Page 1

Express-CB/CBE
User’s Manual
Manual Revision: 2.02
Revision Date: September 7, 2012
Part Number: 50-1J033-1010
Page 2

Revision History
Release Date Change
2.00 Nov. 26, 2010 Initial Release
2.01 Feb. 22, 201 1 Update pinouts, add content for Express-CBE
2.02 Sept. 7, 2012 Add PCI Express x16 Configuration switch SWY1; remove VGA hotplug
feature
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Express-CB/CBE.............................................................................................................1
Preface ............................................................................................................................5
1 Introduction...............................................................................................................7
1.1 Description ...........................................................................................................................7
2 Specifications............................................................................................................8
2.1 General.................................................................................................................................8
2.2 Expansion Busses ...............................................................................................................8
2.3 Video ....................................................................................................................................9
2.4 Audio ....................................................................................................................................9
2.5 LAN.....................................................................................................................................10
2. 6 Multi I/O ..............................................................................................................................10
2. 7 Super I/O ............................................................................................................................10
2.8 TPM (Trusted Platform Module)........................................................................................10
2.9 Power Specifications .........................................................................................................10
2.10 Power Consumption ..........................................................................................................11
2.11 Operating Systems ............................................................................................................12
2.12 Mechanical and Environmental .........................................................................................12
3 Function Diagram ...................................................................................................13
4 Mechanical Dimensions..........................................................................................14
5 Pinout, Signal and Switch Descriptions.................................................................15
5. 1 COM Express® Type 2 compatible pinout ........................................................................15
5. 2 Carrier Board Design Guide ..............................................................................................15
5.3 Pin Definitions ....................................................................................................................16
5.4 Signal Descriptions............................................................................................................18
5. 5 PCI Express x16 Configuration..........................................................................................27
6 Embedded Functions..............................................................................................28
6.1 Watchdog Timer.................................................................................................................28
Page 3Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 3Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 3Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 3
Page 4

6.2 GPIO ...................................................................................................................................29
6.3 Hardware Monitoring.........................................................................................................30
7 System Resources..................................................................................................31
7.1 System Memory Map.........................................................................................................31
7.2 Direct Memory Access Channels ......................................................................................31
7. 3 Legacy I/O Map..................................................................................................................32
7. 4 Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines ...........................................................................................33
7. 5 PCI Configuration Space Map...........................................................................................35
7. 6 PCI Interrupt Routing Map .................................................................................................36
8 BIOS Setup Utility....................................................................................................37
8. 1 Starting the BIOS................................................................................................................37
8.2 Main Setup .........................................................................................................................38
8. 3 Advanced BIOS Setup .......................................................................................................41
8.5 Boot Configuration .............................................................................................................61
8.6 Security Setup....................................................................................................................63
8. 6 Save & Exit .........................................................................................................................64
9 BIOS Checkpoints, Beep Codes.............................................................................66
9.1 Status Code Ranges .......................................................................................................... 67
9.2 Standard Status Codes .....................................................................................................67
9.3 OEM-Reserved Status Code Ranges ...............................................................................73
Important Safety Instructions ........................................................................................................74
Getting Service ..............................................................................................................................76
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 4
Page 5

Preface
Copyright 2010, 2011 ADLINK Technology, Inc.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other
means in any form without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in order to improve
reliability, design, and function and does not represent a commitment on the part of the
manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential
damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product or documentation, even if advised
of the possibility of such damages.
Environmental Responsibility
ADLINK is committed to fulfill its social responsibility to global environmental preservation
through compliance with the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
directive and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directive. Environmental
protection is a top priority for ADLINK. We have enforced measures to ensure that our products,
manufacturing processes, components, and raw materials have as little impact on the
environment as possible. When products are at their end of life, our customers are encouraged to
dispose of them in accordance with the product disposal and/or recovery programs prescribed by
their nation or company.
Trademarks
AMIBIOS®8 is a registered trademark of American Megatrends, Inc. COM Express™, and
PICMG® are registered trademarks of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group.
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 5Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 5Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 5Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 5
Page 6
Conventions
Take note of the following conventions used throughout this manual to make sure that users
perform certain tasks and instructions properly.
Additional information, aids, and tips that help users perform tasks.
Information to prevent minor physical injury, component damage, data loss,
and/or program corruption when trying to complete a task.
Information to prevent serious physical injury, component damage, data
loss, and/or program corruption when trying to complete a specific task.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 6
Page 7

1 Introduction
1.1 Description
The Express-CB and Express-CBE are COM Express™ COM.0 R1.0 Type 2 modules
supporting the 64-bit Intel® Core™ i7/i5 processor with CPU, memory controller, and
graphics processor on the same chip. Based on the latest Mobile Intel® QM57 Express
chipset, the Express-CB is specifically designed for customers who need high-level
processing and graphics performance in a long product life solution.
The Express-CB features the Intel® Core™ i7/i5 processor supporting Intel® Hyper-threading
Technology (2 cores, 4 threads) and up to 8GB of DDR3 dual-channel memory at 1066 MHz
(EEC on Express-CBE) to provide excellent overall performance. Intel® Flexible Display
Interface and Direct Media Interface provide high speed connectivity to the Intel® QM57
Express chipset.
Integrated graphics includes features such as OpenGL 2.1, DirectX10, and Intel® Dynamic
Video Memory Technology (Intel® DVMT 5.0). Graphics outputs include VGA, LVDS and
Embedded DisplayPort. The Express-CB is specifically designed for customers with highperformance processing graphics requirements who want to outsource the custom core logic
of their systems for reduced development time.
The Express-CB has dual stacked SODIMM sockets for up to 8 GB DDR3 memory. The Intel®
Mobile QM57 Express chipset integrates VGA and single/dual-channel 18/24-bit LVDS
display output. In addition to the onboard integrated graphics, a multiplexed PCI Express®
x16 Graphics bus is available for discrete graphics expansion, Embedded DisplayPort, or
general purpose x8, x4 or x1 PCI Express® connectivity.
The Express-CB features a single onboard Gigabit Ethernet port, up to eight USB 2.0 ports and
four SATA 3 Gb/s ports with optional support for RAID 0/1/5/10. Additional storage interfaces
include an optional SATA based Solid State Disk (8/16/32 GB), and a single IDE (PATA)
channel. Legacy support is also provided for 32-bit PCI, LPC, SMBus and I2C. The module is
equipped with an AMI EFI BIOS with CMOS backup, supporting embedded features such as
remote console, CMOS backup, hardware monitor, and watchdog timer.
The Express-CB is a RoHS compliant and lead-free product.
Page 7Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 7Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 7Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 7
Page 8

2 Specifications
2.1 General
f CPU: Penryn Core PGA type
Intel® Core™ i7-610E Processor (4M Cache, 2.53 GHz) 35 W
Intel® Core™ i5-520E Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz) 35 W
Intel® Core™ i7-620LE Processor (4M Cache, 2.00 GHz) 25 W
Intel® Core™ i7-620UE Processor (4M Cache, 1.06 GHz) 18 W
Intel® Celeron® Processor P4500 (2M Cache, 1.86 GHz) 35 W
f Memory: Dual stacked SODIMM socket memory supporting dual channel memory
bandwidth, max. 8 GB of 800/1066 MHz DDR3 (ECC on Express-CBE)
f Chipset: Mobile Intel® QM57 Express
f L2 Cache: 2 MB (Celeron® M), 4/3 MB (Intel® Core™ i7/i5)
f BIOS: AMI EFI with CMOS backup in 16 Mbit SPI BIOS
f Hardware Monitor: Supply voltages and CPU temperature
f Watchdog Timer: Programmable timer ranges to generate RESET
2.2 Expansion Busses
f On Processor:
- PCI Express x16 Graphics bus for discrete graphics solution
or General Purpose PCI Express (2 x8, 2 x4, or 2 x1)
or Embedded Display Port (eDP, see below)
f On Chipset:
- 7 PCI Express x1: 0/1/2/3/4/5 are free, 6 is occupied by GbE LAN
can be optionally configured as 1 x4 (on 0/1/2/3) and 2 x1 (4/5)
- 32-bit PCI: PCI ver. 2.3 at 33MHz, supporting 4 bus masters
- LPC bus: for optional connections to SIO, UART etc
f SMBus (system), I2C (user)
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 8
Page 9

2.3 Video
f Core: Gen 5.75 with 12 execution units
f Integrated Graphics Features:
- DirectX 10 and OpenGL 2.1
- Intel® Dynamic Video Memory Technology (Intel® DVMT 5.0)
- Video capture via concurrent PCI Express x1 port
- PAVP (Protected Audio-Video Path) support for Protected Intel® HD Audio Playback
- High performance MPEG-2 decoding
- WMV9 (VC-1) and H.264 (AVC) support
- Hardware acceleration for MPEG2 VLD/iDCT
- Blu-ray support @ 40 Mb/s
- Hardware motion compensation
- Intermediate Z in classic rendering
f VGA Interface: Analog VGA support up to QXGA, 300MHz DAC
f LVDS Interface: Single or dual channel 18/24-bit at 25~112 MHz
f Embedded DisplayPort: One data pair supporting XGA (1024x768) over two wires
or two data pairs supporting SXGA (1280x1024) over four wires (see Note below).
Embedded DisplayPort (eDP)
DisplayPort is a VESA interface standard for digital display . It defines a new license-free, royalty-free, stateof-the-art digital audio/video interconnect, intended to be used primarily between a computer and its display
monitor, or a computer and a home-theater system. It features 1.62 Gb/s and 2.7 Gb/s transfer rates over 1,
2 or 4 data lanes, 8b 10b coding, Hot-Plug detect support and HDCP support. Embedded DisplayPort does
not offer all features of standard DisplayPort because embedded applications do not require features such
as link training, hot plug detection or logo testing. The eDP standard supports one data pair supporting
XGA (1024x768) over two wires. Optionally 4 wires can be used for two data pairs to support 1280x1024.
2.4 Audio
f Chipset: Integrated in Intel® I/O Controller Hub 9 Mobile (ICH9M)
f Audio Codec: on carrier (ALC888)
Page 9Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 9Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 9Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 9
Page 10

2.5 LAN
f Chipset: Integrated in Intel® QM57 with Intel® 82577 PHY
f Interface: 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet operates in full-duplex at all supported speeds or
half-duplex at 10/100 Mbps; adheres to the IEEE 802.3x Flow Control Specification
2.6 Multi I/O
f PATA: SATA-to-PATA JM20330 controller on SATA channel 0, Master only
f SATA: Four ports SATA 3 Gb/s (2, 3, 4, 5)
f USB: Supports up to eight ports USB 2.0
2. 7 Super I/O
f Connected to LPC bus on carrier if needed
2.8 TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
f Chipset: Infineon SLB9635TT1.2
f Type: TPM 1.2
2.9 Power Specifications
f Input Power: AT mode (12 V +/- 5%) and ATX mode (12 V and 5 Vsb +/- 5%)
f Power States: supporting S0, S1, S3, S4, S5
f Smart Battery Support: yes
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 10
Page 11

2.10 Power Consumption
The 12V measurement is power to the module only (excluding carrier board
power draw). The 5Vsb measurement (in S3/S5 mode) includes both module
power consumption plus active 5Vsb powered peripherals (such as PS/2
and USB) on the carrier that are needed for wakeup. Although all voltages
were measured, only 12 V and 5 VSB are relevant because they are the
only ones used by the Express module. The Idle power level was measured
under Windows XP with no applications running (login screen). Max Load
was measured under Windows XP running BurnIn software. Measurements
were made with two 1GB 1066 MHz DDR3 SODIMM memory modules installed.
Intel® Core™ i7-620UE, 1.06 GHz
Power State +12V +5V
Idle (Windows XP login) 0.70 A N.S. 8.4 W
Max. Load (Windows XP - BurnIn) 2.30 A N.S. 27.6 W
S1 (standby powered on) 0.97 A N.S. 1 1.6 W
S3 (suspend to RAM) - 0.28 A 1.4 W
S5 (soft off) - 0.18 A 0.9 W
SB
Power Consumption
Intel® Core™ i7-620LE, 2.00 GHz
Power State +12V +5V
Idle (Windows XP login) 0.74 A N.S. 8.9 W
Max. Load (Windows XP - BurnIn) 3.01 A N.S. 36.1 W
S1 (standby powered on) 1.08 A N.S. 13.0 W
S3 (suspend to RAM) - 0.29 A 1.5 W
S5 (soft off) - 0.17 A 0.9 W
SB
Power Consumption
Intel® Core™ i7-520E, 2.40 GHz
Power State +12V +5V
Idle (Windows XP login) 0.74 A N.S. 8.9 W
Max. Load (Windows XP - BurnIn) 3.30 A N.S. 39.6 W
S1 (standby powered on) 1.06 A N.S. 12.7 W
S3 (suspend to RAM) - 0.29 A 1.5 W
S5 (soft off) - 0.18 A 0.9 W
SB
Power Consumption
Page 11Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 11Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 11Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 11
Page 12

Power Consumption (cont’d)
®
Core™ i7-610E, 2.40 GHz
Intel
Power State +12V +5V
Idle (Windows XP login) 0.76 A N.S. 9.1 W
Max. Load (Windows XP - BurnIn) 3.10 A N.S. 37.2 W
S1 (standby powered on) 1.13 A N.S. 13.6 W
S3 (suspend to RAM) - 0.28 A 1.4 W
S5 (soft off) - 0.17 A 0.9 W
CMOS Battery Power Consumption
Current (+3V) Power
3.2 µA 0.0000096 W
2.11 Operating Systems
f Standard Support
- Windows XP 32/64-bit
- Windows Vista 32/64-bit
- Windows Server 2003/2008
SB
Power Consumption
f Extended Support (BSP)
- Embedded XP BSP
- WinCE 6.0 BSP
- AIDI I2C Library for Win32, WinCE and Linux
2.12 Mechanical and Environmental
f Form Factor and Type: PICMG COM.0, COM Express™ Basic form factor
f Compatibility: PICMG COM.0 R1, Type 2 pinout
f Dimensions: 95 x 125 mm
f Standard Operating Temperature: 0°C to 60°C
f Relative Humidity: up to 90% at 60°C
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 12
Page 13
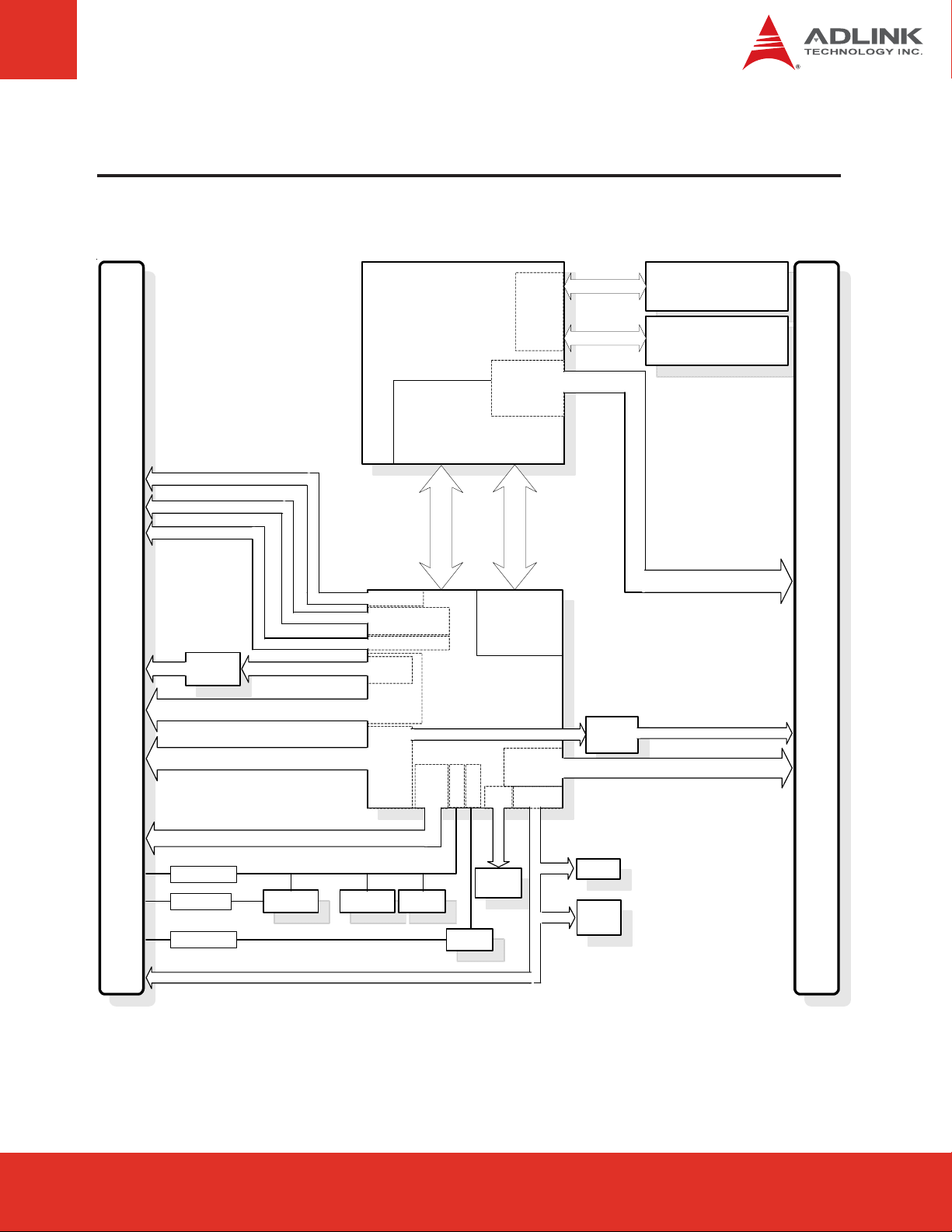
3 Function Diagram
AB
LAN
CRT
LVDS
Audio
Intel
LAN (occupies PCIe x1 port 6)
PHY
82577LM
PCIe x1 (port 0/1/2/3/4/5)
SATA (4 ports)
CPU
DMI
CRT VGA
LVDS
dual 18/24-bit
HD Audio
GbE
MAC
PCI-E x1
6x
SATA 2
8x
USB
2.0
Core i7
Core i5
PCIe x16 Gfx
PCIe 2 x8
Embedded
DisplayPort
Embedded
Graphics Core
SDVO
HDMI x3
DVI x3
DisplayPort x3
PCH
QM57
SATA (1 port)
GPIO
SPI
SMBus
DDR-3
Memory
Controller
(eDP)
FDI
PCI
33 MHz
v2.3
LPC
Channel A
Channel B
JM330
SATA to PATA
DDR3 SODIMM
800/1066/1333
DDR3 SODIMM
800/1066/1333
CD
PATA IDE
PCI
USB
SMBus
LPC
MAX6621
Mon(T)
GPIO
I2C BC
I2C to GPIO
LM87
Mon(T/V)
BIOS
Test
header
TPM
Page 13Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 13Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 13Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 13
Page 14
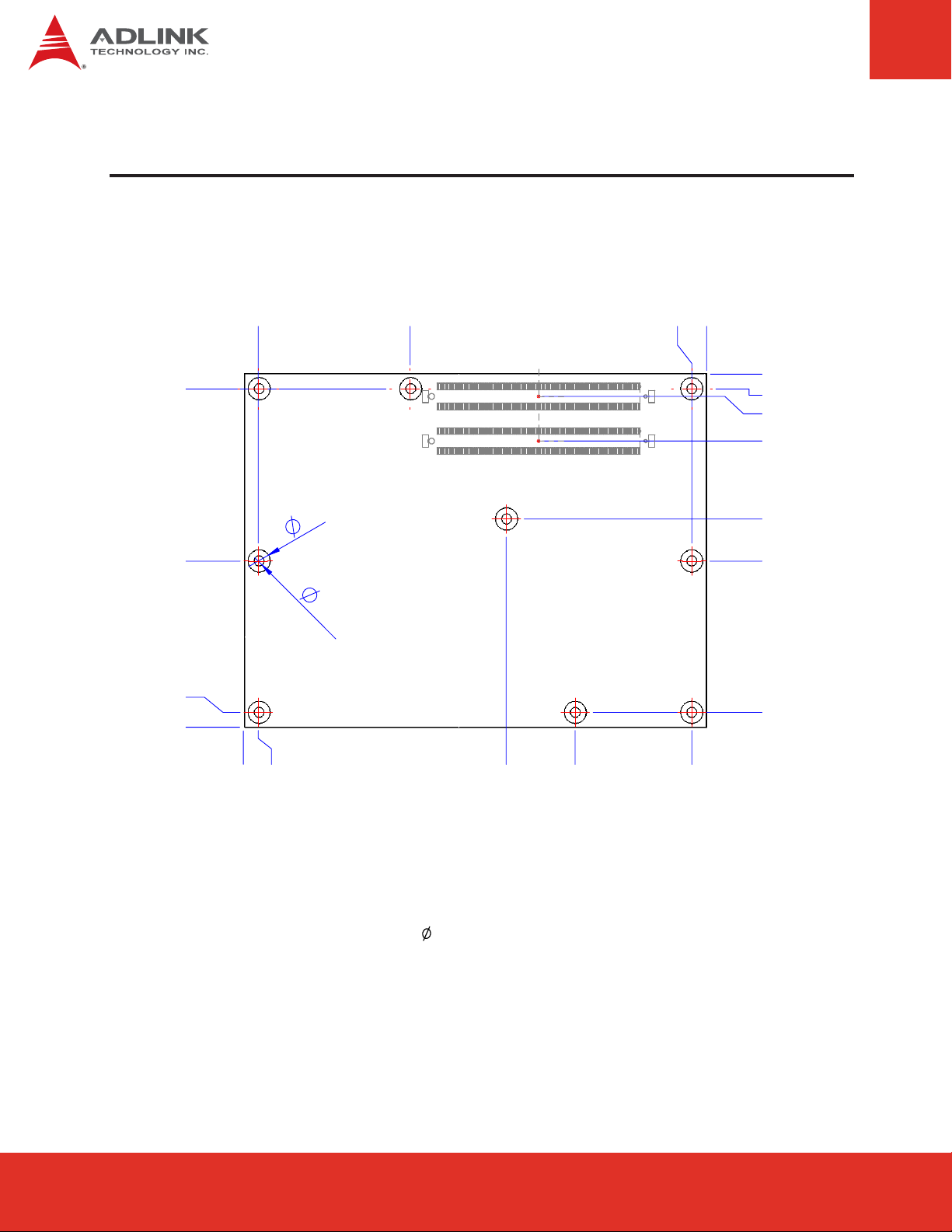
4 Mechanical Dimensions
121
80
0
4
50.3
95
91
4
connector on bottom side
6
2.7
4
121
125
54.08
35.5
0
4
6
18
39
50.3
91
TOP VIEW
All tolerances ± 0.05 mm
Other tolerances ± 0.2 mm
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 14
Page 15
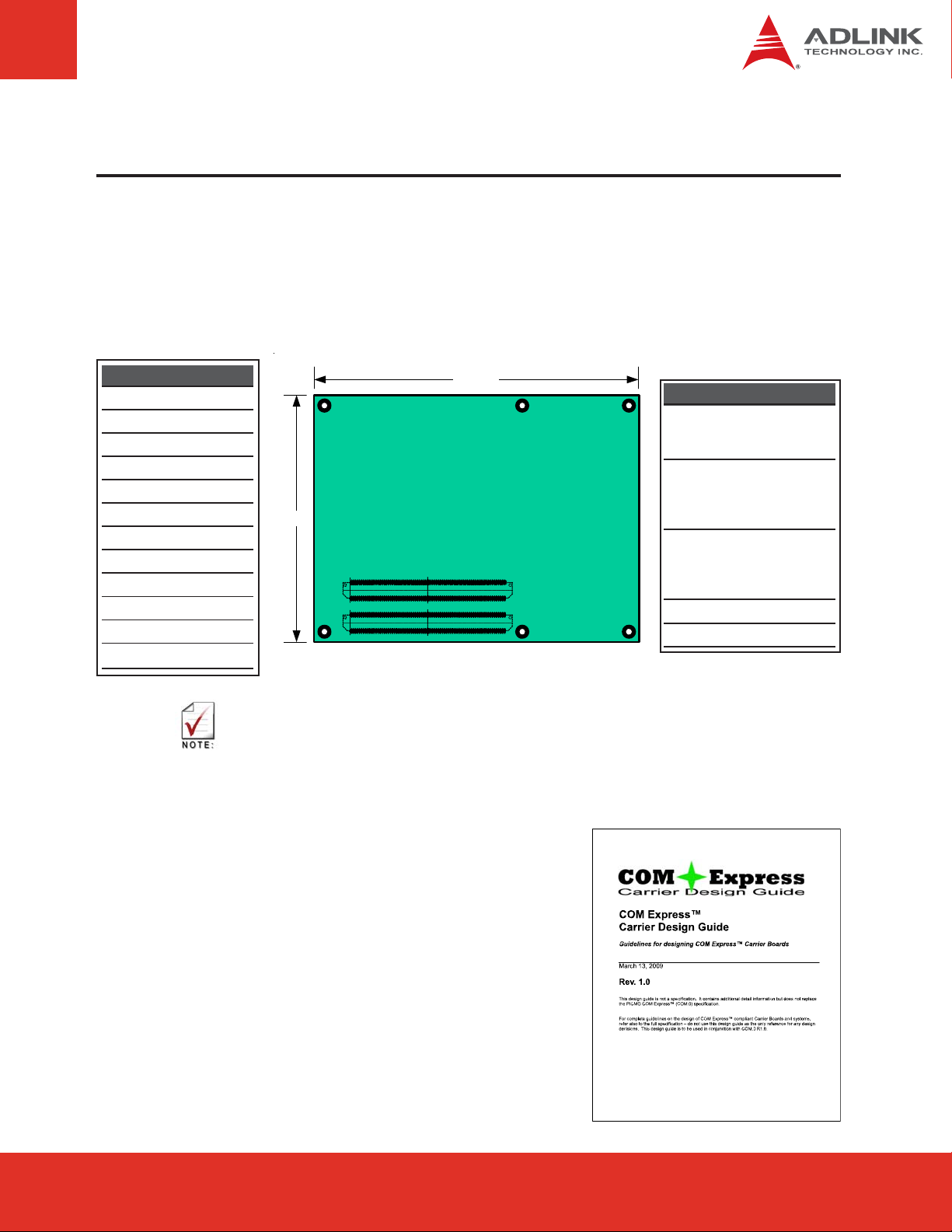
5 Pinout, Signal and Switch Descriptions
5.1 COM Express® Type 2 compatible pinout
All signals on AB and CD connectors of the Express-CB comply with pinouts and conventions
used in the original “PICMG® COM.0 R1.0: COM Express® Module Base Specification”.
AB Connector
1 Gigabit Ethernet port
LPC interface
4 Serial ATA channels
High Definition Audio
8 USB 2.0 ports
5 PCI Express Lanes x1
Dual 24-bit LVDS channels
Analog VGA
8 GPIO pins
SMBus and I2C bus
+12V primary power input
+5V standby and 3V RTC
125mm.
CD Connector
Parallel A T A, IDE port
alternate definition assigns this to
2 additional Gigabit Ethernet ports
32-bit PCI v2.3 bus
alternate definition assigns this to
95mm.
CD
AB
The above function mappings are a generic description of COM Express pinouts, and not
necessarily supported on the module described in this manual.
10 additional PCI Express x1
lanes
PCI Express x16 for Graphics
these pins can also be assigned
to two SDVO extensions
(multiplexed)
Power / Thermal control
+12V primary power input
5.2 Carrier Board Design Guide
The PICMG COM Express Carrier Design Guide is a
160-page document that provides information on
designing a custom carrier board for COM Express
modules. The design guide includes reference
schematics for the external circuitry required to
implement the various COM Express peripheral
functions, explains how to extend the supported buses,
and how to add additional peripherals and expansion
slots to a COM Express-based system. You can
download the document Carrier Design Guide at:
http://www.adlinktech.com/ccps/picmg_comdg_100.pdf
Page 15Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 15Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 15Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 15
Page 16
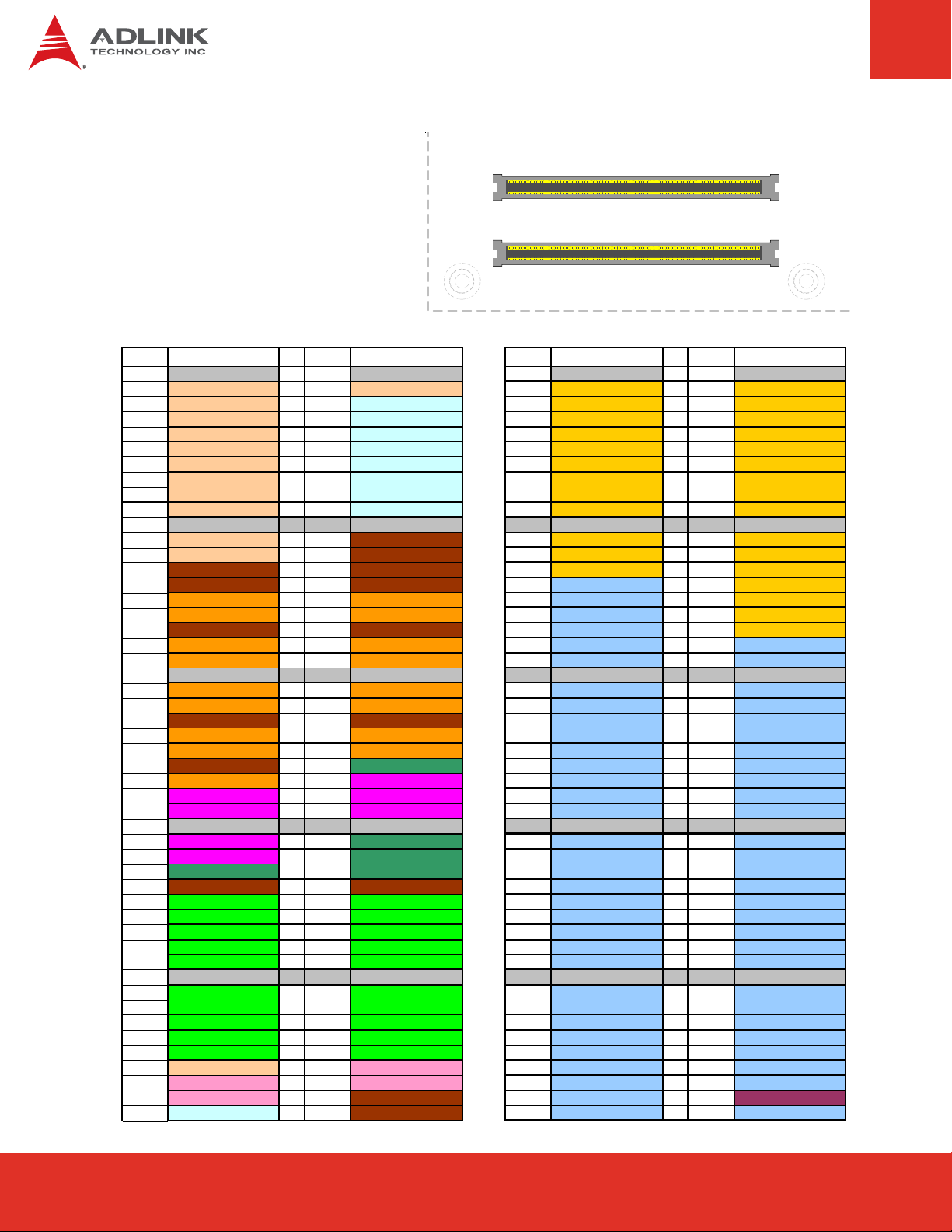
5.3 Pin Definitions
Pinouts for:
D1
D110
C D
C1
C110
B1
COM.0 R1.0 Type 2
A1
B110
A110
A B
Row A Row B Row C Row D
Pin No . Pin Na me Pin No . Pin N ame Pin No. Pin Name Pin No. Pin Na me
A1 GND (FIXE D) B1 GND (FIXED) C1 GND FIXED) D1 GND FIXED)
A2 GBE0_MDI3- B2 GBE0_ACT# C2 IDE_D7 D2 IDE_D5
A3 GBE0_MDI3+ B3 LPC_FRAME# C3 IDE_D6 D3 IDE_D10
A4 GBE0_LINK100# B4 LPC_AD0 C4 IDE_D3 D4 IDE_D11
A5 GBE0_LINK1000# B5 LPC_AD1 C5 IDE_D15 D5 IDE_D12
A6 GBE0_MDI2- B6 LPC_AD2 C6 IDE_D8 D6 IDE_D4
A7 GBE0_MDI2+ B7 LPC_AD3 C7 IDE_D9 D7 IDE_D0
A8 GBE0_LINK# B8 LPC_DRQ0# C8 IDE_D2 D8 IDE_REQ
A9 GBE0_MDI1- B9 LPC_DRQ1# C9 IDE_D13 D9 IDE_IOW#
A10 GBE0_MDI1+ B10 LPC_CLK C10 IDE_D1 D10 IDE_ACK#
A11 GND (FIXED) B11 GND (FIXED) C11 GND (FIXED) D11 GND (FIXED)
A12 GBE0_MDI0- B12 PWRBTN# C12 IDE_D14 D12 IDE_IRQ
A13 GBE0_MDI0+ B13 SMB_CK C13 IDE_IORDY D13 IDE_A0
A14 GBE0_CTREF B14 SMB_DAT C14 IDE_IOR# D14 IDE_A1
A15 SUS_S3# B15 SMB_ALERT# C15 PCI_PME# D15 IDE_A2
A16 SATA0_TX+ B16 SATA1_TX+ C16 PCI_GNT2# D16 IDE_CS1#
A17 SATA0_TX- B17 SATA1_TX- C17 PCI_REQ2# D17 IDE_CS3#
A18 SUS_S4# B18 SUS_STAT# C18 PCI_GNT1# D18 IDE_RESET#
A19 SATA0_RX+ B19 SATA1_RX+ C19 PCI_REQ1# D19 PCI_GNT3#
A20 SATA0_RX- B20 SATA1_RX- C 20 PCI_GNT0# D20 PCI_REQ3#
A21 GND (FIXED) B21 GND (FIXED) C21 GND (FIXED) D21 GND (FIXED)
A22 SATA2_TX+ B22 SATA3_TX+ C22 PCI_REQ0# D22 PCI_AD1
A23 SATA2_TX- B23 SATA3_TX- C23 PCI_RESET# D23 PCI_AD3
A24 SUS_S5# B24 PWR_OK C24 PCI_AD0 D24 PCI_AD5
A25 SATA2_RX+ B25 SATA3_RX+ C25 PCI_AD2 D25 PCI_AD7
A26 SATA2_RX- B26 SATA3_RX- C26 PCI_AD4 D26 PCI_C/BE0#
A27 BATLOW# B27 WDT C27 PCI_AD6 D27 PCI_AD9
A28 ATA_ACT# B28 AC_SDIN2 C28 PCI_AD8 D28 PCI_AD11
A29 AC_SYNC B29 AC_SDIN1 C29 PCI_AD10 D29 PCI_AD13
A30 AC_RST# B30 AC_SDIN0 C30 PCI_AD12 D30 PCI_AD15
A31 GND (FIXED) B31 GND (FIXED) C31 GND (FIXED) D31 GND (FIXED)
A32 AC_BITCLK B32 SPKR C32 PCI_AD14 D32 PCI_PAR
A33 AC_SDOUT B33 I2C_CK C33 PCI_C/BE1# D33 PCI_SERR#
A34 BIOS_DISABLE# B34 I2C_DAT C34 PCI_PERR# D34 PCI_STOP#
A35 THRMTRIP# B35 THRM# C35 PCI_LOCK# D35 PCI_TRDY#
A36 USB6- B36 USB7- C36 PCI_DEVSEL# D36 PCI_FRAME#
A37 USB6+ B37 USB7+ C37 PCI_IRDY# D37 PCI_AD16
A38 USB_6_7_OC# B38 USB_4_5_OC# C38 PCI_C/BE2# D38 PCI_AD18
A39 USB4- B39 USB5- C39 PCI_AD17 D39 PCI_AD20
A40 USB4+ B40 USB5+ C40 PCI_AD19 D40 PCI_AD22
A41 GND (FIXED) B41 GND (FIXED) C41 GND (FIXED) D41 GND (FIXED)
A42 USB2- B42 USB3- C42 PCI_AD21 D42 PCI_AD24
A43 USB2+ B43 USB3+ C43 PCI_AD23 D43 PCI_AD26
A44 USB_2_3_OC# B44 USB_0_1_OC# C44 PCI_C/BE3# D44 PCI_AD28
A45 USB0- B45 USB1- C45 PCI_AD25 D45 PCI_AD30
A46 USB0+ B46 USB1+ C46 PCI_AD27 D46 PCI_IRQC#
A47 VCC_RTC B47 EXCD1_PERST# C47 PCI_AD29 D47 PCI_IRQD#
A48 EXCD0_PERST# B48 EXCD1_CPPE# C48 PCI_AD31 D48 PCI_CLKRUN#
A49 EXCD0_CPPE# B49 SYS_RESET# C49 PCI_IRQA# D49 PCI_M66EN (GND)
A50 LPC_SERIRQ B50 CB_RESET# C50 PCI_IRQB# D50 PCI_CLK
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 16
Page 17
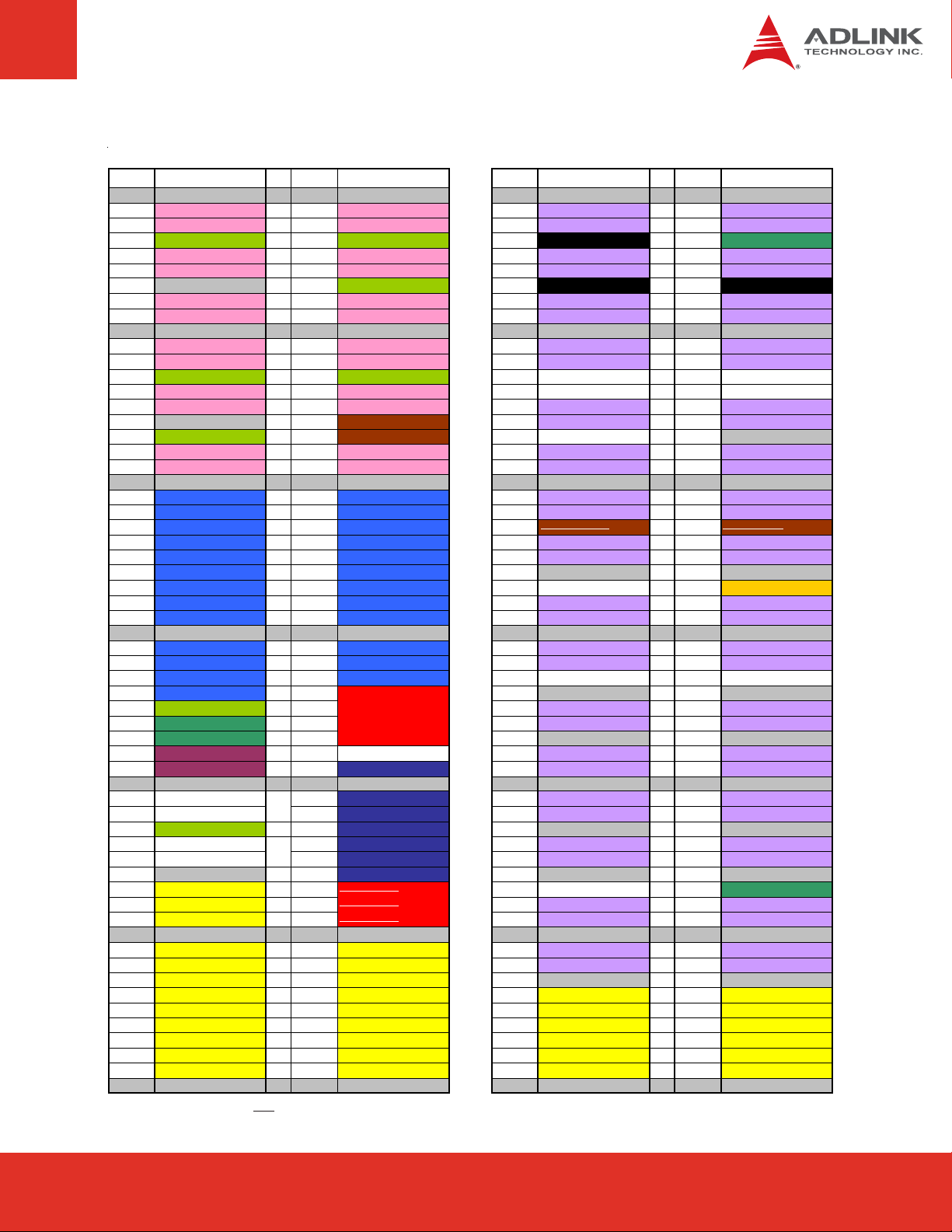
Row A Row B Row C Row D
Pin No . Pin Na me Pin No . Pin N ame Pin No. Pin Name Pin No. Pin Na me
A51 GND (FIXED) B51 GND (FIXED) C51 GND (FIXED) D51 GND (FIXED)
A52 PCIE_TX5+ B52 PCIE_RX5+ C52 PEG_RX0+ D52 PEG_TX0+
A53 PCIE_TX5- B53 PCIE_RX5- C53 PEG_RX0- D53 PEG_TX0A54 GPI0 B54 GPO1 C54 TYPE0# D54 PEG_LANE_RV#
A55 PCIE_TX4+ B55 PCIE_RX4+ C55 PEG_RX1+ D55 PEG_TX1+
A56 PCIE_TX4- B56 PCIE_RX4- C56 PEG_RX1- D56 PEG_TX1A57 GND B57 GPO2 C57 TYPE1# D57 TYPE2#
A58 PCIE_TX3+ B58 PCIE_RX3+ C58 PEG_RX2+ D58 PEG_TX2+
A59 PCIE_TX3- B59 PCIE_RX3- C59 PEG_RX2- D59 PEG_TX2A60 GND (FIXED) B60 GND (FIXED) C60 GND (FIXED) D60 GND (FIXED)
A61 PCIE_TX2+ B61 PCIE_RX2+ C61 PEG_RX3+ D61 PEG_TX3+
A62 PCIE_TX2- B62 PCIE_RX2- C62 PEG_RX3- D62 PEG_TX3A63 GPI1 B63 GPO3 C63 RSVD D63 RSVD
A64 PCIE_TX1+ B64 PCIE_RX1+ C64 RSVD D64 RSVD
A65 PCIE_TX1- B65 PCIE_RX1- C65 PEG_RX4+ D65 PEG_TX4+
A66 GND B66 WAKE0# C66 PEG_RX4- D66 PEG_TX4A67 GPI2 B67 WAKE1# C67 RSVD D67 GND
A68 PCIE_TX0+ B68 PCIE_RX0+ C68 PEG_RX5+ D68 PEG_TX5+
A69 PCIE_TX0- B69 PCIE_RX0- C69 PEG_RX5- D69 PEG_TX5A70 GND (FIXED) B70 GND (FIXED) C70 GND (FIXED) D70 GND (FIXED)
A71 LVDS_A0+ B71 LVDS_B0+ C71 PEG_RX6+ D71 PEG_TX6+
A72 LVDS_A0- B72 LVDS_B0- C72 PEG_RX6- D72 PEG_TX6A73 LVDS_A1+ B73 LVDS_B1+ C73 SDVO_DATA
A74 LVDS_A1- B74 LVDS_B1- C74 PEG_RX7+ D74 PEG_TX7+
A75 LVDS_A2+ B75 LVDS_B2+ C75 PEG_RX7- D75 PEG_TX7A76 LVDS_A2- B76 LVDS_B2- C76 GND D76 GND
A77 LVDS_VDD_EN B77 LVDS_B3+ C77 RSVD D77 IDE_CBLID#
A78 LVDS_A3+ B78 LVDS_B3- C78 PEG_RX8+ D78 PEG_TX8+
A79 LVDS_A3- B79 LVDS_BKLT_EN C79 PEG_RX8- D79 PEG_TX8A80 GND (FIXED) B80 GND (FIXED) C80 GND (FIXED) D80 GND (FIXED)
A81 LVDS_A_CK+ B81 LVDS_B_CK+ C81 PEG_RX9+ D81 PEG_TX9+
A82 LVDS_A_CK- B82 LVDS_B_CK- C82 PEG_RX9- D82 PEG_TX9A83 LVDS_I2C_CK B83 LVDS_ BKLT_CTRL C83 RSVD D83 RSVD
A84 LVDS_I2C_DAT B84 VCC_5V_SBY C84 GND D84 GND
A85 GPI3 B85 VCC_5V_SBY C85 PEG_RX10+ D85 PEG_TX10+
A86 KBD_RST# B86 VCC_5V_SBY C86 PEG_RX10- D86 PEG_TX10A87 KBD_A20GATE B87 VCC_5V_SBY C87 GND D87 GND
A88 PCIE0_CK_REF+ B88 RSVD C88 PEG_RX11+ D88 PEG_TX11+
A89 PCIE0_CK_REF- B89 VGA_RED C89 PEG_RX11- D89 PEG_TX11A90 GND (FIXED) B90 GND (FIXED) C90 GND (FIXED) D90 GND (FIXED)
A91 RSVD B91 VGA_GRN C91 PEG_RX12+ D91 PEG_TX12+
A92 RSVD B92 VGA_BLU C92 PEG_RX12- D92 PEG_TX12A93 GPO0 B93 VGA_HSYNC C93 GND D93 GND
A94 RSVD B94 VGA_VSYNC C94 PEG_RX13+ D94 PEG_TX13+
A95 RSVD B95 VGA_I2C_CK C95 PEG_RX13- D95 PEG_TX13A96 GND B96 VGA_I2C_DAT C96 GND D96 GND
A97 VCC_12V B97 TV_DAC_A
A98 VCC_12V B98 TV_DAC_B
A99 VCC_12V B99 TV_DAC_C
A100 GND (FIXED) B100 GND (FIXED) C 1 00 GND (FIXED) D100 GND (FIXED)
A101 VCC_12V B101 VCC_12V C101 PEG_RX15+ D101 PEG_TX15+
A102 VCC_12V B102 VCC_12V C102 PEG_RX15- D102 PEG_TX15A103 VCC_12V B103 VCC_12V C103 GND D103 GND
A104 VCC_12V B104 VCC_12V C104 VCC_12V D104 VCC_12V
A105 VCC_12V B105 VCC_12V C105 VCC_12V D105 VCC_12V
A106 VCC_12V B106 VCC_12V C106 VCC_12V D106 VCC_12V
A107 VCC_12V B107 VCC_12V C107 VCC_12V D107 VCC_12V
A108 VCC_12V B108 VCC_12V C108 VCC_12V D108 VCC_12V
A109 VCC_12V B109 VCC_12V C109 VCC_12V D109 VCC_12V
A110 GND (FIXED) B110 GND (FIXED) C 1 10 GND (FIXED) D110 GND (FIXED)
C97 RSVD D97 PEG_ENABLE#
C98 PEG_RX14+ D98 PEG_TX14+
C99 PEG_RX14- D99 PEG_TX14-
D73 SDVO_CLK
XXX Strikethrough pin names indicates that the signal is not supported on this module.
Page 17Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 17Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 17Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 17
Page 18
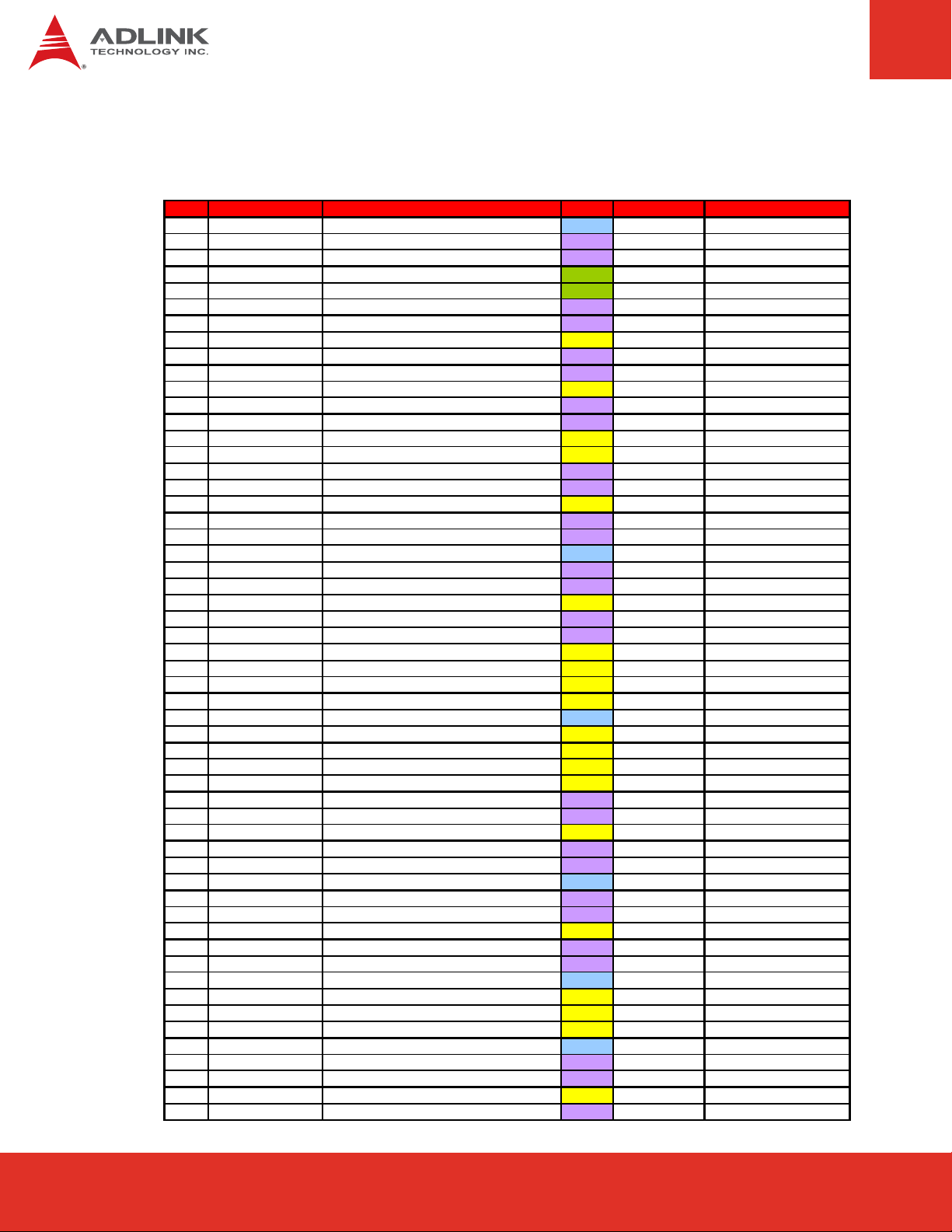
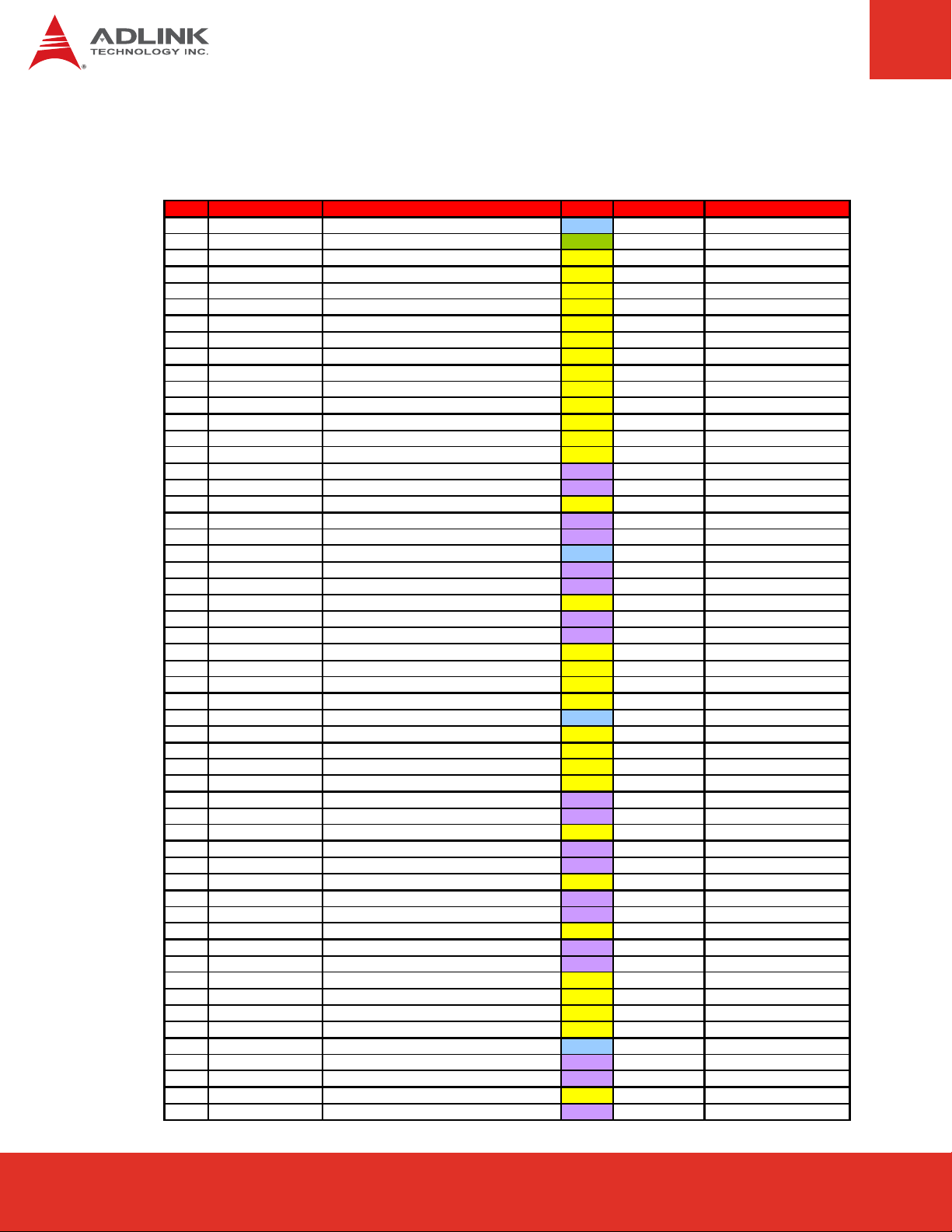
5.4 Signal Descriptions
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
A1 GND Ground PWR - A2 GBE0_MDI3- Ethernet Media Dependent Interface - I/O - DP - A3 GBE0_MDI3+ Ethernet Media Dependent Interface + I/O - DP - A4 GBE0_LINK100# Ethernet Speed LED (100Mb) OD - On at 100Mb/s
A5 GBE0_LINK1000# Ethernet Speed LED (1000Mb) OD - On at 1000Mb/s
A6 GBE0_MDI2- Ethernet Media Dependent Interface - I/O - DP - A7 GBE0_MDI2+ Ethernet Media Dependent Interface + I/O - DP - A8 GBE0_LINK# LAN Link LED O-3.3 -
A9 GBE0_MDI1- Ethernet Media Dependent Interface - I/O - DP - A10 GBE0_MDI1+ Ethernet Media Dependent Interface + I/O - DP - A11 GND Ground PWR - A12 GBE0_MDI0- Ethernet Media Dependent Interface - I/O - DP - A13 GBE0_MDI0+ Ethernet Media Dependent Interface + I/O - DP - A14 GBE0_CTREF ETHCTREF O-1,8 - A15 SUS_S3# PM_SLP_S#3 O-3.3 - A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A22
A23
A24
A25
A26
A27
A28
A29
A30
A31
A32
A33
A34
A35
A36
A37
A38
A39
A40
A41
A42
A43
A44
A45
A46
A47
A48
A49
A50
A51
A52
A53
A54
A55
SATA0_TX+
SATA0_TX-
SUS_S4#
SATA0_RX+
SATA0_RX-
GND
SATA2_TX+
SATA2_TX-
SUS_S5#
SATA2_RX+
SATA2_RX-
BATLOW#
ATA_ACT#
AC_SYNC
AC_RST#
GND
AC_BITCLK
AC_SDOUT
BIOS_DISABLE#
THRMTRIP#
USB6-
USB6+
USB_6_7_OC#
USB4-
USB4+
GND
USB2-
USB2+
USB_2_3_OC#
USB0-
USB0+
VCC_RTC
EXCD0_PERST#
EXCD0_CPPE#
LPC_SERIRQ
GND
PCIE5_TX+
PCIE5_TX-
GPI0
PCIE4_TX+
SATA0_TX+ | SATA 0 Transmit Data + O - DP - SATA0_TX- | SATA 0 Transmit Data - O - DP - PM_SLP_S#4 O-3.3 - SATA0_RX+ | SATA 0 Receive Data + I - DP - SATA0_RX - | SATA 0 Receive Data - I - DP - Ground PWR - SATA2_TX+ | SATA 2 Transmit Data + O - DP - SATA2_TX- | SATA 2 Transmit Data - O - DP - PM_SLP_S#5 O-3.3 - SATA2_RX+ | SATA 2 Receive Data + I - DP - SATA2_RX- | SATA 2 Receive Data - I - DP - PM_BATLOW# | Battery Low I-3.3 PU 8k2 3.3Vsb ATA_LED# | SATA LED O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V
AC_SYNC | A C'97 Sync O- 3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM 57
AC_RST# | AC'97 Reset O-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
Ground PWR AC_BITCLK | AC'97 Clock O-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
AC_SDATAOUT | AC'97 Data O-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
BIOS_DISABLE# I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PM_THRMTRIP#_CON O-3.3 PU 330 3.3V USB_PN6 | USB Data – Port6 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_PP6 | USB Data + Port6 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_OC#_6_7 | USB OverCurrent Port 6/7 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb USB_PN4 | USB Data - Port4 I/O - DP - int. PD 2 0k in QM57
USB_PP4 | USB Data + Port4 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
Ground PWR - USB_PN2 | USB Data - Port2 I/O - DP - int. PD 2 0k in QM57
USB_PP2 | USB Data + Port2 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_OC#_2_3 | USB OverCurrent Port 2/3 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb
USB_PN0 | USB Data - Port0 I/O - DP - int. PD 2 0k in QM57
USB_PP0 | USB Data + Port0 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
V_BAT PWR - Express Card Support [0]|card reset O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb Expr ess Card Support [0]| capable request I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V INT_SERIRQ | Serial Interrupt Request IO-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V Ground PWR - PCI Express 5 Transmit + O - DP - PCI Express 5 Transmit - O - DP - General Purpose Input 0 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 4 Transmit + O - DP - -
Row A
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 18
Page 19
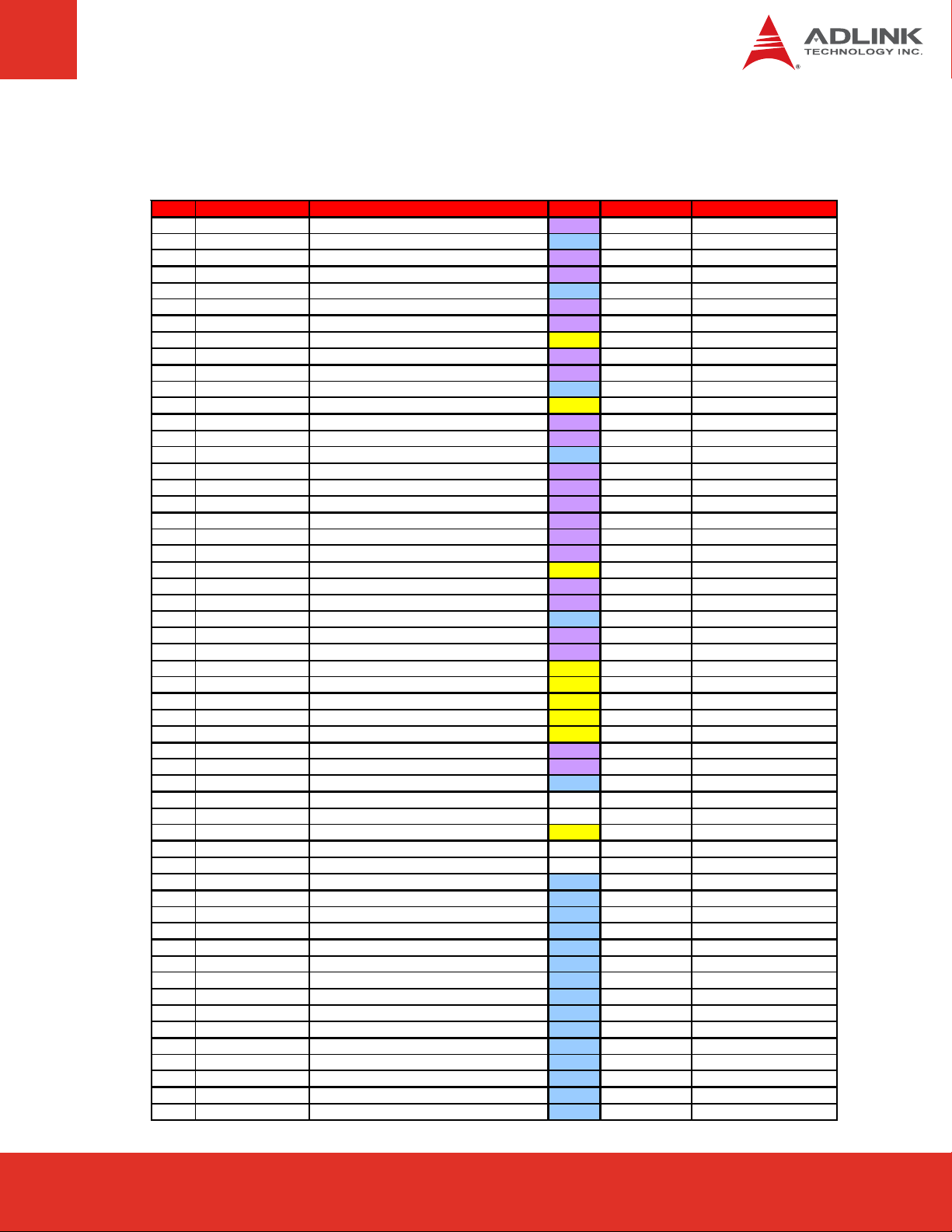
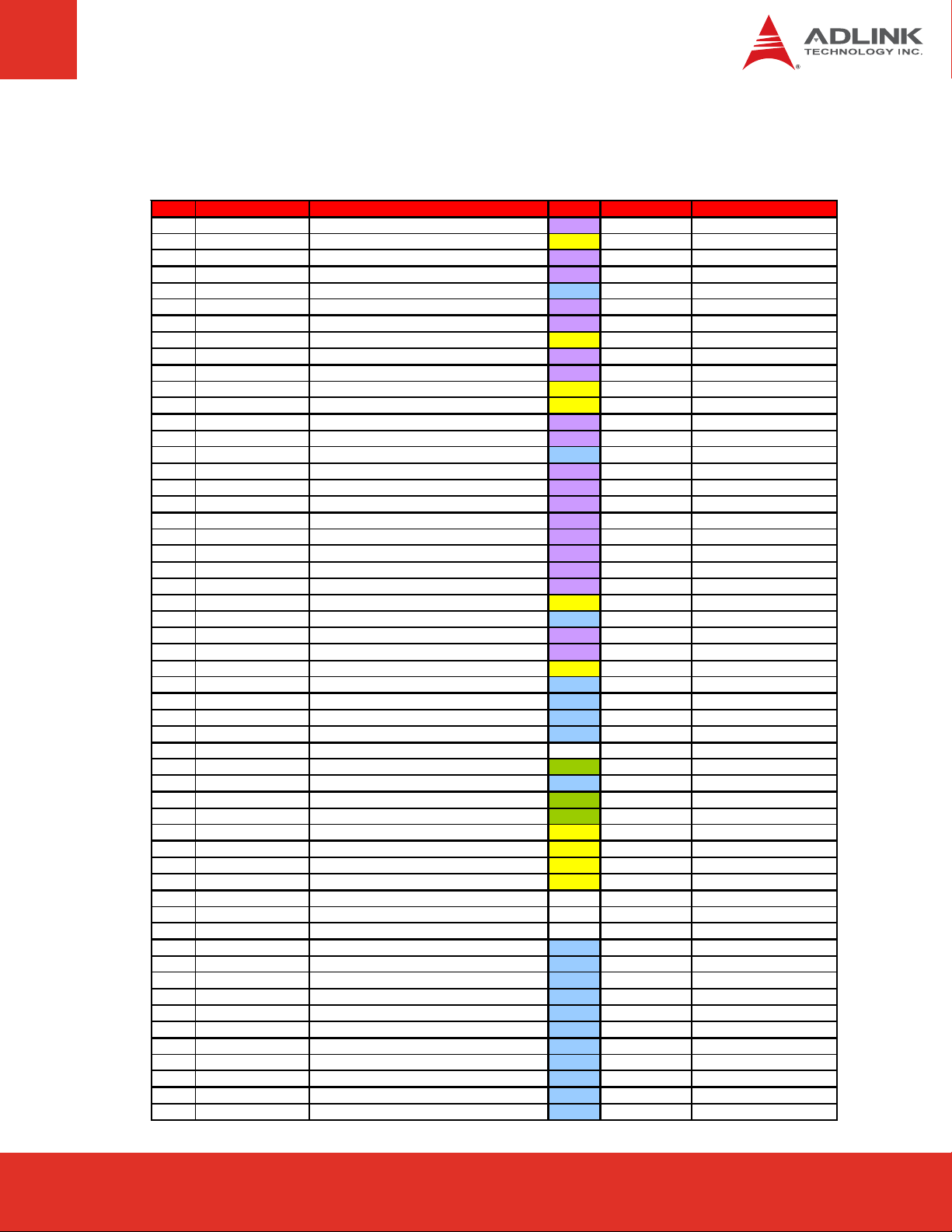
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
Row A
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
A56
A57
A58
A59
A60
A61
A62
A63
A64
A65
A66
A67
A68
A69
A70
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
A77
A78
A79
A80
A81
A82
A83
A84
A85
A86
A87
A88
A89
A90
A91
A92
A93
A94
A95
A96
A97
A98
A99
A100
A101
A102
A103
A104
A105
A106
A107
A108
A109
A110
PCIE4_TX-
GND
PCIE3_TX+
PCIE3_TX-
GND
PCIE2_TX+
PCIE2_TX-
GPI1
PCIE1_TX+
PCIE1_TX-
GND
GPI2
PCIE0_TX+
PCIE0_TX-
GND
LVDS_A0+
LVDS_A0LVDS_A1+
LVDS_A1LVDS_A2+
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_VDD_EN
LVDS_A3+
LVDS_A3-
GND
LVDS_A_CK+
LVDS_A_CK-
LVDS_I2C_CK
LVDS_I2C_DAT
GPI3
KBD_RST#
KBD_A20GATE
PCIE_CK_REF+
PCIE_CK_REF-
GND
RSVD
RSVD
GPO0
RSVD
RSVD
GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND
PCI Express 4 Transmit - O - DP - Ground PWR - PCI Express 3 Transmit + O - DP - PCI Express 3 Transmit - O - DP - Ground PWR - PCI Express 2 Transmit + O - DP - PCI Express 2 Transmit - O - DP - General Purpose Input 1 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 1 Transmit + O - DP - PCI Express 1 Transmit - O - DP - Ground PWR - General Purpose Input 2 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 0 + O - DP - PCI Express 0 - O - DP - Ground PWR - LVDS_AP0 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AN0 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AP1 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AN1 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AP2 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AN2 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_VDDEN | LVDS Panel Power O-2,5 PD 10k LVDS_AP3 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_AN3 | LVDS Channel A O - DP - Ground PWR - LVDS_CLKAP | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LVDS_CLKAN | LVDS Channel A O - DP - LV DS_DDCPCLK | JILI I2C Clock IO-3.3 PU 2k2 3.3V LVDS_DDCPDATA | JILI I2C Data IO-3.3 PU 2k2 3.3V General Purpose Input 3 I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb H_RCIN# | Keyboard R eset I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V H_A20GATE I-3.3 PU 8k2 3.3V CLK_PCIE_REF P O - DP - CLK_PCIE_REF N O - DP - Ground PWR - NC NC - NC NC - General Purpose Output 0 O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb NC NC - NC NC - Ground PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Ground PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Ground PWR - -
Page 19Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 19Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 19Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 19
Page 20
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
_
_RX-
_
AC_
_
_
Row B
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
B1 GND Ground PWR - B2 GBE0_ACT# LAN_ACTLED# | Ethernet Activity LED OD PU 1k 3.3V B3 LPC_FRAME# LPC_FRAME# | LPC Frame Indicator O-3.3 - B4 LPC_AD0 LPC_AD0 | LPC Adre ss & DATA Bus IO-3.3 B5 LPC_AD1 LPC_AD1 | LPC Adre ss & DATA Bus IO-3.3 B6 LPC_AD2 LPC_AD2 | LPC Adre ss & DATA Bus IO-3.3 B7 LPC_AD3 LPC_AD3 | LPC Adre ss & DATA Bus IO-3.3 B8 LPC_DRQ0# SIO_DRQ#0 | LPC Serial DMA Request 0 I-3.3 - int. PU 20k in QM57
B9 LPC_DRQ1# SIO_DRQ#1 | LPC Serial DMA Request 1 I-3.3 - int. PU 20k in QM57
B10 LPC_CLK CLK_SIOE XTPCI O-3.3 - B11 GND Ground I-3.3 - B12 PWRBTN# Power Button I-5 PU 10k 3.3Vsb B13 SMB_C K SMBUS Clock O- 3 .3 PU 2k2 3.3Vsb B14 SMB_DAT S MBUS Data IO-3.3 PU 2k2 3.3Vsb B15 SMB_ALERT# SMB_ALERT# I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb B16
B17
B18
B19
B20
B21
B22
B23
B24
B25
B26
B27
B28
B29
B30
B31
B32
B33
B34
B35
B36
B37
B38
B39
B40
B41
B42
B43
B44
B45
B46
B47
B48
B49
B50
B51
B52
B53
B54
B55
SATA1
TX+
SATA1_TXSUS_STAT#
SATA1_RX+
SATA1
GND
SATA3_TX+
SATA3_TX-
PWR_OK
SATA3
RX+
SATA3_RX-
WDT
AC_SDIN2
SDIN1
AC_SDIN0
GND
SPKR
I2C_CK
I2C
DAT
THRM#
USB7-
USB7+
USB_4_5_OC#
USB5-
USB5+
GND
USB3-
USB3+
USB_0_1_OC#
USB1-
USB1+
EXCD1_PERST#
EXCD1
CPPE#
SYS_RESET#
CB_RESET#
GND
PCIE5_RX+
PCIE5_RX-
GPO1
PCIE4_RX+
SATA1_TX+ | SATA 1 Transmit Data + O - DP - SATA1_TX- | SATA 1 Transmit Data - O - DP - PM_SUS_ STAT# O-3.3 - SATA1_RX+ | SATA 1 Receive Data + I - DP - SATA1_RX - | SATA 1 Receive Data - I - DP - Ground PWR - SATA3_TX+ | SATA 3 Transmit Data + O - DP - SATA3_TX- | SATA 3 Transmit Data - O - DP - Power OK I,3 .3 P U 10k 3.3Vsb SATA3_RX+ | SATA 3 Receive Data + I - DP - SATA3_RX - | SATA 3 Receive Data - I - DP - Watch Dog Timer O-3.3 AC_SDATAIN2 I-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
AC_SDATAIN1 I-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
AC_SDATAIN0 I-3.3 - int. PD 20k in QM57
Ground PWR AC_SPKR O-3.3 - in t. PD 20k in QM57
I2CLK O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V I2DAT IO-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V PM THRM# CON | Over Temperature I-3.3 USB_PN7 | USB Data – Port7 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_PP7 | USB Data + Port7 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_OC#_4_5 | USB OverCurrent Port I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb
USB_PN5 | USB Data- Port5 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_PP5 | USB Data+ Port5 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
Ground I-3.3 - USB_PN3 | USB Data- Port3 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_PP3 | USB Data+ Port3 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_OC#_0_1 | USB OverCurrent Port I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb USB_PN1 | USB Data- Port1 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
USB_PP1 | USB Data+ Port1 I/O - DP - int. PD 20k in QM57
Express Card Support [1]|card reset O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb Expr ess Card Support [1]| capable c. I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3V ETX_SYS_RESET# | Reset Input I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI_RST# | PC I Bus Reset O-3.3 - Ground PWR - PCI Express 5 Recieve + I - DP - PCI Express 5 Receive - I - DP - General Purpose Output 1 O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 4 Recieve + I - DP - -
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 20
Page 21
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
_
_
_
Row B
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
B56
B57
B58
B59
B60
B61
B62
B63
B64
B65
B66
B67
B68
B69
B70
B71
B72
B73
B74
B75
B76
B77
B78
B79
B80
B81
B82
B83
B84
B85
B86
B87
B88
B89
B90
B91
B92
B93
B94
B95
B96
B97
B98
B99
B100
B101
B102
B103
B104
B105
B106
B107
B108
B109
B110
PCIE4_RX-
GPO2
PCIE3_RX+
PCIE3_RX-
GND
PCIE2_RX+
PCIE2_RX-
GPO3
PCIE1_RX+
PCIE1_RX-
WAKE0#
WAKE1#
PCIE0_RX+
PCIE0_RX-
GND
LVDS
B0+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS
B2+
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_BKLT_EN
GND
LVDS_B_CK+
LVDS_B_CK-
LVDS_BKLT_CTRL
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
RSVD
VGA
RED
GND
VGA_GRN
VGA_BLU
VGA_HSYNC
VGA_VSYNC
VGA_I2C_CK
VGA_I2C_DAT
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND
PCI Express 4 Receive - I - DP - General Purpose Output 2 O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 3 Recieve + I - DP - PCI Express 3 Receive - I - DP - Ground PWR - PCI Express 2 Receive + I - DP - PCI Express 2 Receive - I - DP - General Purpose Output 3 O-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 1 Receive + I - DP - PCI Express 1 Receive - I - DP - PCIE_W AK EI# I-3.3 PU 1k 3.3 V sb WAKE1# I-3.3 PU 10k 3.3Vsb PCI Express 0 Receive + I - DP - PCI Express 0 Receive - I - DP - Ground PWR - LVDS_BP0 | LVDS Channel B Data0+ O - DP - LVDS_BN0 | LVDS Channel B Data0- O - DP - LVDS_BP1 | LVDS Channel B Data1+ O - DP - LVDS_BN1 | LVDS Channel B Data1- O - DP - LVDS_BP2 | LVDS Channel B Data2+ O - DP - LVDS_BN2 | LVDS Channel B Data2- O - DP - LVDS_BP3 | LVDS Channel B Data3+ O - DP - LVDS_BN3 | LVDS Channel B Data3- O - DP - LVDS Panel Backlight Enable O-3.3 PD 100k Ground PWR - LVDS_CLKBP | LVDS Channel B O - DP - LVDS_CLKBM | LVDS Channel B O - DP - Backlight Brightness O-3.3 PD 100k 5V Standby PWR - 5V Standby PWR - 5V Standby PWR - 5V Standby PWR - NC
Analog Video RGB-RED OA PD 150R Ground PWR - Analog Video RGB-GREEN OA PD 150R Analog Video RGB-BLUE OA PD 150R Analog Video H-Sync O-3.3 - Analog Video V-Sync O-3.3 - Display Data Channel - Cl ock O - 3.3 Display Data Channel - Data IO- 3.3 NC
NC
NC
Ground PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Ground PWR - -
NC
NC
NC
NC
--
--
--
--
Page 21Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 21Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 21Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 21
Page 22
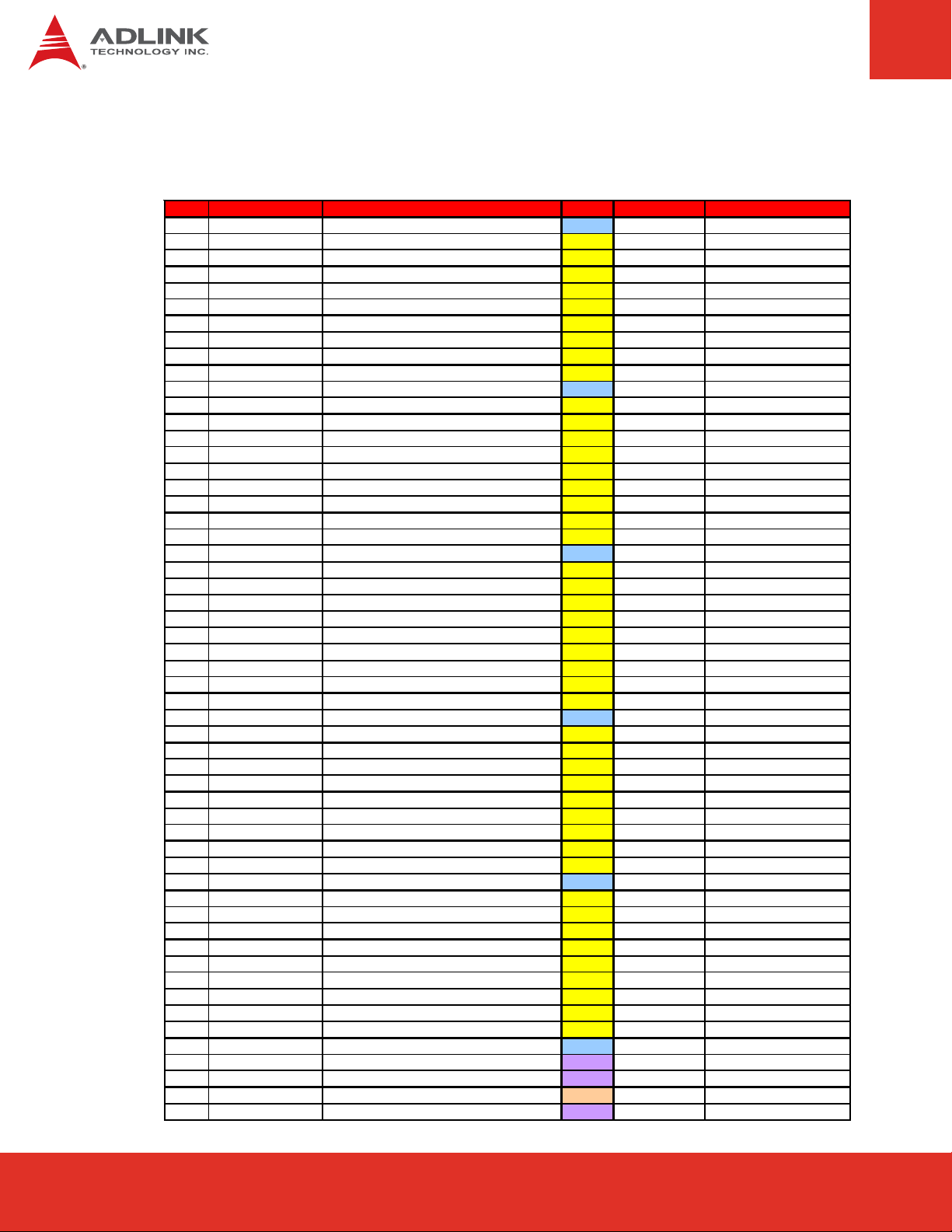
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
r
Row C
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
C10
C11
C12
C13
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
C21
C22
C23
C24
C25
C26
C27
C28
C29
C30
C31
C32
C33
C34
C35
C36
C37
C38
C39
C40
C41
C42
C43
C44
C45
C46
C47
C48
C49
C50
C51
C52
C53
C54
C55
GND
IDE_D7
IDE_D6 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D3 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D15 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D8
IDE_D9 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D2 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D13 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D1 IDE Data Bus
GND
IDE_D14 IDE Data Bus
IDE_IORDY IDE I/O Ready
IDE_IOR# I/O read line to IDE device
PCI_PME#
PCI_GNT2#
PCI_REQ2# PCI Bus Re que st 2
PCI_GNT1# PCI Bus Grant 1
PCI_REQ1# PCI Bus Re que st 1
PCI_GNT0#
GND Ground
PCI_REQ0# PCI Bus Re qes t 0
PCI_RESET# PCI Bus Reset
PCI_AD0 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD2
PCI_AD4 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD6 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD8 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD10
PCI_AD12 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
GND Ground
PCI_AD14 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_C/ BE 1 # PCI Bus Command a nd By t e ena bles
PCI_PERR#
PCI_LOCK# PCI Bus Loc k
PCI_DEVSEL# PCI Bus Device Select
PCI_IRDY# PCI B us Bus Initiator Ready
PCI_C/BE2#
PCI_AD17 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD19 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
GND Ground
PCI_AD21 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD23
PCI_C/ BE 3 # PCI Bus Command a nd By t e ena bles
PCI_AD25 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD27 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD29
PCI_AD31
PCI_IRQA# PCI Bus Interrupt Request A
PCI_IRQB# PCI Bus Interrupt Request B
GND Ground
PEG_RX0+
PEG_RX0- PCIe 0 Recieve -
TYPE0# Module type ID pin 0
PEG_RX1+ PCIe 1 Recieve +
Ground PWR - IDE Data Bus
IDE Data Bus
Ground
PCI Power Management Event
PCI Bus Gra n t 2
PCI Bus Gra n t 0
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Bus Gra n t Erro
PCI Bus Co mm and a nd Byte en ables
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCIe 0 Recieve +
IO PD 10k IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - -
PWR - -
IO - -
I-3.3
O-3.3 -
IO-3.3 int. PU 20k in QM57
O-3.3 int. PU 20k in QM57
I-3.3
O-3.3 int. PU 20k in QM57
I-3.3
O-3.3 int. PU 20k in QM57
PWR -
I-3.3
O-3.3 - -
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - -
PWR - -
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3 IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - -
PWR - -
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 -
I-3.3
I-3.3
PWR I - DP I - DP - -
STO - not connected
I - DP - -
PU 4K7 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 22
Page 23
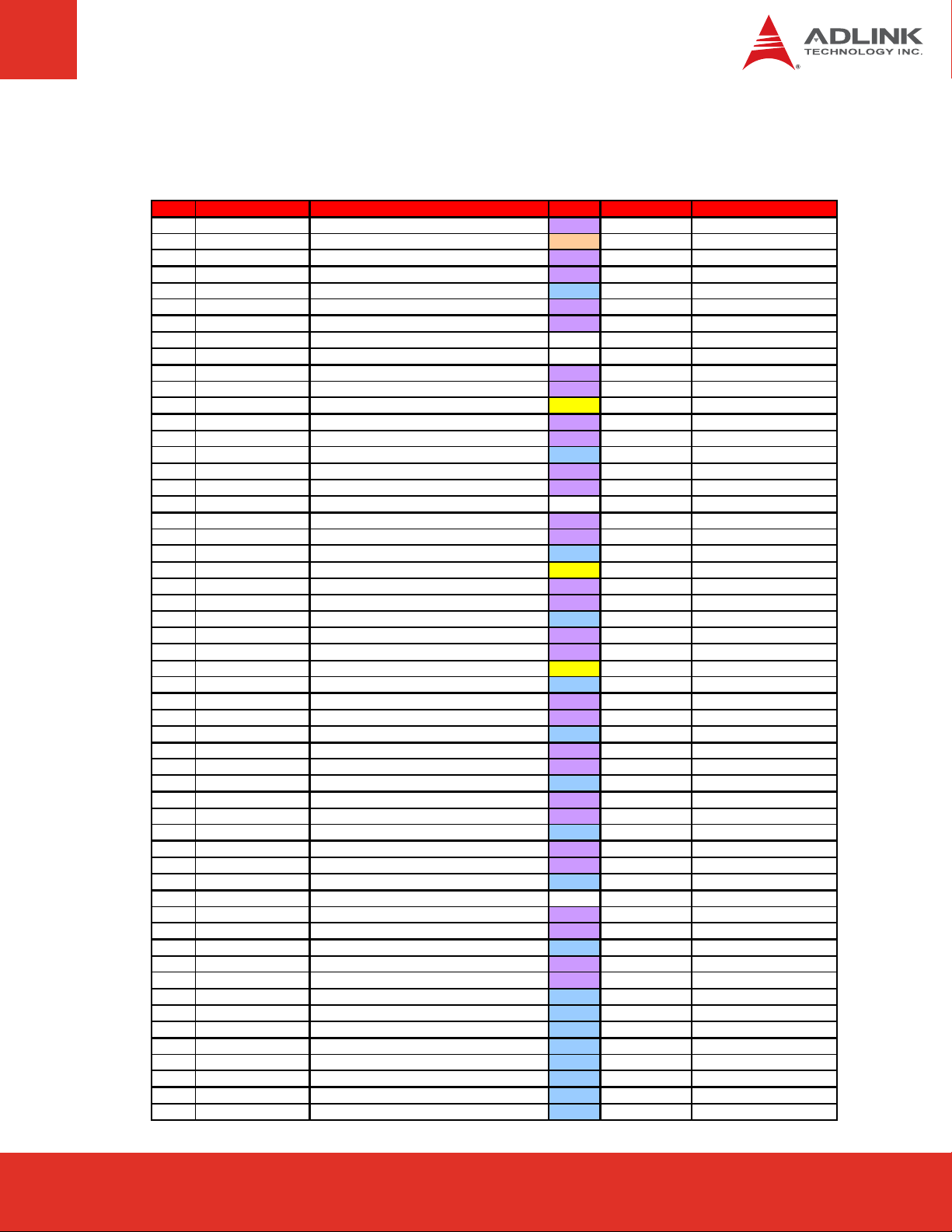
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
yp
Row C
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
C56
C57
C58
C59
C60
C61
C62
C63
C64
C65
C66
C67
C68
C69
C70
C71
C72
C73
C74
C75
C76
C77
C78
C79
C80
C81
C82
C83
C84
C85
C86
C87
C88
C89
C90
C91
C92
C93
C94
C95
C96
C97
C98
C99
C100
C101
C102
C103
C104
C105
C106
C107
C108
C109
C110
PEG_RX1- PCIe 1 Recieve -
TYPE1#
PEG_RX2+ PCIe 2 Recieve +
PEG_RX2- PCIe 2 Recieve -
GND Ground
PEG_RX3+
PEG_RX3- PCIe 3 Recieve -
RSVD
RSVD
PEG_RX4+ PCIe 4 Recieve +
PEG_RX4-
RSVD FAN_PWM_CTRL
PEG_RX5+ PCIe 5 Recieve +
PEG_RX5- PCIe 5 Recieve -
GND
PEG_RX6+
PEG_RX6- PCIe 6 Recieve -
RSVD NC NC
PEG_RX7+ PCIe 7 Recieve +
PEG_RX7-
GND Ground
RSVD FAN_TACH
PEG_RX8+ PCIe 8 Recieve +
PEG_RX8- PCIe 8 Recieve -
GND
PEG_RX9+ PCIe 9 Recieve +
PEG_RX9- PCIe 9 Recieve -
RSVD Physical Presence
GND
PEG_RX10+ PCIe 10 Recieve +
PEG_RX10- PCIe 10 Recieve -
GND Ground
PEG_RX11+ PCIe 11 Recieve +
PEG_RX11-
GND Ground
PEG_RX12+ PCIe 12 Recieve +
PEG_RX12- PCIe 12 Recieve -
GND
PEG_RX13+ PCIe 13 Recieve +
PEG_RX13- PCIe 13 Recieve -
GND Ground
RSVD NC NC
PEG_RX14+
PEG_RX14- PCIe 14 Recieve -
GND Ground
PEG_RX15+ PCIe 15 Recieve +
PEG_RX15-
GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND Ground
Module t
PCIe 3 Recieve +
NC NC - NC NC - -
PCIe 4 Recieve -
Ground
PCIe 6 Recieve +
PCIe 7 Recieve -
Ground
Ground
PCIe 11 Recieve –
Ground
PCIe 14 Recieve +
PCIe 15 Recieve Ground
Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - -
e ID pin 1
I - DP - -
STO - not connected
I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - -
I - DP - I - DP - -
0-5 - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - -
-I - DP - I - DP - PWR - -
I-5 - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - -
I-3.3
PWR - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - -
I - DP - I - DP - PWR - I - DP - I - DP - PWR - -
PWR - -
PU 10k 3.3Vsb
--
-
Page 23Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 23Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 23Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 23
Page 24
Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
p
q
p
Row D
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
D17
D18
D19
D20
D21
D22
D23
D24
D25
D26
D27
D28
D29
D30
D31
D32
D33
D34
D35
D36
D37
D38
D39
D40
D41
D42
D43
D44
D45
D46
D47
D48
D49
D50
D51
D52
D53
D54
D55
GND
IDE_D5
IDE_D10 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D11 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D12 IDE Data Bus
IDE_D4
IDE_D0 IDE Data Bus
IDE_REQ# IDE Device DMA Reques t.
IDE_IOW# IDE IO Write
IDE_ACK# IDE DM A Ac knowledge
GND
IDE_IRQ IDE Inter rupt Request
IDE_A0 IDE Adress Bus
IDE_A1 IDE Adress Bus
IDE_A2
IDE_CS1#
IDE_CS3# IDE Chip Select for 3F0h to 3FFh range
IDE_RESET# IDE Reset Output to Device
PCI_GNT3# PCI Bus Grant 3
PCI_REQ3#
GND
PCI_AD1 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD3 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD5 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD7
PCI_C/ BE 0 # PCI Bus Command a nd By t e ena bles 0
PCI_AD9 PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI_AD11 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD13
PCI_AD15 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
GND
PCI_PAR PCI Bus Parity
PCI_SERR# PCI Bus System Error
PCI_STOP#
PCI_TRDY# PCI Bus Target Ready
PCI _FRAME# PCI Bus C ycle Frame
PCI_AD16 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD18
PCI_AD20 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD22 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
GND
PCI_AD24 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD26
PCI_AD28 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_AD30 PCI Adress & Data Bus line
PCI_IRQC# PCI Bus Interrupt Request C
PCI_IRQD#
PCI_CLKRUN#
PCI_M66EN# Control PCI Speed 33/66 Mhz
PCI_CLK PCI Clock
GND
PEG_TX0+
PEG_TX0- PCIe 0 Transmit -
PEG_LANE_RV# PCIe Lane Reversal
PEG_TX1+ PCIe 1 Transmit +
Ground PWR - IDE Data Bus
IDE Data Bus
Ground PWR - -
IDE Adre ss Bus
IDE Chi
Select for 1F0h to 1FFh range
PCI Bus Re
Ground PWR - -
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
Ground PWR - -
PCI Bus Sto
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
Ground PWR - -
PCI Adre ss & Data Bus line
PCI Bus Interrupt Request D
PCI Clock R u n
Ground PWR - PCIe 0 Transmit +
est 3
IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - IO - -
IO PD 5k6 O-3.3 - O-3.3 - -
I-3.3 PD 10k O-3.3 - O-3.3 - O-3.3 - O-3.3 - O-3.3 - O-3.3 - O-3.3 - int. PU 20k in QM57
I-3.3
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - -
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - -
IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - IO-3.3 - -
I-3.3
I-3.3
I-3.3
I-3.3 - Fixed to 33 MHz
O-3.3 - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
I-3.3 - -
O - DP - -
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
PU 8K2 3.3V
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 24
Page 25

Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
yp
Row D
Pin Signal Description Type PU/PD Comment
D56
D57
D58
D59
D60
D61
D62
D63
D64
D65
D66
D67
D68
D69
D70
D71
D72
D73
D74
D75
D76
D77
D78
D79
D80
D81
D82
D83
D84
D85
D86
D87
D88
D89
D90
D91
D92
D93
D94
D95
D96
D97
D98
D99
D100
D101
D102
D103
D104
D105
D106
D107
D108
D109
D110
PEG_TX1- PCIe 1 Transmit -
TYPE2#
PEG_TX2+ PCIe 2 Transmit +
PEG_TX2- PCIe 2 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX3+
PEG_TX3- PCIe 3 Transmit -
RSVD NC NC
RSVD NC NC
PEG_TX4+ PCIe 4 Transmit +
PEG_TX4-
GND
PEG_TX5+ PCIe 5 Transmit +
PEG_TX5- PCIe 5 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX6+
PEG_TX6- PCIe 6 Transmit -
RSVD NC NC
PEG_TX7+ PCIe 7 Transmit +
PEG_TX7-
GND
IDE_CBLID# IDE Cable Indicator Signal
PEG_TX8+ PCIe 8 Transmit +
PEG_TX8- PCIe 8 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX9+ PCIe 9 Transmit +
PEG_TX9- PCIe 9 Transmit -
RSVD NC NC
GND
PEG_TX10+ PCIe 10 Transmit +
PEG_TX10- PCIe 10 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX11+ PCIe 11 Transmit +
PEG_TX11-
GND
PEG_TX12+ PCIe 12 Transmit +
PEG_TX12- PCIe 12 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX13+ PCIe 13 Transmit +
PEG_TX13- PCIe 13 Transmit -
GND
PEG_ENABLE# PCIe Enable
PEG_TX14+
PEG_TX14- PCIe 14 Transmit -
GND
PEG_TX15+ PCIe 15 Transmit +
PEG_TX15-
GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND
Module t
Ground PWR - PCIe 3 Transmit +
PCIe 4 Transmit -
Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - PCIe 6 Transmit +
PCIe 7 Transmit -
Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - -
PCIe 11 Transmit Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - -
Ground PWR - -
PCIe 14 Transmit +
Ground PWR - -
PCIe 15 Transmit Ground PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Power 12V PWR - Ground PWR - -
e ID pin 2
O - DP - -
STO - not connected
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
--
-O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
-O - DP - O - DP - -
I-3.3 PD 10k O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
--
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
I-3.3
O - DP - O - DP - -
O - DP - O - DP - -
PU 43K2 3.3V
-
Page 25Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 25Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 25Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 25
Page 26

Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
Signal Type Legend
IO-2,5 Bi-direction al 2,5 V Input/Output
IO-3,3 Bi-direction al 3,3 V Input/Output
IO-5 Bi-directional 5 V Input/Output
I-3,3 3,3 V Input
I-5 5 V Input
O-2,5 2,5 V Output
O-3,3 3,3 V Output
O-5 5 V Output
IO In put/Output
OA Analog Output
OD Digital Output
I/O - DP Differential Pair Inpu t/Output
O - DP Differential Pair Output
I - DP Differential Pa ir Input
PWR Power or Ground
STO Strapping Output
PU Pull Up Resistor
PD Pull Down Resistor
NC Not Connected / Reserved
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 26
Page 27

5.5 PCI Express x16 Configuration
Switch SWY1 allows you to configure the PCI Express x16 lanes from the CPU as 1 PCIe x16
or 2 PCIe x8.
SWY1
SWY1: PCI Express Configuration Switch
Mode Pin 1 Pin 2
1x PCIe x16 (default) Off Off
2x PCIe x8 On Off
Page 27Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 27Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 27Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 27
Page 28

6 Embedded Functions
All embedded board functions on ADLINK’s Computer on Modules are supported at the
operating system level using the ADLINK Intelligent Device Interface (AIDI) library. The AIDI API
programming interface is compatible and identical across all ADLINK Computer on Modules and
all supported operating systems. The AIDI library includes a demo program to demonstrate the
library’s functionallity.
6.1 Watchdog Timer
The Express-CB implements a Watchdog timer that can be used to
automatically detect software execution problems or system hangs and
reset the board if necessary. The Watchdog timer consists of a counter
that counts down from an initial value to zero. When the system is
operating normally, the software that sets the intial value periodically
resets the counter so that the it never reaches zero. If the counter
reaches zero before the software resets it, the system is presumed to be
malfunctioning and a reset signal is asserted.
The AIDI Library Watchdog functions support Watchdog control of the board. If the Watchdog
begins countdown and reaches zero, it will access the CPU's RESET signal to reset the system.
This application must call another function named AidiWDogTrigger that triggers the
Watchdog to restart to prevent system reset.
AIDI Demo Program
- Watchdog Tab
The AIDI Demo Program allows
retrieval of the current Watchdog
status and updating of the
Watchdog settings
If the Watchdog is enabled, the
user can click the WDT Trigger
button to manually reset the
counter and prevent the system
from resetting
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 28
Page 29

6.2 GPIO
GPIO library support is limited to GPIO signals that originate from the Computer on Module
and extend to the carrier board. COM Express modules support 4 GPO and 4 GPI signals.
Some of ADLINK’s COM Express boards can configure all 8 ports for GPI or GPO use.
GPIO signals can be monitored and controlled by using the ADLINK Intelligent Device
Interface (AIDI) library that is compatible and identical across all ADLINK COM Express
modules and all supported operating systems.
The COM Express Type 2 standard assigns the following pins for either GPI or GPO
Pin Signal Type # AIDI ID (bit) Remark
A5 4 GPI0 0 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
A6 3 GPI1 1 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
A6 7 GPI2 2 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI andGPO
A8 5 GPI3 3 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI andGPO
A93 GPO0 4 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
B54 GPO1 5 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
B57 GPO2 6 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
B63 GPO3 7 Express-CB can configure this pin for GPI and GPO
AIDI Demo Program
- GPIO Tab
The AIDI Demo Program displays
current GPI or GPO status and
allows reading of GPI and writing
to GPO.
The table above links logical port
numbers in AIDI to physical port
numbers on the COM Express
board-to-board connector.
For boards that support multi-
direction the “SetDirection” button
can configure the port for either
GPI or GPO
Page 29Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 29Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 29Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 29
Page 30

6.3 Hardware Monitoring
To ensure system health of your embedded system ADLINK’s COM Express modules come
with built in support for monitoring and control of CPU and system temperatures, fan speed
and critical module voltage levels.
The AIDI Library provides simple APIs at the application level to support these functions and
adds alarm functions when voltage or temperature levels exceed the upper or lower limit set
by the user.
On the Express-CB the following monitored values can be read from the module:
CPU temperature, system temperature, Vcore, 1.8V, 5V, 3.3V and 12V.
AIDI Demo Program
- HW Monitor Tab
Field 1 displays detected sensors
(number).
Field 2 allows setting of upper and
lower alarm limits.
Field 3 displays read out
information of sensors.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 30
Page 31

7 System Resources
7.1 System Memory Map
Address Range (dec.) Address Range (hex) Size Description
(4GB-2MB) FFE00000 - FFFFFFFF 2 MB High BIOS Area
(4GB-18MB) - (4GB-17MB-1) FEE00000 - FEEFFFFF 1 MB FSB Interrupt Memory Space
(4GB-20MB) - (4GB-19MB-1) FEC00000 - FECFFFFF 1 MB APIC Configuration Space
960 K - 1024 K F0000 - FFFFF 64 KB System BIOS Area
896 K - 960 K E0000 - EFFFF 64 KB Extended System BIOS Area
768 K - 896 K C0000 - DFFFF 128 KB PCI expansion ROM area
640 K - 768 K A0000 - BFFFF 128 KB Video Buffer & SMM space
0 K - 640 K 00000 - 9FFFF 640 KB DOS Area
C0000 - C7FFF: Onboard VGA BIOS
CB800 - CC7FFF: Intel 82577LM
PXE option ROM when onboard
LAN boot ROM is enabled.
7.2 Direct Memory Access Channels
Channel Number Data Width System Resource Comment
0 8-bits Parallel port Note (1)
1 8-bits Parallel port Note (1)
2 8-bits Diskette drive Note (1)
3 8-bits Parallel port Note (1)
4 Reserved - cascade channel
5 16-bits Open
6 16-bits Open
7 16-bits Open
Page 31Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 31Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 31Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 31
Page 32

7.3 Legacy I/O Map
Address Range (hex) Description
000-01F DMA controller 1, 8237A-5 equivalent
020-02D and 030-03F Interrupt controller 1, 8259 equivalent
02E-02F LPC SIO (W83627HG-AW) configuration index/data registers
040-05F Timer, 8254-2 equivalent
060, 062, 064, 066, 068-06F 8742 equivalent (keyboard)
061, 063, 065, 067 NMI control and status
070-07F Real Time Clock Controller( bit 7 -NMI mask)
080-091 DMA page register
93-9F DMA page registers continued
0A0-0B1 and 0B4-0BF Interrupt controller 2, 8259 equivalent
0B2h APM Control I/O Address
0B3h APM Status I/O Address
0C0-0DF DMA controller 2, 8237A-5 equivalent
0F0 Co-processor error register
0F1 N/A
0F2-0F3 N/A
0F4 IDE ID port
0F5-0F7 N/A
0F8 IDE Index port
0F9-0FB N/A
0FC IDE Data port
0FD-0FF N/A
170-177 and 376 Secondary IDE Channel
180-181 Default AIM4 SRAM control register (may be remapped)
1F0-1F7 and 3F6 Primary IDE Controller (AT Drive)
290 SIO_PME_BASE_ADDRESS
2E8-2EF Serial port 4
2F8-2FF Serial port 3
370-377 Secondary Floppy Disk Controller
378- 37F Printer Port (LPT 1)
3B0-3BF Mono/VGA mode video
3C0-3DF VGA registers
3E8-3EF Serial port 2
3F0-3F7 Primary Floppy disk controller
3F8-3FF Serial port 1
400 SMBUS IO base
4D0 Master PIC Edge/Level Trigger register
4D1 Slave PIC Edge/Level Trigger register
500 GPIO base address for SB
800 alias for ACPI I/O base address.
830 SMI Control Registers.
860 alias for ICH TCO base address
CF9 Reset Control register (8 bit I/O)
CF8-CFC The PCI config space index/data ports
0A00-0AFF Reserved for SIO functions base address (eg: Hardware Monitor, GPIO, etc)
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 32
Page 33

7.4 Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines
PIC Mode
IRQ# Typical Interrupt Resource Connected Available
0 Counter 0 N/A No
1 Keyboard controller N/A No
2 Cascade interrupt from slave PIC N /A No
3 Serial Port 2 (COM2) IRQ3 via SERIRQ, IRQ3 at ISA bus Note (1)
4 Serial Port 1 (COM1) / PCI / ISA IRQ4 via SERIRQ, IRQ4 at ISA bus Note (1)
5 PCI / ISA IRQ5 via SERIRQ, IRQ5 at ISA bus Note (1)
6 Floppy Drive Controller IRQ6 via SERIRQ No
7 PCI / ISA IRQ7 via SERIRQ, IRQ7 at ISA bus Note (1)
8 Real-time clock N/A No
9 SCI / PCI IRQ9 via SERIRQ, IRQ9 at ISA bus Note (1), (2)
10 No N/A No
11 No N/A No
12 PS/2 Mouse / PCI / ISA IRQ12 via SERIRQ, IRQ12 at ISA bus Note (1)
13 Math Processor N/A No
14 Primary IDE controller / PCI / ISA IRQ14 via SERIRQ, IRQ14 at ISA bus Note (1)
15 No N/A No
(1) These IRQs can be used for PCI devices when onboard device is disabled. If IRQ is from
ISA, user must reserve IRQ for ISA in BIOS setup menu.
(2) BIOS does not allow IRQ 9 setting for ISA bus.
Page 33Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 33Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 33Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 33
Page 34

APIC Mode
IRQ# Typical Interrupt Resource Connected Available
0 Counter 0 N/A No
1 Keyboard controller N/A No
2 PCI / ISA N/A No
3 Serial Port 2 (COM2) / PCI / ISA IRQ3 via SERIRQ, IRQ3 at ISA bus Note (1)
4 Serial Port 1 (COM1) / PCI / ISA IRQ4 via SERIRQ, IRQ4 at ISA bus Note (1)
5 PCI / ISA IRQ5 via SERIRQ, IRQ5 at ISA bus Note (1)
6 Floppy Drive Controller IRQ6 via SERIRQ No
7 PCI / ISA IRQ7 via SERIRQ, IRQ7 at ISA bus Note (1)
8 Real-time clock N/A No
9 ACPI-Compliant system IRQ9 via SERIRQ, IRQ9 at ISA bus Note (1), (2)
10 PCI / ISA IRQ10 via SERIRQ, IRQ10 at ISA bus Note (1)
11 PCI / ISA IRQ11 via SERIRQ, IRQ11 at ISA bus Note (1)
12 PS/2 Mouse / PCI / ISA IRQ12 via SERIRQ, IRQ12 at ISA bus Note (1)
13 Math Processor N/A No
14 Primary IDE controller / PCI / ISA IRQ14 via SERIRQ, IRQ14 at ISA bus Note (1)
15 Secondary IDE controller / PCI / ISA IRQ15 via SERIRQ, IRQ15 at ISA bus Note (1)
16 N/A PCIE Port 0/1/2/3/4/5/6/7, P.E.G Root Port, Yes
I.G.D, EHCI Controller #2, PCI Slot 0
HECI host 1, HECI host 2
17 N/A PCIE Port 0/1/2/3/4/5/6/7, P.E.G Root Port, Yes
PCI Slot 1, KT Controller
18 N/A PCIE Port 0/1/2/3/4/5/6/7, P.E.G Root Port, Yes
SATA Host controller, SMBus Controller,
Thermal Controller, PCI Slot 2,
IDER Controller
19 N/A PCIE Port 0/1/2/3/4/5/6/7, P.E.G Root Port, Yes
SATA Host controller, SATA
Host controller#1, PCI Slot 3
20 N/A ICH9 internal GbE controller No
21 N/A No
22 N/A ICH9 HDA No
23 N/A EHCI Controller 1 No
(1) These IRQs can be used for PCI devices when onboard device is disabled. If IRQ is from
ISA, user must reserve IRQ for ISA in BIOS setup menu.
(2) BIOS does not allow IRQ 9 setting for ISA bus.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 34
Page 35

7.5 PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus No. Device No. Function No. Routing Description
00h 00h 00h N/A Intel MCH DRAM Controls
00 01H 00 H Internal P.E.G. Root Port
02 00H 0FFH N/A P.E.G. Port
00h 02h 00h Internal Intel Integrated Graphics Device
00h 16h 00h Internal Intel Management Engine Interface #1
00h 16h 01h Internal Intel Management Engine Interface #2
00h 16h 02h Internal IDE-R
00h 16h 03h Internal KT
00h 19h 00h Internal GbE Controller
00h 1Ah 00h Internal Intel USB EHCI Controller #2
00h 1Bh 00h Internal High Definition Audio controller
00h 1C h 00h Internal PCI Express Root port 1
00h 1C h 01h Internal PCI Express Root port 2
00h 1C h 02h Internal PCI Express Root port 3
00h 1C h 03h Internal PCI Express Root port 4
00h 1C h 04h Internal PCI Express Root port 5
00h 1C h 05h Internal PCI Express Root port 6
00h 1C h 06h Internal PCI Express Root port 7
00h 1C h 07h Internal PCI Express Root port 8
00h 1D h 00h Internal Intel USB EHCI Controller #1
00h 1Eh 00h N/ A Intel PCI to PCI Bridge
00h 1Fh 00h N/A Intel LPC Interface Bridge
00h 1 Fh 02h Internal Intel SATA controller #1
00h 1 Fh 03h Internal Intel SMBus Controller
00h 1 Fh 05h Internal Intel SATA controller #2
00h 1 Fh 06h Internal Thermal Controller
11h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #0
12h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #1
13h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #2
14h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #3
15h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #4
16h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #5
17h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #6
18h 00h 0FFh Internal PCIE Port #7
20h 04h 00h Intemal PCI Slot 0
20h 05h 00h Intemal PCI Slot 1
20h 06h 00h Intemal PCI Slot 2
20h 07h 00h Intemal PCI Slot 3
Page 35Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 35Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 35Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 35
Page 36

7.6 PCI Interrupt Routing Map
PIRQ
INT Line
AINTAINTAX X X X
BINTBINTB X
CINTCINTC X X X X
DINTDINTD X X
E X
F
G X
HX
PIRQ
PCIE port 0
A INTA INTB INTC INTD INTA INTB INTA INTB X
B INTB INTC INTD I NTA INTB INTC INTB INTC X
C INTC INTD INTA INTB INTC INTD INTC INTD X
D INTD INTA INTB INTC INTD INTA INTD INTA X
E
F
G
H
VGA
PEG Root Port
PCIE port 1
PCIE port 2
SATA Controller
SATA Controller 1
PCIE port 3
PCIE port 4
SMBus Controller
PCIE port 5
EHCI 1
EHCI 2
Therm. Controller
PCIE port 6
PCI slot 0
PCIE port 7
HAD
PCI slot 1
GbE
HECI Host 1
HECI Host 2
PCI slot 2
PCI slot 3
KT Controller
IDER Controller
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 36
Page 37

8 BIOS Setup Utility
The following chapter describes basic navigation for the AMIBIOS8 BIOS setup utility for the
ADLINK Express-CB COM Express module.
8.1 Starting the BIOS
To enter the setup screen, follow these steps:
1. Power on the motherboard
2. Press the < Delete > key on your keyboard when you see the following text prompt:
< Press DEL or Delete to run Setup >
3. After you press the < Delete > key, the main BIOS setup menu displays. You can
access the other setup screens from the main BIOS setup menu, such as Chipset and
Power menus.
In most cases, the < Delete > key is used to invoke the setup screen. There are
several cases that use other keys, such as < F1 >, < F2 >, and so on.
Page 37Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 37Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 37Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 37
Page 38

8.2 Main Setup
When you first enter the Setup Utility, you will enter the Main setup screen. You can always
return to the Main setup screen by selecting the Main tab. The Main BIOS Setup screen is
shown below.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 38
Page 39

8.2.1 System & Board Info
This screen reports system and board information.
BIOS Rev.
Displays the current BIOS revision.
BC Firmware Rev.
Displays the current firmware revision of board controller (BC).
Manufacture Date
Displays the date which the board was manufactured.
Last Repair Date
Displays the date on which the board was last repaired.
Serial Number
Displays the serial number of board.
Page 39Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 39Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 39Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 39
Page 40

Hardware Rev.
The hardware revision is in XXXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ format. XXXXX represents the ADLINK
internal P/N for this board. YYYY is the board PCB version and ZZZZ represents a special
configuration of the board.
LAN MAC ID
Displays the MAC address of onboard Ethernet controller.
Boot Counter
Displays the number of times the board has been booted-up since production (max.
16777215).
Running Time
Displays the total time the board has been in operation since production. The units are in
hours and the maximum value is 65535.
8.2.2 System Language
Choose the system default language.
8.2.3 System Time/System Date
Use this option to change the system time and date. Highlight System Time or System Date
using the < Arrow > keys. Enter new values using the keyboard. Press the < Tab > key or
the < Arrow > keys to move between fields. The date must be entered in MM/DD/YY
format. The time is entered in HH:MM:SS format.
The time is in 24-hour format. For example, 5:30 A.M. appears as 05:30:00, and 5:30 P.M.
as 17:30:00.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 40
Page 41

8.3 Advanced BIOS Setup
Select the Advanced tab from the setup screen to enter the Advanced BIOS Setup screen.
You can select any of the items in the left frame of the screen, such as SuperIO
Configuration, to go to the sub menu for that item. You can display an Advanced BIOS Setup
option by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The Advanced BIOS Setup screen is
shown below. The sub menus are described on the following pages.
Setting incorrect or conflicting values in Advanced BIOS Setup may cause system
malfunctions.
Page 41Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 41Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 41Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 41
Page 42

8.3.1 CPU Core Configuration
Hyper-Threading
Enabled for Windows XP and Linux (OS optimized for Hyper-Threading Technology) and
Disabled for other OS (OS not optimized for Hyper-Threading Technology).
Active Processor Core
Number of cores to enable in processor. Options: All, 1, 2.
Limit CPUID Maximum
Enable this option to allow compatibility with older operating systems.
Hardware Prefetcher
This feature is used for reducing the wait time of DRAM. The hardware prefetcher looks for
streams of data and tries to predict what data will be needed next by the processor and
proactively tries to fetch these data.
Adjacent Cache Line P
This feature is used to enable optimal use of sequential memory access for performance
purposes. Disable this setting for applications requiring high use of random memory access.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 42
Page 43

Intel Virtualization
Allows a hardware platform to run multiple operating systems separately and simultaneously,
enabling one system to function virtually as several systems. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Power Technology
Power management feature. Configuration options: Disabled, Energy Efficient, Custom.
8.3.2 CPU Configuration
Initial Graphic Adapter
Allows you to select which graphics controller to use as the primary boot device.
Configuration options: IGD, PCI/IGD, PCI/PEG, PEG/IGD, PEG/PCI.
VT-d
The Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Page 43Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 43Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 43Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 43
Page 44

PCI Express Port
This option enables auto negotiation with a PEG device or enables/disables the use of the
PEG port.
IGD Memory
IGD Shared Memory Size. Configuration options: Disable/32M/64M/128M.
PAVP Mode
PAVP (Protected Audio Video Path) is a feature to ensure a robust and secure content
protection path for high-definition video playback including Blu-ray discs on the Microsoft
Windows Vista operating system. It can reduce processor utilization by off-loading the video
decode onto the chipset to free up the processor to perform other tasks. Select Lite mode if
want to use the PAVP feature.
PEG Force Gen1
PCI Express Port Force Gen1. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 44
Page 45

8.3.3 PCH Configuration
SMBus Controller
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
GbE Controller
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Wake on Lan from S5
The GbE wake up system from S5 power mode. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Restore on AC Power Loss
Determines what state the computer enters when AC power is restored after a power loss.
The options for this value are Last State, Power On and Power Off.
Option Description
Power Off Set this value to always power off the system while AC power is restored.
Power On Set this value to always power on the system while AC power is restored.
Last State Set this value to power off/on the system depending on the last system power state while AC power is
restored.
Page 45Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 45Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 45Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 45
Page 46

SLP_S4 Assertion Stre
Select a minimum assertion width of the SLP_S4# signal. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
SLP_S4 Assertion Wid
SLP_S4 Assertion Width help. Configuration options: 1-2 Seconds, 2-3 Seconds, 3-4
Seconds, 4-5 Seconds.
Azalia HD Audio
Onboard HDA Controller. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
High Precision Timer
Set this value to Enable or Disable.
PCI Express Port Configuration
PCI-E Ports 0-3 Config
Configure PCI Express ports 0-3 as four x1 lanes or one x4 lane.
PCI Express Port 1-8
Enable/disable the PCI Express ports in the chipset. Configuration options: Auto, Enable,
Disable.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 46
Page 47

8.3.4 SATA Configuration
SATA Mode
The SATA can be configured as a legacy IDE, RAID and AHCI mode.
Serial-ATA Controller
This item specifies whether SATA Controller 0 is initialized in Compatible or Enhanced mode
of operation. The settings are Disabled, Compatible and Enhanced.
Serial-ATA Controller
This item specifies whether SATA Controller 1 is initialized in Compatible or Enhanced mode
of operation. The settings are Disabled, Compatible and Enhanced.
Jmicron SATA to PATA
When a PATA device is not connected to the SATA-to-PATA bridge, this option should be set
to No PATA IDE Device Connected to avoid delay due to long detection time.
Page 47Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 47Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 47Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 47
Page 48

8.3.5 Video Function Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for Video Function configuration settings. The
video function BIOS Setup screen is shown below.
DVMT/FIXED Memory
Select DVMT/Fixed memory size used by the Internal Graphics Device. Configuration
options: 128MB, 256MB, Maximum.
IGD – Boot Type
Select the Video Device which will be activated during POST. This has no effect if external
graphics present. Configuration options: VBIOS Default, VGA, LFP, VGA+LFP, TV, LFP-SDVO,
EFP, TV-SDVO, VGA+LFP-SDVO, VGA+EFP, VGA+TV+LFP.
LCD Panel Type
When LVDS is selected from Boot Display Device, this option allows you to select resolution
settings for correct timing to the LVDS interface you want to use. The supported resolutions
are: 640x480 1x18-bit, 800x600 1x18-bit, 1024x768 1x18-bit, 1024x768 2x18-bit,1024x768
1x24-bit, 1024x768 2x24-bit, 1280x600 1x18-bit, 1280x768 1x18-bit,1280x800 1x18-bit,
1280x1024 2x24-bit, 1400x1050 2x24-bit 108MHz, 1400x1050 2x24-bit 122MHz, 1600x1200
2x24-bit, 1920x1200 2x24-bit, 2048x1536 2x24-bit.
Panel Scaling
Select the LCD panel scaling option used by the Internal Graphics Device. Configuration
options: Auto, Force Scaling, Maintain Aspect Ratio, Off.
Active LFP
Select the Active LFP Configuration. Configuration options: NO LVDS, Int-LVDS.
Option Description
No LVDS VBIOS does not enable LVDS
Int-LVDS VBIOS enables LVDS driver by integrated encoder
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 48
Page 49

8.3.6 USB Configuration
Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB Support refers to USB mouse and keyboard support. Normally if this option is not
enabled, any attached USB mouse or keyboard will not become available until a USB compatible
operating system is fully booted with all USB drivers loaded. When this option is enabled, any
attached USB mouse or keyboard can control the system even when there is no USB driver
loaded on the system. Set this value to enable or disable the Legacy USB Support (see below).
Option Description
Disabled Set this value to prevent the use of any USB device in DOS or during system boot.
Enabled Set this value to allow the use of USB devices during boot and while using DOS.
EHCI Hand-off
This is a workaround for OSes without EHCI hand-off support. The EHCI ownership change
should be claimed by EHCI driver. Configuration options: Enable, Disable.
Device Reset timeout
USB mass storage device Start Unit command timeout.
Page 49Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 49Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 49Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 49
Page 50

USB Ports Configuration
All USB Devices
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
USB 2.0 (EHCI) Support 1
USB 2.0 (EHCI) support. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
EHCI Controller 1
USB 2.0 (EHCI) controller. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
USB Port 0-7
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 50
Page 51

8.3.7 SuperIO Configuration Screen
The visibility of this SuperIO configuration screen depends on the presence of an onboard
SuperIO (Winbond W83627H). If the Express-CB is used on a carrier w/o a SIO chip, the
legacy-free mode will take effect.
Floppy Disk Controller Configuration
Floppy Disk Controller
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Change Settings
Select an optimal setting for the Floppy Disk Controller.
Options: Auto; IO=3F0, IRQ6, DMA2
Device Mode
Change Mode of Floppy Disk Controller. Select <Read Write> Mode for Normal operation
Select <Write Protect> mode for Read only operation.
Page 51Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 51Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 51Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 51
Page 52

Serial Port 0/1 Configuration
Serial Port 0,1 Configuration
Serial Port
Set parameters of serial port 0/1 (COM A/B). Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Change Settings
This option specifies the base I/O port address and Interrupt Request address of serial port
0, 1. Configuration options: Auto, 3F8, 3E8, 2F8, 2E8.
Device Mode
This option specifies the serial port mode. Configuration options: Standard Serial Port Mode,
IrDA 1.0 (HP SIR) Mode and ASKIR Mode.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 52
Page 53

Parallel Port Configuration
Parallel Port
The parallel Port (LPT/LPTE). Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Change Settings
This option specifies the base I/O port address.
Device Mode
This option specifies the parallel port mode. Options: Standard Parallel Port Mode, EPP
Mode, ECP Mode, EPP Mode & ECP Mode.
Option Description
Standard Set this value to allow the standard parallel port mode to be used.
EPP The parallel port can be used with devices that adhere to the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP)
specification. EPP uses the existing parallel port signals to provide asymmetric bidirectional data
transfer driven by the host device.
ECP The parallel port can be used with devices that adhere to the Extended Capabilities Port (ECP)
specification. ECP uses the DMA protocol to achieve data transfer rates up to 2.5 Megabits per
second. ECP provides symmetric Bidirectional communication.
EPP+ECP Allows the parallel port to support both the ECP and EPP modes simultaneously.
Page 53Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 53Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 53Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 53
Page 54

8.3.8 Intel ME Subsystem Configuration
8.3.9 H/W Monitor
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 54
Page 55

8.3.10 PCI Subsystem Settings
PCI ROM Priority
In case of multiple Option ROMs (Legacy and EFI Compatible), specifies which PCI Option
ROM to launch. Configuration options: Legacy ROM, EFI Compatible ROM.
Launch PXE OpROM
Boot option for legacy network devices. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Launch Storage OpROM
Boot option for legacy mass storage devices with option ROM. Options are Enabled/
Disabled.
PCI Latency Timer
Value to be programmed into PCI Latency Timer Register. Configuration options: 32 PCI Bus
Clocks, 64 PCI Bus Clocks, 96 PCI Bus Clocks, 128 PCI Bus Clocks, 160 PCI Bus Clocks, 192
PCI Bus Clocks, 224 PCI Bus Clocks, 248 PCI Bus Clocks.
Page 55Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 55Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 55Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 55
Page 56

VGA Palette Snoop
The VGA Palette registers snooping. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Relaxed Ordering
Enable/Disable PCI Express device relaxed ordering.
Extended Tag
If enabled, allows device to use 8-bit tag field as a requester. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
No Snoop
Enable/Disable PCI Express Device No Snoop option.
Maximum Payload
Set maximum payload of PCI Express device or allow system BIOS to select the value.
Configuration options: Auto, 128 Bytes, 256 Bytes, 512 Bytes, 1024 Bytes, 2048 Bytes, 4096
Bytes.
Maximum Read Request
Set maximum read request size of PCI Express device or allow system BIOS to select the
value. Configuration options: Auto, 128 Bytes, 256 Bytes, 512 Bytes, 1024 Bytes, 2048
Bytes, 4096 Bytes.
ASPM Support
Set the ASPM support level:
Option Description
Disabled Disable ASPM
Auto BIOS auto configure
Force L0 Force all links to L0 state
Extended Synch
If enabled, allows generation of Extended Synchronization patterns. Options are Enabled/
Disabled.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 56
Page 57

8.3.11 Serial Port Console Redirection
Console Redirection
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Console Redirection Settings
The settings specify how the host computer and the remote computer will exchange data.
Both computers should have the same or compatible settings.
Page 57Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 57Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 57Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 57
Page 58

Console Redirection Settings (cont’d)
Terminal Type
VT-UTF8 is the preferred terminal type for out-of-band management. The next best choice is
VT100+ and then VT100. Configuration options: VT100, VT100+, VT-UTF8, ASNI.
Bits per second
Select the bits per second you want the serial port to use for console redirection. The
options are 115200 ,57600 ,19200, 9600.
Data Bits
Select the data bits you want the serial port to use for console redirection. Set this value to 7
or 8.
Parity
Set this option to select parity for console redirection. The settings for this value are None,
Even, Odd, Mark and Space.
Stop Bits
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. The standard setting is 1 stop bit.
Communication with slow devices may require more than 1 stop bit. Set this value to 1 or 2.
Flow Control
Set this option to select Flow Control for console redirection. The settings for this value are
None, Hardware and Software.
Terminal Resolution
Remote Terminal Resolution. Set this value to 80x25 or 100x31.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 58
Page 59

8.3.12 Trusted Computing
Trusted Computing is an industry standard to make personal computers more secure
through a dedicated hardware chip, called a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). This option
allows you to enable or disable the TPM support.
TPM Support
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
TPM State
Determines whether a TPM state change requires Password Authentication. Options are
Enabled/Disabled.
Pending TPM Operation
Schedule a TPM operation. The settings for this value are None, Enable Take Ownership,
Disable Take Ownership, and TPM Clear.
Page 59Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 59Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 59Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 59
Page 60

8.3.13 ACPI Settings
Enable ACPI Auto Configuration
BIOS ACPI Auto Configuration. Options are Enabled/Disabled.
Enable Hibernation
Options are Enabled/Disabled.
ACPI Sleep State
Select the highest ACPI sleep state the system will enter, when the Suspend button is
pressed. Configuration options: S1, S3, Suspend Disable.
S1 (POS): Power On Suspend - Under this setting the CPU is not executing instructions, all
power resources that supply system level reference of S0 are off, system memory context is
maintained, devices that reference power resources that are on are on, and devices that can
wake-up the system can cause the cpu to continue to execute from where it left off.
S3 (STR): Suspend to RAM - Under this setting the system enters a low power state instead
of being completely shut off. This allows the computer system to boot up in a few seconds.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 60
Page 61

8.5 Boot Configuration
Select the Boot tab from the setup screen to enter the Boot BIOS Setup screen. You can
select any of Boot BIOS options by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The Boot BIOS
Setup screen is shown below.
Quiet Boot
Disabled - Set this value to allow the computer system to display the POST messages.
Enabled - Set this value to allow the computer system to display the OEM logo.
Fast Boot
Disabled - Set this value to allow the BIOS to perform all POST tests.
Enabled - Set this value to allow the BIOS to skip certain POST tests to boot faster.
Setup Prompt Timeout
Number of seconds to wait for setup activation key. 65535 (0xFFFF) means wait indefinitely.
Page 61Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 61Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 61Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 61
Page 62

Bootup Num-Lock
Set this value to allow the Number Lock setting to be modified during boot up.
Off - This option does not enable the keyboard Number Lock automatically. To use the 10-keys
on the keyboard, press the Number Lock key located on the upper left-hand corner of the 10-key
pad. The Number Lock LED on the keyboard will light up when the Number Lock is engaged.
On - Set this value to allow the Number Lock on the keyboard to be enabled automatically when the
computer system is boot up. This allows the immediate use of 10-keys numeric keypad located on
the right side of the keyboard. To confirm this, the Number Lock LED light on the keyboard will be
lit.
GateA20 Active
Upon Request - GA20 can be disabled using BIOS services. Always - do not allow disabling
of GA20; this option is useful when any RT code is executed above 1MB.
Interrupt 19 Capture
Allows option ROMs to trap Int 19. Set this value to Enabled/Disabled.
Hard Drive BBS Priorities
The boot devices are listed in groups by device type. First press <Enter> to enter the submenu. Then you may use the arrow keys to select the desired device, then press <+>, <-> or
<PageUp>, <PageDown> key to move it up/down in the priority list. Only the first device in
each device group will be available for selection in Boot Option.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 62
Page 63

8.6 Security Setup
Administrator Password
Use this option to set a password for administrators with full control of the BIOS setup utility.
User Password
Use this option to set a password for users with limited access to the BIOS setup utility.
Page 63Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 63Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 63Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 63
Page 64

8.6 Save & Exit
Save Changes and Exit
When you have completed the system configuration changes, select this option to save
changes and continue booting the system. New configuration parameters will take effect
after the next system restart.
Discard Changes and Exit
Select this option to quit Setup without saving changes to the system configuration and
continue booting.
Save Changes and Reset
Reset the system after saving the changes.
Discard Changes and Reset
Reset system setup without saving any changes.
Save Changes
Save changes made so far to any of the setup options.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 64
Page 65

Discard Changes
Discard any unsaved changes
Restore Manufacturer Defaults
Restore standard default values for all the setup options.
Save Settings as OEM Defaults
Save the changes made so far as OEM Defaults.
Restore saved OEM Defaults
Restore the OEM Defaults to all the setup options.
Boot Override
Use the up/down arrow keys to highlight a boot device or "Launch EFI Shell" to immediately
exit the BIOS Setup and boot from the selected device.
Page 65Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 65Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 65Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 65
Page 66

9 BIOS Checkpoints, Beep Codes
This section of this document lists checkpoints and beep codes generated by AMIBIOS. The
checkpoints defined in this document are inherent to the AMIBIOS generic core, and do not
include any chipset or board specific checkpoint definitions.
Checkpoints and Beep Codes Definition
A checkpoint is either a byte or word value output to I/O port 80h. The BIOS outputs checkpoints
throughout bootblock and Power-On Self Test (POST) to indicate the task the system is currently
executing. Checkpoints are very useful for debugging problems that occur during the preboot process.
Beep codes are used by the BIOS to indicate a serious or fatal error. They are used when an error
occurs before the system video has been initialized, and generated by the system board speaker.
Viewing BIOS Checkpoints
Viewing all checkpoints generated by the BIOS requires a checkpoint card, also referred to as a
“POST Card” or “POST Diagnostic Card”. These are PCI add-in cards that show the value of
I/O port 80h on a LED display.
Some computers display checkpoints in the bottom right corner of the screen during POST.
This display method is limited, since it only displays checkpoints that occur after the video
card has been activated.
Keep in mind that not all computers using AMIBIOS enable this feature. In most cases, a
checkpoint card is the best tool for viewing AMIBIOS checkpoints.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 66
Page 67

9.1 Status Code Ranges
Status Code Range Description
0x01 – 0x0F SEC Status Codes & Errors
0x10 – 0x2F PEI execution up to and including memory detection
0x30 – 0x4F PEI execution after memory detection
0x50 – 0x5F PEI errors
0x60 – 0xCF DXE execution up to BDS
0xD0 – 0xDF DXE errors
0xE0 – 0xE8 S3 Resume (PEI)
0xE9 – 0xEF S3 Resume errors (PEI)
0xF0 – 0xF8 Recovery (PEI)
0xF9 – 0xFF Recovery errors (PEI)
9.2 Standard Status Codes
SEC Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x0 Not used
Progress Codes
0x1 Power on. Reset type detection (soft/hard).
0x2 AP initialization before microcode loading
0x3 North Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x4 South Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x5 OEM initialization before microcode loading
0x6 Microcode loading
0x7 AP initialization after microcode loading
0x8 North Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0x9 South Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0xA OEM initialization after microcode loading
0xB Cache initialization
SEC Error Codes
0xC – 0xD Reserved for future AMI SEC error codes
0xE Microcode not found
0xF Microcode not loaded
SEC Beep Codes
None.
Page 67Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 67Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 67Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 67
Page 68

PEI Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x0 Not used
Progress Codes
0x10 PEI Core is started
0x11 Pre-memory CPU initialization is started
0x12 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x13 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x14 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x15 Pre-memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x16 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x17 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x18 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x19 Pre-memory South Bridge initialization is started
0x1A Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1B Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1C Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initialization codes
0x2B Memory initialization. Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data reading
0x2C Memory initialization. Memory presence detection
0x2D Memory initialization. Programming memory timing information
0x2E Memory initialization. Configuring memory
0x2F Memory initialization (other).
0x30 Reserved for ASL (see A SL Status Codes section below)
0x31 Memory Installed
0x32 CPU post-memory initialization is started
0x33 CPU post-memory initialization. Cache initialization
0x34 CPU post-memory initialization. Application Processor(s) (AP) initialization
0x35 CPU post-memory initialization. Boot Strap Processor (BSP) selection
0x36 CPU post-memory initialization. System Management Mode (SMM) initialization
0x37 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x38 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x39 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3A Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3B Post-Memory South Bridge initialization is started
0x3C Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3D Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3E Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3F-0x4E OEM post memory initialization codes
0x4F DXE IPL is started
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 68
Page 69

PEI Status Codes (cont’d)
PEI Error Codes
0x50 Memory initialization error. Invalid memory type or incompatible memory speed
0x51 Memory initialization error. SPD reading has failed
0x52 Memory initialization error. Invalid memory size or memory modules do not match.
0x53 Memory initialization error. No usable memory detected
0x54 Unspecified memory initialization error.
0x55 Memory not installed
0x56 Invalid CPU type or Speed
0x57 CPU mismatch
0x58 CPU self test failed or possible CPU cache error
0x59 CPU micro-code is not found or micro-code update is failed
0x5A Internal CPU error
0x5B reset PPI is not available
0x5C-0x5F Reserved for future AMI error codes
S3 Resume Progress Codes
0xE0 S3 Resume is stared (S3 Resume PPI is called by the DXE IPL)
0xE1 S3 Boot Script execution
0xE2 Video repost
0xE3 OS S3 wake vector call
0xE4-0xE7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
0xE0 S3 Resume is stared (S3 Resume PPI is called by the DXE IPL)
S3 Resume Error Codes
0xE8 S3 Resume Failed in PEI
0xE9 S3 Resume PPI not Found
0xEA S3 Resume Boot Script Error
0xEB S3 OS Wake Error
0xEC-0xEF Reserved for future AMI error codes
Recovery Progress Codes
0xF0 Recovery condition triggered by firmware (Auto recovery)
0xF1 Recovery condition triggered by user (Forced recovery)
0xF2 Recovery process started
0xF3 Recovery firmware image is found
0xF4 Recovery firmware image is loaded
0xF5-0xF7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
Recovery Error Codes
0xF8 Recovery PPI is not available
0xF9 Recovery capsule is not found
0xFA Invalid recovery capsule
0xFB – 0xFF Reserved for future AMI error codes
Page 69Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 69Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 69Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 69
Page 70

PEI Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
1 Memory not Installed
1 Memory was installed twice (InstallPeiMemory routine in PEI Core called twice)
2 Recovery started
3 DXEIPL was not found
3 DXE Core Firmware Volume was not found
7 Reset PPI is not available
4 Recovery failed
4 S3 Resume failed
DXE Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x60 DXE Core is started
0x61 NVRAM initialization
0x62 Installation of the South Bridge Runtime Services
0x63 CPU DXE initialization is started
0x64 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x65 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x66 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x67 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x68 PCI host bridge initialization
0x69 North Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x6A North Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x6B North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6C North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6D North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6E North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6F North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x70 South Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x71 South Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x72 South Bridge devices initialization
0x73 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x74 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x75 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x76 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x77 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x78 ACPI module initialization
0x79 CSM initia liza tion
0x7A – 0x7F Reserved for future AMI DXE codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0x90 Boot Device Selection (BDS) phase is started
0x91 Driver connecting is started
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 70
Page 71

DXE Status Codes (cont’d)
Status Code Description
0x92 PCI Bus initialization is started
0x93 PCI Bus Hot Plug Controller Initialization
0x94 PCI Bus Enumeration
0x95 PCI Bus Request Resources
0x96 PCI Bus Assign Resources
0x97 Console Output devices connect
0x98 Console input devices connect
0x99 Super IO Initialization
0x9A USB initialization is started
0x9B USB Reset
0x9C USB Detect
0x9D USB Enable
0x9E – 0x9F Reserved for future AMI codes
0xA0 IDE initialization is started
0xA1 IDE Reset
0xA2 IDE Detect
0xA3 IDE Enable
0xA4 SCSI initialization is started
0xA5 SCSI Reset
0xA6 SCSI Detect
0xA7 SCSI Enable
0xA8 Setup Verifying Password
0xA9 Start of Setup
0xAA Reserved for ASL (see A SL Status Codes section below)
0xAB Setup Input Wait
0xAC Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0xAD Ready To Boot event
0xAE Legacy Boot event
0xAF Exit Boot Services event
0xB0 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP Begin
0xB1 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP End
0xB2 Legacy Option ROM Initialization
0xB3 System Reset
0xB4 USB hot plug
0xB5 PCI bus hot plug
0xB6 Clean-up of NVRAM
0xB7 Configuration Reset (reset of NVRAM settings)
0xB8 – 0xBF Reserved for future AMI codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
Page 71Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 71Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 71Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 71
Page 72

DXE Status Codes (cont’d)
DXE Error Codes
0xD0 CPU initialization error
0xD1 North Bridge initialization error
0xD2 South Bridge initialization error
0xD3 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
0xD4 PCI resource allocation error. Out of Resources
0xD5 No Space for Legacy Option ROM
0xD6 No Console Output Devices are found
0xD7 No Console Input Devices are found
0xD8 Invalid password
0xD9 Error loading Boot Option (LoadImage returned error)
0xDA Boot Option is failed (StartImage returned error)
0xDB Flash update is failed
0xDC Reset protocol is not available
DXE Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
4 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
5 No Console Output Devices are found
5 No Console Input Devices are found
1 Invalid password
6 Flash update is failed
7 Reset protocol is not available
8 Platform PCI resource requirements cannot be met
ACPI/ASL Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x01 System is entering S1 sleep state
0x02 System is entering S2 sleep state
0x03 System is entering S3 sleep state
0x04 System is entering S4 sleep state
0x05 System is entering S5 sleep state
0x10 System is waking up from the S1 sleep state
0x20 System is waking up from the S2 sleep state
0x30 System is waking up from the S3 sleep state
0x40 System is waking up from the S4 sleep state
0xAC System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in PIC mode.
0xAA System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in APIC mode.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 72
Page 73

9.3 OEM-Reserved Status Code Ranges
Status Code Description
0x5 OEM SEC initialization before microcode loading
0xA OEM SEC initialization after microcode loading
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initialization codes
0x3F – 0x4E OEM PEI post memory initialization codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
Page 73Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 73Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 73Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 73
Page 74

Important Safety Instructions
For user safety, please read and follow all instructions, warnings, cautions, and notes
marked in this manual and on the associated equipment before handling/operating the
equipment.
f Read these safety instructions carefully.
f Keep this user’s manual for future reference.
f Read the specifications section of this manual for detailed information on the operating
environment of this equipment.
f When installing/mounting or uninstalling/removing equipment:
- Turn off power and unplug any power cords/cables.
f To avoid electrical shock and/or damage to equipment:
- Keep equipment away from water or liquid sources;
- Keep equipment away from high heat or high humidity;
- Keep equipment properly ventilated (do not block or cover ventilation openings);
- Make sure to use recommended voltage and power source settings;
- Always install and operate equipment near an easily accessible electrical socket-outlet;
- Secure the power cord (do not place any object on/over the power cord);
- Only install/attach and operate equipment on stable surfaces and/or recommended
mountings; and,
- If the equipment will not be used for long periods of time, turn off and unplug the
equipment from its power source.
f Never attempt to fix the equipment. Equipment should only be serviced by qualified
personnel.
f A Lithium-type battery may be provided for uninterrupted, backup or emergency power.
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries
according to the instructions.
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 74
Page 75

f Equipment must be serviced by authorized technicians when:
- The power cord or plug is damaged;
- Liquid has penetrated the equipment;
- It has been exposed to high humidity/moisture;
- It is not functioning or does not function according to the user’s manual;
- It has been dropped and/or damaged; and/or,
- It has an obvious sign of breakage.
Page 75Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 75Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 75Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 75
Page 76

Getting Service
Contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
ᄅקؑխࡉ৬ԫሁ 166 ᇆ 9 ᑔ
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: Ϟ⍋Ꮦ⌺ϰᮄᓴ∳催⾥ᡔು㢇䏃 300 ো(201203)
300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park,
Pudong New Area, Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: ࣫ҀᏖ⍋⎔Ϟഄϰ䏃 1 োⲜ߯ࡼ E ᑻ 801 ᅸ(100085)
Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1,
Shang Di East Rd., Beijing, 100085 China
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8626
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: ⏅ഇᏖቅ⾥ᡔು催ᮄϗ䘧᭄ᄫᡔᴃು
A1 2 ὐ C (518057)
2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7,
High-Tech Industrial Park S., Shenzhen, 518054 China
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
LiPPERT ADLINK Technology GmbH
Address: Hans-Thoma-Strasse 11, D-68163, Mannheim, Germany
Tel: +49-621-43214-0
Fax: +49-621 43214-30
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
Express-CB User’s ManualPage 76
Page 77

ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 15 rue Emile Baudot, 91300 Massy CEDEX, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: ͱ101-0045 ᵅҀ䛑ҷ⬄⼲⬄䤯ފ⬎ 3-7-4
⼲⬄ 374 ɛɳ 4F
KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho,
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 昢殾柢 昢爎割 昢爎壟 1675-12 微汾瘶捒娯 8猻
8F Mointer B/D,1675-12, Seocho-Dong, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-070, Korea
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre,
Singapore 349584
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: 1st Floor, #50-56 (Between 16th/17th Cross) Margosa Plaza,
Margosa Main Road, Malleswaram, Bangalore-560055, India
Tel: +91-80-65605817, +91-80-42246107
Fax: +91-80-23464606
Email: india@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Israeli Liaison Office)
Address: 6 Hasadna St., Kfar Saba 44424, Israel
Tel: +972-9-7446541
Fax: +972-9-7446542
Email: israel@adlinktech.com
Page 77Express-CB User’s Manual
Page 77Express-IA533 User’s Manual Page 77Express-IA533 User’s ManualExpress-CB User’s Manual Page 77
Page 78

 Loading...
Loading...