Acoustic Arc AR0810 Users Manual

User Manual
AirNav® Systems LLC
www.airnavsystems.com
AirNav RadarBox™ 2007
Manual
© Copyright AirNav Systems LLC 2007. All rights reserved.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without prior notice and shall not constitute a
commitment on the part of AirNav Systems. The Product(s) and/or services described in this document shall be
furnished pursuant to the signing of a license, non-disclosure or service agreement and shall be used or copied in
accordance with the terms thereof.

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
1. Welcome
AirNav RadarBox
Welcome to the most Advanced Real-Time Radar Decoder
AirNav RadarBox is the closest you can be to real world aviation without leaving your chair thanks to next generation
Radar decoding.
By decoding ADB-S (Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast) radar signals, you will be able to see on your
computer what real Air Traffic Controllers see on their screens in Real-Time.
Flight number, aircraft type, altitude, heading, speed are all updated each second.
Included is the award winning software interface developed by the world's leader in flight tracking and monitoring
solutions, AirNav Systems.
AirNav RadarBox is equipped to be used in any location all over the world.
3D multi-window maps with worldwide coverage contain more than 200 thousand geographic points included.
Airports, runways, VOR, NDB, FIX, cities, roads, airways and elevation data.
How it works?
1. Install the software from the CD
2. Connect the AirNav RadarBox to your computer using the USB cable provided
3. Start Tracking flights in real-time!
RadarBox Network
AirNav RadarBox Network is an unique feature that enables to view data other RadarBox users are receiving all over
the world.
It is the first worldwide flight data network ever developed. You are experimenting new technology never used
before.
Receive, decode and show real-time flights on your computer.
Share and view data with users all over the world.
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 1
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
1.1. Main Features
AirNav RadarBox - Main Features
Hardware:
• Real-Time Radar ADS-B decoder
• Superior receiver sensitivity
• No need for an external power supply
• Plug-and-play USB connection
• Light weight easy to carry aluminum box
Software:
• Track flights in real-time
• Second by second updates on flight number, aircraft registration, altitude, speed, heading and vertical speed
• Real-Time retrieval of aircraft details including registration, company, aircraft type
• Based on the award winning AirNav Systems 3D multi-window map interface
• Easy plug and play USB connection - no complex time consuming setup
• ACARS Decoder interface
• 5 minute delayed flight data sharing on port 7879
• Automatically Imports Outline Files (.out)
• Real-Time photos of all tracked aircraft
• Real-Time weather information
• Export data and generate reports
• Share screen shots or send logs automatically to your friends
• MyLog feature: log all and share with your friends all the aircraft you receive
• Alert generation for specific aircraft or in-range flights
• Radar player to review airspace recordings
• Editable callsign database included: know the origin and destination of each flight
• 160 thousand flight number database included
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 2

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
Maps:
• High definition worldwide map layer
• Worldwide aviation data included (Airports, Runways, VOR, NDB, FIX, airways and ATC boundaries)
• More than 1 million map locations including detailed shore lines, country boundaries and cities
• Quick locate feature
• Worldwide elevation data
Requirements:
• Microsoft Windows
• PC with 400 Mhz processor (higher recommended)
• 128 MB RAM
• One Available USB Connection
• 50 MB Hard Disk Space Available for Installation
• CD-ROM Drive
Package Contents:
• RadarBox Hardware Unit
• USB Cable
• Antenna
• Quick Installation guide
• Setup Wizard CD with RadarBox Software
1.2. ADS-B Background
ADS-B Background
Putting it in a simple form, AirNav RadarBox consists of an hardware that decodes ADS-B data and sends its to your
computer where a software processes it and shows it on 3D interface.
Received data may be shared between users using the AirNav Systems RadarBox network. This way you will be able
to see data received from users all over the world.
What is ADS-B?
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (also called ADS-B) is a system by which airplanes constantly broadcast
their current position and altitude, category of aircraft, airspeed, identification, and whether the aircraft is turning,
climbing or descending over a dedicated radio datalink. This functionality is known as "ADS-B out" and is the basic
level of ADS-B functionality.
The current ADS-B system was developed in the 1990s though its lineage dates back to the 1960s. It relies on data
from the Global Positioning System, or any navigation system that provides an equivalent or better service. The
maximum range of the system is line-of-sight, typically less than 200 nautical miles (370 km).
The ADS-B transmissions are received by air traffic control stations, and all other ADS-B equipped aircraft within
reception range. Reception by aircraft of ADS-B data is known as "ADS-B in".
The initial use of ADS-B is expected to be by air traffic control and for surveillance purposes and for enhancing pilot
situational awareness. ADS-B is lower cost than conventional radar and permits higher quality surveillance of airborne
and surface movements. ADS-B is effective in remote areas or in mountainous terrain where there is no radar
coverage, or where radar coverage is limited. The outback of Australia is one such area where ADS-B will provide
surveillance where previously none existed. ADS-B also enhances surveillance on the airport surface, so it can also be
used to monitor traffic on the taxiways and runways of an airport.
ADS-B equipped aircraft may also have a display unit in the cockpit picturing surrounding air traffic from ADS-B data
(ADS-B in) and TIS-B (Traffic Information Service-Broadcast) data derived from air traffic radar. Both Pilots and air
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 3

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
traffic controllers will then be able to "see" the positions of air traffic in the vicinity of the aircraft, and this may be
used to provide an ASAS (Airborne Separation Assurance System).
Airborne Collision Avoidance Systems may in the future also make use of "ADS-B in", supplementing the existing TCAS
collision avoidance system by what is called 'hybrid surveillance'.
Airbus and Boeing are expected to include ADS-B out (i.e. the transmitter of information) as standard on new-build
aircraft from 2005 onwards.
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 4
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
2. Getting Started
2.1. Installation
AirNav RadarBox 2007 - Installation
The AirNav RadarBox system is made up of two distinct parts. The hardware and the software.
You will need to install the software first and only after that hardware setup will be performed.
Follow the below steps to properly install the system and start tracking real world flights in real-time on your
computer.
DO NOT CONNECT THE HARDWARE USB CABLE TO YOUR COMPUTER BEFORE INSTALLING THE
SOFTWARE
If you need any help during the installation process visit AirNav Systems Support Page
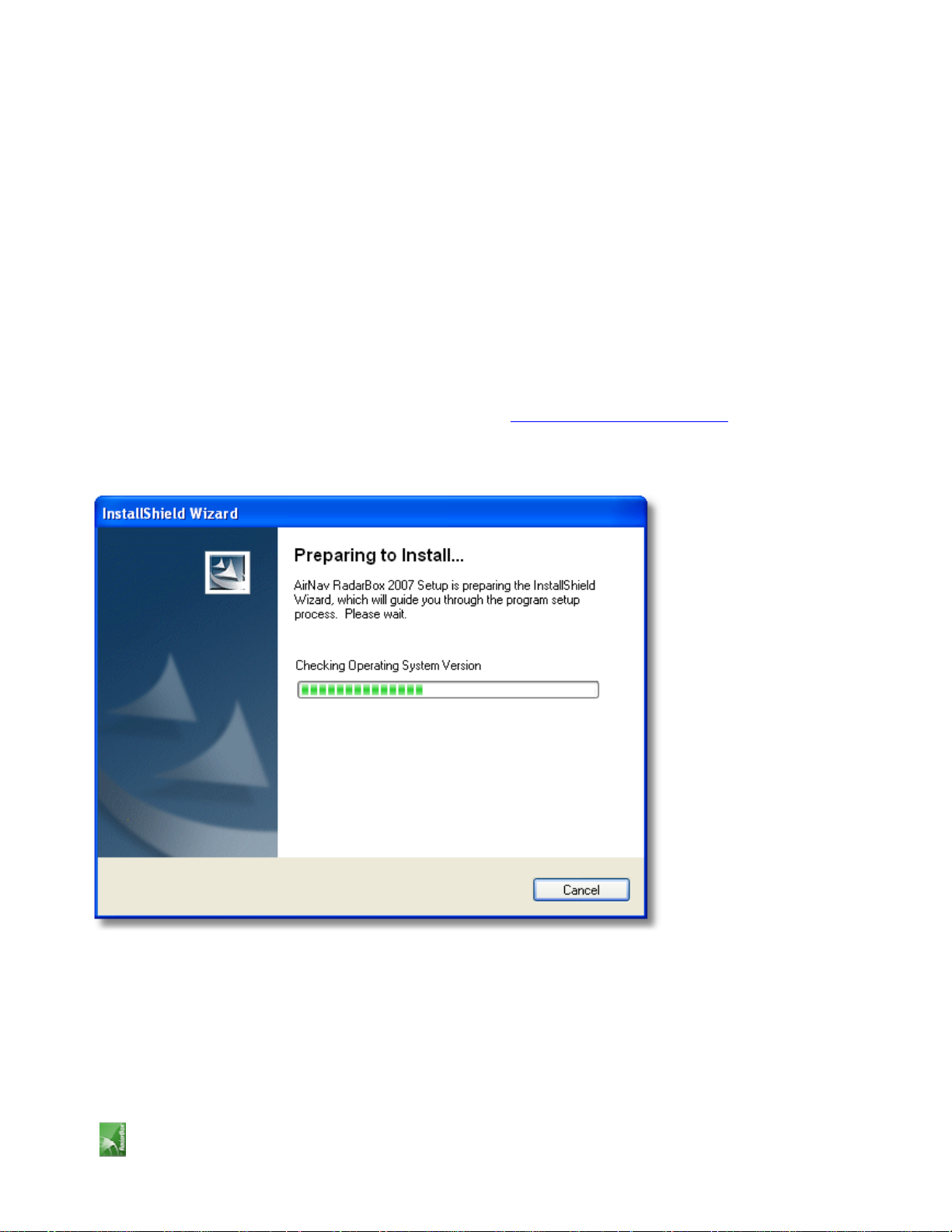
1. Run the setup.exe file located on the root folder of the provided CD. Follow registration instructions paying
special attention to the User Agreement.
2. After the software is installed connect the USB cable from the hardware to your computer. Windows will
detect that AirNav RadarBox is connected.
3. When the below windows appears, under "Can Windows connect to Windows Update for software?" select the
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 5
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
"No, not at this time". Click "Next".
www.airnavsystems.com
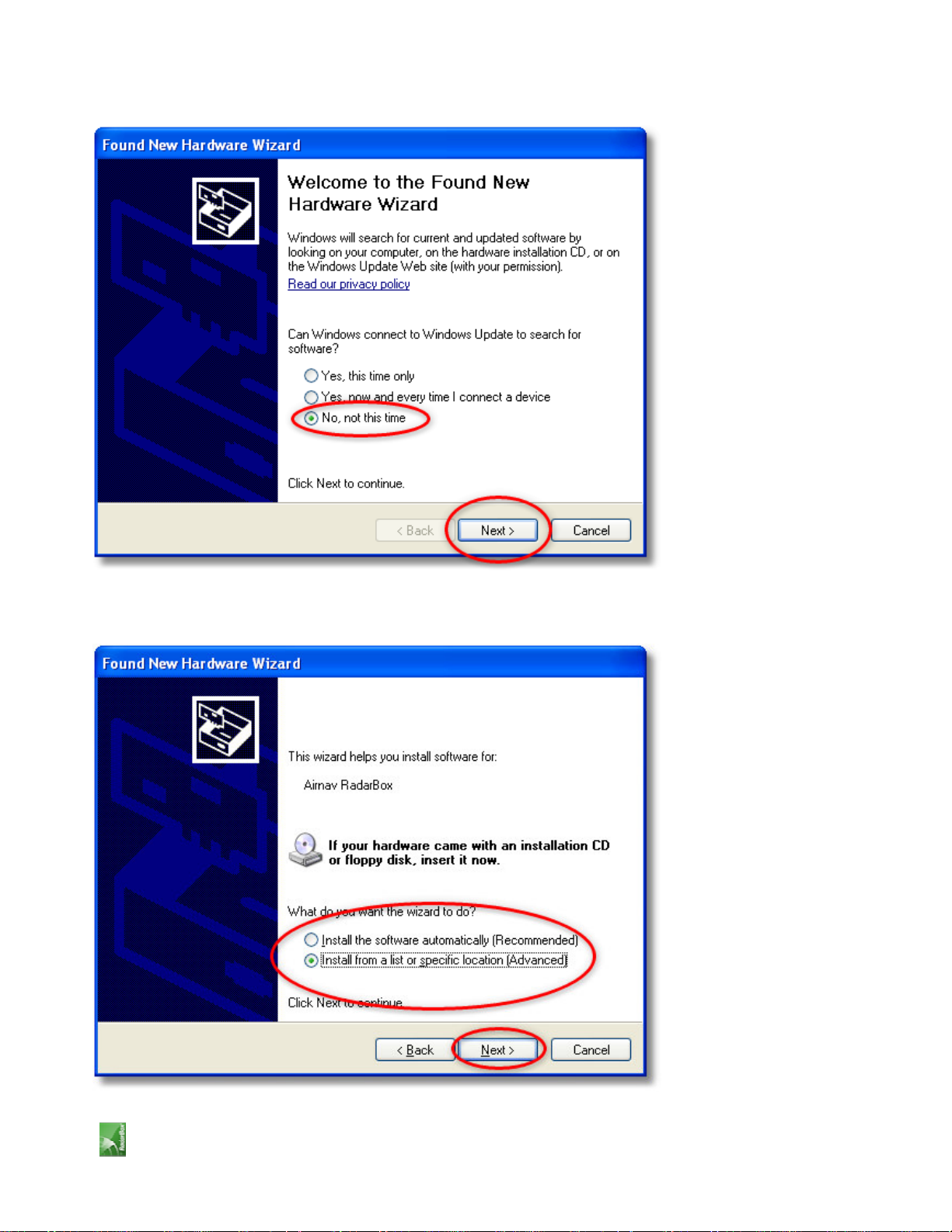
4. Under "What do you want the wizard to do?" select "Install from a list or specific location (Advanced)".
Click "Next".
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 6
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
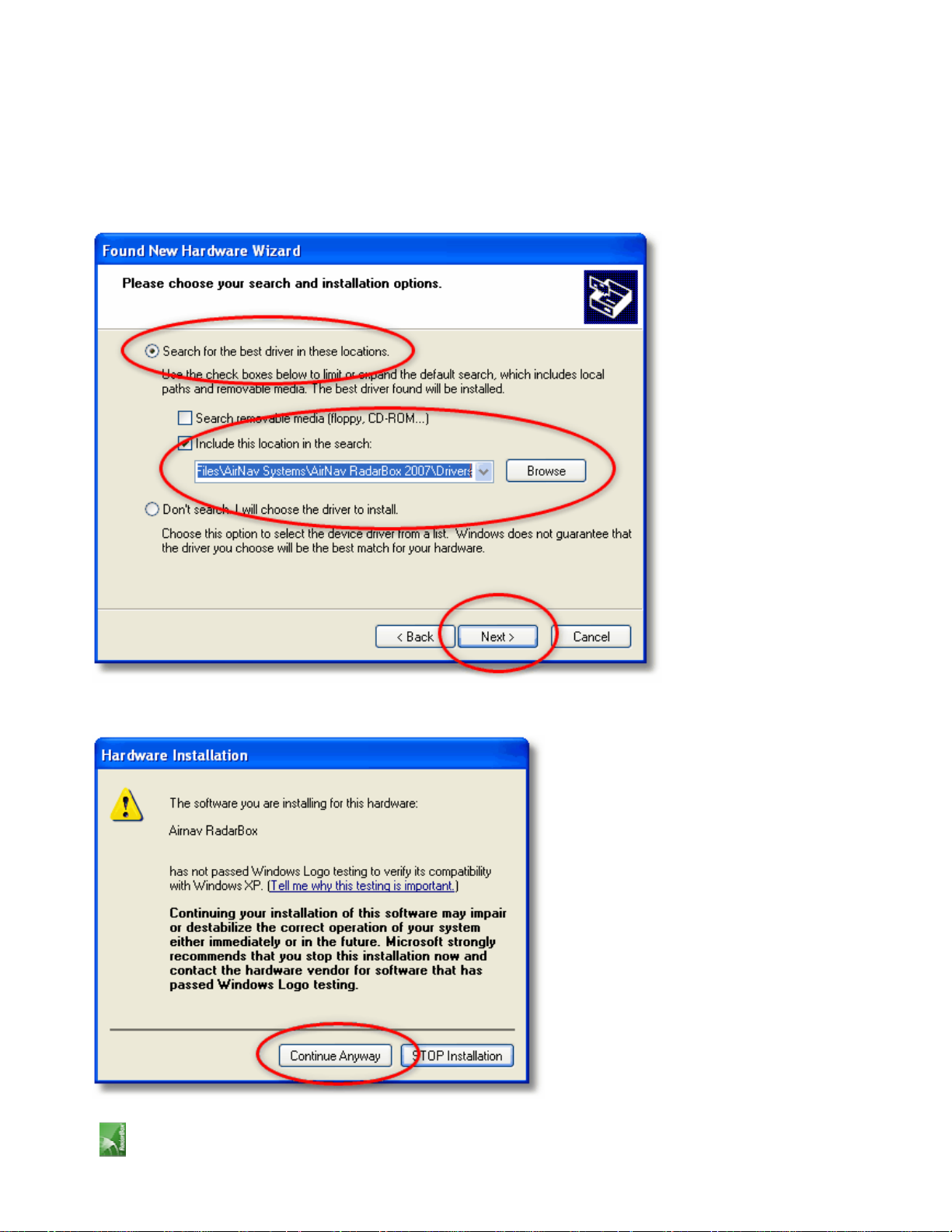
5. Select "Search for the best driver in these locations" and then select "Include this location in the
search". Browse for the folder that contains RadarBox drivers. It is located on a folder named "drivers" that is inside
the folder where AirNav RadarBox software has been installed.
The typical location of drivers would be "C:\Program Files\AirNav Systems\AirNav RadarBox 2007\Drivers".
Click "Next".
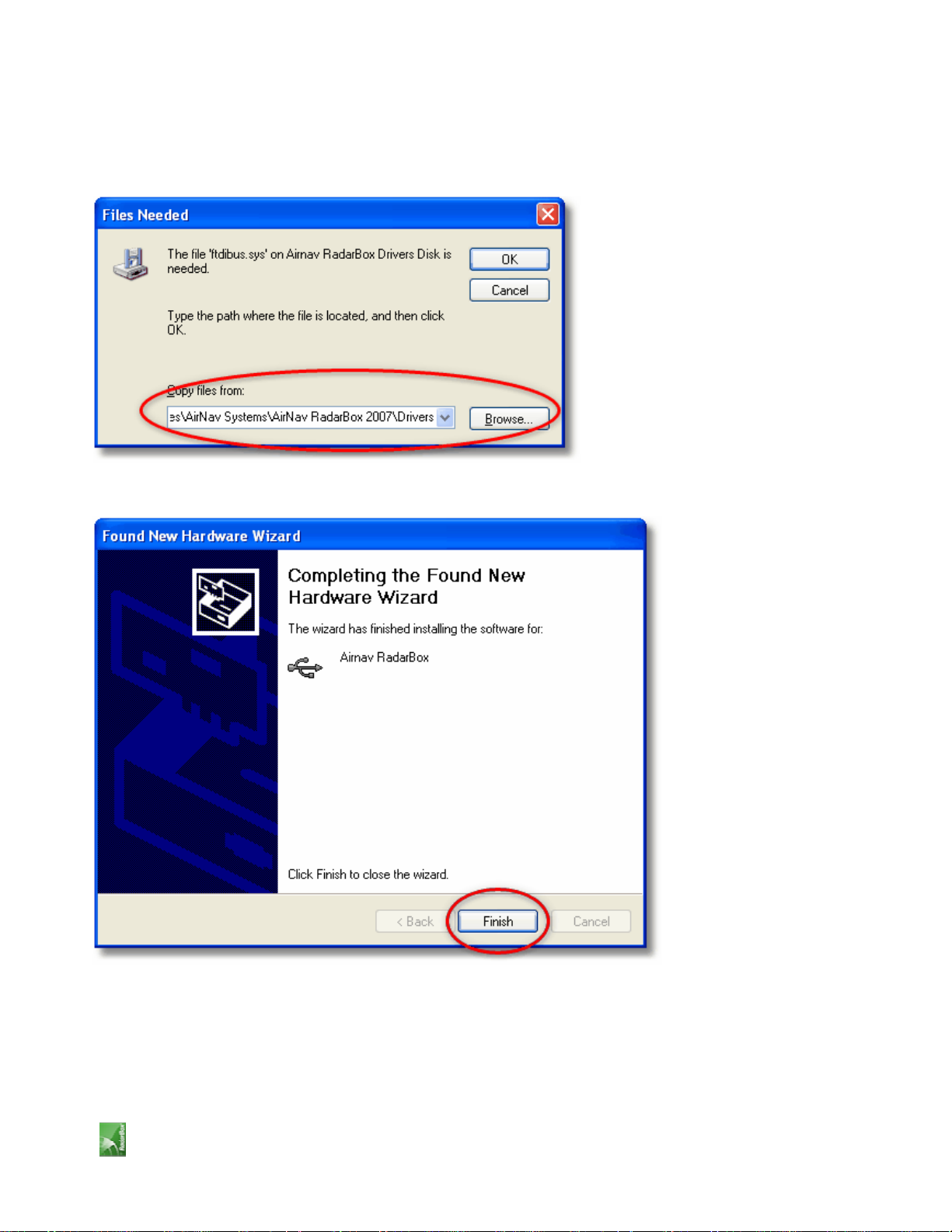
5. Driver installation will start. If the window below appears click "Continue Anyway".
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 7
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
6. If the window below appears select again the RadarBox driver folder, usually located at:
"C:\Program Files\AirNav Systems\AirNav RadarBox 2007\Drivers". Click "OK".
7. That's it! The hardware has been installed successfully. Click the "Finish" button.
2.2. Tutorial
AirNav RadarBox 2007 - Tutorial
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 8

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
AirNav RadarBox 2007 tutorial is a group of step by step instructions that will guide you through the most important
application features.
Note: information between [...] means that the command mentioned can be found in AirNav RadarBox 2007 Menus.
Example: [Tools|Internet|Download Updated Data Now] points you to click on Tools menu, Internet topic, Download
Updated Data Now subtopic.
Step by Step Tutorial
1- Start the software using the windows Shortcut created on your Start Menu or Desktop.
2. The Welcome Window will be shown. Enter your Email/Username and Password. Click the "Start" button
after this. You can check the Remember password checkbox in case you do not want to type your personal details
every time you start the software.
The connection to the Hardware will be started and if you are a subscriber of AirNav RadarBox Network feature, the
software will try to download network data.
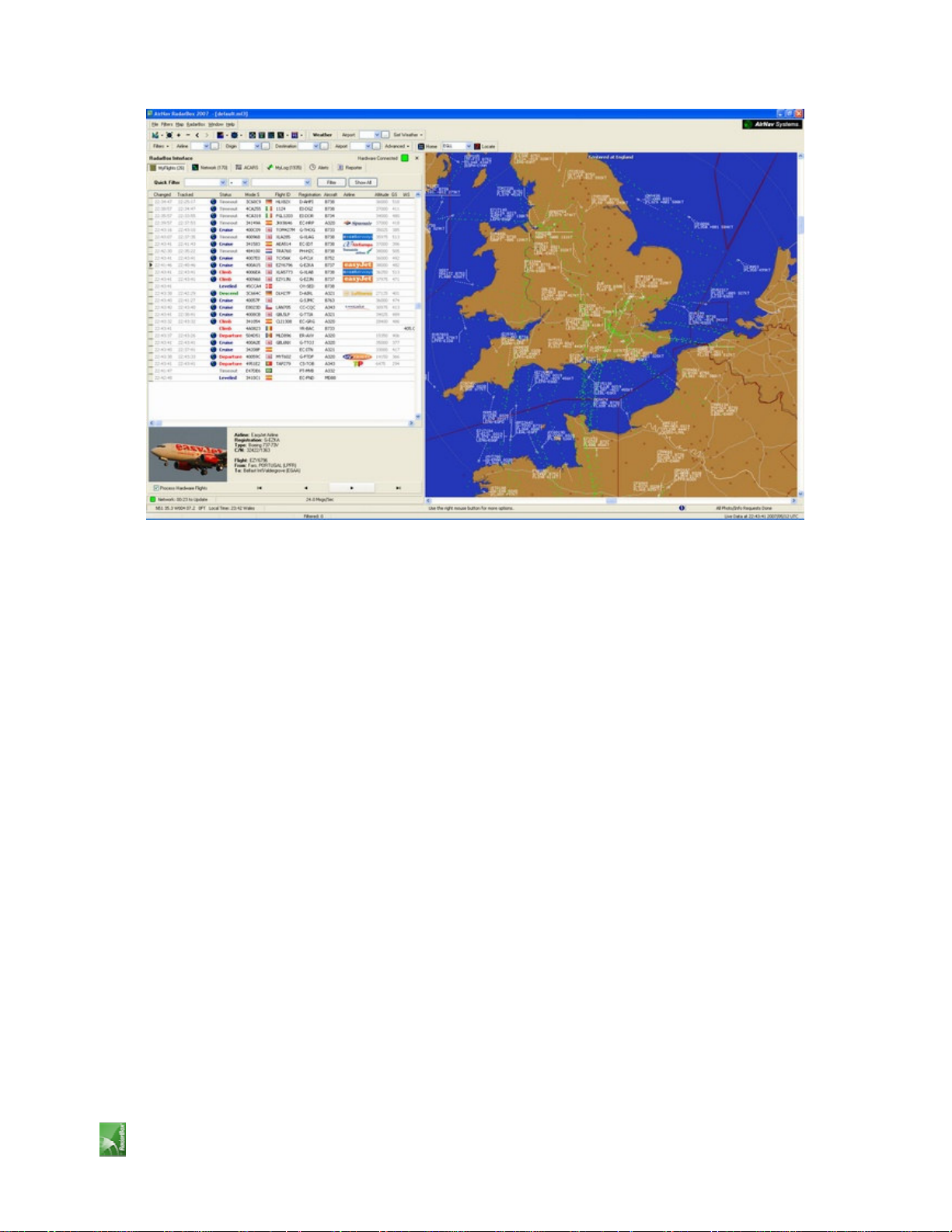
3- The main software window with a world map will be shown as illustrated below.
Dynamic 3D maps are one of AirNav RadarBox 2007 most important features. You are now going to explore some of
the capabilities.
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 9

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
4- First task: you will center the map at your home location, zoom in and save it as your default map.
To center the map at any location let's use the "Locate" feature. It easily centers the map on any airport, city or
navigation facility all over the world.
Imagine you are located near London Heathrow Airport. Enter "EGLL" on the locate box.
This box it at the top of the main screen as on the screen shot below. After this click the Locate button. The map
will now be panned so that London appears on the center.
5- Now Zoom in a more detailed view of the London area is shown. You can do this by clicking the zoom in button
on the map toolbar. The easiest way to pan/zoom your maps is by using your mouse buttons. Learn more here.
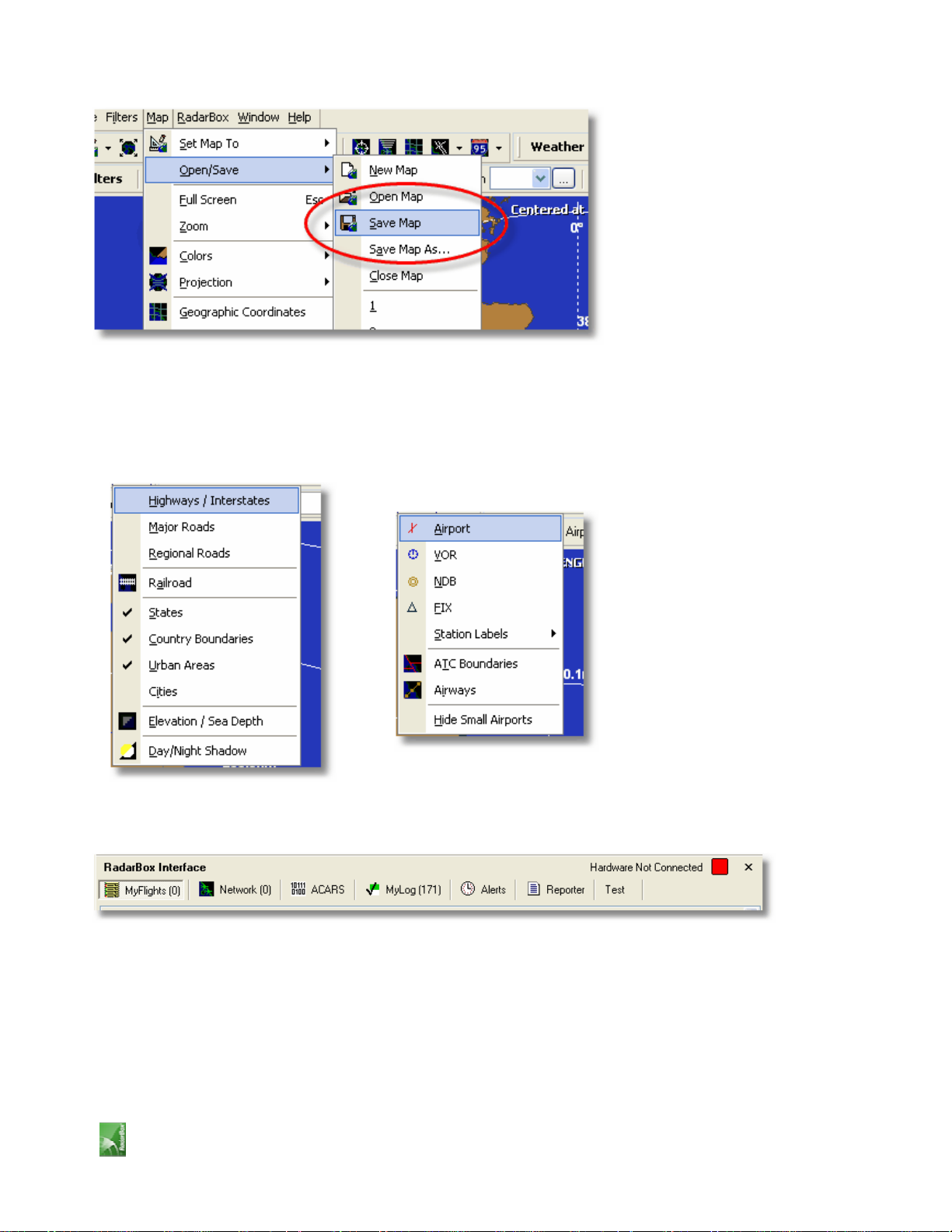
6- Save your map by going to [Map |Open/Save | Save Map]. Answer Yes to the "Are you sure you want to
overwrite your default map file?". This map will be the one that will be always shown after the application is started.
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 10
AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
7- All map functions are located on the map menu or on the map toolbar on the top of the main window. You can
also right mouse click over any map to access map functions in a faster way, including setting you home location. On
these menus there are several map layers that you can choose to be hidden or visible. This includes aviation related
layers (airports, runways, NDBs, VORs, FIXes as well as airways and ATC boundaries). There are also general interest
layers like roads, geographic coordinates, cities and elevations.
General Map Layers Aviation Map Layers
8- Now let's have a look at the RadarBox Interface panel. This is where all the action will take place. It is divided into
6 tabs.
MyFlights: where all the flights received using your hardware will be shown. A grid will show as many flight details
as possible, from aircraft registration to flight route. Photos and aircraft details will appear on the bottom of this tab.
Network: all AirNav RadarBox Network flights (received from other RadarBox users) will be shown on this tab.
ACARS: flights received from AirNav ACARS Decoder interface will be shown here.
MyLog: a collection of all flights received on your hardware will appear on this tab. Details include
Reporter: an easy interface for you to share your reports with other mode-s users.
Alerts: you could receive an email each time a specific registration is received by your decoder. Other types of alerts
are available.
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 11

AirNav® Systems – World Leader in Flight Tracking and Monitoring
www.airnavsystems.com
9- On the top right of the RadarBox interface notice the hardware connection status. You can monitor here if the
hardware is properly connected to your computer.
falar sobre radarbox network com link para a network
falar de acaars decoder com link para acaras decoder sempre com explicacao simples e depois to learn more balh
blah
Let see the entires on mylog and now create a report
tb ha possibilidade de alertas explicada em alertas
ha mtas preferencias vaialable em preferences menu com link
falar nos filtros
falar no weather
10-
3- If you cannot see the map in good conditions (too dark) you may click on the map tool button, the 'Dark/Light'
button which will change the map colors to allow the map to be easily seen in bright locations.
10- Now let's talk about filters. One of AirNav RadarBox 2007 most useful features is the ability to filter what you can
see. To do this you have the
AirNav RadarBox 2007 Manual
Page 12
 Loading...
Loading...