Page 1

1997 RL Online Reference Owner's Manual
Use these links (and links throughout this manual) to navigate through this reference.
For a printed owner's manual, click on authorized manuals or go to www.helminc.com.
Contents
Owner's Identification Form
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... i
A Few Words About Safety.................................................................................................................ii
Driver and Passenger Safety ..............................................................................................................3
Proper use and care of your vehicle's seat belts, and Supplemental Restraint System.
Instruments and Controls.................................................................................................................31
Instrument panel indicator and gauge, and how to use dashboard and steering column controls.
Comfort and Convenience Features ................................................................................................91
How to operate the climate control system, the audio system, and other convenience features.
Before Driving..................................................................................................................................121
What gasoline to use, how to break-in your new vehicle, and how to load luggage and other cargo.
Driving ..............................................................................................................................................131
The proper way to start the engine, shift the transmission, and park, plus towing a trailer.
Maintenance.....................................................................................................................................153
The Maintenance Schedule shows you when you need to take your vehicle to the dealer.
Appearance Care..............................................................................................................................209
Tips on cleaning and protecting your vehicle. Things to look for if your vehicle ever needs body repairs.
Taking Care of the Unexpected......................................................................................................217
This section covers several problems motorists sometimes experience, and how to handle them.
Technical Information.....................................................................................................................241
ID numbers, dimensions, capacities, and technical information.
Warranty and Customer Relations (U.S. and Canada)................................................................253
A summary of the warranties covering your new Acura, and how to contact us.
Authorized Manuals (U.S. only)......................................................................................................259
How to order manuals and other technical literature.
Index...................................................................................................................................................... I
Gas Station Information
A summary of information you need when you pull up to the fuel pump.
Page 2

Your Occupant Protection System
Your Acura is equipped with seat
belts and other features that work
together to protect you and your
passengers during a crash.
Seat belts are the most important
part of your occupant protection
system. When worn properly, seat
belts can reduce the chance of
serious injury or death in a crash.
For added protection during a severe
frontal collision, your Acura has a
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) with airbags and automatic
seat belt tensioners for the driver
and a front seat passenger.
Two indicator lights are also part of
your safety system. One reminds you
to make sure you and your passen-
gers wear seat belts. The other
alerts you to a possible problem with
your supplemental restraint system
(see page 16).
The seats, head restraints and door
locks also play a role in occupant
safety. For example, reclining the
seat-back can decrease the effec-
tiveness of your seat belt. Head
restraints can help protect your neck
and head, especially during rear-end
impacts. Door locks help keep your
doors from being accidentally
opened during a crash.
To get the maximum protection from
your occupant protection system,
check the following before you drive
away:
Everyone in the car is wearing a
seat belt properly (see page 7).
Infants and small children are
properly secured in child safety
seats (see page 20).
All doors are closed and locked
(see page 19).
Seat-backs are upright and head
restraints are properly adjusted
(see pages 18 and 70).
There are no loose items that
could be thrown around and hurt
someone during a crash or sudden
stop (see page 19).
By following these guidelines, you
can reduce injuries to yourself and
your passengers in many crash
situations. Remember, however, that
no safety system can prevent all
injuries or deaths that can occur in
severe crashes.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 3

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
Why Wear Seat Belts
Wearing seat belts, and wearing
them properly, is fundamental to
your safety and the safety of your
passengers.
During a crash or emergency stop,
seat belts can help keep you from
being thrown against the inside of
the car, against other occupants, or
out of the car.
Of course, seat belts cannot com-
pletely protect you in every crash.
But, in most cases, seat belts reduce
your chance of serious injury. They
can even save your life. That is why
many states and all Canadian pro-
vinces require you to wear seat belts.
Important Safety Reminders
Seat belts are designed for adults
and larger children. All infants and
small children must be properly
restrained in child safety seats (see
page 20).
A pregnant woman needs to wear a
seat belt to protect herself and her
unborn child (see page 11).
Two people should never use the
same seat belt. If they do, they could
be very seriously injured in a crash.
Do not place the shoulder portion of
a lap/shoulder belt under your arm
or behind your back. This could
increase the chance of serious
injuries in a crash.
Do not put shoulder belt pads or
other accessories on seat belts. They
can reduce the effectiveness of the
belts and increase the chance of
injury.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Not wearing a seat belt
increases the chance of serious
injury or death in a crash.
Be sure you and your
passengers always wear seat
belts and wear them properly.
Page 4

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
Seat Belt System Components
Your Acura has seat belts in all five
seating positions. The front seats
and the outside positions of the rear
seat have lap/shoulder belts. The
center position of the rear seat has a
lap belt.
Your seat belt system also includes a
light on the instrument panel to
remind you to fasten your seat belt,
and to make sure your passengers
fasten theirs. This light comes on
when you turn on the ignition if you
have not fastened your seat belt. A
beeper also sounds for several
seconds (see page 34).
The following pages cover more
about the seat belt components and
how they work.
Lap/Shoulder Belt
This style of seat belt has a single
belt that goes over your shoulder,
across your chest, and across your
hips.
Each lap/shoulder belt has an
emergency locking retractor. In
normal driving, the retractor lets you
move freely in your seat while it
keeps some tension on the belt.
During a collision or sudden stop,
the retractor automatically locks the
belt to help restrain your body.
The lap/shoulder belt retractor in
each passenger seating position has
an additional locking mechanism
intended to secure a child seat (see
page 24). If the shoulder part of the
belt is pulled all the way out, this
mechanism will engage. The belt will
retract, but it will not allow the
passenger to move freely. If the belt
feels too tight, unlatch it, let it retract
fully, then pull it out as far as needed.
Driver and Passenger Safety
BUCKLE
LATCH PLATE
UPPER
SEAT
BELT
ANCHOR
LAP
PORTION
Page 5

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
Lap Belt
LATCH PLATE
The lap belt has one manually-
adjusted belt that fits across the hips.
It is similar to safety belts used in
airplanes.
Wearing Seat Belts Properly
You can increase the effectiveness of
your seat belts if you take a little
time to read the following pages and
make sure you know how to wear
seat belts properly.
Wearing a Lap/Shoulder Belt
Before putting on the seat belt, move
the driver's seat as far back as is
practical while still allowing you to
maintain full control of the vehicle.
Make sure the seat-back is upright
(see page 18 ). The front seat
passenger should move the seat as
far back as possible.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
Not wearing a seat belt properly
increases the chance of serious
injury or death in a crash.
Be sure you and your
passengers always wear seat
belts and wear them properly.
BELT END
BUCKLE
Page 6

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
1. Pull the latch plate across your
body and insert it into the buckle.
Tug on the belt to make sure the
latch is securely locked.
2. Check that the belt is not twisted.
3. Position the lap portion of the belt
as low as possible across your hips,
not across your stomach. This lets
your strong pelvic bones take the
force of a crash.
4. Pull up on the shoulder part of the
belt to remove any slack. Make
sure the belt goes over your
collarbone and across your chest.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 7

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
RELEASE
BUTTON
5. If the belt crosses your neck, you
need to adjust the belt anchor
height or your seating position.
Front seats:
Adjust the belt anchor by pressing
the release button and sliding the
anchor downward (it has four
positions).
Rear seat:
Move toward the center of the seat
until the belt fits over your collar-
bone.
To unlatch the seat belt, push the
red PRESS button on the buckle.
Guide the belt across your body to
the door pillar.
After you exit the vehicle, make sure
the seat belt is out of the way and
will not get closed in the door.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 8

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
Wearing the Lap Belt
1. Pull the latch plate across your
hips and insert it into the buckle
marked CENTER.
If the belt is too short, hold the
latch plate at a right angle, and
pull it to extend the belt. Insert the
latch plate into the buckle.
2. Position the belt as low as possible
across your hips and pelvic bones,
not across your stomach. Pull the
loose end of the belt to adjust for a
snug but comfortable fit.
To unlatch the belt, push the red
PRESS button on the buckle.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 9

The Seat Belt System and How It Works
Advice for Pregnant Women
Protecting the mother is the best
way to protect her unborn child.
Therefore, a pregnant woman should
wear a properly-positioned seat belt
whenever she drives or rides in a car.
If possible, use a lap/shoulder seat
belt, remembering to keep the lap
portion as low as possible (see page
7 ).
Each time you have a check-up, ask
your doctor if it's okay for you to
drive and how you should position a
lap/shoulder seat belt.
Seat Belt Maintenance
For safety, you should check the
condition of your seat belts regularly.
Pull out each belt fully and look for
frays, cuts, burns, and wear. Check
that the latches work smoothly and
the lap/shoulder belts retract easily.
Any belt not in good condition or not
working properly should be replaced.
If a seat belt is worn during a crash,
have your dealer replace the belt and
inspect the anchors for damage.
For information on how to clean your
seat belts, see page 212 .
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 10

Supplemental Restraint System
Your car is equipped with a Supple-
mental Restraint System (SRS) to
help protect the head and chest of
the driver and front seat passenger
during a severe frontal collision.
This system does not replace your seat
belts. It supplements, or adds to, the
protection offered by seat belts and
other occupant protection features.
SRS Components
Your supplemental restraint system
includes:
One airbag in the steering wheel
for the driver and another in the
dashboard for the passenger.
Automatic seat belt tensioners
that tighten the front seat belts
during a severe frontal collision.
Sensors that can detect a severe
frontal collision.
A sophisticated electronic system
that continually monitors the
sensors, control unit, airbag
activators, and all related wiring
when the ignition is ON (II).
An indicator light on the instru-
ment panel to alert you to a
possible problem with the
system.
Emergency backup power in
case your car's electrical system
is disconnected in a crash.
What Happens In a Crash
If you ever have a severe frontal
collision, the sensors will detect
rapid deceleration and signal the
control unit to instantly inflate the
airbags and activate the automatic
seat belt tensioners.
During a crash, your seat belts will
help to restrain your lower body and
torso, while the tensioners tighten
and lock the seat belts to help keep
you in place. The airbags will provide
a cushion to absorb crash energy
and help keep the head and chest of
the driver and front passenger from
striking the interior of the car.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Not wearing a seat belt
increases the chance of serious
injury or death in a crash, even
if you have airbags.
Be sure you and your
passengers always wear seat
belts and wear them properly.
Page 11

Supplemental Restraint System
After inflating, the airbags will
immediately deflate. The entire
process, from detection to deflation,
takes a fraction of a second. This
process occurs so quickly that you
may not hear the loud noise created
by the airbag inflators, or realize
what has happened.
After the crash, you may see what
looks like smoke. This is actually
powder from the airbag's surface.
People with respiratory problems
may experience some temporary
discomfort from the chemicals used
by the airbag's activators.
Important Facts About Airbags
Airbags inflate only when needed; in
a severe frontal collision. A severe
collision would be similar to a crash
into a parked vehicle of similar size
and weight at 25 mph (40 km/h).
Airbags will not inflate in a moderate
frontal collision, or during a rear
impact, side impact, or rollover —
even if the impact is severe.
Airbags inflate and deflate only once.
They cannot protect you during any
additional impacts that can occur
during a crash sequence.
Injuries, including fatal injuries, can
occur in a severe collision, even if
seat belts are worn properly and the
airbags inflate. No safety system can
provide complete protection in a
severe crash.
Just from viewing the vehicle
damage after a crash, it is very
difficult to accurately determine if
the airbags should or should not
have inflated. In some cases where
the airbag did not inflate, extensive
visible damage indicated that the car
absorbed much of the crash energy,
and the airbags were not needed. In
other cases, a severe jolt, such as an
impact to the undercarriage, may not
cause extensive body damage but
may still cause the airbags to inflate.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Frontal Collision Range
Page 12

Supplemental Restraint System
How the Driver's Airbag Works
If you ever have a severe frontal
collision, your airbag will instantly
inflate to help protect your head and
chest.
To do its job, the airbag inflates with
considerable force. So, while it can
reduce serious injuries and even save
your life, the airbag might cause
some facial abrasions or other
injuries. To reduce the possibility of
injury, you should always sit back as
far from the steering wheel as
practical while still maintaining full
vehicle control.
After the bag completely inflates, it
immediately starts deflating so it
won't interfere with your visibility,
ability to steer, or ability to operate
other controls. The total time for
inflation and deflation is a fraction of
a second. You may not even be
aware that the airbag has been fully
inflated.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 13
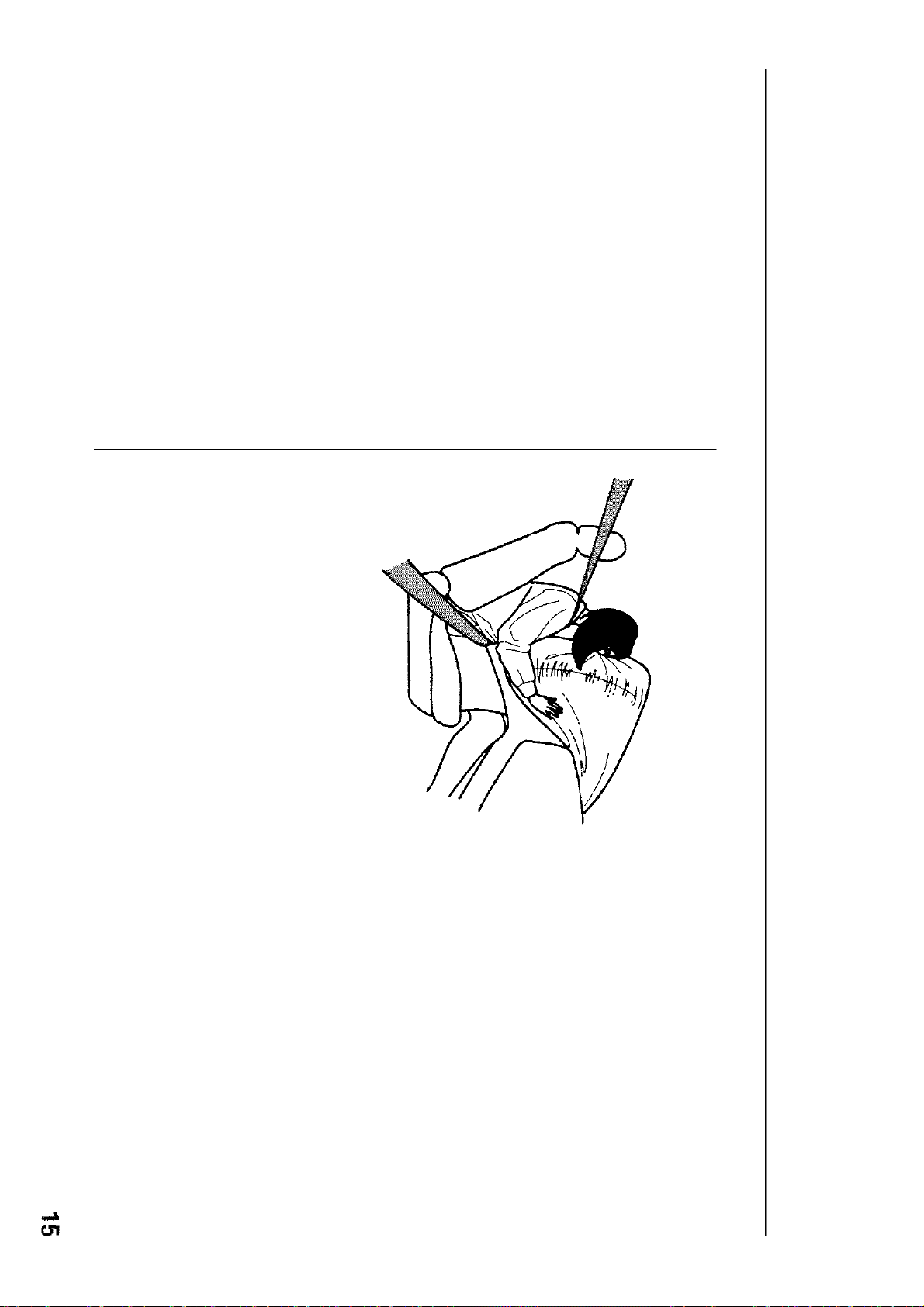
Supplemental Restraint System
The driver's airbag is stored in the
center of the steering wheel. For
your safety, do not attach any items
to the steering wheel. They could
interfere with the proper operation
of the airbag. Or, if the airbag
inflates, they could be propelled
inside the car and hurt someone.
How the Passenger's Airbag
Works
If you ever have a severe frontal
collision, the passenger's airbag will
inflate at the same time as the driver's
airbag.
This airbag is quite large and inflates
with considerable force. It can
seriously hurt a front seat passenger
who is not in the proper position and
wearing the seat belt properly.
Front seat passengers should move
the seat as far back as practical and
sit well back in the seat.
We strongly recommend that you do
not put an infant seat in the front
passenger's seat. If the airbag
inflates, it can hit the infant seat with
great force. The infant seat can be
dislodged or struck with enough
force to cause very serious injury to
the infant.
If a toddler seat is used in the front
passenger's seat, the vehicle seat
should be moved as far back as
possible. If the passenger's bag
inflates, it could seriously hurt a
toddler who is not in the proper
position or properly restrained.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 14

Supplemental Restraint System
The passenger's airbag is stored
near the top of the dashboard, under
a lid marked SRS. Do not place any
objects on top of this lid. If the airbag
inflates, those objects can be
propelled inside the car and possibly
hurt someone.
How the Automatic Seat Belt
Tensioners Work
Your Acura has automatic seat belt
tensioners for added protection
during a severe frontal collision.
If your airbags inflate, the tensioners
immediately tighten the front seat
belts to help hold the occupants in
place. The belts will remain tight
until you unbuckle them in the
normal way.
How the SRS Indicator
Light Works
The purpose of the SRS light on your
instrument panel is to alert you to a
potential problem with your supple-
mental restraint system.
Have the system checked if:
The light does not come on when
you turn the ignition ON (II).
The light stays on after the engine
starts.
The light comes on or flashes
while you are driving.
If you see any of these indications,
the airbags and seat belt tensioners
may not work when needed in an
accident. Take the car to your dealer
promptly for diagnosis and service.
Driver and Passenger Safety
SRS
Page 15

Supplemental Restraint System
System Service
Your supplemental restraint system
is virtually maintenance-free. The
only scheduled maintenance is an
inspection of the system by the
dealer when the car is ten years old.
For your convenience, the car's
production date is on a label on the
driver's doorjamb.
If either of the following happens,
you must have an authorized Acura
dealer service the system. There are
no parts you can safely service.
If your airbags ever inflate, the
airbags, seat belt tensioners and
control unit must be replaced. Do
not try to remove or discard the
airbags yourself. This must be
done by an Acura dealer.
If the SRS indicator light alerts
you to a problem, have the
supplemental restraint system
inspected as soon as possible. If
you ignore this indication, the
airbags might not inflate when you
need them.
System Service Precautions
Do not modify your steering wheel
or any other part of the supplemental
restraint system. Modifications could
make the system ineffective.
Do not tamper with the system's
components or wiring. This could
cause the airbags to inflate inadver-
tently, possibly injuring someone
very seriously.
Tell anyone who works on your car
that you have a supplemental
restraint system. Failure to follow
the procedures and precautions in
the official Acura service manual
could result in personal injury or
damage to the system.
Scrapping an entire car that has
uninflated airbags can be dangerous.
Get assistance from an Acura dealer
if your car must be scrapped.
If you sell your car, please be sure to
tell the new owner that the car has a
supplemental restraint system. Alert
them to the information and precau-
tions in this part of the owner's
manual.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 16

Additional Safety Information
The seat belts and airbags are obvi-
ously important parts of your occu-
pant protection system.
In addition, you should know that
sitting upright, adjusting the head
restraints properly, locking the doors,
and stowing things properly can also
increase your safety and possibly
even save your life.
Seat-back Position
The seat-backs should be in an
upright position for you and your
passengers to get the most protec-
tion from the seat belts.
If you recline a seat-back, you reduce
the protective capability of your seat
belt. The farther a seat-back is
reclined, the greater the risk that
you will slide under the belt in a
severe crash and be very seriously
injured.
For information on how to adjust the
seat-back, see page 68.
Head Restraint Position
Head restraints can help protect you
from whiplash and other injuries. For
the best protection, adjust the top of
the restraint so it is even with the
tops of your ears, or as high as possi-
ble. For instructions on adjusting the
head restraints, see page 70.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 17

Additional Safety Information
Door Locks
It is not safe to leave your car doors
unlocked. A passenger, especially a
child, could open a door and acci-
dentally fall out. Also, there is a
greater chance of being thrown out
of the car during a crash when the
doors are not locked.
Storing Cargo Safely
Before you drive, make sure you
first securely store or tie down any
items that could be thrown around
the car and hurt someone, or
interfere with your ability to operate
the controls.
Do not put any items on top of the
rear shelf. They can block your view
and they could be thrown about the
car in a crash.
Be sure to keep compartment doors
closed when the car is moving. If a
front passenger hits the door of an
open glove box, for example, he
could injure his knees.
For information on loading cargo,
see page 130.
Driving with Pets
Loose pets can be a hazard while you
are driving. An unrestrained pet can
interfere with your ability to drive
the car. In a crash or sudden stop,
loose pets or cages can be thrown
around inside the car and hurt you or
your passengers. It is also for their
safety that pets should be properly
restrained in your car.
The recommended way to restrain a
medium-sized or larger dog is with a
special traveling harness. This har-
ness can be secured to the rear seat
with a seat belt. Travel harnesses are
available at pet stores.
A small dog, cat, or other small
animal will be safest in a pet carrier
with rigid sides. Choose a style that
allows you to secure it to the car's
seat by routing a seat belt through
the carrier's handle.
For further information, contact your
veterinarian or local animal protec-
tion society.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 18

Child Safety
Children depend on adults to protect
them. To help make sure we do,
every state and Canadian province
has laws requiring infants and young
children to be properly restrained
whenever they ride in a car.
Where Should Children Sit?
According to accident statistics,
children of all sizes and ages are
safer when they are properly
restrained in the rear seat rather
than the front seat.
We recommend that, whenever
possible, you secure your child's
infant or toddler seat in the center
position of the rear seat with the lap
belt.
We strongly recommend that you do
not put an infant seat in the front
passenger's seat. If the airbag
inflates, it can hit the infant seat with
great force. The infant seat can be
dislodged or struck with enough
force to cause very serious injury to
the infant.
Driver and Passenger Safety
An infant or child who is not
properly restrained can be killed
or seriously injured in a crash.
Be sure any child too small for
seat belts is properly secured in
a child restraint.
Page 19

Child Safety
If a toddler seat is used in the front
passenger's seat, the vehicle seat
should be moved as far back as
possible. If the passenger's bag
inflates, it could seriously hurt a
toddler who is not in the proper
position or properly restrained.
We also recommend that any child
who is too large to use an infant or
toddler seat ride in one of the out-
side positions of the rear seat. The
child should then wear the lap/
shoulder belt properly for protection.
If the child is not large enough to
wear the lap/shoulder belt properly,
you should use a booster seat.
Important Safety Reminders
Never hold a baby or child on your
lap when riding in a car. If you are
wearing your seat belt, the violent
forces created during a crash will
tear the child from your arms. The
child could be seriously hurt or killed.
If you are holding a child and not
wearing a seat belt in a crash, you
could crush the child against the car's
interior.
Never put your seat belt over
yourself and a child. During a crash,
the belt could press deep into the
child, causing serious internal
injuries.
Two children should never use the
same seat belt. If they do, they could
be very seriously injured in a crash.
If you are driving with small children
in the car, you should use the
childproof door locks to prevent
them from opening the rear doors
(see page 64).
For their safety, do not leave
children alone in your car without
adult supervision.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 20

Child Safety
General Guidelines for
Restraining Children Under
401bs (18 kg)
Use an approved child seat. The seat
must meet Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard 213 (FMVSS-213) or
Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards. Look for the manufac-
turer's statement of compliance on
the box and seat
Use a seat of the right size. Make sure
the seat fits your child. Check the
seat manufacturer's instructions and
labels for height and weight limits.
Secure the child seat to the car. All
approved child seats are designed to
be secured to the car seat by the lap
belt or the lap belt portion of a lap/
shoulder belt. A child whose seat is
not properly secured to the car can
be endangered in a crash.
To properly route a seat belt through
a child seat, follow the seat maker's
instructions. If you use a lap/
shoulder belt, be sure to follow the
instructions for securing a child seat
with a lap/shoulder belt on page 24 .
Secure the child in the child seat. Make
sure the infant or child is firmly
secured to the child seat. Use the
straps provided, and carefully follow
the manufacturer's instructions.
Restraining an Infant Who
Weighs Less Than 20 Ibs
(9 kg)
An infant up to about 20 Ibs (9 kg)
must be restrained in an infant seat
or a convertible seat designed for a
baby. Because infants must ride in a
reclining position, be sure the infant
seat always faces the REAR of the
car as shown.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 21

Child Safety
We recommend that, whenever
possible, you put the infant seat in
the center position of the rear seat
and secure it to the car with the lap
belt.
If you decide to put an infant seat in
any other seating position, be sure to
follow the instructions for securing a
child seat with a lap/shoulder belt on
page 24.
We strongly recommend that you do
not put an infant seat in the front
passenger's seat. If the airbag
inflates, it can hit the infant seat with
great force. The infant seat can be
dislodged or struck with enough
force to cause very serious injury to
the infant.
Restraining a Child Who Weighs
Between 20 and 40 Ibs
(9 and 18 kg)
Toddler seats are designed for
children who weigh between 20 and
40 Ibs (9 and 18 kg).
The preferred place to put a toddler
seat is in the center position of the
rear seat. Use the car's lap belt to
secure the seat to the car.
If you decide to put a toddler seat in
any other seating position, be sure to
follow the instructions for securing a
child seat with a lap/shoulder belt on
page 24.
If you are using a toddler seat in the
front passenger's seat, move the
passenger's seat as far back as
possible before installing the child
seat. If the passenger's bag inflates,
it could seriously hurt a toddler who
is not in the proper position or
properly restrained.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 22

Child Safety
Restraining a Child Who Weighs
Over 40 Ibs (18 kg)
We recommend that, whenever
possible, a child who has outgrown a
toddler seat ride in one of the
outside positions of the rear seat and
use a lap/shoulder belt.
Put the lap/shoulder belt on your
child and check its fit. The shoulder
belt should fit over the collarbone
and across the chest. The lap belt
should sit low on your child's hips,
not across the stomach.
If the shoulder belt crosses the neck,
have your child move toward the
center of the rear seat until the belt
fits properly. If the belt still crosses
the child's neck, you should use a
booster seat.
Several styles of booster seats are
available. We recommend a design
that allows the child to use the car's
lap/shoulder belt.
Whichever style you select, follow
the booster seat manufacturer's
instructions.
Securing a Child Seat with a Lap/
Shoulder Belt
The lap/shoulder belt retractors in
the passenger seating positions have
a built-in locking mechanism in-
tended to secure a child seat. When
you are placing a child seat in one of
these outside seating positions, do
the following:
1. Place the child seat in the desired
seating position. Route the lap/
shoulder belt through the seat
according to the seat manufac-
turer's instructions.
2. Insert the latch plate into the
buckle. Make sure it is fully
latched.
3. Slowly pull the shoulder portion of
the belt out of the retractor until it
stops.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 23

Child Safety
4. Allow the belt to slowly feed back
into the retractor. You should hear
a clicking noise that indicates the
locking mechanism has engaged.
5. After the belt has retracted fully,
pull up on the shoulder portion to
remove any slack.
6. Push and pull on the child seat to
verify that it is held firmly in place.
If not, unlatch the seat belt, allow
it to retract fully, and repeat these
steps.
To unlatch the seat belt, push the
red PRESS button on the buckle.
Guide the belt across to the door
pillar. If the belt doesn't retract
easily, pull it out and check for twists
or kinks.
Using Child Restraints with
Tethers
Your Acura has three attachment
points for a tether-style child seat.
They are located on the rear shelf.
U.S. Models
Use the dimensions in the above
illustration to locate the attachment
point you want to use. As the inside
of the attachment point has a slit,
you can find the attachment point
easily by pushing it slightly with your
finger or a screwdriver. Then cut a
7/8 inch (22 mm) diameter hole in
the rear shelf.
You can also locate the attachment
points by looking in the trunk at the
underside of the rear shelf. Select
the attachment point you want to use.
Take a thin, pointed object, such as
an awl or ice pick, insert it into that
attachment point, and poke a marker
hole in the rear shelf fabric.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 24

Child Safety
Working from inside the car, use a
razor blade to cut a 7/8 inch (22
mm) diameter hole in the fabric at
the marker hole you punched.
Canadian Models
Select the attachment point you want
to use and remove the plug with a
small flat-tipped screwdriver or
fingernail file.
Install the tether hardware that came
with the child seat.
Tighten the bolt to:
16 lbf.ft (2.2 kgf.m, 22 N.m)
If you are not sure how to install the
hardware, have it installed by your
authorized Acura dealer.
If you need an anchor plate and
mounting hardware, contact your
Acura dealer.
Canadian Models
TOOTHED WASHER
The anchor plate and mounting
hardware for a top tether are
supplied with the car. When install-
ing, make sure the toothed washer is
on the bottom of the bolt.
The supplied anchor plate is
designed only for mounting a child
restraint. Do not use it for any other
purpose.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 25

Storing a Child Seat
When you are not using an infant
seat or other child restraint, either
remove it or make sure it is properly
secured so it cannot be thrown
around the car during a crash.
Child Safety
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 26

Alcohol and Drugs
Driving a car requires your full at-
tention and alertness. Traffic condi-
tions change rapidly. You must be
able to react just as rapidly. Alcohol
or drugs directly affect your alert-
ness and ability to react. Even pre-
scription and non-prescription medi-
cines can have this effect.
There are laws that deal with
drunken driving. These laws define
how much alcohol it takes in your
system to be legally "drunk." How-
ever, your judgment and reaction
time get worse with every drink—
even the first one.
The safest thing you can do is never
drink and drive. This can be done if
you plan ahead. If you know you are
going to be drinking, make plans to
ride with a friend who will not be
drinking.
What if you find that you've been
drinking and cannot get a ride from a
friend? Find alternative transpor-
tation. Call a taxi. Take a bus. Many
communities have transportation
services devoted to shuttling people
who have been drinking.
If you have no choice but to drive,
stop drinking and give yourself lots
of time to sober up. Time is the only
thing that can make you sober.
Things like coffee or a cold shower
don't speed up the process.
If you see friends trying to get
behind the wheel after drinking, stop
them. Drive them yourself or
arrange other transportation. If you
think you are interfering, remember
that your interference will keep them
from sharing the road with you.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Page 27

Carbon Monoxide Hazard
Your car's exhaust contains carbon
monoxide gas. You should have no
problem with carbon monoxide
entering the car in normal driving if
you maintain your car properly.
Have the exhaust system inspected
for leaks whenever:
The car is raised for an oil change.
You notice a change in the sound
of the exhaust.
The car was in an accident that
may have damaged the underside.
High levels of carbon monoxide can
collect rapidly in enclosed areas,
such as a garage. Do not run the
engine with the garage door closed.
Even with the door open, run the
engine only long enough to move the
car out of the garage.
With the trunk lid open, air flow can
pull exhaust gas into your car's
interior and create a hazardous
condition. If you must drive with the
trunk lid open, open all the windows
and set the climate control system as
shown below.
If you must sit in your parked car,
even in an unconfined area, with the
engine running, adjust the climate
control system as follows:
1. Push the
button.
2. Select the mode.
3. Set the fan speed to high.
4. Set the temperature control to a
comfortable setting.
Driver and Passenger Safety
Carbon monoxide gas is toxic.
Breathing it can cause
unconsciousness and even kill
you.
Avoid any enclosed areas or
activities that expose you to
carbon monoxide.
Page 28

Safety Labels
These labels are in the locations
shown. They warn you of potential
hazards that could cause serious
injury. Read these labels carefully
and don't remove them.
If a label comes off or becomes hard
to read, contact your Acura dealer
for a replacement.
RADIATOR CAP
Driver and Passenger Safety
BATTERY
Page 29

Control Locations
DOOR LOCK
SWITCHES
(P.60)
DRIVING POSITION
MEMORY
(P.74)
POWER WINDOW
SWITCHES
(P.79)
TRUNK RELEASE
BUTTON
(P.65)
FUEL FILL
DOOR RELEASE
(P.124)
CLIMATE CONTROL
SYSTEM
(P.92)
AUDIO SYSTEM
(P.101)
HOOD RELEASE HANDLE
(P.125)
Instruments and Controls
MIRROR
CONTROLS
(P.72)
DIGITAL
CLOCK
(P.82)
Page 30

Indicator Lights
The instrument panel has many
indicators to give you important
information about your car.
Lamp Check
These indicator lights come on when
you turn the ignition switch ON (II),
allowing you to see that they are
working:
SRS Indicator
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Charging System Indicator
Low Oil Pressure Indicator
Anti-lock Brake System Indicator
Seat Belt Reminder Light
D4 Lamp
Door and Brake Lamp Monitor
Immobilizer System Indicator
Traction Control System Indicator
If an indicator does not light during
this test, it cannot alert you if that
system develops a problem. Have the
dealer check your car for burned-out
bulbs or other problems.
* The U.S. instrument panel is shown. Differences for the Canadian model
are noted in the text.
Instruments and Controls
LOW OIL
PRESSURE
INDICATOR
CHARGING
SYSTEM
INDICATOR
HIGH BEAM
INDICATOR
LOW FUEL
INDICATOR
TRACTION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
INDICATOR
DOOR AND BRAKE
LAMP MONITOR
MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR
LAMP
CRUISE
CONTROL
INDICATOR
PARKING BRAKE
AND BRAKE
SYSTEM
INDICATOR*
LIGHTS ON
INDICATOR
IMMOBILIZER
SYSTEM
INDICATOR
ANTI-LOCK
BRAKE SYSTEM
INDICATOR*
SEAT BELT
REMINDER
LIGHT
SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT
SYSTEM
INDICATOR
Page 31

Indicator Lights
Seat Belt Reminder Light
This indicator lights when you turn
the ignition ON (II). It is a reminder
to you and your passengers to
protect yourselves by fastening the
seat belts. A beeper also sounds if
you have not fastened your seat belt.
If you do not fasten your seat belt,
the beeper will stop after a few
seconds but the light stays on until
you do. Both the light and the beeper
stay off if you fasten your seat belt
before turning on the ignition.
Low Oil Pressure
Indicator
The engine can be severely damaged
if this light flashes or stays on when
the engine is running. For complete
information, see page 230 .
Charging System
Indicator
If this light comes on when the
engine is running, the battery is not
being charged. For complete
information, see page 231.
Parking Brake
and Brake
System
Indicator
This light has two functions:
1. It lights as a reminder that you
have not released the parking
brake. Driving with the parking
brake applied can damage the
brakes and tires, and cause the
Anti-lock brake system to turn off
(see page
142).
2. If it remains lit after you release
the parking brake while the engine
is running, or comes on while
driving, it can indicate that the
brake fluid level is low. This is
normally due to worn brake pads.
Have your dealer check the
braking system for worn pads or
fluid leaks.
Instruments and Controls
U.S.
Canada
BRAKE
Page 32

Indicator Lights
Lights On Indicator
U.S. models only
This indicator reminds you that the
exterior lights are on. It comes on
when the light switch is in either the
or position. If you turn the
ignition switch to ACCESSORY (I)
or LOCK (0) without turning off the
light switch, this indicator will
remain on. A reminder chime will
also sound when you open the driver's
door.
Your vehicle has the Automatic
Lighting feature. This indicator will
come on when the light switch is in
AUTO and the lights turn on auto-
matically.
Immobilizer System
Indicator
This indicator should come on for a
few seconds when you turn the igni-
tion switch ON (II). It will then go
off if you have inserted a properly-
coded ignition key. If it is not a prop-
erly-coded key, the indicator will
blink and the engine will not start
(see page 58).
This indicator also blinks several
times when you remove the key
from the ignition switch.
Supplemental Restraint
System Indicator
This indicator lights when you turn
the ignition ON (II). If it comes on at
any other time, it indicates a problem
in the supplemental restraint system.
For complete information, see page
16 .
Malfunction Indicator
Lamp
See page 232 .
Instruments and Controls
SRS
Page 33

Indicator Lights
Anti-lock Brake
System (ABS)
Indicator
This light normally comes on when
you turn the ignition ON (II) and
goes off after the engine starts. If it
comes on at any other time, there is
a problem in the ABS. If this happens,
take the car to your dealer to have it
checked. With the light on, your car
still has normal braking ability but no
anti-lock.
Traction Control System
(TCS) Indicator
On U.S. 3.5 RL with Premium Package
and Canadian 3.5 RL
This indicator has three functions:
1. It comes on as a reminder that you
have turned off the Traction
Control System.
2. It flashes when the TCS is
regulating the engine power.
3. If it comes on and stays on when
the Traction Control System is on,
it indicates that there is a problem
in the TCS.
This light also comes on when you
turn the ignition ON (II) and goes off
after the engine starts. See page
143 for more information on the
TCS.
Door and Brake Lamp Monitor
The appropriate light comes on in
this display if the trunk or any door
is not closed tightly. If a brake light
does not work, the BRAKE LAMP
indicator comes on when you push
the brake pedal with the ignition
switch ON (II).
A burned out brake light is a hazard
when drivers behind you cannot tell
you are braking. Have your brake
lights repaired right away.
All the lights in the monitor display
come on for a few seconds when you
turn the ignition switch ON (II).
Instruments and Controls
U.S.
Canada
A B S
T
C
S
Page 34

Indicator Lights
Turn Signal and
Hazard Warning
Indicators
The left or right turn signal light
blinks when you signal a lane change
or turn. If the light does not blink or
blinks rapidly, it usually means one
of the turn signal bulbs is burned out
(see page 201 ). Replace the bulb as
soon as possible, since other drivers
cannot see that you are signalling.
When you turn on the Hazard
Warning switch, both turn signal
lights blink. All turn signals on the
outside of the car should flash.
"Daytime Running
Lights" Indicator
Canadian models only
This indicator lights when you turn
the ignition to ON (II) with the
headlight switch off and the parking
brake set. It should go off if you turn
on the headlights or release the
parking brake. If it comes on at any
other time, it means there is a
problem with the DRL. There may
also be a problem with the high
beam headlights.
High Beam Indicator
This light comes on with the high
beam headlights. See page 43 for
information on the headlight
controls.
On Canadian models, this indicator
comes on with reduced brightness
when the Daytime Running Lights
(DRL) are on (see page 45 ).
Cruise Control Indicator
This lights when you set the cruise
control. See page 53 for information
on operating the cruise control.
Low Fuel Indicator
This light comes on as a reminder
that you must refuel soon.
Instruments and Controls
CRUISE
CONTROL
DRL
Page 35

Gauges
The gauges illuminate when you
turn the ignition switch ON (II).
Speedometer
U.S. Models
This shows your speed in miles per
hour (mph). The smaller inner
numbers are the speed in kilometers
per hour (km/h).
Canadian Models
This shows your speed in kilometers
per hour (km/h). The smaller inner
numbers are the speed in miles per
hour (mph).
Tachometer
The tachometer shows the engine
speed in revolutions per minute
(rpm). To protect the engine from
damage, never drive with the
tachometer needle in the red zone.
TACHOMETER SPEEDOMETER
MAINTENANCE
REQUIRED INDICATOR
TRIP METER/OUTSIDE
TEMPERATURE INDICATOR
RESET
BUTTON
Instruments and Controls
ODOMETER
FUEL GAUGE
SELECT
BUTTON
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
Page 36

Gauges
Odometer
The odometer shows the total dis-
tance your car has been driven. It
measures miles in U.S. models and
kilometers in Canadian models.
It is illegal under federal law (in the
U.S.) and provincial regulations (in
Canada) to disconnect, reset, or alter
the odometer with the intent to
change the number of miles or
kilometers indicated.
Trip Meter/Outside Temperature
Indicator
SELECT
BUTTON
RESET
BUTTON
The trip meter and the outside
temperature indicator use the same
display. To switch the display
between the trip meter and the
outside temperature, press the
Select button. When you turn the
ignition switch to ON (II), what you
last selected is displayed.
Trip Meter
The trip meter shows the number of
miles (U.S.) or kilometers (Canada)
driven since you last reset it.
There are two trip meters, Trip A
and Trip B. Switch between these
and the outside temperature display
by pressing the Select button
repeatedly. Each trip meter works
independently, so you can keep track
of two different distances.
To reset a trip meter, display it and
then press the Reset button until you
hear a beep. Both trip meters will re-
set if the car's battery goes dead or
is disconnected.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Page 37

Gauges
Outside Temperature Indicator
This indicator displays the outside
temperature in Fahrenheit in U.S.
models, and in Centigrade in
Canadian models.
The temperature sensor is located in
the front bumper. Therefore, the
temperature reading can be affected
by heat reflection from the road sur-
face, engine heat, and the exhaust
from the surrounding traffic. This
can cause the temperature reading
not to be correct when your speed is
under 19 mph (30 km/h).
In certain weather conditions,
temperature readings near freezing
(32°F, 0°C) could mean that ice is
forming on the road surface.
Temperature Gauge
This shows the temperature of the
engine's coolant. During normal
operation, the pointer should rise
from the bottom white mark to about
the middle of the gauge. In severe
driving conditions, such as very hot
weather or a long period of uphill
driving, the pointer may rise to near
the upper white mark. If it reaches
the red (Hot) mark, pull safely to the
side of the road. Turn to page 228 for
instructions and precautions on
checking the engine's cooling
system.
Fuel Gauge
This shows how much fuel you have.
It is most accurate when the car is on
level ground. It may show slightly
more or less than the actual amount
when you are driving on curvy or
hilly roads.
The gauge stays at the same fuel
level reading after you turn off the
ignition. When you add fuel, the
gauge slowly changes to the new
reading after you turn the ignition
back ON (II).
Instruments and Controls
Page 38

Gauges
MAINTENANCE REQUIRED INDICATOR
This indicator reminds you that it is
time to take your car in for sched-
uled maintenance.
Refer to the Maintenance Schedules
for Normal and Severe Driving
Conditions on pages 158 — 159.
For the first 6,000 miles (9,600 km)
after the Maintenance Required
Indicator is reset, it will come on for
two seconds when you turn the
ignition ON (II).
SELECT
BUTTON
RESET
BUTTON
Between 6,000 miles (9,600 km) and
7,500 miles (12,000 km) this
indicator will light for two seconds
when you first turn the ignition ON
(II), and then flash for ten seconds.
If you exceed 7,500 miles (12,000
km) without having the scheduled
maintenance performed, this
indicator will remain on as a constant
reminder.
Your dealer will reset this indicator
after completing the scheduled
maintenance. If this maintenance is
done by someone other than your
Acura dealer, reset the indicator as
follows.
1. Turn off the engine.
2. Press and hold the select and reset
buttons next to the instrument pan-
el, then turn the ignition ON (II).
3. Hold the buttons for ten seconds,
until the indicator resets.
Instruments and Controls
Maintenance Required Indicator
Page 39

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
The two levers on the steering
column contain controls for driving
features you use most often. The left
lever controls the turn signals,
headlights, and high beams. The
right lever controls the windshield
washers and wipers.
The switch for the hazard warning
lights is on the dashboard to the
right of the steering column.
The controls under the left air vent
are for the cruise control and
instrument panel brightness.
The switches for the rear window
defogger and fog lights are under
the audio system.
The steering wheel adjustment
switch on the side of the steering
column allows you to tilt and
telescope the steering wheel.
On U.S. 3.5 RL with Premium Package
and Canadian 3.5 RL
The TCS On/Off switch is located
under the left air vent.
Instruments and Controls
CRUISE
CONTROL
TCS ON/OFF
HEADLIGHTS/
TURN SIGNALS
HAZARD WARNING
LIGHTS
WINDSHIELD
WIPERS/WASHERS
INSTRUMENT
PANEL
BRIGHTNESS
STEERING WHEEL
ADJUSTMENT
HORN
BUTTONS
FOG
LIGHTS
REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER
Page 40

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Headlights
The rotating switch on the left lever
controls the lights. Turning this
switch to the position turns on
the parking lights, taillights, side
marker lights, and rear license plate
lights. Turning the switch to the
position turns on the
headlights.
U.S. Models
When the light switch is in either of
these positions, the Lights On
indicator comes on as a reminder.
This light remains on if you leave the
light switch on and turn the ignition
switch to ACCESSORY (I) or LOCK
(0). You will also hear a Lights On
reminder chime when you open the
driver's door.
Canadian Models
If you leave the lights on with the
ignition switch in ACCESSORY (I)
or LOCK (0), you will hear a
reminder chime when you open the
driver's door.
To change between low beams and
high beams, pull the turn signal lever
until you hear a click, then let go.
The blue high beam indicator will
light (see page 37).
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Page 41

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
To flash the high beams, pull the
turn signal lever back lightly, then
release it. The high beams will come
on and go off.
The high beams will stay on for as
long as you hold the lever back, no
matter what position the headlight
switch is in.
Automatic Lighting
AUTO POSITION
On
U.S.
3.5 RL
The Automatic Lighting feature
turns on the headlights, all other
exterior lights, and the instrument
panel lights when it senses low
ambient light.
To turn on automatic lighting, turn
the light switch to AUTO at any time.
The lights will come on automatically
when the outside light level becomes
low (at dusk, for example). The
Lights On indicator comes on as a
reminder. The lights and indicator
will turn off automatically when the
system senses high ambient light.
The lights will remain on when you
turn off the ignition switch. They will
turn off automatically when you open
the driver's door. To turn them on
again, either turn the ignition switch
to ON (II) or turn the light switch to
Even with the automatic lighting
feature turned on, we recommend
that you turn on the lights manually
when driving at night or in a dense
fog, or when you enter dark areas,
such as long tunnels or parking
structures.
Instruments and Controls
Page 42

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Do not leave the light switch in
AUTO if you will not be driving the
vehicle for an extended period (a
week or more). You should also turn
off the lights if you plan to leave the
engine idling or the engine off for a
long time. This will prevent the
battery from discharging.
The automatic lighting feature is
controlled by a sensor located on top
of the dashboard. Do not cover this
sensor or spill liquids on it.
Daytime Running Lights
(Canadian Models)
With the headlight switch off, the
high beam headlights come on with
reduced brightness when you turn
the ignition switch to ON (II) and
release the parking brake. They
remain on until you turn the ignition
off, even if you set the parking brake.
The headlights revert to normal
operation when you turn them on
with the switch.
Instruments and Controls
LIGHT
SENSOR
Page 43

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Instrument Panel Brightness
The dial on the dashboard to the left
of the instrument panel is used to
adjust the brightness of the lights in
the controls and displays. Turn the
dial to adjust the brightness.
To reduce glare at night, the instru-
ment panel illumination dims when
you turn the light switch to or
Turning the instrument panel
brightness control fully to the left,
past the detent, will return the instru-
ment panel to its full brightness.
Turn Signals
TURN SIGNAL LEVER
Signal a turn or lane change with this
lever. Push down on the lever to
signal a left turn, and up to signal a
right turn. If you push it up or down
all the way, the turn signal continues
to blink even when you release the
lever. It shuts off automatically as
you complete the turn.
Instruments and Controls
INSTRUMENT PANEL
BRIGHTNESS DIAL
Page 44

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
To signal a lane change, push lightly
on the turn signal lever in the proper
direction and hold it. The lever will
return to the center position as soon
as you release it.
Fog Lights
Turn the fog lights on and off by
pressing the button. The indicator in
the button lights to show the fog
lights are on.
You can use the fog lights only when
the headlights are on low beam.
They will go off when you turn the
headlights off or onto high beam.
On cars with automatic lighting
With the light switch in the AUTO
position, you can also use the fog
lights when the headlights turn on
automatically. They will go off when
the headlights turn off.
Instruments and Controls
Page 45

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Windshield Wipers
The right lever controls the wind-
shield wipers and washers. The
rotary switch at the end of the lever
has three positions:
INT : intermittent
: low speed
: high speed
In intermittent, the wipers operate
every few seconds. The sweep
interval will change slightly with
speed; getting shorter as you drive
faster.
You can vary how often the wipers
sweep the windshield by turning the
INT TIME ring next to the rotary
switch. In low speed and high speed,
the wipers run continuously.
If you turn the INT TIME ring to the
shortest delay, the wipers will
change from intermittent to low
speed operation when vehicle speed
exceeds 12 mph (20 km/h).
Instruments and Controls
Page 46

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
To operate the wipers in mist mode,
push the control lever down. The
wipers run at high speed until you
release the lever. This gives you a
quick way to clear the windshield.
Wiper Arms Waiter Position
The windshield wiper arms have two
parked positions: Winter and
Summer. In the winter position, the
arms sit slightly above the edge of
the hood. This reduces the possibili-
ty of damage to the wiper arms or
windshield wiper motor by a build-up
of snow and ice.
Adjust the wiper arms to the winter
position by grasping either arm near
the pivot. Pull on the arm, parallel to
the windshield, until it locks in the
higher position. Push the arm in the
other direction to return the wipers
to the summer position.
A heavy build-up of snow or ice on
the wiper arms will cause them to
automatically park in the winter
position.
Instruments and Controls
WIPER ARMS
Page 47

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Windshield Washers
To clean the windshield, pull back on
the wiper control lever. The washers
spray until you release the lever. The
wipers run at low speed while you're
pulling the lever, then complete one
more sweep of the windshield after
you release it.
Hazard Warning
Push the red button to the left of the
clock to turn on the hazard warning
lights (four-way flashers). This
causes all four outside turn signals
and both indicators in the instrument
panel to flash. Use the hazard
warning lights if you need to park in
a dangerous area near heavy traffic,
or if your car is disabled.
Rear Window Defogger
The rear window defogger will clear
fog, frost, and thin ice from the
window. Push the defogger button to
turn it on and off. The light in the
button lights to show the defogger is
on. If you do not turn it off, the
defogger will shut itself off after
about 25 minutes. It also shuts off
when you turn off the ignition. You
have to turn it on again when you
restart the car.
Instruments and Controls
Page 48

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
Make sure the rear window is clear
and you have good visibility before
starting to drive.
The defogger and antenna wires on
the inside of the rear window can be
accidentally damaged. When
cleaning the glass, always wipe side
to side.
Steering Wheel Adjustments
Your Acura's steering wheel is
electrically-adjustable for angle and
distance. The adjustment switch is
on the left side of the steering
column. Always adjust the steering
wheel before you begin driving.
1. Adjust the seat so you are a
comfortable distance from the
pedals and can operate them
safely.
2. Locate the adjustment switch on
the left side of the steering column.
Move the steering wheel, in, out,
up, or down by pushing and
holding the adjustment switch in
that direction.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Adjusting the steering wheel
position while driving may
cause you to lose control of the
car and be seriously injured in a
crash.
Adjust the steering wheel only
when the car is stopped.
Page 49

Controls Near the Steering Wheel
3. Release the switch when the
steering wheel reaches the
desired position.
Automatic Movement
AUTO SWITCH
The AUTO switch controls automat-
ic movement of the steering wheel.
When this switch is in the ON posi-
tion, the steering wheel automatical-
ly moves fully in and up when you re-
move the key from the ignition
switch.
The steering wheel then returns to
its original position when you insert
the key back in the ignition switch.
Steering wheel movement is also
controlled by the Driving Position
Memory System (see page 74).
Instruments and Controls
Page 50

Steering Wheel Controls
Cruise Control
Cruise control allows you to maintain
a set speed above 25 mph (40 km/h)
without keeping your foot on the
accelerator pedal. It should be used
for cruising on straight, open
highways. It is not recommended for
conditions such as city driving,
winding roads, slippery roads, heavy
rain, or bad weather. You should
have full control of the car under
those conditions.
Using the Cruise Control
CRUISE CONTROL MASTER SWITCH
1. Push in the Cruise Control Master
Switch to the left of the steering
column. The indicator in the
switch will light.
2. Accelerate to the desired cruising
speed above 25 mph (40 km/h).
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Improper use of the cruise
control can lead to a crash.
Use the cruise control only
when traveling on open
highways in good weather.
Page 51

Steering Wheel Controls
3. Press and hold the SET/decel
button on the steering wheel until
the CRUISE CONTROL light on
the instrument panel comes on.
This shows the system is now
activated.
The set speed may vary slightly,
particularly on hills.
Changing the Set Speed
You can increase the set cruising
speed in either of two ways:
Press and hold the RESUME/
accel button. The car will acceler-
ate slowly. When you reach the
desired cruising speed, release the
button.
Push on the accelerator pedal. Ac-
celerate to the desired cruising
speed and press the SET/decel
button.
You can decrease the set cruising
speed in either of two ways:
Press and hold the SET/decel
button. The car will decelerate.
Release the button when you
reach the desired speed.
Tap the brake pedal lightly with
your foot. The CRUISE
CONTROL light on the instru-
ment panel will go out. When the
car slows to the desired speed,
press the SET/decel button. The
car will then maintain the desired
speed.
Even with the cruise control turned
on, you can still use the accelerator
pedal to speed up for passing. After
completing the pass, take your foot
off the accelerator pedal. The car
will return to the set cruising speed.
Resting your foot on the brake pedal
will cause the cruise control to
cancel.
Instruments and Controls
RESUME/
accel
CANCEL
SET/decel
Page 52

Steering Wheel Controls
Cancelling the Cruise Control
You can cancel the cruise control in
any of these ways:
Tap the brake pedal.
Push the CANCEL button on the
steering wheel.
Press the Cruise Control Master
Switch.
When you push the CANCEL button,
or tap the brake pedal, the CRUISE
CONTROL light on the instrument
panel will go out and the car will
begin to slow down. You can use the
accelerator pedal in the normal way.
The system remembers the
previously-set cruising speed. To
return to that speed, accelerate to
above 25 mph (40 km/h) and then
press the RESUME/accel button
until the CRUISE CONTROL light
comes on. The car will accelerate to
the same cruising speed as before.
Pressing the Cruise Control Master
Switch turns the system completely
off and erases the previous cruising
speed from memory. To use the
system again, refer to Using the
Cruise Control.
Remote Audio Controls
These buttons let you control some
functions of the audio system with-
out removing your hands from the
wheel. Refer to page 118 for a com-
plete explanation.
Instruments and Controls
CANCEL
Page 53

Keys and Locks
Keys
Your vehicle comes with two kinds
of keys: a master key and a valet key.
The master key fits all the locks on
your vehicle:
Ignition
Doors
Trunk
Trunk pass-through cover
Glove box
The valet key works only in the
ignition and the door locks. You can
keep the trunk, trunk pass-through
cover, and the glove box locked
when you leave your vehicle and the
valet key at a parking facility.
You should have received a key
number plate with your keys. You
will need this key number if you ever
have to get a lost key replaced. Keep
the plate stored in a safe place. If you
need to replace a key, use only an
Acura-approved key blank.
These keys contain electronic
circuits that are activated by the
Immobilizer System. They will not
work to start the engine if the
circuits are damaged.
Protect the keys from direct
sunlight, high temperature, and
high humidity.
Do not drop the keys or set heavy
objects on them.
Keep the keys away from liquids.
If they get wet, dry them immedi-
ately with a soft cloth.
The keys do not contain batteries.
Do not try to take them apart.
Instruments and Controls
KEY
NUMBER
PLATE
MASTER
KEY
(Black)
VALET
KEY
(Gray)
LEARNING
KEY
(Red)
Page 54

Keys and Locks
Remote Transmitter
Your car also comes with two remote
transmitters; see page 61 for an
explanation of the operation.
Learning Key
You should also receive a small case
containing a learning key. It is used
by the Acura dealer to code replace-
ment keys to your vehicle's
Immobilizer System. It must not be
used in your vehicle's ignition switch.
Store the learning key with the key
number plate in a safe place.
If you attempt to use the learning
key to start your vehicle's engine, it
may cause a malfunction in the
system that makes your master and
valet keys unusable. If this happens,
you should contact your Acura
dealer.
If you need a new key made, take the
key number plate, the learning key,
and all other keys that came with
your car to your Acura dealer.
Instruments and Controls
Page 55

Keys and Locks
Immobilizer System
The Immobilizer System protects
your vehicle from theft. A properly-
coded master or valet key must be
used in the ignition switch for the
engine to start. If an improperly-
coded key (or other device) is used,
the engine's starting circuit is
disabled.
When you turn the ignition switch to
ON (II), the Immobilizer System
indicator should come on for a few
seconds, then go out. If the indicator
starts to blink, it means the system
does not recognize the coding of the
key. Turn the ignition switch to
LOCK (0), remove the key, reinsert
it, and turn the switch to ON (II)
again.
If the system repeatedly does not
recognize the coding of your key,
contact your Acura dealer.
Do not attempt to alter this system
or add other devices to it. Electrical
problems could result that may make
your vehicle undriveable.
If you have lost your key and you
cannot start the engine, contact your
Acura dealer.
As required by the FCC:
This device complies with Part 15 of the
FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any
interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This device complies with DOC rules in
Canada.
Changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's
authority to operate the equipment.
Instruments and Controls
Page 56

Keys and Locks
Ignition Switch
The ignition switch is on the right
side of the steering column. It has
four positions:
LOCK (0)
ACCESSORY (I)
ON (II)
START (III)
LOCK (0) — You can insert or
remove the key only in this position.
When you turn the key from LOCK
to ACCESSORY, you may have to
turn the steering wheel to release
the anti-theft lock. To switch from
ACCESSORY to LOCK, you must
push the key in slightly as you turn it.
The shift lever must also be in Park.
The anti-theft lock will lock the
steering column when you remove
the key.
ACCESSORY (I) — In this position,
you can operate the audio system
and the cigarette lighter.
ON (II) — This is the normal key
position when driving. All features
and accessories on the car are usable.
Several of the lights on the instru-
ment panel come on as a test when
you turn the ignition switch from
ACCESSORY to ON (see page 33).
START (III) — Use this position
only to start the engine. The switch
returns to ON (II) when you let go of
the key.
The engine will not start if the
Immobilizer System does not
recognize the key's coding (see page
58).
You will hear a reminder beeper if
you leave the key in the ignition
switch in the LOCK (0) or
ACCESSORY (I) position and open
the driver's door. Remove the key to
turn off the beeper.
Instruments and Controls
Page 57

Keys and Locks
MASTER DOOR LOCK SWITCH
Each front door has a master door
lock switch. Either switch locks and
unlocks all doors. Push the switch
down to lock all doors, and up to
unlock them.
LOCK TAB
Each door has a lock tab on the top.
When you push down the lock tab on
the driver's door, all doors lock.
Pulling up the lock tab on the driver's
door only unlocks that door. The
lock tab on each passenger's door
only locks and unlocks that door.
To lock any passenger's door when
getting out of the car, push the lock
tab down and close the door. To lock
the driver's door, remove the key
from the ignition switch and push
the lock tab down or push the master
switch down, then close the door.
All doors can be locked from the
outside by using the key in either
front door. To unlock only the driver's
door from the outside, insert the key
in the driver's door lock, turn the key
and release it. If you turn the key
and hold it, all doors will unlock. All
four doors will unlock when you
unlock the passenger's door with the
key.
Instruments and Controls
Power Door Locks
Page 58

Keys and Locks
Lockout Prevention
If you forget and leave the key in the
ignition switch, Lockout Prevention
will not allow you to lock the driver's
door. With the driver's door open
and the key in the ignition, the
master door lock switches are
disabled. If you try to lock the driver's
door by pushing down the lock tab,
the tabs on all doors immediately pop
up.
You can lock and unlock your vehicle
with the remote transmitter. When
you push the LOCK button, all doors
lock.
When you push the UNLOCK button
once, only the driver's door unlocks.
The remaining doors unlock when
you push the button a second time.
The ceiling lights (if the ceiling light
switch is in the center position) and
the door courtesy lights will come on
when you press the UNLOCK button.
If you do not open any door, the
lights stay on for about 10 seconds,
then fade out. If you relock the doors
with the remote transmitter before
10 seconds have elapsed, the lights
will go off immediately.
If you unlock the doors with the
remote transmitter, but do not open
any of the doors within 30 seconds,
the doors automatically relock and
the security system sets.
You cannot lock any of the doors
with the remote transmitter if any
door is not fully closed or the key is
in the ignition switch. You cannot
unlock any of the doors with the key
in the ignition switch.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Remote Transmitter
LOCK
BUTTON
LED
UNLOCK
BUTTON
TRUNK
RELEASE
BUTTON
PANIC
BUTTON
Page 59

Keys and Locks
To open the trunk, push the Trunk
Release button for approximately
one second.
You can open the trunk with the
remote transmitter regardless of the
position of the main switch in the
glove box. The trunk will not open if
the key is in the ignition switch.
Signal Operation
You can program the remote trans-
mitter so the system will signal you
when the doors lock or unlock.
When you lock the doors, you will
hear a beep, and the parking lights,
side marker lights, and taillights will
flash once.When you unlock the
doors, you will hear two beeps and
the lights will flash twice.
You can turn the signal feature on or
off. To turn this feature on, stand
near the vehicle with the remote
transmitter. Press and hold the
Trunk Release button, then press the
Lock button within one second. You
should see the LED on the remote
transmitter blink twice. Release the
buttons after the LED goes out.
To turn this feature off, repeat the
above procedure. You should see the
LED come on for one second.
After you program the remote
transmitter, make sure the trunk lid
is closed.
Instruments and Controls
Page 60

Keys and Locks
Panic Mode
Panic mode allows you to remotely
activate your vehicle's security
system to attract attention. When
activated, the horn will sound, and
the exterior lights will flash, for
about 30 seconds. To activate panic
mode, press and hold the PANIC
button for about one second.
To cancel Panic mode before 30
seconds, press any button on the
remote transmitter. You can also
turn the ignition switch to ON (II).
Panic mode will not activate if the
ignition switch is in ON (II).
Replacing the Battery
When the remote transmitter's
battery begins to get weak, it may
take several pushes on the button to
lock or unlock the doors, and the
LED will get dim. Replace the
battery as soon as possible.
Battery type: CR2025
To replace the battery, remove the
round cover on the back of the trans-
mitter by turning it counterclockwise
with a coin.
Remove the old battery and note the
polarity. Make sure the polarity of
the new battery is the same (+ side
facing up), then insert it in the
transmitter.
Instruments and Controls
BATTERY
CUSHION
RING
ROUND
COVER
Open
Close
CONTINUED
Page 61

Keys and Locks
Reinstall the cushion ring. Align the
mark on the cover with the
mark on the transmitter,
then set the cover in place and turn it
clockwise.
As required by the FCC:
This device complies with Part 15 of the
FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any
interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This device complies with DOC rules in
Canada.
Changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's
authority to operate the equipment.
Transmitter Care
Avoid severe shock to the trans-
mitter, such as dropping or throwing
it. Also, protect it from extreme hot
or cold temperatures.
Clean the transmitter case with a
soft cloth. Do not use strong
cleaners or solvents that could harm
the case. Immersing the transmitter
in any liquid will harm the trans-
mitter and cause it to not function
properly.
If you lose a transmitter, you will
need to have the replacement
programmed to your vehicle's
system by your Acura dealer. Any
other transmitters you have will also
need to be reprogrammed.
Childproof Door Locks
The childproof door locks are
designed to prevent children seated
in the rear from accidentally opening
the rear doors. Each rear door has a
lock lever near the edge. With the
lever in the LOCK position, the door
cannot be opened from the inside
regardless of the position of the lock
tab. To open the door, pull the lock
tab up and use the outside door
handle.
Instruments and Controls
LEVER
Page 62

Keys and Locks
Trunk
You can open the trunk in three
ways:
Press the trunk release button on
the driver's door.
Use the master key to open the
trunk lock. The valet key does not
work in this lock.
Press and hold the trunk release
button on the remote transmitter
for approximately one second (see
page 62).
To close the trunk, press down on
the trunk lid.
See page 130 for cargo loading and
weight limit information. Keep the
trunk lid closed at all times while
driving to avoid damaging the lid,
and to prevent exhaust gas from
getting into the interior. See Carbon
Monoxide Hazard on page 29 .
TRUNK MAIN SWITCH
To protect items in the trunk when
you need to give the key to someone
else:
1. Disable the trunk release button
on the driver's door by turning off
the trunk main switch in the glove
box.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
MASTER KEY
TRUNK RELEASE BUTTON
Page 63

Keys and Locks
2. Lock the glove box with the
master key.
Make sure the trunk pass-through
cover is locked (see page 71).
3. Give the person the valet key.
Even if the trunk main switch is
turned off, you can open the trunk
with the master key or the remote
transmitter.
Glove Box
Open the glove box by pulling the
bottom of the handle. Close it with a
firm push. Lock or unlock the glove
box with the master key.
The glove box light comes on only
when the parking lights are on.
Instruments and Controls
An open glove box can cause
serious injury to your passenger
in a crash, even if the
passenger is wearing the seat
belt.
Always keep the glove box
closed while driving.
Page 64

Seat Adjustments
Your Acura has power adjustments
for both front seats. The two power
seat adjustment switches are on the
outside edge of the seat bottom.
You can adjust the power seats with
the ignition switch in any position.
Adjust the seat before you start
driving.
Driver's Seat Adjustment
The long horizontal switch adjusts
the seat bottom in several directions.
The short vertical switch adjusts the
seat-back angle.
Push the horizontal switch forward
or backward to adjust the distance to
the steering wheel and pedals.
Pull up or push down on the front of
the switch to move the seat bottom's
front edge up or down. Pull up or
push down on the rear of the switch
to move the rear of the seat bottom
up or down.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Page 65

Seat Adjustments
Pull the center of the horizontal
switch up to raise the seat. Push it
down to lower the seat.
Adjust the seat-back angle by
pushing the rear switch in the
direction you want to move.
The driver's seat includes a memory
feature. Two seat positions can be
stored in separate memories. You
can then select a memorized position-
by pushing the appropriate memory
button. Refer to page 74 for how to
memorize and select the seat
positions.
Instruments and Controls
Reclining the seat-back can
decrease the protection you get
from your seat belt in a crash.
You can slide under the seat
belt and be seriously injured.
Adjust the seat-back to an
upright position and sit well
back in the seat.
Page 66

Seat Adjustments
Driver's Lumbar Support
Vary the lumbar support by moving
the lever on the right side of the
seat-back. Pivot the lever forward
until it stops, then let it return. Doing
this several times adjusts the lumbar
support through its full range.
Front Passenger's Seat
Adjustments
The seat adjustment switches are on
the outside edge of the seat bottom.
Push the long horizontal switch
forward or backward to move the
seat bottom in that direction.
Adjust the seat-back angle by
pushing the vertical switch in the
direction you want to move.
Instruments and Controls
Reclining the seat-back can
decrease the protection you get
from your seat belt in a crash.
You can slide under the seat
belt and be seriously injured.
Adjust the seat-back to an
upright position and sit well
back in the seat.
Page 67

Seat Adjustments, Armrest
Head Restraints
The head restraints help protect you
and your passengers from whiplash
and other injuries. They are most
effective when you adjust them so
the top of the restraint is even with
the top of your ears.
The head restraints adjust for height
and tilt. You need both hands to
adjust the restraint. Do not attempt
to adjust it while driving. To raise it,
pull upward. To lower the restraint,
push the release button sideways
and push the restraint down. To
adjust the tilt, pivot the head
restraint to the desired position.
To remove a head restraint for
cleaning or repair, pull it up as far as
it will go. Push the release button
and pull the restraint out of the seat-
back.
Armrest
The lid of the console compartment
can be used as an armrest at the
high or low position. To raise the
armrest, push the button on the lid.
Make sure the armrest is securely
latched. To lower it, press the button
and push the armrest down until it
latches.
Make sure the passengers' hands or
fingers are away from the armrest
before pushing it down.
Instruments and Controls
Driving your car without head
restraints can lead to serious
injury to you and your
passenger in a crash.
Make sure the head restraints
are in place and adjusted
properly before driving.
Push
RELEASE BUTTON
Page 68

Armrest
Use the low position for your normal
driving or driving in hilly terrain. You
can use the armrest at the high
position when traveling on open
highways or cruising in good
weather.
Make sure you can shift the select
lever smoothly.
The rear seat armrest is located at
the center of the rear seat. Pivot it
down to use it.
Trunk Pass-through Cover
The cover behind the rear seat
armrest allows you to reach small
objects in the trunk from the interior.
The pass-through cover can be
opened from either side; it folds
forward onto the center armrest.
Open the cover by sliding the knob
downward and pushing or pulling on
the cover. To close the cover, swing
it up and push firmly on the top.
Make sure it latches properly.
For security, this cover can be
locked and unlocked only with the
master key. To lock the cover, insert
the key and turn it clockwise.
Never drive with this cover open,
especially if the trunk lid is also open.
See Carbon Monoxide Hazard on
page 29.
Instruments and Controls
KNOB
LID
Page 69

Mirrors
Keep the inside and outside mirrors
clean and adjusted for best visibility.
Be sure to adjust the mirrors before
you start driving.
The inside mirror has day and night
positions. The night position reduces
glare from headlights behind you.
Flip the tab on the bottom edge of
the mirror to select the day or night
position.
Adjusting the Power Mirrors
SELECTOR SWITCH
Adjust the outside mirrors with the
adjustment button on the driver's
door armrest:
1. Turn the ignition switch ON (II).
2. Move the selector switch to L
(driver's side) or R (passenger's
side).
ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
3. Move the mirror right, left, up or
down by pushing the adjustment
button in that direction.
Instruments and Controls
TAB
Page 70

Mirrors
4. When you finish, move the
selector switch to the center (off)
position. This turns off the
adjustment button so you can't
move a mirror out of position by
accidentally bumping the button.
Outside mirror positions can be
stored in the driving position
memory system (see page 74).
On U.S. 3.5 RL with Premium Package
and Canadian 3.5 RL
The outside mirrors are heated to re-
move fog and frost. With the ignition
ON (II), turn on the heaters by
pressing the button. The light in the
button comes on as a reminder.
Press the button again to turn the
heaters off.
Instruments and Controls
HEATED MIRROR BUTTON
Page 71

Driving Position Memory System
Your Acura has a memory feature
for the steering wheel, driver's seat
and outside mirror positions.
Two seat, steering wheel, and
outside mirror positions, for
different drivers or driving
conditions, can be stored in separate
memories. You select a memorized
position by pushing the appropriate
button.
Storing a Driving Position in Memory
Store a driving position as explained
in this section only when the car is
parked.
1. Turn the ignition switch ON (II).
You cannot add a new driving
position in the memory unless the
ignition switch is ON (II). You can
recall a memorized position with
the ignition switch in any position.
2. Adjust the seat to a comfortable
position (see page 67 ). Adjust the
steering wheel to a comfortable
position (see page 51).
Adjust the outside mirrors for best
visibility (see page 72).
3. Press and release the MEMO
button on the control panel. You
will hear a beep. Immediately
press and hold one of the memory
buttons (1 or 2) until you hear two
beeps. The indicator light in the
memory button will come on. The
current positions of the driver's
seat, steering wheel, and outside
mirrors are now stored.
Instruments and Controls
MEMO BUTTON
Page 72

Driving Position Memory System
Doing any of the following after
pressing the MEMO button will
cancel the storing procedure.
Not pressing a memory button
within 5 seconds.
Readjusting the seat or steering
position.
Readjusting the outside mirror
position.
Each memory button stores only one
driving position. Storing a new
position erases the previous setting
stored in that button's memory. If
you want to add a new position while
retaining the current one, use the
other memory button.
All stored driving positions will be
lost if your car's battery goes dead or
is disconnected.
Selecting a Memorized Position
You can select memorized positions
as follows.
1. Make sure the parking brake is set
and the shift lever is in Park.
2. Insert the key in the ignition
switch. If you do not insert the key
in the ignition switch, the steering
wheel will not adjust to the
memorized position until you do.
3. Press the desired memory button
(1 or 2) until you hear a beep, then
release the button.
The system will move the seat,
steering wheel and outside mirrors
to the memorized positions. The
indicator light in the selected
memory button will flash during
movement. When the adjustments
are complete, you will hear two
beeps and the indicator light will
remain on.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
MEMORY BUTTONS
Page 73

Driving Position Memory System, Seat Heaters
To stop the system's automatic ad-
justment;
Press any button on the control
panel: MEMO, 1 or 2.
Push any of the adjustment
switches for the seat or steering
wheel.
Shift out of Park.
Adjust the outside mirrors.
If you select a memorized position
without inserting the key in the
ignition switch, only the seat and
outside mirrors will adjust. To get
the system to also adjust the steering
wheel, insert the key in the ignition
switch. You will hear two beeps
when it is complete.
If desired, you can use the adjust-
ment switches to change the posi-
tions of the seat, steering wheel or
outside mirrors after they are in
their memorized position. To keep
this driving position for later use,
you must store it in the driving posi-
tion memory.
Seat Heaters
3.5 RL with Premium Package in the U.S.
and 3.5 RL in Canada
Both front seats are equipped with
seat heaters. The ignition must be
ON (II) to use them. Push the front
of the switch to turn the power on at
a high temperature setting, and the
rear to set the heater at a low
temperature. The HI or LO lamp
lights and remains on while the
heater is on.
Instruments and Controls
SEAT HEATERS
Page 74

Seat Heaters, Ski Sleeve
To turn the power off, push the
opposite side of the switch lightly.
The lamp will go out.
Follow these precautions whenever
you use the seat heaters:
Use the HI setting only to heat the
seats quickly. Select the LO
setting when the seats feel warm.
The HI setting draws large
amounts of current from the
battery.
Do not use the seat heaters, even
at a low setting, if the engine is left
idling for an extended period.
They can weaken the battery,
causing hard starting.
Ski Sleeve
3.5 RL with Premium Package in the U.S.
and 3.5 RL in Canada
The ski sleeve allows you to carry
skis or other long objects safely
without soiling or damaging the
interior of your car. It attaches to the
trunk pass-through.
To use the ski sleeve:
1. Pull down the rear seat armrest.
Open the trunk pass-through
cover by sliding the knob down-
ward and pulling on the cover.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
LID
KNOB
Page 75

Ski Sleeve
2. Open the trunk. Remove the ski
sleeve from its storage bag.
3. Attach the ski sleeve to the trunk
pass-through.
4. Load the skis into the ski sleeve
from the trunk. Make sure the tip
of the ski sleeve is resting on the
center console.
5. Use the strap on the ski sleeve to
secure it tightly to the rear seat
armrest.
Follow these precautions when you
use the ski sleeve:
Do not transport skis that are
longer or heavier than these limits:
Maximum length: 84 in (215 cm)
Maximum weight: 55 Ibs (25 kg)
After use, make sure the ski
sleeve is dry both inside and out
before folding it up for storage.
This will help to prevent mildew.
Instruments and Controls
Page 76

Power Windows
Your car's windows are electrically-
powered. Turn the ignition switch to
ON (II) to raise or lower any window.
Each door has a switch that controls
its window. To open the window,
push the switch down and hold it.
Release the switch when you want
the window to stop. Close the
window by pulling back on the
switch and holding it.
DRIVER'S WINDOW SWITCH
MAIN SWITCH
The driver's door armrest has a
master power window control panel.
To open any of the passengers' win-
dows, push down on the appropriate
switch and hold it down until the
window reaches the desired position.
To close the window, pull back on
the window switch. Release the
switch when the window gets to the
position you want.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
Closing a power window on a
child's hands or fingers can
cause serious injury.
Make sure your children are
away from the windows before
dosing them.
Page 77

Power Windows, Moonroof
The master control panel also con-
tains these extra features:
AUTO — To open the driver's
window fully, push the window
switch firmly down and release it.
The window automatically goes all
the way down. To stop the window
from going all the way down, pull
back on the window switch briefly.
To open the driver's window only
partially, push the window switch
down lightly and hold it. The window
will stop as soon as you release the
switch.
The AUTO function only works to
lower the driver's window. To raise
the window, you must pull back on
the window switch and hold it until
the window reaches the desired
position.
The MAIN switch controls power to
the passengers'windows. With this
switch off, the passengers'windows
cannot be raised or lowered. The
MAIN switch does not affect the driv-
er's window. Keep the MAIN switch
off when you have children in the car
so they do not injure themselves by
operating the windows unintentional-
ly. The lights inside the switches
come on when you turn the parking
lights or headlights on.
The power window system has a key-
off delay function. The windows will
still operate for up to ten minutes
after you turn off the ignition.
Opening either front door cancels
the delay function. You must turn
the ignition ON (II) again before you
can raise or lower the windows.
OPEN/CLOSE
SWITCH
There are two switches on the
ceiling near the front ceiling light.
The ignition switch must be ON (II).
To open the moonroof, pull the
OPEN/CLOSE switch backward and
hold it until the moonroof reaches
the desired position.
Instruments and Controls
Moonroof
Page 78

Moonroof
To close the moonroof, push the
OPEN/CLOSE switch forward and
hold it. The moonroof will not close
completely; it will stop about 5.1
inches (130 mm) away fro m being
closed. Make sure you r passengers
are clear of th e moonroof, then
release th e switch an d push it
forward again t o close th e moonroof
completely.
The moonroof ha s an AUT O
function. T o open the moonroof fully,
pull the OPEN/CLOSE switch
backward firmly until it clicks, then
release it. Th e moonroof opens
automatically all th e way. To stop th e
moonroof from opening al l th e way,
push th e switch forward briefly. T o
open th e moonroof partially, pull th e
OPEN/CLOSE switch backward
lightly and hold it until th e moonroof
reaches th e desired position. Th e
AUTO function only work s to open
the moonroof.
TILT-UP SWITCH
When you push and hold the TILT-
UP switch, the rear of th e moonroof
will tilt up. T o close it, push th e
OPEN/CLOSE switch forward. If
you pull the switch backward and
hold it, the moonroof wil l tilt down
an d then open. Th e AUT O function
cannot work with the moonroof in
the tilt up position.
If you try to open the moonroof in
below-freezing temperatures, or when
it is covered with snow or ice, you can
damage the moonroof panel or motor.
Instruments an d Controls
NOTICE
Page 79

Parking Brake, Digital Clock
RELEASE LEVER
To apply the parking brake, depress
the pedal fully. To release it, pull the
release lever. The parking brake
light on the instrument panel should
go out when the parking brake is
fully released (see page 34 ). If you
try to drive the car without releasing
the parking brake, the ABS indicator
may come on, and the ABS may not
work properly.
Driving the car with the parking brake
applied can damage the rear brakes
and axles.
Digital Clock
The digital clock displays the time
with the ignition switch ON (II). To
see the time with the ignition off,
press and hold the wide button to the
right of the clock.
Instruments and Controls
NOTICE
PARKING
BRAKE PEDAL
Parking Brake
Page 80

Digital Clock, Sunglasses Holder
HOUR
MIN.
RESET
To set the clock:
1. Turn the ignition switch ON (II) to
display the time.
2. Swing down the front cover of the
wide button to the right of the
clock display. You will see HOUR,
MIN., and RESET buttons.
3. Press and hold the HOUR button
until the hour advances to the
desired time.
4. Press and hold the MIN. button
until the numbers advance to the
desired time.
You can use the RESET button to
quickly set the time to the nearest
hour. If the displayed time is before
the half hour, pressing RESET sets
the clock back to the previous hour.
If the displayed time is after the half
hour, pressing RESET sets the clock
forward to the beginning of the next
hour.
For example:
1:06 would RESET to 1:00.
1:52 would RESET to 2:00.
To open the sunglasses holder, push
on the front edge. It will unlatch and
swing down. To close it, push it until
it latches. Make sure the holder is
closed while you are driving.
CONTINUED
Instruments and Controls
SUNGLASSES HOLDER
Push
Sunglasses Holder
Page 81

Sunglasses Holder, Beverage Holder
Some larger styles of sunglasses
may not fit in the holder.
You may also store small items in
this holder. Make sure they are
small enough to let the holder close
and latch, and that they are not
heavy enough to cause the holder to
pop open while driving.
Beverage Holder
To use the front beverage holder,
push on the lid. The beverage holder
lid is spring-loaded and will swing
open. To close it, push it down until it
latches.
The inner liner can be removed if
you want to hold a larger cup or to
put small items in the beverage
holder.
Use the beverage holder only when
the car is parked. If you place cups in
the holder while driving, the liquid
may spill when you go over bumps or
around corners.
Instruments and Controls
Push
Page 82

Beverage Holder
Be careful when you are using the
beverage holder. A spilled liquid that
is very hot can scald you or your
passengers. Spilled liquids can also
damage the upholstery, carpeting,
and electrical components in the
interior.
The rear seat also has a beverage
holder in the armrest. To use it, pivot
the armrest down.
Instruments and Controls
Page 83

Console Compartment, Coin Box
Console Compartment
LEVER
CONSOLE COMPARTMENT
To open the console compartment,
press the left lever and lift the lid.
To close, lower the lid and push it
down until it latches.
You can put small items in the tray
located in the console compartment
lid. To use the tray, press the right
lever and lift up the armrest pad.
Coin Box
The coin box is located under the air
vent. To open the coin box, push on
the front. To close it, push it in until
it clicks.
Instruments and Controls
LEVER
COIN BOX
Page 84

Vanity Mirror, Cigarette Lighter
Vanity Mirror
To use a vanity mirror on the back of
the sun visor, pull up the cover.
The light beside the mirror comes
on only when the light switch is
turned on.
On cars with automatic lighting
With the light switch in the AUTO
position, the light beside the mirror
will come on when the headlights
turn on automatically.
Cigarette Lighter
The cigarette lighter is next to the
front ashtray under the ashtray lid.
Open the lid by pushing on it.
The ignition switch must be in
ACCESSORY (I) or ON (II) for the
cigarette lighter to work. To heat up
the lighter, push it in. It will pop out
when it is ready for use. Do not hold
the lighter in while it is heating up,
you could cause it to overheat.
Instruments and Controls
Push
CIGARETTE LIGHTER
Page 85

Ashtrays
INNER TRAY
Open the front ashtray by pushing
on the lid. To close the ashtray, push
it in until it clicks shut. To remove it
for emptying, grasp the tab on the
left side of the inner tray and lift it up
and
out.
The rear ashtrays are in the front
lower corner of each door. Open the
ashtray by swinging the upper edge
of the lid down. To remove the
ashtray for emptying, open it, then
lift up and out.
Use the ashtray only for cigarettes,
cigars, and other smoking materials.
To prevent a possible fire and damage
to your car, don't put paper or other
things that can burn in the ashtray.
Instruments and Controls
NOTICE
TAB
ASHTRAY
Page 86

Ceiling Lights
Both front and rear ceiling lights
contain a main light as well as two
spotlights.
The front ceiling light has a three-
position switch. With the switch in
the OFF position (far left), the main
lights do not come on. In the center
position, the main lights come on
when you open any door. After all
doors are closed tightly, they dim
slightly then fade out in about 10
seconds. In the ON position (far
FRONT
right), the main lights stay on
continuously.
Turn on the spotlights in the front
and rear ceiling lights by pushing the
grey button next to each light. Push
the button again to turn it off. You
can use the front spotlights at all
times. The rear spotlights only light
when the parking lights or head-
lights are on.
REAR
On cars with automatic lighting
With the light switch in the AUTO
position, you can use the rear
spotlights only when the headlights
turn on automatically.
Instruments and Controls
Page 87

Courtesy Lights
In addition to the ceiling lights, your
Acura has courtesy lights in each
door and the ignition switch.
The door courtesy lights come on
whenever you open any door. After
all doors are closed tightly, they dim
slightly then fade out in about 10
seconds.
Even if the door is open, the lights
will turn off after three minutes
when the key is not in the ignition
switch or the ignition switch is in the
LOCK (0) or ACCESSORY (I)
position, and the light switch is in the
off position.
The door courtesy lights and ceiling
lights (with the switch in the center
position) come on when you unlock
the door with the key, lock tab on
the driver's door, master door lock
switch, or remote transmitter (see
page 61). If you relock the driver's
door or close the driver's door with
the key in the ignition switch, the
lights turn off immediately.
Otherwise, they remain on, then fade
out in about 10 seconds.
The door courtesy lights and ceiling
lights (with the switch in the center
position) also come on when you
remove the key from the ignition
switch. If you do not open a door,
they stay on, then fade out in about
10 seconds.
The courtesy light in the ignition
switch comes on when you open the
driver's door. It remains on about 10
seconds after the door is closed.
Instruments and Controls
Page 88

Climate Control System
The automatic climate control
system in your Acura picks the
proper combination of air condi-
tioning, heating, and ventilation to
maintain the interior temperature
you select. The system also adjusts
the fan speed and air flow levels.
The direction of air flow from the
vents in the center and each side of
the dashboard is adjustable. Move
the tab in the center of each vent up-
and-down and side-to-side.
The side vents can be opened and
closed with the dials next to them.
In the rear seat, you can also adjust
the ventilation when the climate con-
trol system is on (see page 99 ).
CENTER VENTS
The climate control system draws air
through the exterior vents at the
bottom of the windshield. Keep
these vents clear of leaves and other
debris.
SIDE VENTS
For the climate control system to
provide heating and cooling, the
engine must be running.
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 89

Climate Control System
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 90

Climate Control System
Fully-automatic Operation
To put the Automatic Climate
Control in fully-automatic mode,
press the AUTO button and set the
fan control dial to AUTO, then set
the desired temperature by turning
the temperature control dial. You will
see FULL AUTO in the system's
display. The light in either the
or button also goes
on to show you which is selected.
The system automatically selects the
proper mix of conditioned and/or
heated air that will, as quickly as
possible, raise or lower the interior
temperature from its current level to
the set temperature.
When you set the temperature to its
lower limit (60°F/18°C) or its upper
limit (90°F/32°C), the system runs
at full cooling or heating only. It does
not regulate the interior temperature.
When the temperature is set
between the lower and upper limits,
the system regulates the interior
temperature to the set value.
In cold weather, the fan will not
come on automatically until the
engine has run for a short time and
the heater starts to develop warm air.
Pressing the OFF button shuts the
climate control system completely
off. Keep the system completely off
only for short periods. To keep stale
air and mustiness from collecting,
you should have the fan running at
all times.
Comfort and Convenience Features
AUTO
BUTTON
TEMPERATURE
CONTROL DIAL
FULL AUTO
DISPLAY
OFF
BUTTON
FAN CONTROL
DIAL
Page 91

Climate Control System
Semi-automatic Operation
You can manually select various
functions of the Climate Control
system when it is in FULL AUTO.
All other features remain auto-
matically controlled. Making any
manual selection causes the word
FULL to go out.
Air Conditioning (A/C) Button
Press the A/C button to operate the
air conditioning. Each time you press
the A/C button, the display shows
the mode: A/C ECON, A/C OFF, or
A/C ON.
When you turn the A/C off, the sys-
tem cannot regulate the inside tem-
perature if you set the dial below the
outside temperature. With the A/C
on, use the temperature control dial
to adjust the temperature of the air
flow to a comfortable setting.
With the A/C in economy mode, you
will see A/C ECON in the system's
display. Use this mode to get better
fuel economy.
In this mode, you may feel a slight re-
duction in cooling efficiency. If you
want more cooling, select A/C ON or
FULL AUTO.
CONTINUED
Comfort and Convenience Features
RECIRCULATED AIR FRESH AIR
TEMPERATURE
CONTROL DIAL
AIR CONDITIONING
BUTTON
Page 92

Climate Control System
These two buttons control the
source of the air going into the sys-
tem. In Fresh Air mode
air is brought in from outside the ve-
hicle. In Recirculation mode
air from the vehicle's inte-
rior is sent through the system again.
You can, for example, manually put
the system in recirculation mode
when driving through an area of
smoke or fumes. When you press
the or button, the
light in that button comes on.
You can manually select the fan
speed by turning the fa n control dial.
When you turn the dial to the right,
the fan is taken out of automatic
mode and starts to ran at it s lowest
speed. Turning th e dial t o the fa r
right increases the fan's speed,
which increases air flow.
Mode Button
Use the MODE button to select the
vents the air flows from. Each time
you press the MODE button, the
display shows the mode selected.
Press the button four times to see all
the modes.
Some air will come out of the side
vents in all modes.
Comfort and Convenience Features
FRESH AIR
RECIRCULATED AIR
MODE BUTTON
FAN CONTROL DIAL
Recirculated and Fresh Air
Fan Control Dial
Page 93

The main air flow is divided
between the floor vents and de-
froster vents at the base of the wind-
shield.
The main air flow comes
from the floor vents.
The main air flow is divided
between the dashboard vents and
the floor vents.
The main air flow comes
from the dashboard vents.
CONTINUED
Climate Control System
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 94

Climate Control System
The button directs the main
air flow to the windshield for faster
defrosting. It also overrides any
MODE selection you may have made.
When you select the A/C
turns on automatically and the
system selects fresh air mode. For
faster defrosting, manually set the
fan speed to high. You can also
increase air flow to the windshield by
closing the side vents in the
dashboard.
When you turn off by
pressing the button again, the
system returns to its former settings.
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 95

Climate Control System
Rear Ventilation
The air flow from the rear vents can
be adjusted when the climate control
system is on.
You can adjust the direction of the
air coming from the upper vents in
the center console by moving the tab
in the center of each vent up-and-
down and side-to-side.
You can also adjust the amount of
the air flow by sliding the air flow
control lever under the upper vents.
Slide this lever upward to increase
the amount of air flow.
(Upper position): Maximum
(Center position): Moderate
(Lower position): Off
Mode Control Lever
Use the mode control lever to select
the air flow level. Air flows into the
rear seat at three levels.
(Upper position):
Air flows from the upper vents in the
back of the center console.
(Center position):
Air flow is divided between the upper
vents and the lower vents in the back
of the center console.
(Lower position):
Air flows from the lower vents.
Comfort and Convenience Features
AIR FLOW
CONTROL
LEVER
UPPER
VENTS
MODE
CONTROL
LEVER
LOWER
VENTS
Page 96

Climate Control System
Sunlight Sensor/Temperature
Sensor
The climate control system has two
sensors. A sunlight sensor Is located
in the top of the dashboard and a
temperature sensor is next to the
steering column. Do not cover the
sensors or spill any liquid on them.
Comfort and Convenience Features
SUNLIGHT SENSOR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Page 97

Audio System
AM/FM/Cassette Stereo Audio
System
Your Acura's audio system provides
clear reception on both AM and FM
bands, while the preset buttons allow
you to easily select your favorite
stations.
The cassette system features Dolby
B* noise reduction, automatic
sensing of chromium-dioxide (CrO2)
tape, and autoreverse for continuous
play.
* Dolby noise reduction manufactured under
license from Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corpo-
ration. "DOLBY" and the double-D symbol
are trademarks of Dolby Laboratories
Licensing Corporation.
The Anti-theft feature will disable
the system if it is disconnected from
the car's battery. To get the system
working again, you must enter a
code number (see page 119).
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 98

Audio System
Operating the Radio
The ignition switch must be in
ACCESSORY (I) or ON (II) to
operate the audio system. Turn the
system on by pushing the PWR/
VOL knob or the AM/FM button.
Adjust the volume by turning the
knob.
The band and frequency that the ra-
dio was last tuned to is displayed. To
change bands, press the AM/FM but-
ton. On the FM band, ST will be dis-
played if the station is broadcasting
in stereo. ST will flash if you are driv-
ing in an area where the radio signal
is weak. Stereo reproduction on AM
is not available.
You can use any of three methods to
find radio stations on the selected
band: TUNE, SEEK, or the Preset
buttons.
TUNE — Use the TUNE knob to
tune the radio to a desired frequency.
Turn the TUNE knob to the right to
tune to a higher frequency, or to the
left to tune to a lower frequency.
Turn the knob right or left until the
display reaches the desired frequen-
cy.
SEEK — The SEEK function
searches the band for a station with
a strong signal. To activate it, push ei-
ther of the SEEK/SKIP buttons ( —
or + ). Push the + button to scan up
from the current frequency, and the
— button to scan down. It stops
when it finds a station with a strong
signal.
Preset — You can store the fre-
quencies of your favorite radio
stations in the six preset buttons.
Each button will store one frequency
on the AM band, and two on the FM
band.
Comfort and Convenience Features
Page 99

Audio System
To store a frequency:
1. Select the desired band, AM or
FM. FM1 and FM2 let you store
two frequencies with each Preset
button.
2. Use the TUNE or SEEK function
to tune the radio to a desired
station.
3. Pick the Preset button you want
for that station. Press the button
and hold it until you hear a beep.
4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 to store a total
of six stations on AM and twelve
on FM.
Once a station's frequency is stored,
simply press and release the proper
Preset button to tune to it.
The preset frequencies will be lost if
your vehicle's battery goes dead, is
disconnected or the radio fuse is
removed.
CONTINUED
Comfort and Convenience Features
PWR/VOL
KNOB
AM/FM
BUTTON
STEREO
INDICATOR
TUNE
KNOB
PRESET BUTTONS
SEEK/SKIP
BUTTONS
Page 100

Audio System
AUTO SELECT — If you are
traveling far from home and can no
longer receive the stations you
preset, you can use the Auto Select
feature to find stations in the local
area.
To activate Auto Select, press the
A. SELECT button. A. SELECT win
appear in the display, and the system
will go into scan mode for several
seconds. It automatically scans both
bands, looking for stations with
strong signals. It stores the frequen-
cies of six AM stations and twelve
FM stations in the preset buttons.
You can then use the preset buttons
to select those stations.
If you are in a remote area, Auto
Select may not find six strong AM
stations or twelve strong FM stations.
If this happens, you will see a "0"
displayed when you press any preset
button that does not have a station
stored.
With Auto Select on, you cannot
manually store any frequencies in
the preset buttons. If you do not like
the stations found by Auto Select,
you can use the TUNE and SEEK
functions to find other stations.
Auto Select does not erase the
frequencies that you preset pre-
viously. When you return home, turn
off Auto Select by pressing the
A. SELECT button. The preset
buttons will then select the fre-
quencies you originally set.
Comfort and Convenience Features
AM/FM BUTTON
AUTO SELECT INDICATOR
AUTO SELECT BUTTON
PRESET BUTTONS
SEEK/SKIP
BUTTONS
TUNE
KNOB
 Loading...
Loading...