Page 1
Megabit Modem CRA-C
User Manual
Power
1
0
B
A
S
E
-
T
A
D
S
L
Manual Number: 425-613-150-02
Page 2

Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
P/N 425-613-150-02
Revision 02
May 1998
Copyright © 1998. PairGain Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document contains proprietary information which is protected by
copyright.
Information contained in this document is company private to PairGain
Technologies, Inc. and shall not be modified, used, copied, reproduced or
disclosed in whole or in part without the written consent of PairGain.
PairGain is a registered trademark, and Megabit Modem is a trademark of
PairGain Technologies, Inc.
Other product names mentioned in this manual are used for identification
purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
The information in this publication is believed to be accurate in all respects.
However, PairGain Technologies cannot assume responsibility for any
consequences resulting from the use thereof. The information contained herein
is subject to change. Revision to this publication or new additions to it may be
issued to incorporate such changes.
ii Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 3
FCC NOTICE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with this instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communication.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more
of the following measures:
•
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
•
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the grantee of this device voids
the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual iii
Page 4

DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer’s name
and address:
declares that
Product name:
conforms to the following
Standards:
Application of Council Directives:
I, the undersigned, hereby declare that the equipment specfied above conforms
to the above directives and standards.
Signature:
PairGain Technologies, Inc.
14402 Franklin Ave
Tustin, CA 92780-7013
U.S.A.
Megabit Modem CRA-C
EN55022 (1987), EN50082-1 (1992),
EN60950 (1994)
89/336/EEC, 73/23/EEC
Roy Stephens,
Director of Quality Assurance
Place:
Date:
iv Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Tustin, CA, U.S.A.
March 16, 1998
Page 5

USING THIS MANUAL
This manual helps you:
understand the features of the PairGain® Megabit Modem™ CRA-C
•
and how the unit operates as a component within a network
install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
•
configure your unit to operate within the network
•
contact PairGain if you need additional help
•
Three types of messages with icons appear in the text:
Notes inform you of special circumstances.
Cautions indicate the possibility of damage to equipment.
Warnings indicate the possibility of personal injury.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual v
Page 6

Using This Manual
vi Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 7

CONTENTS
ABOUT THE MEGABIT MODEM CRA-C __________________ 1
INSTALL THE MEGABIT MODEM CRA-C_________________ 7
CONFIGURE AND VIEW STATUS________________________ 17
About Rate Adaptive Transmission..................................... 2
Rate Adaptation.............................................................. 2
Reach, Data Rate, SNR Margin,
and Noise Environment............................................ 4
Unpack and Inspect the Shipment....................................... 7
Identify LEDs and Connectors............................................ 9
Front Panel..................................................................... 9
Rear Panel....................................................................11
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C ..................................12
Connect to the ADSL Line ........................................... 12
Connect to the Data Network ........................................ 13
Power Up and Check LEDs .............................................. 16
Connect to an ASCII Terminal.......................................... 17
How to Log On and Navigate the Menus .......................... 19
How to Configure a Remote Unit...................................... 23
Configure System Settings................................................ 24
Configure ADSL Transceiver ........................................... 26
Configuration ............................................................... 26
Reset ADSL Transceiver .............................................. 29
Configure the Bridge/Router............................................. 30
Configure as a Bridge................................................... 31
Configure as a Router................................................... 34
Configure SNMP..........................................................38
Reset the Ethernet Bridge.............................................40
View Status ...................................................................... 41
System Information ...................................................... 41
ADSL Transceiver Status.............................................. 42
Ethernet Bridge Statistics.............................................. 48
Log Out............................................................................49
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual vii
Page 8

Contents
NETWORK AND MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW____________ 51
MAC Layer Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol............51
Static IP Routing............................................................... 53
Megabit Modem CRA-C IP Addresses..........................59
Management Protocols...................................................... 61
SNMP...........................................................................61
Megabit Modem CRA-C SNMP Agent .........................62
MIB and Trap Support.................................................. 63
Network Configuration and Image Code Download ..........64
BOOTP.........................................................................64
TFTP ............................................................................66
Encapsulation Protocols....................................................66
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS _________________________ 67
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE______________________________ 69
World-Wide Web..............................................................69
FTP ..............................................................................69
LIMITED WARRANTY _________________________________ 71
GLOSSARY____________________________________________ 73
viii Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 9
ABOUT THE MEGABIT MODEM CRA-C
The PairGain® Megabit Modem™ CRA-C uses Asymmetric Digital
Subscriber Line (ADSL) technology to provide, on a single pair telephone line,
a multi-megabit Ethernet connection between the subscriber and the service
provider. The Megabit Modem CRA-C transmits data up to 3.16 Mbps from a
service provider and receives data up to 1.08 Mbps from a subscriber. The
Megabit Modem CRA-C is rate adaptive; its speed is adjusted to the maximum
attainable data rate depending on distance and line condition. Additionally,
ADSL technology allows ordinary telephone service to coexist with the
high-speed data service on the same wire pair.
The rate-adaptive Megabit Modem allows the service provider to deliver the
best possible data rate for any subscriber. Typically, a subscriber closest to the
provider receives the highest data rate available, while subscribers farther
away receive data at a lower transmission rate.
The Megabit Modem CRA-C has field-proven Carrierless
Amplitude-modulation and Phase-modulation (CAP) line coding.
The 2-dimensional, 8-state Trellis coding with Viterbi decoding and
the Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction provide robust transmission
in harsh environments.
Use the Megabit Modem CRA-C for application solutions, particularly those
requiring high-speed transmission to the subscriber, such as:
Internet access
remote Local Area Network (LAN) access
telecommuting
small office or home office
•
Other features of the Megabit Modem CRA-C include:
embedded Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent
IEEE 802.1d transparent MAC level bridging with Spanning Tree
protocol support
static IP routing to provide secure access to the Internet
BOOTP and TFTP to download software
10BASE-T Ethernet port for connection to an Ethernet LAN
line port for Rate-adaptive ADSL single-pair connection
console port for maintenance and management
•
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 1
Page 10
About the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Use the Megabit Modem CRA-C with these other PairGain products:
Megabit Modem CRA (at subscriber site)
•
S1 Network Interface Device (network interface at subscriber site)
•
About Rate Adaptive Transmission
The following definitions are useful for understanding the operation of the
Megabit Modem:
Bit Error Rate (BER) is the ratio of received bits that are in error
•
relative to the total number of bits received, measured over time.
For example, 10
7
10
bits received.
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is the ratio (typically expressed in dB) of
•
the received signal power to the received noise power. It is a measure
of the quality of the transmission. The theoretically achievable BER
can be extrapolated from the measured SNR.
Margin (SNR margin) is the amount of degradation in SNR that the
•
system can tolerate under the current conditions and still achieve a
-7
10
BER. A margin of 6 dB, for example, would mean that the SNR
can degrade by 6 dB and still provide a performance of 10
PairGain Megabit Modem CRA-C has a margin configuration option
that defaults to 6 dB, but may be set anywhere between -3 dB to 9 dB.
-7
BER means that on average one error occurs per
-7
BER. The
Reach is the longest loop length that the system can support with
•
a given margin and a BER of less than 10
-7
at the given data rate.
Rate Adaptation
With PairGain's rate adaptive technology, the Megabit Modem CRA-C
can automatically adjust to the fastest speed possible, given the transmission
distance and line conditions. Alternatively, the provider can manually set
the modem to a specific rate. The available data rates are:
downstream (transmit) rates: 3.168 Mbps, 2.528 Mbps, 2.208 Mbps,
•
1.888 Mbps, 1.568 Mbps, 1.248 Mbps, 928 Kbps, 608 Kbps
upstream (receive) rates: 1.080 Mbps, 944 Kbps, 808 Kbps, 672 Kbps,
•
536 Kbps, 400 Kbps, 264 Kbps, 82.66 Kbps
2 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 11

About the Megabit Modem CRA-C
The Megabit Modem CRA-C can be set to any one of three modes that
determine how the data rate is selected. It is important to note that rate
adaptation occurs only during startup. The Megabit Modem CRA-C will
not change its data rate while the link is up. The three startup modes are:
Full startup always:
•
the highest upstream and downstream data rates it can support under
the current line conditions, with a margin greater than or equal to the
configured margin. This is done during every ADSL startup attempt.
The system will always attempt a full startup where it will set a
transmission rate up to the maximum specified. It determines this rate
by assessing the signal quality data (line length and noise conditions,
for example) and the margin configuration setting. It then comes up
in the highest available rate based on this information.
In the full startup mode, the system figures out
Session startup:
•
rates set during a previous full startup, rather than re-assessing the
signal quality data. In this mode the system performs a full startup
upon every powerup or reset and would also revert back to a full
startup attempt when a session startup is not successful for 30 seconds.
Fixed data rate:
•
programs both the upstream and the downstream data rates using the
Transceiver Configuration Menu. The user can select from available
data rates shown above. Another configuration parameter is the
startup SNR margin that is also configurable using the Transceiver
Configuration Menu. The system will attempt to come up to the
programmed data rates with a margin greater than or equal to the
configured margin. Failure to complete startup with the desired
margin results in repeated attempts to accomplish it.
When a connection is lost in any mode (the cable disconnected, for example),
the system attempts reconnection as if it has been reset.
In session startup mode, the system uses the data
In a fixed-rate mode (fixed data rate), the user
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 3
Page 12
About the Megabit Modem CRA-C
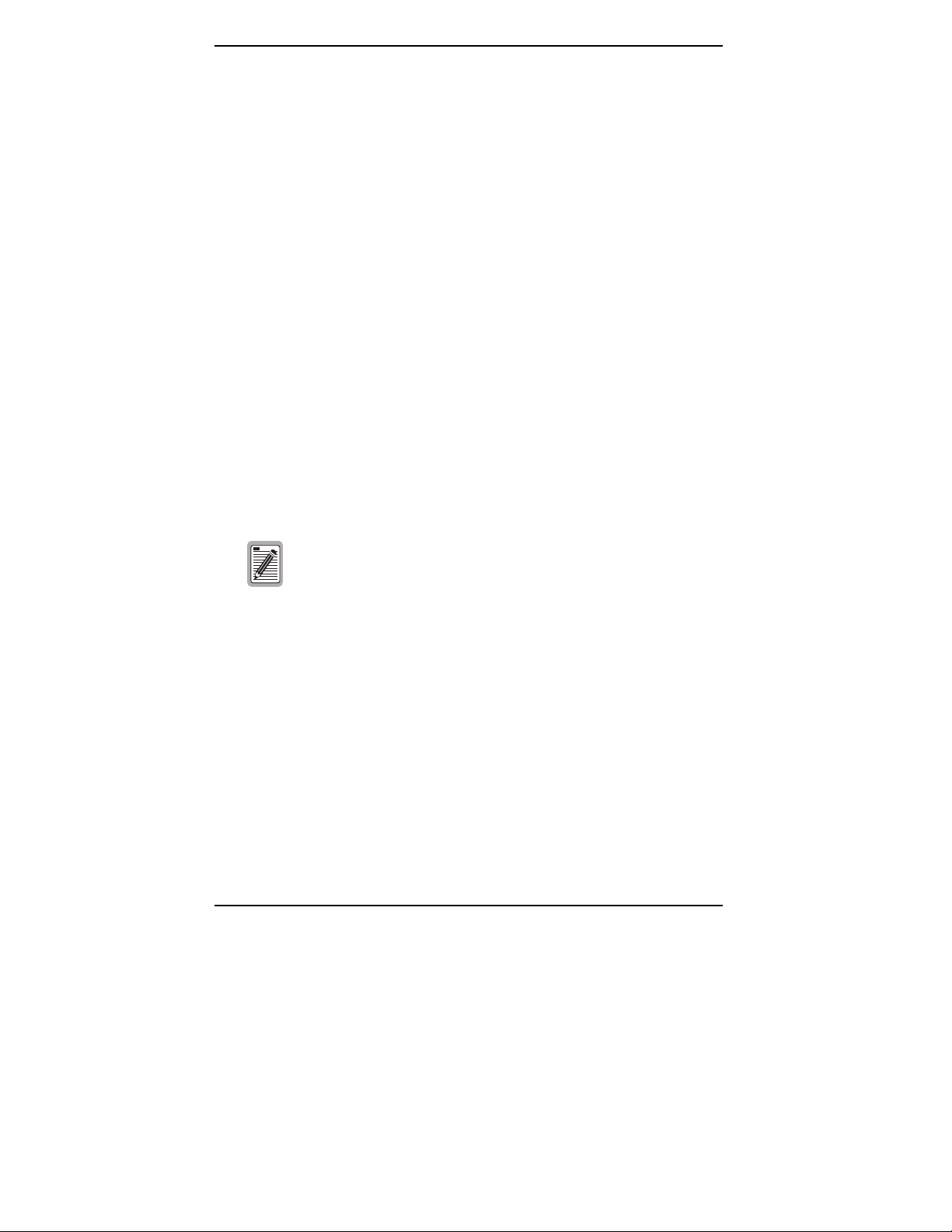
Reach, Data Rate, SNR Margin, and Noise Environment
The maximum transmission rate of the Megabit Modem CRA-C is determined
by distance, SNR margin, and the condition of the line (wire gauge, condition
noise environment). Figure 1 shows the relationship between reach and data
rate for a given set of conditions. The plots can be used to determine the
achievable reach at a given data rate, or they may be used to determined the
achievable data rates at a given distance. In all of the cases except the no
noise case, a margin of 6 dB was allocated above the SNR that provides a Bit
Error Rate (BER) of 10
These line conditions fall within the range of the plots shown in Figure 1:
no noise (0 dB margin)
•
low noise (−140 dBm-Hz Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN))
•
24 ISDN lines in the same binder group
•
24 HDSL lines in the same binder group
•
24 ADSL lines in the same binder group
•
10 T1 lines in an adjacent binder group
•
-7
.
one T1 line in the same binder group
•
The performance shown is "typical" for PairGain Megabit
Modem CRA products. Due to variations in environment and
test setup, PairGain does not guarantee performance to the
figures shown.
One of the configuration options in the Megabit Modem CRA-C is the
startup margin setting. This setting defaults to 6 dB but may be set from
-3 dB to 9 dB. The modems will attempt to come up at the programmed
margin setting. Setting the margin high allows for a cushion against changing
line conditions and impulse noise. Setting the margin low provides less
protection but allows the modems to come up at a higher data rate (if in the
rate-adaptive modes) or at a longer loop length (if in the fixed data rate mode).
The default setting of 6 dB is recommended and provides an overall BER
better than 10
less than 10
4 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
-10
. Reducing the setting to 0 dB will only provide a BER of
-7
and is not recommended.
Page 13
About the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Figure 1.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 5
Reach for a Rate Adaptive ADSL Megabit Modem
Page 14

About the Megabit Modem CRA-C
6 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 15
INSTALL THE MEGABIT MODEM CRA-C
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C using these sections:
For information about this topic Go to page
Unpack and inspect the shipment 7
Identify LEDs and connectors 9
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C 12
Power up and check LEDs 16
Unpack and Inspect the Shipment
Upon receipt of the equipment:
1 Unpack each container and visually inspect it for signs of
damage. If the equipment has been damaged in transit,
immediately report the extent of damage to the transportation
company and to your sales representative. Order replacement
equipment if necessary.
2 Check the contents to the packing list to ensure complete and
accurate shipment. If the shipment is short or irregular, contact
your sales representative. If you must store the equipment for a
prolonged period, store the equipment in its original container.
The shipping carton contains, in addition to the Megabit Modem CRA-C and
this manual, the cables described in Table 1.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 7
Page 16

Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Table 1.
Cables for Megabit Modem CRA-C
Item Description Function
Straight-through
Category 3 cable
Cross-over
Category 5 cable
ADSL cable Gray UTP cable
Console cable Flat, silver, eight-wire
Console adapter A rectangular DB-9 (F)
Black unshielded
twisted-pair (UTP)
cables terminated with
RJ-45 connectors.
Yellow UTP cable
terminated with RJ-45
connectors.
terminated with RJ-11
and RJ-45 connectors.
cable with RJ-45
connectors at each end.
to RJ-48 adapter with
two captive mounting
screws.
Connects the Megabit Modem
CRA-C Ethernet MDI-X port
to a network device with an
MDI port.
Connects the Megabit Modem
CRA-C Ethernet MDI-X port
to a network device with an
MDI-X port.
Connects the Megabit Modem
CRA-C to the ADSL line.
Plugs into the Console port to
connect the Megabit Modem
CRA-C to an ASCII terminal.
Do not use as a 10BASE-T
Ethernet cable.
Optional. Connects the
Megabit Modem CRA-C to an
ASCII terminal for
configuration and viewing
status.
Power supply An AC to DC power
supply that plugs into
the power outlet.
Do not tamper with the power supply safety
prong. It is a critical element for the secondary
lightning protection provided within the Megabit
Modem CRA-C. If you tamper with the safety
prong, you risk serious injury.
8 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Provides primary power to the
Megabit Modem CRA-C and
establishes a safety ground.
Page 17

Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Identify LEDs and Connectors
The Megabit Modem CRA-C front panel has LEDs that show status for power
and data transmission. The rear panel has external interface connectors and a
power switch.
Front Panel
Figure 2 and Table 2 describe the LEDs on the Megabit Modem CRA-C
front panel.
Figure 2. Megabit Modem CRA-C Front Panel
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 9
Page 18
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Table 2.
Front Panel LEDs
LED Mode Description
Power Green Indicates power is on.
10BASE-T
LINK Green
Off
TX Green
Off
COL Green
Off
ADSL
SYNC Solid green
Flashing green
Off
STAT Solid green
Ethernet connection up.
Ethernet connection down.
Transmit activity at port.
No transmit activity at port.
Collisions occurring on the port.
No collisions occurring on the port.
Normal operation.
Training in progress.
Megabit Modem CRA not synchronized with
Megabit Modem CRA-C.
Normal operation.
Flashing green
MAR Solid green
Flashing green
10 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Test/Alarm condition exists.
Margin is above threshold.
Margin is below threshold.
Page 19

Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Rear Panel
Figure 3 and Table 3 describe the Megabit Modem CRA-C rear panel features.
Figure 3.
Megabit Modem CRA-C Rear Panel
Table 3.
Rear Panel Components
Name Function
POWER connector 6-pin mini-DIN type port that supplies power to Megabit
Modem CRA-C.
Do not connect any other wall-plug supply to the
Megabit Modem CRA-C unit, otherwise, you can
permanently damage the unit.
ON/OFF switch Toggle switch used to turn modem ON and OFF.
CONSOLE port RJ-45 connector (RS-232 compatible) used to connect an
ASCII terminal for configuring the Megabit Modem(s).
10BASE-T
MDI-X port
ADSL port RJ-48 port used to connect the Megabit Modem CRA-C to the
RJ-45 MDI-X (cross-over) port used to connect the Megabit
Modem CRA-C to a 10BASE-T port of a data network device.
ADSL transmission line.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 11
Page 20
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Complete the steps in the order listed to install the Megabit Modem CRA-C:
connect to the ADSL line
•
connect to the data network
•
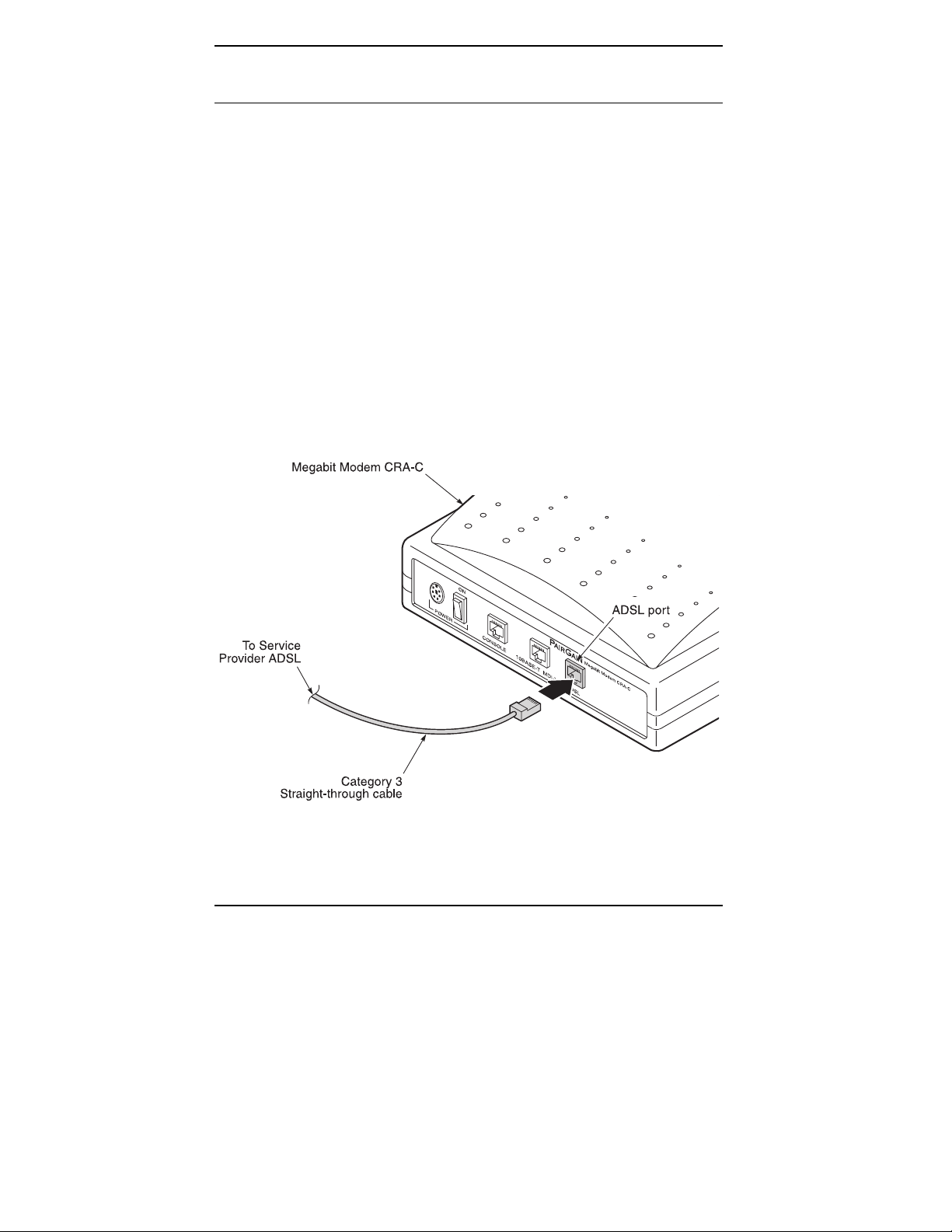
Connect to the ADSL Line
The Megabit Modem CRA-C requires a single pair of telephone wires to
connect the subscriber to the service provider. One wire is the Tip
and the other is the Ring. See Table 4 for pinouts. Connect the Tip and Ring
wires to your Megabit Modem CRA-C:
1 Plug the RJ-45 connector of the ADSL cable (gray) into the
ADSL port on the Megabit Modem CRA-C rear panel (Figure 4).
2 Connect the RJ-11 connector to the ADSL line.
Figure 4.
12 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Connecting to the ADSL Line
Page 21
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Table 4.
ADSL Pin Assignments for RJ-45 Connector
Pin Signal
1 Not Used
2 Not Used
3 Not Used
4 ADSL (Ring)
5 ADSL (Tip)
6 Not Used
7 Not Used
8 Not Used
Connect to the Data Network
The 10BASE-T MDI-X port connects the Megabit Modem CRA-C to the data
network. If the data network has an MDI-X port, use the yellow cross-over
Category 3 or better cable. If the data network has an MDI port, use the black
straight-through Category 3 or better cable.
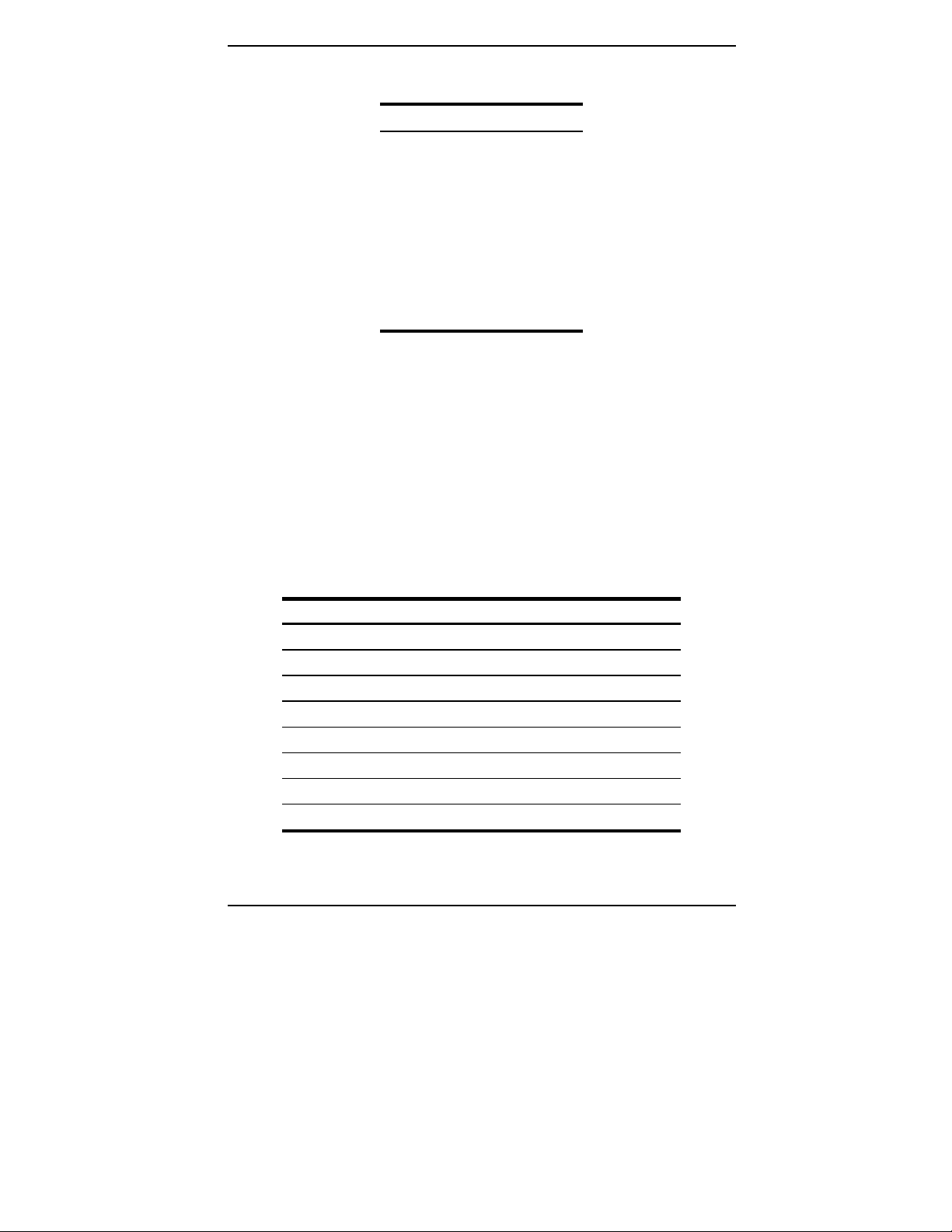
Table 5 and Figure 5 show the 10BASE-T Ethernet interface data signals for
both MDI and MDI-X configurations.
Table 5.
10BASE-T Interface Control Signals
MDI Pin MDI-X Pin Signal Description
1 3 TD+ Transmit Data (+)
2 6 TD- Transmit Data (-)
3 1 RD+ Receive Data (+)
44- 55- 6 2 RD- Receive Data (-)
77- 88- -
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 13
Page 22
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Figure 5
14 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
. Straight-through and Cross-over Cable Pinouts
Page 23
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
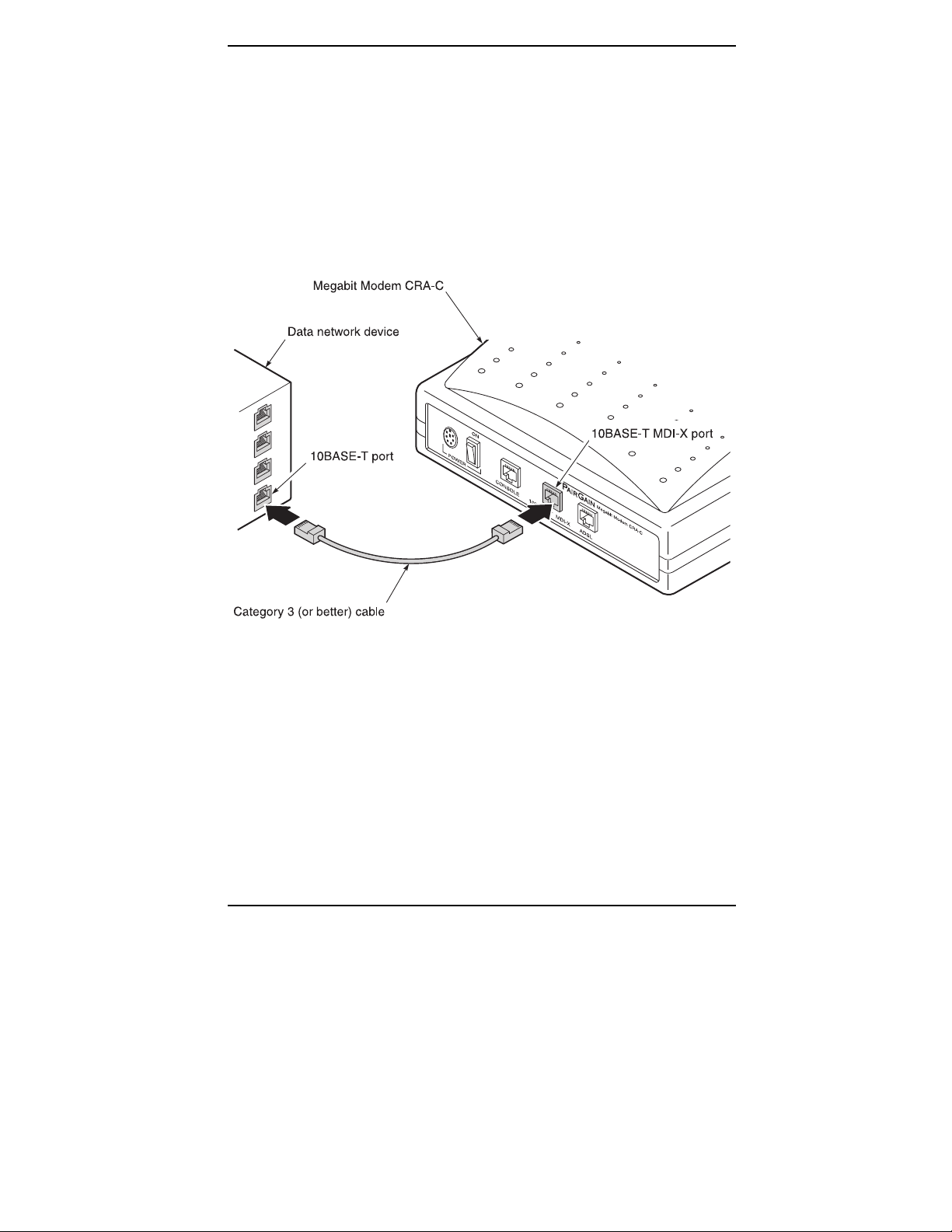
Connect to the data network using either the black straight-through cable or the
yellow cross-over cable:
1 Plug the RJ-45 connector of the Category 3 cable into the
10BASE-T MDI-X connector on the Megabit Modem CRA-C
rear panel (Figure 6).
2 Attach the other end of the Category 3 cable to the 10BASE-T
port of your data network.
Figure 6.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 15
Connecting to the Data Network
Page 24
Install the Megabit Modem CRA-C
Power Up and Check LEDs
Install the power cable and power up the Megabit Modem CRA-C:
1 Plug the mini-DIN connector on the wall-plug supply into the
power connector on the rear of the Megabit Modem CRA-C, then
plug the wall-plug supply into the facility power.
Do not connect any other wall-plug supply to the Megabit
Modem CRA-C. If you use another wall-plug supply, you
can permanently damage the unit.
2 Turn ON the ON/OFF switch on the rear panel. The unit enters a
self-test mode with the following LED indications:
ADSL STAT LED flashes green
•
ADSL SYNC LED flashes green
•
Power LED lit solid green
•
Allow the Megabit Modem CRA-C approximately 30 to 60
seconds to synchronize with the Megabit Modem CRA at the
other end of the ADSL line.
3 Verify the following LED indications (after the self test is
completed):
10BASE-T LINK LED is solid green (when the Ethernet port
•
is connected)
ADSL SYNC LED is solid green
•
ADSL STAT LED is solid green
•
ADSL MAR LED is solid green
•
If conditions other than those listed above exist, check the installation.
See Table 2 for a description of the front panel indications.
16 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 25

CONFIGURE AND VIEW STATUS
In this chapter, you configure the Megabit Modem CRA-C or view system
status using an ASCII terminal connected to the console port. Go to
the following sections:
To complete this task
Connect to an ASCII terminal 17
How to log on and navigate the menus 19
How to configure a remote unit 23
Configure the system settings 24
Configure the ADSL transceiver 26
Configure the Bridge/Router 30
View status 41
Log out 49
Go to page
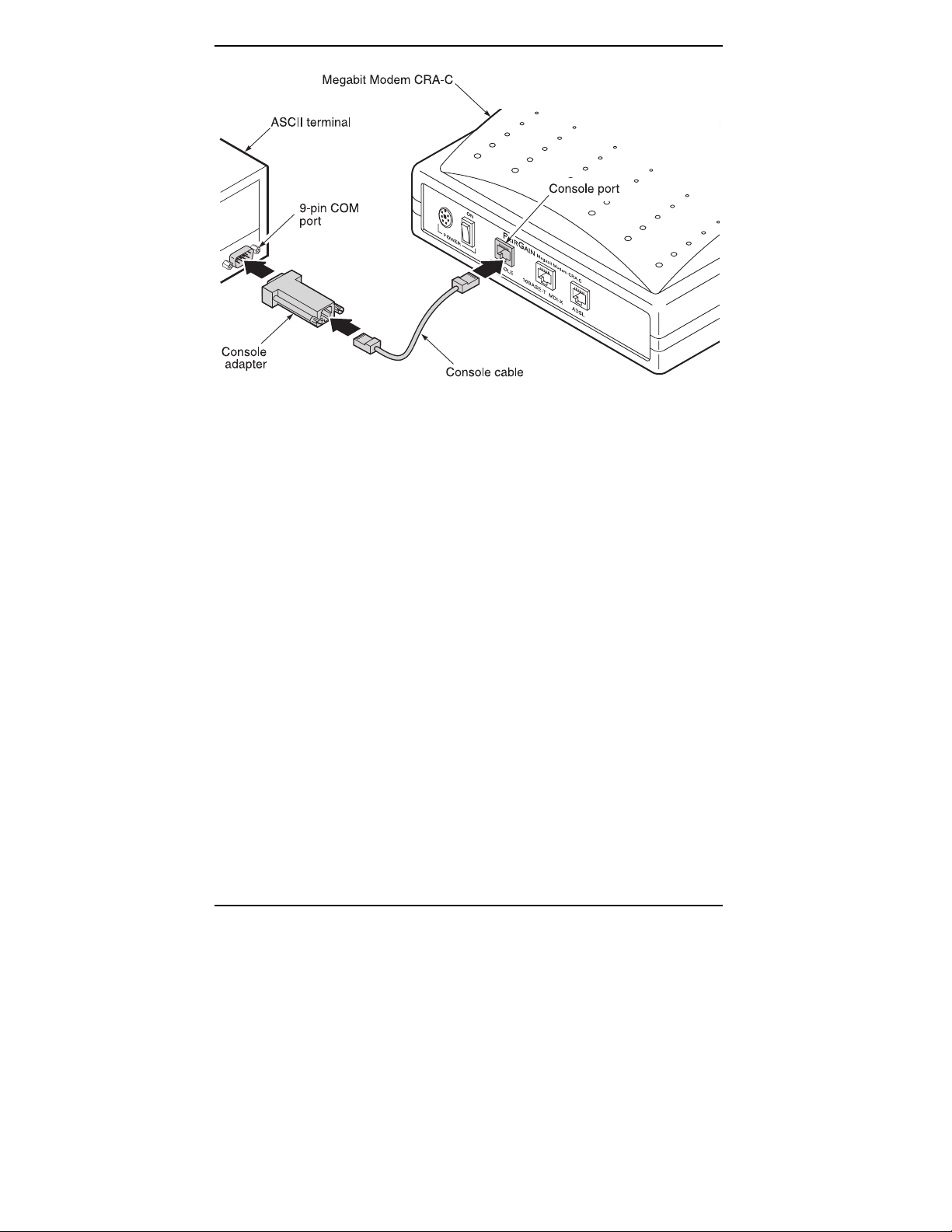
Connect to an ASCII Terminal
Connect the Megabit Modem CRA-C to an ASCII terminal:
1 Plug the console adapter into the standard 9-pin COM port on
the ASCII terminal and tighten the captive screws until they are
snug (Figure 7). (Skip this step if the ASCII terminal has an
RJ-48 jack.)
2 Connect one end of the silver console cable to the
console adapter.
3 Connect the other end of the silver console cable to the console
port on the Megabit Modem CRA-C rear panel.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 17
Page 26
Configure and View Status
Figure 7. Connecting to an ASCII Terminal
4 Configure these communication settings for the ASCII terminal:
9600 to 19,200 baud
•
no parity
•
8 data bits
•
stop bit
•
flow control to OFF
•
5 Select ANSI for terminal emulation.
18 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 27

Configure and View Status
How to Log On and Navigate the Menus
This section shows you how to log on and then how to navigate the menu
structure. Every console screen has a menu header which displays the time in
the upper right corner and the date in the upper left corner.
Through the menus, you can configure a local and a remote modem. The
header on each menu screen identifies the modem being monitored or
configured:
ATU-C is the ADSL Transceiver Unit (ATU) at the service provider
site which is the Megabit Modem CRA-C.
ATU-R is the remote Megabit Modem CRA at the subscriber site
Log on to the Megabit Modem CRA-C:
1 Press the spacebar several times to activate the autobaud feature
and to display the Logon Password screen.
07/2/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:42:36
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
LOGON PASSWORD>
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 19
Page 28

Configure and View Status
ENTER
ENTER
establish a different password, you must type the new
password at the LOGON PASSWORD prompt on a
subsequent log on.
2 Type your password at the password prompt or press
(factory default password) if you have not customized
your password. The Main Menu displays.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:43:18
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
MAIN MENU
1. SYSTEM STATUS AND CONFIGURATION
2. ADSL MENU
3. BRIDGE/ROUTER MENU
4. REMOTE LOGON
Q. LOGOUT
ENTER CHOICE-->
is the factory-default password. If you
ENTER
ENTER
See the section, "Configure System Settings," to establish a new
password.
20 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 29

Configure and View Status
Figure 8 shows the structure for the Megabit Modem CRA-C menus. Type the
number of the menu item you want to view or configure.
Figure 8.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 21
Megabit Modem CRA-C Menu Structure
Page 30

Configure and View Status
Table 6 shows the ASCII terminal key functions used to navigate the menus
and to select settings.
Table 6.
Keyboard Functions
Key Function
ESC
ESC
Restores the parameter to the last saved setting. Applies to
parameters where you type a value but not to parameters you toggle.
M
Q
Q
R
R
Ctrl
Ctrl
Goes to Main Menu.
Performs a log out from the Main Menu.
Returns to the next higher-level menu.
Refreshes the current screen.
R
R
T
Toggles between ATU-C and ATU-R menus.
Status Menus and Reports
C
C
N
N
P
P
U
U
Clears the current values.
Selects the next page.
Selects the previous page.
Restores previous setting by undoing the last action.
When configuring Megabit Modem CRA-C parameters:
Toggle among predefined optional settings (for example, select
STARTUP OPTION in the ADSL Configuration Menu and then
toggle through the choices) as follows:
Type the number of the option.
1
ENTER
Press the spacebar to select the new setting, then press
2
Type required information (for example, to change system time, type
ENTER
.
in the hour, minute, and second as hh:mm:ss) as follows:
Type the number of the option. The screen prompts you to type
1
specific information.
Type the information, following the instructions on the screen,
2
ENTER
ENTER
then press
22 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
.
Page 31

Configure and View Status
How to Configure a Remote Unit
From the Megabit Modem CRA-C, you can view system parameters and set
configuration options for the remote Megabit Modem CRA. The remote
console menu header reflects the remote unit as ATU-R. This shows that the
console program is physically connected to the unit at the service provider site
(ATU-C), but is virtually configuring the unit at the subscriber site (ATU-R).
4
At the Main Menu, type
status menus for Megabit Modem CRA (remote ATU-R).
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:43:18
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
MAIN MENU
1. SYSTEM STATUS AND CONFIGURATION
2. ADSL MENU
3. BRIDGE/ROUTER MENU
4. REMOTE LOGON
Q. LOGOUT
ENTER CHOICE-->
4
for Remote Logon to display the configuration and
The following Remote Logon screen is displayed.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:42:28
ATU-R ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
LOGON PASSWORD>
Optionally, you can press
Ctrl
T at the logon screen or at any menu
shown in the menu tree (Figure 8) to toggle between the local and remote
Megabit Modems.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 23
Page 32

Configure and View Status
Configure the System Settings
This section describes configurable system settings. You can change factory
default settings like time and date, or create a password and unique ID for
the unit.
1
1 On the Main Menu, type
Configuration menu.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:43:23
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
SYSTEM STATUS AND CONFIGURATION
1. SYSTEM INFORMATION
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
1
to display the System Status and
2
2
2 Type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:54:52
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
1. CHANGE SYSTEM TIME
2. CHANGE SYSTEM DATE
3. CHANGE PASSWORD
4. FACTORY DEFAULT CONFIGURATION
(R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
to display the System Configuration menu.
24 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 33

Configure and View Status
g
play
yp
yp
p
g
y
y
y
p
g
g
3 Do the following for each system setting option you want
to change:
Type the number of the option you want to configure.
Type the appropriate information for each option as indicated
ENTER
ENTER
in Table 7 then press
.
Table 7. System Configuration Options
Type
No.
1 Change
2 Change
3 Change
4 Factory
For Option Function
Type the new time in the 24-hour clock format
System Time
System Date
Password
Default
Configuration
hh:mm:ss at the prompt. The new time shows in the
upper right corner of the screen.
Type the month, day, and year in the mm/dd/yy format
at the prompt. The new date shows in the upper left
corner of the screen.
Enter a maximum of ei
password, do the following:
Type
password, press ENTER dis
ENTER
ENTER
When prompted Please enter the new
password, t
ENTER
ENTER
each character of the password.
When prompted Please retype the
password, t
ress
Password accepted.
If you change the default password, write it down and
save it in a secure place. You cannot recover the
password if it is forgotten.
Resets all ADSL transceiver and Ethernet brid
to default. After
ou will reset these values. Select either N (no) or
that
es) to reset. When you select Y, the modem
Y (
restarts. Press the s
You must then lo
Ethernet brid
including the password.
ht characters. To enter a new
3
3
and the message Creating user
s. Press
.
e the new password then press
. An * appears on the screen as you type
e the new password again then
ENTER
ENTER
. You get this confirmation:
e values
4
ou type
4
, a message warns you
acebar several times to autobaud.
in again. All ADSL transceiver and
e values are now at default values,
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 25
Page 34

Configure and View Status
Configure the ADSL Transceiver
The ADSL menu provides access to set ADSL configuration parameters and to
view ADSL performance and alarm status (menu options 1 through 4). See
"View Status" (page 41) for more information on options 1 through 4.
Configure parameters for ADSL data transmission in the "Configuration"
section that follows. Then, reset the Megabit Modem CRA-C to make the
changes effective using the "Reset the ADSL Transceiver" section (page 29).
2
2
From the Main Menu, type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:44:57
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL MENU
1. ADSL PERFORMANCE STATUS
2. 24 HOUR ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
3. 7 DAY ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
4. ADSL ALARM HISTORY
5. ADSL TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION MENU
6. FULL ADSL RESET
7. SESSION ADSL RESET
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
to display the ADSL Menu.
Configuration
Configure ADSL transmission parameters for the Megabit Modem CRA-C
(ATU-C) only. The Megabit Modem CRA (ATU-R) uses the parameters
specified for the Megabit Modem CRA-C.
5
5
Press
1
Configuration Menu.
05/05/98 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:51:00
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL CONFIGURATION MENU
1. STARTUP OPTION SESSION STARTUP
2. MAX UP DATA RATE 1080
3. MAX DOWN DATA RATE 3168
4. STARTUP SNR MARGIN 6dB
5. MARGIN THRESHOLD 4
6. ES THRESHOLD 100
7. ALARM CONFIGURATION LOF=E MAR=E ES=E SES=E SELF=E
8. TRANSMIT SPECTRUM STANDARD
(C)onfirm (U)ndo (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
26 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
at the ADSL Menu to display the ADSL
Page 35

Configure and View Status
Do the following for each system setting option you want
2
to change:
Type the number of the option you want to configure.
•
Select, using the spacebar, or type the appropriate
•
information for each option as indicated in Table 8 then press
ENTER
ENTER
.
R
After you type
3
transceiver, you are prompted
(Y/N)?
Type Y for yes or N for no. You then return to the
R
or M and have made changes to the ADSL
Save current settings
ADSL Menu.
Table 8.
ADSL Transceiver Options
Type
No.
2* Max Up
For
Option
1 Startup
Option
Data
Rate
Function
Select one of three startup options using the spacebar. The unit
uses the option you select to achieve a transmission rate for the
ADSL line at a reboot or if the line is dropped and recovered.
Full startup always
where it will set a transmission rate up to the maximum specified
in options 2 and 3 for maximum upstream and downstream data
rate. It determines this rate by assessing the signal quality data
(line length and noise conditions, for example) and the SNR
value set in option 4 for SNR startup margin. It then uses the
highest available rate based on this information.
Session startup
full startup to achieve a transmission rate, rather than
re-assessing the signal quality data. In this mode, the system
performs a session startup upon every powerup or reset and
would also revert back to a full startup attempt when a session
startup is not successful for 30 seconds. This is the default.
Fixed data rate
rates that you select in options 2 and 3 for maximum upstream
and downstream data rates. The system attempts to come up at
the programmed data rates with a margin greater than or equal to
the configured margin. If the data rates cannot be obtained, then
the system will continue to attempt the data rate. If it does not
achieve it, sync will not occur.
Select a maximum data rate for the upstream channel (from
subscriber to service provider). Use the spacebar to scroll
through the available rates.
- System will always attempt a full startup
- Session startup uses the data acquired during a
- At startup, the system attempts only the data
(continued)
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 27
Page 36

Configure and View Status
ADSL Transceiver Options (continued)
Type
Table 8.
For Option Function
No.
3* Max Down
Data Rate
4 Startup SNR
Margin
5 Margin
Threshold
6 ES Threshold
7 Alarm
Configuration
8 Transmit
Spectrum
* Certain data rate combinations are invalid. If such a combination is selected in fixed
data mode, the modem will change the rates to a valid combination. When such a
combination is selected in full startup mode, the modem accepts it, but the actual data
rate to be achieved will not match the setting regardless of the line quality.
Select a maximum data rate for the downstream channel
(from service provider to subscriber). Use the spacebar to
scroll through the available rates.
Press the spacebar to select a startup SNR margin from
–3 to 9 dB or NA (don't care about startup SNR margin).
The default is 6 dB.
Type a dB value from 0 to 15. The Margin Threshold, in dB,
is the excess SNR relative to the SNR at 10
-7
BER operation.
When the margin falls below the threshold, this causes an
SNR margin alarm and the MAR LED on the front panel to
blink. The default value is 4.
Type in a value from 0 to 255 for the ES (errored second)
Threshold. If the current 15-minute interval ES exceeds the
set value, then this causes an ES alarm. The default is 100.
Configure each alarm as either major or minor alarm or
disable the alarm. Enabling alarms affects the ADSL STAT
LED, but not the alarm history. The available options for
each alarm are (E) for enabled minor alarm, (D) for disabled
alarms, and (M) for enabled major alarm.
Type
7
7
then press
N
N
until you highlight the alarm you
want to configure. Press the spacebar to toggle among the
ENTER
ENTER
choices listed above and press
to select.
When you disable an alarm, it affects the system
ALARM/STATUS LED or alarm relays, but it does
not affect the reporting of alarm information in the
menu displays.
Select downstream power option of either STANDARD
(default) or HI-PERFORMANCE. Unit uses the selected
option to set the upper limit of the downstream power
spectral density (PSD) during data transmission. PSD for
STANDARD is set to -40 dBm/Hz. PSD for
HI-PERFORMANCE is set to -34 dBm/Hz for frequencies
higher than 220 kHz.
28 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 37

Configure and View Status
Reset the ADSL Transceiver
When you change any of the options 1 through 4 at the ADSL Menu, Reset
the ADSL transceiver to make the changes effective and re-establish the
ADSL link.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:44:57
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL MENU
1. ADSL PERFORMANCE STATUS
2. 24 HOUR ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
3. 7 DAY ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
4. ADSL ALARM HISTORY
5. ADSL TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION MENU
6. FULL ADSL RESET
7. SESSION ADSL RESET
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
6
7
6
Type either
Table 9 describes the Reset options.
7
or
from the ADSL Menu to Reset the ADSL transceiver.
Table 9. Reset ADSL Transceiver Options
Type
For Option Function
No.
6 Full ADSL
Reset
7 Session ADSL
Reset
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 29
Select this option to reset and set a transmission rate
up to the maximum specified in options 2 and 3 of
the ADSL Transceiver Configuration Menu. It
determines this rate by assessing the signal quality
data (line length and noise conditions, for example)
and the SNR value set in option 4 of the ADSL
Transceiver Configuration Menu.
Select this option to reset and use the data rates
acquired during the previous full startup rather than
re-assessing the signal quality data and determining
new rates.
Page 38

Configure and View Status
Configure the Bridge/Router
This section describes how to configure the Ethernet interface (bridge) of
the modem as either a bridge or a router. Then, configure the management
protocol options through the SNMP Configuration menu.
3
On the Main Menu, type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:55:55
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE/ROUTER MENU
----------------------------------------------------------ETHERNET MAC ADDRESS: 00-20-A7-20-68-F2
10 BASE-T LINK STATUS: LINK UP
EBM STATUS: READY
----------------------------------------------------------SELECTIONS 1. BRIDGE/ROUTER CONFIGURATION
2. SNMP CONFIGURATION
3. STATISTICS
----------------------------------------------------------SETTINGS 4. RESET
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
3
to display the Bridge/Router Menu.
The Bridge/Router Menu shows the MAC address for the unit you are
viewing and current 10BASE-T and Ethernet Bridge Mode link status.
See "View Status" (page 41) for more information on the Statistics menu.
Through the Bridge/Router Configuration menu, you can configure the
Megabit Modem as either a bridge to forward Ethernet data based on
MAC addresses or as a router to route Ethernet data based on IP addresses.
You must configure both Megabit Modems (local and remote) with the same
mode (both as bridges or both as routers).
Bridge mode can be a less secure method of sending data because the desired
MAC address is broadcast over the network, but it allows protocols other than
IP to be forwarded. Router mode provides security by statically mapping route
entries. Routing can prevent eavesdropping and provide broadcast filtering.
Select either the "Configure as a Bridge" section (page 31) or the "Configure as
a Router" section (page 34).
After you change Bridge/Router Configuration or the SNMP Configuration
options, "Reset the Ethernet bridge" (page 40) to make the changes effective.
30 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 39

Configure and View Status
Configure as a Bridge
Configure Bridge parameters at the Bridge/Router Menu. Bridge configuration
options are maintained and restored through the system's local service port and
are kept in NVRAM to be used in subsequent initializations.
1
1 Type
2 Type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:54:11
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE CONFIGURATION MENU
------------------------------------------------------------SETTINGS 1. BRIDGE/ROUTER MODE BRIDGE
2. LOCAL IP ADDR 192.168.240.10
3. LOCAL SUBNET MASK 255.255.255.0
4. BOOT ROUTER IP ADDR 0.0.0.0
5. DEFAULT ROUTER IP ADDR 192.168.240.1
6. SPANNING TREE DISABLE
7. BOOT SERVER IP ADDR 0.0.0.0
8. BOOT MODE LOCAL
9. IMAGE FILE NAME
A. IMAGE LOAD MODE LOCAL
B. PACKET ENCAPSULATION HDLC
--------------------------------------------------------------
1
at the Bridge/Router Menu to display the Bridge
Configuration Menu.
1
1
, press the spacebar to toggle to Bridge, then press
ENTER
ENTER
. At the prompt, Save current setting (Y/N), type
Y to display this screen. Ensure the mode setting is Bridge.
(C)onfirm (U)ndo (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
3 Do the following for each Bridge Configuration option you want
to change:
Type the number or letter of the option you want
to configure.
Select, using the spacebar, or type in the appropriate
information for each option as indicated in Table 10
ENTER
then press
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 31
ENTER
.
Page 40

Configure and View Status
Bridge Configuration
Type
Table 10.
For Option Function
No.
2 Local IP Addr Configure for the modem to respond to an application
that uses IP protocol including SNMP and TFTP. The
default is 0.0.0.0. You can either type in the address
supplied by a system administrator or get the IP address
via the boot server when boot mode is set to Network.
3 Local Subnet
Mask
4 Boot Router
IP Addr
5 Default Router
IP Addr
6 Spanning Tree Select either Enable or Disable (default) for
7 Boot Server IP
Addr
8 Boot Mode Select either Local (default) or Network for how the
Determines if a host (TFTP server, SNMP management
station, or trap receiver) is on the same local subnet.
If it is, the modem sends messages directly to the host.
If it is not, the Megabit Modem CRA-C sends messages
through a default router. The default is 255.255.255.0
Sets the IP address of the Boot Router used to forward
BOOTP requests to the proper BOOTP server.
When configured, the modem sends its BOOTP
requests directly to this device rather than sending
a broadcast packet. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Sets the address of the router which must be used to
reach a host (TFTP server, SNMP management station,
or trap receiver) located on another network. The
default is 0.0.0.0.
Spanning Tree mode.
Type the IP address of the TFTP server. The default is
the value of the BOOTP server if you have not
configured a different TFTP server address on the
BOOTP configuration file.
Megabit Modem CRA-C learns its protocol and
network configuration (boot information) during
power on or reset. Local Boot configuration is
contained in NVRAM. When Network is selected,
the Megabit Modem CRA-C learns its configuration
over the network via a BOOTP server. It is
recommended that the BOOTP server be connected to
the same segment as the Megabit Modem CRA-C
10BASE-T port.
(continued)
32 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 41

Configure and View Status
Table 10.
Type
For Option Function
No.
9 Image File
Name
A Image Load
Mode
Bridge Configuration (continued)
Read-only value. This parameter can be configured
only in the BOOTP configuration file and is acquired
when Boot Mode and Image Load Mode are set to
network. This name must match the name of a file
on the TFTP server in order for an image file download
to occur.
Specifies how the operational image code is loaded for
the Ethernet bridge. The Megabit Modem CRA-C
supports both local and remote loading. Local image
code is contained in flash devices for local loading of
operation code. When loading over the network, use
BOOTP (RFC 951) and TFTP (RFC 783) to obtain
image files.
Set Local (default) to load the image file from the
application sector of the Megabit Modem CRA-C
non-volatile device, if valid. The code is valid if the
CRC calculated on power-up matches the expected
CRC. If it does not, the Megabit Modem CRA-C
attempts to get a new image using the TFTP.
Set Network (with local backup) to attempt to download
the image file over the network. It first issues a
BOOTP request to get the image filename and image
server IP address, then it initiates a TFTP session. If
the BOOTP fails, the TFTP fails, or the downloaded
image is invalid, the image file is loaded using the
local image mode.
If no image is loaded after cycling through the TFTP
process at least five times, the Megabit Modem CRA-C
resets and repeats the process.
B Packet
Encapsulation
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 33
Indicates the format used to encapsulate the Ethernet
packets over ADSL. Choices are HDLC (default)
and PPP.
Page 42

Configure and View Status
Configure as a Router
Configure Router parameters at the Bridge/Router Menu. Router configuration
options are maintained and restored through the system's local service port and
are kept in NVRAM to be used in subsequent initializations.
1
1 Type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:54:33
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE/ROUTING CONFIGURATION MENU
--------------------------------------------------------------MODE SETTING 1. BRIDGE/ROUTER MODE ROUTER
IP STATIC ROUTING DESTINATION SUBNET MASK GATEWAY ADDRESS
TABLE 2. DEFAULT 192.168.240.1
3. 192.168.242.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
4. 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
5. 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
LAN PORT CONF. 6. LAN IP ADDR: 192.168.240.10
7. LAN SUBNET MASK: 255.255.255.0
LINE PORT CONF. 8. LINE IP ADDR: 172.16.100.1
9. LINE SUBNET MASK: 255.255.255.0
OTHER CONF. A. BOOT SERVER IP ADDR: 0.0.0.0
B. BOOT MODE: LOCAL
C. IMAGE FILE NAME:
D. IMAGE LOAD MODE: LOCAL
E. PACKET ENCAPSULATION: HDLC
-------------------------------------------------------------- C(o)nfirm (U)ndo (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
1
at the Bridge/Router Menu to display the
Bridge/Routing Configuration Menu.
1
1
2 Type
ENTER
ENTER
, press the spacebar to toggle to Router, then press
. At the prompt,
Save current setting (Y/N)
, type
Y to display the screen below. Ensure the mode setting is Router.
The following screen shows configuration for a Megabit Modem
CRA-C (ATU-C) routed toward a remote Megabit Modem CRA
(ATU-R), using IP addresses from the example in Figure 12.
34 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 43

Configure and View Status
The following screen shows configuration for a Megabit Modem
CRA (ATU-R) routed toward a Megabit Modem CRA-C
(ATU-C), using IP addresses from the example in Figure 12.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:54:33
ATU-R ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE/ROUTING CONFIGURATION MENU
--------------------------------------------------------------MODE SETTING 1. BRIDGE/ROUTER MODE ROUTER
IP STATIC ROUTING DESTINATION SUBNET MASK GATEWAY ADDRESS
TABLE 2. DEFAULT 172.16.100.1
3. 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
4. 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
5. 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
LAN PORT CONF. 6. LAN IP ADDR: 192.168.242.1
7. LAN SUBNET MASK: 255.255.255.0
LINE PORT CONF. 8. LINE IP ADDR: 172.16.100.2
9. LINE SUBNET MASK: 255.255.255.0
OTHER CONF. A. BOOT SERVER IP ADDR: 0.0.0.0
B. BOOT MODE: LOCAL
C. IMAGE FILE NAME:
D. IMAGE LOAD MODE: LOCAL
E. PACKET ENCAPSULATION: HDLC
-------------------------------------------------------------- C(o)nfirm (U)ndo (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
3 Do the following for each Router Configuration option you want
to change:
Type the number or letter of the option you want
to configure.
Select, using the spacebar, or type in the appropriate
information for each option as indicated in Table 11 then
ENTER
ENTER
press
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 35
.
Page 44

Configure and View Status
Table 11.
Type
No.
For
Function
Option
2 Default Contains the address of the default gateway
3
IP Static
4
Routing
5
Table
6 LAN IP
Addr
7 LAN Subnet
Mask
8 Line IP
Addr
9 Line Subnet
Mask
Consists of the Destination, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway. Must be configured for the Megabit Modem
CRA-C to operate as a static IP router. 0.0.0.0 is the
format for each field and the default.
Input the network address of the Megabit Modem
CRA-C 10BASE-T port. It is necessary for static IP
mapping to function properly. 0.0.0.0 is the format for
the field.
Input the subnet mask of the Megabit Modem CRA-C
10BASE-T port. Necessary for static IP mapping to
function properly. 0.0.0.0 is the format for the field.
255.255.255.0 is the default.
Input the network address of the Megabit Modem
CRA-C ADSL port. Necessary for static IP mapping
to function correctly.
Input the subnet of the Megabit Modem CRA-C ADSL
port. Necessary for static IP mapping to function
correctly. 255.255.255.0 is the default.
Router Configuration
A Boot Server
IP Addr
B Boot Mode Describes the manner in which the Megabit Modem
36 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Gives the address of the TFTP server. The default is
the value of the BOOTP server if you have not
configured a different TFTP server address on the
BOOTP configuration file.
CRA-C learns its protocol and network configuration
during power-on or reset. Supports both local and
remote loading of Boot information (IP configuration
only). Local Boot configuration is contained in
NVRAM. The Megabit Modem CRA-C obtains its
configuration using values found in NVRAM when
Local (the default) is selected. When Network is
selected, the Megabit Modem CRA-C learns its
configuration over the network via a BOOTP server.
(continued)
Page 45

Configure and View Status
p
g
g
g
g
g
pp
p
g
p
p
g
q
g
g
Type
For Option Function
No.
C Image File
Name
D Image Load
Mode
Table 11.
Router Configuration (continued)
Read-only parameter. The name must match the name
of a file on the TFTP server for an image file download
to occur.
S
ecifies how the Ethernet bridge code is loaded. The
abit Modem CRA-C supports both local and remote
Me
. Local image code is contained in flash devices
loadin
for local loadin
the network, use BOOTP (RFC 951) TFTP (RFC 783) to
obtain ima
Set Local (default) to load the ima
lication sector of the Megabit Modem CRA-C
a
non-volatile device, if valid. The code is valid if the
CRC calculated on
CRC. If it does not, the Me
ts to get a new image via the TFTP.
attem
Set Network (with local backu
the ima
uest to get the image filename and image server IP
re
address, then it initiates a TFTP session. If the BOOTP
fails, the TFTP fails, or the downloaded ima
invalid, the ima
mode.
If no image is loaded after cycling through the TFTP
process at least five times, the Megabit Modem CRA-C
resets and repeats the process.
of operation code. When loading over
e files.
e file from the
ower-up matches the expected
abit Modem CRA-C
) to attempt to download
e file over the network. It first issues a BOOTP
e file is loaded using the local image
e is
E Packet
Encapsulation
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 37
Indicates the encapsulation format used to envelope the
Ethernet packets over ADSL. Choices are HDLC
(default) and PPP.
Page 46

Configure and View Status
Configure SNMP
Configure SNMP parameters and trap addresses at the SNMP
Configuration menu.
2
1 Type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:53:26
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
SNMP CONFIGURATION MENU
---------------------------------------------------------------
SETTINGS 1. SNMP READ ONLY COMM STRING: public
2. SNMP READ WRITE COMM STRING: private
3. AUTHENTICATION TRAP STATUS: ENABLE
4. TRAP RECEIVER 1 IP ADDRESS: 0.0.0.0
5. TRAP RECEIVER 1 COMM STRING: public
6. TRAP RECEIVER 2 IP ADDRESS: 0.0.0.0
7. TRAP RECEIVER 2 COMM STRING: public
---------------------------------------------------------------
(C)onfirm (U)ndo (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER C HOICE-->
2
at the Bridge/Router Menu to display the SNMP
Configuration Menu.
2 Do the following for each SNMP Configuration option you want
to change:
Type the number of the option you want to configure.
Select, using the spacebar, or type in the appropriate
information for each option as indicated in Table 12 then
ENTER
ENTER
press
38 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
.
Page 47

Configure and View Status
Table 12.
SNMP Configuration Options
No. For Option Function
1 SNMP Read
Only Comm
String
2 SNMP Read
Write Comm
String
3 Authentication
Trap Status
Provides the authentication string used for SNMP
read-only operations. At the prompt
COMMUNITY STRING:
community string. Typically, use either Public or
Private. The read-only community string setting
must match the network manager community string
setting of Public or Private. The authentication
string is required for the Megabit Modem CRA-C to
correctly respond to SNMP set and get requests.
Provides the authentication string used for SNMP
read-write operations. At the prompt
COMMUNITY STRING:
or Private. The read-write community string setting
must match the network manager community string
setting of Public or Private. The authentication
string is required for the Megabit Modem CRA-C to
correctly respond to SNMP set and get requests
Select Disable (default) or Enable for use of
authentication error trap generation. The trap is
sent to the trap receiver address when an SNMP
request is received with an invalid or incorrect
community string.
NEW
, type in appropriate
NEW
, type either Public (default)
4 Trap Receiver
1 IP Address
5 Trap Receiver
1 Comm
String
Sets the first IP address for the server receiving
the trap.
Enter the first string used for trap authentication is
entered. Trap Receiver 1 Community String is
blank if no trap is being used. The field is case
sensitive.
6 Trap Receiver
2 IP Address
7 Trap Receiver
2 Comm
String
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 39
Enter the second IP address for the server receiving
the trap.
Enter the second string used for trap authentication.
Trap Receiver 2 Community String is blank if no
trap is being used. The field is case sensitive
Page 48

Configure and View Status
Reset the Ethernet Bridge
Changes you make to the Ethernet bridge through the Bridge/Router
Configuration menus (pages 31 and 37) and SNMP Configuration menu
(page 38) write immediately to flash memory when changes are confirmed.
However, they do not take effect until the Megabit Modem CRA-C Ethernet
bridge is reset. The Reset option causes the bridge to reboot with the new
configuration.
Reset the Megabit Modem CRA-C Ethernet bridge:
3
1 Type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:55:55
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE/ROUTER MENU
----------------------------------------------------------ETHERNET MAC ADDRESS: 00-20-A7-20-68-F2
10 BASE-T LINK STATUS: LINK UP
EBM STATUS: READY
----------------------------------------------------------SELECTIONS 1. BRIDGE/ROUTER CONFIGURATION
2. SNMP CONFIGURATION
3. STATISTICS
----------------------------------------------------------SETTINGS 4. RESET
3
at the Main Menu to display the Bridge/Router menu.
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
WARNING: This will bring down all connections. Are you sure? (Y/N)
2 Make all changes in the Bridge/Routing Configuration menu and
the SNMP Configuration menu.
4
3 Type
4
to select Reset.
4 Type either Y for yes to Reset or N for no to cancel Reset.
When you select Y to Reset, the Megabit Modem CRA-C Ethernet link is
dropped, the bridge is reset, then the Ethernet link is re-established. The
changes made to the Ethernet bridge are now effective.
40 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 49

Configure and View Status
View Status
This section describes status menus. You can view information such as current
alarm status, performance history, and product information. See the following
section for:
system information (page 41)
ADSL transceiver status (page 42)
Ethernet bridge statistics (page 48)
System Information
The System Information screen provides general product information for the
units at both the service provider (ATU-C) and subscriber (ATU-R) sites. This
includes hardware and software revision information as well as the product
number and manufacturing information.
1
Access the System Information screen by typing
1
1
typing
on the System Status and Configuration menu to display the System
Information screen.
1
on the Main Menu then
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:43:44
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
SYSTEM INFORMATION
ATU-C ATU-R
MODEM PRODUCT NUM 1704-01 1704-02
HARDWARE REV P00 P00
MANUF DATE 01/01/96 01/01/96
SERIAL NUM 000000000000 000000000000
SOFTWARE REV 01.01 01.01
PROM CHECKSUM 5D7D/1038 300C/AFF9
TRANSCEIVER HARDWARE NUM 1752-01 1764-01
HARDWARE REV P00 P00
BRIDGE MODULE SOFTWARE REV V2.22 V2.22
PROM CHECKSUM 1234 1234
HISTORY DAY IN OPERATION 4 4
(R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 41
Page 50

Configure and View Status
ADSL Transceiver Status
2
From the Main Menu, type
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:44:57
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL MENU
1. ADSL PERFORMANCE STATUS
2. 24 HOUR ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
3. 7 DAY ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
4. ADSL ALARM HISTORY
5. ADSL TRANSCEIVER CONFIGURATION MENU
6. FULL ADSL RESET
7. SESSION ADSL RESET
(M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
Select options 1 through 4 to view status for the ADSL transceiver. The ADSL
ES counts, UAS counts, and minimum SNR margins are updated every second
and can be viewed from the ADSL Performance History screens shown on
pages 43 through 47.
2
to display the ADSL Menu.
42 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 51

Configure and View Status
ADSL Performance Status. The ADSL Performance Status screen is
updated every second and provides a summary of the ADSL parameters and
outstanding ADSL-related alarms. This screen displays the upstream and
downstream ADSL links. The SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) margin column
displays both the current SNR margins as well as the minimum SNR margins
for the current 24-hour period.
1
1
Press
on the ADSL Menu to display the ADSL Performance Status screen.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:45:10
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL PERFORMANCE STATUS
DOWN ALARMS: NONE
UP ALARMS: NONE
SYSTEM STATE: DATA
DOWNSTREAM UPSTREAM
---------- ------- cur/min cur/min
SNR MARGIN (dB): 13.1/13.1 7.6/7.6
LINE ATTN -0.1 -0.7
24 HOUR ES: 3 3
24 HOUR UAS: 38 38
DATA RATE (kbps): 3168 1080
(C)lear (R)eturn (M)ain
EN TE R C HO ICE-->
C
Do not type
C
unless you want to clear the ADSL
performance and alarm counters in both the local and
remote units.
C
C
Type
to clear the ADSL performance and alarm counters. This also clears
the counts in the remote Megabit Modem CRA.
Table 13 describes the ADSL Performance Status screen fields.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 43
Page 52

Configure and View Status
Table 13.
ADSL Performance Status Screen Fields
Field Meaning
Down Alarms Identifies the current alarms in the path to the subscriber.
Up Alarms Identifies the current alarms in the path from the subscriber.
System State Describes the state of the ADSL system.
Startup states:
DATA (normal operation)
HAND (handshake)
TRAIN (training transceivers for loop conditions)
WSYNC (waiting for frame synchronization)
SNR Margin (dB) Identifies the current (cur) and minimum (min) margin values
for the ADSL loop for the current 24-hour period. The SNR
margin represents the margin relative to the SNR required for
a BER of 10
performance better than 10
margin of 6 dB, which translates to a performance of 10
BER or better. See page 2 for information on SNR margin
and BER.
Line Attn (dB) Indicates the decrease in amplitude of the transmitted
upstream and downstream signals as measured at the ADSL
respective receivers for that channel (upstream or
downstream).
–7
. A margin greater than zero indicates a
–7
. The system provides a default
–10
24 Hour ES Indicates the total number of ES that have been detected on the
ADSL link during the previous 24-hour period.
24 Hour UAS Indicates the total number of unavailable seconds (UAS) that
have been detected on the ADSL link during the previous
24-hour period. This figure represents the amount of time that
the lines were not available for transmission since power on or
last clear.
Data Rate (kbps) Identifies the actual data rates of the ADSL link.
44 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 53

Configure and View Status
24 Hours ADSL Performance History. The 24 Hour ADSL Performance
History report consists of eight screens. Each screen displays three hours of
data, providing a 24-hour report in 15-minute increments.
2
2
Type
on the ADSL menu to open the 24 Hour ADSL Performance
History screen.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:45:54
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
24 HOUR ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
(errored seconds/unavailable seconds/snr)
DOWNSTREAM UPSTREAM
08:45 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
08:30 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
08:15 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
08:00 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
07:45 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
07:30 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
07:15 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
07:00 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
06:45 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
06:30 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
06:15 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
06:00 000/000/ 13.1 000/000/ 7.6
(C)lear (P)revious (N)ext (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
C
C
Type
to clear all ES, UAS counts, including the equivalent counts in the
remote unit. The minimum SNR for the period is reset to the current SNR.
The 24 Hour ADSL Performance History data is lost
when the Megabit Modem CRA-C is turned off.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 45
Page 54

Configure and View Status
7 Days ADSL Performance History. The 7 Day ADSL Performance
History menu displays the ES and UAS counts, and the minimum SNR
margins for the previous 6 days and the current day. The division of the
intervals is based on 12 am midnight as the dividing boundary, and the current
day count is not necessarily equal to the total count for the past 24 hours.
3
3
Type
on the ADSL Menu to open the 7 Day ADSL Performance
History menu.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:46:07
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
7 DAY ADSL PERFORMANCE HISTORY
(errored seconds/unavailable seconds/snr)
DOWNSTREAM UPSTREAM
07/02/97 00000/00000/ 13.1 00000/00000/ 7.6
07/01/97 00003/00038/ 13.1 00003/00038/ 7.6
06/30/97 00000/00000/ NA 00000/00000/ NA
06/29/97 00000/00000/ NA 00000/00000/ NA
06/28/97 00000/00000/ NA 00000/00000/ NA
06/27/97 00000/00000/ NA 00000/00000/ NA
06/26/97 00000/00000/ NA 00000/00000/ NA
(C)lear (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
C
C
Type
to clear all ES and UAS counts, including the equivalent counts in
the remote unit. The minimum SNR for the period is reset to the current SNR.
The 7 Day ADSL Performance History data is lost
when the Megabit Modem CRA-C is turned off.
46 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 55

Configure and View Status
ADSL Alarm History. The ADSL Alarm History screen consists of five
columns. Table 14 describes the information found in each column.
4
4
Type
Type
on the ADSL Menu to open the ADSL Alarm History screen.
09/08/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:47:54
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
ADSL ALARM HISTORY
Type First Last Current Duration(s)
LOF, DOWN 09/08/97-16:50:46 09/08/97-17:53:20 OK
LOF, UP 09/08/97-16:50:46 09/08/97-17:53:20 OK
MARGIN, DOWN OK
MARGIN, UP OK
ES, DOWN OK
ES, UP OK
SES, DOWN OK
SES, UP OK
SELFTEST OK
LAST CLEARED: 09/08/97-16:50:45
(C)lear (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
C
C
to update the first and last date/time stamps and clear the time to 0.
The Alarm History data is lost when the Megabit
Modem CRA-C is turned off.
Table 14.
ADSL Alarm History Screen Columns
Name Description
Type Identifies local, remote, and ADSL link alarms.
LOF: Loss of frame failure
MARGIN: Low SNR margin alarm
ES: Excessive errored seconds
SES: Severely errored seconds
SELF: Self test
First Lists the first time an alarm is detected.
Last Lists the last time an alarm was detected.
Current Identifies the current status of the alarm.
Durations Indicates the total accumulated number of seconds the
system was in alarm condition since the last clear.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 47
Page 56

Configure and View Status
Ethernet Bridge Statistics
The Megabit Modem CRA-C provides real-time, non-disruptive monitoring
of system performance. This menu displays a count of the valid Ethernet and
ADSL frames received and forwarded by the 10BASE-T MDI-X and the line
ports, respectively. The display is updated every 10 seconds and whenever you
access this menu.
3
Access the Statistics screen for the bridge by typing
3
3
then typing
on the Bridge/Router Menu.
07/02/97 PAIRGAIN TECHNOLOGIES 08:55:07
ATU-C ADSL MEGABIT MODEM TERMINAL 01.01
BRIDGE STATISTICS MENU
----------------------------------------------------------ETHERNET PORT: INPUT FRAMES: 10443613
OUTPUT FRAMES: 5277712
DISCARDED FRAMES: 0
ERRORED FRAMES: 0
----------------------------------------------------------ADSL PORT: INPUT FRAMES: 5278375
OUTPUT FRAMES: 10437290
DISCARDED FRAMES: 0
ERRORED FRAMES: 0
---------------------------------------------------------- (R)eturn (M)ain
ENTER CHOICE-->
3
on the Main Menu
Table 15 describes the Bridge Statistics fields.
48 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 57

Configure and View Status
Table 15.
Bridge Statistics Fields
Field Definition
Ethernet Port
Input Frames The number of frames correctly received.
Output Frames The number of frames correctly transmitted.
Discarded Frames The number of frames dropped due to an overflow of the
input or output buffer for the port.
Errored Frames The number of frames received in error (CRC, alignment,
and dribbling bit) from the input buffer.
ADSL Port
Input Frames The number of frames correctly received.
Output Frames The number of frames correctly transmitted.
Discarded Frames The number of frames dropped due to an overflow of the
input or output buffer for the port.
Errored Frames The number of frames received in error (CRC, alignment,
and dribbling bit) from the input buffer.
Log Out
Q
Log out from the Main Menu by pressing
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 49
Q
.
Page 58

Configure and View Status
50 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 59

NETWORK AND MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
Through the console menus, you can configure the Megabit Modem CRA-C
as a bridge to forward Ethernet data based on MAC addresses or as a router
to route Ethernet data based on IP addresses. Additionally, you can configure
parameters for management and encapsulation protocols using the Megabit
Modem CRA-C console menus.
For information about this topic
MAC layer bridging and spanning tree protocol 51
Static IP routing 53
Management protocols 61
Network configuration and image code download 64
Encapsulation protocols 66
Go to page
MAC Layer Bridging and Spanning Tree Protocol
MAC Layer Bridging.
from a source to a destination at the link layer (of an OSI reference model).
The information is sent to a physical address known as a Media Access Control
(MAC) address.
The Megabit Modem CRA-C provides transparent Ethernet MAC level
bridging. It is a completely self-contained bridge with a CPU, memory
subsystems (RAM, Flash, etc.), an Ethernet controller and Ethernet drivers,
and other glue logic. It provides complete main bridging tasks of learning,
forwarding, filtering, and hashing/buffer management. Additionally, it offers
802.1d Spanning Tree protocol, packet encapsulation (via HDLC or PPP
framing), and other local tasks.
Forwarding performance is at 2.7 kpps (kilo packets per second) and filtering
performance is at full Ethernet rate of 14 kpps for 64-byte frames (minimum
size).
A bridge moves information across an internetwork
Spanning Tree.
Spanning Tree protocol eliminates loops in a LAN topology
by partitioning out redundant links between LAN segments. This ensures that
there is only one path, or link, between any two nodes on the network. If this
link goes down, Spanning Tree enables the partitioned links to create a new
loop-free topology, if possible. An example of the active topology is shown
in Figure 9.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 51
Page 60

Network and Management Overview
Figure 9. Spanning Tree Topology
52 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 61

Network and Management Overview
You can enable or disable Spanning Tree on the Bridge/Router Configuration
Menu. The Megabit Modem CRA-C uses the Spanning Tree defaults shown in
Table 16. These values are user-configurable through SNMP as part of the
Spanning Tree group in RFC 1493.
Table 16.
Spanning Tree Defaults
Spanning Tree Attribute Default Value
ST Bridge Priority Hx0000
ST Max Age 30 seconds
ST Hello Time 10 seconds
ST Hold Time 10 second
ST Forward Delay 10 second
ST Port 1 Priority (LAN) 0
ST Port 2 Priority (ADSL) 0
ST Port Path Cost 1
Static IP Routing
Through the static IP routing feature, you can configure the Megabit Modem
CRA-C as an IP router with statically programmed route entries. You can
enable this function as a security feature to prevent eavesdropping and to
provide broadcast filtering, as well as to specify multiple destination gateways.
When static IP routing is enabled, you can access only specific remote IP
subnets or hosts.
Since IP routers make forward or filter decisions based on the network-layer
IP address instead of the MAC hardware address, MAC-level broadcast frames
are prevented from reaching unwanted destinations in the network. The
example in Figure 10 shows a simple Internet Service Provider (ISP) site that
uses the static IP routing feature to filter MAC-level broadcast frames sourced
by ISP Subscriber A from reaching ISP Subscriber B.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 53
Page 62

Network and Management Overview
Figure 10.
54 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Simple Configuration for Static IP Routing
Page 63

Network and Management Overview
Figure 11 shows a more complex example of multiple gateways that use
static IP routing to route packets sourced from specific users to different
destination gateways.
Figure 11.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 55
Multiple Gateways Specified for Static IP Routing
Page 64

Network and Management Overview
When you configure the static IP routing feature, set the parameters defined in
Table 17 through the Megabit Modem CRA-C console menus. Set the
parameters defined in Table 18 in an external router (used as a gateway).
Table 17.
Megabit Modem CRA-C Static IP Routing Parameters
Parameter Definition
Bridge/Router
Mode
Packet
Encapsulation
Default Router
IP Address
IP Static
Routing Table
LAN IP
Address and
Subnet Mask
Line IP
Address and
Subnet Mask
Select router for the Megabit Modem CRA-C to route based
on IP addresses. Both the Megabit Modem CRA-C and
Megabit Modem CRA units connected via ADSL must be set
to router mode.
Select either PPP or HDLC. PPP is the preferred
encapsulation for routing when interfacing with non-PairGain
equipment. HDLC is lower overhead and preferred when
interfacing PairGain to PairGain equipment.
Specify the next hop default router entry. This entry tells
Megabit Modem CRA-C what to do with a packet that has a
destination address which is not in the Static IP Routing table.
Specify up to three static routes and one default route. The
default route specifies where to send packets which do not
match any of the other configured static routes.
Configure the IP address and the Subnet Mask for the
10BASE-T port. These must be configured for static IP
mapping to function properly.
Configure the IP address and Subnet Mask for the ADSL
WAN port
56 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 65

Network and Management Overview
Table 18.
External Router Static Route Entry
Parameter Definition
Static Route
Entry in
External
Routers
Configure a Static Route entry in any of the external routers
which may have been specified as a Default Router or as a
Gateway. This is required because the static IP routing feature
does not send periodic route updates using protocols like
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or Open Shortest Path
First (OSPF) so that other external routers can automatically
update their routing tables. This implementation prevents
other parties from discovering routes through eavesdropping.
The format of this entry will vary among different router
vendors, but it will typically be in the form of Destination,
Mask, and Next Hop Gateway. Destination is the remote IP
subnet or host address. Gateway is the IP address of
the Megabit Modem CRA-C on the same subnet as the
external router.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 57
Page 66

Network and Management Overview
Figure 12 shows an example of a point-to-point ADSL system and hypothetical
values of parameters defined in Tables 17 and 18.
Figure 12.
58 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Example for Static IP Routing
Page 67

Network and Management Overview
Megabit Modem CRA-C IP Addresses
The Megabit Modem CRA-C has two IP addresses, one for the ADSL WAN
port and one for the Ethernet port. In Figure 13, the non-shaded side of the
provider and subscriber modems indicates the LAN address for the Ethernet
(10BASE-T) connection. The shaded side of the provider and subscriber
modems is the IP Line address for the ADSL line connection. Note that the IP
Line address is unique from the LAN addresses. When connecting a Megabit
Modem CRA-C and a Megabit Modem CRA point-to-point via ADSL, the IP
Line addresses are completely isolated and hidden from the rest of the
network. As a result, any valid IP address can be assigned to these ports but
should be on the same subnet.
When routing, data travels one hop at a time. Figure 13 shows destination
and next hop IP addresses. The destination address indicates the network and
subnetwork of the next hop for a common network topology . The default
gateway is the router to which datagrams are sent that do not have an assigned
route in the static routing table.
Use Figure 13 as a worksheet to help you determine/record static IP
routing addresses.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 59
Page 68

Network and Management Overview
Figure 13.
60 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
IP Addresses
Page 69

Network and Management Overview
Management Protocols
SNMP is used for configuring system and bridge parameters, monitoring
statistics, and performing advanced management.
SNMP
This management protocol specifies how to send information between a
Network Management System (NMS) and managed devices on a network.
Managed devices (such as the Megabit Modem CRA-C) run a program called
an agent. The agent interprets SNMP requests and responds to them. The
NMS communicates with the agents in the managed devices to:
set configuration
get configuration
get status
A Management Information Base (MIB) defines these configuration and status
parameters. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) specifies standard
MIBs for certain types of devices, ensuring any NMS can manage them.
Additionally, vendors can issue proprietary MIBs for their devices to fit
specific needs.
Table 19 shows the Megabit Modem CRA-C SNMP configuration parameters
that are maintained and restored through the local console port. These
parameters are kept in the Megabit Modem CRA-C NVRAM and are
parameters that must be configured for SNMP to work.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 61
Page 70

Network and Management Overview
Table 19.
SNMP Configuration Default Values
Attribute Factory Default
Download Image File Name Not configurable via console
Local IP Address 0.0.0.0
Local Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Boot Router IP Address 0.0.0.0
Default Router IP Address 0.0.0.0
Boot Server IP Address 0.0.0.0
Boot Mode (local, network) local
Image Load Mode (local, network) local
SNMP RO Community String public
SNMP RW Community String private
Trap Receiver 1 IP Address 0.0.0.0
Trap Receiver 1 Community String null string
Trap Receiver 2 IP Address 0.0.0.0
Trap Receiver 2 Community String Null string
Authentication Trap enable/disable disable
ST Enable/disable disable
Megabit Modem CRA-C SNMP Agent
An agent is program resident in managed devices (for example, Megabit
Modem CRA-C, modems, nodes, routers and hubs). Agents translate data into
code the NMS can read. Agents and NMS communicate using SNMP as the
transport mechanism. SNMP uses standard Internet Protocol (IP) to transport
incoming and outgoing messages to the appropriate agent or NMS address.
Each SNMP command requires an IP address or NMS from the agent to
transport these messages.
62 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 71

Network and Management Overview
The Megabit Modem CRA-C provides an SNMP agent that supports several
MIBs for the management of the system. The SNMP agent can process
datagrams received from both the Ethernet interface (LAN) and the ADSL
interface (Line). The agent and the protocol stack complies with the following
RFCs:
RFC 1155 Structure of Management Information (SMI)
•
RFC 1157 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
•
RFC 826 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
•
RFC 792 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
•
RFC 791 Internet Protocol (IP)
•
RFC 768 User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
•
MIB and Trap Support
Each managed device has configuration, status, and statistical information that
defines its functionality and operational capabilities. These elements, together,
are the MIB for the device being managed. The MIB defines the kind of
information an NMS can retrieve from a managed device and the settings an
NMS can control in a managed device.
Megabit Modem CRA-C supports the following MIBs:
RFC 1213 MIB II Management Information Base for Network
•
Management of TCP/IP-Based Internet:MIB-II supported groups:
system, interfaces, IP, ICMP, UDP, and SNMP groups
RFC 1215 A Convention for Defining Traps for Use with the SNMP
•
supported objects: ColdStart, linkUp, linkDown, and
authenticationFailure traps. Link status traps are sent for events
related to Ethernet.
RFC 1493 Definition of Managed Objects for Bridges supported
•
objects: Base, Spanning Tree, and transparent bridging groups.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 63
Page 72

Network and Management Overview
The Spanning Tree MIB can only be accessed if the
Spanning Tree protocol is enabled.
PairGain REX MIB an enterprise specific MIB designed for the
agent in the Megabit Modem CRA-C for managing the ADSL portion
of the unit.
The Ethernet interface has the ifIndex value of 1 and the WAN
(ADSL) interface has an ifIndex of 2.
Access any PairGain-specific MIBs through the Internet at ftp.pairgain.com.
Use the following:
FTP ftp.pargain.com
•
login using anonymous as you log-in name
use guest or your e-mail address as you user password
enter cd snmp/rex/mibs
get pgrexmib.txt
•
Network Configuration and Image Code Download
BOOTP
BOOTP is used to supply network configuration information to Megabit
Modem CRA-C from a BOOTP server. Used in conjunction with TFTP, you
can use BOOTP to download image code. The Megabit Modem CRA-C
initiates a BOOTP request in these situations:
current configuration sector is determined to be invalid; this can occur
when the CRC of configuration sector does not match the expected
CRC on power-up
user sets the value of Boot Mode to NETWORK, saves the
configuration to flash, and then reboots the Megabit Modem CRA-C
64 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 73

Network and Management Overview
BOOTP conforms to the following RFCs:
RFC 951: Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
RFC 1533: DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions
RFC 1542: Clarification and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol
(updates 951)
A BOOTP request is broadcast through the Ethernet port to the local network.
The request is not sent from the ADSL port because the boot sector does not
contain the code necessary to transmit over the WAN link. If a BOOTP server
is on the local network and is configured correctly, it returns a BOOTP
response. Once the Megabit Modem CRA-C receives a BOOTP response, it
keeps the IP address, boot server, default router, and any other information
associated with the module in the configuration sector of the flash. Subsequent
BOOTP responses for the Megabit Modem CRA-C are ignored.
When a BOOTP server is not on the local network, the request fails unless
there is a BOOTP agent on the network that recognizes and forwards the
request to the server. The BOOTP server does not contain an entry that
corresponds to the MAC address of the Megabit Modem CRA-C.
From the console interface, you can configure network parameters and
save them to flash so the BOOTP operation can be bypassed. The BOOTP
server should be connected to the same segment as the Megabit Modem
10BASE-T port.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 65
Page 74

Network and Management Overview
TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is used to download networking image
code to the Megabit Modem CRA-C from a TFTP server. This allows
software upgrades to be performed over the network. The Megabit Modem
CRA-C initiates a TFTP download of application code in these situations:
current application code is not valid; this occurs when the CRC
calculated on power-up doesn't match the expected CRC
user sets the value of Image Load Mode to NETWORK, save the
configuration to flash, and reboots the Megabit Modem CRA-C
In either case, the Megabit Modem CRA-C performs a BOOTP request first to
get the most current network configuration. If the BOOTP fails, the TFTP
session is attempted.
TFTP conforms to RFC 1350: The TFTP Protocol (Revision 2)
TFTP uses the connectionless User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for file transfer
with minimum overhead.
Encapsulation Protocols
You can select from two packet encapsulation formats for data transported
across the ADSL WAN link: Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) or High-level
Data Link Control (HDLC), which is the default. HDLC is the preferred
when the system is terminated at each end with PairGain products that have
Ethernet ports. PPP is used when interfacing to a WAN port on non-PairGain
equipment. In PPP mode, the Megabit Modem CRA-C supports the
Bridge Control Protocol (BCP) RFC 1638 when configured as a bridge
and the Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) RFC 1332 when configured
as a router.
66 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 75

TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ADSL Line
Signal Format CAP Line Code
Transmit Signal Power up to 23 dBm
Connector RJ-48
Ethernet Port
Connector RJ-45, 10BASE-T
Bandwidth Filtering 14 Kpps (64-byte packets, both
directions)
Forwarding Performance 2.7 Kpps
Address Learning 2000 MAC addresses with aging
Encapsulation Format Low-overhead HDLC or PPP
Bridging IEEE 802.1d transparent with
Spanning Tree Protocol
Routing Static IP maps
Physical
Height 2.2 inches (5.6 cm)
Width 7.5 inches (19.0 cm)
Depth 9.5 inches (24.13 cm)
Electrical
Power Input 100 to 130 VAC, 60 Hz
Power Dissipation 8 W
Environmental
Temperature 0 to 50°C
Relative Humidity 0 to 85%
Electromagnetic Emissions Per FCC Part 15 Class A
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 67
Page 76

Technical Specifications
Management and Maintenance
Embedded SNMP Agent
BOOTP/TFTP download (with RFC 1542 extensions)
RFC 1533 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
RFC 1213 MIB II, RFC 1493 bridge MIB (base, ST, transparent groups)
PairGain xDSL bridge MIB extensions
RFC 1215 Traps (link state) and ST Traps (newRoot, topology Changed)
ASCII Terminal Maintenance Port
Type RS-232C, RJ-45
Data Rate Autobaud from 2400 to 19,200 baud
Hardware Flow Control Not Supported
Agency Certifications
FCC B
UL
CE
CSA
PairGain reserves the right to change features and
specifications without notice.
68 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 77

TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
PairGain Technical Assistance is available 24-hours-a-day, 7-days-a-week by
contacting PairGain’s Customer Service Engineering group at one of the
following numbers:
Telephone: (800) 638-0031
(714) 832-9922
Fax: (714) 832-9924
During normal business hours (8:00 AM to 5:00 PM, Pacific Time, Monday Friday, excluding holidays), technical assistance calls are normally answered
directly by a Customer Service Engineer. At other times, a request for
technical assistance is handled by an on-duty Customer Service Engineer
through a callback process. This process results in a callback normally within
30 minutes of initiating the request.
World-Wide Web
PairGain product, company, and application information can be found at
http://www.pairgain.com using any Web browser.
FTP
PairGain Management Information Bases (MIBs) are available using the
Internet at ftp.pairgain.com, use:
FTP ftp.pargain.com
•
login using anonymous as you log-in name
use guest or your e-mail address as you user password
enter cd snmp/rex/mibs
get pgrexmib.txt
•
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 69
Page 78

Technical Assistance
70 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 79

LIMITED WARRANTY
PairGain Technologies, Incorporated warrants its products to be free of
defective and faulty workmanship for a period of 60 months, under normal use,
from the date of shipment. PairGain's obligation, under this warranty, is
limited to replacing or repairing, at PairGain's option, any such product which
is returned during the warranty period per PairGain's instructions and which
product, in PairGain's sole option, is determined to be defective upon
examination at our plant.
Do not disassemble the Megabit Modem
CRA-C. The unit’s components are not user
serviceable. Opening the system chassis, or
attempting to modify the unit in any way
voids its warranty.
The transportation charges from the Buyer to PairGain will be prepaid by the
Buyer. When the equipment is shipped back to the Buyer, PairGain will pay
the charges, unless no trouble is found (NTF), in which case the buyer will pay
for the shipment.
PairGain may use reconditioned parts for such repair or replacement. This
warranty
does not
or altered by persons not authorized by PairGain or in PairGain's sole judgment
has subjected to misuse, accident, fire or other casualty, or operation beyond
its design range.
apply to any product which has been repaired, worked upon,
Repaired products have a 90-day warranty, or until the end of the original
warranty period--whichever period is greater.
Modules sent to PairGain for repair will be repaired or replaced and returned to
you as soon as possible. Normally, current products are repaired within 14
calendar days, and out-of-production products are repaired within 30 calendar
days.
To return equipment to PairGain:
Call PairGain Customer Service at (800) 370-9670, or send a
1
fx to (714) 730-2961, to get a
(RMA) Number
and instructions for returning your
Return Material Authorization
equipment.
For other information or questions, PairGain Technologies
can be contacted by telephone at (800) 638-0031 or
(714) 832-9922 or by fax at (714) 832-9924.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 71
Page 80

Limited Warranty
2
3
Provide the following information along with the equipment
you're returning:
Your company name, address, and the name of the person
•
whom we can contact in case we have any questions.
The same Purchase Order Number you gave us when you
•
requested your RMA number.
A description of the equipment, as well as the number of
•
units you're returning to us.
model and part number of each unit.
Shipping address so that we can return your equipment to
•
you.
So we can determine why you're sending the equipment to us, let
us know which of the following applies to you:
The equipment needs an ECO/ECN upgrade.
•
The equipment is defective.
•
Please tell us what you observed just before
the equipment malfunctioned. Be as detailed
in your description as possible.
Don't forget
to include the
If there's another reason for returning the equipment, please let
•
us know what it is so we can help you.
Pack the equipment in a shipping carton.
4
Write clearly on the outside of the carton, PairGain’s address and
5
the assigned
PairGain Technologies, Inc.
14352 Franklin Avenue
Tustin, CA 92780-7013
Attention:
72 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Return Material Authorization Number
Repair and Return Department
:
Page 81

GLOSSARY
The Glossary defines technical terms and abbreviations used in this manual.
Access Provider See Service Provider.
Access Rate The transmission speed, in bits per second, of the
physical access circuit between the end user and
the network.
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. A method
of transmitting at different downstream and
upstream speeds.
Alarm Any valid change of state from its normal condition
detected at an alarm point.
Asymmetric
Transmission Transmission which sends data at different rates in
each direction.
AWG American Wire Gauge.
ATU-C ADSL Terminal Unit at the service provider site.
ATU-R ADSL Terminal Unit at the remote site.
Bandwidth Used to describe the capacity or amount of traffic
(data, voice, or video) a certain communications line
is capable of accommodating.
BER Bit Error Rate. The ratio of received bits that are
in error.
Binder Group A group of 25 or 50 pairs of wires.
Bit In a binary system, the smallest unit of information.
It is represented as a zero or a one.
Bridge A two-port internetworking device that selectively
filters or forwards traffic based or MAC addresses.
Bridged A pair of wires connected in parallel across a single
line to form a "T" Tap configuration.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 73
Page 82

Glossary
CAP Carrierless Amplitude Phase Modulation. A two-
dimensional line code used in ADSL.
Crosstalk Line noise that occurs due to coupling of signals
between pairs in the same bundle.
Downstream The direction of data reception from the Megabit
Modem CRA-C to a remote unit.
Ethernet A baseband LAN specification that has become a
series of standards produced by IEEE referred to as
IEEE 802.3.
HDLC High-level Data Link Control.
Hub A common wiring point for star-topology networks,
and a common synonym for a concentrator.
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
A professional organization that defines network
standards.
I/F Interface or Interface Card.
ISP Internet service provider.
kbps Kilobits per second. A measure of transmission
speed at 1,000 bits per second.
kpps Kilo packets per second.
LAN Local Area Network. The means by which a local
community of users and workgroups can share
information and resources electronically.
LED Light emitting diode.
Line code Any method of converting digital information to
analog form for transmission on a communicaton
line.
Link Another term used for transmission line.
MAC Media Access Control. Associated with Layer 2
or the Data Link Layer of the ISO 7-layer
protocol model.
Margin An ADSL parameter, measured in dB. It indicates
the excess SNR, relative to the performance of 10
–7
BER, at the receiver point.
74 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 83

Glossary
Mbps Megabits per second. 1,000,000 bits per second.
MDI Media Dependent Interface.
MDI-X Media Dependent Interface (cross-over).
MIB Management Information Base.
NVRAM Non-Volatile Random Access Memory.
Port An I/O interface. A point at which signals may be
introduced or extracted in a similar manner.
POTS Plain Old Telephone Service.
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol.
RAM Random Access Memory.
Repeater Connects to line segments to amplify and reshape
the analog waveform to extend network segment
distances.
RFC Request for Comment.
Router Device that decides whether to forward a packet
by looking at the protocol level address.
Service Provider Organization providing and maintaining network
services for subscribers.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol. A network
management standard initially established to allow
multi-vendor networking devices to be managed
more easily with common management tools.
SNR Signal-to-Noise ratio.
Spanning Tree An algorithm used to open bridging loops.
Telecommuter A person who performs work at home while linked
to the office by means of a telecommunicationsequipped computer system.
Upstream The direction of data transmission from the Megabit
Modem CRA-C to a remote unit.
UTP Unshielded Twisted Pair.
Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual 75
Page 84

Glossary
76 Megabit Modem CRA-C User Manual
Page 85

Page 86

Corporate Office
14402 Franklin Avenue
Tustin, CA 92780
Tel: (714) 832-9922
Fax: (714) 832-9924
For Technical Assistance:
(800) 638-0031
 Loading...
Loading...