Page 1
,QVWDOODWLRQ0DQXDO
Y1-03-0177A
9HUVLRQ
31<5HY$
Page 2

Y1-03-0177A
Please read this first!
Warning:
Although ACR strives for accuracy in all its publications; this material may contain errors or
omissions, and is subject to change without prior notice. ACR shall not be made liable for any
specific, indirect, incidental or consequential damages as a result of its use. ACR
components may only be used in safety of life devices or systems, with the express written
approval of ACR, as the failure of such components could cause the failure of the ACR
device or system. If these fail, it is reasonable to assume that the safety of the user or other
persons may be endangered.
Copying of this document, and giving it to others and the use or communication of the contents
thereof, are forbidden without express authority. Offenders are liable to the payment of damages.
Weitergabe sowie Vervielfältigung dieser Unterlage, Verwertung und Mitteilung ihres Inhaltes
nicht gestattet, soweit nicht ausdrücklich zugestanden. Zuwiderhandlungen verpflichten zu
Schadenersatz.
Toute communication ou reproduction de ce document, toute exploitation ou communication
de son contenu sont interdites, sauf autorisation expresse. Tout manquement à cette règle
est illicite et expose son auteur au versement de dommages et intérêts.
Sin nuestra expresa autorización, queda terminantemente prohibida la reproducción total o
parcial de este documento, así como su uso indebido y/o su exhibición o comunicación a
terceros. De los infractores se exigirá el correspondiente resarcimiento de daños y perjuicios.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual I Version 1.0
Page 3

GLOBALWATCHTM UAIS Installation Manual
Y1-03-0177A
Index Page Number
GENERAL INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................... 1
1
1.1 DESCRIPTION OF AIS................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 AIS IN AN OPERATIONAL ENVIRONMENT ................................................................................ 2
1.3 AIS NETWORKS........................................................................................................................ 3
1.4 CARRIAGE REQUIREMENT ........................................................................................................ 4
1.4.1 Chapter V (Safety of Navigation) Regulation 19, of the SOLAS Convention................... 4
1.4.2 Accelerated Implementation of AIS:................................................................................. 4
2 GLOBALWATCHTM UAIS........................................................................................................... 5
2.1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................. 5
3 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................................................... 6
3.1 INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS ............................................................................................... 6
3.2 INSTALLATION OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................... 6
3.3 GENERAL INTERFACE DESCRIPTION......................................................................................... 8
3.4 INTERFACE NMEA DESCRIPTION: ........................................................................................... 9
3.4.1 Sensor Interface CH1, CH2, CH3 .................................................................................... 9
3.4.2 ECDIS – Presentation Interface CH 4 ............................................................................. 9
3.4.3 PILOT Port CH 5 ........................................................................................................... 10
3.4.4 LONG RANGE CH 8...................................................................................................... 10
3.4.5 DGPS – DGNSS Channel 9............................................................................................ 11
3.4.6 ALARM CIRCUIT – BIIT Channel 10............................................................................ 11
3.4.7 Proprietary Sentences .................................................................................................... 11
3.5 SENSOR NOTES........................................................................................................................ 12
3.6 SENSOR INSTALLATION .......................................................................................................... 13
3.6.1 Signal state definitions ................................................................................................... 13
3.6.2 Talker drive circuits ....................................................................................................... 13
3.6.3 Listener receive circuits ................................................................................................. 13
3.6.4 Electrical isolation ......................................................................................................... 13
3.6.5 Maximum voltage on the bus.......................................................................................... 13
3.6.6 Data transmission .......................................................................................................... 13
3.7 SENSOR INSTALLATION EXAMPLE: ......................................................................................... 14
3.7.1 Installation of an RS422 serial interface: ...................................................................... 14
3.7.2 Data format:................................................................................................................... 14
3.8 PIN-DESCRIPTION AIS-CABLE / SOCKET 50-PINS:................................................................. 15
3.9 PIN-DESCRIPTION AIS-CONNECTOR: ..................................................................................... 16
3.10 INSTALLATION OF VHF / GPS ANTENNAS............................................................................. 17
4 STARTING THE GLOBALWATCHTM UAIS ......................................................................... 20
4.1 SERVICE AND USER PASSWORDS: .......................................................................................... 20
4.2 CHANGING THE MMSI / IMO NUMBERS ............................................................................... 24
4.3 INPUTING VOYAGE RELATED DATA – (USER PASSWORD PROTECTED) ................................ 26
4.4 SETTING SHIP RELATED DATA – (USER PASSWORD PROTECTED)......................................... 27
5 TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................................................................... 29
5.1 READING AND UNDERSTANDING ALARMS: ............................................................................ 29
5.2 ALARM CODES........................................................................................................................ 30
5.3 TEXT MESSAGES..................................................................................................................... 31
6 ACCESSORIES............................................................................................................................ 32
7 TECHNICAL INFORMATION ................................................................................................. 33
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual II Version 1.0
Page 4

8 CONTACT AND SUPPORT INFORMATION ........................................................................ 33
Y1-03-0177A
9 APPENDIX ................................................................................................................................... 35
9.1 SAMPLES FOR BATTERY CALCULATION.................................................................................. 35
9.2 DRAWINGS AND APPROVALS ................................................................................................. 37
(1) Dimensional Drawings
(2) Type Approvals
(3) Connection Drawings
(4) Antenna Layout
(5) Sample for data telegrams
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual III Version 1.0
Page 5
History of Changes
Y1-03-0177A
Date
2003-04-30 1.0.2 Released
2003-06-30 1.0.3 Released
Version Status
Comments
Dimensional drawings as Annex
Wheelmark Certificate as Annex
Amendments for:
Power consummation,
Troubleshooting, grounding, external
fuse, battery calculation in Appendix
Responsible
A. Lesch
B. Werner
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual IV Version 1.0
Page 6

1 General Introduction
Y1-03-0177A
1.1 Description of AIS
What does the abbreviation AIS stand for?
AIS stands for:
“Automatic Identification System”
What is AIS?
According to IALA regulations, AIS is defined as follows:
Very simply, the AIS is a broadcast Transponder system, operating in the VHF maritime
mobile Band. It is capable of sending ship information such as identification, position
course, speed and more, to other ships and to shore. It can handle multiple reports at
rapid update rates and uses Self-Organizing Time Division Multiple Access (SOTDMA)
technology to meet these high broadcast rates and ensure reliable and robust ship to ship
operation.
What are the performance standards of AIS?
The IMO defines the performance standards as follows:
- Ship to Ship working
- Ship to Shore working, including Long Range Application
- Automatic and continuous operation
- Provision of information messaging
- Utilization of maritime VHF channels
Which modules make up an AIS-Transponder?
The Modules:
- DGPS / GPS receiver
- VHF Radio
- Antenna
- Computer (CPU)
- Power Supply
Appropriate application software connects the individual modules.
In which modes does AIS function?
AIS is required to function flawlessly in a variety of modes. The relevant regulations require:
The system shall be capable of
- An "autonomous and continuous" mode for operation in all areas. This mode
- An "assigned" mode for operation in an area subject to a competent authority
- A "polling or controlled" mode, where the data transfer occurs in response to
shall be capable of being switched to/from one of the following alternate modes by
a competent authority;
responsible for traffic monitoring such that the data transmission interval and/or
time slots may be set remotely by that authority;
interrogation from a ship or competent authority.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 1 Version 1.0
Page 7

1.2 AIS in an Operational Environment
Y1-03-0177A
This illustration depicts a typical AIS System, where two or more AIS
equipped vessels (and shore based systems) are automatically
communicating with each other.
On the bottom, a typical GlobalWatch
shown. The GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS is connected to the vessels emergency power supply,
TM
UAIS installation in a common environment is
and in connection with the VHF, and GPS-Antennas, the minimal requirements for
Transponder operation are fulfilled.
Both vessels in the above illustration are equipped with a GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS (or any
other certified AIS-Transponder). Due to “Time – Synchronization” they use the same
organization of free and allocated windows (Slots) in the shared VHF Data Link (this
method is called “Self Organized Time Division Multiple Access”) to send and receive
messages.
Without the necessity of any active interaction, both vessels know exactly who or what is
cruising nearby and where the individual object is heading.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 2 Version 1.0
Page 8

1.3 AIS Networks
Y1-03-0177A
The scenario below shows a full AIS coverage area (including all derivates and complete
shore infrastructure).
The Carriage Requirement currently applies exclusively to SOLAS Vessels, but following the
current international discussions on maritime security; it is common understanding that other
possible AIS users will follow very soon. Shore Based infrastructure will be among the first
groups to become AIS equipped.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 3 Version 1.0
Page 9

1.4 Carriage Requirement
Y1-03-0177A
1.4.1 Chapter V (Safety of Navigation) Regulation 19, of the SOLAS Convention.
IMO regulations require sea vessels from a size of 300 GT in international and 500 GT in
national waters to be equipped with an AIS-Transponder. The implementation of this
legislation began on 1. July 2002 and will be enforced in the following stages:
• July 2002 for all vessels built from this period onwards
• July 2003 for all passenger ships and all tankers which were built before 1. July 2002
• July 2004 for all ships of 50.000 GT and above which were built before 1. July 2002
• July 2005 for all ships from 10.000 GT up to under 50.000 which were built before
1. July 2002
• July 2006 for all ships from 3.000 GT up to under 10,000 which were built before
1. July 2002
• July 2007 for all ships from 300 GT up to under 3.000 which were built before
1. July 2002
• July 2008 for all other ships which do not travel in international waters and were built
before July 2002
In some cases, exemptions may be granted to such ships, which will be taken off sea within 2
years of legislation coming into effect.
Refer to IMO Recommendation ITU-R M.1371-1 and IALA-AIS-Guidelines
1.4.2 Accelerated Implementation of AIS:
ANNEX
AMENDMENTS TO THE TO THE INTERNATIONAL CONVENTION FOR THE SAFETY OF
LIFE AT SEA, 1974 AS AMENDED CHAPTER V - SAFETY OF NAVIGATION
Regulation 19 - Carriage requirements for ship borne navigational Systems and equipment
states:
1 The existing subparagraphs .4, .5 and .6 of paragraph 2.4.2 are replaced by the
following:
“4 in the case of ships, other than passenger ships and tankers,
of 300 gross tonnage and upwards, but less than 50.000 gross tonnage, not
later than the first safety equipment survey' after 1 July 2004 or by 31
December 2004, whichever occurs earlier; and”
2 The following new sentence has been added at the end of the existing subparagraph
7 of paragraph 2.4;
“Ships fitted with AIS shall maintain AIS in operation at all times except where
international agreements, rules or standards provide for the protection of
navigational information.”
Refer to the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea, 1974 (SOLAS), held at
IMO, 9-13 December 2002
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 4 Version 1.0
Page 10
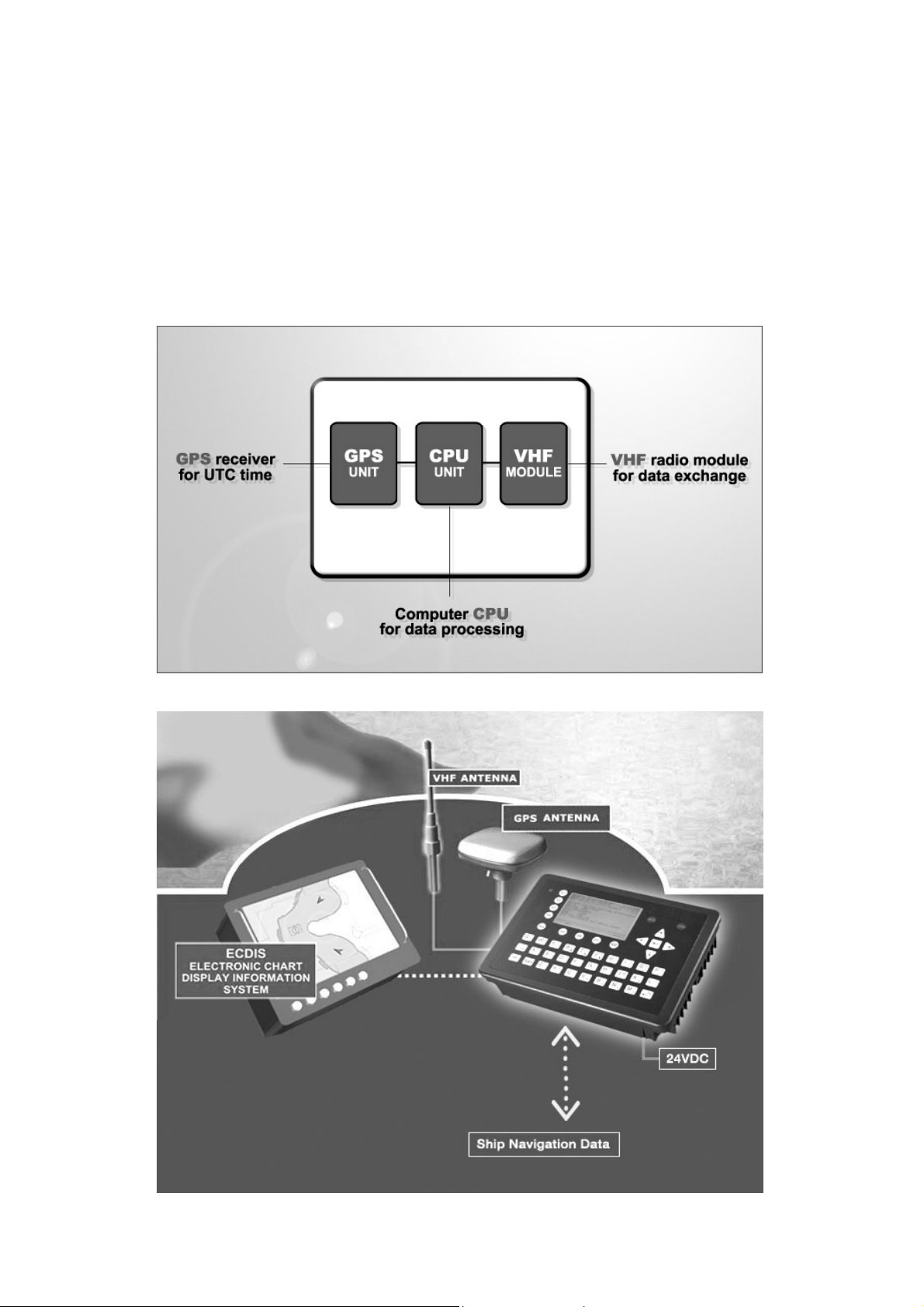
Y1-03-0177A
2 GLOBALWATCHTM UAIS
2.1 System Overview
Unlike other AIS devices, the GlobalWatch
cabinet. Additionally, the GlobalWatch
features (easy mounting & installation, environmental protection, smallest dimensions).
TM
TM
UAIS combines all required functions into one
UAIS gives the operator a number of additional
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 5 Version 1.0
Page 11

Y1-03-0177A
3 Installation
3.1 Installation Requirements
General Requirements
Please note that international conventions, regulations, instructions and guidelines have to be
adhered to when installing the GlobalWatch
The following points must be observed before installation can commence:
- Permission by the local authority to install such a device must be granted.
- Trained service personnel must undertake the installation.
- The GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS must be fitted in a suitable place on the bridge.
- The VHF and GPS Antennas must be installed in a suitable position, where excellent
reception conditions apply (refer to Chapter 3.10 Installation of VHF antenna – page
17)
- All available interfaces must be installed.
- The vessels power supply must suffice, and the GMDSS power supply has to be
used.
- Installation of the pilot plug in conning position (close to the pilot working place).
3.2 Installation Overview
Survey
AIS is considered part of the ship’s radio station and is surveyed together with radio
installation. Surveys on SOLAS Convention ships should be carried out in accordance with
the rules laid down in IMO Res. A 746(18) "Survey Guidelines under the harmonised system
of survey and certification" (R) 8, and "Protocol of 1988 relating to the International
Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea, 1974."
The GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS consists of one unit, which integrates all necessary modules.
TM
UAIS.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 6 Version 1.0
Page 12

Step-by-Step Installation Procedure:
Y1-03-0177A
• Mount the GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS close to ships operator workstation for traffic
surveillance and maneuvering.
• Use the VHF adapter cable together with the VHF plug and TNC plug to
connect the VHF and GPS antenna cables as well as the antennas.
• The sensors, ECDIS, PC, pilot case, long range devices and auxiliary displays can be
connected to the GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS cabinet by the AIS cable respectively the
connection box. The device is driven by a 24V DC 7A supply, which is connected to
the power terminal at the connection box. The AIS should be connected to an
emergency power source. A battery capacity calculation together with GMDSSequipment is needed! Please refer to Appendix 9.1 for examples of battery capacity
calculations.
• After performing these steps, the GlobalWatch
TM
• The GlobalWatch
UAIS has a ground terminal which has to be connected to ship
TM
UAIS automatically starts operation.
ground.
• Now configure the required initial system parameters according to Chapter 4 “Starting
the GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS” on page 20.
Connection Diagram
GPS VHF
Combined Antenna GPS/VHF
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS
Ground
GPS/VHF Interface Cable
AIS Cable
Cable Integrated Splitter
Fuse
Connection Box
Note: The ACR connection box includes a fuse of 6,3A. If it is not used, then the Unit has to
be protected against high current by an external slow blow fuse of 6,3A!
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 7 Version 1.0
Page 13
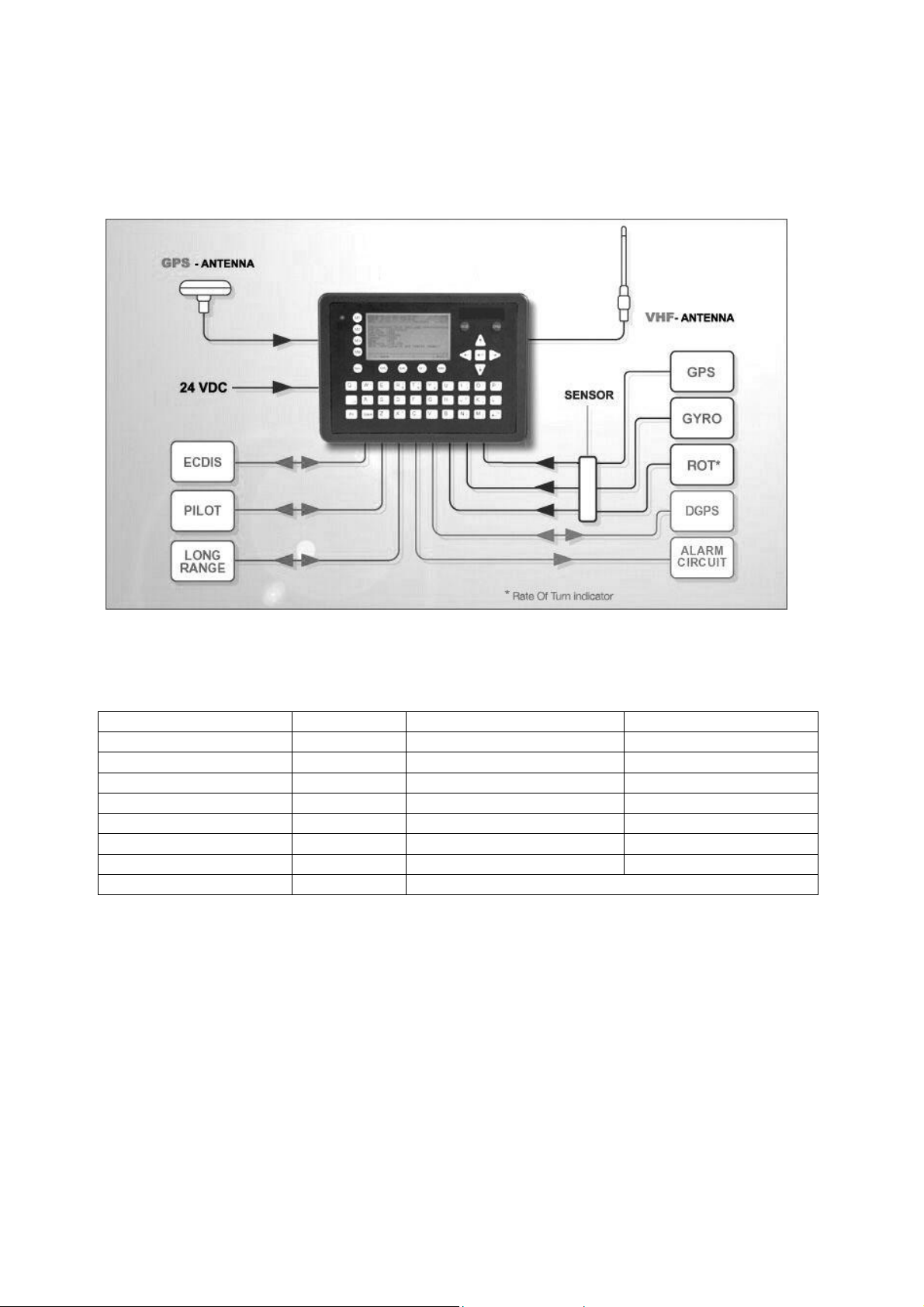
Components and Interfaces
Y1-03-0177A
The diagram below illustrates which devices can be connected to the GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS.
For a detailed description of sensor connecting e.g. an existing Gyro to the GlobalWatch
UAIS refer to Chapter 3 “Sensor Installation” on page 13.
TM
3.3 General Interface Description
Interface Designation Speed Direction
Sensor 1 CH 1 4800bps or 38400bps Input
Sensor 2 CH 2 4800bps or 38400bps Input
Sensor 3 CH 3 4800bps or 38400bps Input
ECDIS CH 4 38400bps Input/Output
PILOT CH 5 38400bps Input/Output
LONG RANGE CH 8 38400bps Input/Output
DGPS (RTCM SC104) CH 9 9600bps Input/Output
ALARM CIRCUIT CH 10 Dry relay contact (power off and alarm state closed)
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 8 Version 1.0
Page 14

3.4 Interface NMEA Description:
Y1-03-0177A
3.4.1 Sensor Interface CH1, CH2, CH3
Sentence Formatters Used Fields
DTM
GBS
GGA
GLL
GNS
HDT
OSD
RMC
ROT
VBW
VTG
3.4.2 ECDIS – Presentation Interface CH 4
Sentence Formatters
ABK
ACA
ACK
AIR
ALR
ABM
BBM
DSC
DSE
DSI
DSR
LRI
LRF
SSD
TXT
VSD
VDM
VDO
Datum Reference 1
GNSS satellite Fault Detection 1 - 5
Global Positioning System Fix Data 1 - 7; 10
Geographic Position – Latitude/Longitude 1 - 7
GNSS Fix Data 1 - 7
Heading, True 1
Own Ship Data 1 - 6; 9
Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data 1 – 6; 9; 12
Rate Of Turn 1 - 2
Dual Ground/Water Speed 4 - 6
Course Over Ground and Ground Speed 1; 5; 7; 9
Direction
UAIS Addressed and binary broadcast acknowledgement out
AIS Channel assignment message in / out
Acknowledge Alarm in
UAIS Interrogation Request in
Set Alarm State out
UAIS Addressed binary and safety related message in
UAIS Broadcast Binary Message in
Digital Selective Calling Information out
Expanded Digital Selective Calling out
DSC Transponder Initialize out
DSC Transponder Response out
UAIS Long-Range Interrogation out
UAIS Long-Range Function out
Station Static Data in
Text Transmission out
Voyage Static Data in
UAIS VHF Data-link Message out
UAIS VHF Data-link Own-vessel report out
Used Fields
All fields are provided
for Input and Output.
For detailed information
please refer to
IEC 61993-2 / NMEA
0183 HS V3.0 for
detailed field
information.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 9 Version 1.0
Page 15

3.4.3 PILOT Port CH 5
Y1-03-0177A
The used sentence Formatters are the same as before described at the ECDIS Port.
Note:
A pilot input/output port is part of an AIS Class A station. A plug connected to this port should
be installed on the bridge near the pilot’s operating position so that a pilot can connect a
Personal Pilot Unit (PPU) if required. Also a power connector for the Pilot Unit should be
available nearby.
The pilot plug should be configured as follows: (Refer to SUB-COMMITTEE ON SAFETY OF
NAVIGATION NAV48/18 2.4.2002)
• AMP/Receptacle (Square Flanged (-1) or Free-Hanging (-2)), Shell size 11, 9-pin,
Std. Sex 206486-1/2 or equivalent with the following terminations:
- Tx A (out-) is connected to Pin 1
- Tx B (out+) is connected to Pin 4
- Rx A (in-) is connected to Pin 5
- Rx B (in+) is connected to Pin 6
- Shield is connected to Pin 9
3.4.4 LONG RANGE CH 8
The AIS long-range function requires a compatible long-range communication system (e.g.
Inmarsat-C or MF/HF radio as part of GMDSS) - a connection between this communication
system and the Class A mobile unit is possible.
This connection is required in order to activate the LR function of the AIS. Its input/output port
must meet the IEC 61162-2 requirements.
Sentence Formatters Direction
UAIS Long Range Interrogation Input
LRI
LRF
LR1
LR2
LR3
UAIS Long-Range Function Input / Output
UAIS Long-Range Reply Sentence l Output
UAIS Long-Range Reply Sentence 2 Output
UAIS Long-Range Reply Sentence 3 Output
Field Information:
All Fields are provided for Input and Output.
For detailed information please refer to
IEC 61993-2 / NMEA 0183 HS V3.0 for detailed field
information.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 10 Version 1.0
Page 16

3.4.5 DGPS – DGNSS Channel 9
Y1-03-0177A
Field / Protocol information:
All Fields are provided, for detailed information please refer to
ITU-R M.823-2 / RTCM SC 104 for detailed field information.
3.4.6 ALARM CIRCUIT – BIIT Channel 10
The AIS requires that an alarm output (relay) must be connected to an audible alarm device
or the ships alarm system, if available.
Alternatively, the BIIT (built-in integrity test) alarm system may use the alarm messages
output on the presentation port (ECDIS Port Channel 5), provided the ECDIS alarm system is
connected and AIS compatible.
3.4.7 Proprietary Sentences
The proprietary ACR NMEA sentences have the NMEA registered manufacture talker ID
“NAU”. The $PNAU sentences are an addition to the standard sentences and offer other
manufactures full remote control to the transponder. The NMEA Interface developer’s manual
includes the full description of how to use the proprietary ACR manufacturer sentences.
List of ACR related proprietary sentences:
Proprietary NMEA-Sentences $PNAU
MID – Mobile (MMS) Id
ASD – Advanced Ship Data
RCS – Read Configuration Settings
CPW – Check Password
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 11 Version 1.0
Page 17

3.5 Sensor notes
Y1-03-0177A
External Sensor
The AIS has interfaces (configurable as IEC 61162-1 or 61162-2) for position, bottom track
(BT) speed, heading and rate of turn (ROT) sensors. In general, sensors installed in
compliance with other carriage requirements of SOLAS Chapter V should be connected to
the AIS System.*1. The sensor information transmitted by AIS should be the same
information being used for navigation of the ship. Interfacing problems might occur if the
existing on board sensors do not have serial (IEC 61162) outputs. A converter is needed to
translate the non conform data to IEC 61162 – sensor data. For Example Raytheon Nav
Data Repeater 133-812
*1)
The fact that AIS is fitted on board a vessel does NOT entail the need to install additional sensors
other that those stated in the carriage requirements.
External GPS
GNSS position sensors normally have IEC 61162 outputs suitable for direct AIS interfacing.
However, it is important to note that:
• The Geodetic Datum of the position data is transmitted by the sensor in WGS84 so that an
IEC 61162 DTM sentence is configured.
• AIS is able to process two reference points for it’s antenna position, one for external, and
one for an internal sensor. If more than one external reference point is used, the appropriate
information needs to be input to the AIS, so that the reference point information is suitably
adjusted.
External Heading
A gyrocompass providing heading information is a mandatory sensor input to the AIS. A
converter unit (synchro or step-signal converter to NMEA 0183 v.3.0 for example Raytheon
converter type: 133-812) will be needed for AIS connection in the case that the ship’s
gyrocompass does not provide IEC 61162 output.
External Speed and Course
If a bottom track (BT)-log for speed over the ground (SOG) is available, it may be connected.
A converter (for example Raytheon converter type: 133-812) is needed if the BT-log does not
provide IEC 61162 outputs
External Rate of Turn
Not all ships will carry a Rate-Of-Turn (ROT) indicator according to IMO A.526. However, if a
rate-of-turn indicator is available and it includes an IEC 61162 interface, it should be
connected to the AIS.
If ROT information is not available from a ROT indicator, it may (optionally) be derived from
heading information through:
• The gyrocompass itself,
• An external converter unit (see Heading),
• The AIS itself (calculated ROT).
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 12 Version 1.0
Page 18

Y1-03-0177A
3.6 Sensor Installation
3.6.1 Signal state definitions
The idle, marking, logical 1, OFF or stop bit state is defined by a negative voltage on line A
with respect to line B, as in IEC 61162-1.
The active, spacing, logical 0, ON or start bit state is defined by a positive voltage on line A
with respect to line B, as in IEC 61162-1.
3.6.2 Talker drive circuits
The drive circuit meets the requirements of ITU-T V.11. The maximum output current is
I
= 50mA on each port.
max
3.6.3 Listener receive circuits
Multiple listeners may be connected to a single talker. The listener's receive circuit complies
with ITU-T V.11. Optional termination resistors (120Ohm) for the Input-lines are provided in
the Connection Box. The input terminals A, B and C are electrically isolated from the
remaining electronics of the listening device.
The input impedance is 30kOhm between A and B lines without the termination resistors. The
minimum input voltage is ±0,3V.
3.6.4 Electrical isolation
Within a listener there are no direct electrical connection between the signal lines A and B,
the signal ground C or the shield to ship's mains ground or power line. This isolation is in
accordance with IEC 60945.
3.6.5 Maximum voltage on the bus
The maximum applied voltage between signal lines A and B and between either line and
ground C is in accordance with ITU-T V.11. For protection against miswiring and for
unintended connection to earlier TALKER designs, all receive circuit devices are capable of
withstanding 15 V between both lines and signal ground for an indefinite period.
3.6.6 Data transmission
Data is transmitted in serial asynchronous form in accordance with 1.2. The first bit is a start
bit and is followed by data bits, least-significant-bit first.
The following parameters are used:
– baud rate 38 400 (bits/s) resp. 4 800 (bits/s)
– data bits 8 (D7 = 0), parity none;
– stop bits 1.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 13 Version 1.0
Page 19
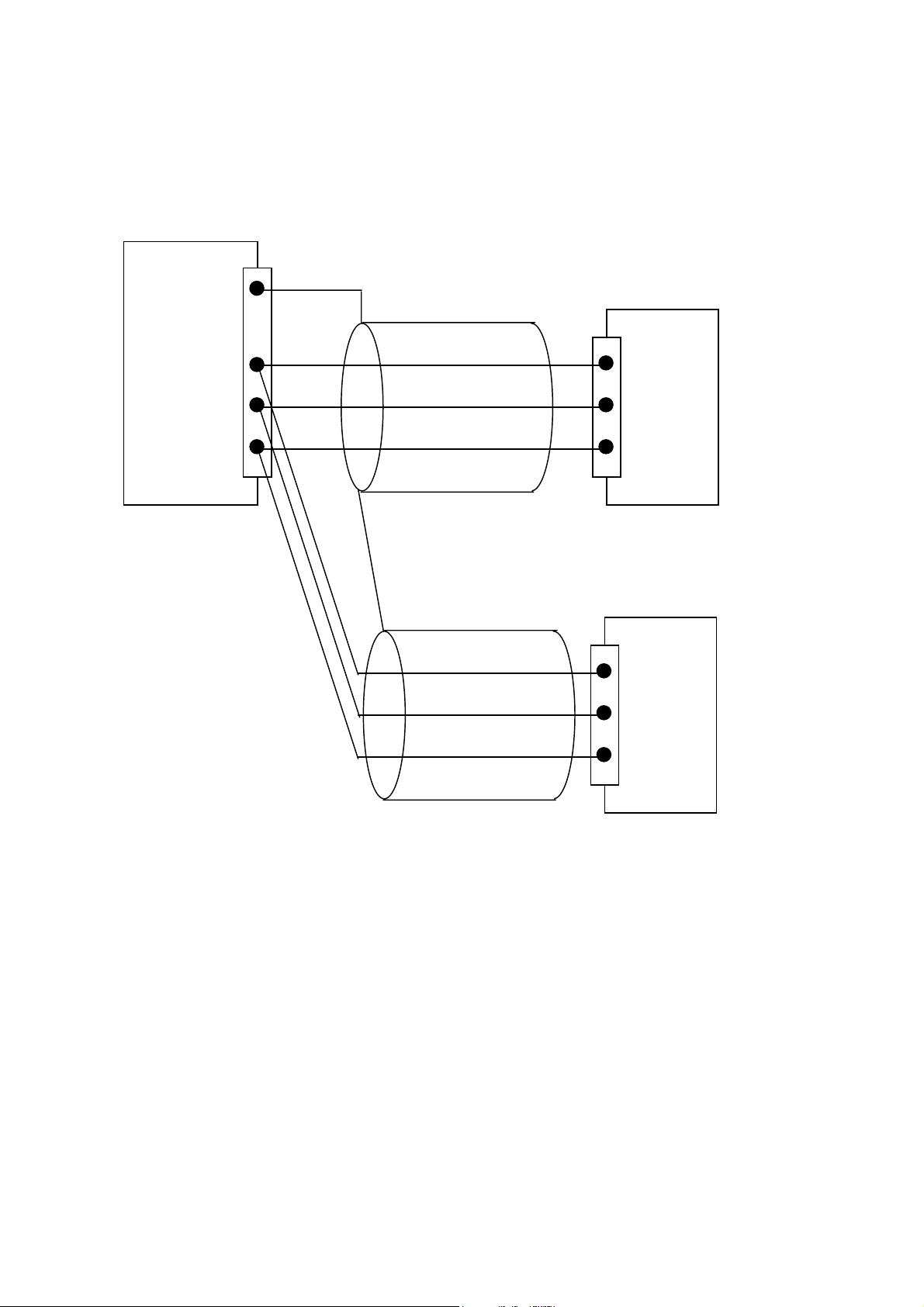
3.7 Sensor installation example:
Y1-03-0177A
3.7.1 Installation of an RS422 serial interface:
Each Interface on the Transponder is a RS422 serial interface!
Shields
A
B
C (GND)
Talker (e.g.: GPS)
A
B
C (GND)
Listener (AIS)
A
B
C (GND)
Listener
3.7.2 Data format:
The talker provides the following data (NMEA 0183 HS V3.0):
$GPDTM,W84,,,,,,,P90*48
$GPGLL,5330.1234,N,01001.2345,E,142555.00,A,A*6A
$GPVTG,350.0,T,,M,10.0,N,,K,A*14
It is recommended that all three (in this case) NMEA Sentences are provided each second.
The maximal delay is about 5sec.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 14 Version 1.0
Page 20

3.8 Pin-Description AIS-Cable / Socket 50-Pins:
Y1-03-0177A
TxA Æ out –
TxB Æ out +
RxA Æ in –
RxB Æ in +
1 CH5_out+ 34 Spare
18 Ch4_out+
2 CH5_out- 35 Spare
19 CH4_out-
3 CH5_gnd 36 Spare
20 CH4_gnd
4 CH5_in+ 37 Spare
21 CH4_in+
5 CH5_in- 38 Spare
22 CH4_in-
6 CH6_Vin 39 CH9_gnd
23 CH8_in+
7 CH6_gnd 40 CH9_out-
24 CH8_in-
8 CH6_CANL 41 CH9_in-
25 CH8_gnd
9 CH6_CANH 42 CH9_in+
26 CH8_in+
10 CH1_in- 43 CH9_out+
27 CH8_in-
11 CH1_gnd 44 Spare
28 Spare
12 CH1_in+ 45 Spare
29 CH3_in-
13 CH2_in- 46 CH10_1
30 CH3_gnd
14 CH2_gnd 47 CH10_2
31 CH3_in+
15 CH2_in+ 48 Vin_gnd
32 Vin_gnd
16 Vin+ (24V) 49 Vin_gnd
33 Vin+ (24V)
17 Vin+ (24V) 50 Spare
CH1 Sensor CH4 ext. Display CH8 Long Range
CH2 Sensor CH5 aux. Display CH9 DGNSS
CH3 Sensor CH6 opt. 61162-3 CH10
Spare Do not use
AIS Cable/Socket ( Sub-D 50 Plug )
BIIT / Relay
(max. 30V DC / 1A)
GlobalWatch
AIS Plug and Socket
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 15 Version 1.0
Page 21

3.9 Pin-Description AIS-Connector:
A
A
Y1-03-0177A
AIS -Cable Sub-D 50 Plug
Note:
TxA Æ out –
TxB Æ out +
RxA Æ in –
RxB Æ in +
CH1_in+ 12
CH1_in- 10
CH1_gnd 11
CH2_gnd 14
CH2_in+ 15
CH2_in- 13
CH3_in+ 31
Sensor 1,2,3 ECDIS Pilot Port Long Range DGPS
CH3_in- 29
CH3_gnd 30
CH4_gnd 20
CH4_in+ 21
CH4_in- 22
CH4_out+ 18
CH4_out- 19
CH5_in+ 4
CH5_in- 5
CH5_out+ 1
CH5_out- 2
CH5_gnd 3
CH8_gnd 25
CH8_in+ 26
CH8_in- 27
CH8_out+ 23
CH8_out- 24
CH9_in+ 42
CH9_in- 41
CH9_out+ 43
CH9_out- 40
CH9_gnd 39
Spare_gnd 36
Spare_in+ 35
Spare_in- 34
Spare_out+ 38
Spare_out- 37
CH6_CANH 9
CH6_CANL 8
CH6_Vin 6
CAN
CH6_gnd 7
CH10_1 46
BIIT Relais
CH10_2 47
16
17
33
48
49
32
+ 24 VDC/max 5A rd
+ 24 VDC rd
+ 24 VDC rd
0 V bl
0 V bl
0 V bl
e.g. GPS
GLL, VTG,
DTM
e.g. GYRO
HDT,ROT
e.g ECDIS
viewer
6
5
4
1
NC
e.g.
Inmarsat
unit
NC
NC
NC
Service
unit
larm unit
SPEED
LOG
VBW
AMP
Pilot
Plug
RTCM
SC104
unit
CAN
unit
Black BK
White WH
Red RD
Green GN
Brown BR
Blue BL
Orange OR
Yellow YL
Violet VI
Gray SL(Slate)
Pink PK
IS-Cable
Open
1 WH/BK
2 BR/BK
3 SL/GN
7 YL/SL
5 PK/GN
6 YL/PK
9 GN/BL
10 YL/BL
11 GN/RD
17 YL/RD
13 GN/BK
14 YL/BK
15 SL/BL
16 PK/BL
19 SL/RD
20 PK/RD
21 SL/BK
22 PK/BK
23 WH/SL
29 SL/BR
25 WH/PK
26 PK/BR
27 WH/BL
28 BR/BL
31 WH/YL
32 YL/BR
33 WH/GN
34 BR/GN
35 SL/PK
41 RD/BL
37 SL
38 PK
39 GN
40 YL
43 WH
44 BR
45 RD
46 BL
49 BK
50 VI
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 16 Version 1.0
Page 22

3.10 Installation of VHF / GPS Antennas
Y1-03-0177A
Interference to the Ship’s VHF Radiotelephone
The AIS ship borne equipment, like any other ship borne transceiver operating in the VHF
maritime band, may cause interference to a ship’s VHF radiotelephone. Because AIS is a
digital system, this interference may occur as a periodic (e.g. every 20 seconds) soft clicking
sound on the ship’s radiotelephone. This affect may become more noticeable if the VHF
radiotelephone antenna is located close to the AIS VHF antenna, and when the
radiotelephone is operating on channels near the AIS operating channels (e.g. channels 27,
28 and 86).
Attention should be paid to the location and installation of the various antennas, in order to
support the antenna characteristics in the best possible way.
VHF Antenna Installation
Antenna Location
Location of the mandatory AIS VHF-antenna should be carefully considered. Digital
communication is more sensitive than analogue/voice communication to interference created
by reflections caused by obstructions such as masts and booms. It may be necessary to
relocate the VHF radiotelephone antenna to minimize interference effects.
To minimise interference effects, the following guidelines apply:
• The AIS VHF antenna should have omni directional vertical polarisation providing 3 to 5
dB gain.
• The AIS VHF antenna should be placed in an elevated position, as free standing as
possible, with a minimum of 2 metres in horizontal direction from constructions made of
conductive materials. The antenna should not be installed close to any large vertical
obstruction. The AIS VHF antenna should have a visible sky of 360°.
• The AIS VHF antenna should be installed at least 3 meters away from interfering highpower energy sources such as radar and other transmitting radio antennas, and out of the
way of the transmitting beam.
• There should not be more than one antenna on each level. The AIS VHF antenna should
be mounted directly above or below the ship’s primary VHF radiotelephone antenna, with
no horizontal separation and a minimum of 2 metres vertical separation. If it is located on
the same level as other antennas, the distance apart should measure at least 10 metres.
• See also sample for antenna layout in Appendix 9.2 (Drawings and Approvals)
Cabling
The cable should be kept as short as possible to minimise attenuation of the signal. Double
shielded coaxial cables equal to or better than RG214 are recommended.
RG214 at VHF attenuation per meter of app. 0,07 dB/m (45m = 3,15db)
VHF AIS frequency app. 162MHz
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 17 Version 1.0
Page 23

All outdoor connectors on the coaxial cables should be fitted with preventive isolation, such
Y1-03-0177A
as shrink-stocking with silicone to protect the antenna cable against water penetration.
Coaxial cables should be installed in separate signal cable channels/tubes, and at least 10
cm away from any power supply cables. Crossing of cables should take place at right angles
(90°). Coaxial cables should not be exposed to sharp bends, which may lead to changes to
the characteristic impedance of the cable. The minimum bend radius should be 5 times the
cables outside diameter.
Grounding
Coaxial down-leads must be used for all receiving antennas, and the coaxial screen should
be connected to the ground at one end.
GNSS Antenna installation
A Class A AIS must be connected to a GNSS antenna.
Location
The GNSS antenna must be installed where it has a clear view of the sky, so that it accesses
the horizon freely through 360°, with a vertical observation of 5 to 90 degrees above the
horizon. Small diameter obstructions, such as masts and booms, do not seriously impair
signal reception, but such objects must not eclipse more than a few degrees of any given
bearing.
The antenna must be located at least three meters away from, and out of the transmitting
beam of high-power transmitters (S-Band Radar and/or Inmarsat systems). This includes the
ship’s own AIS VHF antenna, if it is designed and installed separately. See also sample for
antenna layout in Appendix 9.2 (Drawings and Approvals)
If a DGNSS system is included or connected to the AIS system, the installation of the
antenna should be undertaken in accordance with IEC 61108-4, Edition 1.
Cabling
To achieve optimum performance, the gain of the antenna pre-amplifier should match the
cable attenuation. The resulting installation gain (pre-amplifier gain - cable attenuation)
should be within 0 to 10 dB.
RG214 at GPS attenuation per meter of app. 0,35 dB/m (45m = 15,75dB)
GPS frequency app. 1,2GHz
The coaxial cable between the antenna and the AIS ship borne station connector should be
routed directly, in order to reduce electromagnetic interference. The cable should not be
installed close to high-power lines, such as radar or radio-transmitter lines, or near the AIS
VHF antenna cable. A space of one meter or more is recommended in order to avoid
degradation due to RF-coupling. Crossing of antenna cables should take place at 90 degrees,
to minimise magnetic field coupling.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 18 Version 1.0
Page 24

Y1-03-0177A
Antenna Layout
The position of the VHF und GNSS – antennas must be added to the existing antenna layout
of the vessel.
Power Supply
The GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS must be supplied from the emergency power source. A further
requirement is to connect AIS to the reserve power source of the GMDSS. A new battery
capacity calculation must then be undertaken. See sample in 9.1 (Samples for battery
calculation)
Following documents are needed for the installation approval of the classification
• Antenna Layout (arrangement)
• Battery Calculation
• Connection / Block – Diagram with locations
• Type Approval Certificate
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 19 Version 1.0
Page 25

Y1-03-0177A
4 Starting the GlobalWatchTM UAIS
After completing the hardware, antennas and external equipment installation, the initial
system start-up can commence. To start the system, connect the GlobalWatch
the power supply.
The next step is to enter the configuration like password and the MMSI number.
4.1 Service and User Passwords:
The Transponder system is equipped with two separate Passwords.
1) The User Password, which is the lower security level allows access to all menus except
Menu 6: Service Configuration - please refer to the User Manual for further details on
password protection.
2) The Service Password is required in order to enter the Service Configuration Menu. This is
a higher security level than can be accessed with the User Password and therefore ensures
that the Service Configuration is protected, and limited to authorized service personnel.
The master of the vessel has to ensure that only authorised persons are allowed to make
changes to the Service Configuration and ensures that the newly reset password is stored
very carefully, as it can not be reset from the default “NAUT” a second time.
A master key is not available.
Changing the Service Password
Select “Service Configuration” from the Main Menu with the cursor button [Up] & [Down] or
press Nr. 6 on the keyboard.
TM
UAIS with
N 1^19' E 0^13' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | Menu
-----| |
| +- 1. Messages
View | +- 2. AIS Status
| +- 3. Voyage Settings
-----| +- 4. Ship Settings
| +- 5. Transponder Configuration
Msg. | +- 6. Service Configuration
| +- 7. Display Settings
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
Note:
The User and Service Passwords are set to “NAUT” – please reconfigure them immediately
after Transponder initial operation. Store the new passwords very carefully.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 20 Version 1.0
Page 26

Y1-03-0177A
The password query field appears. Input new Service Password and press [Enter].
N 1^24' E 0^17' |1>0.10|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
----------------------------------------
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Service password protected!
Please enter service password:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--------------------------------------- | Enter | | | Exit
Select Submenu 1 “Change Service Password” with cursor button [Up] & [Down] by pressing
Nr. 1 on the keyboard.
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | 6. Service Configuration
-----| |
| +- 1. Change Service Password
View | +- 2. User Password Settings
| +- 3. Change MMSI / IMO
-----| +- 4. Restore Factory Settings
|
Msg. |
|
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 21 Version 1.0
Page 27

Y1-03-0177A
Enter the new Password:
Repeat the new Password:
A minimum of 4, a maximum of 8 characters are allowed. Should the new password include
numbers, use the shift key to generate them.
N 1^25' E 0^18' |1>0.10|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
******* Change Service Password ********
Enter new password :
Repeat new password:
{Length: 4..8 characters}
--------------------------------------- | Save | | | Back
Press Save to store the change.
Changing the User Password
Select Submenu 2 “User Password Settings” with cursor button [Up] & [Down] by pressing Nr.
2 on the keyboard.
GlobalWatch
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | 6. Service Configuration
-----| |
| +- 1. Change Service Password
View | +- 2. User Password Settings
| +- 3. Change MMSI / IMO
-----| +- 4. Restore Factory Settings
|
Msg. |
|
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 22 Version 1.0
Page 28

Select Submenu 1 “Change User Password” with cursor button [Up] & [Down] by pressing Nr.
Y1-03-0177A
1 on the keyboard.
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | 6-2. User Password Settings
-----| |
| +- 1. Change User Password
View | +- 2. Change Password Protection
|
-----|
|
Msg. |
|
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
Enter the new Password:
Repeat the new Password:
A minimum of 4, a maximum of 8 characters are allowed. Should the new password include
numbers, use the shift key to generate them.
N 1^25' E 0^18' |1>0.10|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
******* Change User Password ***********
Enter new password :
Repeat new password:
{Length: 4..8 characters}
--------------------------------------- | Save | | | Back
Press Save to store the changes.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 23 Version 1.0
Page 29

Y1-03-0177A
4.2 Changing the MMSI / IMO Numbers
Select “Service Configuration” from the Main Menu with the cursor button [Up] & [Down] or
press Nr. 6 on the keyboard.
N 1^19' E 0^13' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | Menu
-----| |
| +- 1. Messages
View | +- 2. AIS Status
| +- 3. Voyage Settings
-----| +- 4. Ship Settings
| +- 5. Transponder Configuration
Msg. | +- 6. Service Configuration
| +- 7. Display Settings
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
Input Service Password and press [Enter].
N 1^23' E 0^16' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
----------------------------------------
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Service password protected!
Please enter service password:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--------------------------------------- | Enter | | | Exit
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 24 Version 1.0
Page 30

Y1-03-0177A
Select Submenu 3 “Change MMSI/IMO” with cursor button [Up] & [Down] by pressing Nr. 3
on the keyboard.
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | 6. Service Configuration
-----| |
| +- 1. Change Service Password
View | +- 2. User Password Settings
| +- 3. Change MMSI / IMO
-----| +- 4. Restore Factory Settings
|
Msg. |
|
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
Input new MMSI / IMO Numbers and press [Save] to store input data. Press [Back] to return
to the Submenu without saving.
Note:
Data input is limited to 9 characters.
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1> N/A|2>0.00|3>0.10nm
********** Change MMSI / IMO ***********
MMSI :1193046
IMO No.:303174162
---------------------------------------NUM| Save | | | Back
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 25 Version 1.0
Page 31

Y1-03-0177A
4.3 Inputing Voyage Related Data – (User Password Protected)
Select “Voyage Settings” from the Main Menu with the cursor button [Up] & [Down]
or press Nr. 3 on the keyboard
Note:
The default User Password is set to “NAUT” – please reconfigure it immediately after
Transponder initial operation
N 1^20' E 0^13' |1> N/A|2>0.00|3>0.10nm
|--------------------------------- | Menu
-----| |
| +- 1. Messages
View | +- 2. AIS Status
| +- 3. Voyage Settings
-----| +- 4. Ship Settings
| +- 5. Transponder Configuration
Msg. | +- 6. Service Configuration
| +- 7. Display Settings
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM|Select->| | |<-Back
The password query field appears. Input new User Password and press [Enter].
N 1^31' E 0^24' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
----------------------------------------
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
User password protected!
Please enter user password:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--------------------------------------- | Enter | | | Exit
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 26 Version 1.0
Page 32

Y1-03-0177A
Scroll the Voyage Data Fields with [Enter] and input own vessel data. Select a default Cargo
Type and NavStat Setting with the cursor buttons [Left] & [Right].
Save the new settings by pressing [Save], and return to the Main Menu Screen by pressing
[Exit]. Press [Back] to return to the Main Menu without saving any changes.
N 1^18' E 0^12' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
*********** Voyage Settings ************
Cargo :<N/A or harmless>
Draught :24.8m
PoB :1
Dest. :CASABLANCA
ETA :10/13 12:31
NavStat.:Engaged in fishing
--------------------------------------- | Save | | | Back
4.4 Setting Ship Related Data – (User Password Protected)
Select “Ship Settings” with cursor button [Up] & [Down]
or press Nr. 4 on the keyboard.
Note:
The default User Password is set to “NAUT” – please reconfigure it immediately after
Transponder initial operation
N 1^23' E 0^16' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
|--------------------------------- | Menu
-----| |
| +- 1. Messages
View | +- 2. AIS Status
| +- 3. Voyage Settings
-----| +- 4. Ship Settings
| +- 5. Transponder Configuration
Msg. | +- 6. Service Configuration
| +- 7. Display Settings
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM| Select->| | |<-Back
Input new User Password and press [Enter].
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 27 Version 1.0
Page 33

N 1^23' E 0^16' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
Y1-03-0177A
----------------------------------------
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
User password protected!
Please enter user password:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
--------------------------------------- | Enter | | | Exit
Scroll the Ship Settings Fields with [Enter] and input own vessel data.
Example: Length = 220m, A = 200m, Beam = 43m, D = 33m
RefPointExt = A200 B20 C10 D33m (location of the external GPS antenna)
A = the distance from bow to the antenna
B= the distance from the antenna to the stern
C = the distance from the port side to the antenna
D = the distance from the antenna to the starboard side
Enter A200D33 (without spaces, no decimals, no commas)
The full line as shown will be displayed: RefPtExt: A200 B20 C10 D33m
B and C are calculated by the AIS.
Enter RetPtInt (location of the internal GPS antenna) in the same way.
Select a default ShipType with the cursor button [Left] & [Right].
Save the new settings by pressing [Save]. Press [Back] return to the Main Menu Screen
without saving any changes.
GlobalWatch
N 1^19' E 0^12' |1>0.01|2>1.30|3>1.80nm
************ Ship Settings *************
/\ +
CallSign:D11233 / \|
ShipName:ANDREA DORIA | |
Length :220m | A
Beam :43m | x--+
RefPtExt:A200 B20 C10 D33m | | B
RefPtInt:A190 B30 C20 D23m +-C-+D-+
ShipType: Pilot vessel
--------------------------------------- | Save | | | Back
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 28 Version 1.0
Page 34

5 Troubleshooting
Y1-03-0177A
5.1 Reading and understanding Alarms:
The GlobalWatch
the user about major system malfunctions and failings in the connected sensors.
The Alarm Status informs the user about all active Alarms. The Alarm will be disabled and
deleted from the Alarm Status, as soon as the displayed problem has been rectified.
The TXT status displays additional sensor information and the UTC clock status.
See tables (page 30) for Alarm and TXT Messages.
Select “AIS Status” with cursor button [Up] & [Down]
or press Nr. 2 on the keyboard.
TM
UAIS differentiates between Alarm and TXT messages. An Alarm informs
N 1^19' E 0^12' |1> N/A|2>0.00|3>0.10nm
|--------------------------------- | Menu
-----| |
| +- 1. Messages
View | +- 2. AIS Status
| +- 3. Voyage Settings
-----| +- 4. Ship Settings
| +- 5. Transponder Configuration
Msg. | +- 6. Service Configuration
| +- 7. Display Settings
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM|Select->| | |<-Back
Select “Alarm Status” or “TXT Status” with cursor button [Up] & [Down]
or press Nr. 4 or 5 on the keyboard.
N 1^21' E 0^14' |1> N/A|2>0.00|3>0.10nm
|--------------------------------- | 2. AIS Status
-----| |
| +- 1. State / Conditions
View | +- 2. Own Ship Data
| +- 3. Own VHF Status
-----| +- 4. Alarm Status
| +- 5. TXT Status
Msg. | +- 6. Version Info
| +- 7. Security Log
-----|
|
Displ|
---------------------------------------NUM|Select->| | |<-Back
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 29 Version 1.0
Page 35

5.2 Alarm Codes
Y1-03-0177A
ID
Description Text
Cause/Source
System Reaction / Remedy
01
AIS: Tx malfunction
AIS: Antenna VSWR
02
exceeds limit
(VSWR - Voltage
Standing Wave Ratio)
AIS: Rx channel 1
03
malfunction
AIS; Rx channel 2
04
malfunction
AIS: Rx channel 70
05
malfunction
06
AIS: General failure
AIS; External EPFS lost
25
(EPFS = electronic
Position Fixing System
such as GPS)
VHF Antenna,
cabling
VHF antenna,
installation
Internal error
Internal error
No valid data on
Ch1, Ch2 or Ch3
is available
Reaction: The transponder unit stops transmission. If Alarm ID 01 and
ID 02 are simultaneously displayed, then a major antenna problem has
arisen.
Remedy:
Check if the antenna is AIS compatible (156-162 MHz) and if the
antenna cabling has a short circuit or is missing any contacts at the
connectors.
If the ID 01 is displayed as a stand alone message, then the unit
requires replacing.
Reaction: The transponder unit continues transmission.
Remedy:
Check the antenna and the antenna cabling (RG214 / 50 Ohm cable
required).
Reaction: The transponder unit stops transmission on the affected
channel,
Remedy;
If this alarm reoccurs regularly, then the transponder unit requires
replacing.
Reaction: The transponder unit stops transmission.
Remedy;
The transponder unit requires replacing.
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation using the position
data of the internal GPS. If there is no valid position data available from
the internal GPS, error 026 is additionally displayed.
Remedy:
Id 25 indicates that the sentences GLL, GNS, GGA, RMC cannot be
received. Check the sensor and the cabling; check if the system that
delivers the data is working. Check the baud rate settings of the sensor
inputs. AIS requires the protocol NMEA 0183 V3.0!
AIS: No sensor position
26
in use
29
AIS: No valid SOG
information
30
AIS: No valid COG
Information
AIS: Heading lost/invalid
32
AIS: No valid ROT
35
Information
No valid position
from internal GPS
or external
position sensor
No valid data from
external speed
sensor or internal
GPS
No valid data from
external sensor or
internal GPS
No valid data from
external sensor
(Gyrocompass)
No ROT indicator
is used.
No valid data from
external sensor
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation.
Remedy:
Check the sensor cabling and the antenna of the internal GPS sensor.
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation and displays SOG:
N/A
Remedy;
The sentences VBW, VTG, RMC cannot be received. Check the
sensor and the cabling; check if the system that delivers the data is
working. Check the baud rate settings of the sensor inputs. AIS
requires the protocol NMEA 0183 V3.0!
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation and displays COG:
N/A
Remedy:
The sentences VBW, VTG, RMC cannot be received. Check the sensor
and the cabling, check if the system that delivers the data is working.
Check the baud rate settings of the sensor inputs. AIS requires the
protocol NMEA 0183 V3.0!
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation
Remedy:
The sentence for HDT cannot be received. Check the sensor and the
cabling, check if the system that delivers the data is working. Check the
baud rate settings of the sensor inputs. Mention AIS accepts true
heading only (no magnetic).
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation
Remedy:
The sentence for ROT cannot be received. If a Rate Of Turn indicator is
not in use, then it suffices to just acknowledge the alarm. The Alarm
Status will store the information that no ROT sensor is available.
Otherwise, check the sensor and the cabling. Check if the system that
delivers the data is working. Check the baud rate settings of the sensor
inputs. AIS requires the protocol NMEA 0183 V3.0!
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 30 Version 1.0
Page 36

5.3 Text Messages
Y1-03-0177A
ID
Description Text
Cause/Source
Reaction of the System / Remedy
07
AIS: UTC clock lost
AIS: external DGNSS in
21
use
AIS: external GNSS in
22
use
AIS: internal DGNSS in
23
use (beacon) 023
AIS: internal DGNSS in
24
use (message 17)
25
AIS: internal GNSS in
use
27
AIS: external SOG/COG
in use
AIS: internal SOG/COG
28
in use
AIS: Heading valid
31
Internal GPS
Information
Information
Information
Information
additional to Alarm
ID 25
Information
Information
additional to Alarm
ID 29 or ID 30
Information
Reaction: the transponder unit continues operation using indirect or
semaphore synchronisation
Remedy:
Check GPS Antenna for AIS.
Reaction: Positioning is fully operational
Remedy: no action required
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation using the position
data from a GNSS receiver
Remedy: no action required
Reaction: The transponder unit uses position data from the internal
source. The internal GNSS receiver is capable of processing DGNSS
corrections.
Remedy: no action required
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation using the position
data from the internal GPS.
Remedy
Check the sensor and the cabling; Check if the system that delivers the
data is working; Check the baud rate settings of the sensor input
Reaction: COG/SOG is in full operation
Remedy: no action required
Reaction: The transponder unit continues operation using the data
from the internal GPS.
Remedy
Check the sensor and the cabling; Check if the system that delivers the
data is working; Check the baud rate settings of the sensor inputs
Reaction: Heading is in full operation
Remedy: no action required
AIS: Rate of Turn
33
Indicator in use
AIS: Other ROT source
34
in use
Information
Information
Reaction: A Rate Of Turn indicator is connected and in full operation
Remedy: no action required
Reaction: The transponder unit is operating with ROT data rather than
with TIROT data - therefore the AIS only differs between + 127 (turning
right at 720 degrees per minute or higher) and – 127 ( turning
left at 720 degrees per minute or higher)
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 31 Version 1.0
Page 37

Y1-03-0177A
6 Accessories
The following material is included to the GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS. For order information please contact ACR.
TM
GlobalWatchTM
UAIS Basic Kit
includes
1 GlobalWatch
1 CD with demo software and documentation
1 installation manual, 1 user Manual, 1 quick user manual
3 caps of plug
1 cable clamp (M5 thread)
1 guide plate Kit
3 angles + 3 mounting screws (screw bolt + square nut)
UAIS Transponder
The GlobalWatchTM UAIS is supplied with some of the components listed below (contents
depend on customer requirements). More information please find on our CD-ROM.
Category
Description Drawing_No
Mountings:
GPS antenna solutions:
VHF antenna solutions:
Single antenna solutions :
Cables and interfaces:
Kit bracket-mounting + 2 wing bolts + 4 screws
Mounting kit retro fit-frame + 3 screws, 3 clips, 3 nuts
19" frame + 3 mounting screws (screw bolt + square nut)
Matsushita GPS antenna marine II
Mounting for GPS-antenna Marine II plastic
Mounting for GPS-antenna Marine II metal
Procom GPS antenna GPS 4
Glomex VHF antenna RA 109 sls + mounting kit
Comrod VHF antenna AV 7 + mounting kit
Procom VHF antenna CLX 2-1 + mounting kit
Comrod AC 17 - AIS (combined GPS/VHF antenna)
+ mounting kit
+ splitter and cable
GPS / VHF extender with N and TNC connection
+ N(m)/RG214 crimp
+ TNC(m)/RG214 crimp
AIS connection box
AIS cable open (3m) with all interfaces
+ pilot plug
Connector N(m)/RG214 crimp
Connector PL(m)/RG214 crimp
Connector TNC(m)/RG214 crimp
Gyro Converter 9028C
NAU-D503
NAU-D500
NAU-D502
NAU-X6011
NAU-X6012
NAU-X6013
NAU-B602
NAU-B610
NAU-B611
NAU-B612 + NAU-X6022
NAU–B620
NAU-B553
NAU-B401
NAU-B503
NAU-X5531
NAU-X5533
NAU-X5534
NAU-Z002
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 32 Version 1.0
Page 38

7 Technical Information
Y1-03-0177A
PHYSICAL
Size in mm / inch (w) 201,26 / 7,92
Size in mm / inch (h) 60 / 2,36
Size in mm / inch (d) 281,26 / 11,07
Weight g / pound 2490 / 5,50
Operating Temperature (Celsius) -15° to +55°
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Voltage (galvanic isolated) 24 V DC (-10% +30%)
Input Current min.7 A (24V)
INTERFACES
Number of Data Ports 3 Input / 4 I-O / 1 Output
IEC 61162-1/2 ( RS422 / NMEA 0183)
ITU-R M.823-2 ( RS422 / RTCM SC104)
Bitrate
CH1 Sensor Input; (i.E.: GPS) 4800 bps or 38400 bps
CH2 Sensor Input; (i.E.: GYRO) 4800 bps or 38400 bps
CH3 Sensor Input; (i.E.: HDG) 4800 bps or 38400 bps
CH4 ECDIS Port (In- / Output)
AIS targets, AIS messages
CH5 Pilot Port (In- / Output)
AIS targets, AIS messages
CH8 Long Range Port (In- / Output) in/out 38400 bps
CH9 DGPS correction (In- / Output)
(RTCM SC104)
Alarm Circuit CH10 Dry relay contact (see BIIT
BUILT IN GPS
Receiver Architecture 12 channel differential
Tracking Capability 12 satellites sim.
Accuracy Horizontal 10m / 2drms *
Accuracy Vertical 15m / 2drms *
GPS Antenna Connector TNC
DGPS Accuracy < 5m / 2drms
*) depends on SA
GPS Solutions
Beacon interoperability
EGNOS interoperability
WAAS interoperability
OMNISTAR interoperability
LongWave interoperability
VHF interop. (DGPS over Msg.17)
optional internal Beacon Receiver
Combined GPS/DGPS Antenna
BIIT – Alarm System
Relay breaking capacity
30V DC 8A
250V AC 8A
OPTIONAL INTERFACES
Number of Data Ports RS232
Bitrate
Simplex / Duplex
Number of Data Ports IEC
61162-3 CAN (RS485)
Bitrate
KEYBOARD
Integrated alphanumerical
in/ out 38400 bps
in/out 38400 bps
in/out 9600 bps
– Alarm System)
up to 5
Up to 115000 bps
Duplex
1
up to 1 Mbps
SPECIFIED STANDARDS
IMO MSC.74(69) Annex 3
ITU-R M.1371 (Class A)
IALA Techn.Clar. of ITU-R M.1371-1
(Ed.1.3)
IEC 61993-2 (2002)
IEC 61162-1 (2000) NMEA 0183-3
IEC 61162-2 (1998) NMEA 0183-3
IEC 61162-3 NMEA 2000
ITU-R M.823-2
IEC 61108-1 (1996)
IEC 60 945 (1996)
ITU-R M.825-3
ITU-R M.1084-3
VHF
Frequency Range 156 MHz - 162MHz
Channel Spacing 12.5 or 25kHz
Number of RF Channels 3 Receiv. / 1 Transm.
Number of AIS Receivers 2
Number of DSC Receivers 1
Frequency Error
VHF TRANSMITTER
Output Power
Receive to Transmit Switching Time < 1ms
Transmit release time < 1ms
Automatic shutdown 1 sec.
Channel switching time < 25ms
Attack Time < 1ms
VHF RECEIVER
Max. Useable Sensitivity < -110dBm
Co-channel Rejection > -8dB (25kHz);
> -12dBm (12.5kHz)
Adjacent Channel Selectivity > 70dB (25kHz);
> 60dB (12.5kHz)
Inter-modulation Rejection > 65dB
Spurious Response Rejection > 70dB
Blocking > 84dB
VHF MODEM
Bitrate GMSK 9600 bps
RF Baud Rate (DSC) 1200bps
Modulation GMSK / FSK
SOFTWARE
Version 2.0.x
- installed and ready for use
- implemented configuration Software
- User friendly Interface
to System and AIS Information
- additional Interface to System
Configuration
(Windows 2000
- Demonstrator
for training purposes
(Windows 2000 Windows XP
HARDWARE
Version 1.0.x
DISPLAY
Integrated graphical 240 x 128
+/- 2.5ppm
2 Watt to 12.5 Watt
(adjustable)
®
)
®
)
adjustable brightness
and contrast
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 33 Version 1.0
Page 39

8 Contact and Support Information
Y1-03-0177A
ACR Electronics
Customer Service
5757 Ravenswood Road
Fort Lauderdale, FL 33312
U.S.A.
Tel.: +1 (954) 981-3333
Fax: +1 (954) 983-5087
info@acrelectronics.com
www.acrelectronics.com
Forms for Problem Report or Installation Checklist can be found on the CD-ROM.
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 34 Version 1.0
Page 40

9 Appendix
Y1-03-0177A
9.1 Samples for battery calculation
GMDSS Reserve Battery Calculation ( 24 V DC )
for Raytheon Marine GmbH GMDSS Compact-Console Area A3 with 250 W MF/HF
According to IMO Regulation COMSAR/Circ.16 4. March 1998
A: with Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate one (1) hour on reserve power
With 50% of time in transmission mode and 50% in receiving mode.
B: without Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate six (6) hours on reserve power
with 50% of time in transmission mode and 50 % of receiving mode.
Equipment Type Transmitting Receiving Additional
MF/HF STR 2000 R 15 A 4 A incl.DSC
Inmarsat C STR 1500 CN 5 A 1,8 A incl.EGC
VHF 1 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
VHF 2 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
AIS RM 808 AIS 5,0 A 1,0 A
Emergency Light 2,5 A
Total 38 A 8,1 A 2.5 A
Calculation:
Case A:
1h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 41.44 Ah
recommend battery capacity is 86 Ah
Charger:
I Charg x 0.1 I Batt/h = 8.6 A
recommend charger is type 20 A
Case B:
6h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 248.66 Ah
The battery calculation should not be used for uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
configuration
_________________________________________________________________________
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 35 Version 1.0
Page 41

GMDSS Reserve Battery Calculation ( 24 V DC )
Y1-03-0177A
for Raytheon Marine GmbH GMDSS Compact-Console Area A3 with 400 W MF/HF
According to IMO Regulation COMSAR/Circ.16 4. March 1998
A: with Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate one (1) hour on reserve power
With 50% of time in transmission mode and 50% in receiving mode.
B: without Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate six (6) hours on reserve power
with 50% of time in transmission mode and 50 % of receiving mode.
Equipment Type Transmitting Receiving Additional
MF/HF STR 2000 18.75 A 4 A incl.DSC
Inmarsat C STR 1500 CN 5 A 1,8 A incl.EGC
VHF 1 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6.5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
VHF 2 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6.5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
AIS RM 808 AIS 5.0 A 1,0A
Emergency Light 2,5 A
Total 41.75 A 8,1 A 2.5 A
Calculation:
Case A:
1h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 44.06 Ah
recommend battery capacity is 86 Ah
Charger:
I Charg x 0.1 I Batt/h = 8.6 A
recommend charger is type 20 A
Case B:
6h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 264.39 Ah
The battery calculation should not be used for uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
configuration
_________________________________________________________________________
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 36 Version 1.0
Page 42

9.2 Drawings and Approvals
Y1-03-0177A
These documents are encluded on the following pages:
(1) Dimensional Drawings
(2) Type Approvals
(3) Connection Drawings
(4) Antenna Layout
(5) Sample for data telegrams
GlobalWatch
TM
UAIS Installation Manual 37 Version 1.0
Page 43

Y1-03-0177A
Page 44

Y1-03-0177A
Page 45

Y1-03-0177A
Page 46

Y1-03-0177A
Page 47

Y1-03-0177A
Page 48

Y1-03-0177A
Page 49

Y1-03-0177A
Page 50

Y1-03-0177A
Page 51

Y1-03-0177A
Page 52

Y1-03-0177A
Page 53

Y1-03-0177A
EG - Konformitätserklärung
CE - Declaration of Conformity
Diese Konformitätserklärung bestätigt, dass das unten benannte Produkt den Auflagen der EC Council Directive
96/98/EC vom 20 Dezember 1996 für maritime Ausrüstung, geändert durch die EC Council Directive 2002/75/EC vom 2.
September 2002 entspricht und von der benannten Stelle Nr. 0735 (BSH) typengeprüft ist.
This declaration of conformity certified that the mentioned equipment is in compliance with EC Council Directive
96/98/EC of 20 December 1996 on Marine Equipment, last amended by EC Council Directive 2002/75/EC of 2
September 2002 and has been type examined by the Notified Body No. 0735 (BSH).
Produktbezeichnung:
name of product
OEM Name:
Trade Name
Zertifikate der benannten
Stelle Nr. 0735 (BSH):
Certificates from the
notified Body No. 0735 (BSH)
Spezifizierte Standards:
Specified Standard(s)
Dokument- Nr.:
document-no :
Jahr, Monat:
Year, month:
Hersteller: Nauticast Schiffsnavigationssysteme AG
manufacturer
Anschrift: Mariahilfer Straße 50/2/11
address 1070 Wien, Austria
Aussteller: Technischer Leiter
Issuer Chief Technology Officer
Ort, Datum: Vienna, 2004-03-24
place, date
Unterschrift:
signature
ISO 9001:2000 Zertifizierung / ISO 9001:2000 Certification
Nauticast hat ein Qualitätsmanagement System nach ISO 9001:2000 implementiert, und ist seit Juli 2003 ISO-zertifiziert.
Nauticast maintains a Quality Management System according to ISO 9001:2000, and received ISO certification in July 2003.
Diese Erklärung bescheinigt die Übereinstimmung mit den genannten Richtlinien, ist jedoch keine Zusicherung von Eigenschaften.
Die Sicherheitshinweise der mitgelieferten Produktdokumentation sind zu beachten.
This declaration certifies the compliance with the indicated directives but implies no warranty of properties.
The safety instructions of the accompanying product documentation shall be observed.
2004/007
2004/03
X-Pack DS
Annex A1 Item: 4.32 Automatic Identification System (AIS)
RM 808 AIS
GlobalWatch UAIS
Bridgemate AIS
EC Type Examination (Module B) Certificate
734.2/0051-1/2003
EC Quality System (Module D) Certificate
BSH-052-03-2003
IMO MSC.74(69) Annex 3
ITU-R M.1371-1 (Class A)
IALA Technical Clarifications of Rec.
ITU-R M.1371-1 (Edition 1.3)
ITU-R M.825-3
ITU-R M1084-3
IEC 61993-2 (2002)
IEC 61162-1 (2000), -2 (1998)
IEC 60945 (1996)
IEC 61108-1 (1996)
EG-Konformitätserklärung Nr.: 2004/007 page 1 of 1 CE Conformity X-Pack DS_007
EC-Declaration of conformity N°:
Page 54

Y1-03-0177A
Page 55

Y1-03-0177A
Page 56

Y1-03-0177A
Page 57

Y1-03-0177A
Page 58

Y1-03-0177A
Source, Draw.-No. 46-EX-D-X00001-C, coyright Raytheon Marine GmbH, Kiel, Germany
Page 59

Sample for battery Calculation
Y1-03-0177A
GMDSS Reserve Battery Calculation ( 24 V DC )
According to IMO Regulation COMSAR/Circ.16 4. March 1998
A: with Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate one (1) hour on reserve power
With 50% of time in transmission mode and 50% in receiving mode.
B: without Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate six (6) hours on reserve power
with 50% of time in transmission mode and 50 % of receiving mode.
Equipment Type Transmitting Receiving Additional
MF/HF STR 2000 18,75 A 4 A incl.DSC
Inmarsat C STR 1500 CN 5 A 1,8 A incl.EGC
VHF 1 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
VHF 2 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
AIS AIS - Unit 5,0 A 1,0A
Emergency Light 2,5 A
Total 41,75 A 8,1 A 2.5 A
Calculation:
Case A:
1h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 44.06 Ah
recommend battery capacity is 86 Ah
Charger:
I Charg x 0.1 I Batt/h = 8.6 A
recommend charger is type 20 A
Case B:
6h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 264.39 Ah
The battery calculation should not be used for uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
configuration
Page 60

Sample for battery calculation
Y1-03-0177A
GMDSS Reserve Battery Calculation ( 24 V DC )
According to IMO Regulation COMSAR/Circ.16 4. March 1998
A: with Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate one (1) hour on reserve power
With 50% of time in transmission mode and 50% in receiving mode.
B: without Emergency Generator ( SOLAS IV 13.2 )
The GMDSS equipment shall be able to operate six (6) hours on reserve power
with 50% of time in transmission mode and 50 % of receiving mode.
Equipment Type Transmitting Receiving Additional
MF/HF STR 2000 R 15 A 4 A incl.DSC
Inmarsat C STR 1500 CN 5 A 1,8 A incl.EGC
VHF 1 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
VHF 2 with DSC VHF1000DSC 6,5 A 0,65 A incl.DSC
AIS AIS - Unit 5,0 A 1,0 A
Emergency Light 2,5 A
Total 38 A 8,1 A 2.5 A
Calculation:
Case A:
1h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 41.44 Ah
recommend battery capacity is 86 Ah
Charger:
I Charge x 0.1 I Batt/h = 8.6 A
recommend charger is type 20 A
Case B:
6h x ( 0.5 I TX + I RX + I Add ) x 1.4 = 248.66 Ah
The battery calculation should not be used for uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
configuration
Page 61

Quick Replacement Guide
1. Prepare the following tools:
Screwdrivers, spanners
User Password: your personal password
(factory default setting is ‘NAUT’)
2. Read out your Transponder conguration
Steps to do this:
Press
Menu
Press
2
2.AIS Status
Press
2
2.Own Ship Data
Write down the current conguration settings here:
IMO No. : Dest :
ShipName : EAT :
ShipType : MMSI :
Length : CS :
Cargo : Beam :
Draught :
Press
Menu
Press
4
4.Ship Settings
Password
[UserPassword] [Enter
]
Write down the current conguration settings here:
RefPtExt: A B C D RefPtInt: A B C D
Press
Menu
Press
5
5.Transponder Conguration
Password
[UserPassword] [Enter
]
Press
5
5.Sensor Settings
Write down the current conguration settings here:
BaudRate Sensor1:
BaudRate Sensor2:
BaudRate Sensor3:
Press
M8
Back
3. Detach the device
3.1. Bracket Mounting
3.2. Frame Mounting
4. Disconnect cables
4.1. AIS-Cable to unscrew
4.2. VHF/GPS Cable to unscrew
5. Unpack the new Transponder
Y1-03-0177A
Page 62

6. Connect cables
6.1. AIS-Cable to screw on
6.2. VHF/GPS Cable to screw on
7. Mount the replacement unit
7.1. Bracket Mounting
7.2. Frame Mounting
8. Key in the conguration settings from above:
Following steps to key in the Conguration
Press
Menu
Press
6
6.Service Conguration
Password
NAUT [Enter
]
(Default Factory Password)
Press
3
3.Change MMSI / IMO
Key in the conguration data from your list: (see page 1)
MMSI: IMO No:
Press
M5
Save
Press
Menu
Press
4
4.Ship Settings
Password
NAUT [Enter
]
(Default Factory Password)
Key in the conguration data from your list: (see page 1)
CallSign: ShipName: Length: Beam:
RefPtExt:
AxxCxx*
RefPtInt:
AxxCxx*
ShipType:
*(B and D are calculated by the AIS)
Press
Menu
Press
5
5.Transponder Conguration
Password
NAUT [Enter
]
(Default Factory Password)
Press
5
5.Sensor Settings
Key in the conguration data from your list: (see page 1)
BaudRate Sensor1: BaudRate Sensor2: BaudRate Sensor3:
Press
M5
Save
9. Check the functionality
Press
M2
You should see correct values for LAT, LON, SOG, COG, and Time
Press
M2
You should see your Own Ship Data as noted down before.
9.1. Change your User Password
Press
Menu
Press
6
6.Service Conguration
Password
NAUT [Enter
]
(Default Factory Password)
Press
2
2.User Password Settings
Press
1
1.Change User Password
Enter
[new password]
Repeat
[new password]
Press
M5
Save
Y1-03-0177A
 Loading...
Loading...