Page 1

4.7 Advanced Setting
Page 2
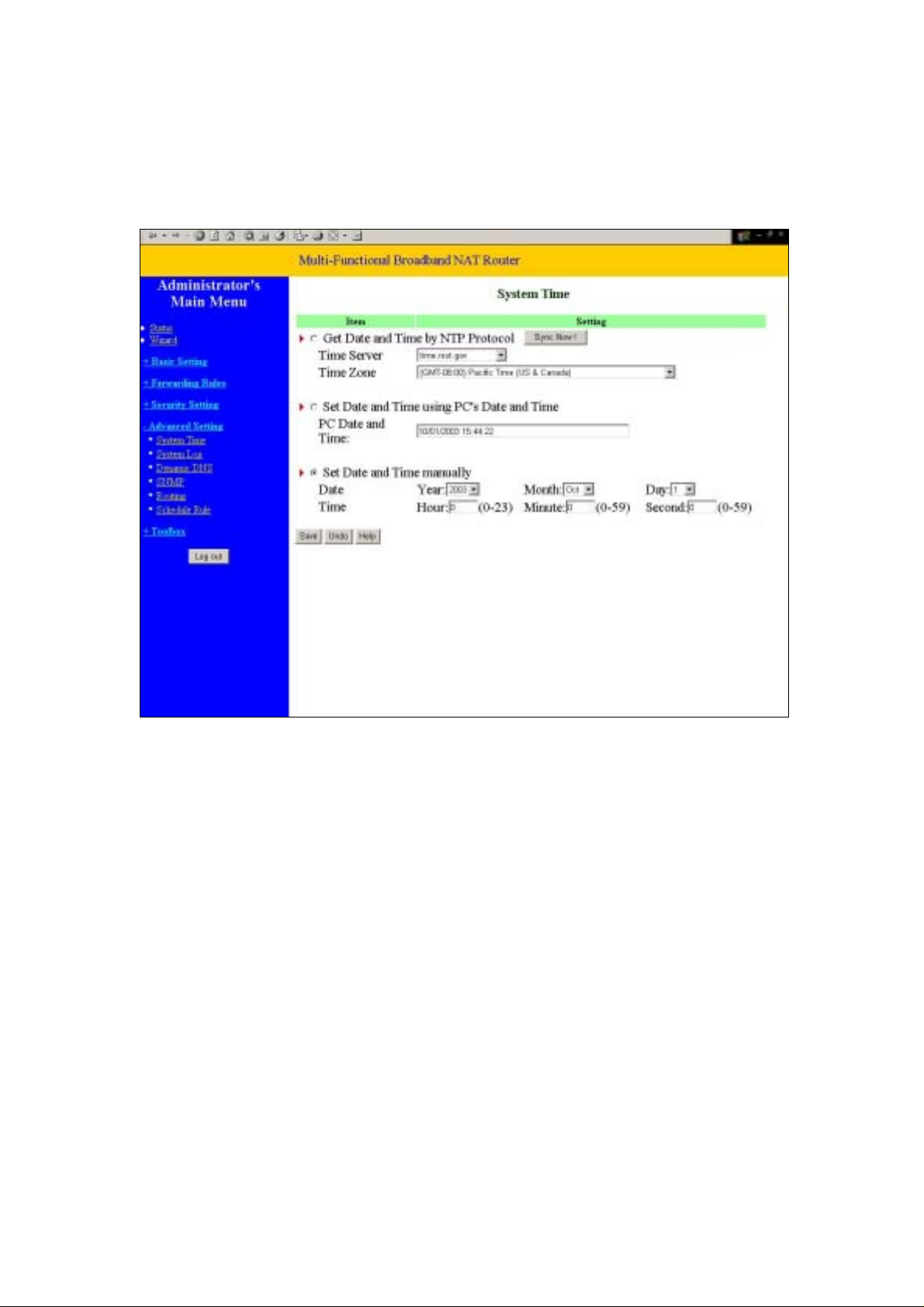
4.7.1 System Time
Get Date and Time by NTP Protocol
Selected if you want to Get Date and Time by NTP Protocol.
Time Server
Select a NTP time server to consult UTC time
Time Zone
Select a time zone where this device locates.
Set Date and Time manually
Selected if you want to Set Date and Time manually.
Function of Buttons
Sync Now: Synchronize system time with network time server
Page 3
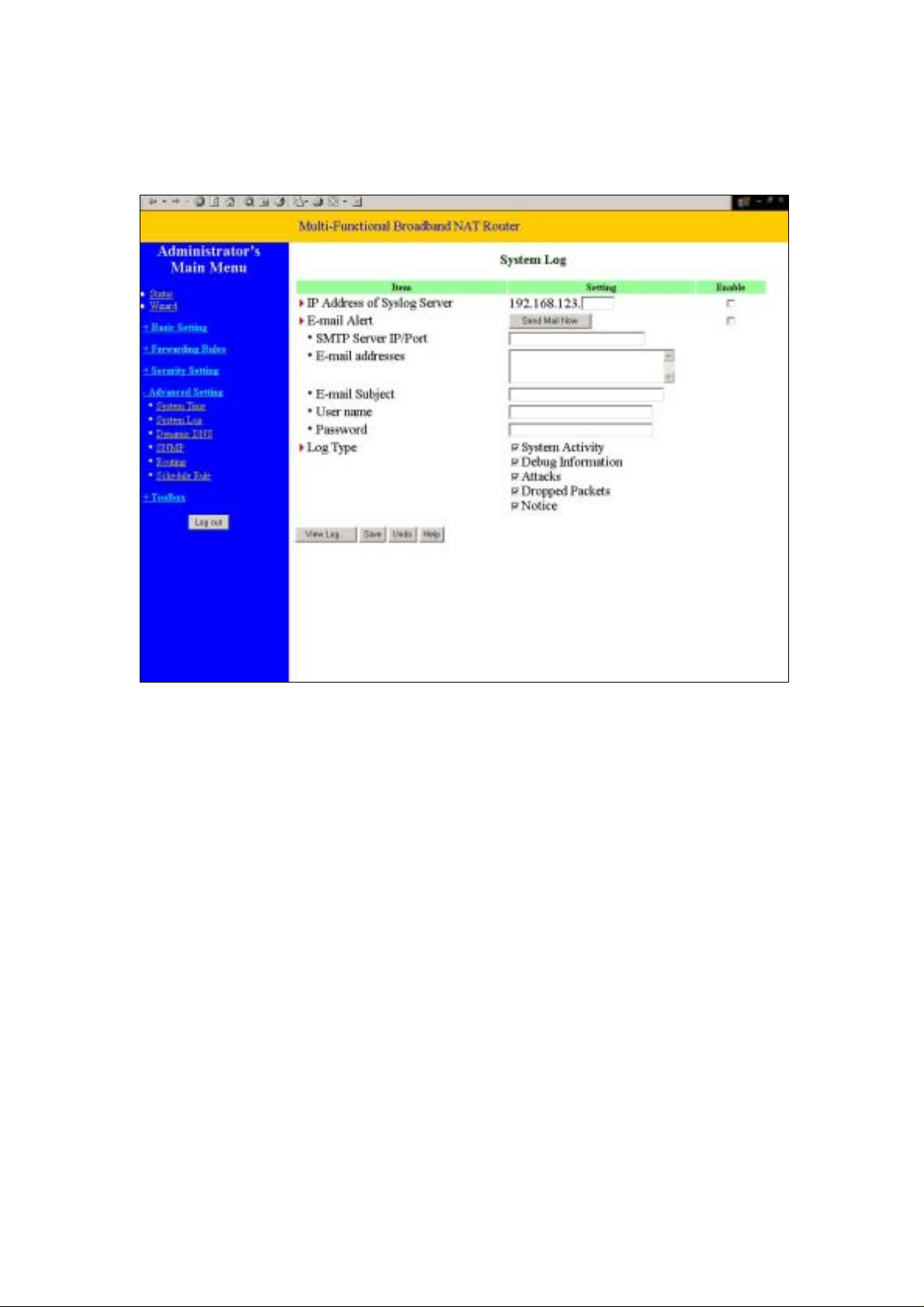
4.7.2 System Log
This page support two methods to export system logs to specific destination by means of
syslog(UDP) and SMTP(TCP). The items you have to setup including:
IP Address for Syslog
Host IP of destination where syslogs will be sent to.
Check Enable to enable this function.
E-mail Alert Enable
Check if you want to enable Email alert(send syslog via email).
SMTP Server IP and Port
Input the SMTP server IP and port, which are concated with ':'. If you do not specify
port number, the default value is 25.
For example, "mail.your_url.com" or "192.168.1.100:26".
Send E-mail alert to
The recipients who will receive these logs. You can assign more than 1 recipient,
using ';' or ',' to separate these email addresses.
Page 4

E-mail Subject
The subject of email alert. This setting is optional.
Username and Password
To fill some SMTP server's authentication requirement, you may need to input
Username and Password that offered by your ISP.
Log type
Please select the activities that should be shown on log.
Page 5

4.7.3 Dynamic DNS
To host your server on a changing IP address, you have to use dynamic domain name service (DDNS).
So that anyone wishing to reach your host only needs to know the name of it. Dynamic DNS will map
the name of your host to your current IP address, which changes each time you connect your Internet
service provider.
Before you enable Dynamic DNS, you need to register an account on one of these Dynamic DNS
servers that we list in provider field.
To enable Dynamic DNS click the check box next to Enable in the DDNS field.
Next you can enter the appropriate information about your Dynamic DNS Server.
You have to define:
Provider
Page 6

Host Name
Username/E-mail
Password/Key
You will get this information when you register an account on a Dynamic DNS server.
Example:
After Dynamic DNS setting is configured, click the save button.
Page 7
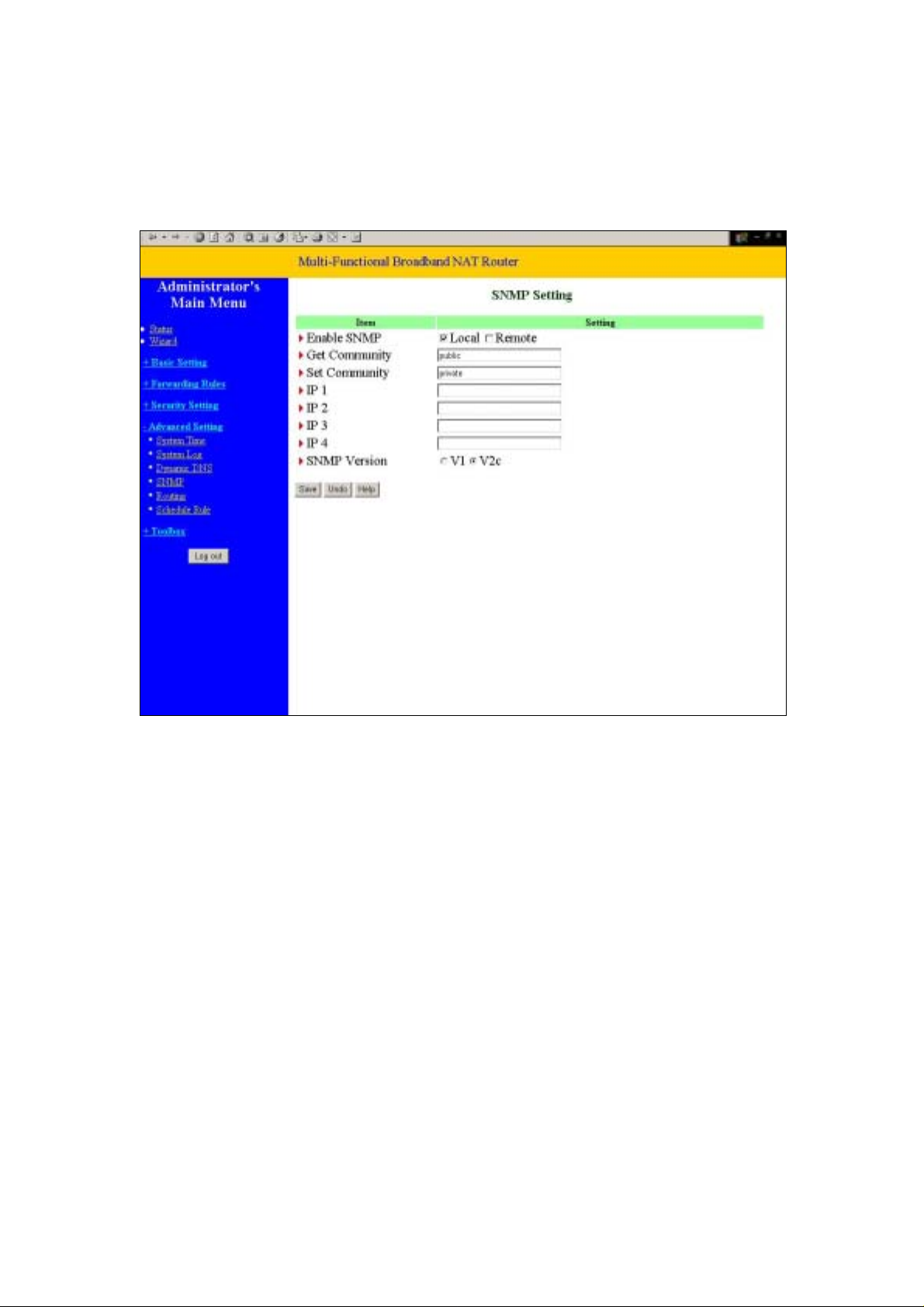
4.7.4 SNMP Setting
In brief, SNMP, the Simple Network Management Protocol, is a protocol designed to give a user the
capability to remotely manage a computer network by polling and setting terminal values and
monitoring network events.
Enable SNMP
You must check either Local or Remote or both to enable SNMP function. If Local is checked, this
device will response request from LAN. If Remote
from WAN.
Get Community
Setting the community of GetRequest your device will response.
Set Community
Setting the community of SetRequest your device will accept.
IP 1,IP 2,IP 3,IP 4
Input your SNMP Management PC’s IP here. User has to configure to where this device should send
SNMP T rap message.
is checked, this device will response request
Page 8
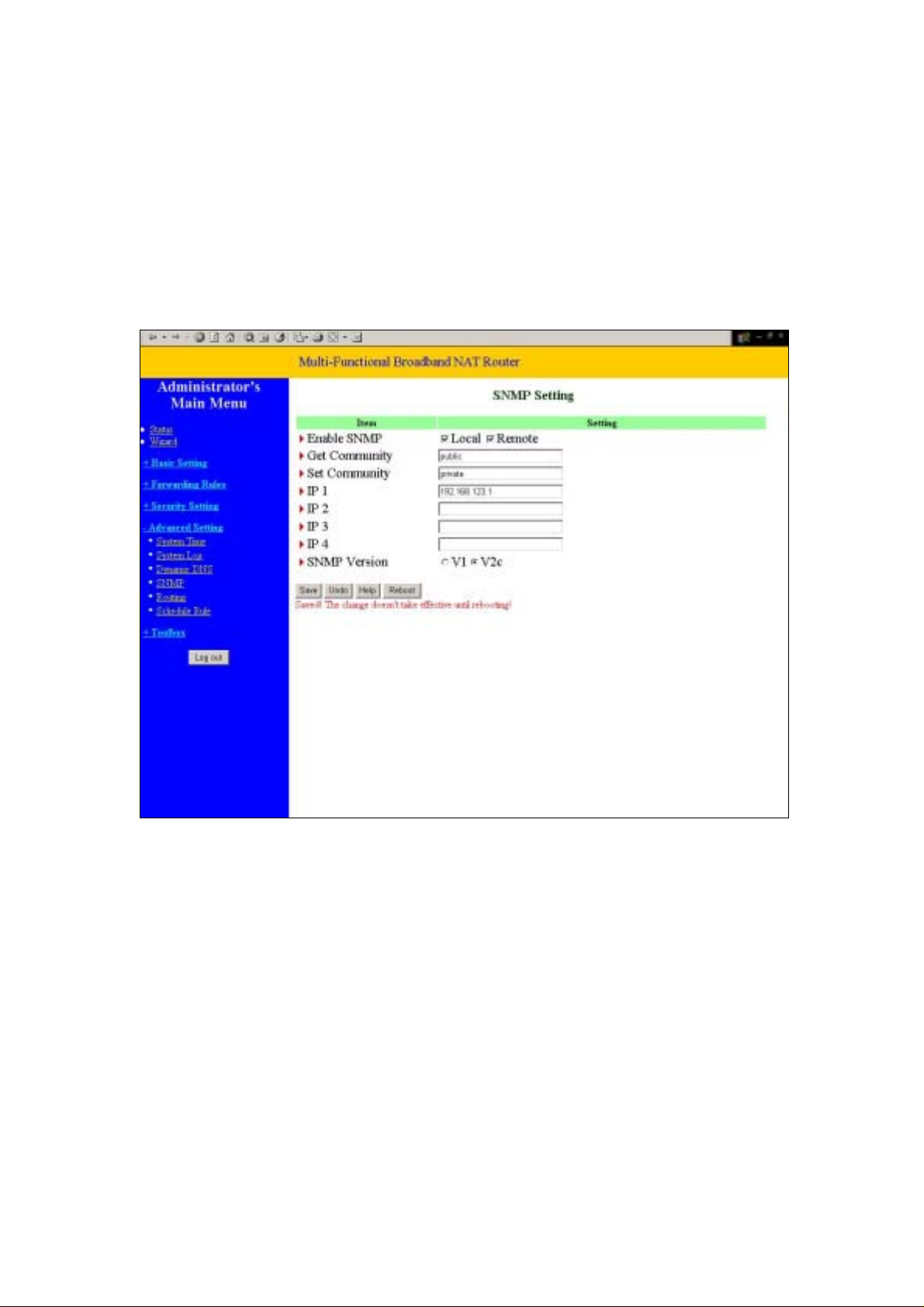
SNMP Version
Please select proper SNMP Version that your SNMP Management software supports
Example:
1. This device will response to SNMP client which’s get community is set as “public”
2. This device will response to SNMP client which’s set community is set as “private”
3. This device will response request from both LAN and WAN
4. This device will send SNMP Trap message to 192.168.123.1 (Use SNMP Version V2c)
Page 9

4.7.5 Routing Table
Routing Tables allow you to determine which physical interface address to use for outgoing IP data
grams. If you have more than one routers and subnets, you will need to enable routing table to allow
packets to find proper routing path and allow different subnets to communicate with each other.
Routing Table settings are settings used to setup the functions of static and dynamic routing.
Dynamic Routing
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) will exchange information about destinations for computing routes
throughout the network. Please select RIPv2 only if you have different subnet in your network.
Otherwise, please select RIPv1 if you need this protocol.
Static Routing: For static routing, you can specify up to 8 routing rules. You can enter the destination
IP address, subnet mask, gateway, hop for each routing rule, and then enable or disable the rule by
checking or unchecking the Enable checkbox.
Page 10
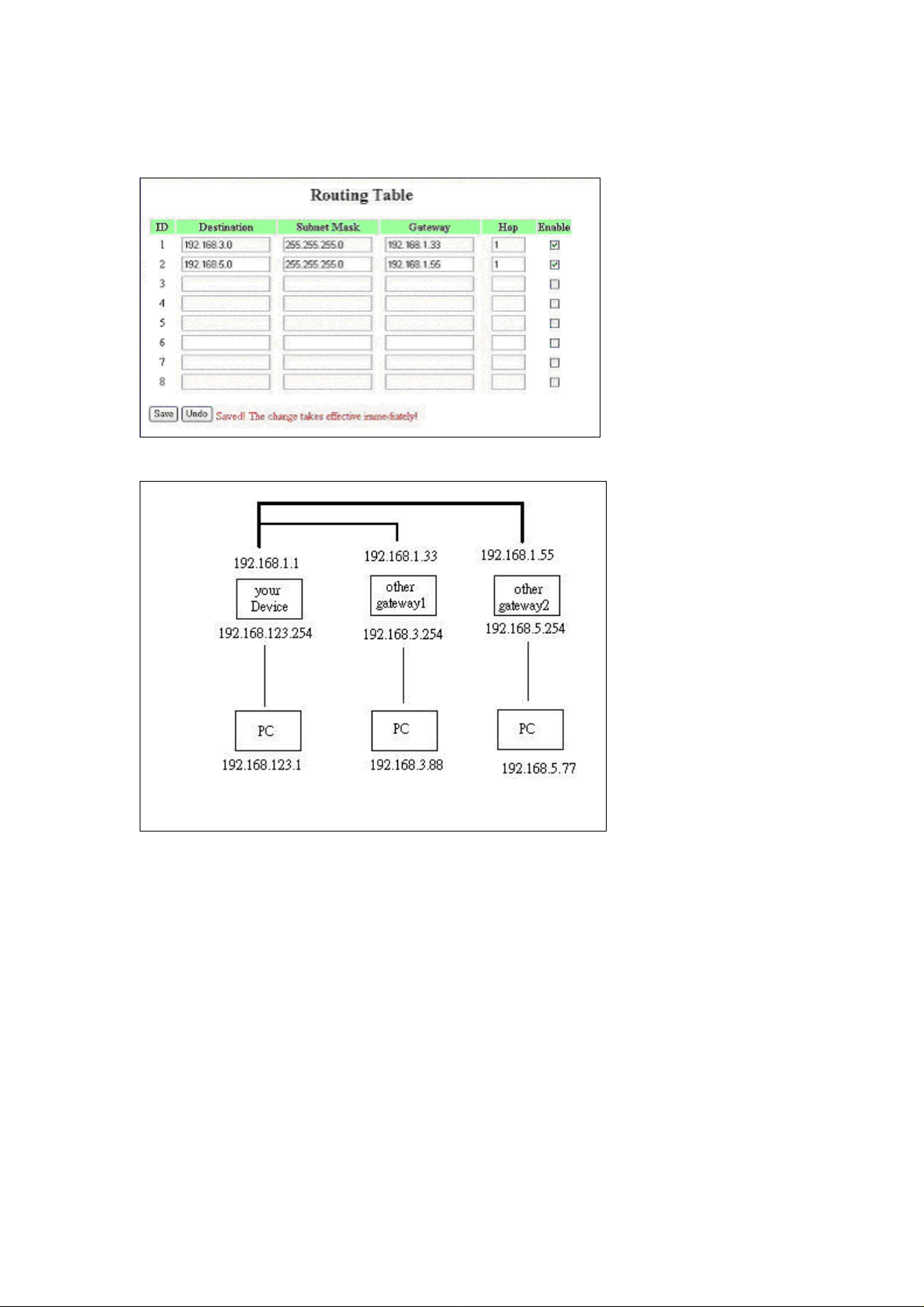
Example:
So if, for example, the host wanted to send an IP data gram to 192.168.3.88, it would use the above
table to determine that it had to go via 192.168.1.33 (a gateway),
And if it sends Packets to 192.168.5.77 will go via 192.168.1.55
Each rule can be enabled or disabled individually.
After routing table setting is configured, click the save button.
Page 11
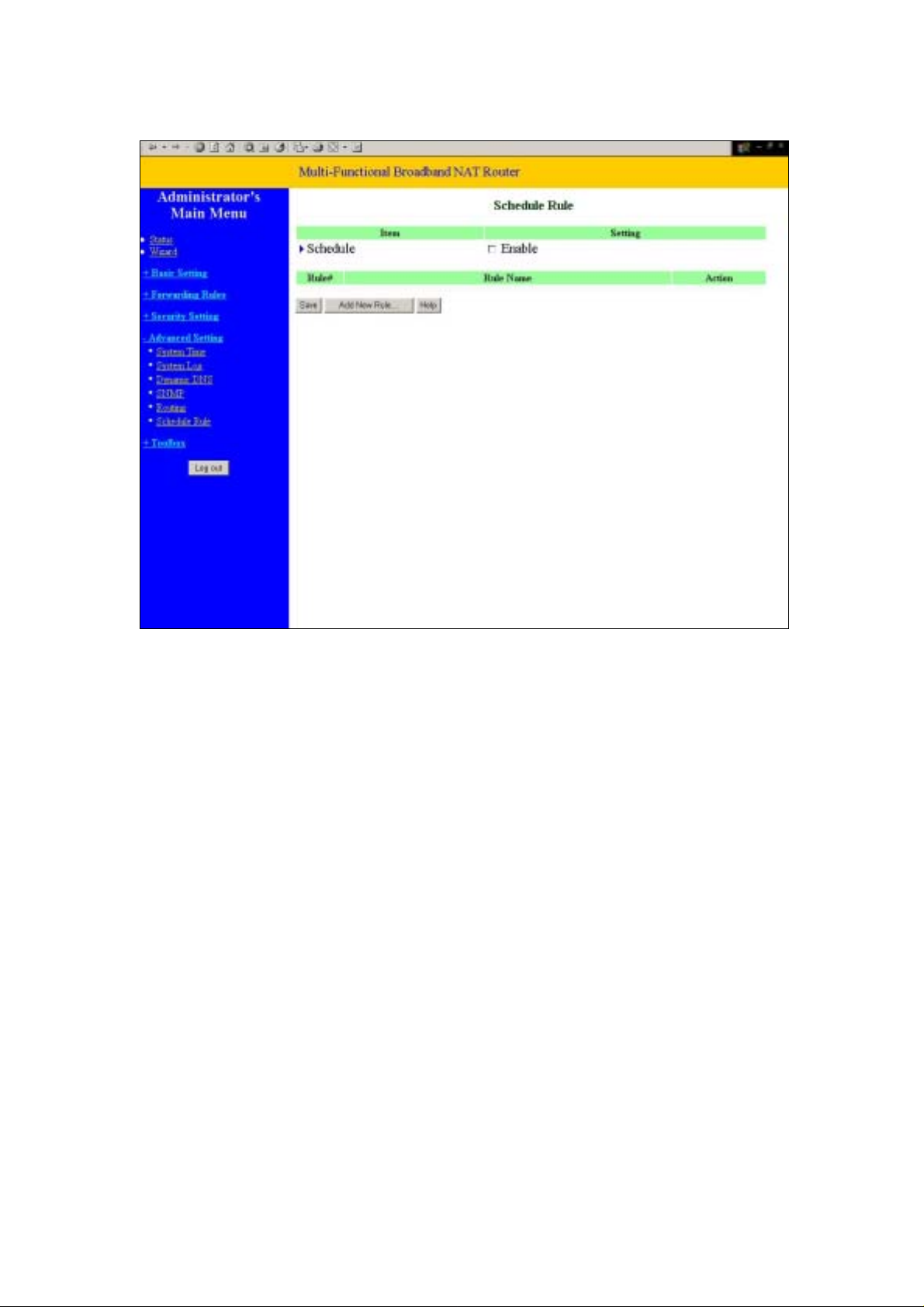
4.7.5 Schedule Rule
You can set the schedule time to decide which service will be turned on or off. Select the “enable” item.
Press “Add New Rule”
You can write a rule name and set which day and what time to schedule from “Start Time” to “End
Time”. The following example configure “ftp time” as everyday 14:10 to 16:20
Page 12
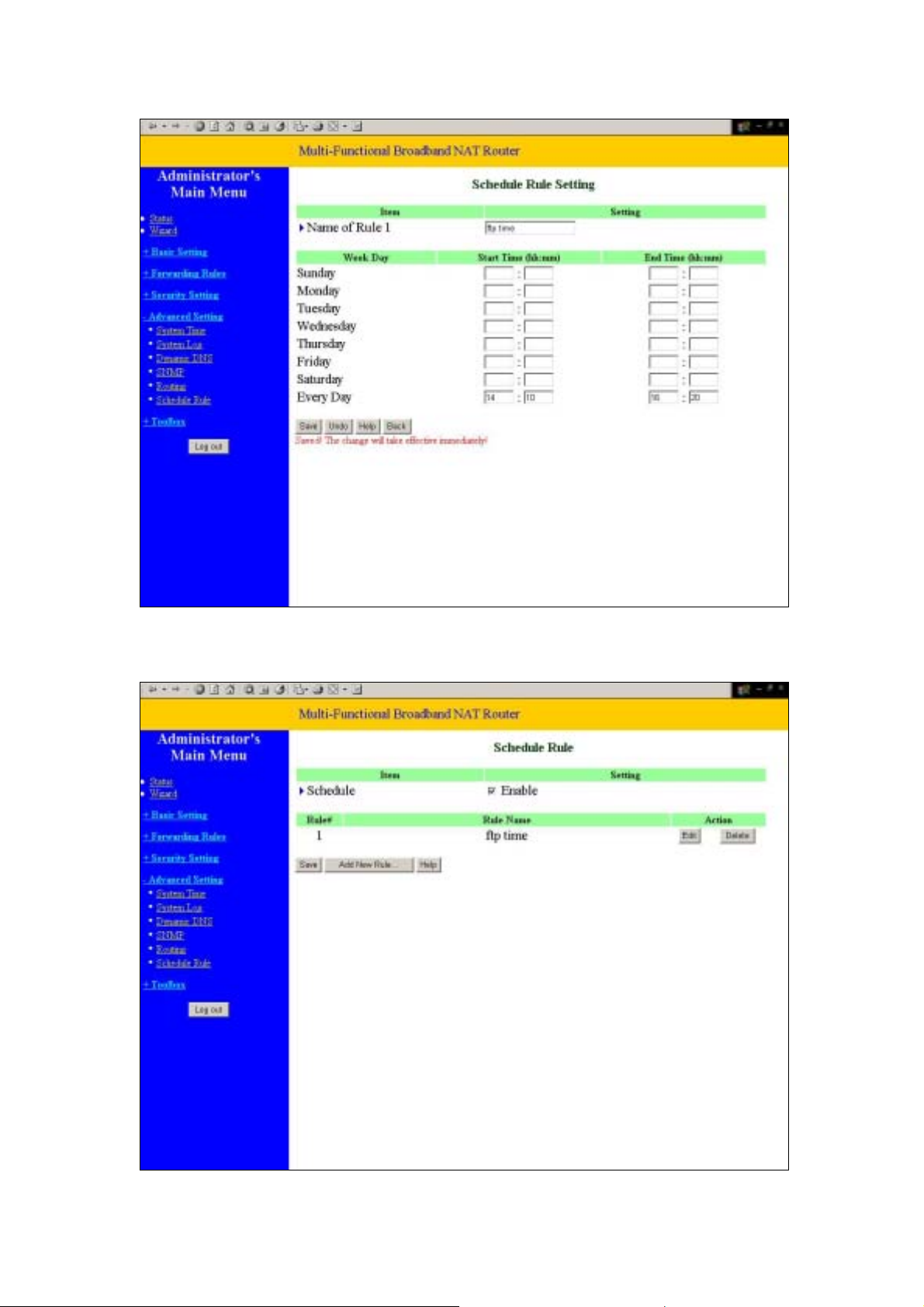
After configure Rule 1
Page 13

Schedule Enable
Selected if you want to Enable the Scheduler.
Edit
To edit the schedule rule.
Delete
To delete the schedule rule, and the rule# of the rules behind the deleted one will decrease one
automatically.
Schedule Rule can be apply to Virtual server and Packet Filter, for example:
Exanple1: Virtual Server – Apply Rule#1 (ftp time: everyday 14:10 to 16:20)
Page 14

Exanple2: Packet Filter – Apply Rule#1 (ftp time: everyday 14:10 to 16:20).
Page 15

4.8 Toolbox
Page 16

4.8.1 System Log
You can View system log by clicking the View Log button
Page 17

4.8.2 Firmware Upgrade
You can upgrade firmware by clicking Firmware Upgrade button.
Page 18

4.8.3 Backup Setting
You can backup your settings by clicking the Backup Setting button and save it as a
bin file. Once you want to restore these settings, please click Firmware Upgrade
button and use the bin file you saved.
4.8.4 Reset to default
You can also reset this product to factory default by clicking the Reset to default button.
4.8.5 Reboot
You can also reboot this product by clicking the Reboot button.
Page 19

4.8.6 Miscellaneous Items
MAC Address for Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN is a technology that enables you to power up a networked device remotely. In order to
enjoy this feature, the target device must be Wake-on-LAN enabled and you have to know the MAC
address of this device, say 00-11-22-33-44-55. Clicking "Wake up" button will make the router to send
the wake-up frame to the target device immediately.
Domain Name or IP address for Ping Test
Allow you to configure an IP, and ping the device. You can ping a specific IP to test
whether it is alive.
Page 20

Chapter 5 Print Server
This product provides the function of network print server for MS Windows 95/98/NT/2000 and Unix
based platforms. (If the product you purchased doesn’t have printer port, please skip this chapter.)
5.1 Configuring on Windows 95/98 Platforms
After you finished the software installation procedure described in Chapter 3, your computer has
possessed the network printing facility provided by this produ ct. For convenience, we call the printer
connected to the printer port of this product as server printer. On a Windows 95/98 platform, open the
Printers window in the My Computer menu:
Now, yon can configure the print server of this product:
Page 21

1. Find out the corresponding icon of your server printer, for example, the HP
LaserJet 6L. Click the mouse’s right button on that icon, and then select the Properties
item:
2. Click the Details item:
Page 22

3. Choose the “PRTmate: (All-in-1)” from the list attached at the Print To item. Be sure that the
Printer Driver item is configured to the correct driver of your server printer.
4. Click on the button of Port Settings:
Type in the IP address of this product and then click the OK button.
5. Make sure that all settings mentioned above are correct and then click the OK button.
Page 23

5.2 Configuring on Windows NT Platforms
The configuration procedure for a Windows NT platform is similar to that of Windows 95/98 except the
screen of printer Properties:
Compared to the procedure in last section, the selection of Details is equivalent to the selection of
Ports, and Port Settings is equivalent to Configure Port.
Page 24

5.3 Configuring on Windows 2000 and XP Platforms
Windows 2000 and XP have built-in LPR client, users could utilize this feature toPrint.
You have to install your Printer Driver on LPT1 or other ports before you preceed the following
sequence.
1. Open Printers and Faxs.
Page 25

2. Select “Ports” page, Click “Add Port…”
Page 26

3. Select “Standard TCP/IP Port”, and then click “New Port…”
4. Click Next and then provide the following information:
Type address of server providing LPD that is our NAT device:192.168.123.254
Page 27

5. Select Custom, then click “Settings…”
Page 28

6. Select “LPR”, type ” lp“ lowercase letter in “Queue Name:”
And enable “LPR Byte Counting Enabled”.
Page 29

7. Apply your settings
Page 30

Page 31

5.4 Configuring on Unix based Platforms
Please follow the traditional configuration procedure on Unix platforms to setup the print server of this
product. The printer name is “lp.”
Page 32

Appendix A TCP/IP Configuration for Windows 95/98
This section introduces you how to install TCP/IP protocol into your personal computer. And suppose
you have been successfully installed one network card on your personal computer. If not, please refer
to your network card manual. Moreover, the Section B.2 tells you how to set TCP/IP values for
working with this NAT Router correctly.
A.1 Install TCP/IP Protocol into Your PC
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
2. Double click Network icon and select Configuration tab in the Network window.
3. Click Add button to add network component into your PC.
4. Double click Protocol to add TCP/IP protocol.
Page 33

5. Select Microsoft item in the manufactures list. And choose TCP/IP in the Network Protocols.
Click OK button to return to Network window.
6. The TCP/IP protocol shall be listed in the Network window. Click OK to complete the install
procedure and restart your PC to enable the TCP/IP protocol.
A.2 Set TCP/IP Protocol for Working with NAT Router
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
Page 34

2. Double click Network icon. Select the TCP/IP line that has been associated to your network card in
the Configuration tab of the Network window.
3. Click Properties button to set the TCP/IP protocol for this NAT Router.
4. Now, you have two setting methods:
A. Get IP via DHCP server
Page 35

a. Select Obtain an IP address automatically in the IP Address tab.
Page 36

b. Don’t input any value in the Gateway tab.
Page 37

c. Choose Disable DNS in the DNS Configuration tab.
Page 38

B. Configure IP manually
a. Select Specify an IP address in the IP Address tab. The default IP address of this
product is 192.168.123.254. So please use 192.168.123.xxx (xxx is b etween 1 and 253)
for IP Address field and 255.255.255.0 for Subnet Mask field.
Page 39

b. In the Gateway tab , add the IP address of this product (default IP is 192.168.123.254)
in the New gateway field and click Add button.
Page 40

c. In the DNS Configuration tab, add th e DNS values which are provided by the ISP into
DNS Server Search Order field and click Add button.
 Loading...
Loading...