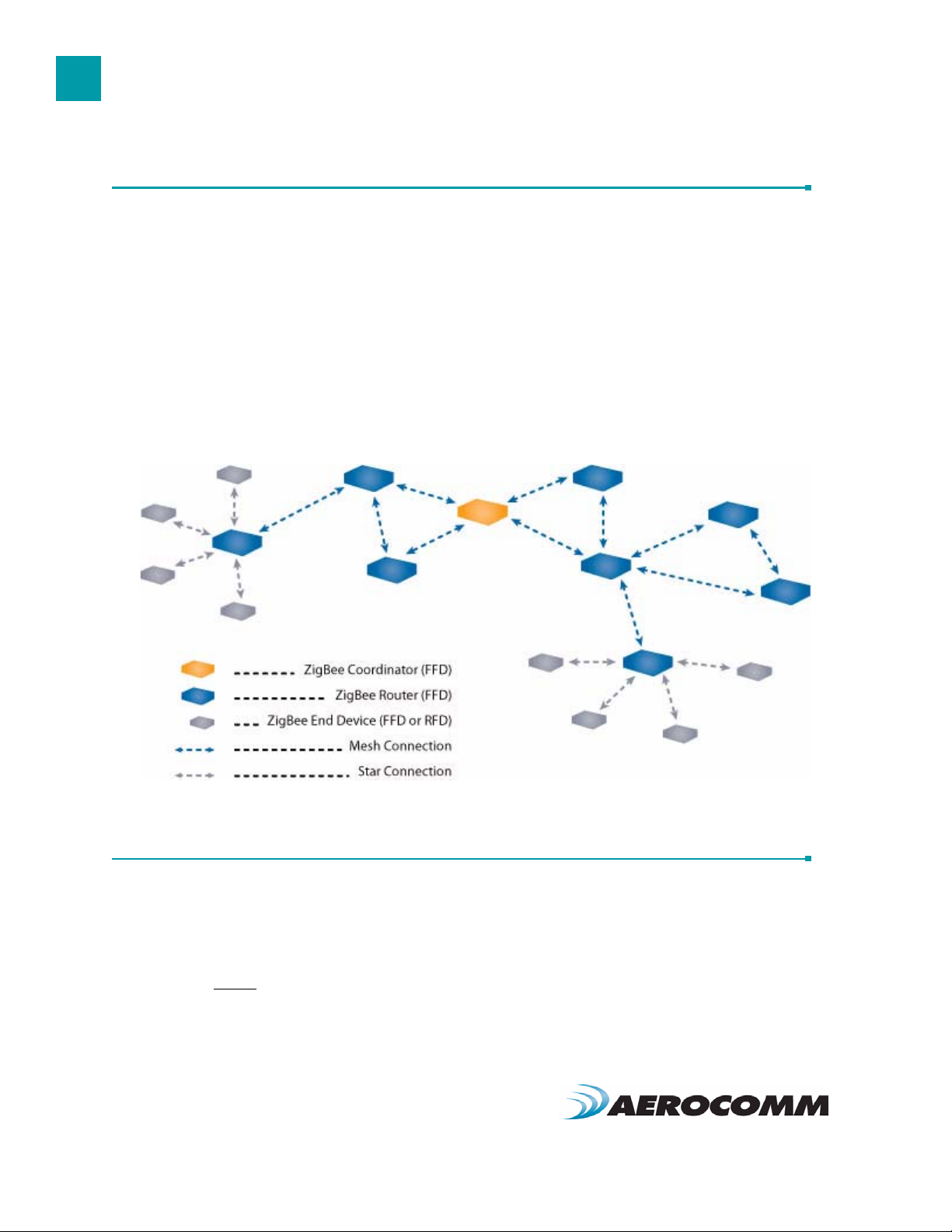
The IEEE 802.15.4 MAC provides support for two wireless network topologies: star and mesh. The management of
these networks is performed by the ZigBee layer. All devices, regardless of topology, participate in the network using
their unique 16-bit address assigned by the Coordinator.
Mesh
The mesh topology allows any Full Function Device (Coordinator or Router) to communicate with any other device
within its range and to have messages relayed to devices which are out of range via multi-hop routing of messages.
While a FFD device can communicate with a Reduced Function Device (RFD), RFD’s cannot directly route messages
and must communicate through their parent device (Coordinator or Router). ZigBee mesh enables the formation of
more complex networks, including ad-hoc, self-organizing, and self-healing structures.
Figure 1 shows a typical ZigBee network architecture.
Figure 1: ZigBee Network Topologies
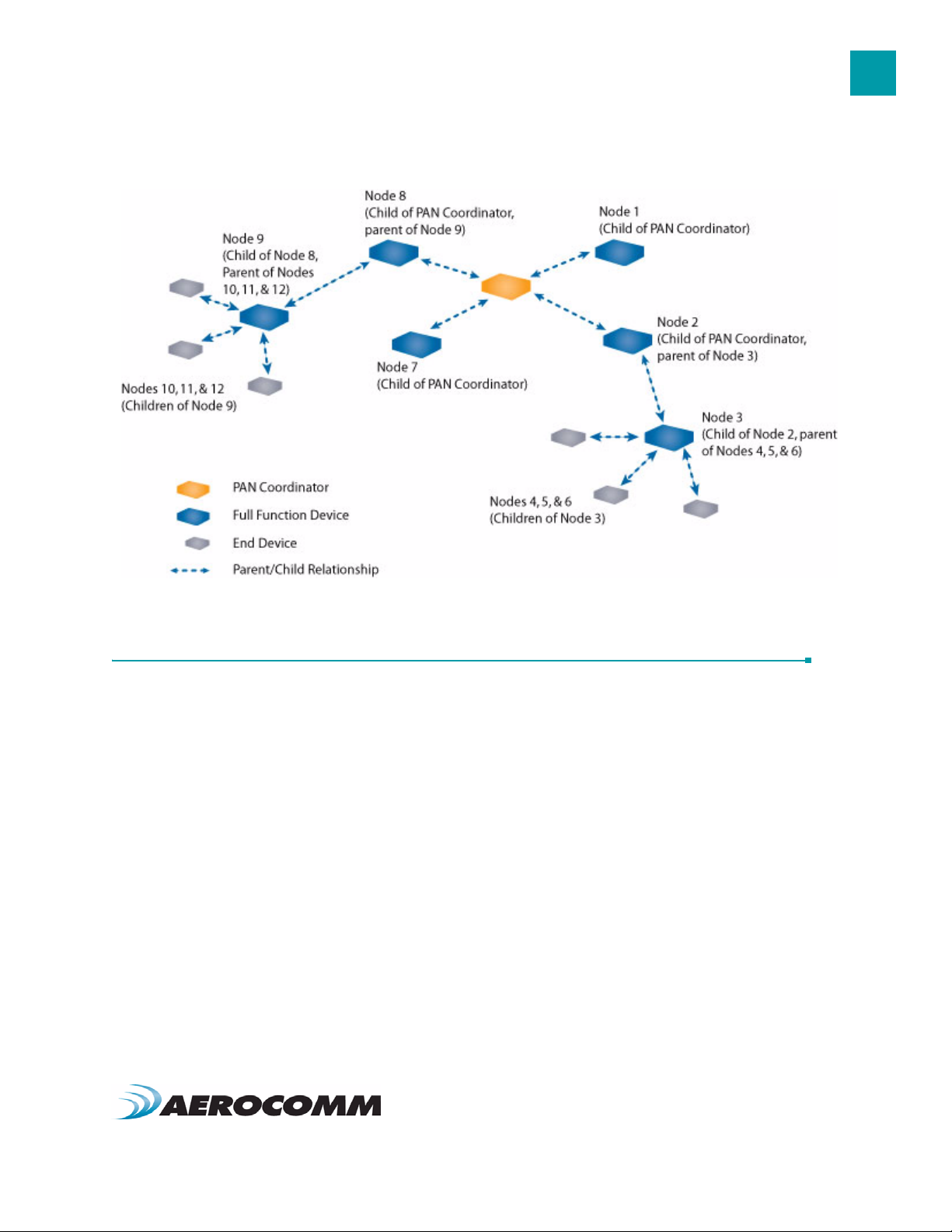
PARENT/CHILD RELATIONSHIP
ZigBee uses a parent/child relationship between network devices. The network begins with the Coordinator as the
first device on the network. When a new device (Router or End Device) associates with the Coordinator, it becomes a
child of the Coordinator and similarly, the Coordinator becomes a parent of that device. If a second device joins the
network, the Coordinator will once again become the parent and the device will become a child of the Coordinator. If
a device is not in range of the Coordinator, it subsequently joins the network through a Router, and becomes a child of
that Router. Network devices can have multiple children, but only one parent. By design, End Devices cannot be
parents and are always
children of the Coordinator or a Router.
Page 18
ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Figure 2: Parent/Child Relationship
THEORY OF OPERATION
13
NETWORK LIMITATIONS
The ZigBee network structure and ultimate size are specified by Stack profiles. The Stack profiles define the
maximum number of Layers, maximum number of Children per Parent, & maximum number of Routers that can be
Children. These parameters are set during code compilation and cannot be altered after compilation. The ZB2430
uses the restricitions specified by the Home Lighting & Controls profile.
The ZigBee Coordinator determines the maximum number of children any device within its network is allowed. Of
these children, a maximum number or routers can be router-capable devices; while the remainder shall be reserved
for end devices. Each device has an associated depth which indicates the minimum number of hops a transmitted
packet must travel to reach the ZigBee Coordinator (see Figure 3: "Network Depth" on page 14).
Maximum Network Depth
The Coordinator has a depth of zero and its Children have a depth of 1. Maximum Network Depth specifies the
maximum number of hops (Routers) that a node can be away from the Coordinator. The Home Lighting & Controls
profile limits the maximum network depth to 5.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 19

THEORY OF OPERATION
14
Figure 3: Network Depth
Maximum Number of Children per Parent
The Maximum Number of Children specifies the total number of Children that can be connected directly to a parent
device on the current Network. The Home Lighting and Control profile specifies the maximum number of children the
Coordinator and Routers can have associated with them to be 20. Of those 20 Children, a maximum of 6 Routers can
be router-capable devices while the remainder shall be End Devices.
ZIGBEE ADDRESSING
The IEEE 802.15.4 standard from which the ZigBee protocol was derived specifies two types of addressing modes:
• 16-bit Network Address
• 64-bit MAC Address
16-bit Network Address
The Network Address is a unique address on the network. The Coordinator always has a Network Address of 0x0000
and it will assign a Network Address to each radio within its range. Routers will then assign Network Addresses to
radios within their range which have not previously been assigned an address. Because the 16-bit address is unique
to each radio on the network, an addressed packet can be sent from any radio on the network to any other radio
located anywhere on the network.
Page 20

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
THEORY OF OPERATION
ENGINEER’S TIP
16-bit Network Addresses.
In a ZigBee network, nodes are assigned a 16-bit NWK address according to how the network
formed. By design, the Coordinator will always have a NWK address of 0x0000. The first
Router to that associates with the Coordinator is assigned a NWK address of 0x0001. The
second Router that associates with the Coordinator is assigned an address of 0x143E.
The 16-bit address is persistent through power loss and resets unless an NV Reset is
performed.
64-bit MAC address
The 64-bit MAC address consists of a 40-bit Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and a 24-bit address
programmed by the manufacturer. All ZB2430 transceivers have the same OUI of 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x50 0x67 which
can be used to distinguish Aerocomm devices on a network but cannot be used to route packets throughout the
network.
When a packet needs to be sent to a specific device through the network, the 16-bit network address must be used.
In order to send data to a specific device in the network, the OEM can compile a table which lists the 64-bit MAC and
the corresponding 16-bit Network address (see Table 3 below). The ZB2430’s built-in Discover IEEE Address and
Discover Network Address commands allow the OEM to query the network and discover all available devices that
respond within a fixed period.
15
Table 3: Device Table Example
Index MAC Address (64-bit) NWK Address (16-bit)
0 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x50 0x67 0x12 0x34 0x56 0x0000
1 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x50 0x67 0x16 0x45 0x34 0x0001
2 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x50 0x67 0x34 0x21 0x78 0x143E
Mesh Routing (AODV)
The ZigBee protocol uses the Ad-Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) routing algorithm. AODV allows nodes to
pass messages through their neighbors to devices which they cannot communicate directly. This is done by
discovering the routes along which messages can be passed using the shortest route possible.
Figure 4 below shows a typical ZigBee network. The circles surrounding the 4 nodes represent the Personal
Operating Space (POS) of each node. Because of the limited range, each node can only communicate with the
neighboring node(s) next to it. When a node needs to send a message to a node which is not a neighbor, it
broadcasts a Route Request (RREQ) message containing the Source Destination Address, the Network Address of
the Destination radio and a path cost metric.
In the example below, Node 0 needs to send a message to Node 3; however the two are not within communication
range of each other. Node 0’s neighbors are Node 1 and Node 2. Since Node 0 cannot directly communicate with
Node 3, it sends out a RREQ which is heard by Nodes 1 and 2 (see Figure 5: "ZigBee Route Request" on page 16).
www.aerocomm.com
Page 21

THEORY OF OPERATION
16
Figure 4: ZigBee AODV
Figure 5: ZigBee Route Request
Page 22

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
One of two things happen when Nodes 1 and 2 receive the RREQ from Node 0:
• If a route is known or if they are the destination radio, they can send a Route Reply (RREP)
back to Node 0.
• If they do not know the route and are also not the destination radio, they will rebroadcast the
RREQ to their neighbors. The message keeps re-broadcasting until the lifespan (specified by
the source radio) expires.
If Node 0 does not receive a reply within a set amount of time, it will rebroadcast the message, this time with a longer
lifespan and a new ID number.
In the example, Node 1 does not have a route to Node 3 and therefore rebroadcasts the RREQ (see Figure 6: "ZigBee
Route Reply" on page 17). Node 2 however, does have a route to Node 3 and therefore replies to the RREQ by
sending out a RREP. Node 2 also sends a RREP to Node 3 so that it knows the route to Node 0.
THEORY OF OPERATION
Figure 6: ZigBee Route Reply
17
Coordinator Addressing
Since the Coordinator’s NWK address is always 0x0000, it can be addressed using its 16-bit NWK address.
Broadcast Transmissions
Since ZigBee is targeted for large-scale applications in which all radios may not be in range of a single radio,
broadcast packets are retransmitted throughout the network. Broadcast transmissions in ZigBee utilize a passive
acknowledgement mechanism; meaning that the Coordinator and all Routers keep track of whether or not their
neighbor(s) have relayed the broadcast packet and will re-broadcast the packet until all of their neighboring devices
have received the packet. Any device can initiate a Broadcast transmission by programming its Destination Address
with a Broadcast Address (see Table 4 on page 18). Subsequent broadcast transmissions occur every 500ms.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 23

THEORY OF OPERATION
18
Table 4: Broadcast Addresses
Broadcast Address Destination Group
0xFFFF All devices in PAN
0xFFFE Reserved
0xFFFD All devices when
0xFFFC All Routers and Coordinator
0xFFF8 - 0xFFFB Reserved
RXOnWhenIdle
= True
ENGINEER’S TIP
Sending a Broadcast packet.
While ZigBee does provide the means for broadcasting data packets throughout the network,
because of the inherent delays associated with broadcast transmissions overall latency may
increase; especially with larger networks. Because of the added latency and overall effect on
the network, broadcast transmissions within a ZigBee network should be limited.
Page 24

SERIAL INTERFACE
The ZB2430 transceiver module interfaces to the OEM Host via an asynchronous 3.3V serial UART interface; allowing
the module to be easily integrated into any 3.3V system without requiring any level translation. The module can
communicate with any logic and voltage compatible UART; or to any serial device with an additional level translator.
6
INTERFACE MODES
The ZB2430 has two different types of interface modes:
• Transparent Mode
•API Mode
Transparent Mode
When operating in Transparent Mode, the ZB2430 can act as a direct serial cable replacement in which received RF
data is forwarded over the serial interface and vice versa. Additionally, many parameters can be configured using
either AT commands or by toggling the Command/Data pin on the transceiver. In transparent mode, the radio needs
to be programmed with the Network Address of the desired recipient. The destination address can be programmed
permanently or on-the-fly.
When Transparent Mode is used, data is stored in the TX buffer until one of the following occurs:
• The RF packet size is reached (EEPROM address 0x5A)
• An Interface Timeout occurs (EEPROM address 0x58)
API Mode
API Mode is an alternative to the default Transparent operation of the ZB2430 and provides dynamic packet routing
and packet accounting abilities to the OEM Host without requiring extensive programming by the OEM Host. API
Mode utilizes specific frame-based packet formats; specifying various vital parameters used to control radio settings
and packet routing on a packet-by-packet basis. The API features can be used in any combination that suits the
OEM’s application specific needs.
API Mode provides an alternative method of configuring modules and message routing at the OEM Host level; without
requiring the use of Command Mode. The ZB2430 has three API functions:
•Transmit API
• Receive API
• API Send Data Complete
For additional details and examples, please refer to the API section on page 38.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 25

SERIAL INTERFACE
20
SERIAL INTERFACE BAUD RATE
In order for the OEM Host and a transceiver to communicate over the serial interface they need to have the same
serial data rate. This value determines the baud rate used for communicating over the serial interface to a transceiver.
For a baud rate to be valid, the calculated baud rate must be within ±3% of the OEM Host baud rate.
Table 5: Baud Rate / Interface Timeout
Desired Baud Rate Baud (0x42)
115,200 0x08 0x02
57,600 0x07 0x02
2
38,400
31,250 0x05 0x02
19,200 0x04 0x02
9,600 0x03 0x03
4,800 0x02 0x05
2,400 0x01 0x09
1,200 0x00 0x12
Non-standard 0xE3 Use equations below
1. Interface timeout = 1 ms per increment
2. Default baud rate
0x06 0x02
Minium Interface Timeout1 (0x58)
For baud rates other than those shown in Table 5 the following equations can be used:
Where
:
FREQUENCY = 32 MHz
BAUD_M = EEPROM Address 0x43
BAUD_E = EEPROM Address 0x44
ENGINEER’S TIP
Using a non-standard baud rate.
The ZB2430 supports a majority of standard as well as non-standard baud rates. To select a
standard baud rate, use the value shown for EEPROM address 0x42 in Table 5 above. To
enable a non-standard baud rate, program EEPROM address 0x42 (Custom Baud Enable) to
0xE3 and then use the equation above to solve for BAUD_M and BAUD_E.
Page 26

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
SERIAL INTERFACE
INTERFACE TIMEOUT / RF PACKET SIZE
Interface Timeout – Interface Timeout specifies a maximum byte gap between consecutive bytes. When that byte gap
is exceeded, the bytes in the transmit buffer are processed as a complete packet. Interface Timeout (EEPROM
address 0x58), in conjunction with the RF Packet Size, determines when a buffer of data will be sent out over the RF
as a complete RF packet, based on whichever condition occurs first.
RF Packet Size - RF Packet Size is used in conjunction with Interface Timeout to determine when to delineate
incoming data as an entire packet based on whichever condition is met first. When the transceiver receives the
number of bytes specified by RF Packet Size (EEPROM address 0x5A) without experiencing a byte gap equal to
Interface Timeout, that block of data is processed as a complete packet. Every packet the transceiver sends over the
RF contains extra header bytes not counted in the RF Packet Size. Therefore, it is much more efficient to send a few
large packets than to send many short packets.
FLOW CONTROL
Although flow control is not required for transceiver operation, it is recommended to achieve optimum system
performance and to avoid overrunning the ZB2430’s serial buffers. The ZB2430 uses seperate buffers for incoming
and outgoing data.
21
RXD Data Buffer and CTS
As data is sent from the OEM Host to the radio over the serial interface, it is stored in the ZB2430’s buffer until the
radio is ready to transmit the data packet. As discussed in “Interface Modes” on page 19, the radio waits to transmit
the data until one of the following conditions occur (whichever occurs first):
• The RF packet size is reached (EEPROM address 0x5A)
• An Interface Timeout occurs (EEPROM address 0x58)
The data continues to be stored in the buffer until the radio receives an RF Acknowledgement (ACK) from the
receiving radio (addressed mode), or all transmit retries/broadcast attempts have been utilized. Once an ACK has
been received or all retries/attempts have been exhausted, the current data packet is removed from the buffer and the
radio will begin processing the next data packet in the buffer.
To prevent the radio’s RXD buffer from being overrun, it is strongly recommended
radio’s CTS
address 0x5C), the radio de-asserts (High) CTS
interface. CTS
CTS_OFF (EEPROM address 0x5D); signalling to the OEM Host that it may resume sending data to the transceiver.
Note: It is recommended that the OEM Host cease all data transmission to the radio while CTS
otherwise potential data loss may occur.
output. When the number of bytes in the RXD buffer reaches the value specified by CTS_ON (EEPROM
to signal to the OEM Host to stop sending data over the serial
is re-asserted after the number of bytes in the RXD buffer is reduced to the value specified by
that the OEM Host monitor the
is de-asserted (High);
TXD Data Buffer and RTS
As data to be forwarded to the OEM Host accumulates, it is stored in the ZB2430’s outgoing buffer until the radio is
ready to begin sending the data to the OEM Host. Once the data packet has been sent to the Host over the serial
interface, it will be removed from the buffer and the radio will begin processing the next data packet in the buffer.
With RTS Mode disabled, the transceiver will send any data to the OEM Host as soon as it has data to send. However,
some OEM Hosts are not able to accept data from the transceiver all of the time. With RTS Mode Enabled, the OEM
Host can prevent the transceiver from sending it a data by de-asserting RTS
(High), causing the transceiver to store
www.aerocomm.com
Page 27

SERIAL INTERFACE
22
the data in its buffer. Once RTS is re-asserted (Low), the transceiver will continue sending data to the OEM Host,
beginning with any data stored in its buffer.
Note: Leaving RTS
ENGINEER’S TIP
NETWORKING
de-asserted for too long can cause data loss once the radio’s TXD buffer reaches capacity.
Can I implement a design using just TXD, RXD and Gnd (Three-wire Interface)?
Yes. However, it is strongly recommended that your hardware monitor the CTS pin of the
radio. CTS
is taken High by the radio when its interface buffer is getting full. Your hardware
should stop sending at this point to avoid a buffer overrun (and subsequent loss of data).
You can perform a successful design without monitoring CTS
. However, you need to take into
account the amount of latency the radio adds to the system, any additional latency caused by
Transmit Retries, how often you send data, non-delivery network timeouts and interface data
rate.
Aerocomm can assist in determining whether CTS
is required for your application.
PAN ID - PAN ID (EEPROM address 0x78) is a 16-bit field and is similar to a password character or network number
and helps differentiate collocated networks.. A transceiver will not be associated with a network unless its PAN ID and
Channel Number match that of the Coordinator. Range is 0x0000 to 0x3FFF.
RF Channel Number - (EEPROM Address 0x40) Channels 0x0B - 0x1A; 5 MHz spacing. The transceiver will operate
only on the RF Channel Number specified in the EEPROM.
Note: The ZB2430-Q is not approved for use on channel 0x1A and the channel number should therefore be selected
accordingly.
Figure 7: IEEE 802.15.4 RF Channels
Table 6: RF Channel Number Settings
Radio Model
ZB2430-D 0x0B - 0x1A 2400 - 2475 MHz
ZB2430-Q 0x0B - 0x19 2400 - 2465 MHz Global
RF Channel Number
Range (0x40)
Frequency Details &
Regulatory requirements
Countries
Page 28

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Channel Select - When enabled in EEPROM (EEPROM address 0x56, bit-3) the Coordinator will select the channel
permitted by the channel mask with the least amount of energy present. The Coordinator will start on the first channel
and if RF energy is detected, it will change to the next channel until a clear channel is found.
When a Router is powered on, it will scan each channel; periodically sending beacons and searching for a parent.
When the parent receives a beacon from the Router, it sends an acknowledgement to the Router, and the Router is
associated with that parent.
When disabled in EEPROM, the Coordinator will use the RF Channel programmed at EEPROM address 0x40 to
establish itself on.
Channel Mask - The Channel Mask (EEPROM Address 0x30) is a 32-bit field which specifies the range of allowable
channels that the radio can select from when choosing an RF channel. In order for two devices to communicate, a
common channel must be selected. At least one channel must be selected (set to 1).
To use the Channel Mask, enable Channel Select (EEPROM Address 0x56, bit 3). When Channel Select is enabled,
the radio disregards the Channel specified at EEPROM address 0x40. When Channel Select is disabled, only the
Channel specified at EEPROM Address 0x40 will be used.
Examples:
The example shown in Figure 8 below enables all 2.4GHz channels for possible use by selecting 0x07FFF800 as the
Channel Mask. The Channel Mask allows you to allow all or to exclude specific channels from selection. The
example in Figure 9 shows channels 0x14-0x1A as the only available channels to select from. Finally Figure 10 below
shows channels 0x0B-0x10 as the only available channels to select from.
SERIAL INTERFACE
Figure 8: Channel Mask - Allow all channels
23
Figure 9: Channel Mask - Allow channels 0x14-0x1A only
www.aerocomm.com
Page 29

SERIAL INTERFACE
24
Note: When Channel Select is enabled in EEPROM, the initial network synchronization time will increase. Channel
Select is disabled in EEPROM by default. All devices on the network should use the same setting for Channel Select.
Figure 10: Allow channels 0x0B-0x10 only
Page 30

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
SERIAL INTERFACE
POWER DOWN MODES
Power down modes allow the ZB2430 to operate at minimum current consumption while not in use. The ZB2430
provides two such modes (End Devices only).
• Cyclic Sleep (Wake periodically based on software-controlled timer)
• Deep Sleep (Wake on pin interrupt)
25
In order for a module to transition into Sleep mode, the Sleep_Int
pin (pin 12) must be logic High or floating. If this pin
is pulled Low, the device will be forced out of Sleep mode and will not be allowed to Sleep until the pin returns to the
High state. While in Sleep mode, the module will not transmit/receive data until after waking up.
Table 7: Sleep Mode Settings
Sleep Mode Transition to Sleep Transition to Wake Current Draw (mA)
Cyclic Sleep Automatic transition to Sleep
Deep Sleep Automatic transition to Sleep
mode after sending Data
Request to Parent Device or
Sleep_Int
is asserted High.
mode occurs after device has
successfully associated with
Network.
Automatic transition to Wake mode
occurs after an EEPROM selectable
period or manual transition when
Sleep_Int
is pulled logic Low.
Manual transition to Wake mode occurs
after Sleep_Int
is pulled logic Low.
ZB2430: 0.5 uA
ZB2430-100: 15.5 uA
ZB2430: 0.5 uA
ZB2430-100: 15.5 uA
Cyclic Sleep
In Cyclic Sleep mode the End Device will wake periodically to request data from its Parent device. The rate at which
the module wakes up to check for data is adjustable in EEPROM (EEPROM address 0x34, 16-bits) in 1 ms increments
with a default setting of 1000ms. The device will wakeup for the period specified, send a data request to its Parent,
and then return to sleep until the next cycle.
Note: Setting the sleep rate to 0x0000 forces the module into Deep Sleep mode (see below).
Deep Sleep
Deep sleep mode is a power-down mode in which the ZB2430 automatically transitions to Sleep mode after having
associated with the Network. While in Deep Sleep mode, the device will not wake up until interrupted by the Sleep_Int
pin. To wake the device out of Deep Sleep mode, Sleep_Int must be pulled logic Low. The device will return to Deep
Sleep mode after Sleep_Int
is returned to the High state.
ENGINEER’S TIP
Transmitting and Receiving data with a sleeping End Device.
• Data sent to the radio over the UART while it is sleeping will be lost. If the module wakes
while receiving data over the UART, it will only see the data received since waking up.
• Incoming data to the module will not keep it awake.
• When sending data for the module to transmit, it is recommended that the module be forced
awake using the Sleep_Int
• While the module is being kept awake using the Sleep_Int
to its Parent Device based on the Poll rate specified in EEPROM for as long as it is awake.
• A Parent will only store data for an End Device for a max. of 2000ms before discarding it.
pin until the module is finished transmitting the data.
pin, it will still send data requests
www.aerocomm.com
Page 31

CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
The ZB2430 can be configured using the CC Configuration Commands. These commands can be issued using either
Hardware or Software Configuration. To use Hardware Configuration, pin 15 of a transceiver must be asserted Low.
Software Configuration can be used by entering AT Command Mode before issuing the CC commands.
7
Figure 11: ZB2430 Configuration Flow
Receive Mode
Yes
Send Enter AT
Command M ode
command
(Software
Configuration)
Send CC
Commands?
Yes
Send CC
Command
Send Another
CC Command?
Use AT
Commands?
Yes
Assert CMD/Data
(Hardware
Configuration)
Yes
Send Exit AT
Command
Pin Low
Exit Command
Mode
In AT
Command
Mode?
De-assert CMD/
Data Pin 15 High
www.aerocomm.com
Page 32

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
AT COMMANDS
The AT Command mode implemented in the ZB2430 creates a virtual version of the Command/Data pin. The “Enter
AT Command Mode” Command asserts this virtual pin Low (to signify Command Mode) and the “Exit AT Command
Mode” Command asserts this virtual pin High (to signify Data). Once this pin has been asserted Low, all On-the-Fly
CC Commands documented in the manual are supported.
On-the-Fly Control Commands
The ZB2430 transceiver contains static memory that holds many of the parameters that control the transceiver
operation. Using the “CC” command set allows many of these parameters to be changed during system operation.
Because the memory these commands affect is static, when the transceiver is reset, these parameters will revert back
to the settings stored in the EEPROM. While in CC Command mode using pin 15 (Command/Data), the RF interface
of the transceiver is still active. Therefore, it can receive packets from remote transceivers while in CC Command
mode and forward these to the OEM Host.
While in Command mode, the incoming RF interface of the transceiver is active and packets sent from other
transceivers will still be received; however no outgoing RF packets will be sent. The transceiver uses Interface
Timeout/RF Packet Size to determine when a CC Command is complete. Therefore, there should be no delay
between each character as it is sent from the OEM Host to the transceiver or the transceiver will not recognize the
command.
When an invalid command is sent, the radio discards the data and no response is sent to the OEM Host. Table 8
below shows a quick summary of the basic configuration & diagnostic commands available on the ZB2430. For
detailed command information, please refer to the command descriptions immedietly following the Quick Reference
Table.
27
Table 8: Command Quick Reference
Command Name Command (All bytes in Hex) Return (All bytes in Hex)
Enter AT Command Mode <0x41> <0x54> <0x2B> <0x2B> <0x2B> <0x0D> <0xCC> <0x43> <0x4F> <0x4D>
Exit AT Command Mode <0xCC> <0x41> <0x54> <0x4F> <0x0D> <0xCC> <0x44> <0x41> <0x54>
Status Request <0xCC> <0x00> <0x00> <0xCC> <Firmware> <Status>
Read Channel <0xCC> <0x02> <0xCC> <Channel> <Channel Mask [3-0]>
Write Destination NWK
Address
Read Destination NWK
Address
Auto Destination <0xCC> <0x15> <Data> <0xCC> <Data>
Read API Control <0xCC> <0x16> <0xCC> <API Control>
Write API Control <0xCC> <0x17> <API Control> <0xCC> <API Control>
Read Digital Input <0xCC> <0x20> <0xCC> <Data>
Read ADC <0xCC> <0x21> <Data> <0xCC> <ADC Hi> <ADC Lo>
Write Digital Outputs <0xCC> <0x23> <Data> <0xCC> <Data>
Set Power Control <0xCC> <0x25> <Power> <0xCC> <Power>
Read NWK Address <0xCC> <0x8A> <0x00> <0xCC> <0x8A> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
<0xCC> <0x10> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo> <0xCC> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
<0xCC> <0x11> <0xCC> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
www.aerocomm.com
Page 33

CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
28
Command Name Command (All bytes in Hex) Return (All bytes in Hex)
Read Parent’s NWK Address <0xCC> <0x8A> <0x01> <0xCC> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Discover NWK Address <0xCC> <0x8D> <00> <MAC [2-0]> <Data> <0xCC> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo> <Data [n-0]>
Discover IEEE Address <0xCC> <0x8E> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo> <Data> <0xCC> <MAC [7-0]> <Data [n-0]>
Read Temperature <0xCC> <0xA4> <0xCC> <Temperature [1-0]>
EEPROM Byte Read <0xCC> <0xC0> <Start> <Length> <0xCC> <Start> <Length> <Data [n-0]>
EEPROM Byte Write <0xCC> <0xC1> <Start> <Length> <Data> <Start> <Length> <Last byte written>
Soft Reset <0xCC> <0xFF> None
Soft Reset with NV reset <0xCC> <0xFF> <0xE3> None
Table 8: Command Quick Reference
Page 34

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
COMMAND DESCRIPTIONS
Enter AT Command Mode
CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
29
Prior to sending this command, the OEM Host must ensure that the
transceiver’s RF transmit buffer is empty. This can be accomplished
by waiting up to one second between the last packet and the AT
command. If the buffer is not empty, the radio will interpret the
command as data and it will be sent over the RF.
Exit AT Command Mode
The OEM Host should send this command to exit AT Command
mode and resume normal operation.
Status Version Request
The OEM Host issues this command to request the firmware and link
status of the transceiver.
Command: <0x41> <0x54> <0x2B> <0x2B> <0x2B> <0x0D>
Number of Bytes Returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x43> <0x4F> <0x4D>
Command: <0xCC> <0x41> <0x54> <0x4F> <0x0D>
Number of Bytes Returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x44> <0x41> <0x54>
Command: <0xCC> <0x00> <0x00>
Number of bytes returned: 3
Response: <0xCC> <Firmware> <Type>
Parameter Range:
<Firmware> = Radio Firmware version
<Type> = 0x00: End Device
0x01: Router
0x02: Coordinator
0x03: Initialized - not started automatically
0x04: Initialized - not connected to anything
0x05: Discovering PAN’s to join
0x06: Joining a PAN
0x07: Rejoining a PAN (only for End Devices)
0x08: Joined but not yet authenticated
0x09: Started a NWK as ZigBee Coordinator
0x0A: Device has lost info about its parent
Read Channel
The OEM Host issues this command to read the channel of the
transceiver.
Write Destination Address
The OEM Host issues this command to the transceiver to change the
Destination Address.
www.aerocomm.com
Command: <0xCC> <0x02>
Number of Bytes Returned: 6
Response: <0xCC> <Channel> <ChMask>
Paramter Range:
<Channel> = RF Channel currently in use
<ChMask> = 32-bit Channel Mask being used
Command: <0xCC> <0x10> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Number of bytes returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Paramter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of destination radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of destination radio’s NWK address
Page 35

CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
30
Read Destination Address
The OEM Host issues this command to the transceiver to read the
Destination Address.
Command: <0xCC> <0x11>
Number of bytes returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Parameter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of destination radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of destination radio’s NWK address
Auto Destination
The Host issues this command to change the Auto Destination
setting. When issuing this command, the Auto Destination setting
will only be changed if the corresponding enable bit is set.
Otherwise, the command performs a read of Auto Destination.
Command: <0xCC> <0x15> <Auto Dest>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: <0xCC> <Auto Dest>
Parameter Range:
<Auto Dest> = bit 7: Ignored
bit 6: Ignored
bit 5: Ignored
bit 4: Enable Modification
bit 3: Ignored
bit 2: Ignored
bit 1: Ignored
bit 0: Auto Destination
Read API Control
The OEM Host issues this command to read the API Control byte. Command: <0xCC> <0x16>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: <0xCC> <API Control>
Parameter Range:
<API Control>= bits 7-3: 0
bit-2: Send Data Complete
bit-1: Transmit API
bit-0: Receive API
Write API Control
The OEM Host issues this command to write the API Control byte to
enable or disable the API features.
Command: <0xCC> <0x17> <API Control>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: <0xCC> <API Control>
Parameter Range:
<API Control>= bits 7-3: Ignored
bit-2: Send Data Complete
bit-1: Transmit API
bit-0: Receive API
Page 36

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Read Digital Input
CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
31
The OEM Host issues this command to read the state of GI0 input
line.
Read ADC
The OEM Host issues this command to read the onboard 12-bit A/D
converters.
The following equations can be used to determine the voltages
associated with the ADC value returned:
ADC value
⎛⎞
Temperature
ADC value
⎛⎞
---------------------------
ADIn
=VCC×
⎝⎠
0x1FFF
---------------------------
⎝⎠
0x1FFF
1.25V×=
Write Digital Outputs
The OEM Host issues this command to write both digital output lines
to particular states.
Command: <0xCC> <0x20>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: <0xCC> <Digital In>
Parameter Range:
<Digital In> = bit-0: GI0
Command: <0xCC> <0x21> <Port>
Number of bytes Returned: 3
Response: <0xCC> <Hi ADC> <Lo ADC>
Parameter Range:
<Port> = 0x00: ADIn
<Hi ADC> = MSB of requested 12-bit ADC value
<Lo ADC> = LSB of requested 12-bit ADC value
Command: <0xCC> <0x23> <Digital Out>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: 0xCC <Digital Out>
Parameter Range:
<Digital Out>= bit-1: GO1
0x01: Temperature
bit-0: GO0
Set Max Power
The OEM Host issues this command to adjust the maximum output
power.
Read 16-bit NWK Address
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 16-bit NWK
address of the device.
www.aerocomm.com
Command: <0xCC> <0x25> <Max Pwr>
Number of Bytes Returned: 2
Response: 0xCC <Max Pwr>
Parameter Range:
<Max Pwr> = High Power
Command: <0xCC> <0x8A> <0x00>
Number of Bytes Returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x8A> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Parameter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of radio’s NWK address
Note: If the device has not yet associated, a NWK address of
0xFFFF will be returned.
0x00: 17 dBm 0x00: 3 dBm
0x01: 11 dBm 0x01: -3 dBm
0x02: 5 dBm 0x02: -9 dBm
0x03: -1 dBm 0x03: -15 dBm
Low Power
Page 37

CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
32
Read 16-bit NWK Address of Parent Device
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 16-bit NWK
address of its’ Parent Device.
Command: <0xCC> <0x8A> <0x01>
Number of Bytes Returned: 4
Response: <0xCC> <0x8A> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Parameter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of Parent’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of Parent’s NWK address
Note: If the device has not yet associated, a NWK address of
0xFFFF will be returned.
Discover 16-bit NWK Address of Remote Radio
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 16-bit NWK
address of a remote radio.
Note: This command is valid only for Coordinators and/or Router
devices. This command will not issue a response if the requested
address is unable to be located in the network. A timeout of several
seconds should be assumed when using this command.
Command: <0xCC> <0x8D> <IEEE [7-0]>
Number of Bytes Returned: 3
Response: <0xCC> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Parameter Range:
<IEEE> = 64-bit IEEE Address of remote radio
<NWK Hi> = MSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of remote radio’s NWK address
Discover 16-bit NWK Address & Children of Remote Radio
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 16-bit NWK
address of a remote radio as well as report a list of that device’s
Children.
Note: This command is valid only for Coordinators and/or Router
devices. This command will not issue a response if the requested
address is unable to be located in the network. A timeout of several
seconds should be assumed when using this command.
Command: <0xCC> <0x8D> <IEEE [7-0]> <0x01>
Number of Bytes Returned: 10+
Response: <0xCC> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo> <Length> <List>
Parameter Range:
<IEEE> = 64-bit IEEE Address of remote radio
<NWK Hi> = MSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<Length> = Length of data to follow
<List> = List of remote radio’s associated devices
[<Index n> <NWK Hi n> <NWK Lo n>]
Discover IEEE Address of Remote Radio
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 64-bit IEEE
address of a remote radio.
Note: This command is valid only for Coordinators and/or Router
devices. This command will not issue a response if the requested
address is unable to be located in the network. A timeout of several
seconds should be assumed when using this command.
Command: <0xCC> <0x8E> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
Number of Bytes Returned: 9
Response: <0xCC> <IEEE [7-0]>
Parameter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<IEEE> = 64-bit IEEE Address of remote radio
Page 38

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Discover IEEE Address & Children of Remote Radio
CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
33
The OEM Host issues this command to discover the 64-bit IEEE
address of a remote radio as well as report a list of that device’s
Children.
Note: This command is valid only for Coordinators and/or Router
devices. This command will not issue a response if the requested
address is unable to be located in the network. A timeout of several
seconds should be assumed when using this command.
Read Temperature
The OEM Host issues this command to read the onboard
temperature sensor.
Note: The temperature sensor is uncalibrated and has a tolerance of
+/- 3C. For calibration instructions, contact Aerocomm’s technical
support.
EEPROM Byte Read
Upon receiving this command, a transceiver will respond with the
desired data from the addresses requested by the OEM Host.
Command: <0xCC> <0x8E> <0x00> <NWK Hi> <NWK Lo>
<0x01>
Number of Bytes Returned: 10+
Response: <0xCC> <IEEE [7-0]> <Length> <List>
Parameter Range:
<NWK Hi> = MSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<NWK Lo> = LSB of remote radio’s NWK address
<IEEE> = 64-bit IEEE Address of remote radio
<Length> = Length of data to follow
<List> = List of remote radio’s associated devices
Command: <0xCC> <0xA4>
Number of bytes returned: 3
Response: 0xCC <+/-> <Temp.>
Parameter Range:
<+/-> = 0x2B: +
<Temp.> = Temperature (Celsius)
Command: <0xCC> <0xC0> <Start> <Length>
Number of Bytes Returned: 4+
Response: <0xCC> <Start> <Length> <Data>
Parameter Range:
<Start> = EEPROM address to begin reading at
<Length> = Length of data to be read
<Data> = Requested data
[<Index n> <NWK Hi n> <NWK Lo n>]
0x2D: -
EEPROM Byte Write
Upon receiving this command, a transceiver will write the data byte
to the specified address but will not echo it back to the OEM Host
until the EEPROM write cycle is complete.
Note: The maximum length of data that can be written in a single
write process is 0x50. If writing the entire 256-byte EEPROM, it is
convenient to perform 64 byte (0x40) writes.
Reset
The OEM Host issues this command to perform a soft reset of the
transceiver. Any transceiver settings modified by CC commands will
revert to the values stored in the EEPROM.
www.aerocomm.com
Command: <0xCC> <0xC1> <Start> <Length> <Data>
Number of Bytes Returned: 3
Response: <Start> <Length> <Last byte>
Parameter Range:
<Start> = EEPROM address to begin writing at
<Length> = Length of data to be written (Max = 0x50)
<Data> = Data to be written
<Last byte> = Value of last byte written
Command: <0xCC> <0xFF>
Number of Bytes Returned: None
Response: None
Page 39

CONFIGURING THE ZB2430
34
Soft Reset with NV reset
The OEM Host issues this command to perform a soft reset of the
transceiver and to erase the network settings stored in the radio’s
non-volatile memory. Any transceiver settings modified by CC
commands will revert to the values stored in the EEPROM.
Command: <0xCC> <0xFF> <0xE3>
Number of Bytes Returned: None
Response: None
Page 40

EEPROM PARAMETERS
8
The OEM Host can program various parameters that are stored in EEPROM and become active after a power-on
reset. The table below gives the locations and descriptions of the parameters that can be read/written by the OEM
Host. Factory default values are also shown. Do not write to any EEPROM addresses other than those listed below.
Do not copy one transceiver’s EEPROM to another transceiver as doing so may cause the transceiver to malfunction.
Table 9: EEPROM Parameters
Parameter
Product ID 0x00 40 Product identifier string. Includes revision infor-
Channel Mask 0x30 4 0x07FFF800 When Channel Select is enabled in EEPROM,
End Device Poll Rate 0x34 2 0x0000 -
Channel Number 0x40 1 0x0B -
Baud Rate 0x42 1 0x00 -
Baud_M 0x43 1 0x00 -
Baud_E 0x44 1 0x00-
EEPROM
Address
Length
(Bytes)
Range Default Description
mation for software and hardware.
tells the radio the available channels to use in
Channel Select mode.
0xFFFF
0x1A
0x08,
0xE3
0xFF
0xFF
0x03E8 Specifies how often the End Device will wakeup
0x0B RF Channel Number. Used when Channel
0x06 0x00: 1200
0xFF Used to calculate baud rate when Custom
0xFF Used to calculate baud rate when Custom
from Sleep Mode. and request data from its
parent. 1 ms per increment.
Note: Valid only for End Devices
Select mode is disabled.
0x01: 2400
0x02: 4800
0x03: 9600
0x04: 19200
0x05: 31250
0x06: 38400
0x07: 57600
0x08: 115200
0xE3: Enable Custom Baud rate
Note: If any value ofther than 0x00-0x08 or 0xE3
is used, the radio will default to 9600 baud.
Baud Rate is enabled.
Baud Rate is enabled.
MAC Retries 0x4B 1 0x00 -
Transmit Attempts 0x4C 1 0x01 -
www.aerocomm.com
0x07
0x07
0x03 Specifies the number of retries to use at the
0x02 Specifies the maximum number of transmit
MAC level. A setting of 0x03 actually sends the
packet up to 4 times. MAC retries can be set to
0x00, but since they occur faster than the transmit retries, the default setting is typically recommended.
retries. When MAC retries is not set to 0x00, the
actual amount of transmit attempts is equal to
MAC retries x Transmit Attempts. Transmit
attempts occur at a slower rate than MAC
retries.
Page 41

EEPROM PARAMETERS
36
Table 9: EEPROM Parameters
Parameter
Broadcast Attempts 0x4D 1 0x00 -
Stale Limit 0x4F 1 0x01-
Control 1 0x56 1 0x01 -
Interface Timeout 0x58 1 0x02 -
RF Packet Size 0x5A 2 0x0001 -
EEPROM
Address
Length
(Bytes)
Range Default Description
0x05
0xFF
0xFF
0xFF
0x0054
0x04 Specified the maximum number of times to
0x32 Specifies amount of time to keep a radio in the
0x43 Settings are:
0x04 Specifies a byte gap timeout, used in conjunc-
0x0054 Specifies the RF packet size.
broadcast a packet. Attempts occur at 500ms
intervals.
Radio Table without having received a packet
from that particular radio. Prevents retries from
being interpreted as new packets. Adjustable
in 100 ms increments.
bit-7: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-6: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-5: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-4: Auto Destination
0 = Use Destination Address
1 = Use Auto Destination
bit-3: Channel Select
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
bit-2: RTS Enable
0 = Ignore RTS
1 = Transceiver obeys RTS
bit-1: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-0: Aerocomm Use Only
tion with RF Packet Size to determine when a
packet coming over the interface is complete.
Note: 1 ms per increment.
Note: RF packet size needs to be set to a minimum of six bytes in order to use the Enter AT
command.
CTS On 0x5C 2 0x0001 -
CTS Off 0x5E 2 0x0001 -
Power Control 0x63 1 0x00 -
Destination ID 0x76 2 0x00 -
PAN ID 0x78 2 0x00 -
0x01C0
0x01C0
0x03
0xFF
0xFF
0x01C0 CTS will be deasserted (High) when the Trans-
0x01B0 Once CTS has been deasserted, CTS will be
0x00 Determines output power of transceiver.
R/E: 0x0000
C: 0x0001
0x0001 Similar to network password. Radios must
mit buffer contains at least this many characters
reasserted (Low) when the transmit buffer contains this many or less characters.
ZB2430-Q ZB2430-D
0x00: 17 dBm 0x00: 3 dBm
0x01: 11 dBm 0x01: -3 dBm
0x02: 5 dBm 0x02: -9 dBm
0x03: -1 dBm 0x03: -15 dBm
Specifies destination for RF packets.
have the same PAN ID to associate with each
other.
Page 42

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Table 9: EEPROM Parameters
EEPROM PARAMETERS
37
Parameter
MAC ID 0x80 8 0x00 -
Part Number 0x90 16 0x00 -
API Control 0xC1 1 0x00 -
RSSI Threshold 0xC8 1 0x00 -
D.O.B. 0xE0 4 Provides factory calibration and test date.
EEPROM
Address
Length
(Bytes)
Range Default Description
0xFF
0xFF
0xF8 Settings are:
0xFF
0xFF
Factory programmed 8 byte unique IEEE MAC
address.
Note: This address is write protected and cannot be modified.
Provides part number information. EEPROM
byte 0x95 can be read to determine device type
(C, R, or E).
bit-7:Aerocomm Use Only
bit-6: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-5: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-4: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-3: Aerocomm Use Only
bit-2: Enable API Send Data Complete
0 = Disabled
1 = Enable
bit-1: Enable Transmit API
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
bit-0: Enable Receive API
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
The minimum RSSI required. Packets sent
from a transceiver whose RSSI does not currently meet this threshold will be discarded.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 43

API OPERATION
API Operation is a powerful alternative to the default Transparent operation of the ZB2430 and provides dynamic
packet routing and packet accounting abilities to the OEM Host without requiring extensive programming by the OEM
Host.. API operation utilizes specific packet formats; specifying various vital parameters used to control radio settings
and packet routing on a packet-by-packet basis. The API features can be used in any combination that suits the
OEM’s specific needs and can be different between radios operating on the same network.
API Transmit Packet
API Transmit Packet is a powerful command that allows the OEM Host to send data to a single or multiple (broadcast)
transceivers on a packet-by-packet basis. This can be useful for many applications; including polling and/or mesh
networks.
API Transmit Packet is enabled when bit-1 of the API Control byte is enabled. The OEM Host should use the format
shown in Figure 12 below to transmit a packet over the RF.
Figure 12: Transmit API packet format
9
Start Delimiter
0x81
Byte 2: Payload Dat a Le ng t h
Byte 3: Reserved. Set to 0x00
Byte 4: Number of Transmit Retries
Byte 5: Reserved. Set to 0x00
Bytes 6-7: 16-bit Network Destination Address
0x - - - -: Unicast (addressed)
0xFFFC: Broadcast to all Routers & Coordinator
0xFFFD: Broadcast to all with RXOnWhenIdle = True
0xFFFF: Broadcast to all Devices
Bytes 8-n: Payload Data
API Send Data Complete
API Send Data complete can be used as a software acknowledgement indicator. When a radio sends an addressed
packet, it will look for a received acknowledgement (transparent to the OEM Host). If an acknowledgement is not
received, the packet will be retransmitted until one is received or all retries have been exhausted.
For applications where data loss is not an option, the OEM Host may wish to monitor the acknowledgement process
using the API Send Data Complete. If an acknowledgement is not received (Failure), the OEM Host can send the
packet to the transceiver once again.
API Send Data Complete is enabled when bit-2 of the API Control byte is enabled. The transceiver sends the OEM
Host the data shown in Figure 13 upon receiving an RF acknowledge or exhausting all attempts.
Request
Data
Data
www.aerocomm.com
Page 44

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
Figure 13: Send Data Complete packet format
API OPERATION
39
Start Delimiter
0x82
Byte 2: TX Cost
Byte 3: RX Cost
Byte 4: Success
0x00: Fail
0x01: Success
Request
Data
Data
API Receive Packet
By default, the source MAC is not included in the received data string sent to the OEM Host. For applications where
multiple radios are sending data, it may be necessary to determine the origin of a specific data packet. When API
Receive Packet is enabled, all packets received by the transceiver will include the MAC address of the source radio as
well as an RSSI indicator which can be used to determine the link quality between the two.
API Receive Packet is enabled when bit-0 of the API Control byte is enabled. Upon receiving a RF packet, the radio
sends its OEM Host the data as shown in Figure 14 below.
Figure 14: Receive API packet format
Start Delimiter
0x81
Request
Data
Data
Bytes 2-3: Payload Data Length. PDL Lo then PDL Hi.
Byte 4: RSSI
Byte 5-6: 16-bit Network Source Address
Bytes 7-n: Payload Data
www.aerocomm.com
Page 45

ZB2430 ADDRESSING
Every ZB2430 transceiver module has a unique static 64-bit MAC address that is programmed at the factory. Upon
joining the network, the device is assigned a 16-bit NWK Address. The NWK address only changes on initial power-up
adn when an NV Reset command is issued to the radio.
In Figure 15 below, 4 nodes with each of their associated MAC addresses are shown.
Figure 15: ZigBee Addressing by MAC - Node 0 to Node 3
10
In previous sections (see “Mesh Routing (AODV)” on page 15), the Ad-Hoc On-Demand Vector routing protocol,
Route Requests and Replies were discussed. Fortunately, the routing, RREQ’s and RREP’s are not left up to the OEM
Host and are all taken care of by the ZigBee protocol embedded in the ZB2430. A message can therefore be sent to
a device anywhere on the network once its 16-bit NWK address is known.
Using the same example as before, assume that Node 0 needs to send a message to Node 3 which is out of Node 0’s
range. This can be done using the procedure below (note that the underlined values will vary from radio to radio):
1. Enter AT Command Mode: .....................................................0x41 0x54 0x2B 0x2B 0x2B 0x0D
2. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x43 0x4F 0x0D
3. Discover NWK Address:.......................................................... 0xCC 0x8D 0x56 0x78 0x90
4. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x00 0x01
5. Write 16-bit Destination NWK address:................................... 0xCC 0x10 0x00 0x00 0x01
6. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x00 0x00 0x01
7. Exit AT Command Mode:........................................................0xCC 0x41 0x54 0x4F 0x0D
www.aerocomm.com
Page 46

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
8. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x44 0x41 0x54
9. Send data to device
Figure 16: ZigBee Addressing by MAC - Node 0 to Node 2
ZB2430 ADDRESSING
41
Next, assume that Node 1 needs to send a message to Node 2, which is also out of it’s range. The procedure is the
essentially the same as above (see Figure 16: "ZigBee Addressing by MAC - Node 0 to Node 2"). Note that the
underlined values will vary from radio to radio.
1. Enter AT Command Mode: .....................................................0x41 0x54 0x2B 0x2B 0x2B 0x0D
2. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x43 0x4F 0x0D
3. Discover NWK Address:.......................................................... 0xCC 0x8D 0x22 0x11 0x33
4. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x14 0x3E
5. Write 16-bit Destination NWK address:................................... 0xCC 0x10 0x00 0x14 0x3E
6. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x00 0x14 0x3E
7. Exit AT Command Mode:........................................................0xCC 0x41 0x54 0x4F 0x0D
8. Wait for command response:.................................................. 0xCC 0x44 0x41 0x54
9. Send data to device
www.aerocomm.com
Page 47

ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
Some applications may require a more extensive knowledge of the Network and its current configuration. For this
reason, the ZB2430 includes several advanced commands which can be issued anytime the radio is in Command
mode. Each of these commands include a 16-bit Return Mask which allows the OEM Host to select the information
returned in the command response.
Note: All unused bits in the Return Mask should be set to “0”.
11
Read Neighbor Table
The Neighbor Table stores information about neighboring devices which are operating on the same RF Channel but
different PAN ID. To read a device’s Neighbor Table, use the command format shown in Figure 17 below.
Command Definitions
• Start Index: Starting index within the Neighbor Table to begin reporting.
• Count: Number of entries to include in Neighbor Table. Maximum number of indexes = 8 (Coordinator and
Routers) and 4 (End Devices).
• Index Number: Index location of radio in Route Table.
• NWK Address: 16-bit NWK address of the neighboring device.
• PAN ID: The 16-bit PAN ID of the network to which the device belongs.
• TX Cost: Counter of transmission (success/failures)
• RX Cost: Average of received RSSI values for the specified device
Figure 17: Read Neighbor Table Command
Start Delimiter
0xCC
After issuing the Read Neighbor Table command, the radio will respond with the requested information as shown in
Figure 18 below. The actual command response format may vary depending on the Return Mask setting used in the
command.
Command Identifier
0x88
Count (Byte 3)
0x00: Show all entries between
Start Index and maximum
0x01: Show entry at Start Index
0x02: Show entries between
Start Index and (Start Index + 1)
etc.
Request
Data
Start Index (Byte 4)
0x00: Index to start
reporting at
Return Mask (Bytes 5-6)
bit 0: Index number
bits 1-2: NWK Address
bits 3-4: PAN ID
bit 5: TX cost
bit 6: RX cost
bits 7: Security Key sequence number
bits 8-11: Security Frame counter
bit 12-15: Reserved. Set to 0.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 48

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
Figure 18: Read Neighbor Table Response
43
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Command Identifier
0x88
Length
1 Byte
Status (Byte 4)
0x00: Success
0x01: Fail
Request
Data
Response (Bytes 5-n)
(Repeated for each radio)
Byte 5: Index number
Bytes 6-7: NWK Address
Bytes 8-9: PAN ID
Byte 10: TX Cost
Byte 11: RX Cost
Byte 12: Security Key Sequence number
Bytes 13-16: Security Frame Counter
www.aerocomm.com
Page 49

ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
44
Read Route Table
ZigBee Coordinators and Routers maintain a routing table which is used to establish a route to a particular destination
device.
Note: This command not valid for End Devices.
Command Definitions
• Count: Number of entries to include in Route Table. Maximum number of indexes = 20 (Coordinator and
Routers)
• Start Index: Starting index within the Route Table to begin reporting.
• Index Number: Index location of radio in Route Table.
• Destination Address: The 16-bit NWK address of the route.
• Next Hop Address: The 16-bit NWK address of the next radio on the way to the destination.
• Expiry Time: A countdown timer indicating the number of milliseconds until route discovery expires.
• Status: The status of the route.
Figure 19: Read Route Table Command
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Command Identifier
0x89
Count (Byte 3)
0x00: Show all entries between
Start Index and maximum
0x01: Show entry at Start Index
0x02: Show entries between Start
Index and (Start Index + 1)
etc.
Figure 20: Read Route Table Response
Command Identifier
0x89
Request
Data
Start Index (Byte 4)
0x00: Index to start
reporting from
Length
1 Byte
Status (Byte 4)
0x00: Success
0x01: Fail
Return Mask (Bytes 5-6)
bit 0: Index number
bits 1-2: Destination Address
bits 3-4: Next Hop Address
bit 5: Expiry Time
bit 6: Status
bits 7-15: Reserved. Set to 0.
Request
Data
Response (Bytes 5-n)
Byte 5: Index number
Bytes 6-7: Destination Address
Bytes 8-9: Next Hop Address
Byte 10: Expiry Time
Byte 11: Status
Page 50

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
Perform Scan
ZigBee Coordinators and Routers can manually scan selected channels for RF activity and other ZigBee devices/PAN
ID’s, etc.
Note: This command not valid for End Devices.
Command Definitions
• Scan Channel: A 32-bit channel mask specifying the channel(s) to include in the scan.
• Scan Type: Specifies the type of scan to perform. If Energy scan is selected, the device will tune to each
channel & perform an energy measurement. If Active scan is selected, the device tunes to each channel,
send a beacon request and listen for beacons from other ZigBee devices.
• Scan Duration: Duration of the Active & Energy scans on each channel selected. Time is measured as:
(48ms) x 2^(Scan Duration + 1)
• Max Results: The maximum number of results to report for Active scans. Ignored with Energy scan command.
• Status: Indicates the status of the current scan.
• Channel Number: 8-bit channel current measurement was taken from.
• Energy: The strength of the RF channel during the Energy scan.
• NWK Address: 16-bit NWK address of the neighboring device.
• PAN ID: The 16-bit PAN ID of the network to which the device belongs.
• Link Quality: The strength of the link between the current device and the device found during the Active scan.
45
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Scan Channel (Bytes 3-6)
32-bit channel mask
describing channels to scan
Figure 21: Perform Scan Command
Command Identifier
0x8B
Scan Type (Byte 7)
0x00: Energy detect scan
0x01: Active scan
Request
Data
Scan Duration (Byte 8)
Range: 0x00-0x0E
Reserved (Byte 9)
Reserved.
Set to 0x00.
Max Results (Byte 10)
Maximum number
of results to return
www.aerocomm.com
Page 51

ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
46
Figure 22: Perform Scan Response
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Status (Byte 5)
0x00: Success
0x1A: Fail – Insufficient RAM Resources
0xFC: Scan already in progress
Command Identifier
0x8B
Length
1 Byte
Scan Type (Byte 6)
0x00: Energy detect scan
0x01: Active scan
Request
Data
Reserved (Byte 7)
Reserved
Response (Bytes 8-n)
if Scan Type = 0x00
Byte 8: Channel Number
Byte 9: Energy
if Scan Type = 0x01
Byte 8: Channel Number
Bytes 9-10: NWK Address
Bytes 11-12: PAN ID
Byte 13: Link Quality
Page 52

ZB2430 User’s Manual - v1.6
ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
Read Radio Table
The Radio Table contains information about the last 8 devices which the radio has received data from. The Radio
Table stores relationship and link-state information which updates everytime the radio receives a packet from that
device. To read a device’s Radio Table, use the command format shown in Figure 23 below.
Note: This command not valid for End Devices.
Command Definitions
• Index Number: Index location of radio in Radio Table (range = 0-20).
• NWK Address: 16-bit NWK address of the device.
• Node Relation: The type/relation of the device.
• Device Status: Status of the link between the two devices.
• TX Cost: Counter of transmission (success/failures)
• RX Cost: Average of received RSSI values for the specified device
Figure 23: Read Radio Table Command
47
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Command Identifier
0x8C
Device Type (Byte 3)
0x00: All
0x01: Parent
0x02: Children
0x03: Radio at index
Request
Data
Index (Byte 4)
Radio Index in table.
(Only valid when Device
Type = 0x03)
Return Mask (Bytes 5-6)
bit 0: Index number
bits 1-2: NWK Address
bits 3-4: Address index
bit 5: Node relation
bit 6: Device Status
bit 7: Association Count
bit 8: TX cost
bit 9: RX cost
bits 10: Security Key sequence number
bits 11-14: Security Frame counter
bit 15: Reserved. Set to 0.
After issuing the Read Radio Table command, the radio will respond with the requested information as shown in
Figure 24 below. The actual command response format may vary depending on the Return Mask setting used in the
command.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 53

ADVANCED NETWORK COMMANDS
48
Figure 24: Read Radio Table Response
Start Delimiter
0xCC
Command Identifier
0x8C
Length
1 Byte
Status (Byte 4)
0x00: Success
Request
Data
Response (Bytes 5-n)
(Repeated for each radio)
Byte 5: Index number
Bytes 6-7: NWK Address
Bytes 8-9: Address index
Byte 10: Node relation
0x00: Parent
0x01: Child RFD
0x02: Child RFD RX Idle
0x03: Child FFD
0x04: Child FFD RX Idle
0x05: Neighbor
Byte 11: Device Status
Byte 12: Association Count
Byte 13: TX Cost
Byte 14: RX Cost
Byte 15: Security Key Sequence number
Bytes 16-19: Security Frame Counter
Page 54

DIMENSIONS
ZB2430 MECHANICAL
Figure 25: ZB2430 Mechanical Drawing
12
0.131
0.031
0.000
1.000
0.985
0.619
22
19
Bottom View
1
18 10
Side View
Top View
9
Bottom Pads
0.060 by 0.050 typ.
RF Shield
0.760
0.675
0.381
0.015
0.000
0.000
0.015
0.205
0.079
typ.
1.040
0.810
0.837
1.350
Notes:
All dimensions are +/- .005 inches
PC Board Material is 0.031 thick FR4
Board edge connections are 1/2 of 0.031 plated holes
www.aerocomm.com
0.325
0.000
Page 55

ORDERING INFORMATION
PRODUCT PART NUMBERS
13
www.aerocomm.com
Page 56

COMPLIANCY INFORMATION
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed below, and having a maximum gain of 5 dB.
Antennas not included in this list or having a gain greater than 5 dB are strictly prohibited for use with this device.
The required antenna impedance is 50 ohms.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain schuld be so chosen that the
equivalent isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that permitted for successful communication.
14
AGENCY IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS
Agency compliancy is a very important requirement for any product development. Aerocomm is in the process of
obtaining modular approval for its ZB2430 product family so that the OEM only needs to meet a few requirements to
use that approval. The corresponding agency identification numbers and approved antennas are listed below.
Table 10: Agency Identification Numbers
Part Number US/FCC CANADA/IC ETSI
ZB2430-D KQL-ZB2430D 2268C-ZB2430D Approved
ZB2430-100 KQL-ZB2430-100 2268C-ZB2430 Pending
APPROVED ANTENNA LIST
Table 11: ZB2430 Approved Antenna List
Aerocomm Part
Number
- FR05-S1-N-o-001 Fractus Integral Chip 2 - X
0600-00039 S151FC-L-(132)PX-2450S Nearson Omni 5 X X
Manufacturer Part
Number
WIC2450-A Laird/Centurion Chip 2 X -
Manufacturer Type
Gain
(dBi)
ZB2430-D
ZB2430-100
FCC / IC REQUIREMENTS FOR MODULAR APPROVAL
In general, there are two agency classifications of wireless applications; portable and mobile.
Portable - Portable is a classification of equipment where the user, in general, will be within 20 cm of the transmitting
antenna. Portable equipment is further broken down into two classes; within 2.5 cm of human contact and beyond
2.5 cm (Note: Ankles, feet, wrists, and hands are permitted to be within 2.5 cm of the antenna even if the equipment is
designated as being greater than 2.5 cm). The ZB2430 is not agency approved for portable applications. The OEM is
required to have additional testing performed to receive this classification. Contact AeroComm for more details.
www.aerocomm.com
Page 57

COMPLIANCY INFORMATION
52
Mobile - Mobile defines equipment where the user will be 20 cm or greater from the transmitting equipment. The
antenna must be mounted in such a way that it cannot be moved closer to the user with respect to the equipment,
although the equipment may be moved. (Note: Ankles, feet, wrists, and hands are permitted to be within 20 cm of
mobile equipment).
OEM EQUIPMENT LABELING REQUIREMENTS
WARNING: The OEM must ensure that FCC labeling requirements are met. This includes a clearly visible label on the
outside of the OEM enclosure specifying the appropriate AeroComm FCC identifier for this product as well as the FCC
notice below. The FCC identifiers are listed above.
Contains FCC ID KQL-ZB2430-100
Contains FCC ID KQL-ZB2430D
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Label and text information should be in a size of type large enough to be readiily legible, consistent with the
dimensions of the equipment and the label. However, the type size for the text is not required to be larger than eight
point.
ANTENNA REQUIREMENTS
WARNING: This device has been tested with a U.FL connector with the above listed antennas. When integrated into
the OEM’s product, these fixed antennas require professional installation preventing end-users from replacing them
with non-approved antennas. Any antenna not listed in the above table must be tested to comply with FCC Section
15.203 for unique antenna connectors and Section 15.247 for emissions. Contact AeroComm for assistance.
Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by AeroComm could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment.
WARNINGS REQUIRED IN OEM MANUALS
WARNING: This equipment has been approved for mobile applications where the equipment should be used at
distances greater than 20 cm from the human body (with the exception of hands, feet, wrists, and ankles). Operation
at distances of less than 20 cm is strictly prohibited and requires additional SAR testing.
CHANNEL WARNING
The OEM must prevent the end-user from selecting a channel not approved for use by the FCC.
 Loading...
Loading...