Page 1

61202.029L2-1D
January 1998
ISU 128
128 kbps ISDN Service Unit
USER MANUAL
Part Numbers
1202029L2 115 VAC
1202029L3 115 VAC with V.34 Modem Option
Page 2

Trademarks:
DMS-100 is a trademark of Northern Telecom.
ISU is trademark of ADTRAN, Incorporated.
Macintosh is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Incorporated.
Stac is a registered trademark and LZS is a trademark of Stac Electronics.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
5ESS is a registered trademark of AT&T.
Windows
MNP
®
95 is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
®
is a registered trademark of Microcom, Incorporated.
901 Explorer Boulevard
P.O. Box 140000
Huntsville, AL 35814-4000
Phone: (205) 963-8000
© 1998 ADTRAN, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in USA.
Page 3

FCC regulations require that the following information be provided to the customer in this manual.
1. If your telephone equipment ( ISU 128) causes harm to the telephone network, the
telephone company may discontinue your service temporarily. If possible, they
will notify you in advance. But if advance notice isn’t practical, you will be notified
as soon as possible. You will be advised of your right to file a complaint with the
FCC.
2. Your telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations,
or procedures that could affect the proper operation of your equipment. If they do,
you will be given advance notice so as to give you an opportunity to maintain uninterrupted service.
3. If you experience trouble with this equipment ( ISU 128), please contact ADTRAN
(see inside back cover) for repair/warranty information. The telephone company
may ask you to disconnect this equipment from the network until the problem has
been corrected, or until you are sure the equipment is not malfunctioning.
4. This unit contains no user-serviceable parts.
To ADTRAN service personnel: For continued protection against risk of fire, replace F1 with the same type and rating of fuse only : .2 A, 250 V.
Page 4

FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE STATEMENT
FCC ID: HDC1202029TL
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
or TV reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on. The
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• R eorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device is FCC Class B certified only on the EIA-232 interface. The
V.35 and RS-530 interfaces are FCC Class B verified.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by ADTRAN will void
the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
Page 5

CANADIAN EMISSIONS REQUIREMENTS
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled
"Digital Apparatus," ICES-003 of the Department of Communications.
Cet appareil nuerique respecte les limites de bruits radioelectriques applicables aux
appareils numeriques de Class B prescrites dans la norme sur le materiel brouilleur:
"Appareils Numeriques," NMB-003 edictee par le ministre des Communications.
CANADIAN EQUIPMENT LIMITATIONS
Notice: The Canadian Industry and Science Canada label identifies certified equipment. This certification means that the equipment meets certain telecommunications
network protective, operational, and safety requirements. The Department does not
guarantee the equipment will operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, ensure that it is permissible to be connected to the facilities of the local telecommunications company. The equipment must also be installed using an acceptable method of connection. In some cases, the company’s inside
wiring associated with a single-line individual service may be extended by means of a
certified connector assembly (telephone extension cord). Compliance with the above
conditions may not prevent degradation of service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized Canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the user
to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of
the power utility, telephone lines, and internal metallic water pipe system, if present,
are connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
Users should not attempt to make such connections themselves, but should contact the
appropriate electric inspection authority, or an electrician, as appropriate.
Load Number (LN) assigned to each terminal device denotes the percentage of the
The
total load to be connected to a telephone loop which is used by the device, to prevent
overloading. The termination on a loop may consist of any combination of devices
subject only to the requirement that the total of the Load Numbers of all devices does
not exceed 100.
Page 6

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128 ..................................................... 1
ISDN Overview .................................................................................................................. 1
The ADTRAN ISU 128....................................................................................................... 1
ISU 128 Interoperability .................................................................................................... 4
Recommended Operating Protocols................................................................................ 6
Chapter 2. ISDN Ordering Codes (IOCs)..................................................................... 9
Ordering ISDN using IOCs............................................................................................... 9
Capability S ......................................................................................................................... 10
Applications.......................................................................................................... 10
Capability R.................................................................................................................. 10
Applications.......................................................................................................... 10
Capability B .................................................................................................................. 10
Capability C.................................................................................................................. 10
Chapter 3. Installation..................................................................................................... 11
Network Connection.......................................................................................................... 11
DTE Data Connection........................................................................................................ 12
Dial Interface Connection.................................................................................................. 12
Maintenance Interface ....................................................................................................... 13
Chapter 4. Operation ....................................................................................................... 15
Menu Navigation ............................................................................................................... 15
Getting Started.................................................................................................................... 16
Status Buffer ................................................................................................................. 16
VT 100 Terminal Menu Support ...................................................................................... 17
Status Screen................................................................................................................. 17
Configuration Screen .................................................................................................. 18
Chapter 5. Testing ............................................................................................................ 19
TEST Options...................................................................................................................... 19
Loopback DTE.............................................................................................................. 20
Loopback Network...................................................................................................... 20
Loopback Protocol....................................................................................................... 20
Loopback Remote ........................................................................................................ 21
Test Remote .................................................................................................................. 21
Loopback Disable ........................................................................................................ 21
No Remote Loopbacks.................................................................................. 21
DDS Accepted................................................................................................ 21
V.54 Accepted ................................................................................................ 21
DDS+V54 Accept........................................................................................... 22
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
i
Page 7

ii
Table of Contents
Near-End Block Errors/Far-End Block Errors (NEBE/FEBE).............................. 22
Software Version.......................................................................................................... 22
Chapter 6. Configuration ................................................................................................. 23
Dial Line Operation............................................................................................................ 23
Switch Protocol ............................................................................................................ 24
Call Type....................................................................................................................... 24
Speech.................................................................................................................... 24
Audio ..................................................................................................................... 25
Data 56 kbps.......................................................................................................... 25
Data 64 kbps (default) ......................................................................................... 25
Terminal Identification ............................................................................................... 25
Setting the SPID.................................................................................................... 25
Setting the LDN.................................................................................................... 26
Dial Options.................................................................................................................. 29
Front Panel............................................................................................................ 29
RS-366 .................................................................................................................... 29
1 sec or EON................................................................................................... 30
2 sec or EON................................................................................................... 30
5 sec or EON (default)................................................................................... 30
10 sec or EON................................................................................................. 30
20 sec or EON................................................................................................. 30
Wait for EON ................................................................................................. 30
AT Commands ............................................................................................................. 30
Using AT Commands ................................................................................... 31
Using S-Registers........................................................................................... 31
Reading S-Registers....................................................................................... 32
Reading S-Register Strings........................................................................... 32
Changing S-Registers.................................................................................... 32
Changing S-Register Strings ........................................................................ 32
Dialing a Call Using the AT Command Processor ................................... 32
V.25 bis .......................................................................................................................... 33
V.25 ASYNC Dialing..................................................................................... 34
V.25 SYNC HDLC Dialing ........................................................................... 35
V.25 SYNC BISYNC Dialing ...................................................................... 35
V.25 HDLC FLAG.......................................................................................... 35
Disabled................................................................................................................. 35
Auto Answer ................................................................................................................ 36
Disabled................................................................................................................. 36
Enabled.................................................................................................................. 36
Dump all calls....................................................................................................... 36
Answer Tone ................................................................................................................ 37
No Answer Tone (Default) ................................................................................. 37
Incoming Tone...................................................................................................... 37
Outgoing Tone...................................................................................................... 37
Always Tone......................................................................................................... 37
Connect Timeout.......................................................................................................... 38
Call Screening............................................................................................................... 38
ISU-128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 8

Table of Contents
Leased Line Service............................................................................................................ 40
Clock Mode: Slave/Master ....................................................................................... 40
Channel rate ................................................................................................................. 41
DTE OPTIONS.................................................................................................................... 42
Bit Rate .......................................................................................................................... 42
Connector Type............................................................................................................ 43
RTS Options.................................................................................................................. 43
CTS Options ................................................................................................................. 43
CD Options................................................................................................................... 43
DTR Options................................................................................................................. 43
DSR Options................................................................................................................. 44
Flow Control (Asynchronous Data Format)............................................................ 44
Data Format (Asynchronous) .................................................................................... 45
Transmit Clock (Synchronous Data Format)........................................................... 45
Chapter 7. Protocol Options ............................................................................................ 47
Protocol Options................................................................................................................. 47
Clear Channel............................................................................................................... 48
BONDING Mode 1...................................................................................................... 48
TXINIT ............................................................................................................ 49
TXFA ............................................................................................................... 49
TXADD01 ....................................................................................................... 50
TXDEQ............................................................................................................ 50
TANULL......................................................................................................... 50
TCID................................................................................................................ 50
V.120 .............................................................................................................................. 50
V.110 .............................................................................................................................. 51
V.34 ................................................................................................................................ 51
Error Control.................................................................................................. 51
Compression .................................................................................................. 52
Microcom™ Network Protocol Block Size (MNP® Blk) ......................... 52
DSU 57.6 ASYNC......................................................................................................... 53
T-Link............................................................................................................................ 53
Simple ADTRAN Protocol (SAP).............................................................................. 53
FALLBACK .................................................................................................................. 54
Point-to-Point (PPP) Async-to-Sync ......................................................................... 56
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)............................................................................. 56
Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol (MP)............................................................ 56
PPP with Compression ....................................................................................... 57
Chapter 8. Quick Setup .................................................................................................... 59
Quick Setup Configuration............................................................................................... 59
Quick Setup .................................................................................................................. 60
Dial 56K sync* ...................................................................................................... 60
Dial 64K sync* ...................................................................................................... 61
Dial 112K sync* .................................................................................................... 61
Dial 128K sync* .................................................................................................... 62
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
iii
Page 9

iv
Table of Contents
Dial PPP* ............................................................................................................... 62
V34 115.2 async*................................................................................................... 63
Dial 57.6 asyn* ...................................................................................................... 63
Dial 115.2 asyn* .................................................................................................... 64
Fallback 57.6k*...................................................................................................... 64
More....................................................................................................................... 65
Leased 128K.................................................................................................... 65
Ldm 128 Master ............................................................................................. 65
Factory Setup.................................................................................................. 66
Chapter 9. Dial Options ................................................................................................... 67
Dialing Options................................................................................................................... 67
Hang Up Line............................................................................................................... 68
Dial Number................................................................................................................. 68
Redial Last Number .................................................................................................... 68
Answer Call.................................................................................................................. 68
Dial Stored Number .................................................................................................... 68
Store/Review Number ............................................................................................... 69
Chapter 10. Remote Configuration ................................................................................ 71
Remote Configuration ....................................................................................................... 71
Configuring with AT Commands ............................................................................. 71
Configuring and Testing with the Front Panel or
VT 100 Terminal ............................................................................................ 72
Configure Remote Unit............................................................................................... 73
Remote Testing............................................................................................................. 74
Loopback Remote 1B ........................................................................................... 74
Loopback Remote 2B ........................................................................................... 74
Set Password......................................................................................................... 74
Chapter 11. Troubleshooting........................................................................................... 77
If Self Test Fails ................................................................................................................... 77
If The ISU 128 Does Not READ READY......................................................................... 77
Chapter 12. Specifications ............................................................................................... 83
Specifications and Features............................................................................................... 83
Network Interface.......................................................................................... 83
DTE Interface ................................................................................................. 83
Dialing Selections .......................................................................................... 83
Data Rates (Network) ................................................................................... 83
Data Rates (DTE) ........................................................................................... 83
Rate Adaption ................................................................................................ 84
Interoperability .............................................................................................. 84
Switch Compatibility .................................................................................... 84
B Channel Aggregation ................................................................................ 84
Display ............................................................................................................ 84
ISU-128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 10

Table of Contents
Environmental ............................................................................................... 85
Physical........................................................................................................... 85
Power .............................................................................................................. 85
Appendix A. AT Commands........................................................................................... 87
Appendix B. Current Status Messages.......................................................................... 93
Appendix C. Status Buffer Messages............................................................................ 97
Appendix D. S-Register List ........................................................................................... 107
Appendix E. Connector Pinouts ..................................................................................... 115
Acronyms ............................................................................................................................ 121
Glossary .............................................................................................................................. 123
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
v
Page 11

Table of Contents
vi
ISU-128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 12

List of Figures
Figure 1-1: ISU 128 Rear Panel ................................................................................ 2
Figure 1-2: ISU 128 Front Panel............................................................................... 3
Figure 1-3: ISU 128 Interoperability........................................................................ 5
Figure 4-1: VT 100 Status Screen ............................................................................. 17
Figure 4-2: VT 100 Configuration Screen............................................................... 18
Figure 5-1: VT 100 Test Screen................................................................................. 19
Figure 5-2: Test Menu Tree ......................................................................................20
Figure 5-3: Loopback Points .................................................................................... 20
Figure 6-1: Dial Line Menu Tree ............................................................................. 23
Figure 6-2: VT 100 Configuration Screen............................................................... 24
Figure 6-3: Configuration Menu Tree..................................................................... 27
Figure 6-4: Dial Options, RS-366 Menu Tree......................................................... 29
Figure 6-5: Dial Options, V.25 bis Menu Tree....................................................... 33
Figure 6-6: Dial Line, Auto Answer Menu Tree ................................................... 34
Figure 6-7: Data Bits Menu Tree.............................................................................. 34
Figure 6-8: V.25 bis ASYNC Menu Tree................................................................. 35
Figure 6-9: Answer Tone Menu Tree...................................................................... 37
Figure 6-10: Connect Timeout Menu Tree............................................................... 38
Figure 6-11: Call Screening Menu Tree .................................................................... 38
Figure 6-12: Leased Line Menu Tree ........................................................................ 40
Figure 6-13: Limited Distance Modem Application............................................... 40
Figure 6-14: Leased Application with Channel Banks........................................... 41
Figure 6-15: Asynchronous DTE Options Menu Tree............................................ 42
Figure 6-16: Synchronous DTE Options Menu Tree ..............................................42
Figure 6-17: Flow Control Menu Tree ...................................................................... 44
Figure 6-18: Data Format Menu Tree ....................................................................... 45
Figure 7-1: Protocol Menu Tree............................................................................... 48
Figure 7-2: BONDING Mode 1 Protocol Menu Tree............................................ 49
Figure 7-3: V.34 Error Control Menu Tree............................................................. 51
Figure 7-4: V.34 Compression Menu Tree .............................................................52
Figure 7-5: V.34 MNP Block Size Menu Tree ........................................................52
Figure 7-6: FALLBACK Menu Tree ........................................................................ 55
Figure 7-7: PPP Menu Tree ...................................................................................... 56
Figure 8-1: Quick Setup Menu Tree........................................................................ 59
Figure 9-1: VT 100 Terminal Dial Options Screen ................................................67
Figure 9-2: Dial Menu Tree ......................................................................................68
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
vii
Page 13

List of Figures
Figure 10-1: Remote Configuration Menu Path...................................................... 72
Figure 10-2: Remote Configuration Screen.............................................................. 72
Figure 10-3: Remote Unit Configuration Screen..................................................... 73
Figure 10-4: Test Menu Path ......................................................................................74
Figure 10-5: Loopback Remote 1B............................................................................. 75
Figure 10-6: Set Password Screen..............................................................................75
Figure E-1: EIA-232/RS-530 Interface..................................................................... 115
Figure E-2: V.35 Interface.......................................................................................... 117
Figure E-3: RS-366 Interface......................................................................................118
Figure E-4: RJ-45 Interface ........................................................................................118
Figure E-5 Maintenance Port...................................................................................119
viii
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 14

List of Tables
Table 1-A: DTE Indicators .......................................................................................3
Table 1-B: Recommended Operating Modes ....................................................... 7
Table 3-A: Maximum DTE Interface Cable Lengths............................................ 12
Table 7-A: Rate Adaption Protocols....................................................................... 54
Table E-A: EIA-232 Interface ................................................................................... 115
Table E-B: RS-530 Interface ..................................................................................... 116
Table E-C: V.35 Interface.......................................................................................... 117
Table E-D: RS-366 Interface ..................................................................................... 118
Table E-E: RJ-45 ISDN IFC ...................................................................................... 118
Table E-F: Maintenance Port................................................................................... 119
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
xi
Page 15

List of Tables
xii
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 16

Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
ISDN OVERVIEW
Chapter 1
The Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a public or private switched
digital network. ISDN is an international standard for digital communications, allowing a full range of enhanced services supporting voice, data, and
image applications through standard interfaces over a single telephone wire.
ISDN provides a means of integrating these services and modernizing communication networks for information movement and management efficiency.
THE ADTRAN ISU 128
The ADTRAN ISU™ 128 is a stand-alone device that connects data terminal
equipment (DTE) to the ISDN network or to a leased digital network for data
transmission. The ISU 128 allows high-speed data transmission (up to 128
kbps) over a single ISDN line. The ISU 128 meets the Microsoft Windows
Plug-an-Play specifications. The file
this file contact our website at URL of www.adtran.com ADTRAN technical
support. The number is located on the inside back cover of this manual.
From the network, ISDN is delivered by a single 2-wire 2B1Q U-interface
which is connected directly to the ISU 128. ISDN network termination is designed into the ISU 128, eliminating the need and expense of a separate NT1.
For network testing, the ISU 128 responds to NT1 test commands from the telephone company central office (CO).
The ISU 128 transmits data over an RS-530, V.35 interface, or EIA-232 interface,
selectable on the front panel. The ISU 128 performs at synchronous data transfer rates of 2400 bps to 128 kbps and asynchronous rates of 300 bps to 115.2
kbps. For speeds over 64 kbps, the industry standard BONDING or MULTILINK PPP protocol aggregates the two 64 kbps B channels for a maximum of
128 kbps. The ISU 128 is intended to support the transfer of data and images
®
95
MDMADTN.INF is required. To obtain
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
1
Page 17
Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
over ISDN. The ISU 128 may be viewed as an ISDN dial modem that allows
cost-effective high-speed data transmission at rates up to 128 kbps.
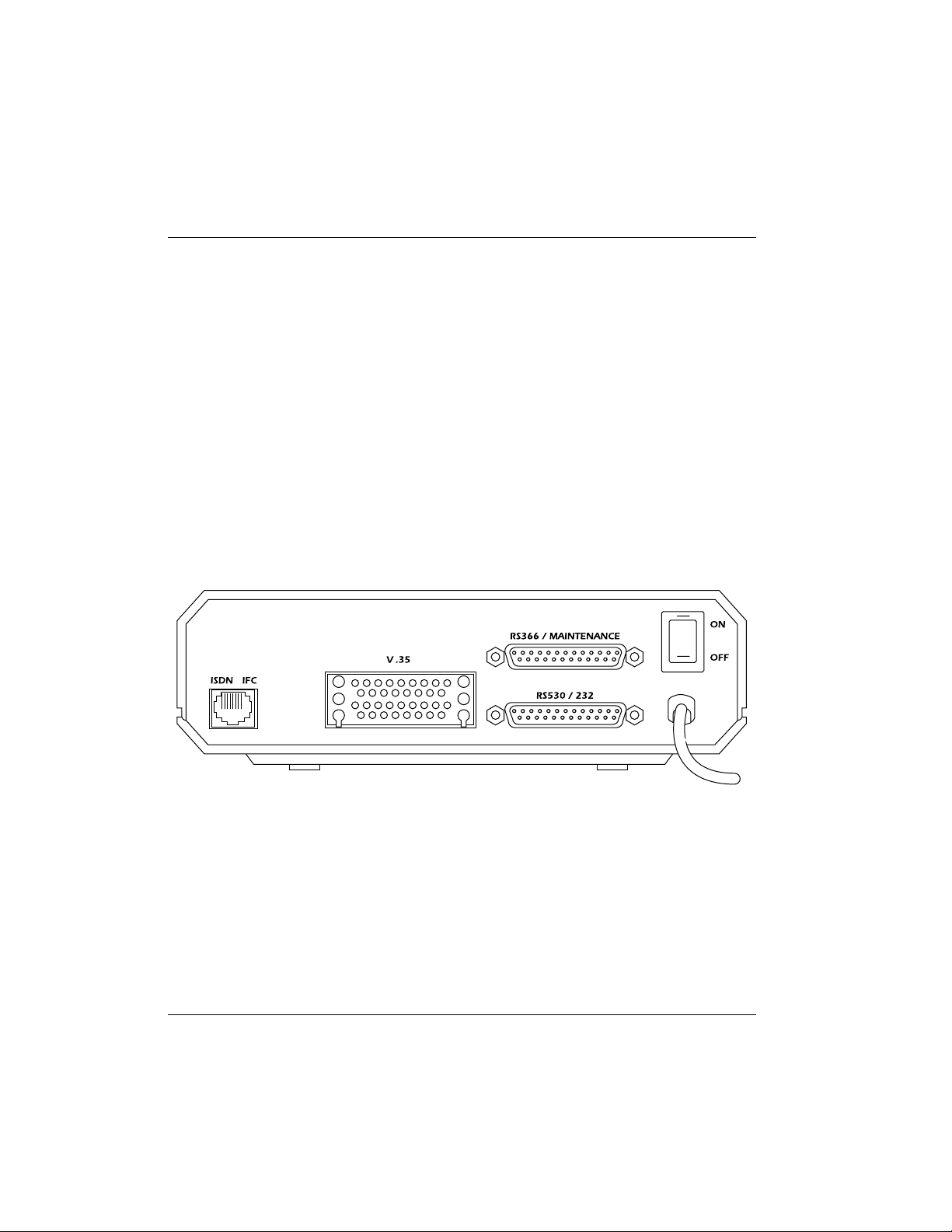
The ISU 128 has one RJ-45 jack available on the rear panel for network connection (see Figure 1-1). The RJ-45 jack labelled ISDN IFC is for ISDN Basic Rate.
ISDN Basic Rate service divides a standard telephone line into three digital
channels capable of simultaneous voice and data transmission. The three
channels are comprised of two bearer (B) channels at 64 kbps and one data (D)
channel at 16 kbps (2B+D).
The ISU 128 also supports a leased digital connection that allows data to be
transferred at up to 128 kbps over a 2-wire facility using the U-interface jack
labelled
ISDN IFC . This type of service is a permanent connection between
end points and is sometimes referred to as a leased connection, a dedicated
connection, a nailed-up connection, a private circuit, or a limited distance modem connection. These types of service are referred to in this manual as
Leased Line Service.
2
Figure 1-1
ISU 128 Rear Panel
Dialing from the ISU 128 is accomplished in a variety of ways:
• From the front panel
• From up to ten stored numbers
• Through an RS-366 dial port used in facsimile and video conferencing applications
• Over the DTE interface using the AT command set
• With V.25 bis in-band dialing (used in applications such as LAN/WAN
bridging)
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 18
Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
• With DTR asserted, some bridges/routers raise DTR when bandwidth on
their dedicated line is exceeded. In high-traffic times, this allows the ISU
128 to dial out over the ISDN for an extra 128 kbps of bandwidth-on-demand.
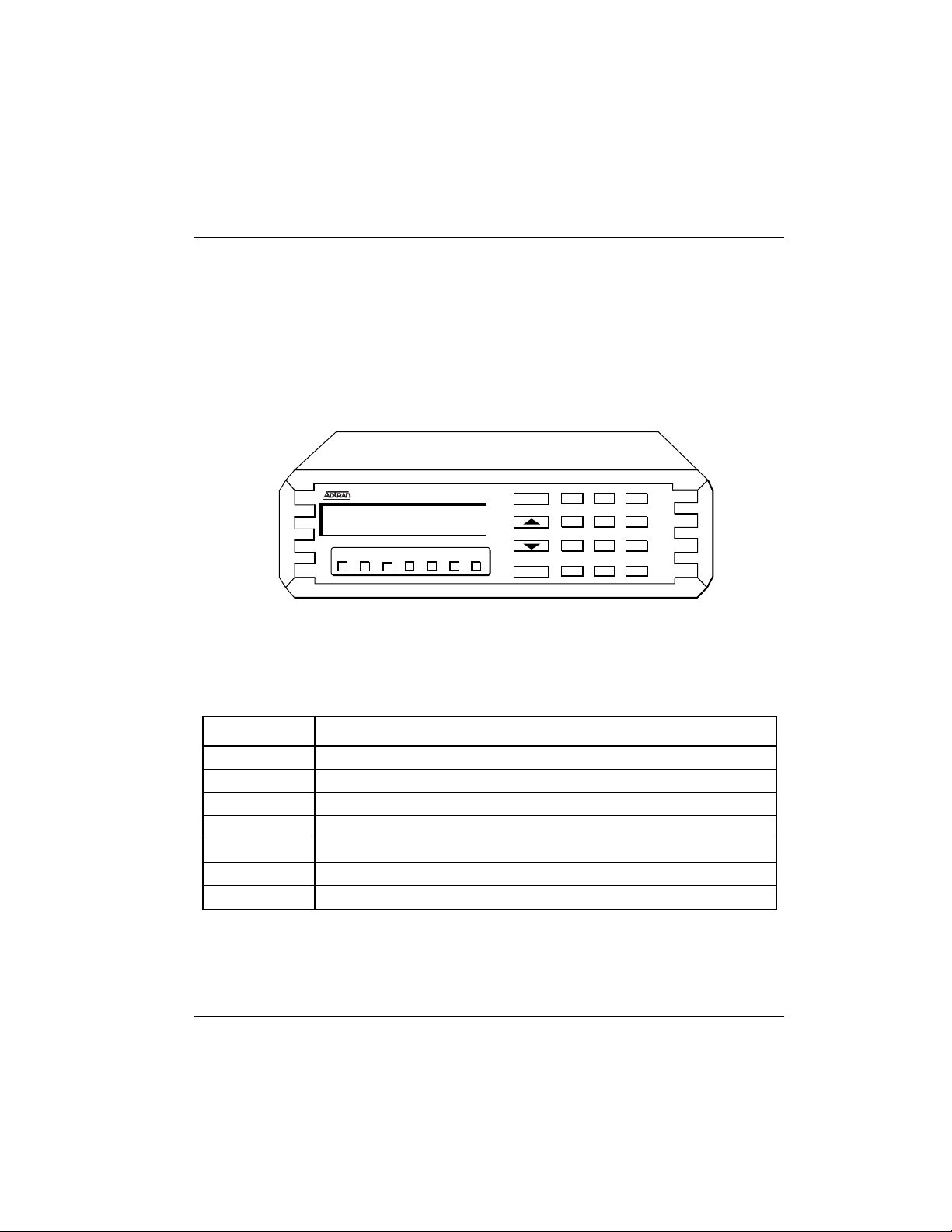
The ISU 128 front panel accommodates a 2-line, 16 character LCD display.
Seven LED indicators monitor data flow and display the status of key DTE interface leads as described in Table 1-A. A front panel keypad supports configuration, test modes, test status, and dialing (see Figure 1-2).
ISU 128
RS CS TD RD CD TR SR
ENTER
CANCEL
123
456
789
0
*
#
ISU 128 Front Panel
Indicator Definition
RS Request to Send. Indicates the DTE is ready to transmit.
CS Clear to Send. Indicates the ISU 128 is ready to transmit.
TD Transmit Data. On when the DTE is transmitting to the ISU 128.
RD Receive Data. On when the ISU 128 is receiving data from the far end.
CD Carrier Detect. On when the ISU 128 is connected to a remote unit.
TR Data Terminal Ready from DTE. On when DTR is active at DTE interface.
SR Data Set Ready.
Figure 1-2
Table 1-A
DTE Indicators
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
3
Page 19

Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
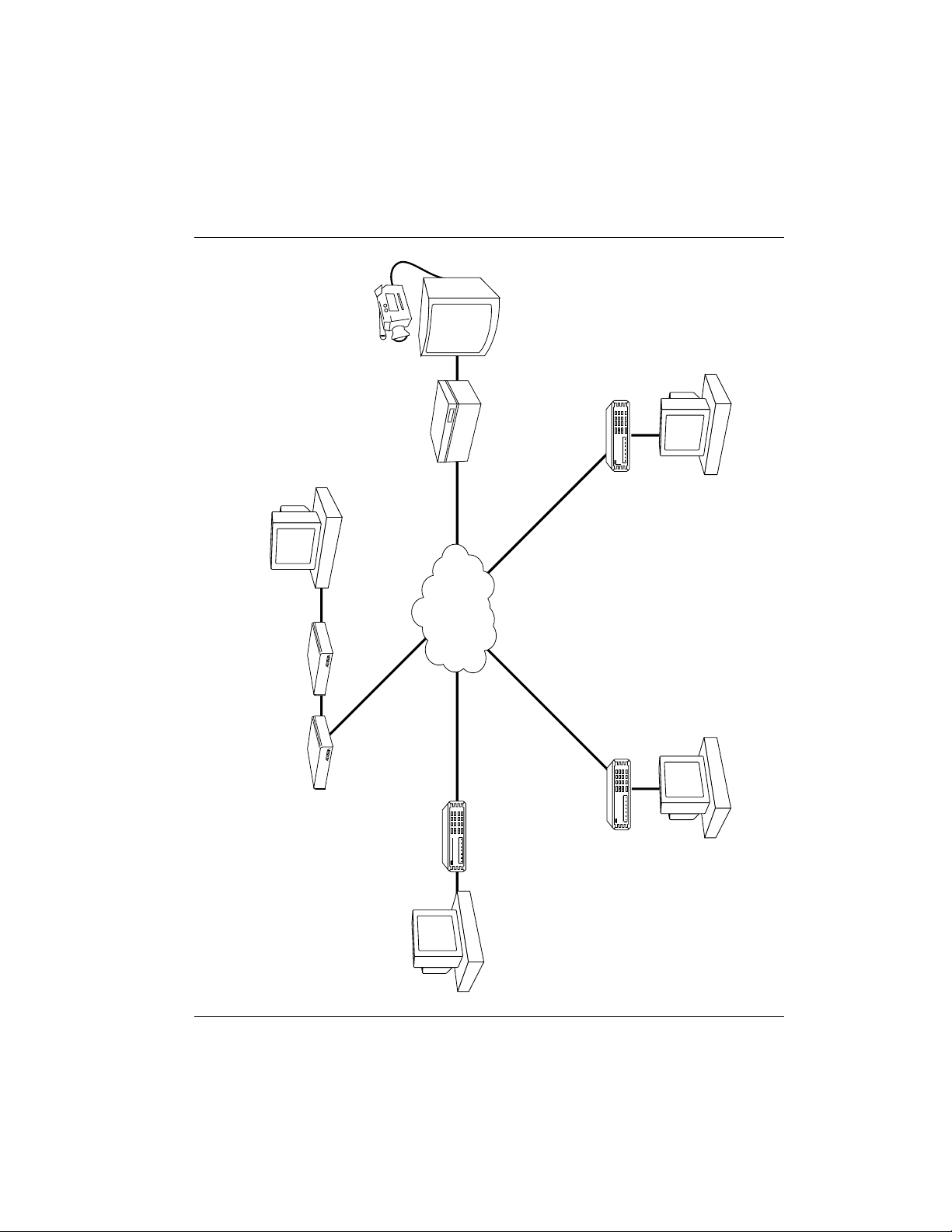
ISU 128 INTEROPERABILITY
Telephone networks are evolving from analog technologies to digital technologies such as ISDN. This transition is time-consuming and costly for the telephone companies. Upgrading all locations and facilities is a lengthy process.
The ISU 128 bridges this transition by supporting communications with existing and future network services and equipment. The ISU 128 supports communications with Switched 56 service, Switched 56 DSUs (2-wire and 4-wire),
various ISDN terminal adapters, ISDN terminal equipment, BONDING compatible inverse multiplexers, and analog modems with the optional V.34 modem (part number 1202029L3).
4
Figure 1-3 illustrates the ISU 128 operation in various switched network services and customer premises products.
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 20
Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
DTE
TANT1
ISDN U-Interface
Inverse MUX
BONDING Compatible
4-Wire Switched 56 DSU
NETWORK
ISDN U-Interface ISDN or SW56
*
123
456
789
#0
ENTER
CANCEL
ISU
ISU 128
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
Video Codec
Data Path
2-Wire Switched 56
*
123
456
789
#0
ENTER
CANCEL
DSU
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
4-Wire
SW56 DSU
2-Wire
SW56 DSU
*
123
456
789
#0
ENTER
CANCEL
DSU
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
Figure 1-3
ISU 128 Interoperability
DTE
DTE
DTE
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
5
Page 21

Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
RECOMMENDED OPERATING PROTOCOLS
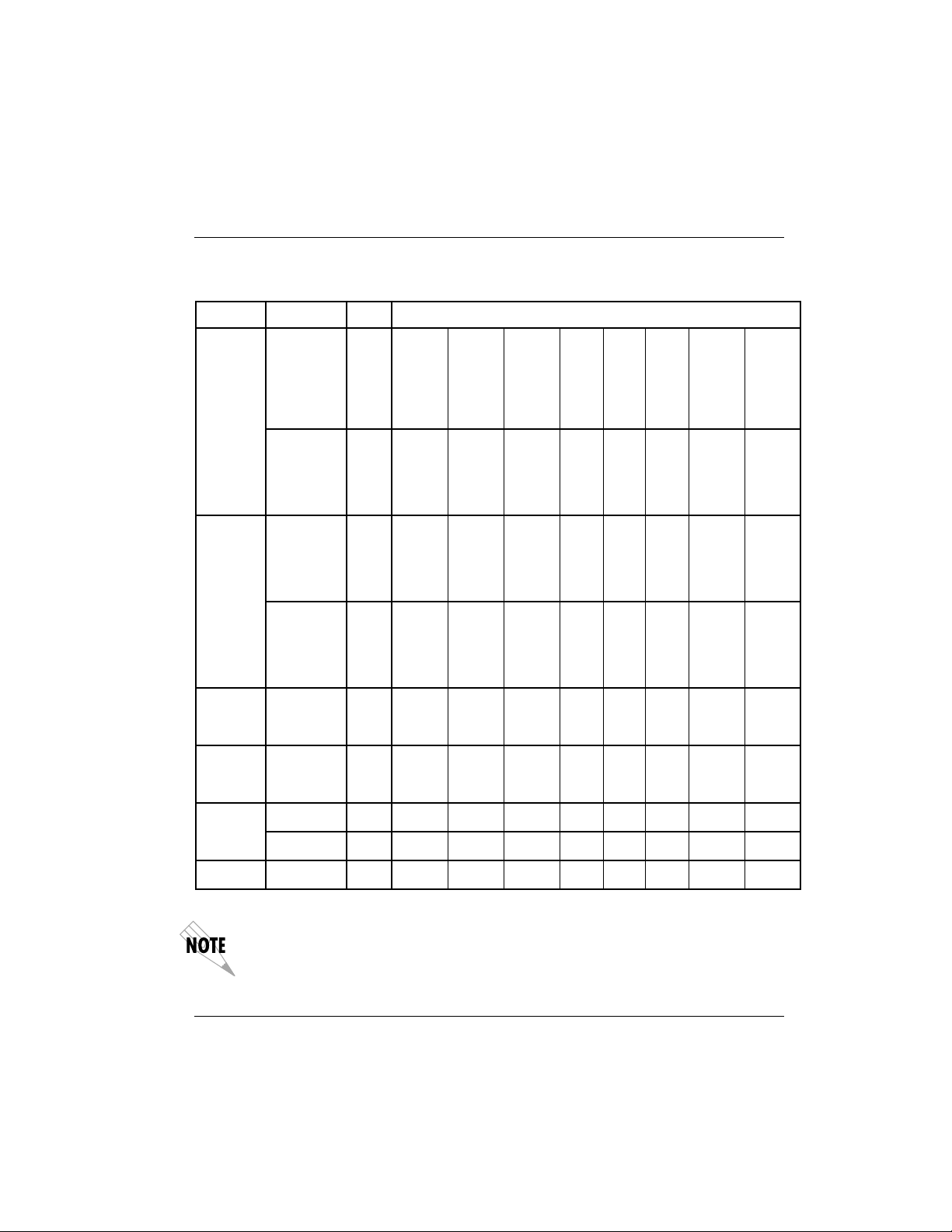
The ISU 128 supports a wide range of operating modes. Many combinations
of circuit type, protocol, and data rate may be selected. However, only the
combinations shown in Table 1-B are recommended. As noted in Table 1-B, all
asynchronous rates will support flow control. Flow control is required when
operating at 115,200 bps using PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol), V.120, SAP (Simple Adtran Protocol), or asynchronous bonding.
Table 1-B shows that a given data rate may be achieved by more than one protocol/rate adaption selection. The table is organized so that selections with
the least transport delay are closer to the top of the table for any given circuit
type. Therefore, users should choose a protocol and rate closer to the top of
the protocol rate list for a given circuit type.
6
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 22
Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
Table 1-B
Recommended Operating Modes
Call Type Protocol
DIAL-64K BONDING Sync 56000 64000
Clear Chan Sync 48000 56000 64000
PPP Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 56000 64000
V.110 Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400
V.120 Sync 9600 19200 38400 48000
Tlink Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 56000 64000
SAP Sync 38400
PPP async-sync Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600 115200
BONDING Async 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600
V.110 Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400
V.120 Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600 115200
Tlink Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200
SAP Async 38400 57600 115200
DIAL-56K BONDING Sync 56000
Clear Chan Sync 48000 56000
PPP Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 56000
V.110 Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200
V.120 Sync 9600 19200 38400 48000
Tlink Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 56000
PPP async-sync Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600 115200
BONDING Async 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600
DSU 57.6 Async 57600
V.110 Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200
V.120 Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600 115200
Tlink Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200
DIAL-64K*2 BONDING Sync 128000
MPPP Sync 128000
MPPP Async 115200
BONDING Async 115200
DIAL-56K*2 BONDING Sync 112000
MPPP Sync 112000
MPPP Async 115200
BONDING Async 115200
LEASED 64K Clear Chan Sync 48000 56000 64000
SAP Sync 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400
DSU 57.6 Async 57600
SAP Async 1200 2400 4800 9600 19200 38400 57600
LEASED 128K Clear Chan Sync 128000
SAP Async 57600
Sync/
Async
f
f
f
f
f
115200
f
1. All asynchronous rates support flow control.
2. All dial-up modes support front panel, DTR, RS-366, AT command, and V.25 bis dialing
methods.
3. Rates marked with f require flow control.
4. Given a choice between two protocols, pick the protocol closer to the top of the list.
5. Multilink PPP supports the same rates as single-link PPP async-sync. Use the recom-
mended rates for PPP async-sync.
Rates Supported (bps)
f
f
v
f
115200
f
f
f
f
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
7
Page 23

Chapter 1. Understanding ISDN and the ISU 128
8
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 24

ISDN Ordering Codes (IOCs)
ORDERING ISDN USING IOCS
Chapter 2
The development of ISDN ordering codes (IOCs) simplifies the process of ordering ISDN service. The ISDN Solutions Group, a consortium of ISDN equipment vendors, service providers, and Bellcore, established these codes to
represent predetermined line configurations for ISDN Basic Rate service for
specific applications.
ADTRAN and Bellcore have registered and tested eight generic IOCs. Of
these, four are recommended for operation of the ISU 128. After reviewing
the following list, order ISDN lines from the local service provider. Request
the appropriate IOC for your application. They are described in detail in this
chapter.
In some areas, ISDN tariffs may warrant the use of ordering codes with less
features. For example, in a particular region, there may be additional monthly
expense associated with having voice service on each B channel. If you have a
data only application,
cost-effective.
If these are not available from your service provider or you would like more
information regarding ordering ISDN see the ADTRAN document Ordering
ISDN Service User Guide part number 60000.015-8 or contact your telephone
company for alternative line configurations. The Ordering ISDN Service User
Guide is available on the ADTRAN home page at http://www.adtran.com or
by calling ADTRAN.
Capability R (previously Generic Data I ) may be more
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual
9
Page 25

Chapter 2. ISDN Ordering Codes (IOCs)
ADTRAN has registered the following ISDN ordering codes to support a variety of tariffs and applications:
Capability S
• 2B service
• Both B channels alternating voice and data
• Two directory numbers
Applications
• Host data center, internet access, bulletin board, and modem pooling applications
• Modem capability
• Generic data transfer, including remote access and LAN/WAN connectivity and telecommuting
10
Capability R
• 2B service
• Data only
• Two directory numbers
Applications
• Host data center, internet access, bulletin board, and modem pooling applications
• Data only applications, no modem capability
• Data transfer applications, including remote access and LAN/WAN connectivity, telecommuting
Capability B
• 1B service
• Data only
• One directory number
•
Capability C
• 1B service
• Alternating voice and data
• One directory number
ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 26
After unpacking the unit, immediately inspect it for possible shipping damage. If damage is discovered, file a claim immediately with the shipping carrier, then contact ADTRAN Repair and Return Department (see the end of this
manual).
Ensure that a grounded, 115 VAC, 60 Hz receptacle is used to provide power.
NETWORK CONNECTION
The ISU 128 supports either dial or leased operation. An eight-pin RJ-45 modular jack labelled ISDN IFC on the rear panel allows connection to ISDN Basic
Rate Service provided by the telephone company or to a leased type of service.
Dial operation uses the ISDN Basic Rate U-interface and allows the ISU 128 to
dial out over the ISDN network. The Leased Line Service can be dedicated
2B1Q data service or a nailed-up circuit (twisted pair) that provides a dedicated connection between end points such as a limited distance modem or pointto-point connection. When using the ISU 128 in either of these types of service,
connect the network interface to the RJ-45 connector labelled ISDN IFC.
See the appendix Connector Pinouts for network connection pin assignments.
Chapter 3
Installation
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 11
Page 27
Chapter 3. Installation
DTE DATA CONNECTION
Data terminal equipment is connected to the ISU 128 by using either the RS530 interface, the V.35 interface, or EIA-232 interface on the rear panel of the
ISU 128. The maximum recommended cable lengths are shown in Table 3-A.
See the appendix Connector Pinouts for each interface pin assignments. Be sure
to configure the menu option for the connector type used in your application.
Refer to the section DTE Options for Asynchronous and Synchronous Operation in
Chapter 6 to configure the connector type.
The RS-530 interface and the V.35 interface support data rates up to 128 kbps.
The DTE rate is configured from the front panel of the ISU 128 or by using AT
commands. See the chapter Configuration to configure the ISU 128 with the appropriate data rates.
Table 3-A
Maximum DTE Interface Cable Lengths
DTE Interface Max Cable Length
RS-530 50 feet
V.35 30 feet
EIA-232 15 feet
To prevent possible radio frequency interference emissions, a shielded V.35
cable is required.
DIAL INTERFACE CONNECTION
If out-of-band RS-366 dialing is required for applications such as videoconferencing or FAX machines, the dialing interface of the host DTE should be connected to the dial port marked RS-366/Maintenance. Pin assignments for the
RS-366 connector are listed in the appendix Connector Pinouts.
12 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 28
MAINTENANCE INTERFACE
The Maintenance Interface is available at 9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, asynchronous format, through the RS-366/Maintenance port. See the appendix
Connector Pinouts for Maintenance port pin assignments. The VT 100 terminal
or null modem can be connected to the RS-366/Maintenance port using an
EIA-232 cable. This interface can be used to set internal S-registers, dial ISDN
connections, and disconnect calls. This port also allows ADTRAN Technical
Support personnel to retrieve vital information from the unit if a problem is
encountered during initial configuration of the ISU 128. Most problems can be
solved without resorting to this port for assistance.
In order to activate the Maintenance port, ensure the dial mode is either Front
Panel or AT commands. When the dial mode is set for RS-366, the Maintenance port is disabled.
The Maintenance port cannot be used to pass data or to remotely configure another
ISU 128 using the Cfg. Rmt. Unit option.
AT commands sent to the Maintenance port are not preceeded by "AT."
Example: To display the unit model number, enter: I0
Chapter 3. Installation
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 13
Page 29

Chapter 3. Installation
14 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 30
MENU NAVIGATION
Four function keys on the left-hand side of the keypad allow the user to enter,
exit, and scroll through the various menu branches. The four function keys are
defined below.
Enter Enters the selected item.
Up Arrow Scrolls up a menu tree.
Down Arrow Scrolls down a menu tree.
Cancel Exits (back one level) from the current branch of
For reading ease, function keys are represented in bold, initial caps text. Selectable
menu items and messages displayed on the LCD are represented in bold type as they
appear on the LCD.
Chapter 4
Operation
the menu tree.
Press either the Up or Down arrow to scroll through the menu tree. To choose
an item, press the corresponding number on the keypad. The item blinks to
show that it is selected and has been stored in non-volatile memory. Press Enter to select the item. Press Cancel to exit back through the menu tree.
It is important to note that some features in the ISU 128 do not immediately
take effect upon selection. This prevents unintentional reconfiguration of the
ISU 128 during an active call. Leased/Dial Line, and ISDN Switch Protocl,
take effect only when the ISU is powered up or the U-interface is bounced (line
broken and restored). To ensure the ISU is actually performing as configured,
cycle the power off, then back on again, after these items are changed. Also,
items such as Bit Rate, Protocol, and Call Type take effect only at the beginning of a new call.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 15
Page 31

Chapter 4. Operation
GETTING STARTED
At power up, the front panel display is in the Current Status mode. This is the
recommended resting place for the display as it shows the current operational
status of the unit. For example, if the ISU 128 is not connected to the network,
the Current Status menu displays ADTRAN ISU 128 Link Down. If the unit
is connected to the network and functioning properly, it displays ADTRAN
ISU 128 Ready. A list of Current Status messages is provided in the appendix
Current Status Messages. Pressing Cancel repeatedly returns the unit to the
Current Status menu. While at the Current Status menu, pressing any key
changes the display to the top of the menu tree.
The menu tree allows for set up and operation of the ISU 128 from the front
panel. The main branches of the menu tree follow:
1. STATUS
2. TEST
3. CONFIG (Configuration)
4. DIAL
Status Buffer
Select 1=STATUS from the top of the menu tree to display the status buffer.
The Up and Down arrows allow viewing of the last fifty status messages gen-
erated during the operation of the unit. The most recent message displays last.
An explanation of Status Buffer Messages can be found in the appendix Status
Buffer Messages. To return to the top of the menu, press Cancel. The buffer can
be cleared by pressing 0.
16 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 32

VT 100 TERMINAL MENU SUPPORT
When connected to an asynchronous VT 100 terminal or VT 100 terminal emulator, use the built-in ISU 128 menu system for configuration. To enter into
the menus, type AT!V Enter. To go to a particular menu, simply press the hot
keys for that menu. The main branches of the menu tree and their hot keys are:
• STATUS (Ctl-V)
• TEST (Ctl-T)
• CONFIG (Ctl-C)
• DIAL (Ctl-D)
Status Screen
To determine the current status of the unit, press Ctrl+V to access the Status
Screen (see Figure 4-1). The Status Screen displays unit information such as
the loop status, software revision, the result of the initial self test, and the status buffer messages. The most recent message always displays as Status Buffer 1. An explanation of status buffer messages can be found in the appendix
Status Buffer Messages.
Chapter 4. Operation
Figure 4-1
VT 100 Status Screen
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 17
Page 33

Chapter 4. Operation
Configuration Screen
Once the unit is selected using the terminal interface, the display shows the
Configuration Menu (see Figure 4-2). This screen shows the current configuration, line, and call status for the selected unit. See the chapter Configuration formore information about configuring the ISU 128.
Figure 4-2
VT 100 Configuration Screen
To configure the ISU 128 quickly and easily for most applications, see the
chapter Quick Setup.
18 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 34

TEST OPTIONS
Pressing Ctl-T from any VT 100 terminal screen or selecting 2=TEST from the
top of the menu tree on the front panel displays local testing options. Figure
5-1 shows the VT 100 terminal test screen and the menu tree is illustrated in
Figure 5-2.
Chapter 5
Testing
Figure 5-1
VT 100 Test Screen
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 19
Page 35

Chapter 5. Testing
1=STATUS
2=TEST
3=CONFIG
4=DIAL
Loopback DTE
Loopback DTE causes the ISU DTE port to loop back toward user equipment.
This allows performance of a bit error rate test (BERT) between the ISU 128
and the end user equipment to verify proper cable connection.
Loopback Network
Loopback Network forces the ISU 128 to loopback both the B1 and B2 channels toward the network. This can be used to allow a far-end user to perform
a BERT all the way through the network.
1=Loopback DTE
2=Loopback Netw.
3=Loopback Proto
4=Loopback Remote
5=Test Remote
6=Lpbk Disable
7=NEBE/FEBE
0=Software Ver
1=No Rem Lpbks
2=DDS Accepted
3=V54 Accepted
4=DDS + V54 Accept
Figure 5-2
Test Menu Tree
Loopback Protocol
Loopback Protocol allows data to loopback toward the network after passing
through a selected protocol such as T-Link or BONDING. See Figure 5-3 for
loopback points.
NETWORK
20 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
NET
IFC
Network
RATE
ADAPTION
Protocol
DTE
DTE
IFC
DTE
Figure 5-3
Loopback Points
Page 36

Loopback Remote
Loopback Remote allows the ISU 128 to issue a V.54 in-band loopback command to a far-end unit while still accepting data from the DTE connector. This
provides bit error rate testing of an entire link using an external BERT test set.
To use this feature, both units must be configured for Clear Channel operation
and the far-end unit must be able to respond to V.54 loopback commands. See
the chapter Protocol Options to configure the unit for Clear Channel operation.
Press the Cancel key to end the test.
Loopback Remote 1B and 2B are only used with the DTE set to asynchronous.
Test Remote
Test Remote allows the ISU 128 to issue a V.54 in-band loopback command to
a far-end unit and BERT the link using a built-in 2047 pattern generator/
checker. This allows for testing a circuit without any extra test equipment. To
use this feature, both units must be configured for Clear Channel operation
and the far-end unit must be able to respond to V.54 loopback commands. See
the chapter Protocol Options to configure the unit for Clear Channel operation.
The built-in 2047 pattern generator/checker displays the number of bytes
transmitted on the top line and the number of errored bytes received on the
lower line of the front panel display. Press 0 to clear the counts. By pressing
the down arrow, you can loop down the far end unit and run a head to head
2047 pattern test. Press Cancel to end the test.
Chapter 5. Testing
Loopback Disable
The following options are available when disabling loopbacks:
No Remote Loopbacks
The ISU 128 ignores all V.54 and DDS loopback commands.
DDS Accepted
The ISU 128 responds to DSU Latching Loopback commands. This option
only takes effect if the unit is in leased line mode.
V.54 Accepted
The ISU 128 responds to V.54 loopback commands.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 21
Page 37

Chapter 5. Testing
DDS+V54 Accept
The ISU 128 responds to both DSU Latching Loopback commands (leased line
mode only) and V.54 loopback commands.
The ISU must be optioned for Clear Channel operation for DSU Latching and V.54
loopback commands to take effect.
Near-End Block Errors/Far-End Block Errors (NEBE/FEBE)
NEBE/FEBE allows the user to determine the quality of the network connection by viewing the number of near-end (NEBE) and far-end (FEBE) block errors occurring on the ISDN interface. A large or incrementing count indicates
problems with network equipment. An incrementing or large count of NEBEs
indicates problems from the switch to the terminal adapter. An incrementing
or large count of FEBEs indicates problems in the direction from the terminal
adapter to the switch.
Software Version
Software Ver displays the software version and checksum in use on the ISU
128.
Press Cancel to exit any of these options.
22 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 38

DIAL LINE OPERATION
This section explains how to configure the ISU 128 when using ISDN basic rate
switched service. Figure 6-3 illustrates the entire CONFIG branch of the menu
tree.
The following are step-by-step procedures for configuring the unit for dial line
operation, switch protocol, call type, terminal ID, dial options, auto answer,
answer tone, connect timeout, and call screening.
To dial calls over the ISDN, the unit must be configured for Dial Line. The
menu path to select Dial line operation is shown in Figure 6-1.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
Chapter 6
Configuration
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
Figure 6-1
Dial Line Menu Tree
When using a VT 100 terminal, press Ctl-C to access the Configuration screen,
then set the Line type option to Dial Line. The Configuration screen appears
as shown in Figure 6-2.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 23
Page 39

Chapter 6. Configuration
Switch Protocol
Find out what kind of ISDN switch your local CO is using by asking the telephone administrator or telephone company representative. Configure the ISU
128 for either a Northern Telecom DMS-100
conforming to the National ISDN-1 standard (usually an AT&T 5ESS, NTI
DMS-100, or Siemens EWSD). In the Far East, configure for the NEC switch.
Figure 6-2
VT 100 Configuration Screen
®
, AT&T 5ESS® switch, or a switch
Call Type
The call type can be configured four different ways, depending on the type of
service used: speech, audio, data 56 kbps, or data 64 kbps.
When placing outgoing calls using the optional V.34 modem, the unit must be optioned for either speech or audio call type.
Speech
Speech directs the call control software to request a Mu-law/A-law speech circuit as the bearer capability for outgoing calls. The Speech option is used with
an ISDN line configured for voice service. In some areas voice service costs
24 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 40

less than data service. A Speech call type does not guarantee an end-to-end
digital connection with some local and long distance carriers.
Audio
Audio directs the call control software to request a 3.1 kHz audio circuit as the
bearer capability for outgoing calls. The Audio option is used with an ISDN
line configured for voice service. In some areas audio service is less expensive
than data service. Selecting an Audio call type guarantees a digital end-to-end
ISDN connection.
Data 56 kbps
Data 56 kbps directs the call control software to request a 64 kbps data circuit
that is rate-adapted to 56 kbps. Data 56 kbps is intended for use in circumstances where interoperability with Switched 56 service is desired.
Data 64 kbps (default)
The default Call type for ISDN service is Data 64 kbps. This directs the call
control software to request an unrestricted 64 kbps circuit.
Terminal Identification
Chapter 6. Configuration
Terminal identification is assigned by the local telephone company and consists of a Service Profile Identifier (SPID) and Local Directory Number (LDN).
Setting the SPID
The SPID is a sequence of digits used to identify ISDN terminal equipment to
the ISDN switch. The SPID is assigned by the local phone company when the
ISDN line is installed and it usually looks similar to the phone number. Obtain
SPIDs from the telephone administrator or local telephone representative.
The number of SPIDs required (0, 1, or 2) depends on how your ISDN line is
configured. For instance, a point-to-point line has no SPID. Multipoint lines
may have one or two SPIDs. The ISU 128 uses the presence of SPID 1 to determine if the line is multipoint. If the line has only one SPID, then it must be entered in SPID 1.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 25
Page 41

Chapter 6. Configuration
When selecting a SPID, use the Up and Down arrows to choose between
SPID 1 and SPID 2. Press Enter to select the SPID and use the keypad to enter
the SPID number. While entering/editing a SPID, the Down arrow allows ou
to backspace through the number string to correct mistakes. The Up arrow
scrolls back to the last digit entered. To cancel a number, use the Down arrow
to backspace through it and press Enter. Press Enter after entering each SPID.
To abort changes at any time, press Cancel.
Disconnect the network interface from the unit before initially entering and/or altering
the SPIDs or LDNs.
Setting the LDN
This option allows the entry of 0, 1, or 2 LDNs. The LDN is used when placing
or receiving BONDING calls. The LDN is the seven-digit local phone number
assigned to the line.
When entering and LDN, use the Up and Down arrows to choose between
LDN 1 and LDN 2. Press Enter to select the LDN and use the keypad to enter
the LDN number. While entering/editing an LDN, the Down arrow allows
you to backspace through the number string to correct mistakes. The Up arrow
scrolls back to the last digit entered. To cancel a number, use the Down arrow
to backspace through it and press Enter. Press Enter after entering each LDN.
To abort changes at any time, press Cancel.
26 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 42

Chapter 6: Configuration
‘Buffer Display’
1=Loopback DTE
2=Loopback Netw.
3=Loopback Proto
4=Loopback Remote
5=Test Remote
6=Lpbk Disable
7=NEBE/FEBE
8=Software Ver
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol 1=Clear Channel
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Hang up line
2=Dial number
3=Redial last #
4=Answer Call
5=Dial Stored #
6=Store/Review #
1=No Rem Lpbks
2=DDS Accepted
3=V54 Accepted
4=DDS + V54 Accept
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP .
9=FALLBACK 1=Fallback Def
0=PPP asyn-sync
1=Dial 56K sync
2=Dial 64Ksync
3=Dial 112K sync
4=Dial 128K sync
5=Dial PPP
6=V.34 1152 async
7=Dial 57.6 asyn
8=Dial 115.2 asy
9=Fallback 57.6k
0=More
1=Cfg. Rmt. Unit
2=Set Password
3=Loopback remote 1B
4=Loopback remote 2B
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID Set SPID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening 1=Answer any
1=Clock mode 1=Slave
2=Channel rate 1=64k
1=Method
2=TBD
1=Leased 128k
2=Ldm 128 Master
3=TBD
4=TBD
5=TBD
6=TBD
7=TBD
1=PPP
2=Multilink PPP
3=PPP w/Comp
1=AT&T 5ESS
2= DMS-100
3=National ISDN1
4=NEC Switch
1=Speech
2=Audio
3=Data 56Kbps
4=Data 64Kbps
Set LDN
1=Front Panel
2=RS-366
3=AT commands
4=V.25
5=Disabled
1=Disabled
2=Enabled
3=Dump all calls
1=No answer tone
2=Incoming tone
3=Outgoing tone
4=Always tone
1=15 sec
2=30 sec (def)
3=1 minute
4=2 minute
5=4 minute
2=ansr if SNO…9
2=Master
2=128k
1=TXINIT
2=TXFA
3=TXADD01
4=TXDEQ
5=TANULL
6=TCID
1=Error Ctrl
2=Compression
3=MNP Blk Size
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=PPP asyn-sync
1=V.25 HDLC
2=V.25 ASYNC
3=V.25 BISYNC
4=V.25 HDLC FLAG
1=1 sec or EON
2=2 sec or EON
3=5 sec (default)
4=10 sec or EON
5=20 sec or EON
6=Wait for EON
1=Normal
2=Direct
3=Reliable MNP
4=Auto-Rel MNP
5=Force LAPM
6=Force MNP
1=No Compression
2=Compress MNP5
3=Compress V42
4=Comp V42/MNP5
1=64 bytes
2=128 bytes
3=192 bytes
4=256 bytes
1=2400
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type 1=RS-530
3=RTS Options 1=1 Ms delay
4=CTS Options 1=Forced CTS
5=CD Options 1=CD Forced on
6=DTR Options 1=Ignore DTR
7=DSR Options 1=DSR forced on
8=Transmit Clock
6=48000
2=4800
7=56000
3=9600
8=64000
4=19200
9=112000
5=38400
0=128000
2=V.35
3=RS-232
2=18 Ms delay
2=Follows RTS
2=Normal
3=Off with LOCD
4=Off with Link Down
2=Cmd when Off
3=Idle when Off
4=Off>On dial #0
5=Dial #0 if On
6=Answer if On
7=Dial/Ans if On
2=OFF Idle+Test
3=OFF Link Down
1=Normal
2=External
6=19200
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Flow Control
9=Data Format 1=Data Bits 1=8 Data Bits
1=300
7=38400
2=1200
8=57600
3=2400
9=115200
4=4800
5=9600
1=RS-530
2=V.35
3=RS-232
1=1 Ms delay
2=18 Ms delay
1=Forced CTS
2=Follows RTS
1= CD Forced on
2=Normal
3=Off with LOCD
4=Off with Link Down
1=Ignore DTR
2=Cmd when Off
3=Idle when Off
4=Off>On dial #0
5=Dial #0 if On
6=Answer if On
7=Dial/Ans if On
1=DSR forced on
2=OFF Idle+Test
3=OFF Link Down
1=Hardware Flow
2=Software Flow
3=No Flow Ctrl
2=Parity Bits
3=Stop Bits
2=7 Data Bits
1=None
2=Odd
3=Even
1=1 Stop bit
2=1.5 Stop bits
3=2 Stop Bits
1 ISU 128 User Manual 27
Configur
Page 43

Chapter 6: Configuration
28 ISU 128 User Manual
Page 44

Dial options
The ISU 128 can be configured to dial using the Front Panel, RS-366 port, AT
Commands, or V.25 bis Commands. Figure 6-4 illustrates the menu tree.
Front Panel
To establish and disconnect calls from the front panel keypad, configure Dial
options for Front Panel. See the section Front Panel Dialing Options for more
detail.
RS-366
To establish and disconnect calls using the RS-366 parallel dialing port, configure the unit for RS-366 dialing. This enables the RS-366 port on the rear of the
unit. Whenever this dialing mode is enabled, DTR must be active before a call
is placed. The call may be disconnected by dropping DTR, or from the front
panel by selecting the # (pound) key to go directly to the Dial menu and select-
ing 1=Hang up line, then Enter.
DTE RS-366 dialers can end a string of dialed numbers in two different ways.
The end of number (EON) alerts the ISU 128 that the entire number has been
sent. Another method is to simply stop sending numbers and allow the ISU to
time out, then dial the number. The ISU 128 supports both methods of dialed
number terminations. The following options in Figure 6-4 allow for fine-tuning the dialed number termination.
Chapter 6. Configuration
1=Switch protocl
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
1=Front Panel
2=RS-366
3=AT commands
4=V.25
5=Disabled
1=1 sec or EON
1=2 sec or EON
3=5 sec or (default)
4=10 sec or EON
5=20 sec or EON
6=Wait for EON
Figure 6-4
Dial Options, RS-366 Menu Tree
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 29
Page 45

Chapter 6. Configuration
1 sec or EON
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered if more than one second
elapses since the last digit was entered, or the unit receives the EON command.
2 sec or EON
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered if more than two seconds
elapse since the last digit was entered, or the unit receives the EON command.
5 sec or EON (default)
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered if more than five seconds
elapse since the last digit was entered, or the unit receives the EON command.
This is the factory default setting.
10 sec or EON
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered if more than 10 seconds
elapse since the last digit was entered, or the unit receives the EON command.
20 sec or EON
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered if more than 20 seconds
elapse since the last digit was entered, or the unit receives the EON command.
Wait for EON
The ISU 128 assumes the dial string is fully entered only if the unit receives the
EON command.
AT Commands
Configuring the ISU 128 for AT commands enables in-band dialing over the
DTE interface using asynchronous AT commands. AT commands can be used
to set up the ISU 128 as well as establish and end a call. Calls can be disconnected from the front panel (as previously described) or from the far-end unit.
When AT commands are selected, the DTE port becomes dual purpose. First,
while a call is not established, the port accepts AT commands. During this
time, the Carrier Detect (CD) signal is inactive. Second, when a call is established, the port is used for data. This data mode is indicated by the CD signal
active. See the appendix AT Commands for a listing of the supported AT commands and their functions. In addition to the front panel, the ISU 128 can be
configured and controlled with in-band AT commands from an asynchronous
DTE port.
30 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 46

Chapter 6. Configuration
To exit the data mode and enter the command mode, the asynchronous DTE
device must transmit a proper escape sequence to the ISU 128. A specified
time delay must occur between the last data character and the first escape sequence character. This is the guard time delay, and it can be changed by writing a value to the S12 register. The default value for the guard time is one
second. For a valid escape sequence to occur, the DTE must transmit the escape code character three times in succession with delay between each character being less than the guard time. The default escape sequence is +++.
Once the command mode is entered, AT commands can be transmitted to the
ISU 128 to configure most of the options, dial remote DSUs, or initiate tests to
check both the ISU 128 and the network connections. All command lines must
begin with the AT character set in either capital or lower case letters and end
with a terminating character. A command line can be terminated at any time
by transmitting the Ctl-X (ASCII 018) after the AT attention code. The ISU 128
ignores this command line and issues an OK response.
The command line may contain a single command or a series of commands after the AT attention code. When a series of commands are used, the individual
commands may be separated with spaces for readability. The maximum
length for a command line is 40 characters. Each command line is executed by
the ISU 128 upon receipt of a terminating character.
The default terminating character is a carriage return (ASCII 013), but it can be
changed by writing a different value to register S3. Before the terminating
character is transmitted, the command line can be edited by using the backspace character (ASCII 008) to erase errors so the proper commands can be entered. Examples of using AT commands are provided in this section.
Using AT Commands
Type AT followed by the letter of the command and numeric value of the setting desired and then press Enter. The following command returns the software version of the unit:
ATI1
Using S-Registers
The configuration of the ISU 128 can be changed and/or reviewed with S-registers. See the appendix S-Register List for a description of each S-register and
its corresponding range of values.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 31
Page 47

Chapter 6. Configuration
Reading S-Registers
Type ATS followed by the number of the S-register to be read followed by a
question mark and press Enter.
Reading S-Register Strings
The ISU 128 uses S-register strings to store strings of digits for stored phone
numbers, SPIDs, etc. Type ATSS followed by the number of the string S-register to be read followed by a question mark and press Enter.
Changing S-Registers
Type ATS followed by the number of the S-register to be changed, an equal
sign, the numeric value to be assigned to the register, then press Enter.
Changing S-Register Strings
Type ATSS followed by the number of the string S-register to be changed, an
equal sign, the numeric string to be assigned to the register, then press Enter.
ATS0?
ATSS80?
ATS0=2
ATSS80=5551212
Dialing a Call Using the AT Command Processor
To dial a number using the DTE terminal and AT commands type ATD and
the telephone number on one line and press Enter.
ATD5551212
When the dialing process begins, the front panel reads Dialing 5551212. If the
call is successful, Connect is displayed on the front panel, followed by the rate
adaption protocol in use and the bit rate. If the call is not successful, the front
panel displays Disconnect followed by Ready. At this point the unit is ready
for another call. The status buffer can be examined to find the reason for an
unsuccessful call.
To end an active call with the AT command processor, press the break in key
sequence (+++) or the redefined key, then type ATH and press Enter to hang
up the line.
32 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 48

V.25 bis
Configuring the ISU 128 for V.25 bis (see Figure 6-5) enables in-band dialing
over a DTE interface using asynchronous or synchronous V.25 bis commands.
V.25 bis can be used to establish and end a call. Disconnecting calls can also
be done from the front panel (as previously described) or from the far-end
unit.
V.25 bis dialing is used primarily by DTE with synchronous interfaces
(HDLC/SDLC or BSC/BISYNC) not supporting the AT command set, which
is commonly used by asynchronous devices. The ISU 128 supports V.25 bis inband dialing in accordance with Fascicle VIII.I - V.25 bis (Malaga-Torremolinos 1984, Melbourne 1988).
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
Chapter 6. Configuration
1=Front Panel
2=RS-366
3=AT commands
4=V.25
5=Disabled
1=V.25 HDLC
2=V.25 ASYNC
3=V.25 BISYNC
4=V.25 HDLC FLAG
Figure 6-5
Dial Options, V.25 bis Menu Tree
Recommendation V.25 uses the following DCE/DTE control signals:
Transmitted data ..........................................................circuit 103
Received data................................................................ circuit 104
Ready for sending ........................................................circuit 106
Data set ready ............................................................... circuit 107
Data terminal ready .................................................circuit 108/2
Calling indicator........................................................... circuit 125
The ISU 128 supports the following V.25 bis commands to control automatic
calling and answering:
CRN..................................... call request (number in command)
CRS.......................................call request (using stored number)
PRN ........................................................program stored number
RLN ..................................................................list stored number
CIC..............................................................connect incoming call
DIC ........................................................disconnect incoming call
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 33
Page 49

Chapter 6. Configuration
When using stored numbers, V.25 bis accesses stored numbers 1 through 9 used by
front panel dialing. See Front Panel Dialing Options.
Auto Answer should be set to Disabled (shown in Figure 6-6) if V.25 bis is in
control of answering incoming calls with the CIC/DIC commands, since the
other settings for Auto Answer will override V.25 control of the answer function.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
V.25 ASYNC Dialing
V.25 bis specifies that the characters should be ASCII, 7 bits, even parity and
one stop bit. However, for versatility the ISU 128 allows the data, parity, and
stop bits as defined under Data bits. (See Figure 6-7.)
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
1=Disabled
2=Enabled
3=Dump all calls
Figure 6-6
Dial Line, Auto Answer Menu Tree
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Flow Control
9=Data Format
1=Data Bits
2=Parity Bits
3=Stop Bits
1=8 Data bits
2=7 Data bits
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
Figure 6-7
Data Bits Menu Tree
34 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 50

3=CONFIG
Chapter 6. Configuration
The setting in Figure 6-8 allows for V.25 bis messages in asynchronous (start/
stop) data format.
1=Switch protocl
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
1=Front Panel
2=RS-366
3=AT commands
4=V.25
5=Disabled
1=V.25 HDLC
2=V.25 ASYNC
3=V.25 BISYNC
4=V.25 HDLC FLAG
Figure 6-8
V.25 bis ASYNC Menu Tree
Although V.25 bis allows asynchronous data format, asynchronous DTE is
more likely to support the AT command set than V.25 bis.
V.25 SYNC HDLC Dialing
This setting provides V.25 bis messages in bit-synchronous format (for example HDLC, SDLC, X.25). The bit-synchronous format is the most commonly
used by V.25 bis.
This option specifies that the characters should be 7-bit ASCII, with the 8th bit
ignored (it may be either 0 or 1).
The first byte of each packet contains all ones (A = FF HEX), and the second
byte of each packet (the C byte) is either 13 HEX or 03 HEX if not the final packet.
V.25 SYNC BISYNC Dialing
This setting allows for V.25 bis messages in byte synchronous format (BISYNC). V.25 bis specifies that the characters should be ASCII, 7 bits, and odd
parity. This setting allows synchronous DTE which does not use HDLC to
support serial in-band dialing.
V.25 HDLC FLAG
Configuring the ISU 128 for HDLC FLAG V.25 bis enables in-band dialing
over a DTE interface using standard synchronous HDLC V.25 bis commands
with 0x7E hex idle.
Disabled
This selection disables in-band dialing over the DTE interface.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 35
Page 51

Chapter 6. Configuration
Auto Answer
The ISU 128 auto answer parameter can be configured in one of three ways:
Disabled, Enabled, or Dump all calls.
Disabled
When Disabled is selected, the ISU 128 will not automatically answer an incoming call. The AT answer command (ATA) must be issued to the ISU 128
before it accepts the incoming call. The ringing call can be dumped using the
Hang up line command, or answered using the Answer Call command.
These commands are listed under the Dial branch of the main tree. See the
chapter Dial Options for more detail.
Enabled
When Enabled is selected, the incoming call is answered. If that call is a
BONDING call and requires two B channels, the second call is answered. If
the unit is configured for a call that uses only one B channel, such as 56 kbps
or 64 kbps, the ISU 128 will not accept a second incoming call.
Dump all calls
When Dump all calls is selected, the ISU 128 will not accept any incoming
calls. This keeps the line clear for outgoing calls.
36 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 52

Answer Tone
The Answer tone option (shown in Figure 6-9) enables the transmission of a
modem answer tone at the start of voice and audio calls. The purpose of this
tone is to disable echo suppression and echo cancelling on the circuit in order
to get a clear digital circuit. This may be necessary on some long distance circuits. The specifics of the tone are 4 seconds, 2100 Hz at a -10 dB level, with
phase reversals every 475 ms.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
No Answer Tone (Default)
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
Answer Tone Menu Tree
Chapter 6. Configuration
1=No answer tone
2=Incoming tone
3=Outgoing tone
4=Always tone
Figure 6-9
This option disables Answer tone on incoming calls.
Incoming Tone
This option enables Answer tone on incoming calls.
Outgoing Tone
This option enables Answer tone on outgoing calls.
Always Tone
This option enables Answer tone on either incoming or outgoing calls.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 37
Page 53

Chapter 6. Configuration
Connect Timeout
Connect Timout sets the length of time that the ISU 128 waits for a far-end unit
to answer an outgoing call. These choices are illustrated in Figure 6-10.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
Call Screening
Call Screening allows the ISU 128 to answer all incoming calls (default) or
only calls originating from phone numbers stored in the DIAL menu as stored
numbers SN0 through SN9. See the section Front Panel Dialing Options, to review how to store numbers. Figure 6-11 illustrates the menu tree for setting
call screening.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
Connect Timeout Menu Tree
1=Switch protocl
2=Call type
3=Terminal ID
4=Dial options
5=Auto answer
6=Answer tone
7=Connect Timout
8=Call Screening
1=15 sec
2=30 sec (default)
3=1 Minute
4=2 Minute
5=4 Minute
Figure 6-10
1=Answer any
2=Ansr if SN0...9
Figure 6-11
Call Screening Menu Tree
When Call Screening is set to answer any numbers if stored in SN0 through
SN9 (Ansr if SN0...9), an incoming call is not answered if the Call ID received
from the switch does not match a stored number. Depending on the switch
protocol, the Call ID may be presented in either a seven- or ten-digit format.
38 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 54

Chapter 6. Configuration
The ISU 128 displays the Call ID for all dumped calls in the Status buffer. See
the section Status Buffer for more information on the Status buffer.
Because different switches handle calls and Call ID differently,
use the following procedure to determine if a seven or ten digit Call ID (phone
number) should be stored:
1. Select Ansr if SN0. . .9 under Call Screening.
2. Store your seven digit number in SN0.
3. Place a call to the ISU 128 with the stored number to determine whether it
answers properly.
4. If the ISU 128 does not answer the call, look at the Call ID message in the
Status buffer. An explanation of Status buffer messages is located in the
appendix Status Buffer Messages. More than likely, the Call ID number is a
ten digit number
5. Reenter the number in SN0 as it is displayed in the Call ID message and
test Call Screening again.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 39
Page 55

Chapter 6. Configuration
LEASED LINE SERVICE
This section explains how to configure the ISU 128 when using a 2B1Q leased
digital service or a service that provides a permanent connection between end
points. Figure 6-12 illustrates the menu tree for setting leased line.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
Selecting leased line configures the unit for leased line service or service that
provides a permanent connection between end points such as limited distance
modem.
Follow this step-by-step procedure to configure the ISU 128 for Leased Line
Clock mode and Channel rate.
Clock Mode:Slave/Master
By configuring the ISU 128 for Master timing, the ISU 128 can provide clocking for both ends of the phone line. This Master option is used at one end of a
limited distance modem application, where two ISU 128 units are directly connected without the use of channel banks (see Figure 6-13). The far-end unit
should be configured for Slave and it derives its clocking from the ISU 128
configured as Master.
1=Dial Line
2=Leased Line
1=Slave
1=Clock mode
2=Channel rate
2=Master
1=64k
2=128k
Figure 6-12
Leased Line Menu Tree
ISU 128
123
ENTER
456
789
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
#0
CANCEL
*
DTE DTE
ISU 128
Master
18,000 Ft
Mixed Gauge Wire
ISU 128
123
ENTER
456
789
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
#0
CANCEL
ISU 128
Leased 128K
*
Figure 6-13
Limited Distance Modem Application
40 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 56

Chapter 6. Configuration
If two ISU 128 units are connected through channel banks, both units should
be configured for Slave mode (see Figure 6-14). To easily configure ISU 128s
for this application, one unit can be optioned using Quick Setup, Ldm 128
Master and the other using Quick Setup, Leased 128k sync. For more information, refer to the chapter Quick Setup.
DTE
Channel Rate
In Leased Line operation, the data rate for the ISU 128 can be configured for
64 kbps or 128 kbps. When 64 kbps is selected, only one bearer channel (B1) is
used. When 128 kbps is selected both bearer channels (B1 and B2) are used.
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
ISU 128
BIMUX DP
or Equivalent
XXXXX
XXXXX
ISU 128
123
ENTER
456
789
#0
CANCEL
*
XXXXXXXXX
T1
BIMUX DP
or Equivalent
XXXXX
XXXXX
XXXXXXXXX
RS CS TD RD LD TR SR
ISU 128
ISU 128
123
ENTER
456
789
#0
CANCEL
*
DTE
Figure 6-14
Leased Application with Channel Banks
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 41
Page 57

Chapter 6. Configuration
DTE OPTIONS
The following procedure configures the DTE options for asynchronous and
synchronous applications. Figure 6-15 and Figure 6-16 illustrate the menu
trees for both asynchronous and synchronous operation.
Ensure your DTE equipment is set for asynchronous operation before attempting to
make an asynchronous call. Failure to do so will cause the call attempt to fail.
3=CONFIG
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
Asynchronous DTE Options Menu Tree
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Flow Control
9=Data Format
Figure 6-15
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Transmit Clock
Figure 6-16
Synchronous DTE Options Menu Tree
Bit Rate
The Bit Rate can be set asynchronously for 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200,
38400, 57600, and 115200 bps.
The Bit Rate can be set synchronously for 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 48000,
56000, 64000, 112000, and 128000 bps.
42 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 58

Connector Type
The ISU 128 can provide an EIA-232, RS-530, or V.35 interface to a DTE by selecting the desired connector type.
RTS Options
Selecting 1 MS delay causes the Clear-to-Send (CTS) signal to change states 1
millisecond after the DTE Ready-to-Send (RTS) signal changes state. The 18
MS delay causes the CTS signal to change state 18 milliseconds after the DTE
RTS signal changes state.
CTS Options
Selecting Forced CTS causes the CTS signal on the DTE connector to be continually asserted. Selecting Follows RTS causes the CTS signal to follow the
state of the RTS lead.
CD Options
Selecting CD Forced on causes the carrier detect (CD) signal to always be asserted. Selecting Normal causes the CD signal to be asserted when a call has
been successfully established. Selecting Off with LOCD causes the CD signal
to be disasserted for a period of 5 seconds, then reasserted at the termination
of a call. Selecting Off with Link Down causes the CD signal to be disasserted
when the U-interface is not present.
Chapter 6. Configuration
DTR Options
Selecting Ignore DTR causes the ISU 128 to disregard the state of the data ter-
minal ready (DTR) pin. Cmd when Off forces the unit into the AT command
processor mode when DTR is not asserted. To return on-line, DTR must be asserted, followed by the AT0 command. Idle when Off forces the unit to end
the current call when DTR is no longer asserted. Off>On dial #0 allows one
call attempt to be automatically established when the DTR signal goes from inactive to active. While DTR is active, front panel dialing is also possible.
When DTR goes inactive, any outgoing call present is disconnected. Off>On
dial #0 uses the phone number in stored number register 0 to establish the call.
To store a number for automatic dialing see the chapter Dialing Options. Selecting Dial #0 if On allows calls to be automatically established when the
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 43
Page 59

Chapter 6. Configuration
DTR signal is in the active state. The unit attempts to establish a call using SN0
until the call is established or DTR goes inactive. Selecting Answer if On only
allows the unit to answer an incoming call if the DTR signal is asserted. Dial/
Ans if On... allows the unit to dial Stored Number 0 or answer if DTR is asserted.
DSR Options
Selecting DSR forced on causes the Data Set Ready (DSR) signal on the DTE
connector to always be asserted. Selecting OFF Idle+Test causes DSR to be
disasserted if the network interface is in test or there is not an active call. OFF
Link Down causes DSR to be disasserted if the network interface is disrupted.
Flow Control (Asynchronous Data Format)
Selecting Hardware Flow (as shown in Figure 6-17) causes the ISU 128 received data to be presented to the DTE interface only when RTS is asserted.
Software Flow control uses Xon/Xoff to control data transferred between the
DTE and the ISU 128. Selecting No Flow Ctrl disables flow control.
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Flow Control
9=Data Format
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
1=Hardware Flow
2=Software Flow
3=No Flow Ctrl
Figure 6-17
Flow Control Menu Tree
44 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 60

Data Format (Asynchronous)
A frame consists of a start bit, 7 or 8 data bits, 0 or 1 parity bit, and 1 to 2 stop
bits. The settings for Data Bits, Parity Bits, and Stop Bits are available as
shown in Figure 6-18.
1=Bit Rate
2=Connector Type
3=RTS Options
4=CTS Options
5=CD Options
6=DTR Options
7=DSR Options
8=Flow Control
9=Data Format
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Asynchronous
2=Synchronous
Transmit Clock (Synchronous Data Format)
Chapter 6. Configuration
1=8 Data Bits
2=7 Data Bits
1=Data Bits
2=Parity Bits
3=Stop Bits
1=None
2=Odd
3=Even
1=1 Stop bit
2=1.5 Stop bits
3=2 Stop bits
Figure 6-18
Data Format Menu Tree
Selecting the Normal option causes the ISU 128 to be the synchronous DTE interface transmit timing source. Transmit data is timed from the transmit clock
provided by the ISU 128 on the DTE connector. Normal clock is the normal
mode of operation for the ISU 128.
With the External option selected, the ISU 128 slaves to an external transmit
timing source. The external clock is provided to the ISU 128 by the external
transmit clock signal at the DTE connector. This signal is echoed by the ISU
128 to the transmit clock signal on the DTE connector.
This option provides for situations where equipment connected to the ISU 128
DTE connector cannot slave to the ISU 128 provided clock. The ISU 128 uses
the U-interface as the frequency standard when it must provide a synchronous
receive or transmit clock. The externally provided clock must be of the same
average frequency as the clock that the ISU 128 would provide if internal clock
were selected. If this is not the case, then bit errors may occur.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 45
Page 61

Chapter 6. Configuration
46 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 62

PROTOCOL OPTIONS
The ISU 128 communicates with many different types of telecommunication
equipment including other ISU 128s, ISDN terminal adapters, Switched 56
DSUs, BONDING-compatible inverse multiplexers, and V.34 (1202029L3 only)
compatible analog modems. Communicating between such diverse types of
equipment requires the use of various rate adaptation protocols to support
various bit rates and DTE settings. Figure 7-1 illustrates the menu tree for setting protocol options. The ISU 128 supports the following rate adaptation protocols:
• Clear Channel (no rate adaption protocol)
• BONDING mode 1 (Bandwidth on Demand Interoperability Group)
• CCITT V.120
• CCITT V.110
Chapter 7
Protocol Options
• V.34 (for communicating with analog modems)
V.34 is only available in PN 1202029L3
• DSU 56.7 Async (for communication with ADTRAN DSUs)
• TLINK (Dial Switched 2-wire 56 or Datapath DSU)
• SAP (Simple ADTRAN Protocol)
• FALLBACK
• Point-to-point protocol (PPP) asynchronous to synchronous conversion
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 47
Page 63

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
3=CONFIG
See the section Recommended Operating Protocols and Table 1-B in Chapter 1 for
more information on recommended modes of operation.
The desired protocol may be selected with AT commands at the DTE port or
from the ISU 128 front panel. A description of each protocol follows.
Clear Channel
Clear Channel provides the entire bearer channel to the DTE without regard
to data format or protocol. This provides a rate adaptation at or near the ISDN
circuit rate. The primary usage for Clear Channel in the dial line mode is for
56 kbps and 64 kbps synchronous. It is useful when the DTE performs its own
internal synchronous protocol/rate adaptation or the ISU 128 is calling a 4wire Switched 56 DSU. In the leased line mode, Clear Channel can provide
synchronous bit rates of 56 kbps, 64 kbps, 112 kbps, and 128 kbps.
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
Figure 7-1
Protocol Menu Tree
BONDING Mode 1
The BONDING mode 1 protocol allows the ISU 128 to communicate at bit
rates in excess of 64 kbps to a maximum of 128 kbps. BONDING provides
high-speed communication between ISU 128s, ISDN TE/TAs, and inverse
multiplexing equipment supporting the BONDING protocol. The protocol allows use of both synchronous and asynchronous bit rates. When the ISU 128
uses the BONDING mode 1 protocol, it must make two separate ISDN phone
calls to seize control of both ISDN bearer channels. The protocol corrects any
delays existing between the two bearer channels and presents a single high
speed data channel to the DTE. For successful high-speed operation, both the
48 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 64

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
near- and far-end DCE need to be configured to use the BONDING mode 1
protocol. Also, if the second B channel number is different from the first B
channel, it is important that the 7-digit LDN is programmed in the answering
unit. The BONDING mode 1 protocol negotiation phase has numerous timers
to allow for transmission delays due to satellite hops, international calls, etc.
The timers may be adjusted if necessary by entering into the BONDING mode
1 submenu. Figure 7-2 illustrates the menu path for setting the timers.
1=TXINIT
2=TXFA
3=TXADD01
4=TXDEQ
5=TANULL
6=TCID
7=BONDING Method 1=ADTRAN Only
2=Multivendor
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
Figure 7-2
BONDING Mode 1 Protocol Menu Tree
The timers are defined as follows:
TXINIT
This option specifies the length of time the originating endpoint attempts to
detect the BONDING negotiation pattern from the answering endpoint before
deciding the BONDING call has failed. In general, this timer value should be
left at the factory default setting of 10 seconds. Values of 1, 2, 5, 10 (default),
20, 50, 100, and 200 seconds may be selected.
TXFA
This option specifies the length of time both endpoints attempt to detect the
BONDING frame pattern when a call is connected before deciding the BONDING call has failed. This timer value should be left at the factory default setting
of 10 seconds. However, when interoperating with other manufacturers’
BONDING equipment, it may be necessary to lengthen this timer so that it
matches TXADD01. Values of 1, 2, 5, 10 (default), 20, 50, 100, and 200 seconds
may be selected.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 49
Page 65

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
TXADD01
This option specifies the length of time both endpoints wait for the additional
call to be connected at the end of negotiation before deciding the BONDING
call has failed. The factory default setting of 20 seconds will be sufficient for
most calls to go through, although when dialing overseas it may be necessary
to lengthen this timer to allow for slower call routing. Values of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20,
50 (default), 100, and 200 seconds may be selected.
TXDEQ
This option specifies the length of time both endpoints attempt to equalize the
network delay between the bearer channels before deciding the BONDING
call has failed. The default setting is 50 seconds. Values of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50
(default), 100, and 200 seconds may be selected.
TANULL
This option specifies the length of time the answering endpoint attempts to detect the BONDING negotiation pattern from the originating endpoint before
aborting to clear channel mode. In general, this timer value should be left at
the factory default setting of 10 seconds. However, it may be necessary to
shorten this timer, if the DTE equipment connected to the ISU also has timer
constraints for completing non-BONDING parameter negotiation. Values of
1, 2, 5, 10 (default), 20, 50, 100, and 200 seconds may be selected.
TCID
This option specifies the length of time both endpoints attempt to negotiate an
agreeable value for bearer channels and channel capacities before deciding the
BONDING call has failed. This timer default setting is 5 seconds. Values of 1,
2, 5 (default), 10, 20, 50, 100, and 200 seconds may be selected.
V.120
The V.120 protocol is a CCITT compliant rate adaption method which provides DTE service between the ISU 128 and other V.120 compliant devices at
rates less than the 64 kbps ISDN bearer channel rate. V.120 supports synchronous and asynchronous DTE rates. See the section Recommended Operating
Modes and Table 1-B in Chapter 1 for available V.120 rates. Figure 7-2 illustrates the menu path for selecting V.120.
50 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 66

V.110
V.34
Chapter 7. Protocol Options
The V.110 protocol is a CCITT compliant rate adaption method which provides DTE service between the ISU 128 and other V.110 compliant devices.
V.110 supports synchronous and asynchronous DTE rates. See the section
Recommended Operating Modes and Table 1-B in Chapter 1 for available V.110
rates. Figure 7-2 illustrates the menu path for selecting V.110.
The V.34 protocol allows the ISU to originate and receive calls to analog modems on POTS lines. The V.34 modem only supports asynchronous DTE rates.
To place an outgoing call to an analog modem, the call type must be changed
to Audio. See Call Type in Chapter 6 to change call types. Figure 7-3 illustrated
the menu path for selecting the V.34 modem operational parameters.
The ISU 128 with optional V.34 modem (part number 1202029L3) must be used for
operation of this protocol.
Error Control
This option sets the type of error control to be negotiated with the far-end modem during train-up. Normal turns all error control off and makes allowances
for flow control. Reliable MNP uses MNP error control. If the far end does
not support MNP then the call is terminated. When Auto-Rel MNP is selected, the ISU 128 attempts to use MNP error control. If the far end does not use
MNP then normal operation is used. Force LAPM allows only LAPM (V.42)
error corrected calls to connect. Force MNP allows only MNP error corrected
calls to connect.
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
1=Error Ctrl
2=Compression
3=MNP Blk Size
1=Normal
2=Direct
3=Reliable MNP
4=Auto-Rel MNP
5=Force LAPM
6=Force MNP
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
Figure 7-3
V.34 Error Control Menu Tree
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 51
Page 67

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
Compression
No Compression turns off the MNP5 compression algorithms in the ISU 128.
Compress MNP5 enables MNP5 data compression. Compress V42 enables
V.42 bis data compression. Compress V42/MNP5 allows the 128 to negotiate
MNP5 or V.42 bis compression.
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
1=Error Ctrl
2=Compression
3=MNP Blk Size
1=No Compression
2=Compress MNP5
3=Compress V42
4=Comp V42 MNP5
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
V.34 Compression Menu Tree
Microcom™ Network Protocol Block Size (MNP® Blk)
When error control is enabled, this option sets the amount of data sent in a single packet during MNP error-controlled stream operation. Options available
are 64, 128, 192, and 256 bytes.
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
1=Error Ctrl
2=Compression
3=MNP Blk Size
1=64 bytes
2=128 bytes
3=192 bytes
4=256 bytes
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
V.34 MNP Block Size Menu Tree
Figure 7-4
Figure 7-5
52 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 68

DSU 57.6 ASYNC
The DSU 57.6 ASYNC or DSTOP protocol allows the ISU 128 to communicate
asynchronously at 57.6 kbps with ADTRAN 2- and 4-wire Switched 56 DSU
products. In addition, the ISU 128 will communicate with other ISUs over dial
and leased connections using this protocol. Figure 7-1 illustrates the menu
path for setting the DSU 57.6 ASYNC protocol.
T-Link
The T-Link protocol allows the ISU 128 to communicate with 2-wire Switched
56 DataPath Data Units (DUs) such as the ADTRAN DSU III 52W. The T-Link
protocol performs two functions:
• The T-link protocol adapts DTE data subrates of 64 kbps to the 64 kbps
bandwidth of the ISDN bearer channel.
• For asynchronous and synchronous DTE rates up to 19.2 kbps, T-Link
transmits the status of the DCE-DTE EIA leads to facilitate flow control
and maintenance.
Chapter 7. Protocol Options
In addition to 2-wire Switched 56 DataPath DUs, the ISU 128 can communicate
with any other device that uses the T-Link protocol. Figure 7-1 shows the
menu path for selecting T-Link.
Simple ADTRAN Protocol (SAP)
Simple ADTRAN Protocol (SAP) is a rate adaption method providing DTE
service between ISU 128 units at a sub 64 kbps ISDN bearer channel rate. Selecting this menu item causes the ISU 128 to use SAP protocol.
The primary usage for SAP is general purpose asynchronous rate adaption in
a dial-up or leased environment. SAP only operates on a 64 kbps data link.
See Figure 7-2 for the menu path to select SAP.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 53
Page 69

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
FALLBACK
The FALLBACK asynchronous rate adaption protocol provides the capability
to automatically establish calls with other ISDN terminal adapters, Switched
56 DSUs, V.34 modems (optional), as well as other ISUs using a single configuration. To communicate with analog modems, the ISU 128 with V.34 modem
option (part numbers 1202029L3) must be used.
The ISU 128 must be optioned as follows for FALLBACK operation:
• Any asynchronous bit rate up to 115.2 kbps which is supported by the
DTE.
• Flow control must be enabled and supported by the DTE.
FALLBACK supports the following protocols based on the call type: BONDING Mode 1, V.120, T-Link, and V.34.
When answering calls, the ISU 128 uses the incoming call type to determine
which rate adaption protocols to support. See Table 7-A for the call type and
the supported rate adaption protocols.
Table 7-A
Rate Adaption Protocols
Call Type
Data 64k BONDING Mode 1 ISUs
Data 56k V.120 ISDN TAs
Speech or Audio V.34 V.34 compatible modems
54 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Rate Adaption
Protocols Supported
V.120 ISDN TAs
PPP PPP compatible bridges/routers
T-Link 2-Wire Switched-56 DSUs
PPP PPP compatible bridges/routers
Typical Units Supported
Page 70

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
When originating calls to unknown units, the ISU begins protocol selection
based on the local call type. Data 64k is used for FALLBACK selected from
Quick Setup menu. Upon connection at 64k call type, BONDING, V.120, and
PPP are attempted. If connection is not made at 64k, the ISU 128 attempts another call at 56k call type. If connection is made at 56k, then V.120, T-Link, and
PPP are attempted. If connection is not made at 56k, then an audio call type is
attempted, provided the ISU 128 with the V.34 modem option is used. If the
ISU connects the audio call type, the V.34 protocol is attempted for V.34 compatible modems. Once a call connects, if the protocol cannot be negotiated, the
protocol is negotiated as specified by S11 register (default is DSTOP). If this
protocol fails, the call is disconnected.
If FALLBACK fails to determine which protocol is running, the user has the
option to select which protocol will run. Figure 7-6 illustrates the FALLBACK
default settings.
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=FALLBACK
0=PPP asyn-sync
1=Fallback Def.
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING Mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=V.110
6=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
7=T-LINK
8=SAP
9=PPP asyn-sync
Figure 7-6
FALLBACK Menu Tree
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 55
Page 71

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
Point-to-Point (PPP) Async-to-Sync
PPP provides a standard method for transporting multi-protocol datagrams
over point-to-point links. The ADTRAN PPP async-sync protocol allows the
ISU 128 and a PC or Macintosh® running PPP software, to communicate with
a PPP-compatible bridge or router. The PPP async-sync protocol complies
with Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) RFC 1662. The menu path to select PPP is shown in Figure 7-7.
The asynchronous control character map (ACCM) option is scanned during
the negotiation. When the ACCM option is seen in a configure ACK link control packet, it is adopted by the ISU 128. In addition, when the ACCM option
is not seen in the configure-request packet from the network, the ISU 128 adds
it to the packet.
1=Clear Channel
2=BONDING mode 1
3=V.120
4=V.34
5=DSU 57.6 ASYNC
6=T-LINK
7=SAP
8=FALLBACK
9=PPP asyn-sync
1=METHOD
1=PPP
2=Multilink PPP
3=PPP w/ Comp
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
PPP Menu Tree
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
The ISU 128 is configured for PPP from the protocol options of the configuration menu by selecting 1=PPP or by setting S-register S27 to a value of 0. Figure 7-6 illustrates the menu path for setting PPP, Multilink PPP, and PPP w/
Comp.
Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol (MP)
Multilink PPP is an extension of point-to-point protocol and is a method for
splitting and recombining data packets across multiple logical data links.
Figure 7-7
56 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 72

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
The ISU 128 is configured for multilink PPP from the protocol options of the
configuration menu by selecting 2=Multilink PPP or by setting S-register S27
to a value of 1. In this mode, the ISU 128 dials a second number to establish a
second point-to-point link. Once the second link is established, multilink PPP
is performed over both B-channels.
The phone number for the second call should be placed in stored number 1
(SN1). If no number is stored in SN1, the same phone number is dialed to establish the second link.
PPP with Compression
The ISU 128 is configured for PPP with compression from the protocol options
of the the configuration menu by selecting 3=PPP w/Comp or by setting S-register S27 to a value of 2.
When setup for PPP with compression, the ISU 128 will negotiate the compression control protocol (CCP) with the network PPP peer. If STAC™ compression is successfully negotiated with the peer, data packets from the DTE are
compressed before being sent out through the network. Likewise, compressed
packets from the network are decompressed before being transmitted through
the DTE.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 57
Page 73

Chapter 7. Protocol Options
58 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 74

QUICK SETUP CONFIGURATION
To configure the DTE Options quickly and easily, the Quick Setup menu is
available to automatically set up the most common DTE configurations (Figure 8-1). For fine-tuning a particular application and DTE settings, see the section DTE Options for Asynchronous and Synchronous Operation in Chapter 6 for
a step-by-step procedure for configuration of the DTE Options.
Chapter 8
Quick Setup
1=Dial 56K sync
2=Dial 64K sync
3=Dial 112K sync
4=Dial 128K sync
5=Dial PPP
6=V34 115.2 async
7=Dial 57.6 asyn
8=Dial 115.2 asy
9=Fallback 57.6k
0=More
1=Leased 128k
2=Ldm 128 Master
3=TBD
4=TBD
5=TBD
6=TBD
7=TBD
3=CONFIG
1=Netw. options
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
Figure 8-1
Quick Setup Menu Tree
Option 1=DIAL 56K sync will always flash upon entry of the Quick Setup Menu re-
gardless of previous configuration selections.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 59
Page 75

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
Quick Setup
To assist in configuring the DTE options for the ISU 128, ten common configurations are preset in Quick Setup. These include:
• Synchronous dial operation for 56, 64, 112, and 128 kbps
• Asynchronous dial operation for 57.6, and 115.2 kbps
• 128 kbps Leased service
• 128 kbps Limited Distance Modem using Master Clocking
• V.34 modem service
• Fallback 57.6
In the following descriptions, an asterisk (*) following the option indicates the option
requires ISDN switch protocol to be configured. Multipoint lines will also require
SPID1 & LDN1. See the chapter Dial Options.
Dial 56K sync*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 56K sync service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
Automatic answering...................................................... Enabled
ISDN call type ..................................................................56 kbps data
Data protocol.................................................................... Clear Channel
DTE mode ......................................................................... Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................56 kbps
DTE flow control.............................................................. none
RTS line .............................................................................1 ms delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Normal clock source
V.54 Loopbacks ................................................................Accepted
60 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 76

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
Dial 64K sync*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 64K sync service the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
Automatic answering...................................................... Enabled
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data protocol ....................................................................Clear Channel
DTE mode .........................................................................Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................64 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................none
RTS line..............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Normal clock source
V.54 Loopbacks ................................................................Accepted
Dial 112K sync*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 112K sync service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
Automatic answering...................................................... Enabled
ISDN call type ..................................................................56 kbps data
Data protocol ....................................................................BONDING mode 1
DTE mode .........................................................................Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................112 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................none
RTS line..............................................................................1 ms delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Internal clock source
BONDING timer TXINIT ...............................................10 seconds
BONDING timer TXFA................................................... 10 seconds
BONDING timer TXADD01........................................... 50 seconds
BONDING timer TXDEQ ...............................................50 seconds
BONDING timer TANULL ............................................ 10 seconds
BONDING timer TCID ...................................................5 seconds
V.54 Loopbacks ................................................................Accepted
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 61
Page 77

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
Dial 128K sync*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 128K sync service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
Automatic answering...................................................... Enabled
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data protocol.................................................................... BONDING mode 1
DTE mode ......................................................................... Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................128 kbps
DTE flow control.............................................................. None
RTS line .............................................................................1 ms delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Internal clock source
BONDING timer TXINIT ...............................................10 seconds
BONDING timer TXFA................................................... 10 seconds
BONDING timer TXADD01........................................... 50 seconds
BONDING timer TXDEQ ...............................................50 seconds
BONDING timer TANULL ............................................ 10 seconds
BONDING timer TCID ...................................................5 seconds
V.54 Loopbacks ................................................................Accepted
Dial PPP*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial PPP service, the following parameters
are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data Protocol.................................................................... PPP asyn-sync
DTE mode ......................................................................... Asynchronous
Data Bits ............................................................................8
Parity Bits.......................................................................... None
Stop Bits............................................................................. 1
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................Hardware
DTE flow control.............................................................. None
RTS line .............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Follow RTS
62 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 78

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
V34 115.2 async*
When the ISU 128 is configured for V34 115.2 async service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
ISDN call type ..................................................................Audio
Data Protocol ....................................................................V.34
DTE mode .........................................................................Asynchronous
Data Bits ............................................................................8
Parity Bits.......................................................................... None
Stop Bits............................................................................. 1
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................115.2 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................Hardware
RTS line..............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Follows RTS
Error Control ....................................................................Auto-reliable
Compression.....................................................................Compress V42/MNP5
MNP block size ................................................................256 bytes
This option is only used with the ISU 128 with V.34 modem option (part numbers
1202029L3).
Dial 57.6 asyn*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 57.6 asyn service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data Protocol ....................................................................V.120
DTE mode .........................................................................Asynchronous
Data Bits ............................................................................8
Parity Bits.......................................................................... None
Stop Bits............................................................................. 1
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................57.6 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................None
RTS line..............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 63
Page 79

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
Dial 115.2 asyn*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Dial 115.2 asyn service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... ISDN dial line
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data Protocol.................................................................... BONDING mode 1
DTE mode ......................................................................... Asynchronous
Data Bits ............................................................................8
Parity Bits.......................................................................... None
Stop Bits............................................................................. 1
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................115.2 kbps
DTE flow control.............................................................. Hardware
RTS line .............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Follows RTS
Fallback 57.6k*
When the ISU 128 is configured for Fallback 57.6k service, the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... Dial line
Automatic answering...................................................... yes
ISDN call type ..................................................................64 kbps data
Data Protocol.................................................................... Fallback
DTE mode ......................................................................... Asynchronous
Data Bits ............................................................................8
Parity Bits.......................................................................... None
Stop Bits............................................................................. 1
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................57.6 kbps
DTE flow control.............................................................. Hardware
RTS line .............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Follows RTS
64 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 80

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
More
More takes the user into the following level of choices:
Leased 128K
When the ISU 128 is configured for Leased 128K service the following parameters are automatically preset:
Service type....................................................................... Leased Line
Network clock source...................................................... Slave
Channel rate...................................................................... 128K
Data Protocol ....................................................................Clear Channel
DDS loopbacks enabled .................................................. Yes
DTE mode .........................................................................Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................128 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................none
RTS line..............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Normal clock source
Ldm 128 Master
When the ISU 128 is configured for a point-to-point application such as a limited distance modem (LDM) arrangement, the Ldm 128 Master option automatically presets the following parameters:
Service type....................................................................... Leased Line
Network clock source...................................................... Master
Channel rate...................................................................... 128K
Data Protocol ....................................................................Clear Channel
DDS loopbacks enabled .................................................. Yes
DTE mode .........................................................................Synchronous
DTE connector bit rate ....................................................128 kbps
DTE flow control..............................................................none
RTS line..............................................................................1 msec delay
CTS line .............................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock .........................................................Normal clock source
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 65
Page 81

Chapter 8. Quick Setup
Factory Setup
This option restores the ISU 128 to the factory default setup:
Service type................................................................ISDN dial line
ISDN switch protocol...............................................AT&T 5ESS
ISDN call type ...........................................................64 kbps data
Dialing Mode.............................................................Front Panel
Data protocol.............................................................Clear Channel
DTE connector bit rate .............................................64 kbps
DTE flow control.......................................................none
RTS line ......................................................................Forced on
CTS line ......................................................................Forced on 1 msec after RTS
CD line........................................................................Turned on when call is up
DSR line......................................................................Forced on
Transmit data clock ..................................................Internal clock source
BONDING timer TXINIT ........................................10 seconds
BONDING timer TXFA............................................10 seconds
BONDING timer TXADD01....................................10 seconds
BONDING timer TXDEQ ........................................50 seconds
BONDING timer TANULL .....................................50 seconds
BONDING timer TXID ............................................5 seconds
AT Commands Escape character............................+
End-of-Line character value....................................13
Line Feed character value........................................10
Backspace character value.......................................8
Transmit Data Clock.................................................Normal clock source
66 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 82

DIALING OPTIONS
Selecting 4=DIAL or pressing the # (pound) key from the Current Status menu
displays the front panel available dialing options. (See Figure 9-2.) Access the
VT 100 terminal dial options screen (Figure 9-1) by pressing Ctl-D from any
screen. The dial options are only available when the ISU is configured for Dial
Line operation (not Leased Line).
Chapter 9
Dial Options
Figure 9-1
VT 100 Terminal Dial Options Screen
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 67
Page 83

Chapter 9. Dial Options
Hang Up Line
Terminates current call.
Dial Number
Enter and dial a number from the keypad. If an error is made while entering a
number, press the Down arrow to correct the mistake. Press Cancel twice consecutively to exit this menu item without dialing a number. Press Enter to dial
the number and save as stored number 9 for redialing purposes.
4=DIAL
1=Hang up line
2=Dial number
3=Redial last #
4=Answer Call
5=Dial stored #
6=Store/Review #
Figure 9-2
Dial Menu Tree
Redial Last Number
Redial the last number called (or attempted). This number is saved as stored
number 9 from the last attempted phone call.
Answer Call
Selectively answer incoming calls when Auto Answer is configured for disable. (Auto Answer is described in the section Auto Answer in Chapter 6.)
Dial Stored Number
Dial one of ten stored phone numbers. The Up and Down arrows permit viewing and selecting of stored number. Press Enter to dial the number and save as
stored number 9 (SN9) for redial purposes.
68 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 84

Store/Review Number
Enter and review stored numbers. Press the Up or Down arrow to scroll
through the 10 stored numbers (SN0 - SN9). To store a number, scroll to the
desired stored number location, enter the number to be stored, and press Enter
to save the number. If a mistake is made, use the Up and Down arrows to edit
the number. Press Enter to save the number and exit. Press Cancel to exit without changing the number.
The Dial Options Menu must be exited after dialing in order for CD (carrier detect)
to be activated.
Chapter 9. Dial Options
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 69
Page 85

Chapter 9. Dial Options
70 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 86

Remote Configuration
Remote Configuration
Remote Configuration allows configuration and testing of a remote unit by
calling the remote unit from a local unit. The remote unit can be configured
using AT commands, the Front Panel, or the VT 100 terminal interface.
There are six items that cannot be set through remote configuration. The items
are Dial Line Mode, SPID(s), LDN(s), Switch Type, Quick Setup, and Factory
Default.
Configuring with AT Commands
A remote unit can be configured by issuing an ATD command with the phone
number of the remote unit plus a dial string modifier. The configuration command syntax is:
ATD nnnnnnn#6#yyyyyy
Where nnnnnnn is the remote number to call, and yyyyyy is a password of up
to six digits.
Chapter 10
After the connection is established, AT commands issued to the local unit are
sent to the remote unit and executed. The remote unit sends response back to
the local unit which then sends the response out of the DTE interface connector. See the appendices AT Commands and S-Registers of the ISU 128 manual
for a complete list of commands.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 71
Page 87

Chapter 10. Remote Configuration
Configuring and Testing with the Front Panel or
VT 100 Terminal
The menu path to follow to select remote configuration on the Front Panel is
shown in Figure 10-1.
1=Netw. options
3=CONFIG
When using the VT 100 terminal interface, select the main menu option Cfg.
Rmt. Unit. The Remote Configuration screen appears as shown in Figure 10-2.
2=DTE options
3=Protocol
4=Quick setup
5=Remote config
1=Cfg. Rmt. Unit
2=Set Password
3=Loopback remote 1B
4=Loopback remote 2B
Remote Configuration Menu Path
Figure 10-1
Figure 10-2
Remote Configuration Screen
72 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 88

Configure Remote Unit
This option allows configuration of a remote ISU 128. The Front Panel will display a prompt for the remote number to dial. Enter a number and press Enter
to continue. A prompt for the remote password is displayed. Enter up to six
digits for the password to access the remote unit and press Enter to continue.
The Front Panel displays status information about the call. When a connection
is established, the Front Panel will display information as if it were the remote
unit. If the connection was not successful, the Front Panel displays information for the local unit connection. Pressing Cancel anytime up to this point
cancels the call. Pressing Cancel at the first remote display screen or selecting
Hang up line disconnects the call.
Figure 10-2 illustrates the VT 100 terminal screen when Cfg. Rmt. Unit is selected from the main menu. Enter the remote number to call and press Enter.
When prompted, enter the password and press Enter. If a password has not
been set for accessing the remote unit, press Enter. The VT 100 terminal will
first display the Status Menu screen as it attempts to connect to the remote
unit. Once successfully connected, the terminal will change back to the Configuration Menu screen and display remote information as if the remote unit
were connected to the VT 100 terminal. Figure 10-3 illustrates the terminal
screen when connected to a remote ISU 128. The call may be terminated by selecting Hang up line from the Dial menu.
Chapter 10. Remote Configuration
Figure 10-3
Remote Unit Configuration Screen
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 73
Page 89

Chapter 10. Remote Configuration
The Front Panel can only be used to configure other ISU devices with front panels. AT
commands and the VT 100 terminal can be used to configure any ISU device that supports remote configuration, such as the Express XR/XRT and the ISU 2x64 Rackmount.
Remote Testing
Two tests may be performed from the local unit before connecting to the remote unit. Figure 10-4 illustrates the menu path for choosing Loopback Remote 1B and Loopback Remote 2B from the Test menu on the front panel.
2=TEST
Loopback Remote 1B
The Lpbk Remote 1B option allows a local unit to call, loopback, and BERT
test a remote unit on one B-channel if both the local and remote units are configured for Fallback protocol. The Front Panel and VT 100 terminal will
prompt for the remote number to dial. When a connection is established, error
information is displayed. Press 1) Exit Test or Escape to exit the test. Figure
10-5 illustrates the VT 100 terminal while testing Loopback Remote 1B.
1=Loopback DTE
2=Loopback Netw.
3=Loopback Proto
4=Loopback Remote
5=Test Remote
6=Lpbk Disable
7=NEBE/FEBE
0=Software Ver
Figure 10-4
Test Menu Path
Loopback Remote 2B
The Lpbk Remote 2B option allows a local unit to call, loopback, and BERT
test a remote unit on two B-channels if both the local and remote units are configured for Fallback protocol. The Front Panel and VT100 terminal will
prompt for the remote number to dial. When a connection is established, error
information will be displayed. Press 1) Exit Test or Escape to exit the test.
Set Password
The Set Password option allows the user to store a password up to six digits
for remote configuration access. If a password is entered, any other unit used
to configure this unit remotely must send a password matching the stored
password. If passwords do not match, the remote configuration fails to
74 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 90

Chapter 10. Remote Configuration
connect. The screen from a VT 100 terminal is illustrated in Figure 10- 6. To
set the password, choose Set Password from the Main Configuration Menu.
Type the six digit (or less) password, then press Enter. To clear the existing
password, do not enter numbers for Set Password. Just press enter.
Figure 10-5
Loopback Remote 1B
Figure 10-6
Set Password Screen
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 75
Page 91

Chapter 10. Remote Configuration
76 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 92

When the ISU 128 powers up, it performs an internal self test. This takes about
10 seconds. At the end of the test, the front panel displays Self Test Passed.
IF SELF TEST FAILS
If Self Test Passed is not displayed, perform the following procedure to verify
if the problem can be fixed locally:
1. Ensure that the ISU 128 is receiving power and is switched on.
2. Turn off the ISU 128. While holding down the 0 key, power back on. Con-
tinue to press 0 for 15 seconds. This will reset all the internal settings to
factory defaults.
3. If the ISU 128 still does not pass self test, call ADTRAN Technical Support
for assistance. See the back of this manual for phone numbers.
IF THE ISU 128 DOES NOT READ READY
Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
When the ISU 128 has been set up and connected to an ISDN line but the front
panel does not read Ready after a few minutes, use the following troubleshooting procedure:
1. Cycle power on the ISU 128, leaving it off for a minimum of two seconds.
Turn the power on for one minute to ensure the unit does not read Ready.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 77
Page 93

Chapter 11. Troubleshooting
2. Disconnect the ISU 128 from the ISDN line. From a functioning voice
phone, call the local directory number(s) provided with your line. Calling
a good ISDN line with nothing connected usually results in a ring or fast
busy tone. If someone answers or a not-in-service intercept is received,
there is probably something wrong with the translation of the ISDN line.
The phone service provider should be able to help.
3. If the ISU 128 continues to read Link Down, there is a physical problem
with the ISDN phone line (more than likely, a problem with the Layer 1
setup). The problem may be one or more of the following:
• The ISU 128 software setup
• The ISU 128 hardware
• The wiring on your premises
• The telephone service provider's wiring
• The telephone service provider's hardware
• The telephone service provider's software setup
To isolate the problem, perform the following procedure:
A. Make sure the ISU 128 is configured for dial line service. Check that
CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial Line, is selected on the menu.
B. Try another piece of functioning ISDN equipment with a U-interface
on the ISDN line.
C. Talk to your service provider and ensure you have an ISDN Basic
Rate U-Interface with 2B1Q line coding (wrong options are an S or T
interface or AMI line coding).
D. Ensure that your ISDN phone line is connected to the actual telephone
line (U-interface) provided by your telephone company. Make sure your
ISDN line is not connected though another piece of equipment such as
an NT1 in a wiring closet somewhere.
E. Make sure nothing else is bridged across the ISDN line pair.
F. With a minimum of extra wiring, try connecting to the ISDN line pair
at the point where service provider's wiring ends.
78 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 94

Chapter 11. Troubleshooting
G. With the ISU 128 connected to the ISDN line and powered up, talk to
your service provider's repair group and inform them that your ISDN
basic rate line has a physical layer 1 problem. Ask them to check the
ISDN line. Tell them that you have an NT1-like device at the end of the
ISDN line.
4. If the ISU 128 continues to read Getting TEI #1, the ISU 128 is physically
connected to your local telephone service provider but is unable to establish logical layer 2. The problem may be one or more of the following:
• The ISU 128 software setup
• The telephone service provider's software setup
• Hardware configuration if the ISDN line is extended from the switch
To isolate the problem, use the following procedure:
A. Ensure the ISU 128 is set up for the correct switch protocol by selecting
CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial Line, Switch protocl.
B. Ensure the line quality is satisfactory by checking for near- and far-end
block errors (NEBEs and FEBEs). To do this, select Test, NEBE/FEBE. If
the counts are non-zero and incrementing, there may be a physical link
problem as described under Link Down (Step 3).
C. Try another piece of functioning ISDN equipment with a U-interface
on the line.
D. With the ISU 128 connected to the line and powered up, talk to your
service provider's repair group and tell them you have an ISDN basic
rate line that appears physically okay but has no terminal endpoint
identifier (TEI). Ask them to check the ISDN line translation and ensure
that the ISDN line supports dynamic TEI allocation. Tell them that you
have an NT1 and terminal adapter device connected to the line.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 79
Page 95

Chapter 11. Troubleshooting
5. If the ISU 128 continues to read Register SPID #1, the ISU 128 is physically
connected to the local telephone service provider and has established logical layer 2. The ISU 128 is unable to establish layer 3. The problem may
be one or more of the following:
• The ISU 128 software setup
• The telephone service provider's software setup
To isolate the problem, use the following procedure:
A. Ensure the ISU 128 is set up for the correct switch protocol by selecting
CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial line, Switch protocl.
B. Ensure the ISDN line is multipoint.
C. Make sure that the ISU 128 is set up with the correct SPID and LDN by
selecting CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial Line, Terminal ID, SPID/LDN.
D. Try another piece of functioning ISDN equipment with a U-interface on
the line.
E. With the ISU 128 connected to the ISDN line and powered up, talk to your
service provider's repair group and tell them you have an ISDN basic rate
line that appears physically okay but has no terminal endpoint identifier
(TEI). Ask them to check the line translation and ensure that the line
supports dynamic TEI allocation. Tell them that you have an NT1 and
terminal adapter device connected to the line.
6. If the ISU 128 continues to read Getting TEI #2, the ISU 128 has completely
initialized the first phone number but is unable to establish logical layer 2
for the second phone number. The problem may be one or more of the following:
• The ISU 128 software setup
• The telephone service provider's software setup
To isolate the problem, use the following procedure:
A. Ensure the ISDN line is multipoint with two phone numbers.
80 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 96

Chapter 11. Troubleshooting
B. Ensure that the ISU 128 is set up with the correct SPID and LDN by
selecting CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial Line, Terminal ID, SPID/LDN.
C. Try swapping SPID1 with SPID2 and LDN1 with LDN2. Determine if
the problem is the second phone number or the quantity of phone
numbers.
D. Try another piece of functioning ISDN equipment with a U-interface
on the ISDN line.
E. With the ISU 128 connected to the ISDN line and powered up, talk to your
service provider's repair group and tell them you have an ISDN basic rate
line that appears physically okay but has no TEI. Ask them to check the
line translation and ensure that the line supports dynamic TEI allocation.
Tell them that you have an NT1 and terminal adapter device connected
to the line.
7. If the ISU 128 continues to read Register SPID #2, the ISU 128 has com-
pletely initialized the first phone number but is unable to establish logical
layer 3 for the second phone number. The problem is in one or more of
the following places:
• The ISU 128 software setup
• The telephone service provider's software setup
To isolate the problem, use the following procedure:
A. Ensure the ISDN line is multipoint with two phone numbers.
B. Ensure that the ISU 128 is set up with the correct SPID and LDN by
selecting CONFIG, Netw. options, Dial Line, Terminal ID, SPID/LDN.
C. Try swapping SPID1 with SPID2 and LDN1 with LDN2.
Determine if the problem is the second phone number or the quantity
of phone numbers.
D. Try another piece of functioning ISDN equipment with a U-interface
on the line.
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 81
Page 97

Chapter 11. Troubleshooting
E. With the ISU 128 connected to the line and powered up, talk to your
service provider's repair group and tell them you have an ISDN basic rate
line that appears physically okay but has no terminal endpoint identifier
(TEI). Ask them to check the line translation and ensure that the line
supports dynamic TEI allocation. Tell them that you have an NT1 and
terminal adapter device connected to the line.
82 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 98

SPECIFICATIONS AND FEATURES
This section describes the standard specifications and features incorporated in
the ISU 128.
Network Interface
• RJ-45 for ISDN Basic Rate U-Interface, and Leased 2B1Q service
DTE Interface
• RS-530
• V.35
• EIA-232
Dialing Selections
• In-band DTE dialing: V.25 or AT commands
• Manual or automatic stored number dialing, DTR assertion
• Dial interface: RS-366
• Front panel manual dialing
Chapter 12
Specifications
Data Rates (Network)
64 kbps (one B channel), 128 kbps (two B channels)
Data Rates (DTE)
• 300 bps to 115.2 kbps asynchronous
• 2400 bps to 128 kbps synchronous
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 83
Page 99

Chapter 12. Specifications
Rate Adaption
• T-Link
• CCITT V.120
• CCITT V.110
• SAP
• DSU 57.6 Async
• BONDING mode 1
• V.34 (optional)
• PPP
•MP
Interoperability
• BONDING Inverse Multiplexers
• Switched 56 DSUs
• ISDN TAs
• V.34 modems (optional)
Switch Compatibility
• AT&T 5ESS
• NTI DMS-100
• National ISDN-1
• NEC
B Channel Aggregation
• BONDING Mode 1
•MP
Display
• Two-line by 16 character LCD
• LED indicators
RS Request to Send.
Indicates the DTE is ready to transmit.
CS Clear to Send.
Indicates the ISU 128 is ready to transmit.
TD Transmit Data.
On when the DTE is transmitting to the ISU 128.
RD Receive Data.
On when the ISU 128 is receiving data from the far end.
CD Carrier Detect.
On when the ISU 128 is connected to a remote unit.
84 ISU 128 User Manual 61202.029L2-1
Page 100

Chapter 12. Specifications
TR Data Terminal Ready from DTE.
On when DTR is active at DTE interface.
SR Data Set Ready.
Environmental
• Operating Temperature: 0 to 50 °C
• Storage Temperature: 20 to 70 °C
• Relative Humidity: Up to 95%, non-condensing
Physical
• Dimensions: 2.25"H x 8.75"W x 11.00"D
• Weight: 3 lbs.
Power
• 115 VAC, 60 Hz, 8 W maximum dissipation (part numbers 1202029L2 and
1202029L3)
61202.029L2-1 ISU 128 User Manual 85
 Loading...
Loading...