Page 1

Networking Gateway
System Manual
S/W Version 2.0
August 2005
P/N 214196
Page 2

Page 3

About This Manual
This manual contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1 – Product Description: Describes the Networking Gateway
and its components.
Chapter 2 – Installation: Describes how to install the system and its
components.
Chapter 3 – Operation and Administration: Describes how to use the
web-based management application for configuring parameters and
managing the Networking Gateway.
Appendix A – Print Server: Describes how to configure the printer
server.
Appendix B – 802.1x Setting.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1 - Product Description .......................................................1
1.1 Introducing the Networking Gateway IDU ......................................................2
1.2 Functions and Features ...................................................................................3
1.2.1 Basic Functions....................................................................................................3
1.2.2 Wireless Functions...............................................................................................4
1.2.3 Security Functions ...............................................................................................4
1.2.4 Advanced Functions ............................................................................................5
1.3 Specifications....................................................................................................6
1.3.1 Radio Specifications ............................................................................................6
1.3.2 Regulatory Standards Compliance ......................................................................6
1.3.3 Environmental ......................................................................................................7
1.3.4 Mechanical ...........................................................................................................7
1.3.5 Electrical...............................................................................................................7
Chapter 2 - Installation .....................................................................9
2.1 Installation Requirements ..............................................................................10
2.1.1 Packing List........................................................................................................10
2.1.2 Additional Installation Requirements .................................................................10
2.2 Panels Layout and Components ...................................................................11
2.2.1 Front Panel.........................................................................................................11
2.2.2 Rear Panel Components....................................................................................13
2.3 Installation.......................................................................................................14
Page 6

Contents
Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server............................ 17
3.1 Introduction .................................................................................................... 18
3.2 Accessing the Web Configuration Server.................................................... 19
3.3 Log in and Log out ......................................................................................... 20
3.3.1 The Main Menu.................................................................................................. 21
3.3.2 Control Buttons .................................................................................................. 21
3.4 Status .............................................................................................................. 23
3.5 Wizard (Administrator only) .......................................................................... 25
3.6 Basic Setting................................................................................................... 33
3.6.1 WAN Setup ........................................................................................................ 33
3.6.2 LAN Setup..........................................................................................................42
3.6.3 Wireless Setting................................................................................................. 48
3.6.4 Change Password .............................................................................................54
3.7 Security Setting .............................................................................................. 55
3.7.1 MAC Control ......................................................................................................55
3.7.2 Packet Filters (Administrator only)..................................................................... 55
3.7.3 URL Blocking (Administrator only)..................................................................... 60
3.7.4 Domain Filter (Administrator only) ..................................................................... 62
3.7.5 Firewall (Administrator only) .............................................................................. 64
3.7.6 Miscellaneous Items (Administrator only).......................................................... 65
3.8 NAT Setting (Administrator only).................................................................. 67
3.8.1 Virtual Server ..................................................................................................... 67
3.8.2 Special AP .........................................................................................................68
3.8.3 DMZ Host...........................................................................................................69
3.8.4 VPN Pass Through ............................................................................................70
3.9 Advanced Settings (Administrator only)...................................................... 72
3.9.1 System Time ...................................................................................................... 72
Page 7

Introducing the Networking Gateway IDU
3.9.2 System Log ........................................................................................................73
3.9.3 Dynamic DNS.....................................................................................................75
3.9.4 SNMP Setting.....................................................................................................76
3.9.5 Routing Table.....................................................................................................77
3.9.6 Schedule Rule....................................................................................................80
3.9.7 UPnP Setting......................................................................................................83
3.10 Toolbox............................................................................................................84
3.10.1 View Log ............................................................................................................84
3.10.2 Firmware Upgrade (Administrator only).............................................................85
3.10.3 Backup Setting...................................................................................................86
3.10.4 Reset to Default .................................................................................................87
3.10.5 Reboot................................................................................................................87
3.10.6 DRAP .................................................................................................................88
3.10.7 Miscellaneous Items ..........................................................................................89
3.11 Web Configuration Server’s Parameters Summary.....................................91
Appendix A - Print Server..............................................................103
A.1 Configuring on Windows 2000 and XP Platforms......................................104
Appendix B - 802.1x Setting..........................................................111
Glossary.........................................................................................119
Manual Revision
vii
Page 8

Page 9

Figures
Figure 1: Front Panel .........................................................................................................................11
Figure 2: Rear Panel (without antenna).............................................................................................13
Figure 3: Log In Window....................................................................................................................20
Figure 4: Networking Gateway Main Window....................................................................................21
Figure 5: System Status ....................................................................................................................23
Figure 6: Setup Wizard ......................................................................................................................25
Figure 7: Setup Wizard - Select WAN Type ......................................................................................25
Figure 8: Setup Wizard – WAN Type - Static IP Address..................................................................26
Figure 9: Setup Wizard - Dynamic IP Address ..................................................................................27
Figure 10: Setup Wizard - Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management..............28
Figure 11: Setup Wizard – PPP over Ethernet ..................................................................................29
Figure 12: Setup Wizard – PPTP.......................................................................................................30
Figure 13: Setup Wizard - Configuration Completed.........................................................................32
Figure 14: Basic Setting.....................................................................................................................33
Figure 15: WAN Setup/Primary Setup...............................................................................................33
Figure 16: Virtual Computers.............................................................................................................34
Figure 17: Choose WAN Type...........................................................................................................35
Figure 18: Primary Setup - Static IP Address....................................................................................36
Figure 19: Primary Setup - Dynamic IP Address...............................................................................37
Figure 20: Primary Setup - Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management.............38
Figure 21: Primary Setup - PPPoE ....................................................................................................40
Figure 22: Primary Setup - PPTP ......................................................................................................41
Figure 23: LAN Setup ........................................................................................................................42
Figure 24: LAN Setup - DHCP Server Enabled.................................................................................44
Page 10

Figures
Figure 25: DHCP Clients List............................................................................................................. 45
Figure 26: MAC Address Control.......................................................................................................46
Figure 27: DHCP Clients Combo Box ...............................................................................................48
Figure 28: Wireless Setting ...............................................................................................................48
Figure 29: Wireless Clients List......................................................................................................... 51
Figure 30: Advanced Wireless Setting .............................................................................................. 52
Figure 31: Change Password ............................................................................................................ 54
Figure 32: Security Setting Window .................................................................................................. 55
Figure 33: Packet Filter Initial Window ..............................................................................................56
Figure 34: Inbound Packet Filter – Example 1 .................................................................................. 58
Figure 35: Inbound Packet Filter - Example 2 ................................................................................... 58
Figure 36: Outbound Packet Filter - Example 1 ................................................................................ 59
Figure 37: Outbound Packet Filter - Example 2 ................................................................................ 60
Figure 38: URL Blocking.................................................................................................................... 60
Figure 39: URL Blocking Example.....................................................................................................61
Figure 40: Domain Filter ....................................................................................................................62
Figure 41: Firewall .............................................................................................................................64
Figure 42: Miscellaneous Items.........................................................................................................65
Figure 43: NAT Setting ......................................................................................................................67
Figure 44: Virtual Server.................................................................................................................... 67
Figure 45: Special Applications ......................................................................................................... 69
Figure 46: DMZ Host ......................................................................................................................... 70
Figure 47: VPN Pass Through...........................................................................................................70
Figure 48: Advanced Setting ............................................................................................................. 72
Figure 49: System Time ....................................................................................................................72
Figure 50: System Log ......................................................................................................................74
Figure 51: Dynamic DNS...................................................................................................................75
Figure 52: SNMP Setting...................................................................................................................76
Figure 53: Routing Table ................................................................................................................... 78
Page 11

Introducing the Networking Gateway IDU
Figure 54: Schedule Rule ..................................................................................................................80
Figure 55: Schedule rule Setting .......................................................................................................81
Figure 56: Schedule Rule Setting – Example Step 1 ........................................................................81
Figure 57: Schedule Rule Setting – Example Step 2 ........................................................................82
Figure 58: Virtual Server - Schedule Rule#1 .....................................................................................82
Figure 59: Packet Filter - Schedule Rule#1.......................................................................................83
Figure 60: UPnP Setting ....................................................................................................................83
Figure 61: Toolbox.............................................................................................................................84
Figure 62: View System Log..............................................................................................................85
Figure 63: Firmware Upgrade............................................................................................................86
Figure 64: Backup..............................................................................................................................87
Figure 65: Reset to Default................................................................................................................87
Figure 66: Reboot ..............................................................................................................................88
Figure 67: DRAP Protocol .................................................................................................................88
Figure 68: Toolbox - Miscellaneous Items.........................................................................................89
Manual Revision
xi
Page 12

Page 13

Tables
Table 1: Radio Specifications ..............................................................................................................6
Table 2: Regulatory Standards Compliance........................................................................................6
Table 3: Environmental Specifications.................................................................................................7
Table 4: Mechanical Specifications .....................................................................................................7
Table 5: Electrical Specifications .........................................................................................................7
Table 6: Front Panel LEDs ................................................................................................................11
Table 7: Rear Panel Connectors .......................................................................................................13
Table 8: Status Window Parameters .................................................................................................23
Table 9: Setup Wizard – Static IP Address Parameters....................................................................27
Table 10: Setup Wizard – Dynamic IP Address Parameters.............................................................28
Table 11: Setup Wizard – Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management
Parameters ........................................................................................................................................29
Table 12: Setup Wizard – PPPoE Parameters..................................................................................30
Table 13: Setup Wizard – PPTP Parameters ....................................................................................31
Table 14: Virtual Computers Parameters ..........................................................................................34
Table 15: Static IP Address Parameters ...........................................................................................36
Table 16: Dynamic IP Address Parameters ......................................................................................38
Table 17: Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management Parameters ....................39
Table 18: PPP over Ethernet Parameters .........................................................................................40
Table 19: PPTP Parameters..............................................................................................................41
Table 20: LAN Setup Parameters......................................................................................................43
Table 21: DHCP Clients List Parameters ..........................................................................................45
Table 22: DHCP Clients List Parameters ..........................................................................................46
Table 23: Wireless Setting Parameters .............................................................................................49
Page 14

Tables
Table 24: Wireless Clients List Parameters ......................................................................................51
Table 25: Advanced Wireless Setting Parameters............................................................................ 52
Table 26: Advanced Wireless Setting Parameters............................................................................ 56
Table 27: URL Blocking Parameters .................................................................................................61
Table 28: Domain Filter Parameters..................................................................................................63
Table 29: Firewall Parameters...........................................................................................................64
Table 30: Miscellaneous Items Parameters ...................................................................................... 65
Table 31: Virtual Server Parameters .................................................................................................68
Table 32: Special Applications Parameters.......................................................................................69
Table 33: VPN Pass Through Parameters ........................................................................................71
Table 34: System Time Parameters .................................................................................................. 73
Table 35: System Log Parameters .................................................................................................... 74
Table 36: Dynamic DNS Parameters ................................................................................................76
Table 37: SNMP Parameters.............................................................................................................77
Table 38: Routing Table Parameters.................................................................................................78
Table 39: Routing Table Parameters.................................................................................................80
Table 40: DRAP Protocol Parameters............................................................................................... 88
Table 41: Miscellaneous Items Parameters ...................................................................................... 90
Table 42: Web Configuration Server’s Parameters Summary .......................................................... 91
Page 15
Chapter 1 - Product Description
In This Chapter:
Introducing the Networking Gateway IDU, page 2
1
1
Functions and Features
Specifications
, page 6
, page 3
Page 16

Chapter 1 - Product Description
1.1 Introducing the Networking Gateway
IDU
The Networking Gateway Indoor Unit (IDU) enables operators and service
providers using a Broadband Wireless Access system to provide subscribers
with a number of broadband services transparently.
The Networking Gateway IDU together with the SU-ODU comprises a
Subscriber Unit that provides data connections to the Base Station. The
four 10/100Base-T Ethernet ports connect to the user’s data equipment,
providing comprehensive routing functionality and supporting various
security features. User’s data equipment equipped with either IEEE
802.11b (11M) or IEEE 802.11g (54M) compatible wireless adapters can
connect to the unit via its built-in Wireless LAN port, functioning as an
Access Point.
The Networking Gateway IDU is powered from the mains. The Networking
Gateway IDU is connected to the ODU via a category 5E Ethernet cable.
This cable carries the Ethernet data between the two units as well as power
(54 VDC) and control signals to the ODU. It also carries status indications
from the ODU.
The Networking Gateway is designed for remote management and
supervision using either the built-in internal web server or SNMP.
The Networking Gateway is easily updated and upgraded as it supports
remote software and configuration file download.
Product Description
2
Page 17

1.2 Functions and Features
1.2.1 Basic Functions
Auto-sensing Ethernet Switch
Equipped with a 4-port auto-sensing Ethernet switch.
Printer sharing
Embedded print server to allow all of the networked computers to share
one printer through the USB host port.
WAN Types
Support of several WAN types: Static, Dynamic, PPPoE, PPTP, and
Dynamic IP with Road Runner Session Management (e.g., Telstra,
BigPond).
Functions and Features
Firewall
All unwanted packets from outside intruders can be blocked to protect
the Intranet.
DHCP Server Support
All of the networked computers can retrieve TCP/IP settings
automatically from the Networking Gateway.
Web-based configuring
Configurable through any networked computer’s web browser using
Netscape or Internet Explorer.
Virtual Server Support
Enables to expose WWW, FTP and other services on your LAN to other
Internet users.
User-Definable Application Sensing Tunnel
Users can define the attributes to support special applications requiring
multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, video conferencing,
Internet telephony and so on. The Networking Gateway can sense the
application type port as a trigger and open a multi-port tunnel for it.
DMZ Host Support
NG System Manual
Lets one specific networked computer be fully exposed to the Internet.
This function is used when special application sensing tunnel feature is
insufficient to allow an application to function correctly. Use with
caution.
3
Page 18

Chapter 1 - Product Description
Statistics of WAN Support
Enables to monitor inbound and outbound packets.
1.2.2 Wireless Functions
High speed for wireless LAN connection
Up to 54 Mbps data rate by incorporating Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing (OFDM).
IEEE 802.11b compatible (11M)
Allowing inter-operation among multiple vendors.
IEEE 802.11g compatible (54M)
Allowing inter-operation among multiple vendors.
Auto fallback
54M, 48M, 36M, 24M, 18M, 12M, 6M data rates with auto fallback in
802.11g mode.
11M, 5.5M, 2M, 1M data rates with auto fallback in 802.11b mode.
1.2.3 Security Functions
Packet Filter
Packet Filter allows controlling access to a network by analyzing the
incoming and outgoing packets and letting them pass or blocking them
based on the source and destination IP addresses and ports.
Domain Filter Support
Enables preventing users from accessing specific domains.
URL Blocking Support
URL Blocking uses keywords to block hundreds of applicable websites
connections.
VPN Pass-through
The Networking Gateway can also support VPN pass-through.
802.1X Support
When the 802.1X function is enabled, the Wireless user must be
authenticated by the Networking Gateway before being allowed to use
the Network services.
Product Description
4
Page 19

SPI Mode Support
When SPI Mode is enabled, the Networking Gateway checks every
incoming packet and detects if this packet has changed its IP address
since initial negotiation.
DoS Attack Detection Support
When this feature is enabled, the Networking Gateway detects and logs
Denial of Service (DoS) attack arriving from the Internet.
1.2.4 Advanced Functions
System Time
Allows synchronizing system time with a network time server, with the
PC, or set the time manually.
E-mail Alert
The Networking Gateway can be configured to send its log file by mail.
Functions and Features
Dynamic DNS
At present, the Networking Gateway supports 3 Dynamic DNSs:
DynDNS.org, TZO.com and dhs.org.
SNMP Support
The Networking Gateway supports SNMP V1 and V2c.
Routing Table
The Networking Gateway supports static routing and two kinds of
dynamic routing: RIP1 and RIP2.
Schedule Rule
Customers can control the schedule (when to allow and when to block)
for several functions, such as virtual server and packet filters.
NG System Manual
5
Page 20
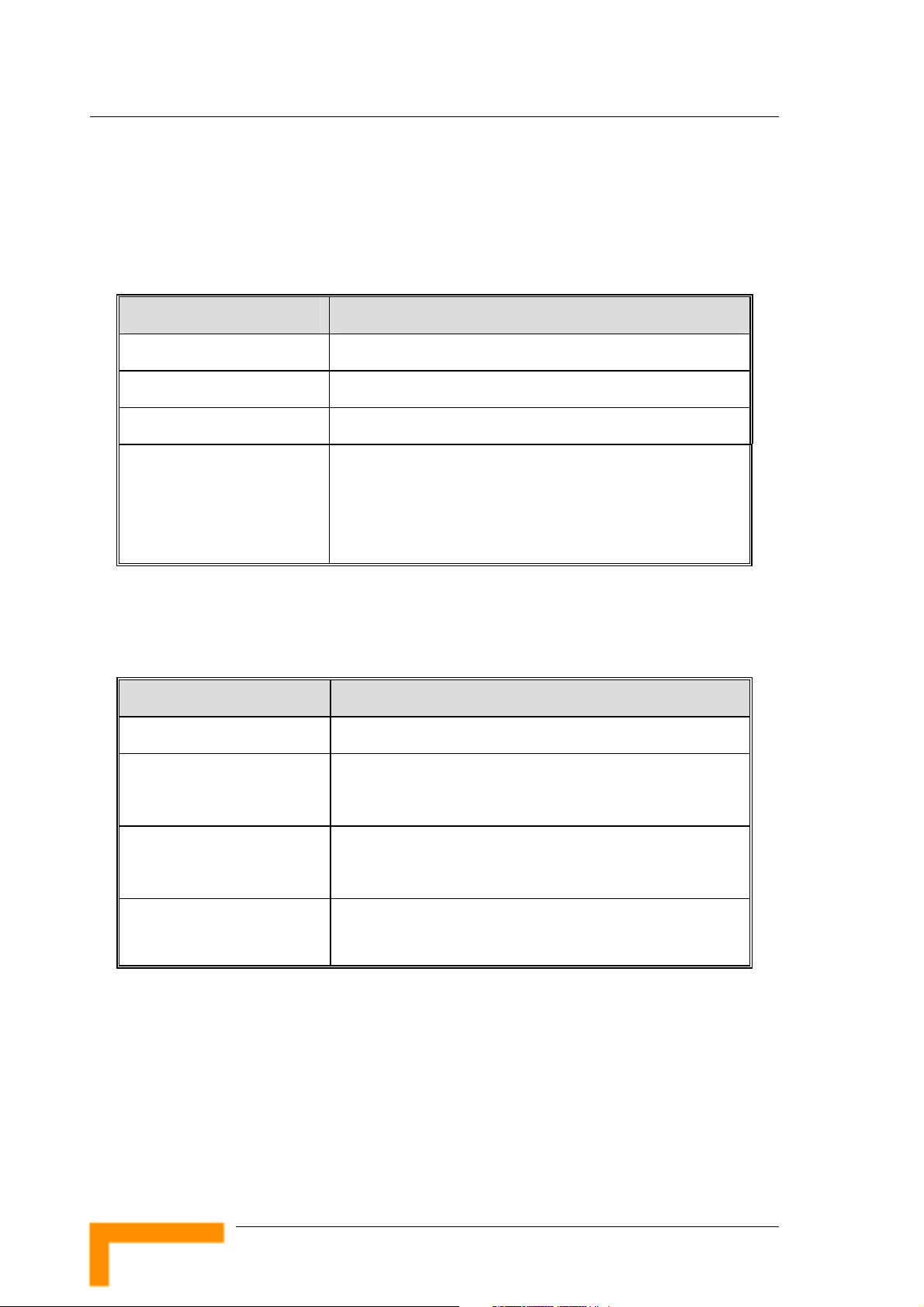
Chapter 1 - Product Description
1.3 Specifications
1.3.1 Radio Specifications
Table 1: Radio Specifications
Item Description
Frequency 2400-2483.5 MHz
Wireless LAN Standards Compliant with IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g
Output Power (Average) 10, 12, 15, 17 dBm
Data Rates IEEE 802.11g mode: 54M, 48M, 36M, 24M, 18M, 12M, 6M
with auto fallback in.
IEEE 802.11b mode: 11M, 5.5M, 2M, 1M with auto fallback
in.
1.3.2 Regulatory Standards Compliance
Table 2: Regulatory Standards Compliance
Type Standard
EMC ETS EN 301 489-17
Safety EN 60950 (CE)
IEC 60 950 US/C UL
Radio ETSI 300 328
FCC Part 15
Immunity EN 55024:1998
Product Description
6
Page 21
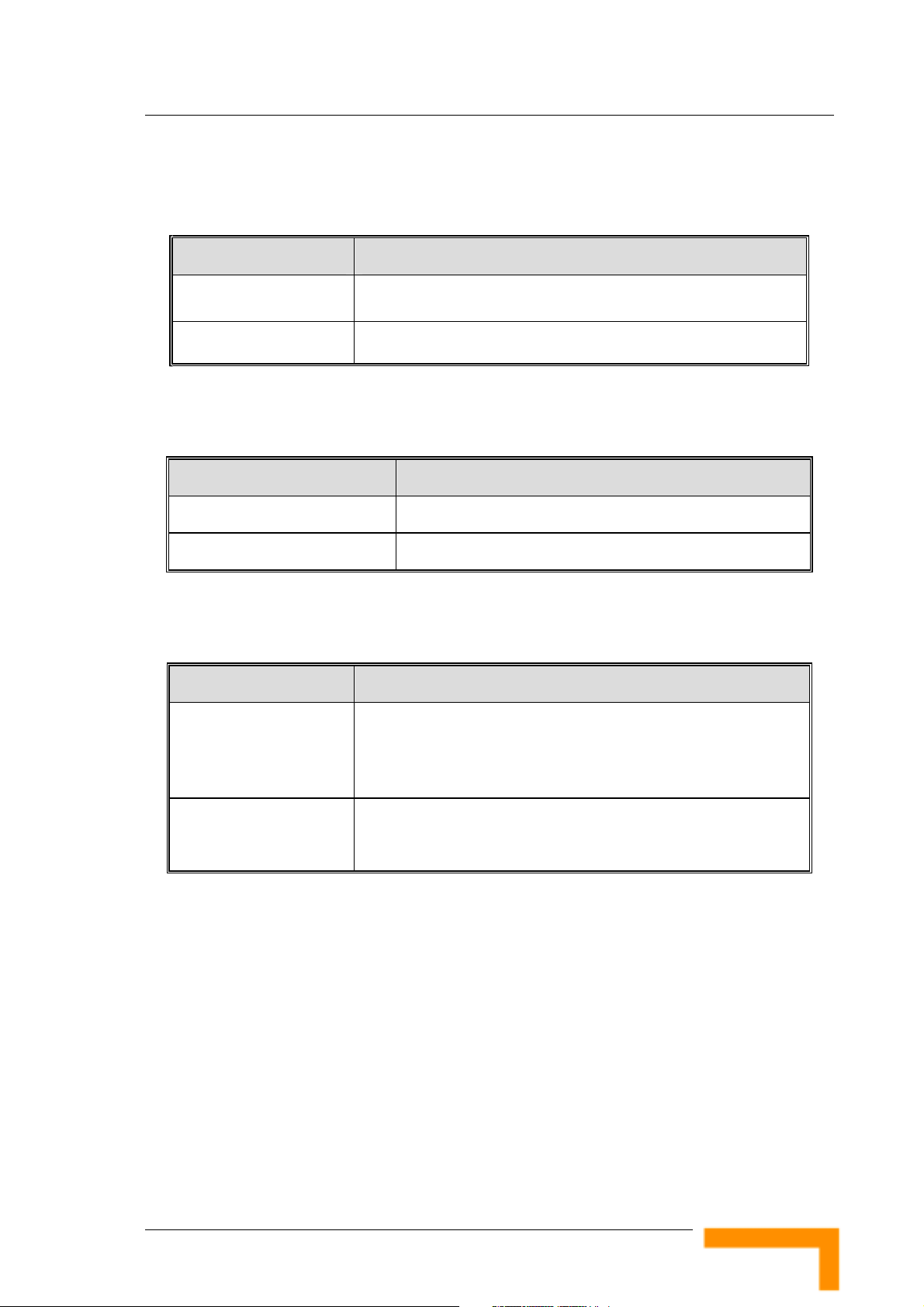
1.3.3 Environmental
Table 3: Environmental Specifications
Item Details
Specifications
Operating temperature 0
Operating humidity 5%-95% non condensing
o
C to 40
o
C
1.3.4 Mechanical
Table 4: Mechanical Specifications
Item Details
Dimensions (W x H x D) 190.5 x 26.2 x 111 mm
Weight 0.62 kg
1.3.5 Electrical
Table 5: Electrical Specifications
Item Details
Power Transformer 100-240 VAC, 50-60 Hz, 2A max.
Supplies 5 VDC (for the Networking Gateway IDU) and 55 VDC (for
the ODU via the RADIO connector)
Power Consumption Networking Gateway IDU (5 VDC): 10W max
ODU (55 VDC): 50W max.
NG System Manual
7
Page 22

Page 23

Chapter 2 - Installation
In This Chapter:
Installation Requirements, page 10
2
2
Panels Layout and Components
Installation
, page 14
, page 11
Page 24

Chapter 2 - Installation
2.1 Installation Requirements
2.1.1 Packing List
Networking Gateway IDU
Antenna
Power Transformer
Mains power cord
2.1.2 Additional Installation Requirements
Ethernet cable(s) for connecting to the end-user’s data equipment.
Mains plug adapter or termination plug (if the power plug on the
supplied AC power cord does not fit local power outlets).
PC with an Ethernet card and an Ethernet cable for configuring the
Networking Gateway IDU parameters using a web browser, and for
configuring the SU-ODU parameters using Telnet.
Other installation tools and materials (e.g., means for securing cables to
walls, etc.)
10
Installation
Page 25
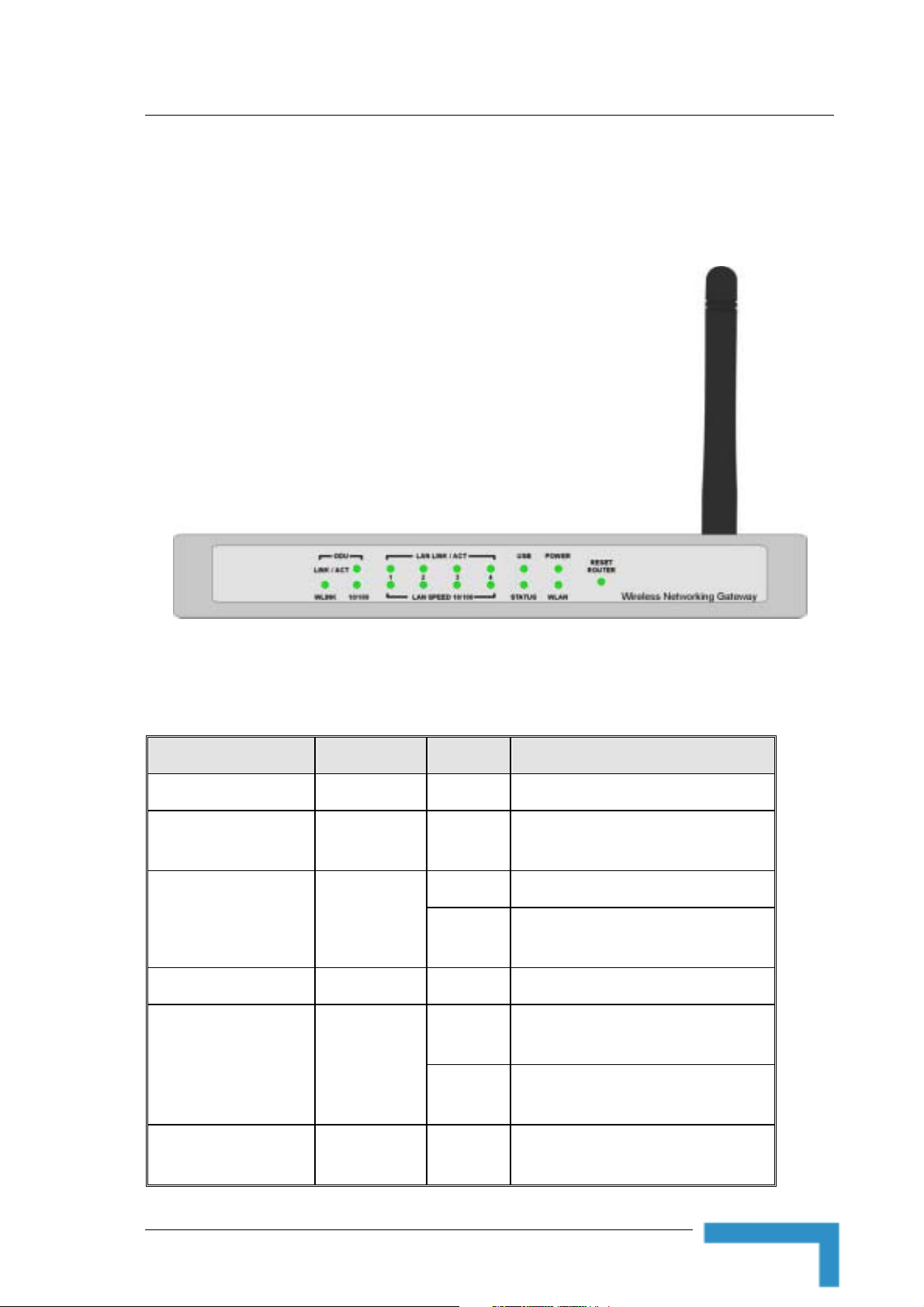
Panels Layout and Components
2.2 Panels Layout and Components
2.2.1 Front Panel
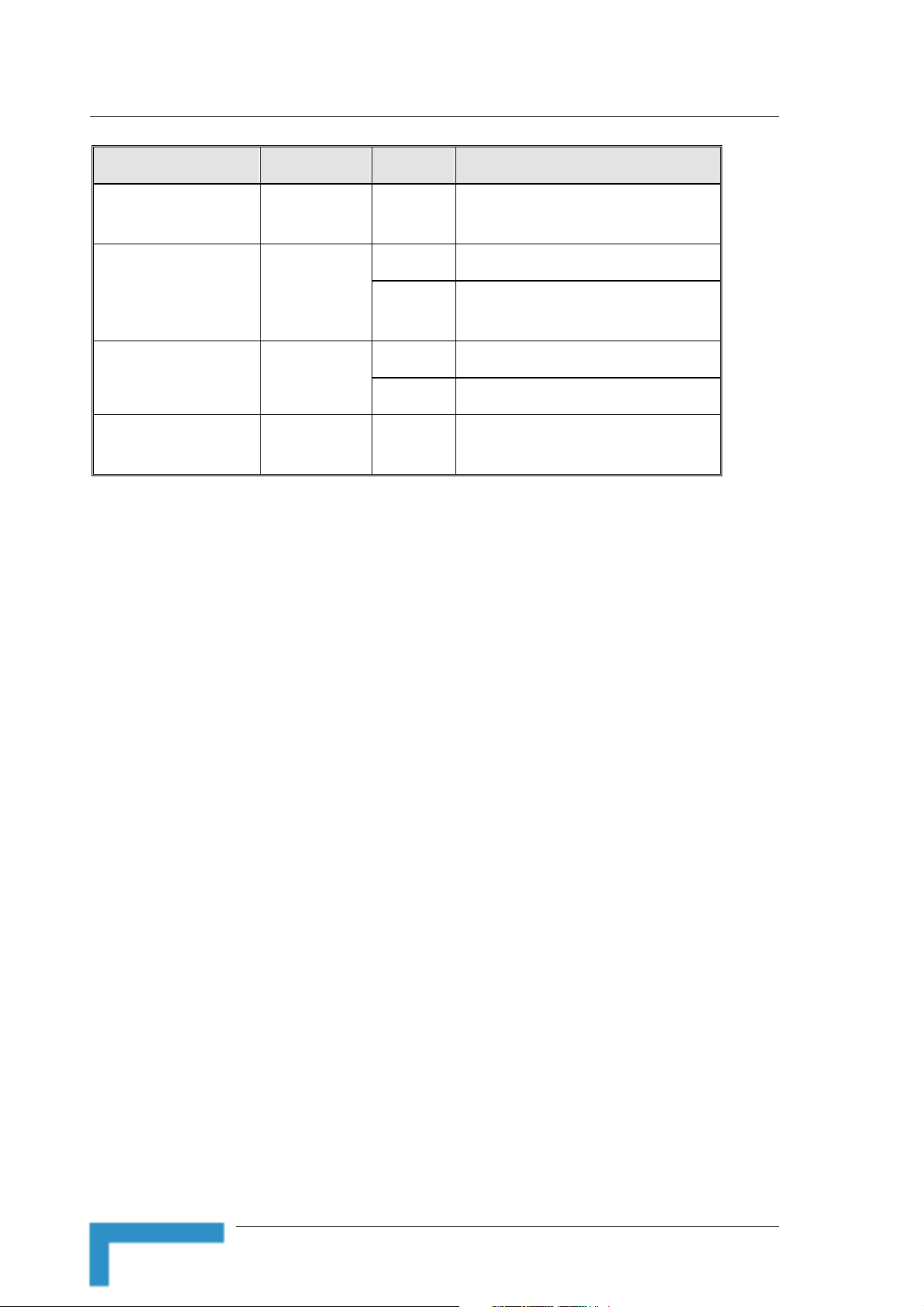
Figure 1: Front Panel
2.2.1.1 Front Panel LEDs
Table 6: Front Panel LEDs
LED Function Status Description
POWER Power Indication On Power is available.
WLAN
USB USB Port Activity
STATUS System Status Blinking The unit is functioning properly.
LAN LINK/ACT
1~4
Wireless LAN
Activity
LAN Status
Blinking
On The USB port is linked.
Blinking
On
Blinking
Sending or receiving data via wireless
LAN.
The USB port is sending or receiving
data.
An active station is connected to the
corresponding LAN port.
The corresponding LAN port is sending or
receiving data.
LAN SPEED 10/100
1~4
NG System Manual
LAN Port Data
Rate
On
Data rate is 100 Mbps on the
corresponding LAN port.
11
Page 26
Chapter 2 - Installation
LED Function Status Description
Data rate is 10 Mbps on the
corresponding LAN port.
The ODU port is sending or receiving
data.
ODU LINK/ACT
ODU 10/100 ODU Port Data
ODU WLINK
ODU Port
Activity
Rate
ODU Wireless
Link Status
Off
On The ODU port is connected to the ODU.
Blinking
On Data rate is 100 Mbps.
Off Data rate is 10 Mbps.
On The ODU is connected with an AU.
2.2.1.2 RESET ROUTER Button
Press momentarily the recessed RESET ROUTER button to reset the
Networking Gateway IDU.
2.2.1.3 Resetting the IDU to Factory Defaults
Press the RESET ROUTER button for at least 5 seconds, until the STATUS
LED flashes 5 times. After releasing the button, the unit will resume
operation with the factory default configuration.
12
Installation
Page 27
Panels Layout and Components
2.2.2 Rear Panel Components
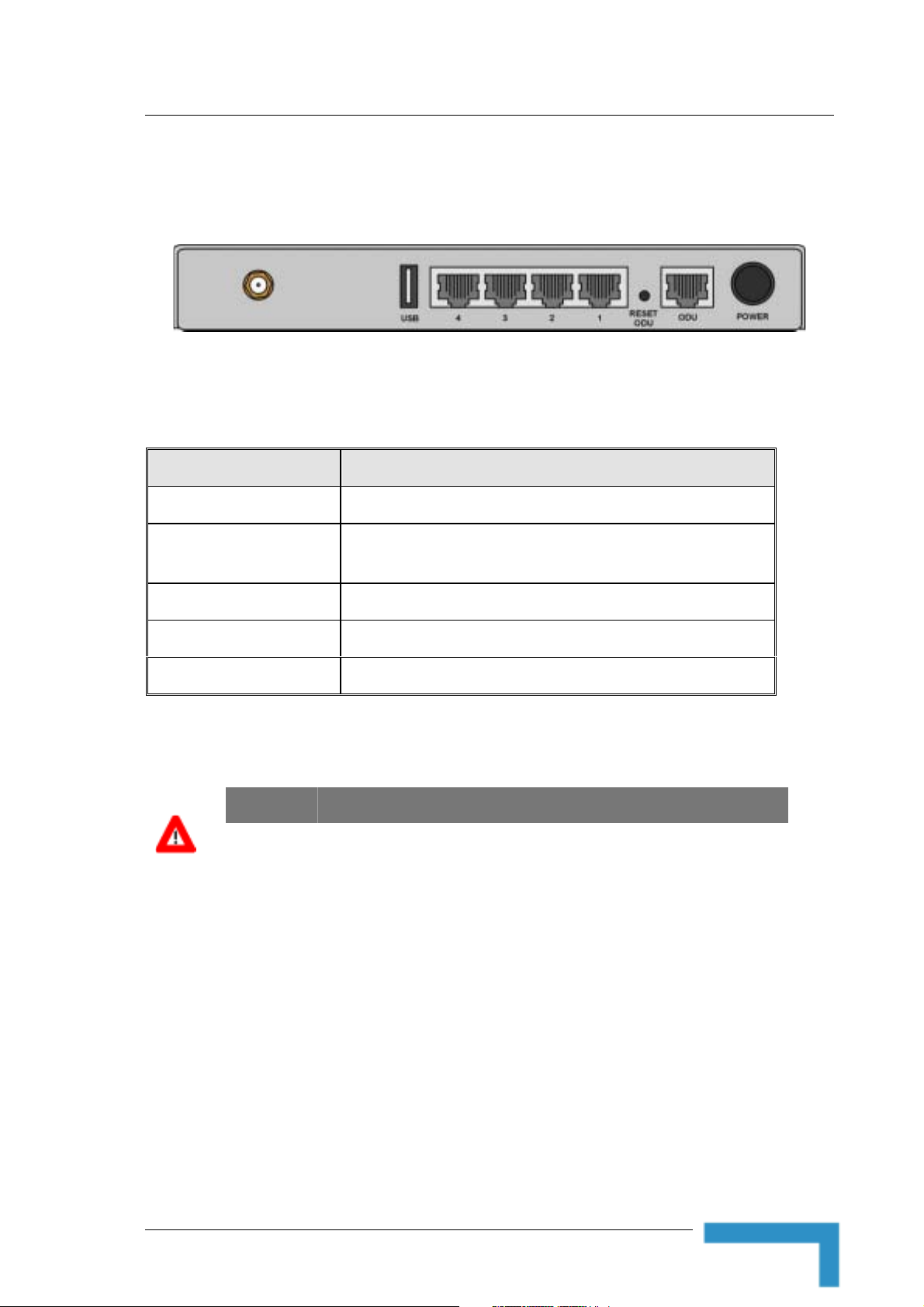
Figure 2: Rear Panel (without antenna)
2.2.2.1 Rear Panel Connectors
Table 7: Rear Panel Connectors
Connector Description
POWER DC Power Inlet from Power Transformer
ODU Connection to the ODU. Carries Ethernet, Power (55 VDC) and
signaling.
Port 1-4 LAN ports for networked computers and other devices.
USB USB Host Port for a USB printer.
Antenna (not marked) An SMA connector for the WLAN antenna
CAUTION
Do not connect data equipment to the ODU port. The ODU port supplies high DC power
to the ODU, and this may harm other equipment connected to it.
2.2.2.2 RESET ODU Button
Press momentarily the recessed RESET ODU button to reset the ODU.
NG System Manual
13
Page 28
Chapter 2 - Installation
2.3 Installation
The unit can be placed on a desktop or a shelf. Alternatively, it may be wallmounted.
For optimal performance, place the Networking Gateway in the center of
your office (or your home), in a location that is away from any potential
source of interference, such as a metal wall or microwave oven. This
location must be close to a mains outlet and network connections.
To install the Networking Gateway IDU:
1 Assemble an RJ-45 connector with a protective cover on the indoor end
of the IDU-ODU cable. The length of the IDU-ODU cable should not
exceed 100m. Refer to the relevant System Manual for instructions on
preparing the cable and for information on the cable type.
2 Connect the IDU-ODU cable to the ODU connector located on the rear
panel.
3 Connect the power cord of the transformer to the unit’s POWER socket,
located on the rear panel. Connect the Mains power cord to the power
transformer and to the AC mains.
NOTE
The color codes of the power cable are as follows:
Brown Phase ~
Blue Neutral 0
Yellow/Green Ground
4 When power is connected, the unit will automatically enter the self-test
phase. When it is in the self-test phase, the STATUS LED will be lit ON
for about 10 seconds, and will then blink 3 times, indicating that the
self-test operation has ended. Finally, the STATUS LED will blink
continuously one blink per second, indicating that the unit is
functioning properly.
5 Connect a PC to one of the LAN ports using an Ethernet cable and
configure the basic parameters of the SU-ODU. Align the antenna of the
ODU. For more information refer to the applicable sections of the
relevant System Manual.
14
6 Use a web browser to configure the parameters of the Networking
Gateway IDU. For details refer to Chapter 3.
Installation
Page 29

Installation
7 If a printer is to be used, connect it to the USB port using a standard
USB cable. To configure the Print Server on your computer(s), refer to
Appendix A - Print Server.
8 Configure the network settings of the computers for proper operation
with the Networking Gateway. The default IP address of the Networking
Gateway LAN is 192.168.254.253, and the default subnet mask is
255.255.255.0.
9 To verify data connectivity, from the end-user’s PC or from a portable
PC connected to the unit, try to connect to the Internet.
10 Verify proper operation using the LED indicators (see Table 6).
NG System Manual
15
Page 30

Page 31

3
3
Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration
Server
In This Chapter:
Start-up and Log in on page 18
Status on page 23
Wizard on page 25
Basic Setting on page 33
Security Setting on page 55
NAT Setting on page 67
Advanced Settings on page 72
Toolbox on page 84
Page 32

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.1 Introduction
The Networking Gateway IDU can be configured using the following
methods:
The Web Configuration Server
A .cfg-file loaded into the unit from the web configuration server or
TFTP.
SNMP
This document describes the configuration using the Web Configuration
Server.
18
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 33

Accessing the Web Configuration Server
3.2 Accessing the Web Configuration
Server
Follow the steps below to access the Web Configuration Server:
1 Connect the unit to the AC mains.
2 Connect PC to LAN port 1.
NOTE
When connecting from WAN, make sure that a remote administrator is enabled (see
section 3.7.6), and enter the WAN IP address specified in the System Status window (see
section 3.4) using TCP port 88.
IMPORTANT
When managing the NG via bwaNMS (using the cut through option), the Remote
Administrator Port must be set to 8080.
3 Open a web browser (Internet Explorer or Netscape Communicator).
NOTE
Be sure to disable the proxy on your Web browser or add the IP address of the product
into the proxy exceptions.
4 Type http://192.168.254.253 in the Address (IE) or Location (Netscape)
field and click Enter.
5 If the Web Configuration Server is password protected, you will be
prompted to enter your password in order to login to the system (see
section 3.3
6 The Web Configuration Server main view appears on the screen.
).
NG System Manual
19
Page 34

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.3 Log in and Log out
After connection is established, the networking gateway web user interface
appears. There are two entry levels: for general users and for system
administrators. The menus and screens vary depending on entry level. The
menus and parameters specified hereinafter, refer to both entry levels,
unless otherwise specified.
To log in, enter the system password in the System Password field and
click the Log in button.
NOTE
The default passwords for the two access levels are:
For Administrators: private
For Users: public
20
Figure 3: Log In Window
Upon successful Log in, the Networking Gateway Main Window appears.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 35

Log in and Log out
Figure 4: Networking Gateway Main Window
3.3.1 The Main Menu
The Web Configuration Server view consists of a number of menu links (to
the left). Clicking on each of them expands the menu node and displays the
selected page with the applicable content (configurable parameters/options
or status information) in the main area.
IMPORTANT
Many pages include a "Save" button. Click on the Save button before selecting another
page/menu item, or before quitting the application. The Save functionality in many cases is per
page. If you leave the page without clicking the Save button, all the changes in the page will be
discarded.
Changes to most of the settings are applied only after restarting the unit
(refer to s ection 3.10.5
).
3.3.2 Control Buttons
A control button causes an immediate action. To activate a control button,
click on it. Certain control buttons only appear in selected windows. Others
are common to most windows.
NOTE
Some control buttons may be disabled for user entry level (public password).
NG System Manual
21
Page 36

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Save – Saves any changes made to the configuration. Most changes
require rebooting the system for them to take effect.
Undo – Recovers the original settings.
Help – Displays a help screen for the specific window.
Refresh – Refreshes the displayed information.
Back – Reverts to a previous step/screen.
<<Previous – In windows that are divided into several pages, use the
<<Previous button to jump to the previous page.
Next>> - In windows that are divided into several pages, use the Next>>
button to jump to the next page.
Cancel – Clears unsaved changes to the configuration.
Reboot – Reboots the Networking Gateway.
22
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 37

3.4 Status
The Status window appears in the main window upon successful log in. The
window can be accessed at any time by clicking on the Status menu on the
menu list.
Status
Figure 5: System Status
The Status window provides information for observing the product's working
status, as follows:
Table 8: Status Window Parameters
Parameter Description
Remaining Lease Time A counter displaying the remaining time (in hh:mm:ss) in
which unit will request a new IP. When the lease time expires,
a new IP address will be automatically allocated, or the lease
will be automatically renewed, depending on the settings (see
and 3.6.1.3.
sections
This field is relevant only for Dynamic IP Address mode and
will not appear in any of the other modes.
Renew (Administrator only) – In Dynamic IP Address
In Static IP Address, PPPoE and PPTP modes, the WAN
3.6.1.2
mode, click to reset the Lease Time. The gateway will
request an IP address from the DHCP server.
type is specified in the sidenote (Static IP, PPPoE, or
PPTP, respectively).
NG System Manual
23
Page 38

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Parameter Description
IP Address The WAN IP address.
Release (Administrator only) – In Dynamic IP Address
mode only, Click to release the WAN IP address.
Subnet Mask The Subnet mask of the device. (The default is
255.255.255.0)
Gateway The default Gateway IP address.
Domain Name Server The DNS Server IP address(es).
Connection Time (PPPoE
and PPTP modes only)
Peripheral Status The USB Printer status:
Traffic Statistics Enables to monitor inbound and outbound packets for WAN,
Connect/ Disconnect – When in PPPoE or PPTP mode, click
Connect to initiate a session, or Disconnect to terminate a
session.
Not ready - no printer is available
Off-line or No Paper – the printer is off-line or the paper
tray is empty
Printing – the printer is currently printing
Ready - a printer is connected and ready to print.
Device error – a general error occurred.
LAN and wireless beginning from last reset.
In addition, the Status window includes the following buttons:
24
View Log – opens the log file for viewing. See section 3.10.1
.
Clients List – opens the list of DHCP assigned clients. See section 3.6.2.1
Using the Web Configuration Server
.
Page 39

Wizard (Administrator only)
3.5 Wizard (Administrator only)
The Setup Wizard will guide you through the basic configuration procedure
(recommended for most users).
Figure 6: Setup Wizard
1 Click on Next. The Select WAN Type window appears.
NOTE
You can click Back at any time to return to previous screens and change your settings.
2 Select the WAN Type from the list:
NG System Manual
Figure 7: Setup Wizard - Select WAN Type
25
Page 40

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Static IP Address – a static IP Address provided by the ISP
Dynamic IP Address – an IP Address automatically obtained from the
ISP (default)
Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management (e.g.
Telstra, BigPond)
PPP over Ethernet – some ISPs require the use of PPPoE to connect
to their services
PPTP – Some ISPs require the use of PPTP to connect to their
services.
3 Click Next. For each WAN type selected, a different WAN Type-specific
window appears:
Static IP Address
26
Figure 8: Setup Wizard – WAN Type - Static IP Address
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 41

Wizard (Administrator only)
Set the following parameters provided by your ISP:
Table 9: Setup Wizard – Static IP Address Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address Sets the local IP address of the device.
Static IP Address The IP address of the WAN port.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Static Subnet Mask The subnet mask of the WAN port.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Static Gateway The Default Gateway IP address of the unit.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Static Primary DNS The IP address of the primary Domain Name Server.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Static Secondary DNS The IP address of the secondary Domain Name Server.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Dynamic IP Address
NG System Manual
Figure 9: Setup Wizard - Dynamic IP Address
27
Page 42

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Set the following parameters:
Table 10: Setup Wizard – Dynamic IP Address Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address The local IP address of the device.
The default IP address is 192.168.254.253. To change the IP
address enter a new value.
Host Name: Optional Some ISPs require a host name, for example, Home.
A string of maximum 39 characters.
The default is an empty field.
WAN's MAC Address The gateway's pre-configured MAC Address.
Clone MAC - Click to replace the Gateway's WAN MAC
Address with the PC's MAC Address.
Restore MAC - When Clone MAC is activated, the button
changes to Restore MAC, to enable to restore the unit's
default MAC Address.
Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management
Figure 10: Setup Wizard - Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management
Using the Web Configuration Server
28
Page 43

Wizard (Administrator only)
Set the following parameters:
Table 11: Setup Wizard – Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management
Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address The local IP address of the device.
The default IP address is 192.168.254.253. To change the IP
address enter a new value.
Account The account provided by the service provider. If you do not
want to change the account, leave empty. At initial entry, you
are required to enter an account.
A string of up to 53 printable characters.
The default is an empty field.
Password The password provided by the service provider. If you do not
want to change the password, leave empty. At initial entry,
you are required to enter a password.
A string of up to 53 printable characters.
Login Server The Login Server (optional). Leave empty if you want the
default server.
PPP over Ethernet
NG System Manual
Figure 11: Setup Wizard – PPP over Ethernet
29
Page 44

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Set the following parameters:
Table 12: Setup Wizard – PPPoE Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address The local IP address of the device.
The default IP address is 192.168.254.253. To change the IP
address enter a new value.
Account The account provided by the service provider.
A string of up to 53 printable characters.
The default is an empty field.
Password The password provided by the service provider. If you do not
want to change the password, leave empty. At initial entry,
you are required to enter a password.
A string of up to 53 printable characters.
Primary DNS The DNS provided by your ISP. To use a specific DNS, enter
a specific address. Leave the default 0.0.0.0 setting to
automatically assign the parameter.
Secondary DNS The backup DNS provided by the service provider. (optional)
PPTP
30
Figure 12: Setup Wizard – PPTP
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 45

Wizard (Administrator only)
Set the following parameters:
Table 13: Setup Wizard – PPTP Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address The local IP address of the device.
The default IP address is 192.168.254.253. . To change the
IP address enter a new value.
IP Mode select one of the following options:
Dynamic IP Address (this is the default setting)
Static IP Address
My IP Address The private IP address assigned by the service provider after
connection. When in Static Mode, the IP address must be
configured manually.
My Subnet Mask The private subnet mask assigned by the service provider
after connection. When in Static Mode, the subnet mask must
be configured manually.
WAN Gateway IP The WAN Gateway IP address after connection. When in
Static Mode, the IP address must be configured manually.
Server IP Address/Name The IP address/Name of the PPTP server.
PPTP Account The user account assigned by the service provider.
A string of up to 53 characters
PPTP Password The password assigned by the service provider. If you do not
want to change the password, leave this field empty. At initial
entry, you are required to enter a password.
A string of up to 53 characters
4 After setting the appropriate parameters, the following window appears:
NG System Manual
31
Page 46

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 13: Setup Wizard - Configuration Completed
5 The configurations will take effect only after rebooting your computer.
Click on Reboot to restart your computer.
For more advance configurations, see details on the specific windows,
below.
32
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 47

3.6 Basic Setting
The Basic Setting window allows to configure the settings for WAN, LAN,
and Wireless and to change the password.
Basic Setting
3.6.1 WAN Setup
Click on WAN Setup from the Basic Setting menu on the menu list. The
Primary Setup window appears. The parameters displayed may vary
depending on the WAN Type selected. The default WAN Type is Dynamic IP
Address.
Figure 14: Basic Setting
NG System Manual
Figure 15: WAN Setup/Primary Setup
33
Page 48

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
NOTE
The WAN setup window is read only for user level entry.
From the WAN Setup window you can:
Set the WAN type – allows to select the WAN connection type of your
ISP.
NAT – Enable/Disable - When disabled, the gateway functions as a
regular router as opposed to a NAT router. This option is available in the
Primary Setup window for all WAN types.
Set Virtual Computers (Administrators only) – Enabled when using NAT.
In addition to the primary WAN address, enables to set up one-to-one
mapping of up to five global IP address and local IP address (see Figure
16 below).
Figure 16: Virtual Computers
The Virtual Computers window includes the following parameters:
Table 14: Virtual Computers Parameters
Parameter Description
Global IP Enter the global IP address assigned by the service provider.
Local IP Enter the local IP address of your LAN PC corresponding to
the global IP address.
Enable Check/Uncheck this item to enable/disable the Virtual
Computer feature.
Using the Web Configuration Server
34
Page 49

Basic Setting
NOTE
The Reboot button is not available at first entry to the Primary Setup window and appears
only after saving your changes.
For user entry level (public password), the parameter fields in all WAN type screens are
disabled (for display only).
IMPORTANT
Changes to the Primary Setup window will take effect only after rebooting the system.
The default WAN type is Dynamic IP Address. However, you can change
the WAN type as follows:
To select a different WAN type:
1 Click Change. The Choose WAN Type window opens.
Figure 17: Choose WAN Type
2 Select one of the following types:
NG System Manual
Static IP Address: The ISP provides you with a static IP address. See
section 3.6.1.1
.
Dynamic IP Address: Automatically obtain an IP address from the
ISP. See section 3.6.1.2
. This is the default setting.
35
Page 50

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management (e.g.
Telstra BigPond). See section 3.6.1.3
PPP over Ethernet: Some ISPs require the us e of PPPoE to connect to
their services. See section 3.6.1.4
PPTP: Some ISPs require the use of PPTP to connect to their services.
See section 3.6.1.5
For each WAN type selected, a different Primary Setup window appears, as
follows. You can change the WAN type by clicking on Change and selecting
a different WAN type.
3.6.1.1 Static IP Address
.
.
.
Figure 18: Primary Setup - Static IP Address
The Setup page for Static IP Address includes the following parameters
provided by the service provider:
Table 15: Static IP Address Parameters
Parameter Description
WAN IP Address The IP address of the WAN port.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
WAN Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask of the WAN port.
The default is 255.255.255.0
WAN Gateway The Default Gateway IP address of the unit.
Using the Web Configuration Server
36
Page 51

Parameter Description
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Primary DNS The IP address of the primary Domain Name Server.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
Secondary DNS The IP address of the secondary Domain Name Server.
The default is 0.0.0.0.
NAT Enable/Disable. When disabled, the gateway functions as a
regular router as opposed to a NAT router. This option is
available in the Primary Setup window for all WAN types.
The default is: Enable
3.6.1.2 Dynamic IP Address
Basic Setting
NG System Manual
Figure 19: Primary Setup - Dynamic IP Address
37
Page 52

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
The Setup page for Dynamic IP Address includes the following parameters:
Table 16: Dynamic IP Address Parameters
Parameter Description
Host Name Optional - Some ISPs require a host name, for example,
Home.
A string of maximum 39 characters.
WAN's MAC Address The gateway's pre-configured MAC Address.
Clone MAC - Click to replace the Gateway's WAN MAC
Address with the PC's MAC Address.
Restore MAC - When Clone MAC is activated, the button
changes to Restore MAC, to enable to restore the unit's
pre-configured MAC Address.
Renew IP Forever When enabled, this feature will automatically renew your IP
address when the lease time expires, even if the system is
idle.
NAT Enable/Disable - When disabled, the gateway functions as a
regular router as opposed to a NAT router.
3.6.1.3 Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session
Management
Figure 20: Primary Setup - Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management
Using the Web Configuration Server
38
Page 53

Basic Setting
The Setup page for Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session
Management provides authentication using dedicated DHCP server and
includes the following parameters:
Table 17: Dynamic IP Address with Road Runner Session Management Parameters
Parameter Description
Account The account provided by your ISP
A string of maximum 53 characters.
Password The password provided by your ISP. If you do not want to
change the password, leave empty.
A string of maximum 53 characters.
Login Server The Login Server (optional). Leave empty if you want the
default server.
A string of maximum 31 characters.
Renew IP Forever Enable/Disable – when enabled, your IP address will
automatically be renewed when the lease time expires, even
if the system is idle.
NAT Enable/Disable - When disabled, the gateway functions as a
regular router as opposed to a NAT router.
3.6.1.4 PPP over Ethernet
Some ISPs require the use of PPPoE to connect to their services. If this is
the case, click Change to select PPPoE as your WAN type. The Primary
Setup window display changes to reflect the parameters for PPPoE.
NG System Manual
39
Page 54

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 21: Primary Setup - PPPoE
The Setup page for PPPoE includes the following parameters:
Table 18: PPP over Ethernet Parameters
Parameter Description
PPPoE Account The account assigned to you by your ISP.
PPPoE Password The password assigned to you by your ISP. This field always
appears blank. If you don't want to change the password,
leave it empty.
Primary DNS The DNS provided by your ISP. To use a specific DNS, enter
a specific address. Leave the default 0.0.0.0 setting to
automatically assign the parameter.
Secondary DNS The backup DNS provided by your ISP. (optional)
Maximum Idle Time The amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your
PPPoE session. To disable this feature, set this parameter to
0 seconds, or enable Auto-reconnect.
The Maximum Idle Time is applicable only when Connection
Control is set to Connect-on-demand or to Manually.
Connection Control Authentication for IP allocation. Select one of the following
options:
Connect-on-demand – An IP address is automatically
allocated whenever the user attempts to make a
connection.
Auto reconnect(Always-on) – The system automatically
connects to the ISP after restart or after connection is
dropped.
Manually – The user manually performs the connection.
Maximum Transmission Unit
(MTU)
More >> Click to display the following parameters:
Most ISPs provide an MTU value to users. The maximum
MTU value allowed is 1492 bytes.
PPPoE Service Name (optional) - Directs to a PPPoE
server.
40
Assigned IP Address (optional) – The fixed IP assigned
by the ISP.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 55

3.6.1.5 PPTP
Some ISPs require th e use of PPTP to connect to their services.
Basic Setting
Figure 22: Primary Setup - PPTP
The Setup page for PPTP includes the following parameters:
Table 19: PPTP Parameters
Parameter Description
IP Mode Select one of the following options:
Dynamic IP Address (this is the default setting)
Static IP Address
My IP Address The private IP address assigned by your ISP. This parameter
is enabled only for Static IP Address mode.
My Subnet Mask The private subnet mask assigned by your ISP. This
parameter is enabled only for Static IP Address mode.
WAN Gateway IP The WAN Gateway IP address. This parameter is enabled
only for Static IP Address mode.
Address/Name The IP address/Name of the PPTP server.
PPTP Account The user account assigned by your ISP.
Connection ID Enter the connection ID if your ISP requires it (optional).
NG System Manual
A string of maximum 53 characters.
41
Page 56

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Parameter Description
Maximum Idle Time The amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your
PPTP session. To disable this feature, set this parameter to 0
seconds, or enable Auto-reconnect.
Connection Control Authentication for IP allocation. Select one of the following
options:
Connect-on-demand – An IP address is automatically
allocated whenever the user attempts to make a
connection.
Auto reconnect(Always-on) – The system automatically
connects to the ISP after restart or after connection is
dropped.
Manually – The user manually performs the connection.
3.6.2 LAN Setup
Select Basic Setting > LAN Setup submenu on the menu list. The LAN Setup
window opens.
42
Figure 23: LAN Setup
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 57

The LAN Setup page includes the following parameters:
Table 20: LAN Setup Parameters
Parameter Description
LAN IP Address Sets the local IP address of the device. The users on your
network must use this LAN IP address as their default
gateway. You can change it as necessary.
LAN Subnet Mask Sets the subnet mask to the LAN IP address.
DHCP Server Enable/Disable to turn off this service. When enabled, the
LAN Setup window display changes (indicated by the red
icon), and the following parameters are displayed (see Figure
24):
Range of IP addresses Pool – Specify the starting and
ending address for DHCP clients. The IP addresses are
allocated from this pool according to calculations based
on the client’s MAC address.
Basic Setting
Domain suffix – Specify the domain suffix for DHCP
clients.
Primary DNS – Specify the primary DNS for DHCP
clients.
Secondary DNS – Specify the secondary DNS for DHCP
clients.
Primary WINS – Specify the primary WINS address for
DHCP clients.
Secondary WINS – Specify the secondary WINS address
for DHCP clients.
Lease Time – The time set (in minutes) for IP allocation.
DHCP Proxy This parameter is available only when DHCP Server is
disabled.
NG System Manual
43
Page 58

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 24: LAN Setup - DHCP Server Enabled
The LAN PC receives a DHCP IP address from the Networking Gateway. To
receive the DHCP IP address from the DHCP server, perform the following
procedure:
3 Set the DHCP Server parameter to Disable.
4 Set the DHCP Proxy parameter to Enable.
5 In the Proxy IP field, enter the IP of the DHCP server.
In addition, the LAN Setup window includes the following control buttons:
Clients List – Opens a list of the current mapping of the IP and MAC
address for each DHCP client (see section 3.6.2.1)
Fixed Mapping – Opens the MAC Address Control window for assigning a
specific IP address to the specified MAC address for DHCP clients (see
MAC Address Control
on page 52 for further details).
44
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 59

3.6.2.1 DHCP Clients List
Figure 25: DHCP Clients List
Basic Setting
The DHCP Clients List displays the following parameters for each DHCP
client:
Table 21: DHCP Clients List Parameters
Parameter Description
IP Address The IP address of the DHCP client.
Host Name The host name of the DHCP client.
MAC Address The MAC address of the DHCP client.
From the DHCP Clients List window you can do the following for the selected
clients:
Wake up – Sends Ethernet packets to turn on the PC, relevant hardware
and configuration is required on NIC and PC
Delete – Delete the selected clients from the list.
NG System Manual
45
Page 60

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.6.2.2 Fixed Mapping
Opens the MAC Address Control window. MAC Address Control allows to
assign different access rights for different users and to assign a fixed IP
address to a specific MAC address.
NOTE
All the settings in this page will take effect only when MAC Address Control is set to
"Enable".
Figure 26: MAC Address Control
The MAC Address Control window includes the following parameters:
Table 22: DHCP Clients List Parameters
Parameter Description
MAC Address Control Check "Enable" to enable the MAC Address Control feature.
Connection control Check the "Connection control" check box to enable
controlling which wired and wireless clients can connect to
this device. If a client is denied the connection to this device,
he will not be able to access the Internet either. Select
allow/deny to allow or deny clients whose MAC addresses
are not in the "Control table" (see below) to connect to this
device. ("deny" is the default setting.)
A wired client who is allowed to connect to the device has full
access to the Internet and to network resources. When
denied the connection to the device, he can communicate
with other clients on the wired LAN, but cannot connect to the
Internet, use the Print Server function, communicate with
46
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 61

Basic Setting
Parameter Description
clients on the wireless LAN, or use the Web configuration.
Association control "Association" refers to the exchanging of information between
wireless clients and the device to establish a link between
them. A wireless client is able to transmit and receive data to
the device only after successful association. Check
"Association control" check box to control which wireless
clients can associate to the wireless LAN. If a client is denied
the association to the wireless LAN, he will not be able to
send or receive any data via this device. Select allow/deny to
allow or deny clients whose MAC addresses are not in the
"Control table" to associate to the wireless LAN.
A wireless client who is allowed both to associate to the
wireless LAN and to connect to the device has full access to
the Internet and to network resources.
When allowed to associate to the wireless LAN, but denied to
connect to the device, he can communicate with other clients
on the LAN (wired and wireless), but cannot connect to the
Internet, use the Print Server function, or use the Web
configuration.
When denied to associate to the wireless LAN, the client
cannot communicate with other clients on the LAN (wired or
wireless), connect to the internet, use the Print Server
function, or use the Web configuration.
NOTE: Association control does not affect wired clients.
Control Table: Each row in the control table indicates the MAC address and the mapped IP
address of a single client.
MAC Address The MAC address of a specific client.
IP Address The expected IP address of the corresponding client. Leave
empty if you do not want to specify an IP address for the
corresponding client.
C When "Connection control" is checked, checking "C" will
A When "Association control" is checked, checking "A" will
NG System Manual
allow/deny (depending on the connection control setting) the
corresponding client to connect to this device.
allow/deny (depending on the association control setting) the
corresponding client to associate to the wireless LAN.
47
Page 62

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
To enter the MAC address:
Use the DHCP clients combo box.
Figure 27: DHCP Clients Combo Box
1 Select a specific client in the "DHCP clients" Combo box and click on
Copy to to copy the MAC address of the selected client to the selected
ID in the "ID" Combo box
NOTE
When the unit has a list of clients connected through DHCP, and the unit is reset, the list
will show empty. In this case renew the PC IP address from DHCP on LAN.
2 The control table is divided into several pages. Use the << Previous
page and Next Page >> buttons to jump to a different page.
3.6.3 Wireless Setting
Wireless settings allow you to set the wireless configuration items.
CAUTION
Changing any of the parameters may cause loss of wireless link connectivity to the unit
if the settings do not match the settings on the WLL subscriber in the User's PC.
48
Figure 28: Wireless Setting
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 63

Basic Setting
The Wireless Setting window includes the following parameters:
Table 23: Wireless Setting Parameters
Parameter Description
Wireless Enable/Disable – Check the Enable box to enable this
service.
The default setting is "Enable".
Network ID (SSID) Network ID is used for identifying the Wireless LAN (WLAN).
Client stations can roam freely over this product and other
Access Points that have the same Network ID.
The factory setting is "default".
Channel The radio channel number. The permissible channels depend
on the Regulatory Domain.
Security Select the data privacy algorithm you want to protect your
data when being transferred from one station to another. The
available security protocols are:
None – No encryption is applied. (default)
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) – Encrypts frames
transmitted through a wireless module using a pre-
entered WEP key. You can configure 4 key sets and
select one to apply as follows:
WEP 64 bit - 10 hexadecimal digits
WEP 128 bit – 26 hexadecimal digits
WEP 256 bit – 58 hexadecimal digits
802.1x – When enabled, the wireless user must be
authenticated before it is allowed to use the network
services. One implementation of 802.1x (the most
common one) is through a RADIUS server on your LAN,
containing an authentication database.
Encryption Key Length – Select either 64 or 128 bits
for the encryption key.
RADIUS Server IP – The 802.1x server's IP address.
NG System Manual
RADIUS Port – The 802.1x server's service port.
WPA-PSK - Accepts WPA clients only. Manually enter a
pre-share key (encryption key) as follows:
49
Page 64

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Parameter Description
Pre-share key mode: ASCII or HEX can be selected.
Pre share key: 32 ASCII characters or 64
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) – improves data protection
and implements access control to Wireless LAN systems.
Frames transmitted through a wireless module are
encrypted using a Pre-share key (PSK) or a key received
from the RADIUS server.
RADIUS Server IP – The 802.1x server's IP address.
RADIUS Port – The 802.1x server's service port.
RADIUS Shared Key – Key value shared by the
hexadecimal digits pre-share key (encryption key).
RADIUS server and the networking gateway. The key
value is consistent with the one in the RADIUS server.
IMPORTANT
If you enable the 802.1x or WPA feature, you must have a RADIUS server available.
50
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 65

3.6.3.1 Wireless Clients List
Clicking on the Wireless Clients List button that appears in the Wireless
Setting window opens the Wireless Clients List window.
Basic Setting
Figure 29: Wireless Clients List
The Wireless Clients List displays the following parameters for each wireless
client:
Table 24: Wireless Clients List Parameters
Parameter Description
Connected Time The connection time.
MAC Address The MAC address of the wireless client.
3.6.3.2 Advanced Wireless Setting
Clicking the Advanced Wireless Setting button that appears in the
Wireless Setting window opens the Advanced Wireless Setting window.
NG System Manual
51
Page 66

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 30: Advanced Wireless Setting
The Advanced Wireless Setting window includes the following parameters:
Table 25: Advanced Wireless Setting Parameters
Parameter Description
Beacon Interval Specify the intervals (in milliseconds) between the packets
sent by the access point to synchronize the wireless network
(beacons).
The range is 1~1000 milliseconds
The default is 100 milliseconds.
RTS Threshold Specify the packet size above which a Request To Send will
be performed. Used to determine whether CSMA/CD or
CSMA/CA will be used.
The range is 256~2432 bytes
The default is 2432 bytes.
Fragmentation Threshold Specify the packet size above which fragmentation will be
performed.
The range is 256~2346 bytes, even numbers only
The default is 2346 bytes.
Using the Web Configuration Server
52
Page 67

Parameter Description
DTIM Interval Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) is a countdown
informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast
and multicast messages.
The range is: 1~65535 seconds.
The default value is 3 seconds.
Wireless Mode The wireless mode supported: 802.11b, 802.11g, or both.
The default is both.
TX Rates Select the wireless transfer rate from the dropdown list,
based on the speed of wireless adapters on the WLAN.
The default is auto rate.
Preamble Type Defines the length of the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
block for communication between the Access Point and
roaming wireless adapters. A long transmit preamble may
provide a more reliable connection or slightly longer range. A
short transmit preamble provides better performance. Select
short/long or automatic preamble to be assigned to each
packet.
Basic Setting
The default is auto mode.
Authentication Type Used for wireless authentication when associated with an AP
router.
Open System
Shared Key
Both
The default is auto mode.
SSID Broadcast Enable/Disable broadcasting the network's ID.
The default is Enable.
Antenna Transmit Power Select the antenna's transmission power from the dropdown
list.
The default is 100% TX power (17 dBm).
NG System Manual
53
Page 68

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.6.3.3 MAC Address Control
MAC Address Control allows to assign different access rights for different
users and to assign a fixed IP address to a specific MAC address. For
further details, see section 3.6.2.2
3.6.4 Change Password
The Change Password window allows to change the system password. For
security reasons, it is strongly recommended that you do so.
To access change password:
1 Select Basic Setting > Change Password submenu on the menu list. The
Change Password window opens.
.
Figure 31: Change Password
2 Type in the old password in the Old Password box.
3 Type in the new password in the New Password box.
4 Re-type the new password in the Reconfirm box. The password should
be identical to the one entered in the New Password field.
5 Click Save to save the new password(s).
Follow this procedure for the Administrator Password level, for the User
Password level, or for both password levels.
NOTE
The Administrator Password is visible to the Administrator entry level only.
Using the Web Configuration Server
54
Page 69

3.7 Security Setting
Click on the Security Setting menu on the menu list to display the
submenus and the Security Setting window.
Security Setting
Figure 32: Security Setting Window
3.7.1 MAC Control
MAC Address Control allows to assign different access rights for different
users and to assign a fixed IP address to a specific MAC address. For
further details, see section 3.6.2.2
.
3.7.2 Packet Filters (Administrator only)
Packet Filter enables to control which packets are allowed to pass through
the networking gateway. When selecting the Packet Filters submenu on the
menu list, the Outbound Packet Filter window opens.
NOTE
The Inbound Filter… button at the bottom of the window toggles between the
Outbound and Inbound Packet Filter windows. The button's text will change from
Inbound Filter… to Outbound Filter… accordingly.
NG System Manual
55
Page 70

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 33: Packet Filter Initial Window
The Outbound filter applies on all outbound packets. The Inbound filter
applies only on packets that are destined to Virtual Servers or DMZ host.
You can select one of the following filtering policies:
Allow all to pass except those match the specified rules
Deny all to pass except those match the specified rules
Up to 8 rules can be specified for each direction, inbound and outbound.
For each rule, you can define the following:
Table 26: Advanced Wireless Setting Parameters
Parameter Description
Source IP address You can define a single IP address (for example, 4.3.2.1) or a
range of IP addresses (for example, 4.3.2.1-4.3.2.254).
An empty field denotes all IP addresses.
Source Ports address You can define a single port (for example, 80) or a range of
ports (for example, 1000-1999).
56
Add a prefix "T" or "U" to specify a TCP or UDP protocol. For
example, T80, U53, U2000-2999. No prefix indicates both
TCP and UDP protocols.
An empty field denotes all port addresses.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 71

Security Setting
Parameter Description
Destination IP address You can define a single IP address (for example, 4.3.2.1) or a
range of IP addresses (for example, 4.3.2.1-4.3.2.254).
An empty field denotes all IP addresses.
Destination port address You can define a single port (for example, 80) or a range of
ports (for example, 1000-1999).
Add prefix "T" or "U" to specify a TCP or UDP protocol. For
example, T80, U53, U2000-2999. No prefix indicates both
TCP and UDP protocols.
An empty field denotes all port addresses.
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled or
disabled individually.
Use Rule# Packet Filter can work with Scheduling Rules. For details,
please refer to Schedule Rule on page 80.
The Schedule Rule option facilitates the process of selecting a scheduling
rule for each Filter ID. Select a specific Schedule Rule from the Schedule
Rule Combo box. Select the Filter ID to which the schedule rule will apply
from the ID Combo box and click Copy to to copy the Schedule Rule
number to t he selected Filter ID.
Click Save to save your Inbound/Outbound Packet Filter settings.
The following paragraphs provide examples for using the
Inbound/Outbound Packet Filter option.
3.7.2.1 Inbound Filter
To enable Inbound Packet Filter click on the Inbound Filter button and
check the Enable box in the Inbound Packet Filter window.
In the following examples, the SMTP Server (port 25), POP Server (p ort 110),
Web Server (port 80), FTP Server (port 21), and News Server (port 119) are
defined in the Virtual Server or DMZ Host.
NG System Manual
57
Page 72

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Example 1:
Figure 34: Inbound Packet Filter – Example 1
In this example, IPs (1.2.3.100-1.2.3.149) are allowed to send mail (port
25), receive mail (port 110), and browse the Internet (port 80).
IPs (1.2.3.10-1.2.3.20) are allowed to perform all operations.
All other IPs are all blocked from performing any operation.
Example 2:
58
Figure 35: Inbound Packet Filter - Example 2
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 73

In this example, IPs (1.2.3.100-1.2.3.119) are allowed to do everything
except read net news (port 119) and transfer files via FTP (port 21).
All other IPs are all allowed to perform all operations.
3.7.2.2 Outbound Filter
To enable Outbound Packet Filter, click on the Outbound Filter button and
check the Enable box in the Outbound Packet Filter window.
Example 1:
Security Setting
Figure 36: Outbound Packet Filter - Example 1
In this example, IP (192.168.123.149) is restricted from sending mail (port
25), receiving mail (port 110), and browsing the Internet (port 80). It is
allowed to perform all other operations.
IP (192.168.123.20) is blocked from performing any operation.
All other IPs are allowed to perform all operations.
NG System Manual
59
Page 74

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Example 2:
Figure 37: Outbound Packet Filter - Example 2
In this example, IPs (192.168.123.100) and (192.168.123.119) can only
read net news (port 119) and send mail (port 25). They are blocked from
performing any other operation.
All other IPs are blocked from performing any operation.
3.7.3 URL Blocking (Administrator only)
When enabled, this feature blocks LAN computers from connecting to predefined Web sites.
60
Figure 38: URL Blocking
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 75

Security Setting
The URL Blocking window includes the following parameters:
Table 27: URL Blocking Parameters
Parameter Description
URL Blocking Enable/Disable - Check to enable the URL Blocking feature.
URL If any part of the Web site's URL matches the pre-defined
word specified in this field, the connection will be blocked.
For example, you can use a pre-defined word "sex" to block
all Web sites whose URLs contain the word "sex".
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled or
disabled individually.
Use Rule# URL Blocking can work with Scheduling Rules. For details,
please refer to Schedule Rule on page 80.
The Schedule Rule option facilitates the process of selecting a scheduling
rule for each Filter ID. Select a specific Schedule Rule from the Schedule
Rule Combo box. Select the Filter ID to which the schedule rule will apply
from the ID Combo box and click Copy to to copy the Schedule Rule
number to t he selected Filter ID.
Click Save to save your settings.
The following section provides an example for using the URL Blocking
option.
3.7.3.1 URL Blocking - Example
NG System Manual
Figure 39: URL Blocking Example
61
Page 76

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
In this example:
1 All URLs which include the string "msn" will be blocked, and the action
will be recorded in the log file.
2 All URLs which include the string "sina" will be blocked, and the action
will be recorded in the log file.
3 All URLs which include the string "cnnsi" will be blocked, and the action
will be recorded in the log file.
4 All URLs which include the string "espn" will be blocked, and the action
will be recorded in the log file.
If the Enable box is not checked for a specific rule, the rule will not be
applied and the matching URLs will not be blocked.
3.7.4 Domain Filter (Administrator only)
When enabled, the Domain Filter feature blocks LAN computers from
connecting to pre-defined Web sites.
NOTE
While URL Blocking uses keywords to block all Web sites whose URL includes the prespecified keyword, Domain Filter blocks a single or multiple domains by specifying the
suffix (such as xxx.com, .org, etc.).
62
Figure 40: Domain Filter
Up to 9 Domain Suffixes can be defined, and for each rule you can specify
the desired action to be taken when a user attempts to access that domain.
For each rule you can define the following:
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 77

Security Setting
Table 28: Domain Filter Parameters
Parameter Description
Domain Filter Check to enable the Domain Filter feature to prevent users
from accessing specific URLs.
Log DNS Query Check to enable logging users' attempts to enter the specified
URLs.
Privilege IP Addresses
Range
Domain Suffix A suffix of URL to be restricted.
Action You can specify the type of action you want performed when
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled/disabled
Sets a group of hosts and allows them to access the network
without restriction.
The range is: From: 1~254, To: 1~254
For example, ".com", "xxx.com".
someone attempts to access the specific URL that meets the
domain-suffix:
Drop – Check to block access.
Log – Check to log the access attempt.
individually.
In the example above (Figure 40):
1 The URL "www.msn.com" will be blocked, and the action will be
2 The URL "www.sina.com" will not be blocked, but any attempt to enter
3 The URL "www.google.com" will be blocked, but the action will not be
4 IP address X.X.X.1~ X.X.X.20 can access network without restriction.
Click Save to save your settings.
NG System Manual
recorded in the log file.
the Web site will be recorded in the log file.
recorded in the log file.
63
Page 78

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.7.5 Firewall (Administrator only)
Firewall rules deny/allow traffic from passing through the device.
Figure 41: Firewall
Up to 8 rules can be specified for each direction of traffic: inbound and
outbound. For each rule, you can define the following:
Table 29: Firewall Parameters
Parameter Description
Source IP address From LAN or WAN
Destination IP address From LAN or WAN
Destination Protocol TCP, UDP or ICMP
Destination Destination port number
Action Allow/Deny
The default is Allow
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled/disabled
individually
64
Click Save to save your settings.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 79

Security Setting
3.7.6 Miscellaneous Items (Administrator only)
Figure 42: Miscellaneous Items
From the Miscellaneous Items window you can set the following parameters:
Table 30: Miscellaneous Items Parameters
Parameter Description
Remote Administrator
Host/Port
Enables the user to perform administration tasks from a
remote host. When enabled, only the specified IP address
can perform remote administration. If the specified IP address
is 0.0.0.0, any host can connect to this device in order to
perform administration tasks. You can use subnet mask bits
"/nn" notation to specify a group of trusted IP addresses.
For example, "10.1.2.0/24".
NOTE - When Remote Administration is enabled, the web
server port will automatically change to 88. You can change
the web server port to another port.
IMPORTANT – When managing the NG via bwaNMS (using
the cut through option), the Remote Administrator Port must
be set to 8080.
Administrator Time-out The time of no activity to logout automatically. Set it to zero to
TFTP Access Client/Port When enabled, the specified IP address can access the
Discard PING from WAN When enabled, any ping packet from WAN will be discarded.
NG System Manual
disable automatic time-out
device through the TFTP client utility.
65
Page 80

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Parameter Description
side
SPI Mode When enabled, the router records the information, such as IP
address, port address, ACK, SEQ number and so on, of the
packets that pass through the WAN, and the Networking
Gateway checks every incoming packet to detect whether it is
valid.
DoS Attack Detection When enabled, the router detects and logs the Denial of
Service (DoS) attack that comes from the Internet. Currently,
the Networking Gateway can detect the following DoS attack:
SYN Attack, WinNuke, Port Scan, Ping of Death, and Land
Attack etc.
66
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 81

NAT Setting (Administrator only)
3.8 NAT Setting (Administrator only)
The NAT Setting page pr ovides access to configuring the virtual server,
special AP, DMZ host and VPN pass through.
Figure 43: NAT Setting
3.8.1 Virtual Server
Virtual Server enables WWW, FTP and other services on your LAN to be
accessible to Internet users.
NG System Manual
Figure 44: Virtual Server
67
Page 82

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Specify the following parameters for each ID:
Table 31: Virtual Server Parameters
Parameter Description
Protocol Select from TCP, UDP, * (all).
The default setting is *.
Service Ports Enter a port number, or a range of ports.
Server IP Enter the server IP on the LAN interface.
The range is 1~254.
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled/disabled
individually.
Use Rule# Virtual Server can work with Scheduling Rules. For details,
please refer to Schedule Rule on page 80.
In addition, the Virtual Server page allows to easily select services from a
pre-defined list, and to assign to them a pre-defined rule.
Well known services – Select a service from the list of pre-defined
services.
The Schedule Rule option facilitates the process of selecting a
scheduling rule for each Virtual Server ID. Select a specific Schedule
Rule from the Schedule Rule Combo box. Select the Virtual Server ID to
which the schedule rule will apply from the ID Combo box and click
Copy to to copy the Schedule Rule number to the selected Virtual
Server ID.
3.8.2 Special AP
Some applications, such as Internet games, Video conferencing, Internet
telephony etc., require multiple connections. Because of the firewall
function, these applications cannot work with a pure NAT router. The
Special Applications window makes some of these applications work with
NAT router.
68
NOTE
Only one PC at a time can use each Special Application.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 83

Figure 45: Special Applications
NAT Setting (Administrator only)
The Special Applications window includes the following parameters:
Table 32: Special Applications Parameters
Parameter Description
Trigger The outbound destination port number issued by the
application.
Incoming Ports When the trigger packet is detected using the destination
port, the inbound packets to the specified port numbers are
allowed to pass through the networking gateway.
Enable Check to enable the rule. Each rule can be enabled/disabled
individually.
Some predefined settings are provided. Select an application from the predefined list, select the ID number (1-10) and click Copy to, to add the
predefined setting to your list.
NOTE
If Special Applications fails to make an application work, try DMZ host instead.
3.8.3 DMZ Host
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Host is a host without the firewall protection. It
allows a computer to be exposed to unrestricted 2-way communication for
NG System Manual
69
Page 84

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Internet games, Video conferencing, Internet telephony (H.323 or SIP), and
other special applications.
CAUTION
This feature exposes your computer and may cause security issues. Make sure your PC is
updated with the last security updates.
Figure 46: DMZ Host
Check the Enable box to enable this feature. One IP address should be set
on the subnet of LAN.
3.8.4 VPN Pass Through
70
Figure 47: VPN Pass Through
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 85

NAT Setting (Administrator only)
The VPN Pass Through window includes the following parameters:
Table 33: VPN Pass Through Parameters
Parameter Description
VPN PPTP Pass-Through Check to enable PPTP connection to pass through the
device. The device can handle up to 8 concurrent sessions.
VPN IPSec Pass-Through Check to enable IPSec connection to pass through the
device. The device can handle up to 16 concurrent sessions.
NG System Manual
71
Page 86

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.9 Advanced Settings (Administrator
only)
The Advanced Settings menu provides access to configuring additional
features, such as System Time, Log, Dynamic DNS, SNMP, Routing,
Scheduling Rules and enabling Universal Plug and Play protocol.
Figure 48: Advanced Setting
3.9.1 System Time
The System Time window enables to set the device time.
72
Figure 49: System Time
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 87

From the System Time window, you can select one of the following ways to
set the date and time of the device:
Table 34: System Time Parameters
Parameter Description
Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
Get Date and Time by NTP
Protocol
Set Date and Time using
PC's Date and Time
Set Date and Time manually Select if you want to manually set the device's internal clock.
Select if you want to set the device's internal clock using the
Network Time Protocol (NTP) from a specific server located
on the internet.
Time Server - Select an NTP time server to consult UTC
time.
Time Zone - Select a time zone where this device is
located.
Sync Now! - Synchronize system time with network time
server (alternatively, synchronization will be performed
automatically from every 10 hours).
Select if you want the device's internal clock to synchronize
with the PC's clock.
You need to specify:
Date: Year, Month, Day
Time: Hours (0-23), Minutes (0-59), Seconds (0-59).
The clock is set upon clicking Save.
NOTE
The device time is displayed at the bottom of the Status window.
In addition, you can specify daylight saving time as follows:
Daylight Saving - Enable/disable Daylight Saving and set start and end
time of daylight saving time range.
3.9.2 System Log
System Log enables to set parameters for exporting system logs to a
specified destination. Two exporting methods are supported: syslog (UDP)
and SMTP (TCP).
NG System Manual
73
Page 88

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 50: System Log
The System Log window includes the following parameters:
Table 35: System Log Parameters
Parameter Description
IP Address for Syslog Server Enter the IP address of the syslog server. It is valid only on
your subnet LAN. Check to Enable this function.
E-mail Alert Enable Check if you want to enable Email alert (send syslog via
email).
SMTP Server IP and Port - Enter the SMTP server IP and
port, which are concatenate with ':'.For example,
"mail.your_url.com" or "192.168.1.100:26". If you do not
specify port number, the default value is 25.
E-mail addresses - The listed recipients will receive these
logs. You can assign more than 1 recipient, using a semi-
colon (;) or a comma (,) to separate the addresses.
E-mail Subject - The subject of email alert. This setting is
optional.
Username and Password - To fill some SMTP server's
authentication requirement, you may need to enter the
Username and Password provided by your ISP.
Log Type Select the activities to be logged.
Using the Web Configuration Server
74
Page 89

NOTE
The changes made in the System Log page become effective upon clicking Save.
Rebooting the system is not required.
To view the system log:
Click on the View Log… button at the bottom of the screen. The System Log
opens (see View Log
on page 84, Figure 62)
3.9.3 Dynamic DNS
To host your server on a changing IP address, you need to use a Dynamic
Domain Name Service (DDNS).
To reach your host, one needs to know its name. Dynamic DNS will map
the name of your host to your current IP address, which changes each time
you connect to your Internet service provider.
Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
Before enabling Dynamic DNS, you need to register an account on of the
Dynamic DNS servers listed here under Provider: DnyDNS.org(Dynamic),
DnyDNS.org(Custom), TZO.com and dhs.org. Upon registration, you will
receive your account details.
NG System Manual
Figure 51: Dynamic DNS
75
Page 90

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
The Dynamic DNS window includes the following parameters:
Table 36: Dynamic DNS Parameters
Parameter Description
DDNS Click Enable or Disable to enable/disable Dynamic DNS.
Provider Select from the list of Dynamic DNS servers on which you
have an account.
Host Name Enter to register a domain name to the DDNS provider. The
full domain name is concatenated with the specified Host
Name and a suffix, specified by the DDNS provider.
Username/E-mail Enter your Username or E-mail address according to the
DDNS provider you selected.
Password/Key Enter your password or key according to the DDNS provider
you selected.
After Dynamic DNS setting is configured, click Save.
3.9.4 SNMP Setting
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides the user with
the capability to remotely manage a computer network by polling and
setting terminal values and monitoring network events.
76
Figure 52: SNMP Setting
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 91

Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
The SNMP Setting window includes the following parameters:
Table 37: SNMP Parameters
Parameter Description
Enable SNMP You must check either Local or Remote or both to enable the
SNMP function.
Local - The device will respond to requests from LAN.
Remote – The device will respond to requests from WAN.
Get Community Set the password for GetRequest access rights to your
device.
Set Community Setting the password for SetRequest access rights to your
device.
IP 1,IP 2,IP 3,IP 4 Enter your IP addresses for allowed managers. SNMP Trap
messages will be sent to this IP address as well. If no IP is
defined, the unit cannot be managed by any PC, from either
LAN or WAN.
SNMP Version Select the proper SNMP Version supported by your SNMP
Management software.
In the above figure:
The device will respond to requests from both LAN and WAN.
The device will respond to SNMP clients whose get community is set as
"public" and coming from IP 192.168.123.33.
The device will respond to SNMP clients whose set community is set as
"private" and coming from IP 192.168.123.33.
This device will send SNMP Trap messages to 192.168.123.33 (Using
SNMP Version V2c).
3.9.5 Routing Table
Routing allows to determine which physical interface address to use for
outgoing IP data grams. If you have more than one gateway and subnet,
you will need to enable Routing Table to allow packets to find the proper
routing path and allow different subnets to communicate with each other.
NG System Manual
77
Page 92

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 53: Routing Table
Routing Table settings are used to setup the functions of static and
dynamic routing. The Routing Table window includes the following
parameters:
Table 38: Routing Table Parameters
Parameter Description
Dynamic Routing Routing Information Protocol (RIP) will exchange information
on destinations for computing routes throughout the network.
Select RIPv2 only if you have a different subnet on your
network. Otherwise, select RIPv1 if you need this protocol.
Static Routing For static routing, you can specify up to 8 routing rules. You
can enter the destination IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway, hop for each routing rule, and enable/disable the
individual rule.
Default Route Sets the default route interface as WAN or LAN. For LAN,
one IP for routing must be set.
78
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 93

Example:
Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
Configuration on NAT Router
Destination Subnet Mask Gateway Hop Enabled
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.123.216 1 ˇ
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.123.103 1 ˇ
If, for example, Client3 wanted to send an IP datagram to 192.168.0.2
(Client2), he would use the above table to determine that he had to go via
192.168.123.103 (Gateway2).
And if he sends Packets to 192.168.1.11 he will go via 192.168.123.216
(Gateway1).
Each rule can be enabled or disabled individually.
After the Routing Table setting is configured, click Save.
NG System Manual
79
Page 94

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.9.6 Schedule Rule
Schedule Rule allows to set the schedule time for which a service will be
turned on or off.
Figure 54: Schedule Rule
The Schedule Rule window includes the following parameters:
Table 39: Routing Table Parameters
Parameter Description
Schedule Click the checkbox to Enable the Scheduler.
Rule # The rule number. Rules are numbered sequentially from the
first rule set to the last. When a rule is deleted, the rules are
automatically renumbered for all unit configurations.
Rule Name The name of the rule.
Action Edit and Delete - Every rule can be edited or deleted
individually.
To add a new rule:
80
1 Click Add New Rule to add a rule to the list. The Schedule Rule Setting
window opens.
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 95

Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
Figure 55: Schedule rule Setting
You can enter a rule name and set which day and what time to schedule
from “Start Time” to “End Time”. In the following example, a rule named
"FTP Time" is scheduled to operate every day between 14:10 and 16:20.
2 After configuring Rule 1, click on Save to save the rule and return to the
NG System Manual
Figure 56: Schedule Rule Setting – Example Step 1
Schedule Rule window. The new rule is now displayed on the list.
81
Page 96

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 57: Schedule Rule Setting – Example Step 2
When rules are set, you can:
Edit – Click to edit the specific rule.
Delete – Click to delete the specific rule. When the rule is deleted, all
subsequent rules are automatically renumbered.
Schedule Rule can be applied to Virtual server and Packet Filter, for
example:
Example1: Virtual Server – Apply Rule#1 using the scheduled rule #1 (ftp
time: every day 14:10 to 16:20).
82
Figure 58: Virtual Server - Schedule Rule#1
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 97

Advanced Settings (Administrator only)
Example2: Packet Filter – Apply Rule#1 using scheduled rule #1 (ftp time:
every day 14:10 to 16:20).
Figure 59: Packet Filter - Schedule Rule#1
3.9.7 UPnP Setting
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a protocol for connecting voice/video
applications through the Networking Gateway when in NAT mode.
UPnP Setting - Enable/Disable – enables/disables the feature. NAT should
be enabled.
NG System Manual
Figure 60: UPnP Setting
83
Page 98

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
3.10 Toolbox
The Toolbox menu provides access to viewing the system log, to firmware
upgrade, backup setting, resetting the system to the factory default values,
to rebooting the system, implementing DRAP protocol, running Wake-onLAN and performing Ping tests.
3.10.1 View Log
Clicking on View Log opens the System Log file. The System Log file can
also be accessed from the System Log window in the Advanced Setting
menu.
The log file logs all the activities performed since the last reset.
Figure 61: Toolbox
84
Using the Web Configuration Server
Page 99

Figure 62: View System Log
While in Log View, you can:
Toolbox
Click Back to return to the System Log window.
Click Refresh to manually update the Log.
Click Download to download the Log file (system.log) and save it
locally, on your PC.
Click Clear to clear the log file of its content.
3.10.2 Firmware Upgrade (Administrator only)
The Firmware Upgrade window displays the currently inst alled firmware
version.
NG System Manual
85
Page 100

Chapter 3 - Using the Web Configuration Server
Figure 63: Firmware Upgrade
To upgrade the firmware:
1 Click on Browse to browse to the upgrade file's location. The upgrade
file is a *.BIN file.
2 Click Upgrade to begin the upgrading process, or Cancel to terminating
it.
When the upgrade process is complete, the unit will automatically restart.
CAUTION
Do not turn off power to the unit during the upgrading process.
3.10.3 Backup Setting
To backup your settings:
1 Click Backup Setting in the menu list. This automatically opens the File
Download window.
86
2 Select the Save this file to disk option and click OK. Follow the
instructions on screen to save the file. The file is saved as a .bin file.
Using the Web Configuration Server
 Loading...
Loading...