Page 1

Wireless
The Barricade also operates as a wireless-to-wired bridge, allowing wireless
computers to access resources available on the wired LAN, and to access
the Internet. To configure the Barricade as a wireless access point for
wireless clients (either stationary or roaming), all you need to do is enable
the wireless function, define the radio channel, the domain identifier, and
the encryption options. Check Enable and click APPLY.
W
IRELESS
4-25
Page 2
C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
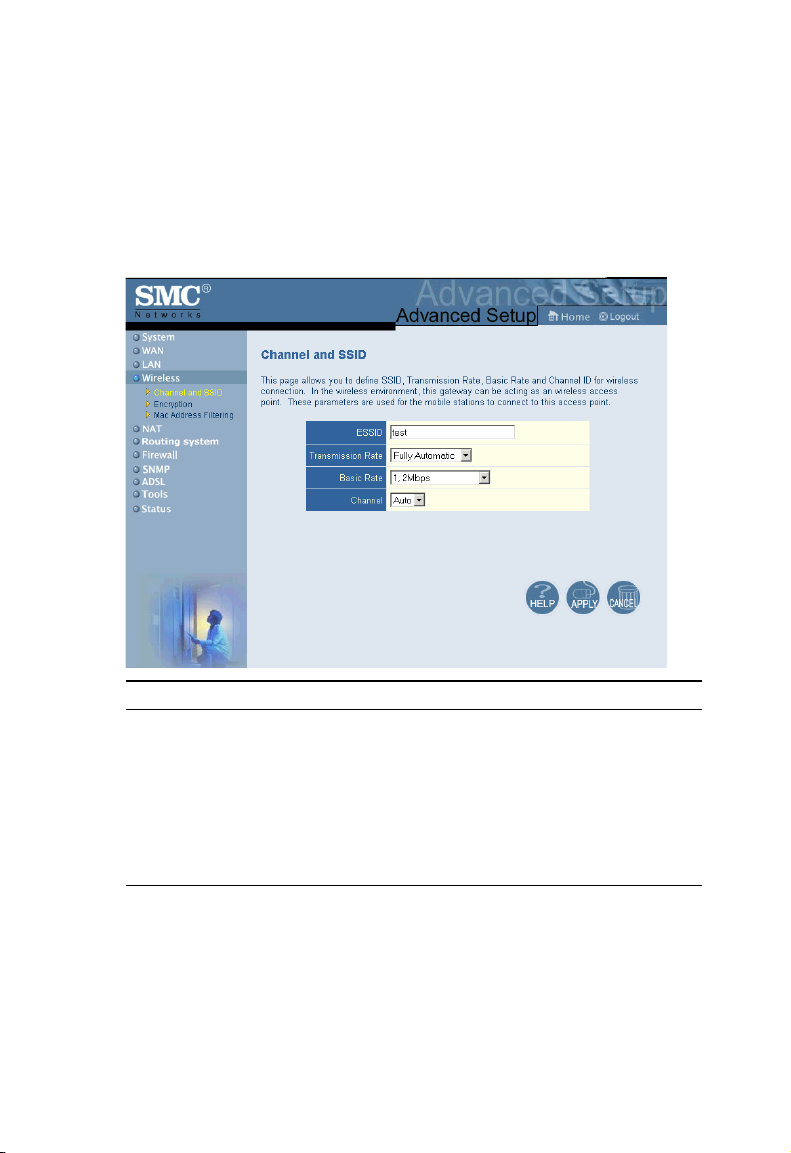
Channel and SSID
You must specify a common radio channel and SSID (Service Set ID) to
be used by the Barricade Wireless Router and all of your wireless clients.
Be sure you configure all of your clients to the same values.
Parameter Description
ESSID Extended Service Set ID. The ESSID must be the same on the
Transmission Rate The default is Fully Automatic. The transmission rate is
Barricade and all of its wireless clients.
automatically adjusted based on the receiving data error rate.
Usually the connection quality will vary depending on the
distance between the wireless router and wireless adapter. You
can also select a lower transmission data rate to maximize the
radio communication range.
4-26
Page 3

W
IRELESS
Parameter Description
Basic Rate The highest rate specified will be the rate that the Barricade will
use when transmitting broadcast/multicast and management
frames. Available options are: All (1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps), and
1, 2Mbps (default is 1, 2Mbps).
Channel The radio channel must be the same on the Barricade and all of
your wireless clients.
The Barricade will automatically assign itself a radio channel, or
you may select one manually.
4-27
Page 4
C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
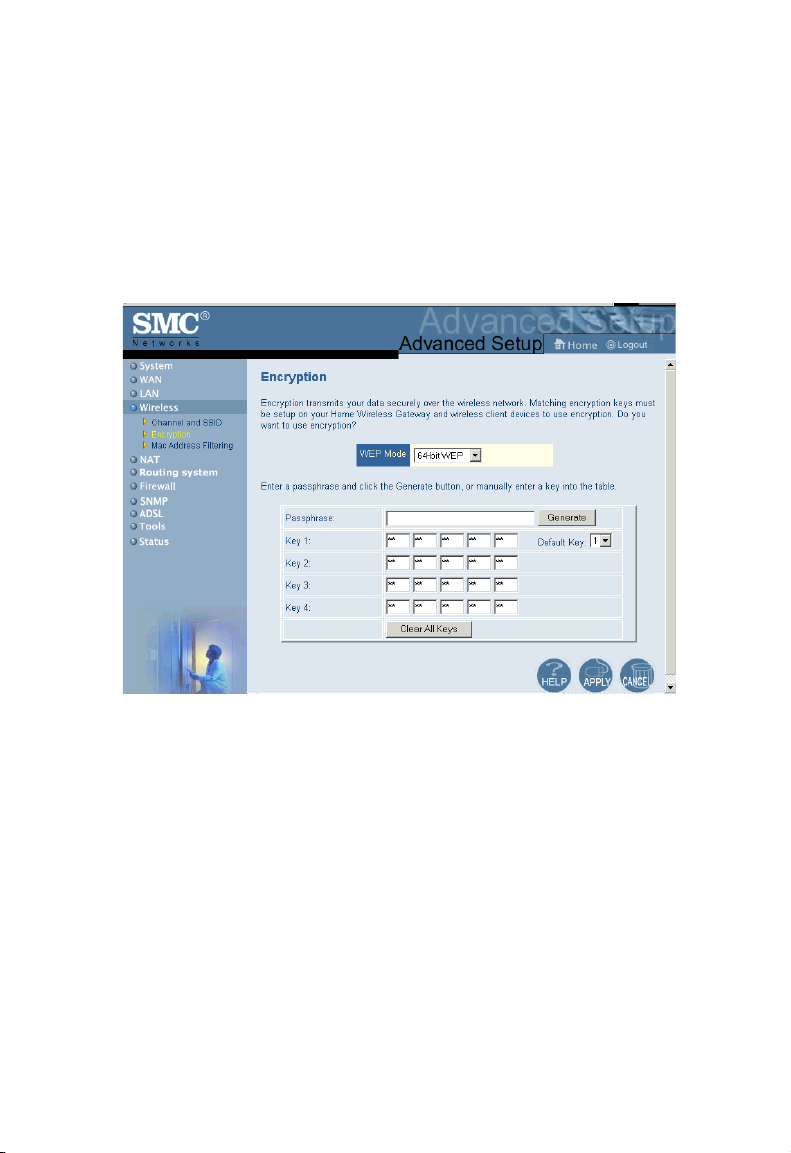
Encryption
If you are transmitting sensitive data across wireless channels, you should
enable encryption. You must use the same set of encryption keys for the
Barricade and all of the wireless clients. Choose between standard 64-bit
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) or the more robust 128-bit encryption.
You may automatically generate encryption keys or manually enter the
keys. For automatic 64-bit security, enter a passphrase and click Generate,
four keys will be generated. Choose a key from the drop-down list or
accept the default key. Automatic 128-bit security generates a single key.
Note: The passphrase can consist of up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
To manually configure the keys, enter five hexadecimal pairs of digits for
each 64-bit key, or enter 13 pairs for the single 128-bit key. (A hexadecimal
digit is a number or letter in the range 0-9 or A-F.)
Note that WEP protects data transmitted between wireless nodes, but
does not protect any transmissions over your wired network or over the
Internet.
4-28
Page 5

MAC Address Filtering
Client computers can be filtered using the unique MAC address of their
IEEE 802.11 network card. To secure an access point using MAC address
filtering, you must enter a list of allowed/denied client MAC addresses into
the filtering table. (See “Finding the MAC address of a Network Card” on
page 4-57.)
W
IRELESS
Parameter Description
Filtering
Disable Disables MAC address filtering.
Enable Enables MAC address filtering.
Setting
Permissions Allows only devices with their MAC address in the list to
connect to the Barricade.
Prohibition Denies access to the Barricade from devices with their
MAC address in the list.
4-29
Page 6

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
NAT
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet gaming,
videoconferencing, and Internet telephony. These applications may not
work when Network Address Translation (NAT) is enabled. If you need to
run applications that require multiple connections, use these pages to
specify the additional public ports to be opened for each application.
Address Mapping
Allows one or more public IP addresses to be shared by multiple internal
users. This also hides the internal network for increased privacy and
security. Enter the Public IP address you wish to share into the Global IP
field. Enter a range of internal IPs that will share the global IP into the
from field.
4-30
Page 7

Virtual Server
If you configure the Barricade as a virtual server, remote users accessing
services such as Web or FTP at your local site via public IP addresses can
be automatically redirected to local servers configured with private IP
addresses. In other words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP
port number), the Barricade redirects the external service request to the
appropriate server (located at another internal IP address).
NAT
If you configure the Barricade as a virtual server, remote users accessing
services such as Web or FTP at your local site via public IP addresses can
be automatically redirected to local servers configured with private IP
addresses. In other words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP
port number), the Barricade redirects the external service request to the
appropriate server (located at another internal IP address).
4-31
Page 8
C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
For example, if you set Type/Public Port to TCP/80 (HTTP or Web) and
the Private IP/Port to 192.168.2.2/80, then all HTTP requests from
outside users will be transferred to 192.168.2.2 on port 80. Therefore, by
just entering the IP Address provided by the ISP, Internet users can access
the service they need at the local address to which you redirect them.
The more common TCP service ports include:
HTTP: 80, FTP: 21, Telnet: 23, and POP3: 110. A list of ports is
maintained at the following link:
http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers.
Note: The WAN interface should have a fixed IP address to best utilize
this function. If your ISP only provides dynamic IP addresses, a
search for “free dynamic IP” on any major search engine will turn
up tools that will allow you to use the same domain name even
though your IP address changes each time you log into the ISP.
4-32
Page 9

R
OUTING SYSTEM
Routing System
These pages define routing related parameters, including static routes and
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) parameters.
Static Route
Click Add to add a new static route to the list, or check the box of an
already entered route and click Modify. Click Delete to remove an entry
from the list.
Parameter Description
Index Check the box of the route you wish to delete or
modify.
Network Address Enter the IP address of the remote computer for
which to set a static route.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask of the remote network for
which to set a static route.
Gateway Enter the WAN IP address of the gateway to the
remote network.
4-33
Page 10

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
RIP
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) sends routing-update messages at regular
intervals and when the network topology changes. When a router receives
a routing update that includes changes to an entry, it updates its routing
table to reflect the new route. RIP routers maintain only the best route to a
destination. After updating its routing table, the router immediately begins
transmitting routing updates to inform other network routers of the
change.
Parameter Description
Interface The WAN interface to be configured.
Operation Mode Disable: RIP disabled on this interface.
Enable: RIP enabled on this interface.
Silent: Listens for route broadcasts and updates its
route table. It does not participate in sending route
broadcasts.
Version Sets the RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
version to use on this interface.
4-34
Page 11

R
OUTING SYSTEM
Parameter Description
Poison Reverse A way in which a router tells its neighbor routers
that one of the routers is no longer connected.
Authentication Required • None: No authentication.
• Password: A password authentication key is
included in the packet. If this does not match
what is expected, the packet will be discarded.
This method provides very little security as it
is possible to learn the authentication key by
watching RIP packets.
MD5: MD5 is an algorithm that is used to verify
data integrity through the creation of a 128-bit
message digest from data input (which may be a
message of any length) that is claimed to be as
unique to that specific data as a fingerprint is to a
specific individual.
Authentication Code Password or MD5 Authentication key.
4-35
Page 12

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
Routing Table
Parameter Description
Flags Indicates the route status:
C = Direct connection on the same subnet.
S = Static route.
R = RIP (Routing Information Protocol) assigned route.
I = ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Redirect route.
Network Address Destination IP address.
Netmask The subnetwork associated with the destination.
This is a template that identifies the address bits in the
destination address used for routing to specific subnets. Each bit
that corresponds to a “1” is part of the network/subnet number;
each bit that corresponds to “0” is part of the host number.
Gateway The IP address of the router at the next hop to which matching
Interface The local interface through which the next hop of this route is
Metric When a router receives a routing update that contains a new or
frames are forwarded.
reached.
changed destination network entry, the router adds 1 to the
metric value indicated in the update and enters the network in
the routing table.
Note: Most modern routers support RIP-2 so there is usually no need for
a static route table.
4-36
Page 13

Firewall
The Barricade Router’s firewall inspects packets at the application layer,
maintains TCP and UDP session information including time-outs and
number of active sessions, and provides the ability to detect and prevent
certain types of network attacks.
F
IREWALL
Network attacks that deny access to a network device are called Denial-ofService (DoS) attacks. DoS attacks are aimed at devices and networks with
a connection to the Internet. Their goal is not to steal information, but to
disable a device or network so users no longer have access to network
resources.
The Barricade protects against the following DoS attacks: IP Spoofing,
Land Attack, Ping of Death, IP with zero length, Smurf Attack, UDP port
loopback, Snork Attack, TCP null scan, and TCP SYN flooding. (See
“Intrusion Detection” on page 4-42 for details.)
The firewall does not significantly affect system performance, so we advise
leaving it enabled to protect your network. Select Enable and click the
APPLY button to open the Firewall submenus.
4-37
Page 14

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
Access Control
Access Control allows users to define the outgoing traffic permitted or
not-permitted through the WAN interface. The default is to permit all
outgoing traffic.
The Barricade can also limit the access of hosts within the local area
network (LAN). The MAC Filtering Table allows the Barricade to enter up
to 32 MAC addresses that are not allowed access to the WAN port.
The following items are on the Access Control screen:
Parameter Description
Normal Filtering Table Displays the IP address (or an IP address range)
MAC Filtering Table Displays the MAC (Media Access Control) address
filtering table.
filtering table.
4-38
Page 15

F
IREWALL
1. Click Add PC on the Access Control screen.
2. Define the appropriate settings for client PC services (as shown on the
following screen).
3. Click OK and then click APPLY to save your settings.
4-39
Page 16

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
URL Blocking
The Barricade allows the user to block access to Web sites from a
particular PC by entering either a full URL address or just a keyword. This
feature can be used to protect children from accessing violent or
pornographic Web sites.
4-40
Page 17

Schedule Rule
You may filter Internet access for local clients based on rules. Each access
control rule may be activated at a scheduled time. Define the schedule on
the Schedule Rule page, and apply the rule on the Access Control page.
F
IREWALL
Follow steps to add schedule rule:
1. Click Add Schedule
Rule.
2. Define the appropriate
settings for a schedule
rule (as shown on the
following screen).
3. Click OK and then
click APPLY to save
your settings.
4-41
Page 18

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
Intrusion Detection
4-42
Page 19

F
IREWALL
• Intrusion Detection Feature
SPI and Anti-DoS firewall protection (Default: Enabled) — The Intrusion
Detection Feature of the Barricade Router limits access for incoming
traffic at the WAN port. When the SPI feature is turned on, all incoming
packets will be blocked except for those types marked with a check in the
Stateful Packet Inspection section.
RIP Defect (Default: Enabled) — If an RIP request packet is not replied
to by the router, it will stay in the input queue and not be released.
Accumulated packets could cause the input queue to fill, causing severe
problems for all protocols. Enabling this feature prevents the packets
accumulating.
Discard Ping from WAN (Default: Disabled) — Prevent a PING on the
Gateway’s WAN port from being routed to the network.
• Stateful Packet Inspection
This is called a “stateful” packet inspection because it examines the
contents of the packet to determine the state of the communications; i.e., it
ensures that the stated destination computer has previously requested the
current communication. This is a way of ensuring that all communications
are initiated by the recipient computer and are taking place only with
sources that are known and trusted from previous interactions. In addition
to being more rigorous in their inspection of packets, stateful inspection
firewalls also close off ports until connection to the specific port is
requested.
When particular types of traffic are checked, only the particular type of
traffic initiated from the internal LAN will be allowed. For example, if the
user only checks “FTP Service” in the Stateful Packet Inspection section,
all incoming traffic will be blocked except for FTP connections initiated
from the local LAN.
4-43
Page 20

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
Stateful Packet Inspection allows you to select different application types
that are using dynamic port numbers. If you wish to use the Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI) to block packets, click on the Yes radio button in the
“Enable SPI and Anti-DoS firewall protection” field and then check the
inspection type that you need, such as Packet Fragmentation, TCP
Connection, UDP Session, FTP Service, H.323 Service, and TFTP Service.
• When hackers attempt to enter your network, we can
alert you by e-mail
Enter your E-mail address. Specify your SMTP and POP3 servers, user
name, and password.
• Connection Policy
Enter the appropriate values for TCP/UDP sessions as described in the
following table.
Parameter Defaults Description
Fragmentation
half-open wait
TCP SYN wait 30 sec Defines how long the software will wait for a
TCP FIN wait 5 sec Specifies how long a TCP session will be
TCP connection
idle timeout
UDP session idle
timeout
H.323 data channel
idle timeout
10 sec Configures the number of seconds that a packet
state structure remains active. When the timeout
value expires, the router drops the unassembled
packet, freeing that structure for use by another
packet.
TCP session to synchronize before dropping the
session.
maintained after the firewall detects a FIN
packet.
3600
seconds
(1 hour)
30 sec The length of time for which a UDP session will
180 sec The length of time for which an H.323 session
The length of time for which a TCP session will
be managed if there is no activity.
be managed if there is no activity.
will be managed if there is no activity.
4-44
Page 21

F
IREWALL
• DoS Criteria and Port Scan Criteria
Set up DoS and port scan criteria in the spaces provided (as shown below).
Parameter Defaults Description
Total incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
HIGH
Total incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
LOW
Incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
(per min) HIGH
Incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
(per min) LOW
Maximum incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
number from same
host
Incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions
detect sensitive time
period
Maximum half-open
fragmentation packet
number from same
host
Half-open
fragmentation detect
sensitive time period
Flooding cracker
block time
300
sessions
250
sessions
250
sessions
200
sessions
10 Maximum number of incomplete TCP/UDP
300
msec
30 Maximum number of half-open fragmentation
10000
msec
300
second
Defines the rate of new unestablished sessions
that will cause the software to start deleting
half-open sessions.
Defines the rate of new unestablished sessions
that will cause the software to stop deleting
half-open sessions.
Maximum number of allowed incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions per minute.
Minimum number of allowed incomplete
TCP/UDP sessions per minute.
sessions from the same host.
Length of time before an incomplete
TCP/UDP session is detected as incomplete.
packets from the same host.
Length of time before a half-open
fragmentation session is detected as half-open.
Length of time from detecting a flood attack to
blocking the attack.
Note: The firewall does not significantly affect system performance, so
we advise enabling the prevention features to protect your
network.
4-45
Page 22

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
DMZ
If you have a client PC that cannot run an Internet application properly
from behind the firewall, you can open the client up to unrestricted
two-way Internet access. Enter the IP address of a DMZ (Demilitarized
Zone) host on this screen. Adding a client to the DMZ may expose your
local network to a variety of security risks, so only use this option as a last
resort.
4-46
Page 23

SNMP
Use the SNMP configuration screen to display and modify parameters for
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Community
A computer attached to the network, called a Network Management
Station (NMS), can be used to access this information. Access rights to the
agent are controlled by community strings. To communicate with the
Barricade, the NMS must first submit a valid community string for
authentication.
SNMP
Parameter Description
Community A community name authorized for management access.
Access Management access is restricted to Read Only (Read) or
Valid Enables/disables the entry.
Note: Up to 5 community names may be entered.
Read/Write (Write).
4-47
Page 24

C
ONFIGURING THE BARRICADE
Trap
Specify the IP address to notify an NMS that a significant event has
occurred at an agent. When a trap condition occurs, the SNMP agent
sends an SNMP trap message to any NMSs specified as the trap receivers.
Parameter Description
IP Address Traps are sent to this address when errors or specific events
Community A community string (password) specified for trap management.
Version Sets the trap status to disabled, or enabled with V1 or V2c.
occur on the network.
Enter a word, something other than public or private, to
prevent unauthorized individuals from reading information on
your system.
The v2c protocol was proposed in late 1995 and includes
enhancements to v1 that are universally accepted. These
include a get-bulk command to reduce network management
traffic when retrieving a sequence of MIB variables, and a more
elaborate set of error codes for improved reporting to a
Network Management Station.
4-48
Page 25

ADSL
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is designed to deliver more
bandwidth downstream (from the central office to the customer site) than
upstream. This section is used to configure the ADSL operation type and
shows the ADSL status.
Parameters
ADSL
Parameter Description
Operation Mode • Automatic
• ETSI DTS/TM-06006 standard
• G.992.1 standard
Address 3C etc. Reserved.
4-49
 Loading...
Loading...