Page 1

Express-BE
User’s Manual
Manual Revision: 1.00
Revision Date:
Part Number: 50-1J060-1000
May 7, 2015
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Description Date By
1.00 Initial release 2015-05-07 JC
Page 2 Express-BE
Page 3

Preface
Copyright 2015 ADLINK Technology, Inc.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by
any mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in order to improve reliability, design, and function and does not
represent a commitment on the part of the manufacturer. In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or
consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product or documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such
damages.
Environmental Responsibility
ADLINK is committed to fulfill its social responsibility to global environmental preservation through compliance with the European Union's
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directive. Environmental
protection is a top priority for ADLINK. We have enforced measures to ensure that our products, manufacturing processes, components, and
raw materials have as little impact on the environment as possible. When products are at their end of life, our customers are encouraged to
dispose of them in accordance with the product disposal and/or recovery programs prescribed by their nation or company.
Trademarks
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
Express-BE Page 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Revision History ............................................................................................................ 2
Preface............................................................................................................................ 3
1. Introduction......................................................................................................... 8
2. Specifications....................................................................................................... 9
2.1. Core System..............................................................................................................................9
2.2. Expansion Busses......................................................................................................................9
2.3. SEMA Board Controller.............................................................................................................9
2.4. Debug Headers .........................................................................................................................9
2.5. Video...................................................................................................................................... 10
2.6. Audio...................................................................................................................................... 10
2.7. LAN ........................................................................................................................................ 10
2.8. Multi I/O and Storage............................................................................................................ 10
2.9. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) ........................................................................................... 10
2.10. Power Specifications ............................................................................................................. 11
2.11. Power Consumption.............................................................................................................. 11
2.12. Operating Temperatures ....................................................................................................... 11
2.13. Environmental ....................................................................................................................... 11
2.14. Specification Compliance ...................................................................................................... 11
2.15. Operating Systems................................................................................................................. 11
2.16. Functional Diagram................................................................................................................ 12
2.17. Mechanical Dimensions......................................................................................................... 13
3. Pinouts and Signal Descriptions......................................................................
3.1. AB/CD Pin Definitions............................................................................................................ 14
3.2. Signal Description Terminology............................................................................................. 17
14
3.3. AB Signal Descriptions ........................................................................................................... 18
3.3.1. Audio Signals ...............................................................................................................................18
3.3.2. Analog VGA (No VGA support)....................................................................................................18
3.3.3. LVDS ............................................................................................................................................18
3.3.4. Gigabit Ethernet ..........................................................................................................................19
3.3.5. SATA ............................................................................................................................................19
3.3.6. PCI Express ..................................................................................................................................20
3.3.7. Express Card................................................................................................................................21
3.3.8. LPC Bus ........................................................................................................................................21
3.3.9. USB ..............................................................................................................................................21
Page 4 Express-BE
Page 5

3.3.10. USB Root Segmentation ..............................................................................................................22
3.3.11. SPI (BIOS only).............................................................................................................................22
3.3.12. Miscellaneous..............................................................................................................................23
3.3.13. SMBus..........................................................................................................................................23
3.3.14. I2C Bus.........................................................................................................................................23
3.3.15. General Purpose I/O (GPIO) ........................................................................................................23
3.3.16. Serial Interface Signals ................................................................................................................24
3.3.17. Power and System Management ................................................................................................24
3.3.18. Power and Ground ......................................................................................................................25
3.4. CD Signal Descriptions ........................................................................................................... 26
3.4.1. USB 3.0 Extension .......................................................................................................................26
3.4.2. PCI Express x1..............................................................................................................................26
3.4.3. DDI Channels ...............................................................................................................................27
3.4.4. DDI to DP/HDMI Mapping...........................................................................................................29
3.4.5. PCI Express Graphics x16 (PEG)...................................................................................................30
3.4.6. Module Type Definition ..............................................................................................................31
3.4.7. Power and Ground ......................................................................................................................31
4. Module Interfaces and Configuration ............................................................ 32
4.1. Connector, Switch and LED Locations ................................................................................... 32
4.1.1. Express-BE and the DB40 Module connected.............................................................................32
4.2. 40-pin Multipurpose Connector ............................................................................................ 33
4.3. Status LEDs ............................................................................................................................ 34
4.4. Fan Connector ....................................................................................................................... 35
4.5. BIOS Setup Defaults Reset Button......................................................................................... 36
4.6. Express-BE Switch Settings .................................................................................................... 37
4.6.1. Switch Locations..........................................................................................................................37
4.6.2. SW1: BIOS Select and Mode Configuration Switch .....................................................................37
4.7. PCIe x 16-to-two-x8 Adapter Card......................................................................................... 38
5. Smart Embedded Management Agent (SEMA) ............................................. 39
5.1. Board Specific SEMA Functions ............................................................................................. 40
5.1.1. Voltages.......................................................................................................................................40
5.1.2. Main Current...............................................................................................................................40
5.1.3. BMC Status..................................................................................................................................40
5.1.4. Exception Codes ..........................................................................................................................41
5.1.5. BMC Flags....................................................................................................................................41
6. System Resources.............................................................................................. 42
6.1. System Memory Map ............................................................................................................ 42
Express-BE Page 5
Page 6

6.2. Direct Memory Access Channels ........................................................................................... 42
6.3. I/O Map.................................................................................................................................. 43
6.4. Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines................................................................................................ 44
6.4.1. PIC Mode.....................................................................................................................................44
6.4.2. APIC Mode...................................................................................................................................45
6.5. PCI Configuration Space Map ................................................................................................ 46
6.6. PCI Interrupt Routing Map .................................................................................................... 47
6.7. SMBus Address Table ............................................................................................................ 47
7. BIOS Setup .........................................................................................................48
7.1. Menu Structure ..................................................................................................................... 48
7.2. Main....................................................................................................................................... 49
7.2.1. System Information.....................................................................................................................49
7.2.2. Memory Information...................................................................................................................49
7.2.3. System Management ..................................................................................................................49
7.2.4. System Date and Time.................................................................................................................52
7.3. Advanced ............................................................................................................................... 52
7.3.1. CPU..............................................................................................................................................52
7.3.2. Memory.......................................................................................................................................53
7.3.3. Graphics ......................................................................................................................................53
7.3.4. SATA ............................................................................................................................................54
7.3.5. USB ..............................................................................................................................................55
7.3.6. Network.......................................................................................................................................57
7.3.7. PCI and PCIe ................................................................................................................................57
7.3.8. Super IO.......................................................................................................................................62
7.3.9. ACPI and Power Management ....................................................................................................62
7.3.10. Sound ..........................................................................................................................................63
7.3.11. Serial Port Console ......................................................................................................................63
7.3.12. Thermal .......................................................................................................................................65
7.3.13. Miscellaneous..............................................................................................................................65
7.4. Boot ....................................................................................................................................... 65
7.4.1. Boot Configuration......................................................................................................................65
7.4.2. Boot Configuration > CSM16 Parameters ...................................................................................66
7.4.3. Boot Configuration > CSM Parameters .......................................................................................66
7.5. Security.................................................................................................................................. 67
7.5.1. Password Description..................................................................................................................67
7.6. Save & Exit ............................................................................................................................. 67
7.6.1. Save and Exit > Reset Options.....................................................................................................67
7.6.2. Save and Exit > Save Options ......................................................................................................67
Page 6 Express-BE
Page 7

7.6.3. Boot Override..............................................................................................................................67
8. BIOS Checkpoints, Beep Codes........................................................................ 68
8.1. Status Code Ranges ............................................................................................................... 69
8.2. Standard Status Codes........................................................................................................... 69
8.2.1. SEC Status Codes .........................................................................................................................69
8.2.2. SEC Beep Codes...........................................................................................................................70
8.2.3. PEI Status Codes..........................................................................................................................70
8.2.4. PEI Beep Codes............................................................................................................................72
8.2.5. DXE Status Codes ........................................................................................................................72
8.2.6. DXE Beep Codes ..........................................................................................................................75
8.2.7. ACPI/ASL Checkpoint...................................................................................................................75
8.3. OEM-Reserved Checkpoint Ranges ....................................................................................... 75
9. Mechanical Information ...................................................................................
9.1. Board-to-Board Connectors .................................................................................................. 76
9.2. Thermal Solution ................................................................................................................... 77
9.2.1. Heat Spreaders............................................................................................................................77
9.2.2. Heat Sinks....................................................................................................................................77
9.2.3. Installation...................................................................................................................................77
9.3. Mounting Methods................................................................................................................ 80
9.4. Standoff Types....................................................................................................................... 81
Safety Instructions ...................................................................................................... 82
Getting Service ............................................................................................................ 83
76
Express-BE Page 7
Page 8

1. Introduction
The Express-BE is a COM Express® COM.0 R2.1 Basic Size Type 6 module supporting the AMD R-Series APU (codename: Bald Eagle)
with A77E Fusion Controller Hub. The Express-BE is specifically designed for customers who need excellent graphics performance and
high-level processing performance with low power consumption in a long product life solution.
The Express-BE features the AMD R-Series APU supporting Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA) and non-ECC type DDR3L dualchannel memory at 1333/1600 MHz to provide excellent overall performance.
AMD Radeon HD 9000 Graphics integrated on the APU includes features such as OpenGL 4.2, DirectX 11.1, OpenCL 1.2, OpenGLES 2.0,
OpenCV, and support for H.264, MPEG2, VC1, MPEG4, WMV9, and MVC hardware decode. Graphics outputs include dual-channel
18/24-bit LVDS and DDI ports supporting HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort and optional eDP
supported. The Express-BE is specifically designed for customers with high-performance processing and graphics requirements who want to
outsource the core logic of their systems for reduced development time.
The Express-BE has dual stacked SODIMM sockets for up to 16 GB non-ECC type DDR3L memory. In addition to the onboard integrated
graphics, a multiplexed PCI Express® x16 Graphics bus is available for discrete graphics expansion. Input/output features include a single
onboard Gigabit Ethernet port, USB 3.0 ports and USB 2.0 ports, and SATA 6 Gb/s ports. Support is provided for SMBus and I2C. The
module is equipped with SPI AMI EFI BIOS with CMOS backup, supporting embedded features such as remote console, hardware monitor,
and watchdog timer.
(TBD). In addition, up to four independent displays are
Page 8 Express-BE
Page 9

2. Specifications
2.1. Core System
¾ CPU: Dual or quad-core AMD R-Series APU (codename: Bald Eagle)
• RX-427BB 2.7 GHz (3.6 GHz boost), 35W (4C/8CU)
• RX-425BB 2.5 GHz(3.4 GHz boost), 35W (4C/6CU)
• RX-225FB 2.2 GHz (3.0 GHz boost), 17W (2C/3CU)
Supporting: AMD-V, Intel® SSE4.1 and SSE4.2, AMD Thermal Monitor (SB-TSI)
Note: The availability of the features may vary between processor SKUs.
¾ Cache: 4MB L2 cache for RX-427BB and RX-425BB, 2MB L2 cache for RX-225FB
¾ Memory: Dual channel non-ECC 1333/1600 MHz DDR3L memory up to 16GB in dual stacked SODIMM sockets
Note: The lower SODIMM slot must be populated.
¾
Chipset: AMD A77E Fusion Controller Hub (codename: Bolton-E4)
¾ Embedded BIOS: AMI EFI with CMOS backup in 8 MB SPI BIOS
2.2. Expansion Busses
¾ PCI Express x 16 Gen3 (can be configured to 2 x8 or 1 x8 and 1 x4)
Note: These lanes are intended for use with a graphics card.
¾ 6 PCI Express x1 (AB): Lanes 0/1/2/3/4/5 (Lanes 0-3 from APU, L anes 4-5 from FCH)
¾ 1 PCI Express x1 (CD): Lane 6 (from FCH)
2
¾ LPC bus, SMBus (system) , I
C (user)
2.3. SEMA Board Controller
¾ Type: ADLINK Smart Embedded Management Agent (SEMA)
¾ Supports:
• Voltage/Current monitoring
• Power sequence debug support
• AT/ATX mode control
• Logistics and Forensic information
• Flat Panel Control
• General Purpose I2C
• Failsafe BIOS (dual BIOS )
• Watchdog Timer and Fan Control
2.4. Debug Headers
¾ 40-pin multipurpose flat cable connector, used in combination with DB-40 debug module providing BIOS POST code LED, BMC
access, SPI BIOS flashing, power testpoints, debug LEDs
Express-BE Page 9
Page 10

2.5. Video
¾ GPU Feature Support: Radeon HD 9000 Series supporting four independent displays and Heterogeneous System Architecture
• 3D graphics hardware acceleration
• Support for DirectX 11.1, OpenCL 1.2, OpenGL 4.2, OpenGLES 2.0 and OpenCV
• Video decode hardware acceleration (UVD 4.2) including support for H.264, MPEG2, VC-1, MPEG4, WMV9 and MVC formats
• Video encode hardware acceleration (VCE 2.0) including support for H.264, SVC formats and specific support for video conferencing and
wireless display applications
• AMD Eyefinity technology
• AMD Dual Graphics technology
Note: the availability of the features may vary between OS (Win 7/8, WES 7/8, Linux)
¾ Display Interface support
• DDI1: supports
• DDI2: supports
• DDI3: supports
DisplayPort, HDMI, DVI (eDP TBD)
DisplayPort, HDMI, DVI
DisplayPort, HDMI, DVI (eDP TBD)
• LVDS: supports up to dual-channel 18/24-bit LVDS (through eDP to LVDS bridge IC)
Note: Display priority follows APU settings, and cannot be defined by the user. The priority is DP0 > DP1 > DP2 > DP3.
à DP0 (from APU) mapped to DDI1
à DP1 (from APU) mapped to DDI3
à DP2 (from APU) mapped to LVDS
à DP3 (from APU) mapped to DDI2
2.6. Audio
¾ Audio Codec: located on carrier Express-BASE6 (ALC886 standard support)
2.7. LAN
¾ Intel MAC/PHY: Intel® i210 Ethernet controller
¾ Interface: 10/100/1000 Mbit/s connection
2.8. Multi I/O and Storage
¾ Integrated in APU and FCH
¾ USB:
• 4x USB 1.1/2.0/3.0 (USB 0,1,2,3)
• 4x USB 1.1/2.0 (USB 4,5,6,7)
¾ SATA: four ports SATA 6Gb/s (SATA 0,1,2,3)
Note: SATA repeater/redriver on carrier board is required for SATA 6Gb/s
¾ Serial: 2 UART ports COM 0/1 with console redirection
¾ GPIO: 4 GPO and 4 GPI with interrupt
2.9. TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
¾ Chipset: Atmel AT97SC3204
¾ Type: TPM 1.2
Page 10 Express-BE
Page 11

2.10. Power Specifica tions
¾ Power Modes: AT and ATX mode (AT mode startup controlled by SEMA)
¾ Standard Voltage Input: ATX @ 12V±5%,/ 5Vsb ±5% or AT @ 12V ±5%
¾ Wide Voltage Input: ATX @ 8.5-20V, 5Vsb ±5% or AT @ 8.5-20V
¾ Power Management: ACPI 4.0 compliant, Smart Battery support
¾ Power States: supports C0, C1, C1E, C6, CC6, S0, S3, S5, S5 ECO mode (Wake-on-USB S3, WOL S3/S5)
¾ ECO mode: supports deep S5 for 5Vsb power saving
2.11. Power Consumption
TBD
2.12. Operating Temperatures
¾ Standard Operating Temperature: °C to 60°C (wide voltage input)
2.13. Environmental
¾ Humidity: 5-90% RH operating, non-condensing
5-95% RH storage (and operating with conformal coating).
¾ Shock and Vibration: IEC 60068-2-64 and IEC-60068-2-27
MIL-STD-202F, Method 213B, Table 213-I, Condition A and Method 214A, Table 214-I, Condition D
¾ Halt: Thermal Stress, Vibration Stress, Thermal Shock and Combined Test
2.14. Specification Compliance
¾ PICMG COM.0: Rev 2.1 Type 6, Basic size 125 x 95 mm
2.15. Operating Systems
¾ Standard Support: Windows 7/8.1 32/64-bit, Linux 32/64-bit
¾ Extended Support (BSP): WES 7/8, Linux
Express-BE Page 11
Page 12
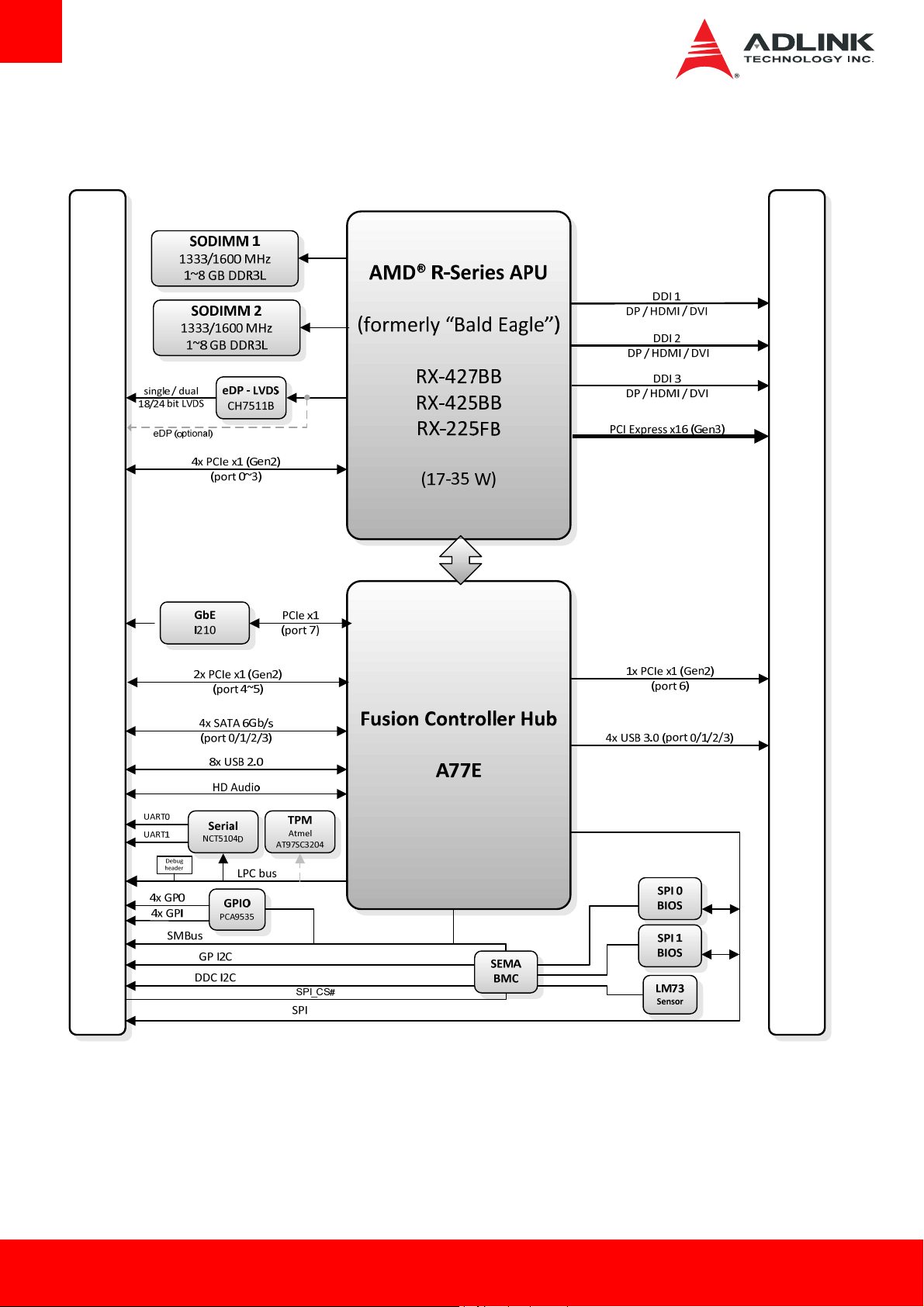
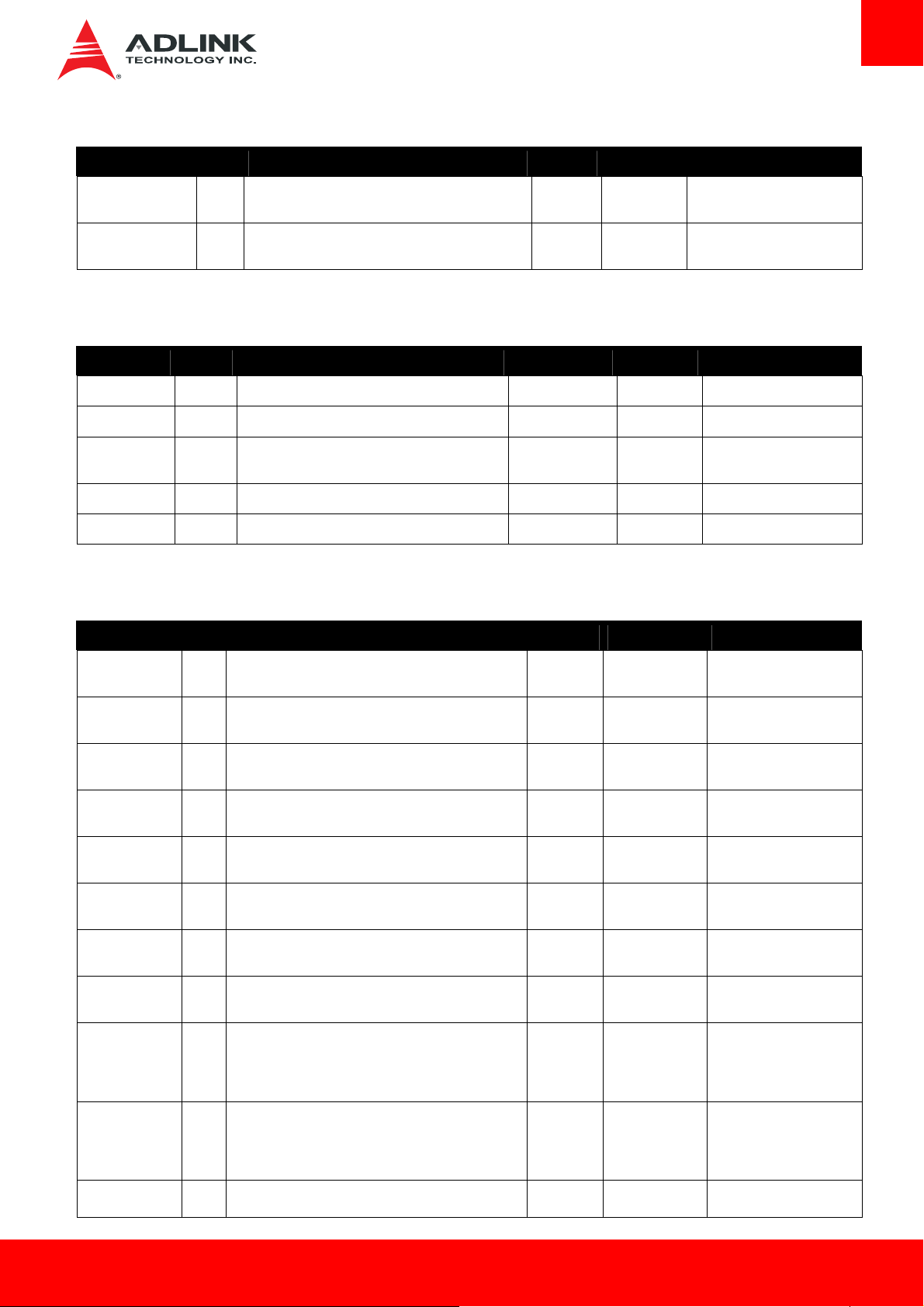
2.16. Functional Diagram
AB
UMI
CD
Page 12 Express-BE
Page 13
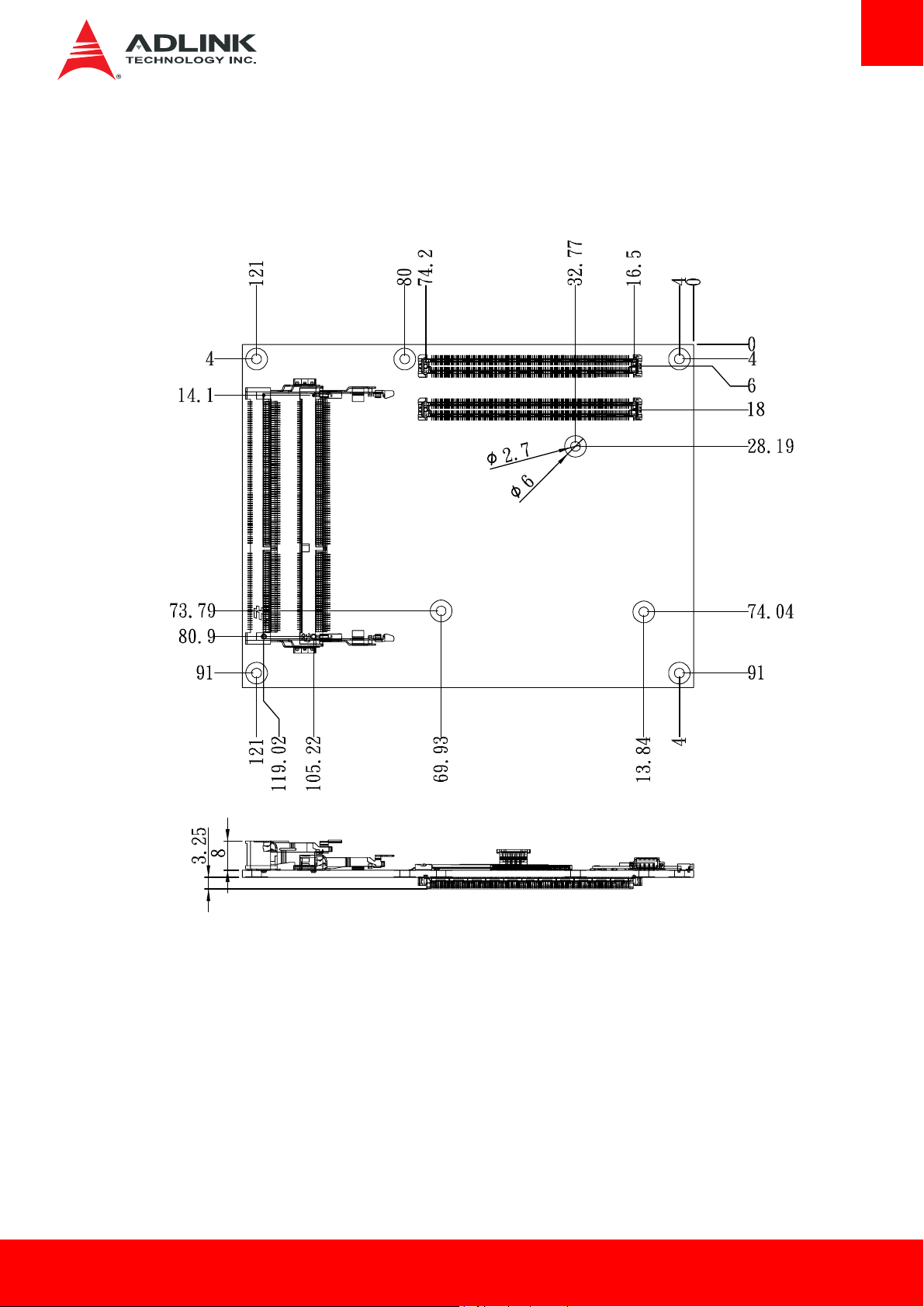
2.17. Mechanical Dimensions
Top View
Side View
All Ø tolerances ± 0.05 mm
Other tolerances ± 0.2 mm
Dimensions in mm
Express-BE Page 13
Page 14
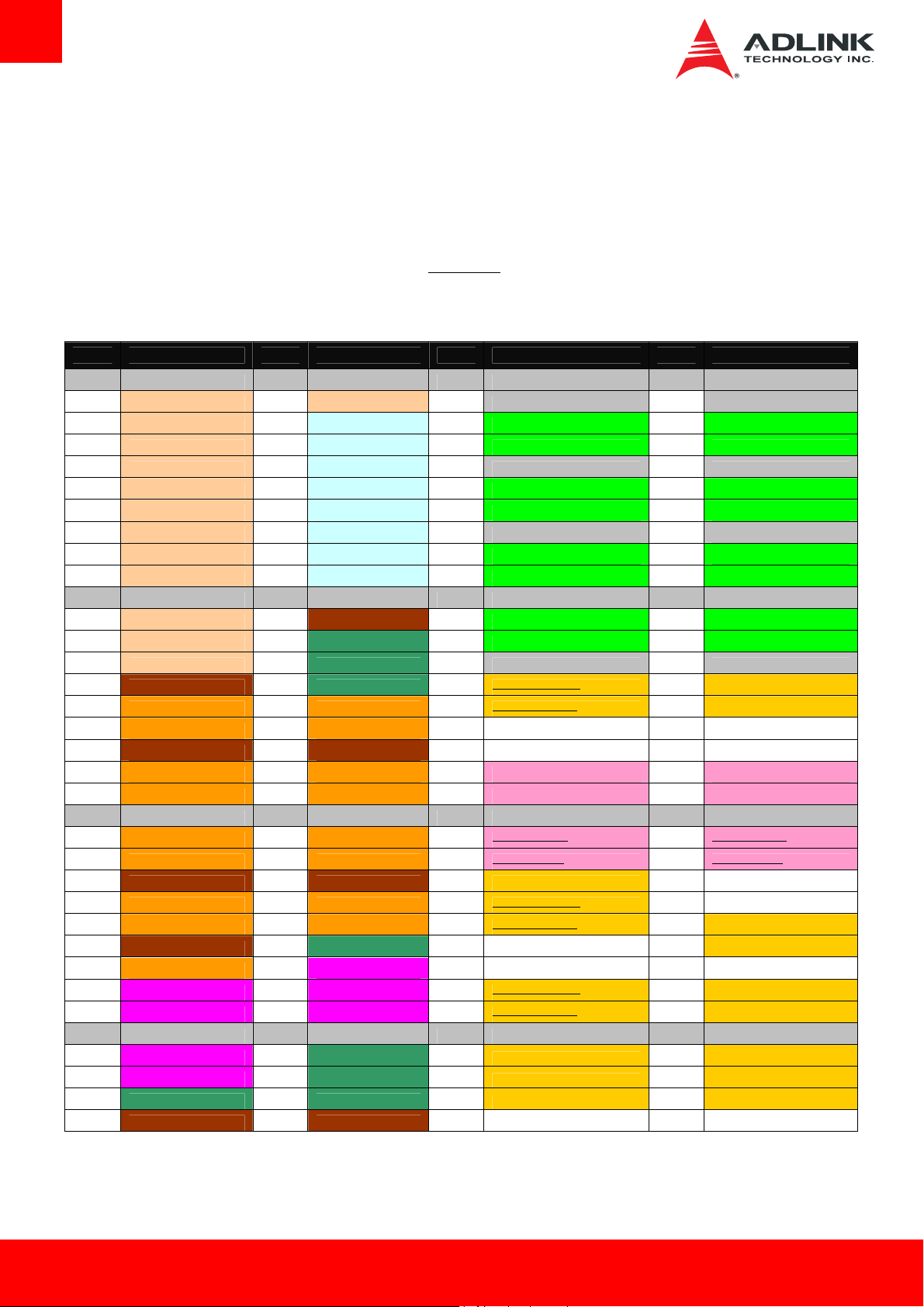
3. Pinouts and Signal Descriptions
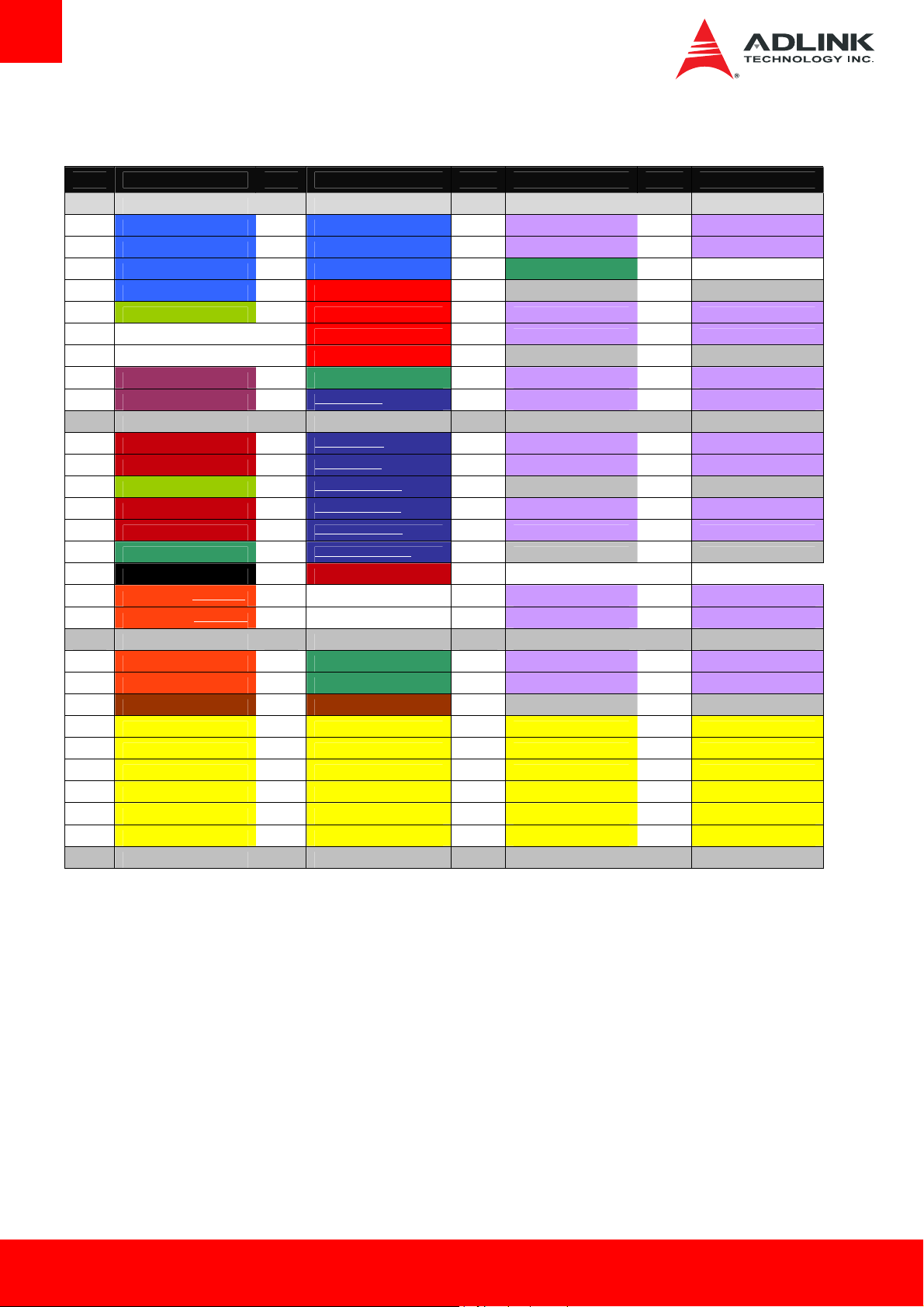
3.1. AB/CD Pin Definitions
The Express-BE is a Type 6 module supporting USB 3.0 and DDI channels on the CD connector. In the table below, all standard pins of the
COM Express specification are described, including those not supported on the Express-BE.
Note: Signals not supported on the Express-BE module are crossed out
Row A Row B Row C Row D
Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A22
A23
A24
A25
A26
A27
A28
A29
A30
A31
A32
A33
A34
A35
GND (fixed)
GBE0_MDI3GBE0_MDI3+
GBE0_LINK100#
GBE0_LINK1000#
GBE0_MDI2GBE0_MDI2+
GBE0_LINK#
GBE0_MDI1GBE0_MDI1+
GND (fixed)
GBE0_MDI0GBE0_MDI0+
GBE0_CTREF
SUS_S3#
SATA0_TX+
SATA0_TX-
SUS_S4#
SATA0_RX+
SATA0_RXGND (fixed)
SATA2_TX+
SATA2_TXSUS_S5#
SATA2_RX+
SATA2_RX-
BATLOW#
(S)ATA_ACT#
AC/HDA_SYNC
AC/HDA_RST#
GND (fixed)
AC/HDA_BITCLK
AC/HDA_SDOUT
BIOS_DIS0#
THRMTRIP#
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B8
B9
B10
B11
B12
B13
B14
B15
B16
B17
B18
B19
B20
B21
B22
B23
B24
B25
B26
B27
B28
B29
B30
B31
B32
B33
B34
B35
GND (fixed)
GBE0_ACT#
LPC_FRAME#
LPC_AD0
LPC_AD1
LPC_AD2
LPC_AD3
LPC_DRQ0#
LPC_DRQ1#
LPC_CLK
GND (fixed)
PWRBTN#
SMB_CK
SMB_DAT
SMB_ALERT#
SATA1_TX+
SATA1_TX-
SUS_STAT#
SATA1_RX+
SATA1_RXGND (fixed)
SATA3_TX+
SATA3_TXPWR_OK
SATA3_RX+
SATA3_RX-
WDT
AC/HDA_SDIN2
AC/HDA_SDIN1
AC/HDA_SDIN0
GND (fixed)
SPKR
I2C_CK
I2C_DAT
THRM#
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
C10
C11
C12
C13
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
C21
C22
C23
C24
C25
C26
C27
C28
C29
C30
C31
C32
C33
C34
C35
GND (fixed)
GND
USB_SSRX0USB_SSRX0+
GND
USB_SSRX1- D6 USB_SSTX1USB_SSRX1+ D7 USB_SSTX1+
GND D8 GND
USB_SSRX2- D9 USB_SSTX2USB_SSRX2+ D10 USB_SSTX2+
GND (fixed) D11 GND (fixed)
USB_SSRX3- D12 USB_SSTX3USB_SSRX3+ D13 USB_SSTX3+
GND
DDI1_PAIR6+
DDI1_PAIR6RSVD
RSVD
PCIE_RX6+ D19 PCIE_TX6+
PCIE_RX6- D20 PCIE_TX6GND (fixed)
PCIE_RX7+
PCIE_RX7-
DDI1_HPD
DDI1_PAIR4+
DDI1_PAIR4RSVD
RSVD
DDI1_PAIR5+
DDI1_PAIR5GND (fixed)
DDI2_CTRLCLK_AUX+
DDI2_CTRLDATA_AUXDDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL
RSVD
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D14
D15
D16
D17
D18
D21
D22
D23
D24
D25
D26
D27
D28
D29
D30
D31
D32
D33
D34
D35
GND (fixed)
GND
USB_SSTX0USB_SSTX0+
GND
GND
DDI1_CTRLCLK_AUX+
DDI1_CTRLDATA_AUX
RSVD
RSVD
GND (fixed)
PCIE_TX7+
PCIE_TX7RSVD
RSVD
DDI1_PAIR0+
DDI1_PAIR0RSVD
DDI1_PAIR1+
DDI1_PAIR1GND (fixed)
DDI1_PAIR2+
DDI1_PAIR2-
DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL
RSVD
Page 14 Express-BE
Page 15
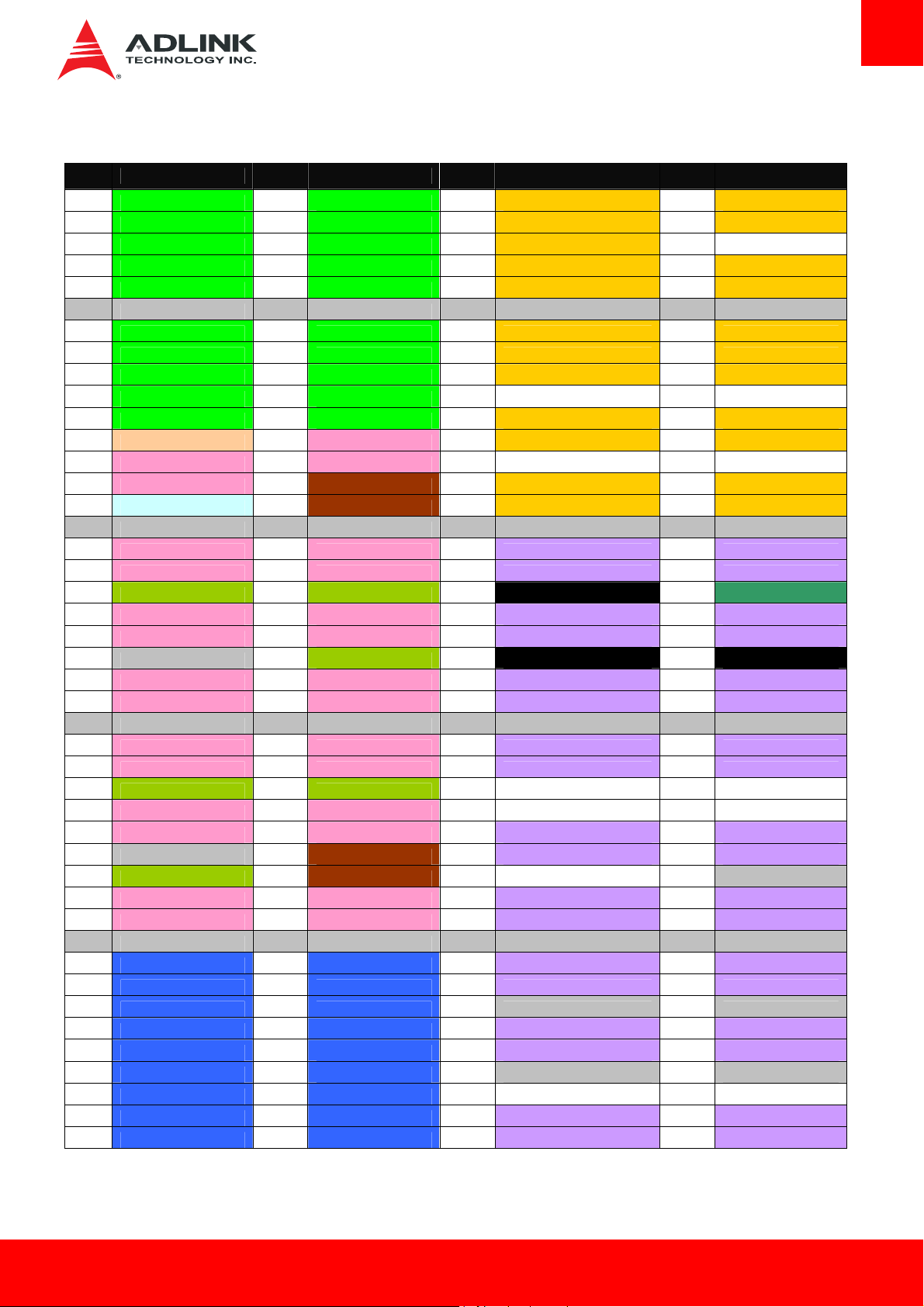
Row A Row B Row C Row D
Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name
A36
A37
A38
A39
A40
A41
A42
A43
A44
A45
A46
A47
A48
A49
A50
A51
A52
A53
A54
A55
A56
A57
A58
A59
A60
A61
A62
A63
A64
A65
A66
A67
A68
A69
A70
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
A77
A78
A79
USB6USB6+
USB_6_7_OC#
USB4USB4+
GND (fixed)
USB2USB2+
USB_2_3_OC#
USB0USB0+
VCC_RTC
EXCD0_PERST#
EXCD0_CPPE#
LPC_SERIRQ
GND (fixed)
PCIE_TX5+
PCIE_TX5-
GPI0
PCIE_TX4+
PCIE_TX4GND
PCIE_TX3+
PCIE_TX3GND (fixed)
PCIE_TX2+
PCIE_TX2GPI1
PCIE_TX1+
PCIE_TX1GND
GPI2
PCIE_TX0+
PCIE_TX0GND (fixed)
LVDS_A0+
LVDS_A0-
LVDS_A1+
LVDS_A1-
LVDS_A2+
LVDS_A2-
LVDS_VDD_EN
LVDS_A3+
LVDS_A3-
B36
B37
B38
B39
B40
B41
B42
B43
B44
B45
B46
B47
B48
B49
B50
B51
B52
B53
B54
B55
B56
B57
B58
B59
B60
B61
B62
B63
B64
B65
B66
B67
B68
B69
B70
B71
B72
B73
B74
B75
B76
B77
B78
B79
USB7USB7+
USB_4_5_OC#
USB5USB5+
GND (fixed)
USB3USB3+
USB_0_1_OC#
USB1USB1+
EXCD1_PERST#
EXCD1_CPPE#
SYS_RESET#
CB_RESET#
GND (fixed)
PCIE_RX5+
PCIE_RX5-
GPO1
PCIE_RX4+
PCIE_RX4GPO2
PCIE_RX3+
PCIE_RX3GND (fixed)
PCIE_RX2+
PCIE_RX2GPO3
PCIE_RX1+
PCIE_RX1-
WAKE0#
WAKE1#
PCIE_RX0+
PCIE_RX0GND (fixed)
LVDS_B0+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_BKLT_EN
C36
C37
C38
C39
C40
C41
C42
C43
C44
C45
C46
C47
C48
C49
C50
C51
C52
C53
C54
C55
C56
C57
C58
C59
C60
C61
C62
C63
C64
C65
C66
C67
C68
C69
C70
C71
C72
C73
C74
C75
C76
C77
C78
C79
DDI3_CTRLCLK_AUX+
DDI3_CTRLDATA_AUX-
DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL
DDI3_PAIR0+
DDI3_PAIR0GND (fixed)
DDI3_PAIR1+
DDI3_PAIR1DDI3_HPD
RSVD
DDI3_PAIR2+
DDI3_PAIR2RSVD
DDI3_PAIR3+
DDI3_PAIR3GND (fixed)
PEG_RX0+ D52 PEG_TX0+
PEG_RX0- D53 PEG_TX0-
TYPE0#
PEG_RX1+ D55 PEG_TX1+
PEG_RX1- D56 PEG_TX1-
TYPE1#
PEG_RX2+ D58 PEG_TX2+
PEG_RX2- D59 PEG_TX2GND (fixed) D60 GND (fixed)
PEG_RX3+ D61 PEG_TX3+
PEG_RX3- D62 PEG_TX3RSVD D63 RSVD
RSVD D64 RSVD
PEG_RX4+ D65 PEG_TX4+
PEG_RX4- D66 PEG_TX4RSVD D67 GND
PEG_RX5+ D68 PEG_TX5+
PEG_RX5- D69 PEG_TX5GND (fixed) D70 GND (fixed)
PEG_RX6+ D71 PEG_TX6+
PEG_RX6- D72 PEG_TX6GND D73 GND
PEG_RX7+ D74 PEG_TX7+
PEG_RX7- D75 PEG_TX7GND D76 GND
RSVD D77 RSVD
PEG_RX8+ D78 PEG_TX8+
PEG_RX8- D79 PEG_TX8-
D36
D37
D38
D39
D40
D41
D42
D43
D44
D45
D46
D47
D48
D49
D50
D51
D54
D57
DDI1_PAIR3+
DDI1_PAIR3RSVD
DDI2_PAIR0+
DDI2_PAIR0GND (fixed)
DDI2_PAIR1+
DDI2_PAIR1DDI2_HPD
RSVD
DDI2_PAIR2+
DDI2_PAIR2RSVD
DDI2_PAIR3+
DDI2_PAIR3GND (fixed)
PEG_LANE_RV#
TYPE2#
Express-BE Page 15
Page 16
Row A Row B Row C Row D
Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name
A80
A81
A82
A83
A84
A85
A86
A87
A88
A89
A90
A91
A92
A93
A94
A95
A96
A97
A98
A99
A100
A101
A102
A103
A104
A105
A106
A107
A108
A109
A110
GND (fixed)
LVDS_A_CK+
LVDS_A_CK-
LVDS_I2C_CK
LVDS_I2C_DAT
GPI3
RSVD
RSVD
PCIE0_CK_REF+
PCIE0_CK_REF-
GND (fixed)
SPI_POWER
SPI_MISO
GPO0
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
TPM_PP
TYPE10#
SER0_TX / CAN_TX
SER0_RX / CAN_RX
GND (fixed)
SER1_TX
SER1_RX
LID# ** B103 SLEEP# **
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND (fixed)
B80
B81
B82
B83
B84
B85
B86
B87
B88
B89
B90
B91
B92
B93
B94
B95
B96
B97
B98
B99
B100
B101
B102
B104
B105
B106
B107
B108
B109
B110
GND (fixed)
LVDS_B_CK+
LVDS_B_CK-
LVDS_BKLT_CTRL
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
VCC_5V_SBY
BIOS_DIS1#
VGA_RED C89
GND (fixed)
VGA_GRN C91
VGA_BLU C92
VGA_HSYNC C93
VGA_VSYNC C94
VGA_I2C_CK C95
VGA_I2C_DAT C96
SPI_CS#
RSVD
RSVD
GND (fixed)
FAN_PWMOUT
FAN_TACHIN
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND (fixed)
C80
C81
C82
C83
C84
C85
C86
C87
C88
C90
C97
C98
C99
C100
C101
C102
C103
C104
C105
C106
C107
C108
C109
C110
GND (fixed)
PEG_RX9+ D81 PEG_TX9+
PEG_RX9- D82 PEG_TX9TPM_PP D83 RSVD
GND D84 GND
PEG_RX10+ D85 PEG_TX10+
PEG_RX10- D86 PEG_TX10GND D87 GND
PEG_RX11+ D88 PEG_TX11+
PEG_RX11- D89 PEG_TX11GND (fixed) D90 GND (fixed)
PEG_RX12+ D91 PEG_TX12+
PEG_RX12- D92 PEG_TX12GND D93 GND
PEG_RX13+ D94 PEG_TX13+
PEG_RX13- D95 PEG_TX13GND D96 GND
RSVD D97 RSVD
PEG_RX14+ D98 PEG_TX14+
PEG_RX14- D99 PEG_TX14GND (fixed) D100 GND (fixed)
PEG_RX15+ D101 PEG_TX15+
PEG_RX15- D102 PEG_TX15GND D103 GND
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND (fixed)
D80
D104
D105
D106
D107
D108
D109
D110
GND (fixed)
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
VCC_12V
GND (fixed)
Page 16 Express-BE
Page 17

3.2. Signal Description Terminology
The following terms are used in the COM Express AB/CD Signal Descriptions below.
I Input to the Module
O Output from the Module
I/O Bi-directional input/output signal
OD Open drain output
I 3.3V Input 3.3V tolerant
I 5V Input 5V tolerant
O 3.3V Output 3.3V signal level
O 5V Output 5V signal level
I/O 3.3V Bi-directional signal 3.3V tolerant
I/O 5V Bi-directional signal 5V tolerant
I/O 3.3Vsb Input 3.3V tolerant active in standby state
P Power Input/Output
REF Reference voltage output that may be sourced from a module power plane.
PDS Pull-down strap. This is an output pin on the module that is either tied to GND or not connected.
The signal is used to indicate the PICMG module type to the Carrier Board.
PU ADLINK implemented pull-up resistor on module
PD ADLINK implemented pull-down resistor on module
Express-BE Page 17
Page 18
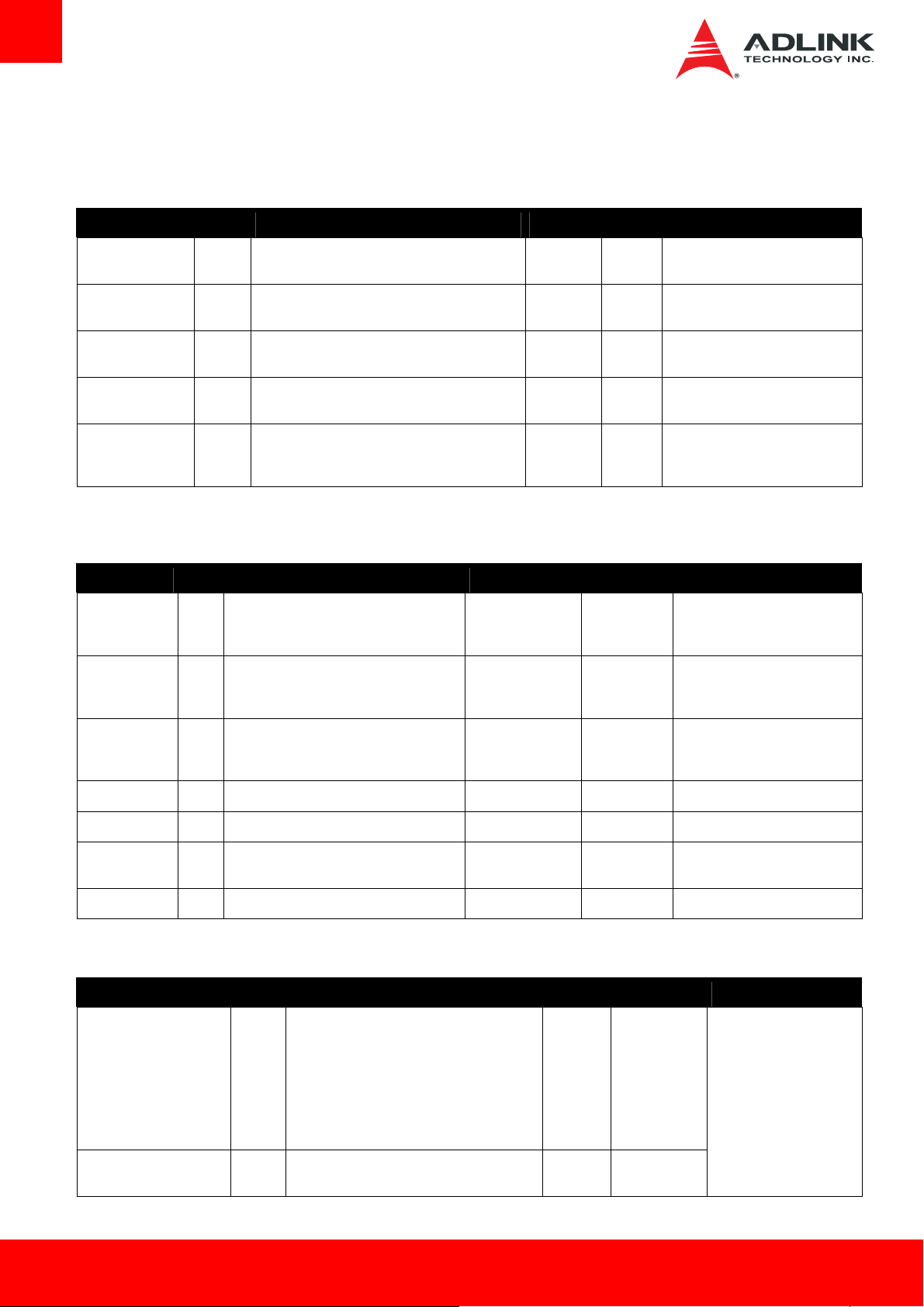
3.3. AB Signal Descriptions
3.3.1. Audio Signals
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
AC_RST# /
HDA_RST#
AC_SYNC /
HDA_SYNC
AC_BITCLK /
HDA_BITCLK
AC _SDOUT /
HDA_SDOUT
AC _SDIN[2:0]
HDA_SDIN[2:0]
A30 Reset output to CODEC, active low. O 3.3VSB
A29 Sample-synchronization signal to the CODEC(s). O 3.3V
A32 Serial data clock generated by the external
CODEC(s).
A33 Serial TDM data output to the CODEC. O 3.3V
B28
B30
Serial TDM data inputs from up to 3 CODECs. I/O 3.3VSB AC_SDIN0: supported
I/O 3.3V
AC_SDIN1: supported
AC_SDIN2: supported
3.3.2. Analog VGA (No VGA support)
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
VGA_RED B89 Red for monitor.
Analog DAC output, designed to drive a
37.5-Ohm equivalent load.
VGA_GRN B91 Green for monitor
Analog DAC output, designed to drive a
37.5-Ohm equivalent load.
O Analog
O Analog
PD 150R
PD 150R
shall also be terminated on the
carrier with 150Ω resistor to
ground close to VGA connector
shall also be terminated on the
carrier with 150Ω resistor to
ground close to VGA connector
VGA_BLU B92 Blue for monitor.
Analog DAC output, designed to drive a
37.5-Ohm equivalent load.
VGA_HSYNC B93 Horizontal sync output to VGA monitor O 3.3V
VGA_VSYNC B94 Vertical sync output to VGA monitor O 3.3V
VGA_I2C_CK B95 DDC clock line (I²C port dedicated to identify
VGA monitor capabilities)
VGA_I2C_DAT B96 DDC data line. I/O OD 3.3V PU 2k2 3.3V
O Analog
I/O OD 3.3V PU 2k2 3.3V
PD 150R
shall also be terminated on the
carrier with 150Ω resistor to
ground close to VGA connector
3.3.3. LVDS
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
LVDS_A0+ / eDP_TX2+
LVDS_A0- / eDP_TX2-
LVDS_A1+ / eDP_TX1+
LVDS_A1- / eDP_TX1LVDS_A2+ / eDP_TX0+
LVDS_A2- / eDP_TX0-
LVDS_A3+
LVDS_A3-
LVDS_A_CK+ / eDP_TX3+
LVDS_A_CK- / eDP_TX3-
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
A78
A79
A81
A82
LVDS Channel A differential pairs O LVDS
LVDS Channel A differential clock O LVDS
Page 18 Express-BE
Page 19
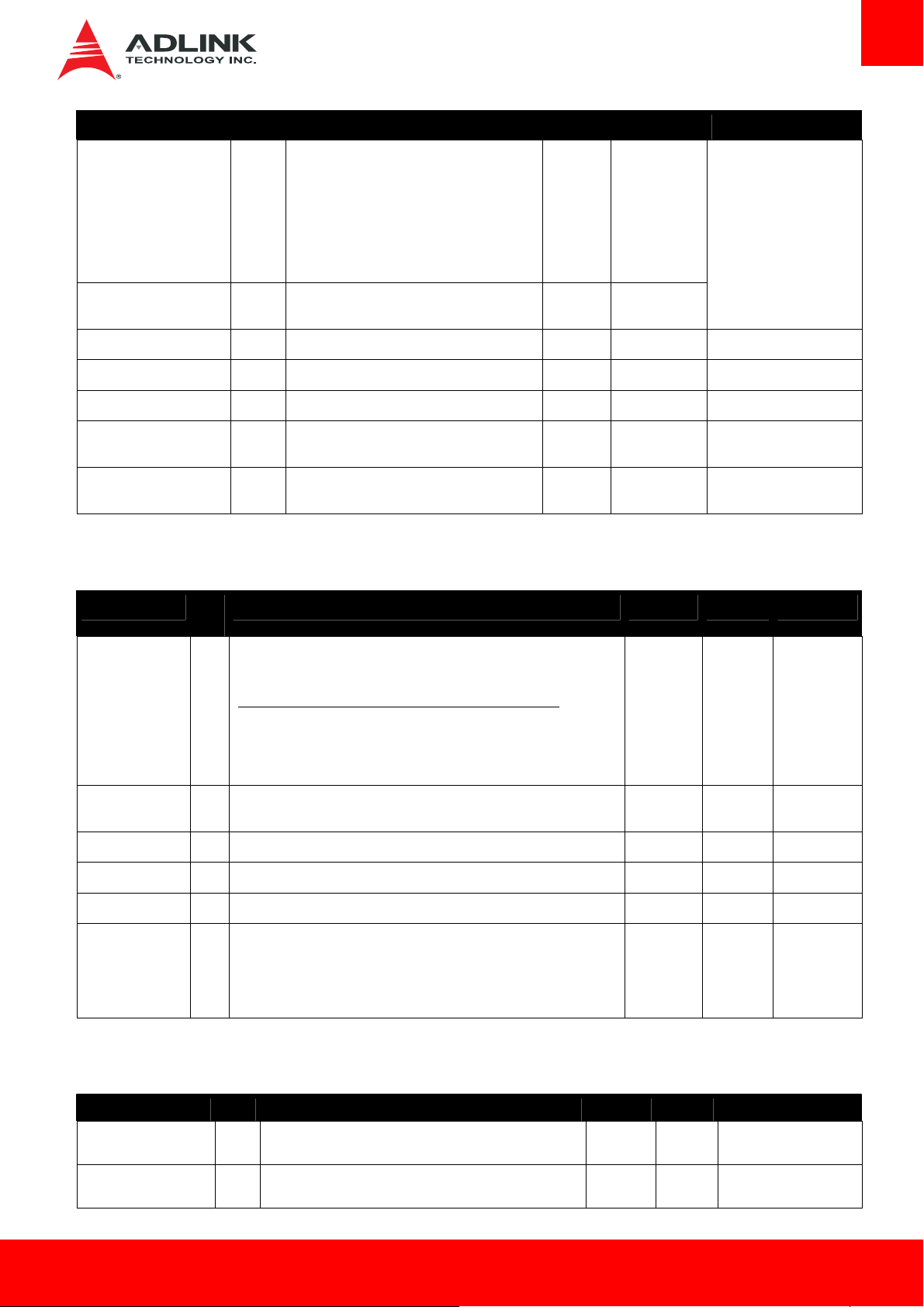
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
LVDS_B0+
LVDS_B0-
LVDS_B1+
LVDS_B1-
LVDS_B2+
LVDS_B2-
LVDS_B3+
LVDS_B3-
LVDS_B_CK+
LVDS_B_CK-
LVDS_VDD_EN A77 LVDS panel power enable O 3.3V
LVDS_BKLT_EN B79 LVDS panel backlight enable O 3.3V
LVDS_BKLT_CTRL B83 LVDS panel backlight brightness control O 3.3V
LVDS_I2C_CK A83 DDC lines used for flat panel detection and
LVDS_I2C_DAT A84 DDC lines used for flat panel detection and
B71
B72
B73
B74
B75
B76
B77
B78
B81
B82
LVDS Channel B differential pairs O LVDS
LVDS Channel B differential clock O LVDS
O 3.3V PU 2k2 3.3V
control.
I/O 3.3V PU 2k2 3.3V
control.
3.3.4. Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
GBE0_MDI0+
GBE0_MDI0-
GBE0_MDI1+
GBE0_MDI1-
GBE0_MDI2+
GBE0_MDI2-
GBE0_MDI3+
GBE0_MDI3-
GBE0_ACT# B2 Gigabit Ethernet Controller 0 activity indicator, active low. O 3.3VSB PU 10k
GBE0_LINK# A8 Gigabit Ethernet Controller 0 link indicator, active low. O 3.3VSB
GBE0_LINK100# A4 Gigabit Ethernet Controller 0 100Mbit/sec link indicator, active low. O 3.3VSB
GBE0_LINK1000# A5 Gigabit Ethernet Controller 0 1000Mbit/sec link indicator, active low. O 3.3VSB
GBE0_CTREF A14 Reference voltage for Carrier Board Ethernet channel 1 and 2 magnetics
A13
Gigabit Ethernet Controller 0: Media Dependent Interface Differential Pairs
A11
0, 1, 2, 3. The MDI can operate in 1000, 100, and 10Mbit/sec modes.
A10
Some pairs are unused in some modes according to the following:
A9
1000 100 10
A7
MDI[0]+/- B1_DA+/- TX+/- TX+/-
A6
MDI[1]+/- B1_DB+/- RX+/- RX+/-
A3
MDI[2]+/- B1_DC+/-
A2
MDI[3]+/- B1_DD+/-
center tap. The reference voltage is determined by the requirements of the
Module PHY and may be as low as 0V and as high as 3.3V. The reference
voltage output shall be current limited on the Module. In the case in which
the reference is shorted to ground, the current shall be 250 mA or less.
I/O Analog Twisted pair
3.3VSB
GND min
3.3V max
Floating on
3.3.5. SATA
signals for
external
transformer.
module, N.C.
pin
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SATA0_TX+
SATA0_TX-
SATA0_RX+
SATA0_RX-
A16
Serial ATA channel 0, Transmit Output differential pair. O SATA AC coupled on Module
A17
A19
Serial ATA channel 0, Receive Input differential pair. I SATA AC coupled on Module
A20
Express-BE Page 19
Page 20
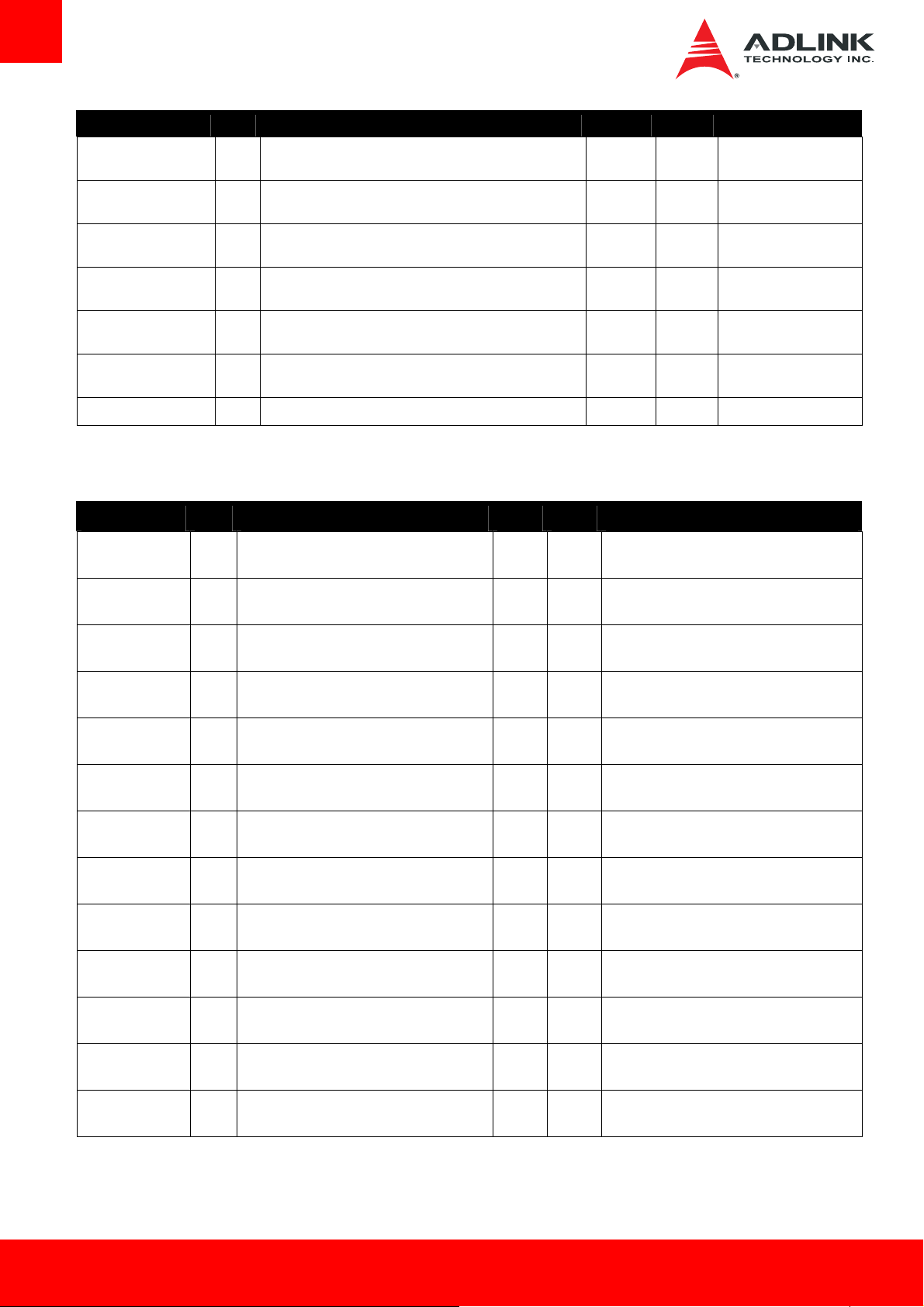
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SATA1_TX+
SATA1_TX-
SATA1_RX+
SATA1_RX-
SATA2_TX+
SATA2_TX-
SATA2_RX+
SATA2_RX-
SATA3_TX+
SATA3_TX-
SATA3_RX+
SATA3_RX-
(S)ATA_ACT# A28 ATA (parallel and serial) or SAS activity indicator, active low. O 3.3V
B16
Serial ATA channel 1, Transmit Output differential pair. O SATA AC coupled on Module
B17
B19
Serial ATA channel 1, Receive Input differential pair. I SATA AC coupled on Module
B20
A22
Serial ATA channel 2, Transmit Output differential pair. O SATA AC coupled on Module
A23
A25
Serial ATA channel 2, Receive Input differential pair. I SATA AC coupled on Module
A26
B22
Serial ATA channel 3, Transmit Output differential pair. O SATA AC coupled on Module
B23
B25
Serial ATA channel 3, Receive Input differential pair. I SATA AC coupled on Module
B26
3.3.6. PCI Express
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
PCIE_TX0+
PCIE_TX0-
PCIE_RX0+
PCIE_RX0-
A68
PCI Express channel 0, Transmit Output
A69
differential pair.
B68
PCI Express channel 0, Receive Input
B69
differential pair.
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
PCIE_TX1+
PCIE_TX1-
PCIE_RX1+
PCIE_RX1-
PCIE_TX2+
PCIE_TX2-
PCIE_RX2+
PCIE_RX2-
PCIE_TX3+
PCIE_TX3-
PCIE_RX3+
PCIE_RX3-
PCIE_TX4+
PCIE_TX4-
PCIE_RX4+
PCIE_RX4-
PCIE_TX5+
PCIE_TX5-
PCIE_RX5+
PCIE_RX5-
A64
PCI Express channel 1, Transmit Output
A65
differential pair.
B64
PCI Express channel 1, Receive Input
B65
differential pair.
A61
PCI Express channel 2, Transmit Output
A62
differential pair.
B61
PCI Express channel 2, Receive Input
B62
differential pair.
A58
PCI Express channel 3, Transmit Output
A59
differential pair.
B58
PCI Express channel 3, Receive Input
B59
differential pair.
A55
PCI Express channel 4, Transmit Output
A56
differential pair.
B55
PCI Express channel 4, Receive Input
B56
differential pair.
A52
PCI Express channel 5, Transmit Output
A53
differential pair.
B52
PCI Express channel 5, Receive Input
B53
differential pair.
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
O PCIE AC coupled on Module
I PCIE AC coupled off Module
PCIE_CLK_REF+
PCIE_CLK_REF-
A88
PCI Express Reference Clock output for all PCI
A89
Express and PCI Express Graphics Lanes.
O PCIE
Page 20 Express-BE
Page 21
3.3.7. Express Card
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
EXCD0_CPPE#
EXCD1_CPPE#
EXCD0_PERST#
EXCD1_PERST#
A49
B48
A48
B47
PCI ExpressCard: PCI Express capable card request I 3.3V PU 10k 3.3V
PCI ExpressCard: reset O 3.3V
3.3.8. LPC Bus
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
LPC_AD[0:3] B4-B7 LPC multiplexed address, command and data bus I/O 3.3V
LPC_FRAME# B3 LPC frame indicates the start of an LPC cycle O 3.3V
LPC_DRQ0#
LPC_DRQ1#
LPC_SERIRQ A50 LPC serial interrupt I/O OD 3.3V PU 8k2 3.3V
LPC_CLK B10 LPC clock output –33MHz nominal O 3.3V
B8
B9
LPC serial DMA request I 3.3V
3.3.9. USB
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
USB0+
USB0-
USB1+
USB1-
USB2+
USB2-
USB3+
USB3-
USB4+
USB4-
USB5+
USB5-
USB6+
USB6-
USB7+
USB7-
USB_0_1_OC# B44 USB over-current sense, USB ports 0 and 1. A pull-up
A46
USB differential data pairs for Port 0 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
A45
B46
USB differential data pairs for Port 1 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
B45
A43
USB differential data pairs for Port 1 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
A42
B43
USB differential data pairs for Port 2 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
B42
A40
USB differential data pairs for Port 3 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
A39
B40
USB differential data pairs for Port 4 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
B39
A37
USB differential data pairs for Port 5 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
A36
B37
USB differential data pairs for Port 6 I/O 3.3VSB USB 1.1/ 2.0 compliant
B37
for this line shall be present on the module. An open
drain driver from a USB current monitor on the carrier
board may drive this line low.
I 3.3VSB PU 10k 3.3VSB Do not pull high on carrier
USB_2_3_OC# A44 USB over-current sense, USB ports 2 and 3. A pull-up
for this line shall be present on the module. An open
drain driver from a USB current monitor on the carrier
board may drive this line low. .
USB_4_5_OC# B38 USB over-current sense, USB ports 4 and 5. A pull-up
for this line shall be present on the module. An open
I 3.3VSB PU 10k 3.3VSB Do not pull high on carrier
I 3.3VSB PU 10k 3.3VSB Do not pull high on carrier
Express-BE Page 21
Page 22
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
drain driver from a USB current monitor on the carrier
board may drive this line low.
USB_6_7_OC# A38 USB over-current sense, USB ports 6 and 7. A pull-up
for this line shall be present on the module. An open
drain driver from a USB current monitor on the carrier
board may drive this line low.
3.3.10. USB Root Segmentation
I 3.3VSB PU 10k 3.3VSB Do not pull high on carrier
USB_SSRX2+ / C10
USB_SSRX0+ / C4
USB_SSTX0+ / D4
USB_SSRX0- / C3
USB0+ / A46
USB1+ / B46
USB2+ / A43
USB3+ / B43
USB4+ / A40
USB5+ / B40
USB6+ / A37
USB0- / A45
USB1- / B45
USB2- / A42
USB3- / B42
USB4- / A39
USB5- / B39
USB6- / A36
USB7+ / B37
USB7- / B36
USB_SSTX0- / D3
USB_SSRX1+ / C7
USB_SSTX1+ / D7
USB_SSRX1- / C6
USB_SSTX1- / D6
USB_SSTX2+ / D10
USB_SSTX2- / D9
3.3.11. SPI (BIOS only)
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SPI_CS# B97 Chip select for Carrier Board SPI BIOS Flash. O 3.3VSB
SPI_MISO A92 Data in to module from carrier board SPI BIOS flash. I 3.3VSB
SPI_MOSI A95 Data out from module to carrier board SPI BIOS flash. O 3.3VSB
SPI_CLK A94 Clock from module to carrier board SPI BIOS flash. O 3.3VSB
SPI_POWER A91 Power supply for Carrier Board SPI – sourced from Module
– nominally 3.3V.
The Module shall provide a minimum of 100mA on
SPI_POWER.
Carriers shall use less than 100mA of SPI_POWER.
SPI_POWER shall only be used to power SPI devices on
the Carrier
O P 3.3VSB
USB_SSRX3+ / C13
USB_SSTX3+ / D13
USB_SSRX3- / C12
USB_SSRX2- / C9
USB_SSTX3- / D12
BIOS_DIS0# A34 Selection strap to determine the BIOS boot device. I PU 10K 3.3VSB Carrier shall pull to GND
or leave not- connected.
BIOS_DIS1# B88 Selection strap to determine the BIOS boot device. I PU 10K 3.3VSB Carrier shall pull to GND
or leave not- connected
Page 22 Express-BE
Page 23
3.3.12. Miscellaneous
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SPKR B32 Output for audio enunciator, the “speaker” in PC-AT
systems
WDT B27 Output indicating that a watchdog time-out event has
occurred.
THRM# B35 Input from off-module temp sensor indicating an over-temp
situation.
THRMTRIP# A35 Active low output indicating that the CPU has entered
thermal shutdown.
FAN_PWMOUT B101 Fan speed control. Uses the Pulse Width Modulation
(PWM) technique to control the fan’s RPM.
FAN_TACHIN B102 Fan tachometer input for a fan with a two pulse output. I OD 3.3V PU 10k 3.3V
TPM_PP C83 Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Physical Presence pin.
Active high. TPM chip has an internal pull down. This
signal is used to indicate Physical Presence to the TPM.
O 3.3V
O 3.3V
I 3.3V
O 3.3V PU 10k 3.3V
O OD 3.3V
I 3.3V
PD 10k 3.3V PD only when TPM on
module
3.3.13. SMBus
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SMB_CK B13 System Management Bus bidirectional clock line. Power
sourced through 5V standby rail and main power rails.
SMB_DAT# B14 System Management Bus bidirectional data line. Power
sourced through 5V standby rail and main power rails.
I/O OD 3.3VSB PU 2k2 3.3VSB
I/O OD 3.3VSB PU 2k2 3.3VSB
SMB_ALERT# B15 System Management Bus Alert – active low input can
be used to generate an SMI# (System Management
Interrupt) or to wake the system. Power sourced
through 5V standby rail and main power rails.
I 3.3VSB PU 10k 3.3VSB
3.3.14. I2C Bus
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
I2C_CK B33 General purpose I²C port clock output/input I/O OD 3.3VSB PU 2k2 3.3VSB Source SEMA BMC
I2C_DAT B34 General purpose I²C port data I/O line I/O OD 3.3VSB PU 2k2 3.3VSB Source SEMA BMC
3.3.15. General Purpose I/O (GPIO)
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
GPO[0] A93 General purpose output pins. O 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V After hardware RESET
output low
GPO[1] B54 General purpose output pins. O 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V After hardware RESET
output low
GPO[2] B57 General purpose output pins. O 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V After hardware RESET
output low
GPO[3] B63 General purpose output pins. O 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V After hardware RESET
output low
GPI[0] A54 General purpose input pins.
Pulled high internally on the module.
I 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V
Express-BE Page 23
Page 24
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
GPI[1] A63 General purpose input pins.
Pulled high internally on the module.
GPI[2] A67 General purpose input pins.
Pulled high internally on the module.
GPI[3] A85 General purpose input pins.
Pulled high internally on the module.
I 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V
I 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V
I 3.3V PU 10K 3.3V
3.3.16. Serial Interface Signals
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
SER0_TX A98 General purpose serial port transmitter (TTL level output) O CMOS Power rail tolerance 5V, 12V
SER0_RX A99 General purpose serial port receiver (TTL level input) I CMOS Power rail tolerance 5V, 12V
SER1_TX A101 General purpose serial port transmitter (TTL level output) O CMOS Power rail tolerance 5V, 12V
SER1_RX A102 General purpose serial port receiver (TTL level input) I CMOS Power rail tolerance 5V, 12V
3.3.17. Power and System Management
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
PWRBTN# B12 Power button to bring system out of S5 (soft off), active on falling edge. I 3.3VSB PU 10k
3.3VSB
SYS_RESET# B49 Reset button input. Active low request for module to reset and reboot. May
be falling edge sensitive. For situations when SYS_RESET# is not able to
reestablish control of the system, PWR_OK or a power cycle may be used.
CB_RESET# B50 Reset output from module to Carrier Board. Active low. Issued by module
chipset and may result from a low SYS_RESET# input, a low PWR_OK
input, a VCC_12V power input that falls below the minimum specification, a
watchdog timeout, or may be initiated by the module software.
PWR_OK B24 Power OK from main power supply. A high value indicates that the power is
good. This signal can be used to hold off Module startup to allow carrier
based FPGAs or other configurable devices time to be programmed.
SUS_STAT# B18 Indicates imminent suspend operation; used to notify LPC devices. O 3.3VSB
SUS_S3# A15 Indicates system is in Suspend to RAM state. Active-low output. An inverted
copy of SUS_S3# on the carrier board (also known as “PS_ON”) may be
used to enable the non-standby power on a typical ATX power supply.
SUS_S4# A18 Indicates system is in Suspend to Disk state. Active low output. O 3.3VSB
SUS_S5# A24 Indicates system is in Soft Off state. O 3.3VSB
WAKE0# B66 PCI Express wake up signal. I 3.3VSB PU 10k
I 3.3VSB PU 10k
3.3VSB
O 3.3VSB
I 3.3V PU 100k
3.3VSB
O 3.3VSB
3.3VSB
Not
supported
connected to
SUS_S5#
Not supported
connected to
WAKE1#
WAKE1# B67 General purpose wake up signal. May be used to implement wake-up on
PS/2 keyboard or mouse activity.
BATLOW# A27 Battery low input. This signal may be driven low by external circuitry to
signal that the system battery is low, or may be used to signal some other
external power-management event.
I 3.3VSB PU 10k
3.3VSB
I 3.3VSB PU 10k
3.3VSB
Page 24 Express-BE
Page 25
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
LID# A103 LID button. Low active signal used by the ACPI operating system for a LID
switch.
SLEEP# B103 Sleep button. Low active signal used by the ACPI operating system to bring
the system to sleep state or to wake it up again.
I OD
3.3VSB
I OD
3.3VSB
PU 10k
3.3VSB
PU 10K
3.3VSB
Emulated on
GPIO (BIOS)
Emulated on
GPIO (BIOS)
3.3.18. Power and Ground
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
VCC_12V A104-A109
B104-B109
VCC_5V_SBY B84-B87 Standby power input: +5.0V nominal. See section 7 “Electrical
VCC_RTC A47 Real-time clock circuit-power input. Nominally +3.0V. P
GND A1, A11, A21, A31, A41, A51,
A57, A66, A80, A90, A96, A100,
A110, B1, B11, B21 ,B31, B41,
B51, B60, B70, B80, B90, B100,
B110
Primary power input: +12V nominal (wide range 5 ~ 20V).
All available VCC_12V pins on the connector(s) shall be used.
Specifications“ for allowable input range. If VCC5_SBY is used,
all available VCC_5V_SBY pins on the connector(s) shall be
used. Only used for standby and suspend functions. May be left
unconnected if these functions are not used in the system design.
Ground - DC power and signal and AC signal return path. P
P 8.5~20 V
P 5Vsb ±5%
Express-BE Page 25
Page 26
3.4. CD Signal Descriptions
3.4.1. USB 3.0 Extension
Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
USB_SSRX0-
USB_SSRX0+
USB_SSTX0-
USB_SSTX0+
USB_SSRX1-
USB_SSRX1+
USB_SSTX1-
USB_SSTX1+
USB_SSRX2-
USB_SSRX2+
USB_SSTX2-
USB_SSTX2+
USB_SSRX3-
USB_SSRX3+
USB_SSTX3-
USB_SSTX3+
C3
C4
D3
D4
C6
C7
D6
D7
C9
C10
D9
D10
C12
C13
D12
D13
Additional Receive signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB0
Additional Transmit signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB0
Additional Receive signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB1
Additional Transmit signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB1
Additional Receive signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB2
Additional Transmit signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB2
Additional Receive signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB3
Additional Transmit signal differential pairs for the
SuperSpeed USB data path on USB3
I PCIE AC coupled off module
O PCIE AC coupled on module
I PCIE AC coupled off module
O PCIE AC coupled on module
I PCIE AC coupled off module
O PCIE AC coupled on module
I PCIE AC coupled off module
O PCIE AC coupled on module
3.4.2. PCI Express x1
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
PCIE_TX6+
PCIE_TX6-
PCIE_RX6+
PCIE_RX6-
D19
D20
C19
C20
PCI Express channel 6, Transmit Output differential pair. O PCIE
PCI Express channel 6, Receive Input differential pair. I PCIE
AC coupled on module
AC coupled off module
PCIE_TX7+
PCIE_TX7-
PCIE_RX7+
PCIE_RX7-
D22
D23
C22
C23
PCI Express channel 7, Transmit Output differential pair. O PCIE Not supported
PCI Express channel 7, Receive Input differential pair. I PCIE Not supported
Page 26 Express-BE
Page 27

3.4.3. DDI Channels
DDI 1
Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
DDI1_PAIR0+
DDI1_PAIR0DDI1_PAIR1+
DDI1_PAIR1DDI1_PAIR2+
DDI1_PAIR2DDI1_PAIR3+
DDI1_PAIR3DDI1_PAIR4+
DDI1_PAIR4DDI1_PAIR5+
DDI1_PAIR5DDI1_PAIR6+
DDI1_PAIR6-
DDI1_HPD C24 Digital Display Interface Hot-Plug Detect I PCIE PD 100K
DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL D34 Selects the function of
D26
D27
D29
D30
D32
D33
D36
D37
C25
C26
C29
C30
C15
C16
Digital Display Interface1 differential pairs O PCIE Pair 4 to Pair 6
IF DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP1_AUX+ DDI1_CTRLCLK_AUX+ D15
IF DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI1_CTRLCLK
IF DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP1_AUX+ DDI1_CTRLCLK_AUX- D16
IF DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI1_CTRLDATA
I/O OD 3.3V PD 1M
DDI1_CTRLCLK_AUX+ and
DDI1_CTRLDATA_AUX-. This pin shall
have a 1M pull-down to logic ground on
the Module. If this input is floating the
AUX pair is used for the DP AUX+/signals. If pulled-high the AUX pair
contains the CRTLCLK and CTRLDATA
signals.
Not supported
Express-BE Page 27
Page 28

DDI 2
Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
DDI2_PAIR0+
DDI2_PAIR0DDI2_PAIR1+
DDI2_PAIR1DDI2_PAIR2+
DDI2_PAIR2DDI2_PAIR3+
DDI2_PAIR3-
DDI2_HPD D44 PD 100K
DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL C34 Selects the function of DDI2_CTRLCLK_AUX+ and
D39
D40
D42
D43
D46
D47
D49
D50
Digital Display Interface2 differential pairs
IF DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP2_AUX+ DDI2_CTRLCLK_AUX+ C32
IF DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI2_CTRLCLK
IF DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP2_AUX+ DDI2_CTRLCLK_AUX- C33
IF DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI2_CTRLDATA
PD 1M
DDI2_CTRLDATA_AUX-. This pin shall have a 1M
pull-down to logic ground on the Module. If this input
is floating the AUX pair is used for the DP AUX+/signals. If pulled-high the AUX pair contains the
CRTLCLK and CTRLDATA signals.
DDI 3
Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
DDI3_PAIR0+
DDI3_PAIR0DDI3_PAIR1+
DDI3_PAIR1DDI3_PAIR2+
DDI3_PAIR2DDI3_PAIR3+
DDI3_PAIR3-
DDI3_HPD C44 PD 100K
DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL C38 Selects the function of DDI3_CTRLCLK_AUX+
C39
C40
C42
C43
C46
C47
C49
C50
Digital Display Interface3 differential pairs
IF DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP2_AUX+ DDI3_CTRLCLK_AUX+ C36
IF DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI2_CTRLCLK
IF DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL is floating I/O PCIe DP2_AUX+ DDI3_CTRLCLK_AUX- C37
IF DDI3_DDC_AUX_SEL pulled high I/O OD 3.3V HDMI2_CTRLDATA
PD 1M
and DDI3_CTRLDATA_AUX-. This pin shall
have a 1M pull-down to logic ground on the
Module. If this input is floating the AUX pair is
used for the DP AUX+/- signals. If pulled-high
the AUX pair contains the CRTLCLK and
CTRLDATA signals.
Page 28 Express-BE
Page 29

3.4.4. DDI to DP/HDMI Mapping
Pin Pin Name DP HDMI \ DVI
D26 DDI1_PAIR0+ DP1_LANE0+ TMDS1_DATA2+
D27 DDI1_PAIR0- DP1_LANE0- TMDS1_DATA2D29 DDI1_PAIR1+ DP1_LANE1+ TMDS1_DATA1+
D30 DDI1_PAIR1- DP1_LANE1- TMDS1_DATA1D32 DDI1_PAIR2+ DP1_LANE2+ TMDS1_DATA0+
D33 DDI1_PAIR2- DP1_LANE2- TMDS1_DATA0D36 DDI1_PAIR3+ DP1_LANE3+ TMDS1_CLK+
D37 DDI1_PAIR3- DP1_LANE3- TMDS1_CLKC25 DDI1_PAIR4+
C26 DDI1_PAIR4-
C29 DDI1_PAIR5+
C30 DDI1_PAIR5-
C15 DDI1_PAIR6+
C16 DDI1_PAIR6-
C24 DDI1_HPD DP1_HPD HDMI1_HPD
D15 DDI1_CTRLCLK_AUX+ DP1_AUX+ HMDI1_CTRLCLK
D16 DDI1_CTRLDATA_AUX- DP1_AUX- HMDI1_CTRLDATA
D34 DDI1_DDC_AUX_SEL
D39 DDI2_PAIR0+ DP2_LANE0+ TMDS2_DATA2+
D40 DDI2_PAIR0- DP2_LANE0- TMDS2_DATA2D42 DDI2_PAIR1+ DP2_LANE1+ TMDS2_DATA1+
D43 DDI2_PAIR1- DP2_LANE1- TMDS2_DATA1D46 DDI2_PAIR2+ DP2_LANE2+ TMDS2_DATA0+
D47 DDI2_PAIR2- DP2_LANE2- TMDS2_DATA0D49 DDI2_PAIR3+ DP2_LANE3+ TMDS2_CLK+
D50 DDI2_PAIR3- DP2_LANE3- TMDS2_CLKD44 DDI2_HPD DP2_HPD HDMI2_HPD
C32 DDI2_CTRLCLK_AUX+ DP2_AUX+ HDMI2_CTRLCLK
C33 DDI2_CTRLDATA_AUX- DP2_AUX- HDMI2_CTRLDATA
C34 DDI2_DDC_AUX_SEL
Express-BE Page 29
Page 30

3.4.5. PCI Express Graphics x16 (PEG)
Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
PEG_RX0+
PEG_RX0-
PEG_RX1+
PEG_RX1-
PEG_RX2+
PEG_RX2-
PEG_RX3+
PEG_RX3-
PEG_RX4+
PEG_RX4-
PEG_RX5+
PEG_RX5-
PEG_RX6+
PEG_RX6-
PEG_RX7+
PEG_RX7-
PEG_RX8+
PEG_RX8-
PEG_RX9+
PEG_RX9-
PEG_RX10+
PEG_RX10-
PEG_RX11+
PEG_RX11-
PEG_RX12+
PEG_RX12-
PEG_RX13+
PEG_RX13-
PEG_RX14+
PEG_RX14-
PEG_RX15+
PEG_RX15
PEG_TX0+
PEG_TX0-
PEG_TX1+
PEG_TX1-
PEG_TX2+
PEG_TX2-
PEG_TX3+
PEG_TX3-
PEG_TX4+
PEG_TX4-
PEG_TX5+
PEG_TX5-
PEG_TX6+
PEG_TX6-
PEG_TX7+
PEG_TX7-
PEG_TX8+
PEG_TX8-
PEG_TX9+
PEG_TX9-
PEG_TX10+
PEG_TX10-
PEG_TX11+
PEG_TX11-
PEG_TX12+
PEG_TX12-
PEG_TX13+
PEG_TX13-
PEG_TX14+
PEG_TX14-
PEG_TX15+
PEG_TX15-
C52
C53
C55
C56
C58
C59
C61
C62
C65
C66
C68
C69
C71
C72
C74
C75
C78
C79
C81
C82
C85
C86
C88
C89
C91
C92
C94
C95
C98
C99
C101
C102
D52
D53
D55
D56
D58
D57
D61
D62
D65
D66
D68
D69
D71
D72
D74
D75
D78
D79
D81
D82
D85
D86
D88
D89
D91
D92
D94
D95
D98
D99
D101
D102
PCI Express Graphics transmit differential pairs. I PCIE AC couple off module
PCI Express Graphics receive differential pairs. O PCIE AC couple on module
Page 30 Express-BE
Page 31

Signal Pin Description I/O PU/PD Comment
PEG_LANE_RV# D54 PCI Express Graphics lane reversal input strap.
Pull low on the Carrier board to reverse lane order.
I 3.3V
3.4.6. Module Type Definition
Signal Pin # Description I/O Comment
TYPE0#
TYPE1#
TYPE2#
C54
C57
D57
The TYPE pins indicate to the Carrier Board the Pin-out Type that is implemented on
the module. The pins are tied on the module to either ground (GND) or are noconnects (NC). For Pinout Type 1, these pins are don’t care (X).
TYPE2# TYPE1# TYPE0#
X X X Pinout Type 1
NC NC NC Pinout Type 2
NC NC GND Pinout Type 3 (no IDE)
NC GND NC Pinout Type 4 (no PCI)
NC GND GND Pinout Type 5 (no IDE, no PCI)
GND NC NC Pinout Type 6 (no IDE, no PCI)
The Carrier Board should implement combinatorial logic that monitors the module
TYPE pins and keeps power off (e.g deactivates the ATX_ON signal for an ATX power
supply) if an incompatible module pin-out type is detected. The Carrier Board logic
may also implement a fault indicator such as an LED.
Type 6
3.4.7. Power and Ground
Signal Pin # Description I/O PU/PD Comment
VCC_12V C104-C109
D104-D109
GND C1, C11, C21, C31, C41,
C51, C60, C70, C76, C80,
C84, C87, C90, C93, C96,
C100, C103, C110, D1,
D11, D21, D31, D41, D51,
D60, D67, D70, D76, D80,
D84, D87, D90, D93, D96,
D100, D103, D110
Primary power input: +12V nominal (wide range 5 ~ 20V).
All available VCC_12V pins on the connector(s) shall be used
Ground - DC power and signal and AC signal return path.
All available GND connector pins shall be used and tied to carrier
board GND plane.
P 8.5 ~ 20V
P
Express-BE Page 31
Page 32

4. Module Interfaces and Configuration
This chapter describes connectors and pinouts, LEDs and switches that are used on the module but are not included in the standard PICMG
specification.
4.1. Connector, Switch and LED Locations
BIOS
Defaults
Reset
Switch
Fan
4-pin
Fan
40-pin Multi-
Purpose
CD
AB
4.1.1. Express-BE and the DB40 Module connected
Page 32 Express-BE
Page 33

4.2. 40-pin Multipurpose Connector
¾ FPC Connector type: FCI 59GF Flex 10042867
¾ Pin Orientation:
1 40
¾ Pin Definitions (on COMe module)
Pin Interface Signal Remark Pin Interface Signal Remark
1 VCC_SPI_IN SPI Power Input from flash tool to
SPI
Program
interface
2 GND 22 RXD6
3 SPI_BIOS_CS0# 23 FUMD0
4 SPI_BIOS_CS1# 24 RESET_IN#
5 SPI_BIOS_MISO 25 DATA
6 SPI_BIOS_MOSI 26 CLK
7
8 3V3_LPC System power 3.3V provide from
LPC Bus
9 GND 29 PWRBTN#
10 BIOS_DIS0 30 SYS_RESET#
11 RST# 31 CB_RESET#
12 CLK33_LPC 32 CB_PWROK
13 LPC_FRAME# 33 SUS_S3#
SPI_BIOS_CLK 27 OCD0A Include a jumper to connect
module. HW need add MOS FET
to switch SPI power for SPI ROM
COM module
21 TXD6
28
BMC Program
interface
(continued)
OCD0A via 1K0 pull-up to
3.3V_BMC
OCD0B Include a jumper to connect
OCD0A via 1K0 pull-up to
3.3V_BMC
Test points
14 LPC_AD3 34 SUS_S4#
15 LPC_AD2 35
16 LPC_AD1 always power 3.3V provide from
COM module
17
BMC
18
Program
interface
19 3.3V_BMC always power 3.3V provide from
20
LPC_AD0 37 SEL_BIOS Connect to Jumper for
3.3V_BMC always power 3.3V provide from
COM module
COM module
GND 40 Reserved
36 POSTWDT_DIS# Connect to Jumper for
38 BIOS_MODE Connect to Jumper for
39
BMC Debug
signals
SUS_S5#
Debug
Debug
Debug
BMC_STATUS
Note: the pin description on the Debug Module is the inverse of that on the COM Express module.
Express-BE Page 33
Page 34

4.3. Status LEDs
To facilitate easier maintenance, status LED’s are mounted on the board.
LED1 LED2 LED3
¾ LED Descriptions:
Name Color Connection Function
LED1 Blue BMC output Power Sequence Status Code (BMC)
Power Changes, RESET
(see 5.1.4 Exception Codes below)
LED2 Green Power Source 3Vcc S0 LED ON
S3/S4/S5 LED OFF
ECO mode LED OFF
LED3 Red BMC output
and same signal as WDT
(B27) on BtB connector
Module power up LED OFF
Watchdog counting LED OFF
Watchdog timed out LED ON
Watchdog RESET LED ON
Rebooted after WD RESET LED ON
Rebooted after PWRBTN LED ON
Rebooted after RESET BTN LED OFF
Note: only a RESET not initiated by the BMC can clear the WD LED (user action)
Page 34 Express-BE
Page 35

4.4. Fan Connector
¾ Connector Type: JVE 24W1125A-04M00
¾ Pin Orientation:
1 2 3 4
¾ Pin Definitions:
Pin Signal
1 FAN_PWMOUT
2 FAN_TACHIN
3 Ground
4 5V
Express-BE Page 35
Page 36

4.5. BIOS Setup Defaults Reset Button
To perform a hardware reset of BIOS default settings, perform the following steps:
1. Shut down the system.
2. Press the BIOS Setup Defaults Reset Button continuously and boot up the system. You can release the button when the BIOS
prompt screen appears
3. The BIOS prompt screen will display a confirmation that BIOS defaults have been reset and request that you reboot the system.
Page 36 Express-BE
Page 37

4.6. Express-BE Switch Settings
4.6.1. Switch Locations
4.6.2. SW1: BIOS Select and Mode Configuration Switch
The module has two BIOS chips and BIOS operation can be configured to "PICMG" and dual-BIOS "Failsafe" modes using SW1, Pin 2.
Setting the module to PICMG mode will configure the BIOS chips on the module as SPI0 and SPI1. In PICMG mode, a BIOS chip cannot
placed in the SPI0 slot on the carrier.
In dual-BIOS Failsafe mode, both BIOS chips on the module are configured as SPI1. Only one of the two is connected to the SPI bus at any
given time. In case of failure of the primary SPI1 BIOS, the system will reboot and switch to the secondary SPI1 BIOS on the module. In
Failsafe mode, the SPI0 BIOS socket on the carrier can be populated.
In either mode, SW1 Pin 1 is used to select whether to boot from SPI0 or SPI1.
Mode Pin 1 Pin 2
Boot from SPI0 (default) On —
Boot from SPI1 Off —
Set BIOS to PICMG mode — On
Set BIOS to Failsafe BIOS mode (default) — Off
be
Express-BE Page 37
Page 38

4.7. PCIe x16-to-two-x8 Adapter Card
The Express-BE can be used with the PCIe x16-to-two-x8 Adapter Card on the Express-BASE6 Reference Carrier to support bifurbication of
the CPU's PEG interface (PCIe x16). The card reroutes the PCIe x16 to two x8 and allows testing of two independent PCIe add-on cards
with x8/x4/x2/x1 width. To use the card, set BIOS > Advanced > Graphics > GFX LINK CFG to "2 x8 " as described in
53.
page
PCIex16-to-two-x8 Adapter Card
(Model: P16TO28, Part No.: 91-79301-0010)
7.3.3 .Graphics on
Page 38 Express-BE
Page 39

5. Smart Embedded Management Agent (SEMA)
The onboard microcontroller (BMC) implements power sequencing and Smart Embedded Management Agent (SEMA) functionality.
The microcontroller communicates via the System Management Bus with the CPU/chipset.
The following functions are implemented
¾ Total operating hours counter counts the number of hours the module has been run in minutes.
¾ On-time minutes counter counts the seconds since last system start.
¾ Temperature monitoring of CPU and board temperature minimum and maximum temperature values of CPU and board are stored in
flash.
¾ Power cycles counter
¾ Boot counter counts the number of boot attempts.
¾ Watchdog Timer (Type-II) Set, Reset, Disable Watchdog Timer. Features auto-reload at power-up.
¾ System Restart Cause Power loss, BIOS Fail, Watchdog, Internal Reset, External Reset
¾ Fail-safe BIOS support In case of a boot failure, hardware signals tells external logic to boot from fail-safe BIOS.
¾ Flash area 1kB Flash area for customer data
¾ 128 Bytes Protected Flash area Keys, IDs, etc. can be stored in a write- and clear-protectable region.
¾ Board Identify Vendor, Board, Serial number, Production Date
¾ Main-current & voltage monitors drawn current and main voltages
For a detailed description of SEMA features and functionality, please refer to the SEMA Technical Manual and SEMA Software Manual,
downloadable at:
http://www.adlinktech.com/PD/web/PD_detail.php?cKind=&pid=1274
Express-BE Page 39
Page 40

5.1. Board Specific SEMA Functions
5.1.1. Voltages
The BMC of the Express-BE implements a voltage monitor and samples several onboard voltages. The voltages can be read by calling the
SEMA function “Get Voltages”. The function returns a 16-bit value divided into high-byte (MSB) and low-byte (LSB).
ADC Channel Voltage Name Voltage Formula [V]
0 Not used
1 +V3.3V (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 1.1 x 3.3 / 1024
2 +V1.05S (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 3.3 / 1024
3 +V3.3V (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 1.1 x 3.3 / 1024
4 +VMEM (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 3.3 / 1024
5 +V5.0V (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 1.833 x 3.3 / 1024
6 +VIN (MSB<<8 + LSB) x 6.000 x 3.3 / 1024
7 (MAIN CURRENT) Use Main Current Function
5.1.2. Main Current
The BMC of the Express-BE implements a current monitor. The current can be read by calling the SEMA function “Get Main Current”. The
function returns four 16-bit values divided in high-byte (MSB) and low-byte (LSB). These 4 values represent the last 4 currents drawn by the
board. The values are sampled every 250ms. The order of the 4 values is NOT in chronological order. Access by the BMC may increase the
drawn current of the whole system. In this case, there are still 3 samples not influenced by the read access.
Main Current = (MSB_n<<8 + LSB_n) x 8.06mA
5.1.3. BMC Status
This register shows the status of BMC controlled signals on the Express-BE.
Status Bit Signal
0 WDT_OUT
1 LVDS_VDDEN
2 LVDS_BKLTEN
3 BIOS_MODE
4 POSTWDT_DISn
5 SEL_BIOS
6 BIOS_DIS0n
7 BIOS_DIS1n
Page 40 Express-BE
Page 41

5.1.4. Exception Codes
In case of an error, the BMC drives a blinking code on the blue Status LED (LED1). The same error code is also reported by the BMC Flags
register. The Exception Code is not stored in the Flash Storage and is cleared when the power is removed. Therefore, a “Clear Exception
Code” command is not needed or supported.
Exception Code Error Message
0 NOERROR
2 NO_SUSCLK
3 NO_SLP_S5
4 NO_SLP_S4
5 NO_SLP_S3
6 BIOS_FAIL
7 RESET_FAIL
8 POWER_FAIL
9 LOW_VIN
10
11 V3.3V
12 V1P05S
13 +V3.3V
14 +VMEM
15 +V5.0V
16 +P12V_5V
18 CRITICAL_TEMP
19 NO_CB_PWROK
20 NO_SYS_GD
21
22 NO_RUNPWR_GD
5.1.5. BMC Flags
The BMC Flags register returns the last detected Exception Code since power-up and shows the BIOS in use and the power mode.
Bit Description
[ 0 ~ 4 ] Exception Code
[ 6 ] 0 = AT mode
1 = ATX mode
[ 7 ] 0 = Standard BIOS
1 = Fail-safe BIOS.
Express-BE Page 41
Page 42

6. System Resources
6.1. System Memory Map
Address Range (decimal) Address Range (hex) Size Description
(4GB-2MB) FFE00000 – FFFFFFFF 2 MB High BIOS Area
(4GB-20MB) – (4GB-19MB-1) FEC00000 – FECFFFFF 1 MB APIC Configuration Space
960 K – 1024 K F0000 – FFFFF 64 KB System BIOS Area
896 K – 960 K E0000 – EFFFF 64 KB Extended System BIOS Area
768 K – 896 K C0000 – DFFFF 128 KB PCI expansion ROM area
C0000 – C7FFF: Onboard VGA BIOS
640 K – 768 K A0000 – BFFFF 128 KB Video Buffer & SMM space
0 K – 640 K 00000 – 9FFFF 640 KB DOS Area
6.2. Direct Memory Access Channels
Channel Number Data Width System Resource
0 8-bits Generic
1 8-bits Generic
2 8-bits Generic
3 8-bits Generic
4 Reserved - cascade channel
5 16-bits Open
6 16-bits Open
Page 42 Express-BE
Page 43

6.3. I/O Map
Hex Range Device
000-01F DMA controller 1, 8237A-5 equivalent
020-02D and 030-03F Interrupt controller 1, 8259 equivalent
02E-02F
04E-04F
040-042
050-052
060, 062, 064, 066 8742 equivalent (keyboard)
061 NMI control and status
070-077 Real Time Clock Controller( bit 7 -NMI mask)
080-091 DMA page register
092 Reset (Bit 0)/ Fast Gate A20 (Bit 1)
093-09F DMA page registers continued
0A0-0B1 and 0B4-0BD Interrupt controller 2, 8259 equivalent
0B2 and 0B3 APM control
0C0-0DF DMA controller 2, 8237A-5 equivalent
0F0
LPC SIO (W83627DHG) configuration index/data registers
Timer, 8254-2 equivalent
Read: PCI and Master abort. (Note 1)
Write: FERR#/ IGNNE# /Interrupt controller
240-247 Serial port 1
248-24F Serial port 2
2F8-2FF Serial port 4
3F8-3FF Serial port 3
B00 SMBUS IO base
E00 SB_SIO_PME_BASE_ADDRESS
CF9 Reset Control register (8 bit I/O)
Note (1): A read to this address will subtractively go to PCI, where it will master abort.
Express-BE Page 43
Page 44

6.4. Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines
6.4.1. PIC Mode
IRQ# Typical Intterupt Resource Connected to Pin Available
0 Counter 0 N/A No
1 Keyboard controller N/A No
2 Cascade interrupt from slave PIC N/A No
3 Serial Port 4 / PCI IRQ3 via SERIRQ Note (1)
4 Serial Port 3 / PCI IRQ4 via SERIRQ Note (1)
5 PCI IRQ5 via SERIRQ Note (1)
6 Floppy Drive Controller IRQ6 via SERIRQ No
7 PCI IRQ7 via SERIRQ Note (1)
8 Real-time clock N/A No
9 SCI / PCI IRQ9 via SERIRQ Note (1)
10 Serial Port 1 IRQ10 via SERIRQ No
11 Serial Port 2 IRQ11 via SERIRQ No
12 PS/2 Mouse / PCI IRQ12 via SERIRQ Note (1)
13 Math Processor N/A No
14 Primary IDE controller / PCI IRQ14 via SERIRQ Note (1)
15 PCI N/A No
Note (1): These IRQs can be used for PCI devices when onboard device is disabled.
Page 44 Express-BE
Page 45

6.4.2. APIC Mode
IRQ# Typical Intterupt Resource Connected to Pin Available
0 Counter 0 N/A No
1 Keyboard controller N/A No
2 PCI N/A No
3 Serial Port 4 / PCI IRQ3 via SERIRQ Note (1)
4 Serial Port 3 / PCI IRQ4 via SERIRQ Note (1)
5 PCI IRQ5 via SERIRQ Note (1)
6 Floppy Drive Controller IRQ6 via SERIRQ No
7 PCI IRQ7 via SERIRQ Note (1)
8 Real-time clock N/A No
9 ACPI-Compliant system IRQ9 via SERIRQ Note (1)
10 Serial Port 1 IRQ10 via SERIRQ Note (1)
11 Serial Port 2 IRQ11 via SERIRQ Note (1)
12 PS/2 Mouse / PCI IRQ12 via SERIRQ Note (1)
13 Math Processor N/A No
14 N/A N/A Note (1)
15 N/A N/A Note (1)
16 N/A HDA controller, AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#1
ATI PCI-to-PCI Bridge#1/2/3/4
17 N/A EHCI USB Controller#0/1/2 Yes
18 N/A AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#3,OHCI USB
Controller#0/1/2
19 N/A HDA controller, AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#4 Yes
Note (1): These IRQs can be used for PCI devices when onboard device is disabled.
Yes
Yes
Express-BE Page 45
Page 46

6.5. PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus Number Device Number Function Number Routing Description
00h 00h 00h N/A AMD Host Bridge
00h 00h 02h Internal AMD System Device
00h 01h 00h Internal ATI VGA Controller(PCI Express)
00h 01h 01h Internal ATI Multimedia(PCI Express)
00h 02h 00h Internal AMD Host Bridge#0
00h 03h 00h Internal AMD Host Bridge#1
00h 04h 00h Internal AMD Host Bridge#2
00h 10h 00h Internal AMD Serial Bus Controller (PCI Express)
00h 10h 01h Internal AMD Serial Bus Controller (PCI Express)
00h 11h 00h Internal AMD AHCI 1.0 Controller
00h 12h 00h Internal ATMD USB OHCI
00h 12h 02h Internal AMD USB2 EHCI
00h 13h 00h Internal AMD USB OHCI
00h 13h 02h Internal AMD USB2 EHCI
00h 14h 00h Internal AMD SMBus
00h 14h 01h Internal AMD IDE Controller
00h 14h 02h Internal AMD Multimedia
00h 14h 03h Internal AMD ISA Bridge
00h 14h 04h Internal AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge
00h 14h 05h Internal AMD USB OHCI
00h 14h 07h Internal AMD System Device
00h 15h 00h Internal AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#0
00h 15h 01h Internal AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#1
00h 15h 02h Internal AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#2
00h 15h 03h Internal AMD PCI-to-PCI Bridge#3
00h 18h 00h N/A AMD Host Bridge#0
00h 18h 01h N/A AMD Host Bridge#1
00h 18h 02h N/A AMD Host Bridge#2
00h 18h 03h N/A AMD Host Bridge#3
00h 18h 04h N/A AMD Host Bridge#4
00h 18h 05h N/A AMD Host Bridge#5
03h 00h 00h Internal Intel Ethernet controller (PCI Express)
Page 46 Express-BE
Page 47

6.6. PCI Interrupt Routing Map
PIRQ
A
B
C
D
ATI VGA
Controller
INTC INTA INTD INTC INTA INTD
INTD INTB INTA
INTA INTB
INTB INTC
ATI IDE
Controller#1
ATI IDE
Controller#0
PIRQ INT Line
A INTA
B INTB
C INTC
D INTD
AMD Host
Bridge#0
INTA INTC INTA INTB INTC INTD
INTB INTD INTB INTC INTD INTA
INTE INTC INTD INTA INTB
INTF INTD INTA INTB INTC
AMD Host
Bridge#1
6.7. SMBus Address Table
SMBUS
Controller
AMD PCI-to-PCI
Bridge#0
OHCI 0/1/2 AMD
AMD PCI-to-PCI
Bridge#1
Multimedia
AMD PCI-to-PCI
Bridge#2
Intel
Ethernet
Controller
AMD PCI-to-PCI
Bridge#3
Device
0x40 PCA9535BS
0x42 CH7511B
0x50 SEMA
0xA0 DIMM A
0xA4 DIMM B
Address
Express-BE Page 47
Page 48

7. BIOS Setup
7.1. Menu Structure
This section presents the six primary menus of the BIOS Setup Utility. Use the following table as a quick reference for the contents of the
BIOS Setup Utility. The subsections in this section describe the submenus and setting options for each menu item. The default setting
options are presented in bold, and the function of each setting is described in the right hand column of the respective table.
Main Advanced Boot Security Save & Exit
- System Information
- Memory Information
- System ►
Management
- System Date
- System Time
Notes:
► indicates a submenu
Gray text indicates info only
- CPU ►
- Memory ►
- Graphics ►
- SATA ►
- USB ►
- Network ►
- PCI and PCIe ►
- Super IO ►
- ACPI and ►
Power Management
- Sound ►
- Serial Port ►
Console
- Thermal ►
- Miscellaneous ►
- Boot Configuration
- CSM16 Parameters ►
- CSM Parameters ►
-
Password
Description
- Secure Boot
Menu ►
- Reset Options
- Save Options
- Boot Override
Page 48 Express-BE
Page 49

7.2. Main
The Main Menu provides read-only information about your system and also allows you to set the System Date and Time. Refer to the tables
below for details of the submenus and settings.
7.2.1. System Information
Feature Options Description
BIOS Version Info only ADLINK BIOS version
Build Date and Time Info only Date the BIOS was built
7.2.2. Memory Information
Feature Options Description
Total Memory Info only Display total memory information
7.2.3. System Management
7.2.3.1. System Management > Board Information
Board Information Info only
SMC Firmware Read only Display SMC firmware
Build Date Read only Display SMC firmware build date
SMC Boot loader Read only Display SMC boot loader
Build Date Read only Display SMC boot loader build date
Hardware Version Read only Display SMC hardware version
PCBA Revision Read only Display PCBA revision
Serial Number Read only Display SMC serial number
Manufacturing Date Read only Display SMC manufacturing date
Last Repair Date Read only Display SMC last repair date
MAC ID Read only Display SMC MAC ID
SEMA Features: Read only Display SEMA features
7.2.3.2. System Management > Temperatures and Fan Speed
Feature Options Description
Temperatures and Fan Info only
Board Temperatures Info only
Current Read only Display current board temperature
Startup Read only Display board startup temperature
Min Read only Display board min. temperature
Max Read only Display board max. temperature
Express-BE Page 49
Page 50

Feature Options Description
CPU Fan Speed Read only Display CPU fan speed
System Fan Speed Read only Display system fan speed
7.2.3.3. System Management > Power Consumption
Feature Options Description
Power Consumption Info only
Current Input Current Read only Display input current
Current Input Power Read only Display input power
V3.30 Read only Display actual V3.30 voltage
V1.05 Read only Display actual V1.05 voltage
V3.30 Read only Display actual V3.30 voltage
VMEM Read only Display actual VMEM voltage
V5.00 Read only Display actual 5.00 voltage
VIN Read only Display actual VIN voltage
AIN7 Read only Display actual AIN7 voltage
7.2.3.4. System Management > Runtime Statistics
Feature Options Description
Runtime Statistics Info only
Total Runtime Read only The returned value specifies the total time in minutes the system
Current Runtime Read only The returned value specifies the time in seconds the system is
Power Cycles Read only The returned value specifies the number of times the external
Boot Cycles Read only The Bootcounter is increased after a HW- or SW-Reset or after a
is running in S0 state.
running in S0 state.
This counter is cleared when the system is removed from the
external power supply.
power supply has been shut down
successful power-up.
Boot Reason Read only The boot reason is the event which causes the reboot of the
system.
Page 50 Express-BE
Page 51

7.2.3.5. System Management > Flags
Feature Options Description
Flags Info only
BMC Flags Read only
BIOS Select Read only Display the selection of current BIOS ROM
ATX/AT-Mode Read only Display ATX/AT-Mode
Exception Code Read only System exception reason
7.2.3.6. System Management > Power Up
Feature Options Description
Power Up Info only
Power Up watchdog
Attention: F12 disables the Power Up
Watchdog.
ECO Mode Disabled
Power-up Mode
Attention: The Power-Up Mode only has
effect, if the module is in ATX-Mode.
Enabled
Disabled
Enable
Turn on
Remain off
Last State
The Power-Up Watchdog resets the system after a certain
amount of time after power-up.
Reduces the power consumption of the system
Turn On: The machine starts automatically when the power
supply is turned on.
Remain Off: To start the machine the power button has to be
pressed.
Last State: When powered on during a power failure the system
will automatically power on when power is restored.
7.2.3.7. System Management > LVDS Backlight
Feature Options Description
LVDS Backlight Info only
LVDS Backlight Bright 255 The value range starts at 0 and ends at 255.
7.2.3.8. System Management > Smart Fan
Feature Options Description
Smart Fan Info only
CPU Smart FanTemperature
Source
CPU Fan Mode AUTO (Smart Fan)
CPU Trigger Point 1 Read only
Trigger Temperature 15 Specifies the temperature threshold at which the BMC turns on
PWM Level 30 Select PWM level
CPU Trigger Point 2 Read only
Trigger Temperature 60 Specifies the temperature threshold at which the BMC turns on
CPU Sensor
System Sensor
Fan Off
Fan On
Select CPU smart fan source
Select CPU fan mode
the CPU fan with the specified PWM level
Express-BE Page 51
Page 52

Feature Options Description
CPU fan the specified PWM level
PWM Level 40 Select PWM level
CPU Trigger Point 3 Read only
Trigger Temperature 70 Specifies the temperature threshold at which the BMC turns on
CPU fan the specified PWM level
PWM Level 63 Select PWM level
CPU Trigger Point 4 Read only
Trigger Temperature 80 Specifies the temperature threshold at which the BMC turns on
CPU fan the specified PWM level
PWM Level 100 Select PWM level
7.2.4. System Date and Time
Feature Options Description
System Date Day of Week, MM/DD/YYYY Requires the alpha-numeric entry of the day of the week, day of
the month, calendar month, and all 4 digits of the year, indicating
the century and year (Fri XX/XX/20XX)
System Time HH/MM/SS Presented as a 24-hour clock setting in hours, minutes, and
seconds
7.3. Advanced
This menu contains the settings for most of the user interfaces in the system.
7.3.1. CPU
Feature Options Description
CPU Info only
Module Version Info only Display Source code version
AGESA Version Info only Display AGESA version
PSS Support Enabled
Disabled
Enable/disable the generation of ACPI _PPC, _PSS, and _PCT
objects.
PSTATE Adjustment PState 0
PState 1
PState 2
PState 3
PState 4
PState 5
PState 6
PState 7
PPC Adjustment PState 0
PState 1
PState 2
PState 3
PState 4
Provide to adjust startup P-state level
Provide to adjust _PPC object.
Page 52 Express-BE
Page 53

Feature Options Description
SVM Mode Enabled
Disabled
C6 Mode Enabled
Disabled
Node Configuration Submenu
Enable/disable CPU Virtualization
Enable/disable C6
7.3.1.1. Node Configuration
Feature Options Description
Node Configuration Info only
7.3.2. Memory
Feature Options Description
Total Memory Info only Display Total Memory.
Memory Clock Submenu
Socket 0 Information Submenu
7.3.2.1. Memory Configuration
Feature Options Description
Memory Clock Auto
800MHz
1066Mhz
1333Mhz
1600MHz
1866Mhz
This option allows user to select a different Memory Clock. Default
value is 800Mhz.
7.3.2.2. Socket 0 Information
Feature Options Description
Socket 0 Configuration Info only
7.3.3. Graphics
Feature Options Description
Graphics Info only
IOMMU Enabled
Disabled
Enable/Disable IOMMU Support
Integrated Graphics Auto
Disable
Force
Primary Video Device Int Graphics (IGD)
Ext Graphics (PEG)
Enable Integrate Graphics Controller
Select Internal/External Graphics
Express-BE Page 53
Page 54

Feature Options Description
PSPP Policy Disabled
PEG Gen Auto
GFX LINK CFG x16
DDI port detection Enabled
Lamar DP0 OutputMode DP Mode
Lamar DP1 OutputMode DP Mode
Lamar DP2 OutputMode DP Mode
7.3.4. SATA
PCIe Speed Power Policy
Performance
Balanced-High
Balanced-Low
Power Saving
Control PEG Gen
Gen 1
Gen 2
PCIe x16 configuration. Set to “x16 or “2 x8”
2 x8
DDI port detection
Disabled
Lamar First Display Port Output Mode, J116-Bottom
Disabled
Lamar Second Display Port Output Mode, J116-Up
Disabled
Lamar Third Display Port Output Mode, J117
Disabled
Feature Options Description
SATA Info only
OnChip SATA Channel Enabled
Disabled
OnChip SATA Type Native IDE
AHCI
Legacy IDE
AHCI as ID 7804
OnChip IDE Mode Legacy mode
Native mode
SATA IDE Combined Mode Enabled
Disabled
SATA Port0 Info only
eSATA PORT on PORT0 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Power on PORT0 Enabled
Disabled
SATA PORT- MODE GEN1
GEN2
SATA HotPlug Port0 Enabled
Disabled
Enable/Disable Serial ATA.
Select AHCI/IDE
SATA port 0 support eSATA Enable/disable
SATA port Power support Enable/disable
SATA Hot-Plug function
SATA Port1 Info only
eSATA PORT on Port1 Enabled
Disabled
SATA port 1 support eSATA Enable/disable
Page 54 Express-BE
Page 55

Feature Options Description
SATA Power on Port1 Enabled
Disabled
SATA PORT- MODE GEN1
GEN2
SATA HotPlug Port1 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Port2 Info only
eSATA PORT on Port2 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Power on Port2 Enabled
Disabled
SATA PORT- MODE GEN1
GEN2
SATA HotPlug Port2 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Port3 Info only
eSATA PORT on Port3 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Power on Port3 Enabled
Disabled
SATA port Power support Enable/disable
SATA Hot-Plug function
SATA port 2 support eSATA Enable/disable
SATA port Power support Enable/disable
SATA Hot-Plug function
SATA port 3 support eSATA Enable/disable
SATA port Power support Enable/disable
SATA PORT- MODE GEN1
GEN2
SATA HotPlug Port3 Enabled
Disabled
SATA Hot-Plug function
7.3.5. USB
Feature Options Description
USB Info only
USB Module Version Info only
USB Devices Info only Drives, keyboards, mouse, hubs
Legacy USB Support Enabled
Disabled
Auto
XHCI Hand-off Enabled
Disabled
EHCI Hand-off Enabled
Disabled
Enables legacy USB support.
Auto option disables legacy support if no USB devices are
connected.
Disable option will keep USB devices available only for EFI
applications and setup.
This is a workaround for OSes without XHCI hand-off support. The
XHCI ownership change should be claimed by the XHCI OS driver.
This is a workaround for OSes without EHCI hand-off support. The
EHCI ownership change should be claimed by the EHCI OS driver.
USB Mass Storage Driver Support Enabled
Disabled
SB USB Configuration Submenu
USB hardware delays and time-outs: Info only
Enable/Disable USB mass storage driver support.
Express-BE Page 55
Page 56

Feature Options Description
USB transfer time-out 1 sec
5 sec
10 sec
20 sec
Device reset time-out 10 sec
20 sec
30 sec
40 sec
Device power-up delay Auto
Manual
Mass Storage Devices Info only List current USB mass storage devices.
The time-out value for control, bulk, and interrupt transfers
USB mass storage device Start Unit command time-out.
Maximum time the device will take before it properly reports itself to
the Host Controller. 'Auto' uses default value: for a Root port it is 100
ms, for a Hub port the delay is taken from Hub descriptor.
7.3.5.1. USB > SB USB Configuration
Feature Options Description
XHCI Controller 0 Enabled
Disabled
XHCI0 Port 0 Enabled
Disabled
XHCI0 Port 1 Enabled
Disabled
XHCI Controller 0 Enable
XHCI Controller 1 Enabled
XHCI1 Port 0 Enabled
XHCI1 Port 1 Enabled
OHCI HC(Bus 0 Dev 18 Fn 0) Enabled
EHCI HC(Bus 0 Dev 18 Fn 2) Enabled
USB Port 0 Enabled
USB Port 1 Enabled
USB Port 2 Enabled
USB Port 3 Enabled
USB Port 4 Enabled
XHCI Controller 1 Enable
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Page 56 Express-BE
Page 57

7.3.6. Network
Feature Options Description
Network Info only
Network Stack Enabled
Disabled
UEFI PXE Driver Enabled
Disabled
LAN device enable/disable Enabled
Disabled
Enable/Disable UEFI network stack.
Enable/Disable UEFI PXE Driver
LAN device enable/disable
7.3.7. PCI and PCIe
Feature Options Description
PCI and PCIe Info only
PCI Common Settings Info only
PCI Latency 32 PCI Bus Clocks
64 PCI Bus Clocks
96 PCI Bus Clocks
128 PCI Bus Clocks
160 PCI Bus Clocks
192 PCI Bus Clocks
224 PCI Bus Clocks
248 PCI Bus Clocks
VGA Palette Snoop Disabled
Enabled
PERR# Generation Disabled
Enabled
SERR# Generation Disabled
Enabled
PCI Express Settings Submenu
Value to be programmed into PCI latency timer register.
Enables or disables VGA palette registers snooping.
Enable or Disable the PCI Express port 1 in the chipset.
Enables or disables PCI Device to generate SERR#.
PCI Express Gen2 Settings Submenu
NB PCI-E Port Submenu
SB GPP Port Configuration Submenu
7.3.7.1. PCI Express Settings
Feature Options Description
Relaxed Ordering Disabled
Enabled
Extended Tag Disabled
Enabled
No Snoop Disabled
Enabled
Maximum Payload Auto
128 Bytes
256 Bytes
512 Bytes
1024 Bytes
2048 Bytes
4096 Bytes
Enables or disables PCI Express device relaxed ordering.
If Enabled, allows device to use 8-bit tag field as a requester.
Enables or disables PCI Express device No Snoop option.
Set maximum payload of PCI Express device or allow system BIOS
to select the value.
Express-BE Page 57
Page 58

Feature Options Description
Maximum Read Request Auto
128 Bytes
256 Bytes
512 Bytes
1024 Bytes
2048 Bytes
4096 Bytes
PCI Express Link Register Settings Info only
ASPM Support
WARNING: Enabling ASPM may cause
some
PCI-E devices to fail
Extended Synch Disabled
Link Training Retry Disable
Link Training Timeout (Us) 100 Defines number of microseconds software will wait before polling
Unpopulated Links Keep Link ON
Disabled
Auto
Force L0s
Enabled
2
3
5
Disabled
Set maximum read request size of PCI Express device or allow
system BIOS to select the value.
Set the ASPM Level: Force L0s - Force all links to L0s
Auto - BIOS auto configure
Disabled - Disables ASPM
If enabled, allows generation of Extended Synchronization patterns.
Defines number of retry attempts software will take to retrain the
link if previous training attempt was unsuccessful.
'Link Training' bit in Link Status register. Value range from 10 to
10000 uS.
In order to save power, software will disable unpopulated PCI
Express links if this option set to Disabled.
Restore PCIE Registers Enabled
Disabled
7.3.7.2. PCI Express Gen2 Settings
Feature Options Description
PCI Express Gen2 Device Register Settings Info only
Completion Timeout Default
Shorter
Longer
Disabled
ARI Forwarding Enabled
Disabled
AtomicOp Requester Enable Enabled
Disabled
On non-PCI Express aware OSes (pre Windows Vista) some
devices may not be correctly reinitialized after S3. Enabling this
restores PCI Express device configurations on S3 resume.
Warning: Enabling this may cause issues with other hardware after
S3 resume.
In device functions that support Completion Timeout
programmability, allows system software to modify the Completion
Timeout value. "Default": 50us to 50ms. If "Shorter" is selected,
software will use shorter timeout ranges supported by hardware. If
"Longer" is selected, software will use longer timeout ranges.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", the Downstream
Port disables its traditional Device Number field being 0
enforcement when turning a Type1 Configuration Request into a
Type0 Configuration Request, permitting access to Extended
Functions in an ARI Device immediately below the Port. Default
value: Disabled"
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this function
initiates AtomicOp Requests only if Bus Master Enable bit is in the
Command Register Set.
AtomicOp Egress Blocking Enabled
Disabled
IDO Request Enable Enabled
Disabled
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", outbound
AtomicOp Requests via Egress Ports will be blocked.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this permits setting
the number of ID-Based Ordering (IDO) bit (Attribute[2]) requests
to be initiated.
Page 58 Express-BE
Page 59

Feature Options Description
IDO Completion Enable Enabled
Disabled
LTR Mechanism Enable Enabled
Disabled
End-End TLP Prefix Blocking Enabled
Disabled
Target Link Speed Auto
Force to 2.5 GT/s
Force to 5.0 GT/s
Clock Power Management Enabled
Disabled
Compliance SOS Enabled
Disabled
Hardware Autonomous Width Enabled
Disabled
Hardware Autonomous Speed Enabled
Disabled
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this permits setting
the number of ID-Based Ordering (IDO) bit (Attribute[2]) requests
to be initiated.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this enables the
Latency Tolerance Reporting (LTR) Mechanism.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this function will
block forwarding of TLPs containing End-End TLP Prefixes.
If supported by hardware and set to "Force to 2.5 GT/s" for
Downstream Ports, this sets an upper limit on Link operational
speed by restricting the values advertised by the Upstream
component in its training sequences. When "Auto" is selected HW
initialized data will be used.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", the device is
permitted to use CLKREQ# signal for power management of Link
clock in accordance to protocol defined in appropriate form factor
specification.
If supported by hardware and set to "Enabled", this will force
LTSSM to send SKP Ordered Sets between sequences when
sending Compliance Pattern or Modified Compliance Pattern.
If supported by hardware and set to "Disabled", this will disable the
hardware"s ability to change link width except width size reduction
for the purpose of correcting unstable link operation.
If supported by hardware and set to "Disabled", this will disable the
hardware"s ability to change link speed except speed rate
reduction for the purpose of correcting unstable link operation.
7.3.7.3. NB PCI-E Port
Feature Options Description
NB GPP Core Config GPP_CORE_x4
GPP_CORE_x2x2
GPP_CORE_x2x1x1
GPP_CORE_x1x1x2
GPP_CORE_x1x1x1x1
Dev2 Fun1 (Lamar J119) Enabled
Disabled
ASPM Mode Control Disabled
L0s Entry
L1 Entry
L0s And L1 Entry
Hotplug Mode Control Disabled
Hotplug Basic
Hotplug Server
Hotplug Enhanced
Hotplug Inboard
Dev2 Fun2 (J3601) Enabled
Disabled
Dev3 Fun1 Enabled
Disabled
ASPM Mode Control Disabled
L0s Entry
L1 Entry
L0s And L1 Entry
NB GPP Core Configuration
Dev2 Fun1 GFX Slot (Lamar J119) Enabled/Disabled
NB Root Port ASPM Mode Control
NB Root Port Hotplug Mode Control
Dev2 Fun2 GFX Slot (J3601) Enabled/Disabled
Dev3 Fun1 Enabled/Disabled
NB Root Port ASPM Mode Control
Express-BE Page 59
Page 60

Feature Options Description
Hotplug Mode Control Disabled
Hotplug Basic
Hotplug Server
Hotplug Enhanced
Hotplug Inboard
Dev3 Fun2 Enabled
Disabled
ASPM Mode Control Disabled
L0s Entry
L1 Entry
L0s And L1 Entry
Hotplug Mode Control Disabled
Hotplug Basic
Hotplug Server
Hotplug Enhanced
Hotplug Inboard
Dev3 Fun3 Enabled
Disabled
ASPM Mode Control Disabled
L0s Entry
L1 Entry
L0s And L1 Entry
Hotplug Mode Control Disabled
Hotplug Basic
Hotplug Server
Hotplug Enhanced
Hotplug Inboard
Dev3 Fun4 Enabled
Disabled
ASPM Mode Control Disabled
L0s Entry
L1 Entry
L0s And L1 Entry
Hotplug Mode Control Disabled
Hotplug Basic
Hotplug Server
Hotplug Enhanced
Hotplug Inboard
NB Root Port Hotplug Mode Control
Dev3 Fun2 Enabled/Disabled
NB Root Port ASPM Mode Control
NB Root Port Hotplug Mode Control
Dev3 Fun3 Enabled/Disabled
NB Root Port ASPM Mode Control
NB Root Port Hotplug Mode Control
Dev3 Fun4 Enabled/Disabled
NB Root Port ASPM Mode Control
NB Root Port Hotplug Mode Control
7.3.7.4. SB GPP Port Configuration
Feature Options Description
SB GPP Function Enabled
Disabled
GPP Port Link Configuration x4 mode
2:2 mode
2:1:1 mode
1:1:1:1 mode
GPP Link ASPM Disabled
L0s
L1
L0s+L1
Page 60 Express-BE
Page 61

Feature Options Description
GPP Gen2 Enabled
Disabled
UMI Gen2 Enabled
Disabled
GPP HW Compliance Mode Disabled
Port A
Port B
Port C
Port D
SB GPP LANE REVERSAL Enabled
Disabled
UMI PHY PLL Power Down Enabled
Disabled
SB GPP PHY PLL Power Down Enabled
Disabled
Hide unused GPP ports Enabled
Disabled
SB GPP Port A Enabled
Disabled
SB GPP Port B Enabled
Disabled
If GPP PORT A is set to "Disabled", other ports will be disabled.
SB GPP Port C Enabled
Disabled
SB GPP Port D Enabled
Disabled
PCIE Posted Pass Non-posted Hudson-1
Hudson-2
UMI ASPM L1 Timer Auto Override Disabled
1us
2us
4us
10us
20us
40us
100us
UMI & GPP TX Drive Strength Disabled
18ma
20ma
22ma
24ma
Express-BE Page 61
Page 62

7.3.8. Super IO
Feature Options Description
Super IO Chip Info only
W83627DHG Super IO Configuration Submenu
NCT5104D Super IO Configuration Submenu
Serial Port 1 Configuration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
Serial Port 2 Configuration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
Enabled
Disabled
IO=3F8h; IRQ=4
Auto
IO=3F8h; IRQ=4
IO=3F8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=3E8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=2E8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
Enabled
Disabled
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3
Auto
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3
IO=3F8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=3E8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
IO=2E8h; IRQ=3,4,5,6,7,10,11,12
Enable/Disable Serial Port 1 (COM0).
Fixed configuration of serial port.
Select an optimal setting for Super IO device.
Enable/Disable Serial Port 2 (COM1).
Fixed configuration of serial port.
Select an optimal setting for Super IO device.
7.3.9. ACPI and Power Management
Feature Options Description
ACPI and Power Management Info only
Enable ACPI Auto Configuration Enabled
Disabled
Enable Hibernation Enabled
Disabled
ACPI Sleep State Suspend Disabled
S3 (Suspend to RAM)
Emulation AT/ATX ATX
AX
Lock Legacy Resources Enabled
Disabled
Page 62 Express-BE
Enables or disables BIOS ACPI Auto Configuration.
Enables or disables system's ability to hibernate (OS/S4 Sleep
State). This option may be not effective with some OSes.
Select the highest ACPI sleep state the system will enter when the
Suspend button is pressed.
Select Emulation AT or ATX function. If this option set to [Emulation
AT], BIOS will report no suspend functions to ACPI OS. In windows
XP, it will make OS show shutdown message during system
shutdown.
Enables or disables Lock of Legacy Resources
Page 63

7.3.10. Sound
Feature Options Description
Sound Info only
HD Audio Azalia Device Disabled
HD Onboard PIN Config Enabled
Azalia Front Panel Auto
SDIN0 Pin Config Azalia
SDIN1 Pin Config Azalia
SDIN2 Pin Config Azalia
SDIN3 Pin Config Azalia
Azalia Snoop Enabled
7.3.11. Serial Port Console
Enabled
Auto
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
Disabled
Feature Options Description
Serial Port Console Info only
COM0 Info only
Console Redirection Disabled
Enabled
Console Redirection Settings Submenu The settings specify how the host computer and the remote
COM1 Info only
Console Redirection Disabled
Enabled
Console Redirection Settings Submenu The settings specify how the host computer and the remote
COM2 Info only
Console Redirection Disabled
Enabled
Console Redirection Settings Submenu The settings specify how the host computer and the remote
Enable or disable Console Redirection.
computer (which the user is using) will exchange data. Both
computers should have the same or compatible settings.
Enable or disable Console Redirection.
computer (which the user is using) will exchange data. Both
computers should have the same or compatible settings.
Enable or disable Console Redirection.
computer (which the user is using) will exchange data. Both
computers should have the same or compatible settings.
COM3 Info only
Console Redirection Disabled
Enabled
Enable or disable Console Redirection.
Express-BE Page 63
Page 64

Feature Options Description
Console Redirection Settings Submenu The settings specify how the host computer and the remote
computer (which the user is using) will exchange data. Both
computers should have the same or compatible settings.
7.3.11.1. Serial Port Console > Console Redirection Settings
Feature Options Description
COM0/COM1/COM2/COM3
Console Redirection Settings
Terminal Type VT100
Bits per second 9600
Data Bits 7
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support Disabled
Recorder Mode Disabled
Resolution 100x31 Disabled
Legacy OS Redirection 80x24
Putty KeyPad VT100
Redirection After BIOS Post Always Enabled
Info only
VT100+
VT-UTF8
ANSI
19200
38400
57600
115200
8
Even
Odd
Mark
Space
2
Hardware RTS/CTS
Enable
Enable
Enable
80x25
LINUX
XTERMR6
SCO
ESCN
VT400
BootLoader
VT100: ASCII char set.
VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc. VTUTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode chars onto 1 or more
bytes.
ANSI: Extended ASCII char set.
Selects serial port transmission speed. The speed must be matched
on the remote computer. Long or noisy lines may require lower
speeds.
Select data bits.
Select parity.
Select number of stop bits.
Select flow control.
Enable VT-UTF8 combination key support for ANSI/VT100
terminals.
With this mode enabled only text will be sent. This is to capture
terminal data.
Enables or disables extended terminal resolution
On legacy OSes, the number of rows and columns supported by
redirection
Select FunctionKey and KeyPad on Putty.
The Settings specify if BootLoader is selected, then legacy console
redirection is disabled before booting to legacy OS. Default value is
Always Enable which means legacy console redirection is enabled
for legacy OS.
Page 64 Express-BE
Page 65

7.3.12. Thermal
Feature Options Description
Thermal Info only
Critical Trip Point Disabled
85 C
95 C
Active Cooling Trip Point Disabled
40 C
50 C
60 C
70 C
BMC Default
Passive Trip Point Disabled
90 C
80 C
This value controls the temperature of the ACPI Critical Trip Point the point at which the OS will shut the system down.
Active Cooling Trip Point.
This value controls the temperature of the ACPI Passive Trip Point the point at which the OS will begin throtting the processor.
7.3.13. Miscellaneous
Feature Options Description
Miscellaneous Info only
Trust Computing Submenu
7.3.13.1. Trust Computing
Feature Options Description
Security Device Support Disabled
Enabled
Current Status Information Info only
Enables or disables BIOS support for security device. O.S. will not
show Security Device. TCG EFI protocol and INT1A interface will not
be available.
7.4. Boot
7.4.1. Boot Configuration
Feature Options Description
Boot Configuration Info only
Setup Prompt Timeout 1 Number of seconds to wait for setup activation key. 65535 (0xFFFF )
means indefinite waiting.
Bootup NumLock State On
Off
Quiet Boot Disabled
Enabled
Fast Boot Disabled
Enabled
Select the keyboard NumLock state.
Enable or disables Quiet Boot option.
Enables or disables boot with initialization of a minimal set of
devices required to launch active boot option. Has no effect on BBS
boot options.
Boot Option Priorities Info only
Express-BE Page 65
Page 66

Feature Options Description
Hard Drive BBS Priorities Info only
CSM16 Parameters Submenu
CSM Parameters Submenu
7.4.2. Boot Configuration > CSM16 Para meters
Feature Options Description
CSM16 Module Version Info only
GateA20 Active Upon Request
Always
Option ROM Messages Force BIOS
Keep Current
INT19 Trap Response Immediate
Postponed
UPON REQUEST - GA20 can be disabled using BIOS services.
ALWAYS - do not allow disabling GA20; this option is useful when
any RT code is executed above 1MB.
BIOS reaction on INT19 trapping by Option ROM: IMMEDIATE execute the trap right away; POSTPONED - execute the trap during
legacy boot.
7.4.3. Boot Configuration > CSM Parameters
Feature Options Description
Launch CSM Enable
Disable
Boot Option filter UEFI and Legacy
Legacy only
UEFI only
Launch PXE OpROM policy Do not launch
Legacy only
UEFI only
Launch Storage OpROM policy Do not launch
UEFI only
Legacy only
This option controls if CSM will be launched.
This option controls what devices system can to boot.
Controls the execution of UEFI and Legacy PXE OpROM.
Controls the execution of UEFI and Legacy Storage OpROM.
Launch Video OpROM policy Do not launch
UEFI only
Legacy only
Other PCI device ROM priority UEFI OpROM
Legacy OpROM
Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy video OpROM.
Determines OpROM execution policy for devices other than network,
storage or video.
Page 66 Express-BE
Page 67

7.5. Security
7.5.1. Password Description
Feature Options Description
Administrator Password Enter password
User Password Enter password
7.6. Save & Exit
7.6.1. Save and Exit > Reset Options
Feature Options Description
Save Changes and Reset Save changes and reset the system. Save Changes and Reset
Discard Changes and Reset Reset the system without saving any changes. Discard Changes and Reset
7.6.2. Save and Exit > Save Options
Feature Options Description
Save Changes Yes No Save Changes done so far to any of the setup options.
Discard Changes Yes No Discard Changes done so far to any of the setup options.
Restore Defaults Yes No Restore/Load Default values for all the setup options.
Save as User Defaults Yes No Save the changes done so far as User Defaults.
Restore User Defaults Yes No Restore the User Defaults to all the setup options.
7.6.3. Boot Override
Feature Options Description
Boot Override Choose boot device Choose the boot device
Express-BE Page 67
Page 68

8. BIOS Checkpoints, Beep Codes
This section of this document lists checkpoints and beep codes generated by AMI Aptio BIOS. The checkpoints defined in this document are
inherent to the AMIBIOS generic core, and do not include any chipset or board specific checkpoint definitions.
Checkpoints and Beep Codes Definition
A checkpoint is either a byte or word value output to I/O port 80h. The BIOS outputs checkpoints throughout bootblock and Power-On Self
Test (POST) to indicate the task the system is currently executing. Checkpoints are very useful for debugging problems that occur during the
preboot process.
Beep codes are used by the BIOS to indicate a serious or fatal error. They are used when an error occurs before the system video has been
initialized, and generated by the system board speaker.
Aptio Boot Flow
While performing the functions of the traditional BIOS, Aptio 5.x core follows the firmware model described by the Intel Platform Innovation
Framework for EFI (“the Framework”). The Framework refers the following “boot phases”, which may apply to various status code &
checkpoint descriptions:
• Security (SEC) – initial low-level initialization
1
• Pre-EFI Initialization (PEI) – memory initialization
• Driver Execution Environment (DXE) – main hardware initialization
2
• Boot Device Selection (BDS) – system setup, pre-OS user interface & selecting a bootable device (CD/DVD, HDD, USB, Network,
Shell, …)
Viewing BIOS Checkpoints
Viewing all checkpoints generated by the BIOS requires a checkpoint card, also referred to as a OST Card or POST Diagnostic Card. These
are PCI add-in cards that show the value of I/O port 80h on a LED display.
Some computers display checkpoints in the bottom right corner of the screen during POST. This display method is limited, since it only
displays checkpoints that occur after the video card has been activated.
Keep in mind that not all computers using AMI Aptio BIOS enable this feature. In most cases, a checkpoint card is the best tool for viewing
AMI Aptio BIOS checkpoints.
1
Analogous to “bootblock” functionality of legacy BIOS
2
Analogous to “POST” functionality in legacy BIOS
Page 68 Express-BE
Page 69

8.1. Status Code Ranges
Status Code
Range
0x01 – 0x0F SEC Status Codes & Errors
0x10 – 0x2F PEI execution up to and including memory detection
0x30 – 0x4F PEI execution after memory detection
0x50 – 0x5F PEI errors
0x60 – 0xCF DXE execution up to BDS
0xD0 – 0xDF DXE errors
0xE0 – 0xE8 S3 Resume (PEI)
0xE9 – 0xEF S3 Resume errors (PEI)
0xF0 – 0xF8 Recovery (PEI)
0xF9 – 0xFF Recovery errors (PEI)
Description
8.2. Standard Status Codes
8.2.1. SEC Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x0 Not used
Progress Codes
0x1 Power on. Reset type detection (soft/hard).
0x2 AP initialization before microcode loading
0x3 North Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x4 South Bridge initialization before microcode loading
0x5 OEM initialization before microcode loading
0x6 Microcode loading
0x7 AP initialization after microcode loading
0x8 North Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0x9 South Bridge initialization after microcode loading
0xA OEM initialization after microcode loading
0xB Cache initialization
SEC Error Codes
0xC – 0xD Reserved for future AMI SEC error codes
0xE Microcode not found
0xF Microcode not loaded
Express-BE Page 69
Page 70

8.2.2. SEC Beep Codes
None
8.2.3. PEI Status Codes
Status Code Description
Progress Codes
0x10 PEI Core is started
0x11 Pre-memory CPU initialization is started
0x12 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x13 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x14 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific)
0x15 Pre-memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x16 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x17 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x18 Pre-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x19 Pre-memory South Bridge initialization is started
0x1A Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1B Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1C Pre-memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initialization codes
0x2B Memory initialization. Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data reading
0x2C Memory initialization. Memory presence detection
0x2D Memory initialization. Programming memory timing information
0x2E Memory initialization. Configuring memory
0x2F Memory initialization (other).
0x30 Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0x31 Memory Installed
0x32 CPU post-memory initialization is started
0x33 CPU post-memory initialization. Cache initialization
0x34 CPU post-memory initialization. Application Processor(s) (AP) initialization
0x35 CPU post-memory initialization. Boot Strap Processor (BSP) selection
0x36 CPU post-memory initialization. System Management Mode (SMM) initialization
0x37 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization is started
0x38 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x39 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3A Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x3B Post-Memory South Bridge initialization is started
Page 70 Express-BE
Page 71

Status Code Description
0x3C Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3D Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3E Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x3F-0x4E OEM post memory initialization codes
0x4F DXE IPL is started
PEI Error Codes
0x50 Memory initialization error. Invalid memory type or incompatible memory speed
0x51 Memory initialization error. SPD reading has failed
0x52 Memory initialization error. Invalid memory size or memory modules do not match.
0x53 Memory initialization error. No usable memory detected
0x54 Unspecified memory initialization error.
0x55 Memory not installed
0x56 Invalid CPU type or Speed
0x57 CPU mismatch
0x58 CPU self test failed or possible CPU cache error
0x59 CPU micro-code is not found or micro-code update is failed
0x5A Internal CPU error
0x5B reset PPI is not available
0x5C-0x5F Reserved for future AMI error codes
S3 Resume Progress Codes
0xE0 S3 Resume is stared (S3 Resume PPI is called by the DXE IPL)
0xE1 S3 Boot Script execution
0xE2 Video repost
0xE3 OS S3 wake vector call
0xE4-0xE7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
0xE0 S3 Resume is stared (S3 Resume PPI is called by the DXE IPL)
S3 Resume Error Codes
0xE8 S3 Resume Failed in PEI
0xE9 S3 Resume PPI not Found
0xEA S3 Resume Boot Script Error
0xEB S3 OS Wake Error
0xEC-0xEF Reserved for future AMI error codes
Recovery Progress Codes
0xF0 Recovery condition triggered by firmware (Auto recovery)
0xF1 Recovery condition triggered by user (Forced recovery)
Express-BE Page 71
Page 72

Status Code Description
0xF2 Recovery process started
0xF3 Recovery firmware image is found
0xF4 Recovery firmware image is loaded
0xF5-0xF7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes
Recovery Error Codes
0xF8 Recovery PPI is not available
0xF9 Recovery capsule is not found
0xFA Invalid recovery capsule
0xFB – 0xFF Reserved for future AMI error codes
8.2.4. PEI Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
1 Memory not Installed
1 Memory was installed twice (InstallPeiMemory routine in PEI Core called twice)
2 Recovery started
3 DXEIPL was not found
3 DXE Core Firmware Volume was not found
7 Reset PPI is not available
4 Recovery failed
4 S3 Resume failed
8.2.5. DXE Status Codes
Status Code Description
0x60 DXE Core is started
0x61 NVRAM initialization
0x62 Installation of the South Bridge Runtime Services
0x63 CPU DXE initialization is started
0x64 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x65 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x66 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x67 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific)
0x68 PCI host bridge initialization
0x69 North Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x6A North Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x6B North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
Page 72 Express-BE
Page 73

Status Code Description
0x6C North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6D North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6E North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x6F North Bridge DXE initialization (North Bridge module specific)
0x70 South Bridge DXE initialization is started
0x71 South Bridge DXE SMM initialization is started
0x72 South Bridge devices initialization
0x73 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x74 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x75 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x76 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x77 South Bridge DXE Initialization (South Bridge module specific)
0x78 ACPI module initialization
0x79 CSM initialization
0x7A – 0x7F Reserved for future AMI DXE codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0x90 Boot Device Selection (BDS) phase is started
0x91 Driver connecting is started
0x92 PCI Bus initialization is started
0x93 PCI Bus Hot Plug Controller Initialization
0x94 PCI Bus Enumeration
0x95 PCI Bus Request Resources
0x96 PCI Bus Assign Resources
0x97 Console Output devices connect
0x98 Console input devices connect
0x99 Super IO Initialization
0x9A USB initialization is started
0x9B USB Reset
0x9C USB Detect
0x9D USB Enable
0x9E – 0x9F Reserved for future AMI codes
0xA0 IDE initialization is started
0xA1 IDE Reset
0xA2 IDE Detect
0xA3 IDE Enable
0xA4 SCSI initialization is started
0xA5 SCSI Reset
Express-BE Page 73
Page 74

Status Code Description
0xA6 SCSI Detect
0xA7 SCSI Enable
0xA8 Setup Verifying Password
0xA9 Start of Setup
0xAA Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0xAB Setup Input Wait
0xAC Reserved for ASL (see ASL Status Codes section below)
0xAD Ready To Boot event
0xAE Legacy Boot event
0xAF Exit Boot Services event
0xB0 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP Begin
0xB1 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP End
0xB2 Legacy Option ROM Initialization
0xB3 System Reset
0xB4 USB hot plug
0xB5 PCI bus hot plug
0xB6 Clean-up of NVRAM
0xB7 Configuration Reset (reset of NVRAM settings)
0xB8 – 0xBF Reserved for future AMI codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
DXE Error Codes
0xD0 CPU initialization error
0xD1 North Bridge initialization error
0xD2 South Bridge initialization error
0xD3 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
0xD4 PCI resource allocation error. Out of Resources
0xD5 No Space for Legacy Option ROM
0xD6 No Console Output Devices are found
0xD7 No Console Input Devices are found
0xD8 Invalid password
0xD9 Error loading Boot Option (LoadImage returned error)
0xDA Boot Option is failed (StartImage returned error)
0xDB Flash update is failed
0xDC Reset protocol is not available
Page 74 Express-BE
Page 75

8.2.6. DXE Beep Codes
# of Beeps Description
4 Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available
5 No Console Output Devices are found
5 No Console Input Devices are found
1 Invalid password
6 Flash update is failed
7 Reset protocol is not available
8 Platform PCI resource requirements cannot be met
8.2.7. ACPI/ASL Checkpoint
Status Code Description
0x01 System is entering S1 sleep state
0x02 System is entering S2 sleep state
0x03 System is entering S3 sleep state
0x04 System is entering S4 sleep state
0x05 System is entering S5 sleep state
0x10 System is waking up from the S1 sleep state
0x20 System is waking up from the S2 sleep state
0x30 System is waking up from the S3 sleep state
0x40 System is waking up from the S4 sleep state
0xAC System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in PIC mode.
0xAA System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in APIC mode.
8.3. OEM-Reserved Checkpoint Ranges
Status Code Description
0x05 OEM SEC initialization before microcode loading
0x0A OEM SEC initialization after microcode loading
0x1D – 0x2A OEM pre-memory initialization codes
0x3F – 0x4E OEM PEI post memory initialization codes
0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes
0xC0 – 0xCF OEM BDS initialization codes
Express-BE Page 75
Page 76

9. Mechanical Information
9.1. Board-to-Board Connectors
To allow for different stacking heights, the receptacles for COM Express carrier boards are available in two heights: 5 mm and 8 mm. When
5 mm receptacles are chosen, the carrier board should be free of components.
Tyco 3-1827253-6
Foxconn QT002206-2131-3H
• 220-pin board-to-board connector with 0.5mm for a stacking height of 5 mm.
• This connector can be used with 5 mm through-hole standoffs (SMT type).
Tyco 3-6318491-6
Foxconn QT002206-4141-3H
• 220-pin board-to-board connector with 0.5mm for a stacking height of 8 mm.
• This connector can be used with 8 mm through-hole standoffs (SMT type).
Common Specifications
• Current capacity: 0.5A per pin
• Rated voltage: 50 VAC
• Insulation resistance: 100M or greater @ 500 VDC
• Temperature rating: -40°C ~ 85°C
• UL certification (ECBT2.E28476)
• Copper alloy (contacts)
• Housing: thermo-plastic molded compound (L.C.P.)
Page 76 Express-BE
Page 77

9.2. Thermal Solution
9.2.1. Heat Spreaders
The function of the heat spreader is to ensure an identical mechanical profile for all COM Express modules. By using a heat spreader, the
thermal solution that is built on top of the module is compatible with all COM Express modules.
9.2.2. Heat Sinks
A heat sink can be used as a thermal solution for a specific COM Express module and can have a fan or be fanless, depending on the
thermal requirements.
9.2.3. Installation
Install a heat spreader or heat sink using the following instructions.
Step 1: Before mounting the heatsink, install the required memory modules onto the SODIMM socket(s) on the COM Express module.
Step 2: Remove the protective membranes from the thermal pads.
Express-BE Page 77
Page 78

Step 3: Assemble the heatsink onto the COM Express module.
Use the four M2.5, L=6mm screws provided to fasten the heatsink to the module.
Step 4: Place the COM Express module and heatsink assembly onto the connectors on the carrier board as shown.
Then press down on the module until it is firmly seated on the carrier board.
Step 5: Use the five M2.5, L=16mm screws provided to secure the COM Express module to the carrier board from the solder side.
Page 78 Express-BE
Page 79

Step 6: If you are installing a heatsink with a fan, plug the fan connector into the carrier board as shown.
Express-BE Page 79
Page 80

9.3. Mounting Methods
There are several standard ways to mount the COM Express module with a thermal solution onto a carrier board. In addition to the choice of
5 mm or 8mm board-to-board connectors, there is the choice of Top and Bottom mounting. In Top mounting, the threaded standoffs are on
the carrier board and the thermal solution is equipped with through-hole standoffs. In Bottom mounting, the threaded standoffs are on the
thermal solution and the carrier board has through-hole standoffs.
Page 80 Express-BE
Page 81

9.4. Standoff Types
The standoffs available for Top and Bottom mounting methods are shown below. Note that threaded standoffs are DIP type and throughhole standoffs are SMT type. Other types not listed are available upon request.
5mm through-hole standoff (SMT type)
P/N: 33-72000-0050
8mm through-hole standoff (SMT type)
P/N: 33-72000-0080
5mm threaded standoff (DIP type)
P/N: 33-72016-0050
8mm threaded standoff (DIP type)
P/N: 33-72015-0050
Express-BE Page 81
Page 82

Safety Instructions
Read and follow all instructions marked on the product and in the documentation before you operate your system. Retain all safety and
operating instructions for future use.
• Please read these safety instructions carefully.
• Please keep this User‘s Manual for later reference.
• The equipment should be operated only from the type of power source indicated on the rating label. Make sure the voltage of the
power source when connect the equipment to the power outlet.
• If your equipment has a voltage selector switch, make sure that the switch is in the proper position for your area. The voltage
selector switch is set at the factory to the correct voltage.
• For pluggable equipment, that the socket-outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily accessible.
• Place the power cord such a way that people can not step on it. Do not place anything over the power cord.
• If the equipment is not use for long time, disconnect the equipment from mains to avoid being damaged by transient overvoltage.
• All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
• Please keep this equipment from humidity.
• Do not use this equipment near water or a heat source.
• Lay this equipment on a reliable surface when install. A drop or fall could cause injury.
• Never pour any liquid into opening; this could cause fire or electrical shock.
• Openings in the case are provided for ventilation. Do not block or cover these openings. Make sure you provide adequate space
around the system for ventilation when you set up your work area. Never insert objects of any kind into the ventilation openings.
• To avoid electrical shock, always unplug all power cables and modem cables from the wall outlets before removing covers.
• Lithium Battery provided (real time clock battery)
“CAUTION – Risk of explosion if battery is replaced with one of an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries according to the
instructions”
• If one of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by a service personnel:
The power cord or plug is damaged.
Liquid has penetrated into the equipment.
The equipment has been exposed to moisture.
The equipment has not work well or you can not get it work according to user‘s manual.
The equipment has dropped and damaged.
If the equipment has obvious sign of breakage.
Page 82 Express-BE
Page 83

Getting Service
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: 300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park,Pudong New Area
Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1, B/D, Shang Di East Rd.
Beijing, 100085 China
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8625
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: 2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7, High-Tech Industrial Park S.
Shenzhen, 518054 China
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
LiPPERT ADLINK Technology GmbH
Address: Hans-Thoma-Strasse 11, D-68163, Mannheim, Germany
Tel: +49-621-43214-0
Fax: +49-621 43214-30
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
Express-BE Page 83
Page 84

ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 6 allée de Londres, Immeuble Ceylan
91940 Les Ulis, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho, Chiyoda-ku
Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 802, Mointer B/D, 326 Seocho-daero, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-881, Korea
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre
Singapore 349584
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: #50-56, First Floor, Spearhead Towers
Margosa Main Road (between 16th/17th Cross), Malleswaram
Bangalore - 560 055, India
Tel: +91-80-65605817, +91-80-42246107
Fax: +91-80-23464606
Email: india@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Israeli Liaison Office)
Address: 27 Maskit St., Corex Building
PO Box 12777
Herzliya 4673300, Israel
Tel: +972-54-632-5251
Fax: +972-77-208-0230
Email: israel@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (UK Liaison Office)
Tel: +44 774 010 59 65
Email: UK@adlinktech.com
Page 84 Express-BE
 Loading...
Loading...