
http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
Advanced AMS500
Monolithic LOW COST 500mA REGULATOR
Systems
RoHS compliant
FEATURES APPLICATIONS
•••• Fixed and Adjustable Versions Available •••• Cellular Telephones
•••• Output Current up to 500mA •••• Portable Consumer Equipment
•••• Very Low Quiescent Current •••• Portable (Notebook) Computers
•••• Reverse Battery Protection •••• Battery Powered Systems
•••• Input-output Differential less than 0.6V •••• Portable Instrumentation
•••• Short Circuit Protection •••• Radio Control Systems
•••• Internal Thermal Overload Protection •••• CD/DVD drives
•••• Overvoltage Protection •••• Automotive
•••• ON/OFF Pin
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AMS500 series consists of positive fixed and adjustable voltage regulators ideally suited for use in battery-powered systems.
The
These devices feature very low quiescent current of 0.8mA or less when supplying 50mA loads. This unique characteristic and the
low input-output differential required for proper regulation (0.2V for output currents of 100mA) make the AMS500 ideal to use
for standby power systems.
Internal circuitry of AMS500 is protected from input fault conditions caused by input voltages that exceed maximum rated input
voltage. During line transients, when the input voltage to the regulator can momentarily exceed the specified maximum operating
voltage, the regulator will automatically shut down to protect both internal circuits and the load. The AMS500 series also includes
internal current limiting, thermal shutdown.
The AMS500 is offered in 3 lead TO-92, SOT-89, SOT-223 and 5 leads SOT-23 packages.
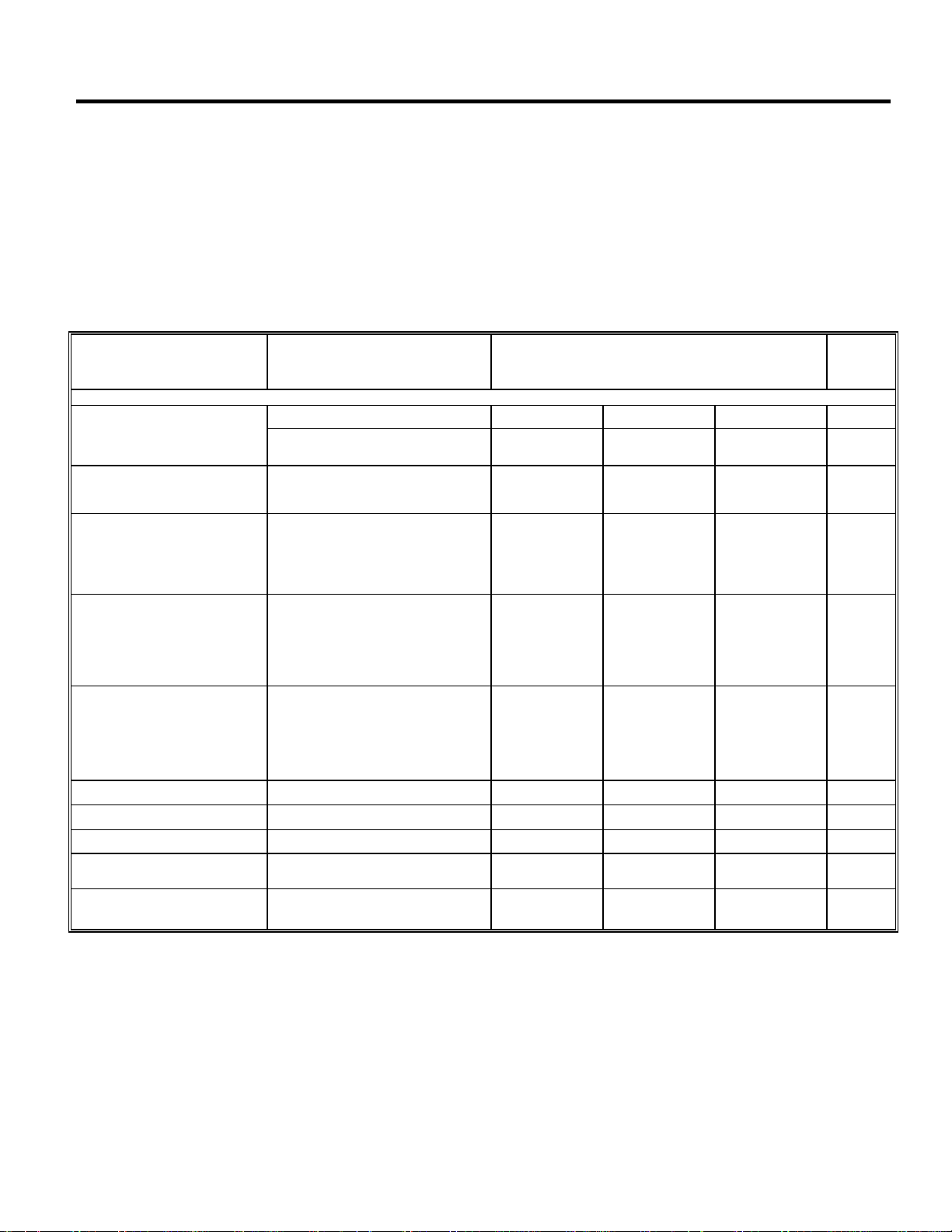
ORDERING INFORMATION
OUTPUT PAC
VOLTAGE
FIXED AMS500N-X AMS500L-X AMS500M1-X AMS500-X (R) -40ºC to +85 ºC
ADJ. AMS500M1 -40ºC to +85 ºC
X = 2.0V, 2.5V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.5V, 4.0V, 5.0V.
3L TO-92 SOT-89 SOT-23-5 SOT-223
KAGE TYPE TEMP.
updated April 24, 2009
RANGE
http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
AMS500
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Note 1)
Input Voltage Maximum Junction Temperature
Operating 25V Storage Temperature
-65°C to +150°C
Overvoltage Protection 26V to 40V Lead Temperature (Soldering 25 sec)
Internal Power Dissipation (Note 4) Internally Limited ESD 2000V
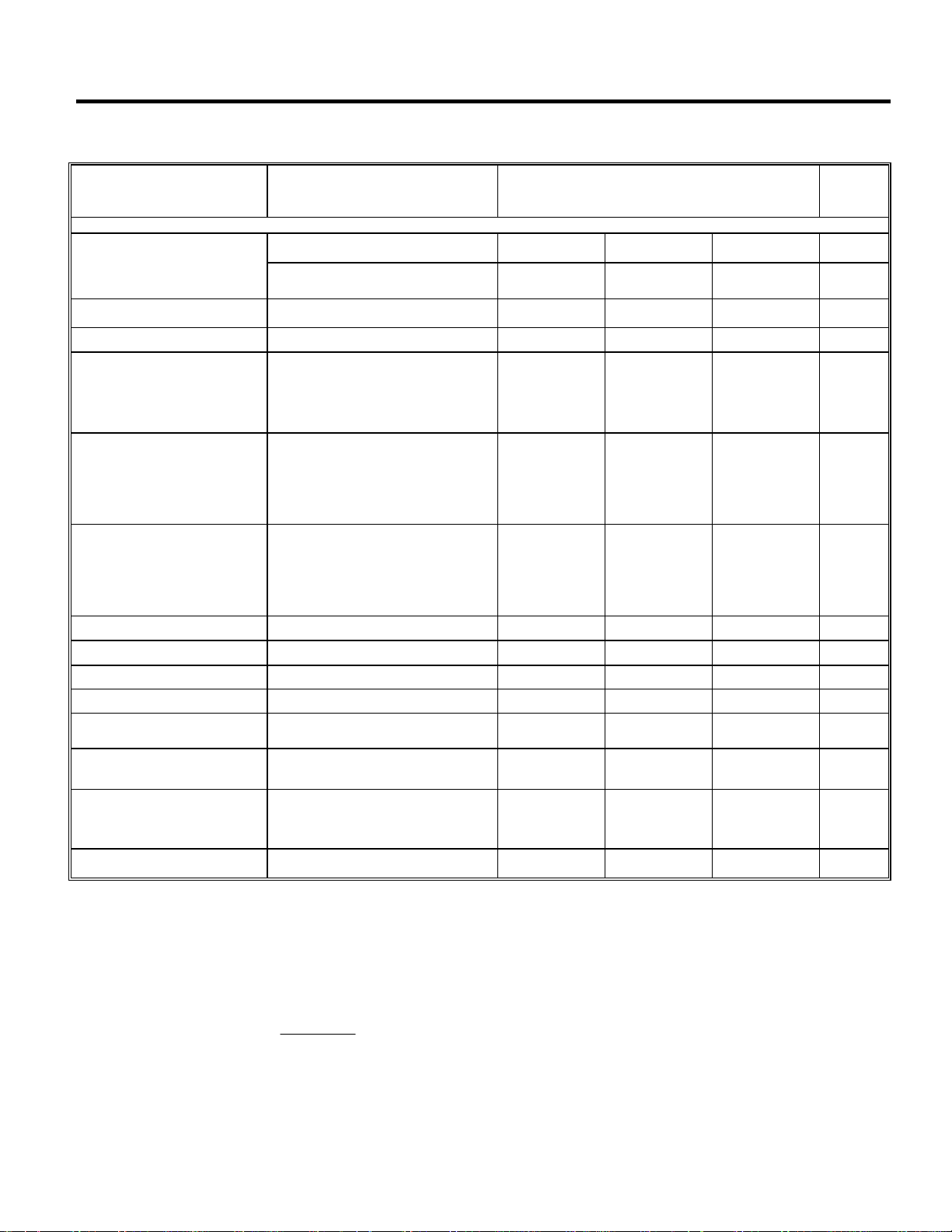
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Characteristics at V
PARAMETER
Fixed Output Voltage Versions
Output Voltage Tolerance -4.0 +4.0 %
=6.3V, IO =5mA, TJ=25°C, C2 = 22µF unless otherwise specified.
N
I
CONDITIONS
6.3V ≤VIN ≤25V, IO=100 mA
AMS500-X
Min. Typ. Max.
±±±± 5.0
%
+125°C
265°C
Units
Line Regulation
Load Regulation
Dropout Voltage
Quiescent Current
Output Noise Voltage
Output Bypass Capacitor
Ripple Rejection fO =120Hz 80 dB
Maximum Operational Input
Voltage
Maximum Line Transient
6V ≤VIN ≤ 15V
15V ≤VIN ≤ 25V
5mA ≤I
5mA ≤10 ≤ 200 mA
5mA ≤10 ≤ 350 mA
5mA ≤10 ≤ 500 mA
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
I
O
10Hz-100kHz, C
ESR=0.1 to 10Ω
25 28 V
RL = 500Ω, VO ≤ 5.5V
T = 1ms, τ ≤100ms
≤ 100 mA
O
= 100 mA
= 200 mA
= 350 mA
= 500 mA
≤ 10 mA,
= 100 mA
≤ 200 mA
= 350 mA
= 100µF
OUT
5
5
5
15
20
20
0.2
50
10
35 40 V
250
400
450
550
2
5
12
10
30
25
40
60
75
400
500
600
800
0.5
4
10
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mV
mA
mA
mA
mA
µV rms
µF
updated April 24, 2009
http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
AMS500
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Characteristics at V
PARAMETER
Adjustable Version
Reference Voltage
Output Voltage Range 2 24 V
Line Regulation
Load Regulation
Dropout Voltage
Quiescent Current
Output Noise Voltage 10Hz-100kHz 100
Output Bypass Capacitor
Long Term Stability T =1000hr 0.4 %/1000hr
Ripple Rejection fO = 120Hz 0.02 dB
Maximum Operational Input
Voltage
Maximum Line Transient
On/Off Threshold Voltage
On
Off
On/Off Threshold Current V
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. For guaranteed performance limits and associated test conditions,
see the Electrical Characteristics tables.
Note 2: To ensure constant junction temperature, low duty cycle pulse testing is used.
Note 3: Limits appearing in boldface type apply over the entire junction temperature range for operation. Limits appearing in normal type apply for TA = TJ =
25°C.
Note 4: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction temperature TJ(MAX), the junction-to ambient thermal resistance θ
and the ambient temperature TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is calculated using:
Where the value of the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance are as follows: 195°C/W for TO-92 (N), 110°C/W for SOT-89 (L), 90°C/W for SOT-223 and
220°C/W for 5 lead SOT-23.
P(MAX)
=6V, V
IN
1.20 1.235 1.27 V
IO ≤ 100 mA, -40°C ≤T
R1=27k, Measured from V
6V ≤VIN ≤ 25V
5mA ≤I
5mA ≤10 ≤ 200 mA
5mA ≤10 ≤ 350 mA
5mA ≤10 ≤ 500 mA
I
= 100 mA
O
I
= 200 mA
O
I
= 350 mA
O
I
= 500 mA
O
I
= 0 mA,
O
I
= 100 mA
O
I
= 200 mA
O
I
= 350 mA
O
ESR=0.1 to 10Ω
IO = 10mA, Reference Voltage ≤ 1.5V
T = 1ms, τ ≤100ms
VO = 3V
OFF
=
=3V IO =5mA, TJ=25°C, R1 =27k, C2 = 2µF unless otherwise specified.
OUT
CONDITIONS
(Note 2)
≤ 125°C,
J
to Adj. Pin
OUT
≤ 100 mA
O
= 2.4V 35 60
AJ
T-(MAX)T
A-J
θ
Min. Typ. Max.
1.180 1.235 1.290
.02 1.5 mV/V
0.3
0.18
10
21 22 V
35 40 V
2.5
AMS500-X
0.5
1.0
1.0
50
300
500
600
2.0
5.0
12
1.8
2.0
0.5
1
1.5
2.0
400
500
600
800
0.5
4
10
1.5
Units
µV
V
%
%
%
%
mV
mV
mV
mV
mA
mA
mA
mA
rms
µF
V
V
µA
/V
J-A
updated April 24, 2009

http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
PIN CONNECTIONS
TO-92
Plastic Package (N)
OUTPUT
GND
Bottom View Top View Top View
SOT-223
INPUT
AMS500
SOT-89
(L)
1 2 3
OUTPUTGNDINPUT
SOT-223
R=
5 Lead SOT-23
(M1)
INPUT OUTPUT
GROUND12
ON/OFF
3
5
4
ADJ / N/C
1 2 3
OUTPUTGNDINPUT
1 2 3
IN PU TGN DOU TPU T
Top View Top View
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Dropout Voltage
0.6
0.5
IO =
350mA
IO =
200mA
IO = 150mA
IO = 100mA
80
INPUT OUTPUT DIFFERENTIAL
120
(V)
INPUT OUTPUT DIFFERENTIAL
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 40
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (° C)
updated April 24, 2009
Dropout Voltage
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
(V)
0.2
0.1
0
0 300
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
400 500200100
600
Low Voltage Behavior
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
AMS500-3.3
IO = 500mA
0
2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)

http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
AMS500
Low Voltage Behavior
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.30
1.28
1.26
1.24
1.22
1.20
1.18
1.16
1.14
1.12
1.10
AMS500-5.0
IO = 500mA
0
2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Reference Voltage
AMS500 ADJUSTABLE
3 6 9 12 15 18 21 240
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Output at Voltage Extremes
6
AMS500-3.3
RL=500mΩ
5
4
3
2
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
-1
-20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Peak Output Current
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
0
TJ= 25°C
0 10
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Output at Voltage Extremes
6
AMS500-5.0
RL=500mΩ
5
4
3
2
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
-1
-20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Ripple Rejection
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
RIPPLE REJECTION (dB)
IO= 10mA
50
45
20
30
1 10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M
C2 = 100µF
ALUM
FREQUENCY (Hz)
C2 = 22µF
TANTALUM
Quiescent Current
17.5
IO= 10mA
15
12.5
10
7.
5
5.
0
2.
5
0
QUIESCENT CURRENT (µA)
-2.5
0 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 10
3 9
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
updated April 24, 2009
QUIESCENT CURRENT (mA)
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 100
Quiescent Current
VIN = 6V
200
50
150
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
250
300
350
Quiescent Current
25
20
15
10
~
~
3
2
1
QUIESCENT CURRENT (mA)
0
-40 40 80 120
0
TEMPERATURE (° C)
IO = 200mA
IO = 100mA
IO = 50mA
IO = 0mA
~
~

http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
APPLICATION NOTES
Definition of Terms
Dropout Voltage: The input-output voltage differential at which
the circuit stops to regulate against further reduction in input
voltage. Measured when the output voltage has dropped 100mV
from the nominal voltage obtained at 1V input, dropout voltage is
dependent upon load current and junction temperature.
Input Voltage: The DC voltage applied to the input terminal with
pect to ground. Input-Output Differential: The voltage
res
difference between the unregulated input voltage and the regulated
output voltage for which the regulator will regulate.
Line Regulation: The change in output voltage for a change in
the input voltage. The line regulation is measured under conditions
of low dissipation or by using low duty cycle pulse testing such
that the average chip temperature is not significantly affected.
Load Regulation: The change in output voltage for a change in
load current at constant chip temperature.
Long term stability: Output voltage stability under accelerated
life-test conditions after 1000 hours with maximum rated voltage
and junction temperature.
Output Noise Voltage: The rms AC voltage at the output, with
constant load and no input ripple, measured over a specified
frequency range.
Quiescent Current: That part of the positive input current that
does not contribute to the positive load current. The regulator
ground lead current.
Ripple Rejection: The ratio of the peak-to –peak input ripple
voltage to the peak-to-peak output ripple voltage at specified
frequency.
Temperature Stability of V
voltage for a thermal variation from room temperature to either
temperature extreme.
External capacitor
AMS500 series require an output capacitor of 10µF or greater
The
to ensure device stability. Without the capacitor the device may
oscillate
: The percentage change in output
O
AMS500
Most type of tantalum or electrolytic capacitor can be used in the
app
lications. A critical characteristic of the capacitors is an ESR
value of 5Ω or less and a resonant frequency above 500kHz. The
value of this capacitor can be increased without limits.
For higher loads, the value of the capacitor should be increased,
specialy when the output voltage is set for 2.5V or less. The
AMS500 lowest fixed output voltage value is 2.0V
Typical application circuit (adjustable output)
V
IN
100k
OFF
10µ
F
ON/OFF
ON
AMS500
ADJUSTABLE
GND
Minimum Load
In circuits using the fixed output voltage versions, minimum load
is not required. For circuits using the adjustable device, the value
of R1 and R2 should be chosen such, that a current of
approximately 40µA flows through the network. The reference
voltage (1.235V) is measured between the adjust pin and V
The output voltage can be set by the two resistors R1 and R2
using the following equation:
+
R2R1
=
VV REFO
R1
The value of R1 is recommended to be between 25kΩ to 30 kΩ,
and the value of R2 will set the output voltage.
OUT
ADJ
R
28k
R
1
+
2
C1
22µF
V
OUT
.
OUT
updated April 24, 2009

http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted.
3L TO-92 PLASTIC PACKAGE (N)
0.060±0.005
(1.524±0.127)
DIA
0.180±0.005
(4.572±0.127)
0.180±0.005
(4.572±0.127)
0.90
(2.286)
NOM
0.060±0.010
(1.524±0.254)
AMS500
0.140±0.010
(3.556±0.127)
10°
NOM
N (TO-92 ) AMS DRW# 042391
0.500
(12.70)
MIN
0.050±0.005
(1.270±0.127)
UNCONTROLLED
0.050
(1.270)
LEAD DIMENSIONS
MAX
0.016±0.003
(0.406±0.076)
5° NOM
0.015±0.002
(0.381±0.051)
5 LEAD SOT-23 PLASTIC PACKAGE (M1)
0.110-0.120
(2.794-3.048)
0.102-0.118
(2.60-3.00)
0.059-0.070
(1.50-1.75)
0.037
(0.95)
TYP
0.018-0.024
(0.457-0.610)
0.036-0.051
(0.090-1.30)
0.003
(0.150)
MAX
updated April 24, 2009
0.075
(1.90)
TYP
0.014-0.020
(0.350-0.50)
10°
NOM
10°
NOM
0.018-0.024
(0.457-0.610)
0.0035-0.0080
(0.090-0.20)
(SOT-23-5 ) AMS DRW# 051001

http://www.BDTIC.com/AMS
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued).
SOT-89 PLASTIC PACKAGE (L)
0.173-0.181
0.155-0.167
(3.94-4.25)
0.090-0.102
(2.29-2.60)
(4.40-4.60)
0.064-0.072
(1.62-1.83)
0.035-0.047
(0.89-1.20)
0.055-0.063
(1.40-1.60)
0.084-0.090
(2.13-2.29)
AMS500
0.014-0.017
(0.35-0.44)
0.264-0.287
(6.71-7.29)
0.130-0.146
(3.30-3.71)
0.059
(1.50)
BSC
0.090
(2.29)
NOM
0.014-0.019
(0.36-0.48)
0.118
(3.00)
BSC
0.017-0.022
(0.44-0.56)
3 LEAD SOT-223 PLASTIC PACKAGE
0.248-0.264
(6.30-6.71)
0.116-0.124
(2.95-3.15)
0.033-0.041
(0.84-1.04)
L (SOT-89 ) AMS DRW# 042392
0.071
(1.80)
MAX
updated April 24, 2009
0.025-0.033
(0.64-0.84)
0.181
(4.60)
NOM
0.012
(0.31)
MIN
10°
MAX
10°-16°
0.025-0.033
(0.64-0.84)
0.010-0.014
(0.25-0.36)
10°-16°
(SOT-223 ) AMS DRW# 042292
 Loading...
Loading...