Page 1

ADTRAN OPERATING SYSTEM (AOS)
Command Reference Guide
AOS Version 11.1
NetVanta 2000 Series Products
November 2005
61202361L1-35E
Page 2

Command Reference Guide
Trademarks
Any brand names and product names included in this manual are trademarks, registered trademarks,
service marks, or trade names of their respective holders.
To the Holder of this Manual
The contents of this manual are current as of th e date of publication. ADTRAN reserves the right to change
the contents without prior notice.
In no event will ADTRAN be liable for any special, incidental, or consequential damages or for
commercial losses even if ADTRAN has been advised thereof as a result of issue of this publication.
Software Licensing Agreement
Each ADTRAN product contains a single license for ADTRAN supplied software. Pursuant to the
Licensing Agreement, you may: (a) use the software on the purchased ADTRAN device only and (b) keep
a copy of the software for backup purposes. This Agreement covers all software installed on the system as
well as any software available on the ADTRAN website. In addition, certain ADTRAN systems may
contain additional conditions for obtaining software upgrades.
Conventions
Notes provide additional useful information.
Cautions signify information that could prevent service interruption or damage to the
equipment.
Warnings provide information that could prevent endangerment to human life.
901 Explorer Boulevard
P.O. Box 140000
Huntsville, AL 35814-4000
Phone: (256) 963-8000
www.adtran.com
Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN
All Rights Reserved.
Printed in the U.S.A.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 2
Page 3

Command Reference Guide
Warranty and Customer Service
ADTRAN will repair and return this product within the warranty period if it does not meet its published
specifications or fails while in service. Warranty information can be found at www.adtran.com
. (Click on
Warranty and Repair Information under Support.)
Product Registration
Registering your product helps ensure complete customer satisfaction. Please take time to register your
products on line at www.adtran.com
. Click Service/Support and then on Product Registration under
Support.
Product Support Information
A return material authorization (RMA) is required prior to returning equipment to ADTRAN. For service,
RMA requests, training, or more information, use the contact information given below.
Repair and Return
If you determine that a repair is needed, please contact our Customer and Product Service (CaPS)
department to have an RMA number issued. CaPS should also be contacted to obtain information
regarding equipment currently in house or possible fees associated with repair.
CaPS Department (256) 963-8722
Identify the RMA number clearly on the package (below the address), and return to the following address:
ADTRAN Customer and Product Service
901 Explorer Blvd. (East Tower)
Huntsville, Alabama 35806
RMA # _____________
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 3
Page 4

Command Reference Guide
Pre-Sales Inquiries and Applications Support
Your reseller should serve as the first point of contact for support. If additional pre-sales support is needed,
the ADTRAN Support website provides a variety of support services such as a searchable knowledge base,
latest product documentation, application briefs, case studies, and a link to submit a question to an
Applications Engineer. All of this, and more, is available at:
http://support.adtran.com
When needed, further pre-sales assistance is available by calling our Applications Engineering
Department.
Applications Engineering (800) 615-1176
Post-Sales Support
Your reseller should serve as the first point of contact for support. If additional support is needed, the
ADTRAN Support website provides a variety of support services such as a searchable knowledge base,
updated firmware releases, latest product documentation, service request ticket generation and
trouble-shooting tools. All of this, and more, is available at:
http://support.adtran.com
When needed, further post-sales assistance is available by calling our Technical Support Center. Please
have your unit serial number available when you call.
Technical Support (888) 4ADTRAN
International Technical Support 1-256-963-8716
Installation and Maintenance Support
The ADTRAN Custom Extended Services (ACES) program offers multiple types and levels of installation
and maintenance services which allow you to choose the kind of assistance you need. This support is
available at:
http://www.adtran.com/aces
For questions, call the ACES Help Desk.
ACES Help Desk (888) 874-ACES (2237)
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 4
Page 5

Command Reference Guide
Training
The Enterprise Network (EN) T echnical T raining Department offers training on our most po pular products.
These courses include overviews on product features and functions while covering applications of
ADTRAN's product lines. ADTRAN provides a variety of training options, including customized training
and courses taught at our facilities or at your site. For more information about training, please contact your
Territory Manager or the Enterprise Training Coordinator.
Training Phone (800) 615-1176, ext. 7500
Training Fax (256) 963-6700
Training Email training@adtran.com
Export Statement
An Export License is required if an ADTRAN product is sold to a Government Entity outside of the EU+8
(Austria, Australia, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary,
Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden,
Switzerland and the United Kingdom). This requirement is per DOC/BIS ruling G030477 issued 6/6/03.
This product also requires that the Exporter of Record file a semi-annual report with the BXA detailing the
information per EAR 740.17(5)(e)(2).
DOC - Department of Commerce
BIS - Bureau of Industry and Security
BXA - Bureau of Export Administration
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 5
Page 6

Command Reference Guide Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Basic Mode Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Common Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Enable Mode Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Global Configuration Mode Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
Line (Console) Interface Config Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
Line (SSH) Interface Config Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
Line (Telnet) Interface Config Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
Ethernet Interface Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
Loopback Interface Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
PPP Interface Configuration Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
Tunnel Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610
VLAN Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 655
VLAN Database Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 659
VLAN Interface Config Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 668
CA Profile Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 715
Certificate Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 726
Crypto Map IKE Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730
Crypto Map Manual Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 739
IKE Client Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750
IKE Policy Attributes Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 754
IKE Policy Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760
AS Path List Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 773
BGP Configuration Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 776
BGP Neighbor Configuration Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 782
Community List Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 798
Router (OSPF) Configuration Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 801
Router (PIM Sparse) Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 816
Router (RIP) Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 821
DHCP Pool Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 832
Quality of Service (QoS) Map Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850
Radius Group Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 856
Route Map Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 858
TACACS+ Group Configuration Command Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 878
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 880
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 6
Page 7

Command Reference Guide CLI Introduction
REFERENCE GUIDE INTRODUCTION
This manual provides information about the commands that are available with all of the NetVanta Series
units.
This manual provides information about the commands that are available with NetVanta 2000 Series units.
For a list of all of the commands available through the CLI, see 61950860L1-35L (All Products).
If you are new to the ADTRAN Operating System’s (AOS) Command Line Interface (CLI), take a few
moments to review the information provided in the section which follows (CLI Introduction).
If you are already familiar with the CLI and you need information on a specific command or group of
commands, proceed to Command Descriptions on page 13 of this guide.
CLI INTRODUCTION
This portion of the Command Reference Guide is designed to introduce you to the basic concepts and
strategies associated with using the AOS CLI.
Accessing the CLI from your PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Understanding Command Security Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Understanding Configuration Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Using CLI Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Performing Common CLI Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Understanding CLI Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Accessing the CLI from your PC
All products using the AOS are initially accessed by connecting a VT100 terminal (or terminal emulator)
CONSOLE port located on the rear panel of the unit using a standard DB-9 (male) to DB-9 (female)
to the
serial cable. Configure the VT100 terminal or terminal emulation software to the following settings:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• No parity
• 1 stop bit
• No flow control
For more details on connecting to your unit, refer to the Quick Configuration Guides and
Quick Start Guides located on the ADTRAN OS Documentation CD provided with your
unit.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 7
Page 8
Command Reference Guide Understanding Command Security Levels
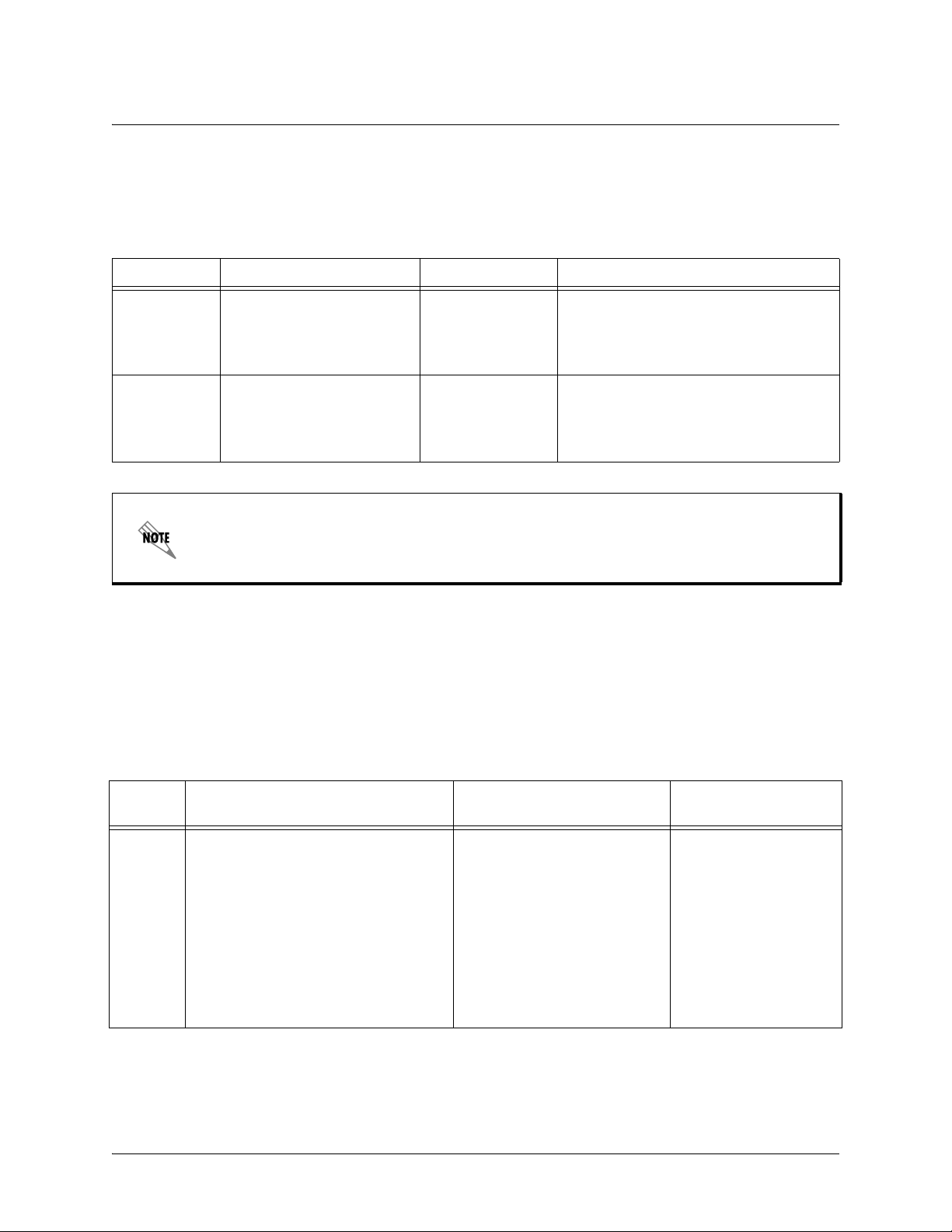
Understanding Command Security Levels
The ADTRAN CLI has two command security levels — Basic and Enable. Both levels support a specific
set of commands. For example, all interface configuration commands are accessible only through the
Enable security level. The following table contains a brief description of each level.
Level Access by... Prompt With this level you can...
Basic beginning an AOS session.
Enable entering
Basic command security level
as follows:
>enable
enable
while in the
> • display system information
• perform traceroute and ping
functions
• open a Telnet session
# • manage the startup and running
configurations
• use the debug commands
• enter any o f the configuration modes
To prevent unauthorized users from accessing the configuration functions of your AOS
product, immediately install an Enable-level password. Refer to the Quick Configuration
Guides and Quick Start Guides located on the ADTRAN OS Documentation CD pr ovided
with your unit for more information on configuring a password.
Understanding Configuration Modes
The ADTRAN CLI has four configuration modes to organize the configuration commands – Global, Line,
Router, and Interface. Each configuration mode supports a set of commands specific to the configurable
parameters for the mode. For example, all Frame Relay configuration commands are accessible only
through the interface configuration mode (for the virtual Frame Relay interface). The following table
contains a brief description of each level.
Mode Access by... Sample Prompt With this mode you
can...
Global entering
command security level prompt.
For example:
>enable
#config term
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 8
config
while at the Enable
(config)# • set the system’s
Enable-level
password(s)
• configure the system
global IP parameters
• configure the SNMP
parameters
• enter any of the
other configuration
modes
Page 9
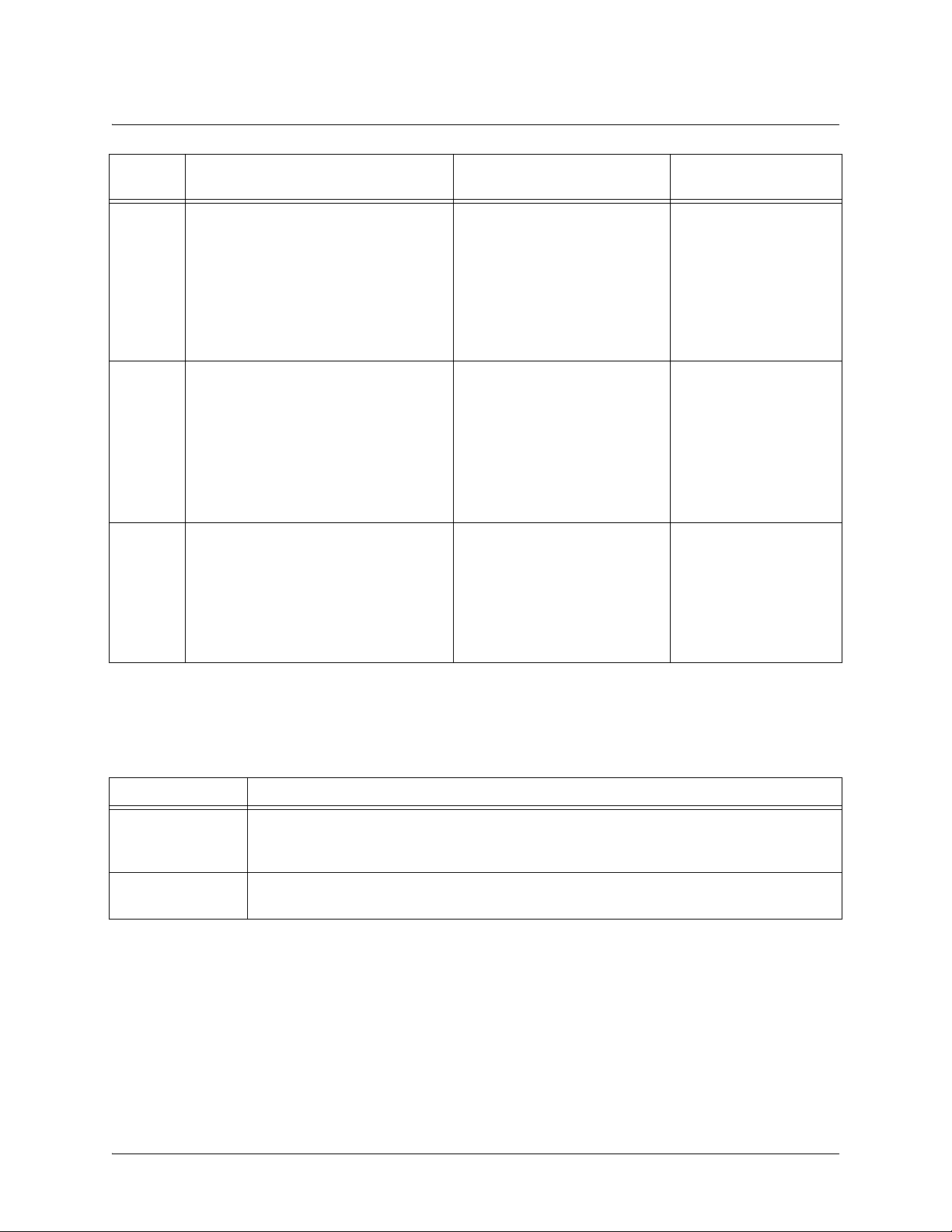
Command Reference Guide Using CLI Shortcuts
Mode Access by... Sample Prompt With this mode you
can...
Line specifying a line (console or Telnet)
while at the Global Configuration mode
prompt.
For example:
>enable
#config term
(config)#line console 0
Router entering
while at the Global Configuration mode
prompt.
For example:
>enable
#config term
(config)#
Interface specifying an interface (T1, Ethernet,
Frame Relay, ppp, etc.) while in the
Global Configuration mode.
For example:
>enable
#config term
(config)#
router rip or
router rip
int eth 0/1
router ospf
(config-con0)# • configure the
console terminal
settings (datarate,
login password, etc.)
• create Telnet log ins
and specify their
parameters (login
password, etc.)
(config-rip)# • configure RIP or
OSPF parameters
• suppr ess route
updates
• redistribute
information from
outside routing
sources (protocols)
(config-eth 0/1)#
(The above prompt is for the
Ethernet
on the rear panel of the unit.)
LAN
interface located
•configure
parameters for the
available LAN and
WAN interfaces
Using CLI Shortcuts
The ADTRAN CLI provides several shortcuts which help you configure your AOS product more easily.
See the following table for descriptions.
Shortcut Description
Up arrow key To re-display a previously entered command, use the up arrow key. Continuing to press the
up arrow key cycles through all commands entered starting with the most recent
command.
<T ab>
key Pressing the
command, display it on the command prompt line, and wait for further input.
<Tab>
key after entering a partial (but unique) command will complete the
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 9
Page 10
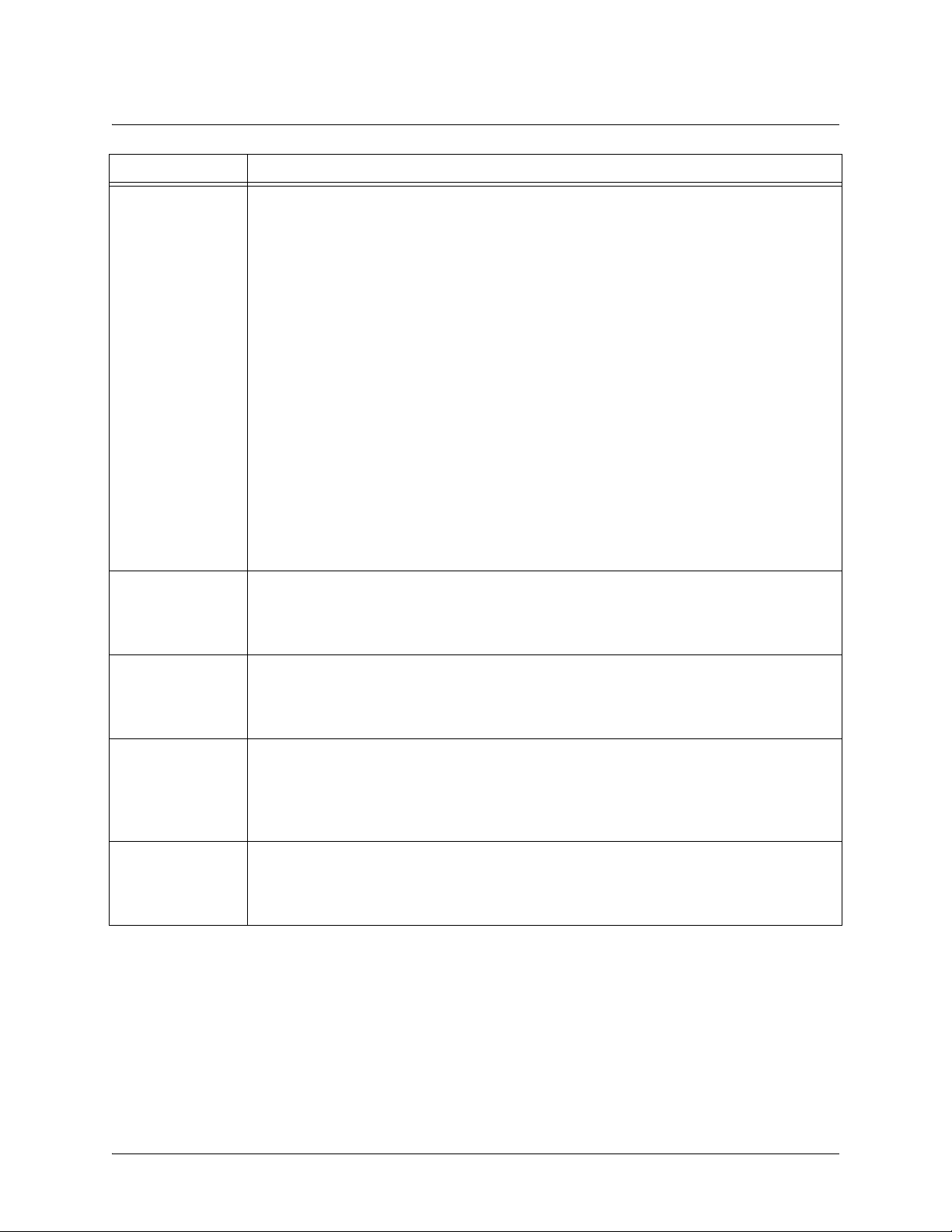
Command Reference Guide Using CLI Shortcuts
Shortcut Description
?
<Ctrl + A>
The ADTRAN CLI contains help to guide you through the configuration process. Using the
question mark, do any of the following:
• Display a list of all subcommands in the current mode. For example:
(config-t1 1/1)#coding ?
ami - Alternate Mark Inversion
b8zs - Bipolar Eight Zero Substitution
• Display a list of available commands beginning with certain letter(s). For example:
(config)#
ip d?
default-gateway dhcp-server domain-lookup domain-name domain-proxy
• Obtain syntax help for a specific command by entering the co mmand, a space, and
then a question mark (?). The ADTRAN CLI displays the range of values and a brief
description of the next parameter expected for that particular command. For
example:
(config-eth 0/1)#mtu ?
<64-1500> - MTU (bytes)
Jump to the beginning of the displayed command line. This shortcut is helpful when using
the
no
form of commands (when available). For example, pressing
following prompt will place the cursor directly after the
#
:
<Ctrl + A>
at the
(config-eth 0/1)#ip address 192.33.55.6
<Ctrl + E>
Jump to the end of the displayed command line. For example, pressing
following prompt will place the cursor directly after the
6
:
<Ctrl + E>
at the
(config-eth 0/1)#ip address 192.33.55.6
<Ctrl + U>
Clears the current displayed command line. The following provides an example of the
<Ctrl + U>
(config-eth 0/1)#ip address 192.33.55.6
feature:
(Press
<Ctrl + U>
here)
(config-eth 0/1)#
auto finish You need only enter enough letters to identify a command as unique. For example,
entering
configuration parameters for the specified T1 interface. Entering
int t1 1/1
at the Global configuration prompt provides you access to the
interface t1 1/1
would
work as well, but is not necessary.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 10
Page 11
Command Reference Guide Performing Common CLI Functions
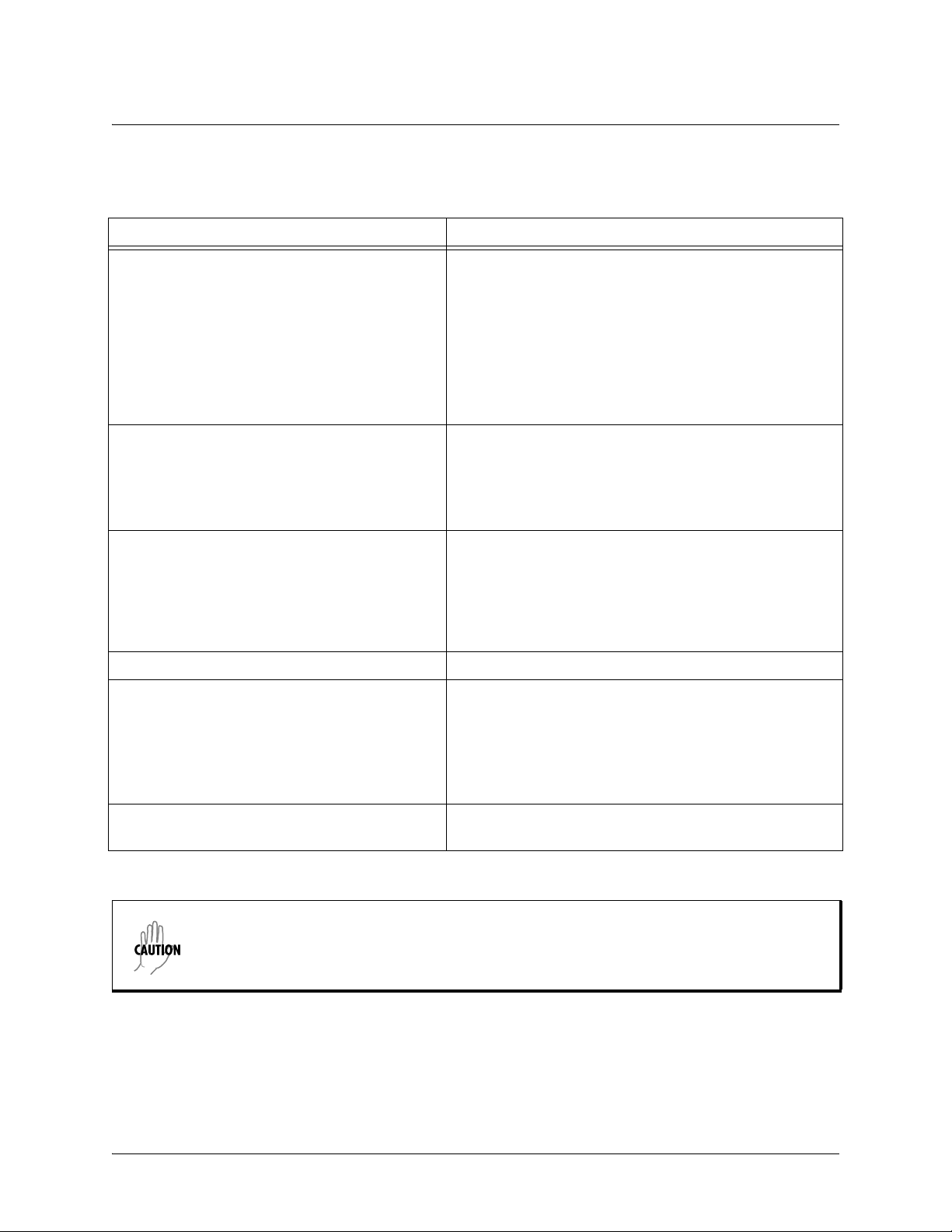
Performing Common CLI Functions
The following table contains descriptions of common CLI commands.
Command Description
do
no
copy running-config startup-config
show running config
debug
The do command provides a way to execute commands in
other command sets without taking the time to exit the
current and enter the desired one. The following example
shows the
interface configuration while currently in the T1 interface
command set:
(config)#interface t1 1/1
(config-t1 1/1)#do show interfaces fr 7
To undo an issued command or to disable a feature, enter
no
before the command.
For example:
no shutdown t1 1/1
When you are ready to save the changes made to the
configuration, enter this command. This copies your
changes to the unit’s nonvolatile random access memory
(NVRAM). Once the save is complete, the changes are
retained even if the unit is shut down or suffers a power
outage.
Displays the current configuration.
Use the
may be experiencing on your network. These commands
provide additional information to help you better interpret
possible problems. For information on specific debug
commands, refer to the section
Set on page 35
do
command used to view the Frame Relay
debug
command to troubleshoot problems you
Enable Mode Command
.
undebug all
To turn off any active debug commands, enter this
command.
The overhead associated with the debug command takes up a large portion of your AOS
product’s resources and at times can halt other processes. It is best to only use the debug
command during times when the network resources are in low demand (non-peak hours,
weekends, etc.).
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 11
Page 12
Command Reference Guide Understanding CLI Error Messages
Understanding CLI Error Messages
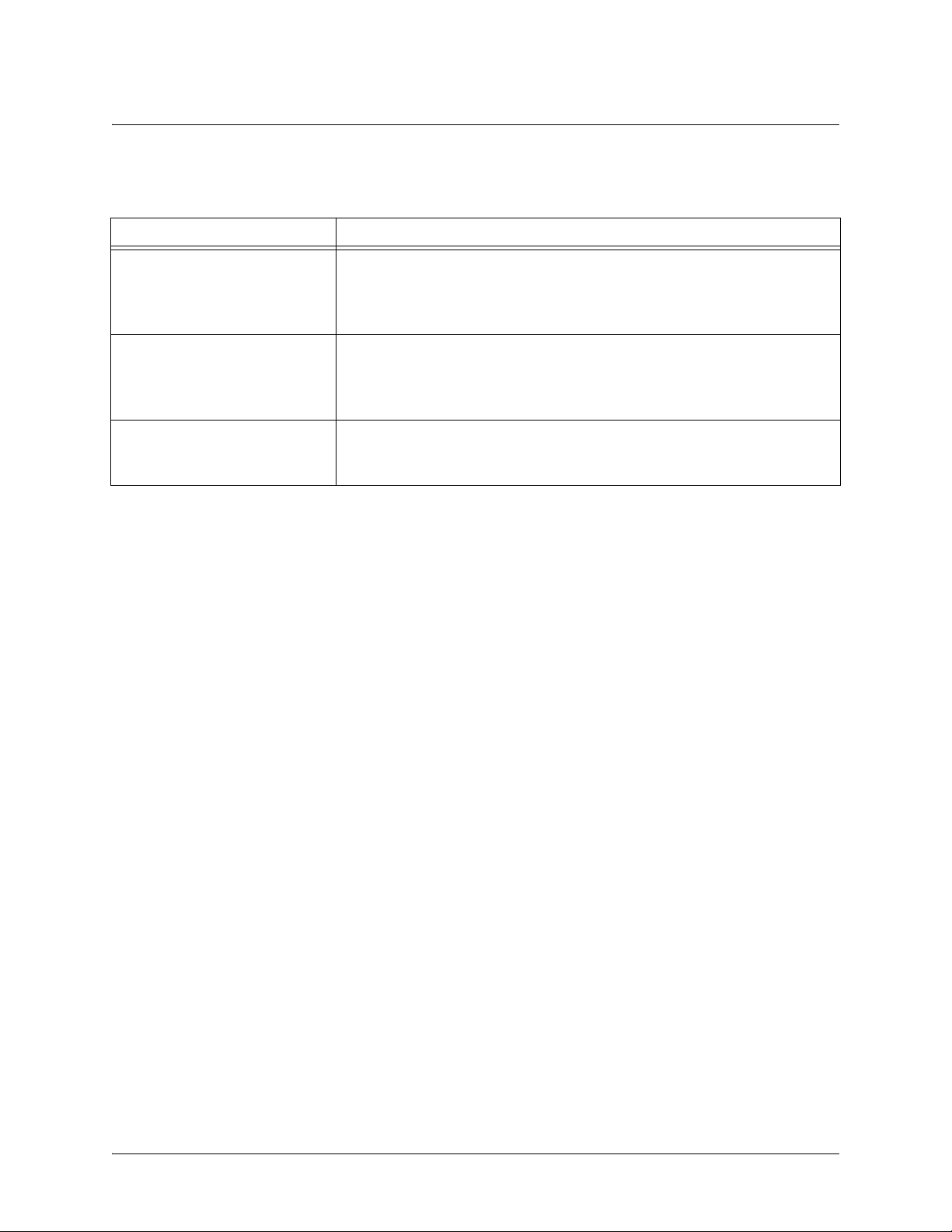
The following table lists and defines some of the more common error messages given in the CLI.
Message Helpful Hints
%Ambiguous command
%Unrecognized Command
%Invalid or incomplete
command
%Invalid input detected at
“^” marker
The command may not be valid in the current command mode, or you may
not have entered enough correct characters for the command to be
recognized. Try using the
CLI Shortcuts on page 9
The command may not be valid in the current command mode, or you may
not have entered all of the pertinent information required to make the
command valid. Try using the
Using CLI Shortcuts on page 9
The error in command entry is located where the caret (^) mark appears.
Enter a question mark at the prompt. The system will display a list of
applicable commands or will give syntax information for the entry.
?
command to determine your error. See
for more information.
?
command to determine your error. See
for more information.
Using
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 12
Page 13

Command Reference Guide Command Descriptions
COMMAND DESCRIPTIONS
This portion of the guide provides a detailed listing of all available commands for the ADTRAN OS CLI
(organized by command set). Each command listing contains pertinent information including the default
value, a description of all sub-command parameters, functional notes for using the command, and a brief
technology review. To search for a particular command alphabetically, use the Index at the end of this
document. To search for information on a group of commands within a particular command set, use the
linked references given below:
Basic Mode Command Set on page 15
Common Commands on page 25
Enable Mode Command Set on page 35
Global Configuration Mode Command Set on page 256
Line Interface Command Sets
Line (Console) Interface Config Command Set on page 430
Line (SSH) Interface Config Command Set on page 443
Line (Telnet) Interface Config Command Set on page 451
Physical Interface Command Sets
Ethernet Interface Configuration Command Set on page 460
Virtual Interface Command Sets
Loopback Interface Configuration Command Set on page 511
PPP Interface Configuration Command Set on page 548
Tunnel Configuration Command Set on page 610
VLAN Configuration Command Set on page 655
VLAN Database Configuration Command Set on page 659
VLAN Interface Config Command Set on page 668
VPN Parameter Command Sets
CA Profile Configuration Command Set on page 715
Certificate Configuration Command Set on page 726
Crypto Map IKE Command Set on page 730
Crypto Map Manual Command Set on page 739
IKE Client Command Set on page 750
IKE Policy Attributes Command Set on page 754
IKE Policy Command Set on page 760
Routing Protocol Command Sets
AS Path List Command Set on page 773
BGP Configuration Command Set on page 776
BGP Neighbor Configuration Command Set on page 782
Community List Command Set on page 798
Router (OSPF) Configuration Command Set on page 801
Router (PIM Sparse) Configuration Command Set on page 816
Router (RIP) Configuration Command Set on page 821
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 13
Page 14

Command Reference Guide Command Descriptions
Security and Services Command Sets
DHCP Pool Command Set on page 832
Quality of Service (QoS) Map Commands on page 850
Radius Group Command Set on page 856
Route Map Command Set on page 858
TACACS+ Group Configuration Command Set on page 878
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 14
Page 15

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
BASIC MODE COMMAND SET
To activate the Basic mode, simply log in to the unit. After connecting the unit to a VT100 terminal (or
terminal emulator) and activating a terminal session, the following prompt displays:
>
The following command is common to multiple command sets and is covered in a centralized section of
this guide. For more information, refer to the section listed below:
exit on page 33
All other commands for this command set are described in this section in alphabetical order.
enable on page 16
logout on page 17
ping <address> on page 18
show clock on page 20
show snmp on page 21
show version on page 22
telnet <address> on page 23
traceroute <address> on page 24
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 15
Page 16

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
enable
Use the enable command (at the Basic Command mode prompt) to enter the Enable Command mode. Use
the disable command to exit the Enable Command mo de. Refer to En able Mode Command Set on page 35
for more information.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The Enable Command mode provides access to operating and configuration parameters and should be
password protected to prevent unauthorized use. Use the enable password command (found in the
Global Configuration mode) to specify an Enable Command mode password. If the password is set,
access to the Enable Commands (and all other “privileged” commands) is only granted when the correct
password is entered. Refer to
enable password [md5] <password> on page 308 for more information.
Usage Examples
The following example enters the Enable Command mode and defines an Enable Command mode
password:
>enable
#configure terminal
(config)#enable password ADTRAN
At the next login, the following sequence must occur:
>enable
Password: ******
#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 16
Page 17

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
logout
Use the logout command to terminate the current session and return to the login screen.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No defaults necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example shows the logout command being executed in the Basic mode:
>logout
Session now available
Press RETURN to get started.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 17
Page 18

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
ping <address>
Use the ping command (at the Basic Command mode prompt) to verify Internet Protocol (IP) network
connectivity.
Syntax Description
<address> Specifies the IP address of the system to ping. Entering the ping command with
no specified address prompts the user with parameters for a more detailed ping
configuration. Refer to Functional Notes (below) for more information.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The ping command helps diagnose basic IP network connectivity using th e Packet InterNet Groper
program to repeatedly bounce Inter ne t Con tr ol Message Protocol (ICMP) echo-request packets off a
system (using a specified IP address). The AOS allows executing a standard ping request to a specified IP
address or provides a set of prompts to configure a more specific ping configuration.
The following is a list of output messages from the ping command:
! Success
- Destination Ho st Unreachable
$ Invalid Host Address
X TTL Expired in Transit
? Unknown Host
* Request Timed Out
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 18
Page 19

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
The following is a list of available extended ping fields with descriptions:
Target IP address Specifies the IP address of the system to ping.
Repeat Count Specifies the number of ping packets to send to the system
(valid range: 1 to 1,000,000).
Datagram Size Specifies the size (in bytes) of the ping packet (valid range: 1 to 1448).
Timeout in Seconds Specifies the timeout period after which a ping is considered unsuccessful
(valid range: 1 to 5 seconds).
Extended Commands Specifies whether additional commands are desired for more ping
configuration parameters.
Source Address (or interface) Specifies the IP address to use as the source address in the ECHO_REQ
packets.
Data Pattern Specifies an alphanumeric string to use (the ASCII equivalent) as the data
pattern in the ECHO_REQ packets.
Sweep Range of Sizes Varies the sizes of the ECHO_REQ packets transmitted.
Sweep Min Size Specifies the minimum size of the ECHO_REQ packet
(valid range: 0 to 1448).
Sweep Max Size Specifies the maximum size of the ECHO_REQ packet
(valid range: Sweep Min Size to 1448).
Sweep Interval Specifies the interval used to determine packet size when performing the
sweep (valid range: 1 to 1448).
Verbose Output Specifies an extended results output.
Usage Examples
The following is an example of a successful ping command:
>ping
Target IP address:192.168.0.30
Repeat count[1-1000000]:5
Datagram Size [1-1000000]:100
Timeout in seconds [1-5]:2
Extended Commands? [y or n]:n
Type CTRL+C to abort.
Legend: '!' = Success '?' = Unknown host '$' = Invalid host address
'*' = Request timed out '-' = Destination host unreachable
'x' = TTL expired in transit
Pinging 192.168.0.30 with 100 bytes of data:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5) round-tri p min /a vg /m ax = 19/2 0. 8/ 25 ms
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 19
Page 20

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
show clock
Use the show clock command to display the sys t em time and date entered using the clock set command.
Refer to the section clock set <time> <day> <month> <year> on page 73 for more information.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example displays the current time and data from the system clock:
>show clock
23:35:07 UTC Tue Aug 20 2002
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 20
Page 21

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
show snmp
Use the show snmp command to display the system Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
parameters and current status of SNMP communications.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following is an example output using the show snmp command for a system with SNMP disabled a nd
the default chassis and contact parameters:
>show snmp
Chassis: Chassis ID
Contact: Customer Service
0 Rx SNMP packets
0 Bad community names
0 Bad community uses
0 Bad versions
0 Silent drops
0 Proxy drops
0 ASN parse errors
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 21
Page 22

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
show version
Use the show version command to display the current AOS version information.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following is a sample show version output:
>show version
AOS version 06.01.00
Checksum: 1F0D5243 built on Fri Nov 08 13:12:06 2002
Upgrade key: de76efcfeb4c8eeb6901188475dd0917
Boot ROM version 03.00.18
Checksum: 7A3D built on: Fri Nov 08 13:12:25 2002
Copyright (c) 1999-2002 ADTRAN Inc.
Serial number C14C6308
UNIT_2 uptime is 0 days 4 hours 59 minutes 43 seconds
System returned to ROM by Warm Start
Current system image file is "030018adv.biz"
Boot system image file is "030018adv.biz"
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 22
Page 23

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
telnet <address>
Use the telnet command to open a Telnet session (through the AOS) to another system on the network.
Syntax Description
<address> Specifies the IP address of the remote system.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example opens a Telnet session with a remote system (10.200.4.15):
>telnet 10.200.4.15
User Access Login
Password:
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 23
Page 24

Command Reference Guide Basic Mode Command Set
traceroute <address>
Use the traceroute command to display the Internet Protocol (IP) routes a packet takes to reach the
specified destination.
Syntax Description
<address> Specifies the IP address of the remote system to trace the routes to.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example performs a traceroute on the IP address 192.168.0.1:
#traceroute 192.168.0.1
Type CTRL+C to abort.
Tracing route to 192.168.0.1 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 22ms 20ms 20ms 192.168.0.65
2 23ms 20ms 20ms 192.168.0.1
#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 24
Page 25

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
COMMON COMMANDS
The following section contains descriptions of commands that are common across multiple command sets.
These commands are listed in alphabetical order.
alias <“text”> on page 26
cross-connect <#> <from interface> <slot/port> <tdm-group#> <to interface> <slot/port>
on page 27
description <text> on page 30
do on page 31
end on page 32
exit on page 33
shutdown on page 34
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 25
Page 26

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
alias <“text”>
Use the alias command to populate the ifAlias OID (Interface Table MIB of RFC2863) for all physical and
virtual interfaces when using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) management stations.
Syntax Description
<“text”> Describes the interface (for SNMP) using an alphanumeric character string
enclosed in quotation marks (limited to 64 characters).
Default Values
No defaults required for this command.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all interface mode command sets.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The ifAlias OID is a member of the ifXEntry object-type (defined in RFC2863) used to provide a
non-volatile, unique name for various interfaces. This name is preserved through power cycles. Enter a
string (using the alias command) which clearly identifies the interface.
Usage Examples
The following example defines a unique character string for the T1 interface:
(config)#interface t1 1/1
(config-t1 1/1)#alias “CIRCUIT_ID_23-908-8887-401”
Technology Review
Please refer to RFC2863 for more detailed information on the ifAlias display string.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 26
Page 27

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
cross-connect <#> <from interface> <slot/port> <tdm-group#>
<to interface> <slot/port>
Use the cross-connect command to create a cross-connect map from a created TDM group on an interface
to a virtual interface.
Changing cross-connect settings could potentially result in service interruption.
Syntax Description
<#> Identifies the cross-connect using a number descriptor or label for (useful in
systems that allow multiple cross-connects).
<from interface> Specifies the interface (physical or virt ual) on one end of the cross-connect. Ente r
cross-connect 1 ? for a list of valid interfaces.
<slot/port> Used when a physical interface is specified in the <from interface> subcommand
(For example: specifying the T1 port of a T1 module would be t1 1/1).
<tdm-group#> Specifies which configured TDM group to use for this cross-connect. This
subcommand only applies to T1 physical interfaces.
<to interface> Specifies the virtual interface on the other end of the cross-connect. Use the ? to
display a list of valid interfaces.
<slot/port> Used when a physical interface is specified in the <to interface> subcommand.
(For example, specifying the primary T1 port of a T1 module would be t1 1/1).
Default Values
By default, there are no configured cross-connects.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Release 5.1 Command was expanded to include the E1 interface.
Functional Notes
Cross-connects provide the mechanism for connecting a configured virtual (layer 2) endpoint with a
physical (layer 1) interface. Supported layer 2 protocols include Frame Relay and point-to-point protocol
(PPP).
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 27
Page 28

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
Usage Examples
The following example creates a Frame Relay endpoint and connects it to the T1 1/1 physical interface:
1. Create the Frame Relay virtual endpoint and set the signaling method:
(config)#
(config-fr 1)#
2. Create the sub-interface and configure the PVC parameters (including DLCI and IP address):
(config-fr 1)#
(config-fr 1.1)#
(config-fr 1.1)#
3. Create the TDM group of 12 DS0s (64K) on the T1 physical interface:
(THIS STEP IS ONLY VALID FOR T1 INTERFACES.)
(config)#
(config-t1 1/1)#
(config-t1 1/1)#
4. Connect the Frame Relay sub-interface with port T1 1/1:
(config)#
interface frame-relay 1
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
interface fr 1.1
frame-relay interface-dlci 17
ip address 168.125.33.252 255.255.255.252
interface t1 1/1
tdm-group 1 timeslots 1-12 speed 64
exit
cross-connect 1 t1 1/1 1 fr 1
Technology Review
Creating an endpoint that uses a layer 2 protocol (such as Frame Relay) is generally a four-step process:
Step 1:
Create the Frame Relay virtual endpoint (using the
method (using the
the applicable Frame Relay timers logging thresholds, encapsulation types, etc. Generally, most Frame Relay
virtual interface parameters should be left at their default state. For example, the following creates a Frame
Relay interface labeled
(config)#
(config-fr 7)#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 28
interface frame-relay 7
frame-relay lmi-type
7
and sets the signaling method to
frame-relay lmi-type ansi
command). Also included in the Frame Relay virtual endpoint are all
interface frame-relay
ansi
.
command) and set the signaling
Page 29

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
Step 2:
Create the sub-interface and configure the PVC parameters. Using the sub-interface, apply access policies to
the interface, create bridging interfaces, configure dial-backup, assign an IP address, and set the PVC data-link
control identifier (DLCI). For example, the following creates a Frame Relay sub-interface labeled
DLCI to
30,
and assigns an IP address of
193.44.69.253
to the interface.
22,
sets the
(config-fr 7)#
(config-fr 7.22)#
(config-fr 7.22)#
interface fr 7.22
frame-relay interface-dlci 30
ip address 193.44.69.253 255.255.255.252
Step 3: (VALID ONLY FOR T1 INTERFACES)
Specify the group of DS0s used for signaling on the T1 interface by creating a TDM group. Group any number of
contiguous DS0s together to create a data pipe for layer 2 signaling. Also use the
specify the per-DS0 signaling rate on the interface. For example, the following creates a TDM group labeled
tdm-group
command to
9
containing 20 DS0s (each DS0 having a data rate of 56 kbps).
(config)#
(config-t1 1/1)#
(config-t1 1/1)#
interface t1 1/1
tdm-group 9 timeslots 1-20 speed 56
exit
Step 4:
Make the association between the layer 2 endpoint and the physical interface using the
cross-connect
command. Supported layer 2 protocols include Frame Relay and point-to-point protocol (PPP). For example, the
following creates a cross-connect (labeled
(
fr 7
) and the TDM group configured on interface t1 1/1 (
(config)#
cross-connect 5 t1 1/1 9 fr 7
5
) to make an association between the Frame Relay virtual interface
tdm-group 9
).
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 29
Page 30

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
description <text>
Use the description command to identify the specified interface (for example, circuit ID, contact
information, etc.).
Syntax Description
<text> Identifies the specified interface using up to 80 alphanumeric characters.
Default Values
No defaults required for this command.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all interface mode command sets.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example enters comment information using the description command:
(config)#interface t1 1/1
(config-t1 1/1)#description This is the Dallas office T1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 30
Page 31

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
do
Use the do command to execute any AOS command, regardless of the active configuration mode. It
provides a way to execute commands in other modes without taking the time to exit the current mode and
enter the desired one.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No defaults required for this command.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all mode command sets.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
Use the do command to view configurations or interface states after config uration changes are made
without exiting to the Enable mode.
Usage Examples
The following example shows the do command used to view the Frame Relay interface configuration while
currently in the T1 Interface Configuratio n mo d e:
(config)#interface t1 1/1
(config-t1 1/1)#do show interfaces fr 7
fr 7 is ACTIVE
Signaling type is ANSI signaling role is USER
Polling interval is 10 seconds full inquiry interval is 6 polling intervals
Output queue: 0/0 (highest/drops)
0 packets input 0 bytes
0 pkts discarded 0 error pkts 0 unknown protocol pkts
0 packets output 0 bytes
0 tx pkts discarded 0 tx error pkts
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 31
Page 32

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
end
Use the end command to exit the current configuration mode and enter the Enable Security mode.
When exiting the Global Configuration mode, remember to perform a copy
running-config startup-config to save all configuration changes.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No defaults necessary for this command.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all mode command sets except Basic mode.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example shows the end command being executed in the T1 Interface Configuration mode:
(config-t1 1/1)#end
#
#- Enable Security mode command prompt
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 32
Page 33

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
exit
Use the exit command to exit the current configuration mode and enter the previous one. For example,
using the exit command in an interface configuration mode will activate the Global Configuration mode.
When using the exit command in the Basic mode, the current session will be terminated.
When exiting the Global Configuration mode, remember to perform a copy
running-config startup-config to save all configuration changes.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No defaults necessary for this command.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all mode command sets.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example shows the exit command being executed in the Global Configuration mode:
(config)#exit
#
#- Enable Security mode command prompt
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 33
Page 34

Command Reference Guide Common Commands
shutdown
Use the shutdown command to disable the interface (both physical and virtual) so that no data will be
passed through. Use the no form of this command to turn on the interface and allow it to pass data. By
default, all interfaces are disabled.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all interfaces are disabled.
Applicable Command Modes
Applies to all interface mode command sets.
Applicable Platforms
Applies to all AOS products.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example administratively disables the modem interface:
(config)#interface modem 1/2
(config-modem 1/2)#shutdown
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 34
Page 35

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
ENABLE MODE COMMAND SET
To activate the Enable mode, enter the enable command at the Basic mode prompt. (If an enable password
has been configured, a password prompt will display.) For example:
>enable
Password: XXXXXXX
#
The following command is common to multiple command sets and is covered in a centralized section of
this guide. For more information, refer to the section listed below:
exit on page 33
All other commands for this command set are described in this section in alphabetical order.
clear commands begin on page 37
clock auto-correct-dst on page 71
clock no-auto-correct-dst on page 72
clock set <time> <day> <month> <year> on page 73
clock timezone <text> on page 74
configure [memory | network | overwrite-network | terminal] on page 77
copy <source> <destination> on page 78
copy console <filename> on page 79
copy flash <destination> on page 80
copy tftp <destination> on page 81
copy xmodem <destination> on page 82
debug commands begin on page 83
dir on page 122
dir [<input> | flash | flash <input>] on page 123
disable on page 124
enable on page 125
erase [<filename> | startup-config] on page 126
events on page 127
exception report generate on page 128
factory-default on page 129
logout on page 130
ping <address> on page 131
reload [cancel | in <delay>] on page 133
show commands begin on page 134
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 35
Page 36

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
sip check-sync on page 249
telnet <address> on page 250
terminal length <text> on page 251
traceroute <address> source <address> on page 252
undebug all on page 253
wall <message> on page 254
write [dynvoice-config | erase | memory | network | terminal] on page 255
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 36
Page 37

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear access-list <listname>
Use the clear access-list command to clear all counters associated with all access lists (or a specified
access list).
Syntax Description
<listname> Optional. Specifies the name (label) of an access list.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all counters for the access list labeled MatchAll:
>enable
#clear access-list MatchAll
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 37
Page 38

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear arp-cache
Use the clear arp-cache command to remove all dynamic entries from the Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP) cache table.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example removes all dynamic entries from the ARP cache:
>enable
#clear arp-cache
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 38
Page 39

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear arp-entry <address>
Use the clear arp-entry command to remove a single entry from the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
cache.
Syntax Description
<address> Specifies the IP address of the entry to remove.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example removes the entry for 10.200.4.56 from the ARP cache:
>enable
#clear arp-entry 10.200.4.56
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 39
Page 40

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear buffers max-used
Use the clear buffers max-used command to clear the maximum-used statistics for buffers displayed in
the show memory heap command.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears the maximum-used buffer statics:
>enable
#clear buffers max-used
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 40
Page 41

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear counters [<interface> <interface id>]
Use the clear counters command to clear all interface counters (or the counters for a specified interface).
Syntax Description
<interface> Optional. Specifies a single interface. Enter clear counters ? or show interface ?
for a complete list of interfaces.
<interface id> Optional. S pecifies the ID of the specific inte rface to clear (e.g., 1 for p ort channel 1).
Default Values
No default values necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Release 9.1 Command was expanded to include HDLC and tunnel interfaces.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all counters associated with the Ethernet 0/1 interface:
>enable
#clear counters ethernet 0/1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 41
Page 42

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear counters vlan <vlan id>
Use the clear counters vlan command to reset counters on the specified virtual local area network
(VLAN) interface.
Syntax Description
<vlan id> Specifies a valid VLAN interface ID (1 to 4094).
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, and 2000 Series units.
Command History
Release 5.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example resets the counters on VLAN interface 7:
>enable
#clear counters vlan 7
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 42
Page 43

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear crypto ike sa <policy priority>
Use the clear crypto ike sa command to clear existing IKE security associations (SAs), including active
ones.
Syntax Description
<policy priority>
Optional. Clears out all existing IKE SAs associated with the designated policy
priority . This number is assigned using the
crypto ike policy
command.
Refer to
crypto ike on page 297 for more information.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 4.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears the entire database of IKE SAs (including the active associations):
>enable
#clear crypto ike sa
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 43
Page 44

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear crypto ipsec sa
Use the clear crypto ipsec sa command to clear existing IPSec security associations (SAs), including
active ones.
Variations of this command include the following:
clear crypto ipsec sa
clear crypto ipsec sa entry <ip address> ah <SPI>
clear crypto ipsec sa entry <ip address> esp <SPI>
clear crypto ipsec sa map <map name>
clear crypto ipsec sa peer <ip address>
Syntax Description
entry
<ip address>
ah
<SPI>
esp
<SPI>
map
<map name>
peer
<ip address>
Clears only the SAs related to a certain destination IP address.
Clears only a portion of the SAs by specifying the authentication header (AH)
protocol and a security parameter index (SPI). You can determine the correct SPI
value using the show crypto ipsec sa command.
Clears only a portion of the SAs by specifying the encapsulating security payload
(ESP) protocol and an SPI. You can determine the correct SPI value using the
show crypto ipsec sa command.
Clears only the SAs associated with the crypto map name given.
Clears only the SAs associated with the far-end peer IP address given.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 4.1 Command was introduced.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 44
Page 45

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Usage Examples
The following example clears all IPSec SAs:
> enable
#clear crypto ipsec sa
The following example clears the IPSec SA used for ESP traffic with the SPI of 300 to IP address
63.97.45.57:
> enable
#clear crypto ipsec sa entry 63.97.45.57 esp 300
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 45
Page 46

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear dump-core
The clear dump-core command clears diagnostic information appended to the output of the show version
command. This information results from an unexpected unit reboot.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears the entire database of IKE SAs (including the active associations):
>enable
#clear dump-core
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 46
Page 47

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear event-history
Use the clear event-history command to clear all messages logged to the local event-history.
Messages cleared fr om the local event-history (using the clear event-history command) are
no longer accessible.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all local event-history messages:
>enable
#clear event-history
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 47
Page 48

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear host [ * | <hostname>]
Use the clear host command to clear a hostname when using the Domain Naming System (DNS) proxy.
Syntax Description
* Clears all dynamic hosts.
<hostname> Clears a specific host name.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 10.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all dynamic hostnames:
>enable
#clear host *
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 48
Page 49

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip bgp [* | <as-number> | <ip address>] [in | out | soft]
Use the clear ip bgp command to clear BGP neighbors as specified.
Syntax Description
* Clears all BGP neighbors.
<as-number> Clears all BGP neighbors with the specified autonomous system (AS) number.
Range is 1 to 65,535.
<ip address> Clears the BGP neighbor with the specified IP address.
in Causes a “soft” reset inbound with a neighbor, reprocessing routes advertised by
that neighbor.
out Causes a “soft” reset outbound with a neighb or, re-sending advertised routes to
that neighbor.
soft Causes a “soft” reset both inbound and outbound.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The clear ip bgp command must be issued to re-initialize the BGP process between the peers matching
the given arguments. Most neighb or changes, including cha nges to prefix- list filters, do not take ef fect until
the clear command is issued. A hard reset clears the TCP connection with the specified peers, which
results in clearing the table. This method of clear ing is disruptive and causes peer routers to record a route
flap for each route.
The out version of this command provides a soft reset ou t to occur by causing all routes to be re-sent to
the specified peer(s). TCP connections are not torn down, so this method is less disruptive. Output
filters/policies are re-applied before sending the update.
The in version of this command provides a soft reset in to occur by allowing the router to receive an
updated table from a peer without tearing down the TCP connection. This method is less disruptive and
does not count as a route flap. Currently, all of the peer's routes are stored permanently, even if they are
filtered by a prefix list. The command causes the peer's routes to be reprocessed with any new
parameters.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 49
Page 50

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Usage Examples
The following example causes a hard reset with peers with an AS number of 101:
>enable
#clear ip bgp 101
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 50
Page 51

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip cache
Use the clear ip cache command to delete cache table entries.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example removes all entries from the cache table:
>enable
#clear ip cache
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 51
Page 52

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip dhcp-server binding [* | <ip address>]
Use the clear ip dhcp-server binding command to clear Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server binding entries from the database.
Syntax Description
* Clears all automatic binding entries.
<ip address> Clears a specific binding entry. Enter the source IP address (format is A.B.C.D).
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 10.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
A DHCP server binding represents an association betwe en a MAC address and an IP address that was
offered by the unit to a DHCP client (i.e., most o ften a PC). Clearing a bi nding allows the unit to of fer that IP
address again, should a request be made for on e .
Usage Examples
The following example clears a DHCP server binding for the IP address 125.25.47.4:
>enable
#clear ip dchp-server binding 125.25.47.4
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 52
Page 53

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip ospf [process | redistribution]
Use the clear ip ospf command to reset open shortest path first (OSPF) information.
Syntax Description
process Restarts the OSPF process.
redistribution Refreshes routes redistributed over OSPF.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example resets the OSPF process:
>enable
#clear ip ospf process
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 53
Page 54

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip policy-sessions
Use the clear ip policy-sessions command to clear policy class sessions. You may clear all the sessions or
a specific session. Use the show ip policy-sessions command to view a current session listing. The
following lists the complete syntax for the clear ip policy-sessions commands:
clear ip policy-sessions
clear ip policy-sessions <classname> [ahp | esp | gre | icmp | tcp | udp | <protocol>] <source ip>
<source port><dest ip><dest port>
clear ip policy-sessions <classname> [ahp | esp | gre | icmp | tcp | udp | <protocol>] <source ip>
<source port><dest ip><dest port> [destination | source] <nat ip><nat port>
Syntax Description
<classname> Alphanumeric descriptor for identifying the configured access policy (access
policy descriptors are not case-sensitive).
ahp Specifies authentication header protocol (AHP).
esp Specifies encapsulating security payload protocol (ESP).
gre Specifies general routing encapsulation protocol (GRE).
icmp Specifies Internet control message protocol (ICMP) protocol.
tcp Specifies transmission control protocol (TCP).
udp Specifies universal datagram protocol (UDP).
<protocol> Specifies protocol ( va lid range: 0 to 255).
<source ip> Specifies the source IP address (format is A.B.C.D).
<source port> Specifies the source port (in hex format AHP, ESP , an d GRE; decimal for all othe r
protocols).
<dest ip> Specifies the destination IP address (format is A.B.C.D).
<dest port> Specifies the destination port (in hex format for AHP, ESP, and GRE; decimal for
all other protocols).
[destination | source] For NAT sessions, this specifies whether to select a NAT source or NAT
destination session.
<nat ip> For NAT sessions, this specifies the NAT IP address (format is A.B.C.D).
<nat port> For NAT sessions, this specifies the NAT port (in hex fo rmat for AHP, ESP, and
GRE; decimal for all other protocols).
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 54
Page 55

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The second half of this command, beginning with the source IP address may be copied and p asted from a
row in the show ip policy-sessions table for easier use.
Usage Examples
The following example clears the Telnet association (TCP port 23) for policy class pclass1 with source IP
address 192.22.71.50 and destination 192.22.71.130:
>enable
#clear ip policy-sessions pclass1 tcp 192.22.71.50 23 192.22.71.130 23
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 55
Page 56

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip policy-stats <classname> entry <policy class #>
Use the clear ip policy-stats command to clear statistical counters for policy classes.
Syntax Description
<classname>
entry <policy class #>
Optional. Specifies the policy class to clear. If no policy class is specified, statistics are
cleared for all policies.
Optional.
Use this keyword to clear statistics of a specific policy class entry.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears statistical counters for all policy classes:
>enable
#clear ip policy-stats
The following example clears statistical counters for the policy class MatchALL:
>enable
#clear ip policy-stats MatchALL
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 56
Page 57

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip prefix-list <listname>
Use the clear ip prefix-list command to clear the IP prefix list hit count shown in the show ip prefix-list
detail command output. Refer to show ip prefix-list [detail | summary] <listname> on page 195 for more
information.
Syntax Description
<listname> Specifies hit count statistics of the IP prefix list to clear.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears the hit count statistics for prefix list test:
>enable
#clear ip prefix-list test
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 57
Page 58

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear ip route [** | <ip address> <subnet mask>]
Use the clear ip route command to remove all learned routes from the IP route table. Static and connec ted
routes are not cleared by this command.
Syntax Description
** Deletes all destination routes.
<ip address> Specifies the IP address of the destination routes to be deleted.
<subnet mask> Specifies the subnet mask of the destination routes to be deleted
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example removes all learned routes from the route table:
>enable
#clear ip route **
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 58
Page 59

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear lldp counters
Use the clear lldp counters command to reset all local loop demarkation point (LLDP) packet counters to
zero on all interfaces.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
There are no default settings for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example resets all LLDP counters:
>enable
#clear lldp counters
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 59
Page 60

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear lldp counters interface <interface>
Use the clear lldp counters interface command to reset all local loop demarkation point (LLDP) packet
counters to zero for a specified interface.
Syntax Description
<interface> Clears the information for the specified interface. Type clear lldp counters
interface ? for a complete list of applicable interfaces.
Default Values
No default values are necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example resets the counters on PPP interface 1:
>enable
#clear lldp counters interface ppp 1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 60
Page 61

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear lldp neighbors
Use the clear lldp neighbors command to remove all neighbors from this unit’s database. As new local
loop demarkation point (LLDP) packets are received, the database will contain information about
neighbors included in those frames.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
There are no default settings for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
This command generates output indicating the names of any neighbors del eted from the data base and the
name of the interface on which the neighbor was learned.
Usage Examples
The following example clears LLDP neighbor Switch_1 from the Ethernet interface 0/7:
>enable
#clear lldp neighbors
LLDP: Deleted neighbor “Switch_1” on interface eth 0/7
#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 61
Page 62

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear pppoe <interface id>
Use the clear pppoe command to terminate the current PPPoE client session and cause the AOS to attempt
to re-establish the session.
Syntax Description
<interface id> Specifies the PPP interface ID number to clear.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 5.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example ends the current PPPoE client session for ppp 1:
>enable
#clear pppoe 1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 62
Page 63

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear processes cpu max
Use the clear processes cpu max command to clear the maximum CPU usage statistic which is displayed
in the show process cpu command output.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 5.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example resets the CPU maximum usage statistics:
>enable
#clear process cpu max
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 63
Page 64

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear qos map
Use the clear qos map command to clear the statistics for all defined quality of service (QoS) maps or to
view detailed information for maps meeting user-configured specifications.
Variations of this command include the following:
clear qos map <map name>
clear qos map <map name> <sequence number>
clear qos map interface <interface id>
Syntax Description
<map name> Specifies the name of a defined QoS map.
<sequence number> Specifies one of the map’s defined sequence numbers.
<interface> Specifies an interface for which to clear QoS map statistics (for just tha t interface).
Type
clear qos map interface ?
for a complete list of applicable interfaces.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 64
Page 65

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Usage Examples
The following example clears statistics for all defined QoS maps:
#clear qos map
The following example clears statistics for all entries in the priority QoS map:
#clear qos map priority
The following example clears statistics in entry 10 of the priority QoS map:
#clear qos map priority 10
The following example clears QoS statistics for a specified interface:
#clear qos map interface frame-relay 1
The clear counters command clears ALL interface statistics (including QoS map interface
statistics).
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 65
Page 66

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear route-map counters <map>
Use the clear route-map counters command to reset route map hit counters.
Syntax Description
<map> Specifies specific route map to be cleared.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all route map counters:
>enable
#clear route-map counters
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 66
Page 67

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear sip location [** | <username>]
Use the clear sip location command to clear session initiation protocol (SIP) location database statistics.
Syntax Description
** Clears all dynamic location entries.
<username> Specifies specific username to clear.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 2000 and 5000 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example deletes all dynamic location entries:
>enable
#clear sip location **
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 67
Page 68

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear sip user-registration
Use the clear sip user-registration command to clear local session initiation protocol (SIP) server
registration information.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 2000 and 5000 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all SIP server registration information:
>enable
#clear sip user-registration
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 68
Page 69

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear tacacs+ statistics
Use the clear tacacs+ statistics command to delete all terminal access controller acce ss control system
(TACACS+) protocol statistics.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example clears all TACACS+ protocol statistics:
>enable
#clear tacacs+ statistics
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 69
Page 70

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clear user [console <user number> | ssh <user number> |
telnet <user number>]
Use the clear user command to detach a user from a given line.
Syntax Description
console <user number> Detaches a specific console user. Valid range is 0 to 1.
ssh <user number> Detaches a specific secure shell (SSH) user. Valid range is 0 to 4.
telnet <user number> Detaches a specific Telnet user. Valid range is 0 to 5.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example detaches the console 1 user:
>enable
#clear user console 1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 70
Page 71

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clock auto-correct-dst
The clock auto-correct-dst command allows the automatic one-hour correction for Daylight Saving Time
(DST). Use the clock no-auto-correct-dst command to disable this feature.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default this command is enabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example allows for automatic DST correction:
>enable
#clock auto-correct-dst
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 71
Page 72

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clock no-auto-correct-dst
The clock no-auto-correct-dst command allows you to override the automatic one-hour correction for
Daylight Saving Time (DST).
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
No default value is necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
Many time zones include an automatic one-hour correction for daylight saving time at the appropriate time.
You may override it at your location using this command.
Usage Examples
The following example overrides the one-hour offset for DST:
>enable
#clock no-auto-correct-dst
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 72
Page 73

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clock set <time> <day> <month> <year>
Use the clock set command to configure the system software clock. For the command to be valid, all fields
must be entered. Refer to the Usage Example below for an example.
Syntax Description
<time> Sets the time (in 24-hour format) of the system software clock in the format
HH:MM:SS (hours:minutes:seconds).
<day> Sets the current day of the month (valid range: 1 to 31).
<month> Sets the current month (valid range: January to December). You need only enter
enough characters to make the entry unique. This entry is not case-sensitive.
<year> Sets the current year (valid range: 2000 to 2100).
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example sets the system software clock for 3:42 pm, August 22 2004:
>enable
#clock set 15:42:00 22 Au 2004
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 73
Page 74

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
clock timezone <text>
The clock timezone command sets the unit’s internal clock to the timezone of your choice. This setting is
based on the difference in time (in hours) between Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) or Central Standard
Time (CST) and the timezone for which you are setting up the unit. Use the no form of this command to
disable this feature.
Syntax Description
Subcommands are specified in the Functional Notes section for this command.
Default Values
No default value is necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
Release 11.1 Command was expanded to include clock timezone 0.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 74
Page 75

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Functional Notes
The following list shows sample cities and their timezone codes.
clock timezone +1-Amsterdam
clock timezone +1-Belgrade
clock timezone +1-Brussels
clock timezone +1-Sarajevo
clock timezone +1-West-Africa
clock timezone +10-Brisbane
clock timezone +10-Canberra
clock timezone +10-Guam
clock timezone +10-Hobart
clock timezone +10-Vladivostok
clock timezone +11
clock timezone +12-Auckland
clock timezone +12-Fiji
clock timezone +13
clock timezone +2-Athens
clock timezone +2-Bucharest
clock timezone +2-Cairo
clock timezone +2-Harare
clock timezone +2-Helsinki
clock timezone +2-Jerusalem
clock timezone +3-Baghdad
clock timezone +3-Kuwait
clock timezone +3-Moscow
clock timezone +3-Nairobi
clock timezone +3:30
clock timezone +4-Abu-Dhabi
clock timezone +4-Baku
clock timezone +4:30
clock timezone +5-Ekaterinburg
clock timezone +5-Islamabad
clock timezone +5:30
clock timezone +5:45
clock timezone +6-Almaty
clock timezone +6-Astana
clock timezone +6-Sri-Jay
clock timezone +6:30
clock timezone +7-Bangkok
clock timezone +7-Kranoyarsk
clock timezone +8-Bejing
clock timezone +8-Irkutsk
clock timezone +8-Kuala-Lumpur
clock timezone +8-Perth
clock timezone +8-Taipei
clock timezone +9-Osaka
clock timezone +9-Seoul
clock timezone +9-Yakutsk
clock timezone +9:30-Adelaide
clock timezone +9:30-Darwin
clock timezone -1-Azores
clock timezone -1-Cape-Verde
clock timezone -10
clock timezone -11
clock timezone -12
clock timezone -2
clock timezone -3-Brasilia
clock timezone -3-Buenos-Aires
clock timezone -3-Greenland
clock timezone -3:30
clock timezone -4-Atlantic-Time
clock timezone -4-Caracus
clock timezone -4-Santiago
clock timezone -5
clock timezone -5-Bogota
clock timezone -5-Eastern-Time
clock timezone -6-Central-America
clock timezone -6-Central-Time
clock timezone -6-Mexico-City
clock timezone -6-Saskatchewan
clock timezone -7-Arizona
clock timezone -7-Mountain-Time
clock timezone -8
clock timezone -9
clock timezone 0
clock timezone GMT-Casablanca
clock timezone GMT-Dublin
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 75
Page 76

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Usage Examples
The following example sets the timezone for Santiago, Chile.
>enable
#clock timezone -4-Santiago
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 76
Page 77

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
configure [memory | network | overwrite-network | terminal]
Use the configure command to enter the Global Configuration mode or to configure the system from
memory. Refer to Global Configuration Mode Command Set on page 256 for more information.
Syntax Description
memory Configures the active system with the commands located in the default
configuration file stored in NVRAM.
network Configures the system from a TFTP network host.
overwrite-network Overwrites NVRAM memory from a TFTP network host.
terminal Enters the Global Configuration mode.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example enters the Global Configuration mode from the Enable mode:
>enable
#configure terminal
(config)#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 77
Page 78

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
copy <source> <destination>
Use the copy command to copy any file from a specified source to a specified destination.
Syntax Description
<source> Specifies the current location of the file to copy.
Valid sources include: running-config (current runnin g co nfig ura tio n file ),
startup-config (configuration file located in NVRAM), or a filename (located in
FLASH memory).
<destination> Specifies the destination of the copied file.
Valid destinations include: running-config (current running configuration file),
startup-config (configuration file located in NVRAM), or a filename (located in
FLASH memory).
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example creates a copy of the file myfile.biz (located in FLASH memory) and names it
newfile.biz:
>enable
#copy myfile.biz newfile.biz
The following example creates a backup copy of the startup configuration file (and places in FLASH
memory):
>enable
#copy startup-config backup.bak
The following example copies the current running-configuration file to the startup configuration file located
in NVRAM:
>enable
#copy running-config startup-config
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 78
Page 79

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
copy console <filename>
Use the copy console command to copy the console’s input to a text file. To end copying to the text file,
type <
Ctrl+D>. The file will be saved in the AOS root directory.
Syntax Description
<filename> Specifies destination file for console input.
Default Values
No default is necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The copy console command works much like a line editor. Prior to pressing <Enter>, changes can be
made to the text on the line. Changes can be made using <Delete> and <Backspace> keys. The text can
be traversed using the arrow keys, <Ctrl+A> (to go to the beginning of a line), and <Ctrl+E> (to go to the
end of a line). To end copying to the text file, type <Ctrl+D>. The file will be saved in the AOS root
directory. Use the dir command to see a list of files in the root directory.
Usage Examples
The following example copies the console input into the file config (located in the AOS ro ot directory):
>enable
#copy console config
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 79
Page 80

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
copy flash <destination>
Use the copy flash command to copy a file located in flash memory to a specified destination.
Syntax Description
<destination> Specifies the destination of the copied file. Valid destinations include tftp and
xmodem.
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example copies the contents of the unit’s flash memory to a TFTP server:
>enable
#copy flash tftp
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 80
Page 81

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
copy tftp <destination>
Use the copy tftp command to copy a file located on a network Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
server to a specified destination.
Syntax Description
<destination> Specifies the destination of the file copied from the TFTP server.
Valid destinations include: flash (FLASH memory), startup-config (the
configuration file stored in NVRAM), or running-config (the current running
configuration file).
After entering copy tftp and specifying a destination, the AOS prompts for
the following information:
Address of remote host: IP address of the TFTP server.
Source filename: Name of the file to copy from the TFTP server.
Destination filename: Specifies the filename to use when storing the copied file to FLASH
memory. (Valid only for the copy tftp flash command.)
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example copies myfile.biz from the TFTP server (10.200.2.4) to flash memory and labels it
newfile.biz:
>enable
#copy tftp flash
Address of remote host?10.200.2.4
Source filename myfile.biz
Destination filename newfile.biz
Initiating TFTP transfer ...
Received 45647 bytes.
Transfer Complete!
#
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 81
Page 82

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
copy xmodem <destination>
Use the copy xmodem command to copy a file (using the XMODEM protocol) to a specified destination.
XMODEM capability is provided in terminal emulation software such as HyperTerminal™.
Syntax Description
<destination> Specifies the destination of the copied file.
Valid destinations include: flash (FLASH memory), startup-config (the
configuration file stored in NVRAM), or running-config (the current running
configuration file).
After entering copy xmodem and specifying a destination, the AOS prompts for
the following information:
Destination filename: Specifies the filename to use when storing the copied file to FLASH memory.
(Valid only for the copy flash command.)
Default Values
No default value necessary for this command.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 1.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example copies a .biz file to flash memory and labels it newfile.biz:
>enable
#copy xmodem flash
Destination filename newfile.biz
Begin the Xmodem transfer now...
Press CTRL+X twice to cancel
CCCCCC
The AOS is now ready to accept the file on the CONSOLE port (using the XMODEM protocol). The next
step in the process may differ depending on the type of terminal emulation software you are using. For
HyperTerminal, you will now select Transfer > Send File and browse to the file you wish to copy. Once the
transfer is complete, information similar to the following is displayed:
Received 231424 bytes.
Transfer complete.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 82
Page 83

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug aaa
Use the debug aaa command to activate debug messages associated with authentication from the AAA
subsystem. Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form
of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 5.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug aaa events include connection notices, login attempts, and session tracking.
Usage Examples
The following is sample output for this command:
>enable
#debug aaa
AAA: New Session on portal 'TELNET 0 (172.22.12.60:4867)'.
AAA: No list mapped to 'TELNET 0'. Using 'default'.
AAA: Attempting authentication (username/password).
AAA: RADIUS authentication failed.
AAA: Authentication failed.
AAA: Closing Session on portal 'TELNET 0 (172.22.12.60:4867)'.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 83
Page 84

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug access-list <listname>
Use the debug access-list command to activate debug messages (for a specified list) associated with access
list operation. Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no
form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
<listname> Specifies a configured access list.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug access-list command provides debug messages to aid in troubleshooting access list issues.
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages for the access list labeled MatchAll:
>enable
#debug access-list MatchAll
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 84
Page 85

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug auto-config
Use the debug auto-config command to activate debug messages associated auto-config events. Debug
messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this command to
disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The example activates debug messages associated with auto-config events:
>enable
#debug auto-config
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 85
Page 86

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug crypto [ike | ike negotiation | ike client authentication |
ike client configuration | ipsec | pki]
Use the debug crypto command to activate debug messages associated with IKE and IPSec functions.
Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this
command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
ike Displays all IKE debug messages.
ike negotiation Displays only IKE key management debug messages (e.g., handshaking).
ike client authentication Displays IKE client authentication messages as they occur.
ike client configuration Displays mode-config exchanges as they take place over the IKE SA. It is
enabled independently from the ike negotiation debug described
previously.
ipsec Displays all IPSec debug messages.
pki Displays all public key infrastructure (PKI) debug messages.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 4.1 Command was introduced.
Release 6.1 Debug pki command introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example activates the IPSec debug messages:
>enable
#debug crypto ipsec
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 86
Page 87

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug data-call
Use the debug data-call command to activate debug messages associated with data call errors and events.
Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this
command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 11.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with data call errors and events:
>enable
#debug data-call
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 87
Page 88

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug dynamic-dns [verbose]
Use the debug dynamic-dns command to display debug messages associated with dynamic domain
naming system (DNS). Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use
the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
verbose Enables detailed debug messages.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example activates dynamic DNS debug messages:
>enable
#debug dynamic-dns verbose
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 88
Page 89

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug firewall
Use the debug firewall command to activate debug messages associated with the AOS firewall operation.
Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this
command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug firewall command activates debug messages to provide real-time information about the AOS
stateful inspection firewall operation.
Usage Examples
The following example activates the debug messages for the AOS stateful inspection firewall:
>enable
#debug firewall
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 89
Page 90

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug interface <interface>
Use the debug interface command to activate debug messages associated with the specified interface.
Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this
command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
<interface> Activates debug messages for the specified interface. Type debug interface ? for
a complete list of applicable interfaces.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
Release 6.1 Command was expanded to include T1 and FXS interfaces.
Release 7.1 Command was expanded to include FXO interface.
Release 9.1 Command was expanded to include tunnel interface.
Functional Notes
The debug interface command activates debug messages to aid in the troubleshooting of physical
interfaces.
Usage Examples
The following example activates all possible debug messages associated with the Ethernet port:
>enable
#debug interface ethernet
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 90
Page 91

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip bgp [events | in | out | keepalives | updates | updates quiet]
Use the debug ip bgp command to activate debug messages associated with IP Border Gateway Protocol
(BGP). Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of
this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
events Displays significant BGP events such as a neighbor state change.
in/out Displays the same information as debug ip bgp, but limits messages to the
specified direction (in or out).
keepalives Displays BGP keepalive packets.
updates Displays detailed information on BGP updates for all neighbors.
updates quiet Displays summary information about BGP neighbor updates. (Note: updates
quiet displays a one-line summary of what update displays in 104 lines.)
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 8.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
If no arguments are given, the debug ip bgp command displays general BGP events such as
sent/received message summaries, route processing actions, and results. Keepalive packets are not
debugged with this command.
Usage Examples
The following example enables debug messages on general outbound BGP messages and events:
>enable
#debug ip bgp out
#07:42:39: BGP OUT 10.15.240.1[2]: Transmitting msg, type=UPDATE (2), len=142
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 91
Page 92

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip dhcp-client
Use the debug ip dhcp-client command to activate debug messages associated with Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client operation in the AOS. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to
the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug ip dhcp-client command activates debug messages to provide information on DHCP client
activity in the AOS. The AOS DHCP client capability allows interfaces to dynamically obtain an IP address
from a network DHCP server.
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with DHCP client activity:
>enable
#debug ip dhcp-client
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 92
Page 93

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip dhcp-server
Use the debug ip dhcp-server command to activate debug messages associated with Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server operation in the AOS. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to
the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 2.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug ip dhcp-server command activates debug messages to provide information on DHCP server
activity in the AOS. The AOS DHCP server capability allows the AOS to dynamically assign IP addresses
to hosts on the network.
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with DHCP server activity:
>enable
#debug ip dhcp-server
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 93
Page 94

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip dns-client
Use the debug ip dns-client command to activate debug messages associated with domain naming system
(DNS) client operation in the AOS. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet)
screen. Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug ip dns-client command activates debug messages to provide information on DNS client
activity in the AOS. The IP DNS capability allows for DNS-based host translation (name-to-address).
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with DNS client activity:
>enable
#debug ip dns-client
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 94
Page 95

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip dns-proxy
Use the debug ip dns-proxy command to activate debug messages associated with domain naming system
(DNS) proxy operation in the AOS. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet)
screen. Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
Functional Notes
The debug ip dns-proxy command activates debug messages to provide informatio n on DNS proxy
activity in the AOS. The IP DNS capability allows for DNS-based host translation (name-to-address).
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with DNS proxy activity:
>enable
#debug ip dns-proxy
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 95
Page 96

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip http [verbose]
Use the debug ip http command to activate debug messages associated with HyperText Transfer Protocol
(HTTP) operation in the AOS. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen.
Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
verbose Activates detailed debug messages for HTTP operation.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, and 2000 and Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 6.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example activates debug messages associated with HTTP activity:
>enable
#debug ip http
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 96
Page 97

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip icmp [send | recv]
Use the debug ip icmp command to show all Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages as they
come into the router or are originated by the router. If an optional keyword (send or recv) is not used, all
results are displayed. Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the
no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
send
recv
Optional. Displays only ICMP messages sent by the router.
Optional. Displays only ICMP messages received by the router.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following example activates the debug ip icmp send and receive messages for the AOS:
>enable
#debug ip icmp
ICMP SEND: From (0.0.0.0) to (172.22.14.229) Type=8 Code=0 Length=72 Details:echo request
ICMP RECV: From (172.22.14.229) to (10.100.23.19) Type=0 Code=0 Length=72 Details:echo reply
ICMP SEND: From (0.0.0.0) to (172.22.14.229) Type=8 Code=0 Length=72 Details:echo request
ICMP RECV: From (172.22.14.229) to (10.100.23.19) Type=0 Code=0 Length=72 Details:echo reply
ICMP RECV: From (172.22.255.200) to (10.100.23.19) Type=11 Code=0 Length=36 Details:TTL equals 0
during transit
ICMP RECV: From (172.22.14.229) to (10.100.23.19) Type=3 Code=3 Length=36 Details:port
unreachable
ICMP RECV: From (172.22.14.229) to (10.100.23.19) Type=3 Code=3 Length=36 Details:port
unreachable
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 97
Page 98

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip mrouting
Use the debug ip mrouting command to activate debug messages associated with multicast table routing
events. Debug messages are displayed (real time) on the terminal (or Telnet) screen. Use the no form of
this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
No subcommands.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and
Total Access 900 Series units.
Command History
Release 10.1 Command was introduced.
Usage Examples
The following sample activates ip mrouting debug messages:
>enable
#debug ip mrouting
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 98
Page 99

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
debug ip ospf
Use the debug ip ospf command to activate debug messages associated with open shortest path first
(OSPF) routing operations. Debug messages are displayed (real time) to the terminal (or Telnet) screen.
Use the no form of this command to disable the debug messages.
Syntax Description
adj Displays OSPF adjacency events.
database-timer Displays OSPF database timer.
events Displays OSPF events.
flood Displays OSPF flooding.
hello Displays OSPF hello events.
lsa-generation Displays OSPF link state advertisement (LSA) generation.
packet Displays OSPF packets.
retransmission Displays OSPF retransmission events.
spf Displays OSPF shortest-path-first (SPF) calculations.
tree Displays OSPF database tree.
Default Values
By default, all debug messages in the AOS are disabled.
Applicable Platforms
This command applies to the NetVanta 300, 1000R, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 and Total Access 900
Series units.
Command History
Release 3.1 Command was introduced.
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 99
Page 100

Command Reference Guide Enable Mode Command Set
Usage Examples
The following is an example of debug ip ospf command results:
>enable
#debug ip ospf flood
OSPF: Update LSA: id=c0a8020d rtid=192.168.2.13 area=11.0.0.0 type=1
OSPF: Update LSA: id=0b003202 rtid=11.0.50.2 area=11.0.0.0 type=1
OSPF: Queue delayed ACK lasid=0b003202 lsartid=11.0.50.2 nbr=11.0.50.2
OSPF: Rx ACK lasid=c0a8020d lsartid=192.168.2.13 nbr=11.0.50.2
OSPF: Received LSA ACK LSA_ID=-64.-88.2.13 LSA_RT_ID=-64.-88.2.13
OSPF: Rx ACK lasid=00000000 lsartid=192.168.2.13 nbr=11.0.50.2
OSPF: Received LSA ACK LSA_ID=0.0.0.0 LSA_RT_ID=-64.-88.2.13
OSPF: Sending delayed ACK
OSPF: Update LSA: id=c0a8020d rtid=192.168.2.13 area=11.0.0.0 type=1
OSPF: Flooding out last interface
OSPF: Update LSA: id=0b003202 rtid=11.0.50.2 area=11.0.0.0 type=1
61202361L1-35E Copyright © 2005 ADTRAN 100
 Loading...
Loading...