Page 1

cPCI-9116®/cPCI-9116R®
64 Ch, 16 bit, 250KS/s
Analog input Card
For 3U CompactPCI
User’s Guide
Recycled Paper
Page 2

Page 3

©Copyright 2002 ADLINK Technology Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Manual Rev. 1.10: April 28, 2003
Part No: 50-15002-101
The information in this document is subject to change without prior n otice in
order to improve reliability, design and function and does not represent a
commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental,
or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product
or documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All
rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any
mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form without prior written
permission of the manufacturer.
Trademarks
NuDAQ®, NuIPC® are registered trademarks of ADLINK Technology Inc.
Other products names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes
only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Page 4
Getting service from ADLINK
Customer Satisfaction is the most important priority for ADLINK Tech Inc. If
you need any help or service, please contact us.
ADLINK Technology Inc.
Web Site http://www.adlinktech.com
Sales & Service Service@adlinktech.com
NuDAQ + USBDAQ nudaq@adlinktech.com
Technical
Support
TEL +886-2-82265877 FAX +886-2-82265717
Address 9F, No. 166, Jian Yi Road, Chungho City, Taipei, 235 Taiwan.
Please email or FAX us of your detailed information for a prompt, satisfactor y
and constant service.
Company/Organization
Contact Person
E-mail Address
Address
Country
TEL FAX
Web Site
Product Model
Environment to Use
Automation automation@adlinktech.com
NuIPC nuipc@adlinktech.com
NuPRO / EBC nupro@adlinktech.com
Detailed Company Information
Questions
OS:
Computer Brand:
M/B: CPU:
Chipset: BIOS:
Video Card:
Network Interface Card:
Other:
Detail Description
Suggestions to ADLINK
Page 5

Table of Contents
Tables..........................................................................................................iv
Figures.........................................................................................................v
Outline of Chapters.................................................................................... vi
Chapter 1 Introduction................................................................................1
1.1 Features..............................................................................................2
Applications ........................................................................................2
1.2
1.3 Specifications......................................................................................3
1.4 Software Support................................................................................6
1.4.1 Programming Library.............................................................6
1.4.2 PCIS-LVIEW: LabVIEW® Driver............................................6
1.4.3 DAQBenchTM: ActiveX Controls.............................................7
Chapter 2 Installation..................................................................................8
2.1 What You Have...................................................................................8
2.2 Unpacking...........................................................................................9
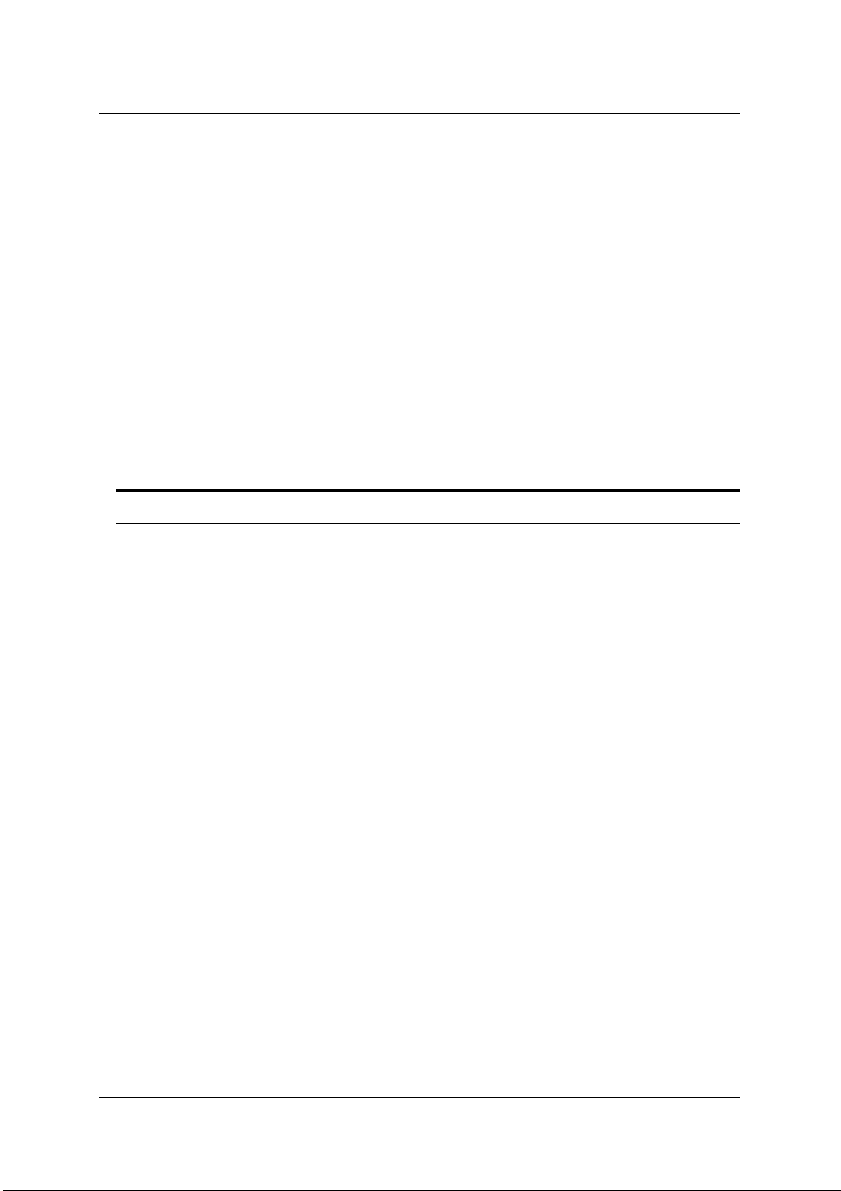
2.3 cPCI-9116 and cPCI-9116R Layout..................................................10
2.4 PCI Configuration..............................................................................12
Chapter 3 Signal Connections.................................................................13
3.1 Connectors and Pin Assignment.......................................................13
3.1.1 100-pin SCSI-type connector (J1) .......................................14
3.1.2 Legend of J1........................................................................15
3.2 Analog Input Signal Connection........................................................16
3.2.1 Types of signal sources.......................................................16
3.2.2 Input Configurations ............................................................16
3.3 Digital I/O Connection....................................................................... 18
Chapter 4 Registers..................................................................................19
4.1 I/O Port Address ...............................................................................19
4.2 Internal Timer/Counter Register........................................................21
4.3 General Purpose Timer/Counter Register.........................................22
4.4 General Purpose Timer/Counter Control Register............................22
4.5 A/D Data Registers...........................................................................24
4.6 Channel Gain Queue Register..........................................................24
4.7 A/D & FIFO Control Register ............................................................26
4.8 A/D & FIFO Status Register..............................................................27
4.9 Digital I/O register.............................................................................29
4.10 A/D Trigger Mode Register ...............................................................30
4.11 Interrupt Control Register..................................................................31
4.12 Interrupt Status Register...................................................................33
Table of Contents • i
Page 6

Chapter 5 Operation Theory.....................................................................34
5.1 A/D Conversion.................................................................................34
5.1.1 A/D Conversion Procedure..................................................34
5.1.2 Software conversion with polling data transfer acquisition
mode (Software Polling)......................................................35
5.1.3 Programmable scan acquisition mode.................................36
5.1.4 A/D Data Transfer Modes....................................................47
5.2 Digital Input and Output....................................................................48
5.3 General Purpose Timer/Counter Operation ......................................49
Chapter 6 C/C++ Library...........................................................................51
6.1 Libraries Installation..........................................................................51
6.2 Programming Guide..........................................................................52
6.2.1 Naming Convention.............................................................52
6.2.2 Data Types..........................................................................52
6.2.3 Sample Programs List (DOS)..............................................53
6.3 Initial functions..................................................................................54
6.3.1 _9116_Initial........................................................................ 54
6.3.2 _9116_AD_Clr_DFIFO........................................................55
6.4 DIO functions....................................................................................56
6.4.1 _9116_DI.............................................................................56
6.4.2 _9116_DO...........................................................................56
6.5 AD Channel Gain Queue configuration functions..............................57
6.5.1 _9116_AD_Clr_CFIFO........................................................57
6.5.2 _9116_AD_Set_CFIFO .......................................................58
6.5.3 _9116_AD_CFIFO_SetDone...............................................60
6.6 AD Software-Polling functions...........................................................61
6.6.1 _9116_AD_Acquire .............................................................61
6.7 AD Trigger control functions .............................................................62
6.7.1 _9116_AD_Trig_Ctrl............................................................62
_9116_AD_Set_TrigMode...................................................62
_9116_AD_Set_TrigPol.......................................................62
_9116_AD_Set_Timebase ..................................................62
_9116_AD_Set_Delay_SRC ...............................................62
_9116_AD_Set_M_enable ..................................................62
6.8 AD Counter setting functions ............................................................64
6.8.1 _9116_AD_Set_SC.............................................................64
6.8.2 _9116_AD_Set_SI...............................................................65
6.8.3 _9116_AD_Set_SI2.............................................................65
6.8.4 _9116_AD_Set_DIV............................................................66
6.8.5 _9116_AD_Set_DLY1.........................................................66
6.8.6 _9116_AD_Set_M...............................................................67
6.8.7 _9116_AD_Set_Retrig.........................................................68
ii • Table of Contents
Page 7

6.9 AD one-shot scan data acquisition with DMA transfer functions.......69
6.9.1 _9116_AD_DMA_Start........................................................69
6.9.2 _9116_AD_DMA_Status .....................................................70
6.9.3 _9116_AD_DMA_Stop........................................................71
6.10 AD one-shot scan data acquisition with interrupt- transfer functions.72
6.10.1 _9116_AD_INT_Start..........................................................72
6.10.2 _9116_AD_INT_Status........................................................73
6.10.3 _9116_AD_INT_Stop ..........................................................74
6.11 AD continuous scan data acquisition with double-buffered DMA
transfer functions ..............................................................................75
6.11.1 _9116_DblBufferMode........................................................75
6.11.2 _9116_DblBufferTransfer ....................................................76
6.11.3 _9116_GetOverrunStatus....................................................77
6.12 General Purpose Timer/Counter functions........................................77
6.12.1 _9116_GP0_Set_Mode.......................................................77
6.12.2 _9116_GP0_Set_Count ......................................................78
6.12.3 _9116_GP0_Set_CLK.........................................................78
6.12.4 _9116_GP0_Set_GATE_SRC.............................................79
6.12.5 _9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN_SRC......................................79
6.12.6 _9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN................................................80
6.12.7 _9116_GP0_EN ..................................................................80
6.12.8 _9116_GP0_Read_Count ...................................................81
Chapter 7 Software Utility & Calibration.................................................82
7.1 Running 9116util.exe program..........................................................82
7.2 Calibration.........................................................................................83
7.2.1 What do you need ...............................................................83
7.2.2 VR Assignment....................................................................84
7.2.3 A/D Adjustment ...................................................................84
7.3 Functional Testing.............................................................................85
Warranty Policy.........................................................................................87
Table of Contents • iii
Page 8

Tables
Table 1. Legend of J1 Connector......................................................15
Table 2. I/O Port Address..................................................................20
Table 3. Timer/Counter Register Address.........................................21
Table 4. General Purpose Timer/Counter Register...........................22
Table 5. General Purpose Timer/Counter Control Register...............22
Table 6. GPTC0’s Mode selection.....................................................23
Table 7. A/D Data Registers..............................................................24
Table 8. Channel Gain Queue Register ............................................24
Table 9. Gain Selection Bits..............................................................25
Table 10. A/D & FIFO Control Register...............................................26
Table 11. A/D & FIFO Status Register ................................................27
Table 12. Digital I/O register (Read)....................................................29
Table 13. Digital I/O register (Write)....................................................29
Table 14. A/D Trigger Mode Register..................................................30
Table 15. Trigger Mode Selection Bits ................................................31
Table 16. Interrupt Control Register....................................................31
Table 17. Interrupt Status Register......................................................33
Table 18. Functions of VRs.................................................................84
iv • Tables
Page 9

Figures
Figure 1: PCB Layout of the cPCI-9116 .............................................10
Figure 2: PCB Layout of cPCI-9116R and Rear I/O adaptor .............. 11
Figure 3: J1 Pin Assignments.............................................................14
Figure 4: Single-ended Mode and Floating sources...........................16
Figure 5: Ground-referenced source and differential input .................17
Figure 6: Floating source and differential input...................................17
Figure 7: Ground-referenced source and User Common Mode
connections.........................................................................18
Figure 8: Digital I/O Connection..........................................................18
Figure 9: Scan Timing ........................................................................37
Figure 10: Pre-trigger (trigger occurs after M scans)............................40
Figure 11: Pre-trigger (trigger with scan is in progress)........................40
Figure 12: Pre-trigger with M_enable = 0 (trigger occurs before M
scans)..................................................................................41
Figure 13: Pre-trigger with M_enable = 1 ............................................. 42
Figure 14: Middle trigger with M_enable = 1.........................................43
Figure 15: Middle trigger (trigger with scan is in progress)...................44
Figure 16: Post trigger..........................................................................44
Figure 17: Delay trigger........................................................................45
Figure 18: Post trigger with re-trigger...................................................46
Figure 19: General-purpose Timer/Counter model...............................49
Figure 20: Mode 0 Operation................................................................50
Figure 21: Mode 1 Operation................................................................50
Figure 22: CPCI-9116 Utility Main Screen............................................83
Figure 23: A/D Adjustment menu Screen.............................................84
Figure 24: cPCI-9116 Function Testing Screen....................................86
Figures • v
Page 10

Outline of Chapters
This manual is designed to help you use the 9116 series. The manual
describes how to modify various settings on the card to meet your
requirements. It is divided into seven chapters:
Chapter1, “Introduction”,
applications, and specifications.
Chapter 2, “Installation”,
layout of 9116 series is shown.
Chapter 3, “Signal Connection”,
assignment and how to connect external signal and devices
to the 9116 series card.
Chapter 4, “Registers”,
structure. This information is important for programmers
who want to control the hardware with low-level
programming.
Chapter 5, “Operation theory”,
9116 series card. The A/D, DIO and timer/counter functions
are introduced. Also, some programming concepts are
specified.
Chapter 6, “Software Utility & Calibration”,
utility program included in the software CD and how to
calibrate the 9116 series card for accurate measurements.
gives an overview of the product features,
describes how to install the 9116 series. The
describes the connectors' pin
describes the details of the registers and its
describes the working theory of the
describes how to run the
vi • Outline of Chapters
Page 11
1
Introduction
The cPCI-9116 series products are advanced data acquisition cards based on
the 32-bit CompactPCI architecture. The 9116 series include:
cPCI-9116: 16-bit 250KHz DAS card for 3U CompactPCI
•
cPCI-9116R: 16-bit 250KHz DAS card for 3U CompactPCI
•
with Rear I/O connector
The 9116 series DAS cards use state-of-the-art technology making it an ideal
for data logging and signal analysis applica tions in medical, process control,
etc.
Introduction • 1
Page 12

1.1 Features
The 9116 series CompactPCI Advanced Data Acquisition Card provides the
following advanced features:
32-bit PCI-Bus, plug and play
•
Up to 64 single-ended inputs or 32 differential inputs, mixing
•
of using SE and DI analog signal sources
16-bit analog input resolution
•
On-board A/D 1K FIFO memory
•
512 words analog input Channel Gain Queue spaces
•
Sampling rate up to 250KS/s
•
Bipolar or Unipolar input signals
•
Programmable gain of x1, x2, x4, x8
•
Jumper-less and software configurable
•
Five A/D trigger modes: software trigger, pre-trigger,
•
post-trigger, middle-trigger and delay-trigger
Software Polling, Interrupt and Bus-mastering DMA data
•
transfer available
8 digital input and 8 digital output channels
•
100-pin D-type SCSI-II connector for cPCI-9116
•
100-pin D-type SCSI-II connector on a rear I/O transition
•
board for cPCI-9116R
Compact size: standard compact PCI 3U size
•
1.2 Applications
Automotive Testing
•
Cable Testing
•
Transient signal measurement
•
ATE
•
Laboratory Automation
•
Biotech measurement
•
2 • Introduction
Page 13
1.3 Specifications
Analog Input (A/D)
♦
Converter:
•
Number of channels: (programmable)
•
64 single-ended (SE)
3
32 differential input (DI)
3
Mixing of SE and DI analog signal between channel allowed
3
A/D Data FIFO Buffer Size:
•
Channel Gain Queue Length:
•
Resolution:
•
Input Range:
•
Bipolar:
3
Unipolar:
3
CMRR (DC to 60 Hz, typical)
•
Input Range CMRR
LT1606 (or equivalent) 250KHz
16-bit
(Controlled by Channel Gain Queue)
± 5V, ±2.5V, ±1.25V, ±0.625V
0~10V, 0~5V, 0~2.5V, 0~1.25
1024 locations
512 words configurations
±5, 0~10V
±2.5, 0~5V
±1.25, 0~2.5V
±0.625, 0~1.25V
Overvoltage Protection:
•
Accuracy:
•
Input Impedance:
•
Time-base source:
•
3
3
Programmable scan interval and sampling rate (divided from
•
0.01% of FSR
Internal 24MHz
External clock Input (fmax: 24MHz, fmin: 1MHz)
87dB
90dB
92dB
93dB
Continuous ± 35V maximum
100 MΩ | 6pF
time-base source)
Introduction • 3
Page 14

Trigger Mode:
•
Software-trigger.
3
Pre-trigger.
3
Post-trigger.
3
Middle-Trigger.
3
Delay Trigger
3
Data Transfer:
•
Polling.
3
EOC interrupt transfer.
3
FIFO half-full Interrupt transfer.
3
Bus-mastering DMA.
3
Data Throughput:
•
Digital I/O (DIO)
♦
Channel:
•
Input Voltage:
•
3
3
Output Voltage:
•
3
3
General Purpose Timer/ Counter
♦
Number of channel:
•
Clock Input:
•
8 TTL compatible digital inputs and outputs
Low: VIL=0.8 V max. IIL=0.2mA max.
High: VIH=2.0V max. IIH=0.02mA max
Low: VOL=0.5 V max. IOL=8mA max.
High: VOH=2.7V min; IOH=400μA
Internal 24MHz or External CLK input up to 20MHz
250KHz (maximum)
One 16-bit Up/Down Timer/Counter
4 • Introduction
Page 15

General Specifications
♦
Connector:
•
Operating Temperature:
•
Storage Temperature:
•
Humidity:
•
Power Consumption:
•
+5V @ 560mA typical
3
+3.3V@ 100mA typical
3
15V (pin35, pin85) Output Current (max):
±
•
+5V(pin49, pin99) Output Current (max):
•
Dimension:
•
100-pin D-type SCSI-II connector
0° C ~ 60° C
-20° C ~ 80° C
5 ~ 95%, non-condensing
Standard Compact PCI 3U size
5mA
500mA
Introduction • 5
Page 16

1.4 Software Support
ADLINK provides versatile software drivers and packages for users’ different
approach to building a system. We not only provide programming libraries
such as DLL for many Windows systems, but also provide drivers for other
software packages such as LabVIEW®.
All software options are included in the ADLINK CD. Non-free software drivers
are protected with licensing codes. Without the software code, you can install
and run the demo version for two hours for trial/demonstration purposes.
Please contact ADLINK dealers to purchase the formal license.
1.4.1 Programming Library
For customers who are writing their own programs, we provide function
libraries for many different operating systems, including:
PCIS-DASK: Include device drivers and DLL for Windows
•
98, Windows NT and Windows 2000. DLL is binary compati bl e
across Windows 98, Windows NT and Windows 2000. That
means all applications developed with PCIS-DASK are
compatible across Windows 98, Windows NT and Windows
2000. The developing environment can be VB, VC++, Delphi,
BC5, or any Windows programming language that allows calls
to a DLL. The user’s guide and function reference manual of
PCIS-DASK are in the CD. Please refer the PDF manual files
under \\Manual_PDF\Software\PCIS-DASK
PCIS-DASK/X: Includes device drivers and shared library for
•
Linux. The developing environment can be Gnu C/C++ or any
programming language that allows linking to a shared librar y.
The user's guide and function reference manual of
PCIS-DASK/X are in the CD.
(\Manual_PDF\Software\PCIS-DASK-X.)
The above software drivers are shipped with the board. Please refer to the
“Software Installation Guide” for installation procedures.
1.4.2 PCIS-LVIEW: LabVIEW® Driver
PCIS-LVIEW contains the VIs, which are used to interface with NI’s
LabVIEW® software package. The PCIS-LVIEW supports Windows
95/98/NT/2000. The LabVIEW® drivers is shipped free with the board. You
can install and use them without a license. For more information about
PCIS-LVIEW, please refer to the user’s guide in the CD.
(\\Manual_PDF\Software\PCIS-LVIEW)
6 • Introduction
Page 17

1.4.3 DAQBenchTM: ActiveX Controls
We suggest customers who are familiar with ActiveX controls and VB/VC++
programming use the DAQBenchTM ActiveX Control component library for
developing applications. The DAQBenchTM is designed under Windows
NT/98. For more information about DAQBench, please refer to the user’s
guide in the CD. (\\Manual_PDF\Software\DAQBench\DAQBench
Manual.PDF).
Introduction • 7
Page 18
2
Installation
This chapter describes how to install the 9116 series cards. The contents of the
package and unpacking information that you should be aware of are described
first.
The 9116 series cards perform an automatic configuration of the IRQ, port
address, and BIOS address. You do not need to set these configurations, as
you would do in ISA form factor DAS cards. Automatic configuration allows
your system to operate more reliable and safe.
2.1 What You Have
In addition to this User's Guide, the package should also include the following
items:
cPCI-9116 or cPCI-9116R with rear I/O adaptor Analog input
•
Data Acquisition Card
ADLINK All-in-one Compact Disc
•
Software Installation Guide
•
If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact the dealer from
whom you purchased the product. Save the shipping materials and carton
in case you want to ship or store the product in the future.
8 • Installation
Page 19
2.2 Unpacking
The card contains electro-static sensitive components tha t can be easily be
damaged by static electricity.
Therefore, the card should be handled on a grounded anti-static mat. The
operator should be wearing an anti-static wristband, grounded at the same
point as the anti-static mat.
Inspect the card module carton for obvious damages. Shipping and handling
may cause damage to your module. Be sure there are no shipping and
handling damages on the modules carton before continuing.
After opening the card module carton, extract the system module and place it
only on a grounded anti-static surface with component side up.
Again, inspect the module for damages. Press down on all the socketed IC's to
make sure that they are properly seated. Do this only with the module place on
a firm flat surface.
Note:
DO NOT APPLY POWER TO THE CARD IF IT HAS BEEN DAMAGED.
You are now ready to install your cPCI-9116/R.
Installation • 9
Page 20

2.3 cPCI-9116 and cPCI-9116R Layout
10 • Installation
Figure 1: PCB Layout of the cPCI-9116
Page 21
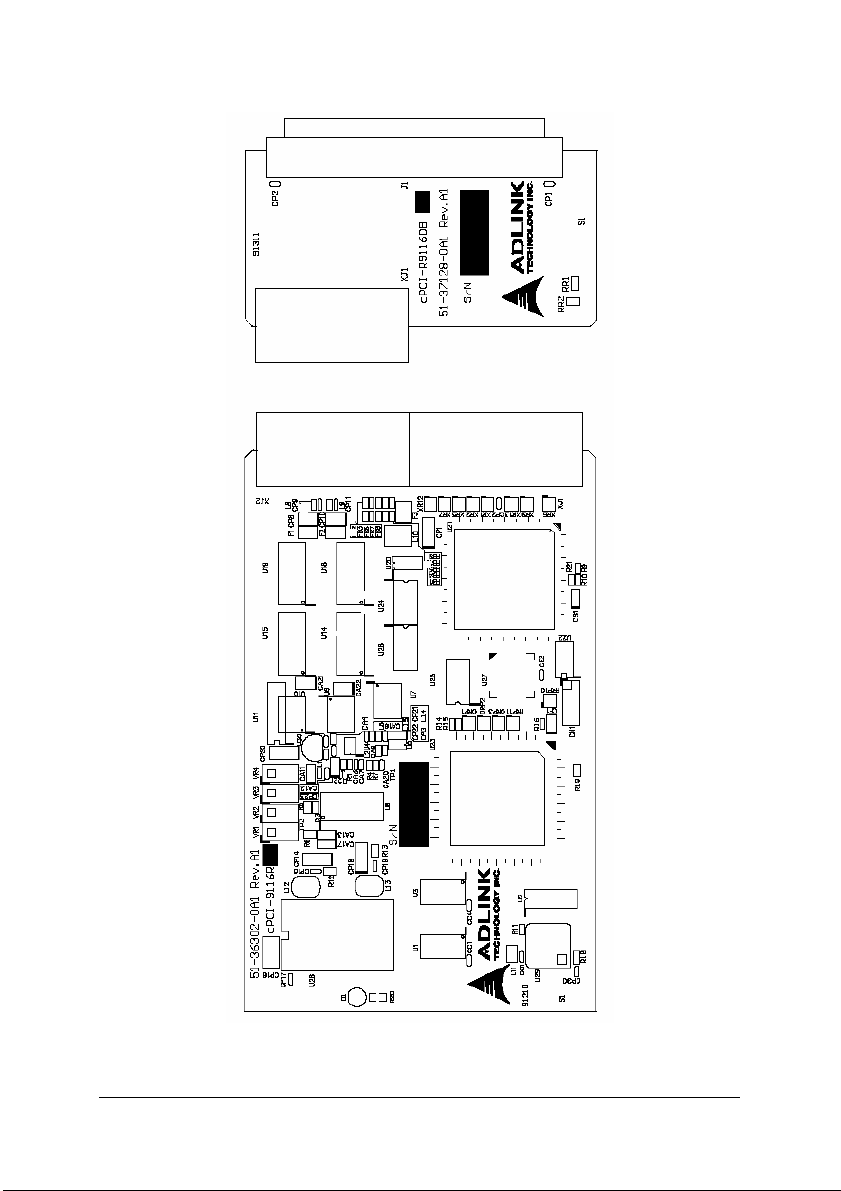
Figure 2: PCB Layout of cPCI-9116R and Rear I/O adaptor
Installation • 11
Page 22

2.4 PCI Configuration
1. Plug and Play:
As a plug and play component, the board requests an interrupt number via a
system call. The system BIOS responds with an interrupt assignment based on
the board information and on known system parameters. These system
parameters are determined by the installed drivers and the hardware load seen
by the system.
2. Configuration:
The board configuration is done on a board-by-boar d basis for all PCI form
factor boards on your system. Because configuration is controlled by the
system and software, so there is no jumpers for base-address, DMA, and
interrupt IRQ need to be set by the user.
The configuration is subject to change with every boot of the s ystem as new
boards are added or boards are removed. So, there is no idea what‘s going on
to be installed.
3. Trouble shooting:
If your system doesn’t boot or if you experience erratic operation with your PCI
board in place, it’s likely caused by an interrupt conflict (perhaps because you
incorrectly configured the BIOS setup). In general, the solution, once you
determine it is not a simple oversight, is to consult the BIOS documentation
that came with your system.
12 • Installation
Page 23
3
Signal Connections
This chapter describes the connectors of the 9116 series. The signal
connections between the 9116 series cards and external devices are also
outlined.
3.1 Connectors and Pin Assignment
The cPCI-9116 is equipped with one 100-pin SCSI-type connector (J1).
J1 is used for digital input/output, analog input, and timer/counter signals. The
pin assignment for the connector is illustrated in the Figure 3.1.
With the REAR I/O adaptor specifically designed for the cPCI-9116R, the
cPCI-9116R connector pin assignments are identical to that of the cPCI-9116.
The red LED positioned on the front panel is used as a power indicator.
Signal Connections • 13
Page 24
3.1.1 100-pin SCSI-type connector (J1)
U_CMMD 1 51 AGND
AIH0 AI0 2 52 AI32 AIL0
AIH1 AI1 3 53 AI33 AIL1
AIH2 AI2 4 54 AI34 AIL2
AIH3 AI3 5 55 AI35 AIL3
AIH4 AI4 6 56 AI36 AIL4
AIH5 AI5 7 57 AI37 AIL5
AIH6 AI6 8 58 AI38 AIL6
AIH7 AI7 9 59 AI39 AIL7
AIH8 AI8 10 60 AI40 AIL8
AIH9 AI9 11 61 AI41 AIL9
AIH10 AI10 12 62 AI42 AIL10
AIH11 AI11 13 63 AI43 AIL11
AIH12 AI12 14 64 AI44 AIL12
AIH13 AI13 15 65 AI45 AIL13
AIH14 AI14 16 66 AI46 AIL14
AIH15 AI15 17 67 AI47 AIL15
AIH16 AI16 18 68 AI48 AIL16
AIH17 AI17 19 69 AI49 AIL17
AIH18 AI18 20 70 AI50 AIL18
AIH19 AI19 21 71 AI51 AIL19
AIH20 AI20 22 72 AI52 AIL20
AIH21 AI21 23 73 AI53 AIL21
AIH22 AI22 24 74 AI54 AIL22
AIH23 AI23 25 75 AI55 AIL23
AIH24 AI24 26 76 AI56 AIL24
AIH25 AI25 27 77 AI57 AIL25
AIH26 AI26 28 78 AI58 AIL26
AIH27 AI27 29 79 AI59 AIL27
AIH28 AI28 30 80 AI60 AIL28
AIH29 AI29 31 81 AI61 AIL29
AIH30 AI30 32 82 AI62 AIL30
AIH31 AI31 33 83 AI63 AIL31
AGND 34 84 AGND
+15V out 35 85 -15V out
N/C 36 86 N/C
DI0 37 87 DO0
DI1 38 88 DO1
DI2 39 89 DO2
DI3 40 90 DO3
DI4 41 91 DO4
DI5 42 92 DO5
DI6 43 93 DO6
DI7 44 94 DO7
ExtTimeBase 45 95 N/C
ExtTrg 46 96 GP_TC_CLK
SSH_OUT 47 97 GP_TC_GATE
GP_TC_OUT 48 98 GP_TC_UPDN
+5V Out 49 99 +5V out
DGND 50 100 DGND
Figure 3: J1 Pin Assignments
14 • Signal Connections
Page 25
3.1.2 Legend of J1
Signal Name Definition
U_CMMD User Common Mode
AIn Analog Input Channel n (single-ended)
AIHn Analog High Input Channel n (differential)
AILn Analog Low Input Channel n (differential)
DIn Digital Input Signal Channel n
DOn Digital Output Signal Channel n
ExtTimeBase External Timebase Clock Input
ExtTrg External Digital Trigger Signal
SSH_OUT SSH Output Signal
GP_TC_CLK General Purpose Timer/Counter Clock Input
GP_TC_GATE General Purpose Timer/Counter Gate Input
GP_TC_UPDN
GP_TC_OUT General Purpose Timer/Counter Output
+5V OUT +5V Output
+15V OUT +15V Output
-15V OUT -15V Output
AGND Analog Ground
DGND Digital Ground
N/C No Connection
Purpose Timer/Counter Up/Down Control Input
(0:down, 1:up)
Table 1. Legend of J1 Connector
Signal Connections • 15
Page 26
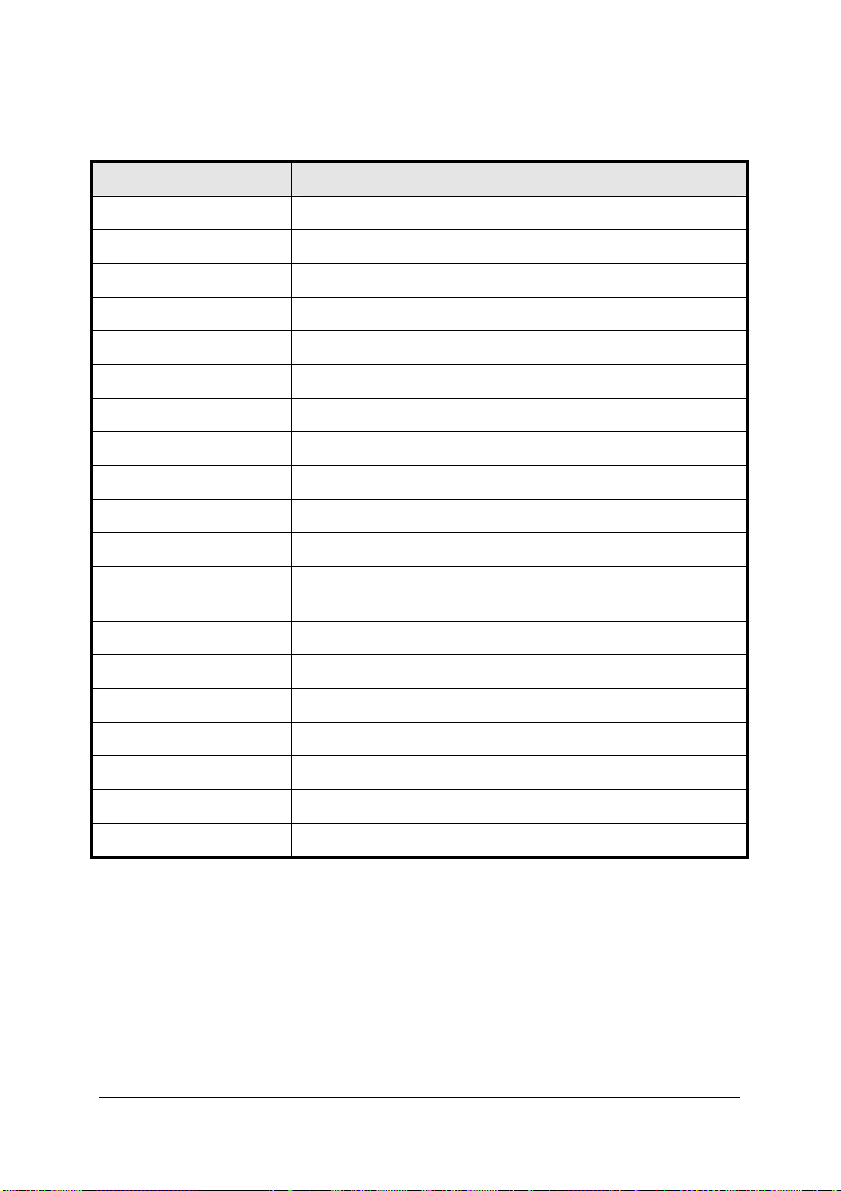
AInA
A
3.2 Analog Input Signal Connection
The 9116 series provides up to 64 single-ended or 32 differential analog input
channels. You can set and fill the Channel Gain Queue to get the desired
combination of the input signal types. The analog signals can be converted to
digital value by the A/D converter. To avoid ground loops and to obtain
accurate measurements from the A/D conversion, it is quite important to
understand the signal source type and how to choose the analog input modes:
Single-ended, Differential, or User Common Mode.
3.2.1 Types of signal sources
Floating Signal Sources
A floating signal source means it is not connected in any way to the buildings
ground system. A device with an isolated output is a floating signal sour ce,
such as optical isolator outputs, transformer outputs, and thermocouples
Ground-Referenced Signal Sources
A ground-referenced signal means it is connected in some way to the buildings
system. That is, the signal source is already connected to a common ground
point with respect to the 9116 card, assuming that the computer is plugged into
the same power system. Non- isolated outputs of instruments and devices that
plug into the buildings power system are ground-referenced signal sources.
3.2.2 Input Configurations
Single-ended Mode
In single-ended mode, all input signals are connected to g round provided by
the 9116 card. It is suitable for connections with floating signal sources. Figure
4 illustrates single-ended connection. Note that when more than t wo floating
sources are connected, these sources will be referenced to the same common
ground.
Floating
Signal
Source
V1
n = 0, ...,63
V2
J1
Input Multipexer
GND
Instrumentation
mplifier
-
To A/D
Converter
-
Figure 4: Single-ended Mode and Floating sources
16 • Signal Connections
Page 27

A
A
x
A
A
r
A
A
x
A
A
r
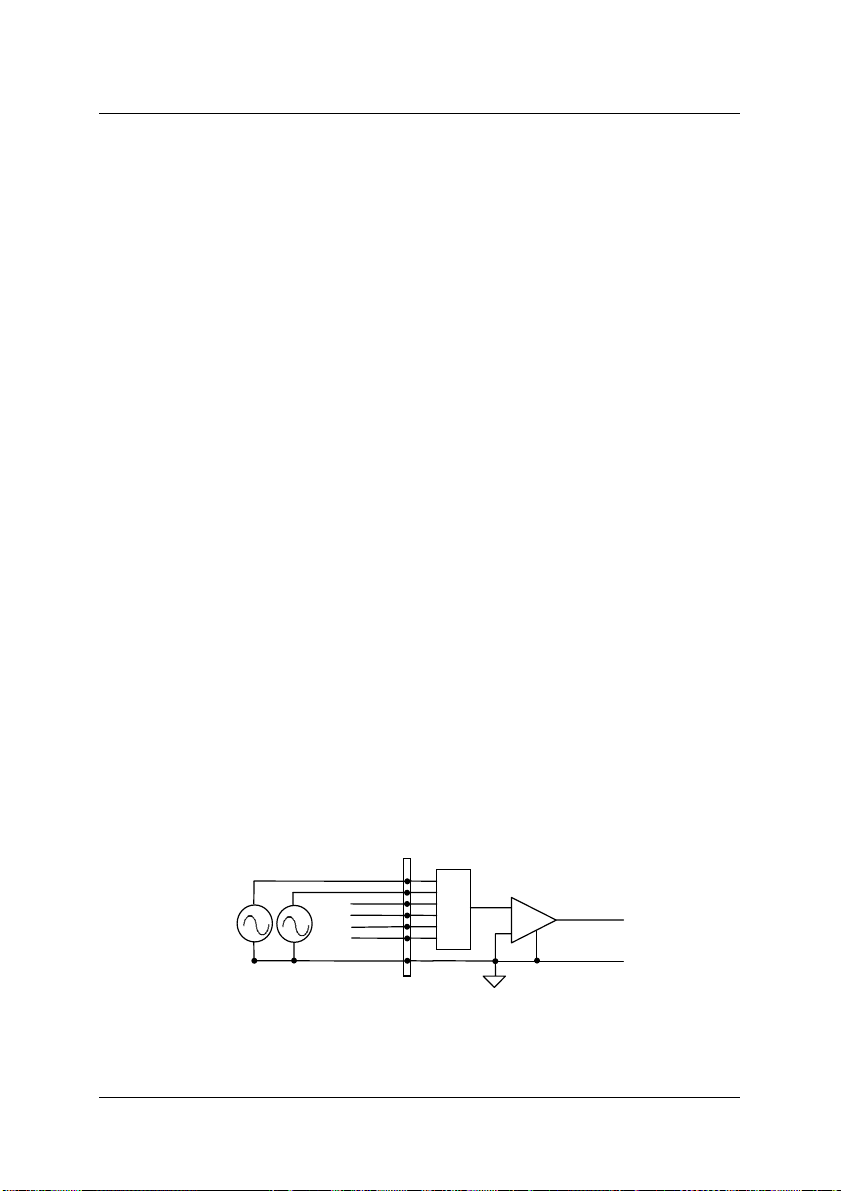
Differential input mode
The differential input mode provides two inputs that respon d to signal voltage
differences between them. If the signal source is ground- referenced, the
differential mode can be used for common-mode noise rejection. Figure 5
shows the connection of ground-referenced signal sources under different ial
input mode.
Ground
Referenced
Signal
Source
Commonmode noise &
Ground
potential
Vcm
= 0, ..., 31
Figure 5: Ground-referenced source a nd differential input
Fig 6 shows how to connect a floating signal source to the 9116 card in
differential input mode. For floating signal sources, a resistor is required on
each channel to provide a bias return path. The resistor value should be about
100 times the equivalent source impedance. If the source impedance is less
than 100ohms, simply connect the negative side of the signal to AGND as well
as the negative input of the Instrumentation Amplifier, without any resistors. In
differential input mode, less noise is coupled into the signal connections than in
single-ended mode.
Ground
Reference d
Signal
Source
= 0, ..., 31
IxH
IxL
IxH
IxL
In put Multipexer
+
-
GND
Inpu t Multipexer
+
-
Instrumentation
mplifie
To A /D
Converter
-
Instrumentation
mplifie
To A /D
Converter
-
GND
Figure 6: Floating source and differential input
Signal Connections • 17
Page 28
A
A
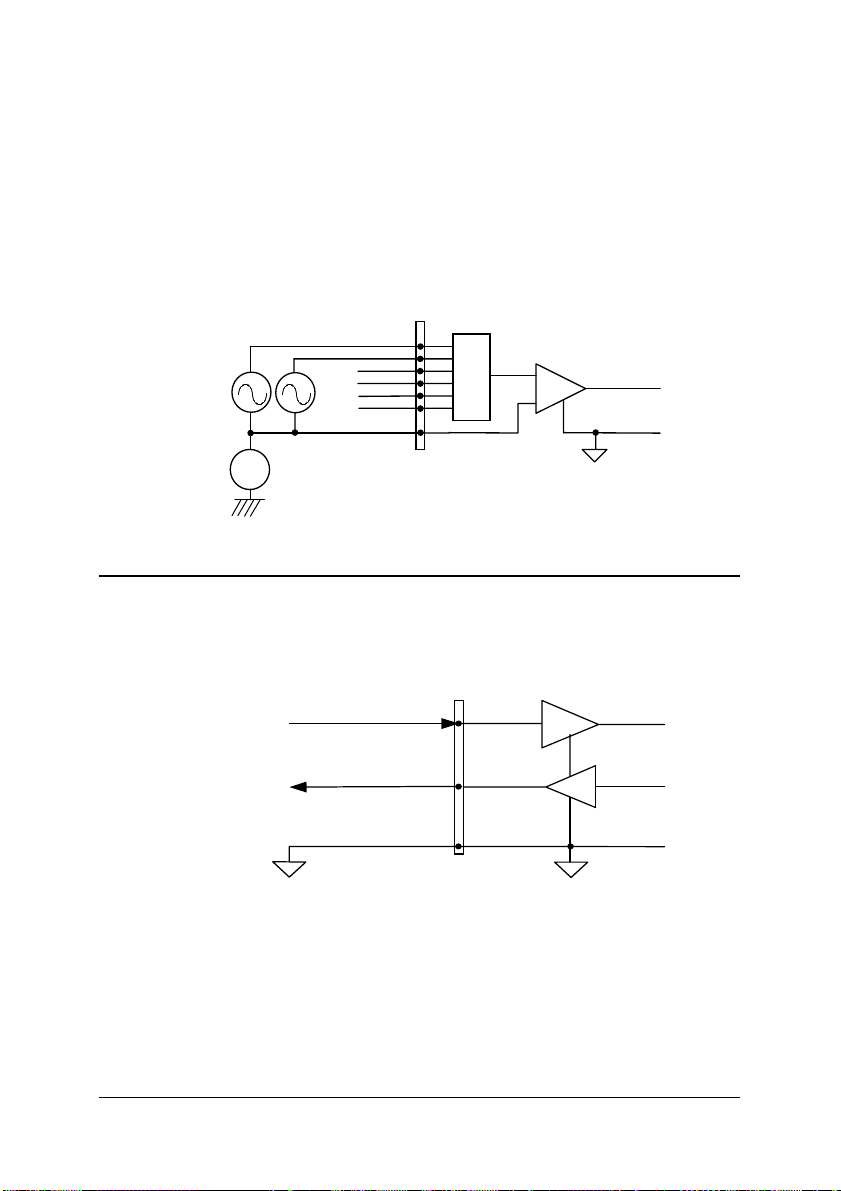
User Common Mode (U_CMMD)
To measure ground-referenced signal sources, which are connected to the
same ground point, you can connect the signals in a User-Common-Mode
(U_CMMD) configuration. Fig 7 illustrates the connections. The signal local
ground reference is connected to the negative input of the instrumentation
Amplifier, and the common-mode ground potential to signal ground. The
instrumentation amplifier will now reject the 9116 series ground.
In
U_CMMD
Input Multipexer
-
Instrumentation
mplifier
To A/D
-
Converter
GroundReferenced
Signal Source
Commonmode noise &
Ground
potential
V1
Vcm
V2
n = 0, ...,63
Figure 7: Ground-referenced source a nd User Common Mode connections
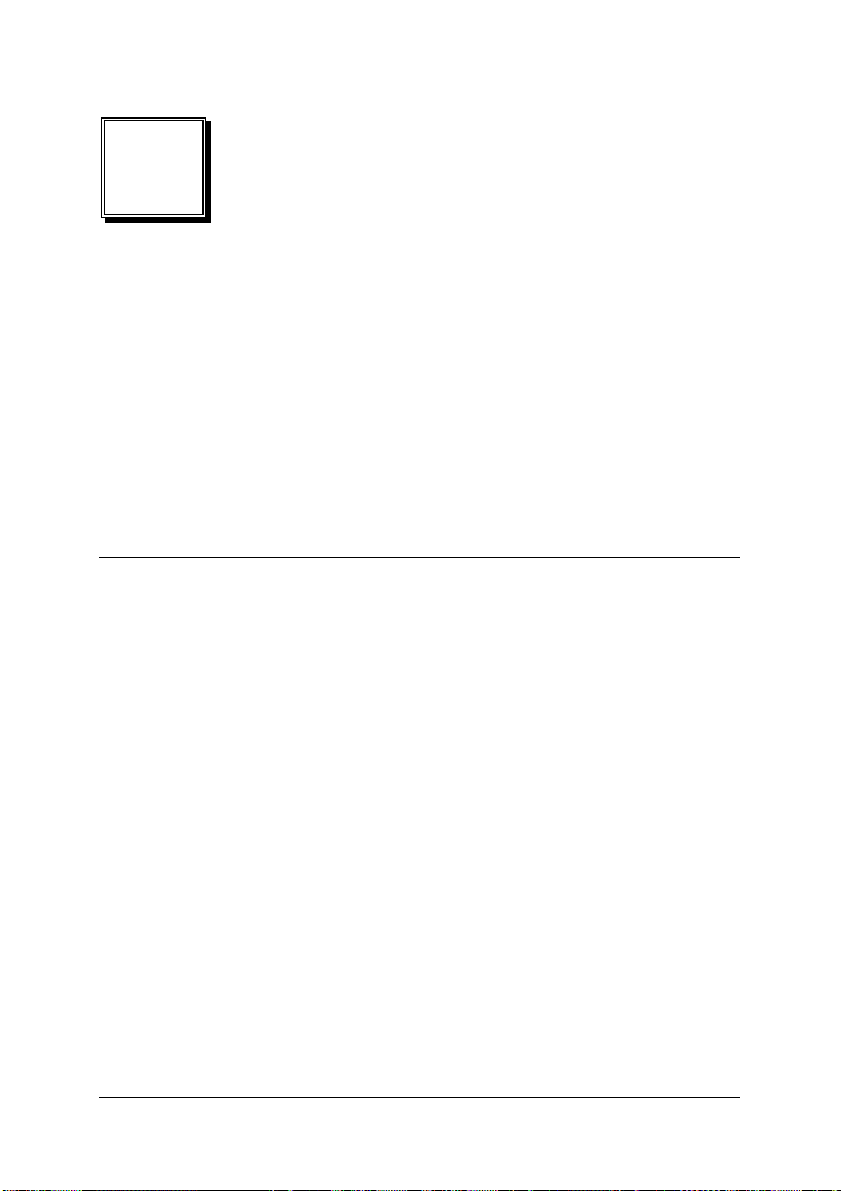
3.3 Digital I/O Connection
The 9116 series card provides 8 digital input and 8 digital output channels. The
digital I/O signals are fully TTL/DTL compatible. The details of the digital I/O
signal specification can be found in section 1.3.
74LS244
From TTL Signal
To TTL Devices
Digital Input(DI)
Digital Output(DO)
Digital GND(DGND)
74LS244
Figure 8: Digital I/O Connection
18 • Signal Connections
Page 29
4
Registers
The descriptions of the registers and structure of the cPCI-9116 are outlined in
this chapter. The information in this chapter will assist programmers, who wish
to handle the card with low-level programs.
In addition, the low level programming syntax is introduced. This information
can help beginners to operate the cPCI-9116 in the shortest possible time.
4.1 I/O Port Address
The 9116 series card functions as a 32-bit PCI master device to any master on
the PCI bus. It supports burst transfer to memory space by using 32-bit data.
All data read and write are based on 32-bit transactions. Table 2 shows the I/O
address of each register with respect to the base address. The function of each
register is also shown.
Registers • 19
Page 30
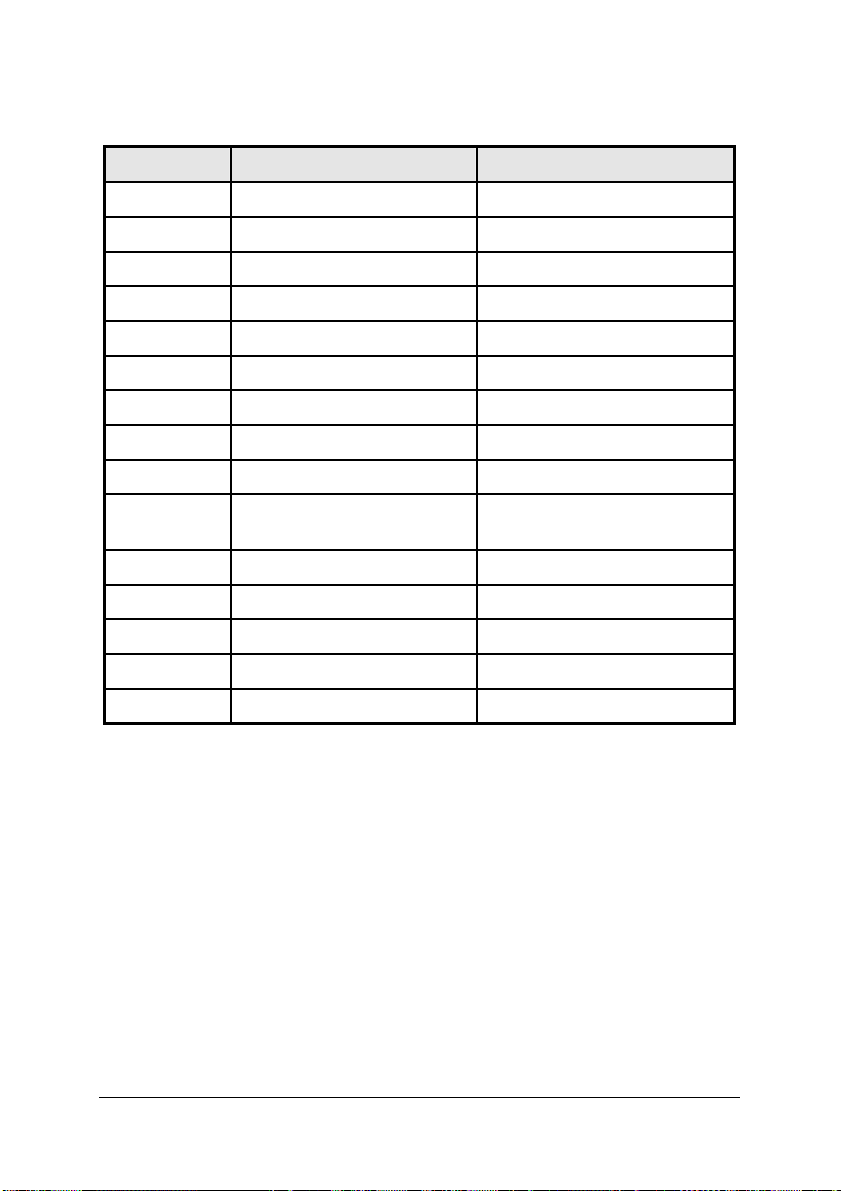
I/O Address Read Write
Base + 0x00 Scan Interval Counter Scan Interval Counter
Base + 0x04 Sample Interval Counter Sample Interval Counter
Base + 0x08 Scan Counter Scan Counter
Base + 0x0C DIV Counter DIV Counter
Base + 0x10 Delay1 Counter Delay1 Counter
Base + 0x14 M Counter M Counter
Base + 0x18 GP Counter/Timer 0 GP Counter/Timer 0
Base + 0x1C X X
Base + 0x20 X GP Counter/Timer Control Reg
Base + 0x24 A/D FIFO Data Reg
Base + 0x28 A/D and FIFO Status Reg. A/D and FIFO Control Reg.
Base + 0x2C X X
Base + 0x30 Digital IN Reg.(Dout) Digital OUT Reg.
Base + 0x34 X A/D Trigger Mode Reg.
Base + 0x38 Interrupt Reason Reg. Interrupt Control Reg.
Table 2. I/O Port Address
Config. Channel Gain Queue
Reg..
20 • Registers
Page 31

4.2 Internal Timer/Counter Register
The 9116 series card basically has 6 counters, which are responsible for the
scan timing of the analog input data acquisition. The 6 counters occupy 6 I/O
address locations in the 9116 card as shown below.
Address: BASE + 0 ~ BASE + 14
Attribute:
Data Format:
Base + 0x00 Scan Interval Count er Register (R/W) 24bit
Base + 0x04 Sample Interval Counter Reg ister (R/W) 16bit
Base + 0x08 Scan Counter Register (R/W ) 24bit
Base + 0x0C DIV Counter Register (R/W) 9bit
Base + 0x10 Delay1 Co unter Register (R/W) 16bit
Base + 0x14 M Counter Register (R/W) 16bit
SI_counter: Scan Interval counter
SI2_counter: Sample Interval counter
SC_counter: total Scan Count counter
DIV_counter: specify the number of samples per scan
DLY1_counter: Delay Interval counter (only used in delay trigger mode)
M_counter: specify the number of scans before a trigger (only used in
read / write
Table 3. Timer/Counter Register Address
pre-trigger and middle-trigger modes)
Registers • 21
Page 32

4.3 General Purpose Timer/Counter Register
One 16-bit, general-purpose timer/counter exists in the 9116 series card.
Writing to this register loads the initial count value into the gen eral-purpose
timer/counter. Reading from this register feedbacks the current count value of
the general-purpose timer/counter
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
BASE + 0x18
write / read
GP7 GP6 GP5 GP4 GP3 GP2 GP1 GP0
GP15 GP14 GP13 GP12 GP11 GP10 GP9 GP8
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 4. General Purpose Timer/Counter Register
4.4 General Purpose Timer/Counter Control Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
--- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
22 • Registers
BASE + 0x20
write only
Counter
en
Up
Down
Table 5. General Purpose Timer/Counter Control Register
Up
Down
src
Gate_sr
c
Clk_src --- MODE1 MODE0
Page 33

Counter en (bit7): GPTC0 count enable
1: enable GPTC0
0: disable GPTC0
UpDown (bit6): GPTC0’s up/down pin software control
1: Up counter
0: Down counter
UpDown src(bit5): GPTC0’s up/down pin selection bit
1: External input (Pin 98)
0: Software Control
Gate_src (bit4): GPTC0’s gate source
1: External Input (Pin 97)
0: gate controlled by setting the enable (bit7)
Clk_src (bit3): GPT C0’s clock source
1: External Input (Pin 96)
0: Internal Timebase
MODE1~MODE0 (bit1 ~ bit0): GPTC0’s Mode selection
MODE1 MODE0 Description
0 0 General Counter
0 1 Pulse Generation
1 0 X
1 1 X
Table 6. GPTC0’s Mode selection
Registers • 23
Page 34

4.5 A/D Data Registers
The digital converted data is 16-bits and is stored into 32-bit registers.
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
BASE +24
read
AD7 AD6 AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0
AD15 AD14 AD13 AD12 AD11 AD10 AD9 AD8
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Table 7. A/D Data Registers
AD15 ~ AD0: Analog to digital data. AD15 is the Most Significant Bit
(MSB). AD0 is the Least Significant Bit (LSB).
4.6 Channel Gain Queue Register
This register is used to fill the Channel Gain Queue. We recommend users use
our call function to avoid any possible errors from these settings.
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
24 • Registers
BASE + 0x24
write
:
EN3 EN2 EN1 EN0 HL_sel UNIP DIFF U_CMMD
--- --- Gain1 Gain0 CH3 CH2 CH1 CH0
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 8. Channel Gain Queue Register
Page 35

CH3 ~ CH0 (bit11~ bit8): Internal A/D Channel selection bits
EN3 ~ EN0 (bit7~ bit4): Multiplexer Enable selection bits
Gain1~Gain0 (bit13~bit12): Gain selection bits
Gain1 Gain0 Gain
0 0 1
0 1 2
1 0 4
1 1 8
Table 9. Gain Selection Bits
HL_sel(bit3): >31 channel selection (single ended)
1: when channel number is larger than 31
0: when channel number is smaller than or equal to 31
DIFF(bit1): Analog Input Signals Type
1: Differential
0: Single ended
UNIP(bit2): Analog Input Signals Polarity
1: Unipolar
0: Bipolar
U_CMMD(bit0): User Defined Common Mode Selection
1: User Defined Common Mode (Pin 1)
0: Local Ground of 9116 series
Registers • 25
Page 36

4.7 A/D & FIFO Control Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
DMA (Bit8): Write Only. Set for DMA transfer
SC_dis (Bit7): Write Only. Set to disable the SC counter
Clear Channel Gain Queue (Bit6): Write Only
Set done (Bit5): Write Only
Clear DFIFO(Bit4) : Write Only
Clear the Data FIFO:
Clear Trg_det(Bit3) : Write 1 to clear
BASE + 28
Write
Clear
SC_dis
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- DMA
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Channel
Gain
Queue
Table 10. A/D & FIFO Control Register
Clear the Channel Gain Queue
0: no effect on the Channel Gain Queue
1: clear the Channel Gain Queue
0: indicate the Channel Gain Queue is not ready
1: indicate the Channel Gain Queue is OK
0: no effect on Data FIFO
1: clear the Data FIFO
Set
done
Clear
DFIFO
Clear
Trg_det
Clear
SC_TC
Clear
ADOR
Clear
ADOS
26 • Registers
Page 37

Write 1 to clear the trigger status:
0: no effect
1: clear trigger detect status
Clear SC_TC(Bit2) : Write 1 to clear
Write 1 to clear Scan Counter Terminal Count status
0: no effect
1: clear the SC_TC status
Clear ADOR(Bit1) : Write 1 to clear
Write 1 to clear the A/D Overrun Status
0: no effect
1: clear the A/D Overrun status
Clear ADOS(Bit0) : Write 1 to clear
Write 1 to clear the A/D Over Speed Status:
0: no effect
1: clear the A/D Over-Speed status
4.8 A/D & FIFO Status Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
BASE + 28
read
ACQ Full HFull Empty Trg_det SC_TC ADOR ADOS
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 11. A/D & FIFO Status Register
Registers • 27
Page 38

ACQ (Bit7): Read Only, set when acquisition is in progress.
Full (Bit6): Read Only A/D FIFO Full status (Fatal Error!)
0: FIFO Full
1: FIFO not Full
HFull(Bit5): Read only A/D FIFO Half Full status
0: FIFO Half Full
1: FIFO not Half Full
Empty (Bit4): Read Only A/D FIFO Empty status
0: FIFO Empty
1: FIFO not Empty
Trg_det (Bit3): Read/ Write 1 to clear External Digital Trigger Status
1: External Digital Trigger
0: No External Digital Trigger
SC_TC(Bit2): Read/ Write 1 to clear Scan Counter Terminal Count Status
1: Scan Counter counts to 0
0: Scan Counter not completed
ADOR(Bit1): Read/ Write 1 to clear A/D Overrun Status (Fatal Error !)
1: A/D Overrun
0: A/D not Overrun
ADOS(Bit0): Read/ Write 1 to clear A/D Over Speed Status (Warning !)
1: A/D Over Speed
0: A/D not Over Speed
28 • Registers
Page 39

4.9 Digital I/O register
There are 8 digital input and 8 digital output channels provided by the 9116
series cards. The address Base + 30 is used to access digital inputs and
control digital outputs.
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
BASE +30
read
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
DO7 DO6 DO5 DO4 DO3 DO2 DO1 DO0
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 12. Digital I/O register (Read)
BASE + 30
write
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DO7 DO6 DO5 DO4 DO3 DO2 DO1 DO0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 13. Digital I/O register (Write)
Registers • 29
Page 40

4.10 A/D Trigger Mode Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
BASE + 0x34
write only
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Retrig DLYSRC
Time
Base
TrgP MODE2 MODE1 MODE0
---
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
--- --- --- --- --- softconv ACQ_EN M_enable
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 14. A/D Trigger Mode Register
softconv (bit10): ADC direct conv ersion control
1: generate 1 convert pulse
0: no effect
ACQ_EN (bit9): Acquisition enable bit
1: enable the acquisition timing
0: disable the acquisition timing
M_enable (bit8): M counter enable bit
1: ignore trigger signals before M counter reaches 0
0: accept the trigger signal anytime
Retrig (bit7): Re-triggerability in an acquisition
1: Re-triggerable
0: trigger only once
DLY SRC (bit6): Delay time unit in delay trigger mode
1: delay in sampling rate (SI2)
0: delay in Timebase
30 • Registers
Page 41

TimeBase(bit5) : The Timebase Selection of 9116 series
1: External Timebase
0: Internal Timebase (24 MHz)
TrgP (bit4): The T r igger polarity selection bit
1: Negative Edge Trigger
0: Positive Edge Trigger
MODE2 ~ 0(bit3 ~ bit1): Trigger Mode Selection Bits
MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 Description
0 0 0 Software Trigger
0 0 1 Post Trigger
0 1 0 Delay Trigger
0 1 1 Pre Trigger
1 0 0 Middle Trigger
Table 15. Trigger Mode Selection Bits
4.11 Interrupt Control Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
--- --- --- Clr_Timer Clr_STTC Clr_Hfull Clr_DTrg Clr_EOC
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
--- --- --- Timer_en STTC_en Hfull_en DTrg_en EOC_en
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Timer_en (bit12): General Purpos e Timer Interrupt Enable Control
BASE + 0x38
write
Table 16. Interrupt Control Register
1: Enable
0: Disable
Registers • 31
Page 42

SCTC_en (bit11): Trigger Complete Interrupt Enable Control
1: Enable
0: Disable
Hfull_en (bit10): A/D FIFO Half Full Interrupt Enable Control
1: Enable
0: Disable
DTrg_en (bit9): Extern al Digital Trigger Interrupt Enable Control
1: Enable
0: Disable
EOC_en (bit8): End of conversion Interrupt Enable Control
1: Enable
0: Disable
Clr_Timer (bit4): writ e 1 to clear the GPTC Interrupt status
1: clear interrupt from the GPTC
0: no effect
Clr_SCTC (bit3): write 1 to clear the SCTC Interrupt
1: clear the interrupt on terminal count of the Scan counter
0: no effect
Clr_HFull (bit2): write 1 to clear the data FIFO half full interrupt
1: clear the interrupt on the data FIFO half full status
0: no effect
Clr_DTrg (bit1): write 1 to clear the Digital Trigger Interrupt
1: clear the interrupt when trigger happens
0: no effect
Clr_EOC (bit0): write 1 to clear the End of Conversion Interrupt
1: clear the interrupt when EOC
0: no effect
32 • Registers
Page 43
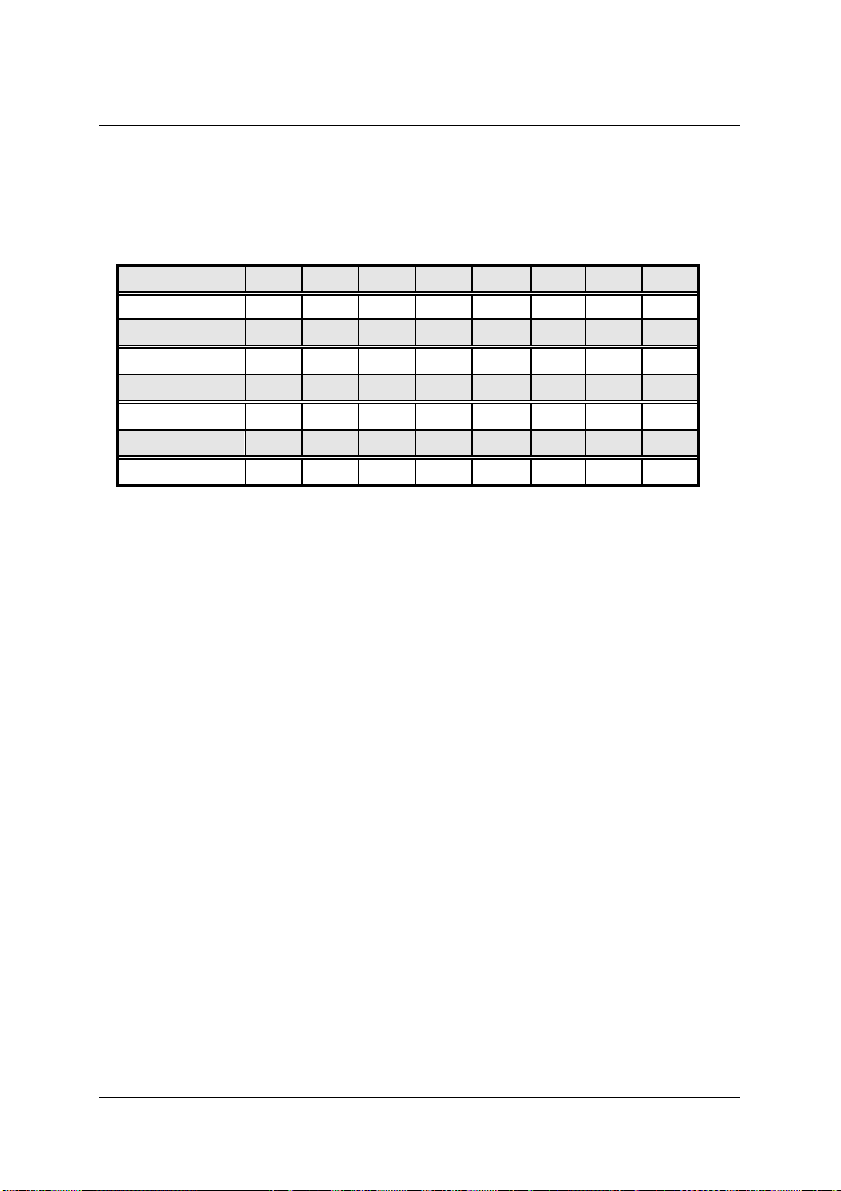
4.12 Interrupt Status Register
Address:
Attribute:
Data Format:
Timer (bit4): GPTC generated Interrupt status
SCTC(bit3): Scan Counter reach Terminal Count Interrupt status
HFull (bit2): data FIFO Half Full Interrupt
DTrg (bit1): Digital Trigger Interrupt status
EOC (bit0): End of Conversion Interrupt status
BASE + 0x38
read
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
--- --- --- Timer STTC Hfull DTrg EOC
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
--- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Table 17. Interrupt Status Register
1: Interrupt Occurs
0: Interrupt not Occur
1: Interrupt Occurs
0: Interrupt not Occur
1: Interrupt Occurs
0: Interrupt not Occur
1: Interrupt Occur
0: Interrupt not Occur
1: Interrupt Occurs
0: Interrupt not Occur
Registers • 33
Page 44

5
Operation Theory
The operation theory of the functions on the 9116 series is described in this
chapter. The functions include the A/D conversion, Digital I/O and General
Purpose Counter / Timer. The operation theory can help you better understand
how to configure and program the 9116 series card.
5.1 A/D Conversion
5.1.1 A/D Conversion Procedure
When using an A/D converter, users should beware of the properties of the
signal to be measured. Users can decide which channel to use and where to
connect the signals to the card. Please refer to 3.2 for signal connections. In
addition, users should define and control the A/D signal configurations,
including channels, gains, and A/D signal types.
The A/D acquisition is initiated by a trigger source; users must decide how to
trigger the A/D conversion. The data acquisition will start when a trigger
condition is met.
After the end of the A/D conversion, the A/D data is buffered in a Data FIFO.
The A/D data is then transferred into PC's memory for further processing.
There are two acquisition modes: Software Polling and Scan acquisition. They
will be described separately in the following section, including the timing, signal
source control, trigger mode, and transfer method.
34 • Operation Theory
Page 45

5.1.2 Software conversion with polling data transfer acquisition
mode (Software Polling)
This is the easiest way to acquire a single A/D data. The A/D converter starts a
conversion when the user writes 1 into bit10 of the A/D trigger mode register
(BASE+34). After the software initializes the A/D conversion, the software polls
the FIFO Empty status (bit4) in the A/D & FIFO Status register (BASE+28)
until it changes to active low logic.
If the Data FIFO is empty before an A/D conversion starts, the Empty bit will be
high. After the A/D conversion is completed, the A/D data is written to the Data
FIFO immediately, thus the Empty becomes low. You can consider the Empty
bit as a flag to indicate the converted data ready status. That is, a low Empty
bit meaning the data is ready. The A/D data is now ready to be transferred to
host memory from the FIFO.
This method is suitable for applications that needs to process AD data in r eal
time. Under this mode, the timing of the A/D conversion is fully controlled by
the software. However, it is difficult to control a fixed A/D conversion rate
unless another timer interrupt service routine is used to generate a fixed
conversion rate trigger.
ADLINK’s software driver provides an integral function to acquire a single data
(That is, it will start an A/D conversion, then poll the Empty flag and read the
data back when the data is ready). We also provide individual functions to
allow users to start an A/D conversion only. Users must read it back from the
A/D data register (BASE+24) by themselves. This method makes it possible to
read A/D converted data without polling. The conversion and acquisition time
of the ADC does not exceed 4μs. Hence, after software conversion, the
software need only wait for a maximum of 4μs to read the A/D Data Register
without polling.
Operation Theory • 35
Page 46

5.1.2.1 Specifying Channels, Gains, and input configurations in the
Channel Gain Queue
In both Software Polling and programmable scan acquisition mode, the
channel, gain, and input configuration (single-end, differential, and U_CMMD),
where you want to acquire samples from, can be specified in the
Gain Queue
any order. Therefore, you can control the channel order from which data is
acquired with different gain and input configuration for each channel. The
maximum number of entries you can set is 512 channels. The channel order of
acquisition is the same as the order you set in the Channel Gain Queue. When
the specified channels are sampled from the beginning to the end in the
Channel Gain Queue, the channels in the Channel Gain Queue will be
sampled again until the specified number of samples has been acquired.
. You can set the channel number in the Channel Gain Queue in
Channel
5.1.3 Programmable scan acquisition mode
5.1.3.1 Scan Timing and Procedure
It's recommended that this mode be used, if your application needs a fixed and
precise A/D sampling rate. You can accurately program the period between
conversions of each individual channel in the scan and the period bet ween
conversions of the entire scan. There are 4 counters, which need to be
specified:
SI_counter(24 bit): Specify the Scan Interval = SI_counter / Timebase
SI2_counter(16 bit): Specify the data Sampling Interval =
SI2_counter/Timebase
SC_counter(24 bit): Specify Scan Count Counter after trigger
DIV_counter(9 bit): Specify the number of samples per scan
The acquisition timing and the meaning of the 4 counters are illustrated in
figure 9.
36 • Operation Theory
Page 47

A
A
(
)(
)
Timebase clock source
In scan acquisition mode, all the A/D conversions start on the output of
counters, which use
specify the Timebase to be either an internal clock source (on board 24MHz) or
an external clock input on pin 45 of J1. The external clock is useful when you
want to acquire data at rates not available with the internal A/D sample clock.
The external clock source must generate TTL-compatible continuous cloc ks,
and the maximum frequency is 24MHz while the minimum is 1MHz.
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
SSH_OUT
cquisition_in_progress
Timebase
as the clock source. With the software you can
3 Scans, 4 Samples per scan
(SC_Counter=3, DIV_Counter=4)
( channel sequences are specified in Channel Gain Queue)
Ch2
Ch3
Ch1
Ch0
Ch2
Ch3
Ch1
Ch0
pin47
Ch2
Ch3
Ch1
Ch0
Sam pling Inte rva l t=
SI2_COUNTER/TimeBase
Scan In te rva l T =
SI_COUNTER/TimeBase
Figure 9: Scan Timing
In the scan acquisition mode, the channel, gain, and input configurations
(single-end, differential, or U_CMMD) must be specified in the hardware
Channel Gain Queue
, please refer to 5.1.3.2 for more details.
There are 5 trigger modes to start the scan acquisition, please refer to 5.1.3.3
details. The data transfer modes will be discussed in 5.1.3.4.
Operation Theory • 37
Page 48

Note:
1. The maximum A/D sampling rate is 250kHz. Therefore, SI2_counter can’t
be smaller than 96 while using the internal Timebase.
2. The SI_counter is a 24-bit counter and the SI2_counter is a 16-bit counter.
Therefore, the maximum scan interval while using the internal Timebase =
24
/24M s = 0.699s, and the maximum sampling interval between 2
2
channels while using the internal Timebase = 2
3. T he scan interval can’t be smaller than the product of the data sampling
interval and the DIV_counter value. The relationship can be represented
as: SI_counter>=SI2_counter*DIV_counter.
Scan with SSH
You can send the SSH_OUT signal on pin 47 of J1 to an external S&H circuits
to sample and hold all signals if you want to simultaneously sample all
channels in a scan, as illustrated in fig 9.
Note: The ‘SSH_OUT’ signal is sent to external S&H circuits to hold the analog
signal. Users must implement external S&H circuits on their own to
carry out the S&H function. There are no on-board S&H circuits.
5.1.3.2 Specifying Channels, Gains, and input configurations in the
Channel Gain Queue
Like software polling acquisition mode, the channel, gain, and input
configurations (single-end, differential, and U_CMMD) must also be specified
in the hardware
Channel Gain Queue
under scan acquisition mode. Please
refer to 5.1.2.1 for details. Note that in scan acquisition mode, the number of
entries in the Channel Gain Queue is normally equivalent to the value of
DIV_counter (that is, the numbers of samples per scan).
Example:
Set
SI2_counter = 240
SI_counter = 960
SC_counter = 3
DIV_counter = 4
Timebase = Internal clock source
Channel entries in the Channel Gain Queue: ch1, ch2, ch0, ch2
16
/24M s = 2.73ms.
38 • Operation Theory
Page 49

Then
Acquisition sequence of channels: 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 0, 2.
Sampling Interval = 240/24M s = 10 us
Scan Interval = 960/24M s = 40 us
Equivalent sampling rate of ch0, ch1: 25kHz
Equivalent sampling rate of ch2: 50kHz
5.1.3.3 Trigger Modes
There are 5 trigger modes (software-trigger, pre-trigger, post-trigger,
middle-trigger, and delay-trigger) to start the data acquisition described in
5.3.1.1. All but software trigger are external digital triggers. An external digital
trigger event occurs when a rising edge or a falling edge (software
programmable) of a digital signal is detected on pin 46 of J1. They are
described as follows.
Software-Trigger Acquisition
This trigger mode does not need any external trigger source. The data
acquisition starts right after you execute the specified function calls to begin
the operation. The scan timing is the same as fig 9. The total acquired data
length = DIV_counter*SC_counter.
Pre-Trigger Acquisition
Use pre-trigger acquisition in applications where you want to collect data
before an external trigger event. The A/D starts when you execute the
specified function calls to begin the operation, and it stops when the external
trigger event occurs. Users must program the value M in the
to specify the amount of stored scans of data before the trigger event. If the
external trigger occurs after M scans of data are converted, the program only
stores the last M scans of data, as illustrated in fig 10, where M_counter = M =3,
DIV_counter =4, SC_counter = 0. The total stored amount of data =
DIV_counter *M_counter =12.
M_counter
(16bit)
Operation Theory • 39
Page 50

A
A
Aq
A
A
A
Aq
A
(M_counter = M = 3, DIV_counter=4, SC_counter=0)
ExtTrg(pin4 6)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(
SSH_OUT
cquisition_in_progress
)(pin47)
uired data
Operation start
cquired & stored data
(M scans)
Figure 10: Pre-trigger (trigger occurs after M scans)
Note: If an external trigger event occurs when a scan is in progress, the data
acquisition won’t stop until this scan completes, and the stored M scans
of data include the last scan. Therefore, the first stored data will al ways
be the first channel entry of a scan (that is, the first channel entry in the
Channel Gain Queue if the number of entries in the Channel Gain
Queue is equivalent to the value of DIV_counter), no matter when the
trigger signal occurs, as illustrated in Fig 11, where M_counter = M =3,
DIV_counter = 4, SC_counter = 0.
(M_counter = M = 3, DIV_counter =4, SC_counter=0)
ExtTrg(pin46)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(SSH_OUT)(pin47)
cquisition_in_progress
Operation start
uired data
cquired & stored data
(M scans)
Trigger occurs
Data acquisition
won’t stop u ntil a
scan completes
Figure 11: Pre-trigger (trigger with scan is in progress)
40 • Operation Theory
Page 51

A
A
A
When an external trigger signal occurs before the first M scans of data are
converted, the amount of stored data could be fewer than the originally
specified amount of DIV_counter * M_counter, as illustrated in fig 12. This
situation can be avoided by setting
M_enable.
trigger signal will be ignored until the first M scans of data are converted, and it
assures user of obtaining M scans of data under pre-trigger mode, as
illustrated in fig 13. However, if
M_enable
is set to 0, the trigger signal will be
accepted in any time, as illustrated in fig 12. Note that the total amount of
stored data is still always a multiple of DIV_counter (number of samples per
scan) because the data acquisition won’t stop until a scan is completed.
(M_Counter = M = 3 , DIV_Counter=4, SC_Counter=0)
ExtTrg(pin46)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(SSH_OUT)(pin47)
cquisition_in_progress
cquired & stored data
(2 scans)
Operation start
Figure 12: Pre-trigger with M_enable = 0 (trigger occurs before M scans)
M_enable
If
is set to 1, the
Operation Theory • 41
Page 52

A
A
Aq
A
(M_counter = M = 3, DIV_counter=4, SC_counter=0)
ExtTrg(pin46)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(
SSH_OUT
cquisition_in_progress
)(pin47)
The first M scans
Trigger signals which occur in the shadow
region(the first M scans) will be ignored
uired data
Operation start
cquired & stored data
(M scans)
Figure 13: Pre-trigger with M_enable = 1
Note: The SC_counter must be set to 0 in pre-trigger acquisition mode.
Middle-Trigger Acquisition
Use middle-trigger acquisition in applications where yo u want to collect data
before and after an external trigger event. The number of scans stored before
the trigger is specified in M_counter, while the number of scans after the trigger
is specified in SC_counter.
Like pre-trigger mode, the number of stored data can be less than the specified
amount of data (DIV_counter *(M_counter+SC_counter)) if an external trigger
occurs before M scans of data is converted. The M_enable bit in middle-trigger
mode takes the same effect as in pre-trigger mode. If M_enable is set to 1, the
tigger signal will be ignored until the first M scans of data are converted, this
assures user of obtaining M+N scans of data under middle-trigger mode.
However, if M_enable is set to 0, the trigger signal will be accepted at any time.
Fig 14 shows the acquisition timing with M_enable=1.
42 • Operation Theory
Page 53

A
A
Aq
A
(M_ Counter=M =3, DIV_ Coun ter=4, SC_C ounter=N=1 )
ExtTrg(pin46)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(
SSH_OUT
cquisition_in_progress
)(pin47)
The first M scans
Trigger signals which occur in the shadow
region(the first M scans) will be ignored
uired data
Operation start
M scans before
trigger
cquired & stored data
(M+N scans)
N scans
after trigger
Figure 14: Middle trigger with M_enable = 1
If an external trigger event occurs when a scan is in progress, the stored N
scans of data would include this scan.
be the first channel entry of a scan,
And the first stored data will always
as illustrated in Fig 15.
Operation Theory • 43
Page 54

A
A
Acq
A
A
A
A
ExtTrg(pin46)
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(SSH_OUT)(pin47)
cquisition_in_progress
(M_Counter=M=2, DIV_C ounter=4, SC_Co unter=N=2)
Trigger occurs when a scan is in progress
uired data
Operation start
M scans before
trigger
(M+N scans)
cquired & stored data
N scans
after trigger
Figure 15: Middle trigger (trigger with scan is in progress)
Post-Trigger Acquisition
Use post-trigger acquisition in applications where you want to collect data after
an external trigger event. The number of scans after the trigger is specified in
SC_counter, as illustrated in fig 16. The total acquired data length =
DIV_counter *SC_counter.
(DIV_Counter=4, SC_Counter=3)
ExtTrg
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(SSH_OUT)
cquisition_in_progress
cquired & stored data
(3 scans)
Operation start
Figure 16: Post trigger
44 • Operation Theory
Page 55

A
A
A
Delay Trigger Acquisition
Use delay trigger acquisition in applications where you want to delay the data
collection after the occurrence of a specified trigger event. The delay time is
controlled by the value, which is pre-loaded in the
counter counts down on the rising edge of Delay_counter clock source after
the trigger condition is met. The clock source can be software program med
either Timebase clock (24MHz) or A/D sampling clock (Timebase
/SI2_counter). When the count reaches 0, the counter stops and 9116 c ard
starts to acquire data. The total acquired data length = DIV_counter *
SC_counter.
(DIV_Counter=4, SC_Counter=3)
ExtTrg
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(
SSH_OUT
cquisition_in_progress
)
Delay_counter
(16bit). The
Delay until
Delay_Counter
reaches 0
Operation start
cquired & stored data
(3 scans)
Figure 17: Delay trigger
Note: When the Delay_counter clock source is set to Timebase, the maximum
delay time = 216/24M s = 2.73ms, and when the source is set to A/D
sampling clock, the maximum delay time = 2
16
* SI2_counter / 24M).
Operation Theory • 45
Page 56

A
A
A
Post-Trigger or Delay-trigger Acquisition with re-trigger
Use post-trigger or delay-trigger acquisition with re-trigger function in
applications where you want to collect data after several external trigger events.
The number of scans after each trigger is specified in SC_count er, and users
could program
illustrates an example. In this example, 2 scans of data is acquired after the
first trigger signal, then the board waits for the re-trigger signal (re-trigger
signals which occur before the first 2 scans of data is acqu ired will be ignored).
When the re-trigger signal occurs, the board scans 2 more scans of data. The
process repeats until the specified amount of re-trigger signals ar e detected.
The total acquired data length = DIV_counter * SC_counter * Retrig_no.
ExtTrg
Scan_start
D_conversion
Scan_in_progress
(SSH_OUT)
cquisition_in_progress
Retrig_no
(DIV_Counter=4, SC_Counter=2, retrig_no=3)
Operation start
to specify the number of re-triggers. Fig 18
cquired & stored data
(6 scans)
Figure 18: Post trigger with re-trigger
46 • Operation Theory
Page 57

5.1.4 A/D Data Transfer Modes
After the end of the A/D conversion, A/D data are buffered into the
memory. The FIFO size on the 9116 series card is 1024 (1K) words. If the
sampling rate is 10 KHz, the FIFO can buffer 102.4 ms of a nalog signal . Aft er
the FIFO is full, any data after this time will be lost.
The data must be transferred to the host memory after the data is ready and
before the FIFO is full. In scan acquisition mode, there are 3 data t ransfer
modes that can be used. They are described below.
EOC Interrupt Transfer
The 9116 series card provides traditional hardware End-Of-Conversion (EOC)
interrupt capability. Under this mode, an interrupt signal is generated when the
A/D conversion has ended and the data is ready to be read into the Data FIFO.
The hardware interrupt will be asserted and its corresponding ISR (I nterrupt
Service Routine) will be invoked and executed. The ISR program can read the
converted data. This method is suitable for data processing applications under
real-time and fixed sampling rate.
FIFO Half-Full Interrupt Transfer
Sometimes, the application does not need real-time processing, cause the
foreground program is busy polling the FIFO data. The FIFO half -full inter rupt
transfer mode is useful for the situation mentioned above.
Under this mode, an interrupt signal is generated when FIFO becomes half-full.
It means that there are 512 words of data in the FIFO ready f or transfer. The
ISR can read the whole block of data when the interrupt occurs. A “block is 512
words long.
Note: In the current version, EOC & FIFO half-full interrupt transfer mode
doesn’t support pre-trigger and middle-trigger mode data acquisition.
Users must use DMA transfer to work with pre-trigger or middle-trigger
data acquisition.
Data FIFO
Operation Theory • 47
Page 58

DMA Transfer
PCI bus-mastering DMA is necessary for high speed DAQ in order to utilize the
maximum PCI bandwidth. The bus-mastering controller, which is built-in into
the AMCC-5933 PCI controller, controls the PCI bus when it becomes the
master on the bus. Bus mastering reduces the size of the on-board memor y
and reduces the CPU loading because data is directly transferred to the
computer’s memory without host CPU intervention.
Bus-mastering DMA provides the fastest data transfer rates on PCI-bus. Once
the analog input operation starts, control returns to your program. The
hardware temporarily stores the acquired data in the on board Data FIFO and
then transfers the data to a user-defined DMA buffer memory in the computer.
Note that even when the acquired data leng th is less than t he Data FIFO, the
AD data will not held in the Data FIFO but directly transferred to the host
memory by bus-mastering DMA.
The DMA transfer mode is very complex to program. We recommend usi ng a
high-level program library to configure this card. If you want to program the
software, which can handle DMA bus master data transf er, please refer to
information about the PCI controller at www.amcc.com.
Note: In DMA transfer mode, the maximum acquired data length in one
acquisition can be up to 64M byte s (32M samples), which is the limit of the
PCI controller. However, the memory that you allocate f or data transfer
must be continuous.
5.2 Digital Input and Output
To program the digital I/O operation is fairly st raightforward. The digital input
(DI) operation is to read data from its corresponding registers, and the digital
output (DO) operation is to write data to its corresponding registers. The digital
I/O registers
reading the DI port. Note that the DIO data channel can only be read or written
to, in the form of 16-bit blocks. It is impossible to access individual bits.
48 • Operation Theory
‘
formats are shown in section 4.9. The DO can be read back when
Page 59

5.3 General Purpose Timer/Counter Operation
An independent 16-bit up/down timer/counter is designed in the FPGA for user
applications. Fig 19 shows a simplified model of the timer/counter on the 9116
series card. It has the following features:
CPCI-9116
Controller
Initial
Count
load
Mode
control
Counter
D0
Count
read back
CLK(pin96)
Gate(pin97)
D15Q0Q15
C
O
G
UP/DOWN(pin98)
OUT(pin48)
Figure 19: General-purpose Timer/Counter model
Count up/Count down controlled by hardware or software
•
(low or 0: counts down, high or 1: counts up)
Programmable counter CLK source selection (Internal
•
24MHz or External CLK input up to 20MHz)
Programmable Gate selection (Internal or External. For
•
Internal control, you can disable counting only by software. For
External gate control, either software or setting Gat e = low on
pin 97 of J1 disables the counting)
Initial Count can be loaded from software
•
Current count value can be read with software without
•
affecting circuit operation
Two programmable timer modes are provided:
•
Operation Theory • 49
Page 60

Mode 0: Interrupt on Terminal Count
Mode 0 is typically used for event counting, as illustrated in fig 20. After the
initial count is written, OUT is initially low, and will remain low until the Counter
counts to zero. OUT then goes high and will remain high until a new count is
written into the Counter.
Mode 0, Initial count=3, Count down
Gate
CLK
Count value
OUT
Mode 1: Rate Generator
This mode operates like a divide-by-N counter, as illustrated in fig 21. After the
initial count is written, initially OUT is low. When the counter reaches 1, OUT
goes high for one clock pulse. OUT then goes low again. The counter reloads
the initial count and the process will be repeated.
mode 1, In itial co un t= 3, C o un t d ow n
Gate
CLK
Count value
OUT
Note: In Mode 1 the initial count value N must be larger than one.
33 2111000
Figure 20: Mode 0 Operation
33 2213213
Figure 21: Mode 1 Operation
50 • Operation Theory
Page 61

6
C/C++ Library
This chapter describes the software library for operating t his card. Only the
functions in DOS library are described. Please refer to the PCIS-DASK
function reference manual, which included in ADLINK CD, for the descriptions
of the Windows 98/NT/2000 DLL functions.
The function prototypes and some us eful constant s are defined in the header
files LIB directory (DOS).
6.1 Libraries Installation
Please refer to the “Software Installation Guide” for the detail information about
how to install the software libraries for DOS or PCIS-DASK for Windows
98/NT/2000.
The device drivers and DLL functions of Win do ws 98/NT / 2000 ar e inc lud e d in
the PCIS-DASK. Please refer the PCIS-DASK user’s guide and function
reference, which included in the ADLINK CD, for detailed programming
information.
C++ Library • 51
Page 62

6.2 Programming Guide
6.2.1 Naming Convention
The functions of the NuDAQ PCI cards or NuIPC CompactPCI cards’ software
driver are using full-names to represent the functions' real meaning. The
naming convention rules are:
In DOS Environment :
_{hardware_model}_{action_name}. e.g. _9116_initial().
6.2.2 Data Types
We defined some data type in 9116.h (DOS). These data types are used b y
NuDAQ Cards’ library. We suggest that you use t hese data types in your
application programs. The following table shows the data type names and their
range.
Type Name Description Range
U8 8-bit ASCII character 0 to 255
I16 16-bit signed integer -32768 to 32767
U16 16-bit unsigned integer 0 to 65535
I32 32-bit signed integer -2147483648 to 2147483647
U32
F32
F64
Boolean Boolean logic value TRUE, FALSE
32-bit single-precision
floating-point
32-bit single-precision
floating-point
64-bit double-precision
floating-point
0 to 4294967295
-3.402823E38 to
3.402823E38
-1.797683134862315E308 to
1.797683134862315E309
52 • C++ Library
Page 63

6.2.3 Sample Programs List (DOS)
You can get sample programs once cPCI-9116 dos driver is installed. The
following is the list of the files and it’s description:
File Name Description
AD_DEMO0 Software polling with single-ended input
AD_DEMO1 Software polling with differential input
AD_DEMO2
AD_DEMO3
AD_DEMO4
AD_DEMO5
AD_DEMO6
AD_DEMO7
AD_DEMO8 Scan data acquisition with post-trigger and DMA transfer
AD_DEMO9
AD_DEMO10
DIO_DEMO DIO test
GP_DEMO0 General purpose timer/counter mode0 operation
GP_DEMO1 General purpose timer/counter mode1 operation
Scan data acquisition with software trigger and EOC
interrupt transfer
Scan data acquisition with software trigger and Half-Full
interrupt transfer
Scan data acquisition with software trigger and DMA
transfer
Scan data acquisition with pre-trigger, M_enable=1 and
DMA transfer
Scan data acquisition with pre-trigger, M_enable=0 and
DMA transfer
Scan data acquisition with middle-trigger, M_enable=1 and
DMA transfer
Scan data acquisition with delay-trigger, re-trigger and
DMA transfer
Continuous scan data acquisition with double buffered
mode DMA transfer
C++ Library • 53
Page 64

6.3 Initial functions
6.3.1 _9116_Initial
@ Description
This function is used to initialize t he cPCI-9116. Each cPCI -9116 card
must be initialized with this function before calli ng other functions is
permitted.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_Initial( I16 card_number, U16 *op_base_address,
U16 *pt_base_address, U16 *irq_no, U16 *pci_master);
@ Argument
card_number :
op_base_address :
pt_base_address :
irq_no :
pci_master :
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_PCIBiosNotExist
ERR_PCICardNotExist
ERR_PCIIrqNotExist
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be
initialized, totally 4 cards can be initialized,
valid card numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2,
CARD_3, CARD_4.
the physical location of the S5933(PCI
controller) operation Registers in I/O space.
the physical location of add-on registers in
pass-through I/O space. (The base address
used in CH4)
the interrupt IRQ level of your cPCI-9116 card,
this available IRQ value is automatically
assigned by the system BIOS.
BIOS enables or disables bus mastering in
PCI Command Register
54 • C++ Library
Page 65

6.3.2 _9116_AD_Clr_DFIFO
@ Description
This function is used to clear the A/D Data FIFO.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Clr_DFIFO( I16 card_number )
@ Argument
card_number :
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
C++ Library • 55
Page 66

6.4 DIO functions
6.4.1 _9116_DI
@ Description
This function is used to read data from the digital input port. There are 8
digital input channels on the cPCI_9116. All 8 channels can be
accessed using this function.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_DI (I16 card_number, unsigned int far *data )
@ Argument
card_number:
data:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError,ERR_BoardNoInit
6.4.2 _9116_DO
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
8-bit data read from the digital input port.
@ Description
This function is used to write data to the digital output port. There are 8
output channels on the cPCI-9116.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_DO (I16 card_number , unsigned int data)
@ Argument
card_number:
data:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
56 • C++ Library
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
data written to the output port.
Page 67

6.5 AD Channel Gain Queue configuration functions
6.5.1 _9116_AD_Clr_CFIFO
@ Description
This function is used to reset the A/D Channel Gai n Queue (Refer to
5.1.2.1 for definition of Channel Gain Queue). Before calling the
_9116_AD_Set_CFIFO function to set the A/D channel and input range,
this function must be call to clear the A/D Channel Gain Queue.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Clr_CFIFO (I16 card_number)
@ Argument
card_number:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
C++ Library • 57
Page 68

6.5.2 _9116_AD_Set_CFIFO
@ Description
This function is used to specify the A/D channel and the input range.
Note: _9116_AD_Clr_CFIFO should be called before you use this
function to set the channels and gains in the Channel-Gain
Queue. After the settings are completed, you have to call
_9116_AD_CFIFO_SetDone to stop filling out the Channel-Gain
Queue. The sequence to call these three functions is:
_9116_AD_Clr_CFIFO();
_9116_AD_Set_CFIFO();
:
: Setting A/D channels
: and gains
_9116_AD_Set_CFIFO();
_9116_AD_CFIFO_SetDone ();
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_CFIFO( I16 card_number, I16 ch, I16 range, U16
diff, U16 cmmd_sel )
@ Argument
card_number:
ch :
range :
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
the channel which is being set, valid values are
between 0 to 63 for single-ended configuration
and 0 to 31 for differential mode configuration.
the A/D input range, possible values are listed in
column ‘AD_INPUT’ of the following table.
58 • C++ Library
Page 69

AD_INPUT GAIN
AD_B_5_V
AD_B_2_5_V
AD_B_1_25_V
AD_B_0_625_V
AD_U_10_V
AD_U_5_V
AD_U_2_5_V
AD_U_1_25_V
Diff:
SINGLE_ENDED (or 0):
DIFFERENTIAL (or 1):
cmmd_sel:
1 Bipolar ±5V
2 Bipolar ±2.5V
4 Bipolar ±1.25V
8 Bipolar ±0.625V
1 Unipolar 0V ~ 10V
2 Unipolar 0V ~ 5V
4 Unipolar 0V ~ 2.5V
8 Unipolar 0V ~ 1.25V
differential/single-ended input selection:
common mode reference selection when
Input type
(Bipolar or Unipolar)
single-ended mode is selected:
0:
1:
@ Return Code
input signals are referenced to system ground
input signals are referenced to U_CMMD (pin1 of
J1)
ERR_NoError
ERR_InvalidADChannel
ERR_BoardNoInit
ERR_InvalidADGain
single-ended
differential
Input Range
C++ Library • 59
Page 70

6.5.3 _9116_AD_CFIFO_SetDone
@ Description
This function is used to stop setting A/D channel gain queue.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _ 9116_AD_CFIFO_SetDone (I16 card_number)
@ Argument
card_number:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
60 • C++ Library
Page 71

6.6 AD Software-Polling functions
6.6.1 _9116_AD_Acquire
@ Description
This function is used to poll the A/D conve rted data. It will trigger an A/D
conversion, and read the A/D data when the data is ready. To perform a
software-polling data acquisition, users must set the Channel Gain
Queue using functions in 6.5, and then performing this function will
retrieve the data in the order the Channel Gain Que ue has been set.
Refer to the sample program AD_DEMO0.C.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Acquire( I16 card_number, U16 far *ad_data )
@ Argument
card_number:
ad_data :
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
16-bit A/D converted values in binary code format.
C++ Library • 61
Page 72

6.7 AD Trigger control functions
6.7.1 _9116_AD_Trig_Ctrl
_9116_AD_Set_TrigMode
_9116_AD_Set_TrigPol
_9116_AD_Set_Timebase
_9116_AD_Set_Delay_SRC
_9116_AD_Set_M_enable
@ Description
These functions are used to set the AD trigger controls. The
_9116_AD_Trig_Ctrl() function provides settings for all trigger
parameters, while the other functions provide individual settings for
each trigger parameter.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Trig_Ctrl( I16 card_number, I16 trig_src, I16
trig_mode, I16 trig_pol, I16 timebase_sel, I16 delay_src, I16
retrig_en, I16 M_enable, I16 ACQ_enable)
int _9116_AD_Set_TrigMode( I16 card_number, I16 trig_mode)
int _9116_AD_Set_TrigPol( I16 card_number, I16 trig_pol)
int _9116_AD_Set_Timebase( I16 card_number, I16 timebase_sel)
int _9116_AD_Set_Delay_SRC( I16 card_number, I 16 delay_src)
int _9116_AD_Set_M_enable( I16 card_number, I16 M_enable)
@ Argument
card_number:
Trig_src:
Trig_mode:
NO_TRIG (or 0):
POST_TRIG (or 1):
DLY_TRIG (or 2):
PRE_TRIG (or 3):
MN_TRIG (or 4):
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
Reserved. Set to 0 for proper operation.
Trigger mode setting. Refer to 5.1.3.3 for details.
when _9116_AD_DMA_Start() or
_9116_AD_INT_Start() is performed(software
trigger)
acquisition starts immediately
post-trigger mode
delay-trigger mode
pre-trigger mode
middle-trigger mode
62 • C++ Library
Page 73

Trig_pol:
RISE_TRIG (or 0):
FALL_TRIG (or 1):
Timebase_sel:
trigger polarity setting:
Timebase source selection. Refer to 5.1.3.1 for
details.
INT_TIMEBASE (or 0):
EXT_TIMEBASE (or 1):
pin45
Delay_src:
Delay source selection in delay-trigger mode.
Refer to 5.1.3.3 for details.
0:
1:
retrig_en:
delay in timebase
delay in samples
Enable/disable re-trigger mode acquisition when
post-trigger or delay-trigger mode is selected.
0:
1:
M_enable:
disable re-trigger
enable re-trigger
Enable/disable M_enable bit when pre-trigger or
middle-trigger mode is selected. Mode acquisition
when post-trigger or delay-trigger is selected.
Refer to 5.1.3.3 (pre-trigger & middle-trigger
section) for definition of M_enable
0:
1:
ACQ_enable:
@ Return Code
set M_enable to 0
set M_enable to 1
Set to 0 for proper operation
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
rising edge trigger
falling edge trigger
internal timebase (24MHz)
external timebase from
C++ Library • 63
Page 74

6.8 AD Counter setting functions
These functions are for the setting of the counter values when usi ng
programmable scan acquisition mode. Refer to Chapter 5 for definitio n
of each counter.
6.8.1 _9116_AD_Set_SC
@ Description
Set SC_Counter value for programmable scan acquisition mode.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_SC( I16 card_number, U32 counter _value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
the SC_Counter value. Range: 1 through to
16777215
64 • C++ Library
Page 75

6.8.2 _9116_AD_Set_SI
@ Description
Set SI_Counter value for programmable scan acquisition mode.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_SI( I16 card_number, U32 counter_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
the SI_Counter value. Range: 96 through to
16777215
6.8.3 _9116_AD_Set_SI2
@ Description
Set SI2_Counter value for programmable scan acquisition mode.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_SI2( I16 card_number, U32 counter_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
the SI2_Counter value. Range: 96 through to
65536
C++ Library • 65
Page 76

6.8.4 _9116_AD_Set_DIV
@ Description
Set DIV_Counter value for programmable scan acquisition mode. Refer
to Chapter 5 for definition of DIV_Count er
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_DIV( I16 card_number, U32 counter_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
6.8.5 _9116_AD_Set_DLY1
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
the DIV_Counter value. Range: 1 through to 512
@ Description
Set DLY1_Counter value when delay-trigger mode is selected.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_DLY1( I16 card_number, U32 counter_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
66 • C++ Library
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
the DLY1_Counter value. Range: 1 through to
65535
Page 77

6.8.6 _9116_AD_Set_M
@ Description
Set M_Counter value when pre-trigger or middle-trigger mode is
selected.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_M( I16 card_number, U32 counter_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
Counter_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4
the M_Counter value. Range: 1 through t o 65535
C++ Library • 67
Page 78

6.8.7 _9116_AD_Set_Retrig
@ Description
Set the number of re-trigger counts when post-trigger or delay-trigger
mode is selected.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_Set_Retrig( I16 card_number, I16 retrig_en, U16
retrig_no);
@ Argument
card_number:
retrig_en:
0:
1:
retrig_no:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
Enable/disable re-trigger mode acquisition when
post-trigger or delay-trigger mode is selected.
disable re-trigger
enable re-trigger
Number of re-trigger counts. Range: 1 through to
65535
68 • C++ Library
Page 79

6.9 AD one-shot scan data acquisition with DMA transfer
functions
These functions are used to start scan data acquisition with DMA
transfer according to the selected trigger mode and condit ions.
6.9.1 _9116_AD_DMA_Start
@ Description
This function will perform programmable scan data acquisition with
DMA data transfer using the pacer trigger. It takes place in the
background and will not stop until the completion of all conversions or
the execution of _9116_AD_DMA_Stop() function to stop the process.
The data acquired will be in the order the Channel Gain Qu eue is set.
After executing this function, it is necessary to check the status of the
operation by using the function _9116_AD_DMA_Status(), and execute
_9116_AD_DMA_Stop() after obtaining the AD_DMA_STOP status
from _9116_AD_DMA_Status().
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_DMA_Start(I16 card_number, U32 SI_value, U32
SI2_value, U32 SC_value, U32 DIV_value, U32
*ad_buffer)
@ Argument
card_number:
SI_value:
SI2_value:
SC_value:
DIV_value:
ad_buffer :
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
Set SI_Counter value. Range: 96 through to
16777215
Set SI2_Counter value. Range: 96 through to
65535
Set SC_Counter value. Range: 1 through to
16777215
Set DIV_Counter value. Range: 1 through to
65535
the start address of the memory buffer to store the
A/D data, the buffer size must be larger then the
numbers of A/D conversions. The memory should
be of double-word length.
C++ Library • 69
Page 80

@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit,
ERR_InvalidADChannel,
ERR_InvalidTimerValue
ERR_AD_InvalidGain
6.9.2 _9116_AD_DMA_Status
@ Description
Since the _9116_AD_DMA_Start() function runs in the background,
this function can be used to check its operation status.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int I16 _9116_AD_DMA_Status( I16 card_number, I16 *status ,
U32 *count, U32 *start_idx);
@ Argument
card_number:
Status:
Count:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_AD_DMANotSet
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
status of the DMA data transfer
AD_DMA_STOP (or 0)
AD_DMA_RUN (or 1)
the number of A/D data that have been
transferred.
: DMA is completed.
: DMA is not completed.
70 • C++ Library
Page 81

6.9.3 _9116_AD_DMA_Stop
@ Description
This function is used to stop the DMA data transfer and obtain the start
index of the data buffer when pre-trigger or middle-tr igger is selected.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_DMA_Stop( I16 card_number, U32 *count, U32
*start_idx )
@ Argument
card_number:
Count:
the number of A/D converted data that have been
start_idx:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
transferred.
The index where the data started from within the
user’s buffer, i.e the sequence of read data is:
buff[start_idx], buff[start_idx+1], _, buff[0],
buff[1],_.,buff[start_idx-1].
C++ Library • 71
Page 82

6.10 AD one-shot scan data acquisition with interrupttransfer functions
These functions are used to start scan data acquisition with
interrupt-transfer according to the selected trigger mode and conditions.
Note that these functions cannot be applied to pre-trigger and
middle-trigger mode.
6.10.1 _9116_AD_INT_Start
@ Description
This function will perform programmable scan data acquisition with
interrupt transfer by using the pacer trigger. It takes place in the
background and will not stop until the completion of all the conversions
or the execution of _9116_AD_INT_Stop() function to stop the process.
The data acquired will be in the order of the Channel Gain Queue
setting.
After executing this function, it is necessary to check the status of the
operation by using the function _9116_AD_INT _Status(), and execute
_9116_AD_INT_Stop() after you obtain the AD_INT_STOP status from
_9116_AD_INT_Status().
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_INT_Start( I16 card_number, U32 SI_value, U32
SI2_value, U32 SC_value, U32 DIV_value, U16 *ad_buffer,
U16 mode)
@ Argument
card_number:
SI_value:
SI2_value:
SC_value:
DIV_value:
ad_buffer :
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card numbers
are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3, CARD_4.
Set SI_Counter value. Range: 96 through to
16777215
Set SI2_Counter value. Range: 96 through to 65535
Set SC_Counter value. Range: 1 through to
16777215
Set DIV_Counter value. Range: 1 through to 65535
the start address of the memory buffer to store the
A/D data, the buffer size must be larger then the
numbers of A/D conversion. The memory should be
of double-word length.
72 • C++ Library
Page 83

Mode:
0: EOC interrupt transfer mode
1: Half-full interrupt transfer mode
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit,
ERR_InvalidADChannel,
ERR_InvalidTimerValue
ERR_AD_InvalidGain
EOC or Half-full interrupt transfer mode selection
6.10.2 _9116_AD_INT_Status
@ Description
Since the _9116_AD_INT_Start() function runs in the background, t his
function can be used to check its operation status.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int I16 _9116_AD_INT_Status( I16 card_number, I16 *status , U32
*count);
@ Argument
card_number:
Status:
Count:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_AD_DMANotSet
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
status of the DMA data transfer
AD_INT_STOP (or 0)
completed.
AD_INT_RUN (or 1)
completed.
the number of A/D data that has been transferred.
: Interrupt transfer is
: Interrupt transfer is not
C++ Library • 73
Page 84

6.10.3 _9116_AD_INT_Stop
@ Description
This function is used to stop the interrupt data being transferred.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_AD_INT_Stop( I16 card_number, U32 *count)
@ Argument
card_number:
Count:
the number of A/D converted data that has been
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
transferred.
74 • C++ Library
Page 85

6.11 AD continuous scan data acquisition with
double-buffered DMA transfer functions
These functions are used to perform continuous scan data acquisition
with double-buffered DMA data transfer. It takes place in the
background and will not stop until the execution of
_9116_AD_DMA_Stop() function to stop the process. (Note these
functions do not apply to pre-trigger and middle-trigger mode.) Refer to
the sample program AD_DEMO10.C.
6.11.1 _9116_DblBufferMode
@ Description
This function is used to enable the double-buffered mode. If
double-buffered mode is set, function _9116_AD_DMA_Start() will
perform continuous scan data acquisition. Otherwise function
_9116_AD_DMA_Start() only performs one-shot scan data acquisition.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_DblBufferMode(I16 card_number, U8 enable)
@ Argument
card_number:
Enable:
0:
1:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
enable/disable double-buffered mode DMA.
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
disabled
enabled
C++ Library • 75
Page 86

6.11.2 _9116_DblBufferTransfer
@ Description
Using this function to copy the converted A/ D data from th e circular to
transfer buffer.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_DblBufferTransfer(I16 card_number, U32 far *user_buffer)
@ Argument
card_number:
userBuffer :
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
user transfer buffer for A/D converted data, each
time _9116_DblBufferTransfer() copies half size
of circular buffer to user’s Buffer. The size of the
circular in samples is specified in
_9116_AD_DMA_Start () function call.
76 • C++ Library
Page 87

6.11.3 _9116_GetOverrunStatus
@ Description
When you perform continuous scan data acquisition with
double-buffered mode DMA transer but you do not use
_9116_DblBufferTransfer() to copy converted data then circular buffer
overrun will occur. You can use this function to check overrun counts.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_GetOverrunStatus(I16 card_number, U32 *overrun_cnt)
@ Argument
card_number:
overrunCount:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
number of overrun counts.
6.12 General Purpose Timer/Counter functions
6.12.1 _9116_GP0_Set_Mode
@ Description
This function is used to select operation mode of GPTC. Please refer to
5.3 for the details.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_GP0_Set_Mode( I16 card_number, U16 mode)
@ Argument
card_number:
Mode: 0
1:
the card number of the cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: mode0 operation
mode1 operation
C++ Library • 77
Page 88

@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
6.12.2 _9116_GP0_Set_Count
@ Description
This function is used to set the initial count value of GPTC
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_GP0_Set_Count ( I16 card_number, U16 GP_value )
@ Argument
card_number:
GP_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
16-bit count initial value
6.12.3 _9116_GP0_Set_CLK
@ Description
This function is used to select the clock source of GPTC
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_GP0_Set_CLK( I16 card_nmber, U8 clk_src)
@ Argument
card_number:
Clk_src : 0
1:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
78 • C++ Library
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: internal clock source(24MHz timebase)
external clock source from pin96 of J1
Page 89

6.12.4 _9116_GP0_Set_GATE_SRC
@ Description
This function is used to select the gate source of GPTC. When internal
gate source is selected, you can use function _9116_GP0_EN to
enable/disable the counting.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
int _9116_GP0_Set_GATE_SRC( I16 card_number, U8 gate_src )
@ Argument
card_number:
gate_src : 0
1:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: internal gate source
external clock source from pin97 of J1
6.12.5 _9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN_SRC
@ Description
This function is used to select the up/down control source of GPT C.
When internal source is selected, you can use function
_9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN() to select up/down counter operation.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
Int 9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN_SRC( I16 card_number, U8
updown_src )
@ Argument
card_number:
Updown_src: 0
1:
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: internal source
external source from pin98 of J1
C++ Library • 79
Page 90

@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
6.12.6 _9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN
@ Description
This function is used to select up/down operation of GPTC when
internal up/down source is selected.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
Int _9116_GP0_Set_UPDOWN(I16 card_number, U8 updown)
@ Argument
card_number:
Updown: 0
1:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: count down
count up
6.12.7 _9116_GP0_EN
@ Description
This function is used to enable the counting of GPTC.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
Int _9116_GP0_EN( I16 card_number, U8 gp0_en)
@ Argument
card_number:
Gp0_en: 0
1:
80 • C++ Library
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
: disable counting
enable counting
Page 91

@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
6.12.8 _9116_GP0_Read_Count
@ Description
This function is used to read back the counter value of GPTC.
@ Syntax
C/C++ (DOS)
Int _9116_GP0_Read_Count( I16 card_number, U16 *GP_value)
@ Argument
card_number:
Gp_value:
@ Return Code
ERR_NoError
ERR_BoardNoInit
the card number of cPCI-9116 to be initialized,
totally 4 cards can be initialized, the valid card
numbers are CARD_1, CARD_2, CARD_3,
CARD_4.
read-backed counter value
C++ Library • 81
Page 92

7
Software Utility & Calibration
This software CD provides a utility program, 9116util.exe, a nd is intended f or:
Calibration and Functional Testing. This utility is a menu-driven design and
operates under the DOS environment. The text messages gives operating
guidance, with graphics to indicate correct hardware configuration and location.
The utility is described in the following sections. Not e that the software driver
for the cPCI-9116 and cPCI-9116R are the same.
7.1 Running 9116util.exe program
After finishing the DOS installation, you can execute the utility by typing the
following command. (Assuming the utility is located in
C:\ADLINK\9116\DOS_BC\Util directory, the following command should be
entered at the DOS prompt.
C> cd\ADLINK\9116\DOS_BC\Util
C> 9116UTIL
The following diagram will be displayed on you screen. The message at the
bottom of each window guides you through the selected item.
82 • Software Utility & Calibration
Page 93

****** cPCI-9116 Utility Rev. 1.0 ******
Copyright © 2001-2002, ADLINK Technology Inc. All rights reserved.
<F1> : Calibration.
<F2> : Function testing.
<Esc>: Quit.
>>> Select function key F1 ~ F2, or press <Esc> to quit. <<<
Figure 22: CPCI-9116 Utility Main Screen
7.2 Calibration
In data acquisition processes, calibration of the measur ement devices is very
important to maintain its accuracy. Users can calibrate the analog input
channels under the operating environment to optimizing t he accuracy of the
9116 series card. The following section will guide you though the calibr ation
process for the 9116 series card.
Note:
For an environment with frequently large flu ctuations in temperature
and vibration, a 3 months re-calibration interval is recommended. For
laboratory conditions, 6 months to 1 year is acceptable.
7.2.1 What do you need
Before calibrating your 9116 series card, you should prepare the following
equipment’s:
A 5 1/2 digital multimeter (6 1/2 is recommended)
•
A voltage calibrator or a very stable and noise free DC
•
voltage generator
Software Utility & Calibration • 83
Page 94
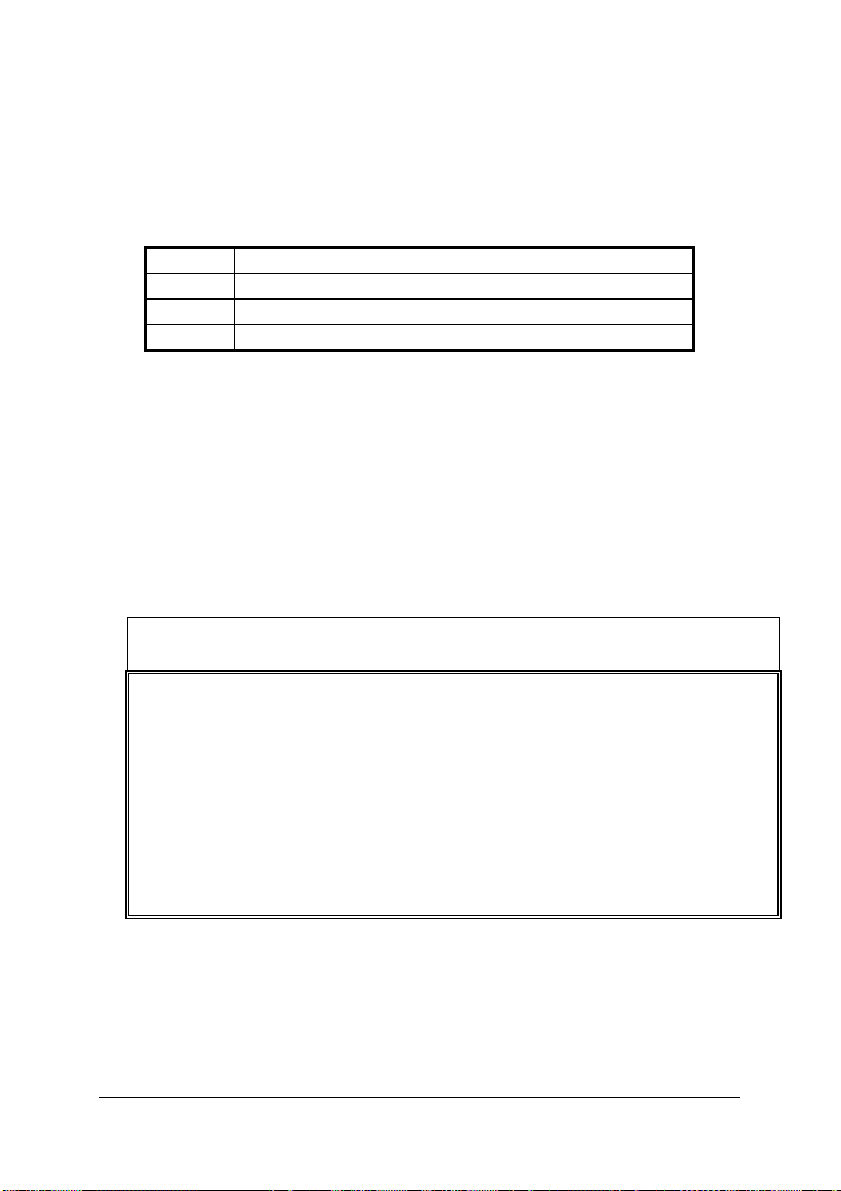
7.2.2 VR Assignment
There are 4 variable resistors (VR) on the 9116 series board that allows you to
make adjustments to the A/D channels. The function of each VR is specified in
Table 18.
VR1 A/D unipolar offset adjustment
VR2 A/D bipolar offset adjustment
VR3 A/D full scale adjustment
VR4 PGA offset adjustment
Table 18. Functions of VRs
7.2.3 A/D Adjustment
When you choose the calibration function from the main menu list, a calibration
items menu is displayed on the screen. After you have select one of the
calibration items from the calibration items menu, a calibration window displays
on the screen. The upper window outlines the
procedures that must be
carefully followed to calibrate the 9116 series card. The instructions will
guide you through the calibration process step by
window shows the layout of the 9116 series card and the Variable Resister (VR)
that needs to be adjusted will blink.
step. The bottom
****** cPCI-9116 Calibration ******
<1> A/D PGA offset adjusting
<2> A/D (Bipolar Gain = 1, -5V ~ 5V) adjusting
<3> A/D (Unipolar Gain = 1, 0V ~ 10V) adjusting
<Esc> Quit
Select 1 to 3 or <Esc> to quit calibration.
Figure 23: A/D Adjustment menu Screen
84 • Software Utility & Calibration
Page 95

7.2.3.1 PGA offset Calibration
1. Short the A/D channel 0 (pin 2 of J1) to ground (pin51 of J1).
2. Use multi-meter to measure the voltage between
VR4
3. Adjust
7.2.3.2 Bipolar input Calibration
1. Calibrate the PGA offset as described in 7.2.3.1.
2. Connect A/D channel 0 (pin 2 of J1) to ground (pin 51 of J1), and Applied a
precise +5V to A/D channel 1 (pin 3 of J1).
3. Trim
Trim
7.2.3.3 Unipolar input Calibration
1. Calibrate the PGA offset as described in 7.2.3.1.
2. Applied a precise +5 V input signal to A/D channel 1 (pin 3 of J1).
3. Trim
to obtain the multi-meter value as close as possible to 0V.
VR2
to obtain the reading of A/D channel 0 flicks between 0 to 1, and
VR3
to obtain reading of A/D channel 1 flicks between 32766~32767.
VR1 to obtain reading flicking between 0~1.
TP1
and
TP2
on board.
7.3 Functional Testing
This function is used to test the functions of the 9116 series card, it includes
Digital I/O testing, A/D polling test, A/D Interrupt Test, A/D with DMA test, A/D
with DMA & pre-trigger test, A/D with DMA & mn-trigger test, A/D with DMA &
post-trigger test, A/D with DMA & delay-trigger with re-trigger=3 test, and A/D
with continuous DMA test (Double buffer mode).
When you choose one of the testing functions from the function menu, a
diagram is displayed on the screen. The figure belo w is the function testing
menu window.
Software Utility & Calibration • 85
Page 96

****** cPCI-9116 Function Testing ******
<0> : DI/DO Test
<1> : A/D with Polling Test (ch0~31)
<2> : A/D with Polling Test (ch32~63)
<3> : A/D with Interrupt Test
<4> : A/D with DMA Test
<5> : A/D with DMA & pre-trigger
<6> : A/D with DMA & mn-trigger
<7> : A/D with DMA & post-trigger
<8>: A/D with DMA & delay-trigger with retrigger=3
<9> : A/D with continuous DMA(Double buffer mode)
<Esc>: Quit.
Select 0 to 9 or <Esc> to quit function testing
Figure 24: cPCI-9116 Function Testing Screen
A calibration utility is supported in the software CD that is included in the
product package. The calibration procedures and descriptions can be found in
the utility. Users only need t o run the s oft war e calibrat ion ut ilit y and f ollo w the
procedures.
The 9116 series card is shipped calibrated from the factor y. Unless the 9116
card is operating in a very hostile environment with high temperature
fluctuation and vibration, users do not need to calibrate t he 9116 series card
when you first receive it.
86 • Software Utility & Calibration
Page 97

Warranty Policy
Thank you for choosing ADLINK. To understand your rights and enjoy all the
after-sales services we offer, please read the following carefully.
1. Before using ADLINK’s products please read the user manual and follow
the instructions exactly. When sending in damaged produ cts for repair,
please attach an RMA application form which can be do wnloaded from:
http://rma.adlinktech.com/policy/.
2. All ADLINK products come with a limited two-year warranty, one year for
products bought in China.
The warranty period starts on the day t he product is shipped from
•
ADLINK’s factory.
Peripherals and third-party products not manufactured by ADLINK will
•
be covered by the original manufacturers' warranty.
For products containing storage devices (hard drives, flash cards,
•
etc.), please back up your data before sending them for repair.
ADLINK is not responsible for any loss of data.
Please ensure the use of properly licensed software with our systems.
•
ADLINK does not condone the use of pirated software and will not
service systems using such software. ADLINK will not be held leg all y
responsible for products shipped with unlicensed software installed by
the user.
For general repairs, please do not include peripheral accessories. If
•
peripherals need to be included, be certain to specify which items you
sent on the RMA Request & Confirmation Form. ADLINK is not
responsible for items not listed on the RMA Request & Co nfirmation
Form.
3. Our repair service is not covered by ADLINK's guarantee in the following
situations:
Damage caused by not following instructions in the User's Manual.
•
Damage caused by carelessness on the user's part during product
•
transportation.
Damage caused by fire, earthquakes, floods, lightening, pollution,
•
other acts of God, and/or incorrect usage of voltage transformers.
Warranty Policy • 87
Page 98

Damage caused by inappropriate storage environments such as with
•
high temperatures, high humidity, or volatile chemicals.
Damage caused by leakage of battery fluid during or after change of
•
batteries by customer/user.
Damage from improper repair by unauthorized ADLINK technicians.
•
Products with altered and/or damaged serial numbers are not entitled
•
to our service.
This warranty is not transferable or extendible.
•
Other categories not protected under our warranty.
•
4. Customers are responsible for all fees necessary to transport damaged
products to ADLINK.
For further questions, please e-mail our FAE staff: service@adlinktech.com
88 • Warranty Policy
 Loading...
Loading...