Page 1

Technical Manual
P/n: RAA022AA
Page 2

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. Revisions
Table 1: Table of Revisions
Index P/N revision Software revision Section Date
RAA022AA RAH912AA < V1.01 All 31/03/02
This document applies to the latest higher software version.
When a subsequent software version changes the information in this document, a new issue will be
released.
1.1. Notice of liability
The information in this manual is distributed on an ’’as is’’ basis, without warranty. While every
precaution has been taken in the preparation of the manual, ABX DIAGNOSTICS shall have any liability to
any person or entity with respect to liability, loss, or damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or
indirectly by the instructions contained in this manual or by the computer software and hardware
products described herein.
1.2. Trademarks
Other product names mentioned within this publication may be trademarks or registered
trademarks of other companies.
1.3. Copyright ® 2002 by ABX DIAGNOSTICS
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of ABX DIAGNOSTIC S.
ABX DI AGNOS TICS
Parc Euromédecine
Rue du caducée
B.P. 7290
34184 MONTPELLIER Cedex 4 - FRANCE
Tel: (33) (0)4 67 14 15 16
Fax: (33) (0)4 67 14 15 17
2/3
Page 3

2. Working conditions
2.1. Environment
The Pentra 80 should be operated in an indoor location only. Operation at an altitude over 3000
meters (9800 feet) is not recommended. Instrument is designed to be safe for transient voltages
according to INSTALLATION CATEGORY II and POLLUTION DEGREE 2.
Please ask your ABX Diagnostics representative service center for any information about the operating
location when it does not comply with the recommended specifications.
2.2. Location
The Pentra 80 should be placed on a clean and leveled table or work station. Please note that the
Pentra 80, printer and reagents weigh approximately 40 kilograms (88 lbs). Avoid exposure to sunlight.
Proper ventilation requires that a space of at least 20 cm (8 inches) must be left behind the instrument.
2.3. Grounding
INTRODUCTION
Proper grounding is required. Check that the wall ground (earth) plug is correctly connected to the
laboratory grounding electricity installation.
If there is no ground then use a ground stake. Current electricity Standards must be applied.
2.4. Humidity and temperature conditions
The Pentra 80 must function between 16 to 34°C (61 to 93°F). Maximum relative humidity 80% for
temperatures up to 31°C (88°F) decreasing linearly to 50% relative humidity at 40°C (104°F). If it is kept
at a temperature of less than 10°C (50°F), the instrument should be allowed to sit for an hour at the
correct room temperature before use.
2.5. Electromagnetic environment check
The Pentra 80 as been designed to produce less than the required level of electromagnetic
interferences in order to operate in conformity with its destination. The electromagnetic interferences
caused by the Pentra 80 are limited to a level allowing the correct operation of other instruments in
conformity with their destination.
In case of problems, check that the instrument is not placed in proximity of electromagnetic fields,
or short wave emissions (radars, X-rays, scanner, etc...).
2.6. Environment protection
Used accessories and consumables must be collected by a laboratory specialized in elimination
and recycling of this kind of material according to the legislation.
3/3
Page 4

Page 5

Specifications
1. Technical specifications ..........................................1-2
1.1. Parameters...................................................................1-2
1.2. Throughput Analyses ...................................................1-2
1.3. Tube identification ......................................................1-2
1.4. Reagents......................................................................1-3
1.5. Internal Computer .......................................................1-3
1.6. Measurements and computation.................................. 1-3
2. Physical specifications.............................................1-3
2.1. Power requirements..................................................... 1-3
2.2. Operating temperature and humidity...........................1-3
2.3. Dimension and weight ................................................1-3
2.4. Minimum specimen volume ........................................1-4
2.5. dilution ratios ..............................................................1-4
2.6. Hgb measurement ....................................................... 1-4
2.7. Counting aperture diameters........................................1-4
2.8. Reagent consumption (ml)...........................................1-4
3. Summary of performance data.................................1-5
3.1. Repeatability ...............................................................1-5
3.2. Linearity ......................................................................1-5
3.3. Carryover ....................................................................1-5
4. Reagents specification .............................................1-6
4.1. ABX DILUENT.............................................................1-6
4.2. ABX ALPHALYSE.........................................................1-6
4.3. ABX BIOLYSE .............................................................. 1-6
4.4. ABX CLEANER.............................................................1-7
4.5. ABX EOSINOFIX..........................................................1-7
4.6. ABX BASOLYSE II........................................................1-7
4.7. Waste handling precautions ........................................1-8
5. Limitations ..............................................................1-8
5.1. Maintenance ...............................................................1-8
5.2. Blood specimens ......................................................... 1-8
5.3. Known interfering substances ......................................1-8
Page 6
PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. Technical specifications
1.1. Parameters
Table 1: CBC Mode
WBC White Blood Cell
RBC Red Blood Cell
Hgb Hemoglobin Concentration
Hct Hematocrit
MCV Mean Corpuscular Volume
MCH Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
MCHC Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
RDW Red Distribution Width
PLT Platelets
PDW Platelets Distribution Width
MPV Mean Platelet Volume
PCT Plateletcrit
Table 2: CBC + 5DIFF Mode
WBC White Blood Cell
LY M Lymphocytes % and #
MON Monocytes % and #
NEU Neutrophils % and #
EOS Eosinophils % and #
BAS Basophils % and #
LIC Large Immature Cell % and #
ALY Atypical Lymphocytes % and #
RBC Red Blood Cell
Hgb Hemoglobin Concentration
Hct Hematocrit
MCV Mean Corpuscular Volume
MCH Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
MCHC Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
RDW Red Distribution Width
PLT Platelets
PDW Platelets Distribution Width
MPV Mean Platelet Volume
PCT Plateletcrit
2/10
1.2. Throughput Analyses
• 80 samples per hour.
1.3. Tube identification
• By mean of Keyboard, internal and external Barcode.
Page 7

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
1.4. Reagents
• ABX DILUENT (20 Litres).
• ABX CLEANER (1 Litre, Integrated).
• ABX EOSINOFIX (1 Litre, Integrated).
• ABX BASOLYSE (1 Litre, Integrate d).
• ABX ALPHALYSE (0.4 Litre, Integrated).
1.5. Internal Computer
• Color LCD touch screen: 12 inches.
• Industrial PC board Windows NT 4.0.
• Processor frequency ..... Celeron 433 MHz.
• Memory capacity ........................... 128 Mo.
• Hard drive ........................................ 10 Go.
• Floppy disck.
• CD ROM drive.
• RS 232C.
• Keyboard.
• Mouse.
1.6. Measurements and computation
• Impedance for Wbc, Plt, Rbc, Baso.
• Photometry for Hgb.
• Impedance and light scattering for Lym, Mon; Neu, Eos, Aly and Lic.
• Computation from stored data that was directly measured for Hct, Mcv, Mch, Mchc, Rdw, Mpv,
Pct and Pdw.
2. Physical specifications
2.1. Power requirements
• Power supply...... from 100 Vac to 240 Vac.
......................50 Hz to 60 Hz.
• Power consumption ..... Maximum 230 VA.
• Printer ........................... Depends of printer.
................................... (See printer’s manual).
2.2. Operating temperature and humidity
• 16 - 34°C (61-93°F) room temperature.
• Maximum relative humidity 80% for temperature up to 31°C (88°F) decreasing linearly to 50%
relative humidity at 40°C (104°F).
2.3. Dimension and weight
• Dimensions ....................... 82 x 57 x 54 cm.
................ 34.1 x 23.3 x 22 in.
• Weight............................................... 55 Kg.
..................................122 lbs.
3/10
Page 8

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
2.4. Minimum specimen volume
• CBC Mode (CBC) ............................... 30µl.
• CBC + 5DIFF Mode (DIF).................... 53µl.
2.5. dilution ratios
• WBC/BASO.......................................1/200.
• LMNE .................................................. 1/80.
• RBC/PLT .......................................1/10000.
• HGB .................................................. 1/250.
2.6. Hgb measurement
• Hgb chamber, LED 555 nm.
• Modified Drabkin method (cyanmethemoglobin).
• Light source .......Electroluminescent diode.
• Wavelenght ..................... 550nm +/- 10nm.
2.7. Counting aperture diameters
• WBC/BASO....................................... 80µm.
• LMNE ................................................ 60µm.
• RBC/PLT ........................................... 50µm.
2.8. Reagent consumption (ml)
Table 3: Reagents consumption
Cycles
CBC/DIFF 0’45’’ 27.4 1.0 2.0 1.0 0.45
CBC 0’45’’ 24.4 - 2.0 1.0 0.45
Prime DILUENT 3’00’’ 44 - - - -
Prime
EOSINOFIX
Prime
BASOLYSE 2
Prime CLEA-
NER
Prime LYSE 1’31’’ 2.7 - - - 8.4
Prime ALL 7’13’’ 50.7 24.0 24.0 25.0 8.4
STARTUP
(1 blank cycle)
SHUT DOWN 2’56’’ 32.2 1.0 1.0 14.2 0.49
Rinse
CYTOMETER
AUTOCLEAN 1’33’’ 27.6 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.50
MINICLEAN 0’21’’ 10.3 1.0 2.0 1.0 0.33
CONCENTRA-
TED cleaning
BACKFLUSH 0’24’’ - - - - -
Estimated
duration (s)
1’34’’ 1.6 23.7 - - -
1’25’’ 1.7 - 23.7 1.0 -
1’24’’ 1.7 - - 24.7 -
2’28’’ 55.2 2.0 3.0 2.0 0.95
1’14’’ 5.0 - - - -
4’00’’ 29.6 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.50
Diluent
(ml)
Eosinofix
(ml)
Basolyse II
(ml)
Cleaner
(ml)
Lyse
(ml)
4/10
Page 9

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
STARTUP cycle estimated duration and consumptions are given for one blank cycle control. It
could be a maximum of three cycles.
3. Summary of performance data
3.1. Repeatability
• Based on 10 consecutive samples of the same fresh whole blood sample without alarm:
Table 4: Repeatibility
PARAMETERS %CV Test Level
3.2. Linearity
Table 5: Linearity
PARAMETERS Linearity Range
PLT Concentrated mode (103/µL) 1500 to 5000 x 103/µL
WBC < 2%
RBC < 2%
Hgb < 1% at 15 g/dL
Hct < 2% at 45%
Plt < 5%
at 10 x 103/µL
at 5 x 106/µL
at 300 x 103/µL
(Which ever is greater)
WBC (103/µL) 0 to 120 x 103/µL
RBC (106/µL) 0 to 8 x 106/µL
RBC (106/µL) 8 to 18 x 106/µL
PLT (103/µL) 0 to 1 900 x 103/µL
HGB (g/dl) 1.3 to 24 g/dl +/- 0.3 or +/- 2%
HCT (%) 2 to 67 % +/- 2 or +/- 3%
+/- 0.3 or +/- 7%
+/- 0.07 or +/- 2%
Reportable range
+/- 10 or +/- 7%
+/- 10 or +/- 7 %
Difference
3.3. Carryover
• Carry-over was tested by analyzing samples with hight concentration of WBCs, RBCs, Hgb and
PLTs. Each sample was run in triplicate, followed by three background cycles. The % carryover is
calculated using the following formula:
Carryover
Background1 Background3–
---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- ---------- ----------- ----------x100=
Sample3 Background3–
Table 6: Carryover
WBC RBC Hgb PLT
Level 43.64 8.56 25.94 739
% Carryover (Actual) 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.28
% Carryover (Claimed) <0.5% <0.5% <0.5% <0.5%
5/10
Page 10

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
4. Reagents specification
In order for the instrument to operate correctly, hight-quality reagents must be used.
ABX DIAGNOSTICS provides all the necessary reagents.
All these reagents have been registered by the A.F.S.S.A.P.S. «Agence Française de Sécurité
Sanitaire des Produits de Santé» according to the procedure relative to laboratory reagents
used for biological analyses.
These reagents are used for in vitro diagnostics.
All these reagents are manufactured by:
ABX DIAGNOSTICS
Rue du caducée - Parc Euromédecine
34184 MONTPELLIER CEDEX - FRANCE
Tel: (33) 4 67 14 15 16 - Fax: (33) 4 67 14 15 17
4.1. ABX DILUENT
• Function: This diluent is necessary for the process involved in counting (and differentiating) the
blood cells. This reagent is used also to rinse the hydraulic parts of the instrument.
• Composition: Stabilized saline solution which contains an organic buffer, an antiseptic and
Sodium Azide < 0.1%.
• Description: Limpid and odourless aqueous solution.
• Physico-chemical properties: Boiling point: About 100°C, pH: neutral.
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Handling Precautions: Avoid skin and eye contact. Use laboratory gloves when handling the
reagents. If a large quantity of reagent is ingested a mucous irritation can result.
• Emergency First aid: If the eyes or skin come into contact with the reagent, rinse thoroughly with
water. If a large quantity is ingested, drink water immediately, and induce vomiting.
• Storage conditions: Stored at 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F) away from light.
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0901020
4.2. ABX ALPHALYSE
• Function: This reagent is used to lyse blood cells and determine hemoglobin concentration.
• Composition:The reagent contains potassium cyanide at 0.03%, a quarternary ammonium salt
and a saline phosphate buffer containing sodium azide < 0.1%.
• Description: Aqueous solution, limpid.
• Physico-chemical properties: Boiling point: approximately 100°C. pH: basic, smells of cyanide.
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Handling Precautions: May be dangerous. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. Wear
laboratory gloves when handling the product. The product may be harmful if ingested. The product
can be absorbed through an open wound, or inhalation.
• Emergency First aid: If the eyes or skin come into contact with the reagent, rinse with water. If
the reagent is inhaled, breathe fresh air immediately. If a large quantity is ingested, drink water
immediately, and induce vomiting. Call anti-poison center, or contact doctor.
• Storage conditions: Stored at 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F) away from light. Product will degrade if
exposed to air, keep cap / probe assembly securely tightened.
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0906004
4.3. ABX BIOLYSE
• Function: This reagent is used to lyse blood cells and determine hemoglobin concentration.
• Composition:Quarternary ammonium chloride.
6/10
Page 11

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
• Description: Colorless, odorless.
• Physico-chemical properties: pH: 6.65
• Handling Precautions: May be dangerous. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. Wear
laboratory gloves when handling the product. The product may be harmful if ingested.
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Emergency First aid: If the eyes or skin come into contact with the reagent, rinse with water. If
the product is ingested, call immediately a doctor.
• Storage conditions: Stored at 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F) away from light..
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0906005
4.4. ABX CLEANER
• Function: Washing agent.
• Composition: Enzymatic solution with proteolytic action.
• Description: Transparent liquid.
• Physico-chemical properties: Boiling point: around 100°C. pH: 9.6
• Handling Precautions: May be harmful. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing.
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Emergency First Aid: In case the product comes into contact with the eyes, rinse with water. If
the product is ingested, call a doctor immediately.
• Storage conditions: Stored at 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F).
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0903010
4.5. ABX EOSINOFIX
• Function: This reagent lyses RBCs, fixes leukocytes and gives a specific coloration to
eosinophils.
• Composition: Alcoholic solution containing propylene-glycol, a formic dye, buffers, alkaline salts,
wetting agents and an aldehyde preservative.
• Description: Deep blue aqueous solution, smells of alcohol.
• Physico-chemical properties: pH: 6.9
• Handling precautions: Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. Wear laboratory gloves when
handling the product. The product may be harmful if ingested or inhalted. Keep the bottle closed
when not in use.
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Emergency First Aid: If the eyes or skin come into contact with the reagent, rinse with water. If
the reagent is inhaled or ingested, call local anti-poison center or contact doctor.
• Storage conditions: Room temperature between 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F).
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0206010
4.6. ABX BASOLYSE II
• Function: This reagent lyses RBCs for the leukocytes and differential count of the polynuclear
basophils.
• Composition: Acidic solution containing a lytic agent.
• Description: Colorless aqueous solution.
• Physico-chemical properties: pH: 2.4
• Handling precautions: Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. Wear laboratory gloves when
handling the product. The product may be harmful if ingested or inhalated. Keep the bottle closed
when not in use.
7/10
Page 12

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
• Mesuring Principles: See user manual.
• Performances: See user manual.
• Results: See user manual.
• Directions for use: See user manual.
• Emergency First Aid: If the eyes or skin come into contact with the reagent, rinse with water. If
the reagent is inhaled, breath fresh air immediately. If a large quantity is ingested, drink water
immediately. Do not induce vomiting. Call local anti-poison center or contact doctor.
• Storage conditions: Room temperature between 18°C (65°F) to 25°C (77°F).
• ABX DIAGNOSTICS Part number: 0906003
4.7. Waste handling precautions
If required, waste can be neutralized before being discarded. Follow your laboratory’s protocol
when neutralizing and disposing of waste.
5. Limitations
5.1. Maintenance
In Chapter 8. Maintenance, specific maintenance procedures are listed. The maintenance
procedures identified are mandatory for proper use and operation of the ABX PENTRA 80.
Failure to execute any of these recommended procedures may result in poor reliability of the
system.
5.2. Blood specimens
Verification of any abnormal test result (including flagged results or results outside of the normal
range) should be performed using reference methods or other standard laboratory procedures for
conclusive verification of the results. The sections below list known limitations of automated blood cell
counters which use the principles of impedance and light absorbance as principles of measurement.
5.3. Known interfering substances
WBC:
• White Blood Cells (Leukocytes):WBC results that exceed the linearity limits of the system will
require dilution of the blood sample (Leukemia sample followed by a leukopenia). Re-assaying the
diluted sample will help to obtain the correct assay value.
• Unlysed Red Cells - In some rare instances, the erythrocytes in the blood sample may not be
completely lysed. These non-lysed red blood cells may be detected on the WBC histogram with an
L1 alarm or as an elevated baseline on the side (leading edge) of the lymphocytes population. Non-
lysed erythrocytes will cause a falsely elevated WBC count.
• Multiple myeloma - The precipitation of proteins in multiple myeloma patients may give high
WBC counts.
• Leukemia - A very low WBC count may result from this disease because of possible increased
fragility of the leukocytes leading to destruction of some of these cells during counting. These white
cell fragments will also interfere with the white cell differential parameters.
• Chemotherapy - Cytotoxic and immunosuppressive drugs may increase the fragility of the
leukocytes which may cause low WBC counts.
• Cryoglobulins - Increased levels of cryoglobulin that may be associated with myeloma,
carcinoma, leukemia, macroglobulinemia, lymphoproliferative disorders, metastic tumors,
autoimmune disorders, infections, aneurism, pregnancy, thromboembolic phenomena, diabetes,
etc, which can increase the WBC, RBC or Plt counts and the Hgb concentration. The specimen
must be warmed up to 37°C (99°F) in a bain marie for 30 minutes and analyzed again immediately
after (analyzer or manual method).
• Macrothrombocytes - in excessive numbers may affect and increase Leukocyte numeration.
8/10
Page 13

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
RBC:
• Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): The red blood cell dilution contains all the formed elements in
the blood: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. During erythrocytes counting (red blood cells),
platelets are not counted as their size falls below the minimum threshold.
• Agglutinated erythrocytes - May cause a low incorrect RBC count. Blood samples containing
the agglutinated red blood cells may be suspected by elevated MCH and MCHC values and shown
by examination of the stained blood film.
• Cold agglutinins - IgM immunoglobulins which are high in cold agglutinin disease may cause
lower RBC and Plt counts and increase MCV.
Hgb (Hemoglobin):
• Turbidity of the blood sample - Any number of physiological and/or therapeutic factors may
produce high incorrect Hgb results. To obtain accurate hemoglobin results when increased turbidity
of the blood sample occurs, determine the cause of the turbidity and follow the appropriate method
below:
• High WBC: An extremely high WBC will cause excessive light scatter. In these cases use
reference (manual) methods.The diluted sample should be centrifuged, and the supernatant fluid
measured with a spectrophotometer.
• High lipid concentration: A high concentration of lipids in the blood sample will give the plasma
a «milky» appearance. This condition can occur with hyperlipidemia, hyperproteinemia (as in
gammapathies) and hyperbilirubinemia. Accurate hemoglobin determinations can be achieved by
using reference (manual) methods and a plasma blank.
• Increased turbidity may also be seen in cases where the red blood cells are resistant to lysing.
This condition will cause an incorrect high Hgb result, but may be detected by observing the
abnormal MCH, MCHC values, and the increased baseline on the leading edge of the WBC
histogram. Erroneous hemoglobin results will cause the results of the MCH and MCHC to be
incorrect as well.
• Fetal bloods - The mixing of fetal and maternal bloods may produce a high inaccurate Hgb value.
Hct (Hematocrit):
• Red blood cells agglutination - May produce an inaccurate Hct and MCV values. Red blood cell
agglutination may be detected by observing abnormal MCH and MCHC values, as well as by
examination of the stained blood film In such cases, manual methods may be required to obtain an
accurate Hct value
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume):
• Red blood cell agglutination - May produce an inaccurate MCV value. Red blood cell
agglutination may be detected by observing abnormal MCH and MCHC values, as well as by
examination of the stained blood film. In such cases, manual methods may be required to obtain an
accurate MCV value.
• Excessive numbers of large platelets and/or the presence of an excessively high WBC count
may interfere with the accurate determination of the MCV value. In such cases, careful examination
of the stained blood film may reveal the error.
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin):
• The MCH is determined according to Hgb value and the RBC count. The limitations listed for the
Hgb and RBC will have an effect on the MCH and may cause inaccurate values.
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration):
• The MCHC is determined according to the Hgb and Hct values. The limitations listed for the Hgb
and Hct will have an effect on the MCHC and may cause inaccurate values.
RDW (Red blood cell Distribution Width):
• The red blood cell distribution width is determined according to the RBC count.
• Nutritional deficiency or blood transfusion - May cause high RDW results due to iron and/or
cobalamin and /or folate deficiency.
Plt (Platelets):
• Very small erythrocytes (microcytes), erythrocyte fragments (schizocytes) and WBC fragments
may interfere with the proper counting of platelets and cause elevated Plt counts.
• Agglutinated erythrocytes - May trap platelets, causing an erroneously low platelet count. The
presence of agglutinated erythrocytes may be detected by observation of abnormal MCH and
MCHC values and by careful examination of the stained blood film.
• Giant platelets in excessive numbers - may cause a low inaccurate platelet count as these large
9/10
Page 14

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
platelets may exceed the upper threshold for the platelet parameter and are not counted.
• Chemotherapy - Cytotoxic and immunosuppressive drugs may increase the fragility of these
cells which may cause low Plt counts. Reference (manual) methods may be necessary to obtain an
accurate platelet count.
• Hemolysis - Hemolysed specimens contain red cell stroma which may increase platelet counts.
• A.C.D. blood - Blood anticoagulated with acid-citrate-dextrose may contain clumped platelet
which could decrease the platelet count.
• Platelet agglutination - Clumped platelets may cause a decreased platelet count and/or a high
WBC count. The specimen should be recollected in sodium citrate anticoagulant to ensure the
anticoagulated character depending on agglutination and reanalyzed only for the platelet count.
The final Plt result must be corrected for the sodium citrate dilution effect. However, these platelet
clumps do trigger flags L1, LL and LL1.
MPV (Mean Platelet Volume):
• Giant platelets that exceed the upper threshold of the Platelet parameter may not be counted as
platelets. Consequently, these larger platelets will not be included in the instrument’s calculation of
Mean Platelet Volume.
• Very small erythrocytes (microcytes), erythrocytic fragments (Schizocytes) and white blood cell
fragments may interfere with the proper counting and sizing of Platelets.
• Agglutinated erythrocytes - May trap Platelets, causing an incorrect MPV result. The presence
of agglutinated erythrocytes may be detected by observation of abnormal MCH and MCHC values
and by careful examination of the stained blood film.
• Chemotherapy - May also affect the sizing of Plts.
Blood samples collected in EDTA will not maintain a stable Mean Platelet Volume. Platelets
collected in EDTA swell depending on the time post-collection and storage temperature.
LYM# (Lymphocyte count absolute value), LYM% (Lymphocyte percentage):
• The Lymphocyte count is derived from the WBC count. The presence of erythroblasts, certain
parasites and erythrocytes that are resistant to lysis may interfere with an accurate LYM count.
Limitations listed for the WBC count pertain to the LYM # and % counts as well.
MON# (mononuclear cell count absolute), MON% (Mononuclear percentage):
• The mononuclear cell count absolute is derived from the WBC count. The presence of large
lymphocytes, atypical lymphocytes, blasts and an excessive number of basophils may interfere
with an accurate monocyte count.
• Limitations listed for the WBC count pertain to the MON # and % counts as well.
NEU# (neutrophil count absolute), NEU% (Neutrophil percentage):
• The neutrophils cell count is derived from the WBC cell count. The excessive presence of
eosinophils, metamyelocytes, myelocytes, promyelocytes, blasts and plasma cells may interfere
with an accurate neutrophils count.
EOS# (Eosinophil cell count absolute), EOS% (Eosinophil percentage):
• The eosinophil cell count is derived from the WBC cell count. The presence of abnormal granules
(degranulated areas, toxic granules...) may interfere with the eosinophil counting.
BAS# (Basophil cell count absolute), BAS% (Basophil percentage):
• The Basophil cell count is derived from the WBC cell count.
10/10
Page 15
Hydraulic & Pneumatic principles
1. Hydropneumatic connections..................................2-2
2. Instrument tubing ....................................................2-5
2.1. Tube list ......................................................................2-5
2.2. Connectors and integrated tubings list .........................2-7
3. Function of valves ...................................................2-7
4. Pneumatic diagram..................................................2-8
Page 16
PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. Hydropneumatic connections
Read this table as follow: LV3_2 means connection to port 2 of valve 3.
Table 1: Hydropneumatic connection
Circuit From F.S . Diameter Length T.S. To
AIR Atmosphere 2.05 140 LV14_2
LV14_1 1.52 70 Count syringe_1
DILUENT REAGENT
Rinse chamber_1 -
Atmos.
LV17_1 1.52 30 T8_1
Atmosphere 2.05 80 LV19_1
LV19_3 1.52 500 Diluent reservoir_2
LV19_2 1.52 60 T8_3
T8_2 1.52 230 Drain syringe # 2_1
Atmosphere 2.05 70 LV21_2
LV21_1 1.30 185 Isolator_2
Rinse chamber_2 -
Atmos.
LV24_1 1.52 90 Drain syringe # 1_1
ABX Diluent contai-
ner
Diluent input 2.54 190 S LV29_2
LV29_1 S 2.54 180 S Diluent reservoir_4
Diluent reservoir_1 2.05 370 LV 2_ 1
LV2_3 S 2.05 120 LMNE syringe_2
LV3_2 S 1.52 50 S LV3_3
LV3_1 S 1.52 60 S LV1_3
LV1_1 S 1.52 200 S Isolator_1
Isolator_2 S 1.52 100 T1_1
T1_2 1.14 35 LMNE flow cell_4
T1_2 Xba403a LMNE flow cell_4
T1_3 1.14 35 LMNE flow cell_2
T1_3 Xba403a LMNE flow cell_2
LV1_2 1.52 300 T6_3
LV2_2 1.02 175 LMNE syringe_4
LMNE syringe_1 1.02 205 LMNE flow cell_5
LMNE flow cell_7 1.02 10 (Cap)
Diluent reservoir_3 2.05 610 LV10_1
LV10_3 2.05 160 Reagent syringe_4
LV10_2 1.52 50 LV11_3
LV11_1 1.52 15 T5_2
T5_1 1.52 760 LV22_3
LV22_1 1.52 50 LV23_3
LV23_1 1.52 190 T3_1
T3_3 1.52 75 Probe rinse block_1
T3_2 1.30 15 Isolator_1
Isolator_3 1.52 215 LV20_1
2.05 550 LV17_2
2.05 300 LV24_2
C 3x6 maxi. 2000 Diluent input
2.05 65 Diluent reservoir_1
2.05 65 Diluent reservoir_3
2/8
Page 17

SECTION 2 HYDRAULIC & PNEUMATIC PRINCIPLES
Table 1: Hydropneumatic connection
Circuit From F.S . Diameter Length T. S . To
LV20_2 1.52 760 T7_1
LV23_2 1.52 300 Probe rinse block_2
LV22_2 1.02 115 Sample syringe_2
LV11_2 1.52 440 LV25_3
LV25_1 1.52 65 LV27_3
LV27_1 1.52 50 LV26_3
LV26_1 1.52 200 S Reagent heater_7
Reagent heater_8 S 1.52 160 RBC chamber_1
LV26_2 1.52 260 S Reagent heater_1
Reagent heater_2 S 1.52 160 DIL1/HGB chamber_1
LV27_2 1.52 50 T10_2
LV25_2 1.52 170 WBC/Baso chamber_4
ABX CLEANER
REAGENT
ABX EOSINOFIX REAGENT
ABX BASOLYSE II REAGENT
ABX ALPHALYS E RE AGENT
SAMPLING Probe_1 1.02 205 Sample syringe_1
LMNE COUNTING
Abx Cleaner bottle 2.05 800 LV8 _1
LV 8_ 3 2.05 160 Reagent syringe_2
LV 8_ 2 1.52 70 LV 6_3
LV 6_ 1 1.52 300 T10_3
T10_1 1.52 180 WBC/Baso chamber_1
LV 6_ 2 1.52 120 T5_3
Abx Eosinofix bottle 2.05 800 LV 9 _1
LV 9_ 3 2.05 160 Reagent syringe_3
LV 9_ 2 1.52 550 S Reagent heater_3
Reagent heater_4 S 1.52 160 LMNE chamber_3
Abx Basolyse II
bottle
LV12_3 2.05 160 Reagent syringe_5
LV12_2 1.52 575 S Reagent heater_10
Reagent heater_9 S 1.52 60 S Reagent heater_11
Reagent heater_12 S 1.52 160 WBC/Baso chamber_2
Abx Alphalyse bottle 1.52 800 LV 7 _1
LV 7_ 3 1.52 160 Reagent syringe_1
LV 7_ 2 1.52 480 DIL1/HGB chamber_2
Probe_1 S Sample syringe_1
LMNE chamber_4 1.30 20 M4_2 photocell
M4_1 photocell 1.30 320 LV4 _1
LV 4_ 2 1.02 130 T2_2
T2_3 1.02 240 LMNE syringe_5
LMNE syringe_3 1.02 85 T4_1
T4_2 1.02 15 LV 5_1
LV 5_ 2 1.52 280 T7_2
T2_1 S 1.85 10 LMNE flow cell_6
2.05 800 LV12_1
0.19 4 LMNE flow cell_6
3/8
Page 18

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
Table 1: Hydropneumatic connection
Circuit From F.S . Diameter Length T.S. To
LMNE flow
cell_output
E1_2 anode fitting 1.52 70 Isolator_1
Isolator_2 1.52 80 E2_1 ground fitting
E2_2 ground fitting 1.52 335 LV28_2
LV28_1 1.52 120 T6_2
T6_1 1.52 160 S Reagent heater_5
Reagent heater_6 S 1.52 160 LMNE chamber_2
WBC/RBC
COUNTING
WASTE Rinse chamber_3 2.05 20 Filter_1
WBC/Baso
chamber_3
RBC chamber_2 1.52 480 LV15_2
LV15_1 1.52 70 Count syringe_2
Filter_2 2.05 100 LV31_2
LV31_1 1.52 30 T12_3
DIL1/HGB
chamber_3
LV32_1 1.52 15 T12_2
T12_1 1.52 35 T13_3
RBC chamber_4 1.52 65 LV34_2
LV34_1 1.52 15 T13_2
T13_1 1.52 180 M2_1 photocell
M2_2 photocell 1.52 15 Isolator # 2_1
Isolator # 2_2 2.05 280 LV30_1
LV30_3 S 2.54 160 S Drain syringe # 1_2
LV30_2 S 2.54 150 T14_3
LMNE chamber_5 1.52 65 LV33_2
LV33_1 1.52 60 E3_1
E3_2 1.52 60 T11_1
T7_3 1.52 100 T11_3
T11_2 1.52 15 M1_1 photocell
M1_2 photocell 1.52 15 Isolator # 1_1
Isolator # 1_2 2.05 500 LV18_1
LV18_3 2.05 210 Drain syringe # 2_2
LV18_2 S 2.54 150 T9_2
WBC/Baso
chamber_5
LV35_1 1.52 130 M3_1 photocell
M3_2 photocell 1.52 15 Isolator # 3_1
Isolator # 3_2 2.05 460 Count syringe_3
T4_3 1.02 150 LV13_1
LV13_2 2.05 140 Count syringe_4
Count syringe_5 2.05 120 LV16_1
LV16_2 S 2.54 150 T9_3
T9_1 2.54 225 T14_2
T14_1 2.54 20 Waste output
Waste ou tput C 4x6 maxi. 2000 Waste container
1.52 20 E1_1 anode fitting
1.52 200 RBC chamber_3
1.52 65 LV32_2
1.52 50 LV35_2
4/8
Page 19

SECTION 2 HYDRAULIC & PNEUMATIC PRINCIPLES
2. Instrument tubing
2.1. Tube list
Table 2: Tube list
Designation Part Numb er Diameter Length Quantity Comment
Y Connector EAB021A 3 2
Y Connector EAB026A 2.5 2
T410-6 Connector EAB033A 1.6 2
T220-6 Connector EAB035A 2.3 8
0.040 TYGON
tubing
0.051 TYGON
tubing
0.060 TYGON
tubing
EAE005A 1.02 10 1
1.02 15 1
1.02 85 1
1.02 115 1
1.02 130 1
1.02 150 1
1.02 175 1
1.02 205 2
1.02 240 1
EAE006A 1.30 15 1
1.30 20 1
1.30 185 1
1.30 320 1
EAE007A 1.52 15 7
1.52 20 1
1.52 30 2
1.52 35 1
1.52 50 6
1.52 60 5
1.52 65 4
1.52 70 4
1.52 75 1
1.52 80 1
1.52 90 1
1.52 100 2
1.52 120 2
1.52 130 1
1.52 160 7
1.52 170 1
1.52 180 2
1.52 190 1
1.52 200 3
1.52 215 1
1.52 230 1
1.52 260 1
5/8
Page 20

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
Table 2: Tube list
Designation Part Num ber Diameter Length Quantity Comment
1.52 280 1
1.52 300 3
1.52 335 1
1.52 440 1
1.52 480 1
1.52 500 1
1.52 550 1
1.52 575 1
1.52 760 2
1.52 800 1
0.081 TYGON
tubing
CRISTAL tubing EAE011A 3x6
CRISTAL tubing EAE028A 4x6
0.045 TYGON
tubing
0.100 TYGON
tubing
0.0075 TYGON
tubing
0.073 TYGON
tubing
Sleevings GAL098A 30
Tube shielding XBA403A 2
EAE008A 2.05 20 1
2.05 65 2 Notched tubing
2.05 70 1 Notched tubing
2.05 80 1 Notched tubing
2.05 100 1
2.05 120 2
2.05 140 1
2.05 140 1 Notched tubing
2.05 160 4
2.05 210 1
2.05 280 1
2.05 300 1
2.05 370 1
2.05 460 1
2.05 500 1
2.05 550 1
2.05 610 1
2.05 800 3
maxi
2000
maxi
2000
EAE033A 1.14 35 2
EAE034A 2.54 20 1
2.54 150 3
2.54 160 1
2.54 180 1
2.54 190 1
2.54 225 1
EAE047A 0.19 4 1
EAE048A 1.85 10 1
1
1
S2x4 Lg=6 tubing
EAE026A
6/8
Page 21

SECTION 2 HYDRAULIC & PNEUMATIC PRINCIPLES
2.2. Connectors and integrated tubings list
The following table shows the connectors and integrated tubings list: Length x Quantity per
diameter.
Table 3: Connectors and integrated tubings list
Designation Part Num b e r Diameter Length Qty Comment
Y Connector EAB021A 3 2
Y Connector EAB026A 2.5 2
T410-6 Connector EAB033A 1.6 2
T220-6 Connector EAB035A 2.3 8
0.040 TYGON
tubing
0.051 TYGON
tubing
0.060 TYGON
tubing
0.081 TYGON
tubing
CRISTAL tubing EAE011A 3x6
CRISTAL tubing EAE028A 4x6
0.045 TYGON
tubing
0.100 TYGON
tubing
0.0075 TYGON
tubing
0.073 TYGON
tubing
Sleevings GAL098A 30
Tube shielding XBA403A 2
EAE005A 1.02 1330 1
EAE006A 1.30 540 1
EAE007A 1.52 11700 1
EAE008A 2.05 7240 1
maxi
2000
maxi
2000
EAE033A 1.14 70 1
EAE034A 2.54 1225 1
EAE047A 0.19 4 1
EAE048A 1.85 10 1
1
1
S2x4 Lg=6 tubing
EAE026A
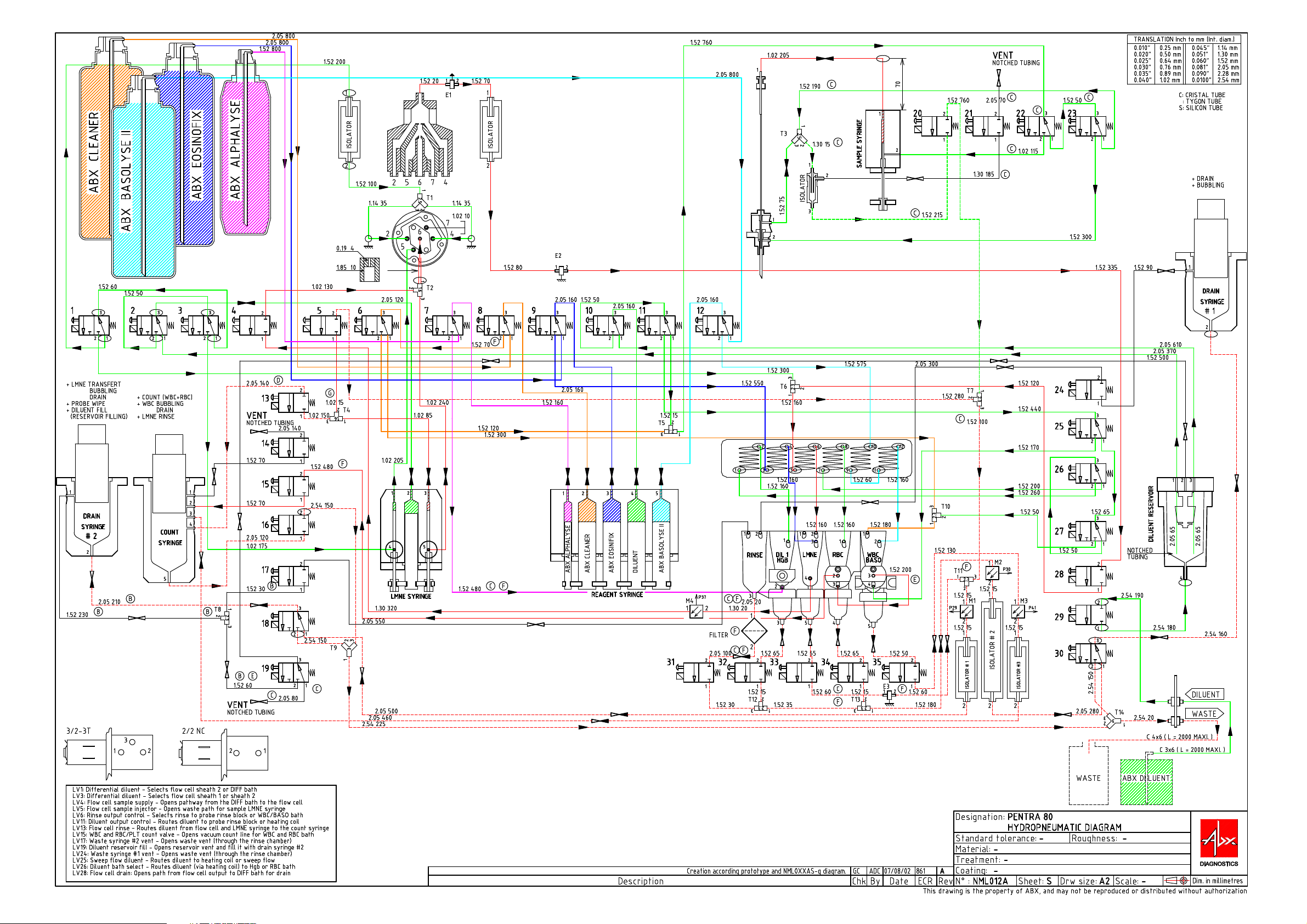
3. Function of valves
Table 4: Function of valves
Valve
number
Subject Functions
1 Differencial diluent Selects flowcell sheath 2 or LMNE chamber
2 Differencial diluent
3 Differencial diluent Selects flowcell sheath 1 or sheath 2
Flowcell sample
4
supply
Flowcell sample
5
injector
Rinse output con-
6
trol
7 Alphalyse Control alphalyse entry\exit reagent syringe
Opens pathway from LMNE chamber to flowcell
Opens waste path for sample LMNE syringe
Selects rinse for probe rinse block or WBC\Baso chamber
7/8
Page 22

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
Table 4: Function of valves
Valve
number
Subject Functions
8 Cleaner Control cleaner entry\exit reagent syringe
9 Eosinofix Control eosinofix entry\exit reagent syringe
10 Diluent Control alphalyse entry\exit reagent syringe
Diluent ouput con-
11
trol
12 Basolyse II Control basolyse II entry\exit reagent syringe
13 Flowcell rinse Routes diluent from flowcell and LMNE syringe to counting syringe
14 Counting syringe Set counting syringe to atmosphere
WBC and RBC\Plt
15
count
16 Counting syringe Drain for counting syringe
17 Draining syringe #2 Set draining syringe #2 to atmosphere (through Rinse chamber)
18 Draining syringe #2 Drain for draining syringe #2
19 Diluent reservoir Fill diluent tank or set diluent tank to atmosphere
20 Probe Probe cleaning
21 Probe Flushing out of probe rinsing block
22 Probe Direct diluent into interior or exterior of probe
23 Probe Probe cleaning
24 Draining syringe #1 Set draining syringe #1 to atmosphere (through Rinse chamber)
WBC\Baso Coun-
25
ting head
Diluent chamber
26
select
27 Diluent circuit Fill WBC\Baso chamber with diluent
28 Flowcell drain Opens path from flowcell output to LMNE chamber for drain
29 Diluent circuit Entry of diluent
30 Counting syringe Flushing\Draining of the counting syringe
31 Chambers Drain for rinse chamber
32 Chambers Drain for first dilution chamber
33 Chambers Drain for LMNE chamber
34 Chambers Drain for RBC chamber
35 Chambers Drain for WBC\Baso chamber
Routes diluent to probe rinse block or heating coil
Opens vacuum count line for WBC and RBC chambers
Routes diluent to heating coil or sweep flow for counting head
Routes diluent (via heating coil) to Hgb or RBC chamber
8/8
4. Pneumatic diagram
See pneumatic diagram on next page.
Page 23
Page 24
Electric & Electronic principles
1. Main board .............................................................3-3
1.1. Main board general view .............................................3-3
2. Motor board ............................................................3-4
2.1. Motor board general view............................................3-4
3. Connectors and other boards...................................3-4
3.1. CBC008A Barcode reader............................................3-5
3.2. DAD075AS Flat cable 350mm. 14pts ..........................3-6
3.3. DAD075AS Flat cable 480mm. 14pts ..........................3-7
3.4. DAD109A Flat cable 560mm. 14pts............................3-8
3.5. DAD112AS Flat cable 930mm. 26pts (Main board\Car-
riage board)........................................................................3-9
3.6. DAD119AS Flat cable 950mm. 8pts ..........................3-10
3.7. DAD120A Flat cable 800mm. 14pts..........................3-11
3.8. DAD121A Flat cable 700mm. 44pts..........................3-12
3.9. DAD122A Flat cable 650mm. 14pts..........................3-13
3.10. DAD123A DSUB 25pts Flat cable 1000mm. ........... 3-14
3.11. DAD124A DSUB 9pts Flat cable 1000mm. ............. 3-15
3.12. XAA428C Carriage board ........................................3-16
3.13. XAA429A LEDs board .............................................3-17
3.14. XAA456A Main board ............................................. 3-18
3.15. XAA458A LMNE amplifier board............................. 3-19
3.16. XAA459A Motor board............................................ 3-20
3.17. XAA478A Solenoid board........................................ 3-21
3.18. XBA322B External waste level detection.................. 3-22
3.19. XBA342A Infrared sensor......................................... 3-23
3.20. XBA387A Reagent heating coil ................................ 3-24
3.21. XBA389A Hemoglobin photometer ......................... 3-25
3.22. XBA393A Upper fan ................................................3-26
3.23. XBA396A Infrared 260mm.......................................3-27
3.24. XBA398B RBC&WBC electrode coaxial cable .........3-28
3.25. XBA399B LMNE flowcell coaxial cable ...................3-29
3.26. XBA425A Chamber heating ..................................... 3-30
3.27. XBA427A Emergency position assy.......................... 3-31
3.28. XBA431A Infrared photocell 600mm. (No tab) ........ 3-32
3.29. XBA432A Infrared photocell 600mm. (2 tabs).......... 3-33
Page 25

3.30. XBA433A Infrared photocell 600mm. (1 tab) ........... 3-34
3.31. XBA458A Switch JST 300mm. .................................3-35
3.32. XBA459A Switch JST 400mm. .................................3-36
3.33. XBA460A Switch Jst 500mm....................................3-37
3.34. XBA461A Switch Jst 700mm....................................3-38
3.35. XBA462A Motor Jst 300mm..................................... 3-39
3.36. XBA463A Motor Jst 400mm..................................... 3-40
3.37. XBA464A Motor Jst 500mm..................................... 3-41
3.38. XBA465A Motor Jst 700mm..................................... 3-42
3.39. XBA469A Horizontal carriage cell extension........... 3-43
3.40. XBA470A Solenoid JST 700mm. ..............................3-44
3.41. XBA471A Solenoid Molex 230mm. ......................... 3-45
3.42. XBA478A Horizontal carriage motor ....................... 3-46
3.43. XBA486A LEDs extension JST 1000mm. ..................3-47
3.44. XBA487A LED JST 200mm. ..................................... 3-48
3.45. XBA488A Waste level detection .............................. 3-49
3.46. XDA605A Diluent reservoir with level detection ..... 3-50
3.47. XDA751C 12 valves assy (LV1-6 & LV7-12)............. 3-51
3.48. XDA752C 7 valves assy (LV13-19)........................... 3-52
3.49. XDA753C Carriage valves assy (LV20-23)................3-53
3.50. XDA754C 7 valves assy (LV24-30)........................... 3-54
3.51. XDA755C 5 valves assy (LV31-35)........................... 3-55
4. Pentra 80 synoptic.................................................3-55
Page 26
SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
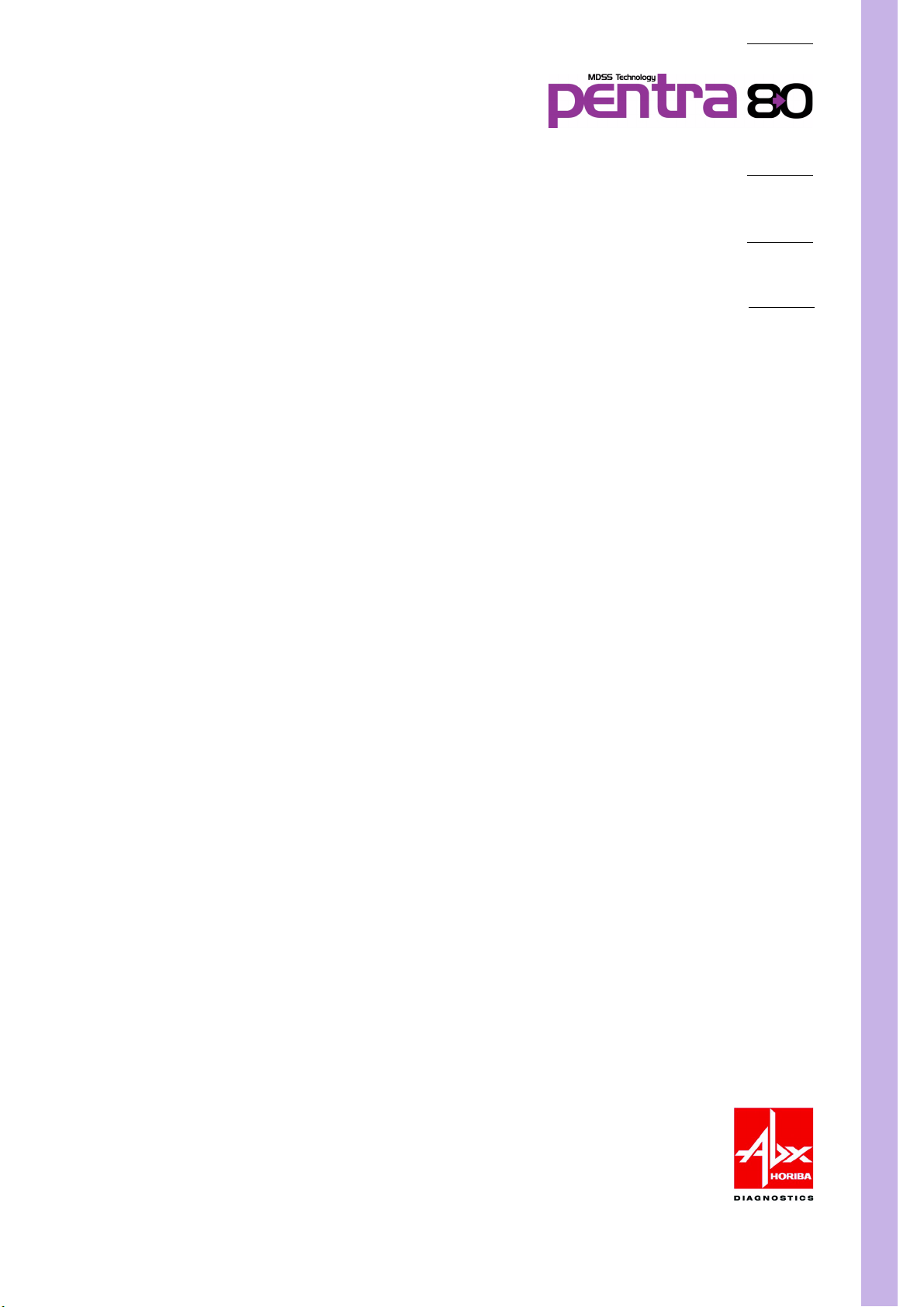
1. Main board
1.1. Main board general view
Diag.1:Main board general view
3/55
Page 27
PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
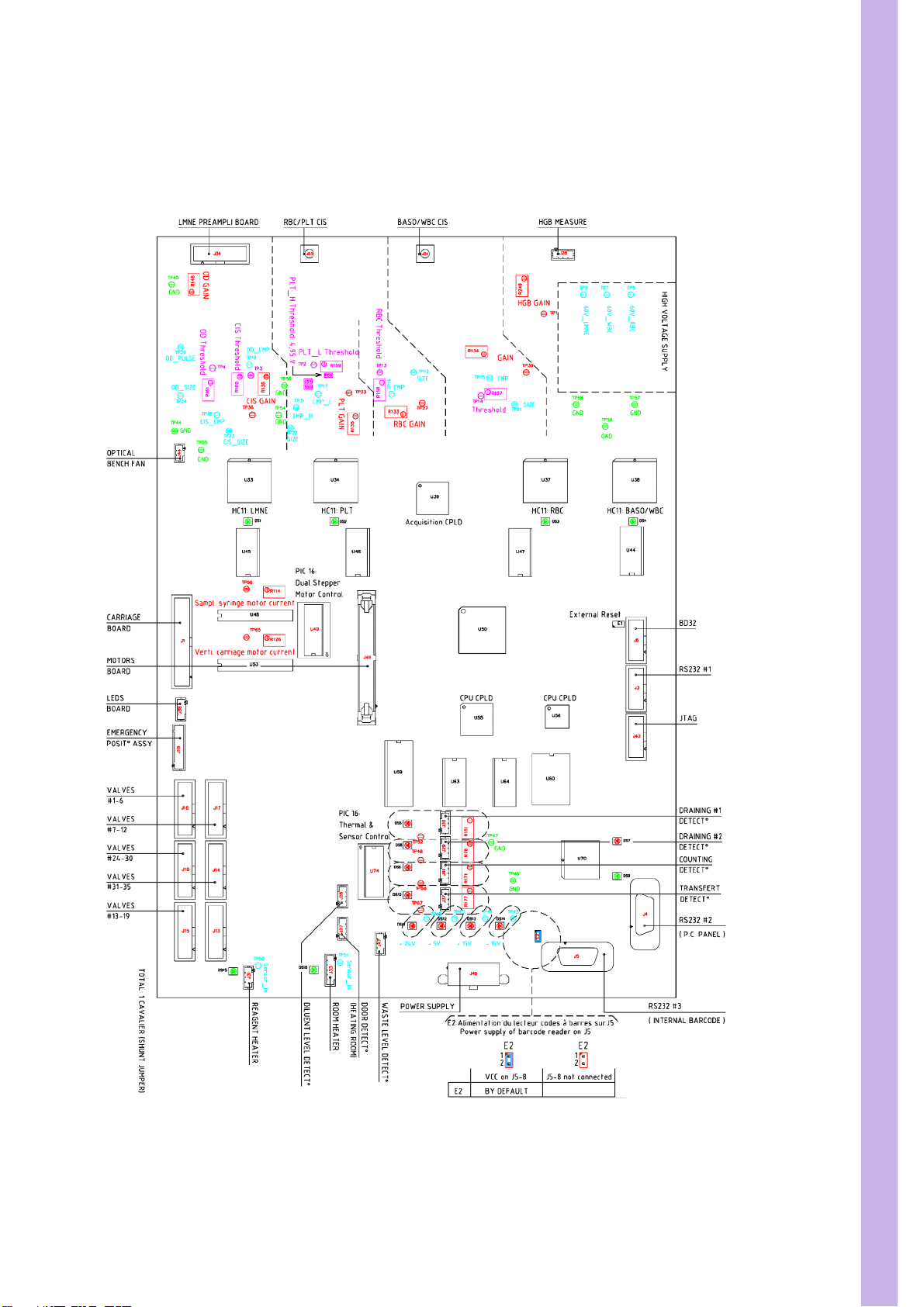
2. Motor board
2.1. Motor board general view
4/55
Diag.2:Motor board general view
3. Connectors and other boards
Page 28
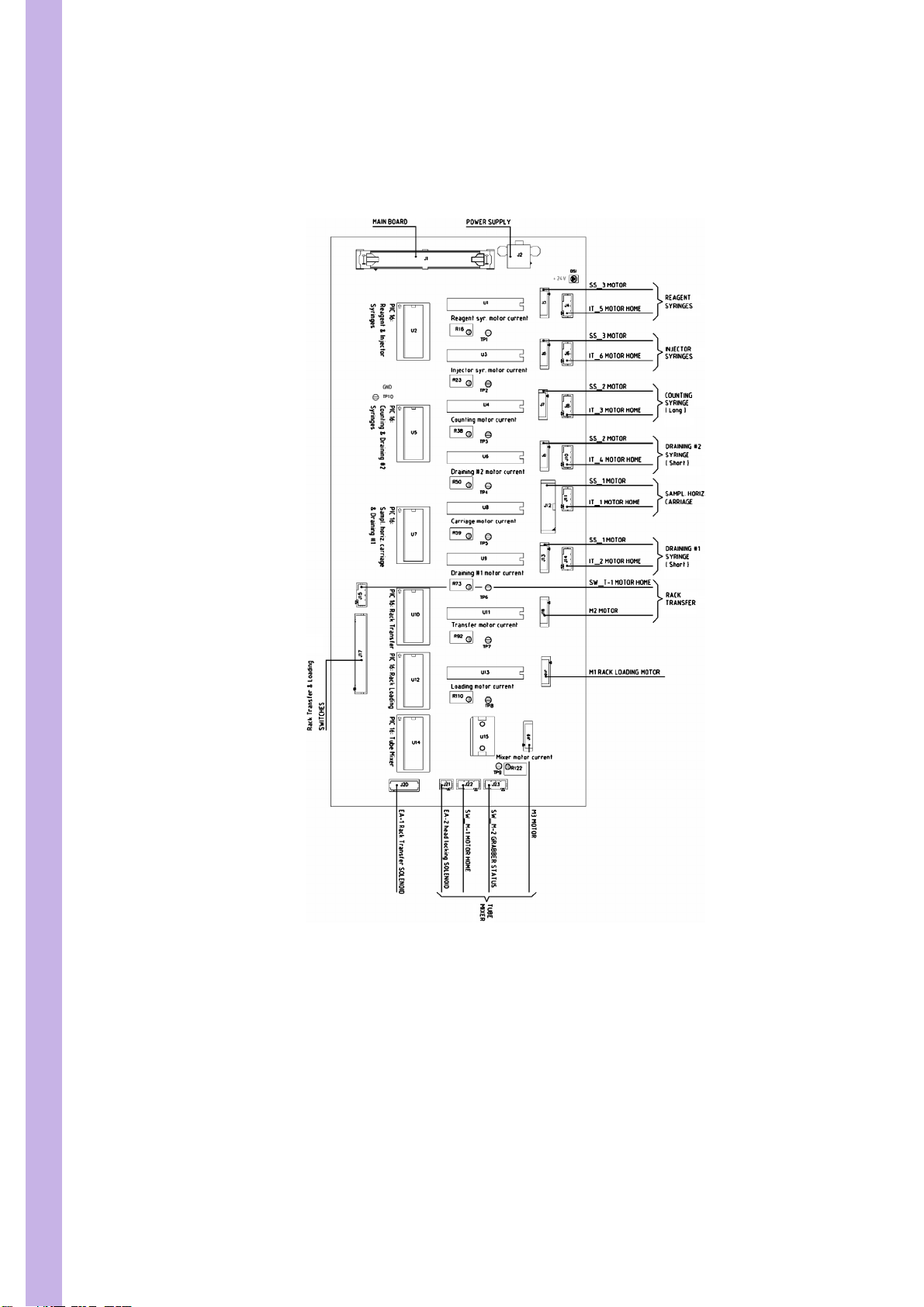
SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.1. CBC008A Barcode reader
Diag.3:CBC008A Barcode reader
5/55
Page 29
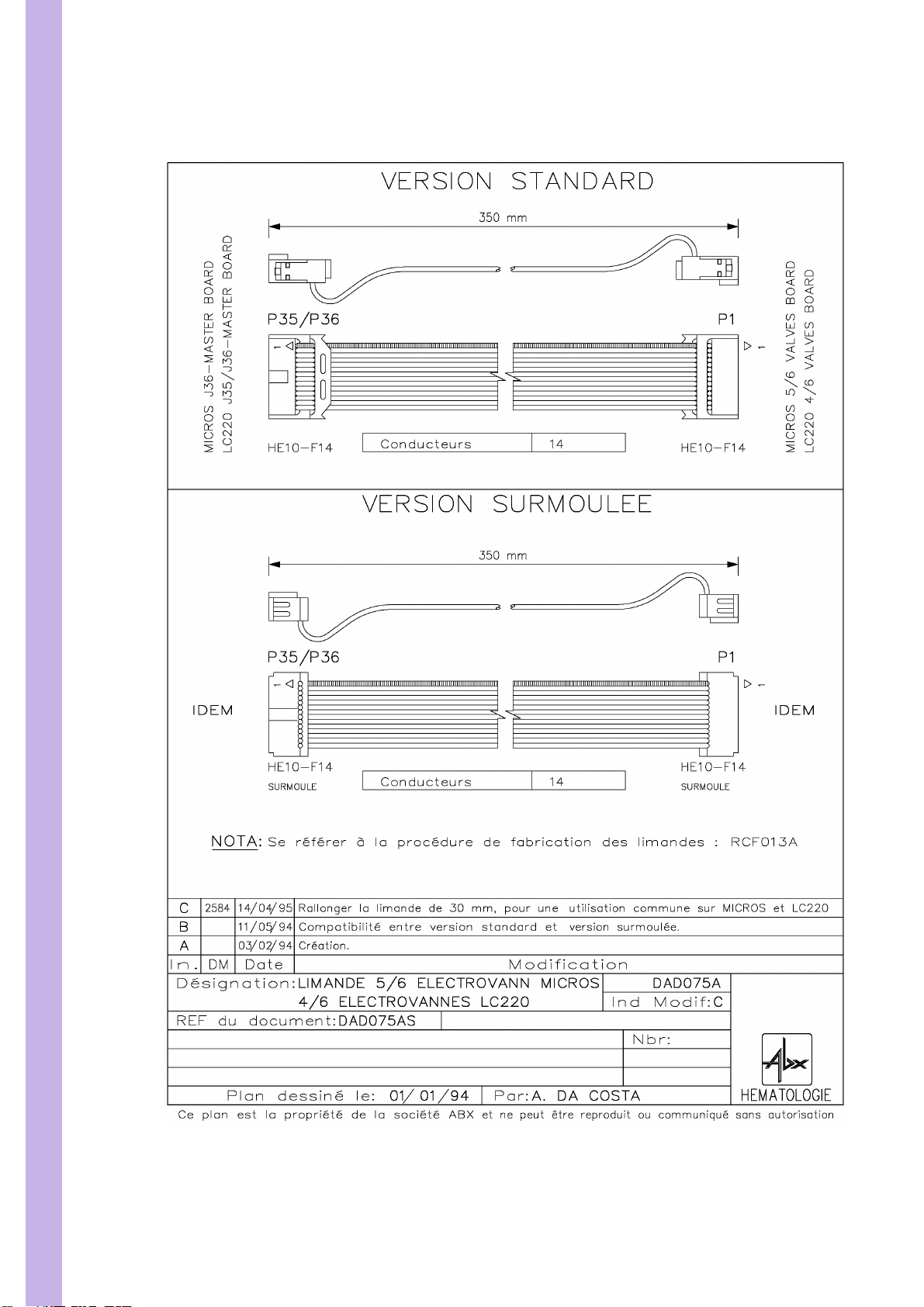
PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.2. DAD075AS Flat cable 350mm. 14pts
6/55
Diag.4:DAD075AS Flat cable 350mm. 14pts
Page 30
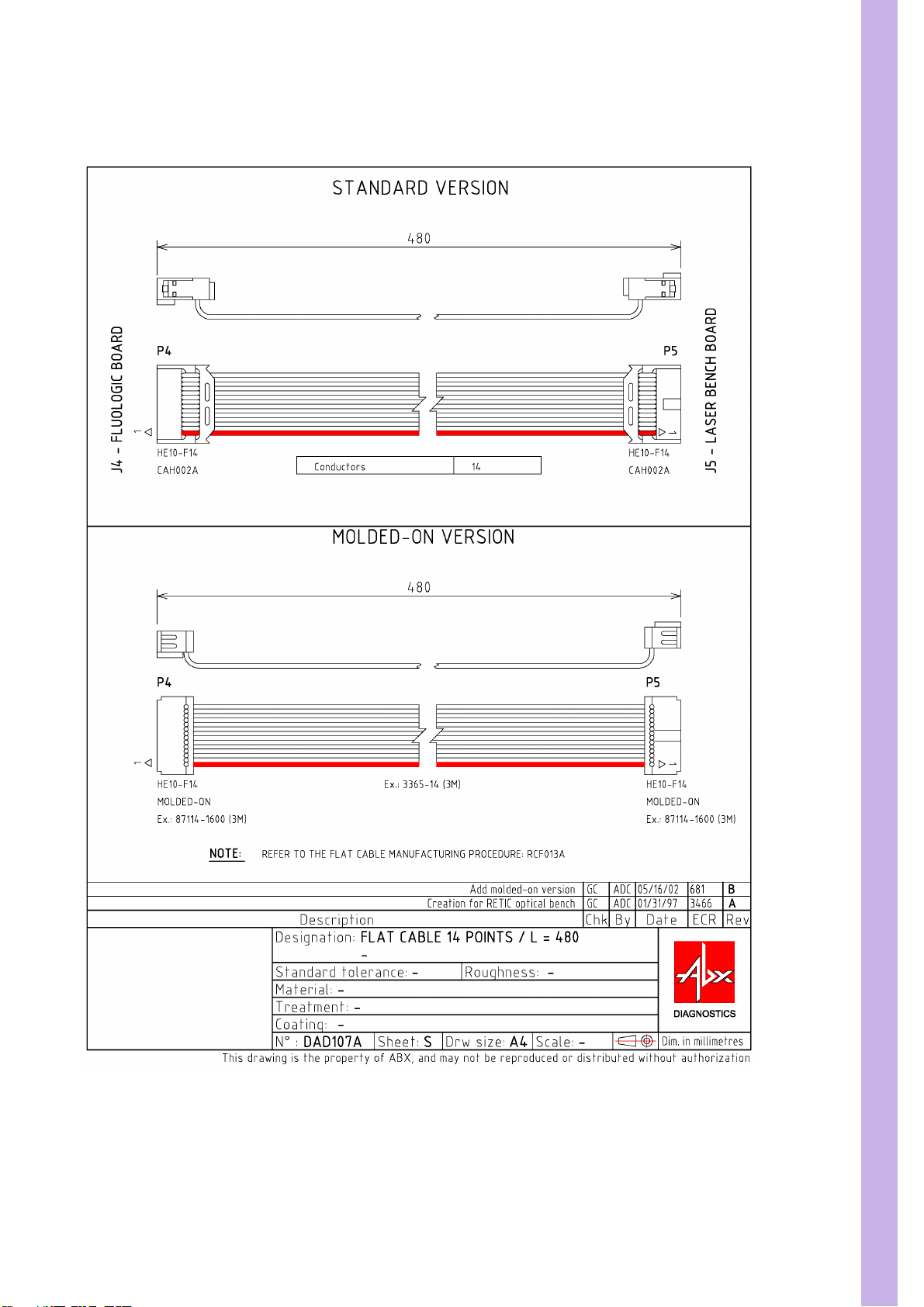
SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.3. DAD075AS Flat cable 480mm. 14pts
Diag.5:DAD075AS Flat cable 480mm. 14pts
7/55
Page 31

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.4. DAD109A Flat cable 560mm. 14pts
8/55
Diag.6:DAD109A Flat cable 560mm. 14pts
Page 32

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.5. DAD112AS Flat cable 930mm. 26pts (Main board\Carriage board)
Diag.7:DAD112AS Flat cable 930mm. 26pts
9/55
Page 33

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.6. DAD119AS Flat cable 950mm. 8pts
10/55
Diag.8:DAD119AS Flat cable 950mm. 8pts
Page 34

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.7. DAD120A Flat cable 800mm. 14pts
Diag.9:DAD120A Flat cable 800mm. 14pts
11/55
Page 35

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.8. DAD121A Flat cable 700mm. 44pts
12/55
Diag.10:DAD121A Flat cable 700mm. 44pts
Page 36

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.9. DAD122A Flat cable 650mm. 14pts
Diag.11:DAD122A Flat cable 650mm. 14pts
13/55
Page 37

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.10. DAD123A DSUB 25pts Flat cable 1000mm.
14/55
Diag.12:DAD123A DSUB 25pts Flat cable 1000mm.
Page 38

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.11. DAD124A DSUB 9pts Flat cable 1000mm.
Diag.13:DAD124A DSUB 9pts Flat cable 1000mm.
15/55
Page 39

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.12. XAA428C Carriage board
16/55
Diag.14:XAA428C Carriage board
Page 40

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.13. XAA429A LEDs board
Diag.15:XAA429A LEDs board
17/55
Page 41

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.14. XAA456A Main board
18/55
Diag.16:XAA456A Main board
Page 42

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.15. XAA458A LMNE amplifier board
Diag.17:XAA458A LMNE amplifier board
19/55
Page 43

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.16. XAA459A Motor board
20/55
Diag.18:XAA459A Motor board
Page 44

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.17. XAA478A Solenoid board
Diag.19:XAA478A Solenoid board
21/55
Page 45

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.18. XBA322B External waste level detection
22/55
Diag.20:XBA322B External waste level detection
Page 46

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.19. XBA342A Infrared sensor
Diag.21:XBA342A Infrared sensor
23/55
Page 47

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.20. XBA387A Reagent heating coil
24/55
Diag.22:XBA387A Reagent heating coil
Page 48

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.21. XBA389A Hemoglobin photometer
Diag.23:XBA389A Hemoglobin photometer
25/55
Page 49

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.22. XBA393A Upper fan
26/55
Diag.24:XBA393A Upper fan
Page 50

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.23. XBA396A Infrared 260mm.
Diag.25:XBA396A Infrared 260mm.
27/55
Page 51

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.24. XBA398B RBC&WBC electrode coaxial cable
28/55
Diag.26:XBA398B RBC&WBC electrode coaxial cable
Page 52

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.25. XBA399B LMNE flowcell coaxial cable
Diag.27:XBA399B LMNE flowcell coaxial cable
29/55
Page 53

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.26. XBA425A Chamber heating
30/55
Diag.28:XBA425A Chamber heating
Page 54

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.27. XBA427A Emergency position assy
Diag.29:XBA427A Emergency position assy
31/55
Page 55

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.28. XBA431A Infrared photocell 600mm. (No tab)
32/55
Diag.30:XBA431A Infrared photocell 600mm. (No tab)
Page 56

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.29. XBA432A Infrared photocell 600mm. (2 tabs)
Diag.31:XBA432A Infrared photocell 600mm. (2 tabs)
33/55
Page 57

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.30. XBA433A Infrared photocell 600mm. (1 tab)
34/55
Diag.32:XBA433A Infrared photocell 600mm. (1 tab)
Page 58

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.31. XBA458A Switch JST 300mm.
Diag.33:XBA458A Switch JST 300mm.
35/55
Page 59

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.32. XBA459A Switch JST 400mm.
36/55
Diag.34:XBA459A Switch JST 400mm.
Page 60

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.33. XBA460A Switch Jst 500mm.
Diag.35:XBA460A Switch Jst 500mm.
37/55
Page 61

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.34. XBA461A Switch Jst 700mm.
38/55
Diag.36:XBA461A Switch Jst 700mm.
Page 62

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.35. XBA462A Motor Jst 300mm.
Diag.37:XBA462A Motor Jst 300mm.
39/55
Page 63

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.36. XBA463A Motor Jst 400mm.
40/55
Diag.38:XBA463A Motor Jst 400mm.
Page 64

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.37. XBA464A Motor Jst 500mm.
Diag.39:XBA464A Motor Jst 500mm.
41/55
Page 65

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.38. XBA465A Motor Jst 700mm.
42/55
Diag.40:XBA465A Motor Jst 700mm.
Page 66

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.39. XBA469A Horizontal carriage cell extension
Diag.41:XBA469A Horizontal carriage cell extension
43/55
Page 67

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.40. XBA470A Solenoid JST 700mm.
44/55
Diag.42:XBA470A Solenoid JST 700mm.
Page 68

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.41. XBA471A Solenoid Molex 230mm.
Diag.43:XBA471A Solenoid Molex 230mm.
45/55
Page 69

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.42. XBA478A Horizontal carriage motor
46/55
Diag.44:XBA478A Horizontal carriage motor
Page 70

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.43. XBA486A LEDs extension JST 1000mm.
Diag.45:XBA486A LEDs extension JST 1000mm.
47/55
Page 71

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.44. XBA487A LED JST 200mm.
48/55
Diag.46:XBA487A LED JST 200mm.
Page 72

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.45. XBA488A Waste level detection
Diag.47:XBA488A Waste level detection
49/55
Page 73

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.46. XDA605A Diluent reservoir with level detection
50/55
Diag.48:XDA605A Diluent reservoir with level detection
Page 74

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.47. XDA751C 12 valves assy (LV1-6 & LV7-12)
Diag.49:XDA751C 12 valves assy (LV1-6 & LV7-12)
51/55
Page 75

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.48. XDA752C 7 valves assy (LV13-19)
52/55
Diag.50:XDA752C 7 valves assy (LV13-19)
Page 76

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.49. XDA753C Carriage valves assy (LV20-23)
Diag.51:XDA753C Carriage valves assy (LV20-23)
53/55
Page 77

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
3.50. XDA754C 7 valves assy (LV24-30)
54/55
Diag.52: XDA754C 7 valves assy (LV24-30)
Page 78

SECTION 3 ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES
3.51. XDA755C 5 valves assy (LV31-35)
Diag.53:XDA755C 5 valves assy (LV31-35)
4. Pentra 80 synoptic
See synoptic diagram on next page.
55/55
Page 79

Page 80

Analysis cycle technology
1. Analysis cycle description (Principles) .....................4-2
2. Measuring principles ...............................................4-4
2.1. Multi distribution sytem (MDSS) .................................. 4-4
2.2. CBC detection principles .............................................4-5
2.3. WBC and differential count .........................................4-7
Page 81

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. Analysis cycle description (Principles)
• Aspiration of blood sample from the tube trough
the cap (53µl)
• Translation of sampling carriage over Rinse
chamber.
Cleaning of the needles:
• Internal cleaning: 1ml inside piercing needle
• External cleaning: 2ml outside piercing needle
• Internal cleaning: 1ml inside piercing needle and
reject of 3µl of blood (not used).
• Translation of sampling carriage DIL1 chamber
(first dilution), descent of the needle.
• Positioning the needle point into a tangential flux
of ABX diluent (1.65ml) and synchronised
distribution of 10µl of blood.
• Translation of sampling carriage over WBC/
BASO count chamber.
• Positioning the needle point into a tangential flux
of 2ml of ABX BASOLYSE II and synchronised
distribution of 10µl of blood.
Dilution
Blood Volume: 10 µl
BASOLYSE II Volume: 2000 µl
Dilution Rate: 1/200
• Translation of sampling carriage over LMNE
mixing chamber.
• Positioning the needle point into a tangential flux
of 1ml of ABX Eosinofix and synchronised
distribution of 25µl of blood.
Dilution
Blood Volume: 25 µl
Eosinofix Volume: 1000 µl
Diluent Volume: 1000 µl
Final Dilution Rate: 1/80
2/11
Page 82

SECTION 4 ANALYSIS CYCLE TECHNOLOGY
• Translation of sampling carriage over Rinse
chamber
• Rinsing of the needles:
• Internal rinsing: 0.8ml inside sampling needle
• External rinsing: 0.5ml outside sampling needle
• Internal rinsing: 0.5ml inside sampling needle
• External rinsing: 0.3ml outside sampling needle
WBC and LMNE counting:
• 1ml of diluent into LMNE chamber
• Dilution transfer trough LMNE flowcell and
counting during 12 seconds
• WBC\BASO counting
• Translation of sampling carriage over DIL1
chamber
• Sample of the 42.5µl of the first dilution.
• Translation of sampling carriage over Rinse
chamber.
• Rinsing of the exterior of sampling needle with
0.4ml of diluent
• Translation of sampling carriage over RBC and
PLT count chamber.
• Distribution of the 42.5µl of first dilution into a
flux of 2.20ml of diluent.
• Distribution of 0.3ml of diluent from the interior
of the needle.
Dilution
Initial Blood Volume: 10 µl
Reagent Volume (RBC chamber): 2500 µl
Final Dilution Rate: 1/10000
Hgb:
• Distribution of 0.36ml of ABX ALPHALYSE into
DIL1 chamber while bubbling.
• WBC\BASO chamber rinsing:
• Draining and filling with 1ml of ABX CLEANER
and 1.5ml of diluent
• RBC\Plt counting and Hgb measurement
• Chambers cleaning and Hgb blank
• Draining and filling of DIL1 chamber with 2.7ml
of diluent
• Measurement of Hgb blank
• Flowcell rinsing (about 1.6ml of diluent)
• Draining and filling of RBC chamber with 2.5ml
of diluent
3/11
Page 83

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
2. Measuring principles
2.1. Multi distribution sytem (MDSS)
2.1.1. CBC mode
In CBC mode, 30µl of whole blood is
aspirated then delivered with reagents into
chambers as follows:
one specimen for the first RBC/Plt dilution
and the Hgb measurement.
another specimen for the BASO/WBC count.
Diag.1:Specimen distribution in CBC mode
2.1.2. Diff Mode
In DIFF mode, 53µl of whole blood is
aspirated, then delivered with reagents into
chambers as follows:
one specimen for the first RBC/Plt dilution
and the Hgb measurement.
another specimen for the BASO/WBC count.
the last specimen for the LMNE matrix.
2.1.3. Specimen distribution
Specimen distribution in the chambers is
carried out in a tangential flow of reagent which
allows perfect mixing of the dilution and avoids
any viscosity problems (this multi distribution in
a reagent flow is an ABX DIAGNOSTICS patent).
Diag.2:Specimen distribution in DIFF mode
4/11
Diag.3:Blood distribution in a tangential flow
Page 84

SECTION 4 ANALYSIS CYCLE TECHNOLOGY
2.2. CBC detection principles
2.2.1. RBC/Plt
Measurement of impedance variation
generated by the passage of cells through a
calibrated micro aperture.
The specimen is diluted in an electrolytic
diluent (current conductor) and pulled through
the calibrated micro-aperture. Two electrodes
are placed on either side of the aperture.
Electric current passes through the electrodes
continuously.
When the cell passes through the aperture,
electric resistance between the two electrodes
increases proportionately with the cell volume.
The generated impulses have a very low
voltage, which the amplification circuit
increases, so that the electronic system can
analyze them and eliminate the background
noise.
Diag.4:Impedance Principles
Results
Number of cells counted per volume unit x
calibration coefficient
Histograms
RBC: Distribution curves on 256 counting
channels from 30fl to 300fl.
Plt: Distribution curves on 256 channels from
2fl to a mobile threshold. This threshold moves
according to the microcyte population present
in the analysis area.
Diag.5:RBC distribution curve
Diag.6:Plt Distribution curve
Dilutions
Table 1: RBC\Plt dilutions
Technical characteristics of the RED BLOOD CELL and PLATELET counts
Initial blood volume 10 µl Method Impedance
Vol . ABX DILU ENT 2500 µl Aperture diameter 50 µm
5/11
Page 85

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
Table 1: RBC\Plt dilutions
Technical characteristics of the RED BLOOD CELL and PLATELET counts
Final dilution rate** 1/10000 Count vacuum 200 mb
Temperature of reaction 35°C Count period 2 X 6 seconds
**: Two successive dilutions are carried out : Primary Dilution for RBC and Plt:
Blood (µl) 10 µl
Vol . ABX DILUENT 1700 dilution 1/170
Secondary Dilution RBC and Plt (from the primary dilution)
Dilution (µl) 42,5 µl
Vol . ABX DILUENT 2500 dilution 1/58,8
Final dilution: 1/170 x 1/58,8 = 1/10000
2.2.2. Hgb Measurement
The hemoglobin released by the lysis of the red blood cells combines with the potassium cyanide to
form the chromogenous cyanmethemoglobin compound. This compound is then measured through
the optical part of the first dilution chamber using a spectrophotometric technique at a wavelength of
550 nm.
Table 2: Hgb measurement
Technical characteristics for the HGB MEASUREMENT
Blood volume 10 µl Method Photometry
Vol . ABX DILUENT 1700 µl Wavelength 550 nm
Vol. ABX ALPHALYSE 400 µl
complement ABX DILUENT 400 µl
Final dilution rate** 1/250
Temperature of reaction 35°C
Results
Final Hgb result represents: Absorbance value obtained x coefficient of calibration.
Hct Measurement
The height of the impulse generated by the passage of a cell through the micro-aperture is directly
proportional to the volume of the analyzed RBC.
The hematocrit is measured as a function of the numeric integration of the MCV.
2.2.3. RDW calculation
The study of the RBC distribution detects erythrocyte anomalies linked to anisocytosis.
A Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) will enable you to follow the evolution of the width of the curve
in relation to the cell number and average volume.
6/11
RDW = (K X SD) / MCV
With:
• K = system constant
• SD = Determined standard deviation according to statistical studies on cell distribution.
• MCV = Mean Corpuscular Volume of erythrocytes
Page 86

SECTION 4 ANALYSIS CYCLE TECHNOLOGY
2.2.4. MCV, MCH, MCHC calculation
• MCV (Mean Cell Volume) is calculated directly from the RBC histogram.
• MCH (Mean Cell Hemoglobin) is calculated from the Hgb value and the RBC number.
• The mean hemoglobin weight in each RBC is given by the formula:
MCH (pg) = Hgb/RBC x 10
• MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Contained) is calculated according to the Hgb and Hct
values. Mean Hgb concentration in the total volume of RBC is given by the formula:
MCHC (g/dL) = Hgb/Hct x 100
2.2.5. MPV Measurement
The MPV (Mean Platelet Volume) is directly derived from the analysis of the platelet distribution
curve.
2.2.6. Pct Calculation
Thrombocrit is calculated according to the formula:
Pct% = Plt (103/µl) x MPV (µm3) / 10 000
2.2.7. PDW calculation
PDW (Platelet Distribution Width) is
calculated from the Plt histogram.
The PDW is represented by the width
of the curve between 15% of the
number of platelets starting from 2 fl
(S1), and 15% of the number of platelets
beginning with the variable top threshold
(S2).
2.3. WBC and differential count
2.3.1. General principles
Diag.7:PDW calculation
The WBC count is carried out twice by two different sensors:
• In the BASO count chamber at the same time as the BASOS count,
• In the optical chamber during the acquisition of the LMNE matrix.
The reference count
is the one obtained in the WBC and BASO count chamber.
7/11
Page 87

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
2.3.2. BASO/WBC Count
Detection principle is the same as for RBC.
Differentiation betwen BASOs and other leukocytes is obtained by means of the BASOLYSE II specific
lysing action.
All the WBCs are counted between the electrical
threshold <0> threshold <BA3>. The basophils are
located from threshold <BA2> to threshold
<BA3>.
Diag.8:WBC/BASO histogram
Table 3: WBC\Baso count
Technical characteristics of the WBC/BASO counts
Initial blood volume 10 µl (CBC or CBC/DIFF) Method Impedance
Vol. ABX BASOLYSE II 2000 µl Aperture diameter 80 µm
Final dilution rate** 1/200 Count vacuum 200 mb
Temperature of reaction 35°C Count period 2 X 6 seconds
Results
WBC: Number of cells per volume x coefficient of calibration.
BASO: Number of cells per volume x coefficient of calibration in percentage regarding the total
number of leukocytes (BASO + WBC nuclei).
8/11
Page 88

SECTION 4 ANALYSIS CYCLE TECHNOLOGY
2.3.3. LMNE Matrix
The WBC and Differential count are based
on 3 essential principles:
• The double hydrodynamic sleeving
«DHSS» (ABX DIAGNOSTICS patent)
• The volume measurement (impedance
changes).
• The measurement of transmitted light
with 0° angle, which permits a response
according to the internal structure of each
element and its absorbance by means of
incident light diffusion.
25µl of whole blood is delivered to the
LMNE chamber in a flow of EOSINOFIX. This
reagent lyses the RBC, stabilizes the WBC in
their native forms and stains the eosinophil
nuclei with a specific coloration.
The solution is then stabilized with diluent
and transferred to the measuring chamber.
Each cell is measured both in absorbance
(cytochemistry) and resistivity (volume).
Diag.9:DHSS principles
Table 4: WBC counts
Technical characteristics of the WBC counts during the acquisition of the matrix
Initial blood volume 25 µl Method Impedance with hydrofocus
Vol . ABX Eosi nofix 1000 µl Aperture diameter 60 µm
Diluent Volume 1000 µl Flow diameter 42 µm
Final dilution rate 1/80 Injection duration 12 s
Temperature of reaction 35°C Volume injected 72µl
Incubation duration 12s
9/11
Page 89

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
No cell in the flowcell Baseline
Poorly-stained (agranular)
cell in the flowcell
Hyper segmented with
complex granularity and
staining
Diag.10:Absorbance measurement
Results
From these measurements, a matrix is drawn up with volumes on the X-axis and optical
transmission on the Y-axis. The study of the matrix image permits the clear differentiation of 4 out of 5
leukocyte populations. As a matter of fact, the basophil population is very small compared to the
others.
Low
absorbance
High
absorbance
10/11
MONOCYTES: The monocytes, being cells with large kidney shaped nuclei and a large non-
granular cytoplasm, will neither be scattered nor absorb a large amount of light. They will therefore be
positioned in the lower part of the optical axis but clearly to the right of the volume axis.
LYMPHOCYTES: The lymphocytes being small with regular shape, are positioned in the lower part
of both the optical axis and volume axis. Normal lymphocyte populations are generally observed with a
good volume homogeneity. The far left side of the lymphocyte zone should normally be empty, but
when small lymphocytes are present, population may exist in this area. The presence of platelet
aggregates is detected by a distribution pattern that moves from the origin of the matrix (background
zone) into the lymphocyte zone. The NRBCs with their cytoplasmic membranes lysed like the
erythrocytes, will have their nuclei situated to the far left side of the lymphocyte zone.
Page 90

SECTION 4 ANALYSIS CYCLE TECHNOLOGY
EOSINOPHILS: With reagent action on cytoplasmic membranes, the leukocytes keep their native
size and only eosinophils are colored for optical separation. Eosinophils will be situated in the upper
part of the optical Y-axis due to their strong absorbance qualities and their size, which is nearly
equivalent to large neutrophils.
NEUTROPHILS: The neutrophils, with their cytoplasmic granules and their generally segmented
nuclei, will scatter light depending on their morphological complexity. A hypersegmented neutrophil will
give an increased optical response with respect to a young neutrophil population which will be in the
upper position of the optical axis depending on the presence of segmentation and/or granules.
Additional parameters: LIC (Large Immature Cells) and ALY (Atypical Lymphocytes) complete the
panel available on the matrix.
The immature granulocytic cells are detected by their larger volumes and by the presence of
granules which increase the intensity of the scattered light. Therefore, cells such as metamyelocytes
will be found clearly to the right of the neutrophils and nearly at the same level. Myelocytes and
promyelocytes will be found in saturation position on the far right of the matrix. These last three
populations will be counted as LIC (Large Immature Cells) and their given results are included in the
neutrophil value. The blast cells will be found generally to the right of the monocytes, and, as such, will
increase the LIC count. Small blasts will be found between the normal lymphocytes and monocytes.
Platelets and debris from erythrocyte lysis represent the background noise population located in the
lower left area of the matrix. Most of the population partition thresholds are fixed and give the limits of
the morphological normality of leukocytes. Changes in the morphology of a population will be
expressed on the matrix by a shifting of the corresponding population.
A Blast alarm is generated from increased counts within the LIC area, this is correlated with Blast
detection on the Basophil curve.
Large lymphocytes are detected in the ALY (Atypical Lymphocytes) zone, where reactive lymphoid
forms, stimulated lymphocytes and plasmocytes are also to be found.
11/11
Page 91

Page 92

Software release
1. Service software overview.......................................5-2
1.1. Super User Menu......................................................... 5-2
1.2. Miniclean ....................................................................5-3
1.3. Autoclean....................................................................5-3
1.4. Technician Menu ........................................................5-3
2. Software releases.....................................................5-4
2.1. Software releases table.................................................5-4
2.2. Software modification.................................................. 5-4
Page 93

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. Service software overview
1.1. Super User Menu
• Mechanical
• Hydraulic
• Others
1.1.1. Mechanical
• Initialisation
• Check Motors
• Check Valves
• Check Sensors
• Sampler test
• Holder Adjustment
• Rack Adjustment
1.1.2. Hydraulic
1.1.3. Others
• Drain Chambers
• Prime Cycles
• Unprime Cycles
• Clean Cycles
• Cycles Counter
• Run Park Syringes Position
• Run Maintenance Carriage Pos.
2/4
Page 94

SECTION 5 SOFTWARE VERSIONS
1.2. Miniclean
• Miniclean
1.3. Autoclean
• Autoclean
1.4. Technician Menu
1.4.1. Measurement
• Measurement
• Gains
• Others
• Gain Adjustment
• LMNE Adjustment
• Aperture Current
• Pulse Adjustment
3/4
Page 95

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1.4.2. Gains
• Thermic Adjustment
• M.D.S.S. Adjustment
• Liquid Sensor Adjustment
• Vacuum Control
• Sampler Adjust.
• Bubbling
1.4.3. Others
• LMNE Calibration
• Cycles
• Calibration Coefficients
• Blank Values
• System Tools
• Burn In Cycles
2. Software releases
2.1. Software releases table
INDEX P/N REVISION SOFTWARE REVISION SECTION DATE
A RAH 919 AA V1.01 ALL 31/03/02
2.2. Software modification
V1.01: First release of technical manual.
4/4
Page 96

Output format
1. ABX format principles..............................................6-2
1.1. Message structure ........................................................6-2
1.2. Details about the structure........................................... 6-2
1.3. Identifier list and their formats .....................................6-3
1.4. Pathology ....................................................................6-5
1.5. Histograms and matrix.................................................6-8
1.6. Patient result identification ........................................6-12
1.7. Packet type................................................................6-13
1.8. Other identifiers ........................................................6-15
2. PIN assignments ....................................................6-16
3. ARGOS format principles ......................................6-17
3.1. Introduction............................................................... 6-17
3.2. Results characteristics................................................ 6-17
3.3. Patient file characteristics ..........................................6-19
3.4. End of communication .............................................. 6-19
4. ASTM Specifications..............................................6-21
4.1. Hardware and software characteristics.......................6-21
4.2. Output data characteristics ........................................6-21
4.3. Communication protocol...........................................6-21
4.4. ASTM frames format ..................................................6-22
4.5. Message packets (General format).............................. 6-22
4.6. Special caracteristics for ABX datas............................6-26
Page 97

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
1. ABX format principles
1.1. Message structure
The ABX format can have a different number of fields according to the transmitted items setup by
the user (results, curves, flags, etc...). The fields have the same characteristics than the ARGOS format.
The result identifier is different according to the type of result: patient result ("RESULT"), re-run result
(RES-RR), QC result (QC-RES) etc...
Example of "abx format":
- STX
- Size + carriage return.
- Identifier followed by a Load Type + carriage return.
- Identifier followed by the Information associated to the Load Type + carriage return.
- Remainder of the other Identifiers and Informations associated to the Load Type + carriage
returns.
- Other Load Type blocs + Associated Informations.
....................................................................................
- Identifier followed by the CheckSum + carriage return.
- ETX
1.2. Details about the structure
Size: 5 bytes representing the total amount of the data except STX and ETX.
Load: An 8 character chain preceeded by a space indicating that this load is a result type.
Identifier: 1 byte (moving about $21 to $FF, it describes the information type which follows this
indicator).
CheckSum: Sum modulo 65535 of all the characters except ETX, STX and all informations about
checksum (identifier - space - checksum - carriage return) in the hexadecimal format on 4 bytes,
preceeded by a space.
Strings of characters having a length smaller than the expected character number have to be
completed on the right handside by "spaces".
2/28
Page 98

SECTION 6 OUTPUT FORMAT
1.3. Identifier list and their formats
1.3.1. Hematology numerical parameters
A- Format description
Numerical field:
For all indicated parameters from $21 to $43, the format is a numerical field of 5 digits
completed with zeros on the left side (ex. : 04.55) and preceeded by a space.
The unit is the standard units (Version V2.2).
When the parameter cannot be calculated by the analyzer, the field is replaced with (--.--).
Parameter status:
Following the numerical field, a first digit gives the counting rejection status or the suspicion, a
second one gives the parameter value status according to high and low normalities, to high and low
extreme values and to the overloading capacities.
Table 1: Identifier First digit
First digit
(letter)
R Parameter rejected for a counting default
B Incorrect balance between the counting methods
S Suspicious parameter value
’s pa c e ’ No anomaly observed
Correspondance
Table 2: Identifier Second digit
Second digit
(letter)
L Parameter < to the lower extreme value
l Parameter < to the low normal value
’s pa c e ’ Parameter normal value
h Parameter > to the high normal value
H Parameter > to the high extreme value
O Parameter exceeding the capacity
Example:
5.5 millions RBC with a counting error in the standard units :
$32 $20 $30 $35 $2E $35 $30 $52 $68 $0D ou “2 05.50Rh” + carriage return.
The length is fixed and is worth 2+7+1, that is to say 10 bytes for one parameter.
Correspondance
1.3.2. Identifier list
Table 3: Identifier list
Identifiers Pa rame t ers Units
$21 ! WBC Standard - SI g/dl - SI mmoles - (or others)
$22 « Lymphocytes (#)
$23 # (%)
$24 $ Monocytes (#)
$25 % (%)
$26 & Granulocytes (#)
3/28
Page 99

PENTRA 80 TECHNICAL MANUAL RAA022AA
Table 3: Identifier list
Identifiers Pa ra me te rs Units
$27 ’ (%)
$28 ( Neutrophils (#)
$29 ) (%)
$2A * Eosinophils (#)
$2B + (%)
$2C , Basophils (#)
$2D - (%)
$2E . Atypical Lymphocytes (#)
$2F / (%)
$30 0 Large Immature Cells (#)
$31 1 (%)
$32 2 RBC Standard - SI g/dl - SI mmoles - (or others)
$33 3 Hgb
$34 4 Hct
$35 5 MCV
$36 6 MCH
$37 7 MCHC
$38 8 RDW
$39 9 reserved
$3A : reserved
$3B ; Reticulocytes (#)
$3C < (%)
$3D = Reticulocytes Low (%)
$3E > Reticulocytes Median (%)
$3F ? Reticulocytes High (%)
$40 @ PLT Standard - SI g/dl - SI mmoles - (or others)
$41 A MPV
$42 B THT
$43 C PDW
$44 D Reserved
$45 E Reserved
$46 F Reserved
$47 G Immatures
$48 H Mean fluorescent index (%)
$49 I
$4A J
$4B K Creactive protein (µg/ml)
$4C L IRF
Mean reticulocyte
volume
Corrected reticulocyte
count
Standard - SI g/dl - SI mmoles - (or others)
(%)
4/28
1.3.3. Parameter extended formats
No restriction on the lentgh for the fields #####. The first 12 parts are followed by the raw counts 1
and 2. For the LMNE channel, only the first 2 parts are initialized with the RA# and CO% values.
Page 100

SECTION 6 OUTPUT FORMAT
Table 4: Parameter extended formats
Identifiers Parameters Formats Lengths
$90 É WBC No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$91 æ RBC No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$92 Æ HGB No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$93 ô HCT No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$94 ö PLT No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$95 ò BASO No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
$96 û LMNE No unit 1+[14 x ($20 #####) +1
1.4. Pathology
1.4.1. Flags associated with parameters
Flags are transmitted in a comprehensive mode (same presentation than on the screen, that is to
say dependant from the language), preceeded by a space. They are replaced with spaces when the
flag has not been detected.
Table 5: Flags associated with parameters (English)
Identifiers Parameters Formats Lengths
$50 P WBC L1M1M2G1G2G3 2 + 12 + 1
$51 Q Differential
$52 R RBC MiMa 2 + 4 + 1
$53 S Plt PcScMc 2 + 6 + 1
$66 f WBC balance
$67 g General MpXbXr 2 + 6 + 1
$68 h Reticulocytes LowLasPitFitNrbc 2 + 16 + 1
$A2 I RUOs RUO message (*) 2 + 76 + 1
COMBLLNLMNLNRMRNN
ONELBLl1
BASO or WBC1 or WBC2
and Lmne+/- and BASO+/-
Table 6: Flags associated with parameters (French)
Identifiers Parameters Formats Lengths
$50 P GB L1M1M2G1G2G3 2 + 12 + 1
$51 Q Formule
$52 R GR MiMa 2 + 4 + 1
$53 S Plaquettes PcScMc 2 + 6 + 1
$66 f Balance GB
$67 g Générales MpXbXr 2 + 6 + 1
$68 h Réticulocytes LowLasPitFitNrbc 2 + 16 + 1
$A2 I RUOs message RUO (*) 2 + 76 + 1
COMBLLNLMNLNRMRNN
ONELBLl1
BASO or GB1 or GB2 and
Lmne+/- and BASO+/-
2 + 25 + 1
2 + 14 + 1
2 + 25 + 1
2 + 14 + 1
The RUO message is a warning message, transmitted allways in english language. Its content
and size depend on the instrument. IN USA AND CANADA, PCT, PDW, ALY AND LIC ARE FOR
5/28
 Loading...
Loading...