Page 1

CardBus
11G WIRELESS Network Adapter
User’s Manual
Page 2

Production component
This WIRELESS production should contain the following items:
1. One piece of CardBus 11G WIRELESS LAN Card
2. One piece of CD which contain drivers, user’s manual, and utility
Quick Installation
1. Insert the product’s CD into CD-ROM.
2. Exit all application programs and insert the 11G WIRELESS adapter into the PCMCIA slot.
3. Following “Found New Hardware Wizard” window to install driver step by step.
4. Install the WIRELESS adapter utility
5. Configure your WIRELESS adapter for connecting to a WIRELESS network.
FCC Information
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. this device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. this device must accept any interference received; including interference that may cause
undesired operation. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement.
This Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
- i -
Page 3

FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
1. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
2. This device has been tested for compliance with FCC RF Exposure (SAR) limits
in a typical laptop configuration with a PCMCIA slot on either the right or left
side of the laptop. In order to comply with the FCC SAR limits, it is recommended
when using a PC card adapter that the integrated antenna is positioned more than
1.5 centimeters from nearby persons during extended periods of operation. If the
antenna is positioned less than 1.5 centimeters from nearby persons, it is
recommended that the user limit exposure time."
Page 4

Contents
CHAPTER 1 TERMINOLOGY INTRODUCTION 1
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS 3
2-1 HARDWARE 3
2-2 SOFTWARE 3
CHAPTER 3 INSTALL DRIVER FOR WINDOWS SERIES 4
3-1 SET UP WIRELESS LAN CARD FOR WINDOWS XP 4
3-2 SET UP WIRELESS LAN CARD FOR WINDOWS 2000 7
3-3 SET UP WIRELESS LAN CARD FOR WINDOWS 98/ ME 11
3-4 UNINSTALL THE WIRELESS LAN CARD 14
CHAPTER 4 CONFIGURE THE WIRELESS LAN ADAPTER 17
4-1 INSTALL UTILITY 17
4-2 CONFIGURE WIRELESS LAN ADAPTER FOR WINDOWS XP 18
4-3 CONFIGURE WIRELESS LAN ADAPTER FOR WINDOWS 98/ME/2000 BY UTILITY 21
- iii -
Page 5

Chapter 1 Terminology Introduction
This chapter will introduce terminology about IEEE802.11 what referred by this manual. And in
this character we will explain terminology according to IEEE802.11 Std.
Ad-Hoc Network(Peer to Peer)
A network composed solely of stations within mutual communication range of each other via
the WIRELESS medium(WM). An Ad Hoc network is typically created in a spontaneous
manner. The principal distinguishing characteristic of an ad hoc network is limited temporal
and spatial extent. These limitations allow the act of creating and dissolving the ad hoc
network to be sufficiently straightforward and convenient so as to be achievable by
nontechnical users of the network facilities; i.e., no specialized “technical skills” are required
and little or no investment of time or additional resources is required beyond the stations that
are to participate in the ad hoc network. The term ad hoc is often used as slang to refer to an
independent basic service set(IBSS).
Infrastructure Network
The infrastructure includes the distribution system medium (DSM), access point(AP), and
portal entities. It is also the logical location of distribution and integration service functions of
an extended service set(ESS). An infrastructure contains one or more APs and zero or more
portals in addition to the distribution system(DS).
Basic Service Set(BSS)
A set of stations controlled by a single coordination function.
BSSID
Basic service set identifier
Station service(SS)
The set of services that support transport of medium access control(MAC) service data
units(MSDUs) between stations within a basic service set(BSS)
SSID
Station service identifier
- 1 -
Page 6
Association
The service used to establish access point/station(AP/STA) mapping and enable STA
invocation of the distribution system services(DSSs).
Authentication
The service used to establish the identify of one station as a member of the set of stations
authorized to associate with another station.
Channel
an instance of medium use for the purpose of passing protocol data units(PDUs) that may be
used simultaneously, in the same volume of space, with other instances of medium use(no
other channels) by other instances of the same physical layer(PHY), with an acceptably low
frame error ratio due to mutual interference. Some PHYs provide only one channel, whereas
others provide multiple channels. Examples of channel types are shown in the following tables
Single channel n-channel
Narrowband radio-frequency(RF) channel Frequency division multiplexed channels
Baseband infrared Direct sequence spread spectrum(DSSS) with
code division multiple access
Wired equivalent privacy(WEP)
The optional cryptographic confidentiality algorithm specified by IEEE 802.11 used to provide
data confidentiality that is subjectively equivalent to the confidentiality of a wired local area
network(LAN) medium that does not employ cryptographic techniques to enhance privacy.
- 2 -
Page 7

Chapter 2 System Requirements
Before installing the adapter and related sof `tware, make sure the computer system meets the
minimum requirements described below.
2-1 Hardware
The adapter can be installed in any recent-model IBM-type microcomputer with a PCMCIA slot
which support CardBus interface. The adapter is a Type II CardBus card, and can be installed in a
Type II or Type III CardBus slot.
2-2 Software
The drivers included with the adapter allow the adapter to be used in Microsoft Windows 98, ME,
2000, and XP.
- 3 -
Page 8
Chapter 3 Install Driver for Windows Series
This section describes the installation of the 11G WIRELESS LAN Card driver for the
Windows98/ME/2000 and Windows XP operating systems. The installation procedures for
Windows XP refer to 3-1 Set up WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows XP; for Windows 2000 please
see 3-2 Set up WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows 2000; for Windows 98/ME refer to 3-4 Set up
WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows 98/ME.
3-1 Set up WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows XP
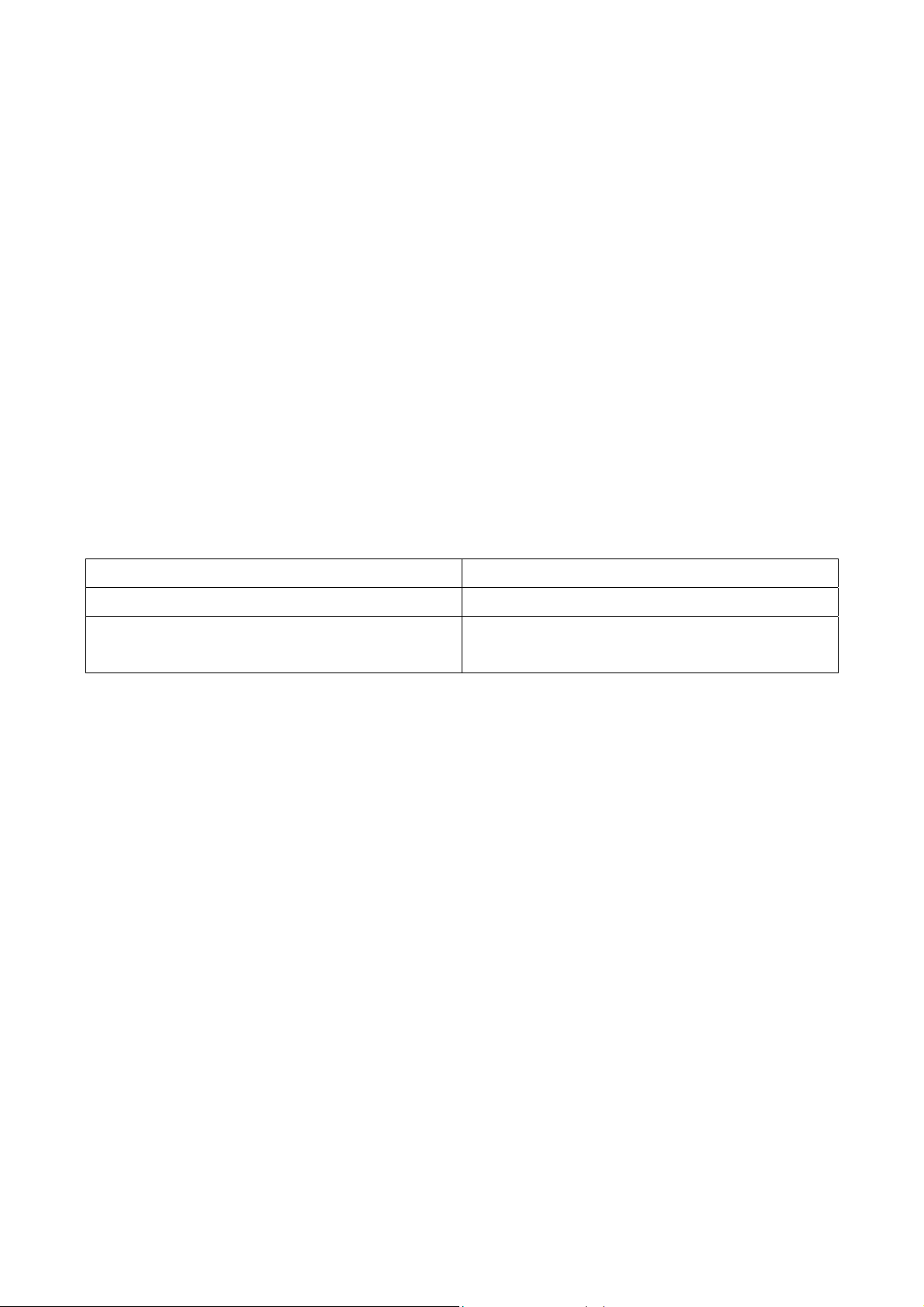
Step 1: After inserting the WIRELESS LAN Card into the PCMCIA slot on your notebook, the
Windows will auto-detect the WIRELESS LAN Card and a “Found New Hardware Wizard”
window will show up. Select “Install from a list or specific location (Advanced)” to install the
driver.
- 4 -
Page 9
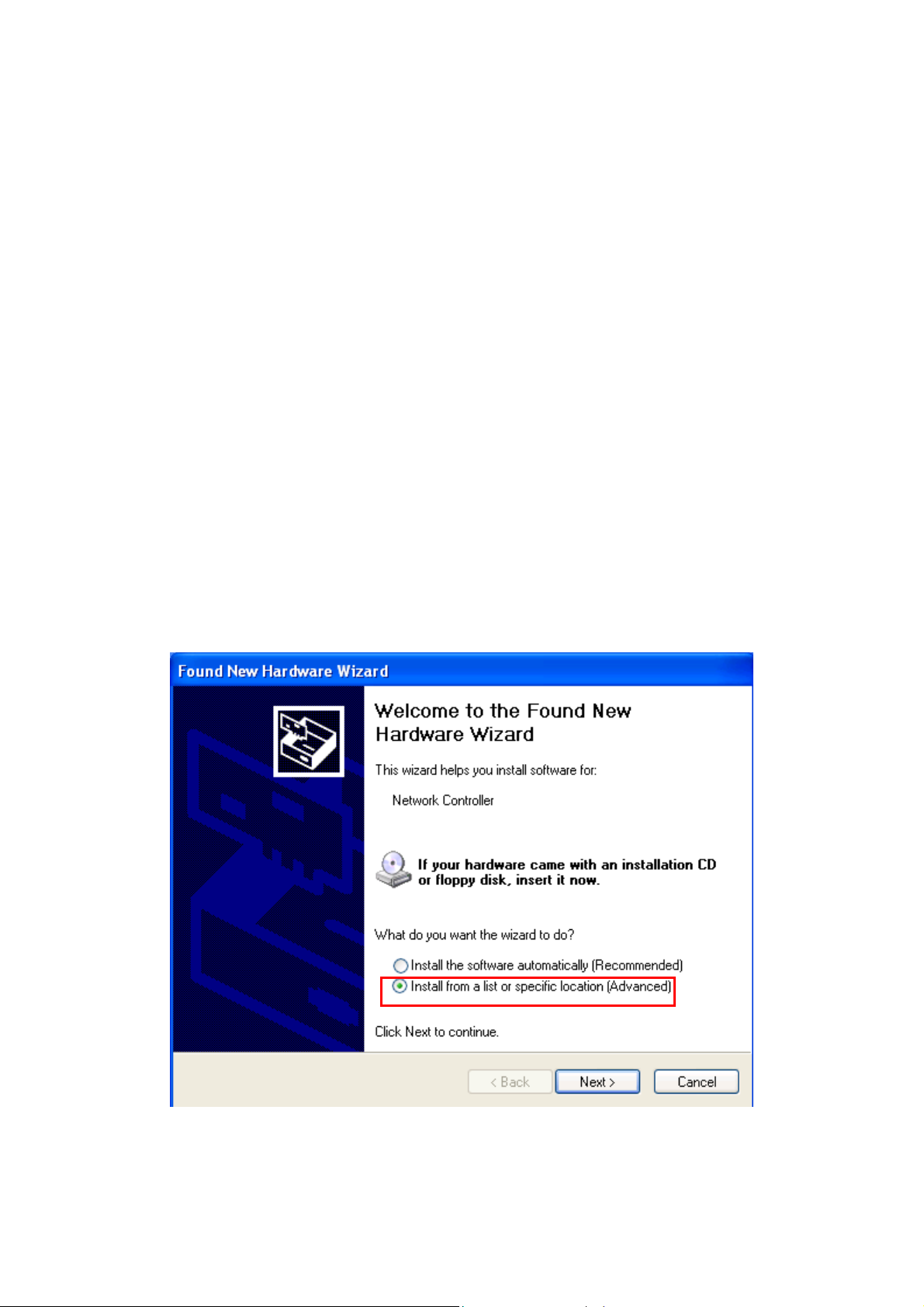
Step 2: Insert the Product CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. Select “Search removable media
[floppy, CD-ROM…]” check box and click on Next to install the driver.
Step 3: The windows will find “TNET1130 WLAN Adapter” and start copying corresponding
files into the system. Click on Next to continue.
- 5 -
Page 10

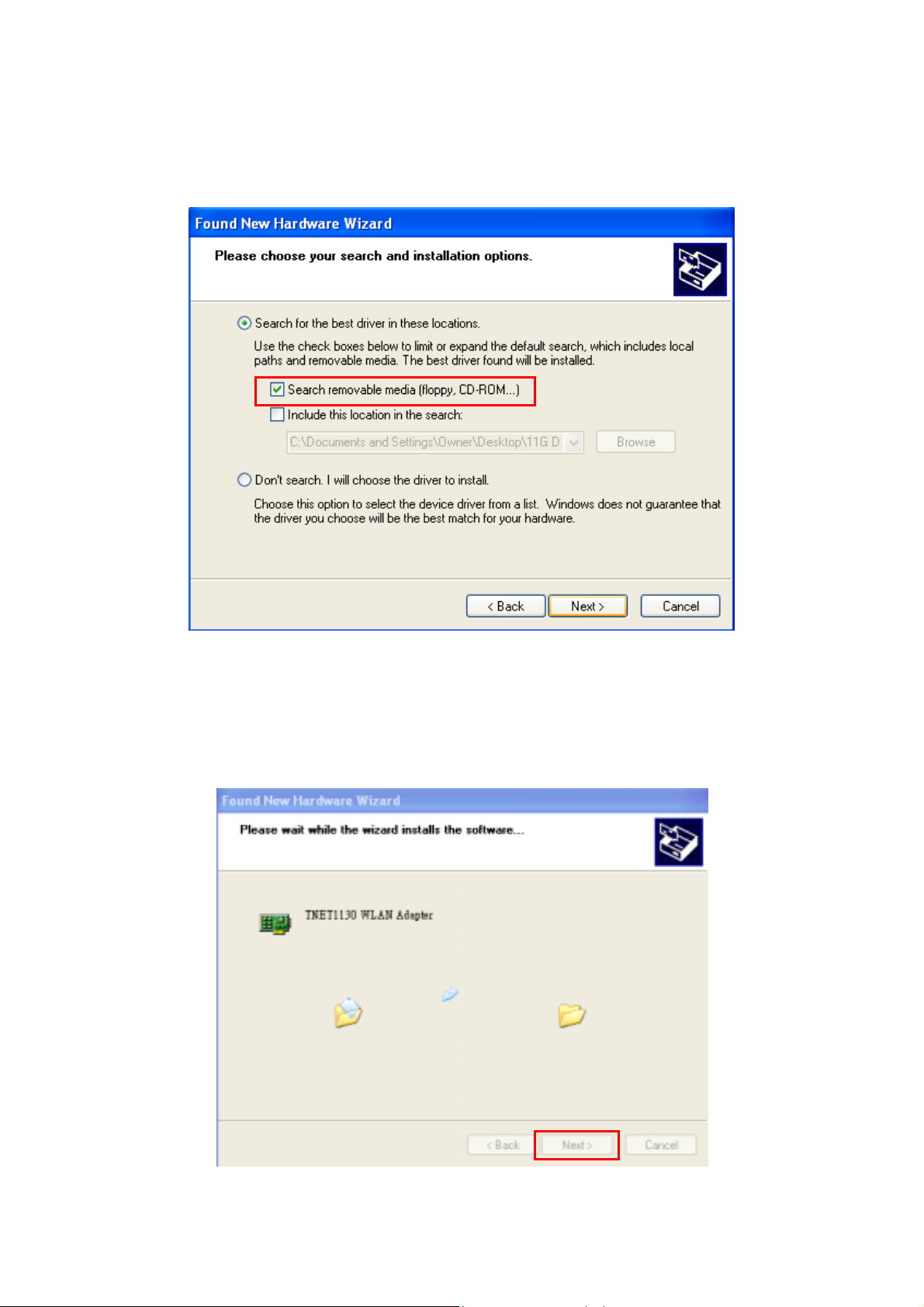
Step 4: Click Continue Anyway to continue the installation.
Step 5: Click Finish to complete the installation.
- 6 -
Page 11

Step 6: Right click “My Computer” from Start, select Properties, go to the Hardware tab and
click the Device Manager button to see if any error icon appears next to the Network
Adapter/WIRELESS LAN Card. If no error, your TNET1130 WLAN Adapter working well.
3-2 Set up WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows 2000
Step 1: After inserting the WIRELESS LAN Card into the PCMCIA slot on your notebook,
Windows will auto-detect the WIRELESS LAN Card.
- 7 -
Page 12

Step 2: A “Found New Hardware Wizard” window shows up. Click Next to proceed.
Step 3: Select “Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended)”.
- 8 -
Page 13

Step 4: Insert the Product CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. Specify the location where the driver
is placed. Click on Next to install the driver.
Step 5: The windows will find “Network Controller”. Click on Next to continue.
- 9 -
Page 14
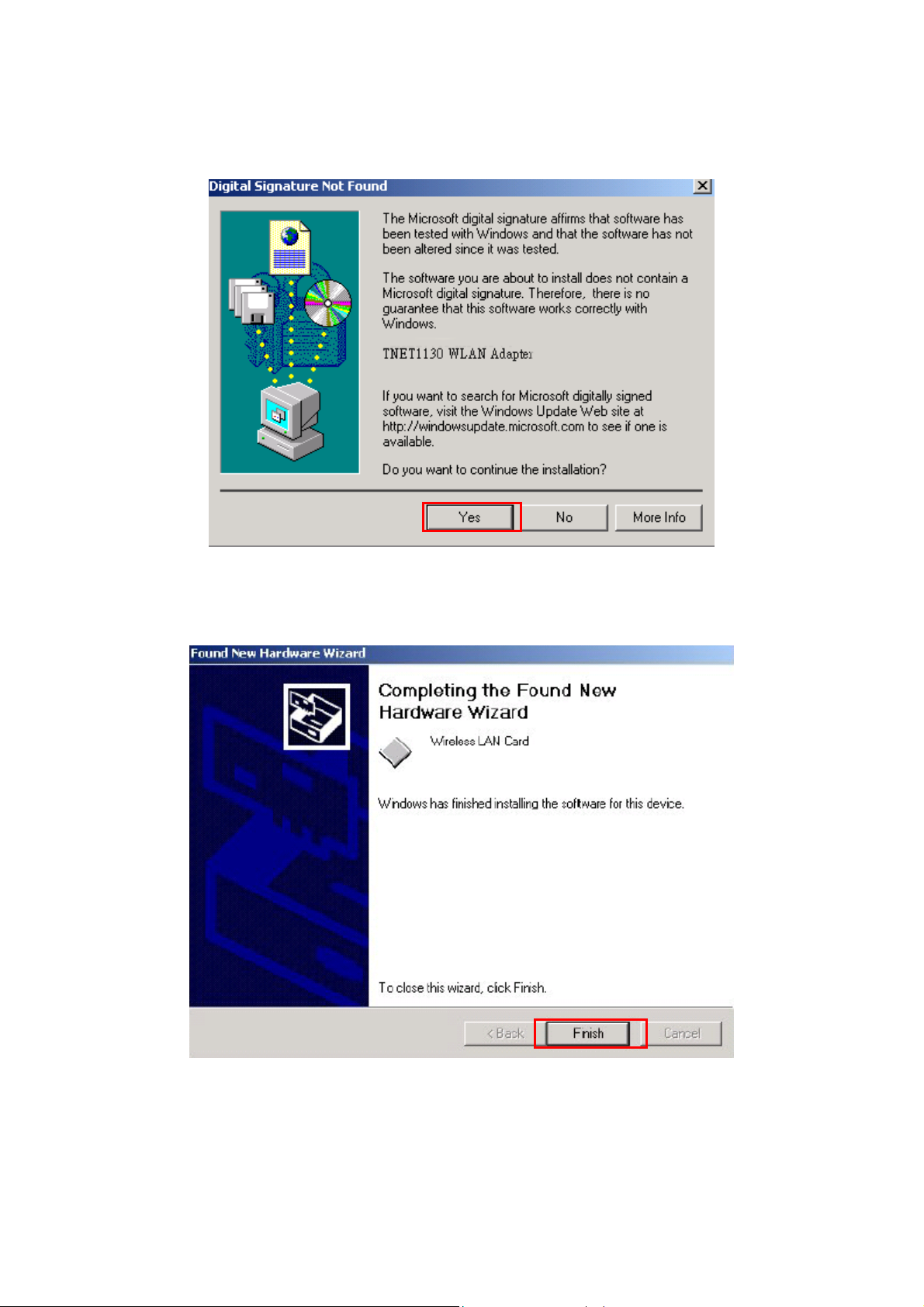
Step 6: Click Yes to continue the installation.
Step 7: Click Finish to complete the installation.
- 10 -
Page 15

Step 8: Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network Adapters to see if
any error icon appears. If no error, your TNET1130 WLAN Adapter is working well.
3-3 Set up WIRELESS LAN Card for Windows 98/ ME
Step 1: After inserting the WIRELESS LAN Card into the PCMCIA slot on your notebook,
Windows will auto-detect new hardware and will display an “Add New Hardware Wizard”
window. Click Next to continue.
- 11 -
Page 16

Step 2: Select “Search for the best driver for your device (Recommended)” and click Next.
Step 3: Insert the Product CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. Select the “CD-ROM drive” check
box and click on Next to install the driver.
- 12 -
Page 17
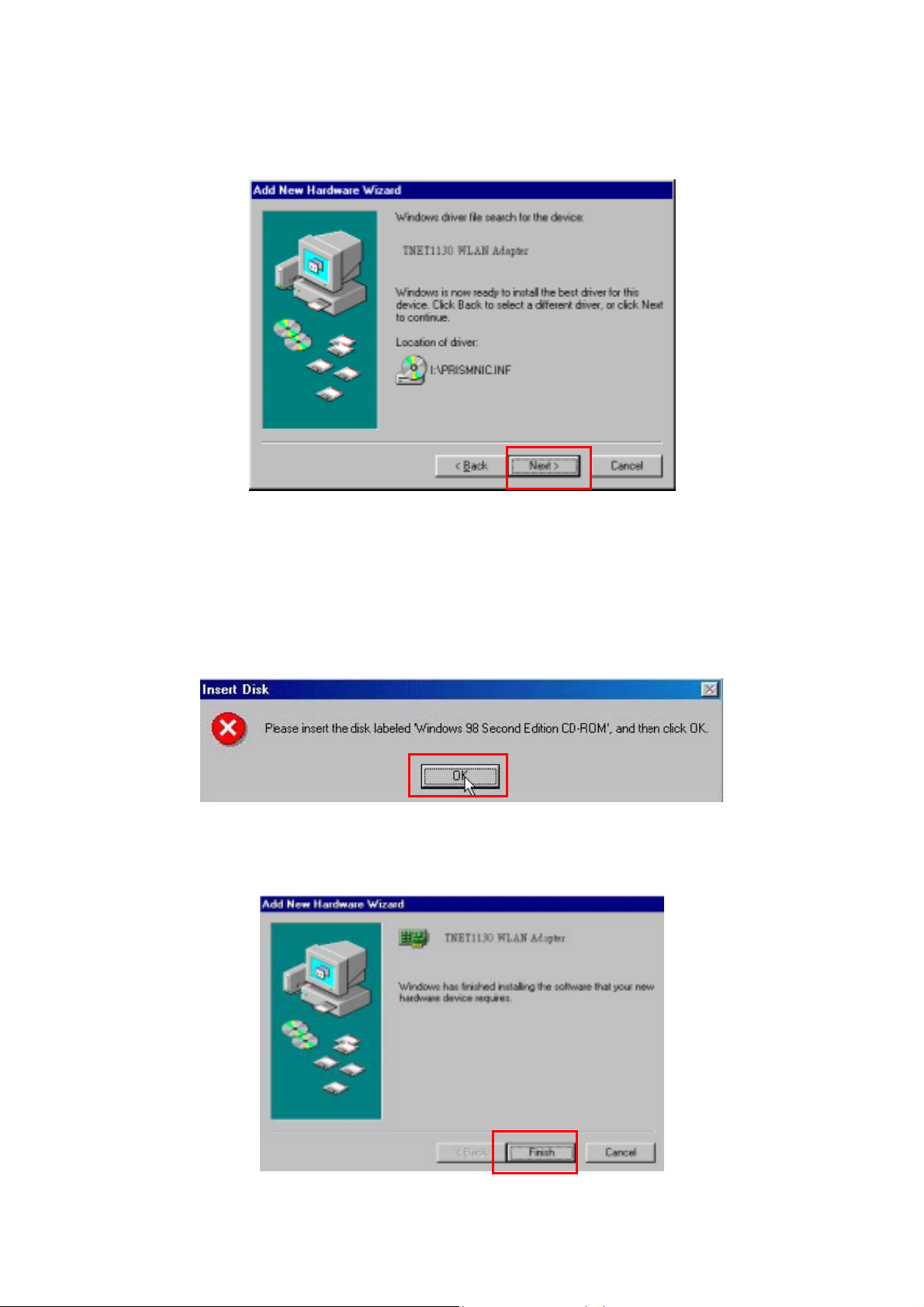
Step 4: The Windows will find “TNET1130 WLAN Adapter”. Click Next to continue.
Step 5: Once the 『 Please insert the disk labeled ‘Windows 98 Second Edition CD-ROM/ME
CD-ROM”, and then click OK』window appears, inset enter the path corresponding to the
appropriate drives and click OK. Usually these files can be found at C:\Windows or
C:\Windows\system.
Step 6: Click Finish to complete the software installation.
- 13 -
Page 18

Step 7: Restart the computer.
Step 8: Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network Adapters to see if
any error icon appears next to the IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS LAN Card. If no error, your
TNET1130 WLAN Adapter is working well.
3-4 Uninstall the WIRELESS LAN Card
If you do not need the WIRELESS connectivity of your WIRELESS LAN Card, it is advised that
you uninstall the card from its slot as described below:
- 14 -
Page 19

1. Open Control Panel/System/Device Manager, and check Network Adapters
2. In the list of Network adapters components, click right to select “TNET1130 WLAN
Adapter”.
- 15 -
Page 20

3. Choose Uninstall.
You will be asked for confirmation and instructed to reboot the computer in operation system
Microsoft Win98 and WinME.
- 16 -
Page 21

Chapter 4 Configure the WIRELESS Lan Adapter
This chapter will show you how to configure your WIRELESS Lan adapter by using utility in the
Product CD Package under Windows series Operation System
4-1 Install Utility
1. Put the CD Package into you CD-Rom, and the install program will autorun the frame as follows,
choose Utility Setup and finish the install process step by step.
2. After finishing the install process, you can execute the utility as follows
- 17 -
Page 22

3. You will see the utility icon after you executing program twlan if your WIRELESS Adapter is
alive
4-2 Configure WIRELESS Lan Adapter for Windows XP
After installing TNET1130 WLAN Adapter, the Windows XP will display a “WIRELESS
Network Connection ” message.
Click on the message and the “Automatic WIRELESS Network Configuration” will then appear
automatically and allow users to connect to an available WIRELESS infrastructure network (Access
Point), shown as follows. You may click the Advanced button to make advanced configuration for
the WIRELESS LAN Card, shown as below.
Choose one
suitable server
- 18 -
Page 23

In order to reconfigure you WIRELESS connection, you can deal as follow procedure
1.click left the network icon.
2. Click Properties to continue
3. Click WIRELESS Networks to reconfigure the WIRELESS network connection.
- 19 -
Page 24

4. If you need a key(WEP) to connect the WIRELESS network, you should keyin the key that
supported by the WIRELESS network router or access point
- 20 -
Page 25

k
Note: Under the Windows XP, it is recommend to use the “Automatic WIRELESS Networ
Configuration” to configure your 11G WIRELESS LAN Card. The WIRELESS LAN Utility
comes with the WIRELESS LAN Card is not support the Windows XP.
4-3 Configure WIRELESS Lan Adapter for Windows 98/ME/2000 by
utility
1. click the utility icon, and you will see the application interface as step 2.
2. main configure window show as follows, in order to connect an access point to communicate
with other station, double click any ssid of access pint, the access point’s information will show
in the group windows “Current Configuration”. You can click the button “Modify” to
configure your connect to the access point in advance.
1
2
3
- 21 -
Page 26

The windows “ Main New Connection “
Modify
The windows “ Main Advanced “
Modify
- 22 -
Page 27

The windows “ Main Security“
Modify
3. After you configure you connection, the related information will show as follows
- 23 -
Page 28

3. When the access point requests the client to authenticate or associate, you should configure the
related information here.
4.
5. this page show wireless LAN card’s state of Transmit and Receive.
- 24 -
Page 29

6. this page show os version、utility version、driver version、firmware version and EEPROM
version.
- 25 -
 Loading...
Loading...