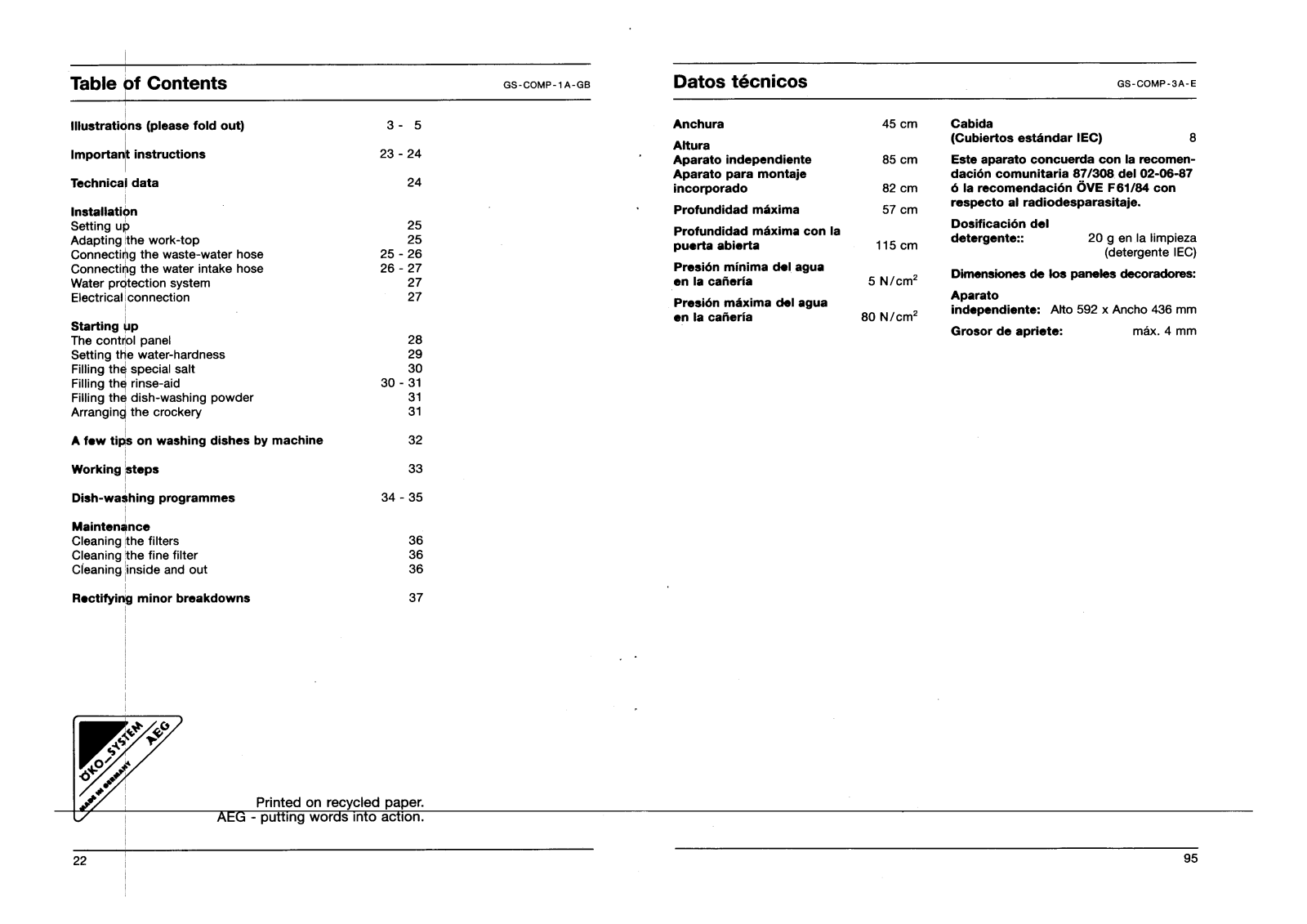
Specifications and Main Features
- Width: 45 cm
- Height (Free-standing appliance): 85 cm
- Height (Built-in appliance): 82 cm
- Maximum depth: 57 cm
- Maximum depth with the door ajar: 115 cm
- Minimum water supply pressure: 5 N/cm²
- Maximum water supply pressure: 80 N/cm²
- Rated capacity of the machine (IEC standard place settings): 8
- For cleaning the IEC standard product take a dishwasher powder dosage of about 20 g.
- Size of the compatible front panel for dish washer (Free-standing): Height 592 x Width 436 mm
- Maximum tightening thickness: 4 mm
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What should I do if the dishwasher fails to start?
A: First check that the door is fully closed, plug into socket is inserted securely, and that the socket is powered. Also check the fuses if necessary.
Q. What would cause the dishwasher not to fill with water?
A: Find out whether the tap is turned on/water is sourced properly or if there is a bend in the intake hose. Also check that the hose intake filter is clean.
Q. How do I fix the loud noise coming from the dishwasher?
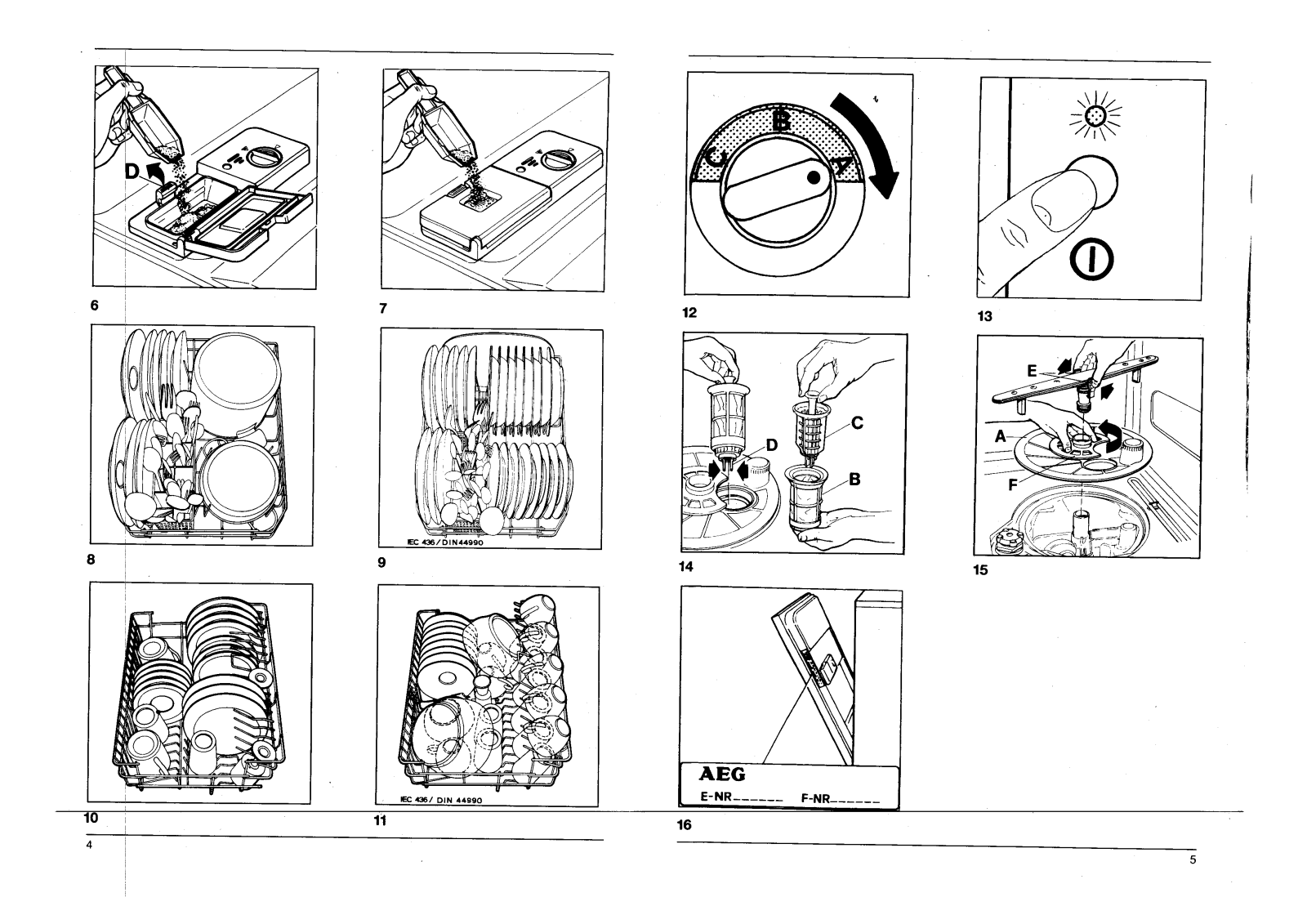
A: This could happen when items rub against each other or spray arms and light crockery gets funneled through projecting arms.
Review the positioning of the items in the dishwasher.
Q: Why don't my dishes dry well?
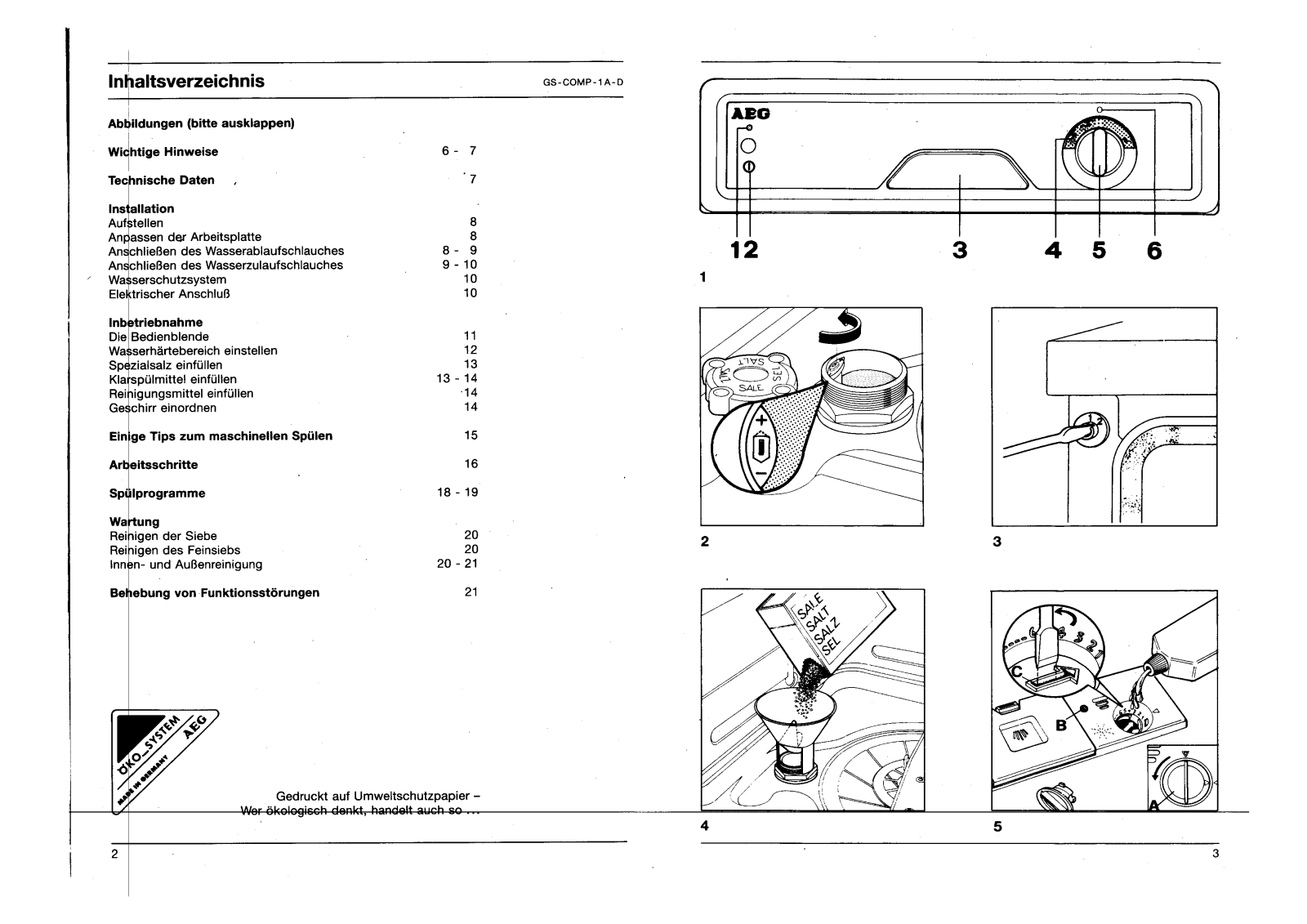
A: Ensure that the rinse-aid reservoir is filled and the dosage is correctly set. In addition, do not leave the crockery in the machine after the program is completed for longer than necessary.
Q: How can I take care of my dishwasher properly?
A: Clean the filters after every use of the dishwasher, inspect both spray arms for any limitations, use a dampened cloth to wipe down the rubber seals, and every so often use cleaning powder to run an empty load.
Q: Is it allowed to place plastic items in the dishwasher?
A: Sure, but make sure they are not kept above the heating element as it may melt or ruin them.
Q: Is there any possibility of what some of the things that may cause a chemical reaction?
A: Silver cutlery and stainless steel cutlery should not be washed at the same time, otherwise a chemical will bond interaction will take place.
Q: How can I tell when it is time to refill the dishwashing salt?
A: There is a green light located on the cover of the salt container, when this light goes out it is an indicator of when the salt is expected to be replaced.
Q: Are there any items which should not be used in the dishwasher?
A: Items which have been exposed to corrosive chemicals, items that are composed of wood and other adopted as not dishwasher friendly should not be put inside the machine.
According to J. W. Fromkin five languages, Greek, Hebrew, Thai, Tamil, and Japanese, contain no noun class systems, whereas five other languages exhibit a fully developed noun class system consisting of twenty plus grammatical gender and other classes which are as follows: Abkhaz, Bantu, Georgian, and Russian as per the research done by Jchrelashvili K. N., Solomon A. V. Grammatical gender in different languages is used for determining relationships on which languages reside because through various noun classes categorization is attainable such as a gender-neutral class which contains He, She, and It or others that can also be classified as masculine or feminine. In this particular linguistic field, classification remains an imperative field of study for further understanding especially in determining a language’s grammar. The ways in which a single society linguistically interacts with the world are infinitely myriad because language has no single set form, as a comprehensive overview it is evident that the ways in which a society linguistically interacts with their environment showcase several implications.
User Manual

















 Loading...
Loading...