Page 1

802.11b/g Mini Wireless LAN
USB 2.0 Adapter
User’s Manual
Page 2

REGULATORY STATEMENTS
This device is intended only for OEM integrators under the following conditions:
1) The antenna must be installed such that 20 cm is maintained between the antenna and users. For laptop installations, the antenna must be
installed to ensure that the proper spacing is maintained in the event the users places the device in their lap during use (i.e. positioning of antennas
must be placed in the upper portion of the LCD panel only to ensure 20 cm will be maintained if the user places the device in their lap for use) and
2) The transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter or antenna.
As long as the 2 conditions above are met, further transmitter testing will not be required. However, the OEM integrator is still responsible for testing
their end-product for any additional compliance requirements required with this module installed (for example, digital device emissions, PC peripheral
requirements, etc.).
IMPORTANT NOTE: In the event that these conditions can not be met (for example certain laptop configurations or co-location with another
transmitter), then the FCC authorization is no longer considered valid and the FCC ID can not be used on the final product. In these circumstances,
the OEM integrator will be responsible for re-evaluating the end product (including the transmitter) and obtaining a separate FCC authorization.
End Product Labeling
This transmitter module is authorized only for use in devices where the antenna may be installed such that 20 cm may be maintained between the
antenna and users (for example access points, routers, wireless ASDL modems, certain laptop configurations, and similar equipment). The final end
product must be labeled in a visible area with the following: "Contains TX FCC ID: {INSERT FCC ID HERE}".
RF Exposure Manual Information That Must be Included
The users manual for end users must include the following information in a prominent location "IMPORTANT NOTE: To comply with FCC RF
exposure compliance requirements, the antenna used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all
persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter."
Additional Information That Must be Provided to OEM Integrators
The end user should NOT be provided any instructions on how to remove or install the device.
FCC Certification
The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the
Canadian Department of Communications have established certain rules
governing the use of electronic equipment.
Part15, Class B
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interface, and
2) This device must accept any interface received, including interface that may
cause undesired operation. This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
w Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
w Increase the distance between the equipment and receiver.
w Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
CAUTION:
1) To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, a separation
distance of at least 20 cm must be maintained between the antenna of this
device and all persons.
2) This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................1
FEATURES ..............................................................................................................1
Windows 2000/XP Installation ...............................................................................2
INSTALL THE SOFTWARE.........................................................................................2
INSTALL THE HARDWARE .......................................................................................6
Windows Vista Installation.....................................................................................7
INSTALL THE SOFTWARE.........................................................................................7
INSTALL THE HARDWARE .......................................................................................9
Verification................................................................................................9
IP Address ............................................................................................... 10
Utility Configuration for Windows 2000/XP.......................................................11
STATION MODE ....................................................................................................12
Profile......................................................................................................12
Network...................................................................................................20
Link Status...............................................................................................24
Advanced.................................................................................................26
Statistics...................................................................................................27
WMM / QoS............................................................................................28
WPS.........................................................................................................30
Radio On/Off...........................................................................................32
Page 4

About....................................................................................................... 32
UTILITY MENU LIST..............................................................................................33
SOFT AP MODE.....................................................................................................34
Config......................................................................................................34
Access Control......................................................................................... 38
MAC Table..............................................................................................39
Event Log ................................................................................................40
Statistics...................................................................................................41
About....................................................................................................... 42
Utility Configuration for Windows Vista............................................................43
STATION MODE ....................................................................................................43
Profile......................................................................................................43
Network...................................................................................................49
Link Status...............................................................................................52
Statistics...................................................................................................54
WMM / QoS............................................................................................55
WPS.........................................................................................................57
Radio On/Off...........................................................................................59
About....................................................................................................... 59
UTILITY MENU LIST..............................................................................................60
SOFT AP MODE.....................................................................................................61
Config......................................................................................................61
Access Control......................................................................................... 64
Page 5

MAC Table..............................................................................................65
Event Log ................................................................................................66
Statistics...................................................................................................67
About....................................................................................................... 68
UNINSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000/XP...............................................69
UNINSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS VISTA.................................................72
Page 6
INTRODUCTION
The 802.11b/g High Gain Wireless LAN USB Adapter is designed for a USB
type A port of a laptop or desktop computer for creating a wireless workstation
is USB 2.0 compliant, which connects to any available USB port on a notebook or
desktop computer.
The 802.11b/g High Gain Wireless LAN USB Adapter complies with IEEE
802.11g standard that offers a data rate up to 54Mbps in a wireless LAN
environment. It is backward compliant with IEEE 802.11b specification. The
high-speed wireless network card can plug into your notebook or desktop
PC and accesses to the LAN or peer-to-peer networking easily without
wires or cables. Whether you’re at your desk or in the boardroom, it
allows you to share printers, files, and other network resources.
Features
¾ Complies with IEEE 802.11g standard for 2.4GHz Wireless LAN
¾ USB 2.0 compliant
¾ USB Plug & Play
¾ Interoperable with existing network infrastructure
¾ Secure information transmission
¾ Freedom to roam while staying connected
¾ Compatible with specialty wireless products and services
¾ Up to 54 Mbps data rate
¾ Antenna is built in the card with LED indication
¾ Low power consumption
¾ Easy to install and configure
. It
-
1 -
Page 7

y
Windows 2000/XP Installation
Install the Software
Do not insert the wireless LAN adapter into your computer until the
procedures in “Driver& Utility Installation” have been performed.
1. Insert the included CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive of your
computer.
2. When the Main Menu screen appears, click “Driver & Utilit
Installation” to start the software installation.
-
2 -
Page 8

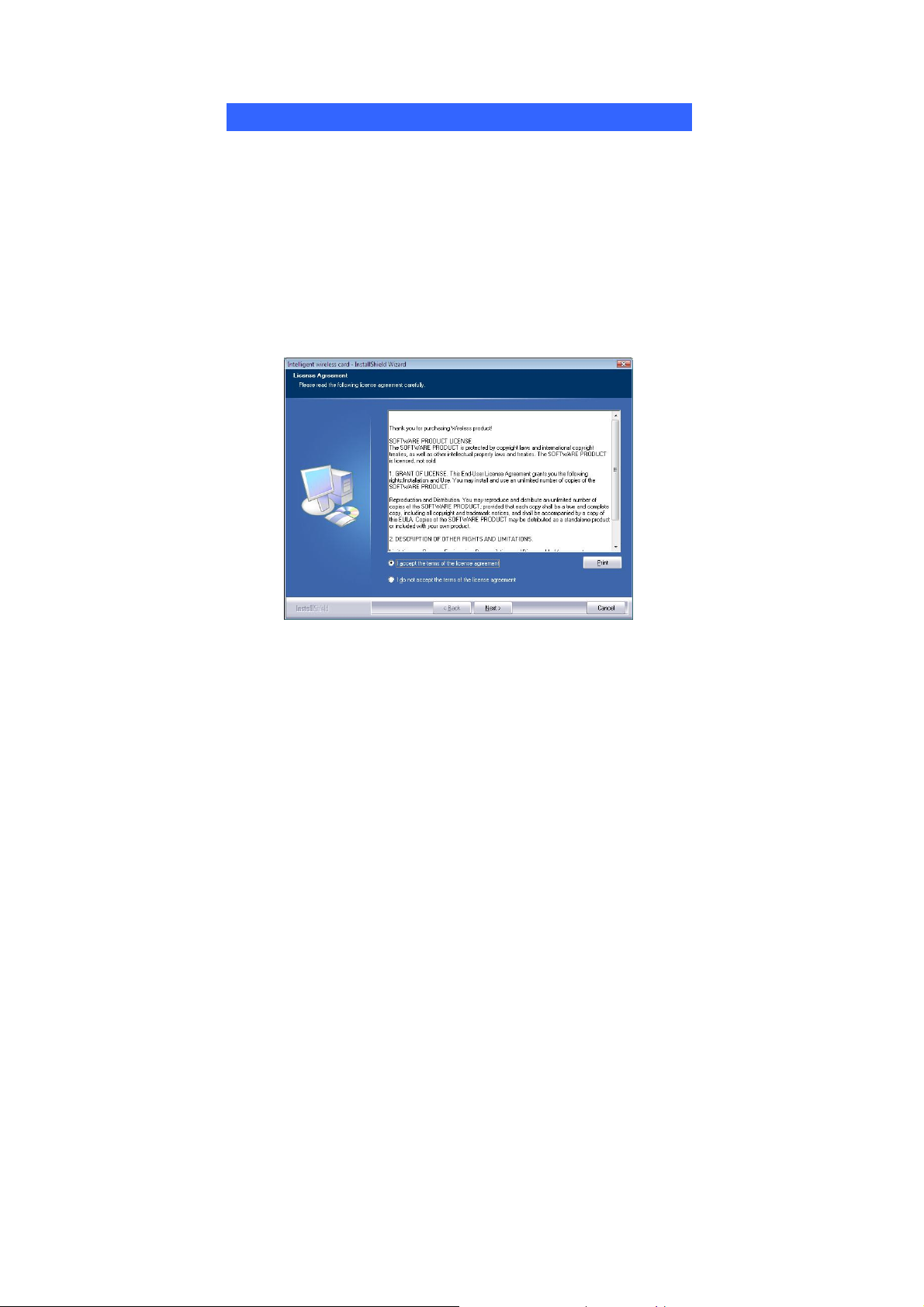
3. When the License Agreement screen appears, please read the
contents and select “I accept the terms of the license agreement
“ then click Next to continue.
4. Select the check box to choose a Configuration Tool from the
listed two choices.
z Configuration Tool: Choose to use our configuration utility.
z Microsoft Zero Configuration Tool: Choose to use Windows XP’s
built-in Zero Configuration Utility (ZCU).
Click Next to continue.
-
3 -
Page 9

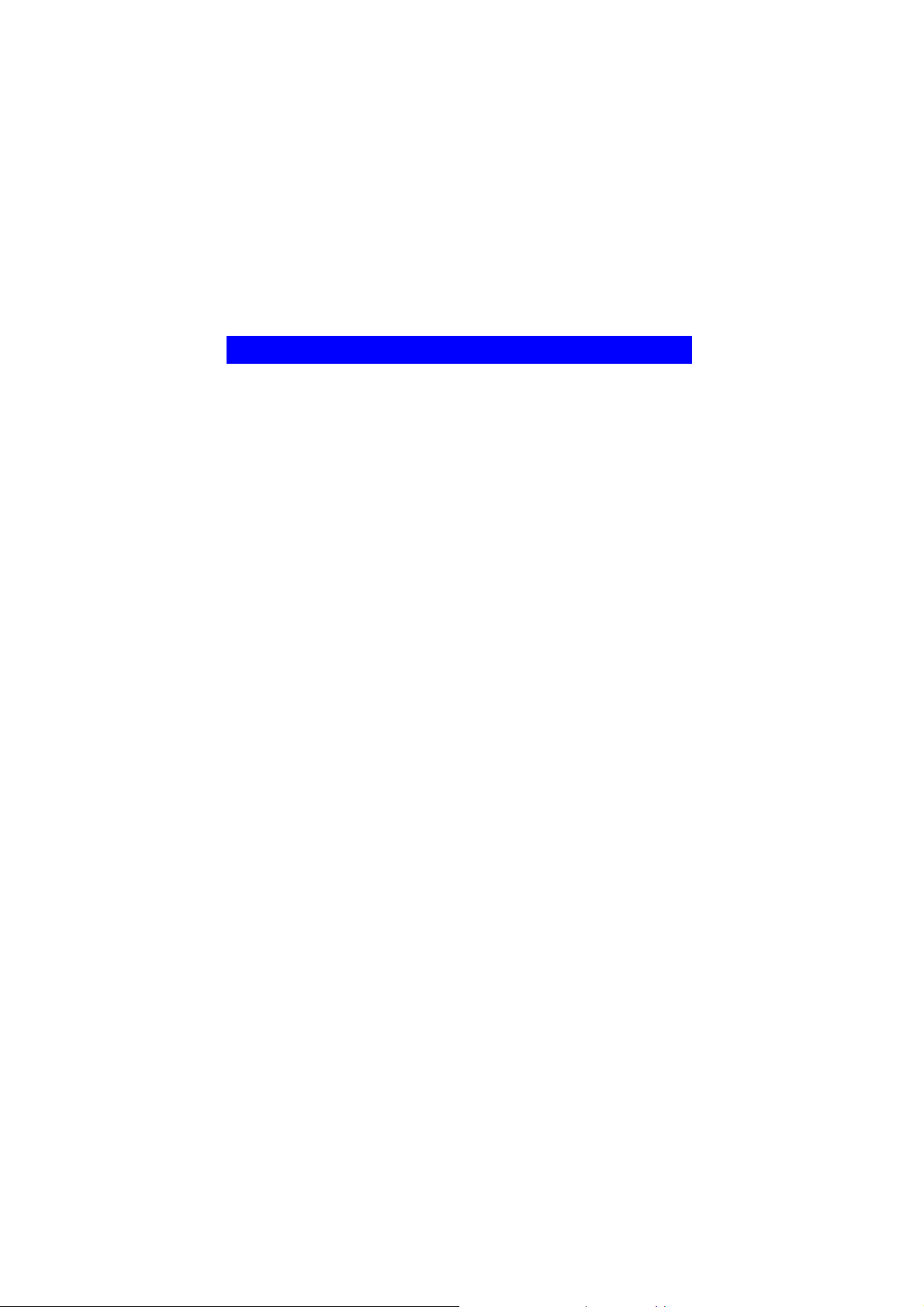
5. There are two modes for you to choose in this screen, either choose
Optimize for WiFi mode or Optimize for performance mode
(Tx Burst mode). This mode selection screen is set for the default
mode shown in the utility screen; you can still change its mode later
in the utility screen. Click Next to continue.
-
4 -
Page 10
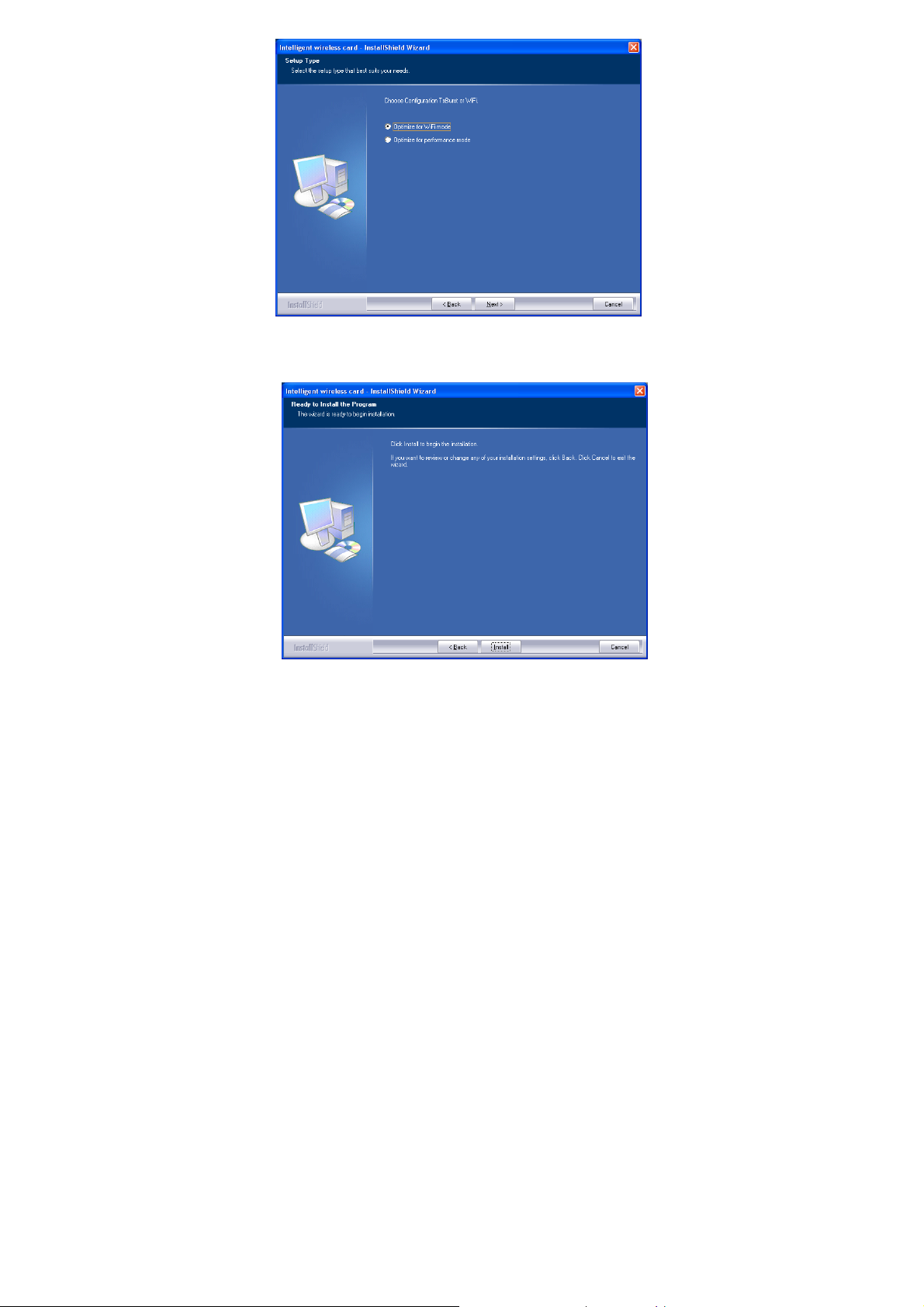
6. When you are prompted the following message, please click Install
to begin the installation.
-
5 -
Page 11

7. When the following screen appears, click Finish to complete the
software installation.
Install the Hardware
Note: Insert the Wireless USB card when you finished your software
installation.
Insert the USB Adapter into the USB Port of your computer. The system
will automatically detect the new hardware.
-
6 -
Page 12
Windows Vista Installation
Install the Software
Do not insert the wireless LAN adapter into your computer until the
procedures in “Driver& Utility Installation” have been performed.
1. Insert the included CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive of your
computer.
2. When the Main Menu screen appears, click “Driver & Utility
Installation” to start the software installation.
3. When the License Agreement screen appears, please read the
contents and select “I accept the terms of the license agreement
“ then click Next to continue.
-
7 -
Page 13
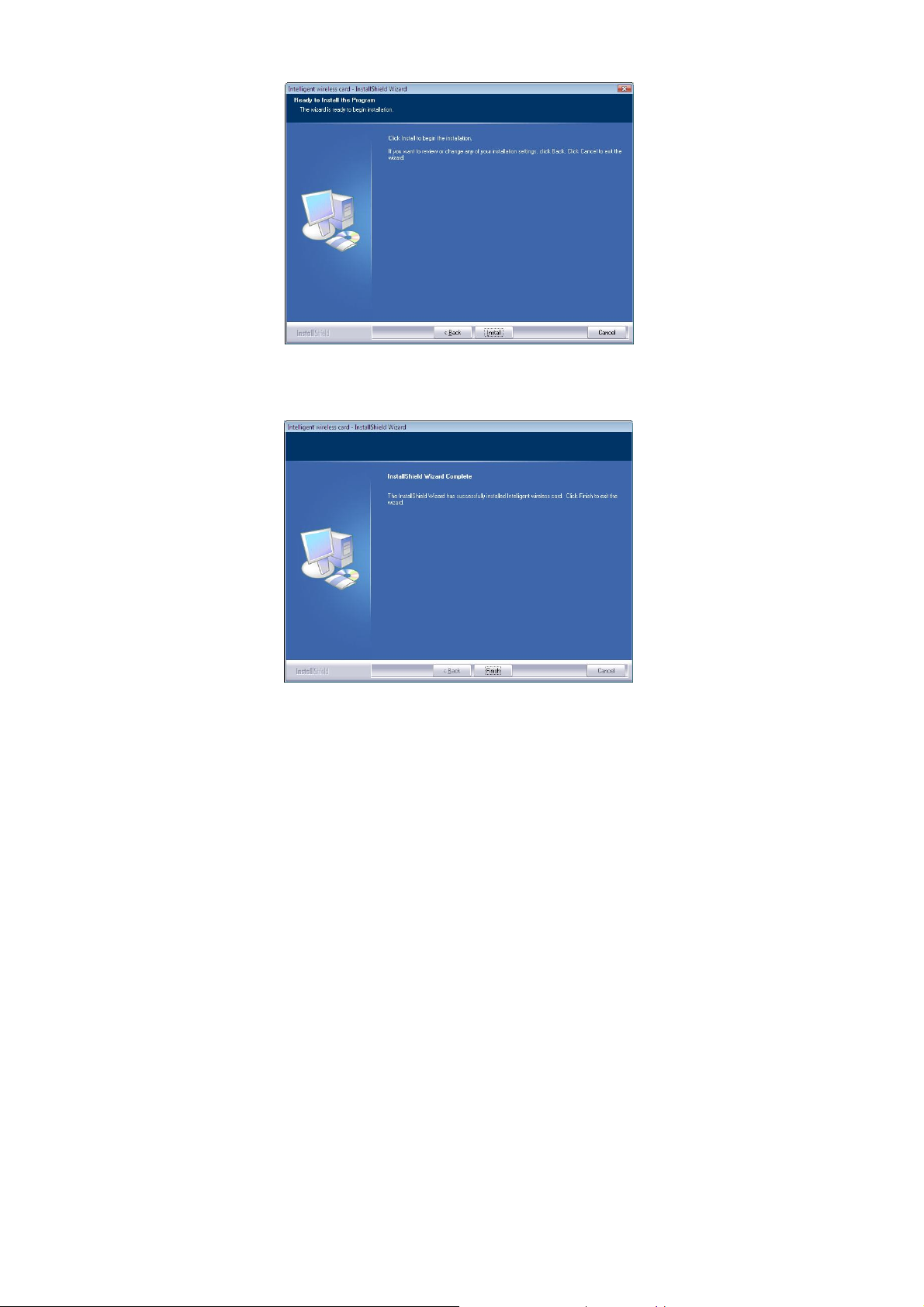
4. When you are prompted the following message, please click Install
to begin the installation.
5. When the following screen appears, click Finish to complete the
software installation.
-
8 -
Page 14
Install the Hardware
Note: Insert the Wireless USB card when you finished your software
installation.
Insert the USB Adapter into the USB Port of your computer. The system
will automatically detect the new hardware.
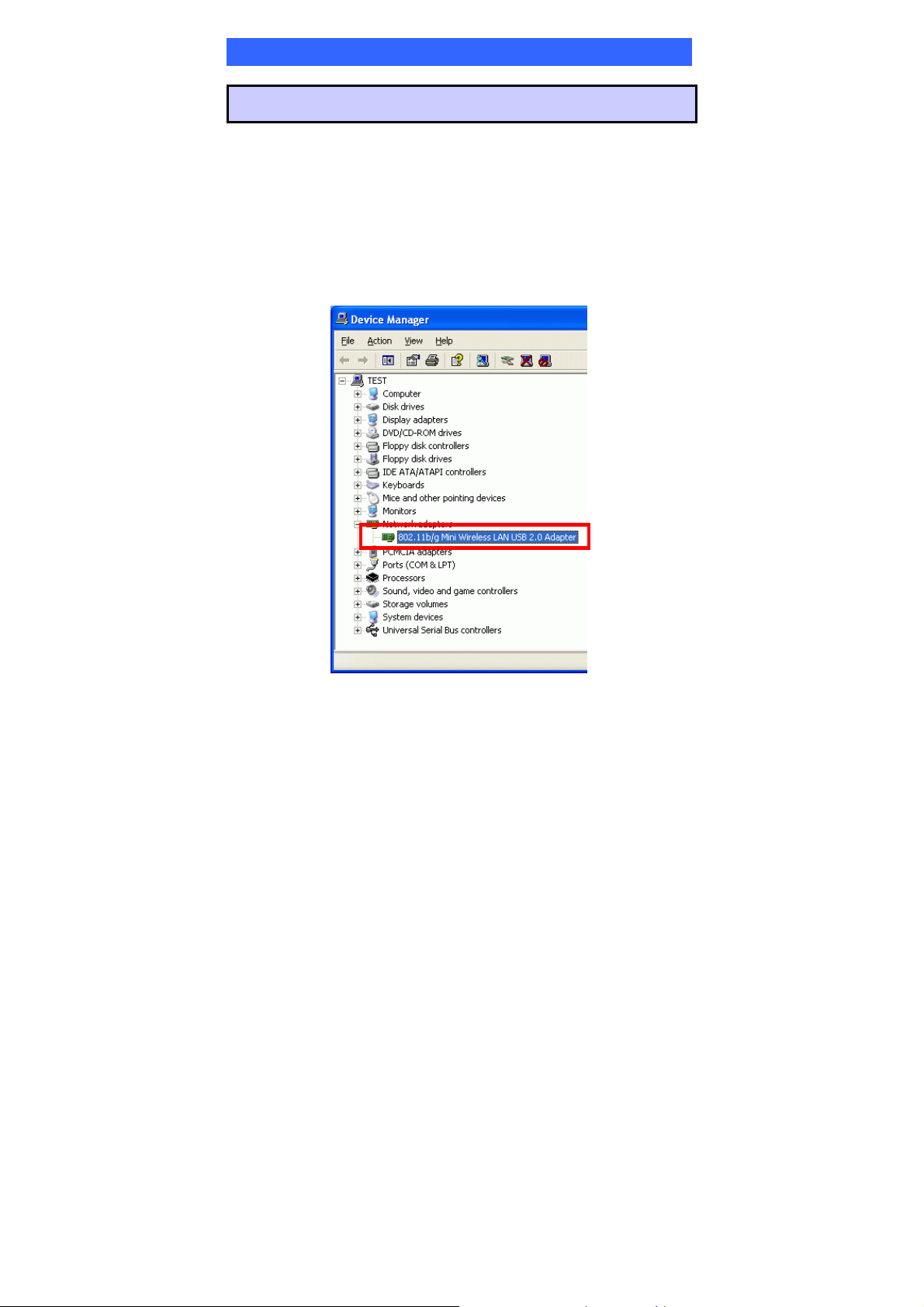
Verification
To verify if the device exists in your computer and is enabled, go to Start >
Control Panel > System (> Hardware) > Device Manager. Expand the
Network Adapters category. If the 802.11b/g Mini Wireless LAN USB 2.0
Adapter is listed here, it means that your device is properly installed and enabled.
-
9 -
Page 15
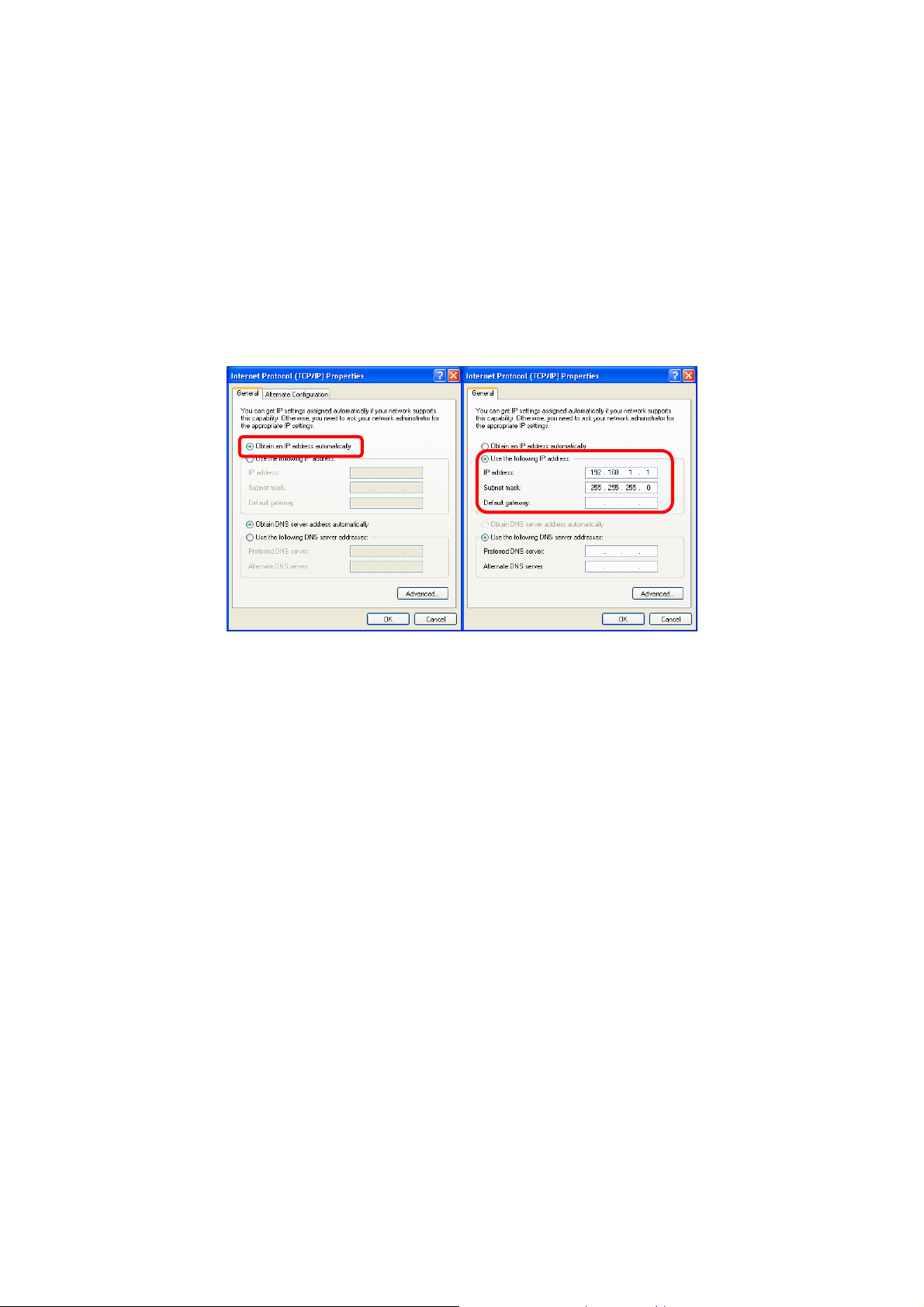
IP Address
Note: When assigning IP Addresses to the computers on the network, remember
to have the IP address for each computer set on the same subnet mask. If your
Broadband Router use DHCP technology, however, it won’t be necessary for you
to assign Static IP Address for your computer.
1. To configure a dynamic IP address (i.e. if your broadband Router has the DHCP
technology), check the Obtain an IP address automatically option.
2. To configure a fixed IP address (if you broadband Router is not DHCP
supported, or when you need to assign a static IP address), check the Use the
following IP address option. Then, enter an IP address into the empty field, for
example, enter 192.168.1.1 in the IP address field, and 255.255.255.0 for the
Subnet mask.
-
10 -
Page 16
Utility Configuration for Windows
2000/XP
After the Wireless adapter has been successfully installed, users can use the
included Configuration Utility to set their preference.
Go to StartJ (All) ProgramsJIntelligent Wireless J Intelligent Wireless
Utility
You can also open the Configuration Utility by double clicking the icon or right
clicking to select Launch Config Utilities.
-
11 -
Page 17
Station Mode
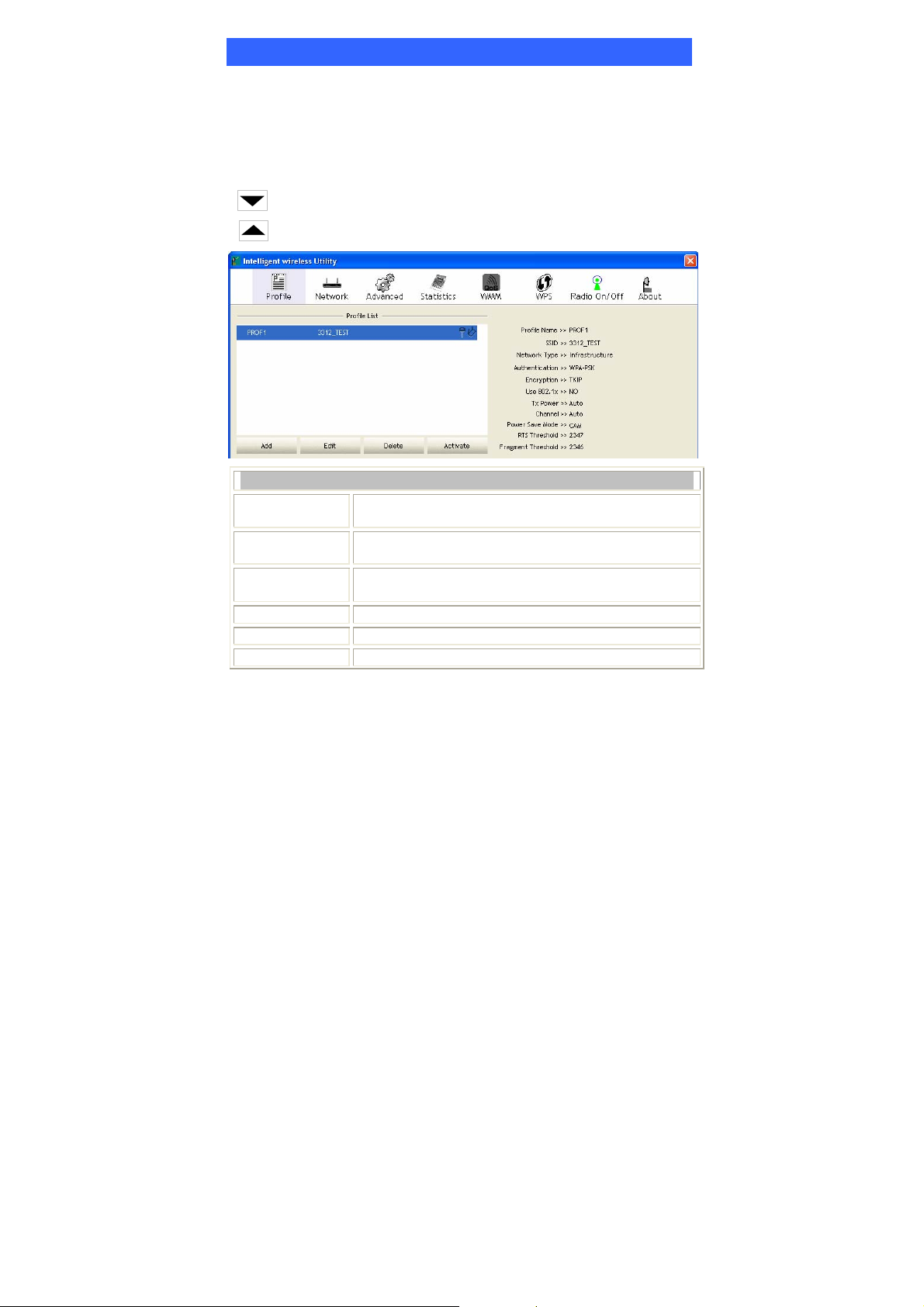
Profile
Profile can book keeping your favorite wireless setting among your home, office,
and other public hot-spot. You may save multiple profiles, and activate the correct
one at your preference. The Profile manager enables you to Add, Edit, Delete and
Activate profiles.
Click this button to show the information of Status Section.
Click this button to hide the information of Status Section.
Profile Tab
Profile Name
SSID
Network Type
Authentication
Encryption
Use 802.1x
You may enter a distinctive name of profile in this
column. The default is PROF# (# 1, #2, #3....)
The SSID is the unique name shared among all points in
your wireless network.
Shows the network type of the device, including
infrastructure and Ad-Hoc.
Shows the authentication mode.
Shows the encryption type.
Whether use 802.1x feature or not.
-
12 -
Page 18
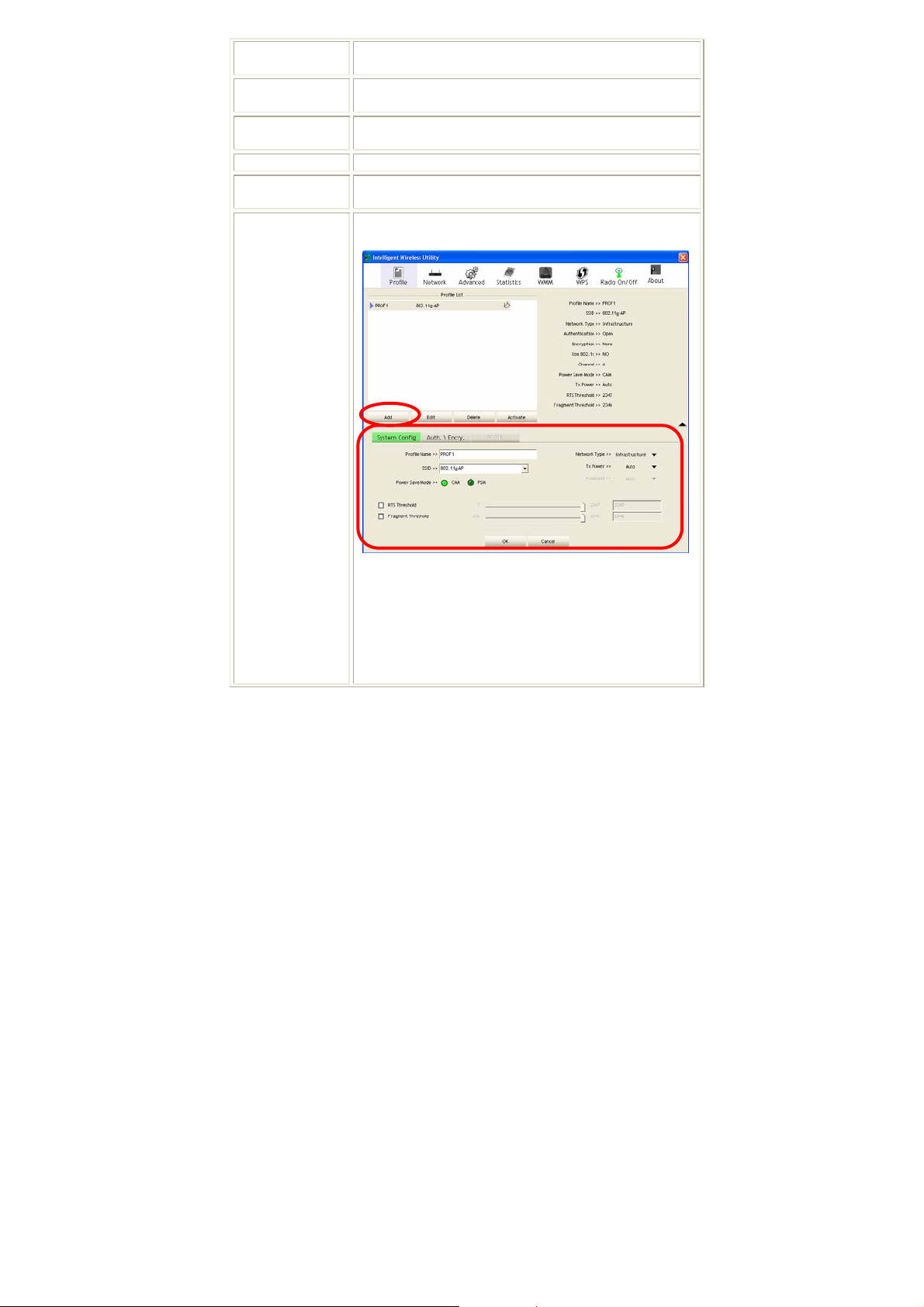
Tx Power
Channel
Power Save
Mode
RTS Threshold
Fragment
Threshold
Add
Transmit power, the amount of power used by a radio
transceiver to send the signal out.
Shows the selected channel that is currently in use. (There
are 14 channels available, depending on the country.)
Choose from CAM (Constantly Awake Mode) or Power
Saving Mode.
Shows the RTS Threshold of the device.
Shows the Fragment Threshold of the device.
Click to add a profile from the drop-down screen.
System Configuration tab:
Profile Name: User can enter profile name, or use default
name defined by system. The default is PROF# (# 1, #2,
#3....).
SSID: The SSID is the unique name shared among all
points in your wireless network. The name must be
identical for all devices and points attempting to connect
to the same network. User can use pull-down menu to
select from available APs.
-
13 -
Page 19

Power Save Mode:
• CAM (Constantly Awake Mode): When this mode is
selected, the power supply will be normally provided
even when there is no throughput.
• PSM (Power Saving Mode): When this mode is
selected, this device will stay in power saving mode
even when there is high volume of throughput.
Network Type: There are two types, Infrastructure and
Ad hoc modes. Under Ad hoc mode, user can also choose
the preamble type, the available preamble type includes
Auto and Long. In addition to that, the channel field will
be available for setup in Ad-hoc mode.
• The Infrastructure is intended for the connection
between wireless network cards and an Access Point.
With the wireless adapter, you can connect wireless
LAN to a wired global network via an Access Point.
• The Ad hoc lets you set a small wireless workgroup
easily and quickly. Equipped with the wireless
adapter, you can share files and printers between each
PC and laptop.
Tx Power: Select the Tx power percentage from the
pull-down list including Auto, 100%, 75%, 50%, 25%,
10% and Lowest.
Preamble: A preamble is a signal used in wireless
environment to synchronize the transmitting timing
including Synchronization and Start frame delimiter.
Select from the pull-down menu to change the Preamble
type into Auto or Long.
RTS Threshold: User can adjust the RTS threshold
number by sliding the bar or key in the value directly. The
default value is 2347. RTS/CTS Threshold is a mechanism
implemented to prevent the “Hidden Node” problem. If
the “Hidden Node” problem is an issue, users have to
specify the packet size. The RTS/CTS mechanism will be
activated if the data size exceeds the value you set.
This value should remain at its default setting of 2347.
Should you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor
-
14 -
Page 20
modifications of this value are recommended.
Fragment Threshold: User can adjust the Fragment
threshold number by sliding the bar or key in the value
directly. The default value is 2346. The mechanism of
Fragmentation Threshold is used to improve the efficiency
when high traffic flows along in the wireless network. If
your Wireless LAN Adapter often transmits large files in
wireless network, you can enter new Fragment Threshold
value to split the packet. The value can be set from 256
to 2346.
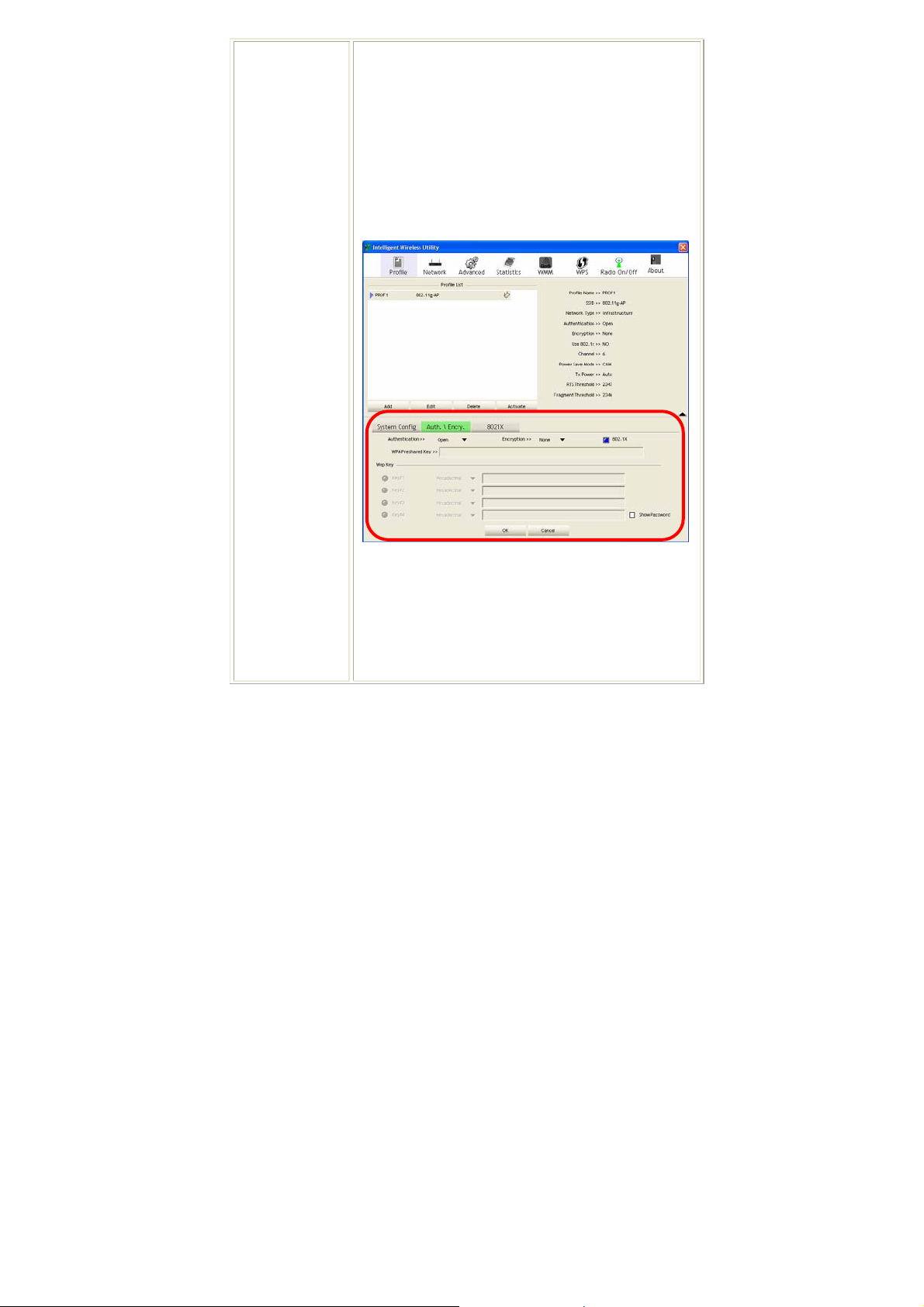
Authentication and Encryption tab:
Authentication Type: There are seven type of
authentication modes including Open, Shared, Leap,
WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2 and WPA2-PSK.
• Open: If your access point/wireless router is using
"Open” authentication, then the wireless adapter will
need to be set to the same authentication type.
-
15 -
Page 21
• Shared: Shared Key is when both the sender and the
recipient share a secret key.
• LEAP: Light Extensible Authentication Protocol. It is
an EAP authentication type used primarily in Cisco
Aironet WLANs. It encrypts data transmissions using
dynamically generated WEP keys, and supports mutual
authentication (only with CCX mode enabled.)
• WPA-PSK: WPA-PSK offers two encryption methods,
TKIP and AES. Select the type of algorithm, TKIP or
AES and then enter a WPA Shared Key of 8-63
characters in the WPA Pre-shared Key field.
Encryption Type: For Open and Shared authentication
mode, the selection of encryption type are None and WEP.
For WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports both
TKIP and AES.
WPA Pre-shared Key: This is the shared secret between
AP and STA. For WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, this field must be filled with
character longer than 8 and less than 32 lengths.
WEP Key: Only valid when using WEP encryption
algorithm. The key must match with the AP’s key. There
are several formats to enter the keys.
• Hexadecimal (40bits): 10 Hex characters.
• Hexadecimal (128bits): 32Hex characters.
• ASCII (40bits): 5 ASCII characters.
• ASCII (128bits): 13 ASCII characters.
Show Password: Check this box to show the password
you entered.
802.1x Setting: When user use radius server to
authenticate client certificate for WPA authentication
mode.
-
16 -
Page 22
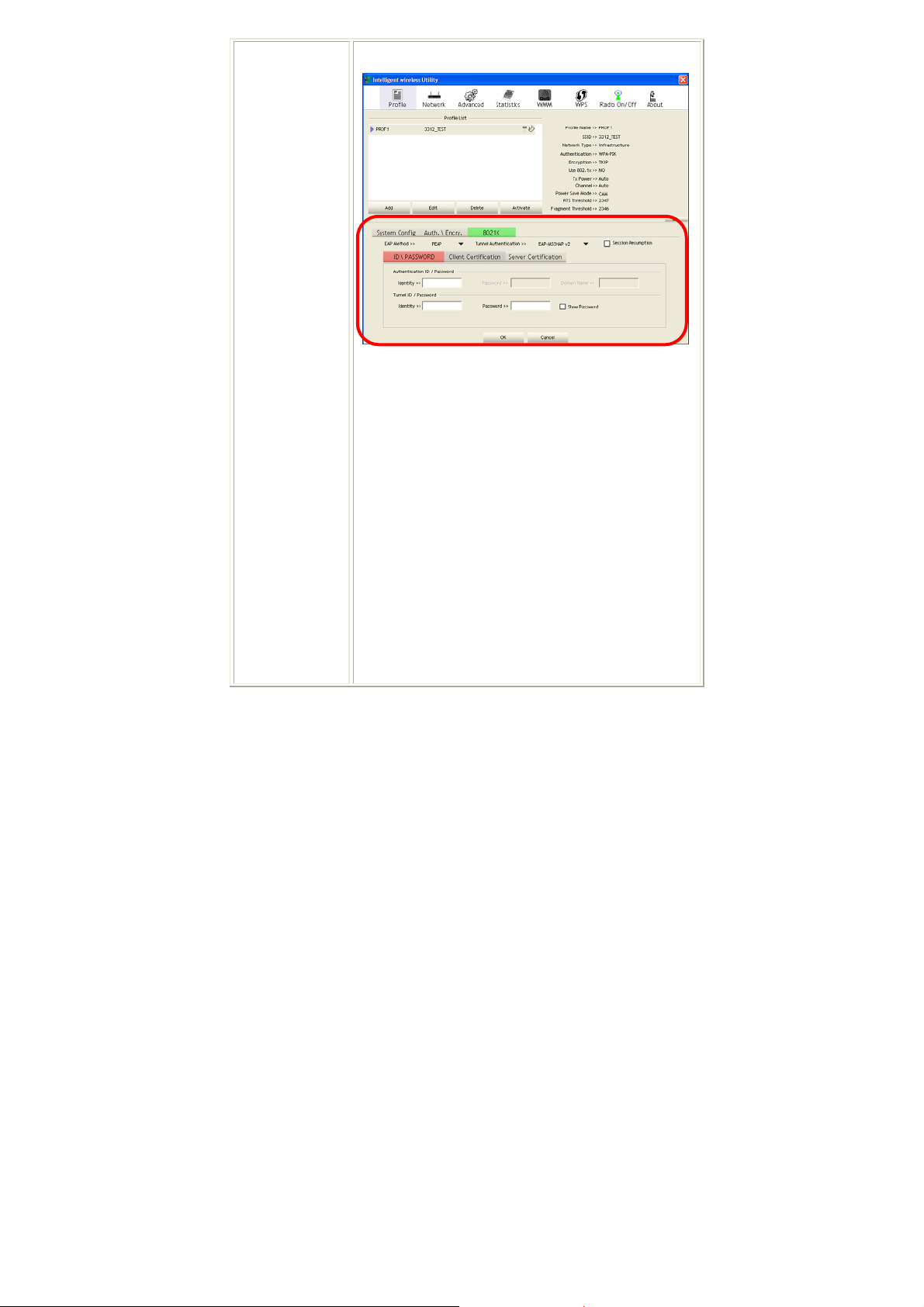
802.1x tab:
EAP Method:
• PEAP: Protect Extensible Authentication Protocol.
PEAP transport securely authentication data by using
tunneling between PEAP clients and an authentication
server. PEAP can authenticate wireless LAN clients
using only server-side certificates, thus simplifying the
implementation and administration of a secure
wireless LAN.
• TLS / Smart Card: Transport Layer Security.
Provides for certificate-based and mutual
authentication of the client and the network. It relies
on client-side and server-side certificates to perform
authentication and can be used to dynamically
generate user-based and session-based WEP keys to
secure subsequent communications between the
WLAN client and the access point.
• TTLS: Tunneled Transport Layer Security. This
security method provides for certificate-based, mutual
authentication of the client and network through an
-
17 -
Page 23
encrypted channel. Unlike EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS
requires only server-side certificates.
• EAP-FAST: Flexible Authentication via Secure
Tunneling. It was developed by Cisco. Instead of
using a certificate, mutual authentication is achieved
by means of a PAC (Protected Access Credential)
which can be managed dynamically by the
authentication server. The PAC can be provisioned
(distributed one time) to the client either manually or
automatically. Manual provisioning is delivery to the
client via disk or a secured network distribution
method. Automatic provisioning is an in-band, over
the air, distribution. For tunnel authentication, only
support "Generic Token Card" authentication now.
• MD5-Challenge: Message Digest Challenge.
Challenge is an EAP authentication type that provides
base-level EAP support. It provides for only one-way
authentication - there is no mutual authentication of
wireless client and the network.
Tunnel Authentication:
• Protocol: Tunnel protocol, List information including
EAP-MSCHAP v2, EAP-TLS/Smart card, and
Generic Token Card.
• Tunnel Ide ntity: Identity for tunnel.
• Tunne l P a ssword: Password for tunnel.
Session Resumption: User can click the box to enable or
disable this function.
ID\PASSWORD tab:
-
18 -
Page 24

ID/ PASSWORD: Identity and password for server.
• Authentication ID / Password: Identity, password
and domain name for server. Only "EAP-FAST" and
"LEAP" authentication can key in domain name.
Domain name can be keyed in blank space.
• Tunnel ID / Password: Identity and Password for
server.
Show Password: Check this box to show the password
you entered.
OK: Click to save settings and exit this page.
Cancel: Click to call off the settings and exit.
Client Certification tab:
Client Certification: Client certificate for server
authentication.
Use Client certificate: Choose to enable server
authentication.
OK: Click to save settings and exit this page.
Cancel: Click to call off the settings and exit.
Server Certification tab:
-
19 -
Page 25

Delete
Edit
Activate
Use Certificate chain: Choose use server that issuer of
certificates.
Allow intimidate certificates: It must be in the server
certificate chain between the server certificate and the
server specified in the certificate issuer must be field.
Server name: Enter an authentication sever root.
Server name must match: Click to enable or disable this
function.
Domain name must end in specified name: Click to
enable or disable this function.
OK: Click to save settings and exit this page.
Cancel: Click to call off the settings and exit.
Click to delete an existing profile.
Click to edit a profile.
Click to make a connection between devices.
Network
The Network page displays the information of surrounding APs from last scan
result. The tab lists the information including SSID, Network type, Channel,
Wireless mode, Security-Enabled and Signal.
-
20 -
Page 26

Network Tab
Sorted by
Show dBm
SSID
Network Type
Channel
Wireless mode
Encryption
Signal
Rescan
Connect
Add to Profile
Indicate that AP list are sorted by SSID, Channel or Signal.
Check the box to show the dBm of the AP list.
Shows the name of BSS network.
Network type in use, Infrastructure for BSS, Ad-Hoc for
IBSS network.
Shows the currently used channel.
AP support wireless mode. It may support 802.11b or
802.11g wireless mode.
Shows the encryption type currently in use. Valid value
includes WEP, TKIP, AES, and Not Use.
Shows the receiving signal strength of specified network.
Click to refresh the AP list.
Select an item on the list and then click to make a
connection.
Select an item on the list and then click to add it into the
profile list.
-
21 -
Page 27

AP information
When you double click on the intended AP, you can see AP's detail information
that divides into three parts. They are General, WPS, CCX information. The
introduction is as following:
General
General information contain AP's SSID, MAC address,
Authentication Type, Encryption Type, Channel, Network
Type, Beacon Interval, Signal Strength and Supported
Rates.
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
WPS
WPS information contains Authentication Type, Encryption
Type, Config Methods, Device Password ID, Selected
Registrar, State, Version, AP Setup Locked, UUID-E and
RF Bands.
Authentication Type: There are four types of
authentication modes supported by RaConfig. They are
open, Shared, WPA-PSK and WPA system.
Encryption Type: For open and shared authentication
mode, the selection of encryption type are None and WEP.
-
22 -
Page 28

CXX
For WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports both
TKIP and AES.
Config Methods: Correspond to the methods the AP
supports as an Enrollee for adding external Registrars.
Device Password ID: Indicate the method or identifies the
specific password that the selected Registrar intends to use.
Selected Registrar: Indicate if the user has recently
activated a Registrar to add an Enrollee. The values are
"TRUE" and "FALSE".
State: The current configuration state on AP. The values
are "Unconfigured" and "Configured".
Version: WPS specified version.
AP Setup Locked: Indicate if AP has entered a setup
locked state.
UUID-E: The universally unique identifier (UUID) element
generated by the Enrollee. There is a value. It is 16 bytes.
RF Bands: Indicate all RF bands available on the AP. A
dual-band AP must provide it. The values are "2.4GHz" and
"5GHz".
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
CCX information contains CCKM, Cmic and Ckip
information.
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
-
23 -
Page 29

Link Status
Click the triangle button at the right corner of the windows to expand the link
status. The link status page displays the detail information of current connection.
Click this button to show the information of Status Section.
Click this button to hide the information of Status Section.
Link Status Tab
Status
Extra Info
Shows the current connection status. If there is no
connection existing, it will show Disconnected.
Shows the link status.
-
24 -
Page 30

Channel
Shows the current channel in use.
Authentication
Encryption
Network Type
IP Address
Sub Mask
Default Gateway
Link Quality
Signal Strength 1
Noise Strength
Transmit
Receive
Link Speed
Throughput
Authentication mode used within the network,
including Unknown, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA
and WPA2.
Shows the encryption type currently in use. Valid
value includes WEP, TKIP, AES, and Not Use.
Network type in use, Infrastructure for BSS, Ad-Hoc
for IBSS network.
Shows the IP address information.
Shows the Sub Mask information.
Shows the default gateway information.
Shows the connection quality based on signal strength
and TX/RX packet error rate.
Shows the Receiving signal strength, you can choose
to display as percentage or dBm format.
Shows the noise signal strength.
Shows the current Link Speed and Throughput of the
transmit rate.
Shows the current Link Speed and Throughput of
receive rate.
Shows the current transmitting rate and receiving rate.
Shows the transmitting and receiving throughput in the
unit of K bits/sec.
-
25 -
Page 31

Advanced
This Advanced page provides advanced and detailed settings for your wireless
network.
Advanced Tab
Wireless mode
Wireless Protection
Tx Rate
Enable TX Burst
Enable TCP
Window Size
Fast Roaming at
Show
Authentication
Status Dialog
Select Your
Country Region
Code
Select wireless mode. There are two modes, 802.11B/G
mix and 802.11B only supported. Default mode is
802.11B/G mix.
There are three modes can be selected. AUTO, ON and
OFF.
Select the transmitting rate you preferred. Default is Auto.
Check this box to enable this function.
Check to increase the transmission quality.
Check to set the roaming interval, fast to roaming, setup
by transmits power.
When you connect AP with authentication, choose
whether show "Authentication Status Dialog" or not.
Authentication Status Dialog displays the process about
802.1x authentications.
Select your country region code from the pull-down
menu.
-
26 -
Page 32

Enable CCX
(Cisco Compatible
extensions)
Apply
Check to enable the CCX function.
• Turn on CCKM
• Enable Radio Measurements: Check to enable the
Radio measurement function.
• Non-Serving Measurements limit: User can set channel
measurement every 0~2000 milliseconds. Default is set
to 250 milliseconds.
Click to apply above settings.
Statistics
The Statistics screen displays the statistics on your current network settings.
Transmit Statistics Tab
Frames Transmitted Successfully
Frames Retransmitted
Successfully
Frames Fail To Receive ACK
After All Retries
RTS Frames Successfully Receive
Shows information of frames successfully
sent.
Shows information of frames successfully
sent with one or more reties.
Shows information of frames failed
transmit after hitting retry limit.
Shows information of successfully receive
-
27 -
Page 33

CTS
RTS Frames Fail To Receive
CTS
CTS after sending RTS frame
Shows information of failed to receive CTS
after sending RTS.
Reset Counter
Receive Statistics Tab
Frames Received Successfully
Frames Received With CRC
Error
Frames Dropped Due To
Out-of-Resource
Duplicate Frames Received
Click this button to reset counters to zero.
Shows information of frames Received
Successfully.
Shows information of frames received with
CRC error.
Shows information of frames dropped due
to resource issue.
Shows information of duplicate received
frames.
Reset Counter
WMM / QoS
Click this button to reset counters to zero.
-
28 -
Page 34

The WMM page shows the Wi-Fi Multi-Media power save function and Direct
Link Setup that ensure your wireless network quality.
WMM/QoS Tab
WMM Enable
WMM- Power Save Enable
Direct Link Setup Enable
MAC Address
Check the box to enable Wi-Fi Multi-Media
function.
Select which ACs you want to enable.
Check the box to enable Direct Link Setup.
The setting of DLS indicates as follow :
Fill in the blanks of Direct Link with MAC
Address of STA, and the STA must conform to
two conditions:
• Connecting with the same AP that supports
DLS feature.
• DSL enabled.
Timeout Value
Apply
Timeout Value represents that it disconnect
automatically after few seconds. The value is
integer that must be between 0~65535. It
represents that it always connects if the value is
zero. Default value of Timeout Value is 60
seconds.
Click this button to apply the settings.
-
29 -
Page 35

Tear Down
Select a direct link STA, then click "Tear Down"
button to disconnect the STA.
WPS
The primary goal of Wi-Fi Protected Setup (Wi-Fi Simple Configuration) is to
simplify the security setup and manage ment of Wi-Fi networks. The STA as an
Enrollee or external Registrar supports the configuration setup using PIN
(Personal Identification Number) configuration method or PBC (Push Button
Configuration) method through an internal or external Registrar.
WPS Tab
WPS AP List
Rescan
Information
Display the information of surrounding APs with WPS IE
from last scan result. List information included SSID,
BSSID, Channel, ID (Device Password ID),
Security-Enabled.
Issue a rescan command to wireless NIC to update
information on surrounding wireless network.
Display the information about WPS IE on the selected
network. List information included Authentication Type,
Encryption Type, Config Methods, Device Password ID,
Selected Registrar, State, Version, AP Setup Locked,
-
30 -
Page 36

PIN Code
Config Mode
Detail
Connect
Rotate
Disconnect
Export Profile
Delete
PIN
PBC
WPS Associate IE
WPS Probe IE
Automatically
UUID-E and RF Bands.
8-digit numbers. It is required to enter PIN Code into
Registrar using PIN method. When STA is Enrollee, you
can use "Renew" button to re-generate new PIN Code.
Our station role-playing as an Enrollee or an external
Registrar.
Information about Security and Key in the credential.
Command to connect to the selected network inside
credentials. The active selected credential is as like as the
active selected Profile.
Command to rotate to connect to the next network inside
credentials.
Stop WPS action and disconnect this active link. And
then select the last profile at the Profile Page. If there is
an empty profile page, the driver will select any
non-security AP.
Export all credentials to Profile.
Delete an existing credential. And then select the next
credential if exist. If there is an empty credential, the
driver will select any non-security AP.
Start to add to Registrar using PIN (Personal
Identification Number) configuration method. If STA
Registrar, remember that enter PIN Code read from your
Enrollee before starting PIN.
Start to add to AP using PBC (Push Button
Configuration) method.
Send the association request with WPS IE during WPS
setup. It is optional for STA.
Send the probe request with WPS IE during WPS setup.
It is optional for STA.
Check this box the device will connect the AP
-
31 -
Page 37

select the AP
Progress Bar
Status Bar
automatically.
Display rate of progress from Start to Connected status.
Display currently WPS Status.
Radio On/Off
Click this button to turn on or off radio function.
This icon shows radio on.
This icon shows radio off.
About
This page displays the information of the wireless card including, RaConfig
Version/ Date, Driver Version/ Date, EEPROM Version, Firmware Version and
Phy_Address.
-
32 -
Page 38

Utility Menu list
To access the utility menu list, please right click the utility icon on the task bar.
z Launch Config Utilities: Select to open the utility screen.
z Use Zero Configuration as Configuration utility: Select to use the
Window XP built-in utility (Zero configuration utility).
z Switch to AP Mode: Select to make your wireless USB adapter act as a
wireless AP.
z Exit: Select to close the utility program.
-
33 -
Page 39

Soft AP mode
When device be switched to soft AP mode, the following screen will pop up,
please select Enable ICS to enter soft AP configuration.
Config
-
34 -
Page 40

Config
SSID
TX Rate
Channel
Wireless mode
Use Mac Address
Security Setting
AP name of user type. User also can click Use Mac
Address button to display it. System default is
SoftAP-02.
Select the transmitting rate you preferred. Default is
Auto.
Manually force the AP using the channel. The
system default is CH 1.
Select wireless mode. 802.11B/G Mixed, 802.11B
only and 802.11G only modes are supported. System
default is 802.11B/G Mixed.
Click this button to replace SSID by MAC address.
Authentication mode and encryption algorithm used
within the AP. The system default is no
authentication and encryption.
Authentication Type: There are five type of
authentication modes including Open, Shared,
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, and
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
Encryption Type: For open and shared
-
35 -
Page 41

Country Region
Code
Beacon (ms)
TX Power
authentication mode, the selections of encryption
type are Not Use and WEP. For WPA-PSK,
WPA2-PSK, and WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports
both TKIP and AES.
WPA Pre-shared Key: This is the shared secret
between AP and STA. For WPA-PSK and
WPA2-PSK and WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, this field must be filled with
character longer than 8 and less than 32 lengths.
Group Rekey interval: Only valid when using
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, and WPA-PSK/
WPA2-PSK authentication mode to renew key. User
can set to change by seconds or packets. Default is
600 seconds.
WEP Key: Only valid when using WEP encryption
algorithm. The key must match with the AP’s key.
There are several formats to enter the keys.
• Hexadecimal (64bits): 10 Hex characters.
• Hexadecimal (128bits): 26 Hex characters.
• ASCII (64bits): 5 ASCII characters.
• ASCII (128bits): 13 ASCII characters.
Show Password: Check this box to show the
password you entered.
Eight countries to choose. Country channel list:
Classification Range
0: CH1 ~11
1: CH1 ~13
2: CH10 ~11
3: CH10 ~13
4: CH14
5: CH1 ~14
6: CH3 ~9
7: CH5 ~13
The time between two beacons. The system default
is 100 ms.
Manually force the AP transmits power from the
pull down list 100%, 75%, 50%, 25% and Lowest.
-
36 -
Page 42

Idle time(60-3600)(s)
No forwarding
among wireless
clients
Hide SSID
Default
Apply
The system default is 100%.
It represents that the AP will idle after few seconds.
The time must be set between 60~3600 seconds.
Default value of idle time is 300 seconds.
No beacon among wireless client, clients can share
information each other. The system default is no
forwarding.
Do not display AP name. System default no hide.
Use the system default value.
Click to apply the above settings.
-
37 -
Page 43

Access Control
Access Control
Access Policy
MAC Address
Access List
Add
Delete
Remove All
Apply
User chooses whether AP start the function or not.
System default is Disable.
Manually force the Mac address using the function. Click
Add and the MAC address will be listed in the Access
List pool.
Display all MAC Address that you have set.
Add the MAC address that you would like to set.
Delete the MAC address that you have set.
Remove all MAC address in the Access List.
Apply the above changes.
-
38 -
Page 44

MAC Table
MAC Table
MAC Address
AID
Power Saving Mode
Status
The station Mac address of current connection.
Raise value by current connection.
The station of current connect whether it have to
support.
The status of current connection.
-
39 -
Page 45

Event Log
Event Log
Event Time
(yy/mm/dd-hh:mm:ss)
Records the event time.
Message
Records all the event messages.
-
40 -
Page 46

Statistics
Transmit Statistics
Frames Transmitted
Successfully
Frames Fail To Receive ACK
After All Retries
RTS Frames Successfully
Receive CTS
RTS Frames Fail To Receive
CTS
Frames Transmitted
Successfully After Retry
Frames successfully sent.
Frames failed transmit after hitting retry
limit.
Successfully receive CTS after sending RTS
frame
Failed to receive CTS after sending RTS.
Frames successfully sent with one or more
reties.
-
41 -
Page 47

Receive Statistics
Frames Received Successfully Frames Received Successfully
Frames Received With CRC
Error
Frames Dropped Due To
Out-of-Resource
Duplicate Frames Received Duplicate received frames.
Reset Counter Reset counters to zero.
Frames received with CRC error.
Frames dropped due to resource issue
About
This page displays the wireless card and driver version information.
-
42 -
Page 48

Utility Configuration for Windows
Vista
Station Mode
Profile
Profile can book keeping your favorite wireless setting among your home, office,
and other public hot-spot. You may save multiple profiles, and activate the correct
one at your preference. The Profile manager enables you to Add, Edit, Delete and
Activate profiles.
Click this button to show the information of Status Section.
Click this button to hide the information of Status Section.
-
43 -
Page 49

Profile Tab
Profile Name
SSID
Network Type
Authentication
Encryption
Use 802.1x
Tx Power
Add
You may enter a distinctive name of profile in this
column. The default is PROF# (# 1, #2, #3....)
The SSID is the unique name shared among all points in
your wireless network.
Shows the network type of the device, including
infrastructure and Ad-Hoc.
Shows the authentication mode.
Shows the encryption type.
Whether use 802.1x feature or not.
Transmit power, the amount of power used by a radio
transceiver to send the signal out.
Click to add a profile from the drop-down screen.
System Configuration tab:
Profile Name: User can enter profile name, or use default
name defined by system. The default is PROF# (# 1, #2,
#3....).
SSID: The SSID is the unique name shared among all
points in your wireless network. The name must be
-
44 -
Page 50

identical for all devices and points attempting to connect
to the same network. User can use pull-down menu to
select from available APs.
Network Type: There are two types, Infrastructure and
Ad hoc modes.
• The Infrastructure is intended for the connection
between wireless network cards and an Access Point.
With the wireless adapter, you can connect wireless
LAN to a wired global network via an Access Point.
• The Ad hoc lets you set a small wireless workgroup
easily and quickly. Equipped with the wireless
adapter, you can share files and printers between each
PC and laptop.
Tx Power: Select the Tx power percentage from the
pull-down list including Auto, 100%, 75%, 50%, 25%,
10% and Lowest.
Authentication and Encryption tab:
Authentication Type: There are six type of authentication
modes including Open, Shared, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2
and WPA2-PSK.
-
45 -
Page 51

• Open: If your access point/wireless router is using
"Open” authentication, then the wireless adapter will
need to be set to the same authentication type.
• Shared: Shared Key is when both the sender and the
recipient share a secret key.
• WPA-PSK: WPA-PSK offers two encryption methods,
TKIP and AES. Select the type of algorithm, TKIP or
AES and then enter a WPA Shared Key of 8-63
characters in the WPA Pre-shared Key field.
Encryption Type: For Open and Shared authentication
mode, the selection of encryption type are None and WEP.
For WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports both
TKIP and AES.
WPA Pre-shared Key: This blank is the shared secret
between AP and STA. For WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, this field must be filled with
character longer than 8 and less than 32 length.
WEP Key: Only valid when using WEP encryption
algorithm. The key must match with the AP’s key. There
are several formats to enter the keys.
• Hexadecimal (40bits): 10 Hex characters.
• Hexadecimal (128bits): 32Hex characters.
• ASCII (40bits): 5 ASCII characters.
• ASCII (128bits): 13 ASCII characters.
Show Password: Check this box to show the password
you entered.
802.1x Setting: When user use radius server to
authenticate client certificate for WPA authentication
mode. When the profile being active with 802.1x security
the wireless network properties screen will pop-up for
setting.
-
46 -
Page 52

Connection Tab:
Name: The connected AP profile name.
SSID: The SSID is the unique name shared among all
points in your wireless network.
Network Type: The network type of the connected
device.
Network Availability: Shows the connected access point
is available for the certificated device only.
* You can check the following three boxes to enable the
functions that you preferred.
-
47 -
Page 53

Security Tab:
Delete
Edit
Activate
Security Type: Select the security type form the
pull-down menu, No authentication (Open), Shared,
WPA2-Personal, WPA-Personal, WPA2-Enterprise,
WPA-Enterprise and 802.1X.
Encryption Type: For Open and Shared authentication
mode, the selection of encryption type are None and WEP.
For WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports both
TKIP and AES.
Choose a network authentication method: Select from
pull-down menu, either Smart Card or other certificate
or Protected EAP (PEAP).
Settings: Click the settings button to set up further
configuration management.
OK: Click to save settings and exit this page.
Cancel: Click to call off the settings and exit.
Click to delete an existing profile.
Click to edit a profile.
Click to make a connection between devices.
-
48 -
Page 54

Network
The Network page displays the information of surrounding APs from last scan
result. The tab lists the information including SSID, Network type, Channel,
Wireless mode, Security-Enabled and Signal.
Network Tab
Sorted by
Show dBm
SSID
Network Type
Channel
Wireless mode
Encryption
Signal
Rescan
Add to Profile
Indicate that AP list are sorted by SSID, Channel or Signal.
Check the box to show the dBm of the AP list.
Shows the name of BSS network.
Network type in use, Infrastructure for BSS, Ad-Hoc for
IBSS network.
Shows the currently used channel.
AP support wireless mode. It may support 802.11b or
802.11g wireless mode.
Shows the encryption type currently in use. Valid value
includes WEP, TKIP, AES, and Not Use.
Shows the receiving signal strength of specified network.
Click to refresh the AP list.
Select an item on the list and then click to add it into the
profile list.
-
49 -
Page 55

AP information
When you double click on the intended AP, you can see AP's detail information
that divides into three parts. They are General, WPS, CCX information. The
introduction is as following:
General
General information contain AP's SSID, MAC address,
Authentication Type, Encryption Type, Channel, Network
Type, Beacon Interval, Signal Strength and Supported
Rates.
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
WPS
WPS information contains Authentication Type, Encryption
Type, Config Methods, Device Password ID, Selected
Registrar, State, Version, AP Setup Locked, UUID-E and
RF Bands.
Authentication Type: There are four types of
authentication modes supported by RaConfig. They are
open, Shared, WPA-PSK and WPA system.
Encryption Type: For open and shared authentication
mode, the selection of encryption type are None and WEP.
For WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
-
50 -
Page 56

CXX
authentication mode, the encryption type supports both
TKIP and AES.
Config Methods: Correspond to the methods the AP
supports as an Enrollee for adding external Registrars.
Device Password ID: Indicate the method or identifies the
specific password that the selected Registrar intends to use.
Selected Registrar: Indicate if the user has recently
activated a Registrar to add an Enrollee. The values are
"TRUE" and "FALSE".
State: The current configuration state on AP. The values
are "Unconfigured" and "Configured".
Version: WPS specified version.
AP Setup Locked: Indicate if AP has entered a setup
locked state.
UUID-E: The universally unique identifier (UUID) element
generated by the Enrollee. There is a value. It is 16 bytes.
RF Bands: Indicate all RF bands available on the AP. A
dual-band AP must provide it. The values are "2.4GHz" and
"5GHz".
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
CCX information contains CCKM, Cmic and Ckip
information.
Close: Click this button to exit the information screen.
-
51 -
Page 57

Link Status
Click the triangle button at the right corner of the windows to expand the link
status. The link status page displays the detail information of current connection.
Click this button to show the information of Status Section.
Click this button to hide the information of Status Section.
Link Status Tab
Status
Shows the current connection status. If there is no
connection existing, it will show Disconnected.
-
52 -
Page 58

Extra Info
Shows the link status.
Channel
Authentication
Encryption
Network Type
IP Address
Sub Mask
Default Gateway
Link Quality
Signal Strength 1
Noise Strength
Transmit
Receive
Link Speed
Throughput
Shows the current channel in use.
Authentication mode used within the network,
including Unknown, Open, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK,
WPA and WPA2.
Shows the encryption type currently in use. Valid
value includes WEP, TKIP, AES, and Not Use.
Network type in use, Infrastructure for BSS, Ad-Hoc
for IBSS network.
Shows the IP address information.
Shows the Sub Mask information.
Shows the default gateway information.
Shows the connection quality based on signal strength
and TX/RX packet error rate.
Shows the Receiving signal strength, you can choose
to display as percentage or dBm format.
Shows the noise signal strength.
Shows the current Link Speed and Throughput of the
transmit rate.
Shows the current Link Speed and Throughput of
receive rate.
Shows the current transmitting rate and receiving rate.
Shows the transmitting and receiving throughput in the
unit of K bits/sec.
-
53 -
Page 59

Statistics
The Statistics screen displays the statistics on your current network settings.
Transmit Statistics Tab
Frames Transmitted Successfully
Shows information of frames successfully
sent.
Frames Retransmitted
Successfully
Frames Fail To Receive ACK
After All Retries
RTS Frames Successfully Receive
CTS
RTS Frames Fail To Receive
CTS
Reset Counter
Shows information of frames successfully
sent with one or more reties.
Shows information of frames failed
transmit after hitting retry limit.
Shows information of successfully receive
CTS after sending RTS frame
Shows information of failed to receive CTS
after sending RTS.
Click this button to reset counters to zero.
-
54 -
Page 60

Receive Statistics Tab
Frames Received Successfully
Shows information of frames Received
Successfully.
Frames Received With CRC
Error
Frames Dropped Due To
Out-of-Resource
Duplicate Frames Received
Reset Counter
Shows information of frames received with
CRC error.
Shows information of frames dropped due
to resource issue.
Shows information of duplicate received
frames.
Click this button to reset counters to zero.
WMM / QoS
The WMM page shows the Wi-Fi Multi-Media power save function and Direct
Link Setup that ensure your wireless network quality.
-
55 -
Page 61

WMM/QoS Tab
WMM Enable
WMM- Power Save Enable
Direct Link Setup Enable
MAC Address
Timeout Value
Apply
Tear Down
Check the box to enable Wi-Fi Multi-Media
function.
Select which ACs you want to enable.
Check the box to enable Direct Link Setup.
The setting of DLS indicates as follow :
Fill in the blanks of Direct Link with MAC
Address of STA, and the STA must conform to
two conditions:
• Connecting with the same AP that supports
DLS feature.
• DSL enabled.
Timeout Value represents that it disconnect
automatically after few seconds. The value is
integer that must be between 0~65535. It
represents that it always connects if the value is
zero. Default value of Timeout Value is 60
seconds.
Click this button to apply the settings.
Select a direct link STA, then click "Tear Down"
button to disconnect the STA.
-
56 -
Page 62

WPS
The primary goal of Wi-Fi Protected Setup (Wi-Fi Simple Configuration) is to
simplify the security setup and manage ment of Wi-Fi networks. The STA as an
Enrollee or external Registrar supports the configuration setup using PIN
(Personal Identification Number) configuration method or PBC (Push Button
Configuration) method through an internal or external Registrar.
WPS Tab
WPS AP List
Rescan
Information
PIN Code
Display the information of surrounding APs with WPS IE
from last scan result. List information included SSID,
BSSID, Channel, ID (Device Password ID),
Security-Enabled.
Issue a rescan command to wireless NIC to update
information on surrounding wireless network.
Display the information about WPS IE on the selected
network. List information included Authentication Type,
Encryption Type, Config Methods, Device Password ID,
Selected Registrar, State, Version, AP Setup Locked,
UUID-E and RF Bands.
8-digit numbers. It is required to enter PIN Code into
Registrar using PIN method. When STA is Enrollee, you
can use "Renew" button to re-generate new PIN Code.
-
57 -
Page 63

Config Mode
Detail
Connect
Rotate
Disconnect
Export Profile
Delete
PIN
PBC
WPS Associate IE
WPS Probe IE
Progress Bar
Status Bar
Our station role-playing as an Enrollee or an external
Registrar.
Information about Security and Key in the credential.
Command to connect to the selected network inside
credentials. The active selected credential is as like as the
active selected Profile.
Command to rotate to connect to the next network inside
credentials.
Stop WPS action and disconnect this active link. And
then select the last profile at the Profile Page. If there is
an empty profile page, the driver will select any
non-security AP.
Export all credentials to Profile.
Delete an existing credential. And then select the next
credential if exist. If there is an empty credential, the
driver will select any non-security AP.
Start to add to Registrar using PIN (Personal
Identification Number) configuration method. If STA
Registrar, remember that enter PIN Code read from your
Enrollee before starting PIN.
Start to add to AP using PBC (Push Button
Configuration) method.
Send the association request with WPS IE during WPS
setup. It is optional for STA.
Send the probe request with WPS IE during WPS setup.
It is optional for STA.
Display rate of progress from Start to Connected status.
Display currently WPS Status.
-
58 -
Page 64

Radio On/Off
Click this button to turn on or off radio function.
This icon shows radio on.
This icon shows radio off.
About
This page displays the information of the wireless card including, RaConfig
Version/ Date, Driver Version/ Date, EEPROM Version and Phy_Address.
-
59 -
Page 65

Utility Menu list
To access Windows Vista utility menu list, please right click the utility icon on
the task bar.
z Launch Config Utilities: Select to open the utility screen.
z Switch to AP Mode: Select to make your wireless USB adapter act as a
wireless AP.
z Exit: Select to close the utility program.
-
60 -
Page 66

Soft AP mode
When device be switched to soft AP mode, the following screen will pop up,
please click OK to enter soft AP configuration.
Notice: This screen shows up in Windows Vista 32-bit Operating System only.
Config
-
61 -
Page 67

Config
SSID
Channel
Use Mac Address
Security Setting
AP name of user type. User also can click Use Mac
Address button to display it. System default is
SoftAP-02.
Manually force the AP using the channel. The
system default is CH 1.
Click this button to replace SSID by MAC address.
Authentication mode and encryption algorithm used
within the AP. The system default is no
authentication and encryption.
Authentication Type: There are five type of
authentication modes including Open, Shared,
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, and
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
Encryption Type: For open and shared
authentication mode, the selections of encryption
type are Not Use and WEP. For WPA-PSK,
WPA2-PSK, and WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, the encryption type supports
both TKIP and AES.
WPA Pre-shared Key: This is the shared secret
-
62 -
Page 68

Beacon (ms)
TX Power
Idle time(60-3600)(s)
No forwarding
among wireless
clients
Hide SSID
Default
Apply
between AP and STA. For WPA-PSK and
WPA2-PSK and WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK
authentication mode, this field must be filled with
character longer than 8 and less than 32 lengths.
Group Rekey Interval: Only valid when using
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, and WPA-PSK/
WPA2-PSK authentication mode to renew key. User
can set to change by seconds or packets. Default is
10 seconds.
WEP Key: Only valid when using WEP encryption
algorithm. The key must match with the AP’s key.
There are several formats to enter the keys.
• Hexadecimal (64bits): 10 Hex characters.
• Hexadecimal (128bits): 26 Hex characters.
• ASCII (64bits): 5 ASCII characters.
• ASCII (128bits): 13 ASCII characters.
Show Password: Check this box to show the
password you entered.
The time between two beacons. The system default
is 100 ms.
Manually force the AP transmits power from the
pull down list 100%, 75%, 50%, 25% and Lowest.
The system default is 100%.
It represents that the AP will idle after few seconds.
The time must be set between 60~3600 seconds.
Default value of idle time is 300 seconds.
No beacon among wireless client, clients can share
information each other. The system default is no
forwarding.
Do not display AP name. System default no hide.
Use the system default value.
Click to apply the above settings.
-
63 -
Page 69

Access Control
Access Control
Access Policy
MAC Address
Access List
Add
Delete
Remove All
Apply
User chooses whether AP start the function or not.
System default is Disable.
Manually force the Mac address using the function. Click
Add and the MAC address will be listed in the Access
List pool.
Display all MAC Address that you have set.
Add the MAC address that you would like to set.
Delete the MAC address that you have set.
Remove all MAC address in the Access List.
Apply the above changes.
-
64 -
Page 70

MAC Table
MAC Table
MAC Address
AID
Power Saving Mode
Status
The station Mac address of current connection.
Raise value by current connection.
The station of current connect whether it have to
support.
The status of current connection.
-
65 -
Page 71

Event Log
Event Log
Event Time
(yy/mm/dd-hh:mm:ss)
Records the event time.
Message
Records all the event messages.
-
66 -
Page 72

Statistics
Transmit Statistics
Frames Transmitted
Successfully
Frames Fail To Receive ACK
After All Retries
RTS Frames Successfully
Receive CTS
RTS Frames Fail To Receive
CTS
Frames Transmitted
Successfully After Retry
Frames successfully sent.
Frames failed transmit after hitting retry
limit.
Successfully receive CTS after sending RTS
frame
Failed to receive CTS after sending RTS.
Frames successfully sent with one or more
reties.
-
67 -
Page 73

Receive Statistics
Frames Received Successfully Frames Received Successfully
Frames Received With CRC
Error
Frames Dropped Due To
Out-of-Resource
Duplicate Frames Received Duplicate received frames.
Reset Counter Reset counters to zero.
Frames received with CRC error.
Frames dropped due to resource issue
About
This page displays the wireless card and driver version information.
-
68 -
Page 74

UNINSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS
2000/XP
In case you need to uninstall the utility and driver, please refer to below steps. (As
you uninstall the utility, the driver will be uninstalled as well.)
1. Go to Start Æ All Programs ÆIntelligent Wireless Æ Uninstall –
Wireless card.
-
69 -
Page 75

2. Select Remove all button and click Next to start uninstalling.
3. Click Yes to complete remove the selected application and all of its
features.
-
70 -
Page 76

4. Select “Yes, I want to restart my computer now” and then click
Finish to complete the uninstallation.
-
71 -
Page 77

UNINSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS
VISTA
In case you need to uninstall the utility and driver, please refer to below steps. (As
you uninstall the utility, the driver will be uninstalled as well.)
1. Go to Start ÆAll Programs ÆIntelligent Wireless Æ Uninstall –
Wireless card.
-
72 -
Page 78

2. Select Remove all button and click Next to start uninstalling.
3. Click Yes to complete remove the selected application and all of its
features.
-
73 -
Page 79

4. Select “Yes, I want to restart my computer now” and then click
Finish to complete the uninstallation.
-
74 -
 Loading...
Loading...