Page 1

CoreModule
TM
430
(PC/104 Single Board Computer)
Reference Manual
P/N 50-1Z006-1010
Page 2
Notice Page
DISCLAIMER
ADLINK Technology, Incorporated makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents of
this manual or of the associated ADLINK products, and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. ADLINK shall under no circumstances be liable for
incidental or consequential damages or related expenses resulting from the use of this product, even if it has
been notified of the possibility of such damages. ADLINK reserves the right to revise this publication from
time to time without obligation to notify any person of such revisions. If errors are found, please contact
ADLINK at the address listed below on the Notice page of this document.
TRADEMARKS
CoreModule and the Ampro logo are registered trademarks, and ADLINK, Little Board, LittleBoard,
MightyBoard, MightySystem, MilSystem, MiniModule, ReadyBoard, ReadyPanel, ReadySystem, and
RuffSystem are trademarks of ADLINK Technology, Inc. All other marks are the property of their
respective companies.
REVISION HISTORY
Revision Reason for Change Date
A, A Initial Release Oct/08
1.0 Added U9 chip to table 2-1; revised description of U7 chip in table 2-1;
revised JP7 default to pins 2-3 in table 2-3; changed document p/n from
5001840 to 50-1Z006-1000; changed rev to 1.0
1010
Changed pitch of J4 header in Tables 2-2 and 3-5 to 0.079
rev of this document from 1.0 to 1010; changed pin 9 in Tabl e 3 -10
from 3.6/4.0V to 3.0V max; added BIOS Setup Screens section to ch 4;
replaced EOL, U14 video memory in Tab le 2- 1 with new component;
changed definition of SPI Flash device
"; changed
Oct/09
June/12
ADLINK Technology, Incorporated
5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110
San Jose, CA 95138-1007
Tel. 408 360-0200
Fax 408 360-0222
http://www.adlinktech.com
© Copyright 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 ADLINK Technology, Incorporated
Audience
This manual provides reference only for computer design engineers, including but not limited to hardware
and software designers and applications engineers. ADLNK Technology, Inc. assumes you are qualified to
design and implement prototype computer equipment.
ii Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 About This Manual ....................................................................................................1
Purpose of this Manual ....................................................................................................................1
References ......................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 2 Product Overview.....................................................................................................3
PC/104 Architecture ........................................................................................................................3
Product Description..........................................................................................................................4
Module Features ........................................................................................................................4
Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................7
Major Components (ICs) .................................................................................................................8
Header, Connector, and Socket Definitions ..................................................................................10
Jumper Header Definitions .......................................................................................................11
Specifications.................................................................................................................................12
Physical Specifications .............................................................................................................12
Mechanical Specifications ........................................................................................................12
Power Specifications ................................................................................................................13
Environmental Specifications....................................................................................................13
Thermal/Cooling Requirements ...............................................................................................13
Chapter 3 Hardware..................................................................................................................15
Overview ........................................................................................................................................15
CPU ..............................................................................................................................................16
Graphics ........................................................................................................................................16
Memory ..........................................................................................................................................16
System Memory .......................................................................................................................16
Video Memory ..........................................................................................................................16
SPI Flash .................................................................................................................................16
Memory Map ..................................................................................................................................17
Interrupt Channel Assignments .....................................................................................................18
I/O Address Map ...........................................................................................................................19
Parallel Interface (LPT) .................................................................................................................20
Serial Interface ..............................................................................................................................21
USB Interface ................................................................................................................................23
Utility Interface ..............................................................................................................................24
Keyboard ..................................................................................................................................24
Mouse .......................................................................................................................................24
Battery ......................................................................................................................................24
Reset Switch.............................................................................................................................24
Speaker ....................................................................................................................................24
Ethernet Interface .........................................................................................................................25
Video (TTL/VGA) Interface ...........................................................................................................26
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) ....................................................................................................28
Low Pin Count Interface (LPC) ......................................................................................................28
Miscellaneous ................................................................................................................................28
Real Time Clock (RTC) ............................................................................................................28
User GPIO Interface ................................................................................................................29
Oops! Jumper (BIOS Recovery) ...............................................................................................29
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual iii
Page 4

Contents
Remote Access ...................................................................................................................... 30
Remote Access Setup ........................................................................................................ 30
Hot (Serial) Cable .............................................................................................................. 30
Watchdog Timer....................................................................................................................... 30
Power Interface ............................................................................................................................ 31
Chapter 4 BIOS Setup .............................................................................................................. 33
Introduction.................................................................................................................................... 33
Entering BIOS Setup (Local Display) ....................................................................................... 33
Entering BIOS Setup (Remote Access) ................................................................................... 33
OEM Logo Utility .......................................................................................................................... 34
Logo Image Requirements....................................................................................................... 34
BIOS Setup Screens ..................................................................................................................... 35
BIOS Main Setup Screen ........................................................................................................ 35
BIOS Advanced Setup Screen................................................................................................. 36
BIOS PCIPnP Setup Screen .................................................................................................... 38
BIOS Boot Setup Screen ......................................................................................................... 40
BIOS Security Setup Screen.................................................................................................... 41
BIOS Chipset Setup Screen..................................................................................................... 42
BIOS Exit Setup Screen........................................................................................................... 45
Appendix A Technical Support .................................................................................................. 47
Index ................................................................................................................................................. 49
List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Stacking PC/104 Modules with the CoreModule 430 .............................................. 3
Figure 2-2. Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 7
Figure 2-3. Component Locations (Top Side)............................................................................ 9
Figure 2-4. Connector Pin Identifications................................................................................. 10
Figure 2-5. Header Locations (Top Side) ................................................................................ 11
Figure 2-6. Mechanical Dimensions (Top Side)....................................................................... 12
Figure 3-1. RS-485 Serial Port Implementation....................................................................... 21
Figure 3-2. Oops! Jumper........................................................................................................29
Figure 3-3. Hot Cable Jumper ................................................................................................. 30
Figure 4-1. BIOS Main Setup Screen ...................................................................................... 35
Figure 4-2. BIOS Advanced Setup Screen .............................................................................. 36
Figure 4-3. BIOS PCIPnP Setup Screen ................................................................................. 38
Figure 4-4. BIOS Boot Setup Screen....................................................................................... 40
Figure 4-5. BIOS Security Setup Screen ................................................................................. 41
Figure 4-6. BIOS Chipset Setup Screen.................................................................................. 42
Figure 4-7. BIOS Exit Setup Screen ........................................................................................ 45
List of Tables
Table 2-1. Major Components (Chips) Descriptions and Functions ......................................... 8
Table 2-2. Header, Connector, and Socket Descriptions ....................................................... 10
Table 2-3. Jumper Settings .................................................................................................. 11
Table 2-4. Weight and Footprint Dimensions ......................................................................... 12
Table 2-5. Power Supply Requirements ................................................................................. 13
Table 2-6. Environmental Requirements ................................................................................ 13
Table 3-1. Memory Map - Vortex 86SX/DX Processor........................................................... 17
Table 3-2. Interrupt Channel Assignments ............................................................................. 18
iv Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 5

Contents
Table 3-3. DMA Map ...............................................................................................................18
Table 3-4. I/O Address Map ....................................................................................................19
Table 3-5. Parallel (LPT) Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J4) .............................................20
Table 3-6. Serial Ports 1 & 2 Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J3, J9) .................................22
Table 3-7. Serial Ports 3 & 4 Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J13, J14) .............................22
Table 3-8. USB0 Interface Pin/Signal Designations (J10) ......................................................23
Table 3-9. USB1 Interface Pin/Signal Designations (J17) ......................................................23
Table 3-10. Utility Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J5) ..........................................................24
Table 3-11. Ethernet Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J2) .....................................................25
Table 3-12. Video Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J11)........................................................26
Table 3-13. SPI Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J19) ...........................................................28
Table 3-14. LPC Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J20)..........................................................28
Table 3-15. User GPIO Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J8) .................................................29
Table 3-16. Power Interface Pin/Signals (J7)............................................................................31
Table 4-1. BIOS Setup Menus ................................................................................................35
Table A-1. Technical Support Contact Information..................................................................47
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual v
Page 6

Contents
vi Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 7

Chapter 1 About This Manual
Purpose of this Manual
This manual is for designers of systems based on the CoreModule™ 430 PC/104 single board computer
(SBC) module. This manual contains information that permits designers to create an embedded system
based on specific design requirements.
Information provided in this reference manual includes:
• CoreModule 430 SBC Specifications
• Environmental requirements
• Major chips and features implemented
• CoreModule 430 SBC connector/pin numbers and definitions
• BIOS Setup information
Information not provided in this reference manual includes:
• Detailed chip specifications
• Internal component operation
• Standard interface pin-out tables
• Internal registers or signal operations
• Bus or signal timing for industry standard busses and signals
References
The following list of references may be helpful for you to complete your custom design successfully. Some
of these references are also available on the Ampro By ADLINK web page. The web page was created for
embedded system developers to share ADLINK’s knowledge, insight, and expertise.
Specifications
• PC/104 Specifications Revision 2.5, November 2003
For latest revision of the PC/104 specifications, contact the PC/104 Consortium, at:
Web site: http://www.pc104.org
Major Integrated Circuit (Chip) Specifications
The following chip specifications are used in the CoreModule 430 processor module:
• DMP Electronics Inc. and the Vortex 86SX/DX CPU
Web site: http://www.vortex86sx.com/
• Winbond Electronics and the W25Q16BV SPI Flash memory
Web site: http://www.winbond.com/hq/enu/ProductAndSales/ProductSearch/?partno=w25q16bv
• Samsung Electronics and DDR2 on-board System Memory
Web site: http://www.samsung.com/global/business/semiconductor/
• Hynix Semiconductor, Inc. and DDR2 on-board Video Memory
Web site: http://www.hynix.com/gl/products/consumer/consumer_info.jsp
NOTE If you are unable to locate the datasheets using the links provided, search the
internet to find the manufacturer’s web site and locate the documents you need.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 1
Page 8

Chapter 1 About This Manual
2 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 9
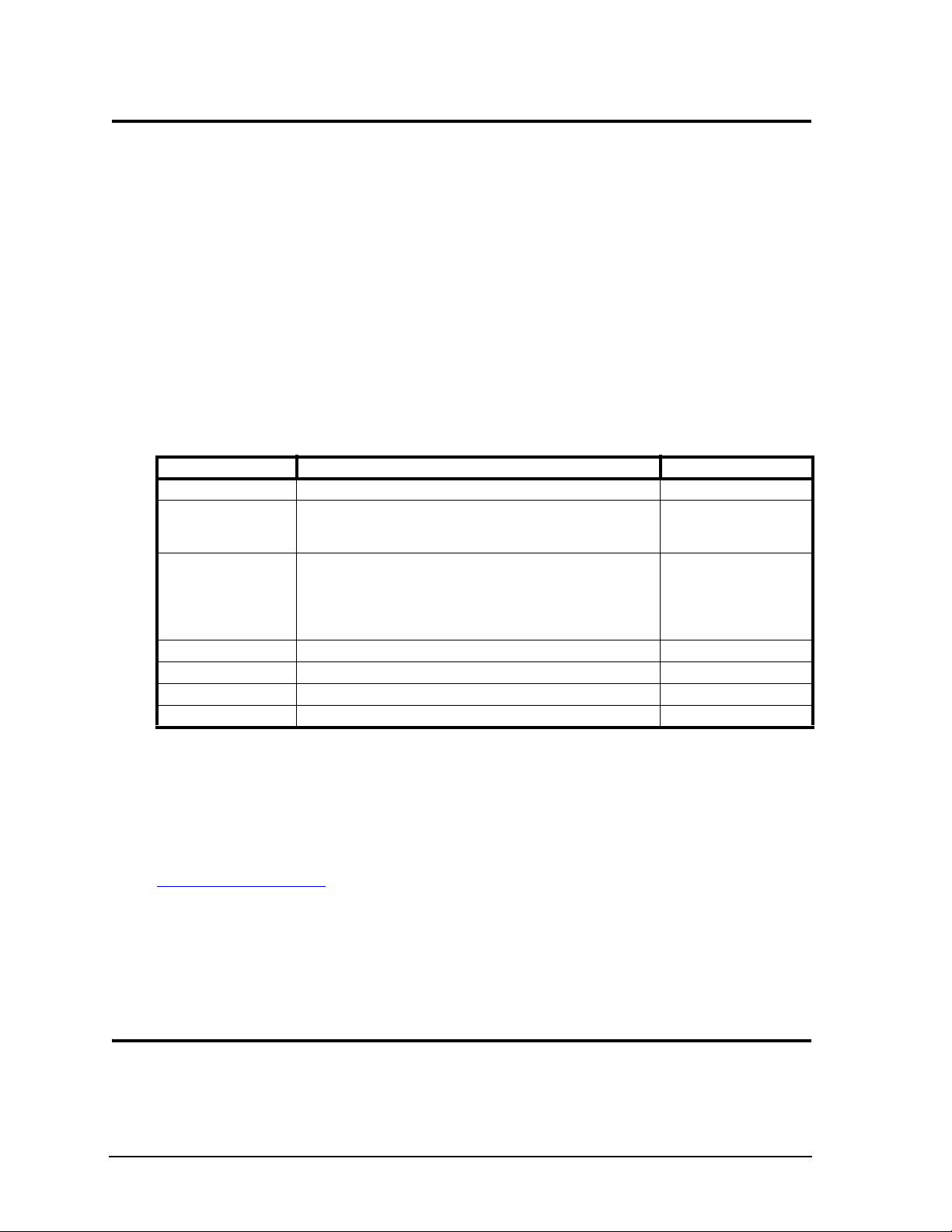
Chapter 2 Product Overview
PC/104 Module
CoreModule 430
PC/104 Module
Stackthrough
Expansion
Bus Headers
4-40 nut (4)
0.6 inch spacer (4)
0.6 inch spacer (4)
4-40 screw (4)
PC/104 Module
CM430stack
This introduction presents general information about the PC/104 architecture and the CoreModule 430
Single Board Computer (SBC). After reading this chapter you should understand:
• PC/104 architecture
• CoreModule 430 product description
• CoreModule 430 features
• Major components
• Header definitions
• Specifications
PC/104 Architecture
The PC/104 architecture affords a great deal of flexibility in system design. You can build a simple system
using only a CoreModule Single Board Computer (SBC), with input/output devices connected to its serial or
parallel ports and a Compact Flash card in the Compact Flash socket. To expand a simple CoreModule
system, simply add self-stacking ADLINK MiniModules or 3rd party PC/104 expansion boards to provide
additional capabilities, such as:
• Additional I/O ports
• Analog or digital I/O interfaces
PC/104 expansion modules can be stacked with the CoreModule 430 avoiding the need for card cages and
backplanes. The PC/104 expansion modules can be mounted directly to the PC/104 bus connector of the
CoreModule 430. PC/104-compliant modules can be stacked with an inter-board spacing of ~0.66" (16.7
mm) so that a 3-module system fits in a 3.6" x 3.8" x 2.4" space. See Figure 2-1.
One or more MiniModule products or other PC/104 modules can be installed on the CoreModule expansion
connectors. When installed on the PC/104 headers, the expansion modules fit within the CoreModule outline
dimensions. Most MiniModule products have stack through connectors compatible with the PC/104 Version
2.5 specification. Several modules can be stacked on the CoreModule headers. Each additional module
increases the thickness of the package by 0.60" (15 mm). See Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1. Stacking PC/104 Modules with the CoreModule 430
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 3
Page 10

Chapter 2 Product Overview
Product Description
The CoreModule 430 SBC is an exceptionally high integration, x86-based PC compatible system in the
PC/104 form factor. This rugged and high quality single board system contains all the component
subsystems of a PC/AT motherboard plus the equivalent of several PC/AT expansion boards.
In addition, the CoreModule 430 SBC includes a comprehensive set of system extensions and enhancements
that are specifically designed for embedded systems. These enhancements ensure fail-safe embedded system
operation, such as a watchdog timer. The CoreModule 430 is designed to meet the size, power consumption,
temperature range, quality, and reliability demands of embedded applications. The CoreModule 430 requires
a single +5V power source.
The CoreModule 430 SBC is particularly well suited to either embedded or portable applications. Its
flexibility makes system design quick and easy. It can be stacked with ADLINK MiniModules or other
PC/104-compliant expansion boards, or it can be used as the computing engine in a fully customized
application.
Module Features
• CPU
Provides x86 based DMP Vortex SX (300 MHz) or DX (800 MHz) microprocessor
Provides integrated Northbridge and Southbridge
Fully supports PC compatible architecture
Provides 8 kB Unified Instruction and Data Cache
Provides Parallel Processing Integrated Floating Point Unit (only in DX version)
Provides Low Power and System Management Modes
• Memory
Provides up to 256 MB standard DDR2 system RAM (soldered on the board)
Provides up to 32 MB standard DDR2 video RAM (soldered on the board)
Supports Memory Bus Speeds of 166 MHz on the SX CPU and 333 MHz on the DX CPU
• PC/104 Bus Interface
Provides standard PC/104 connector
Supports clock speeds up to 8 MHz ISA
• IDE Interface
Provides one IDE channel
Supports two enhanced IDE devices
Provides Fast ATA-capable interface for high-speed PIO modes
(PIO modes 0 to 4)
Supports ATAPI and DVD peripherals
Supports IDE native and ATA compatibility modes
• Compact Flash Socket
Provides Compact Flash socket (Type I or II)
Supports IDE Compact Flash cards
Attached to Primary IDE bus
4 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 11

Chapter 2 Product Overview
• Serial Ports
Provides two 10-pin headers and four buffered RS-232 serial ports with full handshaking and
modem capability
Provides 16C550 or 16C552 UARTs, each with a built-in 16-byte FIFO buffer
Supports RS-232 or RS-485 operation on ports 1 and 2
Supports programmable word length, stop bits, and parity
Supports 16-bit programmable baud-rate generator and an interrupt generator
• Parallel Port (LPT)
Provides parallel port header
Supports standard printer port
Supports IEEE standard 1284 protocols, including SPP, EPP, and ECP modes
Supports 16 byte FIFO for ECP mode
• Ethernet
Supports IEEE 802.3 10BaseT/100BaseT compatible physical layer
Supports Auto-negotiation for speed, duplex mode, and flow control
Supports full duplex or half-duplex mode
• Full-duplex mode supports transmit and receive frames simultaneously
• Supports IEEE 802.3x Flow control in full duplex mode
• Half-duplex mode supports enhanced proprietary collision reduction mode
• Utility Interface
PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Interface
Supports external battery for Real Time Clock operation
Supports standard external 8 speaker interface
Supports external reset switch
• USB Ports
Provides one root USB hub
Provides two USB ports
Supports USB v2.0 and Universal UHCI v1.1
• Video (TTL/VGA) Display
Enhanced 2D graphics controller
Supports BitBLT implementation for all 256 raster operations for Windows support
Provides hardware command queue
Supports all BLT transparency modes
• Bitmap transparency
• Pattern transparency
• Source transparency
• Destination transparency
Supports rectangle clipping
Supports fast line draw engine with styled pattern
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 5
Page 12

Chapter 2 Product Overview
Supports fast rectangle fill engine
Supports 64x64x2 bit-mapped mono hardware cursor
Supports 256MB frame buffer with linear addressing
VGA Interface (DB15)
VGA Controller with 135 MHz triple RAMDACs for 1280 x 1024 x 75 Hz display
Supports 24-bit pixel depth
Interlaced or non-interlaced output
TTL Interface
Supports VESA Flat Panel Display interface
Supports programmable panel size up to 1600x1200 pixel display resolution
Supports internal CRT controller for display mode settings
Supports 12-, 18-, and dual 12-bit interface (1 Pixel/Clock)
Supports 3.3V or 5V LCD panels; jumper selectable
• Miscellaneous
Provides Real Time Clock and CMOS RAM, with support for battery-free operation
Provides General Purpose I/O (GPIO) interface
Supports Oops! Jumper (BIOS Recovery)
Supports Remote Access (Console Redirection)
Supports customizable Splash Screen
Supports Watchdog Timer (WDT)
Provides 16 Mbits of virtual floppy drive capacity
6 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 13
Chapter 2 Product Overview
SPI Header
SPI Flash
(Virtual Floppy)
USB0 and USB1
Header
Ethernet
Transformer
10/100 Ethernet
Header
CRT and TTL
Header
DDR2
Video Memory
DDR2
System Memory
DDR2
System Memory
SiS
Volari
TM
Z9s
PCI Graphics
Controller
DMP Vortex
86DX/SX
CPU
GPIOs (8)
Header
PCI Bus
Parallel (LPT)
Header
PC/104 Connector
Compact Flash
Socket
44-Pin IDE
Header
ISA Bus
Utility Interface
Header
LPC
Header
RTC
COM3 & COM4
Header
COM1 & COM2
Header
RS232
Transceiver (X2)
RS422/485
Transceiver (X1)
COM1 & COM2
Header
RS232
Transceiver (X1)
CM430blkdiag_c
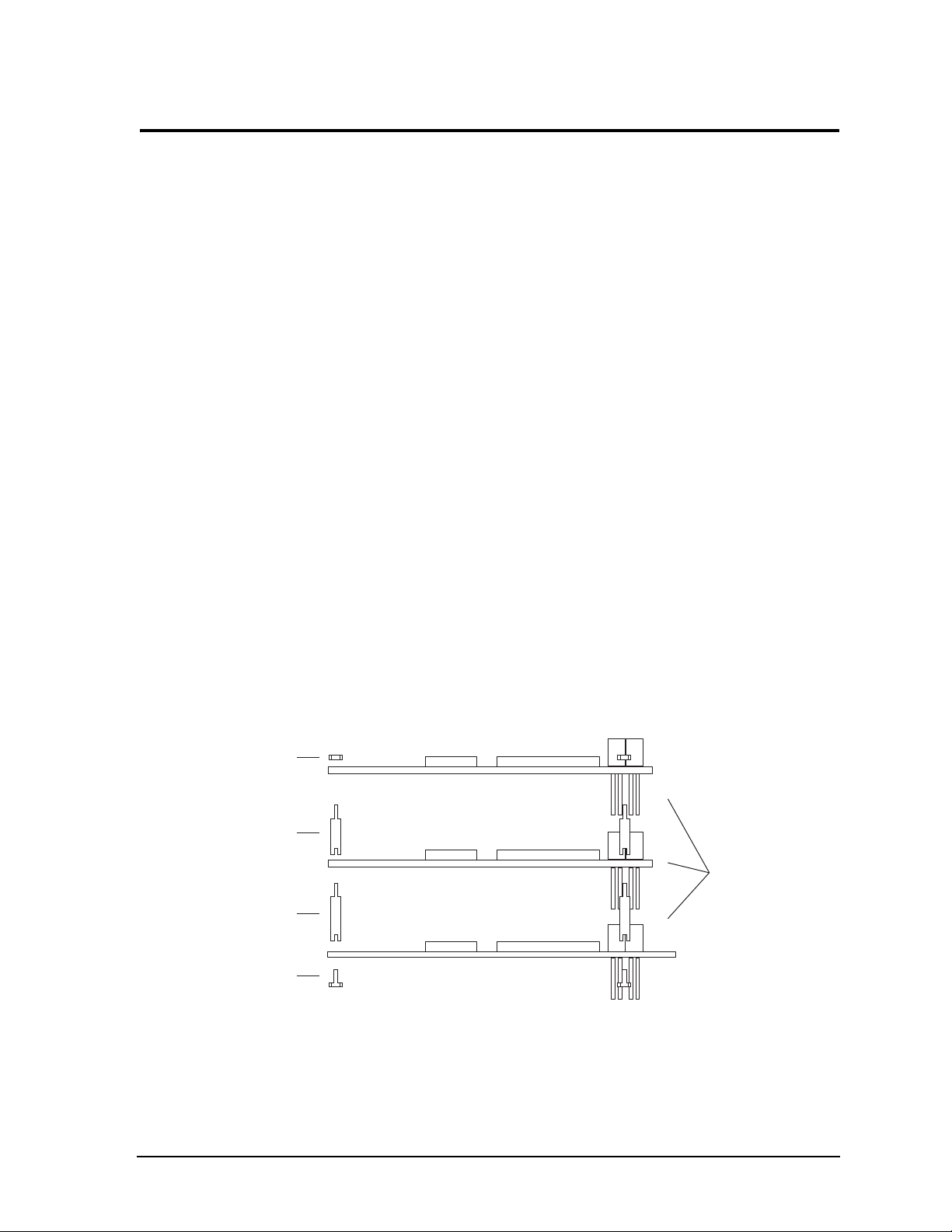
Block Diagram
Figure 2-2 shows the functional components of the module.
Figure 2-2. Block Diagram
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 7
Page 14
Chapter 2 Product Overview
Major Components (ICs)
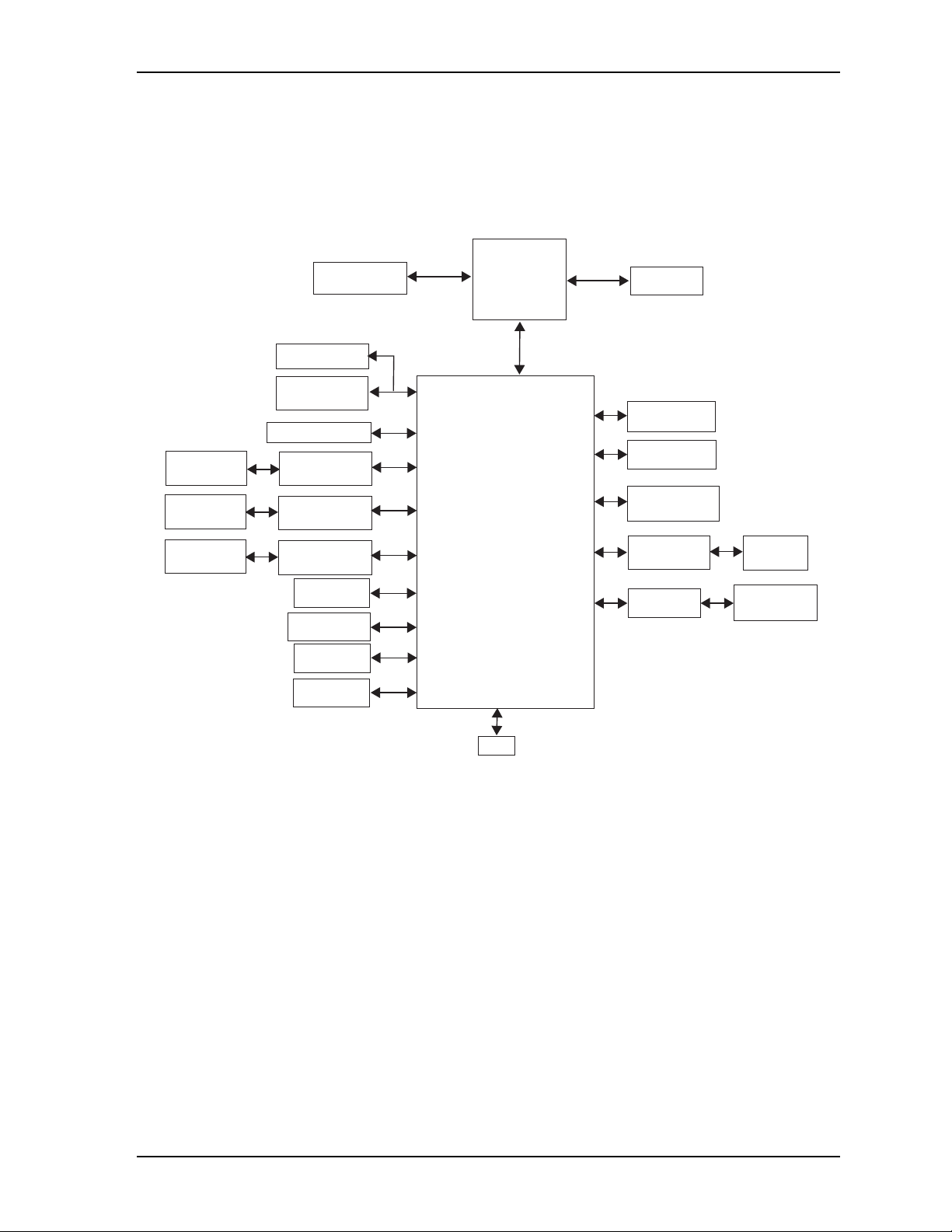
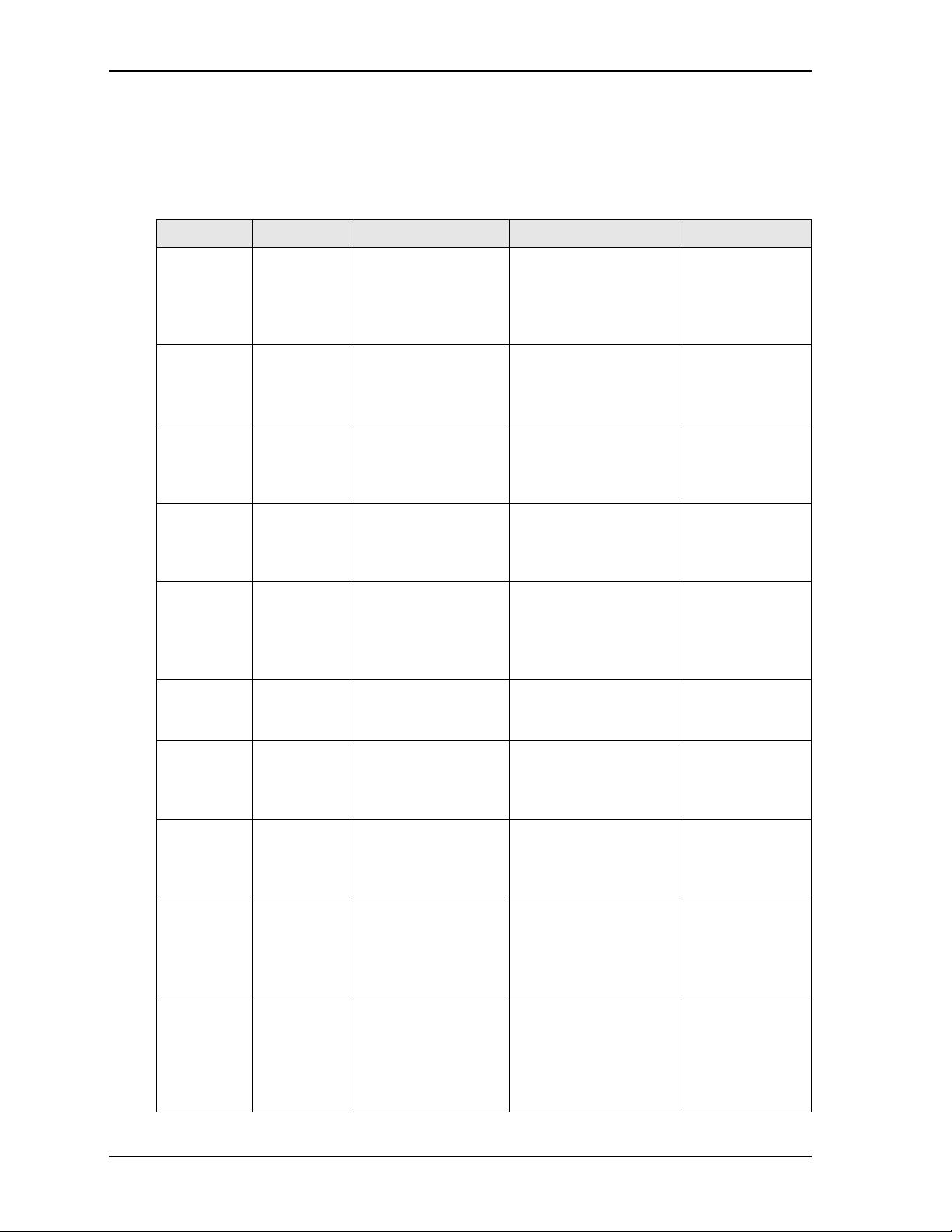
Table 2-1 describes the major integrated circuits (ICs) on the CoreModule 430, and Figure 2-3 shows the
locations of the major ICs on the board.
Table 2-1. Major Components (Chips) Descriptions and Functions
Chip Type Mfg. Model Description Function
CPU (U1) DMP
Electronics,
Inc.
PCI
Graphics
Controller
(U13)
DDR2
System
Memory
(U2 and U3)
DDR2
Vid eo
Memory
(U14)
RS232
Transceiver
(U4 - on
back of the
board)
RS232
Transceiver
(U5)
SPI Flash
(U6)
RS232
Transceiver
(U7)
RS422/485
Transceiver
(U9 - on
back of the
board)
Ethernet
Transfomer
(U12)
SiS
Corporation
Fluctuating Fluctuating On-board DDR2
Fluctuating Fluctuating On-board DDR2
Analog
Devices
Analog
Devices
Winbond W25Q16BV Serial Peripheral
Analog
Devices
Linear LTC1334CG#PBF RS422/485 Transceiver
Pulse H1102NL-T 10/100BaseT Ethernet
Vortex 86SX/DX x86 32-bit processor Integrates
Processor Core,
Memory
Controller, and
I/O Hub
Volari Z9S PCI graphics controller Integrates 2D
Engine and PCI
controller
Provides high128Mx8 System
memory
32Mx16 Video memory
ADM213EARSZ RS232 Transceiver for
COM3
ADM213EARSZ RS232 Transceiver for
COM4
Interface 16 Mbit Flash
Memory
ADM213EARSZ RS232 Transceiver for
COM1 and COM2
for COM1 and COM2
Magnetics
speed data
transfer
Provides high-
speed data
transfer
Transmits and
receives RS232
signals for COM3
Transmits and
receives RS232
signals for COM4
Stores data in
flash memory,
emulating a
floppy drive
Transmits and
receives RS232
signals for COM1
and COM2
Transmits and
receives
RS422/485
signals for COM1
and COM2
Provides
electrical isolation
for Ethernet
controller
contained in the
CPU
8 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 15
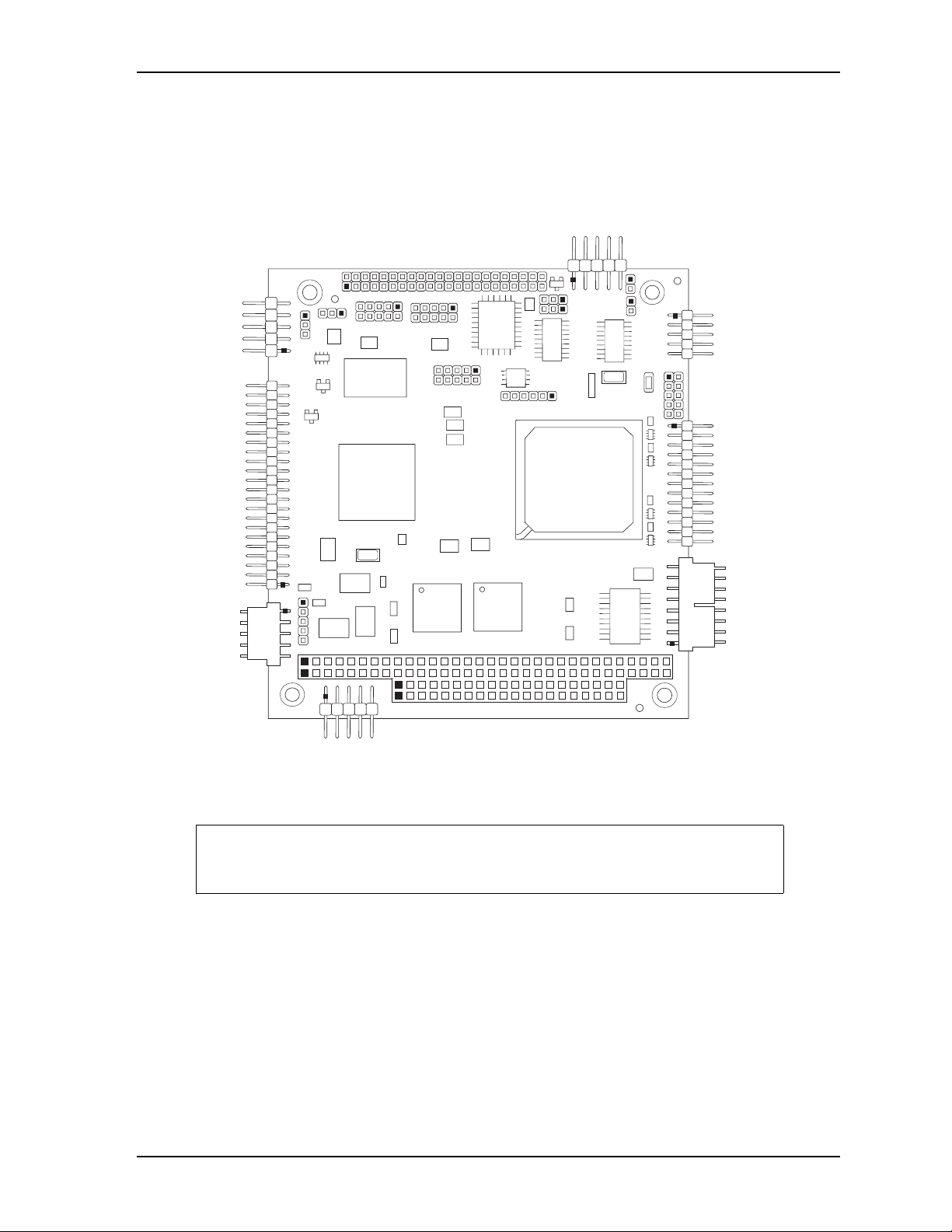
Chapter 2 Product Overview
U1
U2
U14
U3
U13
CM430_comp_top_c
U7
U5
U12
Key:
U1 - CPU
U2 - DDR2 SDRAM - System Memory
U3 - DDR2 SDRAM - System Memory
U5 - RS232 Transceiver - COM4
U6 - SPI Flash - Data Storage
U7 - RS232 Transceiver - COM1 and COM2
U12 - 10/100 Ethernet Transformer
U13 - PCI Graphics Controller
U14 - DDR2 SDRAM - Video Memory
U6
NOTE Pin 1 is shown as a black pin (square or round) on vertical headers or connectors
in all illustrations. Black dots on right-angle headers or connectors indicate pin
2.
Figure 2-3. Component Locations (Top Side)
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 9
Page 16
Chapter 2 Product Overview
20-pin, two rows,
Consecutive, (1, 11)
Or
1
234
5
678910
20
19
124
15 1120
10
53
20-pin, two rows,
Odd/Even, (1, 2)
CM430_ConNum_a
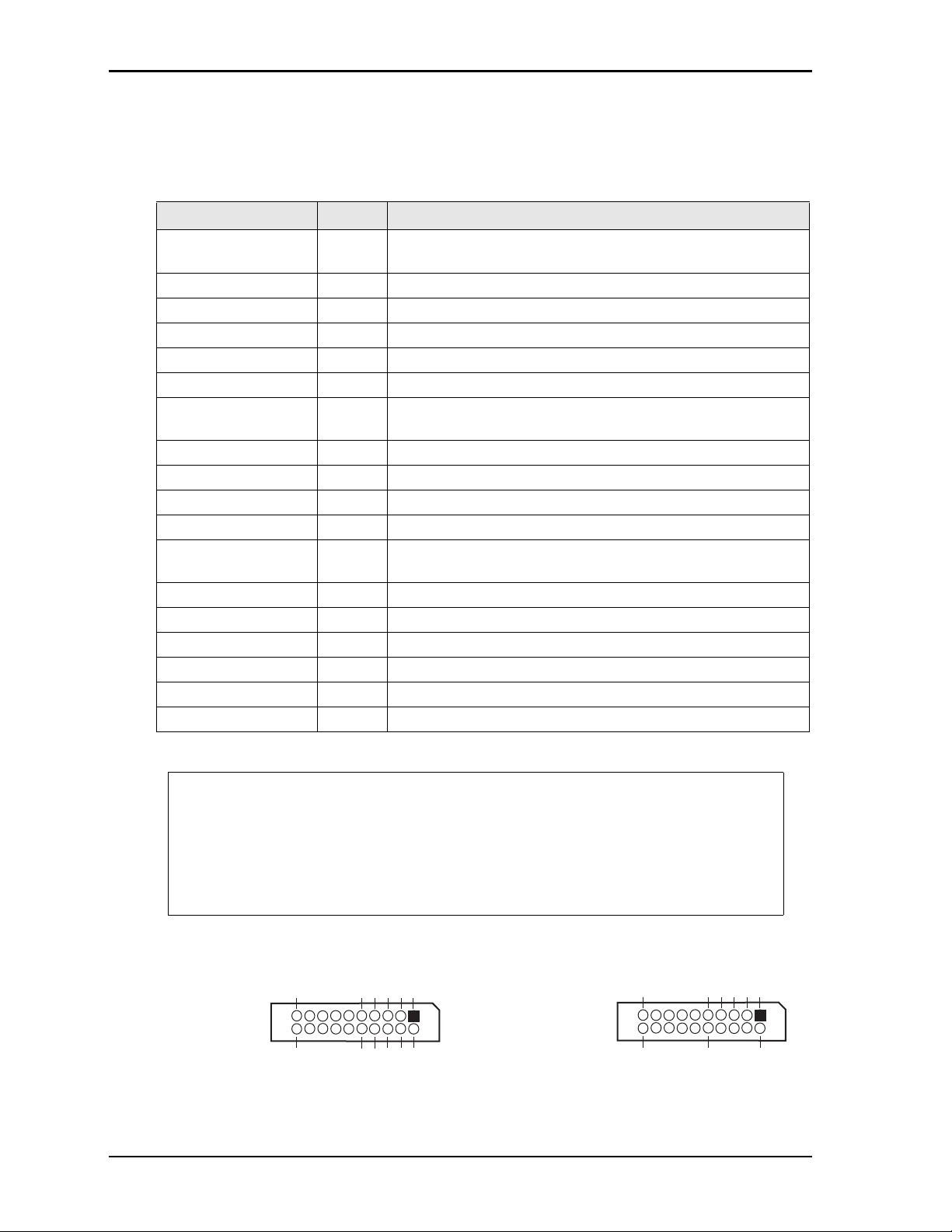
Header, Connector, and Socket Definitions
Table 2-2 describes the headers shown in Figure 2-5.
Table 2-2. Header, Connector, and Socket Descriptions
Jack/Plug # Access Description
P1A/1B & P1C/1D –
PC/104 Bus
J2 – Ethernet Top 8-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for Ethernet interface
J3 – Serial 1 (COM1) Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for Serial 1 interface
J4 – Parallel (LPT) Top 26-pin, 0.079" (2mm), right-angle header for Parallel interface
J5 – Utility Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for Utility interface
J6 – IDE Top 44-pin, 0.079" (2mm) header for IDE interface
J7 – Power Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for Power
J8 – GPIO (User) Top 10-pin, 0.079" (2mm) header for User defined GPIO signals
J9 – Serial 2 (COM2) Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for Serial 2 interface
J10 – USB0 Top 5-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm), right-angle header for USB0 interface
J11 – Video Top 44-pin, 0.079" (2mm), right-angle header for LCD/CRT interface
J12 – Compact Flash Bottom 50-pin, 0.050" (1.27mm) socket for Type I or II Compact Flash
J13 – Serial 4 (COM4) Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm) header for Serial 4 interface
J14 – Serial 3 (COM3) Top 10-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm) header for Serial 3 interface
J15 – DNP Top Do not populate
J17 – USB1 Top 5-pin, 0.079" (2mm) header for USB1 interface
J19 – SPI Top 6-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm) header used for SPI Flash programming
J20 – LPC Top 10-pin, 0.079" (2mm) header for LPC signals
Top/
Bottom
104-pin, 0.100" (2.54mm) connectors for PC/104 (ISA) bus
connection
cards
NOTE The pinout tables in Chapter 3 of this manual identify pin sequence using the
following methods: A 10-pin header with two rows of pins, using odd/even
numbering, where pin 2 is directly across from pin 1, is noted as 10-pin, 2 rows, odd/
even (1, 2). Alternately, a 20-pin connector using consecutive numbering, where pin
11 is directly across from pin 1, is noted in this way: 20-pin, 2 rows, consecutive (1,
11). The second number in the parenthesis is always directly across from pin 1. See
Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4. Connector Pin Identifications
10 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 17
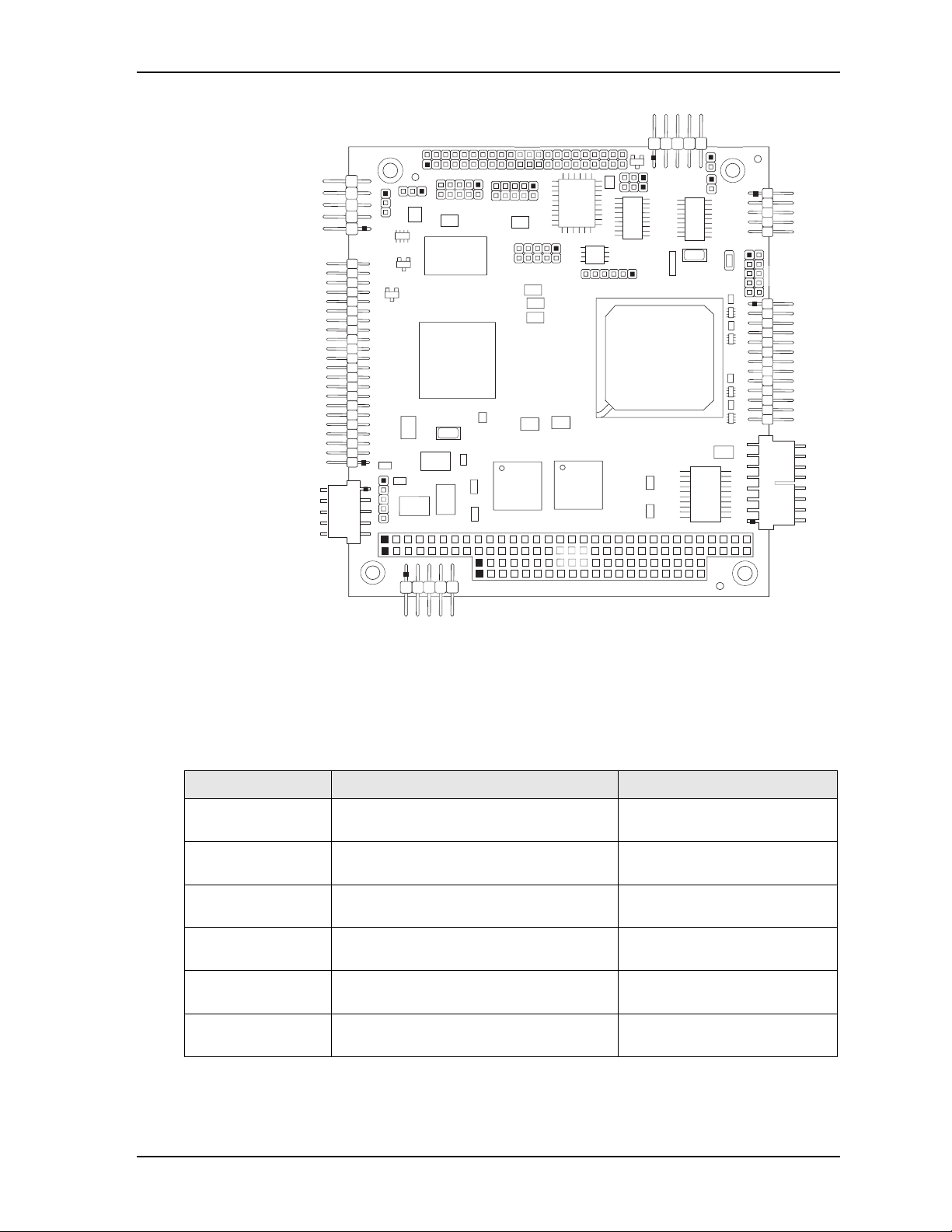
Chapter 2 Product Overview
CM430_conn_top_c
J6
J17
J13
J14
J9
J11
J10
P1
J7
J2
J4
J8
J19
J20
J3
J5
JP2
AB
DC
JP1
JP8
JP5
JP6
JP7
Key:
J2 - Fast Ethernet
J3 - COM1
J4 - Parallel
J5 - Utility
J6 - IDE
J7 - Power
J8 - GPIO
J9 - COM2
J10 - USB0
J11 - TTL and VGA Video
J13 - COM4
J14 - COM3
J17 - USB1
J19 - SPI 16 Mbit Data Storage
JP1 - See jumper table
JP2 - See jumper table
JP5 - See jumper table
JP6 - See jumper table
JP7 - See jumper table
JP8 - See jumper table
P1 - PC/104
Jumper Header Definitions
Table 2-3. Jumper Settings
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 11
Figure 2-5. Header Locations (Top Side)
Table 2-3 describes the jumper headers shown in Figure 2-5.
(Removed) Default setting
(Removed) Default setting
Jumper # Installed Removed/Installed
JP1 – Serial Port 2
Termination
JP2 – Serial Port 1
Termination
JP5 – Backlight
Enable RS-485 Termination (Pins 1-2) Disable RS-485 Termination
Enable RS-485 Termination (Pins 1-2) Disable RS-485 Termination
+5 Volts (Pins 1-2) +12 Volts (Pins 2-3) Default
Voltage Select
JP6 – Flat Panel
Voltage Select
JP7 – Compact Flash
+3.3 Volts (Pins 1-2) Default +5 Volts (Pins 2-3)
+5 Volts (Pins 1-2) +3.3 Volts (Pins 2-3) Default
Voltage Select
JP8 – IDE Select Enable HDD master, CF slave (Pins 1-2)
Default
Note: All jumper headers use 0.079" (2mm) pitch.
Enable HDD slave, CF master
(Pins 2-3)
Page 18

Chapter 2 Product Overview
CM430_mech_dwg_top_b
0
0.200
3.575
3.775
0
0.200
3.350
3.550
0.350
3.250
Specifications
Physical Specifications
Table 2-4 shows the physical dimensions of the module and Figure 2-6 shows the mounting dimensions.
Table 2-4. Weight and Footprint Dimensions
Item Dimension
Weight 0.10 kg. (0.20 lbs.)
Height (upper surface) 10.99mm (0.43")
See Note on page 13.
Width 90.2mm (3.6")
Length 95.9mm (3.8")
Mechanical Specifications
NOTE Height is measured from the
upper board surface to the
highest permanent component
(PC/104 connector) on the
upper board surface. This does
not include the heatsink.
Figure 2-6. Mechanical Dimensions (Top Side)
12 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 19

Chapter 2 Product Overview
NOTE All dimensions are given in inches. Pin 1 is shown as a black pin (square or
round) on vertical headers or connectors in all illustrations. Black dots on rightangle headers or connectors indicate pin 2.
The Compact Flash socket (J12) exceeds the PC/104 height limitation by 0.2
inches.
Power Specifications
Table 2-5 provides the power requirements for the 300 MHz and 800 MHz versions of the CoreModule 430.
Table 2-5. Power Supply Requirements
Parameter Characteristics for 300 MHz CPU Characteristics for 800 MHz CPU
Input Type Regulated DC voltages Regulated DC voltages
Peak In-rush Current 14.80A (74.00W) 14.86A (74.30W)
Idle Current 1.30A (6.51W) 1.42A (7.12W)
BIT Current (Typical) 1.32A (6.58W) 1.44A (7.19W)
Operating configurations:
• In-rush operating configuration includes CRT video, 256MB DDR RAM, and power.
• Idle operating configuration includes the in-rush configuration as well as on-board Compact Flash with
64MB card, and one keyboard.
• BIT = Burn-In-Test. Operating configuration includes idle configuration as well as two serial port loop-
backs, one Ethernet connection, and four USB Compact Flash readers with 64MB Compact Flash.
Environmental Specifications
Table 2-6 provides the operating and storage condition ranges required for this module.
Table 2-6. Environmental Requirements
Parameter Conditions
Temperature
Operating –20° to +70° C (–4° to +158° F)
Extended (Optional) –40° to +85° C (–40° to +185° F)
Storage –55° to +85° C (–67° to +185° F)
Humidity
Operating 5% to 90% relative humidity, non-condensing
Non-operating 5% to 95% relative humidity, non-condensing
Thermal/Cooling Requirements
The CPU is the primary source of heat on the board. The 800 MHz version of the CoreModule 430 CPU is
designed to operate at its maximum speed and requires a heatsink (provided). The 300 MHz version of the
CoreModule 430 CPU does not require a heatsink.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 13
Page 20

Chapter 2 Product Overview
14 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 21

Chapter 3 Hardware
Overview
This chapter discusses the chips and connectors of the module features in the following order:
• CPU
• Graphics
• Memory
System Memory
Vid e o Memory
SPI Flash
• Memory Map
• Interrupt Channel Assignments
• I/O Address Map
• Serial
• Parallel (LPT)
• Utility
Keyboard
Mouse
Battery
Reset Switch
Speaker
• Ethernet
• USB
• Vid eo
• SPI
• LPC
• Miscellaneous
Time of Day/RTC
User GPIO
Oops! Jumper (BIOS Recovery)
Watchdog timer
• Power
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 15
Page 22

Chapter 3 Hardware
NOTE ADLINK Technology, Inc. only supports the features and options listed in this
manual. The main components used on the CoreModule 430 may provide more
features or options than are listed in this manual. Some of these features/options
are not supported on the module and will not function as specified in the chip
documentation.
Only the pinout tables of non-standard headers and connectors are included in
this chapter. This chapter does not include pinout tables for standard headers and
connectors such as PC/104, 44-pin IDE, and Compact Flash.
CPU
The CoreModule 430 offers two versions of an embedded microprocessor—the DMP Vortex 86SX and
86DX—operating at 300 and 800 MHz, respectively, combining a powerful x86 core and a selection of
peripheral interfaces onto one chip. The 86SX and 86DX integrate CPU, Northbridge, and Southbridge
functions. This single chip supports logic including PC/104, EIDE controllers and combines these with
standard I/O interfaces to provide a PC compatible subsystem on a single chip.
Graphics
The CoreModule 430 provides a single PCI graphics controller chip which integrates a 2D engine and a PCI
controller. The graphics controller incorporates a configurable 3.3V/2.5V DVO interface to support a third
party TMDS transmitter and achieves high 2D performance with a DDR2 memory interface supporting a
bandwith of up to 1 GB (DDR2 @ 250 MHz.)
Memory
The CoreModule 430 memory consists of the following element(s):
• System Memory
• Vid e o Memory
• SPI Flash
System Memory
The CoreModule 430 provides two 16-bit, DDR2 memory chips of up to 128MB each for a total of up to
256MB of system memory soldered to the module and operating at 166MHz.
Video Memory
The CoreModule 430 provides one 16-bit, DDR2 memory chip of 32MB of video memory soldered to the
module and operating at 166MHz.
SPI Flash
The CoreModule 430 features an on-board 16Mbit SPI Flash device, operating as a virtual Floppy Disk
Drive. The board supports both the SPI Flash and an SPI header on the external SPI Bus. Enable the SPI
Flash through the Boot screen of the BIOS Setup Utility. Refer to the Chapter 1 for a link to the SPI Flash
data sheet.
16 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 23

Chapter 3 Hardware
Memory Map
The following table provides the common PC/AT memory allocations. These are DOS-level addresses. The
OS typically hides these physical addresses by way of memory management. Memory below 000500h is
used by the BIOS.
Table 3-1. Memory Map - Vortex 86SX/DX Processor
Base Address Function
00000000h - 0009FFFFh Conventional Memory
000A0000h - 000AFFFFh Graphics Memory
000B0000h - 000B7FFFh Mono Text Memory
000B8000h - 000BFFFFh Color Text Memory
000C0000h - 000C7FFFh Standard Video BIOS
000D0000h - 000DFFFFh Reserved for Extended BIOS
000E0000h - 000EFFFFh Extended System BIOS Area
000F0000h - 000FFFFFh System BIOS Area (Storage and RAM Shadowing)
00100000h
FFFC0000h [for SX
processor]
- Top of
DRAM
FFFFFFFFh System Flash
Main DRAM Range
FFE00000h [for DX
processor]
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 17
Page 24

Chapter 3 Hardware
Interrupt Channel Assignments
The interrupt channel assignments are shown in Table 3-2.
Table 3-2. Interrupt Channel Assignments
Device vs IRQ No. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Timer X
Keyboard X
Secondary Cascade X
COM1 D
COM2 D O
COM3 O O O D
COM4 O O D O
Parallel O D
RTC X
IDE D
Math Coprocessor
(only in DX
processor)
PS/2 Mouse X
PCI INTA Automatically Assigned
PCI INTB Automatically Assigned
PCI INTC Automatically Assigned
PCI INTD Automatically Assigned
USB Automatically Assigned
VGA Automatically Assigned
Ethernet Automatically Assigned
X
Legend: D = Default, O = Optional, X = Fixed
NOTE The IRQs for the Ethernet, Video, and Internal Local Bus (ISA) are
automatically assigned by the BIOS Plug and Play logic. Local IRQs assigned
during initialization can not be used by external devices.
Table 3-3. DMA Map
DMA # Use
0-1, 5, 6, 7 Direct Memory Access
3 LPT 1, only in ECP mode (configurable)
4 DMA 1 cascade
18 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 25

Chapter 3 Hardware
I/O Address Map
Table 3-4 shows the I/O address map. These are DOS-level addresses. The OS typically hides these physical
addresses by way of memory management.
Table 3-4. I/O Address Map
Address (hex) Subsystem
0000-000F Primary DMA Controller (#1)
0020-0021 Master Interrupt Controller (#1)
0040-0043 Programmable Interrupt Timer (Clock/Timer)
0060 Keyboard Controller
0061 ISA Standard Port B
0063 ISA Standard Port B alias
0064 Keyboard Controller
0065 ISA Standard Port B alias
0067 ISA Standard Port B alias
0069 ISA Standard Port B alias
006B ISA Standard Port B alias
006D ISA Standard Port B alias
006F ISA Standard Port B alias
0070-0071 RTC/ NMI enable
0080-008F DMA Page
00A0-00A1 Slave Interrupt Controller (#2)
00C0-00DF Secondary DMA Controller (#2)
00F0-00FF Math Coprocessor (only in the DX processor)
01F0-01F7 IDE 0 (can be disabled)
02E8-2FF Serial Port 4 (COM4) (base configuration @
3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h/10)
02F8-02FF Serial Port 2 (COM2) (base configuration @
3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h/10)
0378-037F LPT 1 (only in EPP modes, with default base address)
03E8-3EF Serial Port 3 (COM3) (base configuration @
3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h/10)
03F6 IDE 0 (see 1F0)
03F8-03FF Serial Port 1 (COM1) (base configuration @
3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h/10)
0778-077A LPT 1 (only in EPP modes, with default base address)
0CF8 PCI Configuration Address
0CFC-0CFF PCI Configuration Data
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 19
Page 26

Chapter 3 Hardware
Parallel Interface (LPT)
The Vortex x86 processor chip provides the Parallel Port interface. The Parallel Port supports the standard
parallel, Bi-directional, Standard Printer Port (SPP), Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP), and Enhanced
Capabilities Port (ECP) protocols.
Table 3-5 describes the pin signals of the Parallel interface, which uses a 26-pin, right-angle header with 2
rows, odd/even sequence (1, 2), and 0.079" (2mm) pitch.
Table 3-5. Parallel (LPT) Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J4)
Pin # Signal Description
1 Strobe* Strobe* – This is an output signal used to strobe data into the printer. I/O pin in
ECP/EPP mode.
2 AutoFD* Auto Feed* – This is a request signal into the printer to automatically feed one
line after each line is printed.
3 PD0 Parallel Port Data 0 – These pins (0 to 7) provides parallel port data signals.
4 ERR* Error – This is a status output signal from the printer. A Low State indicates an
error condition on the printer.
5 PD1 Parallel Port Data 1 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
6 INIT* Initialize* – This signal is used to Initialize printer. Output in standard mode,
I/O in ECP/EPP mode.
7 PD2 Parallel Port Data 2 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
8 SLIN Select In – This output signal is used to select the printer. I/O pin in ECP/EPP
mode.
9 PD3 Parallel Port Data 3 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
10
11 PD4 Parallel Port Data 4 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
12
13 PD5 Parallel Port Data 5 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
14
15 PD6 Parallel Port Data 6 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
16
17 PD7 Parallel Port Data 7 – Refer to pin-3, PDO for more information.
18
19 Ack* Acknowledge* – This is a status output signal from the printer. A Low State
20
21 Busy* Busy* – This is a Status output signal from the printer. A High State indicates
22
23 PE Paper End – This is a status output signal from the printer. A High State
24
25 Slct Select – This is a status output signal from the printer. A High State indicates it
26 Key/NC Key Pin/Not Connected
GND Ground
GND Ground
GND Ground
GND Ground
GND Ground
indicates it has received the data and is ready to accept new data.
GND Ground
the printer is not ready to accept data.
GND Ground
indicates it is out of paper.
GND Ground
is selected and powered on.
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
20 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 27

Chapter 3 Hardware
CM430RS485jump_b
Or
1
35
7
9
24
6810
Serial Ports (J3, J9)
(COM1 or COM2)
Side View
Standard DB9 Serial
Port Connector (Female)
Rear View
5
4
3
2
1
9
8
7
6
Serial Interface
The Vortex CPU contains the circuitry for all four serial ports. The CoreModule 430 provides serial ports 1
and 2 through transceivers U7 and U9 (headers J3 and J9), serial port 3 through transceiver U4 (header J14)
and serial port 4 through transceiver U5 (header J13). The serial ports support the following features:
• Programmable word length, stop bits and parity
• 16-bit programmable baud rate generator
• Interrupt generator
• Loop-back mode
• 16-bit FIFOs for each port
• Ports 1, 2, 3, and 4 are supported by the Vortex processor and are 16C550/16C552 compatible
Serial 1 (J3, COM1) supports RS-232/RS-485 with full modem operation
Serial 2 (J9, COM2) supports RS-232/RS-485 with full modem operation
Serial 3 (J14, COM3) supports RS-232 with full modem operation
Serial 4 (J13, COM4) supports RS-232 with full modem operation
NOTE The RS-232/RS-485 mode for Serial Port 1 (COM1) and Serial Port 2 (COM2)
are selected in BIOS Setup Utility. However, the RS-232 mode is the default
(Standard) for any serial port.
RS-485 mode termination is selected with jumper JP2 Serial 1 (COM1) and JP1
Serial 2 (COM2) on the module. Refer to Table 2-3 for more information.
To implement the two-wire RS-485 mode on either serial port, you must tie the equivalent pins together for
the selected port.
For example, you must tie pin 3 (Rx Data –) to 5 (Tx Data –) and pin 4 (Tx Data +) to 6 (Rx Data +) at Serial
Port 1 or 2 (J3 or J9) for the two-wire interface. As an alternate, you may short the equivalent pins on the
DB9 connector attached to respective serial port, as shown in Figure 3-1. Refer also to the following tables
for the specific pins on the connectors. The RS-422 mode uses a four-wire interface and does not require
combining pins for its operation, but you must select RS-485 in BIOS Setup.
Figure 3-1. RS-485 Serial Port Implementation
Table 3-6 provides the signals for the corresponding pins of the two independent serial interfaces (Serial 1 &
2), and Table 3-7 provides the signals for the corresponding pins of two independent serial interfaces (Serial
3 & 4). Both interfaces use 10-pin, right-angle headers with 2 rows, odd/even sequence (1, 2), and 0.100"
(2.54mm) pitch.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 21
Page 28

Chapter 3 Hardware
Table 3-6. Serial Ports 1 & 2 Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J3, J9)
Pin # Signal DB9 # Description
1 DCD* 1 Data Carrier Detect – Indicates external serial device is detecting a
carrier signal (i.e., a communication channel is currently open). In direct
connect environments, this input is driven by DTR as part of the DTR/
DSR handshake.
2 DSR* 6 Data Set Ready – Indicates external serial device is powered, initialized,
and ready. Used as hardware handshake with DTR for overall readiness.
3RXD
2 Receive Data – Serial port receive data input is typically held at a logic 1
(mark) when no data is being transmitted, and is held “Off” for a brief
interval after an “On” to “Off” transition on the RTS line to allow the
transmission to complete.
Rx Data –
4RTS*
7 Request To Send – Indicates serial port is ready to transmit data. Used as
Serial Port 1 or 2 – If in RS-485 mode, this pin is Rx Data Negative.
hardware handshake with CTS for low level flow control.
Tx Data +
5TXD
3 Transmit Data – Serial port transmit data output is typically held to a
Serial Port 1 or 2 – If in RS-485 mode, this pin is Tx Data Positive.
logic 1 when no data is being sent. Typically, a logic 0 (On) must be
present on RTS, CTS, DSR, and DTR before data can be transmitted on
this line.
Tx Data –
6CTS*
8 Clear To Send – Indicates external serial device is ready to receive data.
Serial Port 1 or 2 – If in RS-485 mode, this pin is Tx Data Negative.
Used as hardware handshake with RTS for low level flow control.
Rx Data +
Serial Port 1 or 2 – If in RS-485 mode, this pin is Rx Data Positive.
7 DTR* 4 Data Terminal Ready – Indicates serial port is powered, initialized, and
ready. Used as hardware handshake with DSR for overall readiness.
8 RI* 9 Ring Indicator – Indicates external serial device is detecting a ring
condition. Used by software to initiate operations to answer and open the
communications channel.
9
GND 5 Ground
10 Key/NC NC Key Pin/Not connected
Note: The shaded table cell denotes ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
Table 3-7. Serial Ports 3 & 4 Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J13, J14)
Pin # Signal DB9 # Description
1 DCD* 1 Data Carrier Detect – Indicates external serial device is detecting a
carrier signal (i.e., a communication channel is currently open). In direct
connect environments, this input is driven by DTR as part of the DTR/
DSR handshake.
2 DSR* 6 Data Set Ready – Indicates external serial device is powered, initialized,
and ready. Used as hardware handshake with DTR for overall readiness.
3 RXD 2 Receive Data – Serial port receive data input is typically held at a logic 1
(mark) when no data is being transmitted, and is held “Off” for a brief
interval after an “On” to “Off” transition on the RTS line to allow the
transmission to complete.
22 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 29

Chapter 3 Hardware
Table 3-7. Serial Ports 3 & 4 Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J13, J14) (Continued)
4 RTS* 7 Request To Send – Indicates serial port is ready to transmit data. Used as
hardware handshake with CTS for low level flow control.
5 TXD 3 Transmit Data – Serial port transmit data output is typically held to a
logic 1 when no data is being sent. Typically, a logic 0 (On) must be
present on RTS, CTS, DSR, and DTR before data can be transmitted on
this line.
6 CTS* 8 Clear To Send – Indicates external serial device is ready to receive data.
Used as hardware handshake with RTS for low level flow control.
7 DTR* 4 Data Terminal Ready – Indicates serial port is powered, initialized, and
ready. Used as hardware handshake with DSR for overall readiness.
8 RI* 9 Ring Indicator – Indicates external serial device is detecting a ring
condition. Used by software to initiate operations to answer and open the
communications channel.
9
10 Key/NC NC Key Pin – Not connected
Note: The shaded table cell denotes ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
GND 5 Ground
USB Interface
The CoreModule 430 contains one root USB (Universal Serial Bus) hub and two functional USB ports. The
Vortex CPU provides the USB function including the following features:
• Provides one root hub with two USB ports
• Supports USB EHCI v.2.0 and USB OHCI v.1.1
• Provides over-current detection status
• Provides a fuse (F1, 1.5A) on board for over current protection
Table 3-8 describes the pin signals of the USB0 interface, which uses a single-row, 5-pin, right-angle header
with 0.100" (2.54mm) pitch.
Table 3-8. USB0 Interface Pin/Signal Designations (J10)
Pin # Signal Description
1
2 USB0N USB0 Port Data Negative
3 USB0P USB0 Port Data Positive
4
5SHIELDUSB0 Port shield
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground.
Table 3-9 describes the pin signals of the USB1 interface, which uses a single-row, 5-pin header with 0.079"
(2mm) pitch.
Table 3-9. USB1 Interface Pin/Signal Designations (J17)
USB0PWR USB Power – VCC (+5V +/-5%) power goes to the port through an on board
fuse. Port is disabled if this input is low.
GND USB0 Port ground
Pin # Signal Description
1
2 USB1N USB1 Port Data Negative
3 USB1P USB1 Port Data Positive
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 23
USB1PWR USB Power – VCC (+5V +/-5%) power goes to the port through an on board
fuse. Port is disabled if this input is low.
Page 30

Chapter 3 Hardware
Table 3-9. USB1 Interface Pin/Signal Designations (J17) (Continued)
4
5SHIELDUSB1 Port shield
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground.
GND USB1 Port ground
Utility Interface
The Utility interface provides various utility and I/O signals on the module and consists of a 10-pin, 0.1"
header. The Vortex CPU drives the signals on the Utility interface, and Table 3-10 provides the signal
definitions.
• PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse
• Battery
• Reset Switch
• Speaker
Keyboard
The signal lines for a PS/2 keyboard are provided from the Vortex CPU to the Utility interface.
Mouse
The signal lines for a PS/2 mouse are provided from the Vortex CPU to the Utility interface.
Battery
An external battery input connection is provided through the Utility interface to support a battery backup for
the CMOS RAM and the RTC (Real Time Clock).
Reset Switch
An external reset switch provides the reset signal through the Utility interface to a reset circuit, which drives
the Vortex CPU.
Speaker
The speaker signal provides sufficient signal strength to drive a 1W 8 “Beep” speaker through the Utility
interface at an audible level. The speaker signal is driven from an on board amplifier and the Vortex CPU.
Table 3-10 describes the pin signals of the Utility interface, which uses a 10-pin, right-angle header with 2
rows, odd/even sequence (1, 2), and 0.100" (2.54mm) pitch.
Table 3-10. Utility Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J5)
Pin # Signal Description
1 SPKR Speaker Output
2
3 RESETSW* External Reset Switch signal
4 MDATA Mouse Data input
5 KBDATA Keyboard Data input
6 KBCLK Keyboard Clock input
7
8 KMPWR Keyboard /Mouse power (+5V) output
BATV- Ground return
GND Ground
24 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 31

Chapter 3 Hardware
Table 3-10. Utility Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J5) (Continued)
9
10 MCLK Mouse Clock input
Notes: The shaded table cells denote power or ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
BATV+ Real time battery voltage (3.0V Max) input
Ethernet Interface
The Ethernet solution originates from the Vortex 86SX/DX CPU and consists of both the Media Access
Controller (MAC) and the physical layer (PHY) combined into a single component solution. The Vortex Fast
Ethernet Control Unit is a 32-bit PCI controller that features enhanced scatter-gather bus mastering
capabilities, which enables the processor to perform high-speed data transfers over the internal PCI bus. The
bus master capabilities enable the component to process high-level commands and perform multiple
operations, thereby off-loading communication tasks from the CPU. The Ethernet interface offers the
following features:
• Full duplex or half duplex support
• Full duplex support at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
• In full duplex mode, the Ethernet controller adheres to the IEEE 802.3x Flow Control specification.
• In half duplex mode, performance is enhanced by a proprietary collision reduction mechanism.
• IEEE 802.3 10/100BaseT compatible physical layer to wire transformer
• Two on board LEDs support the speed and the link & activity status
• IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation support
• Fast back-to-back transmission support with minimum interframe spacing (IFS).
• IEEE 802.3x auto-negotiation support for speed and duplex operation
• 3 kB transmit and 3 kB receive FIFOs (helps prevent data underflow and overflow)
• IEEE 802.3x 100BaseTX flow control support
• On-board magnetics (Ethernet isolation transformer)
Table 3-11 describes the pin signals of the Ethernet interface, which uses a single-row, 8-pin header with
0.100" (2.54mm) pitch.
Table 3-11. Ethernet Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J2)
Pin # Signal Description
1 TX+ Analog Twisted Pair Ethernet Transmit Differential Pair – These pins transmit the
2TX-
3 RX+ Analog Twisted Pair Ethernet Receive Differential Pair – These pins receive the
6RX-
4 CT Center Tap – Connected through two 75 ohm resistors in series to center tap of
5CT
7 CT Center Tap – Connected through two 75 ohm resistors in series to center tap of
8CT
serial bit stream through the isolation transformer.
serial bit stream through the isolation transformer.
isolation transformer and then to ground through common 1k PF capacitor.
isolation transformer and then to ground through common 1k PF capacitor.
NOTE The magnetics (isolation transformer, U12) for the Ethernet connector is
included on the CoreModule 430.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 25
Page 32

Chapter 3 Hardware
Video (TTL/VGA) Interface
The Volari Z9s graphics controller provides two graphics display ports for video signals to flat panel
displays and traditional glass CRT monitors. The features are listed below:
• Enhanced 2D Graphics Controller
Full BitBLT Implementation for all 256 Raster Operations Defined for Windows
Supports 4 Transparent BLT Modes
• Bitmap Transparency
• Pattern Transparency
• Source Transparency
• Destination Transparency
Rectangle Clipping
Fast Line Draw Engine with styled pattern
Fast Rectangle Fill Engine
256MB frame buffer with linear addressing
64x64x2 bit-mapped mono hardware cursor
• VGA Output (DB15)
Supports 135 MHz triple RAMDACs for 1280 x 1024 x 75 Hz display
Supports 24-bit pixel depth
Supports interlaced or non-interlaced output
• TTL Output
Conforms with VESA Flat Panel Display Interface FPDI-1B
Supports up to 1600x1200 pixel display resolutions
Uses Internal CRT Controller for display modes settings
Supports 12-, 18-, and dual 12-bit Interface (1 pixel/clock)
Table 3-12 describes the pin signals of the Video interface, which uses a 44-pin, right-angle header with 2
rows, odd/even sequence (1, 2), and 0.079" (2mm) pitch.
Table 3-12. Video Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J11)
Pin # Signal Description
1 TFTDCLK TFT Shift Clock – This clock signal provides the timing for transferring digital
pixel data.
2 TFTDE TFT Data Enable – This signal indicates valid data on any of the FP [23:0] lines.
3 TFTLP TFT Line Pulse – This signal is the digital monitor equivalent of HSYNC.
4 TFTFrame TFT Frame Marker – This signal is the TFT monitor equivalent of VSYNC.
5
6
7 NC Not connected (FP0 = Panel Data 0)
8 NC Not connected (FP1 = Panel Data 1)
9 FP2 Panel Data 2 – These pins (0 to 23) provides digital pixel data output signals.
10 FP3 Panel Data 3 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
11 FP4 Panel Data 4 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
GND Ground
GND Ground
26 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 33

Chapter 3 Hardware
Table 3-12. Video Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J11) (Continued)
12 FP5 Panel Data 5 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
13 FP6 Panel Data 6 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
14 FP7 Panel Data 7 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
15 NC Not connected (FP8 = Panel Data 8)
16 NC Not connected (FP9 = Panel Data 9)
17 FP10 Panel Data 10 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
18 FP11 Panel Data 11 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
19 FP12 Panel Data 12 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
20 FP13 Panel Data 13 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
21 FP14 Panel Data 14 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
22 FP15 Panel Data 15 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
23 NC Not connected (FP16 = Panel Data 16)
24 NC Not connected (FP17 = Panel Data 17)
25 FP18 Panel Data 18 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
26 FP19 Panel Data 19 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
27 FP20 Panel Data 20 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
28 FP21 Panel Data 21 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
29 FP22 Panel Data 22 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
30 FP23 Panel Data 23 – Refer to pin 9, FP2, for more information.
31
TFTEnVcc TFT Power (Vcc) – This signal is the power to flat panel displays.
32 TFTEnVee TFT Backlight Enable – This signal enables power to flat panel displays.
33
34
35
36
+PNLVdd Voltage (+3.3 or +5 volts ±5%) depends on setting of JP6.
+12V Out +12 volts ±5%
GND Ground
GND Ground
37 HSYNC Horizontal Sync – This signal is used for the digital horizontal sync output to the
CRT. Also used (with VSYNC) to signal power management state information to
the CRT per the VESA DPMS standard.
38 VSYNC Vertical Sync – This signal is used for the digital vertical sync output to the CRT.
Also used (with HSYNC) to signal power management state information to the
CRT per the VESA DPMS standard.
39
AGNDR Analog Ground for Red
40 RED Red – This pin provides the Red analog output to the CRT.
41
AGNDG Analog Ground for Green
42 GREEN Green – This pin provides the Green analog output to the CRT.
43
AGNDB Analog Ground for Blue
44 BLUE Blue – This pin provides the Blue analog output to the CRT.
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 27
Page 34

Chapter 3 Hardware
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The CoreModule 430 provides an SPI header for programming the SPI Flash virtual floppy drive.
Table 3-13 describes the pin signals of the SPI header, which provides a single-row of 6 pins with 0.079"
(2mm) pitch.
Table 3-13. SPI Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J19)
Pin # Signal Description
1 EXT_CS* SPI Chip Select
2 EXT_CLK SPI Clock
3 EXT_DO SPI Data Out
4EXT_DISPI Data In
5
6
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground. The * symbol indicates the signal is Active Low.
V.3.3 +3.3 Volts Power
GND Ground
Low Pin Count Interface (LPC)
The LPC interface provides expansion for custom LPC devices.
Table 3-14 describes the pin signals of the LPC interface, which uses a 10-pin header with 2 rows, odd/even
sequence (1, 2), and 0.079" (2mm) pitch.
Table 3-14. LPC Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J20)
Pin # Signal Description
1 AD0 Command, Address, and Data 0
2 SERIRQ Serial Interrupt Request
3 AD1 Command, Address, and Data 1
4 DRQ DMA Request
5 AD2 Command, Address, and Data 2
6 FRAME Frame Signals - indicate start of new cycle or termination of broken cycle
7 AD3 Command, Address, and Data 3
8 CLK_PCI PCI Clock
9
10
Note: The shaded table cells denotes power or ground.
V.3.3 +3.3 Volts Power
GND Ground
Miscellaneous
Real Time Clock (RTC)
The CoreModule 430 contains a Real Time (time of day) Clock (RTC), which can be backed up with an
external cell battery. The CoreModule 430 will function without a battery in those environments which
prohibit batteries. The CoreModule 430 will also continue to operate after the battery life has been
exceeded. Under these conditions all setup information is restored from the on-board Flash memory during
POST along with the default date and time information.
NOTE Some operating systems require a valid default date and time to function.
28 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 35

Chapter 3 Hardware
CM430_Oopsjump_b
Standard DB9 Serial
Port Connector (Female)
Rear View
5
4
32
1
9
87
6
Or
1
35
7
9
24
6810
Serial Port Header
(COM1)
User GPIO Interface
The CoreModule 430 provides GPIO pins for customer use, and the signals are routed to header J8. An
example of how to use the GPIO pins resides in the Miscellaneous Source Code Examples on the
CoreModule 430 Support Software QuickDrive.
The example program can be built by using the make.bat file. This produces a 16-bit DOS executable
application, gpio.exe, which can be run on the CoreModule 430 to demonstrate the use of GPIO pins. For
more information about the GPIO pin operation, refer to the Programming Manual for the Vortex processor
at:
http://www.vortex86sx.com/
Table 3-12 describes the pin signals of the GPIO interface, which uses a 10-pin header with 2 rows, odd/
even sequence (1, 2), and 0.079" (2mm) pitch.
Table 3-15. User GPIO Interface Pin/Signal Descriptions (J8)
Pin # Signal Description
1 GPIO0 User defined
2 GPIO1 User defined
3 GPIO2 User defined
4 GPIO3 User defined
5 GPIO4 User defined
6 GPIO5 User defined
7 GPIO6 User defined
8 GPIO7 User defined
9
10
GND Ground
GND Ground
Note: The shaded table cells denote ground.
Oops! Jumper (BIOS Recovery)
The Oops! jumper is provided in the event you have selected BIOS settings that prevent you from booting
the system. By using the Oops! jumper you can stop the current BIOS settings in the CMOS from being
loaded, allowing you to proceed, using the default settings. Connect the DTR pin to the RI pin on Serial port
1 (COM 1) prior to boot up to prevent the present BIOS settings from loading. After booting with the Oops!
jumper in place, remove the Oops! jumper and go into the BIOS Setup Utility. Change the desired BIOS
settings, or select the default settings, and save changes before rebooting the system.
To convert a standard DB9 connector to an Oops! jumper, short together the DTR (4) and RI (9) pins on the
rear of the connector as shown in Figure 3-2 on the Serial Port 1 DB9 connector.
Figure 3-2. Oops! Jumper
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 29
Page 36

Chapter 3 Hardware
Standard DB9 Serial
Port Cable Connector
(Female)
Rear View
5
4
32
1
9
8
7
6
Or
1
35
7
9
24
6810
Serial Port Header
(COM1 or COM2)
Remote Access
The CoreModule 430 BIOS supports the remote access (or console redirection) feature. This I/O function is
provided by an ANSI-compatible serial terminal, or the equivalent terminal emulation software running on
another system. This can be very useful when setting up the BIOS on a production line for systems that are
not connected to a keyboard and display.
Remote Access Setup
The remote access feature is implemented by connecting a standard null-modem cable or a modified serial
cable (or “Hot Cable”) between one of the serial ports, such as Serial 1 or 2 (J3 or J9), and the serial terminal
or a PC with communications software. The BIOS Setup Utility controls the remote access settings on the
CoreModule 430. Refer to Chapter 4, BIOS Setup for the settings of the remote access option, the serial
terminal, or PC with communications software and the connection procedure.
Hot (Serial) Cable
To convert a standard serial cable to a Hot Cable, specific pins must be shorted together at the Serial port
header or at the DB9 connector. Short together the RTS (4) and RI (8) pins on either serial port (J3 or J9)
header. As an alternate, you can short the equivalent pins (pins 7 and 9) on the back of the respective DB9
port connector as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3. Hot Cable Jumper
Watchdog Timer
The Watchdog Timer (WDT) restarts the system if an error or mishap occurs, allowing the system to recover
from the mishap, even though the error condition may still exist. Possible problems include failure to boot
properly, loss of control by the application software, failure of an interface device, unexpected conditions on
the bus, or other hardware or software malfunctions.
The WDT (Watchdog Timer) can be used both during the boot process and during normal system operation.
• During the Boot process – If the OS fails to boot in the time interval set in the BIOS, the system will
reset.
Enable the Watchdog Timer (sec) field in the Chipset > Southbridge
for a time-out interval in seconds, between 1 and 255, in one second increments. Ensure you allow
enough time for the operating system (OS) to boot. The OS or application must tickle (reset) the WDT
before the timer expires. This can be done by accessing the hardware directly or through a BIOS call.
• During System Operation – An application can set up the WDT hardware through a BIOS call, or by
accessing the hardware directly. Some ADLINK Board Support Packages provide an API to the WDT.
The application must tickle (reset) the WDT before the timer expires or the system will be reset.
• Watchdog Code examples – ADLINK has provided source code examples on the CoreModule 430
Support Software QuickDrive illustrating how to control the WDT. The code examples can be easily
copied to your development environment to compile and test the examples, or make any desired
changes before compiling. Refer to the WDT Readme file in the Sample Code directory on the
CoreModule 430 Support Software QuickDrive.
screen of BIOS Setup. Set the WDT
30 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 37

Chapter 3 Hardware
Power Interface
The CoreModule 430 requires one +5 volt DC power source. If the +5VDC power drops below ~4.65V, a
low voltage reset is triggered, resetting the system.
The power input header (J7) supplies the following voltages and ground directly to the module:
• 5.0VDC +/- 5% @ 1.35 Amps
Table 3-16 describes the pin signals of the Power interface, which uses a 10-pin, right-angle header with 2
rows, odd/even sequence (1, 2), and 0.100" (2.54mm) pitch.
Table 3-16. Power Interface Pin/Signals (J7)
Pin Signal Descriptions
1
2
3
4
5
6 NC Not connected
7
8
9
10
GND Ground
+5V +5 Volts
Key/GND Key Pin on connector/Grounded on board
+12V +12 volts routed to PC/104
GND Ground
GND Ground
+5V +5 Volts
GND Ground
+5V +5 Volts
Note: The shaded table cells denote power or ground.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 31
Page 38

Chapter 3 Hardware
32 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 39

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
Introduction
This chapter assumes the user is familiar with general BIOS Setup and does not attempt to describe the
BIOS functions. Refer to “BIOS Setup Screens” on page 35 in this chapter for a map of the BIOS Setup
settings. If ADLINK has added to or modified any of the standard BIOS functions, these functions will be
described.
Entering BIOS Setup (Local Display)
To access BIOS Setup using a local display for the CoreModule 430:
1. Turn on the display and the power supply to the CoreModule 430.
2. Start Setup by pressing the [Del] key when the following message appears on the boot screen.
Press DEL to run Setup
NOTE If the setting for Quick Boot is [Enabled], you may not see this prompt appear on
screen. If this happens, press the <Del> key early in the boot sequence to enter
BIOS Setup.
3. Follow the instructions on the right side of the screen to navigate through the selections and modify any
settings.
Entering BIOS Setup (Remote Access)
This section describes how to enable the Remote Access in VGA mode and enter the BIOS setup through a
serial terminal or PC.
1. Turn on the power supply to the CoreModule 430 and enter the BIOS Setup Utility in VGA mode.
2. Set the BIOS feature Remote Access Configuration to [Enable] under the Advanced menu.
3. Accept the default options or make your own selections for the balance of the Remote Access fields and
record your settings.
4. Ensure you select the type of remote serial terminal you will be using and record your selection.
5. Select Save Changes and Exit and then shut down the CoreModule 430.
6. Connect the remote serial terminal (or the PC with communications software) to the COM port you
selected and recorded earlier in the BIOS Setup Utility.
7. Turn on the remote serial terminal or PC and set it to the settings you selected in the BIOS Setup Utility.
The default settings for the CoreModule 430 are:
COM1
115200
8 bits
1 stop bit
no parity
no flow control
[Always] for Redirection After BIOS POST
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 33
Page 40

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
8. Restore power to the CoreModule 430 and look for the screen prompt shown below.
Press <space bar> to update BIOS
9. Press the F4 key to enter Setup (early in the boot sequence if Quick Boot is set to [Enabled].)
If Quick Boot is set to [Enabled], you may never see the screen prompt.
10. Use the <Enter> key to select the screen menus listed in the Opening BIOS screen.
NOTE The serial console port is not hardware protected. Diagnostic software that
probes hardware addresses may cause a loss or failure of the serial console
functions.
OEM Logo Utility
The CoreModule 430 BIOS supports a graphical logo utility, which can be customized by the user and
displayed when enabled through the BIOS Setup Utility. The graphical image can be a company logo or any
custom image the user wants to display during the boot process. The custom image can be displayed as the
first image displayed on screen during the boot process and remain there, depending on the options selected
in BIOS Setup, while the OS boots.
Logo Image Requirements
The user’s image may be customized with any image editing tool, and the system will automatically convert
the image into an acceptable format to the tools (files and utilities) provided by ADLINK. The
CoreModule 430 OEM Logo utility supports the following image formats:
• Bitmap image
16-Color, 640x480 pixels
256-Color, 640x480 pixels
• JPG image
16-Color, 640x480 pixels
256-Color, 800x600 pixels
256-Color, 1024x768 pixels
• PCX image
256-Color, 640x480 pixels
• A file size no larger than sample image
34 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 41

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
BIOS Setup Utility
System Overview
AMIBIOS
Version : 08.XX.XX
Build Date: XX/XX/XX
ID : SWXXXXXX_X
Processor
Vortex A91XX
Speed :XXX MHz
+ - Change
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Field
v02.XX (C) Copyright 1985-20XX, American Megatrends, Inc.
System Memory
System Time [XX:XX:XX]
System Date [Xxx XX/XX/20XX]
Size :XXXMB
Speed :XXXMHz
Select Screen
CM430_BIOS_MainScreen_a
Select Item
BIOS Setup Screens
This section provides illustrations of the seven main setup screens in the CoreModule 430 BIOS Setup
Utility. Below each illustration is a bullet list of the screen’s submenus and setting selections. The setting
selections are presented in brackets after each submenu or menu item and the optimal default settings are
presented in bold. For more detailed definitions of the BIOS settings, refer to the AMIBIOS8 manual:
http://www.ami.com/support/doc/MAN-EZP-80.pdf
Table 4-1. BIOS Setup Menus
BIOS Setup Utility Menu Item/Topic
Main Settings Date and Time
Advanced Settings CPU settings, IDE Drive Configurations, Remote Access (Serial
Console), USB Configuration, and Southbridge LAN
PCIPnP (PCI, Plug n' Play) PCI settings, Plug & Play settings, Interrupt settings and DMA channel
settings, Reserved memory size
Boot Boot-up Settings
Security Setting or changing Passwords, Boot Sector Virus Protection
Chipset Northbridge and Southbridge settings
Exit Exiting with or without changing settings, Loading Optimal or Failsafe
conditions
BIOS Main Setup Screen
Figure 4-1. BIOS Main Setup Screen
• Date & Time
System Time (hh:mm:ss) – This is a 24-hour clock setting in hours, minutes, and seconds.
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 35
Page 42

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Advanced Settings
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.XX (C) Copyright 1985-20XX, American Megatrends, Inc.
WARNING: Setting wrong values in below sections
may cause system to malfunction.
CPU Configuration
Board Configuration
IDE Configuration
Remote Access Configuration
USB Configuration
SB LAN [Enabled]
MAC Address XX XX XX XX XX XX
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_AdvancedScreen_a
System Date (day of week, mm:dd:yyyy) – This field requires the alpha-numeric entry of the day of
week, day of the month, calendar month, and all 4 digits of the year, indicating the century plus
year (Fri 10/21/2011).
BIOS Advanced Setup Screen
Figure 4-2. BIOS Advanced Setup Screen
Board Configuration
Chip Serial Number : XX XX XX XX XX XX
CPU Configuration
Manufacture:: DMP
Brand String:: Vortex A91XX
Frequency: : X00MHz
L1 Cache [Disabled; Enabled]
Cache L1 : XX KB
L2 Cache (only on DX model) [Disabled; Enabled]
Cache L2 : XXX KB
IDE Configuration
• OnBoard PCI IDE Controller – [Disabled; Primary; Secondary; Both]
Primary IDE Master : [Not Detected]
• Type – [Not Installed; Auto; CD/DVD; ARMD]
• LBA/Large Mode – [Disabled; Auto]
• Block (Multi-Sector Transfer – [Disabled; Auto]
36 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 43

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
• PIO Mode – [Auto; 0; 1; 2; 3; 4]
• DMA Mode – [Auto]
• S.M.A.R.T. – [Auto; Disabled; Enabled]
• 32Bit Data Transfer – [Disabled; Enabled]
Primary IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
• Type – [Not Installed; Auto; CD/DVD; ARMD]
• LBA/Large Mode – [Disabled; Auto]
• Block (Multi-Sector Transfer) – [Disabled; Auto]
• PIO Mode – [Auto; 0; 1; 2; 3; 4]
• DMA Mode – [Auto]
• S.M.A.R.T. – [Auto; Disabled; Enabled]
• 32Bit Data Transfer – [Disabled; Enabled]
Secondary IDE Master : [Not Detected]
• Type – [Not Installed; Auto; CD/DVD; ARMD]
Secondary IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
• Type – [Not Installed; Auto; CD/DVD; ARMD]
• Hard Disk drive Write Protect – [Disabled; Enabled]
• IDE Detect Time Out (Sec) – [0; 5; 10; 15; 20; 25; 30; 35]
• ATA (PI) 80Pin Cable Detection – [Host & Device; Host; Device]
• Hard Disk Delay – [Disabled; 1 Second; 2 Second; 4 Second; 8 Second]
• OnBoard IDE Operate Mode – [Legacy Mode; Native Mode]
• Not Program PIO mode – [Disabled; Primary Channel; Secondary Channel]
• Primary IDE Pin Select – [Parallel IDE; SD Card]
Remote Access Configuration
• Remote Access – [Hotcable; Enabled]
• Serial port number – [COM1; COM2]
Base Address, IRQ [3F8h, 4]
• Serial Port Mode – [115200 8, n, 1; 57600 8, n, 1; 38400 8, n, 1; 19200 8, n, 1; 09600 8, n, 1]
• Flow Control – [None; Hardware; Software]
• Redirection After BIOS POST – [Disabled; Boot Loader; Always]
• Terminal Type – [ANSI; VT100; VT-UTF8]
: If VT-UTF8 is selected, the following item disappears from the screen.
Note
• VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Sredir Memory Display Delay – [No Delay; Delay 1 sec; Delay 2 sec; Delay 4 sec]
USB Configuration
• USB Port 0, 1 – [Enabled; Disabled]
• USB Port 2, 3 – [Enabled; Disabled]
• USB Device – [Enabled; Disabled]
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 37
Page 44

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Advance PCI/PnP Settings
IRQ3 [Reserved]
IRQ4 [Reserved]
IRQ5 [Available]
IRQ6 [Available]
IRQ7 [Reserved]
IRQ9 [Available]
IRQ10 [Available]
IRQ11 [Available]
IRQ12 [Available]
IRQ14 [Available]
IRQ15 [Reserved]
DMA Channel 0 [Available]
DMA Channel 1 [Available]
DMA Channel 3 [Available]
DMA Channel 5 [Available]
DMA Channel 6 [Available]
DMA Channel 7 [Available]
Reserved Memory Size [Disabled]
Select Screen
Select Item
+ - Change Option
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.XX (C) Copyright 1985-20XX, American Megatrends, Inc.
WARNING: Setting wrong values in below sections
may cause system to malfunction.
Clear NVRAM
Plug & Play O/S
PCI Latency Timer
Allocate IRQ to PCI VGA
Pallette Snooping
PCI IDE BusMaster [Enabled]
OffBoard PCI/ISA IDE Card [Auto]
[No]
[No]
[64]
[No]
[Disabled]
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_PCIPnPScreen_a
• Legacy USB Support – [Disabled; Enabled; Auto]
: If Disabled is selected, the following item disappears from the screen.
Note
• USB 2.0 Controller Mode – [Full Speed; Hi Speed]
• BIOS EHCI Hand-Off – [Disabled; Enabled]
SB LAN
MAC Address
[Enabled; Disabled]
XX XX XX XX XX XX
BIOS PCIPnP Setup Screen
• Clear NVRAM – [No; Yes]
Figure 4-3. BIOS PCIPnP Setup Screen
• Plug & Play O/S – [No; Yes]
• PCI Latency timer – [32; 64; 96; 128; 160; 192; 224; 248]
• Allocate IRQ to PCI VGA – [Yes; No]
• Palette Snooping – [Disabled; Enabled]
38 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 45

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
• PCI IDE BusMaster – [Disabled; Enabled]
• OffBoard PCI/ISA IDE card – [Auto; PCI Slot1; PCI Slot2; PCI Slot3; PCI Slot4; PCI Slot5;
PCI Slot6]
• IRQ3 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ4 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ5 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ6 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ7 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ9 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ10 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ11 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ12 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ14 – [Available; Reserved]
• IRQ15 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 0 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 1 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 3 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 5 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 6 – [Available; Reserved]
• DMA Channel 7 – [Available; Reserved]
• Reserved Memory – [Disabled; 16k; 32k; 64k]
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 39
Page 46

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Boot Settings
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.xx (C) Copyright 1985-20xx, American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot Settings Configuration
Boot Device Priority
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_BootScreen_a
BIOS Boot Setup Screen
Figure 4-4. BIOS Boot Setup Screen
Boot Settings Configuration
• Quick Boot – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Quiet Boot – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Add On ROM Display Mode – [Force BIOS; Keep Current]
• Bootup Num-Lock – [Off; On]
• PS/2 Mouse Support – [Disabled; Enabled; Auto]
• Wait for 'F1' If Error – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Hit 'DEL' Message Display – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Interrupt 19 Capture – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Boot From LAN – [Disabled; Used INT 18h; Used INT 19h; PnP/BEV (BBS); RPL]
• Beep Function – [Disabled; Enabled]
• OnBoard Virtual Flash FDD – [Disabled; Enabled; Diskette Write Protect]
40 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 47

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Security Settings
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Change
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.xx (C) Copyright 1985-20xx, American Megatrends, Inc.
Supervisor Password : Not installed
User Password : Not installed
Change Supervisor Password
Change User Password
Boot Sector Virus Protection [Disabled]
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_SecurityScreen_a
BIOS Security Setup Screen
Figure 4-5. BIOS Security Setup Screen
• Supervisor Password – [Not Installed]
• User Password – [Not Installed]
• Change Supervisor Password
a. Select Change Supervisor Password from the Security Setup menu.
b. Press <Enter> to access the pop-up entry field, Enter New Password.
c. Type the password and press <Enter> again.
The screen will not display the password as you type.
d. Re-type the password when prompted by the pop-up entry field and press <Enter> again.
• Change User Password
stored in NVRAM if you have successfully entered the password.
a. Select Change User Password from the Security Setup menu.
b. Press <Enter> to access the pop-up entry field, Enter New Password.
c. Type the password and press <Enter> again.
If the password is not confirmed when you re-type it, an error message will appear. The password is
The screen will not display the password as you type.
d. Re-type the password when prompted by the pop-up entry field and press <Enter> again.
If the password is not confirmed when you re-type it, an error message will appear. The password is
stored in NVRAM if you have successfully entered the password.
• Boot Sector Virus Protection – [Disabled; Enabled]
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 41
Page 48

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Advance Chipset Settings
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.xx (C) Copyright 1985-20xx, American Megatrends, Inc.
NorthBridge Configuration
SouthBridge Configuration
WARNING: Setting wrong values in below sections
may cause system to malfunction.
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_ChipsetScreen_a
BIOS Chipset Setup Screen
Figure 4-6. BIOS Chipset Setup Screen
NorthBridge Configuration
• NorthBridge Chipset Configuration
DRAM Timing Setting By – [BIOS]
CPU Speed Setting By – [Divide By 1;
Divide By 2;
Divide By 3;
Divide By 4;
Divide By 5;
Divide By 6;
Divide By 7;
Divide By 8]
SouthBridge Configuration
• SouthBridge Chipset Configuration
P.O.S.T. Forward To [Disabled; COM1]
ISA Configuration
• ISA Clock – [8.3MHz; 16.6MHz]
• ISA 16bits I/O wait-state – [1 clock;
2 clock;
3 clock;
4 clock;
5 clock;
6 clock;
7 clock;
8 clock]
42 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 49

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
• ISA 8bits I/O wait-state – [1 clock;
2 clock;
3 clock;
4 clock;
5 clock;
6 clock;
7 clock;
8 clock]
• ISA 16bits Memory wait-state – [0 clock;
1 clock;
2 clock;
3 clock;
4 clock;
5 clock;
6 clock;
7 clock]
• ISA 8bits Memory wait-state – [1 clock;
2 clock;
3 clock;
4 clock;
5 clock;
6 clock;
7 clock;
8 clock]
Serial Port Configuration
• SB Serial Port 1 – [Disabled; 3F8; 2F8; 3E8; 2E8; 10]
- Serial Port IRQ 1 [IRQ3; IRQ4; IRQ9; IRQ10; IRQ11]
- Serial Port Baud Rate [2400 BPS; 4800 BPS; 9600 BPS; 19200 BPS; 38400 BPS;
57600 BPS; 115200 BPS]
- Serial Port Type [RS232; RS485]
• SB Serial Port 2 – [Disabled; 3F8; 2F8; 3E8; 2E8; 10]
- Serial Port IRQ 2 [IRQ3; IRQ4; IRQ9; IRQ10; IRQ11]
- Serial Port Baud Rate [2400 BPS; 4800 BPS; 9600 BPS; 19200 BPS; 38400 BPS;
57600 BPS; 115200 BPS]
- Serial Port Type [RS232; RS485]
• SB Serial Port 3 – [Disabled; 3F8; 2F8; 3E8; 2E8; 10]
• SB Serial Port 4 – [Disabled; 3F8; 2F8; 3E8; 2E8; 10]
WatchDog Configuration
• WatchDog 0 Function – [Enabled; Disabled]
• WatchDog 1 Function – [Enabled; Disabled]
Multi-Function Port Configuration
• Port0 Function – [GPIO; 8051 P0; PWM00 . . PWM07]
• Port0 Bit0 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit1 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit2 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit3 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit4 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit5 Direction – [IN; OUT]
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 43
Page 50

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
• Port0 Bit6 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port0 Bit7 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Function – [GPIO; PWM16. .PWM23]
• Port1 Bit2 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Bit3 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Bit4 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Bit5 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Bit6 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port1 Bit7 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Function – [GPIO; 8051 P2; PWM16. .PWM23]
• Port2 Bit0 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit1 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit2 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit3 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit4 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit5 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit6 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port2 Bit7 Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit0 Function – [GPIO; 8051 P3; SPI]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit1 Function – [GPIO]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit2 Function – [GPIO]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit3 Function – [GPIO]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit4 Function – [GPIO; I2C]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit5 Function – [GPIO]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit6 Function – [GPIO; I2C]
- Direction – [IN; OUT]
• Port3 Bit7 Function – [GPIO]
- Direction – [IN
; OUT]
44 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 51

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup Utility
Exit Options
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
x02.xx (C) Copyright 1985-20xx, American Megatrends, Inc.
Save Changes and Exit
Discard Changes and Exit
Discard Changes
Load Optimal Defaults
Load Failsafe Defaults
Main Advanced PCIPnP Boot Security Chipset Exit
CM430_BIOS_ExitScreen_a
GPCS Configuration
• GPCS0 Function – [Enabled; Disabled]
• GPCS1 Function – [Enabled; Disabled]
Redundancy Control Configuration
• Dual Port 4 KB SRAM – [Enabled; Disabled]
• SB Serial Port 9 – [Disabled; 3F8; 2F8; 3E8; 2E8; 10]
• WatchDog0 Condition – [Disabled; Enabled]
• WatchDog1 Condition – [Disabled; Enabled]
• Invalid OPCODE Condition – [Disabled; Enabled]
• KB/MS System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• GPIO PORT0 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• GPIO PORT1 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• GPIO PORT2 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• UART1 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• UART2 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• UART3 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
• UART4 System Fail – [Normal; TRI-State]
BIOS Exit Setup Screen
Figure 4-7. BIOS Exit Setup Screen
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 45
Page 52

Chapter 4 BIOS Setup
Save Changes and Exit
The < F10 > key can be used for this operation.
Discard Changes and Exit
The < ESC > key can be used for this operation.
Discard Changes
The < F7 > key can be used for this operation.
Load Optimal Defaults
The < F9 > key can be used for this operation.
Load Failsafe Defaults
The < F8 > key can be used for this operation.
46 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 53

Appendix A Technical Support
Contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
ᄅקؑխࡉ৬ԫሁ 166 ᇆ 9 ᑔ
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: Ϟ⍋Ꮦ⌺ϰᮄᓴ∳催⾥ᡔು㢇䏃 300 ো(201203)
300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park,
Pudong New Area, Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. provides a number of methods for contacting Technical Support listed in the
Table A-1 below. Requests for support through the Ask an Expert are given the highest priority, and usually
will be addressed within one working day.
• ADLINK Ask an Expert – This is a comprehensive support center designed to meet all your technical
needs. This service is free and available 24 hours a day through the Ampro By ADLINK web page at
http://www.adlinktech.com/AAE/
which will help you with the common information requested by most customers. This is a good source
of information to look at first for your technical solutions. However, you must register online if you
wish to use the Ask a Question feature.
ADLINK strongly suggests that you register with the web site. By creating a profile on the ADLINK
web site, you will have a portal page called “My ADLINK” unique to you with access to exclusive
services and account information.
• Personal Assistance – You may also request personal assistance by creating an Ask an Expert account
and then going to the Ask a Question feature. Requests can be submitted 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
You will receive immediate confirmation that your request has been entered. Once you have submitted
your request, you must log in to go to the My Question area where you can check status, update your
request, and access other features.
• Download Service – This service is also free and available 24 hours a day at
http://www.adlinktech.com
register online before you can log in to this service.
. This includes a searchable database of Frequently Asked Questions,
. For certain downloads such as technical documents and software, you must
Table A-1. Technical Support Contact Information
Method Contact Information
Ask an Expert http://www.adlinktech.com/AAE/
Web Site http://www.adlinktech.com
Standard Mail
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 47
Page 54

Appendix A Technical Support
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: ࣫ҀᏖ⍋⎔Ϟഄϰ䏃 1 োⲜ߯ࡼ E ᑻ 801 ᅸ(100085)
Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1, B/D
Shang Di East Rd., Beijing, 100085 China
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8625
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: ⏅ഇᏖቅ⾥ᡔು催ᮄϗ䘧᭄ᄫᡔᴃು
A1 2 ὐ C (518057)
2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7,
High-Tech Industrial Park S., Shenzhen, 518054 China
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (Europe) GmbH
Address: Nord Carree 3, 40477 Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: +49-211-495-5552
Fax: +49-211-495-5557
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 15 rue Emile Baudot, 91300 Massy CEDEX, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: ͱ101-0045 ᵅҀ䛑ҷ⬄⼲⬄䤯ފ⬎ 3-7-4
⼲⬄ 374 ɛɳ 4F
KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho,
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 昢殾柢 昢爎割 昢爎壟 1506-25 穢壊 B/D 2 猻
2F, Hando B/D, 1506-25, Seocho-Dong, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-070, Korea
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre,
Singapore 349584
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: No. 1357, "Anupama", Sri Aurobindo Marg, 9th Cross,
JP Nagar Phase I, Bangalore - 560078, India
Tel: +91-80-65605817
Fax: +91-80-22443548
Email: india@adlinktech.com
Table A-1. Technical Support Contact Information (Continued)
48 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
Page 55

Index
A
ADLINK web site ............................................... 47
Advanced BIOS setup screen
assistance
............................................................ 47
............................. 36
B
battery
description and pin signals
function
Real Time Clock (RTC)
BIOS
entering BIOS setup
Hot (Serial) Cable
recovery
remote access
Setup console redirection
Setup Screens
Splash Screen (OEM Logo)
supported features
Watchdog Timer (WDT)
block diagram
Boot BIOS setup screen
......................................................... 28
......................................... 30
......................................................... 29
................................................ 33
................................................ 35
......................................... 35
....................................................... 7
............................ 24
................................ 28
...................................... 33
.............................. 30
.......................... 34
............................... 30
...................................... 40
C
Chipset BIOS setup screen ................................. 42
components
description table
specifications
connectors
locations
pin sequence identification
console redirection
cooling requirements
CPU
cooling requirements
description
features
current capability
......................................................4, 16
.............................................. 8
................................................... 1
........................................................ 10
........................... 10
.............................................. 30
.......................................... 13
..................................... 13
..................................................... 16
................................................ 31
D
dimensions .......................................................... 12
DMA map
........................................................... 18
E
environmental specifications .............................. 13
Ethernet
features
interface description and pin-out table
Exit BIOS setup screen
............................................................ 5
.......... 25
....................................... 45
F
floppy, virtual ..................................................... 16
G
GPIO interface description and pin signals ........ 29
graphics controller
........................................16, 26
H
header description table .......................................10
heatsink requirements
help
......................................................................47
Hot Cable, remote access
..........................................13
....................................30
I
IC (chip) specifications .........................................1
IDE features
Interrupt (IRQs) list
...........................................................4
.............................................18
J
jumper headers ....................................................11
K
keyboard
description and pin signals
miscellaneous feature
............................24
......................................5
L
low voltage limit ..................................................31
LPC interface
.......................................................28
M
Main BIOS setup screen ......................................35
major IC
description table
specifications
mechanical dimensions
memory
descriptions
features
map
system
video
miscellaneous features
modified serial cable
mouse
description and pin signals
miscellaneous feature
.............................................................4
................................................................17
............................................................16
..............................................................16
...............................................8
...................................................1
........................................13
....................................................16
.................................... 6, 28
...........................................30
............................24
......................................5
N
null-modem serial cable ......................................30
O
OEM Logo utility ................................................34
Oops! jumper (BIOS recovery)
...........................29
P
parallel port
description
features
PC/104
architecture
interface
PCIPnP BIOS setup screen
power
interface pin-out
requirements
.....................................................20
.............................................................5
......................................................3
...........................................................4
..................................38
.............................................31
..................................................13
CoreModule 430 Reference Manual 49
Page 56

Index
product description
PS/2 keyboard and mouse
............................................... 4
...................................24
R
Real Time Clock (RTC) ...................................... 28
references
remote access
reset switch description and pin signal
RS-232/RS-485 support
.............................................................. 1
description
entering BIOS setup
..................................................... 30
...................................... 33
...................................... 21
............... 24
S
sample code
GPIO
............................................................. 29
Watchdog Timer (WDT)
SDRAM memory
Security BIOS setup screen
serial
console redirection
null-modem serial cable
port descriptions
port pin-out tables
RS-232/RS-485 support
serial terminal
Single Board Computer
speaker description and pin signal
SPI Flash memory
Splash Screen (OEM Logo)
support contact methods
supported features
battery
Compact Flash
connector list
console redirection
DMA map
Ethernet interface
GPIO interface
Hot Cable
IDE interface
jumpers, on-board
keyboard
major ICs
mechanical dimensions
memory
memory map
mouse
............................................................ 24
Oops! jumper (BIOS recovery)
................................................16
............................................21
................................................ 30
............................................... 16
........................................................5, 24
................................................. 4
................................................. 10
...................................................... 18
..........................................6, 29
...................................................... 30
................................................... 4
....................................................5, 24
......................................................... 8
........................................................... 4
.................................................. 17
............................... 30
................................ 41
........................................30
................................ 30
......................................... 22
................................ 21
........................................ 3
......................24
................................ 34
..................................... 47
....................................6, 30
......................................5, 25
......................................... 11
................................. 13
.................6, 29
parallel port
PC/104 interface
PS/2 keyboard and mouse
Real Time Clock (RTC)
remote access
reset switch
RS-232/RS-485 support
SDRAM
serial ports
speaker
Splash Screen (OEM Logo)
TTL video
USB interface
utility header
VGA video
video display
Vortex CPU
Watchdog Timer (WDT)
system memory
...............................................5, 20
............................................. 4
............................... 5
............................ 6, 28
............................................ 6, 30
................................................... 24
................................ 21
........................................................ 16
.................................................5, 21
.......................................................... 24
...................... 6, 34
.................................................6, 26
............................................5, 23
................................................. 24
................................................ 6, 26
................................................... 5
............................................... 4, 16
.......................... 6, 30
................................................... 16
T
terminal emulation software ............................... 30
thermal cooling requirements
TTL
features
pin signals
............................................................ 6
..................................................... 26
............................. 13
U
USB
features
port descriptions and pin-out tables
utility header
............................................................ 5
.............. 23
....................................................... 24
V
VGA
features
pin signals
video
features
interface descriptions and pin signals
memory
virtual floppy
Volari Z9s graphics controller
voltage requirement
Vortex CPU
............................................................ 6
..................................................... 26
............................................................ 5
........... 26
......................................................... 16
...................................................... 16
...................... 16, 26
........................................ 4, 31
.......................................................... 4
W
Watchdog Timer (WDT) .................................... 30
web site
ADLINK
references
weight
....................................................... 47
........................................................ 1
................................................................. 12
50 Reference Manual CoreModule 430
 Loading...
Loading...