Page 1

USB-7230/7250
USB 2.0-based Digital I/O Module
User’s Manual
Manual Rev.: 2.00
Revision Date: Nov. 16, 2012
Part No: 50-1Z138-2000
Advance Technologies; Automate the World.
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Release Date Description of Change(s)
2.00 Nov. 16, 2012 Initial release
Page 3

USB-7230/7250
Preface
Copyright 2012 ADLINK Technology, Inc.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form
without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without prior
notice in order to improve reliability, design, and function and does
not represent a commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect,
special, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the
use or inability to use the product or documentation, even if
advised of the possibility of such damages.
Environmental Responsibility
ADLINK is committed to fulfill its social responsibility to global
environmental preservation through compliance with the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
directive. Environmental protection is a top priority for ADLINK.
We have enforced measures to ensure that our products, manufacturing processes, components, and raw materials have as little
impact on the environment as possible. When products are at their
end of life, our customers are encouraged to dispose of them in
accordance with the product disposal and/or recovery programs
prescribed by their nation or company.
Conventions
Take note of the following conventions used throughout this
manual to make sure that users perform certain tasks and
instructions properly.
Preface iii
Page 4

NOTE:
NOTE:
CAUTION:
WARNING:
Additional information, aids, and tips that help users perform
tasks.
Information to prevent minor physical injury, component damage, data loss, and/or program corruption when trying to complete a task.
Information to prevent serious physical injury, component
damage, data loss, and/or program corruption when trying to
complete a specific task.
iv Preface
Page 5

USB-7230/7250
Table of Contents
Revision History...................................................................... ii
Preface .................................................................................... iii
List of Figures ....................................................................... vii
List of Tables.......................................................................... ix
1 Introduction ........................................................................ 1
1.1 Overview.............................................................................. 1
1.2 Features............................................................................... 1
1.3 Applications ......................................................................... 2
1.4 Specifications....................................................................... 2
1.4.1 General Specifications................................................ 2
1.4.2 Digital Input (DI).......................................................... 2
1.4.3 Digital Output (DO) ..................................................... 3
1.5 Software Support ................................................................. 4
1.6 Driver Support for Windows................................................. 4
1.7 Utilities for Windows ............................................................ 5
1.8 Schematics and Dimensions ............................................... 6
1.8.1 Module........................................................................ 6
1.8.2 Module Stand ............................................................. 9
1.8.3 Rail Mounting............................................................ 15
1.8.4 Wall Mounting........................................................... 18
1.9 Connector Pin Assignment ................................................ 20
2 Getting Started ................................................................. 23
2.1 Unpacking Checklist .......................................................... 23
2.2 Connecting the USB-7230/7250 Module ........................... 23
2.3 Device ID ........................................................................... 24
Table of Contents v
Page 6

3 Operations ......................................................................... 27
3.1 Isolated Digital Input .......................................................... 28
3.2 Change of State (COS) Detection...................................... 29
3.3 Optical Isolated Frequency/Event Counter ........................ 31
3.4 Digital Filtering ................................................................... 33
3.5 Isolated Digital Output (USB-7230 only) ............................ 34
3.6 Relay Output (USB-7250 only) .......................................... 35
Important Safety Instructions............................................... 37
Getting Service ...................................................................... 39
vi Table of Contents
Page 7

USB-7230/7250
List of Figures
Figure 1-1: USB-7230/7250 Module Rear View............................ 6
Figure 1-2: USB-7230/7250 Module Side View ............................ 7
Figure 1-3: USB-7230 Module Front View .................................... 8
Figure 1-4: USB-7250 Module Front View .................................... 9
Figure 1-5: Module, Stand, Connector, and USB Cable ............. 10
Figure 1-6: Module, Stand, & Wall Mount Kit Side View (w/ connec-
tions)11
Figure 1-7: Module in Stand Front View ..................................... 12
Figure 1-8: Module Stand Top View ........................................... 13
Figure 1-9: Module Stand Side Cutaway View ........................... 14
Figure 1-10: Module Stand Front View ......................................... 14
Figure 1-11: Rail Mount Kit ........................................................... 15
Figure 1-12: Module Pre-Rail Mounting ........................................ 16
Figure 1-13: Module Rail-Mounted ............................................... 17
Figure 1-14: Wall Mount Holes ..................................................... 18
Figure 1-15: Module with Wall Mount Apparatus .......................... 19
Figure 2-1: Device ID Selection Control...................................... 24
Figure 3-1: USB-7230 Functional Block Diagram ....................... 27
Figure 3-2: USB-7250 Functional Block Diagram ....................... 28
Figure 3-3: USB-7230 Isolated Input .......................................... 29
Figure 3-4: USB-7250 Isolated Input .......................................... 29
Figure 3-5: COS Detection Architecture ..................................... 30
Figure 3-6: COS Example........................................................... 31
Figure 3-7: USB-7230/7250 Optical Isolated Frequency/Event Coun-
ter31
Figure 3-8: Frequency Counter Example.................................... 32
Figure 3-9: Frequency Counter Error %...................................... 33
Figure 3-10: Digital Filter Example................................................ 34
Figure 3-11: USB-7230 Isolated Output........................................ 35
Figure 3-12: Form C Relay ........................................................... 35
Figure 3-13: Form A Relay............................................................ 35
List of Figures vii
Page 8

This page intentionally left blank.
viii List of Figures
Page 9

USB-7230/7250
List of Tables
Table 1-1: USB-7230 Pin Assignment ............................................ 20
Table 1-2: USB-7230 I/O Signal Description .................................. 21
Table 1-3: USB-7250 Pin Assignment ............................................ 22
Table 1-4: USB-7250 I/OSignal Description ................................... 22
List of Tables ix
Page 10

This page intentionally left blank.
xList of Tables
Page 11

USB-7230/7250
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
The USB-7230/7250 are USB-based digital I/O modules, featuring
high voltage ON/OFF control and monitoring, and isolation voltage
supported up to 2500V
isolated digital I/O and 2-channel frequency/event counters, and
USB-7250 provides 8-channel isolated digital inputs, 8-channel
solid-state relays, and 2-channel frequency/event counters.
The USB-powered USB-7230/7250 have removable screw-down
terminals for easy device connectivity, and the included multi-functional stand fully supports desktop, rail, or wall mounting.
The USB-7230/7250 are suitable for industrial I/O control applications requiring high voltage and excellent protection. High isolation
voltage protects against damage from accidental contact with high
external voltage and eliminates troublesome ground loops. U-Test,
a free ready-to-use testing program, is included to enable operation or testing of all ADLINK USB DAQ series functions with no
programming requirement.
. The USB-7230 provides 32-channel
RMS
1.2 Features
X High-speed USB 2.0
X USB-powered
X USB-7230: 16CH isolated DI, 16CH isolated DO, 2CH fre-
quency/event counters
X USB-7250: 8CH solid state relays, 8CH isolated DI, 2CH
frequency/event counters
X Programmable digital filter removing unexpected glitches on
input channels
X Programmable initial DO status
X Up to 2500V
X Removable screw-down terminal on module
X Lockable USB cable for secure connectivity
X Ready-to-use testing application (U-Test) included
Introduction 1
isolation voltage
RMS
Page 12
1.3 Applications
X Automotive testing
X Laboratory research
X Industrial I/O control
X Signal switching
1.4 Specifications
1.4.1 General Specifications
Physical, Power, and Operating Environment
Interface
Dimensions
I/O Connector Two 20-pin removable screw-down terminals
Power requirement USB power (5 V @ 400 mA)
Operating environment
Storage environment
High speed USB 2.0 compatible, mini-USB
connector
156.5 (L) x 114 (W) x 41.3 (H) mm (6.16 X 4.49 X
1.63 in.)
Ambient temperature: 0 to 55°C
Relative humidity: 10% to 90%, non-condensing
Ambient temperature: -20 to 70 °C
Relative humidity: 5% to 95%, non-condensing
1.4.2 Digital Input (DI)
USB-7230 USB-7250
Optical Isolated Input
Number of channels 16 8
Polarity Bi-directional (non-polarity)
Logic level VIH=5~24V, VIL=0~1.5V
Or dry contact
Input resistance 2.4k @ 0.5W
Isolated voltage 2500V
2Introduction
(channel to system)
RMS
Page 13
USB-7230/7250
USB-7230 USB-7250
Min. pulse width for change
of state (COS) detection
Data transfer Programmed I/O
Optical Isolated Frequency/Event Counter
Number of channels 2
Logic level VIH=5~12V, VIL=0~1.5V
Event counter width 32-bit
Max. input frequency
(DC coupled)
Min. input frequency
(DC coupled)
Max. frequency error 0.5% (f≤50kHz)
Data transfer Programmed I/O
20.83 ns (software programmable)
1 MHz
0.1 Hz
1% (50kHz<f≤500kHz)
2% (500kHz<f≤1MHz)
1.4.3 Digital Output (DO)
USB-7230
Channels 16 (optical isolation)
Output type Open drain MOSFET
Supply voltage 5-35VDC
Max. sink current 250 mA @ 100% duty (/channel)
Data transfer Programmed I/O
USB-7250
Channels 8 (solid state relay, non-latching)
Contact rating
(/channel)
Relay ON/OFF time Operate time 2 ms
Contact resistance 75mΩ (max.)
Expected lifetime
Introduction 3
Max. switching power 60 W, 125 VA
Max. switching voltage 220 VDC, 250VAC
Max. switching current 2 A
Release time 1 ms
50 VDC 0.1A (resistive), 1x10
6
operations
Page 14

Breakdown voltage 1000 VAC
Data transfer Programmed I/O
1.5 Software Support
ADLINK provides comprehensive software drivers and packages
to suit various user approaches to system building. In addition to
programming libraries, such as DLLs, for most Windows-based
systems, ADLINK also provides drivers for other application environments such as LabVIEW® and MATLAB®. ADLINK also pro
vides ActiveX component ware for measurement and
SCADA/HMI, and breakthrough proprietary software. All software
options are included in the ADLINK All-in-One CD.
Be sure to install the driver & utility before use.
1.6 Driver Support for Windows
UD-DASK
UD-DASK is composed of advanced 32/64-bit kernel drivers for
customized DAQ application development. USB-DASK enables
you to perform detailed operations and achieve superior performance and reliability from the data acquisition system. DASK ker-
nel drivers now support Windows 7/Vista
®
OS.
Only UD-DASK versions 1.0.5 and later support the
USB-7230/7250 module.
NOTE:
NOTE:
DAQPilot
DAQPilot is a SDK with a graphics-driven interface for various
application development environments. DAQPilot represents
ADLINK's commitment to full support of its comprehensive line of
data acquisition products and is designed for novice to most
4Introduction
Page 15

USB-7230/7250
experienced programmers. As a task-oriented DAQ driver, SDK
and wizard for Windows systems, DAQPilot helps shorten development time while accelerating the learning curve for data acquisition programming. Download and install DAQPilot from:
http://www.adlinktech.com/TM/DAQPilot.html
Only UD-DASK versions 2.3.4.1109 and later and later support the USB-7230/7250 module.
NOTE:
NOTE:
1.7 Utilities for Windows
U-Test
U-Test is a free and ready-to-use utility assisting instant testing
and operation of all ADLINK USB DAQ product functions with no
programming requirment. In addition to data collection and monitoring functions, U-Test also supports basic FFT analysis and
direct control of analog output and digital I/O with a user-friendly
interface.
Download and install U-Test from:
http://www.adlinktech.com
Introduction 5
Page 16

1.8 Schematics and Dimensions
All dimensions shown are in millimeters (mm)
NOTE:
NOTE:
1.8.1 Module
Figure 1-1: USB-7230/7250 Module Rear View
6Introduction
Page 17

156.5
Figure 1-2: USB-7230/7250 Module Side View
USB-7230/7250
114
Introduction 7
Page 18

114
41.3
Figure 1-3: USB-7230 Module Front View
8Introduction
Page 19

114
USB-7230/7250
41.3
Figure 1-4: USB-7250 Module Front View
1.8.2 Module Stand
The multi-function USB-7230/7250 stand is compatible with desk,
rail, or wall mounting. To fix the module in the stand, slide the module body into the stand until a click is heard. To remove the module
Introduction 9
Page 20

from the stand, twist the bottom of the stand in a back-and forth
motion and separate from the module.
Figure 1-5: Module, Stand, Connector, and USB Cable
10 Introduction
Page 21

USB-7230/7250
200.1
169.4
156.5
Figure 1-6: Module, Stand, & Wall Mount Kit Side View (w/ connections)
Introduction 11
Page 22

Figure 1-7: Module in Stand Front View
114.3
12 Introduction
Page 23
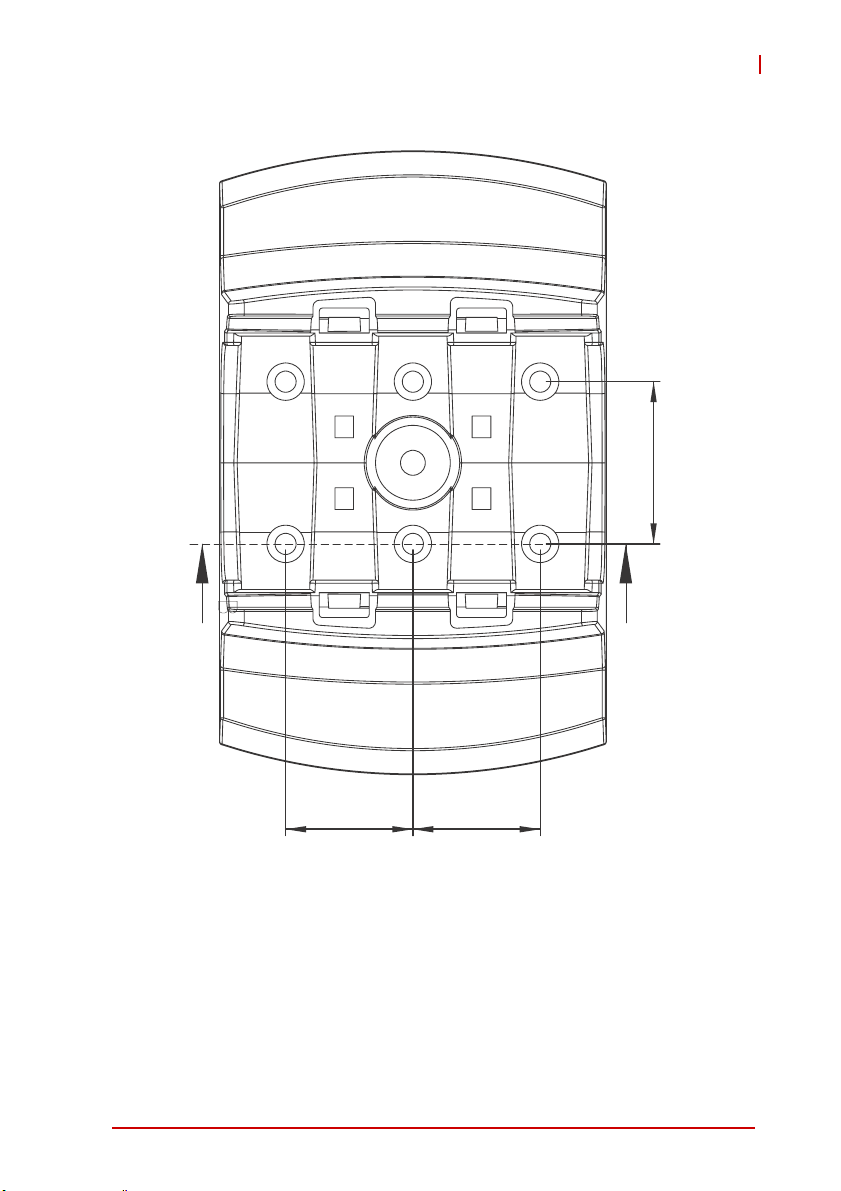
USB-7230/7250
26
B
20.4
Figure 1-8: Module Stand Top View
Introduction 13
20.4
Page 24

Figure 1-9: Module Stand Side Cutaway View
3.4
6
1.5
5.89
100
Figure 1-10: Module Stand Front View
14 Introduction
Page 25

USB-7230/7250
1.8.3 Rail Mounting
The multi-function stand can be mounted on the DIN rail using the
rail-mount kit as shown.
Figure 1-11: Rail Mount Kit
Introduction 15
Page 26

Figure 1-12: Module Pre-Rail Mounting
16 Introduction
Page 27

USB-7230/7250
Figure 1-13: Module Rail-Mounted
Introduction 17
Page 28

1.8.4 Wall Mounting
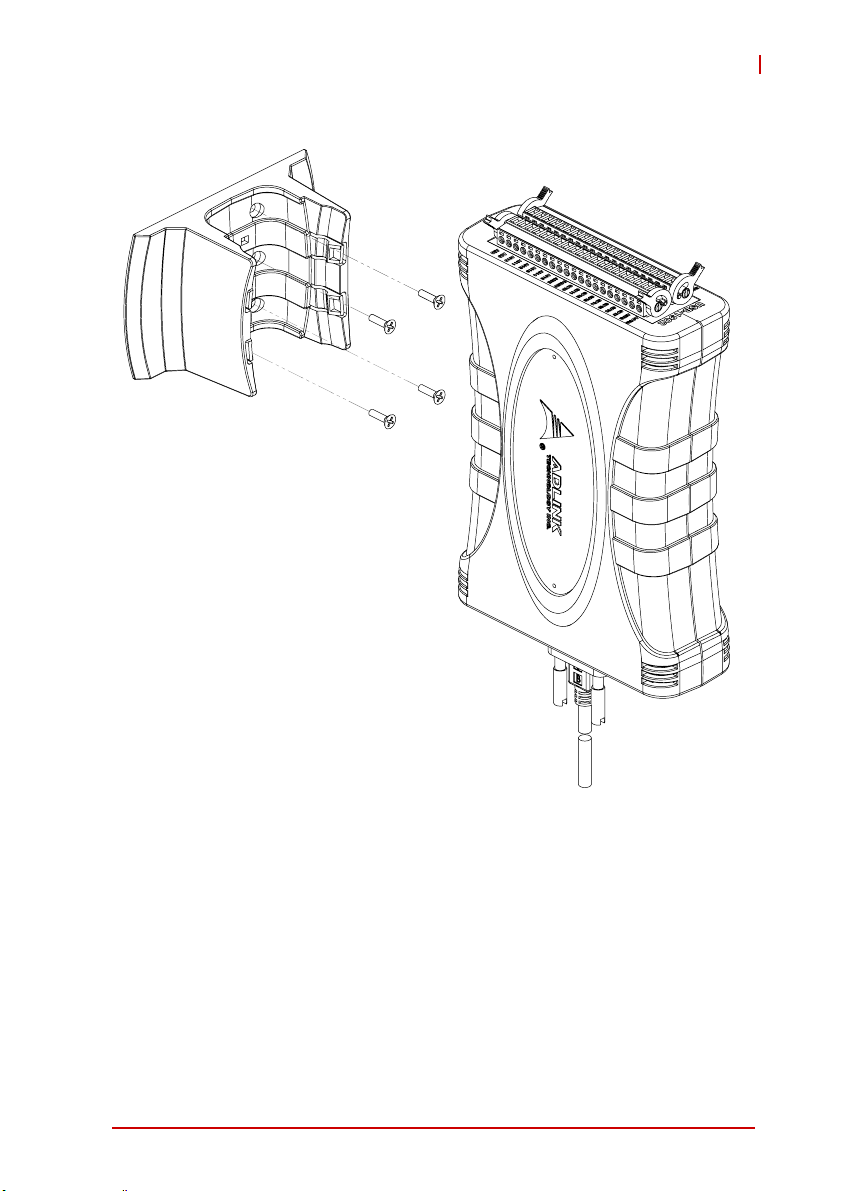
The multi-function stand can be fixed to a wall using four flush
head screws as shown. The four screw holes should be approximately 3.4 mm in diameter.
20.4
13.0
Figure 1-14: Wall Mount Holes
18 Introduction
Page 29
USB-7230/7250
Figure 1-15: Module with Wall Mount Apparatus
Introduction 19
Page 30
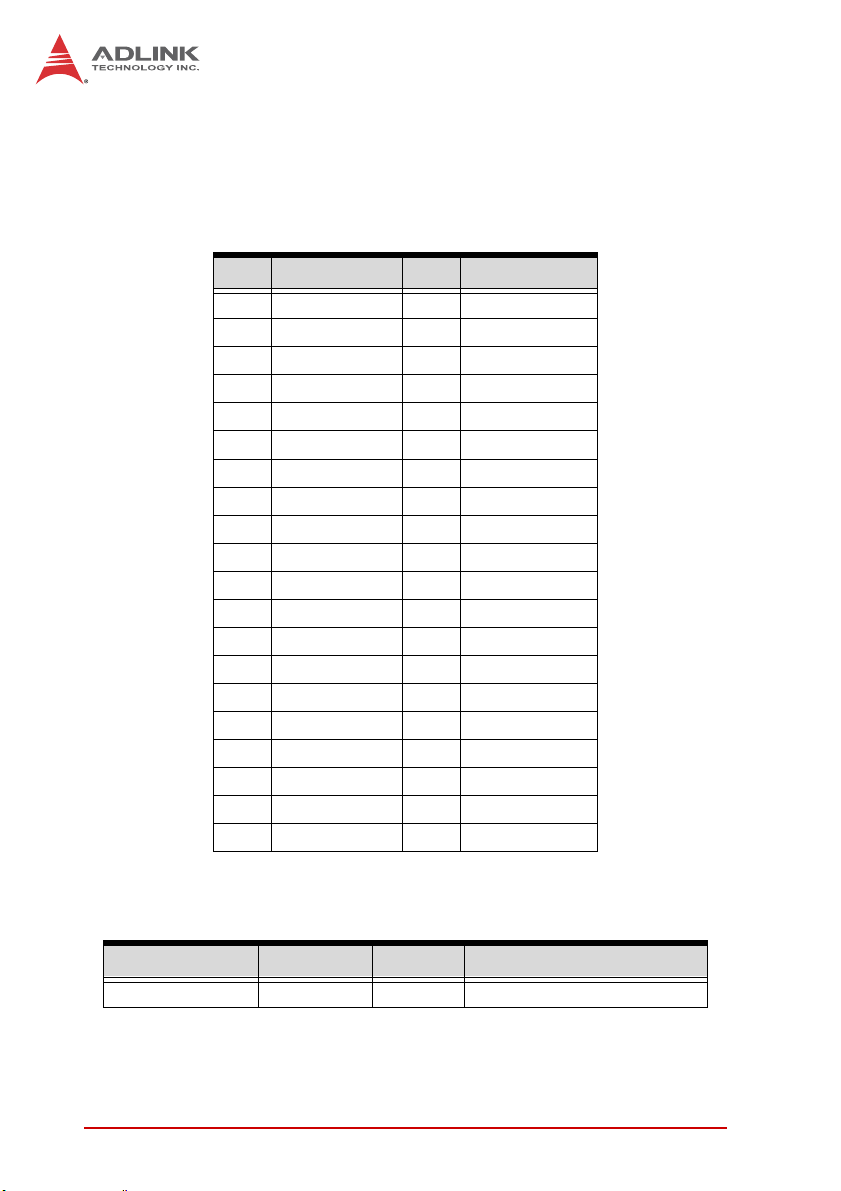
1.9 Connector Pin Assignment
The USB-7230/7250 module is equipped with 40-pin removable
screw-down terminal connectors, with pin assignment as follows.
Pin Function Pin Function
20 VDD 40 DO15
19 DO7 39 DO14
18 DO6 38 DO13
17 DO5 37 DO12
16 DO4 36 DO11
15 DO3 35 DO10
14 DO2 34 DO9
13 DO1 33 DO8
12 DO0 32 IGND
11 IGND 31 IGND
10 CNT0 30 CNT1
9CGND29 COM
8DI728DI15
7DI627DI14
6DI526DI13
5DI425DI12
4DI324DI11
3DI223DI10
2DI122DI9
1DI021DI8
Table 1-1: USB-7230 Pin Assignment
Signal Name Reference Direction Description
DI<0..15> COM I Isolated digital input channel
20 Introduction
Page 31
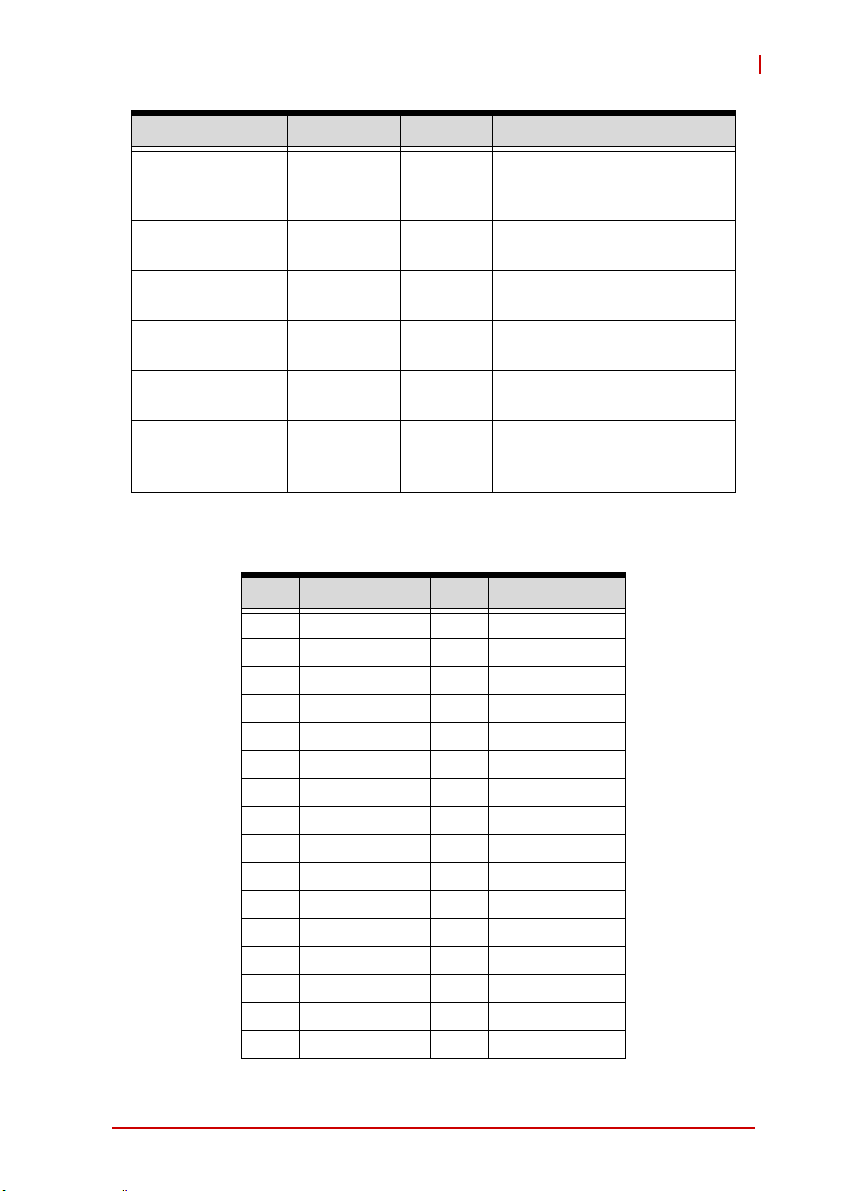
USB-7230/7250
Signal Name Reference Direction Description
COM -------- Common ground or common
power of isolated digital input
channel
CNT<0,1> CGND I Frequency/event counter
channel
CGND -------- Ground of Frequency/event
counter
DO<0..15> IGND O Isolated digital output
channel
IGND -------- Ground return path for
isolated output channel
VDD IGND I Common power input
junction for isolated output
channel
Table 1-2: USB-7230 I/O Signal Description
Pin
20 NO7 40 GND1
19 COM7 39 CNT1
18 NO6 38 GND0
17 COM6 37 CNT0
16 NO5 36 DI7L
15 COM5 35 DI7H
14 NO4 34 DI6L
13 COM4 33 DI6H
12 NC3 32 DI5L
11 N O 3 3 1 D I 5 H
10 COM3 30 DI4L
Introduction 21
Functi
on
9 NC2 29 DI4H
8 NO2 28 DI3L
7COM227 DI3H
6 NC1 26 DI2L
5NO125DI2H
Pin
Fu
ncti
on
Page 32

Pin
Signal Name Reference Direction Description
COM<0..7> ---------- I Common pin of relay <0..7>
NO<0..7> COM<0..7> I Normal open pin of relay
NC<0..3> COM<0..3> I Normal close pin of relay
DI<0..7>H DI<0..7>L I High input of isolated
DI<0..7>L -------- I Low input of isolated
CNT<0,1> GND<0,1> I Frequency/event counter
GND<0,1> -------- Ground of Frequency/event
Table 1-4: USB-7250 I/OSignal Description
Functi
on
4 COM1 24 DI1L
3 NC0 23 DI1H
2NO022DI0L
1 COM0 21 DI0H
Table 1-3: USB-7250 Pin Assignment
Pin
Fu
ncti
<0..7>
<0..3>
differential digital input
differential digital input
channel
counter
on
22 Introduction
Page 33

2 Getting Started
The appropriate driver must be installed before connection to
the computer system. See Section 1.5: Software Support for
WARNING:
2.1 Unpacking Checklist
driver support information.
Before unpacking, check the shipping carton for any damage. If
the shipping carton and/or contents are damaged, inform the
dealer immediately. Retain the shipping carton and packing
materials for inspection. Obtain authorization from the dealer
before returning any product to ADLINK. Ensure that the following items are included in the package.
X USB-7230/7250
X Stand
X Two removable screw terminals
X USB cable (2-meter length)
X Railmount kit
X ADLINK All-in-One CD
X User’s manual
USB-7230/7250
2.2 Connecting the USB-7230/7250 Module
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Connect the USB-7230/7250 module to one USB 2.0
port on the computer using the included USB cable.
3. The first time the USB-7230/7250 module is connected,
a New Hardware message appears. It will take a few
seconds to load the firmware. When loading is complete,
the LED indicator on the rear of the USB DAQ module
changes from amber to green and the New Hardware
message closes.
4. The USB-7230/7250 module can now be located in the
hardware Device Manager.
Getting Started 23
Page 34

The USB-7230/7250 module is exclusively powered by the
USB port and requires 400 mA @ 5 V. If the USB-7230/7250
NOTE:
NOTE:
module cannot be detected, power provided by the USB port
may be insufficient.
2.3 Device ID
A rotary control on the rear of the module (as shown) controls
device ID setting and can be set from 0 to 7. The device ID allows
dedicated control of the USB-7230/7250 module irrespective of
the connected USB port. When more than one USB module of the
same type is connected, each must be set to a different ID to avoid
conflicts and errors in operation.
Figure 2-1: Device ID Selection Control
24 Getting Started
Page 35

USB-7230/7250
All remaining hardware configuration is software programmable,
including sampling/update rate, input/output channel, input range,
and others. Please see the UD-DASK Function Reference manual
for details.
Getting Started 25
Page 36

This page intentionally left blank.
26 Getting Started
Page 37

3 Operations
Figure 3-1: USB-7230 Functional Block Diagram
USB-7230/7250
The USB-7250 provides 8CH optical isolation digital inputs, 8CH
relay outputs (4CH form C and 4CH form A), and 2CH frequency/event counters.
Operations 27
Page 38

Figure 3-2: USB-7250 Functional Block Diagram
3.1 Isolated Digital Input
The USB-7230/7250 support 16 or 8 opto-isolated input channels,as follows, with digital input first routed through a photo-coupler (PC3H4), and normal input voltage range for high state from 5
to 24V.
For USB-7230, all digital inputs share the same common junction (COM), with connections either common power or com-
NOTE:
NOTE:
mon ground, and with USB-7250, each input channel has an
individual differential input pair, preventing connections from
being polarity sensitive, irrespective of the connected voltage.
28 Operations
Page 39

USB-7230/7250
Figure 3-3: USB-7230 Isolated Input
Figure 3-4: USB-7250 Isolated Input
3.2 Change of State (COS) Detection
COS (Change of State) refers to input state (logic level) changing
from low to high or vice versa, wherein the COS detection circuit
registers the edge of the level change.
Operations 29
Page 40

In the USB-7230/7250, the COS detection circuit is applied to all
DI channels, with the channel(s) to enable COS detection selectable by software. When an enabled channel changes logic level,
the COS detection circuit generates an interrupt request to the
USB microcontroller, which, when detected, latches corresponding
DI data into the COS latch register. In COS architecture, DI data is
sampled by a 48 MHz base clock, such that pulse width of the digital input exceeds 21 ns, or the COS latch register cannot latch the
correct input data. The COS latch register is cleared when the register is read out, resuming availability to latch the susequent COS.
Maximum frequency of COS detection depends on software
latency and computer performance, and is not guaranteed if
NOTE:
NOTE:
COS frequency exceeds 1 kHz.
DI0-DI7 DI0-DI7
Digital
Filter
0~7
USB
Bridge
DI8-DI15 DI8-DI15
Digital
CPLD
INT
Filter
8~15
USB
BUS
Figure 3-5: COS Detection Architecture
30 Operations
Page 41

USB-7230/7250
DI
(all channels
enable)
Interrupt
Request
Interrupt
Clear
COS
Latch
register
0027
XXXX
0028 0029 FFFF
0028 FFFF
Figure 3-6: COS Example
3.3 Optical Isolated Frequency/Event Counter
Calculates the number of rising or falling edges occurring on the
input channel, with counter width of 32 bits counting up from 0.
The polarity (rising or falling edge) of valid events is software configurable.
PHOTO COUPLER
n=0,1
Figure 3-7: USB-7230/7250 Optical Isolated Frequency/Event Counter
The frequency counter base clock is 48MHz. The frequency counter calculates base clocks occurring within a period (rising edge to
rising edge or falling edge to falling edge) of the repetitive input
signal, which is then converted to frequency value. Counter polarity can be adjusted to rising edge active or falling edge active.
The following example shows frequency measurement of a 1 MHz
signal by counter0 with rising-edge polarity and 500 kHz signal by
Operations 31
Page 42
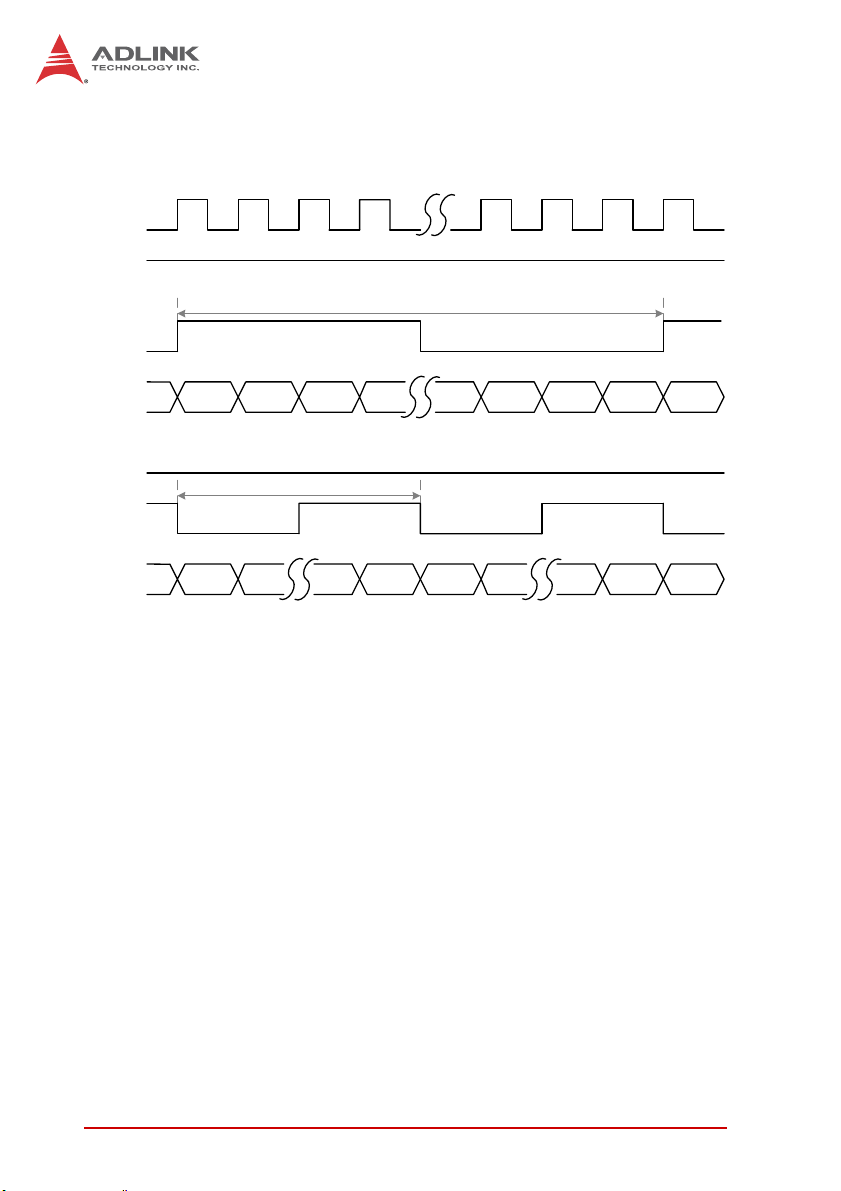
counter1 with falling-edge polarity. Counter value is updated and
reset in every period.
CLK
CNT0
Polarity
CNT0
Freq = 1 MHz
CNT0
FREQ
CNT1
Polarity
CNT1
CNT1
FREQ
1 2 3 46 47 48 1
Freq = 500 KHz
1 24 1
24 1
Figure 3-8: Frequency Counter Example
Since the signals are sampled by a 48MHz base clock, latch timing can generate measurement error, maximum error ratio vs.
input frequency is as follows.
32 Operations
Page 43

Error
(%)
USB-7230/7250
2
1.5
1
.5
1000100
Figure 3-9: Frequency Counter Error %
10000
Frequency (Hz)
100000 1000000
3.4 Digital Filtering
Filters unexpected glitch signals from the input channels. By
default, when enabled, the input channel ignores signal changes
from one state to another when not remaining in the state for a
pre-defined period. The digital filter function is applied on all DI
channels and counters, with the default setting disabled. When
enabled by software,it is necessary to configure the minimum
pulse-width value. This value represents the minimum period of
time guaranteed to pass through the filter when the signal
changes. The digital filter uses an internal 16-bit counter to define
the specified filter value. Data is sampled by a 48 MHz base clock,
with minimum pulse-width value a multiple of 20.83 ns and multiple number from 1 to 65535, representing the minimum
pulse-width from 20.83 ns to 1.365 ms.
In an examplary digital filter operation, as shown, data is sampled
by a 48 MHz base clock, and filter stage is 10, such that minimum
pulse width value is 208.3 ns. The pulse width of the first two signals is 180 ns, shorter than the specified filter value 208.3 ns.
Accordingly, the first two pulses are ignored, and the next two signals, with pulse width of 230 ns (longer than the specified filter
value 208.3 ns) are recognized. When pulse width of last two sig-
Operations 33
Page 44

nals is 180 ns when filter is disabled, definitely, the last two states
are recognized.
12 91282891 891012 8910
CLK
filter
enable
filter
stage
filter_in
filter_out
Pulse Width = 180 ns
Pulse Width = 210 ns
Pulse Width = 180 ns
000A
Pulse Width = 210 ns
Pulse Width = 210 ns
12 8912 8912
Pulse Width = 180 ns
Pulse Width = 180 ns
Pulse Width = 210 ns
XXXX
Pulse Width = 180 ns
Pulse Width = 180 ns
Figure 3-10: Digital Filter Example
To reject a signal deviating from a state for the specified period of
time (minimum pulse width), the filter stage must be set to agree
with: 20.83 ns × filter stage < minimum pulse Width (ns).
3.5 Isolated Digital Output (USB-7230 only)
As shown, when isolated digital output is ON, sink current is conducted through the power MOSFET, and when OFF, no current
flows through the power MOSFET. When the load is of an “inductance nature” such as a relay, coil or motor, the VDD pin must be
connected to an external power source, in order for the flywheel
diode to form a current-release closed loop, protecting the power
MOSFET from high reverse voltage generated by the inductance
load when the output is switched. The DO output status is saved in
the USB microcontroller and can be read back if necessary. The
USB-7230 also features programmable power-up output status,allowing output in a known state when powered on. When the
module is powered off (ejected from the USB port), all digital output reverts to OFF.
34 Operations
Page 45

USB-7230/7250
VDD
DO_n
Controller
(n=0~15)
PHOTO COUPLER
5V
IGND
DOn
IGND
LOAD
Figure 3-11: USB-7230 Isolated Output
3.6 Relay Output (USB-7250 only)
USB-7250 provides Form C and Form A relays, with channels 0 to
3 Form C, and 4 to 7 form A, as shown.
5~35V
Figure 3-12: Form C Relay
Figure 3-13: Form A Relay
Form C relays have NC (Normal Close), NO (Normal Open), and
COM (Common) contacts. The COM terminal, located in the center,must contact either the NO pole or NC pole. When the control
bit is high (1), contact is made between the COM terminal and NO
pole, and if low (0), between the COM terminal and NC pole. Form
Operations 35
Page 46

A relays have only NO (Normal Open) and COM (Common) contacts. When the control bit is high (1), the COM terminal znd NO
pole contact. If the control bit is low (0), no contact takes place.
Current relay output status can be read back by software, and during normal power up, reset, and power down (ejection from USB
port), the relay is low status. In addition, USB-7250 also features
programmable power-up output status, providing output state
when powered up.
36 Operations
Page 47

USB-7230/7250
Important Safety Instructions
For user safety, please read and follow all instructions,
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and NOTES marked in this manual
and on the associated equipment before handling/operating the
equipment.
X Read these safety instructions carefully.
X Keep this user’s manual for future reference.
X Read the specifications section of this manual for detailed
information on the operating environment of this equipment.
X When installing/mounting or uninstalling/removing
equipment:
Z Turn off power and unplug any power cords/cables.
X To avoid electrical shock and/or damage to equipment:
Z Keep equipment away from water or liquid sources;
Z Keep equipment away from high heat or high humidity;
Z Keep equipment properly ventilated (do not block or
cover ventilation openings);
Z Make sure to use recommended voltage and power
source settings;
Z Always install and operate equipment near an easily
accessible electrical socket-outlet;
Z Secure the power cord (do not place any object on/over
the power cord);
Z Only install/attach and operate equipment on stable
surfaces and/or recommended mountings; and,
Z If the equipment will not be used for long periods of time,
turn off and unplug the equipment from its power source.
Important Safety Instructions 37
Page 48

X Never attempt to fix the equipment. Equipment should only
be serviced by qualified personnel.
A Lithium-type battery may be provided for uninterrupted, backup
or emergency power.
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced with an incorrect type;
please dispose of used batteries appropriately.
X Equipment must be serviced by authorized technicians
when:
Z The power cord or plug is damaged;
Z Liquid has penetrated the equipment;
Z It has been exposed to high humidity/moisture;
Z It is not functioning or does not function according to the
user’s manual;
Z It has been dropped and/or damaged; and/or,
Z It has an obvious sign of breakage.
38 Important Safety Instructions
Page 49

USB-7230/7250
Getting Service
Contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: Ϟ⍋Ꮦ⌺ϰᮄᓴ∳催⾥ᡔು㢇䏃 300 ো(201203)
300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park,
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: ࣫ҀᏖ⍋⎔Ϟഄϰ䏃 1 োⲜ߯ࡼ E ᑻ 801 ᅸ(100085)
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8625
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ᄅקؑխࡉ৬ԫሁ 166 ᇆ 9 ᑔ
Pudong New Area, Shanghai, 201203 China
Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1, B/D
Shang Di East Rd., Beijing, 100085 China
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: ⏅ഇᏖቅ⾥ᡔು催ᮄϗ䘧᭄ᄫᡔᴃು
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (Europe) GmbH
Address: Nord Carree 3, 40477 Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: +49-211-495-5552
Fax: +49-211-495-5557
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
A1 2 ὐ C (518057)
2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7,
High-Tech Industrial Park S., Shenzhen, 518054 China
Getting Service 39
Page 50

ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 15 rue Emile Baudot, 91300 Massy CEDEX, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: ͱ101-0045 ᵅҀ䛑ҷ⬄⼲⬄䤯ފ⬎ 3-7-4
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 昢殾柢 昢爎割 昢爎壟 1675-12 微汾瘶捒娯 8猻
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre,
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: 1st Floor, #50-56 (Between 16th/17th Cross) Margosa Plaza,
Tel: +91-80-65605817, +91-80-42246107
Fax: +91-80-23464606
Email: india@adlinktech.com
⼲⬄ 374 ɛɳ 4F
KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho,
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
8F Mointer B/D,1675-12, Seocho-Dong, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-070, Korea
Singapore 349584
Margosa Main Road, Malleswaram, Bangalore-560055, India
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Israeli Liaison Office)
Address: 6 Hasadna St., Kfar Saba 44424, Israel
Tel: +972-9-7446541
Fax: +972-9-7446542
Email: israel@adlinktech.com
40 Getting Service
 Loading...
Loading...