Page 1

Compact Reader ARE i2-LF
Installation Guide
for Systems with a
Serial Interface RS 232
Page 2

1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................ 4
2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW .................................................................................................... 4
3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................. 5
3.1 Mounting of the housing ............................................................................................................................ 5
3.2 Grounding of the reader ............................................................................................................................ 5
3.2.1 Connecting of the plug ........................................................................................................................ 6
3.3 Connecting of the power supply cable ........................................................................................................ 7
3.3.1 Using the pc connection cable ID 70213 ............................................................................................. 7
3.3.2 Using the switchboard cable ID 70212 ................................................................................................ 7
3.3.3 Using a self assembled connecting cable .............................................................................................. 7
3.3.3.1 Assembling of the cable pipe ........................................................................................................ 8
3.3.3.2 Mounting of the cable ................................................................................................................. 8
3.3.3.3 Pin assignment of the SAB connectors ....................................................................................... 10
3.4 Mounting of the external antenna / of the AMP 4 / AMP 8 ...................................................................... 11
4 VISUAL SIGNAL LAMPS ............................................................................................ 12
5 INSTRUCTION SET / STRUCTURE OF THE INSTRUCTION SET ............................... 13
5.1 General ................................................................................................................................................... 13
5.1.1 Entering instuctions ......................................................................................................................... 13
5.1.2 Output format .................................................................................................................................. 13
5.1.2.1 Instruction specific output ......................................................................................................... 14
5.1.2.2 Output after changing a parameter ............................................................................................ 14
5.1.2.3 Output at parameter query ......................................................................................................... 14
5.1.3 Blank instuction ............................................................................................................................... 15
5.1.4 Incorrect instruction / error codes ..................................................................................................... 15
5.1.5 Upper and lower case ....................................................................................................................... 15
5.1.6 Linefeed ........................................................................................................................................... 15
5.2 Instructions for the hardware settings...................................................................................................... 16
5.2.1 BD - baudrate .................................................................................................................................. 16
5.2.2 EC – echo function ........................................................................................................................... 16
5.3 Instructions for the reading settings......................................................................................................... 17
5.3.1 GT – single transponder code reading ............................................................................................... 17
5.3.2 CID – Suppression of ID Codes ......................................................................................................... 17
5.3.3 CN – Suppression of No Reads ......................................................................................................... 18
5.3.4 NID – Failure Protection .................................................................................................................. 19
5.3.5 TOR – Maximum reading time .......................................................................................................... 19
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------2/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 3

5.4 Instructions for the memory settings ........................................................................................................ 20
5.4.1 VER – Reader firmware ................................................................................................................... 20
5.4.2 VS – Show parameter ....................................................................................................................... 20
5.4.3 VSAVE – Save parameter ................................................................................................................ 21
5.4.4 RST – Warm start ............................................................................................................................ 21
5.4.5 INIT – Warmstart with default parameters ....................................................................................... 21
6 OPERATING MODES OF THE READER ...................................................................... 22
6.1 MD 2 - Triggered by an Software Command ............................................................................................ 22
6.2 MD 0 - Continuous Reading ..................................................................................................................... 23
7 STARTUP AND TESTING THE READER .................................................................... 24
8 BASIC DATA EXCHANGE PROCESS .......................................................................... 25
8.1 Selective read RD ................................................................................................................................... 25
8.2 Writing WD............................................................................................................................................. 26
9 INSTRUCTIONS .......................................................................................................... 27
9.1 General Instructions ................................................................................................................................ 27
9.2 Special Instructions for Using a Read / Write System .............................................................................. 28
10 CERTIFICATIONS .................................................................................................... 30
10.1 By FCC, Federal Communications Commission ..................................................................................... 30
10.2 By KCC, Korean Communications Commission ..................................................................................... 31
11 HOTLINE .................................................................................................................. 31
12 REVISIONS .............................................................................................................. 32
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------3/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 4

1 Introduction
This document will describe the components of the Compact Reader System ARE i2 / RS 232 and the
procedure how to do the first set up of the reader.
The main features of the reader are listed below:
• the antenna is placed inside of the housing
• there are algorithm available to read nearly all 125 kHz-transponders on market
• integrated RS232 Interface with tunable baud rate are up to 19200 Bit/s
• the allowed supply voltage is 9 to 30V DC
• low power consumption of reader < 1.2 Watt
• high reliability for reading and writing within an industrial environment
• compact housing of the reader with multiple ways for mounting
• the cabling concept of the reader is optimised to service demands
• the protection class of the housing is IP65
• there is a set of external antennas available to meet special application demands ( X-tended version)
2 System overview
In the base version all electronic components of the reader are placed inside of a small plastic housing.
By means of the integrated antenna the reader generates an alternating magnetic field, which powers the
transponder. Coded signals sent back from the transponder are received and decoded by the reader. The
reader is fully controlled by a master with RS 232 data port, while using the integrated serial RS 232
interface of the reader.
There is a version available without the integrated antenna. On this version it is possible to connect an
external antenna.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------4/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 5
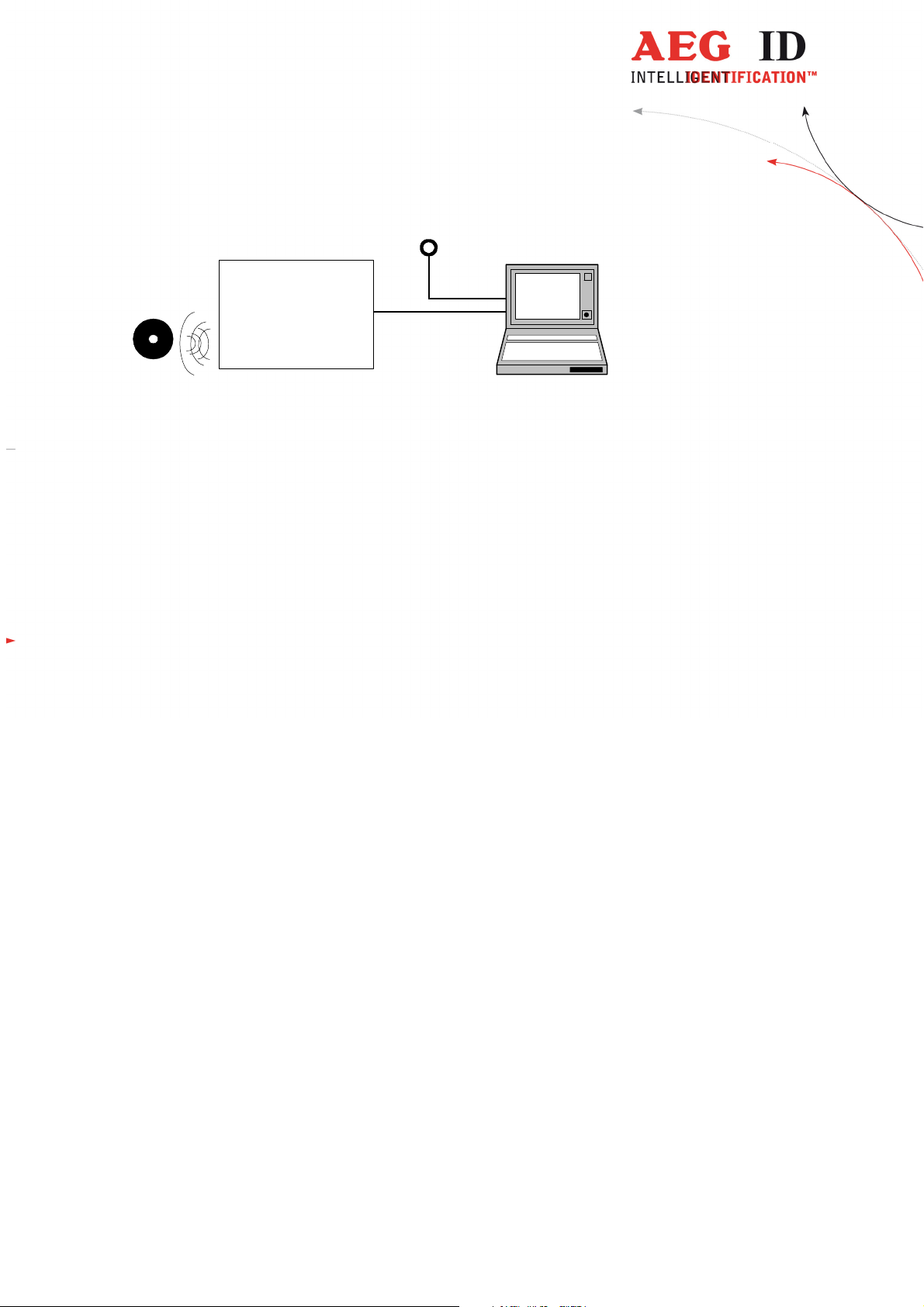
transponder
reader with
integrated
antenna
(9-Pin SubD)
ARE i2
Figure 1: Concept of the reading system
3 Installation
24V
RS232
DC
To get the specified reading performance it is necessary to do the installation carefully step by step as it
is described in the following Chapters. All the work must be done by well educated people.
3.1 Mounting of the housing
The reader can be mounted to any other mechanic construction. The distance between reader and transponder has to tuned
It is recommended to protect the housing against heavy mechanical interactions and drippy fluids.
Attention!
The side of the housing showing the antenna symbol must not be brought next to a metal surface. This
could lead to a significant change of the properties of the antenna circuit, which in turn reduces the
reading range considerably.
With the help of the plastic bars, the reader can mounted or screwed on to the most fastening elements
without open the housing of the device.
3.2 Grounding of the reader
To get reliable reading results, the reader must be grounded. The connector is placed at the side of the
housing (6.35 mm flat contact).
To avoid EMV-problems, the cable to ground ought to be very short with low impedance.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------5/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 6
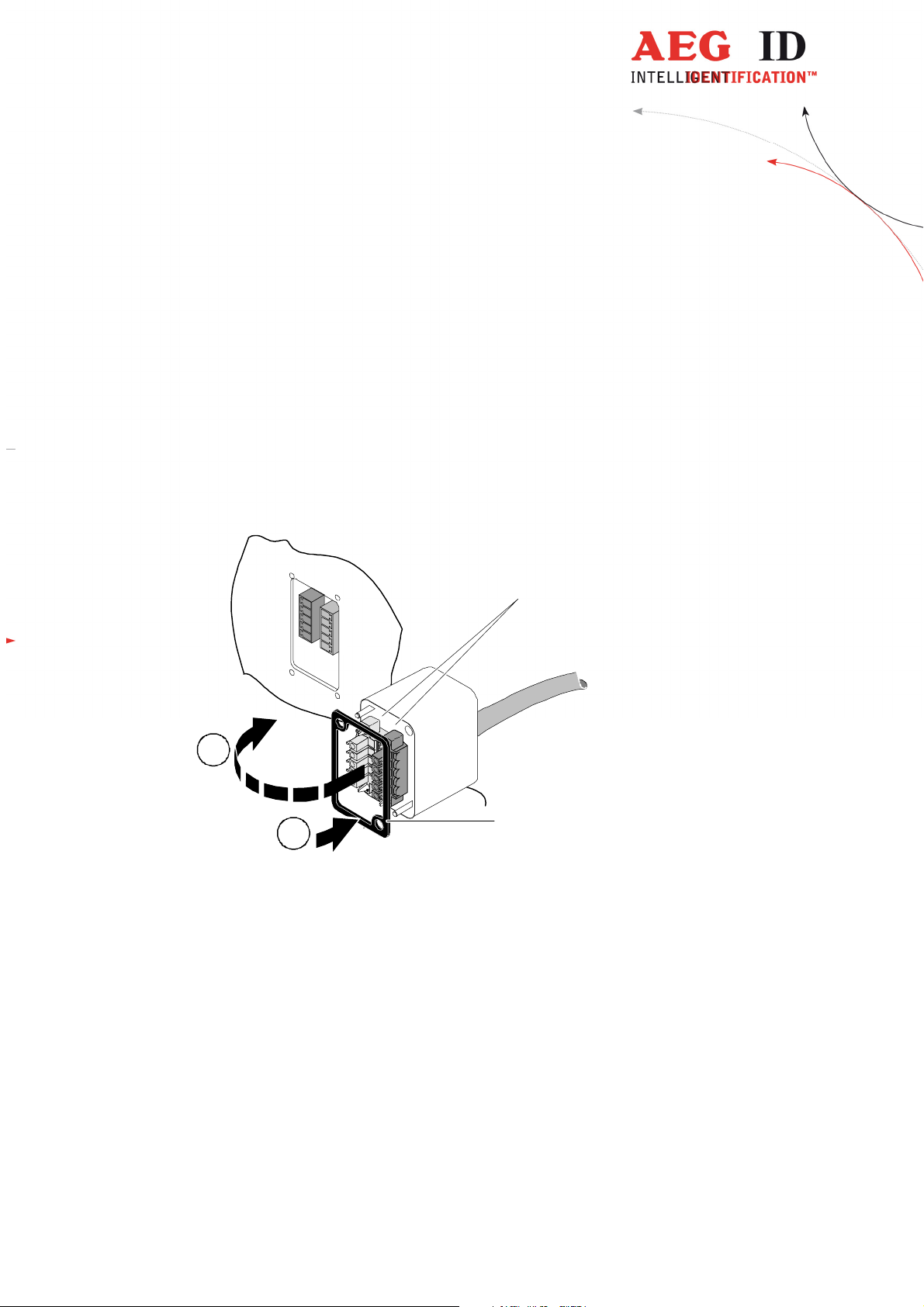
Attention!
The topology of the ground wires must be done in the right way (according state of art).
3.2.1 Connecting of the plug
Attention!
Be sure that the grounding of the reader is well done and the power supply is not connected(chapter 3.2).
Otherwise the electronic may be destroyed by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1
B
A
Figure 2: Connecting of the plug
Put on the sealing 2 to the SAB Cab (A).
Plug in the SAB Cab to the connector at the bottom of the reader device (B).
There is only one way to plug in the SAB Cab to the connector rim of the reader.
Fasten the SAB Cab with the help of the screws.
2
To meet the protection class of IP 65, it’s necessary to apply a turning moment of 0.5 Nm to the screws.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------6/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 7
3.3 Connecting of the power supply cable
The reader has to be supplied with 9..30V DC. The maximum output power of the power supply has to be
1.2 Watt. Be sure that you use the right polarity.
3.3.1 Using the pc connection cable ID 70213
Power supply: brown = + 9 .. 30 Volt
white = ground
3.3.2 Using the switchboard cable ID 70212
Power supply: brown = + 9 .. 30 Volt
white = ground
Data interface: green = RXD (readers data input)
yellow = TXD (readers data output)
grey = ground
3.3.3 Using a self assembled connecting cable
Using the following SAB cabs you can assemble your own connecting cable.
ID 70211 SAB cab with 1 PG9 cable pipe
ID 70215 SAB cab with 2 pre-assembled cable pipes
ID 70219 SAB cab without any cable pipe
You can use any shielded five-pole cable. The allowed diameter of the cable must be in the range from
∅3,5 to ∅8mm. For this case, IP 65 is reached.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------7/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 8
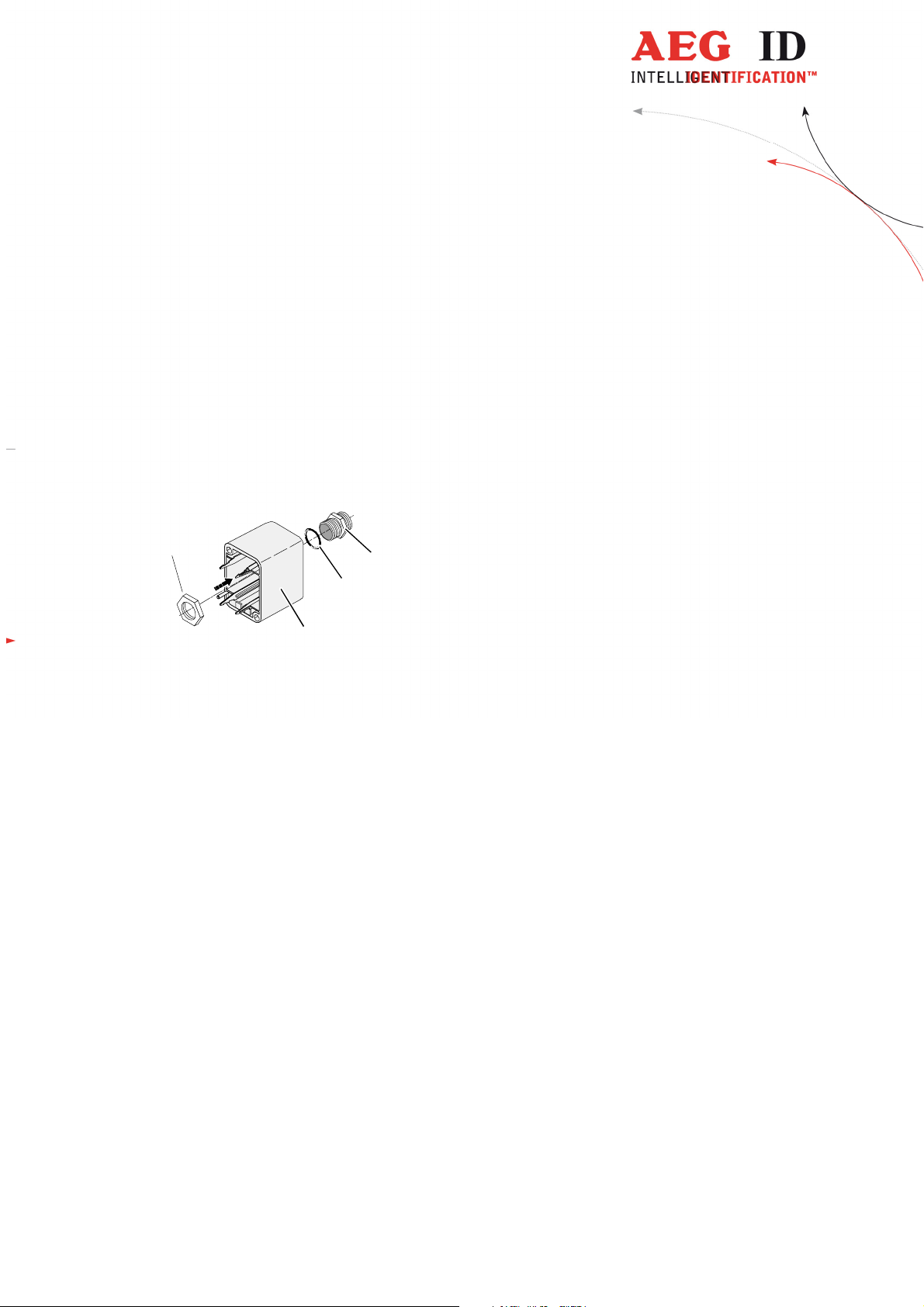
Attention!
The minimum voltage at the readers input mustn’t be lower then 9V.
The maximum length of the serial RS232 cable is 15m.
3.3.3.1 Assembling of the cable pipe
• Breakthrough the prepared areas at the surface of the SAB Cabs. There are two prepared areas seen
at the SAB Cab: central and at one side of the cab.
• The o-ring (3) has to be assembled proberly to the cable pipe (4) to ensure the protection class IP
65.
2
1
4
3
Figure 3: Assembling of the cable pipe
• Bring the nut (2) of the cable pipe inside of the SAB Cab (1).
• To fasten the nut please use the right tool (17mm).
3.3.3.2 Mounting of the cable
The cable must be mounted in following steps:
• Remove all inner parts from the cable pipe at the SAB Cab (1) ( nut (5), cable fastener (3), pipe(4))
(see Figure 4)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------8/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 9
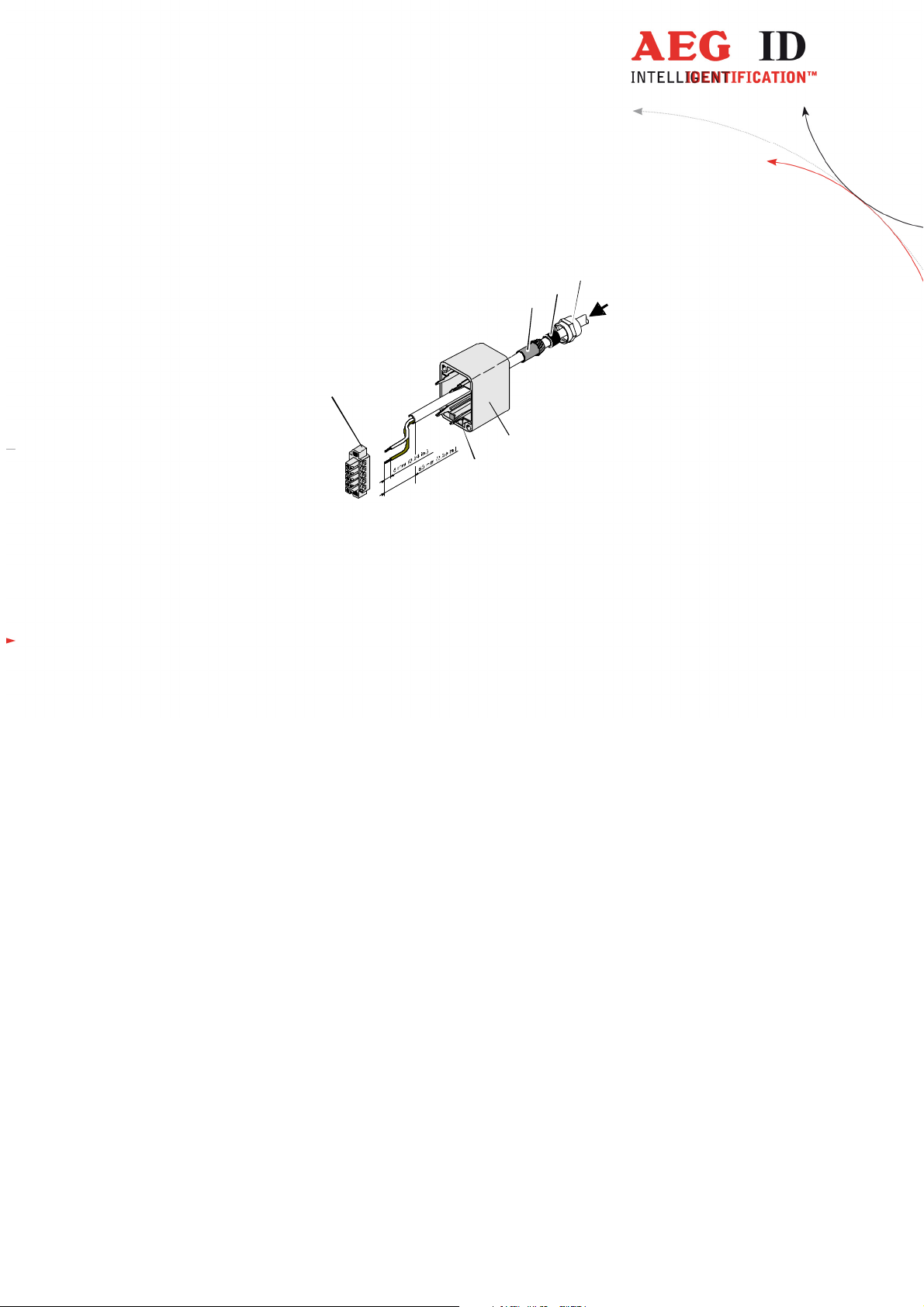
• Put all the removed parts (nut (5), cable fastener (3), pipe (4),) and the cable pipe of the SAB Cab
as well (1 to 4) to the cable.
3
5
4
Cable
6
1
7
Figure 4: Mounting for the cable
• Remove the outer isolation of the cable at a length of 6cm .
• Remove the isolation of the wires at a length of 6mm and stick a covering hull to the litz wire.
• Put the cable to the cable pipe. The length of the cable coming out the SAB Cab must long enough to
do all further installation steps in an easy way.
• Stick the pipe (4) into the cable fastener (3).
• Stick the cable fastener (3) into the cable pipe.
• Connect the cables into the right places of the MINI-COMBICON-Connectors (6).
• The pin assignment is shown in the figure below.
• Put the MINI-COMBICON-Connectors into the SAB cab. Look after the color coding.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------9/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 10
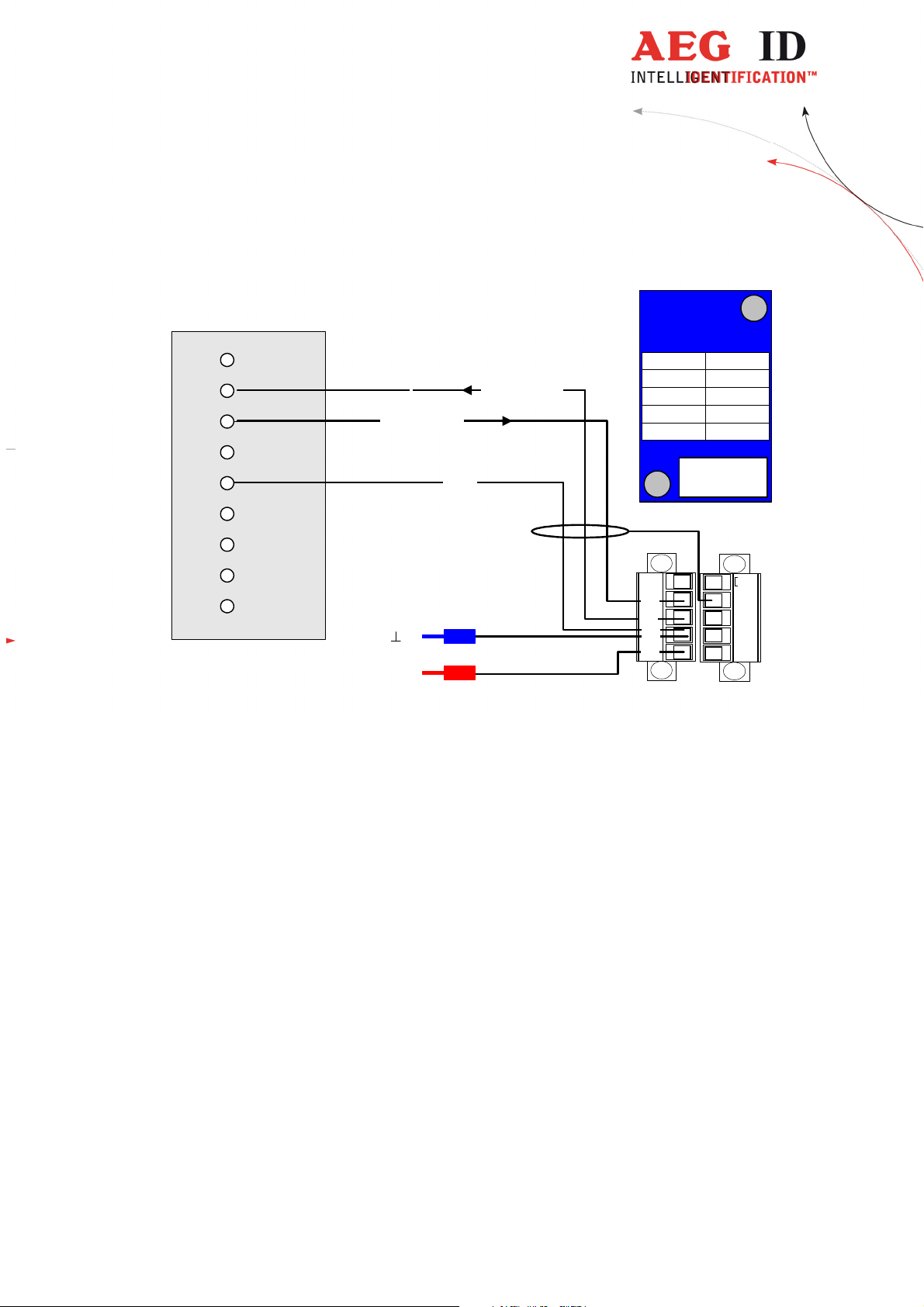
3.3.3.3 Pin assignment of the SAB connectors
RS232
(9 Pins Sub-D female)
1
2
3
4
5
RxD (reader)
GND
TxD (reader)
RXD
TXD
GND (0V)
V+ (+24V)
shielding
ARE I2
6
7
8
9
V+
DC
Figure 5: Pin assignment of the SAB connectors
green
B
A
D
C
E
black
+U
S1
-U
S1
+U
S2
-U
S2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------10/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 11

RS232
(9 Pins Sub-D female)
1
2
3
4
5
6
RxD (reader)
GND
TxD (reader)
RXD
TXD
GND (0V)
V+ (+24V)
shielding
ARE I2
7
8
9
V+
DC
grey
G
F
J
H
K
blue
+U
S
-U
S
L
U
L
Figure 6: Pin assignment of the SAB connectors
3.4 Mounting of the external antenna / of the AMP 4 / AMP 8
If you have an i2 with external antenna the connector is on the topside of the reading device. You just
have to plug the antenna into the connector and bold it on. Alternative you can connect an AMP 4 / AMP
8 with this connector, too.
You may not connect or deconnect an antenna or AMP 4 / AMP 8 while the reader is running. It can
cause, that the reader hangs up.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------11/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 12

4 Visual signal lamps
To show the operational state or results there are 5 LED at the side of the housing.
BFH
ID
L1: twinkles, if the processor works.
ARE i2
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L2: lit, if the last reading process was successful
L3: lit, if the last reading process was not successful
L4: lit, if the reader receives data’s at the serial data port (Rx)
L5: lit, if the reader sends data’s at the serial data port (Tx)
Figure 7: Visual signal lamps
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------12/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 13

5 Instruction set / structure of the instruction set
5.1 General
The command set described below defines the transfer of data on the serial interface.
The commands consist of a command code and optionally of a parameter value. Commands are terminated by the control character <CR> (13h). The control character serves as command line terminator.
Command codes and parameters, that means all letters and numerical values, are principally transmitted as a sequence of ASCII characters (the value 255 (decimal) consequently as 32H, 35H, 35H;
the command RST as 52H, 53H, 54H).
5.1.1 Entering instuctions
The protocol format is as follows
Command <SP> parameter <CR>
The space character <SP> separates commands from parameters and the <CR> character acts as
command line terminator.
For commands without parameter values (e.g. GT ) the <SP> character and parameter values are
omitted. The command line is as short as this:
Command <CR>
5.1.2 Output format
Generally, every input terminated by <CR> is acknowledged by the reader. The following response
protocols are different:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------13/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 14

5.1.2.1 Instruction specific output
After entering a valid command without a parameter value, the system answers by sending the parameter value and <CR>. Example:
Command: GT <CR>
Output: Transponder number or No Read <CR>
Command: RST <CR>
Output: If EC is active the boot message, else <CR>
5.1.2.2 Output after changing a parameter
After entering a valid command together with a parameter value, the system answers by sending the
parameter value and <CR>. Example:
Command: MD <SP> 2 <CR>
Output: 2 <CR>
After entering an invalid parameter value, the system answers with the corresponding error code. Error
message:
Command: MD <SP> 4 <CR>
Output: <NAK> #02 <CR>
5.1.2.3 Output at parameter query
Parameter settings can be queried by sending the command without adding a parameter value. Example:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------14/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 15

Command: MD <CR>
Output: 1 <CR>
5.1.3 Blank instuction
If a single <CR> is input, the reader answers with a single <CR>. Example:
Command: <CR>
Output: <CR>
Please note: If echo mode is active, a single <CR> forces the reader to output <CR> <CR> (echo plus
output).
5.1.4 Incorrect instruction / error codes
If a command is not entered correctly, the reader sends one of the following error codes:
Wrong command: <NAK> #00 <CR>
Wrong parameter: <NAK> #02 <CR>
Antenna failure: <NAK> #10 <CR>
5.1.5 Upper and lower case
The instruction set isn’t case-sensitiv.
5.1.6 Linefeed
The reader does never send a linefeed. If you use a terminal your terminal programme can add the
linefeed. You have to choose the option “displace CR with CR LF”.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------15/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 16

5.2 Instructions for the hardware settings
5.2.1 BD - baudrate
The command BD enables the change of the baud rate. The settings are effective after the next warm or
cold start.
Input format: BD <SP> parameter <CR>
Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 4800 baud
1 9600 baud
2 19200 baud
3 38400 baud
Output (example): 2 <CR>
5.2.2 EC – echo function
The command EC changes of the echo function setting.
Input format: EC <SP> parameter <CR>
Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 Echo inactive
1 Echo active
Output (example): 0 <CR>
Note: The default value of the parameter EC depends on the particular reader.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------16/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 17

5.3 Instructions for the reading settings
5.3.1 GT – single transponder code reading
The instruction GT executes one reading and sends back the transponder code of a transponder or the No
Read error code (e.g. „FFFFFFFFFF“ oder „XXXXXXXXXX“).
Input format: GT <CR>
Output (example): 0420212E5F <CR>
5.3.2 CID – Suppression of ID Codes
With CID=1 only the first of in succession identical transponder numbers is output on the serial interface. The possibly following identical transponder numbers are suppressed, as long as no new valid
transponder number is received, processed and output. NoReads do not influence the data filtering.
Input format: CID <SP> parameter <CR>
Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 No suppression
1 Suppression of equal transponder numbers
Output (example): 0 <CR>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------17/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 18

Example: A, B, C are different transponder codes, N is NoRead error code:
Sequence of reading cycles Output sequence
after filtering with
CN=0 und CID=1
N, N, ......,N, A, A, A, ....A, N,N,
.........
N. N, N, A, A, A, N, A, A, B, A,
C, C, C, .......
N, N, ......,N, A, N,
N, .......
N. N, N, A, N, B,
A, C, .....
The settings are directly effective.
Note: The internal reference number is deleted in the following conditions:
• after a cold start
• after a warm start (command line RST <CR>)
• after entering the command line CID <SP> 1 <CR>
This causes that the next transponder code is output definitely.
Output sequence
after filtering with
CN=1 und CID=1
A
A, B, A, C
Note: The filter function CID picks up the results of the complete reading cycles, while the parameter
NID proceeds from the results of single readings! The filter function CID has effect on the serial interface only.
5.3.3 CN – Suppression of No Reads
Through the setting CN=1 all NoRead results are suppressed on the serial interface.
Input format: CN <SP> parameter <CR>
Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 No suppression
1 Suppression of equal transponder numbers
Output (example): 0 <CR>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------18/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 19

5.3.4 NID – Failure Protection
NID specifies the number of identical transponder numbers, which have to appear for the result “successful reading“ within a reading cycle. In the setting NID = 1, two successive readings have to show
the same transponder number.
Input format: NID <SP> parameter <CR>
Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 One out of one
1 Two out of two
Output (example): 1 <CR>
Sequence of readings Lenght of the read-
ing cycle
Result of the reading cycle
NoRead 1 reading NoRead
0000125ED1, 0000125ED1 2 readings 0000125ED1
0000125ED1, 0000126ED1 2 readings NoRead
5.3.5 TOR – Maximum reading time
Timeout for the reader. TOR is used in operation mode 2 as maximum gating time for a reading process. The length of the maximum gating time results from the equation gating_time = TOR * TB.
Default value = Tor 50
The time constant TB (Time Base) has always the default value 100ms.
Input format: TOR <SP> parameter <CR>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------19/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 20

Parameter:
PARAMETER FUNCTION
0 limits the reading process duration of exactly one reading cycle
1 limits the reading process duration to maximum 1 times TB
2 limits the reading process duration to maximum 2 times TB
...
255 limits the reading process duration to maximum 255 times TB
Output (example): 2 <CR>
5.4 Instructions for the memory settings
5.4.1 VER – Reader firmware
With the command VER you get the actual reader firmware.
Input format: VER <CR>
Output (example): V_2.08 <CR>
Note: If the EC = 1 you will get the same message after each system start.
5.4.2 VS – Show parameter
The command VS lists all current parameter settings.
Input format: VS <CR>
Output (example): EC <SP> 0 <CR>
BD <SP> 2 <CR>
MD <SP> 2 <CR>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------20/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 21

5.4.3 VSAVE – Save parameter
All operating parameters temporarily stored are saved permanently using VSAVE.
Input format: VSAVE <CR>
Output: ok <CR>
5.4.4 RST – Warm start
The command RST causes a warm start of the reader.
Input format: RST <CR>
Output: If EC = 1 you get the startup message, else you get <CR>
RST
system initialization
system start with the actual
parameters saved in the
EEPROM
Figure 7: Workflow RST
5.4.5 INIT – Warmstart with default parameters
This command starts the reader new with the default parameters.
Input format: INIT <CR>
Output: <CR>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------21/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 22

6 Operating Modes of the Reader
There are two operational modes defined:
• MD 0 - continuous mode
• MD 2 - the reading process is triggered by the serial interface
In the next capters can you find a detailed functional description.
The default mode is MD 0.
6.1 MD 2 - Triggered by an Software Command
The master sends the command to read a transponder code. The reader answers with the code or an error
code.
If you use “read- and writable”-transponders you just get the transponder code using the command “Get
Tag” (GT).
You can execute specific commands “Read” (RD) and “Write” (WD) just in mode MD2. (capter 8)
In operating mode 2, the exciter is always turned off. Triggered by the software command (GT; RD ;
WD), the exciter is activated. After successful reading or writing of a transponder number the exciter is
turned off automatically.
exciter
processor
interface
Figure 9: Software triggered reading operation
If the first reading cycle yields no result (NoRead), the on-time of the exciter is limited by the parameter TOR (time out reader): Reading cycles are continuously started until either a transponder is read
successfully or the time span corresponding to the value of the parameter TOR has expired. The reader will not interrupt the last running readout cycle. If no transponder number has been read, a
NoRead is output.
GT
reading cycle
ID
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------22/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 23

TOR
exciter
processor
interface
reading cycle reading cycle reading cycle
GT
reading process
NoRead
Figure 10: Software triggered reading operation with TOR>0
Please note: The TOR parameter is only active, if the GT-Command is applied. Within the time span
defined by the value of TOR no NoRead will be output on the interface!
6.2 MD 0 - Continuous Reading
When operating continuously the exciter is switched on permanently. The reading cycles are initiated
periodically.
After an accomplished reading cycle the reading information is evaluated. After that data (either transponder number or NoRead code) is output to the serial interface
exciter
processor
interface
reading cycle
reading cycle reading cycle
ID ID ID
Figure 11: continuous operation
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------23/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 24

7 Startup and testing the reader
• Connect the reader via cable with the serial interface (COM) from your notebook or pc.
• Connect the reader with your power supply (9..30V DC). Look after the polarity!
• Switch the power supply on. The yellow LED OP of the reader starts to blink.
• Start your terminal programme. You have to set the following settings: 8 data bits, 1 start bit
und 1 stop bit, no parity check (often called 8N1), baud rate 19200 baud, no flow control(e.g.
XOFF/XON).
• Send the command „VER <CR>“ to the reader. The reader answers with the actual firmware
version (e.g. AEG ID V1.23).
• Send the command “MD <SP> 0 <CR>” to the reader. The reader sends No Read messages
(e.g. „FFFFFFFFFF“ or „XXXXXXXXXX“), while there is no transponder in the antenna field
available. The red LED L3 is active. If there is a transponder in the antenna field available the
reader sends its transponder code. The green LED L2 starts to glow.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------24/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 25

8 Basic data exchange process
The master has to send an software command to start an read or write process of the reader. After doing
all the necessary work at the readers site, the result of the reading or writing process or an failure code
is sent back to the master.
If there is used an read/write transponder, only the serial number of the transponder will be read if the
basic read command „Get Tag“ („GT <CR>“) is applied.
The data exchange of the whole memory can only be done, if the reader is set to the Mode 2 ( „selective
Read (RD) “ and „write (WD)“).
8.1 Selective read RD
• Start the reader with the command RD plus parameters (plus <CR>). You can read out just one
block (with one parameter) or several blocks (with two parameters, first and last block number).
• Wait for the answer
• Analyse the received answer: 8 characters plus <CR>. Allowed characters 0 to F.
The NoRead code is set to ( „XXXXXXXX“).
The result of the reading process may also be seen at the LED’s.
• LED L2 lit, if there was a successful read.
• LED L3 lit, if there was a No Read.
Example: RD <SP> 20 <CR> read block 20
RD <SP> 16 <SP> 33 <CR> read all blocks from 16 to 33
Allowed values (block numbers of the transponder IC):
ALGO 9 (1 kBit; P4150, P4450, P4550) 3 ... 33
ALGO 6 (2 kBit; Hitag 1) 16 ... 63
ALGO 14 (2, 4; kBitEM4305, EM4569) 5 … 15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------25/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 26

8.2 Writing WD
The memory of the transponder is organised in blocks, containing 32 bits. The data’s of every single
block must be changed separately.
• Start the reader with the command WD plus parameters ( plus <CR>). The sent parameter consists
of the block address and writing data’s (8 ASCII characters).
• Wait for the answer
• Analyse the received answer: 3 characters plus <CR>.
ACK <CR> Writing process was successful
NAK <CR> Writing process was not successful.
NOT <CR> The response of the transponder was not readable.
The result of the writing process may also seen at the LED’s.
• LED L2 lit, if there was a successful write
• LED L3 lit, if there was no successful write.
Example: WD <SP> 20 <SP> < 0 1 2 7 A C D F > <CR> write to block 20
Allowed values (block numbers of the transponder IC):
ALGO 9 (1 kBit; P4150, P4450, P4550) 3 ... 33
ALGO 6 (2 kBit; Hitag 1) 16 ... 63
ALGO 14 (2, 4; kBitEM4305, EM4569) 5 … 15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------26/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 27

9 Instructions
9.1 General Instructions
To avoid any reduction of the reading distance of the reader, the housing must not be brought next to a
metal surface. This could lead to a significant change of the properties of the antenna circuit, which in
turn reduces the reading range considerably!
To get reliable readings, the distance between reader and transponder must be within the specified reading volume.
The reading characteristic in front of the reader is not isotropic. It depends also strongly on the orientation between Reader and Transponder. To get the maximum reading distance, the orientation between
reader and transponder must be well suited. The best orientation depends on the type of antenna inside of
the housing ( ferrite – type or plane coil type) and the applied transponder (disc or glass transponder)
To get a reliable readings or writings, the time of transponder while crossing the sensitive area of the
antenna must be co-ordinated to the data transfer characteristics of transponder
In general the time depends on the speed of the transponder, the size of the transponder and the way the
transponder is mounted on the vehicle and must be verified by field tests.
Environmental electromagnetic noise may also reduce the read and write range consid-erably.
Arrangement to eliminate such troubles must be done specific to the application by the help of engineers
of the manufacturer.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------27/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 28

9.2 Special Instructions for Using a Read / Write System
To transfer the data to the transponder or to control the selective read process, all standard transponder
types uses a 100%-pulse-gap-modulation technique.
The modulation of the magnetic field comming from the transponder and the write pattern done by the
base station, shows a lot of similarities. Therefore, read write systems may interfere each other.
Because of the antenna cable transfers the energy for the antenna field it radiates also the gap modulation. Therefore they should keep also a minimum distance, and shouldn’t lay parallel.
The minimum distance between two antennas mounted next to each other and the size of the interference
must be determined for each application itself.
Below there are listed several parameters that will influence the size of the interaction:
• size of the antennas
• orientation of the antennas (f.e. parallel or rectangular to each other)
• size of transponder; distance between transponder and antenna
• the chronological orders for reading or writing.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------28/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 29

F -Ty p- Re ad in g C oi l-
B es t O ri en tat ion
Ro d
Tra ns po nd er
0
1020308
10203
C om pa c t Re ad er A R E i2
In ter na l A nt en na F- Ty p
L- Typ -Re ade r C oil-
Di sc
0
Tr an sp ond er
25 30
2
0
1
5
1
0
5
1
Be st Ori ent atio n
Ro d
Tr ans pon der
0
1020308
10203
Baut eilna me
C om pa ct R ea de r AR E i 2
In tern al A nte nna L- Typ
0
25 30
Tr ans pon der
2
0
1
5
1
0
5
Dis c
1
Figure 12: Orientation between transponder and reader
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------29/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 30

10 Certifications
10.1 By FCC, Federal Communications Commission
Name of Grantee AEG Identifiaktionssysteme GmbH
Equipment Class Part 15 Low Power Transceiver, Rx Verified
Notes Compact Reader ARE I2
FCC Rule Parts 15C
FCC IDENTIFIER Frequency Range Model
V7IAREI2 0.125 ARE i2 - 1X/RS232
V7IAREI2 0.125 ARE i2 - 4X/RS232
V7IAREI2LF-2 0.134 ARE i2 - 17X/USB
V7IAREI2LF-3 0.134 ARE i2 - 23X/RS232
V7IAREI2LF-4 0.134 ARE i2 - 17X/RS232
Federal Communications Commissions (FCC) Statement
15.21
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the part responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
15.105(b)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connect-
ed.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------30/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 31

- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
10.2 By KCC, Korean Communications Commission
KCC ID MSIP-RRM-Ai2-AREI2
Applicant AEG Identifiaktionssysteme GmbH
Equipment Name Radio Frequency Transmitter
Model ARE i2 – 1X / RS232
Manufacturer AEG Identificationssysteme GmbH
Origin Germany
11 Hotline
If there are questions or suggestions please call the hotline:
Sales und Marketing: +49 (0)731-140088-0
Fax: +49 (0)731-140088-9000
e-mail: sales@aegid.de
http://
www.aegid.de
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------31/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 32

12 Revisions
19.12.01 Revision 00: Initial edition
09.09.03 Revision 01: Chapter 8.2 added
09.12.04 Revision 02: Chapter 4.3.6.
26.09.07 Revision 03: Chapter 8.2 note for antenna cable added
10.04.08 Revision 04: New structure, based on revision 07 of the german manual
02.10.09 Revision 05: Answer of EC changed (FW)
13.01.10 Revision 06: Chapter 3.4
22.03.10 Revision 07: Orientation
12.10.10 Revision 08: Orientation Antenna to Transponder
07.02.11 Revision 09: Certifications (MK)
25.02.11 Revision 10: Tor 50 (MM)
14.03.14 Revision 11: KCC (MM)
18.05.16 Revision 12: FCC Information (MK)
22.06.16 Revision 13: FCC Information correction (MK)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------32/32--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Loading...
Loading...