Page 1

InterReach Fusion®
Installation, Operation,
and Reference Manual
ADCP-77-042 x Issue 2 x 12/2008
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 2

ADCP-77-042 • Issue 2 • 12/2008 • Preface
COPYRIGHT
© 2008, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
REVISION HISTORY
ISSUE DATE REASON FOR CHANGE
1 7/2008 First ADC release
2 12/2008 Update compliance section
LIST OF CHANGES
The technical changes incorporated into this issue are listed below.
PAGE IDENTIFIER DESCRIPTION OF CHANGE
- Update compliance section
TRADEMARK INFORMATION
ADC is a registered trademark and InterReach, InterReach Unison, InterReach Fusion, WAVEXchange, FlexWave are registered
trademarks and trademarks of ADC Telecommunications, Inc. All other products, company names, service marks, and trademarks
mentioned in this document or website are used for identification purposes only and may be owned by other companies.
DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
Contents herein are current as of the date of publication. ADC reserves the right to change the contents without prior notice. In no
event shall ADC be liable for any damages resulting from loss of data, loss of use, or loss of profits and ADC further
disclaims any and all liability for indirect, incidental, special, consequential or other similar damages. This disclaimer of
liability applies to all products, publications and services during and after the warranty period.
This publication may be verified at any time by contacting ADC’s Technical Assistance Center at 1-800-366-3891, extension 73476
(in U.S.A. or Canada) or 952-917-3476 (outside U.S.A. and Canada), or by e-mail to wireless.tac@adc.com.
Page ii
ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
2540 Junction Avenue, San Jose, California 95134-1902 USA
P.O. Box 1101, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55440-1101
In U.S.A. and Canada: 1-800-530-9960
In U.S.A. and Canada: 1-800-366-3891
Outside U.S.A. and Canada: 1-408-952-2400
Outside U.S.A. and Canada: (952) 938-8080
Fax: 1-408-952-2410
Fax: (952) 917-1717
Page 3

Table of Contents
SECTION 1 General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.1 Firmware Release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Purpose and Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.3 Conventions in this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.4 Standards Conformance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.5 Related Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
SECTION 2
InterReach Fusion
System Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.1 System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2 System Hardware Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.3 System OA&M Capabilities Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.3.1 System Monitoring and Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.3.2 Using Alarm Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.4 System Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.5 System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2.6 System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.6.1 RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
SECTION 3 Fusion Main Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1 Fusion Main Hub Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 Fusion Main Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.2.1 Optical Fiber Uplink/Downlink Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.2.2 Communications RS-232 Serial Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.2.3 Main Hub LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.3 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.3.1 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.3.1.1 9-pin D-sub Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.3.1.2 N-type Female Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
3.4 Main Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
3.5 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 4
CONFIDENTIAL
3.5.1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
3.5.2 View Preference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
SECTION 4 Fusion Expansion Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1 Expansion Hub Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 Expansion Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.2.1 75 Ohm Type F Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.2.2 Manufacturing RS-232 Serial Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.2.3 Optical Fiber Uplink/Downlink Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.2.4 LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.3 Expansion Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.4 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.5 Expansion Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
SECTION 5
SECTION 6
Remote Access Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.1 RAU Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.2 Remote Access Unit Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.2.1 50 Ohm Type-N Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.2.2 75 Ohm Type-F Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.3 RAU LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5.4 Faults and Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.5 Remote Access Unit Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Designing a Fusion Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.2 Downlink RSSI Design Goal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.3 Maximum Output Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.3.1 850 MHz Cellular . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
6.3.2 800 MHz or 900 MHz SMR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
6.3.3 900 MHz EGSM and EDGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.3.4 1800 MHz DCS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
6.3.5 1900 MHz PCS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
6.3.6 2.1 GHz UMTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
6.3.7 2.1 GHz UMTS High Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
6.4 System Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
6.5 Estimating RF Coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
6.5.1 Path Loss Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
6.5.2 RAU Coverage Distance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-16
6.5.3 Examples of Design Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.6 Link Budget Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-25
6.6.1 Elements of a Link Budget for Narrowband Standards . . . . . 6-25
6.6.2 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis
for a Microcell Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.6.3 Elements of a Link Budget for CDMA Standards . . . . . . . . . 6-30
2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 5
CONFIDENTIAL
6.6.4 CDMA Link Budget Analysis for a Microcell Application . 6-33
6.6.5 Considerations for Re-Radiation (Over-the-Air) Systems . . 6-36
6.7 Optical Power Budget . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
6.8 Connecting a Main Hub to a Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-38
6.8.1 Uplink Attenuation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-38
6.8.2 RAU Attenuation and ALC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-39
6.8.2.1 Using the RAU 10 dB Attenuation Setting . . . . . . . . . 6-40
6.8.2.2 Using the Uplink ALC Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
SECTION 7 Installing Fusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.1 Installation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.1.1 Component Location Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.1.2 Cable and Connector Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.1.3 Distance Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.2 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.2.1 Installation Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.2.2 General Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.3 Fiber Port Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.3 Preparing for System Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.3.1 Pre-Installation Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.3.2 Installation Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.3.3 Tools and Materials Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
7.3.4 Optional Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.4 Fusion Installation Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
7.4.1 Installing a Fusion Main Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.4.2 Installing Expansion Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
7.4.3 Installing RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-32
7.4.3.1 Troubleshooting Using RAU LEDs
During Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-35
7.4.3.2 Installing RAUs in a Multiple Operator System . . . . . 7-36
7.4.4 Configuring the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-36
7.5 Splicing Fiber Optic Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-42
7.6 Interfacing the Fusion Main Hub to an RF Source . . . . . . . . 7-44
7.6.1 Connecting a Single Fusion Main Hub to an RF Source . . . 7-44
7.6.2 Connecting Multiple Fusion Main Hubs to an RF Source . . 7-49
7.7 Connecting Contact Alarms to a Fusion System . . . . . . . . . 7-54
7.7.1 Alarm Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-55
7.7.2 Alarm Sense . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-58
7.7.3 Alarm Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-59
7.8 Alarm Monitoring Connectivity Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-60
7.8.1 Direct Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-60
7.8.2 Modem Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-61
7.8.2.1 Setting Up Fusion Modem (USR Modem)
Using AdminBrowser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-61
7.8.2.2 Setting Up a PC Modem Using Windows . . . . . . . . . . 7-62
7.8.3 100 BASE-T Port Expander Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-70
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 3
Page 6
CONFIDENTIAL
7.8.4 POTS Line Sharing Switch Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-71
7.8.5 Ethernet RF Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-72
7.8.6 Ethernet LAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-73
7.8.7 SNMP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-74
SECTION 8 Replacing Fusion Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.1 Replacing an RAU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.2 Replacing a Fusion Expansion Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3 Replacing a Fusion Main Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
SECTION 9
APPENDIX A
APPENDIX B
Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Technical
Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
9.1 Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
9.2 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
9.3 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9.3.1 Troubleshooting Using AdminBrowser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
9.3.1.1 Troubleshooting Recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
9.3.1.2 Fault/Warning/Status Indications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
9.3.2 Troubleshooting Using LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
9.4 Troubleshooting CATV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-10
9.5 Technical Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-10
Cables and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.1 75 Ohm CATV Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.2 Fiber Optical Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-7
A.3 Coaxial Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-8
A.4 Standard Modem Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-9
A.5 TCP/IP Cross-over Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-10
A.6 DB-25 to DB-9 Null Modem Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-11
Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
B.1 Fusion System Approval Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
B.2 Human Exposure to RF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-3
APPENDIX C
Faults, Warnings, Status Tables for Fusion,
Fusion Wideband, Fusion Singlestar . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1 Faults Reported by Main Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.2 Faults Reported for System CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-5
C.3 Faults for Expansion Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
C.4 Faults for RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-9
C.5 Messages for Main Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-10
C.6 Messages for System CPUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-15
4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 7
CONFIDENTIAL
C.7 Messages for Expansion Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-16
C.8 Messages for RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-19
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 5
Page 8
CONFIDENTIAL
6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 9
CONFIDENTIAL
List of Figures
Figure 2-1 Fusion System Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
Figure 2-2 Fusion One Port System Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
Figure 2-3 Three Methods for OA&M Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Figure 2-4 System Monitoring and Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Figure 2-5 Fusion’s Double Star Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Figure 2-6 Downlink (Base Station to Wireless Devices) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Figure 2-7 Uplink (Wireless Devices to Base Station) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Figure 3-1 Main Hub in a Fusion System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
Figure 3-2 Main Hub Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Figure 3-3 Fusion Main Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Figure 3-4 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-8
Figure 3-5 Preferences Check Boxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
Figure 4-1 Expansion Hub in a Fusion System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
Figure 4-2 Expansion Hub Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
Figure 4-3 Expansion Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
Figure 4-4 Expansion Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7
Figure 5-1 Remote Access Unit in a Fusion System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-2
Figure 5-2 Remote Access Unit Block Diagram (Multiband) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-2
Figure 6-1 Determining APL between the Antenna and the Wireless Device .6-14
Figure 6-2 ALC Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-40
Figure 7-1 Flush Mounting Bracket Detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-12
Figure 7-2 Bracket Detail For Wall Mount Rack (PN 4712) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-13
Figure 7-3 Installing Directly to the Wall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-14
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 1
Page 10
CONFIDENTIAL
Figure 7-4 Using Hub Rack-Mounting Brackets for Direct Wall Installation . 7-15
Figure 7-5 Protective Ground Wire Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
Figure 7-6 DC Terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
Figure 7-7 Power Screw Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
Figure 7-8 Pan Head Screw Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
Figure 7-9 Recommended Hub Wire Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
Figure 7-10 Compression Lug and Mounting Screw Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
Figure 7-11 Grounding Wire Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
Figure 7-12 Power Wires and Studs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
Figure 7-13 Wire Polarity Illustration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
Figure 7-14 DC Illustration Detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
Figure 7-15 Flush Mounting Bracket Detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
Figure 7-16 Bracket Detail For Wall Mount Rack (PN 4712) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-26
Figure 7-17 Using Hub Rack-Mounting Brackets for Direct Wall Installation . 7-27
Figure 7-18 Installing Directly to the Wall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-28
Figure 7-19 800/850 MHz Spectrum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-33
Figure 7-20 Guideline for Unison RAU Antenna Placement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-33
Figure 7-21 Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-37
Figure 7-22 Local Area Connection Properties Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-38
Figure 7-23 Set Time and Date Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-39
Figure 7-24 AdminBrowser Configuration Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-39
Figure 7-25 AdminBrowser Configuration Window (continued) . . . . . . . . . . . 7-40
Figure 7-26 Simplex Base Station to a Fusion Main Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-45
Figure 7-27 Duplex Base Station to a Fusion Main Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-46
Figure 7-28 Connecting a Fusion Main Hub to Multiple Base Stations . . . . . . 7-47
Figure 7-29 Connecting a Fusion Main Hub to a Roof-top Antenna . . . . . . . . . 7-48
Figure 7-30 Connecting Two Fusion Main Hub’s RF Band Ports
to a Simplex Repeater or Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-51
Figure 7-31 Connecting Two Fusion Main Hub’s RF Band Ports
to a Duplex Repeater or Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-53
Figure 7-32 Connecting FlexWave to Fusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-55
Figure 7-33 Using a BTS to Monitor Fusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-56
Figure 7-34 Using a BTS and AdminBrowser to Monitor Fusion . . . . . . . . . . . 7-57
Figure 7-35 Using Fusion to Monitor Unison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-58
Figure 7-36 Alarm Sense Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-58
Figure 7-37 5-port Alarm Daisy-Chain Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-59
Figure 7-38 OA&M Direct Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-60
Figure 7-39 OA&M Modem Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-61
Figure 7-40 Default Dial-in Settings (Fusion Hub) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-62
2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 11
CONFIDENTIAL
Figure 7-41 Network Connections Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-63
Figure 7-42 New Connection Wizard - Welcome Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-63
Figure 7-43 New Connection Wizard - Network Connection Type Window . . .7-64
Figure 7-44 New Connection Wizard - Network Connection Window . . . . . . .7-64
Figure 7-45 New Connection Wizard - Connection Name Window . . . . . . . . . .7-65
Figure 7-46 New Connection Wizard - Phone Number to Dial Window . . . . . .7-65
Figure 7-47 New Connection Wizard - Connection Availability Window . . . . .7-66
Figure 7-48 New Connection Wizard - Completing New Connection Window .7-66
Figure 7-49 Connect Fusion Hub Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-67
Figure 7-50 Fusion Hub Properties Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-67
Figure 7-51 Modem Configuration Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-68
Figure 7-52 Fusion Hub Properties - Security Tab Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-68
Figure 7-53 Fusion Hub Properties - Networking Tab Window . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-69
Figure 7-54 Internet Protocol Properties Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-69
Figure 7-55 OA&M Connection using a 232 Port Expander . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-70
Figure 7-56 OA&M Connection Using a POTS Line Sharing Switch . . . . . . . .7-71
Figure 7-57 Cascading Line Sharing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-72
Figure 7-58 OA&M Connection Using Ethernet and ENET/232 Serial Hub . . .7-73
Figure 7-59 Fusion SNMP Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-74
Figure A-1 CommScope 2065V for RG-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Figure A-2 CommScope 2279V for RG-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Figure A-3 CommScope 2293K for RG-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
Figure A-1 Standard Modem Cable Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-9
Figure A-2 Wiring Map for TCP/IP Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-10
Figure A-3 DB-9 Female to DB-9 Female Null Modem Cable Diagram . . . . A-11
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 3
Page 12
CONFIDENTIAL
4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 13

List of Tables
Table 2-1 Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Table 2-2 Wavelength and Laser Power Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Table 2-3 Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Table 2-4 Frequency Bands Covered by Fusion RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Table 2-5 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Table 2-6 1900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Table 2-7 900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Table 2-8 1800 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Table 2-9 900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Table 2-10 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Table 2-11 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Table 2-12 1800 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Table 2-13 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Table 2-14 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Table 2-15 800 MHz (SMR) RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Table 2-16 900 MHz (SMR) RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Table 2-17 1900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Table 2-18 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Table 2-19 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Table 3-1 Fusion Hub Status LED States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Table 3-2 Fusion Hub Port LED States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Table 3-3 9-pin D-sub Pin Connector Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Table 3-4 Main Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Table 4-1 Expansion Hub Unit Status and DL/UL Status LED States . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Table 4-2 Fusion Expansion Hub Port LED States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Table 4-3 9-pin D-sub Pin Connector Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Table 4-4 Expansion Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
Table 5-1 Frequency Bands Covered by Fusion RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 14
CONFIDENTIAL
Table 5-2 System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length (All RAUs
except 800/900/1900) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Table 5-4 Remote Access Unit LED States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Table 5-5 Remote Access Unit Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Table 6-1 Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Table 6-2 GSM/EGSM and EDGE Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Table 6-3 DCS Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Table 6-4 PCS Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Table 6-5 UMTS Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
Table 6-6 UMTS Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
Table 6-7 System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length (All RAUs
except 800/900/1900) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
Table 6-8 System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length
for 800/900/1900 RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
Table 6-9 Coaxial Cable Losses (Lcoax) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
Table 6-10 Average Signal Loss of Common Building Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
Table 6-11 Frequency Bands and the Value of the First Term in Equation (3) . . . 6-16
Table 6-12 Estimated Path Loss Slope for Different In-Building Environments . 6-17
Table 6-13 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 800 MHz SMR Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
Table 6-14 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 850 MHz Cellular Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
Table 6-15 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 900 MHz SMR Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
Table 6-16 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 900 MHz EGSM Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-19
Table 6-17 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 1800 MHz DCS Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-19
Table 6-18 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 1900 MHz PCS Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-20
Table 6-19 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 2.1 GHz UMTS Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-20
Table 6-20 Link Budget Considerations for Narrowband Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-26
Table 6-21 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis: Downlink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
Table 6-22 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis: Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-29
Table 6-23 Distribution of Power within a CDMA Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-30
Table 6-24 Additional Link Budget Considerations for CDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
Table 6-25 CDMA Link Budget Analysis: Downlink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-33
Table 6-26 CDMA Link Budget Analysis: Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
Table 7-1 Distance Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 15
CONFIDENTIAL
Table 7-2 Installation Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Table 7-3 Tools and Materials Required for Component Installation . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Table 7-4 Optional Accessories for Component Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Table 7-5 Troubleshooting Main Hub LEDs During Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-24
Table 7-6 Troubleshooting Expansion Hub LEDs During Installation . . . . . . . . 7-31
Table 7-7 Troubleshooting RAU LEDs During Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-35
Table 7-8 Alarm Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-54
Table 9-1 Troubleshooting Main Hub Port LEDs During Normal Operation . . . . 9-6
Table 9-2 Troubleshooting Main Hub Status LEDs During Normal Operation . . 9-7
Table 9-3 Troubleshooting Expansion Hub Port LEDs During Normal Operation 9-8
Table 9-4 Troubleshooting Expansion Hub Status LEDs
During Normal Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-9
Table 9-5 Summary of CATV Cable Wiring Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-10
Table C-2 Faults for System CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-5
Table C-4 Faults for RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
Table C-5 Warnings/Status Messages for Main Hubs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-11
Table C-6 Warning/Status Messages for System CPUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-15
Table C-8 Warning/Status Messages for RAUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-19
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 3
Page 16
CONFIDENTIAL
4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 17

SECTION 1 General Information
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 1.1 Firmware Release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
• Section 1.2 Purpose and Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
• Section 1.3 Conventions in this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
• Section 1.4 Standards Conformance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
• Section 1.5 Related Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.1 Firmware Release
For the latest Software and Firmware Release and associated documentation, access
the ADC Customer Portal at adc.com.
1.2 Purpose and Scope
This document describes the InterReach Fusion system.
• Section 2 InterReach Fusion System Description
This section provides an overview of the Fusion hardware and OA&M capabilities.
This section also contains system specifications and RF end-to-end performance
tables.
• Section 3 Fusion Main Hub
This section illustrates and describes the Fusion Main Hub. This section includes
connector and LED descriptions, and unit specifications.
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 1-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 18

Conventions in this Manual
• Section 4 Fusion Expansion Hub
This section illustrates and describes the Expansion Hub, as well as connector and
LED descriptions, and unit specification.
• Section 5 Remote Access Unit
This section illustrates and describes the Remote Access Unit. This section also
includes connector and LED descriptions, and unit specifications.
• Section 6 Designing a Fusion Solution
This section provides tools to aid you in designing your Fusion system, including
tables of the maximum output power per carrier at the RAU and formulas and
tables for calculating path loss, coverage distance, and link budget.
• Section 7 Installing Fusion
This section provides installation procedures, requirements, safety precautions,
and checklists. The installation procedures include guidelines for troubleshooting
using the LEDs as you install the units.
• Section 8 Replacing Fusion Components
This section provides installation procedures and considerations when you are
replacing an Fusion component in an operating system.
• Section 9 Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Technical Assistance
This section provides contact information and troubleshooting tables.
• Appendix A Cables and Connectors
This appendix provides connector and cable descriptions and requirements. It also
includes cable strapping, connector crimping tools, and diagrams.
• Appendix B Compliance
This section lists safety and radio/EMC approvals.
• Appendix C Faults, Warnings, Status Tables
This section lists all system alarm messages.
1.3 Conventions in this Manual
The following table lists the type style conventions used in this manual.
Convention Description
bold Used for emphasis
BOLD CAPS
MALL CAPS Software menu and window selections
S
Labels on equipment
1-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 19

Standards Conformance
This manual lists measurements first in metric units, and then in U.S. Customary System of units in parentheses. For example:
0° to 45°C (32° to 113°F)
This manual uses the following symbols to highlight certain information as described.
NOTE: This format emphasizes text with special significance or importance, and provides supplemental information.
CAUTION: This format indicates when a given action or omitted
action can cause or contribute to a hazardous condition. Damage
to the equipment can occur.
WARNING : This format indicates when a given action or omitted
action can result in catastrophic damage to the equipment or cause
injury to the user.
Procedure
This format highlights a procedure.
1.4 Standards Conformance
• Fusion uses the TIA-570-B cabling standards for ease of installation.
• Refer to Appendix B for compliance information.
1.5 Related Publications
• AdminBrowser User Manual, ADC part number D-620607-0-20
• FlexWave Focus Configuration, Installation, and Reference Manual; ADC part
number 8500-10
• InterReach Unison Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual; ADC part
number 8700-50
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 1-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 20
Related Publications
1-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 21

SECTION 2 InterReach Fusion
System Description
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 2.1 System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
• Section 2.2 System Hardware Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
• Section 2.3 System OA&M Capabilities Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
• Section 2.4 System Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
• Section 2.5 System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
• Section 2.6 System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.1 System Overview
InterReach Fusion is an intelligent fiber optics/CATV, multi-band (frequencies) wireless networking system designed to handle both wireless voice and data communications over licensed frequencies. It provides high-quality, ubiquitous, seamless access
to the wireless network in smaller buildings.
Fusion provides RF characteristics designed for large public and private facilities
such as campus environments, airports, shopping malls, subways, convention centers,
sports venues, and so on. Fusion uses microprocessors to enable key capabilities such
as software-selectable band settings, automatic gain control, ability to incrementally
adjust downlink/uplink gain, end-to-end alarming of all components and the associated cable infrastructure, and a host of additional capabilities.
The Fusion system supports major wireless standards and air interface protocols in
use around the world, including:
• Frequencies: 800 MHz, 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz, 2100 MHz
• Voice Protocols: AMPS, TDMA, CDMA, GSM/EGSM,WCDMA, iDEN
• Data Protocols: CDPD, EDGE, GPRS, WCDMA, CDMA2000, 1xRTT, EV-DO,
and Paging
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 2-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 22
System Overview
The Fusion system supports three configurable bands:
• Band 1 in 35 MHz and can be configured for 850 MHz, or 900 MHz.
• Band 2 in 75 MHz and can be configured for 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz, or 2100 MHz
Both bands support all protocols.
Fusion remote access units contain combinations of Band 1, Band 2, and Band 3
frequencies to support various world areas, that is 800 MHz/900 MHz/1900MHz
for North America or 900 MHz/2100 MHz and 900 MHz/1800 MHz for Europe
and Asia. Refer to Figure 2-7 on page 2-8 for a specific list of these RAU frequency combinations.
• Band 3 (only used for the North American FSN-809019-2 RAU) whose Band 3 is
a 6 MHz sub-band of the 35 MHz Band with Band 1 being an 18 MHz sub-band of
the 35 MHz Band.
Key System Features
• Multi-Band, supports two or more full band frequencies for spectrum growth.
• Superior RF performance, particularly in the areas of IP3 and noise figure.
• High downlink composite power and low uplink noise figure enables support of
a large number of channels and larger coverage footprint per antenna.
• Software configurable Main and Expansion Hubs allow the frequency bands to
be configured in the field.
• Either single-mode or multi-mode fiber can be used, supporting flexible cabling
alternatives (in addition to standard CATV 75 Ohm cabling). You can select the
cabling type to met the resident cabling infrastructure of the facility and unique
building topologies.
• Extended system “reach.” Using single-mode fiber, fiber runs can be a long as 6
kilometers (creating a total system “wingspan” of 12 kilometers). Alternatively,
with multi-mode fiber, fiber runs can be as long as 500 meters.
• Standard 75 Ohm CATV cable, can be run up to 150 meters for RG-59 cable
(170 meters for RG-6; 275 meters for RG-11 using CommScope 2065V, 2279V,
and 2293K cables).
• Flexible RF configuration capabilities, including:
• System gain:
– Ability to manually set gain in 1 dB steps, from 0 to 15 dB, on both down-
link and uplink.
•RAU:
– RAU uplink and downlink gain can be independently attenuated 0 or 10 dB.
– Uplink level control protects the system from input overload and can be
optimized for either a single operator or multiple operators/protocols.
2-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 23

– VSWR check on RAU reports if there is a disconnected antenna.
• Firmware Updates are downloaded (either locally or remotely) to the system
when any modifications are made to the product, including the addition of new
software capabilities and services.
• OA&M capabilities, including fault isolation to the field replaceable unit, reporting of all fault and warning conditions, and user-friendly web browser user interface OA&M software package.
2.2 System Hardware Description
The InterReach Fusion system consists of three modular components:
• 19" rack-mountable Main Hub (connects to up to 4 Expansion Hubs, except for
the One Port Main Hub configuration that supports 1 Expansion Hub)
• Converts RF signals to optical IF on the downlink; optical IF-to-RF on the
uplink
• Microprocessor controlled (for alarms, monitoring, and control)
• Auto-configurable bands
• Simplex interface to RF source
• Periodically polls all downstream RAUs for system status, and automatically
reports any fault or warning conditions
System Hardware Description
• 19” rack mountable Expansion Hub (connects to up to 8 Remote Access Units)
• Optical signal conversion to electrical on the downlink; electrical to optical on
the uplink
• Microprocessor controlled (for alarms, monitoring, and control)
• Software configurable band (based on commands from the Main Hub)
• Supplies DC power to RAUs over CATV cable.
• Remote Access Unit (RAU)
• Converts IF signals to RF on the downlink; RF-to-IF on the uplink
• Microprocessor controlled (for alarms, monitoring, and control)
• Multi-band protocol independent, frequency specific units
The minimum configuration of a Fusion system is one Main Hub, one Expansion
Hub, and one RAU (1-1-1). The maximum configuration of a system is one Main
Hub, four Expansion Hubs, and 32 RAUs (1-4-32). Multiple systems can be combined to provide larger configurations.
NOTE: The Fusion One Port Main Hub (PN: FSN-1-MH-1P) configuration
is a cost reduced version of the Fusion Main Hub and supports only one
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 24

System Hardware Description
Expansion Hub (up to 8 RAUs).
The Fusion One Port Main Hub is “software locked” to 1 port 2 fiber ports.
Additional ports are disabled internally. Please do not attempt to remove the
front panel fiber port plate, since doing so will void the product warranty.
Figure 2-1 Fusion System Hardware
Figure 2-2 Fusion One Port System Hardware
2-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 25
System OA&M Capabilities Overview
2.3 System OA&M Capabilities Overview
InterReach Fusion is microprocessor controlled and contains firmware to enable much of
the operations, administration, and maintenance (OA&M) functionality.
Complete alarming, down to the field replaceable unit (that is, Fusion Main Hub,
Expansion Hub, and Remote Access Unit) and the cabling infrastructure, is available.
All events occurring in a system, defined as a Fusion Main Hub and all of its associated Expansion Hubs and Remote Access Units, are automatically reported to the
Main Hub. The Main Hub monitors system status and communicates that status using
the following methods:
• Normally closed (NC) alarm contact closures can be tied to standard NC alarm
monitoring systems or directly to a base station for basic alarm monitoring.
• Connection Methods:
• The Main Hub’s front panel RJ-45 port connects directly to a PC (for local
Ethernet access).
• The Main Hub’s front panel RS-232 serial port connects directly to a modem
(for remote access).
• Remote access is also available with an optional 100BASE-T LAN switch connections to the RJ-45 port.
Use AdminBrowser to configure
or monitor a local or a remote
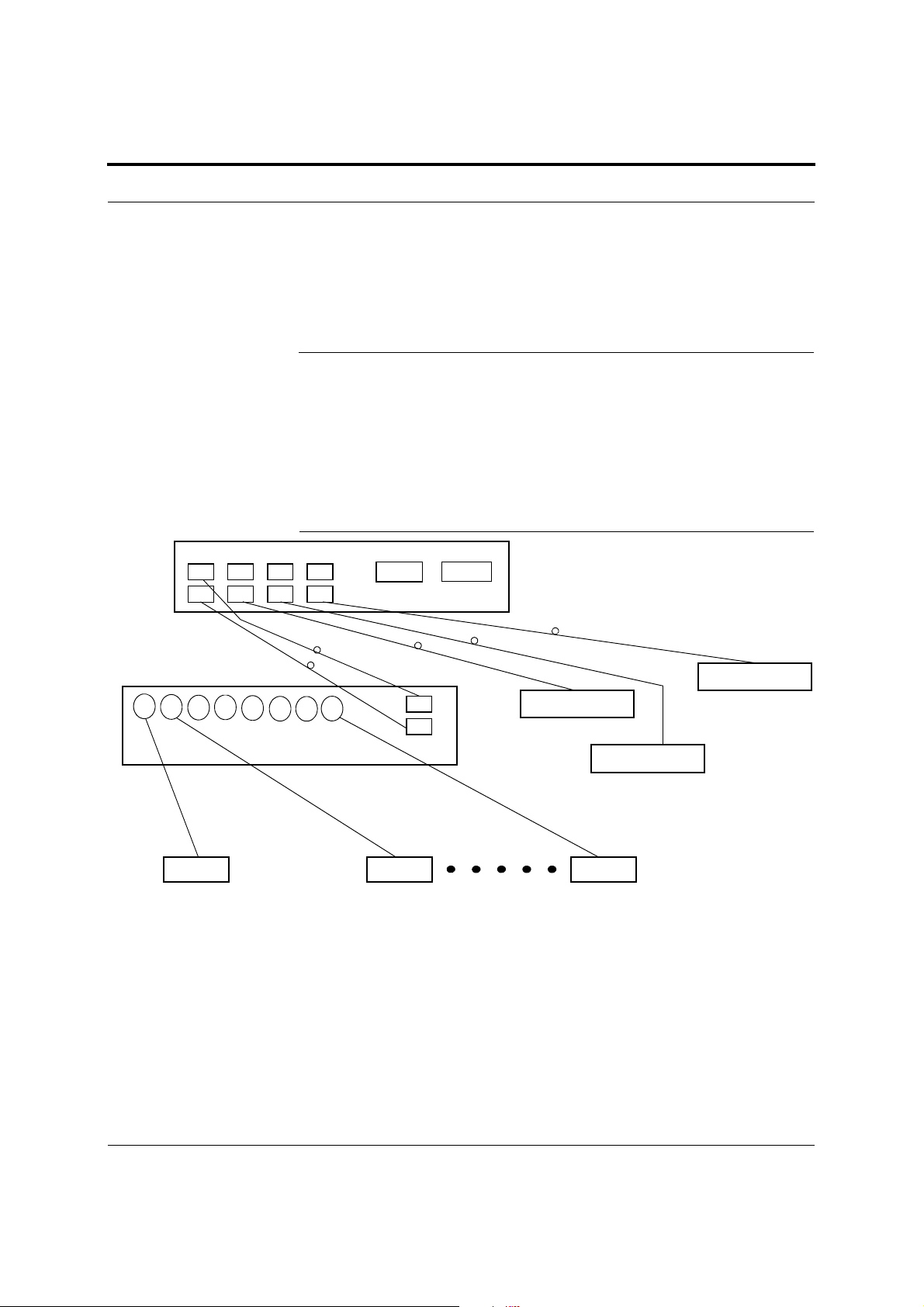
Fusion system.
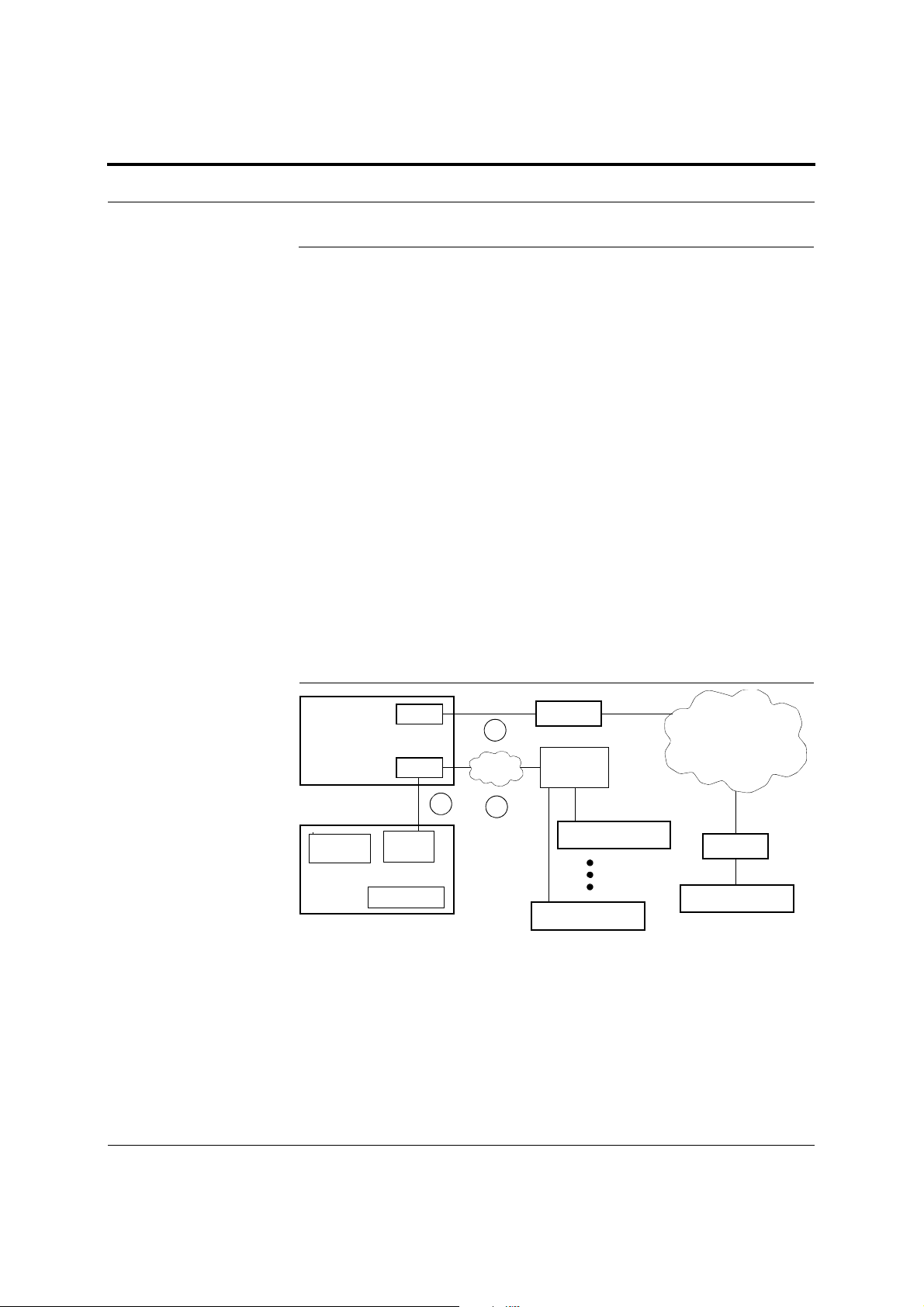
Figure 2-3 Three Methods for OA&M Communications
PC/Laptop
running a
Standard Browser
RS-232 Ethernet
RS-232
Modem
Fusion Main Hub
F-conn.
RS-232
R-J-45
Ethernet
t
Admin Browser
Modem
2
TCP/IP
1
3
LAN
Switch
Ethernet
Fusion Main Hub
Fusion Main Hub
PSTN
Modem
Fusion Main Hub
AdminBrowser OA&M software runs on the Fusion Main Hub microprocessor and
communicates to its downstream Expansion Hubs and associated RAUs. Using
AdminBrowser, you can perform the following from any standard web browser
(Internet Explorer) running on your PC/laptop system:
• Configure a newly installed system
• Change system parameters
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-5
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 26
System OA&M Capabilities Overview
• Perform an end-to-end system test
• Query system status
Refer to the AdminBrowser User Manual (D-620607-0-20 Rev A) for information
about installing and using AdminBrowser software.
2.3.1 System Monitoring and Reporting
Each Fusion Main Hub in the system constantly monitors itself, its Expansion Hubs,
and their downstream RAUs for internal fault and warning conditions. The results of
this monitoring are stored in memory and compared against new results.
When a Main or Expansion Hub detects a change in status, it reports a fault or warning alarm. Faults are also indicated locally by red status LEDs. Both faults and warnings are reported to AdminBrowser software and displayed on a PC/laptop connected
to the Main Hub’s RJ-45 port. Passive antennas connected to the RAUs are not monitored automatically. Perform a System Test to retrieve status information about
antennas.
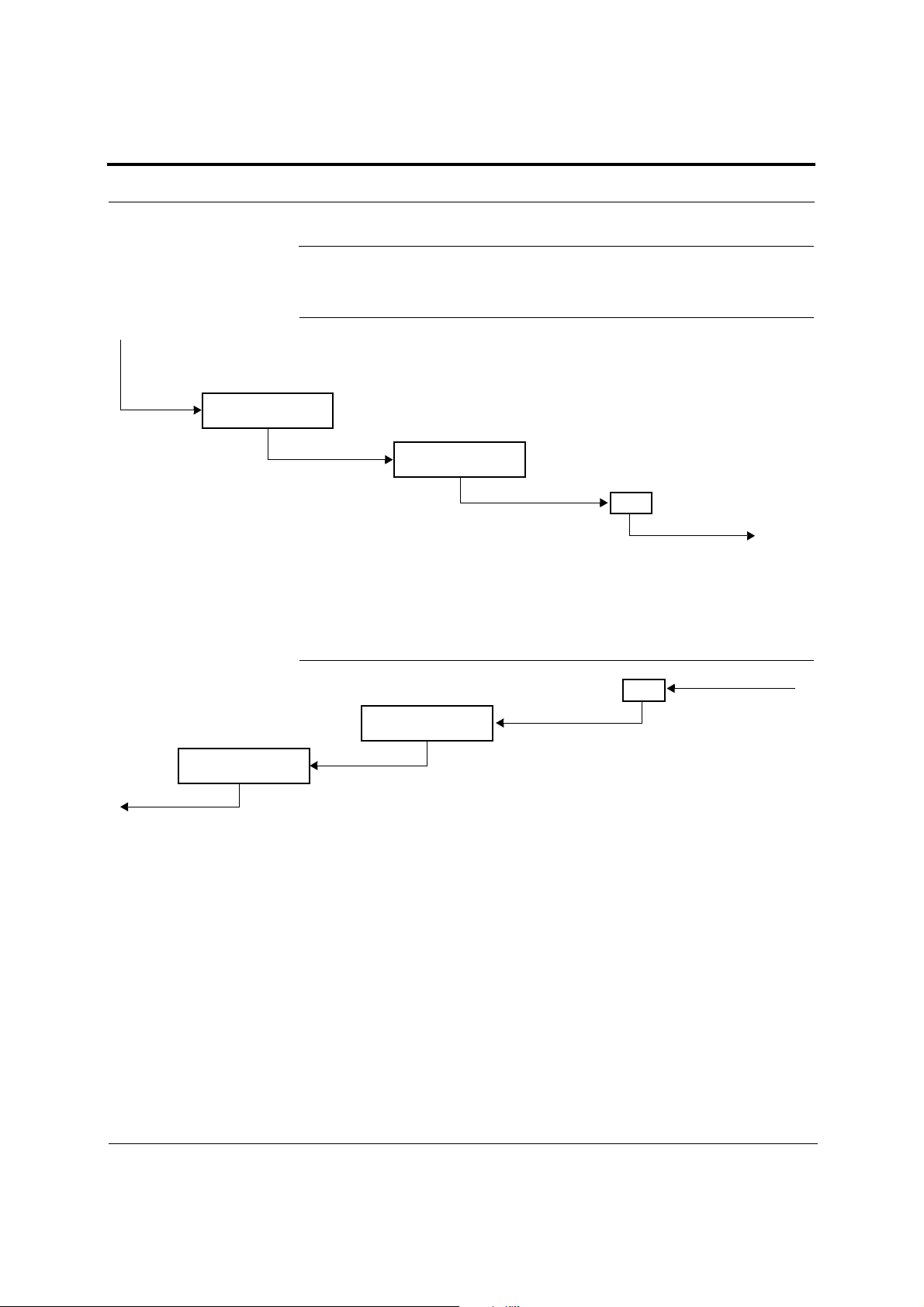
Using AdminBrowser, you can install a new system or new components, change system parameters, and query system status. Figure 2-4 illustrates how the system
reports its status to AdminBrowser.
PC/Laptop
running a
standard
web browser
Use a standard
browser to communicate with remotely or
locally installed Fusion
systems running
AdminBrowser.
If a fault or warning
condition is reported,
the AdminBrowser
graphical user interface indicates the problem on your standard
PC browser.
2.3.2 Using Alarm Contacts
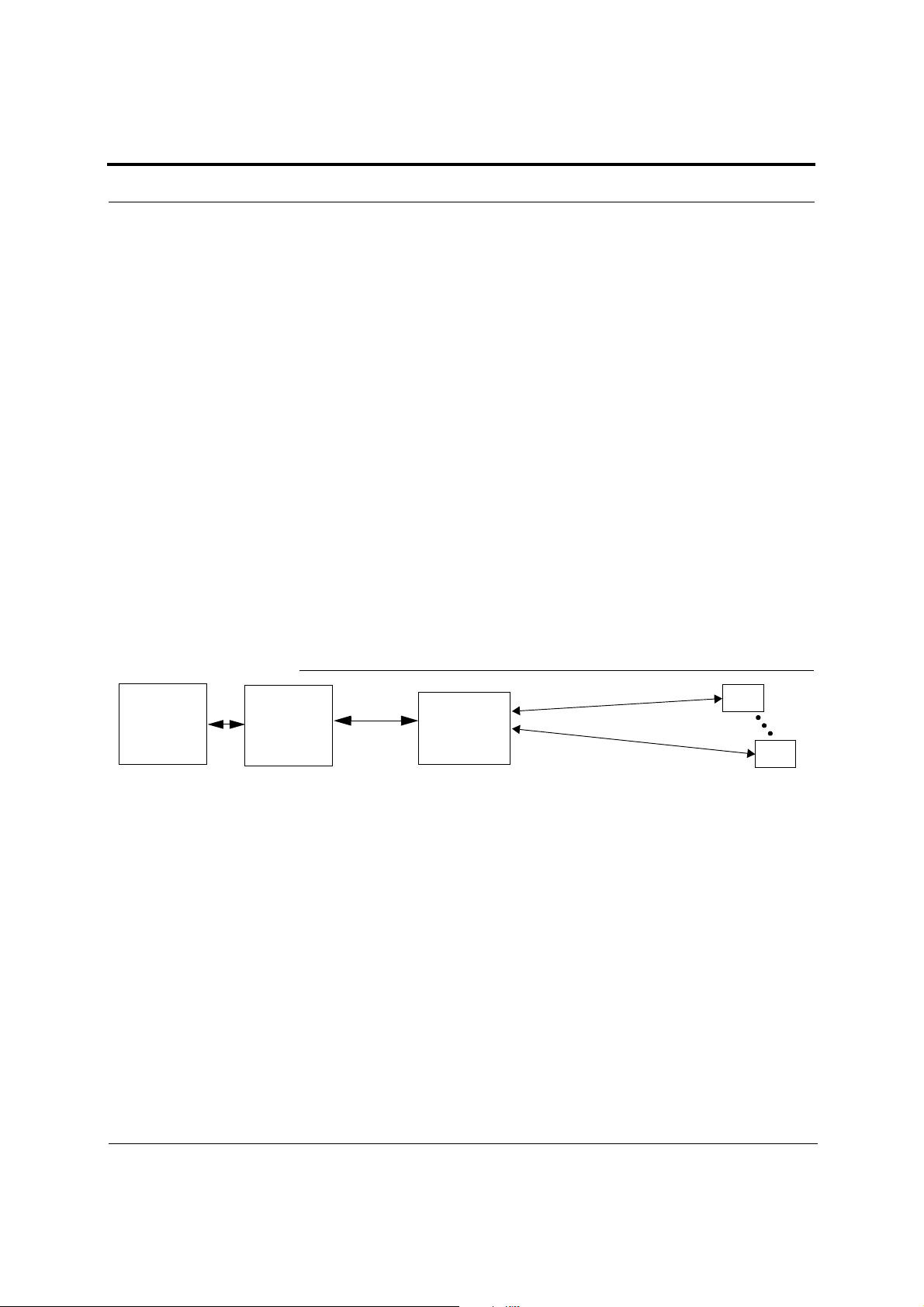
Figure 2-4 System Monitoring and Reporting
Fusion Main
Hub
AdminBrowser
The Main Hub queries
status of each Expansion Hub and each
RAU and compares it
to previously stored
status.
If a fault is detected,
LEDs on the front panel
turn red.
You can connect the DB-9 female connector on the rear panel of the Fusion Main
Hub to a local base station or to a daisy-chained series of Fusion and/or FlexWave
Focus systems.
Fusion
Expansion
Hub
AdminBrowser
The Expansion Hub queries
the status of each RAU and
compares it to the previously
stored status.
If a fault is detected, LEDs on
the front panel turn red.
RAU
RAU
Each RAU passes its status to
the Hub.
If a fault is detected, the
ALARM LED is red. If no fault
is detected, the LED is green.
2-6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 27
When you connect FlexWave Focus or a BTS to the Fusion, the Fusion Main Hub
outputs the alarms (alarm source) and FlexWave Focus or the BTS receives the
alarms (alarm sense). This is described in Section 7.7.1 on page 7-56.
2.4 System Connectivity
The double star architecture of the Fusion system, illustrated in Figure 2-5, provides
excellent system scalability and reliability. The system requires only one pair of
fibers for eight antenna points. This makes any system expansion, such as adding an
extra antenna for additional coverage, potentially as easy as pulling an extra CATV
cable.
Figure 2-5 Fusion’s Double Star Architecture
PORT 1 PORT 2 PORT 3 PORT 4
RS-232
System Connectivity
RJ-45
Main Hub
Fiber
Expansion Hub
Expansion Hub
CATVCATV (RG-59, 6, or 11) CATV
RAU RAU RAU
up to 8 RAUs per Expansion Hub
Expansion Hub
Expansion Hub
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-7
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 28
System Operation
2.5 System Operation
Figure 2-6 Downlink (Base Station to Wireless Devices)
The Main Hub receives downlink RF signals from
a base station using 50 Ohm coaxial cable.
Main Hub
The Main Hub converts the RF signals to IF, then
to optical signals and sends them to Expansion
Hubs (up to four) using optical fiber cable.
The Expansion Hub converts the optical sig-
Expansion Hub
nals to electrical signals and sends them to
RAUs (up to eight) using 75 Ohm CATV cable.
RAU
The RAU converts the IF signals
to RF and sends them to passive
antennas using 50 Ohm coaxial
cable.
Main Hub
The Main Hub sends
uplink RF signals to a
base station using
50 Ohm coaxial cable.
Figure 2-7 Uplink (Wireless Devices to Base Station)
Expansion Hub
The Main Hub receives
the optical signals from
the Expansion Hubs (up
to four) using optical
fiber cable and converts them to RF signals.
The Expansion Hub
receives the IF signals
from the RAUs (up to
eight) using CATV cable
and converts them to
optical signals.
RAU
The RAU receives uplink RF
signals from the passive
antenna using 50 Ohm coaxial
cable and converts them to IF
signals.
2-8 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 29
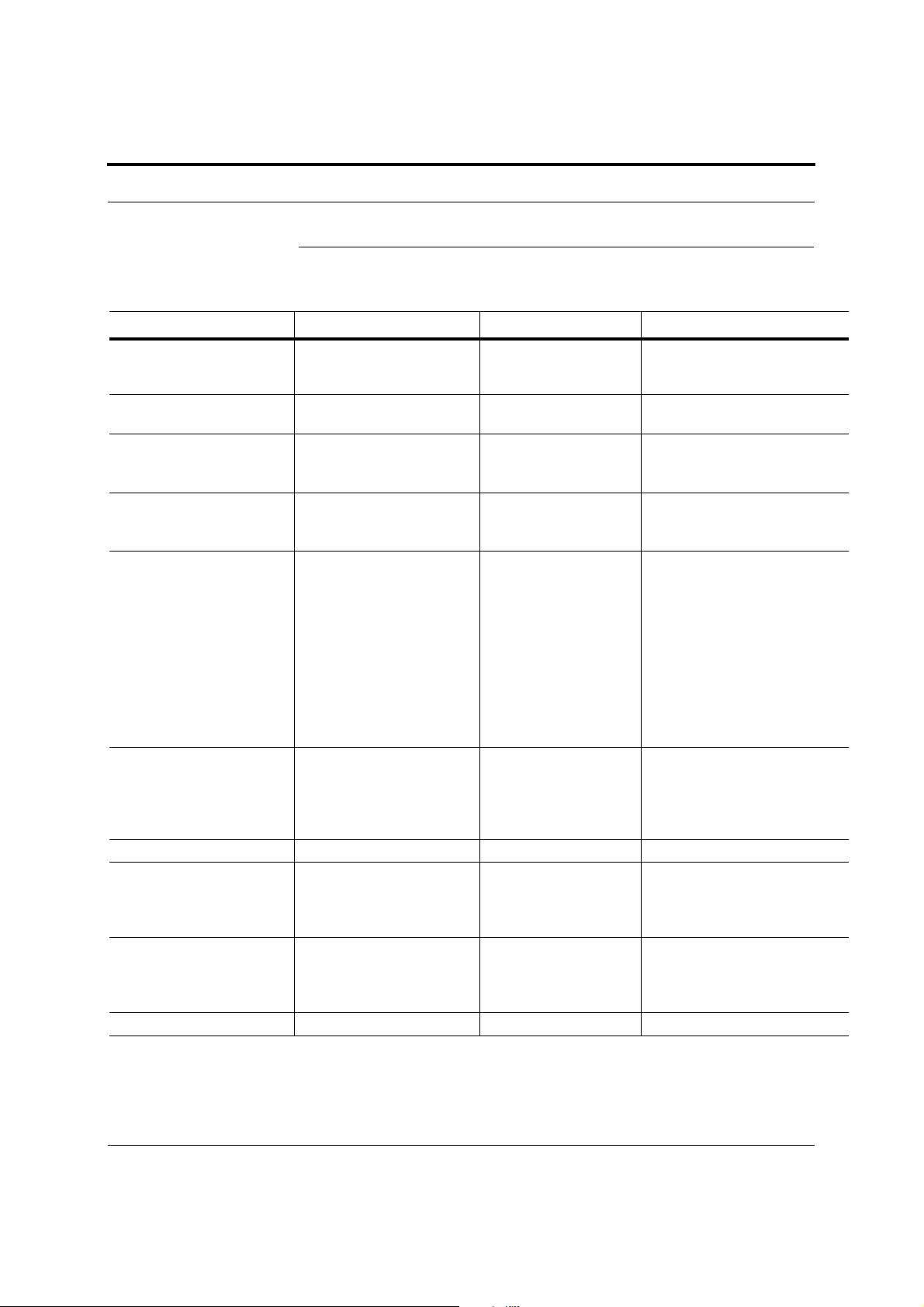
System Specifications
2.6 System Specifications
Tab le 2-1 Physical Specifications
Parameter Main Hub Expansion Hub Remote Access Unit
IF/RF Connectors 6-type “N”, female (50 Ohm),
1 Downlink/Uplink pair per
band
External Alarm Connector
One, 9-pin D-sub, female One, 9-pin D-sub, female —
(contact source)
ADMIN/LAN Interface Connectors
One RJ-45, female
One 9-pin D-sub, male for
optional modem
Fiber Connectors*
4 pair, SC/APC
(FSN-1-MH-1P supports only
1 pair, SP/APC fibers.)
LED Alarm and Status Indicators
Unit Status (One pair):
•Power
• Main Hub Status
Downstream Unit Status
(One per fiber port):
• Expansion Hub/RAU
Power (AC Option) Rating: 100–240V AC, 1A,
50–60 Hz
Operating Range: 90–132V
AC/170-250V
AC auto-ranging
Power (DC Option) Rating: 38–64V DC, 2.5A Rating: 38-64V DC, 14A
Power Consumption (W) 30 4 RAUs: 240 typical, 310
Enclosure Dimensions
u width u depth)†
(height
89 mm × 438 mm × 381 mm
(3.5 in. × 17.25 in. × 15 in.)
(2U)
Weight < 5.5 kg (< 12 lbs.) < 6.6 kg (< 14.5 lbs.) < 2.1 kg (< 4.6 lbs.)
* It is critical to system performance that only SC/APC fiber connectors are used throughout the fiber network, including fiber distribution panels.
† Excluding angle-brackets for 19'' rack hub mounting of the hub.
Note: The Fusion Main Hub’s typical power consumption assumes that the CATV RG-59 cable length is no more than 150 meters, the RG-6 cable
length is no more than 170 meters, and RG-11 cable length is no more than 275 meters using CommScope 2065V, 2279V, and 2293K cables.
8-type “F”, female (CATV
75 Ohm)
One RJ-45, female
One F, female (CATV -75 Ohm)
One N, female (antenna-50 Ohm)
—
One 9-pin D-sub, male
One pair, SC/APC —
Unit Status (One pair):
•Power
• Expansion Hub Status
Unit Status (One pair):
•Link
•Alarm
Fiber Link Status (One
pair):
•DL Status
•UL Status
Port Status:
• One per F connector port
• Link/RAU
Rating: 100–240V AC,
—
6A, 50–60 Hz
Operating Range:
90–132V AC/170-250V
AC auto-ranging
—
max.
8 RAUs: 400 typical, 530
Max.
89 mm × 438 mm × 381
mm
54 mm x 286 mm x 281 mm
(2.13 in. × 11.25 in. × 11.13 in.)
(3.5 in. × 17.25 in. × 15
in.) (2U)
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-9
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 30

System Specifications
Tab le 2- 2 Wavelength and Laser Power Specifications
Measured Output Power
Wavelength Main Hub Expansion Hub
1310 nm +
Tab le 2- 3 Environmental Specifications
20 nm 890 uW 3.8 mW
Parameter Main Hub and Expansion Hub RAU
Operating Temperature 0° to +45°C (+32° to +113°F) –25° to +45°C
(–13° to
+113°F)
Non-operating Temperature –20° to +85°C (–4° to +185°F) –25° to +85°C
(–13° to
+185°F)
Operating Humidity; non-con-
5% to 95% 5% to 95%
densing
Tab le 2- 4 Frequency Bands Covered by Fusion RAUs
RF Passband
MAIN
Fusion
RAU Part Number
Fusion
Band
Downlink
(MHz)
Uplink
(MHz)
HUB/
RAU
Band
RAU
Bandwidth
850/1900 FSN-8519-1 850 869–894 824–849 1 25 MHz
1900 1930–1990 1850–1910 2 60 MHz
900/1800 FSN-9018-1 900 925–960 880–915 1 35 MHz
1800 1805–1880 1710–1785 2 75 MHz
900/2100 FSN-9021-1 900 925–960 880–915 1 35 MHz
2100 2110–2170 1920–1980 2 60 MHz
850/1800 FSN-8518-1 850 869-894 824-849 1 25 MHz
1800 1805-1880 1710-1785 2 75 MHz
850/2100 FSN-8521-1 850 869-894 824-849 1 25 MHz
2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
2-10 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 31

System Specifications
Tab le 2-4 Frequency Bands Covered by Fusion RAUs (continued)
RF Passband
Fusion
RAU Part Number
800/900/
FSN-809019-2 800
1900
Fusion
Band
SMR
900
Downlink
(MHz)
851-869 806-824 1 (sub
935-941 896-902 3 (sub
Uplink
(MHz)
SMR
1900
1930-1995 1850-1915 2 65 MHz
(A-G)
2100
FSN-2100-1 2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
(Single
band RAU)
2100 High
FSN-21HP-1 2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
Power
(Single
band RAU)
MAIN
HUB/
RAU
Band
band
1A)
band
1B)
RAU
Bandwidth
18 MHz
6 MHz
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-11
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 32

System Specifications
2.6.1 RF End-to-End Performance
The following tables list the RF end-to-end performance of each protocol.
NOTE: The system gain is adjustable in 1 dB steps from 0 to 15 dB, and the
gain of each RAU can be attenuated 0 or 10 dB.
850/1900 RAU
Tab le 2- 5 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Parameter
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 2.5 3
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 16
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 22
Typical
Downlink Uplink
Tab le 2- 6 1900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 3.5 4
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) -5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Downlink Uplink
2-12 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 33

System Specifications
900/1800 RAU
Tab le 2-7 900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typ ica l
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 3 4
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Tab le 2-8 1800 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB)
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
4.5
5
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-13
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 34

System Specifications
900/2100 RAU
Tab le 2- 9 900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 3 4
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Tab le 2- 10 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 4.5 5
Spurious Output Levels (dBm) <–30
UMTS TDD Band Spurious Output Level
1900–1920 MHz, 2010–2025 MHz (dBm/MHz)
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Downlink Uplink
<–52
850/1800 RAU
Tab le 2- 11 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 2.5 3
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 16
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 22
2-14 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 35

System Specifications
Tab le 2-1 2 1800 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 4.5 5
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
850/2100 RAU
Tab le 2-1 3 850 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typ ica l
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 2.5 3
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 16
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 22
Tab le 2-1 4 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 4.5 5
Spurious Output Levels (dBm) <–30
UMTS TDD Band Spurious Output Level
1900–1920 MHz, 2010–2025 MHz (dBm/MHz)
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Downlink Uplink
<–52
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-15
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 36

System Specifications
800/900/1900 RAU
Tab le 2- 15 800 MHz (SMR) RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 2.5 3
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 25
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Tab le 2- 16 900 MHz (SMR) RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 2.5 3
Output IP3 (dBm) 35
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 23
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Tab le 2- 17 1900 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter Downlink Uplink
Average gain with 150 m RG-59 at 25°C (77°F) (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 3.5 4
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
2-16 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 37

System Specifications
2100 RAU
Tab le 2-1 8 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter
Average gain with 150 meters RG-59 @ 25qC (dB) 15 15
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 4.5 5
Spurious Output Levels (dBm) <–30
UMTS TDD Band Spurious Output Level
1900–1920 MHz, 2010–2025 MHz (dBm/MHz)
Output IP3 (dBm) 38
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 26
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
Downlink Uplink
<–52
2100 High Power RAU
Tab le 2-1 9 2100 MHz RF End-to-End Performance
Typical
Parameter
Average gain with 150 meters RG-59 @ 25qC (dB)*
Ripple with 150 m RG-59 (dB) 4.5 5
Output IP3 (dBm) 44
Input IP3 (dBm) –5
Output 1 dB Compression Point (dBm) 33
Noise Figure 1 MH, 1 EH, 8 RAUs (dB) 17
Noise Figure 1 MH, 4 EH, 32 RAUs (dB) 23
* The system Downlink gain is adjustable in 1 dB steps from 7 to 22 dB (the High Power RAU adds 7
dB Downlink gain).
The system Uplink gain is adjustable in 1 dB steps from 0 to 15 dB.
Downlink Uplink
22 15
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 2-17
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 38

System Specifications
2-18 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 39

SECTION 3 Fusion Main Hub
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 3.1 Fusion Main Hub Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
• Section 3.2 Fusion Main Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
• Section 3.3 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
• Section 3.4 Main Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
• Section 3.5 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
3.1 Fusion Main Hub Overview
The Fusion Main Hub (shown in Figure 3-1) distributes up to three individual (Band
1, 2, or 3) downlink RF signals from a base station, repeater, or FlexWave Focus system to up to four Expansion Hubs, which in turn distribute the signals to up to 32
Remote Access Units. The Main Hub also combines uplink signals from the associated Expansion Hubs.
Fusion is a multi-band system. One RF source (Band 1 or RF1) goes to the 35 MHz
band and the other RF source (Band 2 or RF2) goes to the 75 MHz band. Band 3 (or
RF3) goes to a 6 MHz sub-band of the 35 MHz band and is functional only with the
800/900/1900 RAU. The system installs in a 19" equipment rack and is usually
co-located with the RF source in a telecommunications closet.
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 3-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 40

Fusion Main Hub Overview
Figure 3-1 Main Hub in a Fusion System
Downlink Path: The Main Hub receives up to 3 individual (Band1, 2, or 3) downlink RF signals from a base station, repeater,
or FlexWave Focus system using 50 Ohm coaxial cable. It converts the signals to IF then to optical and sends them to up to
four Expansion Hubs using fiber optic cable.
The Main Hub also sends OA&M communication to the Expansion Hubs using the fiber optic cable. The Expansion Hubs, in
turn, communicate the OA&M information to the RAUs using CATV cable.
RF1, 2, and 3
Downlink to Main Hub
Fusion Main Hub
Uplink from Main Hub
RF1, 2, and 3
Uplink Path: The Main Hub receives uplink optical signals from up to four Expansion Hubs using fiber optic cables. It converts the signals to IF then to RF and sends them to the respective Band1, 2, or 3 base station, repeater, or FlexWave
Focus system using 50 Ohm coaxial cable.
The Main Hub also receives status information from the Expansion Hubs and all RAUs using the fiber optic cable.
Downlink from Main Hub
Fusion Expansion Hub RAU
Uplink to Main Hub
Figure 3-2 shows a detailed view of the major RF and optical functional blocks of the
Main Hub.
NOTE: The Fusion One Port Main Hub (PN: FSN-1-MH-1P) configuration
is a cost reduced version of the Fusion Main Hub and supports only one
Expansion Hub (up to 8 RAUs).
3-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 41

Figure 3-2 Main Hub Block Diagram
Fusion Main Hub Overview
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 3-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 42

Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
3.2 Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
Figure 3-3 Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
1
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
6
1. Four fiber optic ports (labeled PORT 1, PORT 2, PORT 3, PORT 4)
3
4
5
• One standard female SC/APC connector per port for MMF/SMF input (labeled
UPLINK)
• One standard female SC/APC connector per port for MMF/SMF output
(labeled
2. Four sets of fiber port LEDs (one set per port)
DOWNLINK)
• One LED per port for port link status and downstream unit status
3. One set of unit status LEDs
• One LED for unit power status (labeled
• One LED for unit status (labeled
4. One 9-pin D-sub male connector for system remote dial-up communication and
diagnostics using a modem (labeled
5. One RJ-45 female connector for system communication and diagnostics using a
PC/laptop with direct connect or using a LAN switch (labeled
6. Power switch
POWER)
MAIN HUB STATUS)
MODEM)
ADMIN/LAN)
NOTE: The Fusion One Port Main Hub (PN: FSN-1-MH-1P) configuration
is a cost reduced version of the Fusion Main Hub and supports only one
Expansion Hub (up to 8 RAUs).
3-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 43

3.2.1 Optical Fiber Uplink/Downlink Ports
The optical fiber uplink/downlink ports transmit and receive optical signals between
the Main Hub and up to four Expansion Hubs using industry-standard SMF or MMF
cable. There are four fiber ports on the front panel of the Main Hub; one port per
Expansion Hub. Each fiber port has two female SC/APC connectors:
• Optical Fiber Uplink Connector
This connector (labeled
an Expansion Hub.
• Optical Fiber Downlink Connector
This connector (labeled
nals to an Expansion Hub.
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the Main Hub’s fiber connector ports,
use only SC/APC fiber cable connectors when using either single-mode
or multi-mode fiber. Additionally, it is critical to system performance
that only SC/APC fiber connectors are used throughout the fiber network, including fiber distribution panels.
UPLINK) is used to receive the uplink optical signals from
DOWNLINK) is used to transmit the downlink optical sig-
Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
3.2.2 Communications RS-232 Serial Connector
Remote Monitoring
Use a standard serial cable to connect a modem to the 9-pin D-sub male serial connector for remote monitoring or configuring. The cable typically has a DB-9 female
and a DB-25 male connector. Refer to Appendix A.6 on page A-11 for the cable
pinout diagram.
Remote monitoring is also available by connecting the RJ-45 (ADMIN/LAN) port to
a LAN switch for remote Ethernet LAN access or direct dial-up router access.
Local Monitoring
Use a crossover Ethernet cable (PN-4069-ADB) to connect a laptop or PC to the
RJ-45 female connector for local monitoring or configuring using the AdminBrowser
resident software. The cable typically has a RJ-45 male connector on both ends. Refer
to Appendix A.5 on page A-10 for the cable pinout.
3.2.3 Main Hub LED Indicators
The unit’s front panel LEDs indicate faults and commanded or fault lockouts. The
LEDs do not indicate warnings or whether the system test has been performed. Use the
LEDs to provide basic information only, or as a backup when you are not using AdminBrowser.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 3-5
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 44

Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
Upon power up, the Main Hub goes through a 20-second test to check the LED
lamps. During this time, the LEDs blink through the states shown in Table 3-1, letting
you visually verify that the LED lamps and the firmware are functioning properly.
Upon completion of initialization, the LEDs stay in one of the first two states shown
in Table 3-1.
The Main Hub automatically sends the program bands command to all connected
RAUs. A mismatched band causes a fault message to be displayed in AdminBrowser
and places the RAU in a disabled condition.
NOTE: Refer to Section 9.3.2 for troubleshooting using the LEDs.
NOTE: AdminBrowser should be used for troubleshooting the system.
Only use LEDs for backup or confirmation. However, if there are communication problems within the system, the LEDs may provide additional information that is not available using AdminBrowser.
Unit Status LEDs
The Main Hub has one pair of status LEDs, labeled POWER and STATUS, which can
be in one of the states shown in Table 3-1. These LEDs can be:
steady green
steady red
off - no color (valid only during 90 second power cycle)
flashing red (60 ppm)
There is no off state when the unit’s power is on.
3-6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 45

POWER
STATUS
POWER
STATUS
POWER
STATUS
POWER
STATUS
POWER
STATUS
Tab le 3-1 Fusion Hub Status LED States
LED State Indicates
Green
Green
• The Main Hub is connected to power and all power supplies are operating.
• The Main Hub is not reporting a fault; however, the system test may need to
be performed or a warning condition may exist. Use AdminBrowser to determine this.
Green
Red
• The Main Hub is connected to power and all power supplies are operating.
Use AdminBrowser to power status.
• The Main Hub is reporting a fault.
Green
Green
(60-ppm)
Green
Red
• The Main Hub is connected to power and all power supplies are operating.
Use Admin Browser to determine power status.
• The Main Hub is reporting a lockout condition.
• The Main Hub is connected to power and all power supplies are operating.
• The Main Hub DL input signal level is too high.
(60-ppm)
Red
• One or more power supplies are out-of-specification.
Red
Fusion Main Hub Front Panel
PORT
PORT
PORT
Fiber Port LEDs
The Main Hub has one fiber port LED for each of the four fiber ports. The LED can
be in one of the states shown in Table 3-2. This LED can be:
off
steady green
steady red
flashing red (60 ppm)
Tab le 3-2 Fusion Hub Port LED States
LED State Indicates
Off • The Expansion Hub is not connected.
• The Expansion Hub is connected.
Green
Red
(60 PPM)
• There are no faults from the Expansion Hub or any connected RAU.
• There was a loss of communications with the Expansion Hub.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 3-7
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 46

Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel
PORT
PORT
3.3 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel
Tab le 3- 2 Fusion Hub Port LED States
LED State Indicates
Red
(Steady)
Green
• The Expansion Hub is disconnected.
• The Expansion Hub or any connected RAU reported a fault.
• The Expansion Hub or any connected RAU reported a lockout condition.
(60-ppm)
Figure 3-4 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel
Band 1
UL1 UL2
Alarms
DL1
4
DL2
UL3
Band 3
DL3
3
2
Band 2
1. AC power cord connector
2. Two air exhaust vents
3. Three N-type, female connectors for each band (Band 1, Band 2, and Band 3):
• Uplink (labeled
• Downlink (labeled
UL1, UL2, and UL3)
DL1, DL2, and DL3)
4. One 9-pin D-sub female connector for contact alarm monitoring (labeled
ALARMS)
5. Ground lug for connecting unit to frame ground (labeled GROUND)
3.3.1 Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel Connectors
AC Power
1
5
3.3.1.1 9-pin D-sub Connector
The 9-pin D-sub connector (labeled ALARMS) provides a contact alarm for fault and
warning system alarm monitoring.
3-8 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 47

Fusion Main Hub Rear Panel
Table lists the function of each pin on the 9-pin D-sub connector.
Tab le 3-3 9-pin D-sub Pin Connector Functions
Pin Function
1 Alarm Sense Input (DC Ground)
2 Alarm Sense Input 3
3 Alarm Sense Input 2
4 Warning Source Contact (positive connection)
5 Warning Source Contact (negative connection)
6 DC Ground (common)
7 Fault Source Contact (positive connection)
8 Alarm Sense Input 1
9 Fault Source Contact (negative connection)
This interface can both generate two source contact alarms (Fault and Warning) and
sense 3 single external alarm contacts (Alarm Sense Input 1 through 3).
3.3.1.2 N-type Female Connectors
There are two 50 Ohm N-type connector pairs for each of the 3 bands on the rear
panel of the Hub:
• The
DOWNLINK connector receives downlink RF signals from a repeater, local
base station, or FlexWave Focus system.
• The
UPLINK connector transmits uplink RF signals to a repeater, local base sta-
tion, or FlexWave Focus system.
CAUTION:The UPLINK and DOWNLINK ports cannot handle a DC power
feed from the local base station. If DC power is present, a DC block must be
used or the Fusion hub may be damaged.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 3-9
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 48

Main Hub Specifications
Specification Description
Enclosure Dimensions (H
Weight <5.5 kg (<12 lb)
Operating Temperature 0° to +45°C (+32° to +113°F)
Non-operating Temperature –20° to +85°C (–4° to +185°F)
Operating Humidity, non-condensing 5% to 95%
External Alarm Connector
(contact closure)
ADMIN/LAN Interface Connector 1 RJ-45, female
Fiber Connectors
RF Connectors 6 N, female (50 Ohm), 1 Downlink/Uplink pair per band
LED Fault and Status Indicators Unit Status (1 pair):
AC Power Rating 100/240V AC, 1A, 50-60 Hz
Power Consumption (W) 30
MTBF 117,972 hours
a. Excluding angle brackets for the 19” rack mounting of the Hub.
b. It is critical to system performance that only SC/APC fiber connectors are used throughout the fiber network, including
fiber distribution panels.
3.4 Main Hub Specifications
Tab le 3- 4 Main Hub Specifications
u W u D)
a
:
89 mm x 438 mm x 381 mm (3.5 in. x 17.25 in. x 15 in.) 2U
1 9-pin D-sub, female
Maximum: 40 mA @ 40V DC
Typical: 4 mA @ 12V DC
1 9-pin D-sub, male for optional modem
4 Pair, SC/APC
•Power
• Main Hub Status
Downstream Unit/Link Status (1 per fiber port):
• Link/E-Hub/RAU
Operating Range: 90-132V AC/170-250V AC auto-ranging
b
NOTE: The Fusion One Port Main Hub (PN:
FSN-1-MH-1P) configuration is a cost reduced version of the
Fusion Main Hub and supports only one Expansion Hub (up
to 8 RAUs).
3-10 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 49

Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages
3.5 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages
3.5.1 Description
The Fusion Main Hub monitors and reports changes or events in system performance
to:
• Ensure that fiber receivers, amplifiers and IF/RF paths are functioning properly.
• Ensure that Expansion Hubs and Remote Access Units are connected and function-
ing properly.
An event is classified as fault, warning, or status message.
• Faults are service impacting.
• Warnings indicate a possible service impact.
• Status and informational messages are generally not service impacting.
The Fusion Main Hub periodically queries attached Expansion Hub and Remote
Access Units for their status. Both faults and warnings are reported to a connected
PC/laptop running a standard browser communicating with the AdminBrowser software. Only faults are indicated by the faceplate LEDs.
For more information regarding the events, refer to:
• Appendix C for Main Hub faults.
• Appendix C for Main Hub warnings.
• Appendix C for Main Hub status messages.
• Section 9 for troubleshooting Main Hub LEDs.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 3-11
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 50

Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages
J
3.5.2 View Preference
AdminBrowser 1.0 or higher enables you to select (using the screen shown in
Figure 3-5) the type of events to be displayed.
Figure 3-5 Preferences Check Boxes
To modify the setting, using AdminBrowser, select Alarms
and select the desired choice. After you click
OK, AdminBrowser refreshes and
Set Alarm Preference
updates the tree view according to the new setting.
NOTE: The setting is strictly visual and only in AdminBrowser. There is
no affect on the hardware itself. By default, the event filtering is set to
“Enable viewing of Faults only”.
The only exception to when the event filtering is ignored is during the Install/Configure command. All events are displayed regardless of the event filtering setting. This
ensures a smooth installation.
3-12 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 51

SECTION 4 Fusion Expansion Hub
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 4.1 Expansion Hub Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
• Section 4.2 Expansion Hub Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
• Section 4.3 Expansion Hub Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
• Section 4.4 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
• Section 4.5 Expansion Hub Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
4.1 Expansion Hub Overview
The Expansion Hub acts an interface between the Main Hub and the Remote Access
Unit(s) by converting optical signals to electrical signals and vice versa, as shown in
Figure 4-1. It also supplies control signals and DC power to operate the Remote
Access Unit(s) as well as passing status information from the RAUs to the Main Hub.
Figure 4-1 Expansion Hub in a Fusion System
Downlink Path: The Expansion Hub receives downlink (Band1, 2, and 3) optical signals from the Main Hub using fiber
optic cable. It converts the signals to electrical and sends them to up to eight Remote Access Units (RAUs) using CATV
cables. The Expansion Hub also receives configuration information from the Main Hub using the fiber optic cable and
relays it to the RAUs using CATV cable.
Downlink to Expansion Hub
Fusion Main Hub
Uplink from Expansion Hub
Uplink Path: The Expansion Hub receives uplink (Band1, 2, and 3) IF signals from up to eight RAUs using CATV cables. It
converts the signals to optical and sends them to a Main Hub using fiber optic cable.
The Expansion Hub also receives RAU status information using CATV cable and sends it and its own status information to
the Main Hub using the fiber optic cable.
Fusion Expansion Hub
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 4-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Downlink from Expansion Hub
RAU
Uplink to Expansion Hub
Page 52

Expansion Hub Overview
Figure 4-2 Expansion Hub Block Diagram
4-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 53

Expansion Hub Front Panel
4.2 Expansion Hub Front Panel
Figure 4-3 Expansion Hub Front Panel
1 2 3 4 5
7
8
6
1. One port LED per type F connector port for link status and downstream RAU sta-
tus (8 pair total).
2. Eight CATV cable, type F connectors (labeled PORT 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
3. One pair of unit status LEDs
• One LED for unit power status (labeled
• One LED for unit status (labeled
4. One set of fiber connection status LEDs
• One LED for fiber downlink status (labeled
• One LED for fiber uplink status (labeled
5. One fiber optic port which has two connectors
POWER)
E-HUB STATUS)
DL STATUS)
UL STATUS)
• One standard female SC/APC connector for MMF/SMF output (labeled
UPLINK)
• One standard female SC/APC connector for MMF/SMF input (labeled
DOWNLINK)
6. One 9-pin D-sub male connector for ADC factory testing (labeled CONSOLE)
7. One RJ-45 female connector for system communication and diagnostics using a
PC/laptop with direct connect or using a LAN switch (labeled
8. Power Switch
ADMIN/LAN)
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 4-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 54

Expansion Hub Front Panel
4.2.1 75 Ohm Type F Connectors
4.2.2 Manufacturing RS-232 Serial Connector
The eight type F connectors on the Expansion Hub are for the CATV cables used to
transmit and receive signals to and from RAUs. Use only 75 ohm type F connectors
on the CATV cable.
The CATV cable also delivers DC electrical power to the RAUs. The Expansion
Hub’s DC voltage output is 54V DC nominal. A current limiting circuit protects the
Hub if any port draws excessive power.
NOTE: For system performance, it is important to use only low loss solid copper center conductor CATV cable with quality type F connectors that use captive
centerpin connectors. Refer to Appendix A for approved cables and connectors.
Console Port
This console port is only used by ADC manufacturing test purposes. DO NOT CONNECT ANYTHING TO IT.
Local Monitoring
Use a crossover Ethernet cable (PN-4069-ADB) to directly connect a laptop or PC to
the RJ-45 female connector for local monitoring or configuring the Expansion Hub
and associated RAUs using the AdminBrowser-EH resident software. The cable typically has a RJ-45 male connector on both ends. Refer to Appendix A.4 on page A-8
for the cable pinout and the AdminBrowser manual.
4.2.3 Optical Fiber Uplink/Downlink Connectors
The optical fiber uplink/downlink port transmits and receives optical signals between
the Expansion Hub and the Main Hub using industry-standard SMF or MMF cable.
The fiber port has two female SC/APC connectors:
• Optical Fiber Uplink Connector
This connector (labeled
to the Main Hub.
• Optical Fiber Downlink Connector
This connector (labeled
nals from the Main Hub.
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the Expansion Hub’s fiber connector
ports, use only SC/APC fiber cable connectors. Additionally, use only
UPLINK) is used to transmit (output) uplink optical signals
DOWNLINK) is used to receive (input) downlink optical sig-
4-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 55

SC/APC fiber connectors throughout the fiber network, including fiber distribution panels. This is critical for ensuring system performance.
4.2.4 LED Indicators
The unit’s front panel LEDs indicate fault conditions and commanded or fault lockouts.
The LEDs do not indicate warnings or whether the system test has been performed.
Only use the LEDs to provide basic information or as a backup when you are not using
AdminBrowser.
Upon power up, the Expansion Hub goes through a five-second test to check the LED
lamps. During this time, the LEDs blink through the states shown in Table 4-2, letting
you visually verify that the LED lamps and the firmware are functioning properly.
NOTE: Refer to Section 9 for troubleshooting using the LEDs.
Unit Status and DL/UL Status LEDs
The Expansion Hub unit status and DL/UL status LEDs can be in one of the states
shown in Table 4-1. These LEDs can be:
Expansion Hub Front Panel
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
Tab le 4- 1 Expansion Hub Unit Status and DL/UL Status LED States
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
steady green
steady red
off
LED State Indicates
Green / Green
Green / Green
Green / Green
Red / Green
• The Expansion Hub is connected to power and all power supplies are
operating.
• The Expansion Hub is not reporting a fault or lockout condition; but
the system test may need to be performed or a warning condition
could exist (use AdminManager to determine this).
• Optical power received is above minimum (the Main Hub is connected) although the cable optical loss may be greater than recommended maximum.
• Optical power transmitted (uplink laser) is normal and communications with the Main Hub are normal.
• Optical power received is above minimum (the Main Hub is connected) although the cable optical loss may be greater than recommended maximum.
• Optical power transmitted (uplink laser) is normal and communications with the Main Hub are normal.
• The Expansion Hub is reporting a fault.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 4-5
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 56

Expansion Hub Front Panel
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
POWER
EH STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
DL STATUS
UL STATUS
Tab le 4- 1 Expansion Hub Unit Status and DL/UL Status LED States (continued)
LED State Indicates
Green / Green
Green / Green
(60-ppm)
• Optical power received is above minimum (the Main Hub is connected) although the cable optical loss may be greater than recommended maximum.
• Optical power transmitted (uplink laser) is normal and communications with the Main Hub are normal.
• The Expansion Hub is reporting a commanded lockout.
Green / Red
Red / Green
• A fault condition was detected, optical power received is below minimum.
(the Main Hub is not connected, is not powered, or the Main Hub’s
downlink laser has failed, or the downlink fiber is disconnected or
damaged.)
Green / Green
Red / Red
• The Expansion Hub is reporting a fault condition.
• Optical power received is above minimum (Main Hub is connected)
although the cable optical loss may be greater than recommended
maximum.
• Optical power transmitted is below minimum (Expansion Hub uplink
laser has failed; unable to communicate with Main Hub).
UL STATUS
LED state must be checked within the first 90 seconds after power on.
If initially green, then red after 90 seconds, it means that there is no
communication with the Main Hub. If red on power up, replace the
Expansion Hub.
Green / Red
Red / Red
• Optical power received is below minimum (the Main Hub is not connected, is not powered, or the Main Hub’s downlink laser has failed,
or the downlink fiber is disconnected or damaged.)
• Optical power transmitted is below minimum (the Expansion Hub
uplink laser has failed; is unable to communicate with the Main Hub).
UL STATUS LED state must be checked within the first 90 seconds
after power on. If initially green, then red after 90 seconds, it means
that there is no communication with the Main Hub. If red on power
up, the uplink laser has failed, replace the Expansion Hub.
Green /Off
• Expansion Hub is in factory test mode, return it to the factory.
Green / Off
Red/ Don’t
Care
• One or more power supplies are out of specification. The hub needs to
be replaced.
Red/ Don’t
Care
Green/ Red
• Expansion Hub failure. The Hub must be replaced.
Off/ Off
RJ-45 Port LEDs
The Expansion Hub has a port LED, labeled PORT, for each of the eight 75 Ohm,
Type F ports. The port LEDs can be in one of the states shown in Table 4-2. These
LEDs can be:
off
4-6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 57

PORT
Expansion Hub Rear Panel
steady green
steady red
flashing red (60 pulses per minute [PPM])
Tab le 4- 2 Fusion Expansion Hub Port LED States
LED State Indicates
Off • The RAU is not connected.
PORT
PORT
PORT
PORT
• The RAU is connected.
Green
Red
(60 PPM)
• No faults from the RAU.
• The RAU was disconnected.
• The RAU is not communicating.
• The RAU port power is tripped.
Red
(Steady)
Green
(60-ppm)
• The RAU is disconnected.
• The RAU is reporting a fault.
• The RAU is disconnected.
• The RAU is reporting a lockout condition.
4.3 Expansion Hub Rear Panel
Figure 4-4 Expansion Hub Rear Panel
1
1. AC power cord connector
2. Two air exhaust vents
2
3
4
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 4-7
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 58

Expansion Hub Rear Panel
3. One 9-pin D-sub female connector for contact alarm monitoring (labeled
ALARMS)
4. Ground lug for connecting unit to frame ground (labeled GROUND)
4-8 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 59

Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages
Tab le 4- 3 9-pin D-sub Pin Connector Functions
Pin Function
1 Alarm Sense Input (DC Ground)
2 Alarm Sense Input 3
3 Alarm Sense Input 2
4N/C
5N/C
6 DC Ground (common)
7N/C
8 Alarm Sense Input 1
9N/C
This interface can monitor three single external alarm contacts (Alarm Sense Input 1
This interface monitors the output contact closures from a Universal Power Supply
(UPS). Verify the output contact closure state (normally closed or normally open) of
the UPS, and set the appropriate contact definition using AdminBrowser.
• Faults are service impacting.
• Warnings indicate a possible service impact.
• Status messages are generally not service impacting.through 3).
4.4 Faults, Warnings, and Status Messages
Both fault and warning conditions of the Expansion Hub and attached RAUs are
reported to the Main Hub. Only faults are indicated by LEDs.
For more information, refer to Appendix C, “Faults, Warnings, Status Tables,” on
page C-1.
NOTE: You can select what type of events AdminBrowser displays. Refer
to Section 3.5.2 View Preference 3-12.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 4-9
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 60

Expansion Hub Specifications
4.5 Expansion Hub Specifications
Specification Description
Enclosure Dimensions (H
Weight < 6.6 kg (< 14.5 lb.)
Operating Temperature
Non-operating Temperature
Operating Humidity, non-condensing 5% to 95%
CATV Connectors
Fiber Connectors
LED Alarm and Status Indicators Unit Status (1 pair):
External Alarm Connector (contact sense
monitor)
AC Power (Volts) (47–63 Hz) Rating: 100/240V AC, 6A, 50-60 Hz
Power Consumption (W) 4 RAUs: 275 typical, 335 maximum
MTBF 54,477 hours
a. It is important that you use only recommended CATV 75 Ohm cable with quality F connectors.
b. It is critical to system performance that only SC/APC fiber connectors are used throughout the fiber network, including
fiber distribution panels.
Tab le 4- 4 Expansion Hub Specifications
u W u D) 89 mm x 438 mm x 381 mm
(3.5 in. x 17.25 in. x 15 in.) 2U
0° to +45°C (+32° to +113°F)
–20° to +85°C (–4° to +185°F)
a
b
8 F, female (CATV - 75 Ohm)
1 Pair, SC/APC
•Power
• E-Hub Status
Fiber Link Status (1 pair):
•DL Status
•UL Status
Port Status (1 pair per CATV port):
• Link/RAU
1 9-pin D-sub, female
Operating Range: 90-132V AC/170-250V AC auto-ranging
8 RAUs: 475 typical, 585 maximum
4-10 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 61

SECTION 5 Remote Access Unit
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 5.1 RAU Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
• Section 5.2 Remote Access Unit Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
• Section 5.3 RAU LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
• Section 5.4 Faults and Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
• Section 5.5 Remote Access Unit Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.1 RAU Overview
The Remote Access Unit (RAU) is an active transceiver that connects to an Expansion Hub using industry-standard CATV cable, which delivers RF signals, configuration information, and electrical power to the RAU.
An RAU passes converted 1F to RF (Downlink) and converted RF to 1F (Uplink) signals between an Expansion Hub and an attached passive antenna where the signals
are transmitted to wireless devices as shown in Figure 5-1.
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 5-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 62

RAU Overview
Figure 5-1 Remote Access Unit in a Fusion System
Downlink Path: The RAU receives downlink IF signals from a Fusion Hub using 75 Ohm CATV cable. It converts the sig-
nals to RF and sends them to a passive RF antenna using 50 Ohm coaxial cable. Also, the RAU receives configuration
information from the Fusion Hub using the 75 Ohm CATV cable.
Fusion Main Hub
Fusion Expansion Hub
Downlink to RAU
Uplink from RAU
RAU
Downlink to antenna
Uplink from antenna
Uplink Path: The RAU receives uplink RF signals from a passive RF antenna using 50 Ohm coaxial cable. It converts the
signals to IF and sends them to a Fusion Hub using 75 Ohm CATV cable. Also, the RAU sends its status information to the
Fusion Hub using CATV cable.
The RAU receives 54VDC power from the Fusion Hub port through the 75 Ohm CATV cable center pin.
Figure 5-2 Remote Access Unit Block Diagram (Multiband)
,2,3*
* for FSN-W2-808519-1 RAU when Band 3 is active.
5-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 63

RAU Overview
The Fusion RAUs are manufactured to a specific set of bands: one 35 MHz Band 1
(split into two sub-bands 1A and 1B for FSN-809019-1 RAU), and one 75
MHz-Band 2. Table 5-1 lists the Fusion RAUs, the Fusion Band, and the frequency
bands they cover.
Tab le 5-1 Frequency Bands Covered by Fusion RAUs
RF Passband
MAIN
Fusion
RAU Part Number
Fusion
Band
Downlink
(MHz)
Uplink
(MHz)
850/1900 FSN-8519-1 850 869–894 824–849 1 25 MHz
1900 1930–1990 1850–1910 2 60 MHz
900/1800 FSN-9018-1 900 925–960 880–915 1 35 MHz
1800 1805–1880 1710–1785 2 75 MHz
900/2100 FSN-9021-1 900 925–960 880–915 1 35 MHz
2100 2110–2170 1920–1980 2 60 MHz
850/1800 FSN-8518-1 850 869-894 824-849 1 25 MHz
1800 1805-1880 1710-1785 2 75 MHz
850/2100 FSN-8521-1 850 869-894 824-849 1 25 MHz
2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
800/900/
1900
FSN-809019-2 800
SMR
900
851-869 806-824 1 (sub
935-941 896-902 3 (sub
SMR
1900
1930-1995 1850-1915 2 65 MHz
(A-G)
2100
FSN-2100-1 2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
(Single
band
RAU)
2100
FSN-21HP-1 2100 2110-2170 1920-1980 2 60 MHz
High
Power
(Single
band
RAU)
HUB/
RAU
Band
band
1A)
band
1B)
RAU
Bandwidth
18 MHz
6 MHz
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 5-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 64

RAU Overview
Tab le 5- 2 System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length (All RAUs except
800/900/1900)
Distance
Cable
Typ e
CommScope
Part
Number
Plenum
Rated
Solid
Copper
Conductor
Copper
Clad
Conductor
Zero-loss
RF
Maximum
Length
(meters)
RF is
10dB
Below
Input RF
(meters)
RG-59
2065V Yes X 150 210
2022V Yes X 120 120*
5572R No X 110 110*
5565 No X 150 210
RG-6
2279V Yes X 170 230
2275V Yes X 170 175*
5726 No X 170 170*
5765 No X 170 230
RG-11
2293K Yes X 275 375
2285K Yes X 275 370*
5913 No X 275 370*
* Exceeding the distance of copper-clad cable will result in the attached RAU becoming
non-functional. If the distance of a cable run is at its maximum and is of concern, ADC recommends the use of solid copper cable to ensure successful operation.
5-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 65

Remote Access Unit Connectors
Tab le 5-3 System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length for 800/900/1900
RAUs
Distance
Where
RF is
10dB
Below
Input RF
(meters)
Cable
Typ e
RG-59
RG-6
Zero-loss
CommScope
Part
Number
2065V Yes X 150 210
2022V Yes X 80 80*
5572R No X 70 70*
5565 No X 150 210
2279V Yes X 170 230
2275V Yes X 115 115*
5726 No X 110 110*
5765 No X 170 230
Plenum
Rated
Solid
Copper
Conductor
Copper
Clad
Conductor
RF
Maximum
Length
(meters)
RG-11
2293K Yes X 275 375
2285K Yes X 240 240*
5913 No X 240 240*
* Exceeding the distance of copper-clad cable will result in the attached RAU becoming non-functional. If
the distance of a cable run is at its maximum and is of concern, ADC recommends the use of solid copper
cable to ensure successful operation.
5.2 Remote Access Unit Connectors
5.2.1 50 Ohm Type-N Connector
The RAU has one female type-N connector. The connector is a duplexed RF
input/output port that connects to a standard 50: passive antenna using coaxial cable.
5.2.2 75 Ohm Type-F Connector
The RAU has one type-F female connector that connects it to a Fusion Hub using
CATV 75 Ohm cable. Use RG-59, 6, or 11 solid copper center conductor cables.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 5-5
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 66

RAU LED Indicators
NOTE: For system performance, it is important that you use only low loss,
solid copper center conductor CATV cable with quality F connectors that use
captive centerpin conductors. Refer to Appendix A for specific information.
5.3 RAU LED Indicators
Upon power up, the RAU goes through a two-second test to check the LED lamps.
During this time, the LEDs blink green/green red/red, letting you visually verify that
the LED lamps and the firmware are functioning properly.
NOTE: Refer to Section 9 for troubleshooting using the LEDs.
Status LEDs
The RAU status LEDs can be in one of the states shown in Table 5-4. These LEDs
can be:
off
steady green
steady red
There is no off state when the unit’s power is on.
Tab le 5- 4 Remote Access Unit LED States
LED State Indicates
LINK
ALARM
LINK
ALARM
LINK
ALARM
LINK
ALARM
LINK
ALARM
Off
Off
Green
Green
Green
Red
Red
Red
Green (60-ppm)
Green (60-ppm)
• The RAU is not receiving DC power.
• The RAU is powered and is not indicating a fault
condition. Communication with the Fusion Hub
is normal; however, the system test may need to
be performed or a warning condition may exist
(use AdminBrowser to determine this).
• The RAU is indicating a fault or lockout condition, but communication with the Fusion Hub is
normal.
• The RAU is reporting a fault and is not able to
communicate with the Fusion Hub
• The RAU is reporting a lockout condition, but
communication with the Fusion Hub is normal.
5-6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 67

5.4 Faults and Warnings
Both fault and warning conditions are reported to the Fusion Hub where they are
stored. Only faults are indicated by the faceplate LEDs.
For more information, refer to Appendix C.
5.5 Remote Access Unit Specifications
Tab le 5-5 Remote Access Unit Specifications
Specification Description
Dimensions (H
Weight < 2.1 kg (< 4.6 lb.)
Operating Temperature –25° to +45°C (–13° to +113°F)
Non-operating Temperature –25° to +85°C (–13° to +185°F)
Operating Humidity, non-condensing 5% to 95%
RF Connectors One Type-F, female (CATV - 75 ohms)
LED Alarm and Status Indicators Unit Status (1 pair):
Maximum Heat Dissipation (W) 50 typical, 64 max (from the Hub)
MTBF 211,600 hours (All Dual Band RAUs)
u W u D)
54 mm × 286 mm × 281 mm
(2.13 in. × 11.25 in. × 11.13 in.)
One Type-N, female (antenna 50 ohms)
• Link
• Alarm
144,409 hours (800/900/1900 Tri-Band RAUs)
Faults and Warnings
NOTE: For system performance, it is important that you use only low loss,
solid copper center conductor CATV cable with quality F connectors that use
captive centerpin conductors. Refer to Appendix A for more information.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 5-7
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 68

Remote Access Unit Specifications
5-8 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 69

SECTION 6 Designing a Fusion Solution
This section contains the following subsections:
• Section 6.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
• Section 6.2 Downlink RSSI Design Goal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
• Section 6.3 Maximum Output Power per Carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
• Section 6.4 System Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
• Section 6.5 Estimating RF Coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
• Section 6.6 Link Budget Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-25
• Section 6.7 Optical Power Budget . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
• Section 6.8 Connecting a Main Hub to a Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-38
6.1 Overview
Designing a Fusion solution is a matter of determining coverage and capacity needs.
This requires the following steps:
1. Determine the wireless service provider’s requirements: Refer to Section 6.2,
“Downlink RSSI Design Goal,” on page 6-3.
The following information is typically provided by the service provider:
• Frequency (for example, 1900 MHz)
• Band (for example, “A-F” band in the PCS spectrum)
• Protocol (for example, CDMA, GSM, 1xRTT, GPRS, and so on)
• Number of sectors and peak capacity per sector (translates to the number of RF
carriers that the system will have to transmit)
• Downlink RSSI design goal (RSSI, received signal strength at the wireless
handset, for example, –85 dBm)
InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual 6-1
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 70

Overview
The design goal is always a stronger signal than the mobile phone needs. It
includes inherent factors which affect performance.
• RF source (base station or bidirectional amplifier or repeater), type of equipment if possible.
2. Determine the downlink power per carrier from the RF source through the
DAS: Refer to Section 6.3, “Maximum Output Power per Carrier,” on page
6-4.
The maximum power per carrier is a function of modulation type, the number of
RF carriers, signal quality issues, regulatory emissions requirements, and
Fusion’s RF performance. Power per carrier decreases as the number of carriers
increases.
3. Develop an RF link budget: Refer to Section 6.5, “Estimating RF Coverage,”
on page 6-14.
Knowing both the power per carrier and RSSI design goal, you can develop an RF
downlink link budget which estimates the allowable path loss from an RAU’s
antenna to the wireless handset.
allowable path loss = power per carrier + antenna gain – design goal
Satisfactory performance can be expected as long as path loss is below this level.
4. Determine the in-building environment: Refer to Section 6.5, “Estimating RF
Coverage,” on page 6-14.
• Determine which areas of the building require coverage (entire building, public
areas, parking levels, and so on.)
• Obtain floor plans to determine floor space of building and the wall layout of
the proposed areas to be covered. Floor plans are also useful when you are
selecting antenna locations.
• If possible, determine the building’s construction materials (sheetrock, metal,
concrete, and so on.)
• Determine the type of environment:
– Open layout (for example, a convention center)
– Dense, close walls (for example, a hospital)
– Mixed use (for example, an office building with hard wall offices and cubi-
cles)
5. Determine the appropriate estimated path loss slope that corresponds to the
type of building and its layout, and estimate the coverage distance for each
RAU: Refer to Section 6.5, “Estimating RF Coverage,” on page 6-14.
Use the path loss slope (PLS), which gives a value to the RF propagation characteristics within the building, to convert the RF link budget into an estimate of the
coverage distance per antenna. This helps establish the quantities of Fusion equipment you need. The actual path loss slope that corresponds to the specific RF
environment inside the building can also be determined empirically by performing an RF site-survey of the building. This involves transmitting a calibrated tone
6-2 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 71

for a fixed antenna and making measurements with a mobile antenna throughout
the area surrounding the transmitter.
6. Determine the items required to connect to the base station: Refer to
Section 6.8, “Connecting a Main Hub to a Base Station,” on page 6-38.
Once you know the quantities of Fusion equipment to be used, you can determine
the accessories (combiners/dividers, surge suppressors, repeaters, attenuators, circulators, and so on.) required to connect the system to the base station.
The individual elements that must be considered in designing a Fusion solution are
explained in the following sections.
NOTE: Access the ADC Customer Portal at adc.com for on-line dimensioning and design tools.
6.2 Downlink RSSI Design Goal
Downlink RSSI Design Goal
Wireless service providers typically provide a minimum downlink signal level and an
associated confidence factor when specifying coverage requirements. These two figures of merit are a function of wireless handset sensitivity and margins for fading and
body loss. Wireless handset sensitivity is the weakest signal that the handset can process reliably and is a combination of the thermal noise in the channel, noise figure of
the handset receiver front end and minimum required SNR. Fade margins for multipath fading (fast or small-scale) and log-normal shadow fading (slow or large-scale)
are determined by the desired confidence factor, and other factors. Downlink RSSI
design goal calculations for the GSM protocol are shown below for a 95% area coverage confidence factor.
Noise Power
10 Log (KT)+10 Log (200 KHz); K=1.38X10
–23
, T=300 degrees Kelvin
Wireless Handset Noise Figure 8 dB
Required SNR 9 dB
Multipath Fade Margin
95% Reliability for Rician K=6 dB
Log-normal Fade Margin
95% Area/87% Edge Reliability for 35 dB PLS and 9 dB Sigma
Body Attenuation + 3 dB
Downlink RSSI Design Goal (P
Signal level received by wireless handset at edge of coverage area
DesignGoal
)
–121 dBm
6dB
10 dB
–85 dBm
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-3
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 72

Maximum Output Power per Carrier
Downlink design goals on the order of –85 dBm are typical for protocols, such as
GSM and iDEN. Wireless service providers may choose a higher level to ensure that
in-building signal dominates any macro signal that may be leaking into the building.
6.3 Maximum Output Power per Carrier
The following tables show the recommended maximum power per carrier out of the
RAU 50 Ohm Type-N connector for different frequencies, protocols, and numbers of
carriers. These maximum levels are dictated by RF signal quality and regulatory
emissions issues. In general, as the number of RF carrier increases, the maximum
power per carrier decreases. If these levels are exceeded, signal quality will be
degraded and/or regulator requirements will be violated. The maximum input power
to the Hub is determined by subtracting the system gain from the maximum output
power of the RAU. System gain is software selectable from 0 dB to 15 dB in 1 dB
steps. Additionally, both the uplink and downlink gain of each RAU can be attenuated 0 or 10 dB.
When connecting a Hub to a base station or repeater, attenuation on the downlink is
typically required to avoid exceeding Fusion’s maximum output power recommendations.
WARNING: Exceeding the maximum input power may cause permanent damage to the Hub. Do not exceed the maximum composite input
power of 1W (+30 dBm) to the Hub at any time.
NOTE: These specifications are for downlink power at the RAU output (excluding
antenna).
6-4 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 73

Maximum Output Power per Carrier
6.3.1 850 MHz Cellular
Cellular Power per Carrier
Power per Carrier (dBm)
No. of
Carriers
1 16.5 16.5 16.5 16.5 16.0 15.0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
20
30
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
AMPS TDMA GSM EDGE CDMA WCDMA
16.5 16.5 13.5 13.5 13.0 11.0
16.5 15.0 11.5 11.5 11.0 8.0
13.5 13.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 6.5
12.0 11.5 9.0 9.0 9.0 5.0
10.5 10.5 8.5 8.5 8.0
9.5 9.5 8.0 8.0 7.5
8.5 8.5 7.5 7.5 7.0
8.0 8.0 7.0 7.0
7.0 7.5 6.5 6.5
7.0 7.0 6.5 6.5
6.5 6.5 6.0 6.0
6.0 6.5 5.5 5.5
5.5 6.0 5.5 5.5
5.5 5.5 5.0 5.0
5.0 5.5 5.0 5.0
4.0 4.5 4.5 4.0
2.0 2.5 3.0 2.0
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-5
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 74

Maximum Output Power per Carrier
6.3.2 800 MHz or 900 MHz SMR
Tab le 6- 1 Power per Carrier
Power per Carrier (dBm) - 800MHz/900 MHz
No. of
Carriers
1 16.6/14.5 24.0/23.0 21.0/19.0 24.0/23.0 24.0/23.0 23.0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
iDEN Analog FM CQPSK C4FM
13.0/11.0 19.0/17.0 16.0/14.0 18.5/16.5 18.5/16.5 16.5
10.5/8.5 15.5/13.5 13.5/11.5 15.0/13.0 15.0/13.0 13.0
9.0/7.0 12.5/10.0 11.5/9.5 12.5/10.5 12.5/10.5 10.5
8.0/6.0 11.0/9.0 10.0/8.0 10.5/8.5
7.0/5.0 9.5/7.5 8.5/6.5 9.0/7.0
6.0/4.0 8.5/6.5 8.0/6.0 8.0/6.0
5.5/3.5 7.5/5.5 7.0/5.0 7.5/5.5
5.0/3.0 7.0/5.0 6.5/4.5 6.5/4.5
4.5/2.5 6.0/4.0 6.0/4.0 6.0/4.0
4.0/2.0
3.5/1.5
3.0/1.0
3.0/1.0
2.5/0.5
2.0/0
DataTac/
Mobitex
POCSAG/
REFLEX
6-6 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 75

6.3.3 900 MHz EGSM and EDGE
Tab le 6-2 GSM/EGSM and EDGE Power per Carrier
Power per Carrier (dBm)
No. of
Carriers
1 16.0 16.0
2 13.0 13.0
3 11.0 11.0
4 10.0 10.0
59.09.0
68.08.0
77.57.5
87.07.0
96.56.5
10 6.0 6.0
11 5.5 5.5
12 5.0 5.0
13 5.0 5.0
14 4.5 4.5
15 4.0 4.0
16 4.0 4.0
20 3 3
30 1 1
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion
from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022
emissions requirements.
GSM EDGE
Maximum Output Power per Carrier
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-7
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 76

Maximum Output Power per Carrier
6.3.4 1800 MHz DCS
Tab le 6- 3 DCS Power per Carrier
Power per Carrier (dBm)
No. of
Carriers
1 16.5 16.5
2 14.5 14.5
3 12.5 12.5
4 11.5 11.5
5 10.5 10.5
69.5 9.5
79.0 9.0
88.5 8.0
98.0 7.5
10 7.5 7.0
11 7.0 6.5
12 6.5 6.0
13 6.5 6.0
14 6.0 5.5
15 5.5 5.0
16 5.5 5.0
20 4.5 4.0
30 2.5 2.0
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC
Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
GSM EDGE
6-8 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 77

6.3.5 1900 MHz PCS
Tab le 6-4 PCS Power per Carrier
No. of
Carriers
1 16.5 16.5 16.5 16.0 15.0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
20
30
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
TDMA GSM EDGE CDMA WCDMA
Maximum Output Power per Carrier
Power per Carrier (dBm)
16.5 15.5 15.5 13.0 11.0
15.0 13.5 13.5 11.0 8.0
13.0 12.0 12.0 10.0 6.5
11.5 11.0 10.5 9.0 5.0
10.5 10.5 9.5 8.0
9.5 10.0 9.0 7.5
8.5 9.0 8.0 7.0
8.0 8.5 7.5
7.5 8.0 7.0
7.0 7.5 6.5
6.5 7.0 6.0
6.5 6.5 6.0
6.0 6.5 5.5
5.5 6.0 5.0
5.5 5.5 5.0
4.5 4.5 4.0
2.5 3.0 2.0
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-9
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 78

Maximum Output Power per Carrier
6.3.6 2.1 GHz UMTS
Tab le 6- 5 UMTS Power per Carrier
No. of
Carriers
1
211.0
38.0
46.5
55.0
64.0
73.0
Note: measurements taken with no baseband clipping.
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meeting RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
Power per
Carrier (dBm)
6.3.7 2.1 GHz UMTS High Power
Tab le 6- 6 UMTS Power per Carrier
No. of
Carriers
1
2 18.0
3 15.0
4 13.5
5 12.0
611.0
7 10.0
Note: Measurements taken with no baseband clipping.
Note: Operation at or above these output power levels may prevent Fusion from meet-
ing RF performance specifications or FCC Part 15 and EN55022 emissions requirements.
Power per
Carrier (dBm)
WCDMA
15.0
WCDMA
22.0
Designing for Capacity Growth
Fusion systems are deployed to enhance in-building coverage and/or to off-load
capacity from a macro cell site. In many instances, subscriber usage increases with
time and the wireless provider responds by increasing the load on the installed Fusion
system. For example, the initial deployment might only require two RF carriers, but
four RF carriers may be needed in the future based on capacity growth forecasts.
There are two options for dealing with this scenario:
1. Design the initial coverage with a maximum power per carrier for four RF carri-
ers. This will likely result in additional RAUs.
6-10 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 79

2. Design the initial coverage for two RF carriers, but reserve RAU ports on the Hub
for future use. These ports can be used to fill potential coverage holes once the
power per carrier is lowered to accommodate the two additional carriers.
6.4 System Gain
The system gain of the Fusion defaults to 0 dB or can be set up to 15 dB in 1 dB
increments. In addition, uplink and downlink gains of each RAU can be independently attenuated by 0 or 10 dB using AdminBrowser.
The recommended maximum lengths of CATV cable are as follows:
• For RG-59 cable 150 meters for CommScope PN 2065V.
• For RG-6 cable 170 meters for CommScope PN 2279V.
• For RG-11 cable 275 meters for CommScope PN 2293K.
If the maximum distance is not required, then copper-clad over steel center-conductor
cable may be use to reduce cable costs.
System Gain
If the CATV cable is longer than the recommended distance per cable type, the gain
of the system will decrease, as shown in Table 6-7 and Table 6-8.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-11
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 80

System Gain
Tab le 6- 7
System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length (All RAUs except
800/900/1900)
Comm-
Cable
Typ e
RG-59
RG-6
RG-11
Scope
Part
Number
2065V Yes X 150 210
2022V Yes X 120 120*
5572R No X 110 110*
5565 No X 150 210
2279V Yes X 170 230
2275V Yes X 170 175*
5726 No X 170 170*
5765 No X 170 230
2293K Yes X 275 375
2285K Yes X 275 370*
5913 No X 275 370*
Plenum
Rated
Solid
Copper
Conductor
Copper
Clad
Conductor
Zero-loss
RF
Maximum
Length
(meters)
Distance
Where
RF is
10dB
Below
Input RF
(meters)
* Exceeding the distance of copper-clad cable will result in the attached RAU becoming non-functional. If
the distance of a cable run is at its maximum and is of concern, ADC recommends the use of solid copper
cable to ensure successful operation.
6-12 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 81

System Gain
Tab le 6-8
RAUs
Cable
Typ e
RG-59
RG-6
RG-11
System Gain (Loss) Relative to CATV Cable Length for 800/900/1900
Distance
Where
CommScope
Part
Number
Plenum
Rated
Solid
Copper
Conductor
Copper
Clad
Conductor
RF
Maximum
Length
(meters)
2065V Yes X 150 210
2022V Yes X 80 80*
5572R No X 70 70*
5565 No X 150 210
2279V Yes X 170 230
2275V Yes X 115 115*
5726 No X 110 110*
5765 No X 170 230
2293K Yes X 275 375
2285K Yes X 240 240*
5913 No X 240 240*
Zero-loss
RF is
10dB
Below
Input RF
(meters)
* Exceeding the distance of copper-clad cable will result in the attached RAU becoming non-functional. If
the distance of a cable run is at its maximum and is of concern, ADC recommends the use of solid copper
cable to ensure successful operation.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-13
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 82

Estimating RF Coverage
6.5 Estimating RF Coverage
The maximum output power per carrier (based on the number and type of RF carriers
being transmitted) and the minimum acceptable received power at the wireless device
(that is, the RSSI design goal) essentially establish the RF downlink budget and, con-
sequently, the maximum allowable path loss (APL) between the RAU’s antenna and
the wireless device. Since in-building systems, such as the Fusion, are generally
downlink-limited, this approach is applicable in the majority of deployments.
Figure 6-1 Determining APL between the Antenna and the Wireless Device
G = Antenna Gain
L
= Coaxial cable loss
coax
RAU
P = power per
carrier from the RAU
Distance = d
RSSI = power at the
wireless device
APL = (P – L
+ G) – RSSI (1)
coax
where:
• APL = the maximum allowable path loss in dB
• P = the power per carrier transmitted by the RAU in dBm
•L
= the coaxial cable loss between the RAU and passive antenna in dB
coax
• G = the gain of the passive antenna in dBi
Coaxial cable is used to connect the RAU to an antenna. Table 6-9 lists coaxial cable
loss for various cable lengths.
Tab le 6- 9 Coaxial Cable Losses (
Length of Cable
(.195 in. diameter)
0.9 m (3 ft) 0.6 0.8
1.8 m (6 ft) 1.0 1.5
3.0 m (10 ft) 1.5 2.3
Loss at
850 MHz (dB)
L
coax)
Loss at
1900 MHz (dB)
You can calculate the distance, d, corresponding to the maximum allowable path loss
using equations introduced in the following sections.
6-14 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 83

6.5.1 Path Loss Equation
In-building path loss obeys the distance power law1 in equation (2):
Estimating RF Coverage
PL = 20log
(4Sd0f/c) + 10nlog10(d/d0) + &
10
s
where:
• PL is the path loss at a distance, d, from the antenna
• d = the distance expressed in meters
•d
= free-space path loss distance in meters
0
• f = the operating frequency in Hertz.
• c = the speed of light in a vacuum (3.0 × 10
8
m/sec).
• n = the path loss exponent and depends on the building “clutter” and frequency
of operation
•
&s= a normal random variable that depends on partition material and geome-
tries inside the building and is accounted for by the log-normal fade margin
used in the downlink RSSI design goal calculation
As a reference, Table 6-10 provides estimates of signal loss for some RF barriers
Tab le 6-1 0 Average Signal Loss of Common Building Materials
Partition Type Loss (dB) Frequency (MHz)
Metal wall 26 815
Aluminum siding 20 815
Foil insulation 4 815
Cubicle walls 1.4 900
Concrete block wall 13 1300
Concrete floor 10 1300
Sheetrock 1 to 2 1300
Light machinery 3 1300
General machinery 7 1300
Heavy machinery 11 1300
Equipment racks 7 1300
Assembly line 6 1300
Ceiling duct 5 1300
Metal stairs 5 1300
(2)
1
.
1. Rappaport, Theodore S. Wireless Communications, Principles, and Practice. Prentice Hall PTR, 1996.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-15
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 84

Estimating RF Coverage
6.5.2 RAU Coverage Distance
Use equations (1) and (2), on pages 6-14 and 6-15, respectively, to estimate the dis-
tance from the antenna to where the RF signal decreases to the minimum acceptable
level at the wireless device.
With d
set to one meter and path loss slope (PLS) defined as 10n, Equation (2) can
0
be simplified to:
PL(d) = 20log
Table 6-11 gives the value of the first term of Equation (3) (that is., (20log
(4Sf/c) + PLS·log10(d) (3)
10
(4Sf/c))
10
for various frequency bands.
Tab le 6- 11 Frequency Bands and the Value of the First Term in Equation (3)
Band (MHz)
Frequency
800 MHz SMR 806-824 851-869 838 30.9
900 MHz SMR 896-902 935-941 919 31.9
850 MHz Cellular 824–849 869–894 859 31.1
900 MHz GSM 890–915 935–960 925 31.8
900 MHz EGSM 880–915 925–960 920 31.7
1800 MHz DCS 1710–1785 1805–1880 1795 37.5
1900 MHz PCS 1850–1910 1930–1990 1920 38.1
2.1 GHz UMTS 1920–1980 2110–2170 2045 38.7
Uplink Downlink
Mid-Band
Frequency
(MHz)
20log
(4Sf/c)
10
6-16 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 85

Estimating RF Coverage
Table 6-12 shows estimated PLS for various environments that have different “clut-
ter” (that is, objects that attenuate the RF signals, such as walls, partitions, stairwells,
equipment racks, and so.).
Tab le 6-1 2 Estimated Path Loss Slope for Different In-Building Environments
Environment Type Example
Open Environment
very few RF obstructions
Moderately Open Environment
low-to-medium amount of RF
obstructions
Mildly Dense Environment
medium-to-high amount of RF
obstructions
Moderately Dense Environment
medium-to-high amount of RF
obstructions
Dense Environment
large amount of RF obstructions
Parking Garage, Convention Center 33.7 30.1
Warehouse, Airport, Manufacturing 35 32
Retail, Office Space with approximately 80% cubicles and 20% hard
walled offices
Office Space with approximately
50% cubicles and 50% hard walled
offices
Hospital, Office Space with approximately 20% cubicles and 80% hard
walled offices
By setting the path loss to the maximum allowable level (PL = APL), equation (3) can
be used to estimate the maximum coverage distance of an antenna connected to an
RAU, for a given frequency and type of in-building environment.
For reference, Tables 6-14 through 6-18 show the distance covered by an antenna for
various in-building environments. The following assumptions were made:
d = 10^((APL - 20log
PLS for
850/900 MHz
36.1 33.1
37.6 34.8
39.4 38.1
(4Sf/c))/PLS) (4)
10
PLS for
1800/1900 MHz
• Path loss Equation (4)
• 6 dBm output per carrier at the RAU output
• 3 dBi antenna gain
• RSSI design goal = –85 dBm (typical for narrowband protocols, but not for
spread-spectrum protocols)
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-17
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 86

Estimating RF Coverage
Tab le 6- 13 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 800 MHz SMR Applications
Distance from Antenna
Environment Type
Meters Feet
Open Environment 75 244
Moderately Open Environment 64 208
Mildly Dense Environment 56 184
Moderately Dense Environment 48 156
Dense Environment 40 131
Tab le 6- 14 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 850 MHz Cellular Applications
Distance from Antenna
Environment Type
Meters Feet
Open Environment 73 241
Moderately Open Environment 63 205
Mildly Dense Environment 55 181
Moderately Dense Environment 47 154
Dense Environment 39 129
Tab le 6- 15 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 900 MHz SMR Applications
Distance from Antenna
Facility
Meters Feet
Open Environment 70 230
Moderately Open Environment 60 197
Mildly Dense Environment 53 174
Moderately Dense Environment 45 148
Dense Environment 38 125
6-18 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 87

Tab le 6-1 6 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 900 MHz EGSM Applications
Distance from Antenna
Estimating RF Coverage
Facility
Meters Feet
Open Environment 70 231
Moderately Open Environment 60 197
Mildly Dense Environment 53 174
Moderately Dense Environment 45 149
Dense Environment 38 125
Tab le 6-1 7 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 1800 MHz DCS Applications
Distance from Antenna
Facility
Open Environment 75 246
Moderately Open Environment 58 191
Mildly Dense Environment 50 166
Moderately Dense Environment 42 137
Dense Environment 30 100
Meters Feet
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-19
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 88

Estimating RF Coverage
Tab le 6- 18 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 1900 MHz PCS Applications
Distance from Antenna
Facility
Meters Feet
Open Environment 72 236
Moderately Open Environment 56 183
Mildly Dense Environment 49 160
Moderately Dense Environment 40 132
Dense Environment 29 96
Tab le 6- 19 Approximate Radiated Distance from Antenna
for 2.1 GHz UMTS Applications
Distance from Antenna
Facility
Open Environment 69 226
Moderately Open Environment 54 176
Mildly Dense Environment 47 154
Moderately Dense Environment 39 128
Dense Environment 28 93
Meters Feet
6-20 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 89

6.5.3 Examples of Design Estimates
Example Design Estimate for an 850 MHz TDMA Application
1. Design goals:
• Cellular (859 MHz = average of the lowest uplink and the highest downlink
frequency in 800 MHz Cellular band)
•TDMA provider
• 12 TDMA carriers in the system
• –85 dBm design goal (to 95% of the building) — the minimum received power
at the wireless device
• Base station with simplex RF connections
2. Power Per Carrier: The tables in Section 6.3, “Maximum Output Power per Car-
rier,” on page 6-4 provide maximum power per carrier information. The 850 MHz
TDMA table (on page 6-5) indicates that Fusion can support 10 carriers with a
recommended maximum power per carrier of 7.0 dBm. The input power should
be set to the desired output power minus the system gain.
3. Building information:
• Eight floor building with 9,290 sq. meters (100,000 sq. ft.) per floor; total
74,322 sq. meters (800,000 sq. ft.).
• Walls are sheetrock construction, suspended ceiling tiles.
• Antennas used will be omni-directional, ceiling mounted.
• Standard office environment, 50% hard wall offices and 50% cubicles.
Estimating RF Coverage
4. Link Budget: In this example, a design goal of –85 dBm is used. Suppose 3 dBi
omni-directional antennas are used in the design. Then, the maximum RF propagation loss should be no more than 94.5 dB (6.5 dBm + 3 dBi + 85 dBm) over
95% of the area being covered. It is important to note that a design goal such as
–85 dBm is usually derived taking into account multipath fading and log-normal
shadowing characteristics. Thus, this design goal will only be met “on average”
over 95% of the area being covered. At any given point, a fade may bring the signal level underneath the design goal.
Note that this method of calculating a link budget is only for the downlink path.
For information to calculate link budgets for both the downlink and uplink paths,
refer to Section 6.6 on page 6-25.
5. Path Loss Slope: For a rough estimate, Table 6-12, “Estimated Path Loss Slope for
Different In-Building Environments” on page 6-17, shows that a building with 50%
hard wall offices and 50% cubicles, at 859 MHz, has an approximate path loss slope
(PLS) of 37.6. Given the RF link budget of 95.5 dB, the distance of coverage from
each RAU will be 52 meters (170.6 ft). This corresponds to a coverage area of
8,494 sq. meters (91,425 sq. ft.) per RAU (refer to Section 6.5.1 for details on path
loss estimation). For this case we assumed a circular radiation pattern, though the
actual area covered depends upon the pattern of the antenna and the obstructions in
the facility.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-21
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 90

Estimating RF Coverage
Equipment Required: Since you know the building size, you can now estimate
the Fusion equipment quantities that will be needed. Before any RF levels are
tested in the building, you can estimate that two antennas per level will be needed.
This assumes no propagation between floors. If there is propagation, you may not
need antennas on every floor.
a. 2 antennas per floor × 8 floors = 16 RAUs
b. 16 RAUs ÷ 8 (maximum 8 RAUs per Expansion Hub) = 2 Expansion Hubs
c. 2 Expansion Hubs ÷ 4 (maximum 4 Expansion Hubs per Main Hub) = 1 Main
Hub
Check that the fiber and CATV cable distances are as recommended. If the distances differ, use the tables in Section 6.4, “System Gain,” on page 6-11 to determine system gains or losses. The path loss may need to be recalculated to assure
adequate signal levels in the required coverage distance.
The above estimates assume that all cable length requirements are met. If Expansion
Hubs cannot be placed so that the RAUs are within the distance requirement, additional Expansion Hubs may need to be placed closer to the required RAUs locations.
An RF Site Survey and Building Evaluation is required to accurately establish the
Fusion equipment quantities required for the building. The site survey measures the
RF losses within the building to determine the actual PLS, which are used in the final
path loss formula to determine the actual requirements of the Fusion system.
6-22 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 91

Estimating RF Coverage
Example Design Estimate for an 1900 MHz CDMA Application
1. Design goals:
• PCS (1920 MHz = average of the lowest uplink and the highest downlink frequency in 1900 MHz PCS band)
•CDMA provider
• 8 CDMA carriers in the system
• –85 dBm design goal (to 95% of the building) — the minimum received power
at the wireless device
• Base station with simplex RF connections
2. Power Per Carrier: The tables in Section 6.3, “Maximum Output Power per Car-
rier,” on page 6-4 provide maximum power per carrier information. The 1900
MHz CDMA table (on page 6-9) indicates that Fusion can support eight carriers
with a recommended maximum power per carrier of 6.5 dBm. The input power
should be set to the desired output power minus the system gain.
3. Building information:
• 16 floor building with 9,290 sq. meters (100,000 sq. ft.) per floor; total
148,640 sq. meters (1,600,000 sq. ft.).
• Walls are sheetrock construction, suspended ceiling tiles.
• Antennas used are omni-directional, ceiling mounted.
• Standard office environment, 80% hard wall offices and 20% cubicles.
4. Link Budget: In this example, a design goal of –85 dBm is used. Suppose 3 dBi
omni-directional antennas are used in the design. Then, the maximum RF propagation loss should be no more than 94.5 dB (6.5 dBm + 3 dBi + 85 dBm) over
95% of the area being covered. It is important to note that a design goal such as
–85 dBm is usually derived taking into account multipath fading and log-normal
shadowing characteristics. Thus, this design goal will only be met “on average”
over 95% of the area being covered. At any given point, a fade may bring the signal level underneath the design goal.
Note that this method of calculating a link budget is only for the downlink path.
For information to calculate link budgets for both the downlink and uplink paths,
refer to Section 6.6 on page 6-25.
5. Path Loss Slope: For a rough estimate, Table 6-12, “Estimated Path Loss Slope for
Different In-Building Environments” on page 6-17, shows that a building with 80%
hard wall offices and 20% cubicles, at 1920 MHz, has an approximate path loss
slope (PLS) of 38.1. Given the RF link budget of 94.5 dB, the distance of coverage
from each RAU will be 30.2 meters (99 ft). This corresponds to a coverage area
of 2,868 sq. meters (30,854 sq. ft.) per RAU (refer to Section 6.5.1 for details on
path loss estimation). For this case we assumed a circular radiation pattern, though
the actual area covered depends upon the pattern of the antenna and the obstructions
in the facility.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-23
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 92

Estimating RF Coverage
6. Equipment Required: Since you know the building size, you can now estimate
the Fusion equipment quantities needed. Before you test any RF levels in the
building, you can estimate that four antennas per level will be needed. This
assumes no propagation between floors. If there is propagation, you may not need
antennas on every floor.
a. 4 antennas per floor × 16 floors = 64 RAUs
b. 64 RAUs ÷ 8 (maximum 8 RAUs per Expansion Hub) = 8 Expansion Hubs
c. 8 Expansion Hubs ÷ 4 (maximum 4 Expansion Hubs per Main Hub) = 2 Main
Hubs
Check that the fiber and Cat-5/5E/6 cable distances are as recommended. If the
distances differ, use the tables in Section 6.4, “System Gain,” on page 6-11 to
determine system gains or losses. The path loss may need to be recalculated to
assure adequate signal levels in the required coverage distance.
The above estimates assume that all cable length requirements are met. If Expansion
Hubs cannot be placed so that the RAUs are within the distance requirement, additional Expansion Hubs may need to be placed closer to the required RAUs locations.
An RF Site Survey and Building Evaluation is required to accurately establish the
Fusion equipment quantities required for the building. The site survey measures the
RF losses within the building to determine the actual PLS, used in the final path loss
formula to determine the actual requirements of the Fusion system.
6-24 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 93

6.6 Link Budget Analysis
A link budget is a methodical way to account for the gains and losses in an RF system
so that the quality of coverage can be predicted. The end result can often be stated as
a “design goal” in which the coverage is determined by the maximum distance from
each RAU before the signal strength falls beneath that goal.
One key feature of the link budget is the maximum power per carrier explained in
Section 6.3. While the maximum power per carrier is important as far as emissions
and signal quality requirements are concerned, it is critical that the maximum signal
into the Main Hub never exceed 1W (+30 dBm). Composite power levels above this
limit will cause damage to the Main Hub.
WARNING : Exceeding the maximum input power of 1W (+30 dBm)
could cause permanent damage to the Main Hub.
NOTE: Visit the ADC customer portal at adc.com for the on-line Link Budget Tool.
Link Budget Analysis
6.6.1 Elements of a Link Budget for Narrowband Standards
The link budget represents a typical calculation that might be used to determine how
much path loss can be afforded in a Fusion design. This link budget analyzes both the
downlink and uplink paths. For most configurations, the downlink requires lower
path loss and is therefore the limiting factor in the system design. It is for this reason
that a predetermined “design goal” for the downlink is sufficient to predict coverage
distance.
The link budget is organized in a simple manner: the transmitted power is calculated,
the airlink losses due to fading and body loss are summed, and the receiver sensitivity
(minimum level a signal can be received for acceptable call quality) is calculated. The
maximum allowable path loss (in dB) is the difference between the transmitted
power, less the airlink losses, and the receiver sensitivity. From the path loss, the
maximum coverage distance can be estimated using the path loss formula presented
in Section 6.5.1.
Table 6-20 provides link budget considerations for narrowband systems.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-25
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 94

Link Budget Analysis
Tab le 6- 20 Link Budget Considerations for Narrowband Systems
Consideration Description
BTS Transmit Power The power per carrier transmitted from the base station output
Attenuation between
BTS and Fusion
This includes all losses: cable, attenuator, splitter/combiner, and so forth.
On the downlink, attenuation must be chosen so that the maximum power per carrier going into the
Main Hub does not exceed the levels given in Section 6.3.
On the uplink, attenuation is chosen to keep the maximum uplink signal and noise level low enough
to prevent base station alarms but small enough not to cause degradation in the system sensitivity.
If the Fusion noise figure minus the attenuation is at least 10 dB higher than the BTS noise figure,
the system noise figure is approximately that of Fusion alone. Refer to Section 6.8 for ways to independently set the uplink and downlink attenuations between the base station and Fusion.
Antenna Gain The radiated output power includes antenna gain. For example, if you use a 3 dBi antenna at the
RAU that is transmitting 0 dBm per carrier, the effective radiated power (relative to an isotropic radiator) is 3 dBm per carrier.
BTS Noise Figure This is the effective noise floor of the base station input (usually base station sensitivity is this effec-
tive noise floor plus a certain C/I ratio).
Fusion Noise Figure This is Fusion’s uplink noise figure, which varies depending on the number of Expansion Hubs and
RAUs, and the frequency band. Fusion’s uplink noise figure is specified for a 1-1-8 configuration.
Thus, the noise figure for a Fusion system (or multiple systems whose uplink ports are power combined) is NF(1-1-8) + 10*log(# of Expansion Hubs). This represents an upper-bound because the
noise figure is lower if any of the Expansion Hub’s RAU ports are not used.
Thermal Noise This is the noise level in the signal bandwidth (BW).
Thermal noise power = –174 dBm/Hz + 10Log(BW).
Protocol
Signal
Bandwidth
Thermal
Noise
TDMA 30 kHz –129 dBm
GSM 200 kHz –121 dBm
iDEN 25 kHz –130 dBm
Required C/I ratio For each wireless standard, a certain C/I (carrier to interference) ratio is needed to obtain acceptable
demodulation performance. For narrowband systems, (TDMA, GSM, EDGE, iDEN, AMPS) this
level varies from about 9 dB to 20 dB.
Mobile Transmit
The maximum power the mobile can transmit (power transmitted at highest power level setting).
Power
Multipath Fade
Margin
This margin allows for a certain level of fading due to multipath interference. Inside buildings there
is often one or more fairly strong signals and many weaker signals arriving from reflections and diffraction. Signals arriving from multiple paths add constructively or destructively. This margin
accounts for the possibility of destructive multipath interference. In RF site surveys the effects of
multipath fading are typically not accounted for because such fading is averaged out over power
level samples taken over many locations.
6-26 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 95

Tab le 6-2 0 Link Budget Considerations for Narrowband Systems (continued)
Consideration Description
Log-normal Fade
Margin
This margin adds an allowance for RF shadowing due to objects obstructing the direct path between
the mobile equipment and the RAU. In RF site surveys, the effects of shadowing are partially
accounted for since it is characterized by relatively slow changes in power level.
Body Loss This accounts for RF attenuation caused by the user’s head and body.
Minimum Received
Signal Level
This is also referred to as the “design goal”. The link budget says that you can achieve adequate coverage if the signal level is, on average, above this level over 95% of the area covered, for example.
Link Budget Analysis
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-27
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 96

Link Budget Analysis
6.6.2 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis for a Microcell Application
Tab le 6- 21 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis: Downlink
Line Downlink
Transmitter
a. BTS transmit power per carrier (dBm) 33
b. Attenuation between BTS and Fusion (dB) –23
c. Power into Fusion (dBm) 10
d. Fusion gain (dB) 0
e. Antenna gain (dBi) 3
f. Radiated power per carrier (dBm) 13
Airlink
g. Multipath fade margin (dB) 6
h. Log-normal fade margin with 9 dB std. deviation, 95% area coverage,
87% edge coverage
i. Body loss (dB) 3
j. Airlink losses (not including facility path loss) 19
10
Receiver
k. Thermal noise (dBm/30 kHz) –129
l. Mobile noise figure (dB) 7
m. Required C/I ratio (dB) 17
n. Minimum received signal (dBm) –105
p. Maximum path loss (dB) +99
• c = a + b
• f = c + d + e
• j = g + h + i
• n = k + l + m
• k: in this example, k represents the thermal noise for a TDMA signal, which
has a bandwidth of 30 kHz
• p = f – j – n
6-28 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 97

Link Budget Analysis
Tab le 6-2 2 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis: Uplink
Line Uplink
Receiver
a. BTS noise figure (dB) 4
b. Attenuation between BTS and Fusion (dB) –10
c. Fusion gain (dB) 0
d. Fusion noise figure (dB) 1-4-32 22
e. System noise figure (dB) 22.6
f. Thermal noise (dBm/30 kHz) –129
g. Required C/I ratio (dB) 12
h. Antenna gain (dBi) 3
i. Receive sensitivity (dBm) –97.4
Airlink
j. Multipath fade margin (dB) 6
k. Log-normal fade margin with 9 dB std. deviation, 95% area coverage,
87% edge coverage
l. Body loss (dB) 3
m. Airlink losses (not including facility path loss) 19
10
Transmitter
n. Mobile transmit power (dBm) 28
p. Maximum path loss (dB) 106.4
• e: enter the noise figure and gain of each system component (a, b, c, and d) into
the standard cascaded noise figure formula
F
– 1
F
= F1 + + + ....
sys
where
F = 10
G = 10
(See Rappaport, Theodore S. Wireless Communications, Principles, and Practice. Prentice Hall PTR, 1996.)
2
G
(Noise Figure/10)
(Gain/10)
F3 – 1
G
1
1G2
• i = f + e + g – h
• m = j + k + l
• p = n – m – i
Therefore, the system is downlink limited but the downlink and uplink are almost
balanced, which is a desirable condition.
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-29
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 98

Link Budget Analysis
6.6.3 Elements of a Link Budget for CDMA Standards
A CDMA link budget is slightly more complicated because you must consider the
spread spectrum nature of CDMA. Unlike narrowband standards such as TDMA and
GSM, CDMA signals are spread over a relatively wide frequency band. Upon reception, the CDMA signal is de-spread. In the de-spreading process the power in the
received signal becomes concentrated into a narrow band, whereas the noise level
remains unchanged. Hence, the signal-to-noise ratio of the de-spread signal is higher
than that of the CDMA signal before de-spreading. This increase is called processing
gain. For IS-95 and J-STD-008, the processing gain is 21 dB or 19 dB depending on
the user data rate (9.6 Kbps for rate set 1 and 14.4 Kbps for rate set 2, respectively).
Because of the processing gain, a CDMA signal (comprising one Walsh code channel
within the composite CDMA signal) can be received at a lower level than that
required for narrowband signals. A reasonable level is –95 dBm, which results in
about –85 dBm composite as shown below.
An important issue to keep in mind is that the downlink CDMA signal is composed of
many orthogonal channels: pilot, paging, sync, and traffic. The composite power
level is the sum of the powers from the individual channels. Table 6-23 shows an
example.
Tab le 6- 23 Distribution of Power within a CDMA Signal
Channel Walsh Code Number Relative Power Level
Pilot 0 20% –7.0 dB
Sync 32 5% –13.3 dB
Primary Paging 1 19% –7.3 dB
Traffic 8–31, 33–63 9% (per traffic channel) –10.3 dB
This table assumes that there are 15 active traffic channels operating with 50% voice
activity (so that the total power adds up to 100%). Notice that the pilot and sync channels together contribute about 25% of the power. When measuring the power in a
CDMA signal you must be aware that if only the pilot and sync channels are active,
the power level will be about 6 to 7 dB lower than the maximum power level you can
expect when all voice channels are active. The implication is that if only the pilot and
sync channels are active, and the maximum power per carrier table says that you
should not exceed 10 dBm for a CDMA signal, for example, then you should set the
attenuation between the base station and the Main Hub so that the Main Hub receives
3 dBm (assuming 0 dB system gain).
An additional consideration for CDMA systems is that the uplink and downlink paths
should be gain and noise balanced. This is required for proper operation of soft-handoff to the outdoor network as well as preventing excess interference that is caused by
mobiles on the indoor system transmitting at power levels that are not coordinated
with the outdoor mobiles. This balance is achieved if the power level transmitted by
the mobiles under close-loop power control is similar to the power level transmitted
under open-loop power control. The open-loop power control equation is
P
+ PRX = –73 dBm (for Cellular, IS-95)
TX
6-30 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
Page 99

PTX + PRX = –76 dBm (for PCS, J-STD-008)
Link Budget Analysis
where P
is the mobile’s transmitted power and PRX is the power received by the
TX
mobile.
The power level transmitted under closed-loop power control is adjusted by the base
station to achieve a certain E
ence between these power levels, '
ated from the RAU, P
= P
'
P
downink
= P
'
P
downink
+ P
+ P
downink
uplink
uplink
It’s a good idea to keep –12 dB < '
(explained in Table 6-24 on page 6-31). The differ-
b/N0
, can be estimated by comparing the power radi-
P
, to the minimum received signal, P
, at the RAU:
uplink
+ 73 dBm (for Cellular)
+ 76 dBm (for PCS)
< 12 dB.
P
Table 6-24 provides link budget considerations for CDMA systems.
Tab le 6-2 4 Additional Link Budget Considerations for CDMA
Consideration Description
Power
per carrier,
downlink
Information Rate This is simply
Process Gain The process of de-spreading the desired signal boosts that signal relative to the noise and interference.
Eb/No This is the energy-per-bit divided by the received noise and interference. It’s the CDMA equivalent of sig-
This depends on how many channels are active. For example, the signal is about 7 dB lower if only the
pilot, sync, and paging channels are active compared to a fully-loaded CDMA signal. Furthermore, in the
CDMA forward link, voice channels are turned off when the user is not speaking. On average this is
assumed to be about 50% of the time. So, in the spreadsheet, both the power per Walsh code channel (representing how much signal a mobile will receive on the Walsh code that it is de-spreading) and the total
power are used.
The channel power is needed to determine the maximum path loss, and the total power is needed to determine how hard the Fusion system is being driven.
The total power for a fully-loaded CDMA signal is given by (approximately):
total power =
voice channel power + 13 dB + 10log
10
(50%)
= voice channel power + 10 dB
10log
(9.6 Kbps) = 40 dB for rate set 1
10
10log
(14.4 Kbps) = 42 dB for rate set 2
10
This gain needs to be included in the link budget. In the following formulas, P
P
= 10log10(1.25 MHz / 9.6 Kbps) = 21 dB rate set 1
G
= 10log10(1.25 MHz / 14.4 Kbps) = 19 dB rate set 2
P
G
Note that the process gain can also be expressed as 10log
(CDMA bandwidth) minus the information
10
= process gain:
G
rate.
nal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This figure depends on the mobile’s receiver and the multipath environment.
If the receiver noise figure is NF (dB), then the receive sensitivity (dBm) is given by:
P
= NF + Eb/No + thermal noise in a 1.25 MHz band – P
sensitivity
= NF + E
– 113 (dBm/1.25 MHz) – P
b/No
G
G
Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 6-31
D-620610-0-20 Rev D CONFIDENTIAL
Page 100

Link Budget Analysis
Tab le 6- 24 Additional Link Budget Considerations for CDMA (continued)
Consideration Description
Noise Rise On the uplink, the noise floor is determined not only by the Fusion system, but also by the number of
mobiles that are transmitting. This is because when the base station attempts to de-spread a particular
mobile’s signal, all other mobile signals appear to be noise. Because the noise floor rises as more mobiles
try to communicate with a base station, the more mobiles there are, the more power they have to transmit.
Hence, the noise floor rises rapidly:
noise rise = 10log
where loading is the number of users as a percentage of the theoretical maximum number of users.
Typically, a base station is set to limit the loading to 75%. This noise ratio must be included in the link
budget as a worst-case condition for uplink sensitivity. If there are less users than 75% of the maximum,
then the uplink coverage will be better than predicted.
Hand-off Gain CDMA supports soft hand-off, a process by which the mobile communicates simultaneously with more
than one base station or more than one sector of a base station. Soft hand-off provides improved receive
sensitivity because there are two or more receivers or transmitters involved. A line for hand-off gain is
included in the CDMA link budgets worksheet although the gain is set to 0 dB because the in-building
system will probably be designed to limit soft-handoff.
(1 / (1 – loading))
10
Other CDMA Issues
• Never combine multiple sectors (more than one CDMA signal at the same frequency) into a Fusion system. The combined CDMA signals will interfere with
each other.
• Try to minimize overlap between in-building coverage areas that utilize different
sectors, as well as in-building coverage and outdoor coverage areas. This is important because any area in which more than one dominant pilot signal (at the same
frequency) is measured by the mobile will result in soft-handoff. Soft-handoff
decreases the overall network capacity by allocating multiple channel resources to
a single mobile phone.
6-32 InterReach Fusion Installation, Operation, and Reference Manual
CONFIDENTIAL D-620610-0-20 Rev D
 Loading...
Loading...