Page 1

BCR
BARCODE / CONTACTLESS
READER
___________________
USER MANUAL
PRODUCED BY
ADEL S.r.l.
Legal address: Via Saffi
Operative address Via Nonantolana N. 970/1
41100 MODENA
Tel 059-2550137 Fax 059-2551207
e-mail adel@adel2000.it
Rif. BCR TECHM 1_3.ENG.PDF TECHNICAL DATA ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT ADVISE
N. 58
Page 2
ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
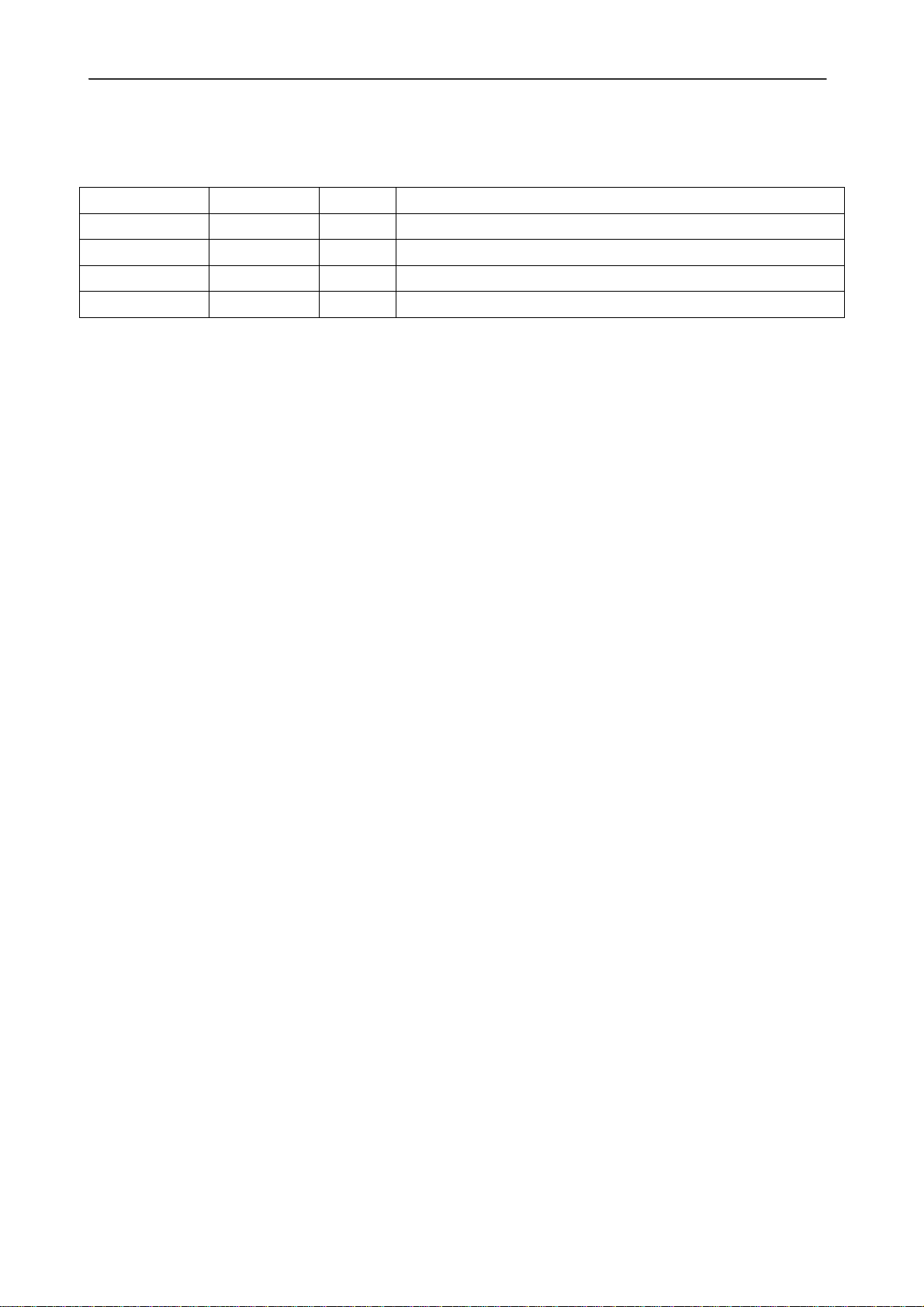
REVISIONS
DATE AUTHOR VER. CHANGES
12/03/2005 FC 1.0 First edition
27/11/2006 SM 1.1 Modified paragraph 3.1.4
01/07/2008 GB 1.2 Modified paragraphs 5.2 and 5.3
18/09/2008 AC 1.3 Modified paragraphs 3.1.4 and 3.1.5
pag. 2
Page 3

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
INDICE
1. GENERALITIES.....................................................................................................................................................4
2. ELECTRIC AND MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS.....................................................................................4
2.1 DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT; BASE AND COMBO VERSIONS .........................................................4
2.2 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY ......................................................................................................................4
2.3 INTERFACE ...................................................................................................................................................4
2.4 AVERAGE LIFE .............................................................................................................................................4
2.5 ENVIRONMENT CONDITIONS..................................................................................................................4
3. MODULE DESCRIPTION..................................................................................................................................... 4
3.1 MECHANICAL STRUCTURE......................................................................................................................4
3.1.1 FLANKS FOR TITLE TRANSPORT.............................................................................................................5
3.1.2 TICKET AND CARD TRANSPORT.............................................................................................................. 5
3.1.3 LASER SCANNER ........................................................................................................................................5
3.1.4 CCD IMAGER SCANNER............................................................................................................................5
3.1.5 LONGITUDINAL SCANNER .......................................................................................................................5
3.1.6 R/W CONTACTLESS UNIT..........................................................................................................................5
4. ELECTRONIC CONTROL ...................................................................................................................................5
4.1 CPU BOARD ..................................................................................................................................................5
4.2 MANAGING FIRMWARE .............................................................................................................................6
5. ELECTRIC CONNECTIONS AND PREARRANGEMENTS...........................................................................6
5.1 ELECTRIC CONNECTIONS .......................................................................................................................6
5.1.1 POWER SUPPLY CONNECTOR.................................................................................................................6
5.1.2 SERIAL INT. RS232 CONNECTOR ............................................................................................................6
5.1.3 I/O SIGNAL CONNECTORS........................................................................................................................6
5.1.4 I/O SIGNAL CONNECTOR..........................................................................................................................7
5.1.5 OPTO #3 CONNECTOR ..............................................................................................................................7
5.1.6 STEPPING MOTOR CONNECTOR............................................................................................................. 7
5.1.7 SCANNER CONNECTOR.............................................................................................................................7
5.1.8 CONTACLESS MODULE CONNECTOR....................................................................................................7
5.1.9 PROGRAMMING CONNECTOR.................................................................................................................8
5.2 BUTTONS.......................................................................................................................................................8
5.3 DIP SWITCH...................................................................................................................................................8
5.4 SIGNALLING LED..........................................................................................................................................8
6. PROGRAMMING PROCEDURE.........................................................................................................................9
7. BCR CPU LAYOUT..............................................................................................................................................10
8. ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS.....................................................................................................................10
8.1 BARCODE AND CONTACTLESS READER SETTING........................................................................10
8.2 BARCODE READING POSITION SETUP .............................................................................................. 10
9. DIMENSIONS........................................................................................................................................................11
10. CONNTACTLESS TICKET AND CARD FORMAT...................................................................................14
pag. 3
Page 4

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
1. GENERALITIES
The BCR module is a motorized device for barcode reading of ISO format tickets.
Barcode reading occurs by a laser scanner for transversal printed codes or with a CCD scanner for codes
printed longitudinally.
Optionally and in alternative the version with contactless card and ticket reader is available.
The BCR COMBO version, ideal for automatic cashers and payment operations allows to install both the
barcode reader and the contactless card reader.
In this way you can realize parking systems with barcode tickets for occasional parkers and contactless card
for season parkers or pre-paid cards for habitual users.
2. ELECTRIC AND MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT; BASE AND COMBO VERSIONS
BASE VERSION COMBO VERSION
Length: 144.5 mm. 224.5 mm
Width: 104.2 mm. 104.2 mm. .
Height: 115 mm. 115 mm.
Weight: 1.2 Kg. 1.4 Kg.
2.2 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY
Tension: 24 Vcc +/- 10% Current: at rest < 100 mA in activity 2.5 A max.
2.3 INTERFACE
Standard: RS232
2.4 AVERAGE LIFE
Mechanical parts subject to wear: > 1.000 000 cycles
2.5 ENVIRONMENT CONDITIONS
Working temperature: from + 10 °C to + 50 °C.
Stocking temperature: from - 10 °C to + 60 °C.
Relative humidity: from 10 % a 85 %. RH not condensing
3. MODULE DESCRIPTION
3.1 MECHANICAL STRUCTURE
The module is composed by the following mechanical groups:
• Flanks for title transport
• Card and ticket transport
• Laser scanner
• CCD scanner
• R/W contactless unit
pag. 4
Page 5

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
3.1.1 FLANKS FOR TITLE TRANSPORT
The flanks are realized in inox steel and they host the symmetrical transport guides trough which title to be
read passes; the right flak hosts the stepping motor and the paper transport devices.
The control electronic board is fixed to the left flank.
3.1.2 TICKET AND CARD TRANSPORT
The transport is guarantied by rubber roller that adapt automatically to card and ticket width between 0.18
and 0.76 mm.
Title movement during insertion, returning to user or swallowing is managed by a stepping motor.
3.1.3 LASER SCANNER
Transversal barcode reader: reading is activated automatically by the BCR module after ticket positioning.
After reading, the code read is available and it can be required by apposite command (rif. Communication
protocol of the BCR) sent by the host on the serial communication line.
This scanner can read all kinds of barcodes.
3.1.4 CCD IMAGER SCANNER
Also this device, in alternative to the laser scanner, allows the reading of barcodes.
The IMAGER scanner is more performing than the laser scanner because it can read also bad resolution
barcodes.
The reading resolution is higher and there is a high tolerance in the reading position.
The reading is activated automatically from the BCR module sliding the ticket under the reader. After
reading the code is available and it can be required by apposite command (rif. Communication protocol of
the BCR) sent by the host on the serial communication line.
This scanner can read all kind of barcodes and two-dimensional barcodes (pdf).
3.1.5 LONGITUDINAL SCANNER
Optionally the CCD IMAGER scanner can be mounted longitudinally in order to read longitudinally printed
barcodes.
3.1.6 R/W CONTACTLESS UNIT
For reading and writing of MIFARE contactless cards in the BCR reader a module in accordance with
following standards is employed: ISO 14443-A and ISO 15693. On request the ISO 14443-B standard is
available. This module is installed between the two flanks at a distance that allows communication with the
card.
The device is connected to the CPU board by the means of the C_LESS connector and it is managed by the
CPU board FW trough special protocol encapsulated in the BCR module protocol.
NOTE: during assembling the module is set and tested for optimal functioning; the set changing can
compromise the correct functioning of the device.
4. ELECTRONIC CONTROL
4.1 CPU BOARD
pag. 5
Page 6

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
All elaboration and management tasks are entrusted to this control board.
The base circuit modules are:
• Microprocessor Fujitsu 16 bit
• Laser Scanner and IMAGER driver interface
• Set of optical sensor for title position survey within the module
• Stepping motor driving circuit
• RS232 serial interface
4.2 MANAGING FIRMWARE
The managing FW controls all functions performed by the module, such as:
• Host communication management trough RS232 serial communication port
• Title movement control within the module
• Laser scanner, IMAGER and R/W contactless module communication management.
5. ELECTRIC CONNECTIONS AND PREARRANGEMENTS
5.1 ELECTRIC CONNECTIONS
5.1.1 POWER SUPPLY CONNECTOR
Power supply is given by the connector SUPPLY (JST PH 4x1 PM 90°) with the following pinout:
Pin 1 +24V
Pin 2 +24V
Pin 3 GND
Pin 4 GND
5.1.2 SERIAL INT. RS232 CONNECTOR
The serial interface used for communication with the BCR module is available in the connector RS232 (JST
PHD 2x5 PM 90°), with the following pinout:
Pin 1 NC Pin 2 NC
Pin 3 Tx RS232 Pin 4 NC
Pin 5 Rx RS232 Pin 6 GND
Pin 7 NC Pin 8 NC
Pin 9 GND Pin 10 NC
5.1.3 I/O SIGNAL CONNECTORS
It is possible to connect to the BCR module three input digital signals and three output signals open collector
type. The I/O connector 1 (JST PHD 6x2 PM 90°) pinout is the following:
Pin 1 OUT 0B Pin 2 GND
Pin 3 OUT 1B Pin 4 GND
Pin 5 OUT 2B Pin 6 GND
Pin 7 IN 0B Pin 8 GND
Pin 9 IN 1B Pin 10 GND
Pin 11 IN 2B Pin 12 GND
pag. 6
Page 7

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
5.1.4 I/O SIGNAL CONNECTOR
Besides the I/O signals present on the I/O 1 connector, on the I/O 2 connector an input digital signal and a
power output signal are available and ideal to drive a ralay.
The I/O 2 (JST PH 4x1 PM 90°) connector pinout is the following:
Pin 1 OUT 3B
Pin 2 GNDPP
Pin 3 IN 3B
Pin 4 GND
5.1.5 OPTO #3 CONNECTOR
On the OPTO #3 connector the connection for a optional external optical sensor is available.
The OPTO #3 (JST PH 4x1 PM 90°) connector pinout is the following:
Pin 1 VCC
Pin 2 OSC
Pin 3 VCC
Pin 4 OPTO
5.1.6 STEPPING MOTOR CONNECTOR
The connection of the stepping motor occurs by the means of the connector MOTOR (AMP MODII 4 PM
90°) with the following pinout
Pin 1 OUT 1
Pin 2 OUT 2
Pin 3 OUT 3
Pin 4 OUT 4
5.1.7 SCANNER CONNECTOR
The laser scanner is connected to the CPU board by the means of the connector BCR (JST PH 4x1 PM 90°)
with the following pinout:
Pin 1 VCC
Pin 2 GND
Pin 3 LASER_TRIGGER
Pin 4 TX
5.1.8 CONTACLESS MODULE CONNECTOR
The contactless module is connected to the CPU board by the means of the connector C_LESS (JST PHD
2x5 PM 90°) with the following pinout:
Pin 1 VCC Pin 2 Rx1
Pin 3 Rx1_RS232 Pin 4 Tx1
Pin 5 Tx1_RS232 Pin 6 I/O AUX1B
Pin 7 C_GND Pin 8 C_GND
Pin 9 I/O AUX0B Pin 10 I/O AUX2B
Following drawing and form show the pinout of the connector that must be inserted in the contactless
module.
pag. 7
Page 8

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
Pin N°
3 TxD RS232 TTL –Transmit data
4 GND GND
5 RxD RS232 TTL –Receive Data
8 VCC +5V DC
9 GND GND
Function
Description X1
ID CPR.M02 –B/-BA
5.1.9 PROGRAMMING CONNECTOR
The firmware download occurs by the means of the connector FLASHPRG (JST PH 4x1 PM 90°)
Pin 1 GND
Pin 2 TX
Pin 3 GND
Pin 4 RX
5.2 BUTTONS
The RESET button allows to reset the board without disconnecting power supply.
The SWP1 button activates the ticket issue function.
The SWP2 button activates the barcode scanner.
5.3 DIP SWITCH
The dip switch SW1 allows the execution of special statements and to activate the firmware download.
The dip switch function is the following:
Dip 1 On = Contactless reader Off = Barcode reader
Dip 2 On = Activates the reverse ticket reading function Off = Disabled function
Dip 3 On = Activates the barcode slow reading function Off = Disabled function
Dip 4 On = Disabled function Off = Activates an Output switch off timer
Dip 5 RESERVED
Dip 6 On = firmware Download
See paragraph 6 for programming procedure
5.4 SIGNALLING LED
DL1 Photo sensor status display OP1
DL2 Photo sensor status display OP2
DL3 Photo sensor status display OP3
DL4 On in programming
DL5 Display trough flash sequences machine status and possible alarms
FIXED ON Regular functioning
pag. 8
Page 9

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
1 FLASH Command in execution
2 FLASHES Command not executed for title not present in the module
3 FLASHES Command not executed for title already present in the module
4 FLASHES Command not executed for reading already enabled
5 FLASHES Position error
7 FLASHES Title jammed
8 FLASHES Configuration not valid
6. PROGRAMMING PROCEDURE
For FW download, after setting dip 4-5-6 follow these instructions:
a. Connect serial cable to connector FLASHPRG (JST 4 P.M. a 90°).
b. Keep RESET button pressed and, at the same time, move the dipswitch 6 to On position; verify that
the DL4 led is on and release RESET button.
c. Execute the FUJITSU FLASH MCU Programmer program.
• Select in the Target Microcontroller field the MB90F497/G model.
• Select in the Cristal Fquency field the value of 4MHz.
• Open the file with MHX extension.
• Select the COM port to which the serial cable is connected.
• The screen appears as the one on the button if the COM1 port is used.
• Press the “Full Operation(D+E+B+P)” button.
• When the Flash window appears press “OK”.
• Wait for procedure to finish.
d. At the end of the procedure press OK and close the program.
e. Select in the Target Microcontroller field the MB90F497/G model.
f. Press reset button and at the same time move the dipswitch 6 in Off position and verify that the LED
DL4 switches off. Release the reset button.
pag. 9
Page 10

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
7. BCR CPU LAYOUT
8. ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
8.1 BARCODE AND CONTACTLESS READER SETTING
The barcode reader is regulated in the position that guaranties best reading performances of barcodes.
The change of this position can reduce or compromise reading realibility.
8.2 BARCODE READING POSITION SETUP
The communication protocol provides a special command to define the ticket position under the
scanner.
It is recommended to position barcode printing near the front edge f the ticket.
pag. 10
Page 11

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
9. DIMENSIONS
CONTACTLESS VERSION
pag. 11
Page 12

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
BARCODE VERSION
pag. 12
Page 13

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
COMBO VERSION
pag. 13
Page 14

ADEL S.r.l. – BCR Barcode / Contactless reader - User Manual Rev. 1.3
10. CONNTACTLESS TICKET AND CARD FORMAT
The contactless card in paper or in plastic format is ISO.
The paper ticket with barcode can be in fan fold or cut directly from roll and with following dimensions:
54x85,6 mm.
Here following is the recommended barcode ticket printing layout.
TRANSVERSAL BARCODE
LONGITUDINALE BARCODE
pag. 14
 Loading...
Loading...