Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
Do This First ................................................................................................................. 3
For Windows 3.1X Installation.............................................................................. 3
For Windows 95/98 Installation ............................................................................ 4
For Windows NT 4.0 Installation .......................................................................... 6
Installing the Modem ................................................................................................... 7
Jumper Settings ...................................................................................................... 7
Hardware Installation............................................................................................ 8
Connecting Devices to the Modem ........................................................................ 10
Configuring Windows 95...................................................................................... 10
Configuring Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2 ............................................. 11
Configuring Windows 98...................................................................................... 11
Configuring Windows NT 4.00 ............................................................................ 12
Installing and Configuring Communications Software .......................................... 14
Using the Modems Voice Features ....................................................................... 14
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 15
Appendix A - AT Commands and S-Registers ............................................................ 20
AT Commands ........................................................................................................ 21
S Registers .............................................................................................................. 28
Appendix B - Communications Regulations .............................................................. 31
Proprietary Notice and Disclaimer
Unless otherwise noted, this document and the information herein disclosed are proprietary to ActionTec Electronics, Inc. Any person or entity to whom this document is furnished or who otherwise has possession thereof, by acceptance agrees that it will not be
copied or reproduced in whole or in part, nor used in any manner except to meet the
purposes for which it was delivered.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be
construed as a commitment by ActionTec. Although ActionTec will make every effort to
inform users of substantive errors, ActionTec disclaims all liability for any loss or damage
resulting from the use of this document or any hardware or software described herein,
including without limitation contingent, special or incidental liability.
Note: PC is a trademark of IBM Corporation. Windows 3.1, Windows 95, and Windows NT are trademarks of
Microsoft, Inc. K56flex is a trademark of Lucent Technologies, Inc. and Rockwell International.
2
Page 3

Do This First
Please read the following tips carefully before attempting to
install your new modem.
For WINDOWS 3.1 INSTALLATION
Because Windows 3.1 and 3.11 are not Plug-N-Play operating systems, it is
suggested that you do not rely on the Plug-N-Play capabilities of your computer to automatically configure the modem. Instead, manually select the COM
Port and IRQ setting by changing the jumpers. The jumper setting definitions
can be found in the Installing The Modem section under the heading Jumper
Settings. It is recommended that you disable an existing COM Port that you
are not using, like COM 2, and set the modems jumpers for COM 2 -IRQ 3.
This will avoid many of the pitfalls associated with installing a modem in
Windows 3.1X. If you cannot disable an existing COM Port, then you must
use COM Ports 3 or 4 and select an interrupt that does not cause a conflict
with another device. If you do not know the available interrupts on your system, you will have to use trial-and-error to get the modem properly configured.
To disable one of your computers existing COM Ports, you need to enter
your System BIOS Setup routine (read your Computers User Manual for
instructions on how to invoke the BIOS Setup). [If you have a seperate I/O
card, use the cards jumbers to disable a COM Port]. Once inside the BIOS
Setup, look for a section called Integrated Peripherals. Locate the entry for
COM 2 or COM Port B and disable it. Save your settings before exiting.
Install your modem into the computer and start Windows 3.1 or 3.11.
Since you have manually selected the COM Port and IRQ settings of the
modem using the jumpers, you will have to manually assign the IRQ and
COM Port address in Windows 3.1X to the same settings as the modem. In
Windows 3.1X Program Manager, double-click on Main and then on Con-
trol Panel. Double-click on Ports. Select the COM Port your modem is us-
ing by clicking once on the icon for that port. Click on Settings and then on
Advanced. The COM Port is represented as an I/O address in hexadecimal
format. Select 3F8 for COM 1, 2F8 for COM 2, 3E8 for COM 3, or 2E8 for
COM 4 depending on which COM Port you selected your modem for. The
IRQ setting will be selected by setting the IRQ box to the appropriate number. If you have set your modem to COM 2, then you would set the IRQ to 3.
If you had chosen COM 3, then you would have set the IRQ jumper on the
modem to an available IRQ setting, one that did not interfere with another
device. You will need to set the Windows IRQ setting to this same number.
After you have configured Windows 3.1X, close Windows and reboot your
system. Install your communications software.
3
Page 4
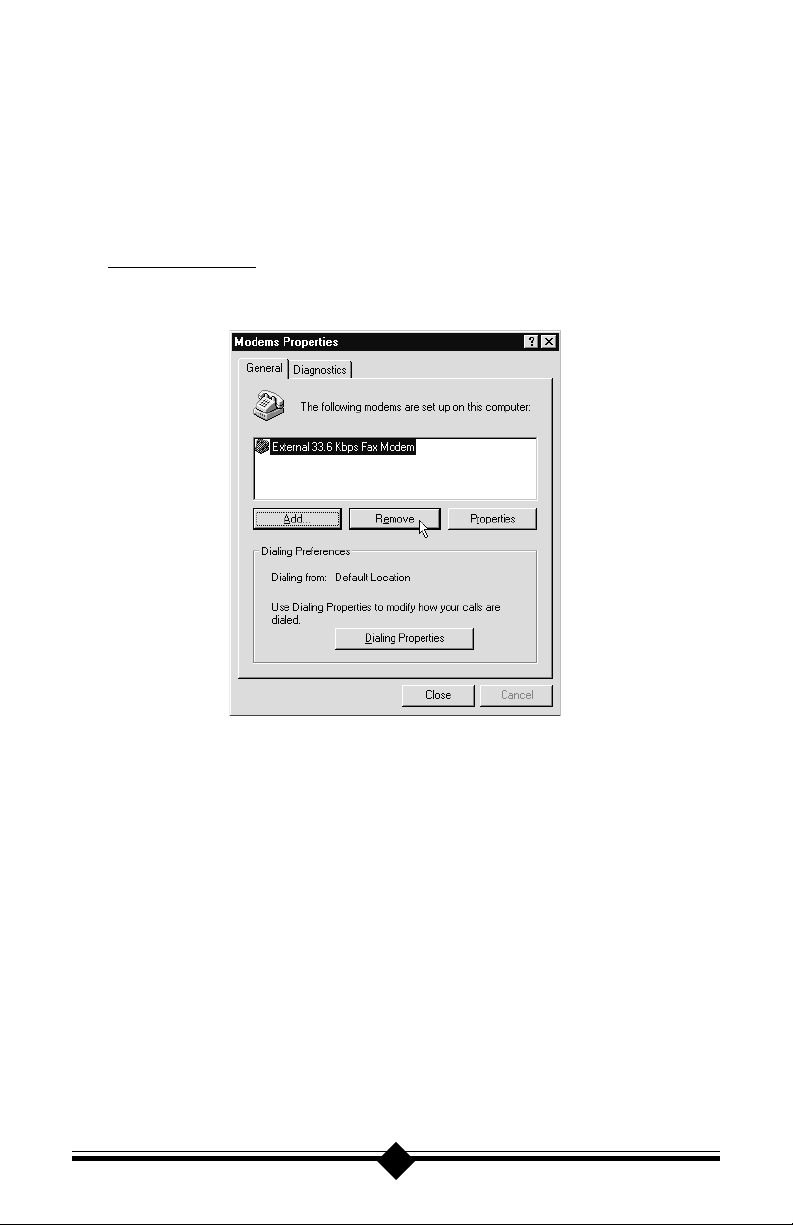
For WINDOWS 95/98 INSTALLATION
If you are replacing an existing modem in your computer system with this
modem, be sure to remove all other modem drivers. Go to: Start-Settings-
Control Panel and double-click on the System icon. Select the Device Manager tab. Double-click on the Modems icon in the device tree to show the
modems installed. Highlight each modem listed by clicking once on the icon
next to the modem and then click the Remove button. It is also a good idea to
physically remove your old modem from the system. Note: once you remove
the old modem and its drivers from your system, you will need the old modem
driver diskette if you wish to reinstall it at a later date.
Figure 1: Win95 Modems Properties Panel
If you are going to use the TAM (Telephone Answering Machine) or speaker-
phone functions of the modem, you need to install the Unimodem V components of Windows 95. If you have Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2 (Version 4.00.950 B or above) or Windows 98, you do not need to install this
component as it is already built into the operating system.
To find the Windows 95 Version on your system, select: Start-Settings-Control Panel. Double-click on the System icon and select the General tab. If
the version of Windows 95 is 4.00.950 or 4.00.950A, go to: Start-Programs
and select Windows Explorer. Go to the UNIMODEM directory of the CDROM (the UNIMODEM driver is sometimes supplied on a separate floppy)
that came with your modem and right-click on UNIMODV.INF (or
UNIMODV, whichever is displayed) then click on Install. Restart your computer to enable the drivers.
4
Page 5

(Note: If you are using the default Play-N-Play jumper settings and not manu-
ally configuring the COM Port and IRQ jumpers, the following step may be
skipped. Refer back to this area only if Plug-N-Play cannot successfully configure your modem.)
The modem will need one IRQ (interrupt) and one COM Port to function. To
check for any available interrupts in your system, go to Start-Settings-Con-
trol Panel. Double-click the System icon and select the Device Manager
tab. Click the Properties button to view the System Resources. There are 16
(0-15) interrupts available in a system. Make a note of any interrupt not listed.
If you do not have any free interrupts you may need to disable an existing
device that you are not currently using, such as COM2 on your motherboard.
This will free up I/O port 0x2F8 and IRQ 3.
To disable COM2, boot your system and enter your BIOS setup. You can
normally invoke the BIOS setup menu by pressing a key or a combination of
keys at the first boot up screen. Some of the common keys are Del, F1, F2,
Ctrl+Alt+S, Ctrl+Alt+Esc. If none of the mentioned key combinations work,
please refer to your computer system manual for instructions on how to invoke the BIOS setup. (note: if your system uses a serate I/O Card, use the
cards jumpers to disable a COM Port.)
Once inside the BIOS setup, find the menu for integrated peripherals, locate
the COM port settings, then disable COM2 or Comport B. If unsure, please
consult your computer users manual. Be sure to Save the settings before
exiting the BIOS Setup. The computer will then reboot. Set your modems
jumpers to COM 2 - IRQ 3 (See Jumper Settings in the Installing the Mo-
dem section for jumper setting diagrams.).
You will also need to disable the COM Port from the device manager. Go to
Start-Settings-Control Panel double-click on the System icon, select the
Device Manager tab. Double-click the Ports (COM & LPT) icon to expand
the Ports tree and highlight Communication Port (COM2). Now click on
the Properties button. Put a Check mark in Disable in this hardware profile
(Windows 95 OEM SR2 only) or uncheck Original Configuration (cur-
rent) (for Windows 95 or Windows 95a). Exit Windows 95 and restart your
system. (Note: If COM 3 and or COM 4 are present and you have nothing
installed on these ports, delete them first before deleting COM 2).
(Note: If you are not familiar with changing the settings within your system
BIOS setup, you should skip the following system preinstallation procedure
and go to the Installing the Modem section. Refer back to this area only if
you have a problem installing the modem.)
5
Page 6

Go to your system BIOS Setup routine and find the Plug-N-Play settings.
These settings can be found within the Advanced, PNP/PCI Configuration,
or Plug and Play Configuration sections depending on the BIOS Manufac-
turer. Next, verify that one free IRQ has been set so that the ISA bus has
access to it (some BIOS dont allow individual selection of interrupts to ISA,
Plug-N-Play, or PCI). These settings can be called ICU, ICU/PCI, or PNP
depending on your BIOS version and manufacturer. Do not set this interrupt
to PCI only. Pay attention to the IRQ usage of the other peripherals in your
system. Do not reassign an interrupt that is already in use by another device.
Since each BIOS manufacturer has a different way of handling these configurations, you may have to use trial-and-error to get your modem properly configured. Be sure to Save the settings before exiting the BIOS Setup.
You are now ready to install the modem. Proceed to the Installing the Mo-
dem section.
For WINDOWS NT 4.0 INSTALLATION
If you are replacing the current modem in your computer system with this
new modem, be sure to remove all other modem drivers from your operating
system. Go to: Start-Settings-Control Panel and double-click on the Mo-
dems icon. Highlight the modem you wish to remove and click the Remove
button. Shutdown the computer, power-down, and physically remove the old
modem from your system. Do not install your new modem at this time. Follow the procedures below to help insure a trouble-free installation. Note:
once you remove the old modem and its drivers from your system, you will
need the old modem driver diskette if you wish to reinstall it at a later date.
It is seriously recommended that you DO NOT use the Plug-N-Play capabili-
ties of the modem for a Windows NT installation. Instead, manually set the
modems jumpers to COM 2 - IRQ 3 (see Jumper Settings in the Installing
The Modem section). The use of a COM 2 - IRQ 3 setting will provide the
least amount of system reconfiguration and aggravation for the installer. This
setting will require that you disable your computers on-board COM2 Port.
To disable COM2, boot your system and enter your BIOS setup. You can
normally invoke the BIOS setup menu by pressing a key or a combination of
keys at the first boot up screen. Some of the common keys are Del, F1, F2,
Ctrl+Alt+S, Ctrl+Alt+Esc. If none of the mentioned key combinations work,
please refer to your computer system manual for instructions on how to invoke the BIOS setup.
Once inside the BIOS setup, find the menu for integrated peripherals, locate
the COM port settings, then disable COM2 or Comport B. If unsure, please
6
Page 7
consult your computers user manual. Be sure to Save the settings before
exiting the BIOS Setup. The computer will then reboot. Set your modems
jumpers to COM 2 - IRQ 3. (See Jumper Settings in the Installing the Mo-
dem section for jumper setting diagrams.)
You are now ready to install the modem. Proceed to the next section.
Installing The Modem
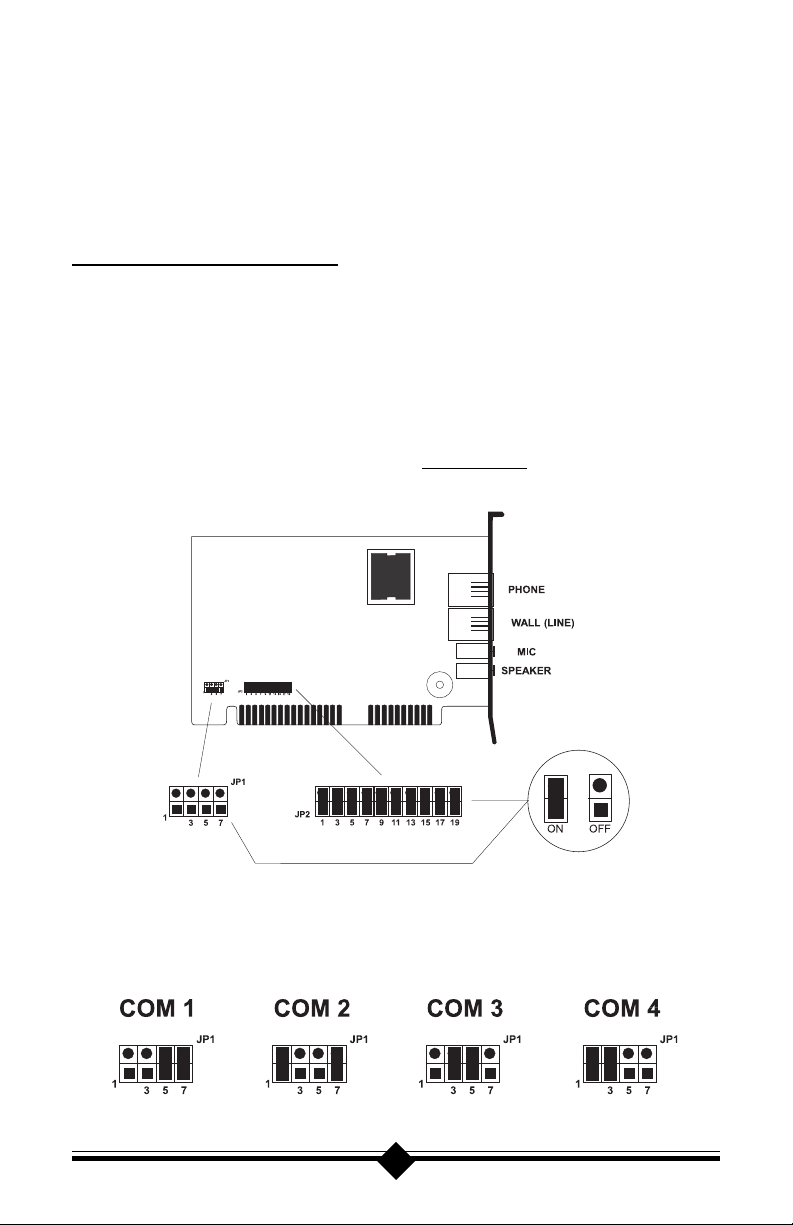
JUMPER SETTINGS
This modem has two sets of jumper blocks used for manual COM Port and IRQ
(interrupt) selection. These are made available for users of non Plug-N-Play operating systems where the default jumper setting cannot be used. It also makes possible manual installation in a system where the installer wishes to use a specific
COM Port and IRQ. Figure 2 shows the default jumper setting for JP1 and JP2 as
shipped from the factory. This setting is for Plug-N-Play and will auto-configure
in computers with operating systems that support this feature, like Windows 95
Figure 2: Jumpers Set To Plug-N-Play (default setting)
The Jumper Block JP1 is used to select the desired COM Port for the modem.
Figure 3: shows the selections for each COM Port.
Figure 3: JP1 COM Port Options
7
Page 8
Jumper Block JP2 is used to select the IRQ (interrupt request) settings for the
modem. Figure 4: below details the possible selections.
Figure 4: JP2 IRQ (interrupt request) Options
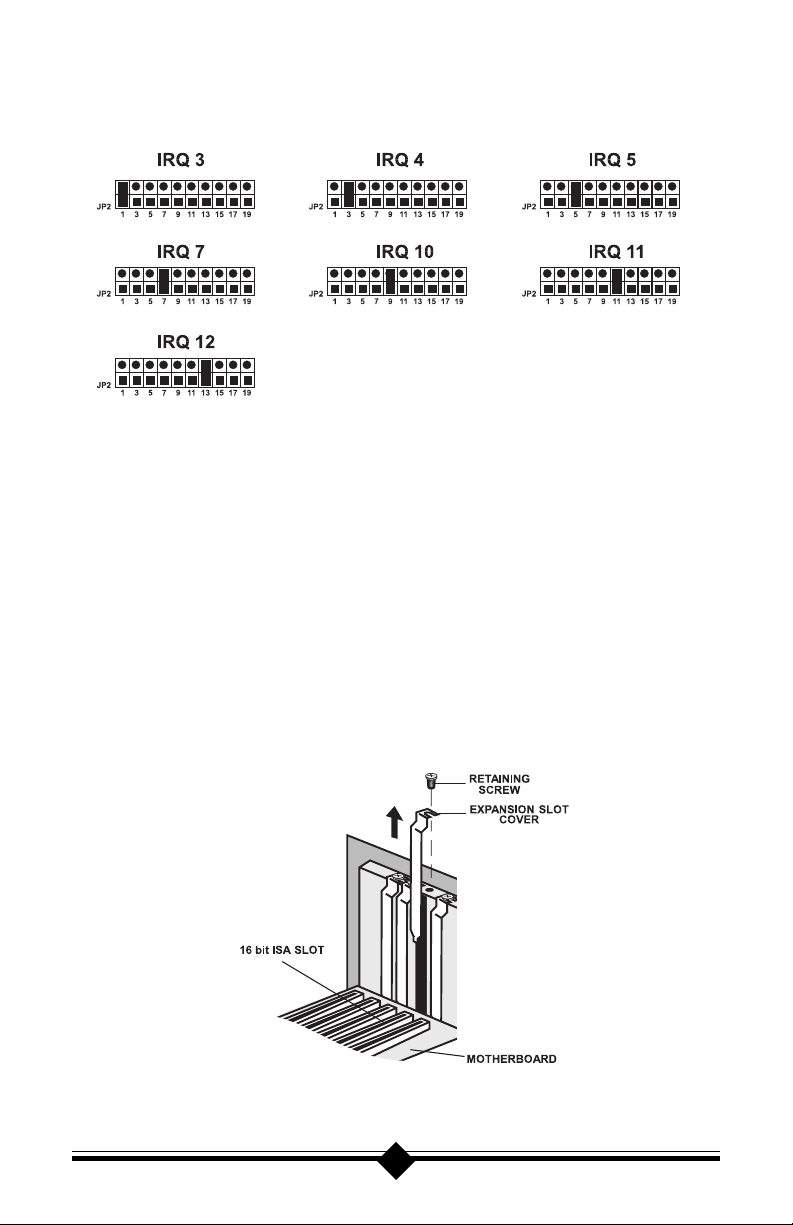
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
1. Turn off the computer and all peripheral devices connected to it.
2. Unplug the computer power cord from the wall receptacle.
3. Remove the computers cover. Refer to your computer owners manual for
instructions.
4. Remove the screw securing the expansion slot cover behind one of the
computers available 16-bit ISA expansion slots. Lift the expansion slot cover
out as shown below.
Figure 5: Removing the Backplate
8
Page 9
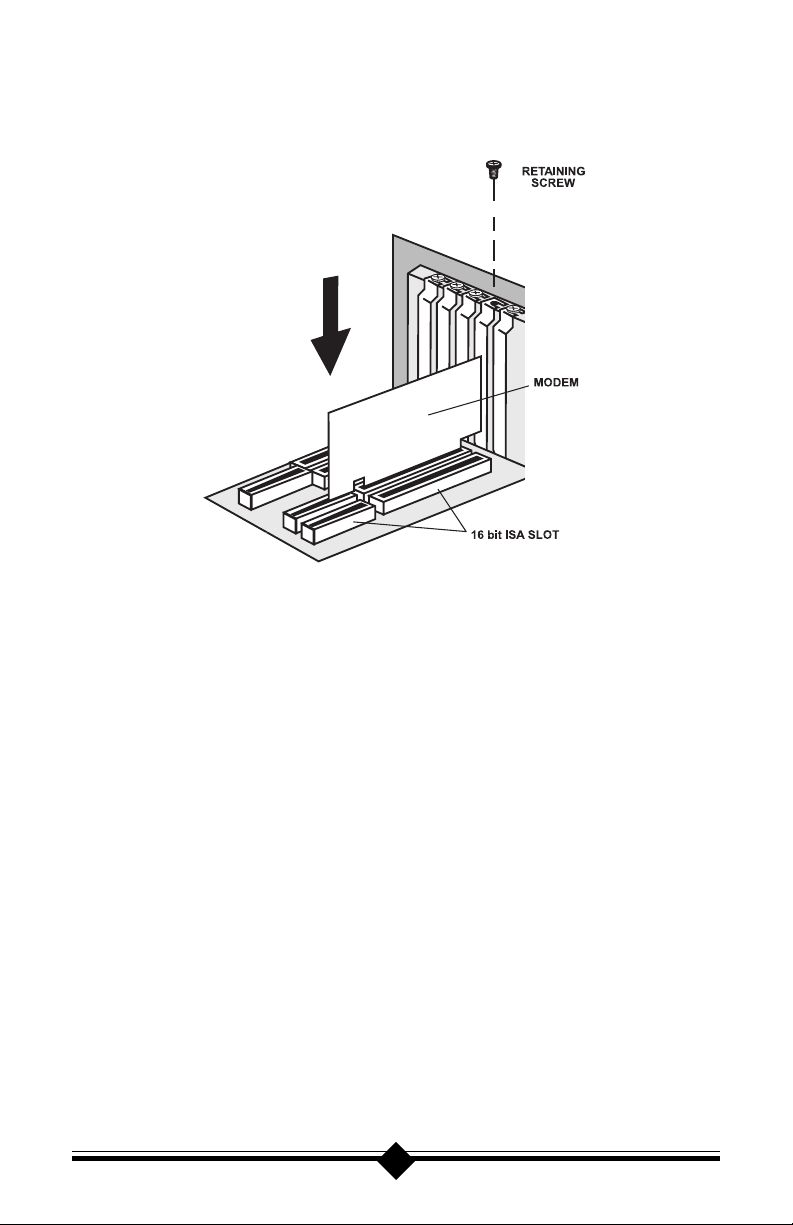
5. Firmly, but gently, insert the modem into the available 16-bit expansion slot.
Ensure that the card is seated properly before securing it with the screw removed in Step 4, as shown in the following diagram:
Fig. 6: Installing The Modem
6. Put the chassis cover back on the computer.
7. Be sure that all power switches are in the OFF position, then reconnect the
power cables to the computer and its peripherals.
8. Connect the telephone line cable to the Line (Telco) jack as shown in Fig.7.
9. Turn on the computer and proceed to the following sections to configure
your modem to the operating system you are using.
Caution. Always discharge static electricity before handling your modem.
You may discharge static electricity by touching a grounded metal structure
or by using any commercially available grounding strap.
Make sure the expansion slot type is 16-bit, which has two slots to fit the ISA
card. 8-bit slots have only one connector. If you use an 8-bit slot, the modem
will not have access to the higher interrupts (IRQ 9-15).
The position of the expansion slots in your computer may differ from the
illustrations shown but the installation procedure should be the same.
9
Page 10
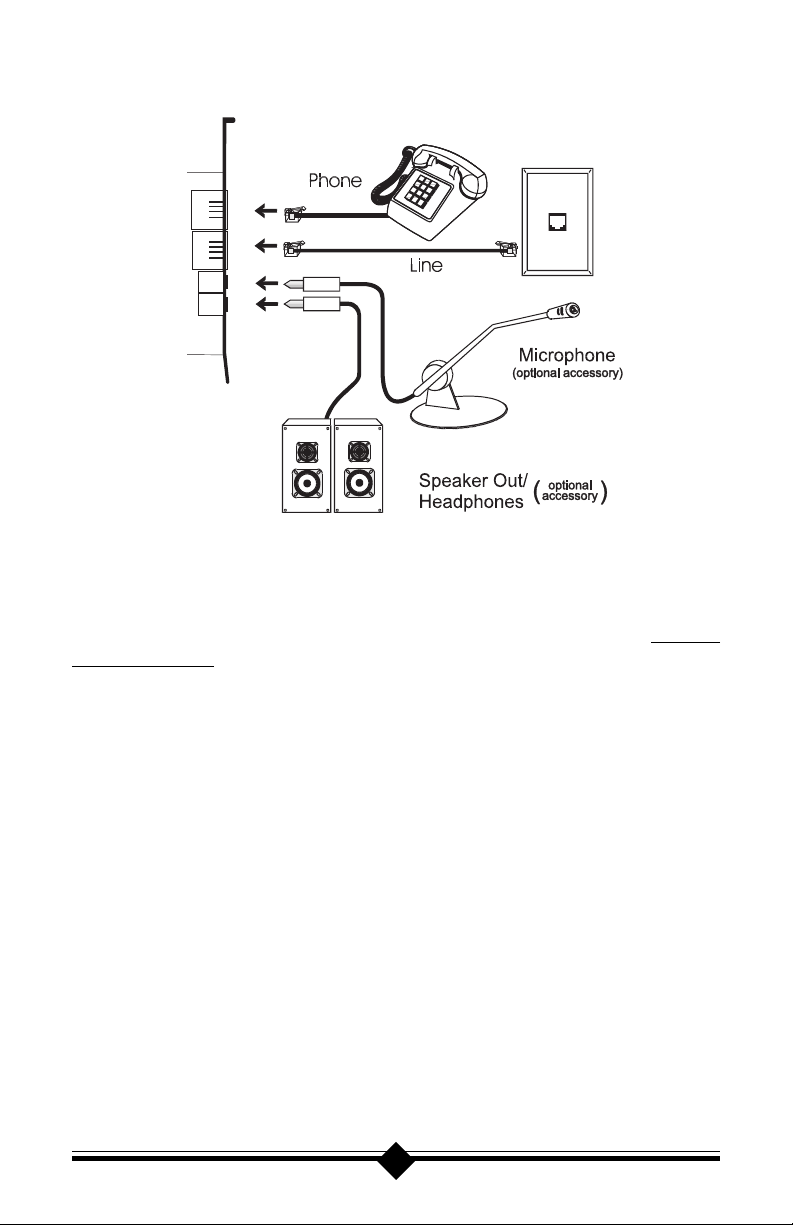
CONNECTING DEVICES TO THE MODEM
Fig.7: Connecting Devices
On the rear panel of your modem are input jacks to connect devices to the modem.
As shown in the diagram, there are jacks for connection to a phone and to a phone
line. The connector labeled Line (Telco) is meant to be connected to a standard
analog phone line. To help reduce the load on your phone line, it is recommended
that all other devices be disconnected from the phone line while the modem is in
use.
CONFIGURING WINDOWS 95
Step 1 Upon start-up, Windows 95 detects the modem and displays the New
Hardware Found dialog box. Select Driver from disk provided by hard-
ware manufacturer then Click OK.
Step 2 Insert the diskette (or CD-ROM) containing the modems Windows 95
.INF files and click OK
Step 3 If Windows asks for an installation disk, click OK and type A: (or CD-
ROM drive letter) in the dialog box that appears and click OK again.
Step 4 After the installer has copied the .INF files to the hard disk, a New Hard-
ware Found dialog box should appear prompting for the Wave Device
for Voice Modem. Click OK. (see the Do This First section for information on UNIMODEM.INF if this screen does not appear).
10
Page 11

Step 5 Click OK to copy the Wave Device .INF file from the A:\ drive to the
hard drive.
Step 6 To determine what COM port and IRQ is assigned to the modem in Win-
dows 95, click on the Modems icon in Control Panel and select the
Diagnostic tab. Click on the COM Port icon and then on the More Info
button to view the modem properties.
CONFIGURING WINDOWS 95 OEM SR2
Step 1 Upon start-up, Windows 95 detects the modem and launches the Update
Device Driver Wizard dialog box. Insert the diskette (or CD-ROM)
containing the modems .INF files and click Next >.
Step 2 After Windows 95 has found the updated drivers for your modem, click
Finish.
Step 3 If Windows asks for an installation disk, click OK and type A: (or the
CD-ROM drive letter) in the dialog box that appears and click OK.
Step 4 After the Wizard has copied the .INF files to the hard disk, it should
detect Wave Device for Voice Modem and prompt for its driver. Click
Next>.
Step 5 Click Finish to copy the Wave Device .INF file from the A:\ drive (or
CD-ROM) to the hard drive.
Step 6 To determine what COM port and IRQ is assigned to the modem in Win-
dows 95, click on the Modems icon in Control Panel and select the
Diagnostics tab. Select your modem and then click on the More Info
button to view the modem properties.
Step 7 Remember this COM port number. When you install your Data/Fax soft-
ware or internet browser program, you may need to set your softwares
modem port location to this same number.
CONFIGURING WINDOWS 98
Step 1 Turn on the computer and load Windows 98. Windows 98 will detect
new hardware and start building the driver database.
Step 2 An Add New Hardware Wizard should appear. Insert the installation
11
Page 12

diskette or CD-ROM into the appropriate drive. Click Next>.
Step 3 Windows will show a screen asking What do you want Windows to do?.
Select: search for the best driver for your device. Click Next>.
Step 4 A search screen will display options to do your search. Put a check on
Floppy disk drives and CD-ROM drive. Click Next>.
Step 5 Windows 98 will find the Fax/Modem driver on the floppy drive. If your
modem came with a CD-ROM, Windows 98 will find the driver on the
CD-ROM. Click Next>.
Step 6 At the next screen, click Finish.
Step 7 A new Add New Hardware Wizard should appear again prompting for
wave device for voice modem. Click Next>.
Step 8 Windows will show another What do you want Windows to do? screen.
Select: search for the best driver for your device. Click Next>.
Step 4 A search screen will display options to do your search. Check to see that
a check still appears on Floppy disk drives and CD-ROM drive. Click
Next>.
Step 5 Windows 98 will find the wave driver on the floppy drive. If you have
installation CD-ROM, Windows 98 will find the driver on the CD-ROM.
Click Next>.
Step 6 Windows 98 will finish the installation. Your modem is now ready to
use. Install or reconfigure your communications program or Internet
Browser for the new modem.
Note: If you have installed your modem in Windows 95 and are upgrading your
operating system to Windows 98, uninstall the modem and its drivers
before attempting the upgrade. After you have finished and verified that
your system is working properly, reinstall the modem into Windows 98
using the driver files provided in your modem package.
CONFIGURING WINDOWS NT 4.00
This installation assumes that you have manually set the modems jumpers to a
COM 2 - IRQ 3 setting as outlined in the Do This First section at the beginning of
the manual. COM 2, IRQ 3 is the preferred installation setting for Windows NT.
12
Page 13

Step 1 Reboot the computer and log in to Windows NT 4.00.
Step 2 Go to: Start-Settings-Control Panel and double-click on the Modems
icon. At the Modems Properties dialog box, click Add.
Step 3 An Install New Modem window should appear. Allow Windows NT to
detect your modem. Click on the Next> button.
Step 4 If a modem is found, Windows NT will query it. In most cases Windows
NT will detect the modem as a Standard Modem. Click on the Change
button.
Step 5 Insert the diskette (or CD-ROM) containing the modems .inf files and
click the Have Disk button. When prompted for the path, type A:\ (or the
CD-ROM Drive letter) and then click the OK button.
Step 6 When prompted to select the manufacturer and model of the modem,
click the OK button. At the next screen click the Next> button.
Step 7 Click on the Modems icon in the Control Panel. Verify that Windows
NT has correctly found the modem.
Step 8 If you wish to use your modem to dial into a Windows NT Remote Ac-
cess Server or wish to connect to the Internet, you will need to configure
Dial-up Networking. Go to: Start-Settings-Control Panel and doubleclick the Network icon. Click on the Services folder and select Remote
Access Service. If the Remote Access Service option is not listed (if
present, go to Step 9), click on the Add button. Scroll-down the menu
and select Remote Access Service. Click on the OK button. Windows
NT may ask for its own disks or CD-ROM for some files. Insert as required. After you have installed Remote Access Service add the appropriate protocols as directed (i.e.. TCP/IP for Internet Access).
Step 9 At the Remote Access Setup dialog box, click on Add. Select the
RAS Device you wish to add and Click OK.
Step 10 Click Continue to finish the Installation.
Step 11 After Windows NT has completed the binding process, allow Windows
NT to shut down and restart the computer.
13
Page 14

Installing and Configuring Communications Software
If your modem came with a communications software package, it is strongly recommended that you use this software for your modem. Its default installation
parameters have been specially configured to work with this modem. The Users
Guide for this program can be found inside the modem package. It can be supplied in either soft-bound copy or on CD-ROM (depending on the model you
purchased). Some configurations are packaged without communications software.
Check your packaging to see if communications software is included.
If you wish to use another software package, please be sure that it supports this
modem. Most Software Manufacturers have a listing of supported modems on
their websites or BBSs. Check these sites to see if this model is supported. If you
are unsure or your brand of software supports only a few modems, try selecting
Hayes Compatible or Standard Modem. This may work in certain cases.
Some software programs allow manual input of parameters. For the users of these
programs, here is a listing of the Data/Fax/Voice Command Standards supported.
Data: TIA/EIA-602
Fax: TIA/EIA-578 for Class 1 Fax
Voice: TIA IS-101 support for TAD (Telephone Answering Device)
and Full-Duplex Speakerphone.
Init String: AT&F&C1&D2W2
TIA IS-101 Commands not supported:
Caller ID
VoiceView
Note: some programs must be configured to communicate with the modem on the same COM port and or IRQ setting used by the modem. See
the Installing the Modem section for instructions on how to determine
your COM Port and IRQ settings in Windows 95.
Using the Modems Voice Features
This modem supports TIA IS-101 commands applicable to a Full Duplex Speakerphone and Telephone Answering Device. In order to take advantage of these
features, you will need an external microphone and external speakers. A software
application; such as the one supplied with the modem; which supports these functions is also required. If you wish to immediately take advantage of these features,
install the enclosed Cheyenne BitWare Software and attach a microphone and
pair of speakers to the modem. (see the CONNECTING DEVICES TO THE MO-
DEM section)
14
Page 15

Troubleshooting
Most problems encountered during the Windows 95/98/NT installation process
are a result of inadequate system resources. If you skipped some of the recommended preinstallation procedures outlined in the Do This First section, return to
the beginning of that section and carefully follow all steps outlined for the operating system you are using. These steps have been thoughtfully chosen to help minimize difficulties during the installation of the modem in both Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT 4.00. Take seriously the recommendation to physically remove any
previously installed modems from your computer. This step alone can help prevent many potential problems from occurring.
If you have used the default Plug-N-Play jumper settings and the modem has
installed but is not functioning, try the troubleshooting procedure listed below.
The information provided by following these steps can help point the way to fixing your difficulty.
Windows 95/98
STEP 1: Check System Resources.
Go to Start-Settings-Control Panel and double-click the System icon.
Select the Device Manager tab. From the device tree, double-click the
Modems icon to show what modems are installed. If there is no Modems icon, your modem did not install (see Does Not Install section). If
your modem is listed, check that there is no yellow exclamation mark or
red X over the modems telephone icon (if there is, go to STEP 2). If
any other modems are listed, highlight the modem by clicking once on
the telephone icon next to the listed modem and then click on the Re-
move button. Shutdown the system and turn off the power. Wait 5 seconds and turn your computer back on and repeat STEP 1.
STEP 2: Check Modem Properties.
From the Device Manager tab within System Properties, double-click
the Modems icon in the device tree to show what modems are installed.
Highlight your modem by clicking once on the icon and then click the
Properties button. Read the Device Status under the General tab to see
if the device is working properly. Check the Device Usage box and make
sure there is no check mark on Disable in this hardware profile (Win-
dows 95 OEM SR2 only) or (for Windows 95 or 95a) the box labeled
Original Configuration, Current has a check mark . If either of these
conditions are not as they should be, correct them. Make a note of the
COM Port and IRQ the modem is using. If the Device Status box shows
some error message, it will generally be about a conflict. Go to the Re-
15
Page 16

sources tab and read the Conflicting Device List. If a conflict is present,
uncheck the box Use automatic settings and select a configuration
that does not cause conflicts. Manually change the IRQ settings if needed
(see your Windows 95 on-line help file for a more detailed discussion on
changing these settings). Click on the OK button. If there is no setting
free of conflicts, go to the Does Not Install section.
STEP 3: Modem Diagnostics.
Go to Start-Settings-Control Panel and double-click the Modems icon.
Your modem should be listed. If any other modem is listed, click once on
each old modem and then click the Remove button. It is a good idea to
shutdown Windows 95, turn off your computer, wait 5 seconds and turn
the power back on (do not use the Shutdown and Restart option). Return
to STEP 3: Modem Diagnostics and click on the Diagnostics tab. High-
light the modem by clicking once on the COM Port icon next to its listing. Now click on the More Info button. You should see the panel below.
Figure 8: More Info Panel
If you receive an error message or the panel is blank, go to the Does Not
Install section.
STEP 4: Does Not Install.
The most likely reason for a non-installation in Windows 95/98 is a lack
of IRQ resources. The modem needs one IRQ and one COM Port in
order to function. Modern computer systems are usually equipped with
soundcard, CD-ROM drive, Hard-drive, floppy drive, video card, two
16
Page 17

COM Ports, one LPT port, keyboard, and a mouse. Each of these devices require at least one IRQ (interrupt) in order to function. Some models
of sound card require three interrupts. It is little wonder that when it
comes time to install a modem, there is nothing left. The addition of
special purpose peripherals (SCSI, Network cards, etc.) makes matters
worse. This section deals with the process of freeing IRQs and configuring the system P-N-P (Plug-N-Play) which requires that you know how
to enter your computer systems BIOS Setup Routine (read your computers user manual for information on how to invoke and use the BIOS setup).
Once inside the BIOS Setup, find the Plug-N-Play configuration. This
can be found within the Advanced, PNP/PCI Configuration, or Plug and
Play Configuration section depending on the BIOS Manufacturer. Next,
from the information you noted in STEP 2: Modem Properties, find the
interrupt selection for the IRQ your modem is using (some BIOS dont
allow individual selection of interrupts to ISA, Plug-N-Play, or PCI).
You want to set this to a Plug-N-Play setting. This can be called ICU/
PCI, ISA, or PNP depending on your BIOS version and manufacturer.
Do not set this interrupt to PCI only or to Legacy ISA. Since each
system manufacturer has a different way of handling this configuration,
you may have to use trial-and-error to get your modem properly configured.
If you do not have any free interrupts available, you will have to disable
some unused function of your computer system. If you are using a PS/2
style mouse, you probably can spare one of your internal COM Ports. To
disable a COM Port, find the BIOS Setup section for Integrated Periph-
erals. Locate the Serial Port settings and disable an unused port that has
nothing connected to it (usually serial port 2). This should free one IRQ
for your modem to use. You will also have to disable the COM Port in
Windows 95 (see the Do This First Section).
Special Situations: Under some situations, you will find that freeing an
interrupt does not solve your installation difficulties. This could be due
to another peripheral device stealing the interrupt you just provided.
Certain full-featured sound cards require three IRQs to support all their
functions. When one becomes available, they take it. This situation requires that you remove your sound card, free an interrupt, install the
modem and verify its operation, and then reinstall the sound card. This
procedure may also work for sound cards that have lost their sound after
the modem has been installed or if the modem will not install in a system
with a sound card.
17
Page 18

Common Problems:
No Dialtone Error
Make sure you have connected the phone cable into the right connector
on the back of the modem. See Figure 7: Connecting Devices.
You may have too many devices connected to the phone line. Remove all
other equipment.
Your modem may not recognize overseas dialtone. Use ATX0 to have
the modem ignore (not look for) the dialtone before dialing.
Communications Software Does Not Work
Some communications software packages need to be configured to the
same COM Port and or IRQ as the modem. See the Installing the Mo-
dem section for information on how to determine your COM Port and
IRQ number.
Does the communications software support this modem? See the Install-
ing and Configuring Communications Software section.
If you are using a different software from the one supplied with the modem (some models of this modem may be shipped without communications software), try installing the supplied software and verify its functionality with the modem.
Nothing Appears On The Screen When I Type in Terminal Mode
Issue the command ATE1 to the modem to enable command echo. This
will let you see what you type.
The Modem Wont Answer the Phone (Cannot Detect Ring)
Issue the command ATS0=1 to the modem to enable auto-answer mode.
Entering the above command will cause the modem to answer on the first
ring.
After Upgrading to Windows 98, The Modem Wont Work
Uninstall the modem and its drivers BEFORE upgrading to Windows 98.
After you have finished the upgrade and verified that your system is working
properly, reinstall the modem and its drivers.
Cant Connect at 56K
Note: Current FCC regulations limit your maximum connection rate to
53K bits / s.
18
Page 19

The number you are calling may not support V.90 protocols. Some ISPs
(Internet Service Providers) have special numbers that you must call to
connect to V.90. Contact your service provider and ask if the number you
are calling supports V.90 connections to their service.
Check the maximum speed setting in the Modem Properties window.
Go to Start-Settings-Control Panel and double-click the Modems icon.
Highlight your modem by clicking once on the icon next to the modem
and then click the Properties button. Select the General tab and look at
the setting in the Maximum speed box. Make sure this is set to 115200.
You may have other telephone devices connected to the phone line. To
help your modem achieve the best connection possible, remove all extra
devices connected to the telephone line when the modem is in use. This
includes extension phones, answering machines, cordless phone bases,
caller ID boxes, etc. Dont just disconnect the phone cable from the units.
Disconnect the phone cable from the wall. This reduces the load on your
phone line and keeps signal attenuation to a minimum. Not having loose
phone line cords coming from your phone line sockets will help reduce
the possibility of interference being transmitted to the phone line.
Keep the length of your phone line cable to 10 feet or less. Dont use an
unusually long cable to connect to the phone line socket. If necessary,
move the computer closer to the phone socket. Dont lay your cabling
close to an electrical appliance like a refrigerator or air conditioner unit.
High current devices can transmit 60 cycle hum to your modem through
the phone cord. This may cause frequent renegotiations or line disconnects while the appliance is running.
If you are attempting to make a call from an office, are you using a direct
outside line or are you using a PBX hookup? If you have to dial 9 to
reach an outside number, you are using a PBX. Do not use this modem
on a digital or PBX system. The modem is not compatible with these
types of phones systems. Try using the line that is connected to a fax
machine. Fax machines are normally connected to a dedicated line and
not through the PBX.
Your phone line may not support a 56K connection.
19
Page 20

Appendix A: AT Command Set
AT Commands
AT commands are issued to the modem to control the modems operation and
software configuration. AT commands can only be entered while the modem is in
command mode. The format for entering AT commands is:
TYPE: ATXn
where X is the AT command, and n is the specific value for that command.
PRESS: Enter
Any command issued is acknowledged with a response in text format known as
result codes. For multiple AT commands in the same command line, the commands are executed in the order received from the DTE. Should execution of a
command result in an error, or a character not be recognized as a valid command,
execution is terminated, the remainder of the command line is ignored, and the
ERROR result code is issued. Otherwise, if all commands execute correctly, only
the result code associated with the last command shall be issued; result codes for
preceding commands are suppressed.
In the following listing, commands and command values accepted by the modem
are shown; any entries other than those shown cause the ERROR result code. AT
Commands may be entered in upper or lower case letters but you should not mix
upper case and lower case letters within the same command line.
+++AT<CR> Escape sequence
The escape sequence allows the modem to exit data mode and enter on-line command mode. While in on-line command mode, you may communicate directly to
your modem using AT commands. Once you are finished, you may return to data
mode using the ATO command. If you are in data mode and wish to enter command mode, you must type the escape character (the value stored in S2, typically
+) three times followed by a valid AT Command and the carriage return character specified by S-Register S3 (typically <enter>). Using the default values of S2
and S3, the escape sequence would be like this: +++at<enter>
S-Registers
S-registers generally affect how the AT commands perform. Contents of the registers can be displayed or modified when the modem is in command mode.
To display the value of an S-register:
20
Page 21

TYPE: ATSn?<enter>
where n is the register number.
To modify the value of an S-register:
TYPE: ATSn = r<enter>
where n is the register number, and r is the new register value.
Common AT Commands and S Registers
The following are some common AT Commands. If you require a complete listing
of the AT Command and S Register options, they are sometimes included as text
files in the Installation Diskette or CD-ROM that came with your modem.
A/ Repeat Last Command
This command repeats the last command string entered. Do not precede this command with an AT prefix or conclude it by pressing Enter.
A Answer Command
This command instructs the modem to go off-hook and answer an incoming call.
Bn Communication Standard Setting
This command determines CCITT vs. Bell standard.
B0: Selects CCITT V.22 mode when the modem is at 1200 bits/s.
B1: Selects Bell 212A when the modem is at 1200 bits/s (default).
B2: Selects V.23 Orig: (75bps trans - 1200bps rec). Answr: (75bps rec - 1200
trans).
B3: Selects V.23 reverse channel ( opposite of B2).
Cn Carrier Control
C0: Transmit carrier always off.
C1: Normal transmit carrier switching.
Dn Dial
This command instructs the modem to begin the dialing sequence. The dial string
(n, the telephone number) is entered after the ATD command.
En Echo Command
21
Page 22

This command controls whether or not the characters entered from your computer
keyboard are echoed back to your monitor while the modem is in command mode.
E0: Disables echo to the computer.
E1: Enables echo to the computer (default).
Fn On-line Data Character Echo Command
This command determines if the modem will echo data from the DTE.
F0: On-line data character echo enabled (NOT SUPPORTED, ERROR).
F1: On-line character echo disabled. (default)
Hn Hook Control
This command instructs the modem to go on-hook to disconnect a call, or offhook to make the phone line busy.
H0: Modem goes on-hook (default).
H1: Modem goes off-hook.
In Request ID Information
This command displays specific product information about the modem.
I0: Reports product code.
I1: Reports modem chip firmware version.
I2: Performs a ROM check and calculates and verifies the checksum dis-
playing OK or ERROR.
I3: Reports chipset name.
I4: Reserved.
I5: Reserved.
I6 Country code.
I7 Reports board version number.
I8 Reports modem firmware features.
Ln Monitor Speaker Volume
This command sets speaker volume to low, medium, or high.
L0: Selects lowest volume.
L1: Selects low volume.
L2: Selects medium volume (default).
L3: Selects high volume.
22
Page 23

Mn Monitor Speaker Mode
This command turns the speaker on or off.
M0: The speaker is off.
M1: The speaker is on until the modem detects the carrier signal (default).
M2: The speaker is always on when modem is off-hook.
M3: The speaker is on until the carrier is detected, except while dialing.
On Return On-line to Data Mode
O0: Instructs the modem to exit on-line command mode and return to data
mode (see AT Escape Sequence, +++).
O1: This command issues a retrain before returning to on-line data mode.
O3: This command issues a rate renegotiation before returning to on-line
data mode.
P Select Pulse Dialing
This command configures the modem for pulse (non-touch-tone) dialing. Dialed
digits are pulsed until a T command or dial modifier is received. Tone dial is the
default setting.
Qn Result Code Control
Result codes are informational messages sent from the modem and displayed on
your monitor. Basic result codes are OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, and
ERROR. The ATQ command allows the user to turn result codes on or off.
Q0: Enables modem to send result codes to the computer (default).
Q1: Disables modem from sending result codes to the computer.
T Select Tone Dialing
This command instructs the modem to send DTMF tones while dialing. Dialed
digits are tone dialed until a P command or dial modifier is received. This is the
default setting.
Vn DCE Response Format
This command controls whether result codes (including call progress and negotiation progress messages) are displayed as words or their numeric equivalents.
V0: Displays results as numbers.
23
Page 24

V1: Displays result codes as text (default).
Wn Result Code Option
W0: CONNECT result code reports DTE (modem to computer) speed.
W1: CONNECT result code reports DTE speed.
W2: CONNECT result code reports DCE (modem to modem) speed.
W3: CONNECT result code reports DTE speed and information on error cor-
rection and data compression.
W4: Reports protocol., data compression, and DTE data rate.
Zn Recall Stored Profile
This command instructs the modem chip set to go on-hook and restore the profile
specified by the n parameter. Z0 restores profile 0 and Z1 restores profile 1.
&Cn Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Control
Data Carrier Detect is a signal from the modem to your computer indicating that
the carrier signal is being received from a remote modem. DCD normally turns off
when the modem no longer detects the carrier signal.
&C0: The state of the carrier from the remote modem is ignored. DCD circuit is
always on.
&C1: DCD turns on when the remote modems carrier signal is detected, and off
when the carrier signal is not detected (default).
&Dn DTR Control
This command interprets how the modem responds to the state of the DTR
signal and changes to the DTR signal.
&D0: Ignore. The modem ignores the true status of DTR and treats it as always
on. This should only be used if your computer does not provide DTR to the
modem.
&D1: Modem switches from data mode to command mode when an on-to-off
transition of DTR occurs.
&D2: When DTR switches off, the modem goes on-hook and disables auto-an-
swer mode; when DTR switches on, auto-answer is enabled.
&D3: Turning off DTR re-initializes the modem and resets values except for the
UART registers.
24
Page 25

&F Load Factory Settings
This command loads the configuration stored and programmed at the factory. This
operation replaces all of the command options and the S-register settings in the
active configuration with factory values.
&F: Recall factory setting as active configuration. (default)
&Gn V.22bis Guard Tone Control
This command determines which guard tone, if any, to transmit while transmitting
in the high band (answer mode). This command is only used in V.22 and V.22bis
mode.
&G0: Guard tone disabled (default).
&G1: Sets guard tone to 550 Hz.
&G2: Sets guard tone to 1800 Hz.
&Kn Serial Port Flow Control Selection
&K0: Disable flow control.
&K3: Enable RTS/CTS flow control (default).
&K4: Enable XON/XOFF flow control.
&Mn Asynchronous Communications Mode
&M0: Modem only supports asynchronous mode.(default)
&Pn Pulse Dial Make-to-Break Ratio Selection
This Command sets pulse-dial make-break ratio.
&P0 39%/61% make/break ratio, 10PPS
&PI 33%/67% make/break ratio, 10PPS (default)
&Qn Asynchronous Communications Mode
&Q0: Modem only supports asynchronous mode.
&Sn Data Set Ready (DSR) Option
This command selects DSR action.
&S0: DSR always ON (default).
25
Page 26

&S1: DSR comes on when establishing a connection and when carrier is lost.
&Vn View Active Configuration and Stored Profile
This command is used to display the active profiles.
&V0: View stored profile 0.
&V1: View stored profile 1.
&V3: View relay and general-purpose input-output status.
&Wn Store Current Configuration
This command stores certain command options and S-register values into the
modems nonvolatile memory. The ATZ command or a power-up reset of the modem restores this profile.
&W0: Store in user profile 0.
&W1: Store in user profile 1.
&Yn Select Stored Profile On Power-UP
This command selects user profiles on power-up:
&Y0: Recall stored profile 0 on power-up
&Y1: Recall stored profile 1 on power-up.
&Zn=x Store Telephone Number
This command is used to store up to four dialing strings in the modems nonvolatile memory for later dialing. The format for the command is &Zn = stored number where n is the location 0-3 to which the number should be written. The dial
string may contain up to 30 digits. The ATDS = n command dials using the string
stored in location n.
%En Auto-Retrain Control
This command enables-disables auto-retrain:
%E0: Disables auto-retrain.
%E1: Enables auto-retrain (default)..
%Gn Rate Renegotiation
This Command enables-disables rate-renegotiation.
26
Page 27

%G0: Disabled.
%G1: Enabled.
-Cn Data Calling Tone
Data Calling Tone is a tone of certain frequency and cadence as specified in V.25
which allows remote Data/FAX/Voice discrimination. The frequency is 1300 Hz
with a cadence of .5 s on and 2 s off.
-CO: Disabled.
-C1: Enabled. (default)
-C2: Enable V.8 and 1300 Hz calling tone.
+MS=m Modulation Selections.
This Command selects modulation standards and transmit-receive speeds. To display the current setting, type AT+MS?. The proper command syntax is:
AT+MS=<carrier>,<automode>,<min rate>,<max rate>
<carrier> This parameter specifies the type of modulation standard used. The list
below shows approved codes:
V21 V.21 (300 bps)
V22 V.22 (1200 bps)
V22B V.22 bis (1200 and 2400 bps)
V23C V.23, constant carrier (1200 bps forward and 300 bps reverse)
V32 V.32 (4800 and 9600 bps)
V32B V.32 bis (7200, 9600, 12200, and 14400)
V34 V.34 asymmetrical (2400, 4800, 7200, 9600, 12200, 14400, 16800,
19200, 21600, 24000, 26400, 28800, 31200, and 33600 bps)
V34S V.34 symmetrical only (2400, 4800,7200, 9600, 12200, 14400, 16800,
19200, 21600, 24000, 26400, 28800, 31200, and 33600 bps)
V34B V.34 extended asymmetrical (2400, 4800, 7200, 9600, 12200, 14400,
16800, 19200, 21600, 24000, 26400, 28800, 31200, and 33600 bps)
V90 V.90 asymmetrical [transmit speeds (4800, 7200, 9600, 12000, 14400,
16800, 19200, 21600, 24000, 26400, 28800, and 31200 bps)]; [receive
speeds (33333, 37333, 41333, 42667, 44000, 45333, 46667, 48000,
49333, 50667, 52000, and 53333 bps)]
<automode> This parameter allows the modem to negotiate modulation speeds
automatically.
0= disabled (modem will not negotiate speeds automatically)
1= enabled (automatic negotiation allowed)
27
Page 28

<min rate> This entry specifies the lowest data transfer rate which the modem
may establish a connection.
<max rate> This parameter specifies the highest speed at which the modem may
establish a connection.
S0 Number of Rings to Auto-answer
The modem automatically goes off-hook and initiates a data mode-answer mode
handshake after detecting the specified number of rings. A value of zero ( 0 )
disables auto-answer mode. Entering a value from 1 to 255 enables auto-answer
mode.
Range: 0-255 rings
Default: 0
S2 Escape Character
The value of S2 specifies an ASCII value for the character used to enter command
mode. A value over 127 disables the escape sequence.
Range: 0-127
Default: 43
S3 Carriage Return Character
S3 specifies the AT command string terminator and modem response code terminator. The default is <CR> or carriage return (ASCII 13).
Range: 0-127
Default: 13
S4 Line Feed Character
The value of S2 specifies the line feed character.
Range: 0-127
Default: 10
S5 Backspace Character
S5 specifies the backspace character that is used to delete the last entered character. The default value is <backspace> (ASCII 8).
28
Page 29

Range: 0-127
Default: 8
S6 Wait Before Blind Dialing
The value of S6 specifies the amount of time that must elapse after the modem
goes off-hook before the modem starts dialing the telephone number. The modem
waits for at least 2 seconds before dialing even if the register is set for a value less
than two.
Range: 2-255
Default: 2
S7 Wait for Carrier/Dial Tone
S7 specifies the length of time the modem waits to detect the remote modem carrier after dialing. If the remote modem is not detected within that time, the modem
hangs up and sends the NO CARRIER response.
Range: 1-255 seconds
Default: 60 seconds
S10 Lost Carrier Hang Up Delay
S10 is used to specify the length of time the modem waits before hanging up if the
remote modem carrier signal is lost. When set to 255, the modem does not hang
up when it loses the remote modem.
Range: 1-255 (1/10 of a second)
Default: 14 (1.4 seconds)
S11 DTMF Dialing Speed
S11 specifies the duration of DTMF (tone) dialing. This register is not used for
pulse dialing.
Range: 50-255 ms.
Default: 70 ms.
S12 Guard Time
S12 is used to specify guard and detect times used for the escape sequence.
Range: 1-255 (1/50 of a second)
29
Page 30

Default: 50 (1 second)
S25 Detect DTR Change
S25 defines the minimum amount of time that DTR has to remain off before the
modem performs the function specified by the &Dn command. A change in DTR
that persists for a shorter time than that specified will be ignored by the modem.
Range: 1-255 1/100 of a second
Default: 5 (1/20 of a second)
S30 Disconnect Inactivity Timer
This register sets the length of time that the modem stays on-line/off-hook before
disconnecting when no data is being sent or received.
Range: 1-255 minutes
Default: 1 minute
S33 Sleep Mode Timer
S33 determines when the modem enters sleep or power-down mode. When enabled ( any value other than zero), the controller enters sleep mode whenever the
modem has been inactive for a user-programmed time delay. The modem exits
sleep mode whenever the host computer reads or writes to the modem or when a
ring signal is detected.
Range: 0-90 seconds
Default: 0 (disabled)
S37 Maximum Line Speed Attempted
This register sets the maximum line speed allowed. S37 provides the same information as the AT+MS=m command. Using the +ms=m parameter automatically
changes the value of S37. For example, setting AT+MS=0 sets S37 to 0 (zero).
Using the AT+MS=m command to change the value of S37 provides greater flex-
ibility than changing the S register directly. See the AT+MS=m command for more
information.
30
Page 31

Appendix B: Communications Regulations
FCC REGULATIONS
The following statements are provided in accordance with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations. Please read these statements carefully
before installing your modem.
FCC PART 68 REQUIREMENTS
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC Rules. On the bottom of this
equipment is a label that contains, among other information, the FCC Registration
Number and Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) for this equipment. If requested,
this information must be given to the telephone company.
The REN is used to determine the maximum number of devices connected to
your telephone line that will ring in response to an incoming call. In most, but not
all, areas, the total REN of devices connected to a line should not exceed five
(5.0). To find out the total permitted in your area, contact your local telephone
company.
If your telephone equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company can discontinue your service temporarily. If possible, the company will
notify you in advance. But if advance notice isnt practical, you will be notified as
soon as possible. You will be informed of your right to file a complaint with the
FCC.
Your telephone company can make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures that could affect the operation of your equipment. If so, you
will be notified in advance so you can make the changes needed to maintain uninterrupted service.
If you experience trouble with this equipment, please contact the manufacturer at
the address given in this manual. The telephone company may ask that you disconnect this equipment from the network until the problem has been corrected or
until you are sure that the equipment in is not malfunctioning.
31
Page 32

DECLARATION of CONFORMITY
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio and television reception, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CAUTION: CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EX-
PRESSLY APPROVED BY THE PARTY RESPONSIBLE FOR
COMPLIANCE COULD VOID THE USERS AUTHORITY TO
OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
32
Page 33

CANADIAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNICATIONS (CDOC):
Requirements for End Users:
Notice: The Canadian Department of Communications label
identifies certified equipment. This certification means the equip-
ment meets certain telecommunications network requirements.
The Department does not guarantee the equipment will operate
to the users satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment users should ensure that connection to the line is
allowed by the local telecommunications company. The equipment must also be
installed using an acceptable method of connection. In some cases, the companys
inside wiring associated with a single line individual service may be extended by
means of a telephone extension cord. Compliance with the above conditions may
not prevent degradation of service in certain situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized Canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the
user to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of the power utility, telephone lines, and internal metallic water pipe system,
if present, are connected together. This precaution may be particularly important
in rural areas.
Caution: Users should not attempt to make
such connections themselves, but should contact the appropriate electric inspection authority, or electrician, as appropriate.
33
 Loading...
Loading...