Page 1
Revision: 1.0
AR-ES6050FLD
System Guide
Revision Description Date
1.0 Release 2010/08/20
1
Page 2

Revision: 1.0
Content s
1 Introduction to AR-ES6050FLD................................................3
1.1 Specifications.................................................................................... 3
1.2 Packing List....................................................................................... 3
1.3 System Dissection............................................................................ 4
2 Procedures of Assembly/Disassembly .....................................7
2.1 Installing the CF card ....................................................................... 7
2.2 Installing the Mini PCI-e interface card........................................... 9
2.3 Installing the DDR2 SO-DIMM procedures ................................... 12
2.4 Assemble/Disassemble the DIN mounting bracket. .................... 14
3 Appendix ....................................................................................16
Cable Pin Define ................................................................................... 16
4 AR-B6050 Board Guide.............................................................18
4.1 Block Diagram................................................................................. 18
4.2 AR-B6050 H/W Information............................................................ 20
4.3 Components and Jumps Setting List ........................................... 22
4.4 BIOS Setting.................................................................................... 26
4.5 WATCHDOG, GPIO, AND BYPASS PROGRAMMING.................... 35
2
Page 3
Revision: 1.0
1 Introduction to AR-ES6050FLD
AR-ES6050FLD is a fan-less embedded system that could be used by DIN mount for
factory uses, VESA mount for medical/multimedia display and wall mount for automatic
control. It is designed with Intel Atom N450 and supports up to 2GB of DDR2 memory.
AR-ES6050FLD has diverse physical interface for different peripheral, e.g. VGA port,
LVDS pin header, 4 *USB 2.0 ports, 2 *USB 2.0 pin header, 1 *COM port, 1 *COM pin
header, 2 *GBbps ports, 2 *SATA ports, CF type I/II slot and Realtek audio output port. It is
also equipped with industrial standard PCI-104 and mini-PCIe interface. Users can
purchase suitable add-on cards to satisfy their needs.
1.1 Specifications
Item Description
System AR-ES6050FLD
CPU Board AR-B6005
System Dimensions 220*128*78(mm)
1.2 Packing List
Description Quantity Remark
AR-ES6050FLD 1
1GB DDR2 SDRAM pre-installed 1
Quick User Guide
Utility CD
CD ROM
DIN mounting bracket
1
1
1
1
3
Page 4

1.3 System Dissection
(1) Dimensions
Revision: 1.0
(2) Front Panel
AUDIO LAN 1~2
USB 1~4
Power switch
(3)System Configuration
COM CF BKT VGA Power LED
ANTENNA HOLE
TERMINAL BLOCK
4
Page 5
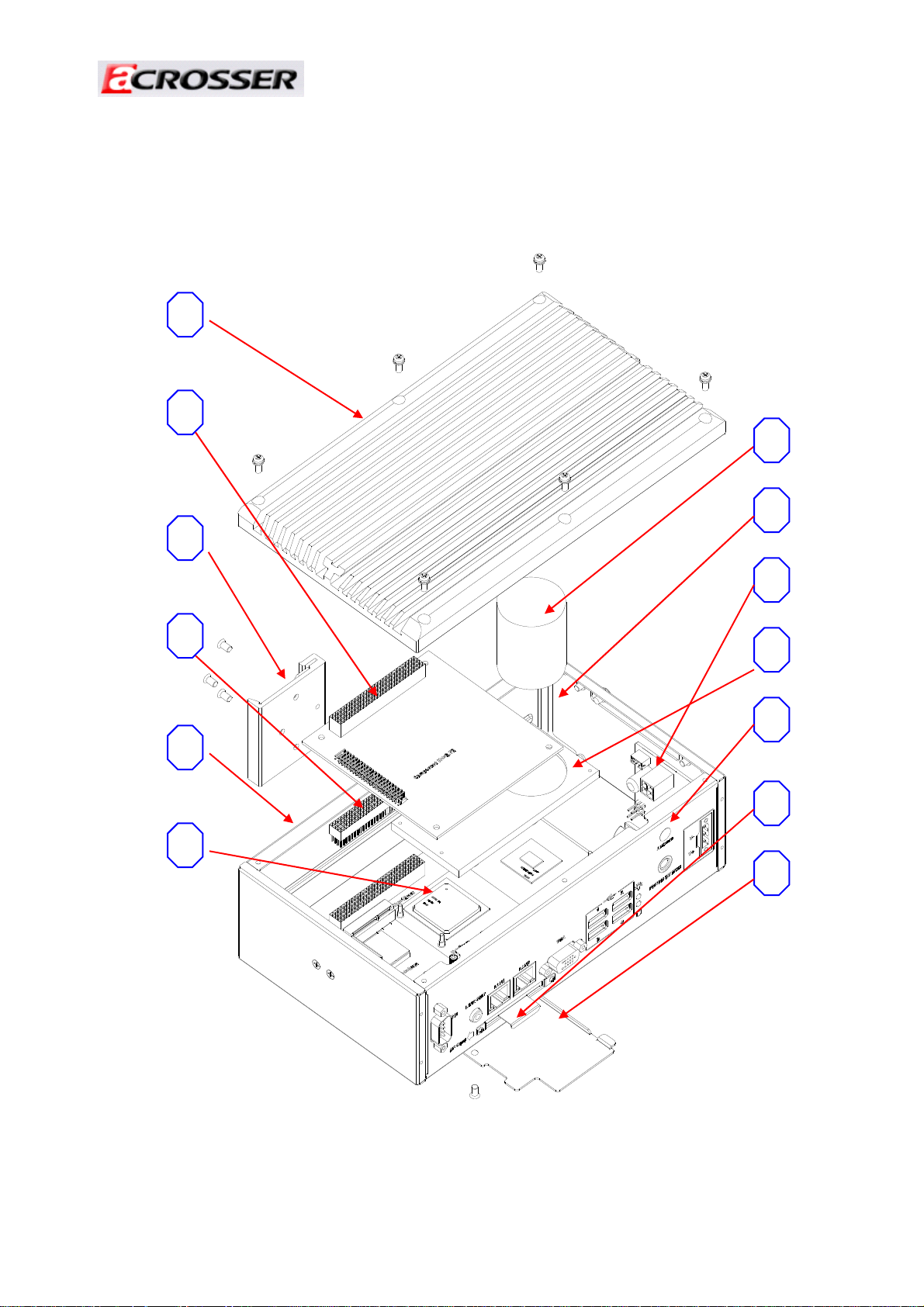
(3) System Configuration
1
2
Revision: 1.0
7
8
3
4
5
6
9
10
11
12
13
5
Page 6
Item Description Quantity
1 LEFT COVER 1
2 PCI-104 CARD 1
3 DIN MOUNTING BRACKET 1
4 PCI-104 TAIL CONNECTOR 1
5 BASE 1
6 AR-B6050 1
7 HEAT COLUMN 1
8 POWER BOARD BRACKET 1
Revision: 1.0
9 AR-PW9427B 1
10 HEAT PLATE 1
11 SWITCH BUTTON 1
12 CF CARD BRACKET
1
13 BASE DDR DOOR 1
6
Page 7

2 Procedures of Assembly/Disassembly
2.1 Installing the CF card
1. Unfasten two screws of CF bracket and then take out the CF card bracket.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 1
2. Put the CF card into CF bracket (figure 2).
Please note that the direction of CF card and CF bracket (figure 3).
Figure 2 figure 3
7
Page 8

Revision: 1.0
3. Push CF card to the bottom of bracket to stop the forwarding at the bend of bracket.
Figure 4
4. Push them into the CF slot of system machine and then fasten the two original screws to
fix CF bracket.
Figure 5
8
Page 9

2.2 Installing the Mini PCI-e interface card
1. Unfasten the six screws to take out the heat sink cover.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 6
2. Maybe you need to force open the heat sink cover.
Figure 7
9
Page 10

3. Align the notch key on the Mini PCI-e card with rib on the slot.
Figure 8
4. Push Mini PCI-e card horizontally
.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 9
10
Page 11

5. Using two M2 screws to fasten Mini PCI-e card.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 10
6. Close the heat sink cover using the original screws to fasten heat sink cover and base.
(Please refer to figure 6)
11
Page 12

2.3 Installing the DDR2 SO-DIMM procedures
1. Unfasten the screw of the DDR cover and open the cover.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 11
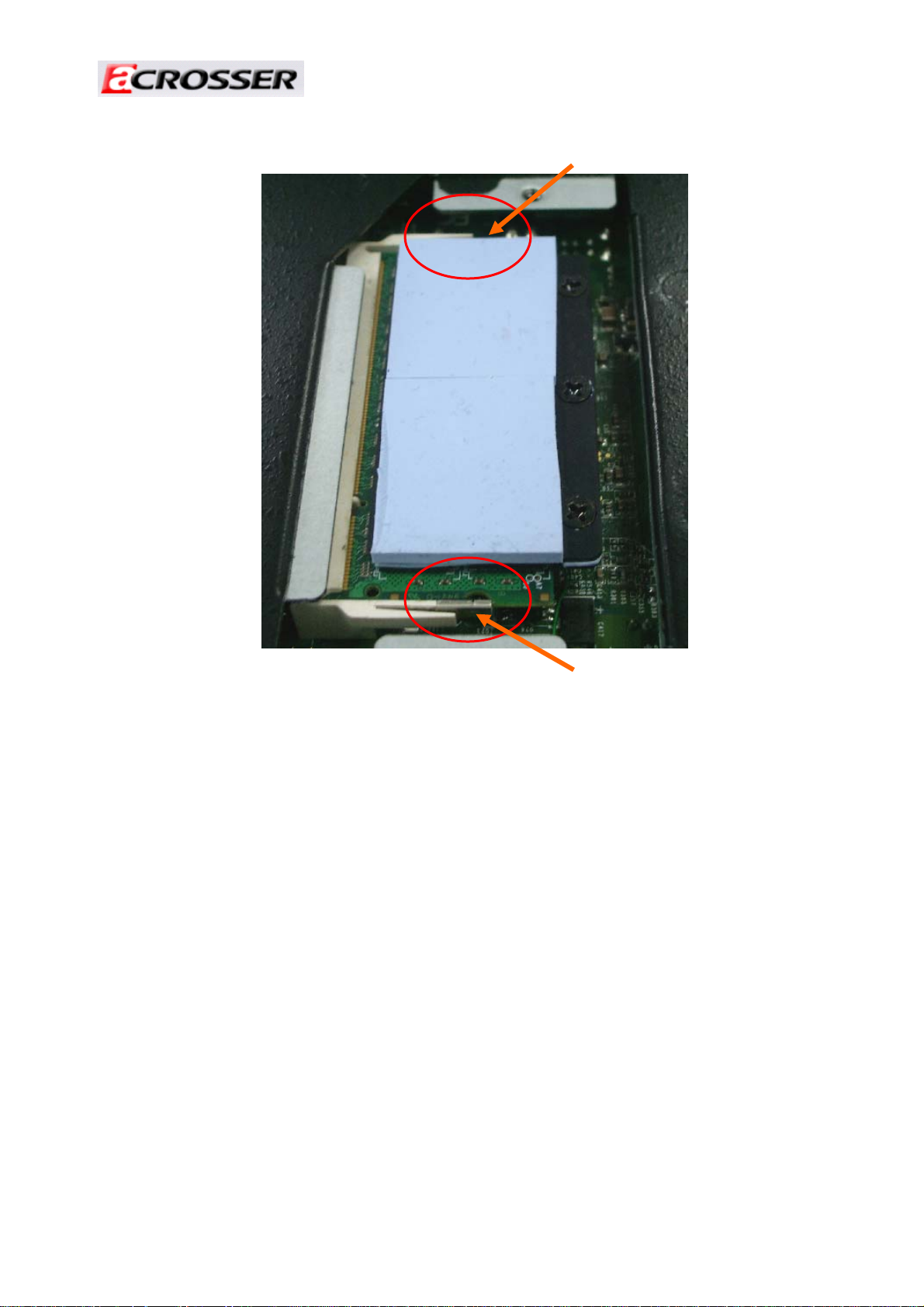
2. Align the notch key on DDR2 SO-DIMM with rib on the DDR2 socket.
Figure 12
12
Page 13
Revision: 1.0
3. Push DDR2 SO-DIMM horizontally and make sure it is locked by hooks of two sides of
DDR2 socket.
Figure 13
4. Recover the DDR cover and fasten it with the screw.
.
13
Page 14

2.4 Assemble/Disassemble the DIN mounting bracket.
1. Hook the spring of the DIN mounting bracket onto the upper of DIN rail.
Revision: 1.0
Figure 14
2. Press down the AR-ES6050FLD system machine and push it forward lightly.
STEP 1
STEP 2
Figure 15
14
Page 15

Revision: 1.0
3. Make sure they are locked together.
Figure 16
4. Disassemble the DIN mounting bracket of AR-ES6050FLD system. Press down the
AR-ES6050FLD system machine and pull it back lightly.
STEP 1
STEP 2
Figure17
15
Page 16

3 Appendix
Cable Pin Define
1. Com cable
Revision: 1.0
110mm
2. Power Cable
BLACK
BLACK
YELLOW
YELLOW
16
Page 17
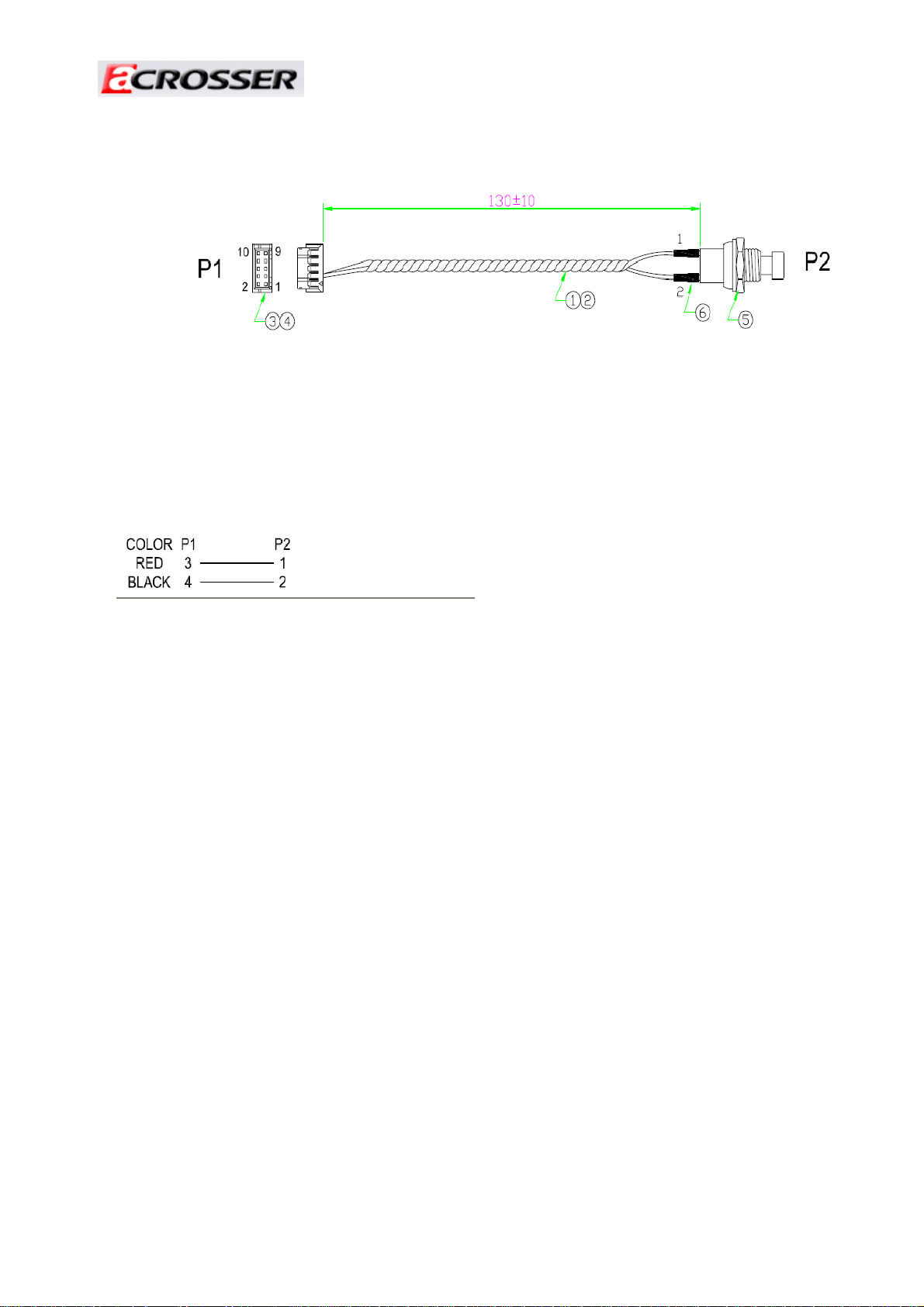
3. Switch Cable
Revision: 1.0
17
Page 18

4 AR-B6050 Board Guide
4.1 Block Diagram
Revision: 1.0
18
Page 19

AR-B6050 Board Specifications
Revision: 1.0
Intel Atom N450 1.66GHz
Intel Graphics Media Accelerator 950
1 x SO-DIMM supports DDRII up to 2GB(Memory DDR2 data transfer rates of 667
MT/s)
1 x VGA
4 x USB2.0
2 x SATA
1 x CF II
2 x RS-232
2 x GbE (Realtek RTL8111D)
1 x PCI-104 & 1 x Mini-PCIe
8-bit GPIO
19
Page 20

Revision: 1.0
4.2 AR-B6050 H/W Information
This section describes the installation of AR-B6050. At first, it shows the Function
diagram and the layout of AR-B6050. It then describes the unpacking information
which you should read carefully, as well as the jumper/switch settings for the
AR-B6050 configuration.
4.2.1 AR-B6050 LAYOUT (Top side)
JP1
ATX1
BAT1
SYSFAN1
CN2
CN3
JP2
J7
GPIO1
COM1
COM2 J1
SATA2 USB3
SATA1 USB1
CN4 USB2
JP3 LED1
LAN1 LVDS1
LAN2 CN1
J6
20
VGA1
Page 21

4.2.2 AR-B6050 LAYOUT (Bottom side)
Revision: 1.0
SODIMM1
CF
21
Page 22

4.3 Components and Jumps Setting List
Revision: 1.0
1. JP1: LCD panel driving
voltage selection.
STATUS SETTING
1-2
2-3 +5V
+3.3V
(Default).
4. SYSFAN1: System DC
Fan connector.
PIN SETTING
1 GND
2 +12V
3 Fan speed data
2. A TX1: AT power input
3. BAT1: CMOS battery holder.
connector.
PIN SETTING
1 GND
2 GND
3 +12V
4 +12V
CMOS battery holder.
5. CN2: PCI-104 connector. 6. CN3: MINI PCI-E connector.
PCI-104 connector.
MINI PCI-E connector.
7. JP2: Signal SERIRQ
connects to PCI-104 pin
#B1 selection.
STATUS SETTING
Open
Short Connected.
Disconnected.
(Default)
8. J7: COM1/2 SELECT RI OR
+12V
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 RI#1 2 RI#1_12V
3 +12V 4 RI#1_12V
5 RI#2 6 RI#2_12V
7 +12V 8 RI#2_12V
9. GPIO1: GPIO connector.
PIN SETTING PIN SETTING
1 GPIO0 2 +5V
3 GPIO1 4 GPIO7
5 GPIO2 6 GPIO6
7 GPIO3 8 GPIO5
9 GND 10 GPIO4
22
Page 23

Revision: 1.0
10. COM1: RS232 signal
connector for port #1.
PIN SETTING PIN SETTING
1 DCD #1 2 DSR #1
3 RX #1 4 RTS #1
5 TX #1 6 CTS #1
7 DTR #1 8 RI #1
9 GND 10 GND
13. SATA2: SATA device
connector #2.
SATA device connector #2.
11. COM2: RS232 signal
connector for port #2.
PIN SETTING PIN SETTING
1 DCD #2 2 DSR #2
3 RX #2 4 RTS #2
5 TX #2 6 CTS #2
7 DTR #2 8 RI #2
9 GND 10 GND
14. CN4: Audio signal
connector.
Audio line out
12. SATA1: SATA device
connector #1.
SATA device connector
#1.
15. JP3: CF MASTER
SELECT
SET SIGNAL
SHORT MASTER
OPEN SLAVE
16. LAN1: RJ45 connector for
Gigabit Ethernet port #1.
RJ45 connector for Gigabit
Ethernet port #1.
17. LAN2: RJ45 connector for
Gigabit Ethernet port #2.
RJ45 connector for
Gigabit Ethernet port #2.
18. J6: Front panel
connector.
STATUS SETTING
1-2 Hardware reset
3-4
5-6 Power Button
AT Mode - Short
ATX Mode - Open
23
Page 24
Revision: 1.0
19. VGA1: D-SUB-15 female
connector for VGA output.
D-SUB-15 female connector
for VGA output.
20. J1: CMOS data clear 21. USB3: Internal USB2.0
connector
PIN SETTING PIN SETTING
1 +5V 2 +5V
SHORT CMOS data clear
3 USB5- 4 USB6-
5 USB5+ 6 USB6+
7 GND 8 GND
9 GND 10 GND
22. USB1: USB connector 23. USB2: USB connector 24. LED1: System power and
HDD access indicators.
Green: System power
Upper: Port #2.
Lower: Port #1.
Upper: Port #4.
Lower: Port #3.
indicator.
Yellow: HDD access
indicator.
25. LVDS1: LCD panel inverter
power connector.
PIN SETTING PIN SETTING
1 LCD VDD 2 GND
3 NC 4 NC
5 GND 6 NC
7 NC 8 GND
9 NC 10 NC
11 NC 12 NC
13 NC 14 NC
15 GND 16 O CLK+
17 CLK- 18 GND
19 Data2+ 20 Data2-
21 I2C CLK 22 Data1+
23 Data1- 24 I2C Data
25 Data0+ 26 Data0-
27 NC 28 NC
29 LCD VDD 30 LCD VDD
26. CN1: LCD panel inverter
power connector.
PIN SETTING
1
+12V
2
+12V
3
GND
4
BKL ON
5
GND
6
Reserved.
24
Page 25

Revision: 1.0
27. DIMM1: DDR-II SODIMM
Socket.
DDR-II SODIMM
Socket.
28. CF1: Type-II compact flash
card socket.
+3.3V CF card only and
UDMA mode supported.
25
Page 26

Revision: 1.0
4.4 BIOS Setting
The BIOS Setup Utility is a hardware configuration program built into your computer’s BIOS.
To activate the BIOS Utility, press F2 during POST (when “Press <F2> to enter Setup”
message is prompted on the bottom of screen). Press <F12> during POST to enter
multi-boot menu. In this menu, user can change boot device without entering BIOS SETUP
Utility.
This chapter describes the BIOS menu displays and explains how to perform common
tasks needed to get the system up and running. It also gives detailed explanation of the
elements found in each of the BIOS menu. The following topics are covered:
Main Setup
Advanced Setup
Security Setup
Power Setup
Boot Setup
Exit Setup
26
Page 27

Revision: 1.0
4.4.1 Main Setup
Once you enter the InsydeH2O BIOS™ Setup Utility, the Main Menu will appear on the
screen. Use the arrow keys to highlight the item and then use the <F5> <F6> keys to select
the desired value in each item.
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
Set the system date. Note that the ‘Day’
automatically changes when you set the
date.
Set the system time.
This field shows the CPU type and speed
of the system.
This field displays the bus speed of the
system.
System Date
System Time
Processor
Type
System Bus
Speed
Format : MM/DD/YYYY
(month/day/year)
Format: HH:MM:SS
(hour:minute:second)
N/A
N/A
System
Memory
N/A
Speed
This field displays the real speed of the
memory.
27
Page 28

Revision: 1.0
Cache RAM
Total Memory
SODIMM 0
BIOS Revision
N/A
This field displays the cache ram of the
CPU.
N/A Displays the total memory available.
N/A
This field displays the memory of the
SODIMM0.
N/A Displays system BIOS version.
28
Page 29

4.4.2 Advanced Chipset Setup
Revision: 1.0
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
Peripheral
Configuration
IDE
Configuration
Serial Port A
Serial Port B
Azalia Audio control
IDE Controller
HDC Configure as
Enter the Peripheral Configuration
menu.
Enter the IDE Configuration menu.
Init Display First
IGD-Device2, Function1
Video
Configuration
IGD-Frame Buffer Size
IGD-DVMT Size
Enter the Video Configuration menu.
IGD-Boot Type
IGD-LCD Panel type
Hardware
Monitor
N/A
This field displays the Hardware
Monitor of the system.
29
Page 30

4.4.3 Security Setup
Revision: 1.0
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
Supervisor
Password
Not Installed
Installed
Shows the setting of the Supervisor
password
Press Enter to set the user password. When
user
password is set, this password protects the
Set
Supervisor
Password
N/A
BIOS Setup
Utility from unauthorized access. The user
can enter
Setup menu only and does not have right to
change the
value of parameters.
30
Page 31

Setting a Password
Follow these steps as you set the user or the supervisor password:
1. Use the ↑ and ↓ keys to highlight the Set Supervisor Password parameter and press the
Enter key. The Set Supervisor Password box appears:
Revision: 1.0
2. Type a password in the “Enter New Password” field. The password length can not exceed 8
alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9, not case sensitive). Retype the password in the
“Confirm New Password” field.
IMPORTANT: Be very careful when typing your password because the characters do not
appear on the screen.
3. Press Enter. After setting the password, the computer sets the User Password parameter to
“Set”.
4. If desired, you can opt to enable the Password on boot parameter.
5. When you are done, press F10 to save the changes and exit the BIOS Setup Utility.
Removing a Password
Follow these steps:
1. Use the ↑ and ↓ keys to highlight the Set Supervisor Password parameter and press the
Enter key. The Set Password box appears:
2. Type the current password in the Enter Current Password field and press Enter.
3. Press Enter twice without typing anything in the Enter New Password and Confirm New
Password fields. The computer then sets the Supervisor Password parameter to “Clear”.
4. When you have changed the settings, press u to save the changes and exit the BIOS Setup
Utility.
31
Page 32

4.4.4 Power Setup
Revision: 1.0
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
ACPI S3
Support
Wakeup on
PME
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
ACPI S1/S3 Sleep State.
Wake up when the system power is off
and a PCI Power Management Enable
wake up event occurs.
32
Page 33

4.4.5 Boot Setup
Revision: 1.0
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
Boot Device
Priority
Hard disk
Drive
CD/DVD-ROM
Drive
USB Drive
Other
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Select Boot Devices to select specific
devices to support boot.
(The item can't display when no device.)
Show the Hard disk drives.
(The item can't display when no device.)
Show the CD/DVD-ROM drives.
(The item can't display when no device.)
Show the USB diskette drives.
(The item can't display when no device.)
Show the other drives.
(The item can't display when no device.)
PXE Boot to
LAN
Enabled
Disabled
Disables or enables PXE boot to LAN.
33
Page 34

4.4.6 Exit Setup
Revision: 1.0
Note: The control keys are listed at the bottom of the menu. If you need any help with the item fields,
you can press the <F1> key, and the relevant information will be displayed.
Item Option Description
Exit Saving
changes
Save change
without Exit
Exit
Discarding
changes
Load Optimal
Defaults
Discarding
changes
Yes
NO
Yes
NO
Yes
NO
Yes
NO
Yes
NO
Exit System Setup and save your changes.
Save Your changes and without exiting
system.
Exit system setup and without saving your
changes.
Load default values for all SETUP item.
Load previous values from CMOS for all
SETUP items.
34
Page 35
Revision: 1.0
4.5 WATCHDOG, GPIO, AND BYPASS PROGRAMMING
4.5.1 Watchdog Programming
This section describes the usage of WATCHDOG. AR-B6050 integrated the
WATCHDOG that enable user to reset the system after a time-out event. User can use a
program to enable the WATCHDOG and program the timer in range of 1~255
second(s)/minute(s). Once user enables the WATCHDOG, the timer will start to count down
to zero except trigger the timer by user’s program continuously. After zeroize the timer (stop
triggering), the WATCHDOG will generate a signal to reset the system. It can be used to
prevent system crash or hang up. The WATCHDOG is disabled after reset and should be
enabled by user’s program.
Intel also provides a Linux watchdog driver to access the feature on AR-B6050. It can
be accessed via /dev/watchdog. About the related operations of Linux watchdog, please
refer Linux website.
Please refer to the following table to program WATCHDOG properly, and user could test
WATCHDOG under ‘Debug’ program.
Address port: 2E and Data port: 2F
C:>debug
-o 2E 87
-o 2E 01
-o 2E 55
-o 2E 55
-o 2E 07
-o 2F 07
-o 2E 72
-o 2F 40
-o 2E 72
-i 2F
-o 2F xx
-o 2E 73
-o 2F ##
-q
To enter debug mode.
To enter configuration.
To point to Logical Device Number Reg.
To select logical device 7 (WATCHDOG).
To select “keyboard reset” as WATCHDOG output to reset system.
Preparing to select the unit of timer equals minute or second.
To read the value of index “2F”.
The value “xx” equals [(value of index “2F”) OR (80)].
OR (80): unit is second.
OR (00): unit is minute.
Preparing to set the WATCHDOG timer value.
The value “##” ranges between 01 ~ FF (1 ~ 255 seconds).
00: To disable WATCHDOG.
To quit debug mode
Notice: The “actual” timer value may not match with the “theoretical”. That is
because of the tolerance of internal oscillating clock and cannot be adjusted or
optimized.
35
Page 36

Revision: 1.0
The WATCHDOG sample code of C language as below:
//====================================================================
=======
// Rev Date Name Description
//====================================================================
=======
// 1.0 12/16/2009 Willy W83627EHF WatchDog timer test
//====================================================================
=======
//====================================================================
=======
// Language include files
//====================================================================
=======
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
//====================================================================
=======
// Normal procedure
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Help();
//====================================================================
=======
// Main procedure
//====================================================================
=======
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned char IO_Port_Address=0x2E;
unsigned char Time;
unsigned char Temp;
if ( argc != 2 )
{ Show_Help(); return 1; }
clrscr();
Time=atoi(argv[1]);
// Set Watchdog
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0x87); // (EFER) Extended Functions Enable Register
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0x87);
36
Page 37

Revision: 1.0
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0x2D); // Point to Global Reg.
// Select Multi-Function pin, (Bit0=0 Watchdog Function)
outportb(IO_Port_Address+1,(inportb(IO_Port_Address+1)&0xFE));
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0x07); // Point to Logical Device Number Reg.
outportb(IO_Port_Address+1,0x08); // Select logical device 8, (Watchdog Function)
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0x30); // Device Active register
outportb(IO_Port_Address+1,0x01);
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0xF5); // Select Watchdog count mode seconds or
minutes
outportb(IO_Port_Address+1,0x02); // Default is second and KBRST mode.
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0xF6); // Set Watchdog Timer Value
outportb(IO_Port_Address+1,Time); // 0x00 to disable, max 0xFF
textcolor(YELLOW);
for(Temp=Time;Temp>0;Temp--)
{
outportb(IO_Port_Address,0xF6); // Read Watchdog Timer Value
Time=inportb(IO_Port_Address+1);
gotoxy(20,10);
cprintf(">>> After %3d Second will reset the system. <<<",Time);
delay(1000);
}
textcolor(LIGHTRED);
gotoxy(18,10);
cprintf("If you can see this message, Reset system is Fail");
return 1;
}
//====================================================================
=======
// Function : Show_Help()
// Input : -
// Change : -
// Return : -
// Description : Show Help string.
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Help()
{
clrscr();
printf("WatchDog Test for W83627EHF\n\n");
printf("Sample: \n");
printf(" WDT.EXE 10 \n");
37
Page 38

Revision: 1.0
printf("( For 10 seconds to reset. )\n");
}
//====================================================================
=======
38
Page 39

Revision: 1.0
4.5.2 GPIO Programming
This section describes the usage of GPIOs. AR-B6050 integrated eight bits, 5V TTL
level, bidirectional, and software programmable GPIOs for user’s application. They are all
capable of 5 mA source current for output and 8 mA sink current for input individually. The
electrical characteristics of GPIOs as following table:
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 GPO0 2 VCC
3 GPO7 4 GPI7
5 GPO2 6 GPI6
7 GPO3 8 GPI5
9 GND 10 GPI4
To quickly understand the GPIO programming under Linux, we also provide a sample
application source code in product CD, naming gpio.c. It can be used to control GPIO pin
described above and also LED.
The GPIO sample code of C language as below:
//====================================================================
=======
// Rev Date Name Description
//====================================================================
=======
// 1.0 03/17/10 Willy GPIO10~GPIO17 Test utility for W83627EHF.
//====================================================================
=======
//====================================================================
=======
// Turbo C++ Version 3.0 Copyright(c) 1990, 1992 by Borland International,Inc.
//====================================================================
=======
//====================================================================
=======
// Language include files
//====================================================================
=======
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//====================================================================
=======
// Normal procedure
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Help();
39
Page 40

Revision: 1.0
void Show_Fail();
void Show_Pass();
//====================================================================
=======
// Main procedure
//====================================================================
=======
int main(int argc)
{
char *Model_Name="AR-B6050";
char *Version="v1.0";
unsigned char IO_PORT_BASE=0x2E; // DATA_PORT = IO_PORT_BASE + 1;
unsigned char data;
int result=0;
if ( argc > 1 )
{ Show_Help(); return 1; }
clrscr();
textcolor(WHITE);
gotoxy(1, 1);
cprintf("<>=============================================================
=============<>");
gotoxy(1, 2); cprintf("|| W83627EHF GPIO Test Utility %s Acrosser Technology Co., Ltd.
||",Version);
gotoxy(1, 3);
cprintf("<>=============================================================
=============<>");
gotoxy(1, 4);
cprintf("<>=============================================================
=============<>");
gotoxy(1, 5); cprintf("|| Model Name :
||");
gotoxy(1, 6); cprintf("|| SIO IO Base :
||");
gotoxy(1, 7);
cprintf("<>=============================================================
=============<>");
// Show Got Parameter Informat
textcolor(LIGHTGRAY);
gotoxy(18,5); cprintf("%s",Model_Name);
gotoxy(18,6); cprintf("%X",IO_PORT_BASE);
// Enter W83627EHF Config
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0x87);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0x87);
// Set Multi-function Pins to GPIO
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0x29);
40
Page 41

outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,(inportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1) | 0x01));
// Select GPIO Port device
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0x07);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x07);
// Set GPIO Port Active
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0x30);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x01);
// Set GPIO I/O Register to 00h
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF3);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x00);
// Set W83627EHF GPIO10~13 to Output, GPIO14~GPIO17 to Input
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF0);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0xF0);
// Set W83627EHF GPIO10~13 to High
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF1);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x0F);
// Read W83627EHF GPIO14~17 Status, if not High error.
data=inportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1)&0xF0;
if(data!=0xF0)
result=1;
// Set W83627EHF GPIO10~13 to Low
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF1);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x00);
// Read W83627EHF GPIO14~17 Status, if not Low error.
data=inportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1)&0xF0;
if(data!=0x00)
result=1;
// Set W83627EHF GPIO10~13 to input, GPIO14~GPIO17 to Output
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF0);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x0F);
// Set W83627EHF GPIO14~17 to High
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF1);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0xF0);
// Read W83627EHF GPIO10~13 Status, if not High error.
data=inportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1)&0x0F;
if(data!=0x0F)
result=1;
// Set W83627EHF GPIO14~17 to Low
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xF1);
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1,0x00);
// Read W83627EHF GPIO14~17 Status, if not Low error.
data=inportb(IO_PORT_BASE+1)&0x0F;
if(data!=0x00)
result=1;
Revision: 1.0
41
Page 42

Revision: 1.0
// Exit W83627EHF Config
outportb(IO_PORT_BASE,0xAA);
if(result)
Show_Fail();
else
Show_Pass();
return result;
}
//====================================================================
=======
// Function : Show_Help()
// Input : -
// Change : -
// Return : -
// Description : Show Title string.
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Help()
{
clrscr();
printf("GPIO Test utility for W83627EHF\n\n");
printf("GPIO0 迋迋迋芼 Vcc\n");
printf("GPIO1 迋迋迋銀迋迋 GPIO7\n");
printf("GPIO2 迋迋芼 迋迋 GPIO6\n");
printf("GPIO3 迋迋銀迋迋迋 GPIO5\n");
printf("GND 迋迋迋 GPIO4\n");
}
//====================================================================
=======
// Function : Show_Fail()
// Input : -
// Change : -
// Return : -
// Description : Show Fail Message.
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Fail()
{
textcolor(LIGHTRED);
gotoxy(20,10); cprintf(" 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗 詗詗 詗 ");
gotoxy(20,11); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗 詗 ");
gotoxy(20,12); cprintf(" 詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗 詗 詗 ");
gotoxy(20,13); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗 詗 ");
gotoxy(20,14); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗詗 詗詗詗詗");
}
42
Page 43

Revision: 1.0
//====================================================================
=======
// Function : Show_Pass()
// Input : -
// Change : -
// Return : -
// Description : Show Pass Message.
//====================================================================
=======
void Show_Pass()
{
textcolor(LIGHTGREEN);
gotoxy(20,10); cprintf(" 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗");
gotoxy(20,11); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗 詗 詗 ");
gotoxy(20,12); cprintf(" 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗");
gotoxy(20,13); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗 詗");
gotoxy(20,14); cprintf(" 詗 詗 詗 詗詗詗詗 詗詗詗詗");
}
//====================================================================
=======
43
Page 44

檔名: ES6050_M10_0820_10am.doc
目錄: Z:\共用區\RD 交流區\Manual 暫存區(勿刪)
範本: C:\Documents and Settings\Roger_Nan\Application
Data\Microsoft\Templates\Normal.dot
標題: AR-ES0631
主旨:
作者: new
關鍵字:
註解:
建立日期: 2010/8/20 9:46:00 AM
修訂版編號: 5
前次更新日期: 2010/8/20 9:54:00 AM
前次存檔人員: Roger_Nan
編輯總時間: 9 分鐘
最後列印在: 2010/8/20 9:54:00 AM
最後列印的字數
頁數: 43
字數: 4,128 (約)
字元數: 23,532 (約)
 Loading...
Loading...