Page 1

User’s Manual
Wireless Super-G
Router
Page 2

1
Index
FCC Part 68....................................................................................................................................................... 3
FCC Part 15....................................................................................................................................................... 4
Chapter 1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 5
1.2 Features...................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 System Requirements ................................................................................................................. 6
Chapter 2 Installation ......................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Checklist ..................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 The Front LEDs ........................................................................................................................... 8
2.3 The Rear Ports ............................................................................................................................ 8
Chapter 3 Configuration ..................................................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Determine your connection settings ............................................................................................. 9
3.2 Connecting the Wireless Broadband Router to your network........................................................ 9
3.3 Configuring with Web Browser..................................................................................................... 9
3.3.1 Host Name Setting ................................................................................................................. 12
3.3.2 System Time .......................................................................................................................... 13
3.3.3 Admin Setting ......................................................................................................................... 14
3.3.4 Firmware Update .................................................................................................................... 15
3.3.5 System Log ............................................................................................................................ 16
3.3.6 System Reset ......................................................................................................................... 17
3.4.1 WAN Configuration ................................................................................................................. 18
3.4.2 Dynamic IP............................................................................................................................. 19
3.4.3 Static IP.................................................................................................................................. 20
3.4.4 PPPoE ................................................................................................................................... 21
3.4.5 PPTP Setting.......................................................................................................................... 22
3.4.6 DNS ....................................................................................................................................... 23
3.5.1 LAN Configuration .................................................................................................................. 25
3.5.2 DHCP Client List..................................................................................................................... 26
3.5.3 UPnP Setting.......................................................................................................................... 27
3.6.1 Wireless Setting ..................................................................................................................... 28
3.6.2 Wireless Security.................................................................................................................... 29
3.6.3 WDS Configuration ................................................................................................................. 30
3.7.1 Firewall Setting....................................................................................................................... 31
3.7.2 Client Filtering ........................................................................................................................ 32
3.7.3 MAC Control........................................................................................................................... 33
3.8.1 Static Routing ......................................................................................................................... 34
Page 3

2
3.8.2 Dynamic Routing .................................................................................................................... 35
3.8.3 Routing Table ......................................................................................................................... 36
3.9.1 System Status ........................................................................................................................ 37
3.10.1 TCP/IP Settings for Windows Operating System ................................................................... 38
Appendix A Troubshooting................................................................................................................................ 45
Appendix B Frequency Asked Questions.......................................................................................................... 48
Appendix C Specification ................................................................................................................................. 50
Appendix D Glossary ....................................................................................................................................... 51
Page 4

3
FCC Part 68
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC Rules. On the bottom of this equipment is a label that contains
the FCC Registration Number and Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) for this equipment. You must provide this
information to the telephone company upon request.
The REN is useful to determine the quantity of devices you may connect to the telephone line and still have those
entire devices ring when your number is called. In most, but not all areas, the sum of the REN of all devices
connected to one line should not exceed five (5.0). To be certain of the number of devices you may connect to
your line, as determined by the REN, you should contact your local telephone company to determine the
maximum REN for your calling area.
If the modem causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company may discontinue your service
temporarily.
If possible, they will notify you in advance. But if advance notice isn't practical, you will be notified as soon as
possible.
You will be advised of your right to file a complaint with the FCC.
The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures that could
affect the proper operation of your equipment. If they do, you will be notified in advance to give you an opportunity
to maintain uninterrupted telephone service.
If you experience trouble with this modem, please contact your dealer for repair/warranty information. The
telephone company may ask you to disconnect this equipment from the network until the problem has been
corrected or you are sure that the equipment is not malfunctioning.
This equipment may not be used on coin service provided by the telephone company. Connection to party lines is
subject to state tariffs.
Page 5

4
FCC Part 15
The modem generates and uses radio frequency energy. If it is not installed and used properly in strict
accordance with the user's manual, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. The modem has
been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class B computing devices in accordance with the
specifications in Subpart B, Part 15 of the FCC regulations. These specifications are designed to provide
reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. FCC regulations require that shielded interface cables be
used with your modem.
If interference does occur, we suggest the following measures be taken to rectify the problem:
1) Move the receiving antenna.
2) Move the modem away from the radio or TV.
3) Plug the modem into a different electrical outlet.
4) Discuss the problem with a qualified radio / TV technician.
CAUTION:
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance to the FCC Rules could
void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Cable connections:
All equipment connected to this modem must use shielded cable as the interconnection means.
Notes:
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2) This device must accept any interference received including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Page 6

5
Chapter 1 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of a Instant Wireless Super-G Router with 4-port Fast Ethernet Switch for cable
and DSL application. The Wireless Super-G Router is the perfect option to connect a small group of PCs to a
high-speed Broadband Internet connection or to an Ethernet backbone. Configurable as a DHCP server, the
Broadband Router acts as the only externally recognized Internet device on your local area network (LAN). The
Router serves as an Internet firewall, protecting your network from being accessed by outside users.
1.1 Overview
Unlike a simple hub or switch, the setup of the Cable/DSL Router consists of more than simply plugging
everything together. Because the Router acts as a DHCP server, you will have to set some values within the
Router, and also configure your networked PCs to accept the IP Addresses the Router chooses to assign them.
The wireless data rates supports up to 108Mbps, better than IEEE 802.11g. User can very easy to share the
internet connection via wireless and get the best performance..
1.2 Features
Router Mode
‧
PPP over Ethernet (RFC-2516)
‧
DHCP Server and Client
‧
PPTP Client
‧
NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)
‧
NAT (Network Address Translation)
‧
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
Standards
‧
IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
‧
IEEE 802-3u 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet
‧
IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, Super-G
‧
WiFi compliance
Internet Access
‧
TCP/IP, UDP, ICMP, ARP, RARP, PPPoE, NAT, DHCP (client/server), PPTP client, Static IP assignment
Security Features
‧
Password protected configuration access
‧
User authentication (PAP/CHAP) for PPP connection
Page 7

6
Wireless Features
Wireless Frequency Range
‧
2.400GHz to 2.500GHz
Wireless Spreading
‧
DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum), CCK OFDM, QPSK, BPSK
Wireless Transmit Power
‧
+15 dBm
Wireless Security
‧
Supports the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) 64-bit and optional 128-bit, WPA/WPA2 (802.1x, TKIP, AES)
Wireless Operating Range
‧
Open Space : 100-300m
‧
Indoor : 35-100m
Wireless data rate
‧
Up to 108Mbps
Management Features
‧
Plug & Play Installation
‧
Local & Remote Management
‧
Web-based configuration
‧
Firmware upgrade
‧
Alarm Status & Power Indicators
‧
Event & History log
1.3 System Requirements
1) Personal computer (PC)
2) Pentium II 233 MHz processor minimum
3) 32 MB RAM minimum
4) 20 MB of free disk space minimum
5) Ethernet Network Interface Controller (NIC) RJ45 Port
6) Internet Browser
Page 8

7
Chapter 2 Installation
This chapter offers information about installing your router. If you are not familiar with the hardware or software
parameters presented here, please consult your service provider for the values needed.
2.1 Checklist
Check the shipping box carefully to ensure that the contents include the items you ordered. If any of the items are
missing or damaged, contact your local distributor. The contents of your carton may vary depending on your
service provider.
Contents description
1) Wireless Super-G Router for home/office use
2) Wireless Super-G Router Installation and Operation Guide (this publication)
3) Power supply with 9VDC / 1.5 Ampere power adapter
4) Ethernet cable Ethernet category 5 twisted pair cable (6 ft)
Page 9
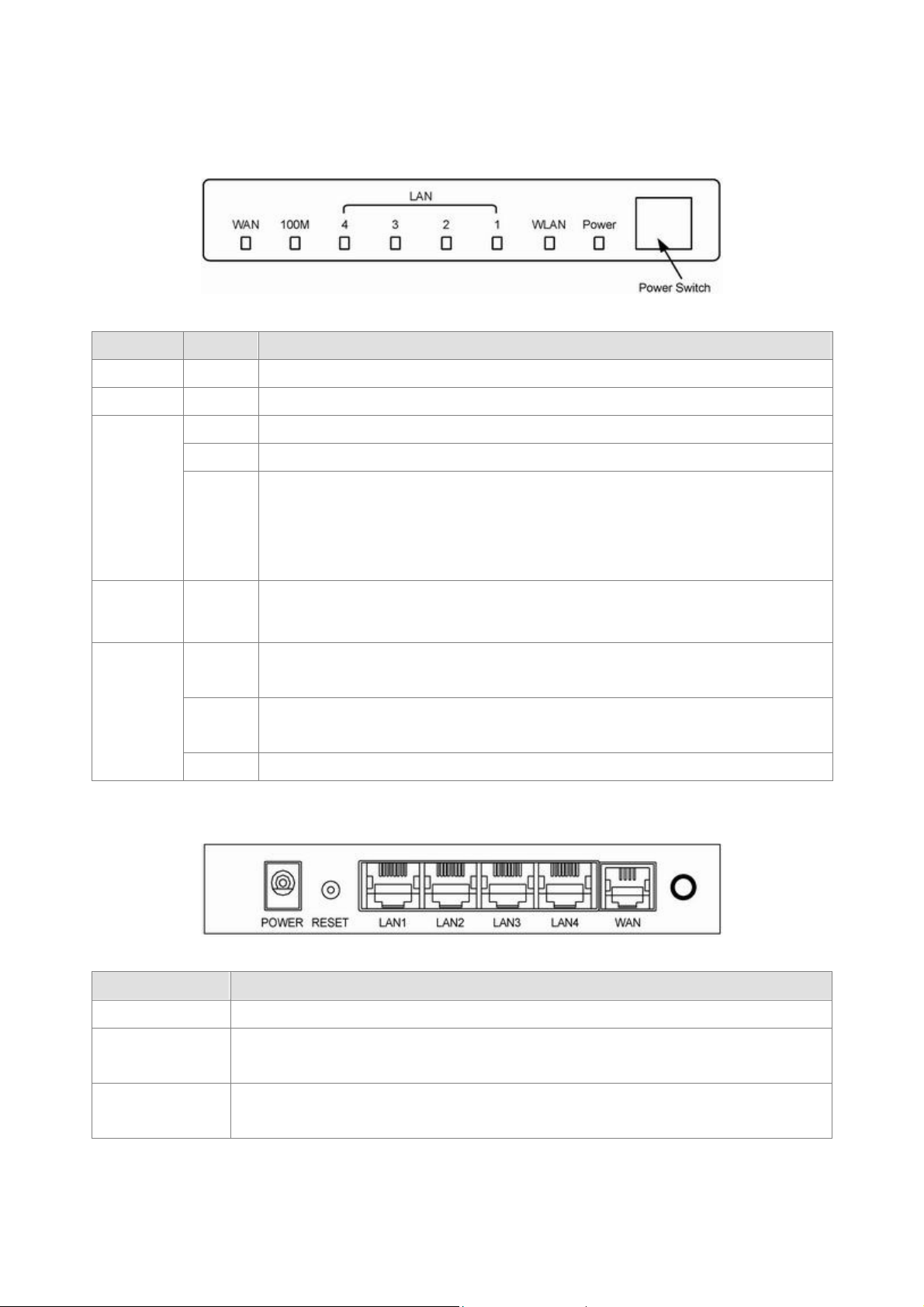
8
2.2 The Front LEDs
devices, such as PCs, print servers remote hard drives, and anything else you want to
modem is trying to establish a connection to telco's network Modem is
DSL modem or
LED State Description
POWER ON Press the button to power one the router.
WLAN ON When wireless AP is ready.
ON Link
Flashing TX or RX activity
LAN
1-4
OFF
100M ON
ON
WAN
Flashing
OFF No link.
2.3 The Rear Ports
No Link
These four LAN (Local Area Network) ports are where you will connect networked
put on your network.
1. WAN DHCP Client link is 100Mbps
2. PPPoE link connected
"Showtime"-successful connection between ADSL modem and telephone company's
network.
"Handshaking"-
powered OFF ADSL Carrier Detect if LED is flash.
Connector Description
POWER Power connector with 9VDC/ 1.5 Ampere.
Router is successfully connected to a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3 or 4).
LAN (1-4)
If the LED is flashing, the Router is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
The WAN (Wide Area Network) Port is where you will connect your cable,
WAN
Ethernet backbone.
Page 10

9
Chapter 3 Configuration
3.1 Determine your connection settings
Before you configure the router; you need to know the connection information supplied by your service provider.
3.2 Connecting the Wireless Broadband Router to your network
Unlike a simple hub or switch, the setup of the Super-G Router consists of more than simply plugging everything
together.
Because the Router acts as a DHCP server, you will have to set some values within the Router, and also
configure your networked PCs to accept the IP Addresses the Router chooses to assign them. Generally there
are several different operating modes for your applications. And you can know which mode is necessary for your
system from ISP. These modes are router, bridge, PPPoE+NAT and NAT.
3.3 Configuring with Web Browser
It is advisable to change the administrator password to safeguard the security of your network.
To configure the router, open your browser, type 'http://192.168.1.1' into the address bar and click 'Go' to get to
the login page. Save this address in your Favorites for future reference.
Page 11
10
At the Password prompt, the User name is 'admin' and the password is ’admin’. You can change these later if
you wish. Click 'OK' to login.
Page 12
11
You can use "Quick Setup" to setup the router, and choose the connect mode you prefer.
Page 13
12
3.3.1 Host Name Setting
Enter the host name representing your host and the domain name you want to configuration, then you can doing
web configuration by typing the whole name you configuration instead by typing the IP address.
Page 14
13
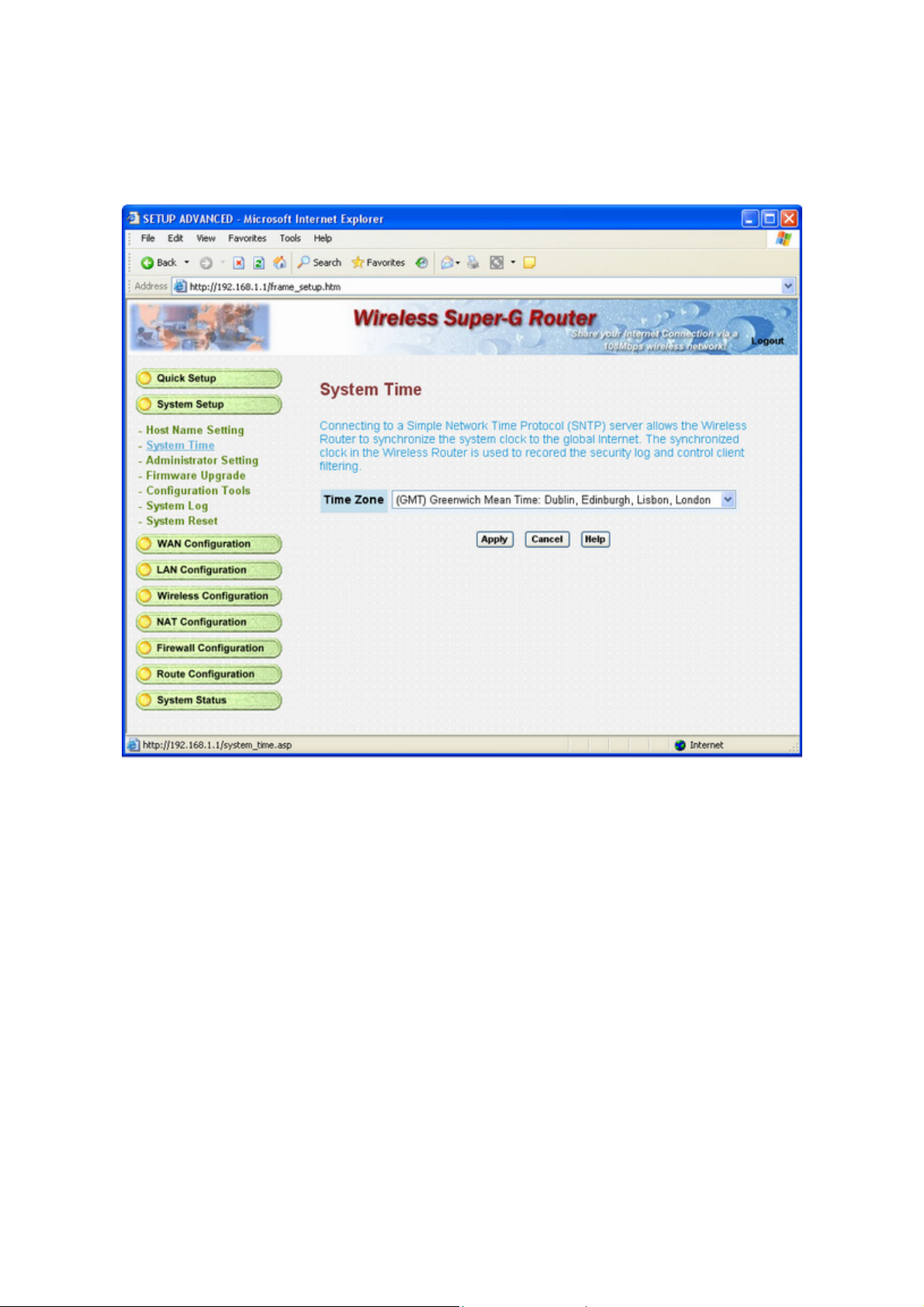
3.3.2 System Time
Connecting to a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server allows the router to synchronize the system clock
to the global Internet. The synchronized clock in the router is used to recorded the security log and control client
filtering.
Page 15
14
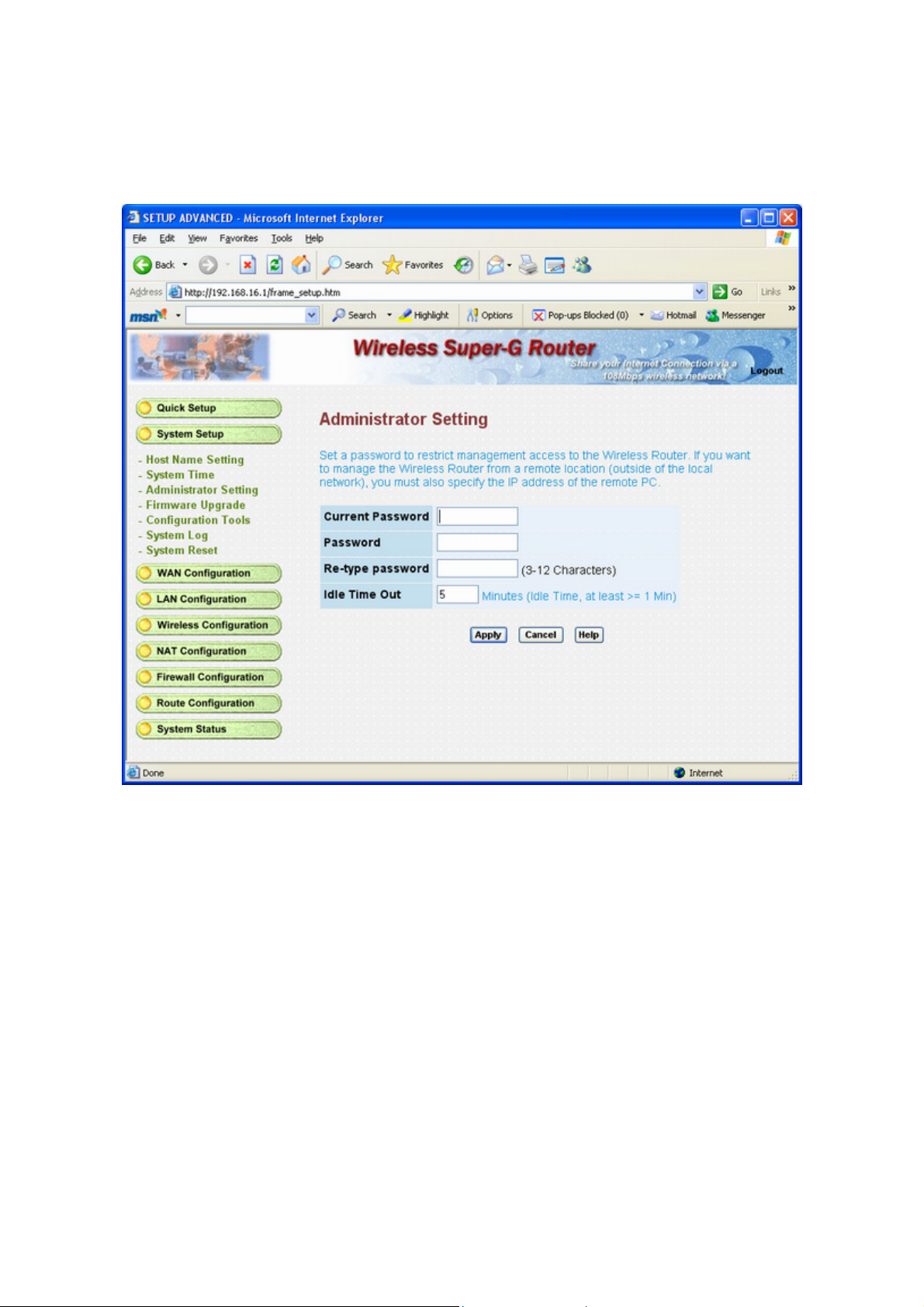
3.3.3 Admin Setting
Set a password to restrict management access to the router. The default is admin.
Page 16
15
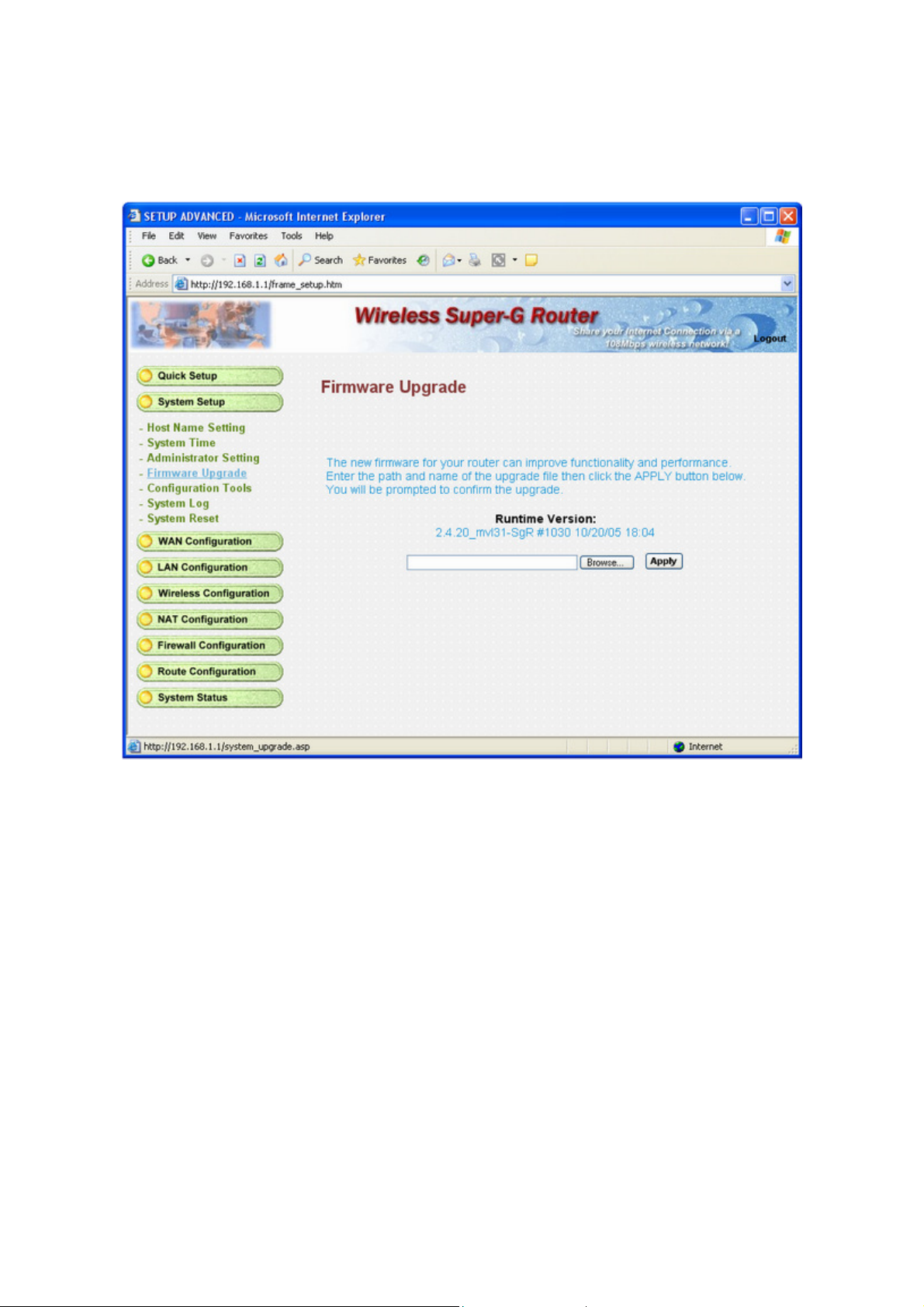
3.3.4 Firmware Update
The new firmware for your router can improve functionality and performance.
Enter the path and name of the upgrade file then click the Apply button below. You will be prompted to confirm
the upgrade.
Page 17
16
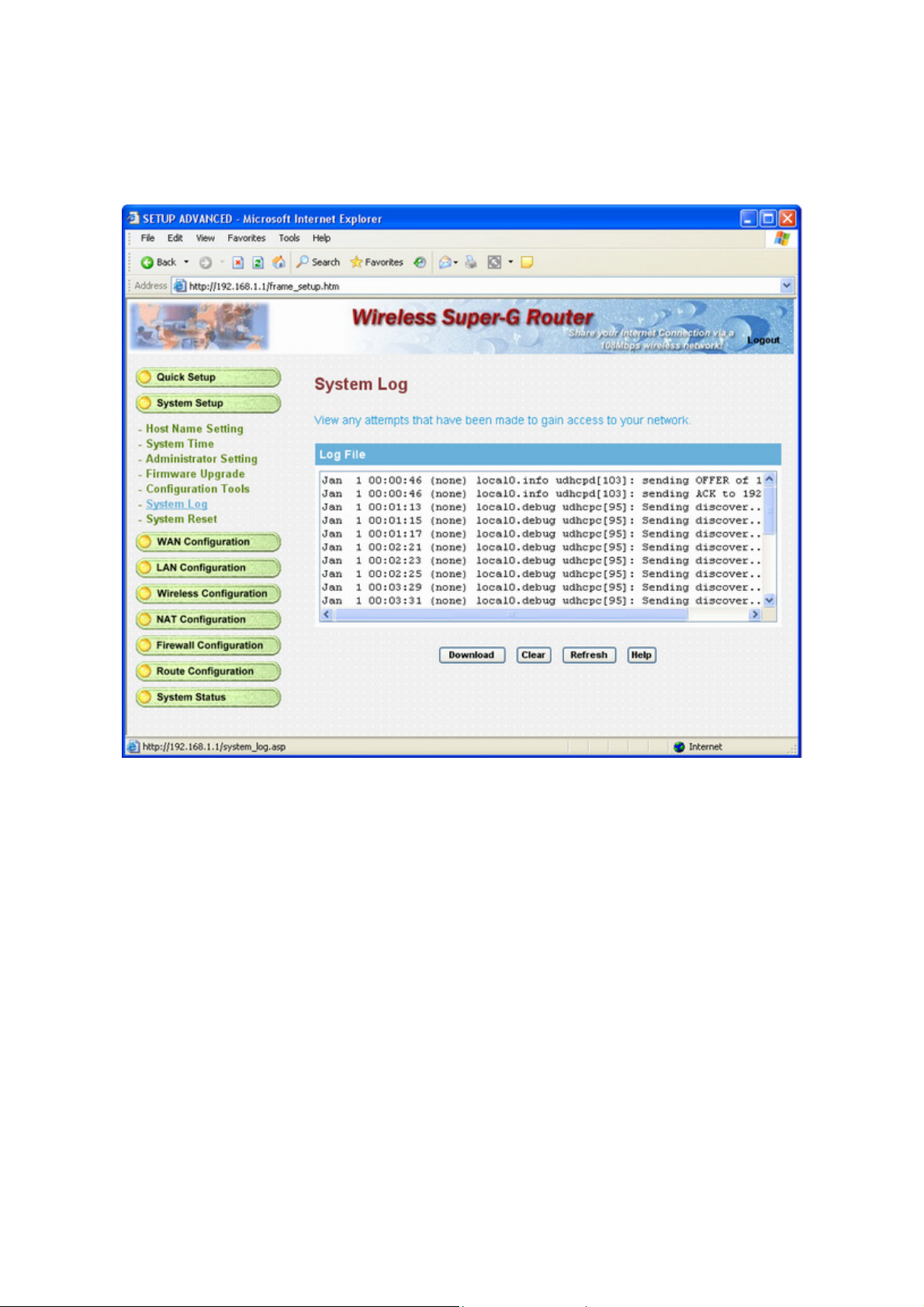
3.3.5 System Log
Click “Download” to save or open system log file.
Page 18
17
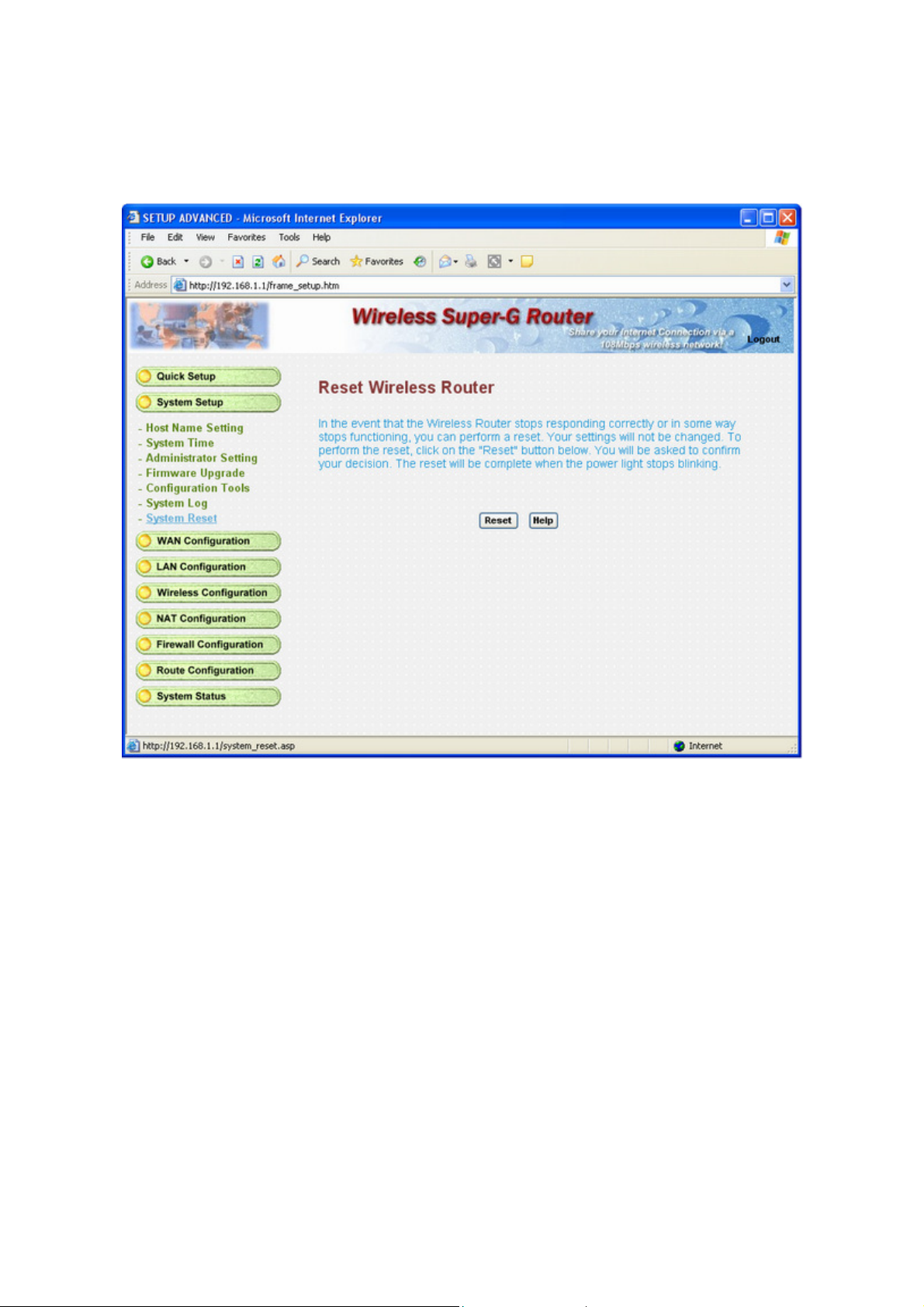
3.3.6 System Reset
In the event that the router stops responding correctly or in some way stops functioning, you can perform a reset.
Your settings will not be changed. To perform the reset, click on the "Reset" button below. You will be asked to
confirm your decision.
Page 19

18
3.4.1 WAN Configuration
The router can be connected to your service provider in any of the following ways.
Page 20

19
3.4.2 Dynamic IP
Dynamic IP Address : Obtain an IP address automatically from your service provider.
Page 21

20
3.4.3 Static IP
Static IP Address : Uses a static IP address. Your service provider gives a static IP address to access Internet
services.
Page 22
21
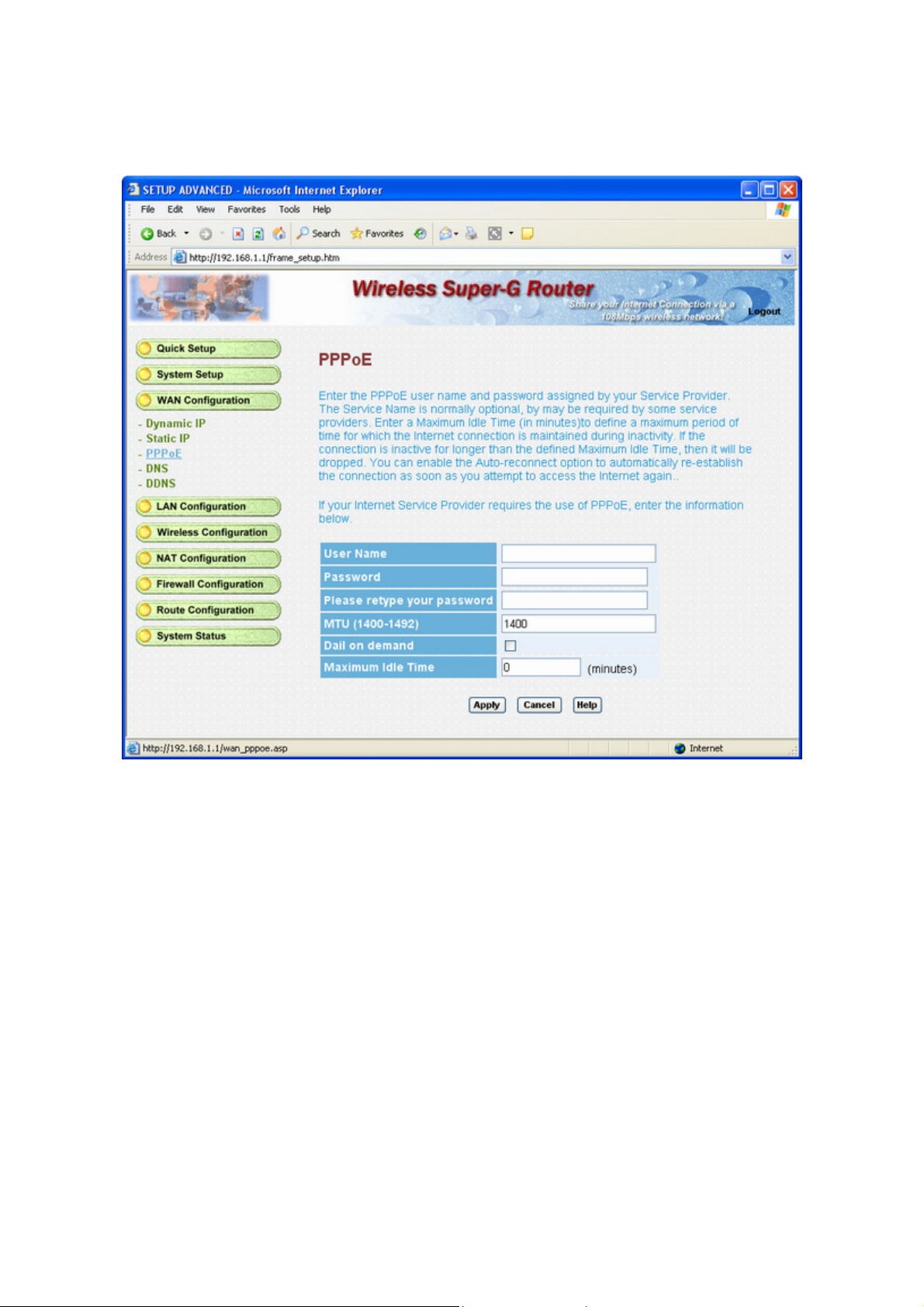
3.4.4 PPPoE
PPPoE : PPP over Ethernet is a common connection method used for xDSL.
Page 23

22
3.4.5 PPTP Setting
PPTP : Point-to-Point Tunnel Protocol is a connection method used for specific area.
Page 24

23
3.4.6 DNS
A Domain Name system (DNS) server is like an index of IP addresses and Web addresses. If you type a Web
address into you browser, a DNS server will find that name in its index and find the matching IP address.
Most ISPs provide a DNS server for speed and convenience. Since your Service Provider many connect to the
Internet with dynamic IP settings, it is likely that the DNS server IP addresses are also provided dynamically.
However, if there is a DNS server that you would rather use, you need to specify the IP address below.
Page 25

24
3.4.7 DDNS
Dynamic DNS allows you to update your dynamic IP address with one or many dynamic DNS services.
So anyone can access your FTP or Web service on your computer using DNS-like address.
Page 26

25
3.5.1 LAN Configuration
The 'LAN Settings' option enables you to assign IP address to the router. If the DHCP Server is selected, the
router will auto assign the IP address to the PC which connect to the router and setting as a DHCP client.
Page 27

26
3.5.2 DHCP Client List
The DHCP client list allows you to see which clients are connected to the router via IP address and MAC address.
Page 28
27
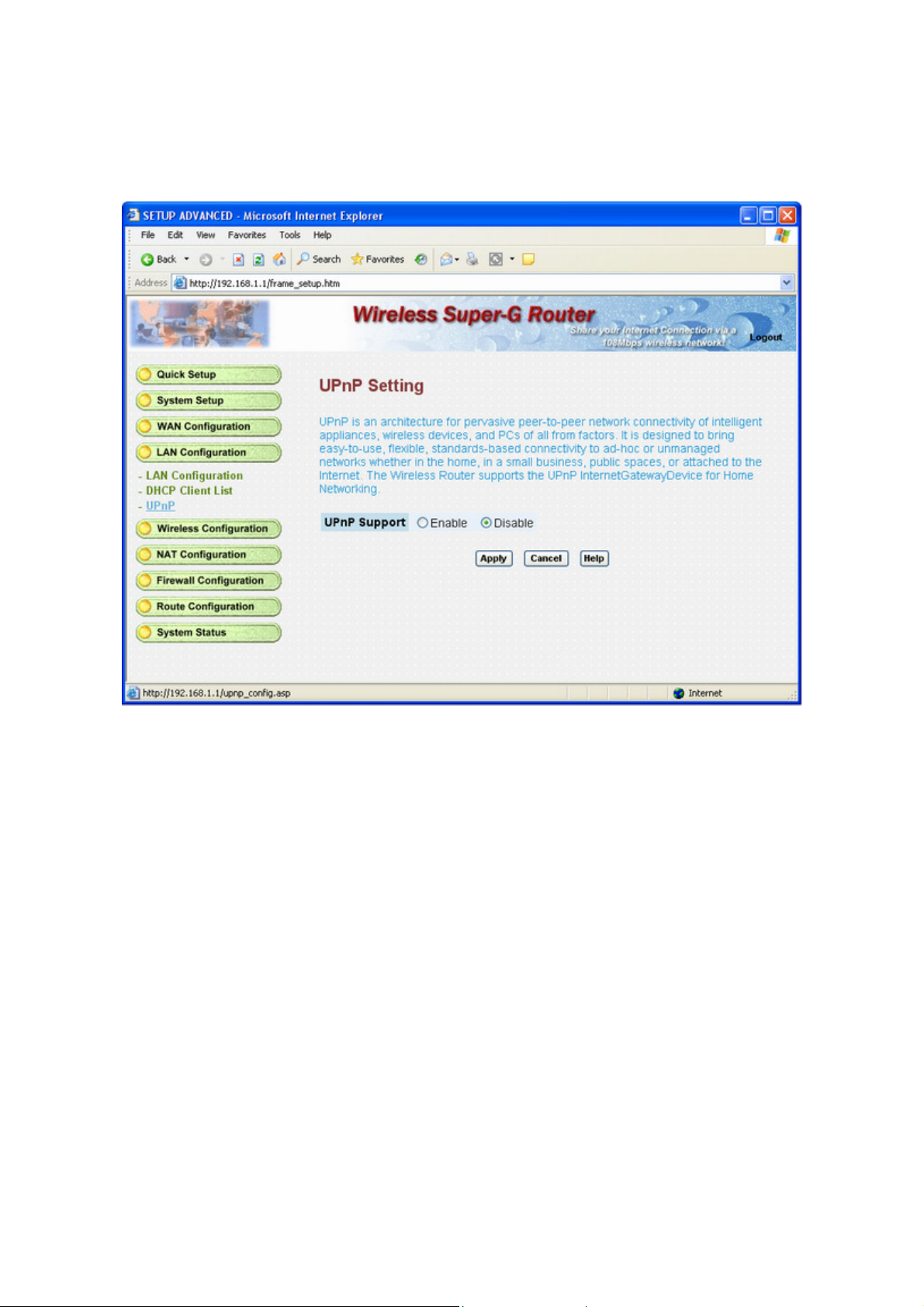
3.5.3 UPnP Setting
You can Enable or Disable the UPnP function.
Page 29

28
3.6.1 Wireless Setting
SSID
The identifier for the network. You can change the SSID. Only devices with the same SSID can interconnect.
Channel ID
The channel number used for networking. The channel setting of the wireless devices within a network should be
the same.
When operation rate set to Super G or Auto, the channel ID will fix in channel 6.
Operation Rate
Support 802.11g , Super G (static) and Super G (dynamic).
Page 30

29
3.6.2 Wireless Security
The Authentication type supports “Open system”, “Shared key”, “WPA-802.1x”, “WPA-PSK”, “WPA2-802.1x” and
"WPA2-PSK".
Page 31

30
3.6.3 WDS Configuration
Enter the MAC Address of another AP you want to connect to and choose Enable to enable the WDS link.
Click the Apply button to save the setting.
Page 32

31
3.7.1 Firewall Setting
The router provides extensive firewall protection by restricting connection parameters to limit the risk of intrusion
and defending against a wide array of common hacker attacks. However, for applications that require unrestricted
access to the Internet.
Page 33

32
3.7.2 Client Filtering
You can block certain clients accessing the internet via Client Filtering.
Page 34

33
3.7.3 MAC Control
You can block certain client PCs accessing the Internet based on MAC address.
Page 35

34
3.8.1 Static Routing
The static routing function determines the path that router follows over your network before and after it passes
through your router. You can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to access the Internet through
this device.
Page 36
35
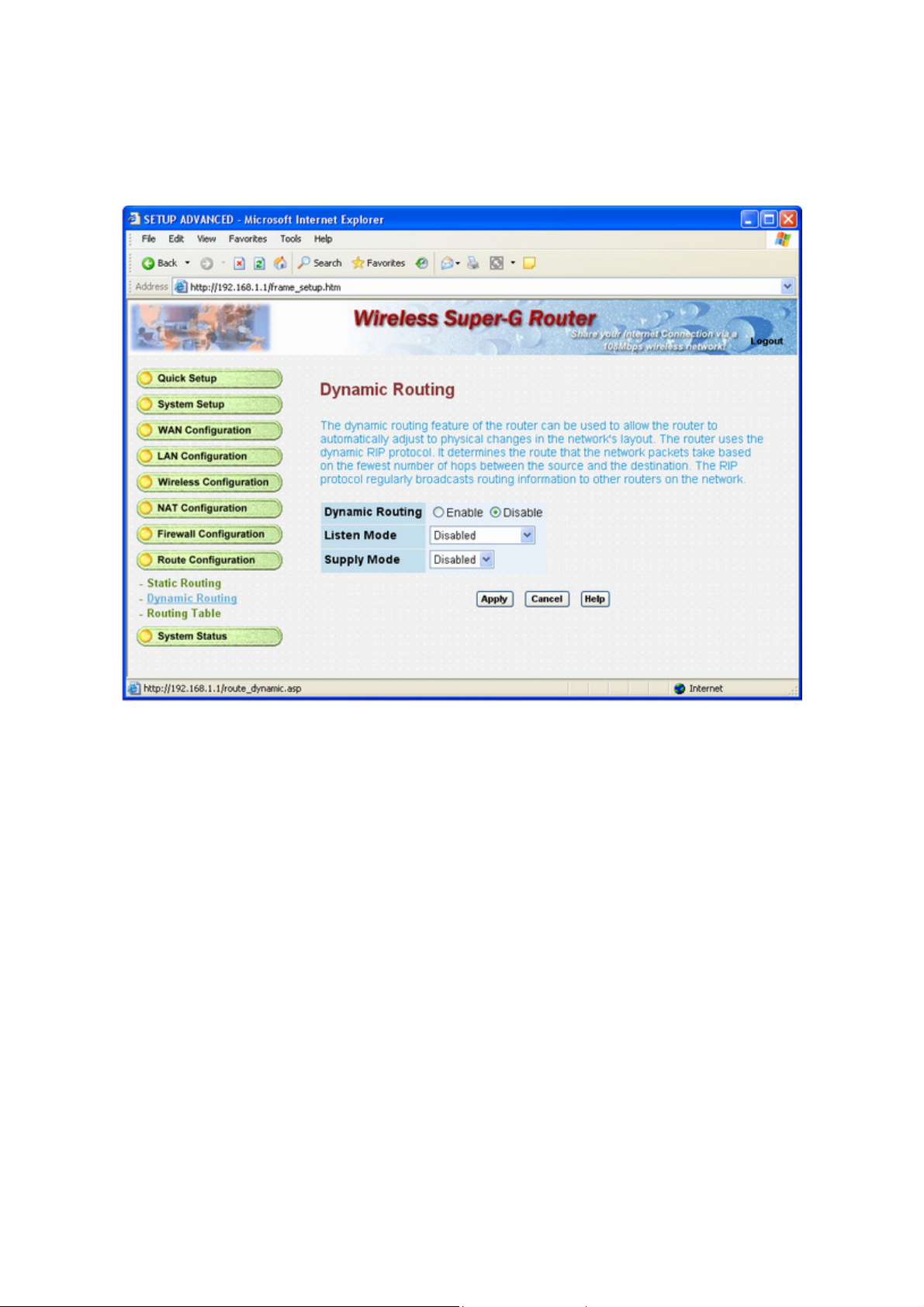
3.8.2 Dynamic Routing
The dynamic routing feature of the router can be used to allow the router to automatically adjust to physical
changes in the network's layout. The router uses the dynamic RIP protocol. It determines the route that the
network packets take based on the fewest number of hops between the source and the destination. The RIP
protocol regularly broadcasts routing information to other routers on the network.
Page 37

36
3.8.3 Routing Table
The Routing table allows you to see how many routings on your routing table and interface information.
Page 38

37
3.9.1 System Status
The System Status page shows the WAN, LAN and router's firmware version.
Page 39
38
3.10.1 TCP/IP Settings for Windows Operating System
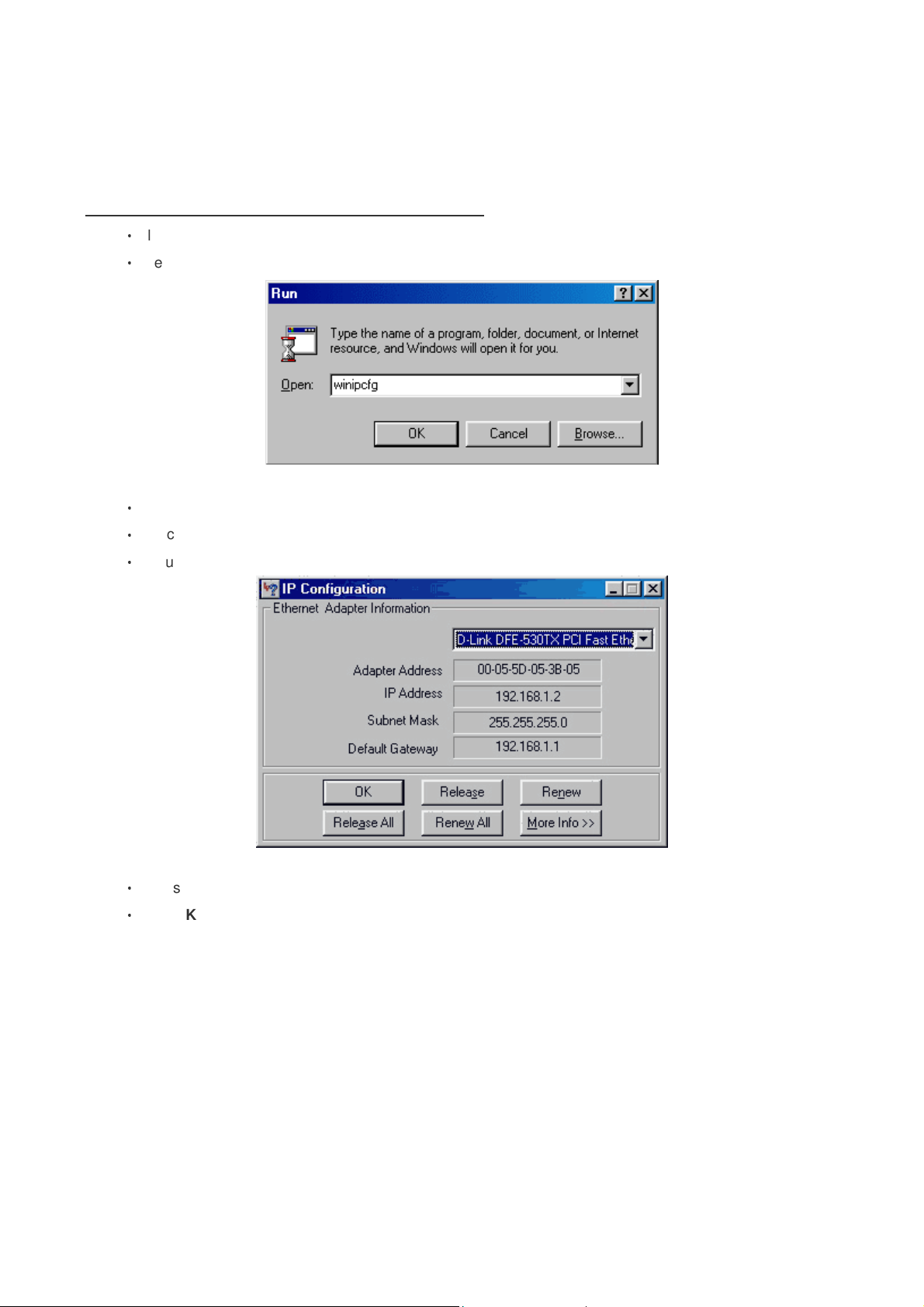
1. How can I find my IP Address in Windows 95, 98, or Me?
‧
Click on Start, then click on Run.
‧
The Run Dialogue Box will appear. Type winipcfg in the window as shown then click OK
‧
The IP Configuration window will appear, displaying your Ethernet Adapter Information.
‧
Select your adapter from the drop down menu.
‧
If you do not see your adapter in the drop down menu, your adapter is not properly installed.
‧
After selecting your adapter, it will display your IP Address, subnet mask, and default router.
‧
Click OK to close the IP Configuration window.
Page 40

39
2. How can I find my IP Address in Windows 2000/XP?
‧
Click on Start and select Run.
‧
Type cmd then click OK.
‧
From the Command Prompt, enter ipconfig. It will return your IP Address, subnet mask, and default
router.
‧
Type exit to close the command prompt.
‧
Make sure you take note of your computer´s Default Router IP Address. The Default Router is the IP
Address of the router. By default, it should be 192.168.0.1
Page 41
40
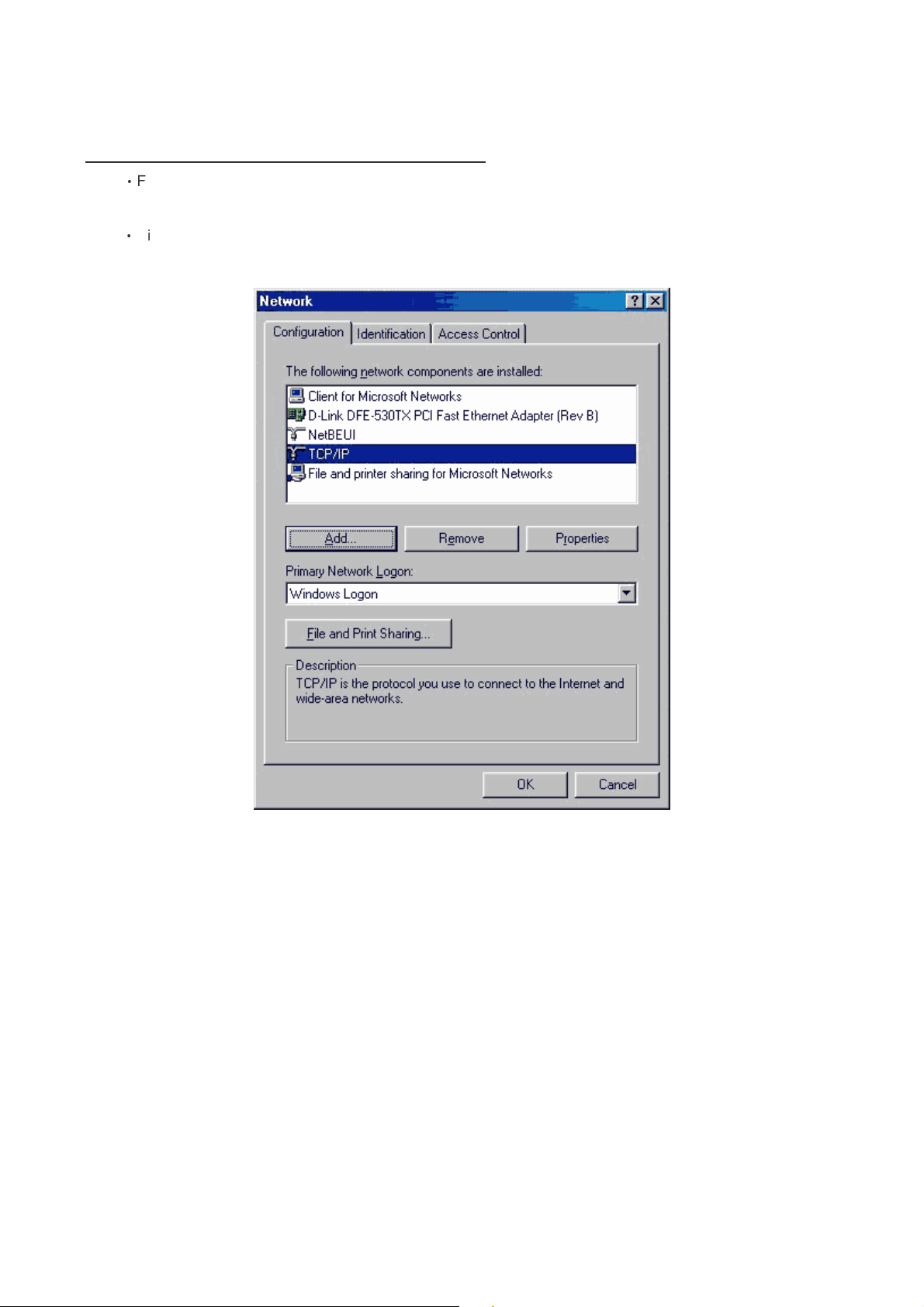
3. How can I assign a Static IP Address in Windows 98/Me?
‧
From the desktop, right-click on the Network Neighborhood icon (Win ME - My Network Places) and
select Properties.
‧
Highlight TCP/IP and click the Properties button. If you have more than 1 adapter, then there will be a
TCP/IP “Binding” for each adapter. Highlight TCP/IP > (your network adapter) and then click Properties.
Page 42
41
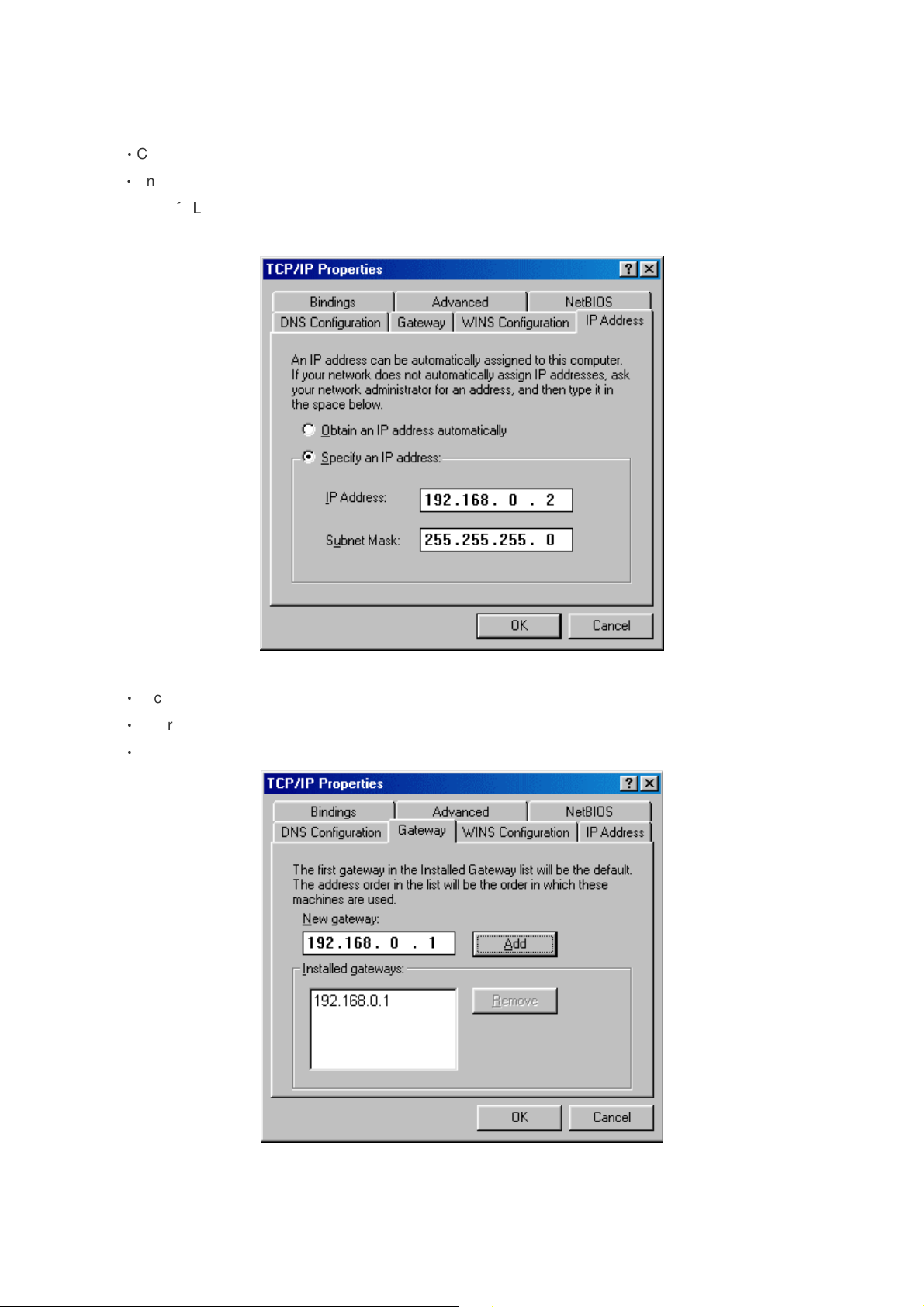
‧
Click Specify an IP Address.
‧
Enter in an IP Address that is on the same subnet as the LAN IP Address on your router. Example: If the
router´s LAN IP Address is 192.168.0.1, make your IP Address 192.168.0.X where X is between 2-99.
Make sure that the number you choose is not in use on the network.
‧
Click on the Router tab.
‧
Enter the LAN IP Address of your router here (192.168.0.1).
‧
Click Add when finished.
Page 43

42
‧
Click on the DNS Configuration tab.
‧
Click Enable DNS. Type in a Host (can be any word). Under DNS server search order, enter the LAN IP
Address of your router (192.168.0.1). Click Add.
‧
Click OK twice.
‧
When prompted to reboot your computer, click Yes. After you reboot, the computer will now have a static,
private IP Address.
Page 44

43
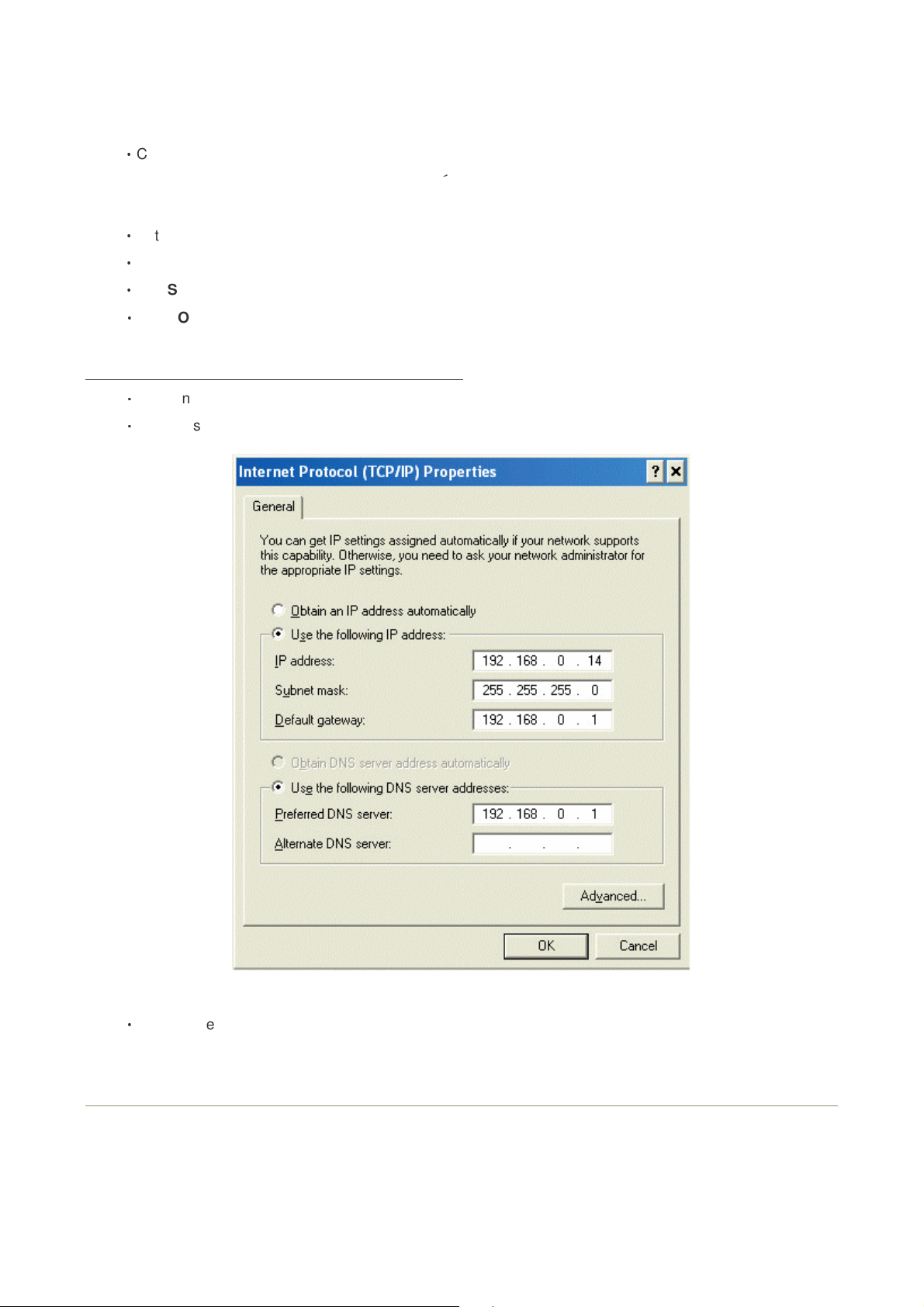
4. How can I assign a Static IP Address in Windows 2000?
‧
Right-click on My Network Places and select Properties.
‧
Right-click on the Local Area Connection which represents your network card and select Properties.
‧
Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
Page 45
44
‧
Click Use the following IP Address and enter an IP Address that is on the same subnet as the LAN IP
Address on your router. Example: If the router´s LAN IP Address is 192.168.0.1, make your IP Address
192.168.0.X where X = 2-99. Make sure that the number you choose is not in use on the network.
‧
Set the Default Router to be the same as the LAN IP Address of your router (192.168.0.1).
‧
Set the Primary DNS to be the same as the LAN IP address of your router (192.168.0.1).
‧
The Secondary DNS is not needed or enter a DNS server from your ISP.
‧
Click OK twice. You may be asked if you want to reboot your computer. Click Yes.
5. How can I assign a Static IP Address in Windows XP?
‧
Click on Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections > Network connections.
‧
See the steps for assigning a static IP address in Windows 2000 and continue from there.
‧
Access the Web management. Open your Web browser and enter the IP Address of your router device in
the address bar. This should open the login page for the Web management. Follow instructions to login
and complete the configuration.
Page 46

45
Appendix A Troubshooting
This chapter gives information about troubleshooting your Wireless Super-G Router. After each problem
description, instructions are provided to help you diagnose and solve the problem.
Basic Function
After you turn on power to the Router, the following sequence of events should occur:
‧
The Router performs a self-test for 30 seconds. The Power LED must always on.
‧
If the Local Ethernet connections are correctly made to operational devices, each LAN LED should be on.
And it will flash when there are data transferring.
‧
If a WAN Ethernet port is connected to the Router WAN port, the WAN LED should be on.
And the WAN LED will flash when there are data transferring.
If any of these conditions does not occur, refer to the appropriate following section.
Power LED Not On
‧
Make sure that the power cord is properly connected to your Router and that the power supply adapter is
properly connected to a functioning power outlet.
‧
Check that you are using the 9V DC (1.5A) power adapter for this product. If the error persists, you have a
hardware problem and should contact technical support.
LAN LED Not On
If the LAN LED does not light when the Ethernet connection is made, check the following:
‧
Be sure you are using the correct cable.
‧
Make sure that the Ethernet cable connections are secure at the Router and at the hub or workstation.
‧
Make sure that power is turned on to the connected hub or workstation.
Troubleshooting the ISP Connection
If your Router is unable to access the Internet, you should first determine whether the Router is able to obtain a
WAN IP address from the ISP. Unless you have been assigned the static IP address, your Router must request an
IP address from the ISP.
You can determine whether the request was successful using either the Browser interface or the Console
interface.
Page 47

46
To check the WAN IP address from the Browser interface:
1. Launch your Browser and select an external site such as www.yahoo.com
2. Access the Main Menu of the Router's configuration at http://192.168.1.1
3. Click on System status
4. Check that an IP address is shown for the WAN Port
5. If it is "NO" on active table, your Router has not obtained an IP address from your ISP.
If your Router is unable to obtain an ISP address from the ISP, the problem may be one of the following:
‧
Your Router may be set incorrectly the login name and password for PPPoE mode.
‧
Your ISP may check for your PC's Host Name.
Assign the PC Host Name of your ISP account to the Router as System Name, or as Host Name in the System
setup.
If your Router can obtain an IP address, but your PC is unable to load any web pages from the Internet:
‧
Your PC may not recognize any DNS server addresses.
A DNS server is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names (such as www addresses) to numeric IP
addresses. Typically your ISP will provide the addresses of one or two DNS servers for your use. If you entered a
DNS address in WAN Configuration, reboot your PC and verify the DNS address. Alternatively, you may configure
your PC manually with DNS addresses, as explained in your operating system documentation.
‧
Your PC may not have the Router configured as its TCP/IP gateway.
If your PC obtains its information from the Router by DHCP, reboot the PC and verify the gateway address.
Testing the LAN Path to Your Router
You can ping the Router from your PC to verify that the LAN path to your Router is set up correctly. To ping the
Router from a PC running Windows system.
‧
From the Windows toolbar, click on the Start button and select Run.
‧
In the field provided, type Ping followed by the IP address of the Router , as in this example: ping 192.168.1.1
‧
Click on OK.
You should see a message like this one:
Pinging < IP address > with 32 bytes of data
If the path is working, you see this message:
Reply from < IP address >: bytes=32 time=NN ms TTL=xxx
Page 48

47
If the path is not working, you see this message:
Request timed out
If the path is not functioning correctly, you could have one of the following problems:
‧
Wrong physical connections
-Make sure the Local LAN LED is on.
-Check that the corresponding Link LEDs are on for your network interface card and for the hub ports (if any)
that are connected to your workstation and Router.
‧
Wrong network configuration
-Verify that the Ethernet card driver software and TCP/IP software are both installed and configured on your PC
or workstation.
-Verify that the IP address for your Router and your workstation are correct and that the addresses are on the
same subnet.
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device
After verifying that the LAN path works correctly, test the path from your PC to a remote device:
‧
From the Windows run menu, type PING -n 10 followed by the IP address of a remote device such as your ISP's
DNS server.
If the path is functioning correctly, replies as in the previous section are displayed.
If you do not receive replies:
‧
Check that your PC has the IP address of your Router listed as the default gateway. If the IP configuration of
your PC is assigned by DHCP, this information will not be visible in the control panel network utility. Go to the
Run... window and run ipconfig.
The IP address of t he Router should appear as the Default Gateway.
‧
Check to see that the network address of your PC (the portion of the IP address specified by the netmask) is
different from the network address of the remote device.
‧
Check console to verify the WAN status. If the menu indicates the WAN status as down, check that your ADSL
line is connected and functioning.
‧
If your ISP assigned a host name to your PC, enter that host name as the Router name.
Restoring the factory default configuration
You can erase the current configuration and restore factory setting by press reset button over 5 seconds at rear
panel.
Page 49

48
Appendix B Frequency Asked Questions
What should I do when WAN's IP won't get IP address with Dynamic IP mode?
Make sure WAN LED is light when you use the router. If it's dark, check the cable you used. (This problem can be
solved by this step for most of users.)
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that the Wireless Super-G Router will support?
The Router will support to 253 IP addresses.
Where is the Broadband Router installed on the network?
In a typical environment, the Router is installed between the Cable/DSL Modem and the WAN. Plug the Wireless
Super-G Router into the Cable/DSL Modem's Ethernet port.
What is Network Address Translation and what is it used for?
Network Address Translation (NAT) translates multiple IP addresses on the private LAN to one public address
that is sent out to the Internet.
This adds a level of security since the address of a PC connected to the private LAN is never transmitted on the
Internet. Furthermore, NAT allows the Wireless Super-G Router to be used with low cost Internet accounts, such
as DSL or cable modems, where only one TCP/IP address is provided by the ISP. The user may have many
private addresses behind this single address provided by the ISP.
Does the Wireless Super-G Router support any operating system other than Windows 95/98/Me,
or Windows NT/2000/XP?
Yes, it provides technical support for setup, configuration or trouble shooting of any non-windows operating
systems.
How can I not receive corrupted FTP downloads?
If you are experiencing corrupted files when you download a file with your FTP client, try using another FTP
program.
Web page hangs, corrupt downloads, or nothing but junk characters is being displayed on the screen.
What do I need to do?
Force your NIC to 10Mbps or half duplex mode, and turn off the "Auto-negotiate" feature of your NIC as a
temporary measure.
(Please look at the Network Control Panel, in your Ethernet Adapter's Advanced Properties tab.).
Does the Wireless Super-G Router support IPsec?
Yes, but only pass through IPSec supported.
Page 50

49
Will the Router function in a Macintosh environment?
Yes.
With which type of firewall is the Wireless Super-G router equipped?
The Wireless Super-G Router uses NAT and TCP/IP port inspections.
Is the Router cross-platform compatible?
Any platform that supports Ethernet and TCP/IP is compatible with the Router.
Which modems are compatible with the Router?
The router is compatible with any cable or DSL modem that supports Ethernet.
How can I check whether I have static DHCP IP Addresses?
Consult your ISP to confirm the information.
What is the default IP address of the router for LAN port?
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Why does the router dial out for PPPoE mode very often?
Normally some of game, music or anti-virus program will send out packets that trigger the router to dial out, you
can close these program. Or you can set the idle time to 0, then control to dial out manually.
Why can't I connect to the Web Configuration?
you can remove the proxy server settings in your web browser.
Why is that I can ping to outside hosts, but not access Internet websites?
Check the DNS server settings on your PC. You should get the DNS servers settings from your ISP. If your PC is
running a DHCP client, remove any DNS IP address setting. As the router will assign the DNS settings to the
DHCP-client-enabled PC.
What is DMZ Hosting?
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) allows one IP address (computer) to be exposed to the Internet. Some applications
require multiple TCP/IP ports to be open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP if you
want to use DMZ Hosting.
Does the Router pass PPTP packets or actively route PPTP sessions?
The Router allows PPTP packets to pass through.
Page 51

50
Appendix C Specification
General Specifications
Network Protocol and Standards Compatibility
Data and Routing Protocols:
TCP/IP, RIP-1, RIP-2, DHCP
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Power Adapter
North America:
United Kingdom, Australia:
Europe:
Japan:
All regions (output):
120V, 60 Hz, input
240V, 50 Hz, input
230V, 50 Hz, input Japan
100V, 50/60 Hz, input
9 V DC @ 1.5A output
Environmental Specifications
Operating temperature:
Operating humidity:
Electromagnetic Emissions
Meets requirements of:
Interface Specifications
LAN:
WAN:
Wireless:
0°C to 55°C
90% maximum relative humidity, Non-condensing
FCC Part 15 Class B
VCCI Class B
EN 55 022 (CISPR 22), Class B
10BASE-T or 100BASE-Tx, RJ-45
10BASE-T or 100BASE-Tx, RJ-45
802.11b/g and Atheros Wireless Super-G AP
Page 52

51
Appendix D Glossary
Static IP Addresses
A static IP address is an IP address permanently assigned to computer in a TCP/IP network. Static IP addresses
are usually assigned to networked devices which are consistently accessed by multiple users, such as Server
PCs, or printers. If you are using your Router to share your cable or DSL Internet connection, contact your ISP to
see if they have assigned your home a static IP address. You will need that address during your Router's
configuration.
Dynamic IP Addresses
A dynamic IP address is an IP address that is automatically assigned to a client station (computer, printer, etc.) in
a TCP/IP network. Dynamic IP addresses are typically assigned by a DHCP server, which can be a computer on
the network or another piece of hardware, such as the Router. A dynamic IP address may change every time your
computer connects to the network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP is software that automatically assigns IP addresses to client stations logging onto a TCP/IP network.
DHCP eliminates having to manually assign permanent IP addresses to every device on your network. DHCP
software typically runs in servers and is also found in network devices such as Routers.
10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3 specification for 10 Mbps Ethernet over twisted pair wiring.
100BASE-Tx
IEEE 802.3 specification for 100 Mbps Ethernet over twisted pair wiring.
Dynamic Host Configuration
An Ethernet protocol that provides a centralized administration point for assigning network configuration
information.
IP Address
A 4-byte number uniquely defining each host on the Internet. Ranges of addresses are assigned by Internic, an
organization formed for this purpose. Usually written in dotted-decimal notation with periods separating the bytes
(for example, 210.167.34.77).
Internet Packet Exchange
Novell's internetworking protocol.
Page 53

52
Internet Protocol
The main internetworking protocol used in the Internet. Used in conjunction with the Transfer Control Protocol
(TCP) to form TCP/IP.
Local area network
A communications network serving users within a limited geographical area, such as one floor of a building,
controlled by a network operating system and using a transport protocol.
Maximum Receive Unit
The size in bytes of the largest packet that can be sent or received.
NAT
See Network Address Translator.
netmask
A number that explains which part of an IP address comprises the network address and which part is the host
address on that network. It can be expressed in dotted-decimal notation or as a number appended to the IP
address. For example, a 28-bit mask starting from the MSB can be shown as 255.255.255.192 or as /28
appended to the IP address.
Network Address Translator (or Translation)
A proposal for IP address reuse, where the local IP address is mapped to a globally unique address. See also
masquerading.
PPP over Ethernet
PPPoE PPP over Ethernet is a protocol for connecting remote hosts to the Internet over an always-on connection
by simulating a
dial-up connection.
Point-to-Point Protocol
PPP A protocol allowing a computer using TCP/IP to connect directly to the Internet.
RFC
Request For Comment. Refers to documents published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) proposing
standard protocols and procedures for the Internet. RFCs can be found at www.ietf.org.
Routing Information Protocol
A protocol in which routers periodically exchange information with one another so that they can determine
minimum distance paths between sources and destinations.
Page 54

53
unnumbered links
LANs by way of a WAN, where the two WAN A method of connecting two end points do not have their own IP
addresses.
wide area network
A long distance link used to extend or connect remotely located local area networks.
Page 55

54
Declaration of Conformity
The following
Equipment: Super-G Broadband Router
Report No.: S940762
is herewith confirmed to comply with the requirements set out in the Council
Directive on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States relating to
Electromagnetic Compatibility(89/336/EEC) (1999/5/EC).
For the evaluation of above mentioned Directives, the following standards were applied:
ETSI EN 301 489-17 : V1.2.1 (2002-08).
Declaration of Conformity
The following
Equipment : Super-G Broadband Router
Report No. : E940762
is herewith confirmed to comply with the requirements of its Harmonised Standards for
CE Marking which have been set out in the Council Directive, and published as below:
1) The EMC Directives of 89/336/EEC, 92/31/EEC and 93/68/EEC;
2) The R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
For the evaluation of above mentioned Harmonised Standards,
the following technical and test standards were applied:
ETSI EN 300328-1 : 2001
Declaration of Conformity for CE Marking
The following
Equipment : Super-G Broadband Router
Report No. : S940146
is herewith confirmed to comply with the requirements set out in the Council
Directive on the harmonization of the Laws of the Member States relating to
electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits(73/23/EEC).
For the evaluation of above mentioned Directives, the following standards were applied:
EN 60950-1: 2001
Testing Laboratory:
PEP TECHNOLOGIES LTD.
12FL-3, NO.27-1, LANE 169, KANG NING ST., HSI CHIH CITY, TAIPEI HSIEN, TAIWAN, R.O.C.
 Loading...
Loading...