Page 1
Digivance® NXD
Radio Access Node (RAN)
Installation and Maintenance Manual
ADCP-75-210
Issue 1
March 2007
21227-A
1356011 Rev A
Page 2

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
COPYRIGHT
© 2006, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the U.S.A.
REVISION HISTORY
ISSUE DATE REASON FOR CHANGE
1 02/2007 Original.
TRADEMARK INFORMATION
Digivance is a registered trademark of ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
ADC is a trademark of ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
Contents herein are current as of the date of publication. ADC reserves the right to change the contents without prior notice. In no
event shall ADC be liable for any damages resulting from loss of data, loss of use, or loss of profits and ADC further
disclaims any and all liability for indirect, incidental, special, consequential or other similar damages. This disclaimer of
liability applies to all products, publications and services during and after the warranty period.
This publication may be verified at any time by contacting ADC’s Technical Assistance Center at 1-800-366-3891, extension 73475
(in U.S.A. or Canada) or 952-917-3475 (outside U.S.A. and Canada), or by e-mail to connectivity_tac@adc.com.
Page ii
ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
P.O. Box 1101, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55440-1101
In U.S.A. and Canada: 1-800-366-3891
Outside U.S.A. and Canada: (952) 938-8080
Fax: (952) 917-1717
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Content Page
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
RELATED PUBLICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
AdmonishmentS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
General Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Safe Working Distances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ix
STANDARDS CERTIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ix
LIST OF ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 General Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 System Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.3 High-Level View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.4 User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.5 Dimensions and Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.6 RAN Cabinet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.7 RAN Chassis and Electronic Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.8 Rectifier Shelf. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.9 Power Amplifier Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.10 Multiplexer System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.11 Circuit Breaker Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.12 Backup Batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.13 Antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2 STANDARD INSTALLATION PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.1 Installation Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.2 Unpacking and Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
1.6.1 Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.6.2 Fiber Optic Cable Entry. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.6.3 Antenna Cable Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.6.4 AC Power Wiring Entry and Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.6.5 Ventilation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.7.1 cPCI Power Supply Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.7.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.7.3 System Interface (STF2) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.7.4 Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.7.5 Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Optical Transceiver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.7.6 RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.7.7 RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.7.8 Fan Access Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.7.9 800 MHz Multicoupler (C/MCPLR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.7.10 1900 MHz Multicoupler (P/MCPLR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.8.1 Rectifier Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.8.2 Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page iii
Page 4

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Content Page
2.3 Required Materials and Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.4 Site Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.4.1 Space Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.4.2 Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.4.3 Antenna Requirement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.4.4 RF Cable Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.4.5 Fiber Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.5 Installing a RAN Cabinet on a Wooden Utility Pole . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.5.1 Site Requirements Unique to Pole Mounting Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.5.2 Pole Loading Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2.5.3 Installing the Cabinet Mounting Bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2.5.4 Mounting the RAN Cabinet on the Bracket. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.5.5 Installing the Rain Shields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.6 Installing a RAN Cabinet on a Concrete Pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.6.1 Pouring a Concrete Pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2.6.2 Mounting the Cabinet on a Concrete Pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2.6.3 Installing the Pedestal Enclosure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.7 Other Standard Installation Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
2.7.1 Installing a Solar Shield . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
2.7.2 Installing a Ground Wire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
2.7.3 Installing RF Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
2.7.3.1 Weatherproofing RF Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
2.7.3.2 Routing and Securing RF Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
2.7.4 Installing Pre-Connectorized Indoor/Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
2.7.5 Installing AC Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
2.7.6 Installing Backup Batteries (Extended or Glitch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.7.6.1 Battery Safety Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.7.6.2 Battery Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3 INSTALLING AN EXTENSION RAN (POLE MOUNT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
4 NON-STANDARD INSTALLATION PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4.1 Installing an Electronic Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4.1.1 Installing a Central Processing Unit (CPU) Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4.1.2 Installing a Systems Interface (STF2) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4.1.3 Installing a Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
4.1.4 Installing a Small Form-Factor Optical Transceiver (SFP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.1.5 Installing a RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.1.6 Installing a RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
4.2 Installing cPCI Chassis Air Baffles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
4.3 Installing a Rectifier Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
4.4 Installing a Compact PCI Power Supply (cPCI P/S) Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
4.5 Installing a Power Amplifier Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Page iv
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Content Page
5 MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
5.1 cPCI Fan Replacement Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
5.2 Cleaning or Replacing an Air Inlet Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
6 CUSTOMER INFORMATION AND ASSISTANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page v
Page 6

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Content Page
Page vi
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 7

ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual provides the following information:
• An overview of the Digivance NXD system;
• A description of the NXD system Radio Access Node (RAN);
• Installation procedures for the RAN;
• Maintenance procedures for the RAN;
• Product support information.
Procedures for installing and operating other NXD system components including the system
“Hub” and the EMS software that provides a user interface for the system, are available in other
ADC publications, listed under “Related Publications” below, and at appropriate points within
this manual.
RELATED PUBLICATIONS
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
Listed below are related manuals, their content, and their publication numbers. Copies of these
publications can be ordered by contacting the Technical Assistance Center at 1-800-366-3891,
extension 73476 (in U.S.A. or Canada) or 952-917-3476 (outside U.S.A. and Canada). All ADC
technical publications are available for downloading from the ADC web site at www.adc.com.
Title/Description ADCP Number
Digivance CXD/NXD Hub Installation and Maintenance Manual 75-193
Provides instructions for installing and operating the NXD system Hub.
Digivance CXD/NXD SNMP Agent and Fault Isolation User Guide 75-195
Describes how to troubleshoot the system using the parameters accessed
through the NXD system SNMP agents.
Digivance CXD/NXD Element Management System User Manual 75-199
Provides instructions for installing and using the Element Management System
(EMS) software for the NXD system.
Digivance NXD Multi-Band Distributed Antenna System Operation Manual 75-209
Provides instructions for turning up and operating NXD equipment.
2 in. O.D. Quad Cellular/PCS Omni-Directional Antenna Installation Manual 75-215
Provides instructions for installing an RF antenna for the NXD system
9 in. O.D. Quad Cellular/PCS Omni-Directional Antenna Installation Manual 75-221
Provides instructions for installing an RF antenna for the NXD system
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page vii
Page 8

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
ADMONISHMENTS
Important safety admonishments are used throughout this manual to warn of possible hazards to
persons or equipment. An admonishment identifies a possible hazard and then explains what
may happen if the hazard is not avoided. The admonishments — in the form of Dangers,
Warnings, and Cautions — must be followed at all times.
These warnings are flagged by use of the triangular alert icon (seen below), and are listed in
descending order of severity of injury or damage and likelihood of occurrence.
Danger: Danger is used to indicate the presence of a hazard that will cause severe personal
injury, death, or substantial property damage if the hazard is not avoided.
Warn ing: Warning is used to indicate the presence of a hazard that can cause severe personal
injury, death, or substantial property damage if the hazard is not avoided.
Caution: Caution is used to indicate the presence of a hazard that will or can cause minor
personal injury or property damage if the hazard is not avoided.
GENERAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
-
Warn ing: Wet conditions increase the potential for receiving an electrical shock when
installing or using electrically-powered equipment. To prevent electrical shock, never install or
use electrical equipment in a wet location or during a lightning storm.
Danger: This equipment uses a Class 1 Laser according to FDA/CDRH rules. Laser radiation
can seriously damage the retina of the eye. Do not look into the ends of any optical fiber. Do not
look directly into the optical transceiver of any digital unit or exposure to laser radiation may
result. An optical power meter should be used to verify active fibers. A protective cap or hood
MUST be immediately placed over any radiating transceiver or optical fiber connector to avoid
the potential of dangerous amounts of radiation exposure. This practice also prevents dirt
particles from entering the adapter or connector.
Caution: This system is a RF Transmitter and continuously emits RF energy. Maintain 3 foot
(91.4 cm) minimum clearance from the antenna while the system is operating. Wherever
possible, shut down the RAN before servicing the antenna.
Caution: Always allow sufficient fiber length to permit routing of patch cords and pigtails
without severe bends. Fiber optic patch cords or pigtails may be permanently damaged if bent
or curved to a radius of less than 2 inches (5.1 cm).
Caution: Exterior surfaces of the RAN may be hot. Use caution during servicing.
Page viii
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 9

SAFE WORKING DISTANCES
The Digivance NXD antenna, which is mounted on top of a pole, radiates radio frequency
energy.
For the occupational worker, safe working distance from the antenna depends on the workers
location with respect to the antenna and the number of wireless service providers being serviced
by that antenna.
Emission limits are from OET Bulletin 65 Edition 97-01, Table 1 A.
STANDARDS CERTIFICATION
FCC: The Digivance NXD complies with the applicable sections of Title 47 CFR Part 15, 22,
24 and 90.
The Digivance NXD Hub has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
Changes and modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer or registrant of this
equipment can void your authority to operate this equipment under Federal Communications
Commissions rules.
In order to maintain compliance with FCC regulations, shielded cables must be used with this
equipment. Operation with non-approved equipment or unshielded cables is likely to result in
interference to radio & television reception.
ETL: This equipment complies with ANSI/UL 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment.
This equipment provides the degree of protection specified by IP24 as defined in IEC
Publication 529. Ethernet signals are not for outside plant use.
FDA/CDRH: This equipment uses a Class 1 LASER according to
FDA/CDRH Rules. This
product conforms to all applicable standards of 21 CFR Part 1040.
IC: This equipment complies with the applicable sections of RSS-131. The term “IC:” before
the radio certification number only signifies that Industry Canada Technical Specifications
were met.
Wind Loading: The NXD RAN is able to withstand wind loads up to 150 mph.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page ix
Page 10

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
LIST OF ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
The acronyms and abbreviations used in this manual are detailed in the following list:
AC Alternating Current
ANT Multiband Antenna
BIM Base Station Interface Module
BTS Base Transceiver Station
C Centigrade
CDRH Center for Devices and Radiological Health
C/MCPLR Cellular SMR Multicoupler
CM Centimeter
cPCI CompactPCI
CPU Central Processing Unit
CXD Compact RAN
DAS Distributed Antenna System
dB(FS) decibals (Full Scale – digital reading)
DC Direct Current
Div Diversity
EMS Element Management System
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
F Fahrenheit
FDA U.S. Food and Drug Administration
FCC U.S. Federal Communications Commission
GPS Global Positioning System
IC Industry Canada
IN Inch
IP Internet Protocol
KG Kilogram
LED Light Emitting Diode
LSE Location Services Equipment
LV D Low Voltage Disconnect
MHz Mega Hertz
MTBF Mean Time Between Failure
MUX Multiplexer
Node Any CPU in the Digivance NXD system
NXD Digivance Neutral Host Product Line
OSP Outside Plant
PA Power Amplifier
PAA Power Amplifier Assembly
PC Personal Computer
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect bus
PIC PA Interface Controller
Page x
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 11

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
P/MCPLR PCS Multicoupler
RAN Radio Access Node
RDC RAN Down Converter
RDC2 RAN Down Converter Version 2
RF Radio Frequency
RUC RAN Up Converter
RUC2.X RAN Up Converter Version 2.X
RUC3 RAN Up Converter Version 3
SFP Small Form-Factor Pluggable Optical Transceiver
SIF Sonet Interface Module
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SONET Synchronous Optical Network
STF2 System Interface Module
UL Underwriters Laboratories
VA C Volts Alternating Current
VDC Volts Direct Current
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
WDM Wave Division Multiplex
WSP Wireless Service Provider
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page xi
Page 12

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007 • Preface
Page xii
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 13
1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
This section describes the Digivance Neutral Host (NXD) Radio Access Node (RAN).
1.1 General Description
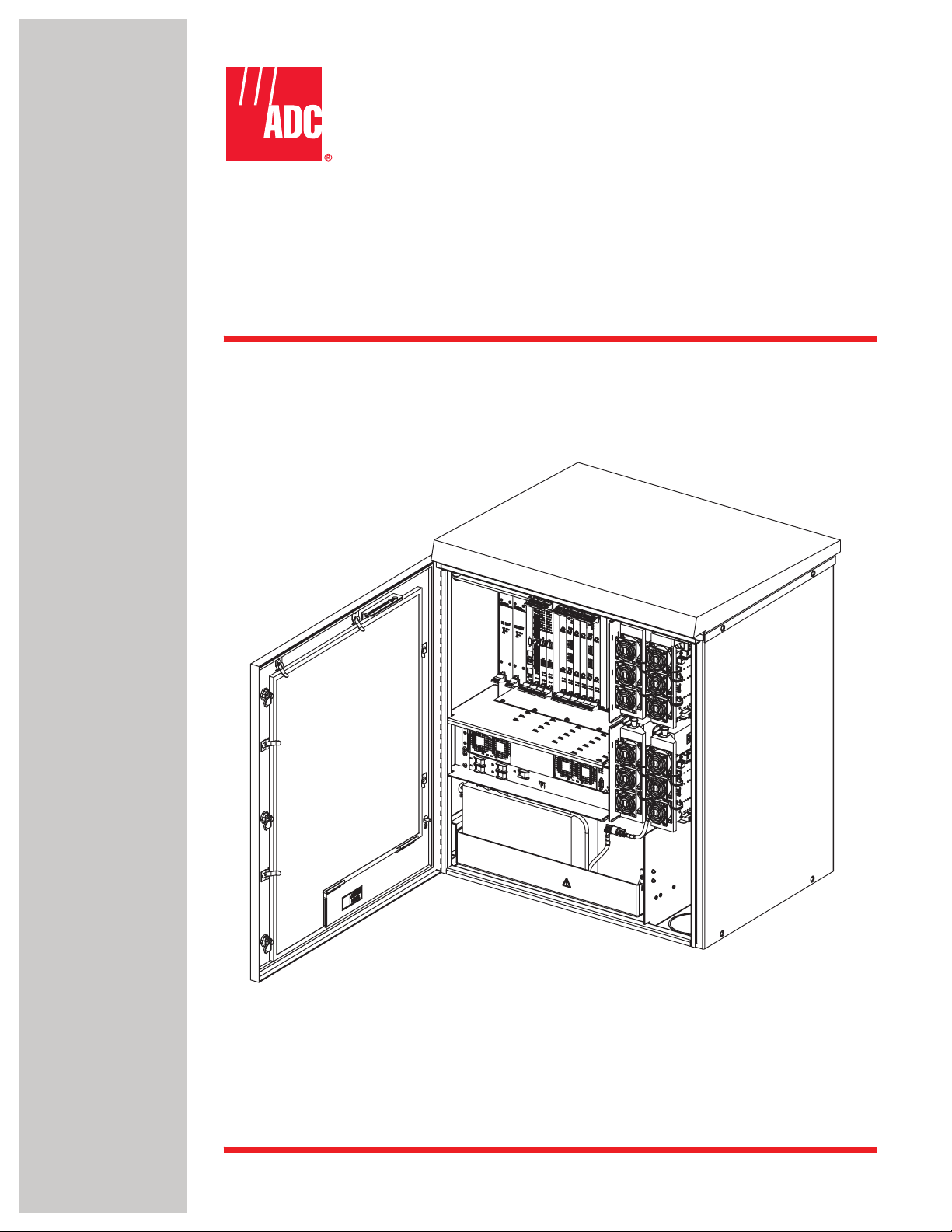
The RAN, shown in Figure 1, is the remote component in the Digivance NXD Multi-Band
Distributed Antenna System. The RAN is a pole-mounted or pad-mounted, weather-resistent
cabinet, housing electronic modules that operate on an internal cPCI backplane. Included are a
central processing unit, a system interface, an optical interface, optical to RF data converters,
RF multicouplers, and DC power supplies. The RAN also houses rectifiers, backup batteries,
power amplifiers, and optical wave division multiplexers. Optical and RF functions are both
required because the RAN exchanges data with the system Hub using an optical link and
exchanges data with wireless users using RF signals. Each RAN provides the system with an RF
antenna and can accommodate up to four bands (
RANs installed at the same location can accommodate up to eight bands using a common
antenna.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
PCS A-F, SMR A, Cell A”/A, or Cell B/B’). Dual
Figure 1. NXD RAN
21227-A
Page 1
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 14
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.2 System Function
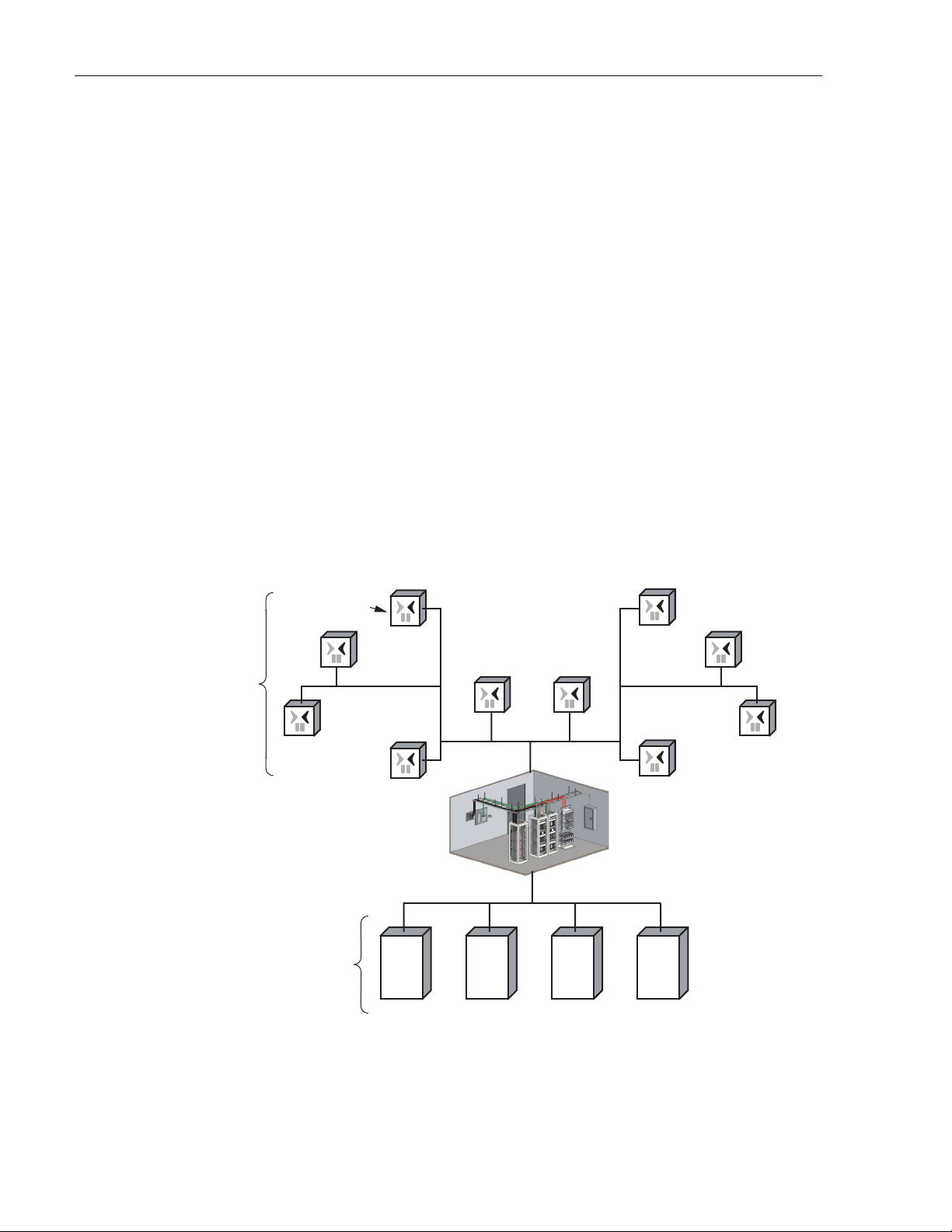
The NXD Distributed Antenna System (DAS), in which the RAN is the remote component, is a
multi-frequency, multi-protocol RF access network providing microcellular Cellular and PCS
coverage via a distributed RF access system. In a typical configuration, such as shown in
Figure 2, multiple RANs are connected to a central Hub where multiple Base Transceiver
Station (BTS) interfaces are located. Signals received at the Hub are distributed to the RANs in
digital form by way of a fiber optical link. Within the RANs, the signals are converted from
digital to RF format to be transmitted from the RAN antennas. Signals also travel in a reverse
direction, from the RANs to the Hub, with a reverse data conversion.
Physically, the DAS consists primarily of electronic modules located in the Hub and RANs. At
the Hub, these modules are mounted in an equipment rack typically housed in a common
telecommunications structure with the base station electronics for Wireless Service Providers
(WSPs), either in the same room or nearby. These modules include high power attenuators, base
station modules, a power distribution unit, an Ethernet hub, a Hub reference module, an RF
chassis, and one or more digital chassis. The RAN electronic modules, mounted in the RAN
cabinet, perform the remote system functions of optical to RF data conversion and RF access.
These modules are described in subsequent topics within this product description. Digivance
Element Management System (EMS) software, running on a computer located at the Hub,
provides a graphical user interface to monitor system performance.
RF
SIGNALS
Access
WIRELESS
SERVICE
PROVIDERS
(WSPs)
Radio
Node
Digital
Fiber
Distribution Hub - EMS Server,
located on Hub Master, monitors
Hub Nodes and RANs
BTS BTS BTS BTS
21013-A
Page 2
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Figure 2. System Function
Page 15
1.3 High-Level View
The RAN consists of the main components shown in a high-level view in Figure 3. These
components include:
• RAN Cabinet: exterior shell of the RAN containing cable connection points, ground
studs, and slots or shelves supporting other RAN components.
• RAN Chassis: standard Compact PCI (cPCI) shelf capable of housing 21 industry
standard cPCI circuit card modules. The modules are plugged into a common backplane
providing data bussing between them.
• Related Electronics: including rectifiers, Power Amplifier Assemblies (PAAs), batteries,
multiplexers, and a circuit breaker panel.
All components called out in the figure except for the multiplexers are separately installable in
the field. In most cases, however, the RAN is shipped with a basic set of components having
been ordered in advance by the customer and installed in the factory.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
RAN
CABINET
RAN CHASSIS
AND ELECTRONIC
MODULES
RELATED
ELECTRONICS:
RECTIFIERS
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
PANEL
BACKUP
BATTERIES
POWER
AMPLIFIER
ASSEMBLIES
(PAAs)
MULTIPLEXERS
21281-A
Figure 3. High Level View
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 3
Page 16
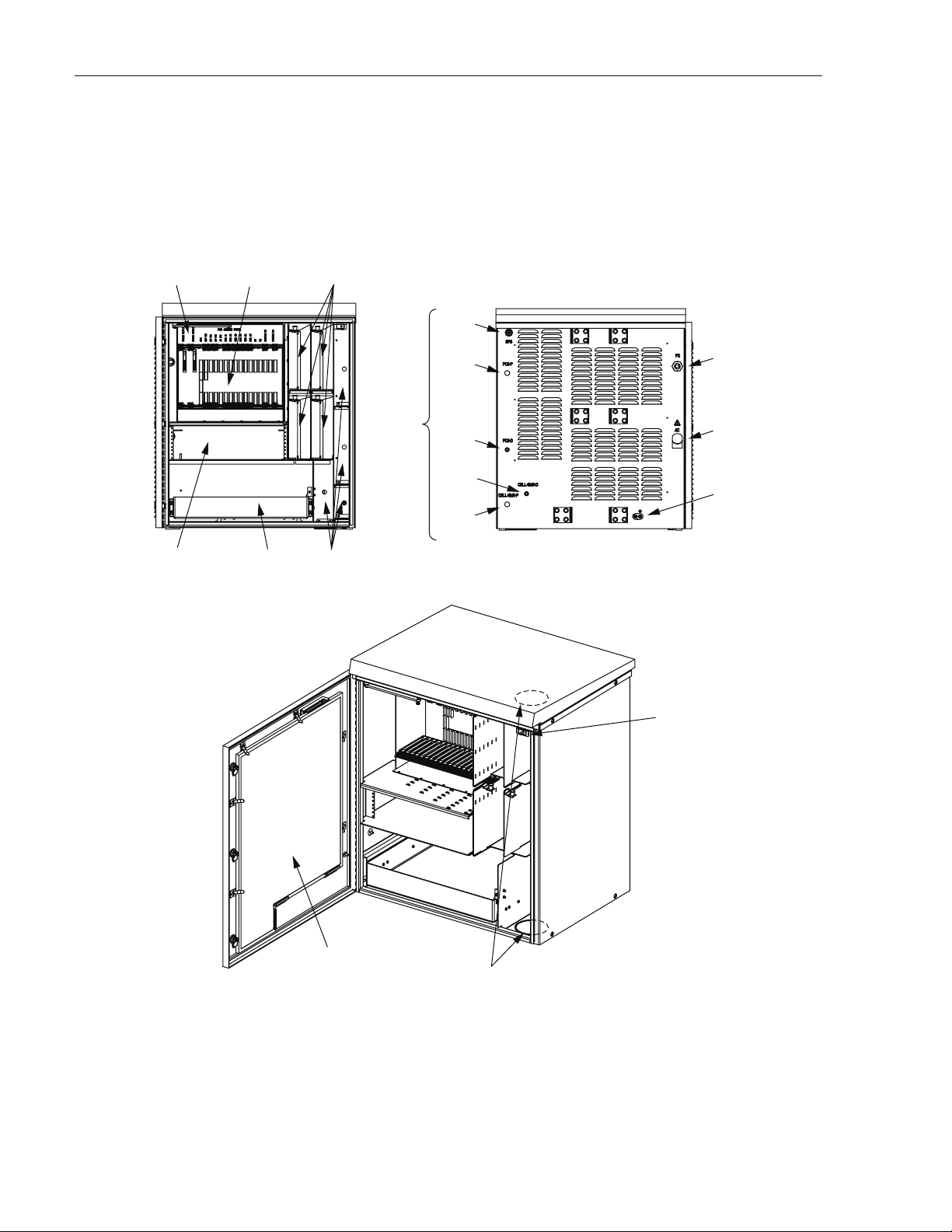
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.4 User Interface
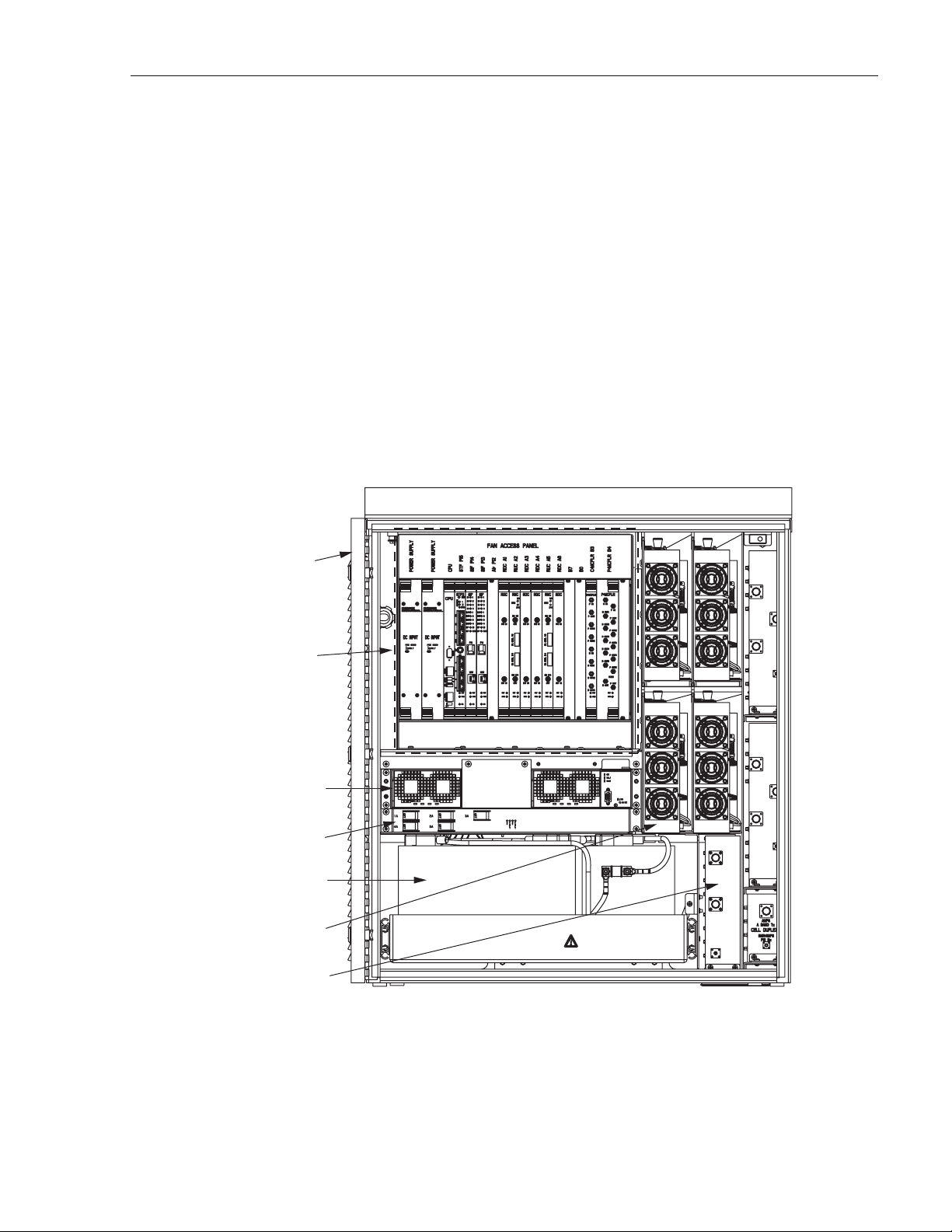
The RAN user interface consists of the various connectors, fittings, mounting slots, power
cords, switches, and indicators that are of relevance to the user in installation and operation
procedures. The user interface is shown in Figure 4 and described in Tabl e 1.
FAN ACCESS
PANEL (1)
RECTIFIER
COMPARTMENT
(UP TO 3)
ELECTRONIC
MODULES (21)
COMPARTMENT
(UP TO 4)
POWER AMPLIFIER
ASSEMBLIES (4)
RF
CABLES
MUXs BATTERY
GPS
PCS-P
PCS-D
CELL/
SMR-D
CELL/
SMR-P
FIBER
PORT
PRIME
POWER
PORT
EARTH
GROUND
STUDS
REAR FRONT
DOOR
ALARM
(1)
Page 4
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
AIR INLET
FILTER (1)
21290-A
KNOCK-OUTS FOR
2nd RAN WIRING FROM
RAN A TO RAN B
Figure 4. User Interface
Page 17
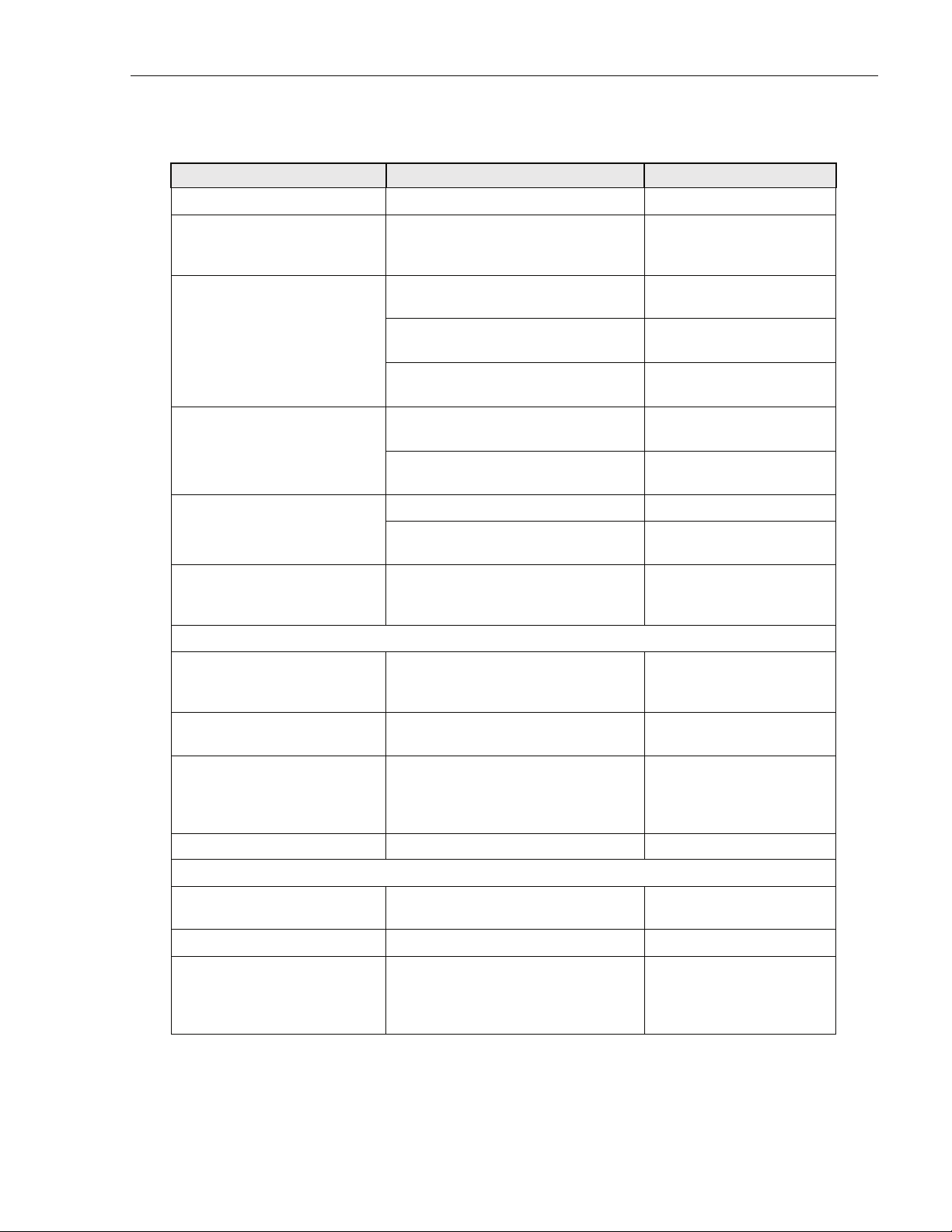
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 1. RAN Cabinet User Interface
COMPONENT WHY RELEVANT FOR MORE INFORMATION
Front View
Fan Access Panel Panel swings down providing access to
Section 1.7.8 on Page 20
internal fan compartment; fans can be
replaced as required
Electronic Modules Electronic modules have indicators
Section 1.7 on Page 10
monitored by the user
Electronic modules can be installed and
Section 4.1 on Page 57
replaced as required
Interconnection diagram summarizes
connections between modules
Power Amplifier Assemblies PAAs have indicators monitored by
Figure 40 on Page 58;
Figure 41 on Page 59
Section 1.9 on Page 25
user
PAAs can be installed or replaced as
Section 4.5 on Page 68
required
Rectifier Compartment Rectifiers have four unmarked LEDs Section 1.8 on Page 23
Rectifiers can be individually installed
Section 4.3 on Page 66
and replaced as required
Battery Compartment Batteries are packaged separately and
Section 2.7.6 on Page 50
installed in a standard installation; they
can be replaced as required
Rear Access
GPS, PCS-P, PCS-D,
CELL/SMR-D,
CELL/SMR-P
Connection points for RF cables connecting RAN with GPS antenna and RF
antenna.
Section 2.7.3 on Page 45;
Table 21 on page 47
Fiber Optic Cables Connection
Point
Prime Power Contact Contact point for power ingress. RAN
Connection point for fiber optic cable
from Hub
Section 2.7.4 on Page 47
Section 2.7.5 on Page 49
requires 240 VAC, single phase, 20
Amps service, typically routed from a
pole- or pad-mounted junction box
Earth Ground Studs Connection point for ground wires Section 2.7.2 on Page 44
Oblique View
Air Inlet Filter Filters are replaced per maintenance
Section 5.2 on Page 70
schedule
Door Alarm Replaceable switch
Knock-Outs for 2nd RAN Wiring from RAN A to RAN B
When two RANs are installed at the
same location, an omnibus cable is
Section 3 on Page 54
routed from RAN A to RAN B through
these knockout holes
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 5
Page 18
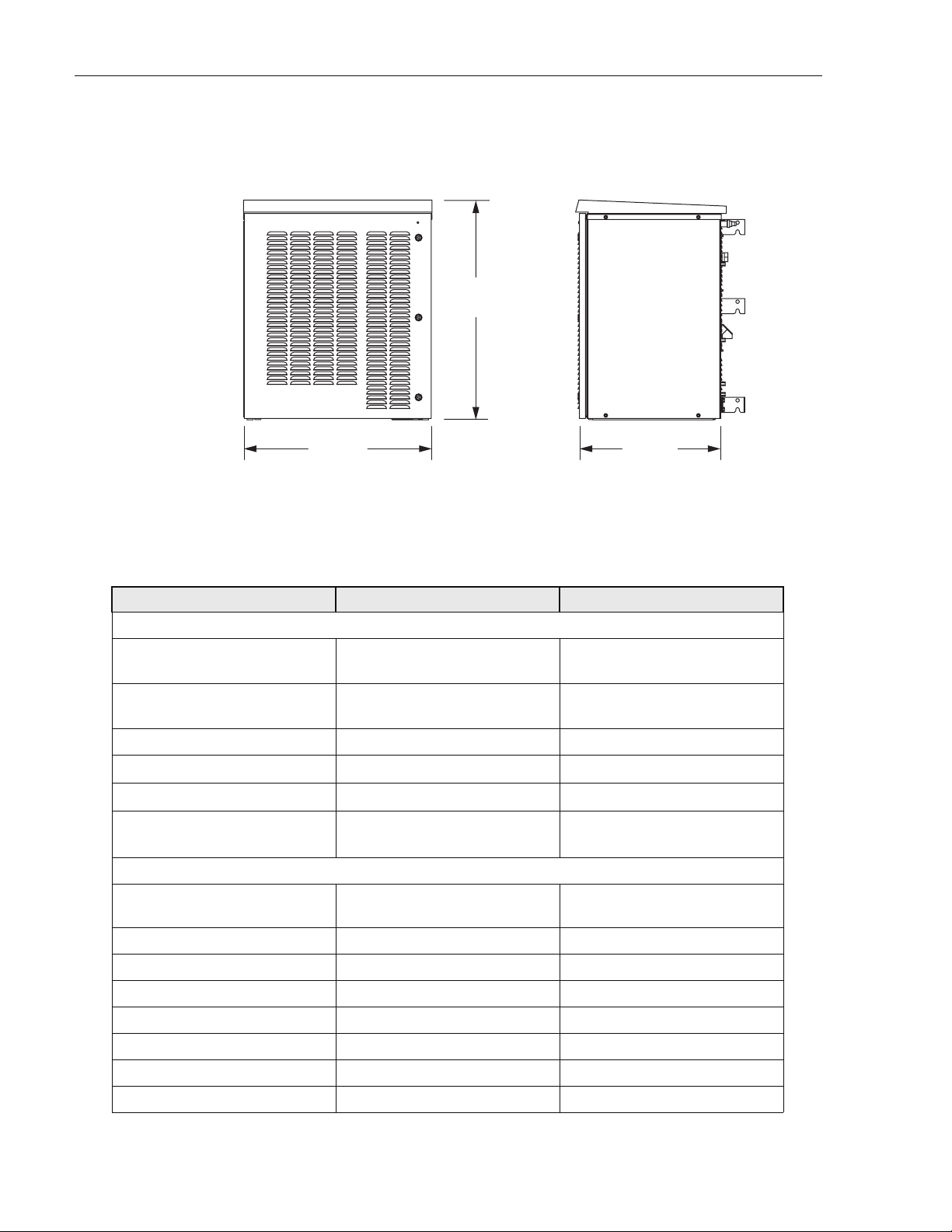
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.5 Dimensions and Specifications
FRONT SIDE
36.5 IN.
(92.7 CM)
31.0 IN.
(78.7 CM)
Figure 5. NXD RAN Dimensions
Table 2. RAN Specifications
ITEM SPECIFICATION COMMENT
Physical and Mechanical
Dimensions (HxWxD) 36.5 x 31.0 x 24.0 inches
See also Figure 5
(92.7 x 78.7 x 60.1 cm)
Weight
with extended batteries (4)
300 lbs. (136.4 kg)
625 lbs. (284.1 kg)
RAN without batteries
Total RAN + 4 batteries
Color Putty white
Bands per box
Boxes per RAN site
RF connections
Up to 4
Up to 2 RANs
RAN cabinet has
5 Type N plugs
Cable type: CommScope PN
540ANM or equivalent
Environmental and Thermal
24.0 IN.
(60.1 CM)
21228-A
Box thermal management External air Variable speed fans (PIC/PA
Assembly and cPCI)
Operating temperature -40 to +50 degrees C -40 to 122 degrees F
Cold-start temperature -20 to +50 degrees C -4 to 122 degrees F
Storage temperature -40 to +85 degrees C -40 to 185 degrees F
Internal air temperature 0 to 60 degrees C 32 to 140 degrees F
Weather resistance NEMA-3R
Operational humidity 95%
Acoustic emissions 63 dBA
Page 6
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 19
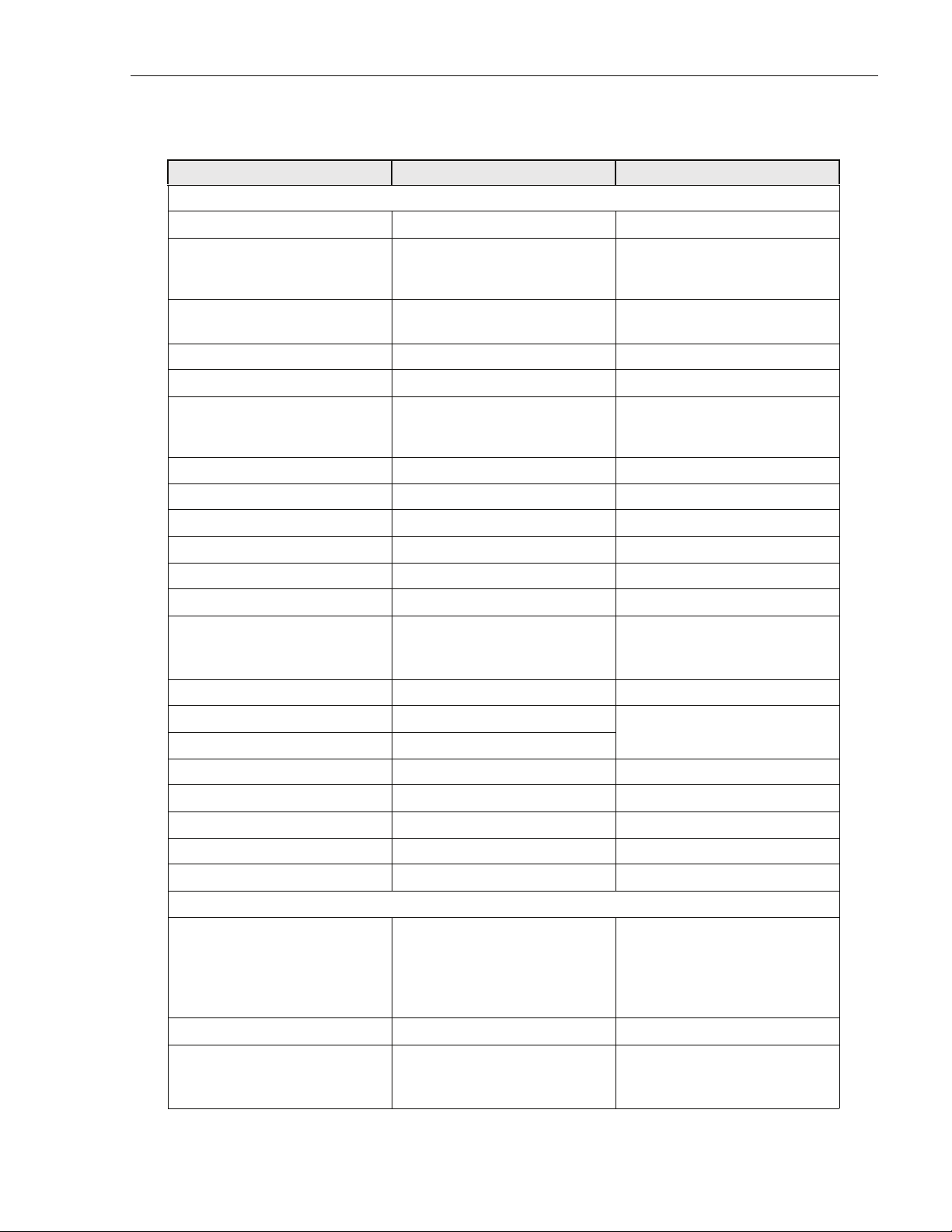
Table 2. RAN Specifications
ITEM SPECIFICATION COMMENT
Power
AC power ingress 240 VAC, 20 Amps, single phase
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Battery backup options
extended
glitch
120 minutes
5 minutes
-48 volts
@25 degrees C (degrees F)
for four bands
RAN box power use 2700 Watts Max.
16 Amps Max.
cPCI rack power -48 VDC
Optical
Fiber cable ingress Nylon connector accommodates
cable diameters in range 0.38-
For larger cable sizes, refer to the
note in Section 1.6.2 on Page 9.
0.50 inches (0.97-1.27 cm).
Fiber type Corning SMF-28 or equivalent
Optical connectors LC Standard on SFP transceivers
Insertion loss 0.2 dB Typical, 0.4 dB Max.
Number of fibers required 1-4 fiber runs per RAN
Fiber configuration Star (point to point) or ring Ran ring limited to 3 SIFs
Fiber data link protocol OC-48
Wavelengths per fiber
with WDM option
with CWDM option
1 (1310 nm)
2 (1310/1550)
8 (1470-1610)
Without WDM/CWDM option
20 nm increments (ITU-GRID)
Optical transceiver type SFP Dual LC connector
Optical Tx power -3 dBm Max, -10 dBm Min. Finistar FTRJ-1320-1
Optical Rx sensitivity -22 dBm Typical, -18 dBm Max.
(or equivalent)
Optical link margin 2 dB Estimated
Optical link loss 6 dB Estimated
Optical Rx saturation level -3 dBm Min. Max. operational power
Optical Rx damage level -3 dBm Min. Max survivable power
Optical safety class 1 ANSI Z 136.2
RF
Tuning frequency
PCS band
Cellular band
SMR 800 band
SMR 900 band
Receive Path
1850-1910 MHz
824-849 MHz
806-824 MHz
896-901 MHz
Transmit Path
1930-1990 MHz
869-894 MHz
851-869 MHz
935-940 MHz
Instantaneous bandwidth 15 MHz
Receiver noise figure
PCS band
Cellular band
6 dB
5 dB
Measured at Hub output connector (BIM, RxP) without BTS at 10
dB gain and a single RAN
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 7
Page 20
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 2. RAN Specifications
ITEM SPECIFICATION COMMENT
Input IP3 -21 dBm Two tone tests at -56 dBm
Received signals
In band
Out of band +/- 8.5 MHz
Out of band +11/-13 MHz
Out of band +13/-16 MHz
-41 dBm
-3 dB
-43 dB
-83 dB
RDC capability (at cabinet input)
A/D clip level, single RF channel
Selectivity
Selectivity
Selectivity
(function of SAW filter)
Automatic gain control
Detector integration time
Attack time
Decay time
Gain control range
Gain in series with BTS -10 to +10 dB Lower limit for simulcast with a
Gain parallel to BTS 0 to +30 dB Allows injection after BTS
Gain stability +/- 2dB Over temperature, frequency, and
System Bandwidth
Forward Path
Reverse Path
Impedance 50 ohm
Output Power
Cellular/SMR 10 Watt MCPA
PCS 20 Watt MCPA
Gain resolution 1 dB
Gain measurement Configured at startup using fac-
10 usec
0 usec
0 usec
30 dB
15 MHz block increments
15 MHz block increments
6.5 Watts (+38 dBm) composite
12.5 Watts (+41 dBm) composite
Activated if A/D clips, changes
gain of A/D and gain in digits.
Design ensures analog gain and
digital gain change will be timed
correctly. 15 dB noise figure at
-14 dB gain
host tower site, the max reduces
effect of cascaded noise figure
amplifiers
aging valid for input signals
below AGC threshold
At antenna port
At antenna port
tory calibration of modules and
user data
Note: The Manufacturer’s rated output power of this equipment is for single carrier
operation. For situations when multiple carrier signals are present, the rating would have
to be reduced by 3.5 dB, especially where the output signal is re-radiated and cause
interference to adjacent band users. The power reduction is to be by means of input power
or gain reduction and not by an attenuator at the output of the device.
1.6 RAN Cabinet
The RAN cabinet is a NEMA-3R enclosure designed to protect its electronic components from
weather and human tampering. The cabinet is weather-tight but contact with salt-air mist should
be avoided as it may decrease the mean time between failure of some components. The cabinet
has ventilation openings to allow entry of cool air and escape of hot air. The cabinet provides
Page 8
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 21

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
termination points for the coaxial antenna cable, fiber optic cable, ground cable, and AC cable.
The cabinet has inbuilt AC power surge protection and limited storage for fiber optic cables.
1.6.1 Mounting
The RAN cabinet may be mounted on a wood pole or on a concrete pad. Mounting bracket kits
(available from ADC) are required for each type of installation.
1.6.2 Fiber Optic Cable Entry
A nylon connector is provided on the rear of the RAN cabinet for routing a fiber optic cable into
the cabinet. The cord connector provides cable strain relief and a watertight seal at the fiber
optic cable entry point. As the connector nut is tightened, a soft neoprene bushing compresses to
tightly grip the cable without applying excessive force to the fibers. The connector
accommodates cables of a diameter in the range .38 to .50 inches (.97 to 1.27 cm).
Note: If the installer has a larger cable, the manufacturer (Hubbell Inc.) makes bushings
that fit this connector in the following size ranges: .500-.625, .625-.750, .750-.875, .875-
1.00, 1.00-1.125 inches.
In a typical installation, the connectorized end of a multi-fiber OSP cable is routed into the
cabinet through the cord connector and the individual fibers are connected to the optical
transceiver on the Synchronous Interface Card (SIF). Excess slack is stored inside the cabinet.
The stub end of the cable is routed to an external splice enclosure (not provided) for splicing to
the outside plant fiber optic cable.
1.6.3 Antenna Cable Connections
Five N-type plugs are provided on the rear of the RAN cabinet for connecting the antenna
coaxial cables. On the inside of the cabinet, coaxial jumper cables (included with the cabinet)
are used for connecting to the antenna port on the appropriate multiplexer.
1.6.4 AC Power Wiring Entry and Grounding
The NXD RAN uses 240 VAC power. A one inch (2.54 cm), 90 degree rigid elbow conduit
fitting is provided on the rear of the cabinet. The conduit should be routed to an external
junction box (not provided). It is suggested that an external AC outlet (not provided) be installed
near the cabinet to power test equipment and power tools. The AC source should supply 50/60
Hz, single-phase power through a circuit breaker rated at 20 Amps.
1.6.5 Ventilation
Ventilation openings are provided in the front door of the RAN cabinet to permit entry of air for
cooling. A filter removes dirt particles so that only clean air enters the cabinet. The heated air
exits the cabinet through the rear side. The four PAAs are each equipped with three cooling fans
that pull air through the module and exhaust it to the rear of the cabinet. A fan assembly at the
top of the RAN chassis forces the air out the rear side of the cabinet.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 9
Page 22
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
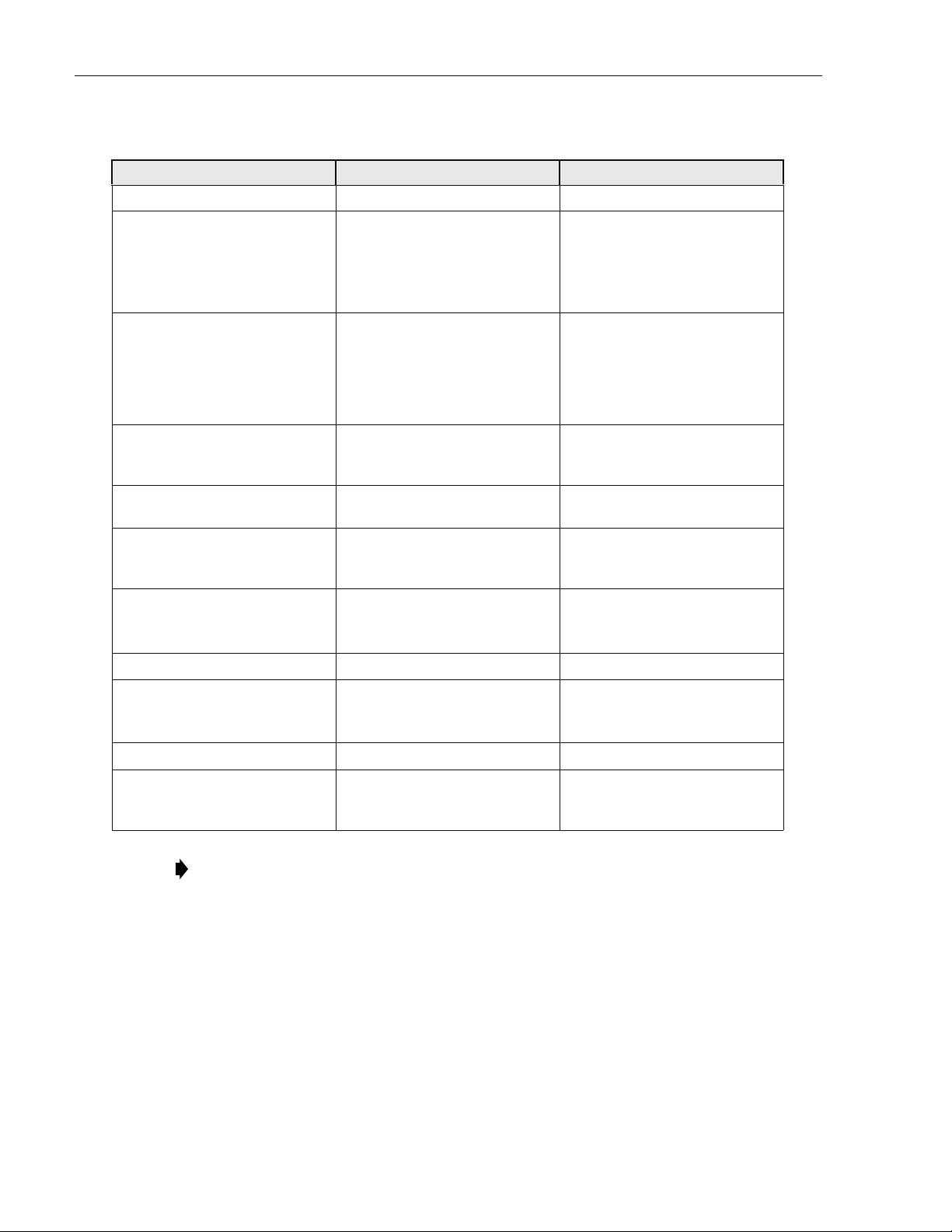
1.7 RAN Chassis and Electronic Modules
The RAN chassis, shown in Figure 6, is a standard Compact PCI (cPCI) shelf capable of
housing 21 industry standard cPCI circuit cards (called “electronic modules” in this manual).
The backplane supports the basic cPCI functions and it has been extended to allow the routing
TM
of DIF
cooling fans within the Fan Access Panel on the top of the chassis. Tab le 3 identifies the
electronic modules using the callout reference numbers from Figure 6.
, reference clocks and I2C signals between I2C modules. The RAN chassis also houses
123 67 891045
REF # MODULE NAME FOR DETAILS REFER TO
1 cPCI Power Supplies Section 1.7.1 on Page 12
2 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Section 1.7.2 on Page 13
3 System Interface (STF2) Section 1.7.3 on Page 14
4 Synchronous Interface (SIF) Section 1.7.4 on Page 15
5 Small Form-Factor Pluggable Optical Transceiver (SFP) Section 1.7.5 on Page 17
Page 10
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
21282-A
Figure 6. RAN Chassis
Table 3. RAN Chassis Electronic Modules
Page 23
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
U
Table 3. RAN Chassis Electronic Modules
REF # MODULE NAME FOR DETAILS REFER TO
6 RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Section 1.7.6 on Page 17
7 RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Section 1.7.7 on Page 19
8 800 MHz Multi-Coupler Section 1.7.9 on Page 20
9 1900 MHz Multi-Coupler Section 1.7.10 on Page 22
10 Fan Access Panel Section 1.7.8 on Page 20
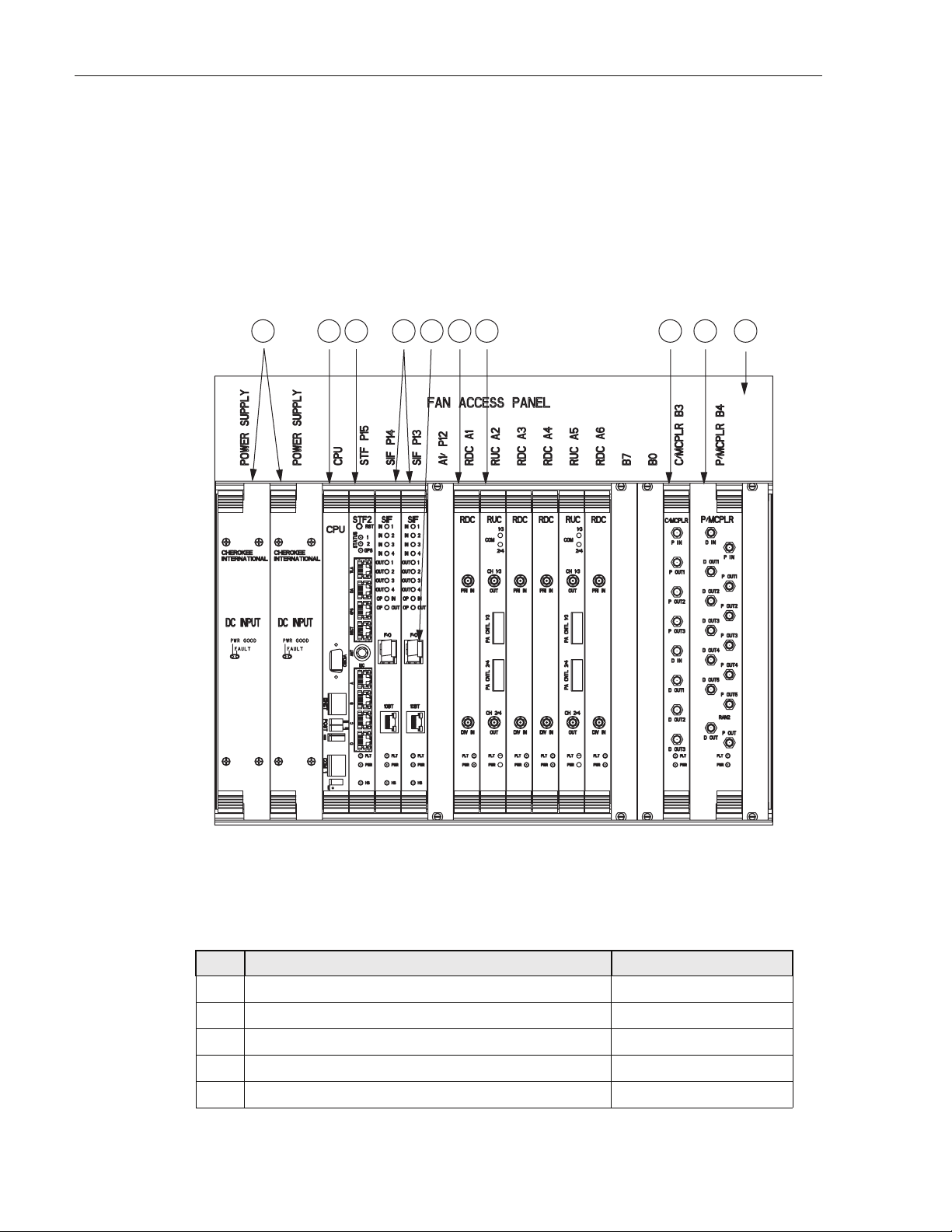
Figure 7 is a schematic showing the data flow in the RAN chassis, as represented by the PCS-A
band. As shown, data flows in two directions, from the Hub through the RAN to the antenna,
and from the antenna through the RAN back to the Hub. In each direction, data conversion
occurs, with optical data “upconverted” to RF data in the up direction in the schematic, and RF
data “downconverted” to optical data in the down direction. In an up direction, the RUC module
converts Digitized Intermediate Frequency (DIF) data into PCS, Cellular, and SMR frequency
RF bands. The RF signals are amplified and then transmitted from the RF antenna. In the down
direction, the RDC module converts PCS, Cellular, and SMR frequency bands into DIF data.
The overall series of events is managed by the CPU using an Ethernet connection to the chassis
backplane.
RAN
MB
ANT
1900-P 1900-D
ANT
PCS QUADPLEXER
AB FRX
MCPA
RF
RUC RDC
DIF
SIF
Fiber Fiber
ANT
PCS QUADPLEXER
DECRX
Pri Div
1900
MUL
66
Pri Div
DIF
DIF
Ethernet
RAN = Radio Access Node
DIF = Digital Intermediate
Frequency
SIF = Synchronous Interface
RUC = RAN Up Converter
MCPA = Munti-Carrier Power
Amplifier
MB ANT = Multi Band Antenna
MUL = Multi-Coupler
RDC = RAN Down Converter
CPU
21777-A
B
H
Figure 7. RAN Chassis Schematic
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 11
Page 24
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
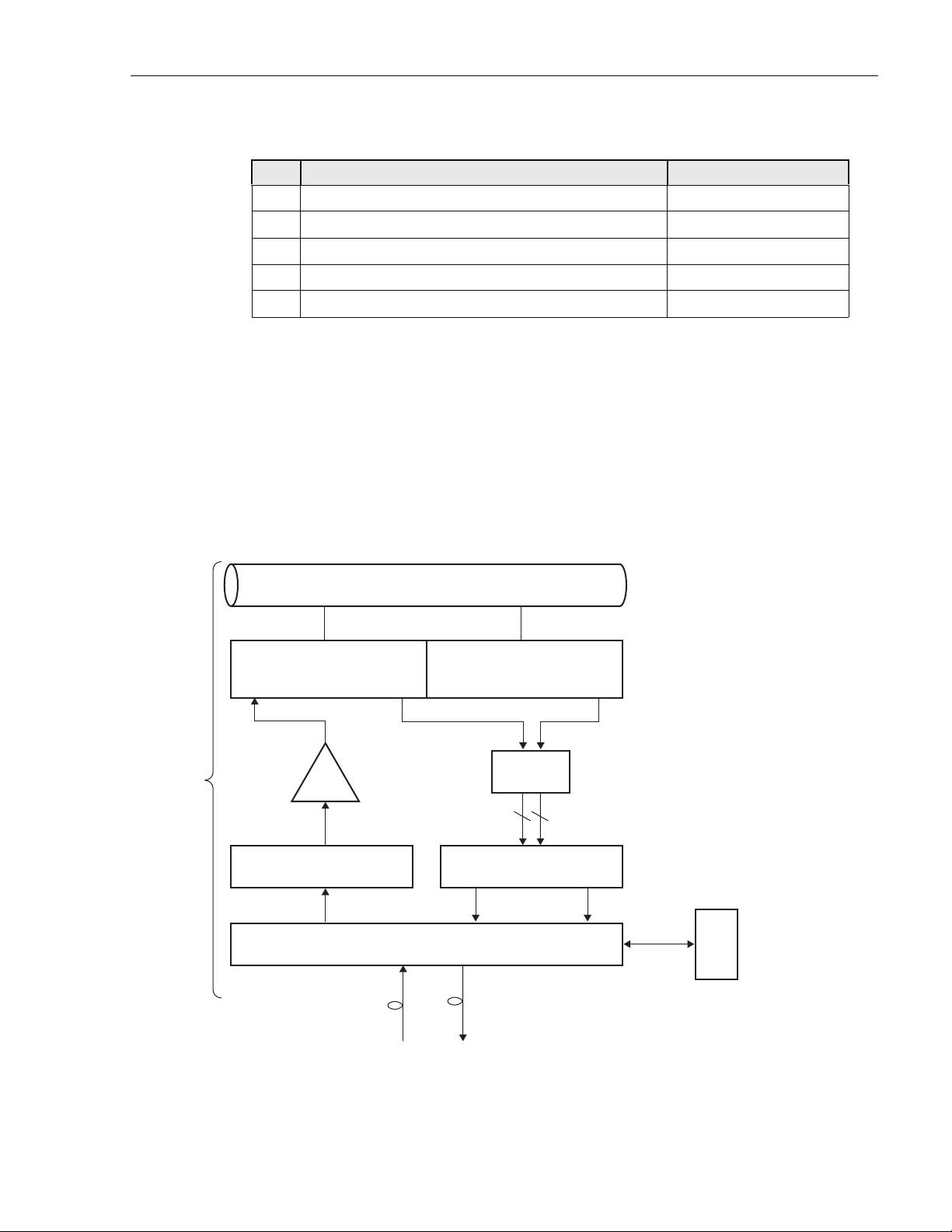
1.7.1 cPCI Power Supply Modules
The Compact PCI (cPCI) Power Supply Modules provide +/-12V, 5V, and 3.3V DC power to
the cPCI backplane for use by the cPCI electronic modules. Each RAN requires one power
supply module. Two modules can be used to provide redundancy if desired. These modules are
hot swappable. Figure 8 shows the cPCI Power Supply Module faceplate. Table 4 describes the
faceplate components called out in the figure.
POWER
1
GOOD LED
FAULT
2
LED
21240-A
Figure 8. cPCI Power Supply Module Faceplate
CPU
Table 4. cPCI Power Supply Module Faceplate
Ref #
DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 PWR GOOD Single-color LED
(green)
2 FAULT Single-color LED
(red)
Power Good. Turns green when module has
power
Fault. Turns red when module has
insufficient power to perform its function
Page 12
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 25
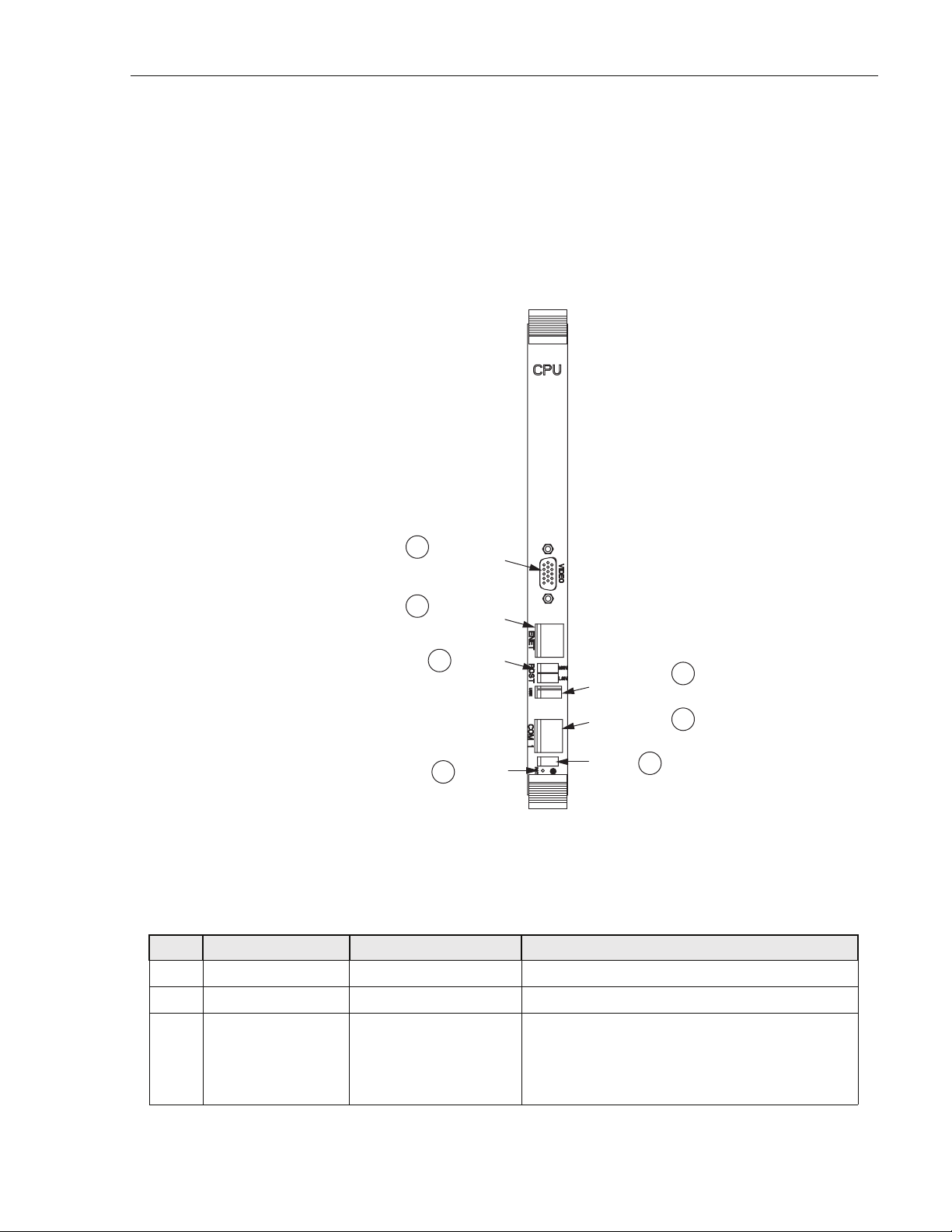
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.7.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Module
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Module is a cPCI-based, single-board x86 computer with
disk running on a Linux operating system. Each RAN chassis has one CPU module. The CPU
runs a process management program that manages all RAN hardware including RF and digital
equipment. The program also manages RF signal gain and monitors signal presence and quality.
Figure 9 shows the CPU module faceplate. Tab le 5 describes the faceplate components called
out in the figure.
VIDEO
7
CONNECTOR
ETHERNET
6
CONNECTOR
ACTICITY
5
4
LEDs
RESET
BUTTON
21251-A
UNIVERSAL
SERIAL BUS
CONNECTOR
COM 1
CONNECTOR
STATUS
LEDs
3
1
2
Figure 9. CPU Module Faceplate
CPU
Table 5. CPU Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 USB1 USB connector Front panel input/output for USB connectivity
2 COM 1 RJ-11C connector Front panel interface for COM1
3 (Unmarked) Status LEDs LED 1 is POST (red on start-up, turns green on
successful completion of start-up self test); LED 2
& 3 are undefined; LED 4 (blinking green) indicates
disk or flash memory activitity
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 13
Page 26
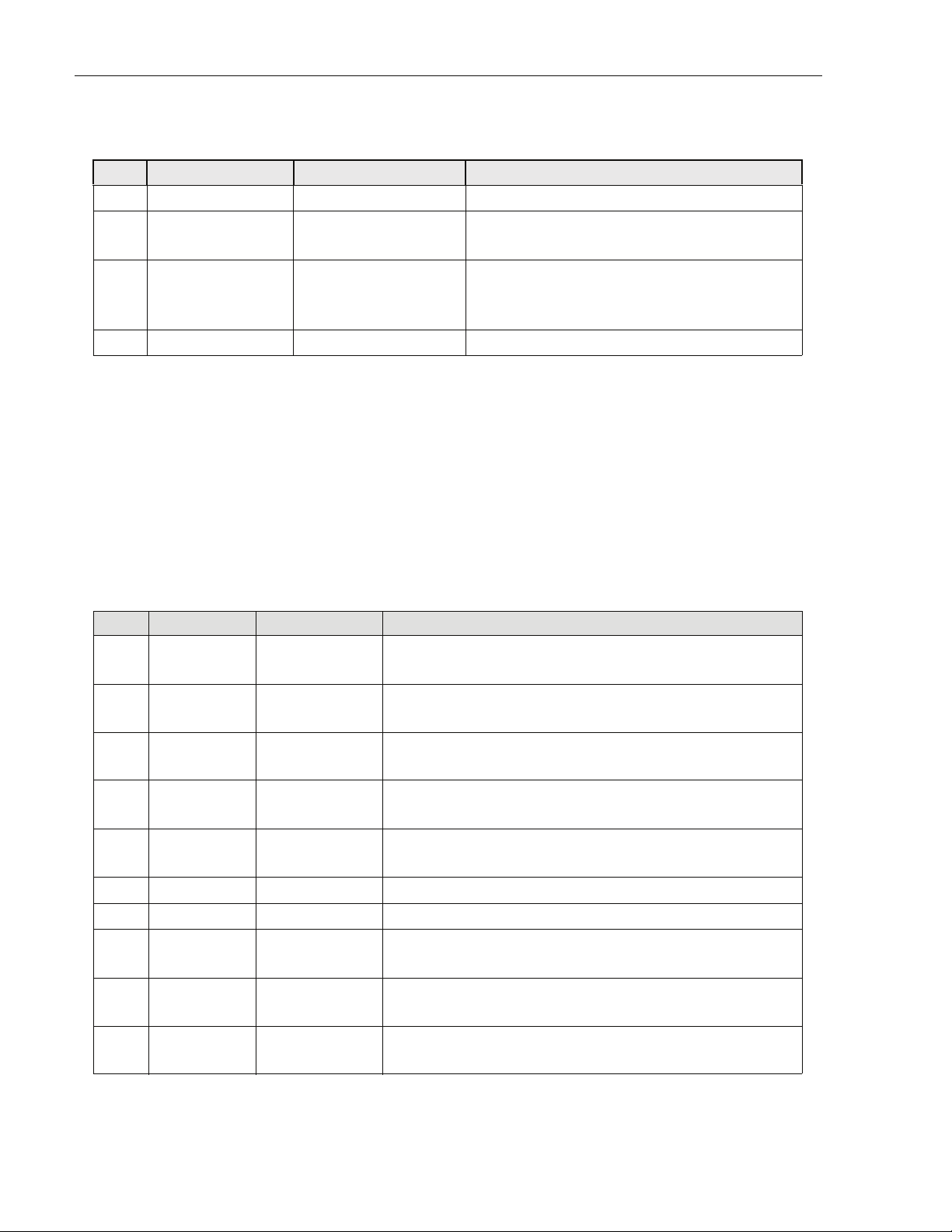
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 5. CPU Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
4 RST Recessed switch Reset. Used to manually reset the CPU
5 POST Single-color LEDs
(yellow)
Post. Top four LEDs give status of CPU during initial
boot process; bottom four give board operation status
6 ENET RJ-45 connector with
single-color LEDs (green
and yellow)
Ethernet. 10 BaseT. Connects to RJ-45 connector on
SIF module (10BT port) using cable 1001478P001.
Connection status (green) and 100 BT (yellow)
7 VIDEO 15-PIN VGA connector Video. Not used by Digivance system
1.7.3 System Interface (STF2) Module
The System Interface (STF2) Module is a cPCI electronic module that provides the CPU and
other electronic modules with the ability to communicate with one another using the four I2C
buses on the cPCI backplane. One STF2 is used per RAN. The STF2 also has the GPS antenna
input port located in the center of the module faceplate. STF2 modules are specified according
to the number of qualifying communications devices being utilized. Tab le 6 describes the
module faceplate components. Figure 10 shows the location of the faceplate components.
Table 6. System Interface Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 RST Recessed switch Reset. Used to halt operation of the CPU operating system. A
power ON reset is required to restart the CPU
2 STATUS 1 Single-color LED
(yellow)
3 STATUS 2 Single-color LED
(yellow)
Reserved for future use. Indicator turns yellow when the CPU is
not installed or has malfunctioned
Reserved for future use. Indicator turns yellow when the CPU is
not installed or has malfunctioned
4 STATUS GPS Single-color LED
(green)
Indicator showing that 1PPS signal is available. Led toggles once
per second (RAN only)
5 DA RJ-45 connector Door Alarm. Input using cable 1001474P001; small LED on this
connector lights (red) when door is open
6 GPS RJ-45 connector Not used
7 RECT RJ-45 connector Rectifier. Communications to rectifier using cable 1001476P001
8 (Unmarked) Single-color LED
(red)
9 (Unmarked) Single-color LED
(green)
10 FLT Single-color LED
(red)
Page 14
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
I2C Error LEDs. One on each I2C RJ-45 connector. Indicator turns
red when there is no response on port
I2C Comm LEDs. One on each I2C RJ-45 connector. Indicator
turns green when an I2C message sent on the port
Fault. Indicator turns red when module has failed or upon startup
until the module has completed initialization
Page 27

Table 6. System Interface Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
11 HS Single-color LED
Not used
(blue)
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
12 PWR Single-color LED
Power. Indicator turns green when module has power
(green)
13 I2C A-D RJ-45 connectors I2C (Bus). Connectors to I2C buses
14 ANT SMA connector Antenna. Input for GPS antenna signal
15 TLA RJ-45 connector Tower Light Alarm (unused)
RESET
1
TOWER LIGHT
15
ALARM CONNECTOR
GPS ANTENNA
CONNECTOR
14
(RAN ONLY)
SWITCH
GPS
4
LED
STATUS
LED 1
STATUS
LED 2
DOOR ALARM
CONNECTOR
GPS COMMS
CONNECTOR
CONNECTOR
I2C ERROR LED
2
3
RECTIFIER
COMMS
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
CONNECTOR
POWER LED
12
I2C COMM LED
I2C
FAULT LED
HOT SWAP LED
21253-A
n
Figure 10. System Interface Module Faceplate
1.7.4 Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module
The Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module provides the optical interface between the Hub and
the RAN. This interface provides for exchange of digitized RF signal information and 10BaseT
Ethernet command and control information. Each RAN can have up to two SIFs, each handling
two bands with diversity receive paths.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 15
Page 28

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
The SIF module is equipped with a small form-factor pluggable optical transceiver (SFP)
module. (For more information on the SFP, see Section 1.7.5.) Figure 11 shows the SIF module
faceplate. Ta ble 7 describes the faceplate components.
OPTICAL
9
INPUT LED
OPTICAL
8
OUTPUT LED
SFP FIBER
7
CONNECTOR
6
5
OPTIC
FAU LT
LED
POWER
LED
DIF INPUT
LED 1-4
DIF OUTPUT
LED 1-4
ETHERNET
CONNECTOR
HOT SWAP
LED
21238-A
1
2
3
4
Figure 11. Synchronous Interface Module Faceplate
Table 7. Synchronous Interface Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 IN 1-4 Tri-color LED
(green/yellow/red)
In. Indicates if DIF input is not enabled (off), good (green),
degraded (yellow), clock issue (blinking), or no DIF tone
lock or unused channel (red)
2 OUT 1-4 Tri-color LED
(green/yellow/red)
Out. Indicates if DIF output is not enabled (off), good
(green), degraded (yellow), clock issue (blinking), or bad
data on output of unused channel (red)
3 10BT RJ-45 connector 10BaseT (Ethernet). Communications between SIF and CPU
using cable 1001478P001
4 HS Blue LED Not used
5 PWR Green LED Power. Lights when module has power
6 FLT Red LED Fault. Lights when module has failed and during start-up
until module is initialized
Page 16
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 29

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 7. Synchronous Interface Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7 F/O Dual-LC connectors Fiber/Optics. Optics connector on SFP optical transceiver
8 OP IN Tri-color LED
(green/yellow/red)
9 OP OUT Tri-color LED
(green/yellow/red)
Optical In. Indicates input status of the SFP interface: not
enabled (off), good (green), degraded (yellow), or bad output
signals (red)
Optical Out. Indicates output status of SFP interface: not
enabled (off), good (green), degraded (yellow), or bad framing, bad parity, no signal, or no signal lock (red)
1.7.5 Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Optical Transceiver
The Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Optical Transceiver, located on the SIF module and
shown in Figure 12, provides the optical interface between the Hub equipment and the RAN
hardware. The SFP has a laser transmitter and an optical receive detector.
The Digivance NXD system uses industry standard SFP optics which offer a number of
configuration options depending on the requirements of the project. The SFP modules are
available separately and may or may not be installed in the SIF depending on the configuration
ordered. The SFP module is specified as up to two per RAN and is able to support two bands
with receive diversity.
The standard SFP module has an optical budget of 9 dB. The SFP module is factory and field
replaceable with optical transceivers having extended optical budgets up to 26 dB or Coarse
Wave-Division Multiplexing (CWDM) optical wavelengths.
21316-A
Figure 12. Small Form-Factor Optical Transceiver
1.7.6 RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Module
The RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Module is a cPCI electronic module housing a
dual-diversity wideband RF receiver. This module takes PCS, Cellular, SMR A, and SMR B
signals from a primary and secondary antenna (via the appropriate multicoupler) and converts
the signals to Digitized Intermediate Frequency (DIF).
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 17
Page 30

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
This module also provides a CW test tone for use in reverse continuity testing. The RF signals
are input into the module by way of coax cables terminated with SMA connectors on the
faceplate (at the ports labeled PRI IN and DIV IN). Figure 13 shows the module faceplate.
Tab le 8 describes the module faceplate components called out in the figure.
PRIMARY
DIVERSITY
FAULT
LED
POWER
LED
21236-A
1
IN
IN
2
3
4
Figure 13. RAN Down Converter Module Faceplate
Table 8. RAN Down Converter Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 PRI IN SMA connector Primary In. Receives RF primary output from either C/PMC-
PLR or P/MCPLR module. Connection is made using cable
1955000P081
2 DIV IN SMA connector Diversity In. Receives RF diversity output from either C/
PMCPLR or P/MCPLR module. Connection is made using
cable 1955000P081
3 FLT Red LED Fault. Lights when module has failed and during start-up until
module has initialized; blinks after module receives a system
clock and is awaiting initialization
4 PWR Green LED Power. Lights when module has power
Page 18
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 31

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.7.7 RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Module
The RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Module is a cPCI electronic module that takes
Digitized Intermediate Frequency (DIF) signals from a DIF signal generated by the SIF and
converts the signals to RF (PCS, Cellular, SMR A, and SMR B frequency bands). Each module
supports two simultaneous bands via wideband outputs. The RUC also provides clocking for its
neighboring RDC. For module faceplate and callouts, see Figure 14 and Tab le 9 .
1
8
CHANNEL
1/3 OUT
CHANNEL
2/4 OUT
COM 1/3
COM 2/4
PA CNTL 1/3
PA CNTL 2/4
FAULT LED
POWER LED
21234-A
2
3
4
5
6
7
Figure 14. RAN Up Converter Module Faceplate
Table 9. RAN Up Converter Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 CH 1/3 OUT SMA connector Channel 1/3 Out*
2 COM 1/3 Yellow LED COM Port 1/3. Turns yellow when DIF is locked to SIF channel
1 or 3*
3 COM 2/4 Yellow LED COM Port 2/4. Turns yellow when DIF is locked to SIF channel
2 or 4*
4 PA CNTL 1/3 I2C flatpack
connector
PA Control Channel 1 or 3. Outputs control data to the PIC card
on the PAA for the channel being provided (using cable
1955000P079)*
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 19
Page 32

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 9. RAN Up Converter Module Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
5 PA CNTL 2/4 I2C flatpack
connector
PA Control Channel 2 or 4. Outputs control data to the PIC card
on the PAA for the channel being provided (using cable
1955000P079)*
6 FLT Red LED Fault. Turns red when the module has failed. Indicator is lit dur-
ing start-up until module has initialized. Indicator will blink
after module receives system clock and is awaiting initialization
7 PWR Green LED Power. Turns green when module has power
8 CH 2/4 OUT SMA connector Channel 2 or 4 OUT*
* An RUC in slot A2 will connect to PAAs 1 and 2. An RUC in slot A5 will connect to PAAs 3 and 4.
Therefore, the RUC front panel indicators of 1/3 and 2/4 will map to PAAs 1 and 2 connections in slot
A2 and PAA 3 and 4 connections in slot A5.
1.7.8 Fan Access Panel
The Fan Access Panel, shown in Figure 15, has a hinged front panel that swings down providing
access to the two fans cooling the RAN chassis. These fans are user-replaceable. This panel has
labels identifying the electronic modules located in the cPCI shelf below the panel.
LABELS FOR CPCI
ELECTRONIC MODULES
21318-A
Figure 15. Fan Access Panel
1.7.9 800 MHz Multicoupler (C/MCPLR)
The 800 MHz (C/MCPLR) Module is a cPCI electronic module that houses the dual-diversity,
receive unit for the 800 MHz bands. This module interfaces to the multiplexer system and
contains the front end low noise amplifiers for the reverse path. The module has six outputs
(Cell bands A, B, and 800 MHz, with diversity).
Figure 16 shows the location of the faceplate components. Tab le 10 describes the faceplate
components.
Page 20
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 33

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 10. C/MCPLR Modules Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 P IN SMA connector Primary In. Receives RF primary reverse path input from primary
antenna
2 D IN SMA connector Diversity In. Receives RF diversity reverse path input from second-
ary antenna
3 P OUT SMA connectors Primary Out. 3 primary outputs (Cell bands A, B, and SMR-A). Each
output being used connects to one RDC electronic module, either in
the same RAN or in the extension RAN if present. Connection is
made using cable 1955000P081
4 D OUT SMA connectors Diversity Out. 3 diversity outputs (Cell bands A, B, and SMR-A).
Each output being used connects to one RDC electronic module,
either in the same RAN or in the extension RAN if present. Connec-
tion is made using cable 1955000P081
5 FLT Red LED Fault. Lights when module has failed and during start-up until mod-
ule has initialized
6 PWR Green LED Power. Lights when module has power
PRIMARY IN
CONNECTOR
PRIMARY OUT
CONNECTORS
DIVERSITY IN
CONNECTOR
DIVERSITY OUT
CONNECTORS
1
3
2
4
FAULT LED
POWER LED
21242-A
5
6
Figure 16. C/MCPLR Module Faceplate
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 21
Page 34

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1.7.10 1900 MHz Multicoupler (P/MCPLR)
The 1900 MHz (P/MCPLR) Module is a cPCI electronic module that houses the dual-diversity,
receive unit for the PCS band. This module interfaces to the multiplexer system and contains the
front end low noise amplifiers for the reverse path. The PCS band has 12 outputs (bands A-F,
with diversity). Figure 17 shows the location of the faceplate components. Tab le 1 1 describes
the module faceplate components.
DIVERSITY OUT
4
CONNECTORS
DIVERSITY IN
CONNECTOR
PRIMARY IN
CONNECTOR
PRIMARY OUT
CONNECTORS
FAULT LED
POWER LED
21245-A
2
1
3
5
6
Figure 17. P/MCPLR Modules Faceplates
Table 11. P/MCPLR Modules Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 P IN SMA connector Primary In. Receives RF primary reverse path input from primary
antenna
2 D IN SMA connector Diversity In. Receives RF diversity reverse path input from secondary
antenna
3 P OUT SMA connectors Primary Out. 6 primary outputs (bands A-F); each output being used
connects to one RDC module, in either same RAN or extension RAN
if present. Connection is made using cable 1955000P081
Page 22
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 35

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 11. P/MCPLR Modules Faceplate Components
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
4 D OUT SMA connectors Diversity Out. 6 diversity outputs (bands A-F); each output being
used connects on one RDC module, in either same RAN or extension
RAN if present. Connection is made using cable 1955000P081
5 FLT Red LED Fault. Lights when module has failed and during start-up until mod-
ule has initialized
6 PWR Green LED Power. Lights when module has power
1.8 Rectifier Shelf
The Rectifier Shelf, shown in Figure 18, is a chassis/backplane device that contains rectifier
modules and a Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) unit. The shelf interconnects the rectifier
modules and LVD unit, and provides an interface to external connectors.
Typically, the rectifier shelf contains two rectifier modules. The center panel on the shelf can be
removed to add a third rectifier, providing N+ redundancy as more equipment is added to the
RAN chassis.
LOW VOLTAGE
DISCONNECT
(LVD) UNIT
21319-A
OVER
TEMPERATURE
PROTECTION
LED
AC OK
LED
RECTIFIER
DC OK
LED
PROTECTION
21
OVER
VO LTAGE
LED
34
Figure 18. Rectifier Shelf
1.8.1 Rectifier Module
The rectifier module converts 240 VAC prime power into -48 VDC for use within the RAN.
Each rectifier has four LEDs, shown in Figure 18 and described in Tab le 12. The rectifiers are
controlled by the LVD unit under command of the STF2 module.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 23
Page 36

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 12. Rectifier Indicators
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 (Unmarked) Green LED AC OK. Lights when AC power is present
2 (Unmarked) Green LED DC OK. Lights when rectifier is limiting current
3 (Unmarked) Red LED Over Voltage Protection. Lights when rectifier has failed
4 (Unmarked) Red LED Over Temperature Protection. Lights when over temperature compen-
sation circuit is active
1.8.2 Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) Unit
The Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) Unit (Figure 19) disconnects power automatically when
the RAN voltage falls below a specified minimum. The LVD unit also manages the backup
batteries (extended or glitch).
OK LED
1
2
MAJOR FAULT LED
3
MINOR FAULT LED
4
LVD ON LED
6
21334-A
5
Figure 19. Low Voltage Disconnect Unit
Table 13. LVD Indicators
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 OK Green LED Okay. Lights when power system is functioning correctly
2 MAJ Red LED Major Fault. Lights when a major fault exists
3 MIN Yellow LED Minor Fault. Lights when a minor fault exists
4 (Unmarked) 9-pin connector Connector for cable 1001476P001 to the RECT (RJ45 connector)
port on the STF module
5 LVD Red LED Low Voltage Disconnect. Lights when switch has closed due to low
voltage
6 DISC Switch Disconnect. Pressing this switch disconnects the backup batteries
Page 24
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 37

1.9 Power Amplifier Assembly
The Power Amplifier Assembly (PAA) is an electronic device that amplifies RF signals in the
forward path just before they are transmitted to the RAN antenna. Up to four PAAs may be
mounted in the RAN, each providing one band. Each PAA consists of a Power Amplifier (PA), a
control board called the PA Interface Controller (PIC), and a cooling system. The PA is multichannel. Different units are used for PCS, Cellular, and SMR 800 bands.
The PIC interfaces to the discrete signals of the PA. The PIC also provides DC power to the PA
by converting from -48 VDC to +12 VDC or +28 VDC depending upon which PA is being used.
Each PA has its own PIC. The PIC is managed is managed by the CPU over an I2C connection
through its corresponding RUC. The cooling system consists of a heat sink and three fans that
provide cooling for the PA by blowing external air across the heat sink. The fans are softwarecontrolled. The PIC module monitors the tachometer outputs of the fan.
Figure 20 shows the PA assembly connection points and indicators. Tabl e 14 describes the items
called out in the figure.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
PIC LED
INDICATORS
1
DC_ FAULT
2
3
DC_ IN
DC_ OUT
8
RF IN
48V
5
PWR
12C
4
21276-A
RF
OUT
POWER
AMPLIFIER
6
7
Figure 20. Power Amplifier Assembly
Page 25
Page 38

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 14. PAA Connection Points and Indicators
REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 DC_IN Green LED DC In. Lighted when PIC has -48 VDC input
2 PA _FAU LT Red LED PA Fault. Lighted when PA has failed
3 DC_OUT Green LED DC Out. Lighted when PIC has +28 VDC output
4 I2C RJ-45 connector
(J1)
I2C (Bus). Connection to RUC module P/A CNTRL using
cable 1001475P001
5 48V PWR Positronic 3-pin
connector (J2)
6 RF OUT SMA connector RF Out. Output of PA for cable 1955000P080 to one of the
7 (Unmarked) Power Amplifier Power amplifier (see description on preceding page)
8 RF IN SMA connector RF In. Input from RUC for cable 19559999P079
48 Volt DC Power. Input to PIC for -48 VDC using PIC
power harness 1001471P001
four plexers (depending on band), connector port TX
1.10 Multiplexer System
The NXD RAN multiplexer system consists of four units that interface to the antenna, PAs, and
multicouplers:
• Quadplexer Primary (PCS Bands A, B, F), interfaces to PCS primary antenna;
• Quadplexer Diversity (PCS Bands D, E, C), interfaces to PCS diversity antenna;
• Triplexer Primary, either of two types:
– Type one (Cellular Band B, SMR800 Band), interfaces to 800 MHz primary antenna;
– Type two (SMR800 Band, SMR900 Band), interfaces to 800 MHz primary antenna;
• Diplexer Diversity (Cellular Band A), interfaces to 800 MHz diversity antenna.
For a schematic of the PCS multiplexers, see Figure 21. For a schematic of the Cellular/SMR
multiplexers, see Figure 22 (showing Cellular B, SMR800 triplexer) or Figure 23 (showing
SMR800, SMR900 triplexer).
Page 26
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 39

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Quadplexer
PCS Band
A/B/F
Rx
1850-1910
Rx
A
B
C
D
E
F
Primary
Tx
1930-1945
MCPA
Tx
A
RUC
Primary
Antenna
Antenna Assembly
Tx
1950-1965
MCPA
Tx
B
RUC
Multicoupler
1850/1910
Tx
1970-1975
MCPA
Tx
F
RUC
Figure 21. PCS Multiplexers
Rx
1850-1910
Rx
A
B
C
D
E
F
Diversity
Tx
1945-1950
MCPA
Tx
D
RUC
Diversity
Antenna
Tx
1965-1970
MCPA
Tx
E
RUC
Quadplexer
PCS Band
D/E/C
Tx
1975-1990
MCPA
Tx
C
RUC
21270-A
Duplexer
800 Mhz Band
Rx
810-849Tx869-880
Rx
SMR
A”
A
B
B’
Figure 22. Cell/SMR Multiplexers (With Cell/SMR 800 Triplexer)
Primary
Antenna
MCPA
Tx
A” A
RUC
Antenna Assembly
Multicoupler
810-849
Rx
810-849
Rx
SMR
A
CELL
A”
A
B
Diversity
Antenna
Tx
855-866
MCPA
Tx
SMR-A
RUC
Triplexer
800 Mhz Band
Tx
880-894
MCPA
Tx
B B’
RUC
21271-B
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 27
Page 40

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Duplexer
800 Mhz Band
Rx
810-849Tx869-880
Rx
SMR A
A”
A
Primary
Antenna
Diversity
Antenna
Antenna Assembly
Rx
810-901Tx851-869
MCPA
Tx
A” A
RUC
Rx
SMR A
SMR B
A”
A
MCPA
Tx
SMR-A
RUC
Multicoupler
810-901
Figure 23. SMR Multiplexers (With SMR 800/900 Triplexer)
Triplexer
800 Mhz Band
Tx
935-940
MCPA
Tx
SMR-B
RUC
21779-A
1.11 Circuit Breaker Panel
The Circuit Breaker Panel, shown in Figure 24, contains five circuit breakers. It distributes the
RAN’s -48 VDC power and protects the RAN’s electronics. Table 15 gives the circuit breaker
functions. Table 16 describes the panel LEDs.
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
(5 PLACES)
SYSTEM OK
12
LEDs
FAULT
LEDs
21320-A
Figure 24. Circuit Breaker Panel
Page 28
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 41

REF # DESIGNATION DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1 OK Green LED Okay. Lights when AC power is present
2 FAU LT Red LED Fault. Lights when rectifier is limiting current
1.12 Backup Batteries
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 15. Circuit Breaker Functions
BREAKER FUNCTION
1A PA1
2A PA2
3A PA3
4A PA4
5A cPCI chassis
Table 16. Circuit Breaker Panel LEDs
The NXD RAN has two backup battery options:
1.13 Antenna
ADC provides a pole-mount antenna kit for use when the RAN is mounted on a wooden utility
pole. The kit must be separately ordered from the RAN. Pole mounting is the most common
type of RAN installation.
The antenna offered interfaces with the PCS and Cellular/SMR bands and supports two branch
diversity receive paths. Also included in the kit is the GPS antenna used by the RAN.
The RAN may also be mounted outdoors on a concrete pad. This type of installation may use a
conventional directional antenna in either a sector or quasi-omni antenna configuration,
depending on the coverage objective and design. Proper antenna selection and the mounting
installation are the responsibility of the design engineer.
Antenna installation is covered in separate publications, available for downloading from the
ADC web site, www.adc.com. Refer to RELATED PUBLICATIONS on Page vii.
• Extended Batteries: provide backup protection for up to two hours. These are four 12V,
85-100 AH internal batteries connected in series for a -48V system. The four batteries
together with associated wiring and hardware weigh 325 pounds (147.7 kg).
• Glitch Batteries: provide backup protection for up to five minutes. These are small,
motorcycle type batteries connected in a series configuration.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 29
Page 42

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2 STANDARD INSTALLATION PROCEDURES
This section provides the standard procedures for a typical installation. The RAN may be
installed either on a wooden pole or on a concrete pad.
This section is organized as follows:
• Sections 2-1 through 2-4 provide information that is relevant before installing the cabinet.
These subsections contain an installation overview, unpacking instructions, a list of
required material and tools, and site preparation guidelines.
• Section 2-5 tells how to install a cabinet on a wooden utility pole. Included are instructions
for installing the pole mount bracket and then installing the cabinet on the bracket. Also
included are instructions for installing the rain shields.
• Section 2-6 tells how to install the RAN on a concrete pad. Included are instructions for
pouring the concrete pad, mounting the RAN on the pad, and installing the pedestal
enclosure.
• Section 2-7 contains other standard procedures typically done at every installation. These
procedures describe how to install the solar shield, grounding wire, RF cables, fiber optic
cable, AC power, and backup batteries.
Note: Section 3 contains instructions for installing a second RAN at the same location.
Section 4 provides information on non-standard installation procedures such as installing
an electronic module.
Installation of the RAN cabinet may proceed separately from the installation of the
corresponding Hub equipment. When the installation of the RAN is completed, refer to the
Digivance NXD Multi-Band Distributed Antenna System Operation Manual (ADCP-75-209)
for system turn-up and test procedures.
The procedures in this section assume that the required Outside Plant (OSP) fiber optic cable
has already been routed between the Hub and the RAN, that the required antenna has been
installed, and that a coaxial cable terminated with an N-type connector has been routed to the
RAN from the antenna.
Danger: Wet conditions increase the potential for receiving an electrical shock when installing
or using electrically-powered equipment. To prevent electrical shock, never install or use
electrical equipment in a wet location or during a lightning storm.
Caution: Always allow sufficient fiber length to permit routing of patch cords and pigtails
without severe bends. Some fiber optic patch cords or pigtails may be permanently damaged if
bent or curved to a radius of less than 2 inches (50 mm).
2.1 Installation Overview
A standard (typical) installation of the RAN consists of the following steps:
Warn ing: Electronic components can be damaged by static electrical discharge. To prevent
ESD damage, always wear an ESD wrist strap when handling electronic components.
Page 30
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 43

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Note: To insure that all optical connectors and optical ports remain dust-free during
installation, leave all dust caps and dust protectors in place until directed to remove them
for installation.
1. Checking out and preparing the installation site.
2. Unpacking and inspecting the shipped items.
3. Installing a pole mount frame or pedestal mount.
4. Installing the RAN cabinet on the pole or pad.
5. Installing the rain shields (pole mount) or pedestal enclosure (pad mount).
6. Installing the solar shield.
7. Installing a ground wire.
8. Connecting RF cables between the antenna and RAN.
9. Installing the fiber optical cable that connects the RAN to the Hub.
10. Installing AC power.
11. Installing backup batteries in the cabinet.
2.2 Unpacking and Inspection
The RAN is shipped to the field pre-configured with all modules and components that the
customer has ordered. Electronic modules except for the batteries are shipped already installed
in the cabinet.
The following optional accessories may also be shipped with the RAN:
• Back-up batteries
• Non-standard SFP optical transceiver
Use the following procedure to unpack and inspect the RAN components:
1. Open the shipping cartons and carefully unpack each component from the protective
packing material.
2. Check each component for broken or missing parts. If there are damages, contact ADC for
an RMA (Return Material Authorization) and to reorder if replacement is required. For
contact information, refer to Section 6 on Page 72.
2.3 Required Materials and Tools
The following materials must be supplied by the installer:
• (Pole mount only) Three galvanized steel square headed bolts with minimum tensile
strength of 20,050 lbs., 3/4 in. diameter, and of a length appropriate to pole diameter;
Three nuts for bolts, three flat washers, three split ring washers, and three 3-in. square
curved washers (see Figure 27 on Page 39)
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 31
Page 44

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
• (Pad mount only) Four 1/2 in. diameter galvanized steel bolts with four lock washers, four
flat washers, and four concrete anchors (see Figure 29 on Page 41)
• 3M 8426-9M cold shrink
• 3M Skothkote Electrical Coating 14853
• Ten Type N plugs (CommScope PN: 540ANM or equivalent)
• Coaxial cable (CommScope PN: FXL540OPE or equivalent)
• Electrician’s tape
• Water seal
• Electrical conduit
• Conduit fittings
• Connector sealant material
• Panduit LLCF6-14B-L or equivalent (X2)
• Two-hole compression lug terminal for #6 AWG wire
• Ground rod
• Connector for attaching #6 AWG grounding wire to approved ground source
The following tools are required to perform this procedure:
• Torque wrench
• Drill
• Drill bit (appropriate for pole width and 3/4 in. bolts)
• 7/16 in. open-end wrench
• Compression pliers for #6 AWG grounding lug
• Wire cutters
• Wire strippers
• Conduit cutter
• Conduit bender
2.4 Site Preparation
This section describes site preparation for installation and is presented only as a guideline for a
typical RAN installation.
2.4.1 Space Requirements
When an installation site for the RAN is selected, either on a utility pole or concrete pad, care
must be exercised to ensure that the site provides adequate space and clearance to accommodate
the current installation and any future upgrades. Tab le 17 gives RAN dimensions.
Page 32
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 45

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Table 17. RAN Dimensions
CONFIGURATION WIDTH HEIGHT DEPTH
RAN 31.35 in. (76.7 cm) 36.5 in. (92.7 cm) 27.5 in. (69.9 cm)
Dual RAN 31.25 in. (76.7 cm) 73 in. (185.4 cm) 27.5 in. (69.9 cm)
2.4.2 Power Requirements
Power must be available at the RAN site. The RAN requires 240 VAC, single phase, 20 Amps
service. Included with the power meter must be surge protection and circuit breakers.
The RAN can have up to three 1500 watt rectifiers. For the minimum specified voltage (176
VAC), each can draw up to 10 amps. The RAN will draw up to 1800 watts normally, but when
batteries are re-charging that amount will increase the current draw into a RAN to up to 16
Amps. Therefore, one 20 Amps service is required per four band RAN.
In a pole mount installation, the power meter is typically installed on the pole below the unit in
separate boxes. In a concrete pad installation, an external junction box is typically placed near
the RAN providing AC power, surge protection, and circuit breakers.
2.4.3 Antenna Requirement
ADC offers a pole-mount antenna kit (accessory) for use when the RAN is mounted on a
wooden utility pole. Either a 2 in. (5.08 cm) O.D. model or a 9 in. (22.86 cm) O.D. model can
be ordered. Pole mounting is the most common installation. The antenna interfaces with the
PCS and Cellular/SMR bands and supports two branch diversity receive paths. Also included in
the kit is the GPS antenna used by the RAN. Installation instructions for the pole mount antenna
are included with the kit.
When the RAN is mounted on a concrete pad, a conventional directional antenna may be used
(customer supplied). The antenna may be set to operate in either a sector or quasi-omni
configuration, depending on the coverage objective and design. Proper antenna selection and the
mounting installation are the responsibility of the design engineer.
2.4.4 RF Cable Requirements
RF cables are required at the installation site to provide the physical link between the RAN and
the antenna. In a pole-mount installation, U-duct of an appropriate size is also required to cover
the RF cables on the pole. The U-duct provides only physical protection. It should not be
considered to provide electrical isolation from conductors on the pole. Adequate clearance must
be obtained for the routing of these cables past the existing services as defined in the previous
topic. In a concrete pad installation, RF cables from the antenna are routed and protected per the
installation plan provided by the design engineer.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 33
Page 46

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2.4.5 Fiber Requirements
Optical fibers are required at the site to provide the physical link between the RAN and the Hub.
In a typical installation, the identified fibers are broken out of a multi-fiber sheath and routed to
a splice box where they are spliced to pigtails connecting the main sheath to the RAN. The
actual fiber bundle location on the utility pole may vary per the agreed to attachment point.
Refer to Figure 25. The nylon cable connector on the rear of the RAN accommodates cables of
a diameter in the range .38 to .50 inches (.97 to 1.27 cm). For larger size cables, refer to
Section 1.6.2 on Page 9.
2.5 Installing a RAN Cabinet on a Wooden Utility Pole
Figure 25 shows the main components and their spatial placement in a typical NXD RAN pole
mount installation.
2.5.1 Site Requirements Unique to Pole Mounting Locations
If power lines are present at the top of the pole, spacing requirements applicable to the RF
cabling and any other hardware installed in the electric space must be considered. Per the
National Electrical Safety Code, vertical clearance at supports for primary-supply conductors
above other facilities is required to be 16 in. (40.64 cm) above neutrals and 40 in. (101.6 cm)
above communications (60 in. [152.4 cm] if above 8700V).
For supply conductors at voltages up to 8700 between conductors, the minimum horizontal
clearance provided by the NESC ANSI C2 is 12 in. (30.5 cm). For higher voltages, it is required
that .4 in. (10.2 mm) be added for every 1000V above 8700. Tabl e 18 lists the required
clearances for some common high voltages.
Table 18. Antenna Clearance vs. Voltage
VOLTAGE HORIZONTAL CLEARANCE
8700V 12.0 in. (30.5 cm)
15 kV 14.52 in. (36.9 cm)
28 kV 19.72 in. (50.1 cm)
38 kV 23.72 in. (60.2 cm)
This information is from the Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, 13th Edition,
McGraw Hill, Chapter 18, Section 151, Pages 18-65.
Page 34
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 47

ANTENNA ANTENNA
ANTENNA
MOUNTING
BRACKET
GROUND WIRE
TO ANTENNA
PRIMARY
POWER
SECONDARY
POWER
FIBER
2 IN. SCHEDULE 40
CONDUIT FOR POWER IN
CARLTON PT. NO.
49011-010 OR
EQUIVALENT
27.5 IN.
(69.85 CM)
100 IN.
(254 CM)
38.6 FT.
(11.8 M)
TYPICAL
1.5 IN. SCHEDULE 40
POLE RISER FOR
FIBER OPTIC LINES
CARLTON PT. NO.
59010N OR
EQUIVALENT
31.25 IN.
(79.4 CM)
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
RF CABLES
TO RA N
(5 REQUIRED)
PRIMARY POWER
SECONDARY POWER LINE
FIBER OPTIC LINE
FIBER SPLICE CAN
3 IN. SCHEDULE 40
CONDUIT FOR
RF CABLES
CARLTON PT. NO.
49013-010 OR
EQUIVALENT
JUNCTION
BOX
#6 AWG COPPER
GROUND WIRE TO
METER BOX, RAN,
AND ANTENNA
COPPER
GROUND
ROD
7 FT. (2.1 M)
SIDE
VIEW
10 FT. (3 M)
TYPICAL
TYPICAL
FRONT
VIEW
21285-A
Figure 25. Typical Pole-Mount Installation
2.5.2 Pole Loading Analysis
A pole loading analysis should be performed before the RAN is mounted on the pole to verify
that the pole can support the weight of the RAN in various conditions. The analysis should take
into account the pole top antenna, the RAN and batteries, and the possibility of an expansion
RAN with batteries. Tab le 1 9 lists the weights of various NXD components and configurations.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 35
Page 48

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Three load types should be considered: static weight loading, ice loading, and wind loading.
These types should be considered on the pole, wires, and any equipment installed on the pole.
A qualified engineer should perform the pole loading analysis, taking into account both vertical
and horizontal forces. The specified horizontal load is applied 2 ft. (60.1 cm) from the top and
the assumption is that the pole acts as a cantilever with maximum stresses applied at the ground
level. Table 20 provides acceptable loads by pole class.
Table 19. RAN Component Weights
CONFIGURATION OR COMPONENT WEIGHT
Base RAN without batteries 379 lbs. (172.3 kg)
Base RAN with four batteries 679 lbs. (308.6 kg)
Expansion RAN with four batteries 619 lbs. (281.4 kg)
Antenna pole-mount bracket (9 inch) 56 lbs. (25.5 kg)
Antenna pole-mount bracket (2 inch) 57 lbs. (25.9 kg)
Pole-top antenna (9 inch) 47 lbs. (21.4 kg)
Pole-top antenna (2 inch) 12 lbs. (5.5 kg)
Table 20. Loading by Pole Class
POLE
CLASS HORIZONTAL LOAD
1 5400 lbs. (2454.5 kg)
2 3700 lbs. (1681.8 kg)
3 3000 lbs. (1363.6 kg)
The strength of the wood pole is defined in Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, 13th
Edition, McGraw Hill, Chapter 18, Section 135, “Strength of Wood Poles,” Pages 18-57. The
wood pole strength calculation is defined in Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, 13th
Edition, McGraw Hill, Chapter 18, Section 136, Reference NEC.
2.5.3 Installing the Cabinet Mounting Bracket
The Digivance NXD Wood Pole Mounting Bracket, shown in Figure 26, is an accessory item
that is used to attach the Digivance NXD cabinet to a power distribution pole or related object.
The bracket is attached to the pole using galvanized steel square head bolts that are attached
through holes drilled through the wooden pole. An example of an installed NXD wood pole
mounting bracket is shown in Figure 26.
Use the following procedure to install the RAN wood pole mounting bracket:
1. Determine the mounting height of the RAN and mark the pole at the desired location of
the base of the RAN.
Note: Install the RAN pole mount bracket on the side of the utility pole assigned by the
utility company or required by local zoning.
Page 36
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 49

34.5 IN.
(87.6 CM)
10 FT.
(3 M)
TYPICAL
UTILITY POLE
MOUNTING BRACKET
2.63 IN.
(6.7 CM)
13.5 IN.
(34.3 CM)
29.25 IN.
(74.3 CM)
HOT DIPPED GALVANIZED MACHINE
BOLT SQUARE HEAD 3/4 x 16.00 LG
W/NUT (J9816) 3 REQUIRED
ROUND FLAT WASHER 2.00 O.D.
(J1089) 3 REQUIRED
SQUARE CURVED WASHER
3 x 3 x 1/4 (J6823) 3 REQUIRED
SPRING LOCK WASHER
.234 x.188 (J140) 3 REQUIRED
OR EQUIVALENT
ATTA CH ME NT
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
RAN
POINTS
21286-A
Figure 26. Cabinet Mounting Bracket
2. Place the pole mount bracket against the pole.
3. Strap or otherwise hold the bracket in place.
4. Using a level, adjust the bracket to make it vertically level.
5. Mark the three holes to be drilled through the wood pole.
6. Remove the pole mount bracket.
7. Drill three holes through the pole using a 7/8 in. wood bit.
8. Using a 3/4 in. machine bolt, put a 2 in. flat washer on the bolt.
9. Place the pole mounting bracket against the pole.
10. Align the holes in the bracket with the holes drilled in the pole.
11. Install one bolt through the bracket and pole (using any of the three holes).
12. Place a 3 in. square curved washer, lock washer, and 3/4 in. nut on the other end of the
machine bolt; do not tighten.
13. Repeat steps 8-12 for the other two holes.
14. Using a 1-1/8 in. wrench, tighten the mounting hardware to 103 ft.-lbs.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 37
Page 50

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2.5.4 Mounting the RAN Cabinet on the Bracket
The cabinet is shipped with the mounting hardware required for mounting the RAN cabinet on
the RAN wood pole mounting bracket. The hardware consists of six 1/2 in. bolts, six nuts, 12
lock washers, and 12 flat washers. Use the following procedure to mount the cabinet. Refer to
Figure 27.
Caution: Do not install batteries in the RAN prior to mounting the RAN securely on the utility
pole.
1. Remove the RAN from the mounting pallet.
2. Securely attach the boom truck cable to the four hoist eyes of the RAN.
3. Carefully raise the RAN toward the cabinet mounting bracket.
4. With a person in the bucket truck and positioned at the RAN pole mounting bracket, guide
the RAN onto the RAN pole mounting bracket so that the RAN holds onto the studs on the
mounting bracket.
Note: Once the RAN is hung on the studs, the through bolts will self-align.
5. Place a lock washer and a flat washer on a 1/2 in. by 1-3/4 in. bolt.
6. Screw the bolt in hand tight.
7. Repeat the previous two steps for the remaining five mounting holes.
8. Install a flat washer, lock washer, and nut on each of the six studs.
9. Using a 3/4 in. wrench, tighten the bolts to 75 ft.-lbs.
10. Carefully detach the boom truck cable from the hoist eye of the RAN.
11. Remove the hoist eyes by unscrewing from the RAN top.
2.5.5 Installing the Rain Shields
There are two rain shields to be installed on the rear of the RAN. They are identified as “rain
shield right” and “rain shield left.” Use the following procedure to install the rain shields. Refer
to Figure 27.
1. Using the supplied hardware, place the left rain shield over the three studs in the pole
mount bracket and three studs on the RAN.
2. Place a lock washer then a nut on each stud.
3. Using a nut driver or wrench, tighten to 6 ft.-lbs.
Page 38
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 51

RAIN
SHIELD
RIGHT
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
UTILITY
POLE
RAN
CABINET
POLE MOUNT
RAIN
SHIELD
LEFT
Figure 27. Pole Mount Components
2.6 Installing a RAN Cabinet on a Concrete Pad
This section contains the procedures for installing the RAN on a concrete pad.
BRACKET
21345-A
Choose an installation site that conforms to all local codes. Obtain all required permits prior to
starting installation. Situate the concrete pad along the trench that was used for routing the OSP
fiber cables for the system.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 39
Page 52

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2.6.1 Pouring a Concrete Pad
Prepare a base for the concrete pad that meets all local code requirements. The base must have a
footing of 4 to 6 inches (10.2 to 15.2 cm) of sand or gravel on firmly compacted soil. Concrete
pad height is site and climate dependent. Height should be based on keeping the front door air
intake louvers and rear bottom exhaust vent free of obstruction. For dimensions of pad, refer to
Figure 28.
CLEARANCE
(234 CM)
31.0 IN.
(79 CM)
DOOR
92.0 IN.
3.5 IN.
(8.9 CM)
15.38 IN.
(39.07 CM)
4.3 IN.
(10.9 CM)
HOLES FOR
PEDESTAL
MOUNT
29.00 IN.
(73.66 CM)
Figure 28. Concrete Pad Dimensions
RAN CABINET/
PEDESTAL ENCLOSURE
FOOT PRINT
CONCRETE PAD
(MINIMUM SIZE)
24.0 IN.
(61 CM)
36.0 IN.
(91 CM)
21308-A
2.6.2 Mounting the Cabinet on a Concrete Pad
Use the following procedure to mount the cabinet on the concrete pad.
1. Fasten the pedestal mounts to the concrete pad using the customer-supplied hardware
identified in Figure 29.
Page 40
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 53

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
1/2 x 13
BOLT
LOCK
WASHER
FLAT
WASHER
CONCRETE
ANCHOR
TYPICAL CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED HARDWARE
(4 PLACES)
21306-A
Figure 29. Installing Pedestal Mount and Cabinet
Warn ing: Use appropriate lifting equipment when moving or installing the cabinet. Do not
stand under the cabinet as it is being hoisted into position for installation. A failure of the lifting
equipment could result in serious personal injury.
2. Using appropriate lifting equipment, lower the cabinet into position on the cabinet mounts.
3. Secure the cabinet from the side, as shown, using the four bolts, four flat washers, and four
lock washers from the shipping pallet mounting brackets.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 41
Page 54

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2.6.3 Installing the Pedestal Enclosure
The pedestal enclosure, shown in Figure 30, mounts on the back of the cabinet.
PEDESTAL
ENCLOSURE
Use the following procedure to install the pedestal enclosure:
1. Orient the pedestal enclosure as shown and attach it to the back of the cabinet using the
four bolts provided.
2. Close the pedestal enclosure door and secure the door with the key provided.
Page 42
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
OPTIONAL FITTINGS
Figure 30. Installing Pedestal Enclosure
21309-A
Page 55

2.7 Other Standard Installation Procedures
This section contains other procedures done at every installation after the RAN is mounted on a
wooden pole or concrete pad.
2.7.1 Installing a Solar Shield
Each RAN has a solar shield that mounts on top of the cabinet. Hardware for the solar shield can
be found in a bag fastened to the inside of the battery compartment. The hardware consists of
two 1/4 in. bolts, each with flat washer and sealing washer. Use the following procedure to
install the solar shield. Refer to Figure 31.
1. Remove the solar shield from its packaging.
2. Place a lock washer and flat washer and then the sealing washer on each 1/4 in. machine
bolt.
3. Using the key provided, open the RAN door.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
SOLAR
SHIELD
RUBBER
SEALING
WASHER
FLAT
WASHER
1/4 x 20
HEX HEAD
BOLT
EACH SIDE
TAN GS
21339-A
Figure 31. Installing the Solar Shield
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 43
Page 56

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4. Locate the two 1/4 in. machine bolts, each with flat washer and sealing washer, in a bag
fastened to the inside of the battery compartment.
5. Place the solar shield on the top of the RAN.
6. Push the solar shield backward until it extends slightly beyond the back of the cabinet then
pull it forward catching the two tangs of the solar shield on the top of the RAN.
7. Locate the two clearance holes on the left and right sides just inside the door frame.
8. Align the solar shield threaded holes with the clearance holes and insert the two 1/4 in.
machine bolts in the hole.
9. Using a 7/16 in. nut driver or socket screw, tighten the two 1/4 in. machine bolts to secure
the solar shield. Tighten to 6 ft.-lbs.
2.7.2 Installing a Ground Wire
Each RAN is designed with provisions for connecting to earth ground. Earth grounding is to be
done in accordance with the National Electric Code and local building code. Two ground studs
for connecting the ground wire are located on the back of the RAN (Figure 32). A 2-hole
compression type lug terminal should be installed on the ground studs for connecting a #6 AWG
copper grounding wire.
The following material must be supplied by the installer:
• Panduit LLCF6-14B-L or equivalent (X2)
• Two-hole compression lug terminal for #6 AWG wire
• #6 AWG wire
• Connector for attaching the wire to an approved ground source
The following tools are required to perform this procedure:
• Compression pliers for #6 AWG grounding lug
• Wire cutters
• Wire stripper
Use the following procedure to install the ground wire:
Caution: For proper equipment operation, an approved earth ground connection must be
provided. The recommended minimum wire size is #6 AWG copper wire.
1. Obtain a length of #6 AWG (4 mm) copper wire for use as a cabinet grounding wire.
2. Crimp the #6 AWG copper grounding wire to the compression lug.
3. Secure the compression lug to the back of the cabinet.
4. Route the free end of the grounding wire to an approved earth ground source.
5. Cut the grounding wire to length and connect it to the earth ground source as specified by
local code.
Page 44
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 57

RF LINE CONDUIT
(FROM ANTENNA)
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
FIBER OPTIC
CONDUIT
FIBER OPTIC
ENTRANCE
LEFT
RAIN
SHIELD
TYPE N CONNECTORS
FOR ANTENNA AND
GPS CONNECTORS
RIGHT
RAIN
SHIELD
POWER ENTRANCE
220 VAC PRIME POWER
GROUND
LUG
GROUND
WIRE
220 VAC RIGID
CONDUIT
21287-A
Figure 32. Cable Connection Points
2.7.3 Installing RF Cabling
RF cabling on the RAN connects the RF antenna to the RF input on the back of the RAN. There
are five Type N receptacles on the antenna and five Type N receptacles on the back of the RAN,
identified in Table 21 on page 47.
There are two main steps in installing RF cables: weatherproofing the cables, and routing and
securing the cables.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 45
Page 58

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
2.7.3.1 Weatherproofing RF Cables
RF cables should be weatherproofed before being installed. The following materials are
required (customer supplied):
Note: Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions prior to using these products.
• 3M 8426-9M cold shrink
• 3M Skothkote Electrical Coating 14853
Use the following procedure to weatherproof the RF cables:
1. Prior to connecting the RF cables to either the RAN or antenna, place one 3M 8426-9M
cold shrink kit over the cable end, then connect the cable end to its intended termination
point. Follow the manufacturer’s directions, which are included with each kit.
2. After the cold shrink has been applied, coat the entire length of the cold shrink material
with the 3M Scotchkote Electrical Coating, number 14853.
2.7.3.2 Routing and Securing RF Cables
For cable installation, the following materials are required (customer supplied):
• 10 Type N male plugs (CommScope PN: 540ANM or equivalent)
• Coax cable (CommScope PN: FXL540OPE or equivalent)
• Electrician’s tape
• Water seal
Use the following procedure to route and secure the RF cabling:
1. Measure from the antenna base connectors to the RAN connectors to determine the coax
cable length including service loops and drip loops. Refer to Figure 25 on Page 35.
2. Install the Type N plugs on each end of each of the RF cables.
Note: Right angle connectors may not be needed if there is enough space or if the coax
cable is flexible enough to create a proper bend radius in the cable. Reference the coax
cable manufacturer specifications for allowable bend radii.
Note: A cable sweep test is highly recommended. When testing the RF and GPS coaxial
cables, use a matched load. The VSWR should be 1:1:1. The return loss should be 26.444
dB or better.
3. Attach each end of the cables to the appropriate connectors on the antenna base and the
RAN. Refer to Figure 33 and Ta bl e 21 .
4. Tighten each connector to 20 ft.-lbs.
5. After each connector is tightened, cover the entire connection with electrician’s tape, then
wrap the connection in water seal and finally cover the water seal with wraps of
electrician’s tape.
Page 46
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 59

GPS
PCS-P
PCS-D
CELL/SMR-P
CELL/SMR-D
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
21278-A
Figure 33. Installing the RF Cables
Table 21. RAN Antenna Ports and Antenna Base Ports
LABEL ON RAN LABEL ON ANTENNA BAND
GPS GPS Global Positioning System (GPS)
PCS-P PCS-T PCS primary receive path and transmits from PCS A, B or F
PCS-D PCS-B PCS diversity receive path and transmits from PCS D, E or C
CELL/SMR-D CELL/SMR-D Cell/SMR primary receive path and transmits from Cell A”/A
CELL/SMR-P CELL/SMR-P Cell/SMR diversity receive path and transmits from SMR A or
Cell B/B’
Note: When building out RANs, connect the quadplexers that will contain the first PCS
bands to the top of the PCS antenna element. On the Phasar antenna, this is marked on the
base PCS-T.
2.7.4 Installing Pre-Connectorized Indoor/Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cable installation consists of routing a pre-connectorized outdoor-rated fiber optic
cable from an external splice enclosure to the NXD RAN cabinet, routing the cable into the
cabinet, and then breaking out the individual fibers for connection. The NXD RAN has a fiber
interface on the front of the Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module in the RAN chassis. The fiber
enters the cabinet on the rear side.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 47
Page 60

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
All fiber optic cable connections require single-mode Dual-LC type connectors.
Figure 34 shows the basic configuration of the optical path between the Hub SIF and the RAN
SIF. For optical specifications, refer to Table 2 on page 6.
FIBER PORT
BASIC CONFIGURATION BETWEEN HUB SIF SFP AND RAN SIF SFP
FIBER PORT
TX RX
REVERSE PATH
FORWARD PATH
END-TO-END OPTICAL CONNECTOR/CABLE ASSEMBLY DIAGRAM
TX RX
21353-A
Figure 34. Optical Path Between Hub SIF and RAN SIF
For fiber cable ingress, the RAN is equipped with a nylon fiber optic connector located on the
rear side of the cabinet. The connector accommodates cables of a diameter in the range .38 to
.50 inches (.97 to 1.27 cm).
Note: If the installer has a larger cable, the manufacturer (Hubbell Inc.) makes bushings
that fit this connector in the following size ranges: .500-.625, .625-.750, .750-.875, .875-
1.00, 1.00-1.125 inches.
Use the following procedure to install the fiber optic cable:
Note: The routing of an Outside Plant (OSP) fiber optic cable from the Hub to a splice
enclosure in the vicinity of the RAN cabinet and the splicing of selected OSP cable fibers
to the fibers in the outdoor-rated cable is the responsibility of the installer.
Warn ing: This equipment uses a Class 1 Laser according to FDA/CDRH rules. Laser radiation
can seriously damage the retina of the eye. Do not look into the ends of any optical fiber. Do not
look directly into the optical transmitter of any unit or exposure to laser radiation may result.
An optical power meter should be used to verify active fibers. A protective cap or hood MUST
be immediately placed over any radiating transmitter or optical fiber connector to avoid the
potential of dangerous amounts of radiation exposure. This practice also prevents dirt particles
from entering the connector.
1. Route the connectorized end of the fiber optic cable from the splice enclosure (not
provided) to the rear side of the cabinet. Estimated length of cable is 30 feet (9 meters)
although this is dependent upon distance from the splice enclosure.
Page 48
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 61

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Note: The fiber should not have armored jacketing which may be a source for ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI).
2. Install the compression nut and an appropriate sized split ring and bushing over the cable
end. Note that the beveled side of the split ring should face toward the compression nut.
3. Insert the end of the cable into the fiber entry opening on the bottom of the cabinet and
pull the cable into the cabinet.
4. Connect fiber to the LC receptor located on the SIF electronic module. For location, refer
to Figure 11 on Page 16.
5. Pull back any excess fiber from within the NXD cabinet.
6. Tighten the compression nut on the fiber entry connector body to secure the cable.
7. Seal all connections.
2.7.5 Installing AC Power
Note: Power interfacing for the RAN must be performed by a licensed electrician.
Prime power for the RAN is 240 VAC, 20 Amps, single phase. A separate service disconnect
and lightning arrestor for each RAN must be installed with proper grounding. An electric meter
is optional depending on local agreements.
A non-connectorized #14 AWG 3-wire power cable is provided with the RAN cabinet for the
AC power connections. The power cable is connected to a wiring harness within the cabinet and
is approximately 20 feet (6 meters) long. The stub end of the cable must be routed out of the
cabinet through conduit to an external junction box (not provided). At the junction box, the
power cable must be connected to the AC power system wiring. The RAN electrical input fitting
is located on the right rear of the cabinet, labeled “AC.”
The AC power cable provides three wire leads for Line, Neutral, and Ground connections. All
AC wires must be run within conduit. The interface at the RAN is a 1 in. (2.54 cm) 90 degree
receptor elbow.
For installation of AC power, the following materials are required (customer provided):
• Electrical conduit
• Conduit fittings
• Connector sealant material
The following tools are required to perform this procedure:
• Wire cutters
• Wire strippers
• Conduit cutter
• Conduit bender
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 49
Page 62

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Note: All electrical work must comply with local codes and requirements. A locally
licensed electrical contractor is best qualified to perform this work. For operation at less
than 20 Amps, consult with ADC Technical Service.
Danger: Use extreme caution when working with high voltage AC power. Ensure all power is
disconnected before working on power circuits.
Use the following procedure to install the AC power wiring:
1. Install outdoor conduit between the the AC power junction box and the AC power fitting
(rigid 90 degree receptor elbow) on the back of the cabinet.
2. Use a UL approved outdoor conduit connector (not provided) to connect the conduit to the
AC power junction box.
Note: A reducer fitting must be provided to accommodate any size change to the conduit.
3. Route the AC power cable through the conduit to the AC junction box.
4. Install the required AC power supply wires between the AC junction box and the AC
circuit breaker box (by the junction box not within the RAN).
5. Strip off the insulation from the AC power cable wire leads and from the AC supply wires
and connect the AC power cable wires to the AC supplier cable.
6. Connect the AC power to the AC wiring harness.
7. At the AC circuit breaker box, connect the AC power supply load wire(s) to a 20 Amp
circuit breaker.
8. Place the circuit breaker in the ON position and then test the connectorized AC power
cable within the cabinet for proper voltage levels and correct polarity.
9. Place the circuit breaker in the OFF position when testing is complete.
2.7.6 Installing Backup Batteries (Extended or Glitch)
Backup batteries for the RAN may be either two-hours-extended or five minutes glitch. The
batteries will need to be installed and under charge before they will be able to provide full
service. Battery storage life is one year in an environmentally controlled area. Batteries should
be checked prior to installation. Each battery should measure 12.6 V or greater across terminals.
Any battery that measures less should not be used. Refer to the battery manufacturer’s manual
for specific information including charging recommendations, tests, and maintenance.
2.7.6.1 Battery Safety Rules
For safety purposes, observe the following DO’s and DON’T’s when installing the batteries or
performing battery tests and maintenance:
• DO use qualified personnel only for battery maintenance
• DO follow all battery and charger manufacturer maintenance instructions
Page 50
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 63

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
• DO wear protective equipment (face shield, goggles, gloves) when working with or
around battery systems.
• DO use proper lifting techniques when working with batteries.
• DO use insulated tools when working on batteries.
• DO remove all rings and metal watchbands before working on batteries.
• DON’T service batteries individually. Replace pack as a unit.
• DON’T replace a defective pack with an alternate type. Use only the replacement packs
provided by ADC.
• DON’T lift batteries by their terminals.
• DON’T place tools, unconnected cables, or metal objects to rest on top of the batteries.
• DON’T use any chemical cleaners (ammonia, bleach, etc.) to clean batteries.
• DON’T remove vent caps or add anything to sealed, maintenance-free batteries.
• DON’T smoke, cause sparks, or carry an open flame near any battery system.
• DON’T approach any energized battery system that shows signs of over-charging or over
discharging (severe swelling, cover deformation, vent caps popping off). Disconnect and
isolate the battery system from all charging and discharging circuitry before approaching
the system.
• DON’T circumvent any device installed by the battery or charger manufacturer for the
purpose of protecting the battery system. These devices include fuses, circuit breakers,
disconnects, switches, etc.
2.7.6.2 Battery Installation
Use the following procedure to install the batteries:
Warn ing: Do not short battery connections together or to ground. The battery pack has high
current capacity and can cause burns or serious personal injury when shorted.
Warn ing: To avoid personal injury or fire damage, do not incinerate or mutilate the battery. Do
not short the battery terminals and do not store or operate the battery in an airtight container.
Warn ing: The batteries contain hazardous materials. Deliver defective batteries to an
authorized disposal center for disposal or recycling.
Caution: Before connecting batteries, be sure to turn off the low voltage connect switch located
on the rectifier. The LED will be OFF.
1. Open the RAN door.
2. Turn off the battery disconnect switch (labeled DISC) on the low voltage disconnect unit
in the RAN chassis. For location, refer to Figure 19 on Page 24. The LVD LED will light
up (red) when the batteries are disconnected.
3. Move the gravity latch in the battery drawer to the up position. Refer to Figure 35.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 51
Page 64

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4. Pull out the battery drawer.
5. Move the gravity latch to the down position. Lock the telescopic slide into the locked out
position.
6. Install the batteries in the drawer as follows, referring to Figure 36 for extended batteries
and Figure 37 for extended batteries:
a. Place the batteries in the drawer in the configuration shown.
b. Wire the batteries in series as shown.
c. Find the wiring harness coiled up on the floor of the battery back up drawer and plug
the Anderson connectors together as shown.
7. Move the gravity latch up, push the battery drawer in, and move the gravity latch down.
8. Reconnect the battery disconnect switch (DISC) on the LVD unit. For location, refer to
Figure 19 on Page 24. The LVD LED on the low voltage disconnect unit should will turn
off when the batteries are reconnected.
Page 52
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
BATTERY
DRAWER
21277-A
GRAVITY
LATCH
Figure 35. Open Battery Drawer
Page 65

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
70 AMP
FUSE
21288-A
ANDERSON
CONNECTOR
Figure 36. Extended Batteries in Drawer
70 AMP
FUSE
NOTE:
CUSTOMER TO COVER
EXPOSED TERMINALS
WITH ELECTRICAL TAPE.
ANDERSON
CONNECTOR
Figure 37. Glitch Batteries in Drawer
21289-A
Page 53
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 66

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
3 INSTALLING AN EXTENSION RAN (POLE MOUNT)
Two RANs can be installed at the same location to provide up to eight bands at that location
using a common antenna. Each RAN requires its own separate power and RF cables and fiber
optical cable. Figure 38 shows a typical dual RAN pole mount installation.
ANTENNA
ANTENNA
MOUNTING
BRACKET
GROUND WIRE
TO ANTENNA
PRIMARY
POWER
SECONDARY
POWER
FIBER
2 IN. SCHEDULE 40
CONDUIT FOR POWER IN
CARLTON PT. NO.
49011-010 OR
EQUIVALENT
27.5 IN.
(69.85 CM)
100 IN.
(254 CM)
6 FT. (1.8 M)
TYPICAL
38.6 FT.
(11.8 M)
TYPICAL
ANTENNA
1.5 IN. SCHEDULE 40
POLE RISER FOR
FIBER OPTIC LINES
CARLTON PT. NO.
59010N OR
EQUIVALENT
31.25 IN.
(79.4 CM)
RF CABLES
TO RA N
(5 REQUIRED)
PRIMARY POWER
SECONDARY POWER LINE
FIBER OPTIC LINE
FIBER SPLICE CAN
3 IN. SCHEDULE 40
CONDUIT FOR RF CABLES
CARLTON PT. NO.
49013-010 OR
EQUIVALENT
JUNCTION
BOX
#6 AWG COPPER
GROUND WIRE TO
METER BOX, RAN,
AND ANTENNA
COPPER
GROUND
ROD
SIDE
VIEW
Materials Required (Customer Supplied):
• Three galvanized steel bolts with tensile strength of 20,500 lbs. or greater, 3/4 inch
diameter, of a length appropriate to pole diameter
Page 54
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
10 FT. (3 M)
TYPICAL
7 FT. (2.1 M)
TYPICAL
FRONT
VIEW
21295-A
Figure 38. Typical Dual RAN Pole-Mount Installation
Page 67

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
• Three nuts, three flat washers, three 3 in. square curved washers, and three split ring
washers for bolts
Materials Required, ADC Supplied:
• RAN fixturing angle P/N 1001509P001 (X2)
• 1/4-20 X 3/4 hex bolts (X4)
• 2 in. through hull bulkhead fitting
• Flexible grommet
Use the following procedure to install an expansion RAN. Refer to Figure 39.
Note: This procedure assumes that the expansion RAN is installed on a utility pole
directly above the existing RAN.
1. Open the existing RAN door.
2. Remove the solar shield from the existing RAN. Refer to the solar shield installation
procedure in Section 2.7.1 on Page 43 and do the steps in a reverse order.
2 IN. (5.08 CM)
BULKHEAD FITTING
SUPPLIED WITH
EXTENSION RAN
1.50 IN.
(3.8 CM)
KENNARD
FLEXIBLE GROMMET
SUPPLIED WITH
EXTENSION RAN
Figure 39. Dual RAN Pole Mount
21296-A
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 55
Page 68

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
3. If RF cables will be routed from the existing RAN M/MCPLR or P/MCPLR module to the
extension RAN, remove the hole seal plugs located on the top right of the existing RAN
and on the bottom right of the extension RAN.
Note: In this case, the multicoupler modules, the PAAs, and the GPS in the existing RAN
will be providing input into the extension RAN RDC module, the PAAs, and the STF
module (ANT input) for some or all of bands 5-8. The associated RF cables from the
multicouplers will be routed out of the top of the existing RAN and into the bottom of the
extension RAN.
4. Bolt the fixturing angle to each side the expansion RAN pole mount bracket bottom holes
using the two 1/4-20 X 3/4 hex bolts.
5. Raise the assembly above the existing RAN and align the bottom of the fixturing angle
with the top of the existing pole mount bracket.
6. Bolt the fixturing angle to each side of the existing RAN pole mount bracket top holes
using the two 1/4-20 X 3/4 hex bolts.
7. Install the extension RAN pole mount bracket, RAN cabinet, and rain shields following
the instructions in Section 2.5.3 on Page 36, Section 2.5.4 on Page 38, and Section 2.5.5
on Page 38, respectively.
8. Install a solar shield on the extension RAN following the instructions in Section 2.7.1 on
Page 43.
9. Install a grounding wire on the extension RAN following the instructions in Section 2.7.2
on Page 44.
10. Install the RF cables from the antenna to the extension RAN following the instructions in
Section 2.7.3 on Page 45.
11. Install the fiber optic cable from the Hub to the extension RAN following the instructions
in Section 2.7.4 on Page 47.
12. Install AC power in the extension RAN following the instructions in Section 2.7.5 on Page
49.
13. Install backup batteries in the extension RAN following the instructions in Section 2.7.6
on Page 50.
14. Close and secure both RANs.
Page 56
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 69

4 NON-STANDARD INSTALLATION PROCEDURES
This section contains other installation procedures that are not typically done at a RAN
installation. These procedures cover field installation of electronic modules and other
components like the RAN chassis fans.
4.1 Installing an Electronic Module
If installing an electronic module in the field, refer to the appropriate procedure in this section.
There is a procedure for each type of electronic module. For a comprehensive description of the
electronic modules including function, controls, and indicators, refer to the appropriate topic in
Section 1.7 on Page 10.
Typically, the RAN chassis is shipped populated with the appropriate modules based on the preordered system configuration. Installation of electronic modules is only required when
installing a new electronic module or when changing the the system configuration.
Note: Not all options and features are supported in combination.
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
The electronic modules install into predetermined slots in the chassis identified by the labels on
the fan access panel above the chassis. For an illustration of the fan access panel labels and a
listing of the slots, refer to Section 1.7 on Page 10.
Warn ing: Electronic components can be damaged by static electrical discharge. To prevent
ESD damage, always wear an ESD wrist strap when handling electronic components.
The interconnection diagram shown in Figure 40 and Figure 41 on the next two pages
summarizes the interconnections between the RAN chassis electronic modules and other
electronic components of the RAN such as rectifiers and PAAs.
Note: The interconnection diagram shows a typical configuration. Other configurations
are possible that would be interconnected slightly differently.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 57
Page 70

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Page 58
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
21372-A
Figure 40. RAN Interconnection Diagram Part 1
Page 71

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Figure 41. RAN Interconnection Diagram Part 2
21373-A
Page 59
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 72

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4.1.1 Installing a Central Processing Unit (CPU) Module
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) module installs into Slot 5 of the RAN chassis. Only one
CPU may be installed in the RAN chassis.
Note: For a description of the CPU module including function, controls, and indicators,
refer to Section 1.7.2 on Page 13. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to
Figure 40 on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install the CPU module (Figure 42):
1. Open the RAN door.
2. Locate the designated slot for the CPU module. The CPU module installs into Slot 5,
which is identified with a red colored card guide.
3. Remove the CPU module from the anti-static packaging and orient the module for
installation as shown in the figure.
4. Slide the CPU module into the designated slot within the RAN chassis.
5. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the CPU module into the cPCI chassis.
6. Tighten the two Phillips head screws inside the handles.
7. Connect the short CAT5e jumper (cable 1001478P001) between the “ENET” port on the
CPU module the “10BT” port on the SIF module.
Note: If there are two SIF modules present, connect the cable to the first SIF module
(leftmost SIF module when viewed from the front of the chassis).
21250-AX
Page 60
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Figure 42. Installing a CPU Module
Page 73

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4.1.2 Installing a Systems Interface (STF2) Module
The System Interface module (STF2) is installed into Slot 6 of the RAN Chassis. Only one
STF2 module may be installed per RAN chassis.
Note: For a description of the STF2 module including function, controls, and indicators,
refer to Section 1.7.3 on Page 14. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to
Figure 40 on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install the STF2 module (Figure 43):
1. Open the RAN door.
2. Locate the designated slot for the STF2 module. The module installs into Slot 6.
3. Remove the STF2 module from the anti-static packaging and orient for installation.
4. Slide the STF2 module into the designated slot within the RAN chassis.
5. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the STF2 module into the cPCI chassis and
tighten the handle screws.
6. Using cable 1001474P001, connect the RAN door switch to the RJ-45 connector labeled
DA (Door Alarm) on the front of the STF2 module.
7. Using cable 1955000P084, connect the GPS antenna to the SMA connector labeled ANT
(Antenna) in the center of the module.
8. Using cable 1001476P001, connect the RECT port on the STF2 module to the unlabeled
9-pin port on the Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) unit. For location of the LVD port, refer
to Section 1.8.2 on Page 24.
21252-AX
Figure 43. Installing an STF2 Module
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 61
Page 74

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4.1.3 Installing a Synchronous Interface (SIF) Module
The Synchronous Interface Module (SIF) is installed into Slot 7 or Slot 8 of the RAN chassis.
One SIF module is required for each two bands installed in the RAN. For the first two bands use
Slot 7. For the second two bands, use Slot 8.
Note: For a description of the SIF module, including function, controls, and indicators,
refer to Section 1.7.4 on Page 15. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to
Figure 40 on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install the SIF module (Figure 44):
1. Open the RAN door.
2. Locate the designated slot for the SIF module. The module installs into Slot 7 or Slot 8.
Refer to the introductory text above for more information.
3. Remove the SIF from the anti-static packaging and orient for installation.
4. Slide the SIF into the designated slot within the RAN chassis.
5. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the SIF module into the cPCI chassis and
tighten handle screws.
21252-AX
6. If this SIF module is being installed into Slot 7, connect the short CAT5e jumper (cable
1001478P001) between the “10BT” port on the SIF and the “ENET” port on the CPU
module. (For a slot 8 SIF, no cable is required.)
7. Carefully route the internal fibers to the front of the SIF module.
Page 62
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Figure 44. Installing an SIF Module
Page 75

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
8. If the optical transceiver is mounted into the SIF module, then connect the fiber to the dual
LC connector. If optical transceiver is not mounted into the SIF module, follow the SFP
installation procedure in Section 4.1.4 on Page 63.
4.1.4 Installing a Small Form-Factor Optical Transceiver (SFP)
The SFP installs in the front center of the SIF module.
Note: For a description of the SFP, refer to Section 1.7.5 on Page 17. See also the
description of the SIF module faceplate in Section 1.7.4 on Page 15.
Use the following procedure to install an SFP:-
1. Locate the transceiver socket on the front of the SIF and remove the port cover from the
socket.
2. The color of the transceiver extractor handle corresponds to the optical specifications of
the SFP and CWDM designations. Select the optical transceiver that is to be used to
communicate with the target RAN.
Note: For CWDM systems, it is extremely important that the correct wavelength be
installed in each SIF. Consult the site fiber plan for details
3. Remove the transceiver from the anti-static packaging and orient for installation.
4. Insert the optical transceiver into the socket until it locks into place.
5. Connect fiber or replace the optical transceiver dust cap if it was removed for installation.
4.1.5 Installing a RAN Down Converter (RDC or RDC2) Module
The RAN Down Converter (RDC) module may be installed into any of four slots in the RAN
chassis, depending on the band for which the module will be used. One RDC module is required
for each band. The four slots are:
• Slot 10 (labeled RDC A1): used for first band
• Slot 12 (labeled RDC A3): used for second band
• Slot 13 (labeled RDC A4): used for third band
• Slot 15 (labeled RDC A6): used for fourth band
Note: For a description of the module including function, controls, and indicators, refer to
Section 1.7.6 on Page 17. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to Figure 40
on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install an RDC or RDC2 module (Figure 45):
1. Identify the slot designated RAN chassis slot for the RDC module. This will be Slot 10,
12, 13, or 15. For more information, refer to the introductory text above.
2. Remove the RDC module from the anti-static packaging and orient the module for
installation.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 63
Page 76

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
3. Slide the RDC module into the designated slot within the RAN chassis.
4. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the RDC module into the chassis and
tighten the handle screws.
5. Using an SMA coaxial cable (1955000P081), connect one end to the PRI IN port on the
RDC module and the other end to the appropriate P OUT port on the C/MCPLR or P/
MCPLR module. Each P OUT port is associated with a different band.
Note: For more information on the C/MCPLR module ports, see Section 1.7.9, 800 MHz
Multicoupler (C/MCPLR), on page 20. For more information on the P/MCPLR module
ports, see Section 1.7.10, 1900 MHz Multicoupler (P/MCPLR), on page 22.
6. Using an SMA coaxial cable (1955000P081), connect one end to the DIV IN port on the
RDC module and the other end to the appropriate D OUT port on the C/MCPLR or P/
MCPLR module. Each D OUT port is associated with a different band. For more
information on these ports, refer to the sections identified in the note above.
21235-AX
4.1.6 Installing a RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) Module
The RAN Up Converter (RUC2.X or RUC3) module may be installed into either of two slots in
the RAN chassis, depending on the band for which the module will be used. One module is
required for each two bands. The two slots are:
• Slot 11 (labeled RUC A2): used for first and second bands
• Slot 14 (labeled RUC A5): used for third and fourth bands
Page 64
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Figure 45. Installing an RDC Module
Page 77

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Note: For a description of the module including function, controls, and indicators, refer to
Section 1.7.7 on Page 19. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to Figure 40
on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install an RUC2.X or RUC3 module (Figure 46):
1. Identify the designated chassis slot for the RUC module. This will be Slot 11 or 14. For
more information, see introductory text above.
2. Remove the RUC module from the anti-static packaging and orient for installation.
3. Slide the RUC module into the designated slot within the RAN cPCI chassis.
4. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the RUC module into the cPCI chassis and
tighten handle screws.
21233-AX
Figure 46. Installing an RUC Module
5. Using cable 1955000P079, connect the CH1/3 connector on the RUC module to either of
the following as appropriate:
– RF IN port on PAA1 if RUC module is in slot A2
– RF IN port on PAA3 if RUC module is in slot A5
6. Using cable 1955000P079, connect the CH 2/4 connector on the RUC module to either of
the following as appropriate:
– RF IN port on PAA2 if RUC module is in slot A2
– RF IN port on PAA4 if RUC module is in slot A5
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 65
Page 78

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
7. Using cable 1001475P001, connect the PA CTL1/3 connector on the RUC module to
either of the following as appropriate:
– CNTL port on PAA1 if RUC module is in slot A2
– CNTL port on PAA3 if RUC module is in slot A5
8. Using cable 1001475P001, connect the CTL 2/4 connector on the RUC module to either of
the following as appropriate:
– CNTL port on PAA2 if RUC module is in slot A2
– CNTL port on PAA4 if RUC module is in slot A5
4.2 Installing cPCI Chassis Air Baffles
The air baffles for the RAN chassis are used in all empty chassis slots. This is done to maintain
airflow around the chassis modules.
Use the following procedure to install air baffles:
1. Identify designated RAN Chassis cPCI slot for the cPCI air baffle.
2. Insert air baffle into designated slot on chassis and tighten screws.
4.3 Installing a Rectifier Module
To install a rectifier module, use the following procedure (Figure 47):
Note: For a description of the rectifier including function, controls, and indicators, refer
to Section 1.8 on Page 23. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to Figure 40
on Page 58.
1. Connect cables following Section 22 on Page 66.
2. Slide the rectifier into the rectifier compartment.
3. Turn the gravity latch down to lock the rectifier in place.
Table 22. Rectifier Ports and Connections
RECTIFIER PORT CONNECTS TO USING CABLE COMMENTS
L1, L2, L3 EMI Line Filter
F-L1, F-L2
RECT GND GND Stud 1001473P001 Connect to cabinet ground stud
+B AT, - BAT Anderson con-
nector
1001473P001 Connect black wire to F-L1 (on EMI Line Filter); connect
brown wire to FL-2
1001477P001 Connect to Anderson connector in battery compartment;
connect black wire to 0V (+BAT) and blue wire to -BAT
OV OUT,
-OV OUT
Page 66
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
temp sensor,
circuit breakers REC+ and
REC-
1001477P001
1001469P001
1001470P001
Place temperature sensor in battery compartment; connect
1001477P001 black wire to OV OUT and blue wire to OV OUT; connect 1001469P001 from rectifier OV OUT
to circuit breaker POS; connect 1001470P001 from rectifier -OV OUT to circuit breaker NEG
Page 79

Table 22. Rectifier Ports and Connections
RECTIFIER PORT CONNECTS TO USING CABLE COMMENTS
25 Pin D Circuit breaker
panel N/C port
1001477P001 Connect white wire to circuit breaker N/C and brown wire
to COM
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
RS232 STF module
RECT port
LOCK
UNLOCK
1001476P001 Connect to STF module connector labeled RECT in RAN
chassis and RS-232 connector on the rectifier
Figure 47. Installing a Rectifier
21274-A
Page 67
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 80

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
4.4 Installing a Compact PCI Power Supply (cPCI P/S) Module
The cPCI Power Supply Module installs into Slots 1 and 2 or Slots 3 and 4 of the RAN chassis.
One module is required per RAN chassis. Either set of two slot can be used. A second module
can be installed for redundancy.
Note: For a description of the cPCI P/S module including function, controls, and
indicators, refer to Section 1.7.1 on Page 12. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram,
refer to Figure 40 on Page 58.
Use the following procedure to install a cPCI Power Supply Module:
1. Identify the designated chassis slots for the module. This will be Slots 1 or 2 or Slot 3 and
4.
2. Remove the module from the anti-static packaging and orient for installation.
3. Slide the module into the designated slots within the RAN cPCI chassis.
4. Lock the IEL handles on the top and bottom of the RUC module into the cPCI chassis and
tighten handle screws.
4.5 Installing a Power Amplifier Assembly
The RAN holds up to four PAAs. One PAA is required for each band being supported. Use the
following procedure to install a PAA:
Note: For a description of the PAA including function, controls, and indicators, refer to
Section 1.9 on Page 25. For a RAN chassis interconnection diagram, refer to Figure 40 on
Page 58.
1. Connect cables per Table 23.
2. Slide the PAA into place.
Table 23. PAA Connections
PAA PORT CONNECTS TO USING CABLE TYPE COMMENTS
I2C (J2) RUC module P/A
CNTL 2/4 or 1/3
48V PWR (J1) Circuit breaker
1A, 2A, 3A, or
4A port
1001475P001 RJ-45 connector. Connect cable from
1001471P001 Positronic 3-pin connector. Connect
PIC module port J2 (CNTL) to RUC
P/A CNTL 1/3 or P/A CNTL 2/4
cable from PIC module J1 port to circuit breaker 1A, 2A, 3A, or 4A port;
the circuit breaker has an individual
output for each of the four PAAs
RF OUT Plexer module
TX port
RF IN RUC module CH
1/3 or CH 2/4
port
Page 68
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
1955000P080 SMA connector. Connect cable from
PAA RF OUT to plexer port TX
1955000P079 SMA connector. Connect cable from
PAA RF IN port to RUC module
CH 1/3 or CH 2/4 port
Page 81

RAISE KNOB TO
UNLATCH RECTIFIER
ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
Figure 48. Installing a PAA
21246-A
Page 69
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 82

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
5 MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
This section provides procedures for completing various maintenance tasks at the RAN. Refer
to the procedures in this section as necessary when scheduled maintenance is required. For fault
and troubleshooting procedures, refer to the system operation and maintenance manual, ADCP75-209.
5.1 cPCI Fan Replacement Procedure
The RAN chassis is equipped with a cooling fan that exhausts heated air from the chassis
assembly. Cool air enters the cPCI chassis through vent openings on the front door of the
cabinet. The recommended replacement interval is 60 months.
Use the following procedure to remove and replace the cPCI cooling fan.
1. Loosen the two thumbscrews that secure the fan access panel front door.
2. Open the hinged door (it swings down) to access the fan compartment.
3. Slide out the fan being replaced, note how it is connected, and then disconnect the fan.
4. Connect the new fan like the previous fan and slide it into the fan compartment.
5. Verify that the fan is running properly.
6. Close the fan panel door and secure it with the thumbscrews.
5.2 Cleaning or Replacing an Air Inlet Filter
The RAN cabinet air filter cleans the intake air before it enters the cabinets. The filter should be
cleaned approximately once per year and more often in extremely dirty environments. If the
cabinet temperature gradually rises over a long period of time and there are no fan failures, it is
possible that the filter is dirty and requires cleaning. Use the following procedure to clean the
cabinet air filter:
1. Open the RAN enclosure door and remove the inlet air filter tray door as shown in
Figure 49.
2. Pull the filter and away from its mounting slot at the bottom of the cabinet.
3. Gently tap the filter against your hand to dislodge the dirt. If necessary, use compressed air
or a vacuum cleaner to remove the dirt.
4. Carefully inspect the filter for holes or tears and replace if it is damaged.
5. Orient the filter with the airflow arrows pointed inside the RAN.
6. Close and secure the inlet air filter tray.
Page 70
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 83

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
FILTER
Figure 49. Air Inlet Filter Tray
21275-A
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Page 71
Page 84

ADCP-75-210 • Issue 1 • March 2007
6 CUSTOMER INFORMATION AND ASSISTANCE
PHONE:
U.S.A. OR CANADA
Sales: 1-800-366-3891 Extension 73000
Technical Assistance: 1-800-366-3891
Connectivity Extension 73475
Wireless Extension 73476
EUROPE
Sales Administration: +32-2-712-65 00
Technical Assistance: +32-2-712-65 42
EUROPEAN TOLL FREE NUMBERS
Germany:
UK:
Spain:
France:
Italy: 0800 782374
ASIA/PACIFIC
Sales Administration: +65-6294-9948
Technical Assistance: +65-6393-0739
ELSEWHERE
Sales Administration: +1-952-938-8080
Technical Assistance: +1-952-917-3475
WRITE:
ADC TELECOMMUNICATIONS, INC
PO BOX 1101,
MINNEAPOLIS, MN 55440-1101, USA
0180 2232923
0800 960236
900 983291
0800 914032
ADC TELECOMMUNICATIONS (S'PORE) PTE. LTD.
100 BEACH ROAD, #18-01, SHAW TOWERS.
SINGAPORE 189702.
ADC EUROPEAN CUSTOMER SERVICE, INC
BELGICASTRAAT 2,
1930 ZAVENTEM, BELGIUM
PRODUCT INFORMATION AND TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE:
connectivity.tac@adc.com
wireless.tac@adc.com
euro.tac@adc.com
asiapacific.tac@adc.com
Contents herein are current as of the date of publication. ADC reserves the right to change the contents without prior notice.
In no event shall ADC be liable for any damages resulting from loss of data, loss of use, or loss of profits and ADC further
disclaims any and all liability for indirect, incidental, special, consequential or other similar damages. This disclaimer of
liability applies to all products, publications and services during and after the warranty period. This publication may be
verified at any time by contacting ADC's Technical Assistance Center.
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
13944-RM
All Rights Reserved
Printed in U.S.A.
Page 72
© 2007, ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...