Page 1

aTCA-9710
Dual Intel Xeon E5-2658 v3
40G AdvancedTCA Processor Blade
User’s Manual
Manual Revision: 0.10 Preliminary
Revision Date: January 27, 2015
Part No.: 50-1G040-1000
Advance Technologies; Automate the World.
Page 2
Revision History
Revision Release Date Description of Change(s)
0.10 27/01/2015 Preliminary release
Copyright 2015 ADLINK Technology, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in order to improve
reliability, design, and function and does not represent a commitment on the part of the
manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or
consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product or documentation,
even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other means in
any form without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Trademarks
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Revision History ......................................................................................................................2
1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................5
1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................5
1.2 Block Diagram.............................................................................................................................6
1.3 Package Contents.......................................................................................................................7
2 Specifications ...................................................................................................................8
2.1 aTCA-9710 Specifications...........................................................................................................8
2.1.1 CPU/ Chipset/ Memory........................................................................................................................ 8
2.1.2 Standard and Interface ........................................................................................................................ 8
2.1.3 Software............................................................................................................................................... 9
2.1.4 Mechanical & Environmental ............................................................................................................... 9
2.2 Power Consumption..................................................................................................................10
2.3 Board Layout............................................................................................................................. 11
2.3.1 aTCA-9710 Board Layout - Component Side.....................................................................................11
2.3.2 aTCA-9710 Board Layout - Solder Side............................................................................................ 12
2.3.3 aTCA-9710 Front Panel..................................................................................................................... 13
2.3.4 Status LED Definitions ....................................................................................................................... 14
2.4 Compliance ...............................................................................................................................17
3 Functional Description...................................................................................................18
3.1 CPU, Memory and Chipset .......................................................................................................18
3.1.1 CPU ................................................................................................................................................... 18
3.1.2 Memory.............................................................................................................................................. 19
3.1.3 Intel® C612 Chipset Overview .......................................................................................................... 19
3.1.4 Silicon Motion SM750 Graphics Controller........................................................................................ 20
3.2 Peripherals................................................................................................................................20
3.2.1 Reset ................................................................................................................................................. 20
3.2.2 SMBus Devices ................................................................................................................................. 21
3.3 I/O Interfaces ............................................................................................................................22
3.3.1 USB ................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.2 VGA Interface .................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.3 Ethernet Connection .......................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.4 Serial Port .......................................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.5 Onboard mSATA Module ................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.6 Switch And Jumper Settings .............................................................................................................. 25
4 Intelligent Platform Management System.........................................................................26
4.1 IPMI Sensors ............................................................................................................................26
4.1.1 Sensor Reading (FRU Hotswap Sensor)........................................................................................... 28
4.1.2 Get Sensor Reading (Physical IPMB-0 Sensor)................................................................................ 29
4.1.3 Watchdog Timer Sensor .................................................................................................................... 30
4.1.4 Version Change Sensor..................................................................................................................... 31
4.1.5 System Firmware Progress Sensor................................................................................................... 32
4.1.6 Get Sensor Reading Command ........................................................................................................ 33
4.2 IPMI Commands .......................................................................................................................35
5 Getting Started................................................................................................................37
5.1 Safety Requirements.................................................................................................................37
5.2 Installing and Removing the aTCA-9710 ..................................................................................38
5.2.1 Installing the Blade ............................................................................................................................ 38
5.2.2 Removing the Blade .......................................................................................................................... 42
3
Page 4

5.3 Firmware Update Procedure.....................................................................................................45
5.3.1 Update Over Serial Interface ............................................................................................................. 45
5.3.2 Update over KCS............................................................................................................................... 46
5.3.3 Update over LAN ............................................................................................................................... 47
6 BIOS ................................................................................................................................48
6.1 Entering the BIOS Setup Screen ..............................................................................................48
6.1.1 Navigation.......................................................................................................................................... 48
6.2 Main BIOS Setup Screen..........................................................................................................50
6.3 Advanced Setup Screen ...........................................................................................................52
6.3.1 ACPI Settings .................................................................................................................................... 54
6.3.2 NCT5104D Super IO Configuration................................................................................................... 55
6.3.3 Serial Port Console Redirection ........................................................................................................ 57
6.3.4 PCI Subsystem Settings.................................................................................................................... 60
6.3.5 Network Stack Configuration ............................................................................................................. 61
6.3.6 CSM Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 62
6.3.7 Trusted Computing ............................................................................................................................ 63
6.3.8 ADLINK IPMI settings........................................................................................................................ 64
6.4 Intel RC Setup...........................................................................................................................66
6.4.1 Processor Configuration .................................................................................................................... 66
6.4.2 Advanced Power Management Configuration................................................................................... 69
6.4.3 Common RefCode Configuration ...................................................................................................... 71
6.4.4 Memory Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 72
6.4.5 IIO Configuration................................................................................................................................ 74
6.4.6 PCH Configuration............................................................................................................................. 76
6.5 Server Mgmt Setup Screen.......................................................................................................78
6.6 Boot Setup Screen....................................................................................................................79
6.7 Security Setup Screen ..............................................................................................................79
6.8 Save & Exit Setup Screen.........................................................................................................81
7 Serial Over LAN ..............................................................................................................83
7.1 Preparation For SOL Connection..............................................................................................83
7.2 Configure The Remote Client....................................................................................................83
7.2.1 Install IPMItool For The Remote Client.............................................................................................. 83
7.3 Configure The Target aTCA-9710 .............................................................................................84
7.3.1 BIOS Configuration............................................................................................................................ 84
7.3.2 Linux grub Setting.............................................................................................................................. 84
7.3.3 Linux System Setting......................................................................................................................... 85
7.4 Establish SOL Connection ........................................................................................................85
8 Drivers.............................................................................................................................87
Safety Instructions ................................................................................................................88
Getting Service ......................................................................................................................89
4
Page 5

1 Overview
1.1 Introduction
The ADLINK aTCA-9710 is a high performance AdvancedTCA® (ATCA) processor blade
featuring dual 12-core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2658 v3, Intel® C612 Chipset, eightchannel memory up to 256GB of DDR4 memory and 400W power supply subsystem. Versatile
connectivity includes four 40GbE Fabric Interfaces, dual GbE Base Interfaces, dual front panel
10GbE egress ports, front panel dual COM and USB 2.0 ports and front panel VGA connector.
An onboard SATA connector supports a mSATA up to 256GB and the optional RTM (aTCAR9700) supports six 10GbE SFP+ ports and one hot-swappable SATA bay providing additional
network throughput and storage capacities.
The aTCA-9710's thermal solution (including VRM heat sink) ensures stable operation under
extreme operating environments and allows for compliance to the NEBS Level 3 standard
(design only). The robust computing power and reliability of the aTCA-9710 meets the
requirements of telecom equipment manufacturers (TEMs) and network equipment providers
(NEPs), allowing them to build the next-generation telecom networks and communication
infrastructures.
Detailed features are outlined below and a functional block diagram is shown in the next
section.
Two 12-core Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2658 v3
Server-class Intel® C612 Chipset
DDR4-2133 JEDEC standard VLP RDIMM (REG/ECC), up to 256 GB
Onboard bootable 32GB mSATA module (max. 256GB)
One Intel® I350 AM2 dual-port PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet controller
Two Intel® XL-710-AM2 dual-port PCI Express 40Gigabit Ethernet controllers
One Intel 82599ES 10Gigabit Ethernet Controller to front panel via SFP+ ports
Optional three Intel® 82599ES 10Gigabit Ethernet Controllers (6 SFP+ ports) on RTM
(aTCA-R9700)
Optional SATA 6G interface drive bay on RTM (aTCA-R9700)
PICMG 3.1 Option 9-KR four Fabric Interface channels supporting dual dual-star
Failover system BIOS
Analog VGA output up to 1920x1440 resolution
5
Page 6
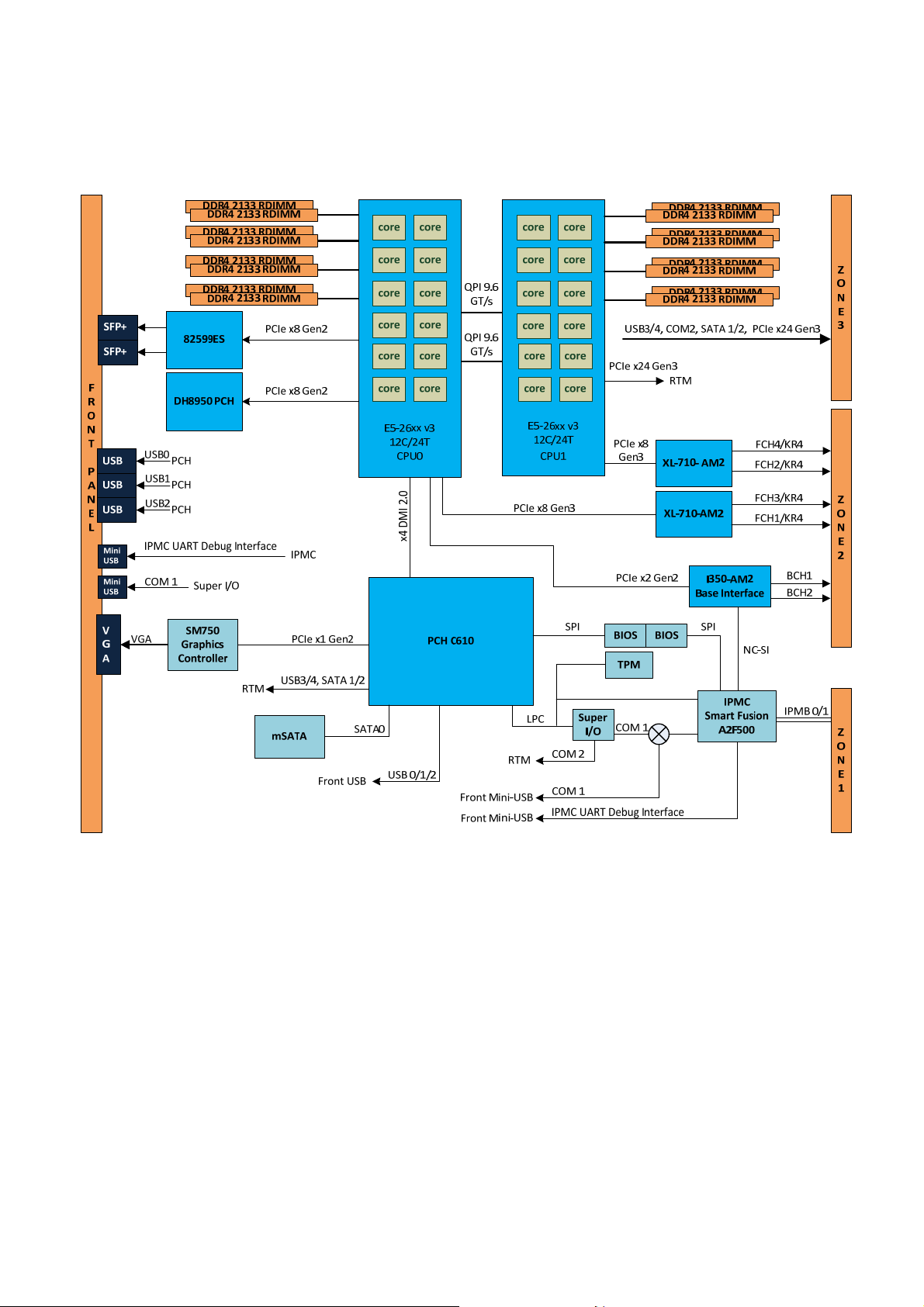
1.2 Block Diagram
6
Page 7

1.3 Package Contents
Before opening, please check the shipping carton for any damage. If the shipping carton and
contents are damaged, notify the dealer for a replacement. Retain the shipping carton and
packing material for inspection by the dealer. Obtain authorization before returning any
product to ADLINK.
Check that the following items are included in the package. If there are any missing items,
contact your dealer:
aTCA-9710 AdvancedTCA processor blade (CPU, RAM specifications may differ
depending on options selected)
USB Mini-B to DB-9 cable (for front panel serial port)
7
Page 8
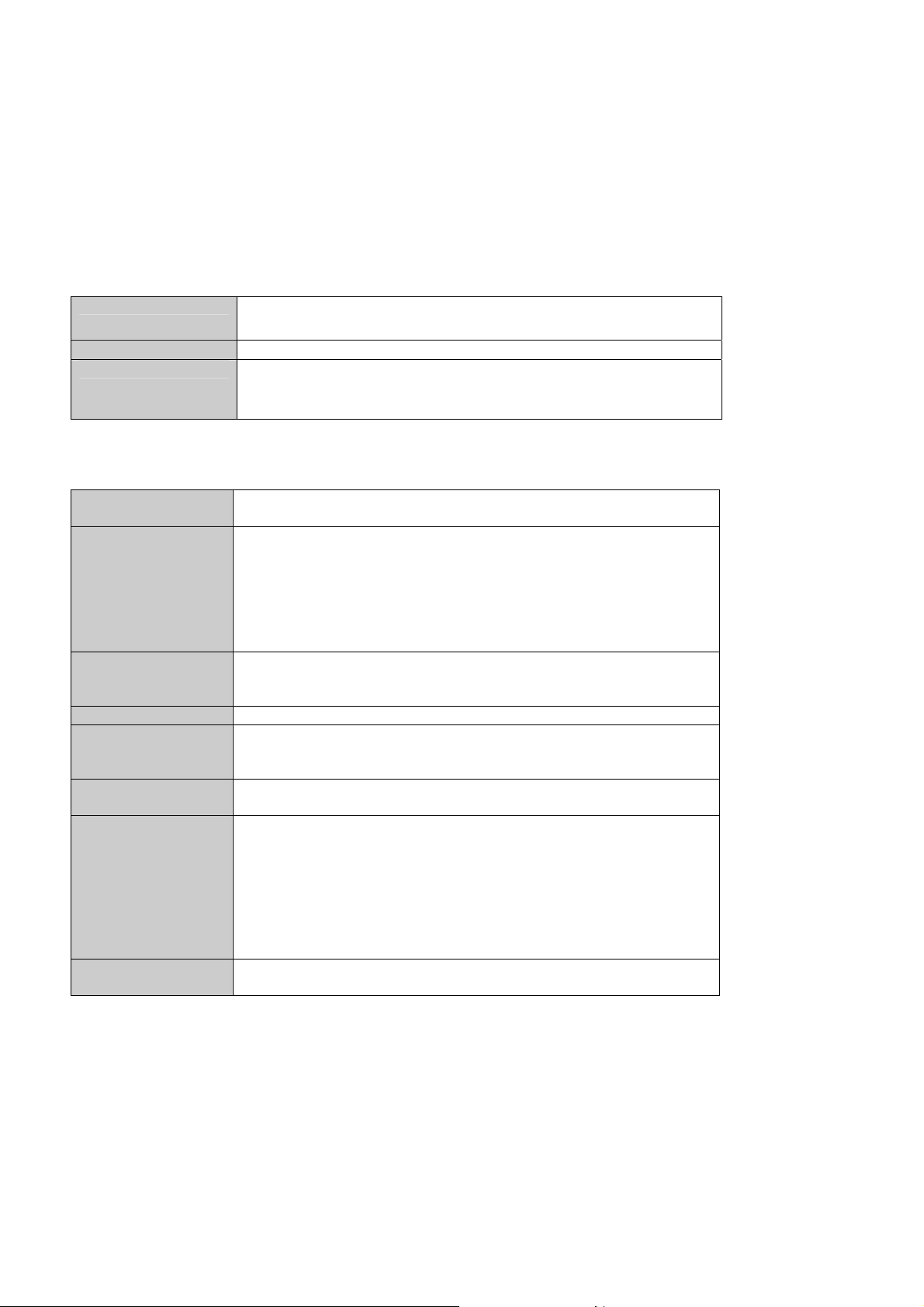
2 Specifications
2.1 aTCA-9710 Specifications
2.1.1 CPU/ Chipset/ Memory
CPU
Chipset
Memory
Dual 12-core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2658 v3,
(2.2/2.9GHz QPI 9.6GT/s, 30MB L2 cache, LGA2011 Socket)
Intel® C612 Chipset
Registered ECC DDR4-1600/1866/2133 VLP RDIMM
16x RDIMM sockets
Up to 256GB
2.1.2 Standard and Interface
Standards
Networking
Display
USB
Serial
Storage
Front Panel I/O
Rear I/O
(aTCA-R9700)
PICMG 3.0 R3.0 AdvancedTCA
PICMG 3.1 AdvancedTCA Ethernet, Option 9-KR
1x dual-port Intel® I350 AM2 Gigabit Ethernet Controller
1x dual-port Intel® 82599ES 10Gigabit Ethernet Controller
2x 10GbE SFP+ ports on face plate
2x 10/100/1000BASE-T Base Interface channels
4x 10GBASE-KR4 Fabric Interface channels via two XL-710-AM2
40G Ethernet Controllers (Option 9-KR)
6x 10GBASE SFP+ ports on RTM (aTCA-R9700)
Silicon Motion SM750 graphics controller
Front panel analog VGA connector supports up to 1920x1440
resolution
2x USB 2.0 ports on front panel, two USB 2.0 ports to RTM
1x IPMC serial debug port (USB Mini-B)
1x RS-232 ports on front panel (USB Mini-B)
1x RS-232 port to RTM
Onboard mSATA module 32GB, up to 256GB
2x SATA channels to RTM
1x VGA port (DB-15)
3x USB 3.0 port (Type-A)
1x IPMC serial debug port (USB Mini-B connector)
1x RS-232 port (USB Mini-B connector)
2x 10GbE ports (SFP+)
LEDs: OOS, BIOS/OS boot OK, IPMC payload power authorization
and IPMC chassis identify command
Recessed reset button
6x SFP+ ports (three Intel® 82599ES 10G Ethernet Controllers)
1x SATA port from Intel® C612 PCH
8
Page 9

2.1.3 Software
BIOS
Supported OS
AMI BIOS with 8Mbit flash memory
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.x/7.0
Contact ADLINK for other OS availability
2.1.4 Mechanical & Environmental
Dimensions
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
Humidity
Shock
Vibration
Compliance
322.25mm x 280mm x 30.48mm (H x D x W) - 6HP slot
Standard: 0°C to 55°C
NEBS short-term: 0°C to 61°C (sea level)
-40°C to 85°C
5% to 90% non-condensing
15G peak-to-peak, 11ms duration, non-operation
Non-operating: 1.88 Grms, 5 to 500 Hz, each axis
Operating: 0.5 Grms, 5 to 500Hz, each axis
CE, FCC Class A, UL, NEBS Level 3 (design)
9
Page 10

2.2 Power Consumption
This section provides information on the power consumption of the aTCA-9710.
System configuration
(1) Memory: 16x 8GB DDR4-2133 ECC REG
(2) Graphics: Silicon Motion SM750
(3) Power Supply: Chroma DC Power supply 62012P-80-60
(4) CPU: 2x 12-core Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2658 v3
The following table lists power consumption under different operating systems and
applications with a 48V power rail.
OS and Application Power Consumption
Windows Server 2008 R2, idle 81.12 W
Windows Server 2008 R2, BurnIn Test, CPU 100% usage 316.32 W
Windows Server 2008 R2, Power Thermal Utility, CPU 100% Usage 365.76 W
10
Page 11
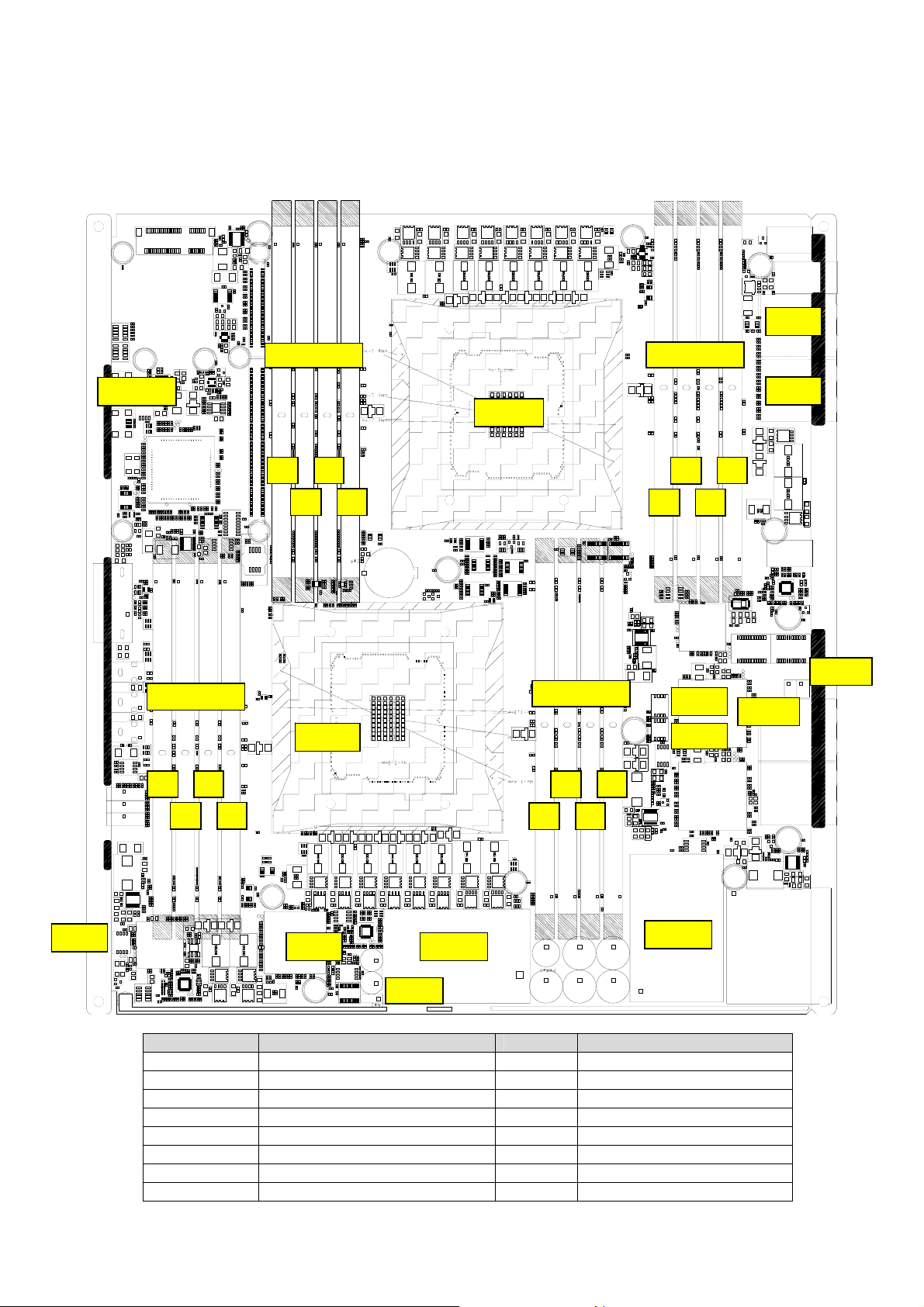
2.3 Board Layout
2.3.1 aTCA-9710 Board Layout - Component Side
SW3
DIMM_EF
SW1
CPU2
E2 F2
DIMM_CD
DIMM_AB
CPU1
C1 D1
C2 D2
SW4
PSU1
A2
A1
B2
CN7
Location Description Location Description
CN1
CN2
CN7
DIMM_AB/CD
DIMM_EF/GH
J3/4
PSU1
PSU2
XL710 JTAG debug header
XL710 JTAG debug header
Ground connection
DDR4 DIMM A-D
DDR4 DIMM E-H
Zone 3 to RTM
400W -48V DC/DC module
400W Hot Swap Power Module
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
SW6
SW7
SW8
Reserved for PCH debug
Clear CMOS
IPMC Programming mode
IPMC Mode Select
HW Reset Button
Reserved for XL710 debug
Reserved for XL710 debug
B1
DIMM_GH
G2
H2
SW7
SW8
PSU2
J3
J4
H1 G1 E1 F1
CN2
CN1
11
Page 12
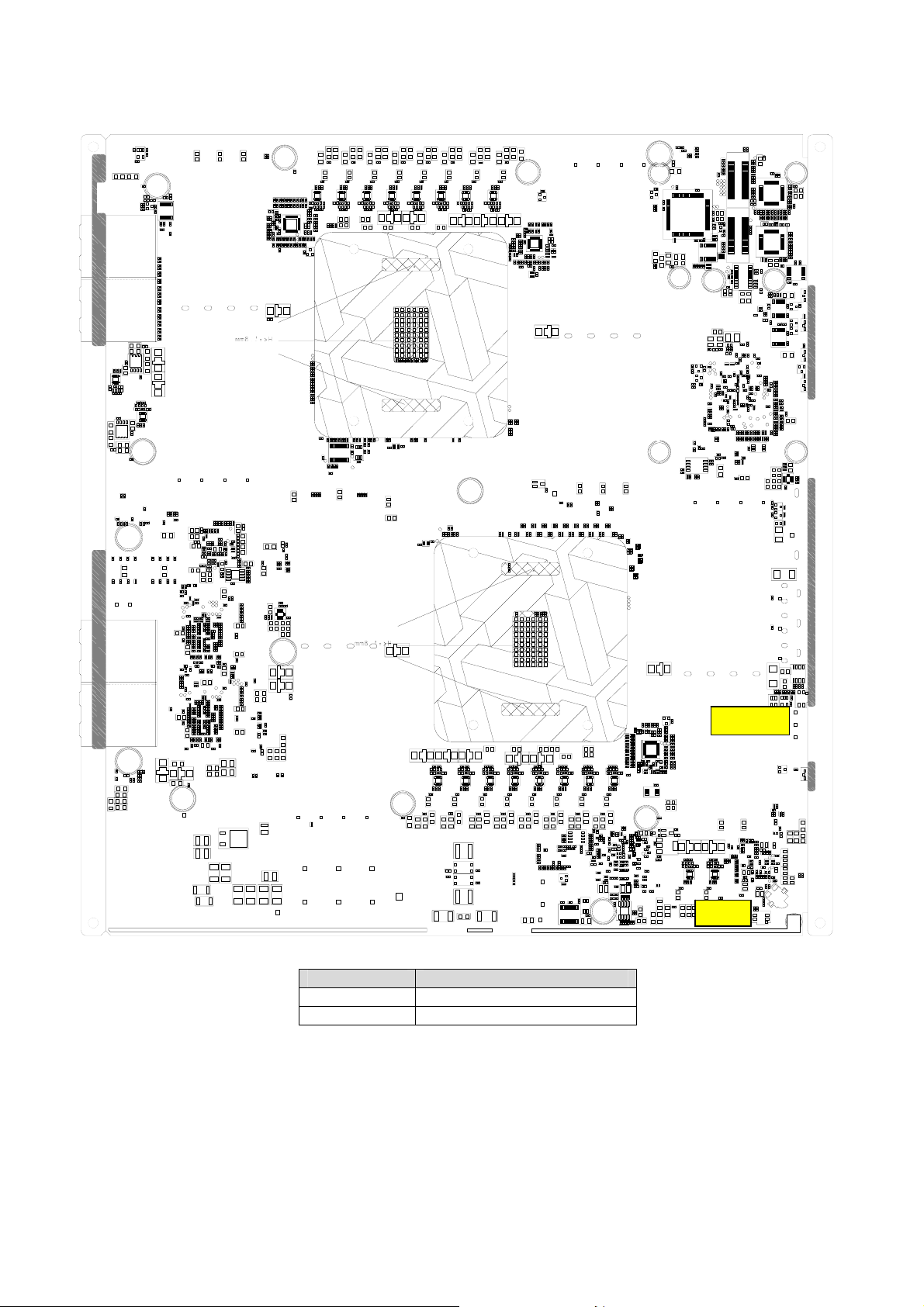
2.3.2 aTCA-9710 Board Layout - Solder Side
Location Description
SW2
SW6
Clear CMOS
HW Reset Button
SW6
SW2
12
Page 13

2.3.3 aTCA-9710 Front Panel
BIOS/OS Boot OK
IPMC Payload Power Authorized
IPMC Chassis Identify Command
OOS LED
10GbE (SFP)
IPMC Serial Debug Port
RS-232 Serial Port
VGA
Hot-Swap LED
USB
Reset button
Base and Fabric Channel LEDs
13
Page 14
2.3.4 Status LED Definitions
The following sections describe the front panel Status LEDs: Hot-swap LED, OOS LED,
BIOS/OS Boot OK LED, IPMC Payload Power Authorized LED and IPMC Chassis Identify
Command LED.
2.3.4.1 Out of Service (OOS) LED
Out of Service LED (Red) State Remark
Blinking During BIOS POST M4
Off BIOS POST OK M4
On After OS shutdown M1
2.3.4.2 BIOS/OS Boot OK
BIOS/OS Boot OK (Green) State Remark
Blinking During OS Boot
Off During BIOS POST
On OS Boot OK
2.3.4.3 IPMC Payload Power Authorized
IPMC Payload Power Authorized
(Amber)
On Payload Power Authorized
Off Payload Power Not
Authorized
State Remark
14
Page 15

2.3.4.4 IPMC Chassis Identify Command LED
IPMC Chassis Identify Command
(Amber)
Off Default Off
Blinking Chassis Identify Command
Active
State Remark
2.3.4.5 Hot-swap LED
Hot-swap LED
(Blue)
Off M0 FRU not installed
On M1 FRU inactive
Long blink M2 FRU activation request
Off M3 FRU activation in process
Off M4 FRU active
Short blink M5 FRU deactivation request
Short blink M6 FRU deactivation in process
FRU State
number
FRU State Name
15
Page 16
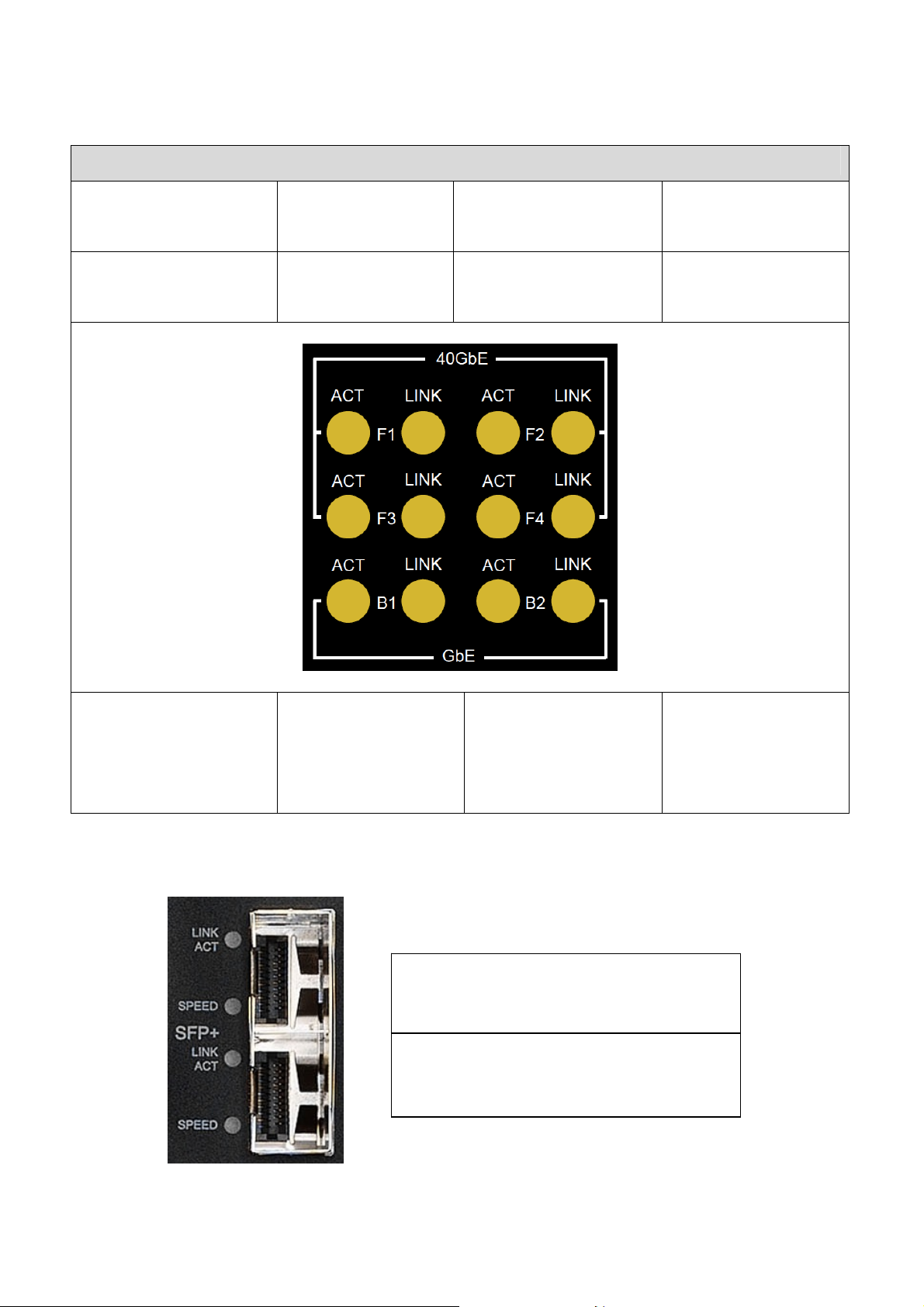
2.3.4.6 Base and Fabric Channels LEDs
Base and Fabric Channels LEDs
FCH1 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
FCH 3 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
Fabric 1 Link
(Amber)
40Gbps – ON
Fabric 3 Link
(Amber)
40Gbps – ON
FCH 2 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
FCH 4 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
Fabric 2 Link
(Amber)
40Gbps – ON
Fabric 4 Link
(Amber)
40Gbps – ON
BCH1 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
BCH1 Speed and
Link
100 Mbps: Green
BCH2 ACT (Amber)
Blink when accessing
Ethernet I/O
1Gbps: Amber
2.3.4.7 Front Panel 10GbE SFP+ LEDs
Left LED: Speed and Link
1Gbps: Amber,
100Mbps: Green
Right LED: ACT
Blinking while data exchanging
Color: Amber
BCH2 Speed and
Link
100 Mbps: Green
1Gbps: Amber
16
Page 17

2.4 Compliance
The aTCA-9710 conforms to the following specifications:
PICMG 3.0 R2.0 ECN0002 AdvancedTCA
PICMG 3.1 Ethernet over AdvancedTCA Option 9-KR
NEBS Level 3 (design)
17
Page 18

3 Functional Description
3.1 CPU, Memory and Chipset
3.1.1 CPU
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2658 v3 implements several key technologies:
Four channel Integrated Memory Controller supporting DDR4
Integrated I/O with up to 40 lanes for PCI Express Generation 3.0
Two point-to-point link interface based on Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI) up
to 9.6GT/s
30 MB of shared cache
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2658 v3 supports several advanced technologies:
Intel® 64 Technology
Enhanced Intel® SpeedStep® Technology
Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology)
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2658 v3 has a maximum TDP of 105W and has an elevated
case temperature specification. The elevated case temperatures are intended to meet the
short-term thermal profile requirements of NEBS Level 3. The Intel® Xeon® processor E52658 v3 is ideal for thermally constrained form factors in embedded servers, communications
and storage markets.
Supported Processors, Maximum Power Dissipation
The following table describes the Intel® Xeon® processor E5 family CPUs supported by the
aTCA-9710:
Name E5-2658 v3
L2 cache 30MB
Clock 2.2GHz
QPI 9.6 GT/s
TDP 105W
18
Page 19

3.1.2 Memory
The aTCA-9710 is a dual processor system with each Intel® Xeon® processor E5 2600 v3
series providing four memory channels supporting DDR4, 1600, 1866, 2133 MT/s DIMMs. The
maximum memory capacity is 256GB with memory interleaving support. The
400/533/667/800/933 MHz differential memory clocks are driven by the Intel® Xeon®
processor E5-2658 v3 CPU with length-matching and impedance controlled through all the
DIMM slots.
The DDR4 DIMMs support the I2C interface. They are connected together and routed to the
PCH for the management.
Memory configuration changes are only permitted to be performed at the factory.
Failure to comply with the above may result in damage to your board or improper
operation.
3.1.3 Intel® C612 Chipset Overview
The Intel® C612 Chipset provides a connection point between various I/O components and
DMI based processors. Functions and capabilities include:
PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 2.0 support for up to eight ports with transfers
up to 5 GT/s.
ACPI Power Management Logic Support, Revision 4.0a Enhanced DMA controller,
interrupt controller, and timer functions
Integrated Serial ATA host controller switch independent DMA operation on up to 10 ports.
USB host interface with two EHCI high-speed USB 2.0 Host controllers and 2 rate
matching hubs provide support for support for up to fourteen USB 2.0 ports
Integrated 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet MAC with System Defense
System Management Bus (SMBus) Specification, version 2.0 with additional support for
2
C devices
I
Intel® High Definition Audio Supports
Intel® Rapid Storage Technology enterprise (Intel® RSTe)
Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT)
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
Low Pin Count (LPC) interface Firmware Hub (FWH) interface
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Intel® Anti-Theft Technology (Intel® AT)
JTAG Boundary Scan support
19
Page 20

3.1.4 Silicon Motion SM750 Graphics Controller
The aTCA-9710 provides an analog VGA port on the front panel powered by a Silicon Motion
SM750 2D graphics controller with the following features:
• PCI-Express x1 architecture
• 16MB integrated video DDR memory
• Low power consumption < 1.5W
• 300 MHz DAC supports up to 1920x1440 resolution
• 128-bit 2D graphic engine
• ROPs, BitBLT, transparent BLT, pattern BLT, Color expansion, and Line drawing
• YUV-16/32-bit RGB conversion
• Support 7 layers of display frames (2 hardware cursors, primary graphic, video, video
alpha, alpha, and secondary graphic)
• Two 8-bit portsorone16-bitvideocaptureportsupportsITU601
• and ITU 656 specifications UV-16/32-bit RGB conversion
• ReduceOn Power Management Technology
• Quick-Rotation features allow for 90°, 180°, and 270° rotation of on-screen images
3.2 Peripherals
The following peripherals are available on the aTCA-9710 blade
3.2.1 Reset
The aTCA-9710 is automatically reset by a precision voltage monitoring circuit that detects a
drop in voltage below the acceptable operating limit of 4.85V for the 5V line and below 3.2V for
the 3.3V line. Other reset sources include the Watchdog Timer, the face plate push-button
switch and also the RESET signal from the IPMC. The aTCA-9710 responds to any of these
sources by initializing local peripherals.
A reset will be generated by the following conditions:
Power failure, +5 V supply falls below 4.1 V (typ.) or +3.3 V supply falls below
2.93 V (typ.)
Pushbutton "RESET" pressed
Watchdog time-out
IPM controller reset
20
Page 21
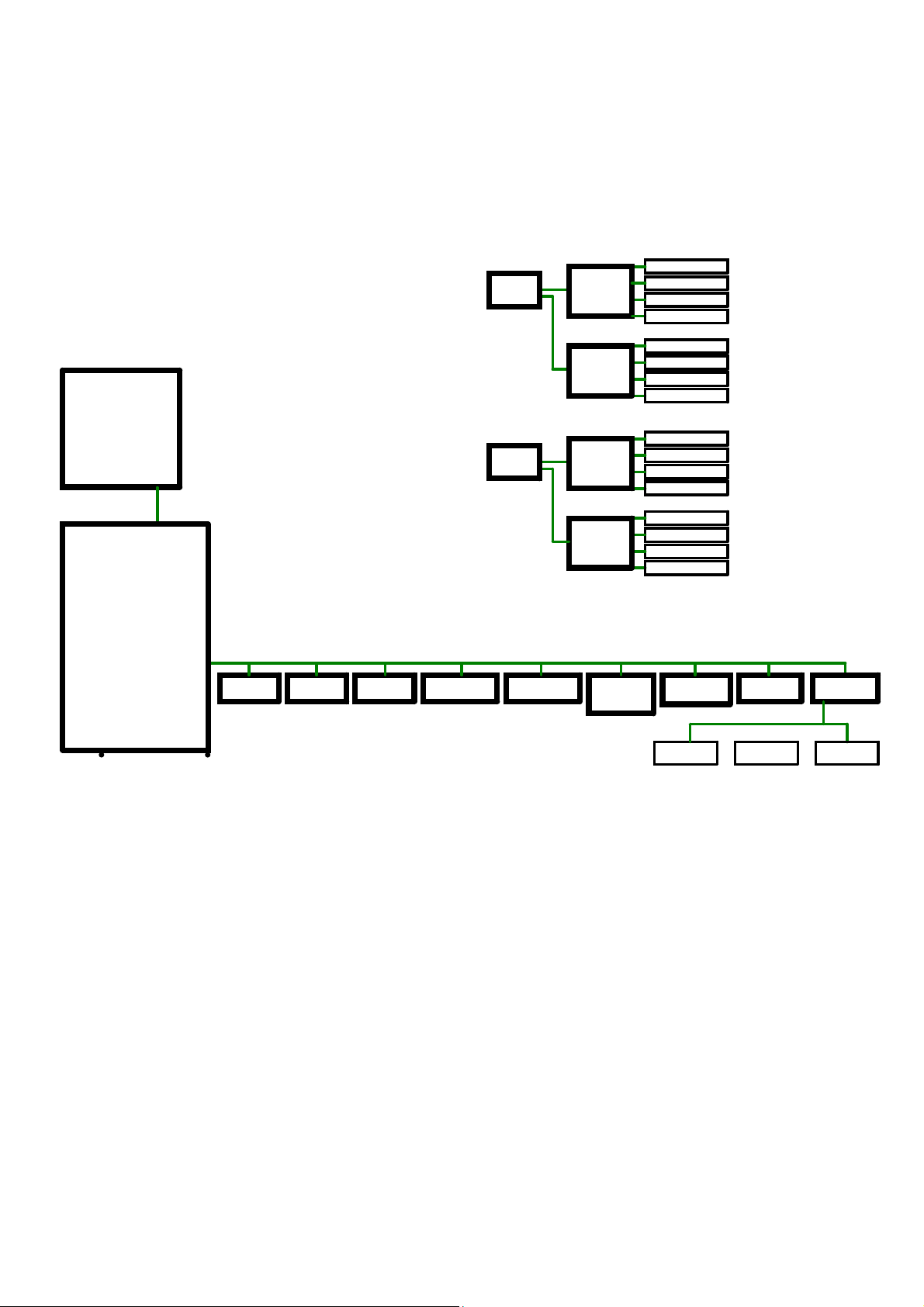
3.2.2 SMBus Devices
The aTCA-9710 provides a System Management Bus (SMBus) hosted by the Intel® C612
PCH. The topology is shown in the diagram below.
PCHHostI2CBus
PCH
IPMCI2CBus
IPMC
SMBus
I2CCLK_IPM
I2CDAT_IPM
SMBus I/ O
PCA9555
SMBUSADD RESS = SUBMS04x0 ADDR ESS= 0xA6
SMBus I/ O
PCA9555
SMBUSADDRES S=0x42
SMBus I/ O
PCA9555
SMBUSADD RESS =0x46
EEPROM (FRU)
24C256
CPU DDR I2CBus
CPU 0
CPU 1
EEPROM(SEL)
24C256
SMBUSADD RESS =0xAA
PCA9617
PCA9617
PCA9617
PCA9617
HOT SW AP
IQ65033
PIM400KZ
SMBUSADDRESS= 0x5E
DIMM A1
DIMM A2
DIMM B1
DIMM B2
DIMM C1
DIMM C2
DIMM D1
DIMM D2
DIMM E1
DIMM E2
DIMM F1
DIMM F2
DIMM G1
DIMM G2
DIMM H1
DIMM H2
SMBUS ADDRES S =0x90/92/94
0xA0
0xA2
0xA8
0xAA
0xA0
0xA2
0xA8
0xAA
0xA0
0xA2
0xA8
0xAA
0xA0
0xA2
0xA8
0xAA
RTC
DS1339U-33
SMBUSADD RESS =0xD0
Thermal Sensor
LM73 x3
HW Monitor
NCT7904D
SMBUSADD RESS =0x5A
Thermal Sensor
LM73 x3
SMBUS ADDRES S = 0x90/92/9 4 SMBUS ADD RESS = 0x 90/92/94
I2C SWI TCH
PCA9545A
SMBUSADDRESS= 0xE0
Thermal Sensor
LM73 x3
21
Page 22
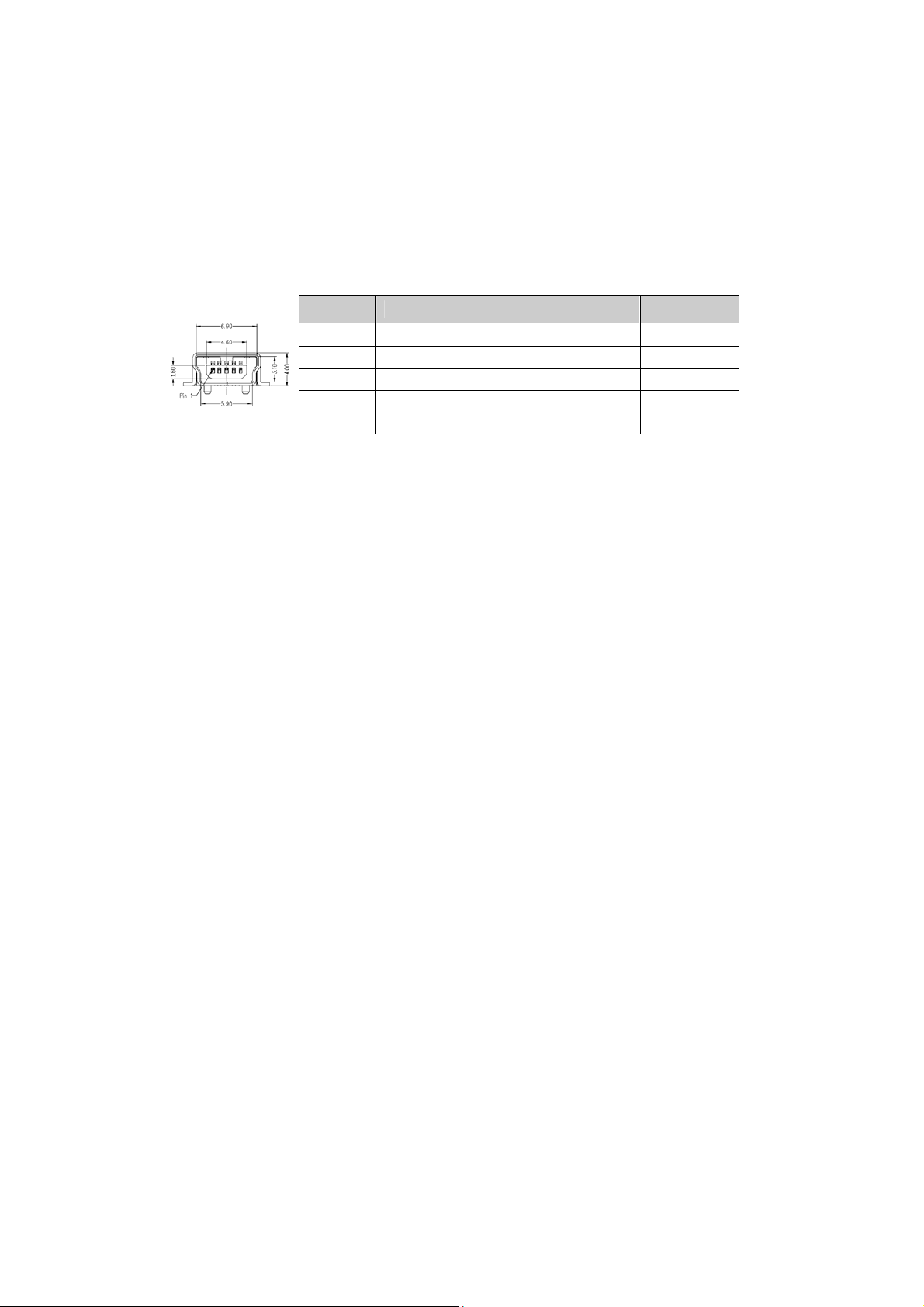
3.3 I/O Interfaces
3.3.1 USB
The aTCA-9710 supports Five USB 2.0 ports:
3x Type-A ports on front panel
Two ports routed to RTM (available on the aTCA-R6280 RTM)
On the USB 2.0 front panel port, a USB cable up to 5 meters in length can be used.
On the USB 2.0 Rear I/O ports, it is strongly recommended to use a cable less than 3 meters
in length for USB 2.0 devices.
The USB 2.0 ports are high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed capable. Hi-speed USB 2.0
allows data transfers of up to 480 Mb/s, 40 times faster than a full-speed USB (USB 1.1).
One USB peripheral may be connected to each port.
With the aTCA-R6280 RTM, the aTCA-9710 supports two additional USB ports on the I/O
panel of the RTM.
USB Connector Pin Definition (Type A)
Pin Signal
1 5V USB VCC
2 USB3 USB+
Note: The aTCA-9710 host interfaces can be used with a maximum 500mA continuous load
current as specified in the Universal Serial Bus Specification, Revision 2.0. Short circuit
protection is provided. All the signal lines are EMI filtered.
4 GND USB
22
Page 23
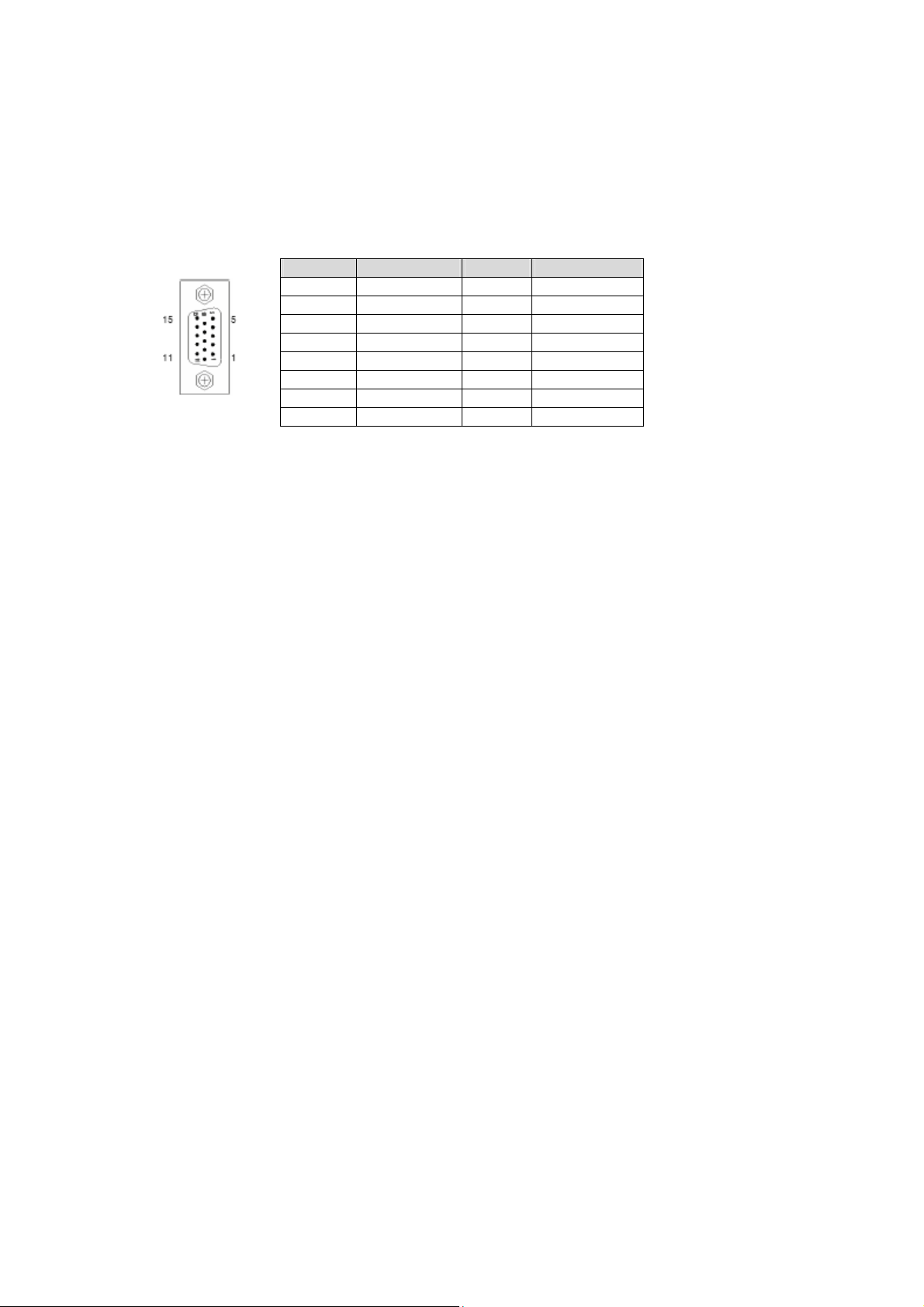
3.3.2 VGA Interface
A DB-15 female connector on the front panel provides analog display output.
Front Panel VGA Pin Definition (DB-15)
Pin Name Pin Name
1 RED 9 +5v
2 GREEN 10 GND
3 BLUE 11 NC
4 NC 12 DDC_DATA
5 GND 13 HSYNC
6 GND 14 VSYNC
7 GND 15 DDC_CLK
8 GND
3.3.3 Ethernet Connection
The aTCA-9710 is equipped with one Intel® 82599ES 10Gigabit Ethernet Controller and
one dual-port Intel® I350AM2 Gigabit Ethernet Controller which provide 2x 10GbE ports
and 2x GbE ports in total. In default configuration, two ports from the Intel® 82599ES
10Gigabit Ethernet Controller are connected to the front panel SFP+ ports. Two GbE ports
from the Intel® I350AM2 Gigabit Ethernet Controller are connected to Zone 2 Base
Channels 1 and 2 (BCH1/BCH2).
Two Intel XL-710-AM2 40G network controllers are installed on the aTCA-9710 providing
four 40GBASE KR4 links to Fabric Channels 1, 2, 3 and 4. The four 40GBASE-KR4 links
are divided into two groups. FCH1/3 are connected to one of the XL-710-AM2 40G network
controllers while FCH2/4 are connected to the other.
Note: The bandwidth of each XL-710 40G network controller is limited by the PCIe x8 Gen3
link to the CPU. The total bandwidth of each XL-710 40G network controller is
approximately 50Gb/s.
With the aTCA-R9700 RTM installed, the aTCA-9710 supports six 10GbE SFP+ ports from
the Intel 82599ES Network Interface Controllers.
23
Page 24
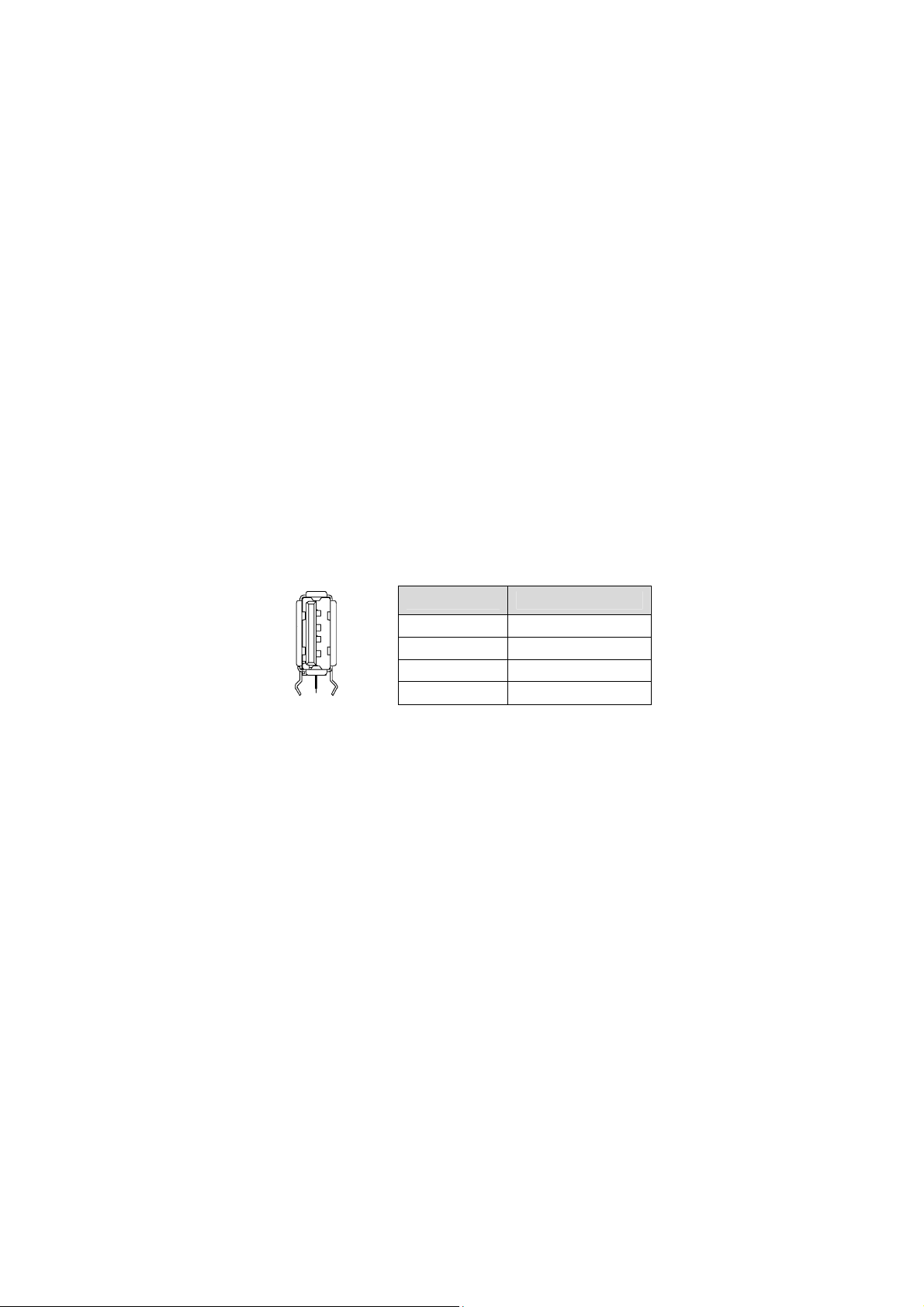
3.3.4 Serial Port
Two serial ports are output to USB Mini-B connectors on the front panel for use as service
terminals. The port labeled IPMI is an "IPMC" debug port and the port labeled CPU" is
connected to COM 1 of the Super IO chip.
Serial Port Pin Definition (USB Mini-B)
PIN Signal Name In/Out
1 Signal Ground
2 Transmitted Data (TxD) Out
3 Received Data (RxD) In
4 Signal Ground
5 Signal Ground
3.3.5 Onboard mSATA Module
The aTCA-9710 is equipped with an mSATA flash module (32GB, up to 256GB available)
which supports a SATA 6.0Gb/s interface with sustained read to 550MB per second and
sustained write up to 500MB per second.
24
Page 25

3.3.6 Switch And Jumper Settings
3.3.6.1 Set Blade Operation Mode
Use switch SW4 to set the Blade Operation Mode. Normal operation requires a shelf
manager for the blade to boot. Standalone mode allows the blade to boot without a shelf
manager.
SW4 Blade Operation Pin 1 Pin 2 Pin 3 Pin 4
Normal Mode (default) OFF OFF OFF OFF
Standalone Mode OFF OFF ON OFF
3.3.6.2 IPMC JTAG Signal
The switch SW3 is designed for hardware debug purposes. Do not change the default
settings. Doing may result in an abnormal boot, failure to boot, and or damage to the board.
SW3 IPMC JTAG Pin 1 Pin 2 Pin 3 Pin 4
Default Setting OFF ON ON ON
3.3.6.3 Shelf/Logic Ground Jumper
Use CN7 to short Shelf Ground to Logic Ground.
Shelf/Logic GND CN7 Setting
Shorted 1-2
Open (default) 2-3
The locations of SW3, SW4 and CN7 are shown below:
SW12
SW4
CN7
25
Page 26
4 Intelligent Platform Management System
The purpose of the intelligent platform management system is to monitor, control, and assure
proper operation of AdvancedTCA® Boards and other Shelf components. The intelligent
platform management system watches over the basic health of the system, reports anomalies,
and takes corrective action when needed. The intelligent platform management system can
retrieve inventory information and sensor readings as well as receive event reports and failure
notifications from Boards and other Intelligent FRUs. The intelligent platform management
system can also perform basic recovery operations such as reset of managed entities.
The IPMC controller on aTCA-9710 supports an “intelligent” hardware management system,
based on the Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification. The intelligent
management system provides the ability to manage the power, cooling, and interconnect
needs of intelligent devices; to monitor events; and to log events to a central repository.
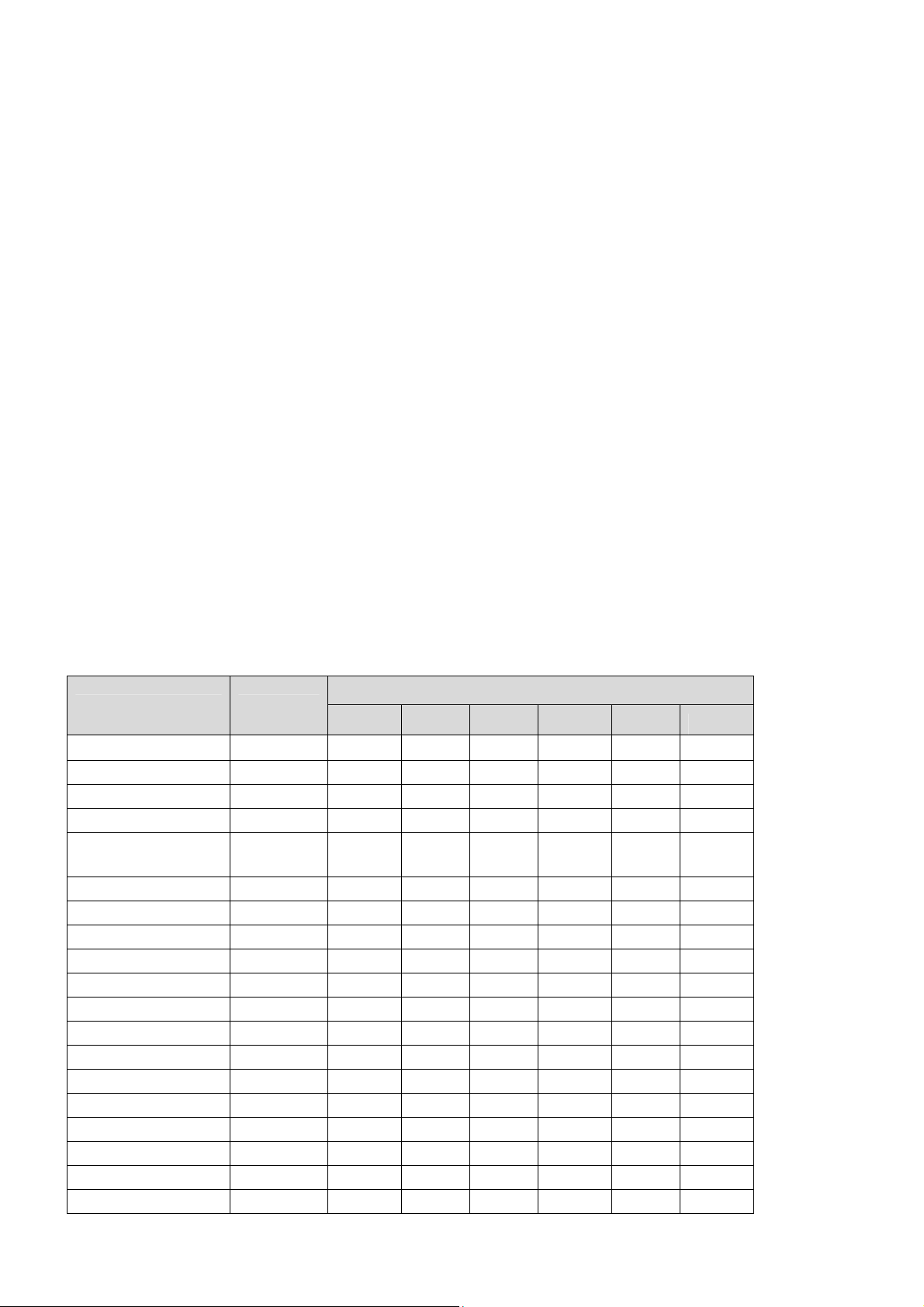
4.1 IPMI Sensors
The following table lists all the sensors supported by the aTCA-9710. Six thresholds including
Lower Non-Recoverable (LNR), Lower Critical (LC), Lower Non-Critical (LNC), Upper NonCritical (UNC), Upper Critical (UC) and Upper Non-Critical (UNR) are defined for each voltage
or temperature sensor.
Sensor Type
LNR LC LNC UNC UC UNR
Hot Swap Discrete na na na na na na
IPMB Physical Discrete na na na na na na
BMC Watchdog Discrete na na na na na na
Version change Discrete na na na na na na
System FW
PROG
Health Status Discrete na na na na na na
BIOS Boot Discrete na na na na na na
48V Current(A) Amps na na na na na na
48V_A Power(V) Volts 75.075 72.15 57.2 43.225 39 36.075
48V_B Power(V) Volts 75.075 72.15 57.2 43.225 39 36.075
1.8V I350 Volts 1.985 1.945 1.915 1.695 1.665 1.625
0.85V XL710_1 Volts 1.235 1.215 1.205 0.605 0.585 0.565
0.85V XL710_2 Volts 1.235 1.215 1.205 0.605 0.585 0.565
1.05V PCH Volts 1.215 1.155 1.105 0.995 0.945 0.895
1.50V PCH Volts 1.655 1.625 1.595 1.305 1.245 1.215
1.20V VGA Volts 1.385 1.345 1.315 1.095 1.065 1.025
3.30V MGMT Volts 3.633 3.573 3.513 3.105 3.044 2.984
3.30V SYS Volts 3.633 3.573 3.513 3.105 3.044 2.984
5.00V SYS Volts 5.502 5.408 5.314 4.703 4.609 4.515
Discrete na na na na na na
Threshold
26
Page 27
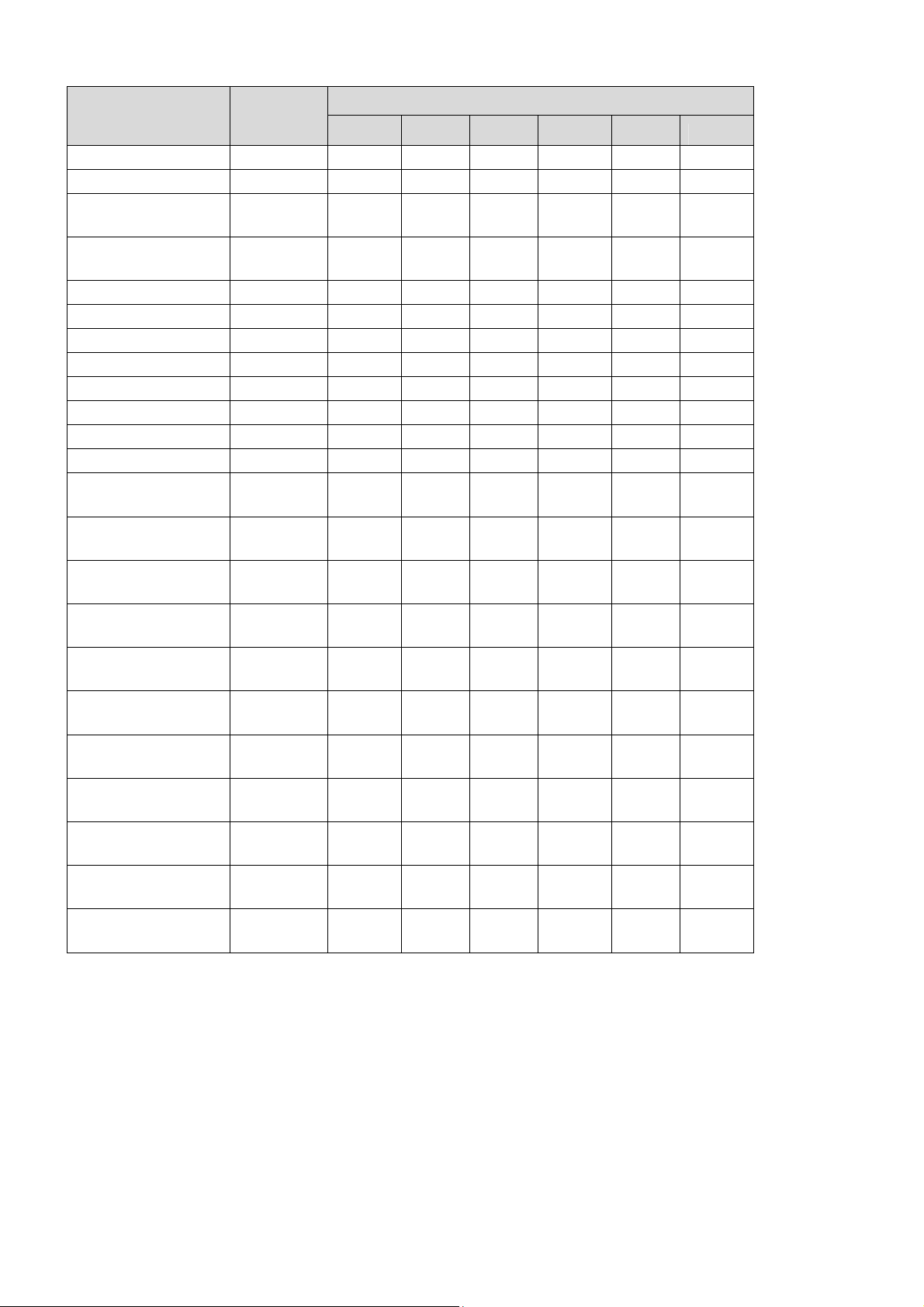
Sensor Type
Threshold
LNR LC LNC UNC UC UNR
12.0V SYS Volts 13.24 13 12.76 11.32 11.08 10.84
1.05V VCCIO Volts 1.216 1.168 1.104 0.992 0.96 0.896
1.80V
VCCIN_CPU0
1.80V
VCCIN_CPU1
Volts 1.856 1.84 1.824 1.6 1.536 1.456
Volts 1.856 1.84 1.824 1.6 1.536 1.456
1.20V VDDQ_AB Volts 1.392 1.344 1.312 1.104 1.056 1.024
1.20V VDDQ_CD Volts 1.392 1.344 1.312 1.104 1.056 1.024
1.20V VDDQ_EF Volts 1.392 1.344 1.312 1.104 1.056 1.024
1.20V VDDQ_GH Volts 1.392 1.344 1.312 1.104 1.056 1.024
0.60V VTT_AB Volts 0.72 0.688 0.64 0.576 0.528 0.496
0.60V VTT_CD Volts 0.72 0.688 0.64 0.576 0.528 0.496
0.60V VTT_EF Volts 0.72 0.688 0.64 0.576 0.528 0.496
0.60V VTT_GH Volts 0.72 0.688 0.64 0.576 0.528 0.496
CPU1 Temp
CPU2 Temp
PCH Temp
DC/DC Temp
XL710 Temp
CPU1 VRM1
Tem p
CPU1 VRM2
Tem p
CPU1 VRM3
Tem p
CPU2 VRM1
Tem p
CPU2 VRM2
Tem p
CPU2 VRM3
Tem p
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
degrees
C
107 97 87 -5 -10 -15
107 97 87 -5 -10 -15
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
95 85 75 0 -5 -10
27
Page 28
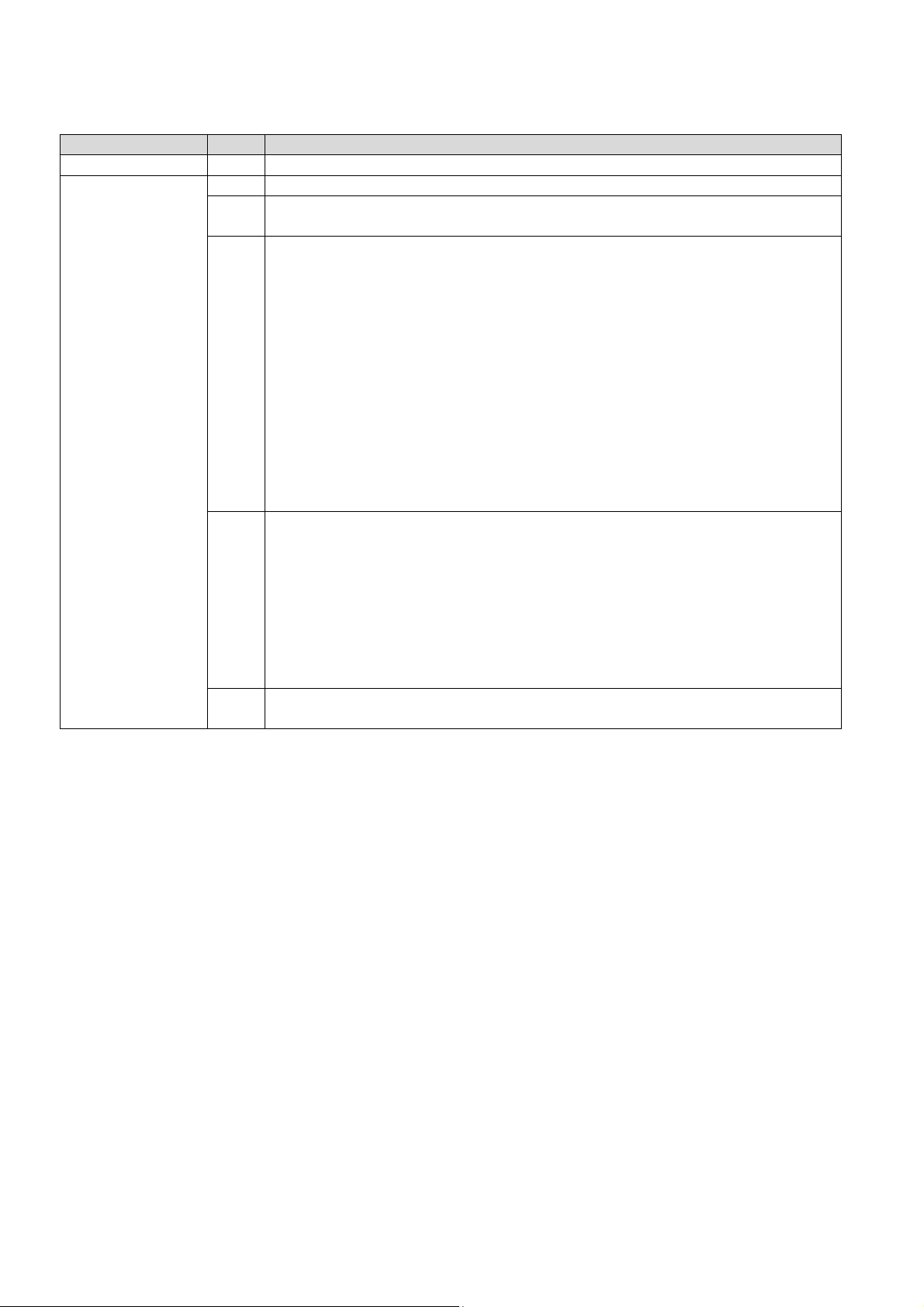
4.1.1 Sensor Reading (FRU Hotswap Sensor)
Request data 1 Sensor Number (FFh = reserved)
Response data
Byte Data field
1 Completion Code
2 Sensor Reading.
[7:0] - Not used. Write as 00h.
3 Standard IPMI byte (See “Get Sensor Reading” in IPMI specification):
[7] - 0b = All Event Messages disabled from this sensor
[6] - 0b = sensor scanning disabled
[5] - 1b = initial update in progress. This bit is set to indicate that a “Rearm Sensor Events” or “Set Event Receiver” command has been used to
request an update of the sensor status, and that update has not occurred
yet. Software should use this bit to avoid getting an incorrect status while
the first sensor update is in progress. This bit is only required if it is
possible for the IPM
Controller to receive and process a “Get Sensor Reading or Get Sensor
Event Status” command for the sensor before the update has completed.
This is most likely to be the case for sensors, such as fan RPM sensors,
that may require seconds to accumulate the first reading after a re-arm.
[4:0] – reserved. Ignore on read.
4 Current State Mask
[7] – 1b = FRU Operational State M7 - Communication Lost
[6] – 1b = FRU Operational State M6 - FRU Deactivation In Progress
[5] – 1b = FRU Operational State M5 - FRU Deactivation Request
[4] – 1b = FRU Operational State M4 - FRU Active
[3] – 1b = FRU Operational State M3 - FRU Activation in Progress
[2] – 1b = FRU Operational State M2 - FRU Activation Request
[1] – 1b = FRU Operational State M1 - FRU Inactive
[0] – 1b = FRU Operational State M0 - FRU Not Installed
(5) [7:0] – Optional/Reserved. If provided, write as 80h (IPMI restriction).
Ignore on read.
28
Page 29

4.1.2 Get Sensor Reading (Physical IPMB-0 Sensor)
Request data 1 Sensor Number (FFh = reserved)
Response data
Byte Data field
1 Completion Code
2 [7] – IPMB B Override State
0b = Override state, bus isolated
1b = Local Control state - IPM Controller determines state of bus.
[6:4] = IPMB B Local Status
0h = No Failure. Bus enabled if no override in effect.
1h = Unable to drive clock HI
2h = Unable to drive data HI
3h = Unable to drive clock LO
4h = Unable to drive data LO
5h = Clock low timeout
6h = Under test (the IPM Controller is attempting to determine if it is
causing a bus hang).
7h = Undiagnosed Communications Failure
[3] – IPMB A Override State
0b = Override state, bus isolated
1b = Local Control state - IPM Controller determines state of bus.
[2:0] = IPMB A Local Status
0h = No failure. Bus enabled if no override in effect.
1h = Unable to drive clock HI
2h = Unable to drive data HI
3h = Unable to drive clock LO
4h = Unable to drive data LO
5h = Clock low timeout
6h = Under test (the IPM Controller is attempting to determine
if it is causing a bus hang).
7h = Undiagnosed Communications Failure
3 Standard IPMI byte (see “Get Sensor Reading” in IPMI specification)
[7] – 0b = All Event Messages disabled from this sensor
[6] – 0b = Sensor scanning disabled
[5] – 1b = Initial update in progress. This bit is set to indicate that a
“Re-arm Sensor Events” or “Set Event Receiver” command has been
used to request an update of the sensor status, and that update has not
occurred yet. Software should use this bit to avoid getting an incorrect
status while the first sensor update is in progress. This bit is only required
if it is possible for the controller
to receive and process a “Get Sensor Reading” or “Get Sensor
Event Status” command for the sensor before the update has completed.
This is most likely to be the case for sensors, such as
fan RPM sensors, that may require seconds to accumulate the first
reading after a re-arm.
[4:0] – Reserved. Ignore on read.
4 [7:4] – Reserved. Write as 0h, ignore on read
[3] 1b = IPMB A enabled, IPMB-B enabled
[2] 1b = IPMB A disabled, IPMB-B enabled
[1] 1b = IPMB-A enabled, IPMB-B disabled
[0] 1b = IPMB A disabled, IPMB-B disabled
(5) [7:0] – Optional/Reserved. If provided, write as 80h (IPMI restriction).
Ignore on read.
29
Page 30

4.1.3 Watchdog Timer Sensor
Sensor Type Sensor
Type
Code
Watchdog 2 23h
Sensor
Specific
Offset
00h
01h
02h
03h
04h-07h
08h
Event
This sensor is recommended for new IPMI v1.0 and later
implementations.
Timer expired, status only (no action, no interrupt)
Hard Reset
Power Down
Power Cycle
reserved
Timer interrupt
The Event Data 2 field for this command can be used to
provide an
event extension code, with the following definition:
7:4 interrupt type
0h = none
1h = SMI
2h = NMI
3h = Messaging Interrupt
Fh = unspecified
all other = reserved
3:0 timer use at expiration:
0h = reserved
1h = BIOS FRB2
2h = BIOS/POST
3h = OS Load
4h = SMS/OS
5h = OEM
Fh = unspecified
all other = reserved
30
Page 31

4.1.4 Version Change Sensor
Sensor Type Sensor
Type
Code
Version
Change
2Bh 00h
Sensor
Specific
Offset
01h
02h
03h
04h
05h
06h
07h
Event
00h Intelligent change detected with associated Entity.
Informational. This offset does not imply whether the
intelligent change was successful or not. Only that a
change occurred.
01h Firmware or software change detected with associated
Entity.Informational. Success or failure not implied.
02h Intelligent incompatibility detected with associated
Entity.
03h Firmware or software incompatibility detected with
associated Entity.
04h Entity is of an invalid or unsupported intelligent
version.
05h Entity contains an invalid or unsupported firmware or
software version.
06h Intelligent Change detected with associated Entity was
successful. (deassertion event means unsuccessful’).
07h Software or F/W Change detected with associated
Entity was successful. (deassertion event means
‘unsuccessful’)
Event data 2 can be used for additional event information
on the type of version change, with the following definition:
Event Data 2
7:0 Version change type
00h unspecified
01h management controller device ID (change in one
or more fields from ‘Get Device ID’)
02h management controller firmware revision
03h management controller device revision
04h management controller manufacturer ID
05h management controller IPMI version
06h management controller auxiliary firmware ID
07h management controller firmware boot block
08h other management controller firmware
09h system firmware (EFI / BIOS) change
0Ah SMBIOS change
0Bh operating system change
0Ch operating system loader change
0Dh service or diagnostic partition change
0Eh management software agent change
0Fh management software application change
10h management software middleware change
11h programmable intelligent change (e.g. FPGA)
12h board/FRU module change (change of a module
plugged into associated entity)
13h board/FRU component change (addition or
removal of a replaceable component on the
board/FRU that is not tracked as a FRU)
14h board/FRU replaced with equivalent version
15h board/FRU replaced with newer version
16h board/FRU replaced with older version
17h board/FRU intelligent configuration change (e.g.
strap, jumper, cable change, etc.)
31
Page 32

4.1.5 System Firmware Progress Sensor
Sensor Type Sensor
Type
Code
System
Firmware
Progress
(formerly
POST
Error)
0Fh 00h
Sensor
Specific
Offset
01h
02h
Event
System Firmware Error (POST Error)
The Event Data 2 field can be used to provide an event
extension code, with the following definition:
Event Data 2
00h Unspecified.
01h No system memory is physically installed in the
system.
02h No usable system memory, all installed memory has
experienced an unrecoverable failure.
03h Unrecoverable hard-disk/ATAPI/IDE device failure.
04h Unrecoverable system-board failure.
05h Unrecoverable diskette subsystem failure.
06h Unrecoverable hard-disk controller failure.
07h Unrecoverable PS/2 or USB keyboard failure.
08h Removable boot media not found
09h Unrecoverable video controller failure
0Ah No video device detected
0Bh Firmware (BIOS) ROM corruption detected
0Ch CPU voltage mismatch (processors that share same
supply have mismatched voltage requirements)
0Dh CPU speed matching failure
0Eh to FFh reserved
System Firmware Hang (uses same Event Data 2 definition
as
following System Firmware Progress offset)
System Firmware Progress
The Event Data 2 field can be used to provide an event
extension
code, with the following definition:
Event Data 2
00h Unspecified.
01h Memory initialization.
02h Hard-disk initialization
03h Secondary processor(s) initialization
04h User authentication
05h User-initiated system setup
06h USB resource configuration
07h PCI resource configuration
08h Option ROM initialization
09h Video initialization
0Ah Cache initialization
0Bh SM Bus initialization
0Ch Keyboard controller initialization
0Dh Embedded controller/management controller
initialization
0Eh Docking station attachment
0Fh Enabling docking station
10h Docking station ejection
11h Disabling docking station
12h Calling operating system wake-up vector
32
Page 33

Sensor Type Sensor
Type
Code
Sensor
Specific
Offset
Event
13h Starting operating system boot process, e.g. calling
Int 19h
14h Baseboard or motherboard initialization
15h reserved
16h Floppy initialization
17h Keyboard test
18h Pointing device test
19h Primary processor initialization
1Ah to FFh reserved
4.1.6 Get Sensor Reading Command
Request data 1 Sensor Number (FFh = reserved)
Response data
Byte Data field
1 Completion Code
2 Sensor reading
Byte 1: byte of reading. Ignore on read if sensor does not return an
numeric (analog) reading.
3 [7] - 0b = All Event Messages disabled from this sensor
[6] - 0b = sensor scanning disabled
[5] - 1b = reading/state unavailable (formerly “initial update in progress”).
This bit is set to indicate that a ‘re-arm’ or ‘Set Event Receiver’ command
has been used to request an update of the sensor status, and that update
has not occurred yet. Software should
use this bit to avoid getting an incorrect status while the first sensor
update is in progress. This bit is only required if it is possible for the
controller to receive and process a ‘Get Sensor Reading’ or ‘Get Sensor
Event Status’ command for the sensor before the update has completed.
This is most likely to be the case for sensors, such as fan RPM sensors,
that may require seconds to accumulate the first reading after a re-arm.
The bit is also used to indicate when a reading/state is unavailable
because the management controller cannot obtain a valid reading or state
for the monitored entity, typically because the entity is not present. For
more in formation, please see Section 16.4, Event Status, Even
Conditions, and Present State and Section 16.6, Re-arming on the
PICMG specification 3.0.
[4:0] - reserved. Ignore on read.
4 For threshold-based sensors
Present threshold comparison status
[7:6] - reserved. Returned as 1b. Ignore on read.
[5] - 1b = at or above (≥) upper non-recoverable threshold
[4] - 1b = at or above (≥) upper critical threshold
[3] - 1b = at or above (≥) upper non-critical threshold
[2] - 1b = at or below (≤) lower non-recoverable threshold
[1] - 1b = at or below (≤) lower critical threshold
[0] - 1b = at or below (≤) lower non-critical threshold
For discrete reading sensors
[7] - 1b = state 7 asserted
[6] - 1b = state 6 asserted
[5] - 1b = state 5 asserted
[4] - 1b = state 4 asserted
[3] - 1b = state 3 asserted
33
Page 34

Byte Data field
[2] - 1b = state 2 asserted
[1] - 1b = state 1 asserted
[0] - 1b = state 0 asserted
(5) For discrete reading sensors only. (Optional)
(00h Otherwise)
[7] - reserved. Returned as 1b. Ignore on read.
[6] - 1b = state 14 asserted
[5] - 1b = state 13 asserted
[4] - 1b = state 12 asserted
[3] - 1b = state 11 asserted
[2] - 1b = state 10 asserted
[1] - 1b = state 9 asserted
[0] - 1b = state 8 asserted
34
Page 35

4.2 IPMI Commands
The following table presents all the commands which are supported by the aTCA-9710 in
different interfaces and compatible with IPMI v1.5 and PICMG 3.0 R2.0 ECN001.
There are two interfaces implemented with IPMI command support.
(1) KCS: OpenIpmi; (2) IPMB0: IPMBa & IPMBb
KCS IPMB0
IPMI Command
IPM Device “Global” Commands
Get Device ID
Cold Reset
Warm Reset
Get Self Test Results
Get Device GUID
IPMI Messaging Support Commands
Set BMC Global Enables
Get BMC Global Enables
Clear Message Flags
Get Message Flags
Get Message
Send Message
Master Write-Read
BMC Watchdog Timer
Reset Watchdog Timer
Set Watchdog Timer
Get Watchdog Timer
Chassis Device Commands
Chassis Identify
Set System Boot Option
Get System Boot Option
Event Commands
Set Event Receiver
Get Event Receiver
Platform Event
Sensor Device Commands
Get Device SDR Info
Get Device SDR
Reserve Device SDR Repository
Get Sensor Reading Factors
Set Sensor Hysteresis
Get Sensor Hysteresis
Set Sensor Threshold
Get Sensor Threshold
Set Sensor Event Enable
Get Sensor Event Enable
Rearm Sensor Events
Get Sensor Event Status
Get Sensor Reading
FRU Device Commands
Get FRU Inventory Area Info
Read FRU Data
Write FRU Data
35
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
Page 36

PICMG Command
HPM.1 Upgrade Commands (HPM.1)
Get target upgrade capabilities
Get component properties
Abort Firmware Upgrade
Initiate upgrade action
Upload firmware block
Finish firmware upload
Get upgrade status
Activate firmware
Query Self-test Results
Query Rollback status
Initiate Manual Rollback
AdvancedTCA
Get PICMG Properties
Get Address Info
FRU Control
FRU Control Capabilities
Get FRU LED Properties
Get LED Color Capabilities
Set FRU LED State
Get FRU LED State
Set IPMB State
Set FRU Activation Policy
Get FRU Activation Policy
Set FRU Activation
Get Device Locator Record ID
Get Port State
Set Port State
Compute Power Properties
Set Power Level
Get Power Level
Bused Resource Control
Get IPMB Link Info
SET_CLOCK_STATE
GET_CLOCK_STATE
Get AMC-Port State
Set AMC-Port State
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
●
●
●
● ●
●
● ●
● ●
● ●
●
●
36
Page 37

5 Getting Started
The aTCA-9710 has been designed for easy installation. However, the following standard
precautions, installation procedures, and general information must be observed to ensure
proper installation and to preclude damage to the board, other system components, or injury
to personnel.
5.1 Safety Requirements
The following safety precautions must be observed when installing or operating the aTCA9710.
ADLINK assumes no responsibility for any damage resulting from failure to comply with these
requirements.
Exercised due care when handling the board as the heat sink can get very hot. Do not touch
the heat sink when installing or removing the board. The board should not be placed on any
surface or in any form of storage container until the board and heat sink have cooled down to
room temperature.
This ATCA blade contains electrostatic sensitive devices. Please observe the necessary
precautions to avoid damage to your board:
Discharge your clothing before touching the assembly. Tools must be discharged before
use.
Do not touch components, connector-pins or traces.
If working at an anti-static workbench with professional discharging equipment, please do
not omit to use it.
37
Page 38

5.2 Installing and Removing the aTCA-9710
5.2.1 Installing the Blade
Follow these steps to install the aTCA-9710 blade to the chassis.
Step 1
Carefully align the board edges with the chassis guide rails and push the blade inwards.
38
Page 39

Step 2
Check if the catch hooks and alignment pins at both ends of the module are correctly
inserted into the proper openings. Push inwards on the handles until the blade is firmly
seated in the chassis. (Do not force the handles if there is any abnormal resistance or it
could damage the connectors and/or backplane.)
39
Page 40

Step 3
Push the ejector handles inwards until it is locked.
40
Page 41

Step 4
Lock both ends of the captive screws.
41
Page 42

5.2.2 Removing the Blade
Follow these steps to remove the aTCA-9710 blade from the chassis.
Step 1
Unlock both ends of the captive screws.
42
Page 43

Step 2
Pinch the lever and latch together then pull outwards to release the ejector handles at both
ends.
Lever
Latch
43
Page 44

Step 3
Pull the blade outwards from the chassis until it is removed.
44
Page 45

5.3 Firmware Update Procedure
The aTCA-9710 supports firmware update (IPMC FW, BIOS, FRU) over various interfaces
(LAN, KCS, serial interface or IPMB). Please follow the procedures listed below to update
the IPMC firmware.
Note: IPMB-0 will be disabled during the process of upgrading IPMC firmware. This is a
limitation of the IPMC controller (SmartFusion A2F500)
5.3.1 Update Over Serial Interface
The following IPMItool command line parameters are used for communicating with the carrier
IPMC via a serial interface:
-I serial-terminal
This parameter instructs the IPMItool utility to use the serial interface for communications
with the carrier IPMC.
-D <dev[:baudrate]>
This parameter specifies the serial device and baud rate settings to use. For Linux hosts, the
serial device is the system path to the device node (e.g. /dev/ttyS0).
Perform the following steps to update the IPMC firmware:
Step 1: Prepare an external host PC with Linux OS and connect it to the serial port on the
aTCA-9710 via the COM port (USB Mini-B on the front panel). Put the IPMItool utility and
new firmware image on the host PC. Enter the following command:
Step 2: Enter “y” when prompted and wait until the string “firmware update procedure
successful” is displayed.
To update other images (BIOS, FRU, etc), just replace the target image and the file name
while typing command.
Item File name
IPMC firmware hpm1fw.img
BIOS hpm1bios.img
Note:
1. The hpm1bios.img always updates the backup BIOS image.
2. Make sure the payload power is off (M1 state) before updating the IPMC firmware
45
Page 46

5.3.2 Update over KCS
Step1: Prepare an aTCA-9710 with Linux system. Enter the following command to make
sure the ipmi_si and ipmi_devintf modules are loaded before the IPMItool utility can be
used.
Step2: Put IPMItool and “target image” in the Linux system then enter the following
command:
Step3: Select “y” and wait until the string of “firmware update procedure successful”
is displayed.
To update other images (BIOS, FRU, etc), just replace the target image and the file name
while typing command.
Item File name
IPMC firmware hpm1fw.img
BIOS hpm1bios.img
46
Page 47

5.3.3 Update over LAN
The following IPMItool command line parameters are used for communicating with the carrier
IPMC via LAN:
-I lan
The parameter instructs the IPMItool utility to use the RMCP protocol for communicating with
the IPMC.
-H <IP address >
The parameter specifies the IP address of the IPMC.
Please follow the step to update firmware:
Step1: Prepare an external x86 PC and connect the target aTCA-9710 via BASE Interface.
Put IPMItool and “target image” on the x86 PC with Linux system. Enter the following
command:
Step2: Select “y” and wait until the string of “firmware update procedure successful”
is displayed.
To update other images (BIOS, FRU, etc), just replace the target image and the file name
while typing command.
Item File name
IPMC firmware hpm1fw.img
BIOS hpm1bios.img
47
Page 48

6 BIOS
This chapter will guide you how to configure BIOS setup items. There will be detailed
description for each BIOS setup item in the following sections.
6.1 Entering the BIOS Setup Screen
To enter the setup screen, follow these steps:
Step 1: Power on the aTCA-9710.
Step 2: Press the <DEL> key on a USB keyboard when you see the following text prompt on
boot up screen.
Step 3: After you press the <DEL> key, the Main BIOS setup menu will be displayed. You
can access the other setup screen from the BIOS setup utility, such as CPU configuration,
USB configuration and so on.
6.1.1 Navigation
The BIOS setup/utility uses a key-based navigation system called hot keys. Most of
the BIOS setup utility hot keys can be used at any time during the setup navigation
process. These keys include <F1>, <F2>, <F3>, <F4>, <ESC>, <Enter>, <Arrow>
48
Page 49

keys, and so on.
There is a hot key legend located in the right frame on most setup screens..
→← Left/Right. The Left and Right < Arrow > keys allow you to select a setup
screen.
↑↓ Up/Down The Up and Down < Arrow > keys allow you to select a setup item
or sub-screen.
+- Plus/Minus the Plus and Minus < Arrow > keys allow you to change the field
value of a particular setup item.
For example: Date and Time.
ESC The < Esc > key allows you to discard any changes you have made and exit
the Setup. Press the < Esc > key to exit the setup without saving your
changes. Press the < Enter > key to discard changes and exit. You can
also use the < Arrow > key to select Cancel and then press the < Enter >
key to abort this function and return to the previous screen.
Enter The < Enter > key allows you to display or change the setup option listed for
a particular setup item. The < Enter > key can also allow you to display the
setup sub-screens.
49
Page 50

6.2 Main BIOS Setup Screen
The Main BIOS setup menu is the screen where you start navigation of the BIOS setting
menus. You can always return to the Main setup screen by selecting the Main tab. Each
BIOS setup menu option is described in the following sections.
There are two parts of the Main BIOS setup menu screen. The left part of the screen
displays the available options. The user can configure the options in blue text. The selected
option will appear highlighted in white text. Options in gray text are for information only
The upper right part of the screen displays the description of the selected option. The lower
right part of the screen shows the navigation keys that user can use.
The Main setup screen is shown below.
System Language
Choose the language of BIOS setup utility. So far, there is only “English” is supported
on aTCA-9710.
System Time/System Date
Use these two options to change system time and date. Highlight System Time or
System Date using the <Arrow> keys. Enter new values using the keyboard. Press
the <Tab> key or the <Arrow> keys to move between fields. The date must be
entered in MM/DD/YY format. The time is entered in HH:MM:SS format.
50
Page 51

The time is in 24-hour format. For example, 5:30 A.M. appears as 05:30:00, and 5:30 P.M. as
17:30:00.
System & Board Information
The Main BIOS setup screen reports memory and board information.
BIOS Vendor
It reports the BIOS vendor of aTCA-9710’s BIOS. American Megatrend, Inc. is the
BIOS vendor that aTCA-9710 is using.
Core Version
It shows what core version is used from AMI to develop aTCA-9710’s BIOS.
Compliancy
It shows what version of EFI specification is compliant with aTCA-9710’s BIOS.
BIOS Revision
It shows revision of aTCA-9710’s BIOS.
Build Date and Time
It shows date and time that aTCA-9710 BIOS is released.
Total Memory
It shows the memory size on aTCA-9710.
51
Page 52

6.3 Advanced Setup Screen
Select the Advanced tab from the setup screen to enter Advanced BIOS setup
screen. You can select any of items in the left frame of the screen, such as CPU
configuration, to go to the sub menu for that item. You can select an Advanced BIOS
sub menu or option by highlighting it using the <Arrow> keys. The Advanced BIOS
setup screen is shown below.
The sub menus are described in the following sections.
Front 10G LAN1/2 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF FRONT 10G LAN.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Base 1G LAN1/2 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF BASE 1G LAN.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Fabric 40G LAN1/2 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF Fabric 40G LAN1/2.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
52
Page 53

Fabric 40G LAN3/4 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF Fabric 40G LAN3/4.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
RTM 10G LAN1/2 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF RTM 10G LAN1/2.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
RTM 10G LAN3/4 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF RTM 10G LAN3/4.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
RTM 10G LAN5/6 PXE ROM
Enable or Disable PXE ROM OF RTM 10G LAN5/6.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Coleto Creek Control
Enable or Disable Coleto Creek plug-in card.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
53
Page 54

6.3.1 ACPI Settings
You can use this screen to select options for the ACPI Advanced Configuration
Settings. Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and <
- > keys to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item
appears on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The
screen is shown below.
Enable ACPI Auto Configuration
Enables or Disables BIOS ACPI Auto Configuration. Set this value to Enabled /
Disabled.
Enable Hibernation
Enables or Disables System ability to Hibernate (OS/S4 Sleep State). This option
may be not effective with some OS. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Lock Legacy Resources
Enables or Disables Lock of Legacy Resources. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
54
Page 55

6.3.2 NCT5104D Super IO Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the NCT5104D Super IO Configuration.
Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys
to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears
on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below
Serial Port 1 Configuration
Set Parameters of Serial Port 1 (COMA). The screen is shown below
Serial Port 2 Configuration
Set Parameters of Serial Port 2 (COMB). The screen is shown below
55
Page 56

Serial PortGSIO200
Enable or Disable Serial Port (COM). Set this value to Enabled / Disabled
56
Page 57

6.3.3 Serial Port Console Redirection
You can use this screen to select options for the serial port console redirection
settings. Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and <
- > keys to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item
appears on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on the following
pages. An example of the Serial Port Console Redirection screen is shown below.
Console Redirection
The BIOS Console Redirection feature here. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
Console Redirection Settings
The settings specify how the host computer and the remote computer (which the user
is using) will exchange data. Both computers should have the same or compatible
settings. The screen is shown below.
57
Page 58

Terminal Type
VT100+ is the preferred terminal type for out-of-band management. Configuration
options: VT100, VT100+, VT-UTF8 , ANSI.
Bits per second
Select the bits per second you want the serial port to use for console redirection. The
options are 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600.
Data Bits
Select the data bits you want the serial port to use for console redirection. Set this
value to 7 / 8.
Parity
Set this option to select Parity for console redirection. The settings for this value are
None, Even, Odd, Mark, Space.
Stop Bits
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit indicates the beginning).
The standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices may require
more than 1 stop bit. Set this value to 1 and 2.
58
Page 59

Flow Control
Set this option to select Flow Control for console redirection.
The settings for this value are None, Hardware RTS/CTS.
VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
Enable VT-UTF8 Combination Key support for ANSI/VT100 terminals.
The settings for this value are Enabled, Disabled.
Recorder Mode
Enabled this mode, only text will be sent. This is to capture terminal data.
Set this value to Enable/Disable.
Resolution 100x31
Set this option to extended terminal resolution. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
Legacy OS Redirection
On Legacy OS, the number of rows and columns supported redirection.
Set this value to 80x24 / 80x25.
Putty KeyPad
Select function key and keypad on putty.
Set this value to VT100 / LINUX / XTERMR6 / SCO / ESCN / VT400.
Redirection After BIOS POST
The settings specify if BootLoader is selected than legacy console redirection is
disabled before booting to legacy O.S. Default value is Always Enable which means
legacy console redirection is enabled for legacy O.S.
Set this value to Always Enable / BootLoader.
59
Page 60

6.3.4 PCI Subsystem Settings
You can use this screen to select options for the PCI Subsystem Settings. Use the up
and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change
the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the
right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
SR-IOV Support
If system has SR-IOV capable PCIe Devices, this option Enables or Disables Single
Root IO Virtualization Support. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
60
Page 61

6.3.5 Network Stack Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Network Stack Configuration. Use
the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to
change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears
on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
Network Stack
Enable/Disable UEFI Network Stack.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
IPv4 PXE Support
Enable Ipv4 PXE Boot Support. If disabled IPV4 PXE boot option will not be created.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
IPv6 PXE Support
Enable Ipv6 PXE Boot Support. If disabled IPV6 PXE boot option will not be created.
Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
PXE boot wait time
Wait time to press ESC key to abort the PXE boot.
Set this value to integer.
61
Page 62

Media detect count
Number of times presence of media will be checked.
Set this value to integer.
6.3.6 CSM Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the CSM Configuration. Use the up and
down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change the
value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the right
side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is shown
below.
CSM Support
Enable/Disable CSM Support. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Boot option filter
This option controls whether to hide Legacy/UEFI boot options. Set this value to UEFI
and Legacy / Legacy only /UEFI only.
Network
Controls the execution of UEFI and Legacy PXE OpROM. Set this value to Do not
launch / UEFI / Legacy.
62
Page 63

Storage
Controls the execution of UEFI and Legacy PXE OpROM. Set this value to Do not
launch / UEFI / Legacy
6.3.7 Trusted Computing
Trusted computing is an industry standard to make personal computers more secure
through a dedicated hardware chip, called a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). This
option allows enabling or disabling the TPM support.
Security Device Support
Enable for BIOS support for security device. O.S. will not show Security Device. TCG
EFI protocol and INT1A interface will be available.
TPM State
Enable/Disable Security Device. Note: Your computer will reboot during restart in
order to change State of the device.
Pending operation
Schedule an Operation for the Security Device. NOTE: your computer will reboot
during restart in order to change state of Security Device.
63
Page 64

6.3.8 ADLINK IPMI settings
You can use this screen to select options for the ADLINK IPMI settings. Use the up
and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change
the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the
right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
POST Watchdog Timer
Enable or Disable POST Watchdog Timer. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
POST Watchdog Timeout
Select the time value for POST Watchdog Timer Expiration value.
Set this value to 3 minutes / 4 minutes /5 minutes /6minutes.
POST Watchdog Timer Policy
Configure how the system should respond if the POST Watchdog Timer expires. Not
available if POST Watchdog Timer is disabled.
Set this value to Reset / Power Down / Do Nothing.
OS Load Watchdog Timer
Enable or Disable OS Watchdog Timer. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
64
Page 65

OS Load Watchdog Timeout
Select the time value for OS Watchdog Timer Expiration value.
Set this value to 5 minutes / 10 minutes / 15 minutes / 20 minutes.
OS Load Watchdog Timer Policy
Configure how the system should respond if the OS Watchdog Timer expires. Not
available if OS Watchdog Timer is disabled.
Set this value to Reset / Power Down / Do Nothing.
65
Page 66

6.4 Intel RC Setup
Select the Inte lRC Setup tab from the setup screen to enter the Intel RC Setup
screen. You can select any of the items in the left frame of the screen, such as
Processor Configuration, to go to the sub menu for that item. You can display an
IntelRCSetup option by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The IntelRCSetup
screen is shown below.
6.4.1 Processor Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Processor Configuration settings.
Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys
to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears
on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
66
Page 67

Hyper-Threading [ALL]
Enables Hyper Threading (Software Method to Enable/Disable Logical Processor
threads. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
Enable Intel TXT Support
Enables Intel Trusted Execution Technology Configuration. Please disable "EV DFX
Features" when TXT is enabled. Set this value to Enabled / Disabled.
VMX
Enables the Vanderpool Technology, takes effect after reboot. Set this value to
Enabled / Disabled.
Per-Socket Configuration
Change Per-Socket settings. The screen is shown below
67
Page 68

Cores Enabled
Number of Cores to Enable. 0 means all cores.
68
Page 69

6.4.2 Advanced Power Management Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Advanced Power Management
Configuration. Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + >
and < - > keys to change the value of the selected option. A description of the
selected item appears on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on
this page. The screen is shown below
Power Technology
Enable the power management features. Set this value to Disable / Energy Efficient
/ Custom.
Config TDP
Option to disable/enable Config TDP. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
CPU P State Control
The screen is shown below
69
Page 70

EIST (P-states)
When enabled, OS sets CPU frequency according load. When disabled, CPU
frequency is set at max non-turbo. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
Turbo Mode
Enable or Disable CPU Turbo mode. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
CPU T State Control
The screen is shown below
70
Page 71

ACPI T-States
Enable/Disable CPU throttling by OS. Throttling reduces power consumption. Set this
value to Enable/Disable.
6.4.3 Common RefCode Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Common RefCode Configuration.
Use the up and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys
to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears
on the right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
71
Page 72

Numa
Enable or Disable Non uniform Memory Access (NUMA). Set this value to
Enable/Disable.
6.4.4 Memory Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Memory Configuration. Use the up
and down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change
the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the
right side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is
shown below.
72
Page 73

Memory Ma p
Set memory mapping settings. The screen is shown below
73
Page 74

Socket Interleave Below 4GB
Splits the 0-4GB address space between two sockets, so that both sockets get a
chunk of local memory below 4GB. Set this value to Enable/Disable.
Channel Interleaving
Select Channel Interleaving setting. Set this value to Auto/1-way Interleave/2-way
Interleave/3-way Interleave/4-way Interleave.
Rank Interleaving
Select Rank Interleaving setting. Set this value to Auto/1-way Interleave/2-way
Interleave/4-way Interleave/8-way Interleave.
6.4.5 IIO Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the IIO Configuration. Use the up and
down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change the
value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the right
side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is shown
below.
IIO0 Configuration
The screen is shown below
IIO1 Configuration
74
Page 75

The screen is shown below
Intel VT for Directed I/O (VT-d)
The screen is shown below
PCIe x8 to aDB-9710
Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). Set this value to Auto/x8/x4x4.
PCIe x16 to aDB-9710
Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). Set this value to Auto/ x16/ x8x8/
x8x4x4/ x4x4x8/ x4x4x4x4.
Socket 0 PcieD0xFx - Port xx
Settings related to PCI Express Ports (0/1A/1B/2A/2B/2C/2D/3A/3B/3C/3D/).The
screen is shown below
75
Page 76

6.4.6 PCH Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the PCH Configuration. Use the up and
down < Arrow > keys to select an item. Use the < + > and < - > keys to change the
value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the right
side of the screen. The settings are described on this page. The screen is shown
below.
76
Page 77

Configure SATA as
This will configure SATA as IDE ,RAID or AHCI. Set this value to IDE/AHCI/ RAID .
77
Page 78
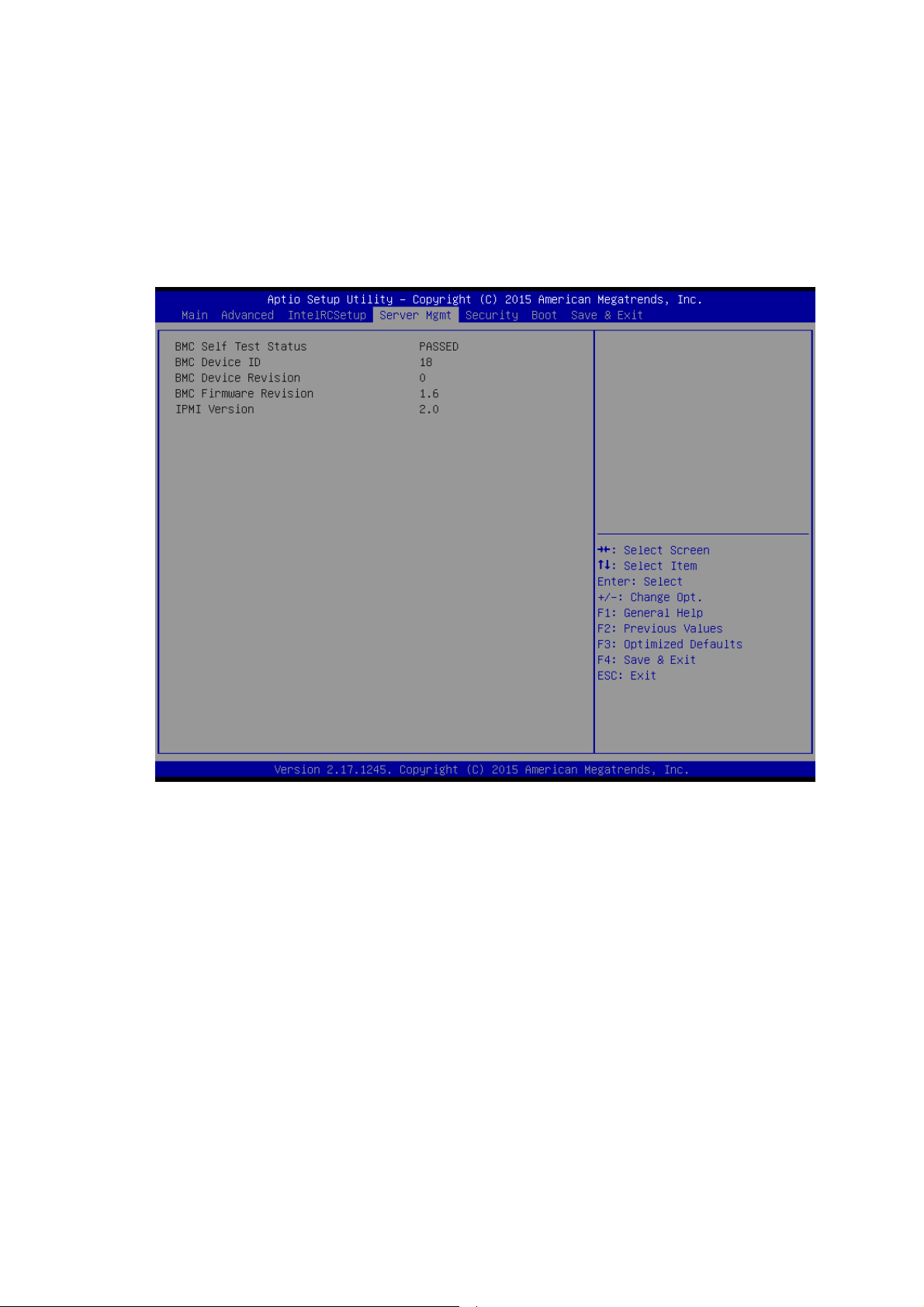
6.5 Server Mgmt Setup Screen
You can use this screen to specify options for the Server Management settings. Use
the up and down <Arrow> keys to select an item. Use <+> and <-> keys to change
the value of the selected option. The settings are described in the following pages.
The screen is shown as below.
78
Page 79

6.6 Boot Setup Screen
You can use this screen to specify options for the Boot configuration settings. Use
the up and down <Arrow> keys to select an item. Use the <+> and <-> keys to
change the value of the selected option. The settings are described in the following
pages. The screen is shown as the below.
Setup Prompt Timeout
It’s the number of seconds to wait for setup activation key. 65535 (0xFFFF) means
indefinite waiting. Use the <+> and <-> keys to change the value of this item.
Quiet Boot
This item allows system BIOS to show the boot up splash logo. When it is set to
“Enabled”, the logo that in system BIOS will be shown during display outputs.
Boot Option Priorities
It shows the boot priority of boot devices. User can adjust the order to make
customized boot priority of found bootable devices.
79
Page 80

6.7 Security Setup Screen
System BIOS provides two levels of password protection. They are Administrator
password and User password. The system can be configured that all users must
enter password every time the system boots or when setup utility is executed, using
either Administrator password or User password.
The Administrator and User passwords activate two different levels of password
security. If you select password support, you are prompted for 3 to 20 characters
password. Type the password on the keyboard. The password doesn’t appear on the
screen when typed. Make sure you write it down. If you forget it, you must drain
NVRAM and re-configure it.
Administrator Password
Use this option to set a password for administrator with full control of the BIOS setup
utility.
User Password
Use this option to set a password for user with limited access to the BIOS setup utility.
80
Page 81

6.8 Save & Exit Setup Screen
Select Save & Exit tab from setup utility to enter Save & Exit BIOS setup screen.
You can select an item by highlighting it using the <Arrow> keys. The Save & Exit
BIOS setup screen is shown below.
Save Changes and Exit
When you have completed the system configuration changes, select this option to
leave setup utility and reboot the computer to let new system configuration
parameters can take effect. When selecting this item and then press <Enter>. The
below message will be shown up and wait for the confirmation.
Save Changes and Exit?
[OK] [Cancel]
Select OK and press <Enter> to save changes and exit. It will keep booting the
system to OS if no changes need to reset system.
Discard Changes and Exit
Select this option to quit setup without making any permanent changes to the system
configuration. When selecting this item and then press <Enter>. The below message
will be shown up and wait for the confirmation.
81
Page 82

Discard Changes and Exit?
[OK] [Cancel]
Select OK and press <Enter> to discard changes and exit. It will keep booting the
system to OS.
Save Changes and Reset
It has the same function as Save Changes and Exit except resetting system. System
will always be reset after selecting this item no matter what change is made,
Discard Changes and Reset
It has the same function as Discard Changes and Exit except resetting system.
System will always be reset after selecting this item and will not save any
configuration.
Save Changes
Save the changes done so far to any of setup options.
Discard Options
Discard the changes done so far to any of setup options.
Restore Defaults
Load BIOS built-in default value for all setup options.
Save as User Defaults
Save the changes done so far as user defaults.
Restore User Defaults
Restore the saved user default to all the setup options.
82
Page 83

7 Serial Over LAN
Serial Over LAN (SOL) is a remote management feature that allows the IPMC (Smart Fusion
A2F500) to redirect the serial console from the blade via an IPMI session over the network
with RMCP+ protocol.
The aTCA-9710 supports SOL on the Base Interface which is powered by the Intel 82576
Gigabit Ethernet Controller. The Intel 82576 Gigabit Ethernet Controller is connected to the
IPMC (Smart Fusion A2F500) via the NC-SI interface, which provides remote management
capability before the payload power is authorized. Users can use the SOL feature to
transmit/receive serial console message from a remote site with full console management
functionality.
The aTCA-9710 supports 2 channels (channel 1/2) and 2 user IDs for SOL. You can refer to
the following sections for more detailed information.
Note: SOL does not support simultaneous login of more than one user.
7.1 Preparation For SOL Connection
First of all, you need to prepare a remote client with Linux OS and connect to the network.
7.2 Configure The Remote Client
7.2.1 Install IPMItool For The Remote Client
You can download the latest IPMItool and document from the following website
http://IPMItool.sourceforge.net
Click on either the *bz or *gz version of IPMItool to download the bzipped or gzipped
IPMItool source code tarball respectively.
To build IPMItool, unzip and untar the downloaded IPMItool package, configure IPMItool for
your system, and change to the created IPMItool directory to build IPMItool.
Example using the gzipped tarball:
tar xvzf IPMItool*.tar.gzcd IPMItool*
Run the following to configure IPMItool for your system:
./configure
83
Page 84

Build the source code and install IPMItool:
make
make install
Now your remote client is ready to connect to the target the aTCA-9710.
Note: The install must be run with root permissions to overlay the existing IPMItool utility in
/usr/local/bin.
7.3 Configure The Target aTCA-9710
7.3.1 BIOS Configuration
You can refer to section 6.3.8/6.3.9 to enable Serial Port Console Redirection on COM0
Note: The aTCA-9710 supports SOL on COM0 only
7.3.2 Linux grub Setting
GRUB supports sending its messages to the serial console. The following lines should be
added to the top of the /boot/grub/grub.conf file.
default=1
timeout=5
serial --unit=1 --speed=115200 --word=8 --parity=no --stop=1
terminal --timeout=15 serial console
The following parameters need to be passed to each instance of the Linux kernel. They
should be added to the kernel line.
console=tty0 console=ttyS1,115200n8
An example is shown below:
title SOL (2.6.18-128.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.18-128.el5 ro root=LABEL=/ console=tty0
console=ttyS1,115200n8
initrd /boot/initrd-2.6.18-128.el5.img
84
Page 85

7.3.3 Linux System Setting
Linux needs to be told to listen for logins on the serial port. This is done by adding the
following line to /etc/inittab.
Add the following line to the init configuration file /etc/inittab.
s1:12345:respawn:/sbin/agetty –L ttyS1 115200 vt100
Now the target aTCA-9710 is ready for SOL connection.
7.4 Establish SOL Connection
Execute the following command from your remote client to establish the SOL Connection
Command:
ipmitool -I lanplus -H <Target IPMC IP > -C < Cipher Suite Id > -U <User Name> -P
<Password> sol activate
Note: Please refer to the following table for the Cipher Suite Id
ID characteristics Cipher Suite
0
1 S 01h, 00h, 00h None None
2 S, A 01h, 01h, 00h None
3 S, A, E 01h, 01h, 01h AES-CBC-128
4 S, A, E 01h, 01h, 02h xRC4-128
5 S, A, E 01h, 01h, 03h
6 S 02h, 00h, 00h None None
7 S, A 02h, 02h, 00h None
8 S, A, E 02h, 02h, 01h AES-CBC-128
9 S, A, E 02h, 02h, 02h xRC4-128
10 S, A, E 02h, 02h, 03h
11 S, A 02h, 03h, 00h None
12 S, A, E 02h, 03h, 01h AES-CBC-128
13 S, A, E 02h, 03h, 02h xRC4-128
14 S, A, E 02h, 03h, 03h
“straight
password"
00h, 00h, 00h RAKP-none None None
Authentication
Algorithm
RAKP-HMAC-
SHA1
RAKP-HMAC-
MD5
Integrity
Algorithm(s)
HMAC-SHA1-
96
HMAC-MD5-
128
MD5-128
Confidentiality
Algorithm(s)
xRC4-40
xRC4-40
xRC4-40
80h-BFh OEM specified OEM specified OEM specified OEM specified OEM specified
C0h-FFh reserved - - - -
85
Page 86

The default values of the aTCA-9710 SOL parameters are listed in the table below
Parameter Default Value
Channel 1 IP Address 172.17.172.134
Channel 2 IP Address 172.17.172.135
User ID 2
User Name adlinkuser
Password adlinkuser
Below are 2 samples to establish the SOL session via channel 1 with default user name and
password:
Sample:
Establish a non-nncrypted RMCP+ SOL session
./ipmitool -I lanplus -H 172.17.172.134 -C 0 -U "adlinkuser" -P "adlinkuser" sol activate
Establish an encrypted RMCP+ SOL session
./ipmitool -I lanplus -H 172.17.172.134 -C 3 -k gkey -U "adlinkuser" -P "adlinkuser" sol
activate
For more details on IPMI commands, please visit the following site:
http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net.
86
Page 87

8 Drivers
The drivers for aTCA-9710 are available on the ADLINK website. Please visit the aTCA-9710
product web site for more details:
www.adlinktech.com/PD/web/PD_detail.php?cKind=&pid= 1453
We recommend using all the drivers provided on the ADLINK website to ensure driver
compatibility. Contact ADLINK to get support for other operating system..
87
Page 88

Safety Instructions
1. Please read these safety instructions carefully.
2. Please keep this User‘s Manual for later reference.
3. One AC Inlets provided and service as Disconnect Devices, disconnect the equipment
from both AC outlets use these AC Inlets before servicing or clearing. Use moisture
sheet or cloth for cleaning.
4. For pluggable equipment, that the socket-outlet shall be installed near the equipment
and shall be easily accessible.
5. Please keep this equipment from humidity.
6. Lay this equipment on a reliable surface when install. A drop or fall could cause injury.
7. Make sure the voltage of the power source when connect the equipment to the power
outlet.
8. Place the power cord such a way that people can not step on it. Do not place anything
over the power cord.
9. All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
10. If the equipment is not use for long time, disconnect the equipment from mains to
avoid being damaged by transient overvoltage.
11. Never pour any liquid into openings; this could cause fire or electrical shock.
12. Never open the equipment. For safety reason, the equipment should only be opened
by qualified service personnel.
13. If one of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by a service
personnel:
a. The Power cord or plug is damaged.
b. Liquid has penetrated into the equipment.
c. The equipment has been exposed to moisture.
d. The equipment has not work well or you can not get it work according to user‘s
manual.
e. The equipment has dropped and damaged.
f. If the equipment has obvious sign of breakage.
14. The equipment can be operated at an ambient temperature of 55°C.
15. Lithium Battery provided (real time clock battery), contact ADLINK for replacement.
CAUTION – Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by one of an incorrect type.
Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions.
88
Page 89

Getting Service
Contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
新北市中和區建一路 166 號 9 樓
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: 上海市浦东新区张江高科技园区芳春路 300 号 (201203)
300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Pudong New Area
Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: 北京市海淀区上地东路 1 号盈创动力大厦 E 座 801 室(100085)
Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1, B/D, Shang Di East Rd.
Beijing, 100085 China
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8625
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: 深圳市南山区科技园南区高新南七道 数字技术园 A1 栋 2 楼 C 区 (518057)
2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7
High-Tech Industrial Park S., Shenzhen, 518054 China
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
LiPPERT ADLINK Technology GmbH
Address: Hans-Thoma-Strasse 11, D-68163, Mannheim, Germany
Tel: +49-621-43214-0
Fax: +49-621 43214-30
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
89
Page 90

ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 6 allée de Londres, Immeuble Ceylan
91940 Les Ulis, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: 〒101-0045 東京都千代田区神田鍛冶町 3-7-4
神田 374 ビル 4F
KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho,
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 137-881 서울시 서초구 서초대로 326, 802 (서초동, 모인터빌딩)
802, Mointer B/D, 326 Seocho-daero, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-881, Korea
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre,
Singapore 349584
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: #50-56, First Floor, Spearhead Towers
Margosa Main Road (between 16th/17th Cross)
Malleswaram, Bangalore - 560 055, India
Tel: +91-80-65605817, +91-80-42246107
Fax: +91-80-23464606
Email: india@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Israeli Liaison Office)
Address: 27 Maskit St., Corex Building
PO Box 12777
Herzliya 4673300, Israel
Tel: +972-77-208-0230
Fax: +972-77-208-0230
Email: israel@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (UK Liaison Office)
Tel: +44 774 010 59 65
Email: UK@adlinktech.com
90
 Loading...
Loading...