Page 1

mikroC
Develop your applications quickly and easily with the world's
most intuitive C compiler for PIC Microcontrollers (families
PIC12, PIC16, and PIC18).
Highly sophisticated IDE provides the power you need with the
simplicity of a Windows based point-and-click environment.
With useful implemented tools, many practical code examples,
broad set of built-in routines, and a comprehensive Help, mikroC
makes a fast and reliable tool, which can satisfy needs of experienced engineers and beginners alike.
C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroElektronika
Development tools - Books - Compilers
www.mikroelektronika.co.yu
User’s
manual
Making it simple
Page 2
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
ii
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
DISCLAIMER:
mikroC and this manual are owned by mikroElektronika and are protected by copyright law
and international copyright treaty. Therefore, you should treat this manual like any other copyrighted material (e.g., a book). The manual and the compiler may not be copied, partially or
as a whole without the written consent from the mikroEelktronika. The PDF-edition of the
manual can be printed for private or local use, but not for distribution. Modifying the manual
or the compiler is strictly prohibited.
HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES
The mikroC compiler is not fault-tolerant and is not designed, manufactured or intended for
use or resale as on-line control equipment in hazardous environments requiring fail-safe performance, such as in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication
systems, air traffic control, direct life support machines, or weapons systems, in which the failure of the Software could lead directly to death, personal injury, or severe physical or environmental damage ("High Risk Activities"). mikroElektronika and its suppliers specifically disclaim any express or implied warranty of fitness for High Risk Activities.
LICENSE AGREEMENT:
By using the mikroC compiler, you agree to the terms of this agreement. Only one person
may use licensed version of mikroC compiler at a time.
Copyright © mikroElektronika 2003 - 2005.
This manual covers mikroC version 2.1 and the related topics. Newer versions may contain
changes without prior notice.
COMPILER BUG REPORTS:
The compiler has been carefully tested and debugged. It is, however, not possible to
guarantee a 100 % error free product. If you would like to report a bug, please contact us at
the address office@mikroelektronika.co.yu. Please include next information in your bug
report:
- Your operating system
- Version of mikroC
- Code sample
- Description of a bug
CONTACT US:
mikroElektronika
Voice: + 381 (11) 30 66 377, + 381 (11) 30 66 378
Fax: + 381 (11) 30 66 379
Web: www.mikroelektronika.co.yu
E-mail: office@mikroelektronika.co.yu
Reader’s note
PIC, PICmicro and MPLAB is a Registered trademark of Microchip company. Windows is a
Registered trademark of Microsoft Corp. All other trade and/or services marks are the
property of the respective owners.
Page 3

MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 mikroC IDE
CHAPTER 2 Building Applications
CHAPTER 3 mikroC Reference
CHAPTER 4 mikroC Libraries
mikroC User’s manual
Page 4

CHAPTER 1: mikroC IDE 1
Quick Overview 1
Code Editor 3
Code Explorer 6
Debugger 7
Error Window 11
Statistics 12
Integrated Tools 15
Keyboard Shortcuts 19
CHAPTER 2: Building Applications 21
Projects 22
Source Files 23
Search Paths 23
Managing Source Files 24
Compilation 26
Output Files 26
Assembly View 26
Error Messages 27
CHAPTER 3: mikroC Language Reference 29
PIC Specifics 30
mikroC Specifics 32
ANSI Standard Issues 32
Predefined Globals and Constants 33
Accessing Individual Bits 33
Interrupts 34
Linker Directives 35
Lexical Elements 36
Tokens 38
Constants 39
Integer Constants 39
Floating Point Constants 41
Character Constants 42
String Constants 44
Enumeration Constants 45
Pointer Constants 45
Constant Expressions 45
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
iv
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 5

Keywords 46
Identifiers 47
Punctuators 48
Objects and Lvalues 52
Scope and Visibility 54
Name Spaces 56
Duration 57
Types 59
Fundamental Types 60
Arithmetic Types 60
Enumeration Types 62
Void Type 64
Derived Types 65
Arrays 65
Pointers 68
Pointer Arithmetic 70
Structures 74
Unions 79
Bit Fields 80
Types Conversions 82
Standard Conversions 82
Explicit Typecasting 84
Declarations 85
Linkage 87
Storage Classes 89
Type Qualifiers 91
Typedef Specifier 92
asm Declaration 93
Initialization 94
Functions 95
Function Declaration 95
Function Prototypes 96
Function Definition 97
Function Calls 98
Operators 100
Precedence and Associativity 100
Arithmetic Operators 102
Relational Operators 104
Bitwise Operators 105
Logical Operators 107
Conditional Operator ? : 109
Assignment Operators 110
sizeof Operator 112
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
v
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 6

Expressions 113
Statements 115
Labeled Statements 115
Expression Statements 116
Selection Statements 116
Iteration Statements 119
Jump Statements 122
Compound Statements (Blocks) 124
Preprocessor 125
Preprocessor Directives 125
Macros 126
File Inclusion 130
Preprocessor Operators 131
Conditional Compilation 132
CHAPTER 4: mikroC Libraries 135
Built-in Routines 136
Library Routines 138
ADC Library 139
CAN Library 141
CANSPI Library 153
Compact Flash Library 162
EEPROM Library 172
Ethernet Library 174
Flash Memory Library 186
I2C Library 188
Keypad Library 193
LCD Library (4-bit interface) 197
LCD8 Library (8-bit interface) 203
Graphic LCD Library 208
Manchester Code Library 219
Multi Media Card Library 224
OneWire Library 233
PS/2 Library 237
PWM Library 240
RS-485 Library 243
Secure Digital Library 249
Software I2C Library 254
Software SPI Library 258
Software UART Library 260
Sound Library 264
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
vi
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 7

SPI Library 266
USART Library 271
USB HID Library 275
Util Library 280
ANSI C Ctype Library 281
ANSI C Math Library 285
ANSI C Stdlib Library 291
ANSI C String Library 295
Conversions Library 299
Trigonometry Library 303
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
vii
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 8

mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
viii
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 9

CHAPTER
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
1
mikroC IDE
mikroC is a powerful, feature rich development tool for PICmicros. It is designed
to provide the customer with the easiest possible solution for developing applications for embedded systems, without compromising performance or control.
PIC and C fit together well: PIC is the most popular 8-bit chip in the world, used
in a wide variety of applications, and C, prized for its efficiency, is the natural
choice for developing embedded systems. mikroC provides a successful match
featuring highly advanced IDE, ANSI compliant compiler, broad set of hardware
libraries, comprehensive documentation, and plenty of ready-to-run examples.
QUICK OVERVIEW
Page 10
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
2
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
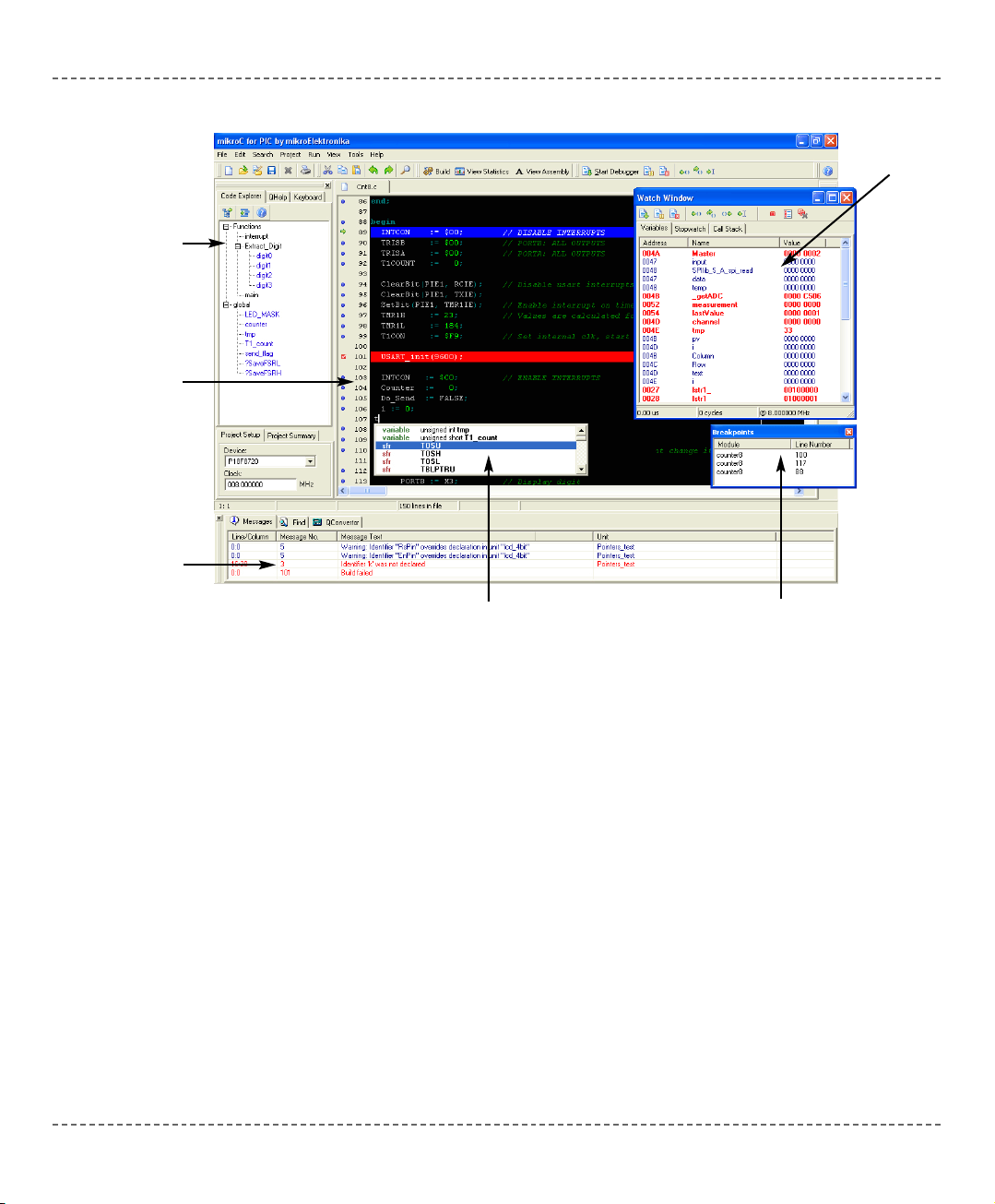
mikroC allows you to quickly develop and deploy complex applications:
- Write your C source code using the highly advanced Code Editor
- Use the included mikroC libraries to dramatically speed up the development:
data acquisition, memory, displays, conversions, communications…
- Monitor your program structure, variables, and functions in the Code Explorer.
Generate commented, human-readable assembly, and standard HEX compatible
with all programmers.
- Inspect program flow and debug executable logic with the integrated Debugger.
Get detailed reports and graphs on code statistics, assembly listing, calling tree…
- We have provided plenty of examples for you to expand, develop, and use as
building bricks in your projects.
Code
Explorer
Error
Window
Watch
Window
Code
Editor
Breakpoints
Window
Code
Assistant
Page 11
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
3
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
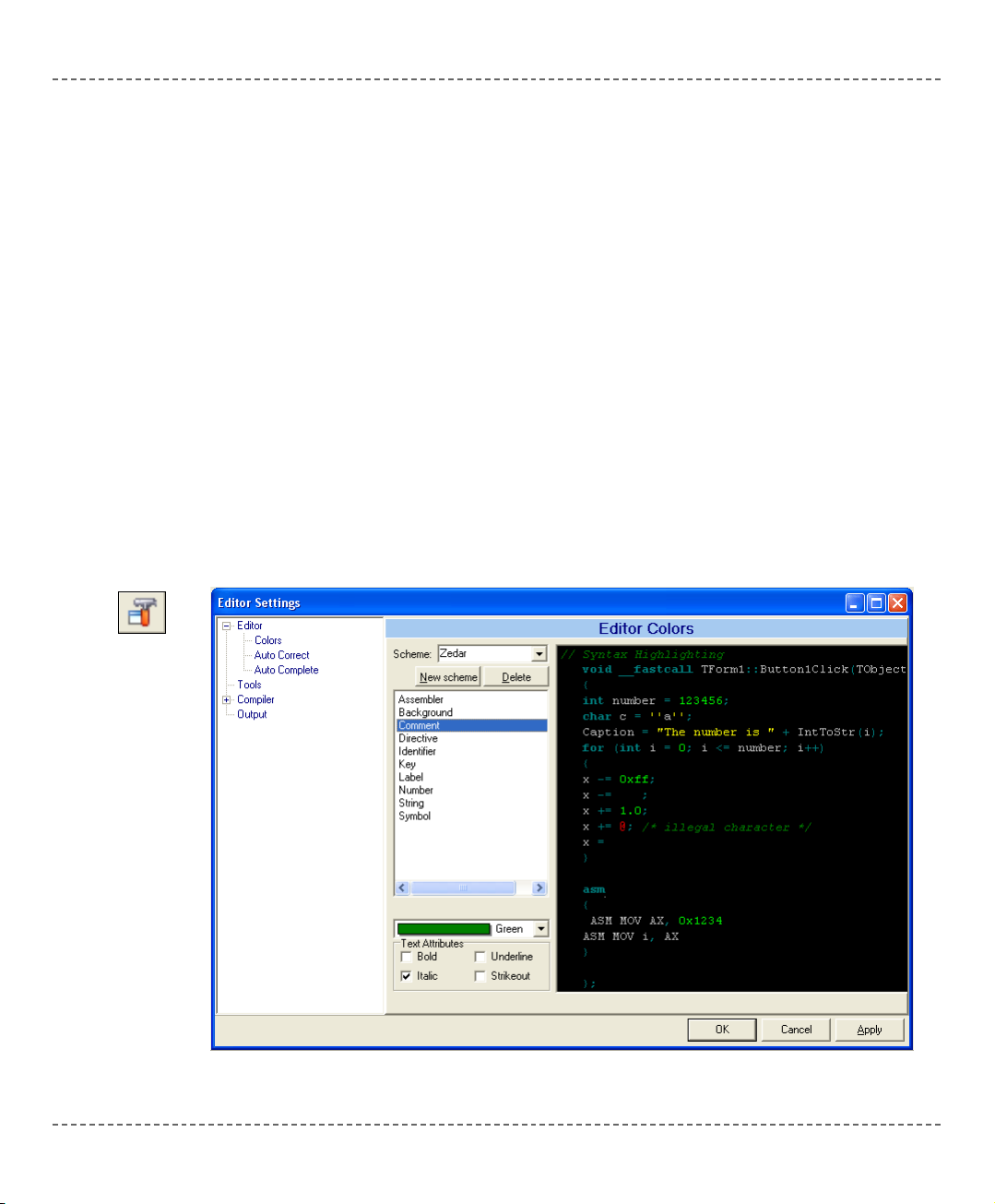
The Code Editor is an advanced text editor fashioned to satisfy the needs of professionals. General code editing is same as working with any standard text-editor,
including familiar Copy, Paste, and Undo actions, common for Windows environment.
Advanced Editor features include:
- Adjustable Syntax Highlighting
- Code Assistant
- Parameter Assistant
- Code Templates (Auto Complete)
- Auto Correct for common typos
- Bookmarks and Goto Line
You can customize these options from the Editor Settings dialog. To access the
settings, choose Tools > Options from the drop-down menu, or click the Tools
icon.
CODE EDITOR
Tools Icon.
Page 12
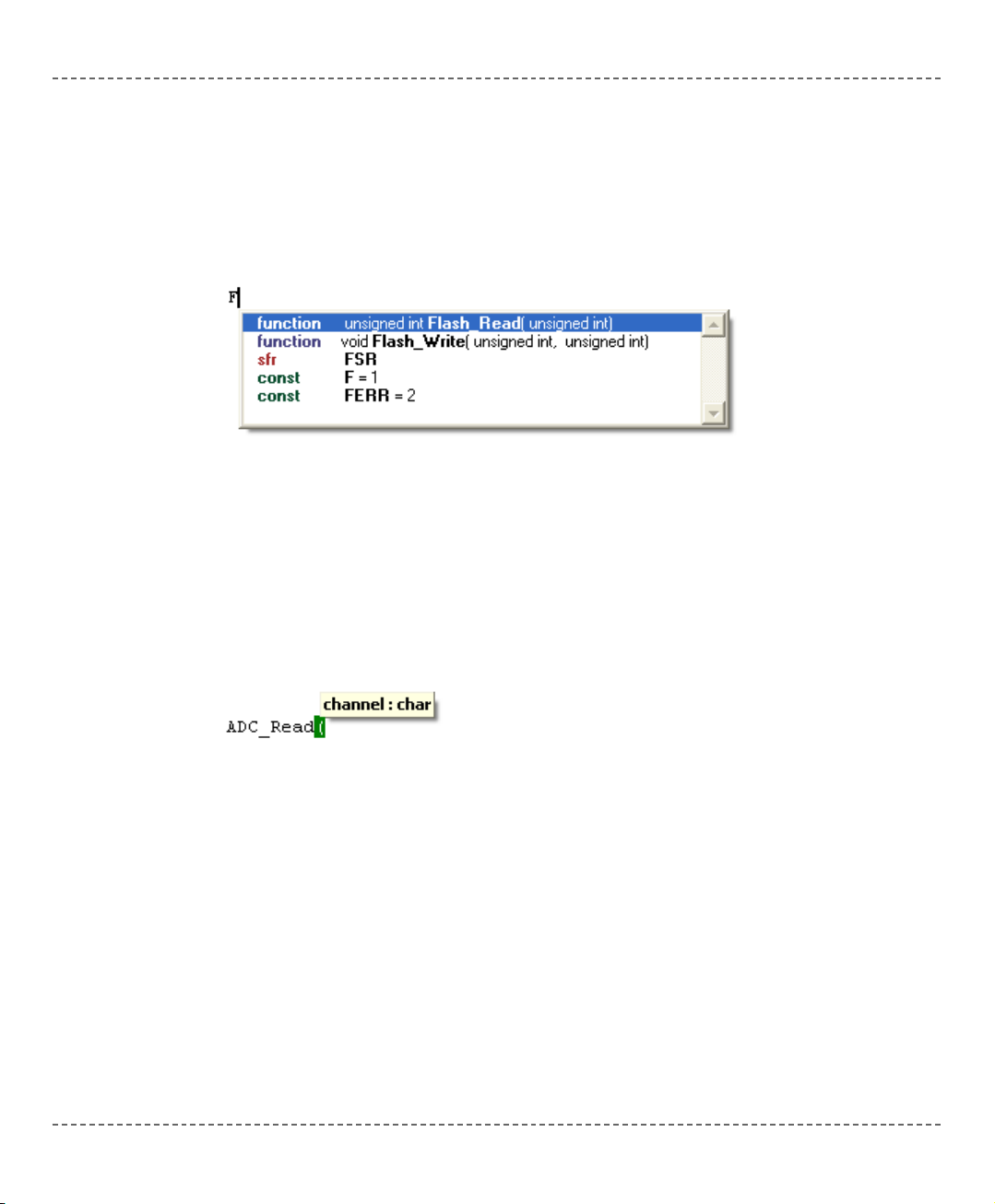
Code Assistant [CTRL+SPACE]
If you type a first few letter of a word and then press CTRL+SPACE, all the valid
identifiers matching the letters you typed will be prompted in a floating panel (see
the image). Now you can keep typing to narrow the choice, or you can select one
from the list using the keyboard arrows and Enter.
Parameter Assistant [CTRL+SHIFT+SPACE]
The Parameter Assistant will be automatically invoked when you open a parenthesis "(" or press CTRL+SHIFT+SPACE. If name of a valid function precedes the
parenthesis, then the expected parameters will be prompted in a floating panel. As
you type the actual parameter, the next expected parameter will become bold.
Code Template [CTR+J]
You can insert the Code Template by typing the name of the template (for
instance, whileb), then press CTRL+J, and the Code Editor will automatically
generate the code. Or you can click a button from the Code toolbar and select a
template from the list.
You can add your own templates to the list. Just select Tools > Options from the
drop-down menu, or click the Tools Icon from Settings Toolbar, and then select
the Auto Complete Tab. Here you can enter the appropriate keyword, description,
and code of your template.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
4
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 13

Auto Correct
The Auto Correct feature corrects common typing mistakes. To access the list of
recognized typos, select Tools > Options from the drop-down menu, or click the
Tools Icon, and then select the Auto Correct Tab. You can also add your own preferences to the list.
Comment/Uncomment
The Code Editor allows you to comment or uncomment selected block of code by
a simple click of a mouse, using the Comment/Uncomment icons from the Code
Toolbar.
Bookmarks
Bookmarks make navigation through large code easier.
CTRL+<number> : Go to a bookmark
CTRL+SHIFT+<number> : Set a bookmark
Goto Line
Goto Line option makes navigation through large code easier. Select Search >
Goto Line from the drop-down menu, or use the shortcut CTRL+G.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
5
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Comment /
Uncomment Icon.
Page 14
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
6
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
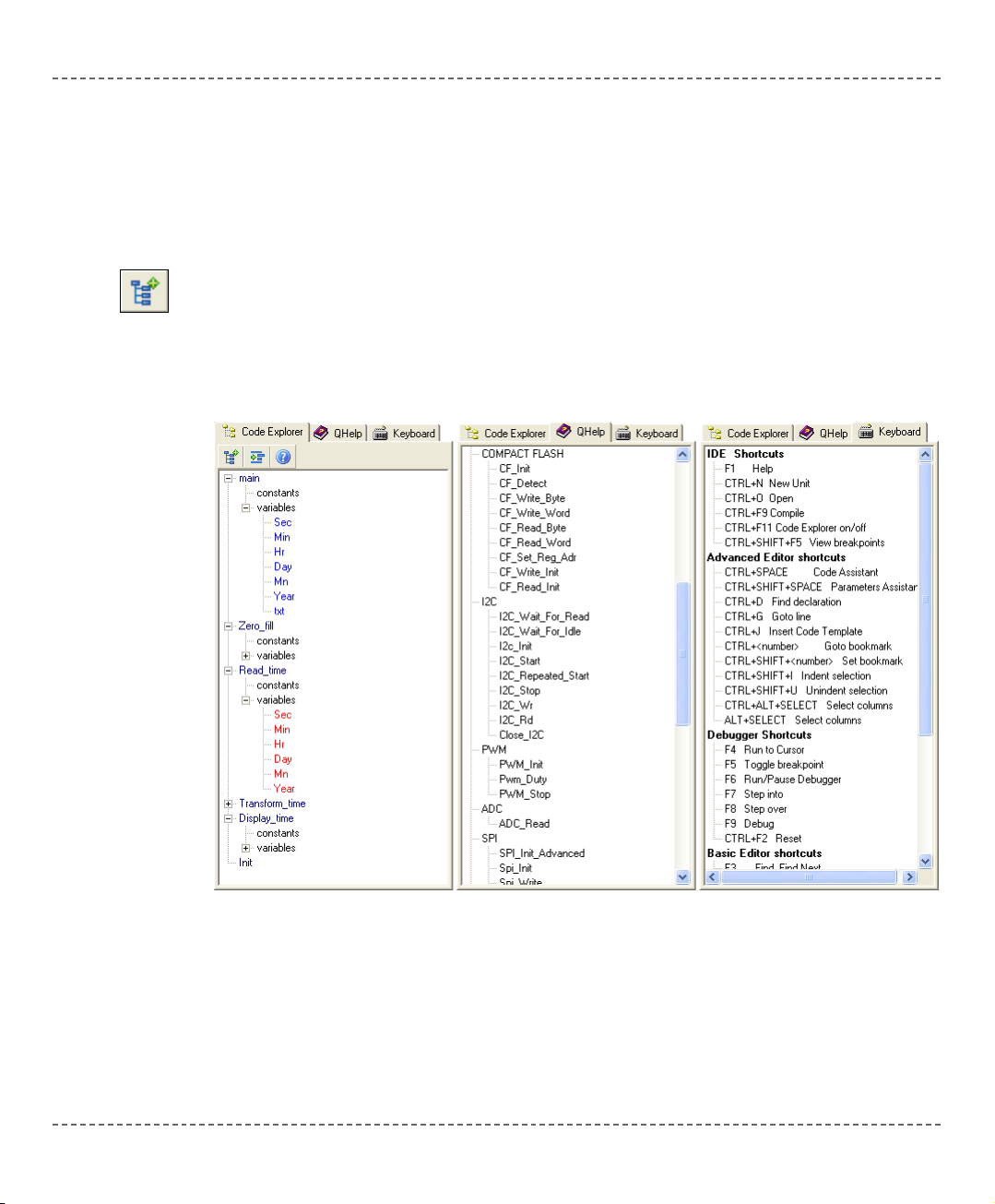
The Code Explorer is placed to the left of the main window by default, and gives a
clear view of every declared item in the source code. You can jump to a declaration of any item by clicking it, or by clicking the Find Declaration icon. To expand
or collapse treeview in Code Explorer, use the Collapse/Expand All icon.
Also, two more tabs are available in Code Explorer. QHelp Tab lists all the available built-in and library functions, for a quick reference. Double-clicking a routine
in QHelp Tab opens the relevant Help topic. Keyboard Tab lists all the available
keyboard shortcuts in mikroC.
CODE EXPLORER
Collapse/Expand
All Icon.
Page 15

MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
7
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
The source-level Debugger is an integral component of mikroC development environment. It is designed to simulate operations of Microchip Technology's
PICmicros and to assist users in debugging software written for these devices.
The Debugger simulates program flow and execution of instruction lines, but does
not fully emulate PIC device behavior: it does not update timers, interrupt flags,
etc.
After you have successfully compiled your project, you can run the Debugger by
selecting Run > Debug from the drop-down menu, or by clicking the Debug Icon .
Starting the Debugger makes more options available: Step Into, Step Over, Run to
Cursor, etc. Line that is to be executed is color highlighted.
Debug [F9]
Start the Debugger.
Run/Pause Debugger [F6]
Run or pause the Debugger.
Step Into [F7]
Execute the current C (single– or multi–cycle) instruction, then halt. If the instruction is a routine call, enter the routine and halt at the first instruction following the
call.
Step Over [F8]
Execute the current C (single– or multi–cycle) instruction, then halt. If the instruction is a routine call, skip it and halt at the first instruction following the call.
Step Out [Ctrl+F8]
Execute the current C (single– or multi–cycle) instruction, then halt. If the instruction is within a routine, execute the instruction and halt at the first instruction following the call.
Run to cursor [F4]
Executes all instructions between the current instruction and the cursor position.
DEBUGGER
Start Debugger
Step Into
Step Over
Step Out
Pause Debugger
Run to Cursor
Page 16
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
8
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Toggle Breakpoint [F5]
Toggle breakpoint at current cursor position. To view all the breakpoints, select
Run > View Breakpoints from the drop-down menu. Double clicking an item in
window list locates the breakpoint.
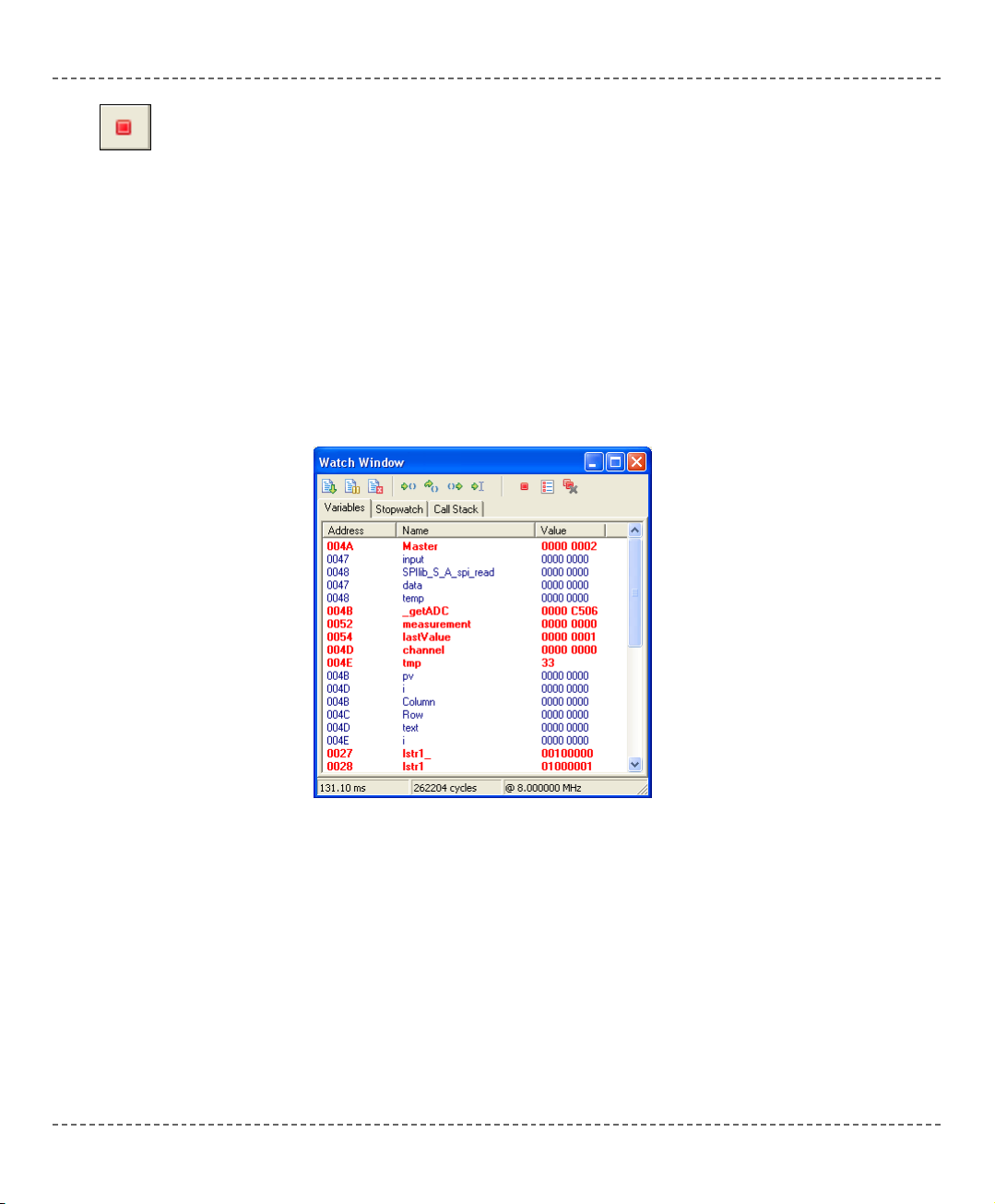
Watch Window
Variables
The Watch Window allows you to monitor program items while running your program. It displays variables and special function registers of PIC MCU, their
addresses and values. Values are updated as you go through the simulation.
Double clicking one of the items opens a window in which you can assign a new
value to the selected variable or register and change number formatting.
Toggle
Breakpoint.
Page 17
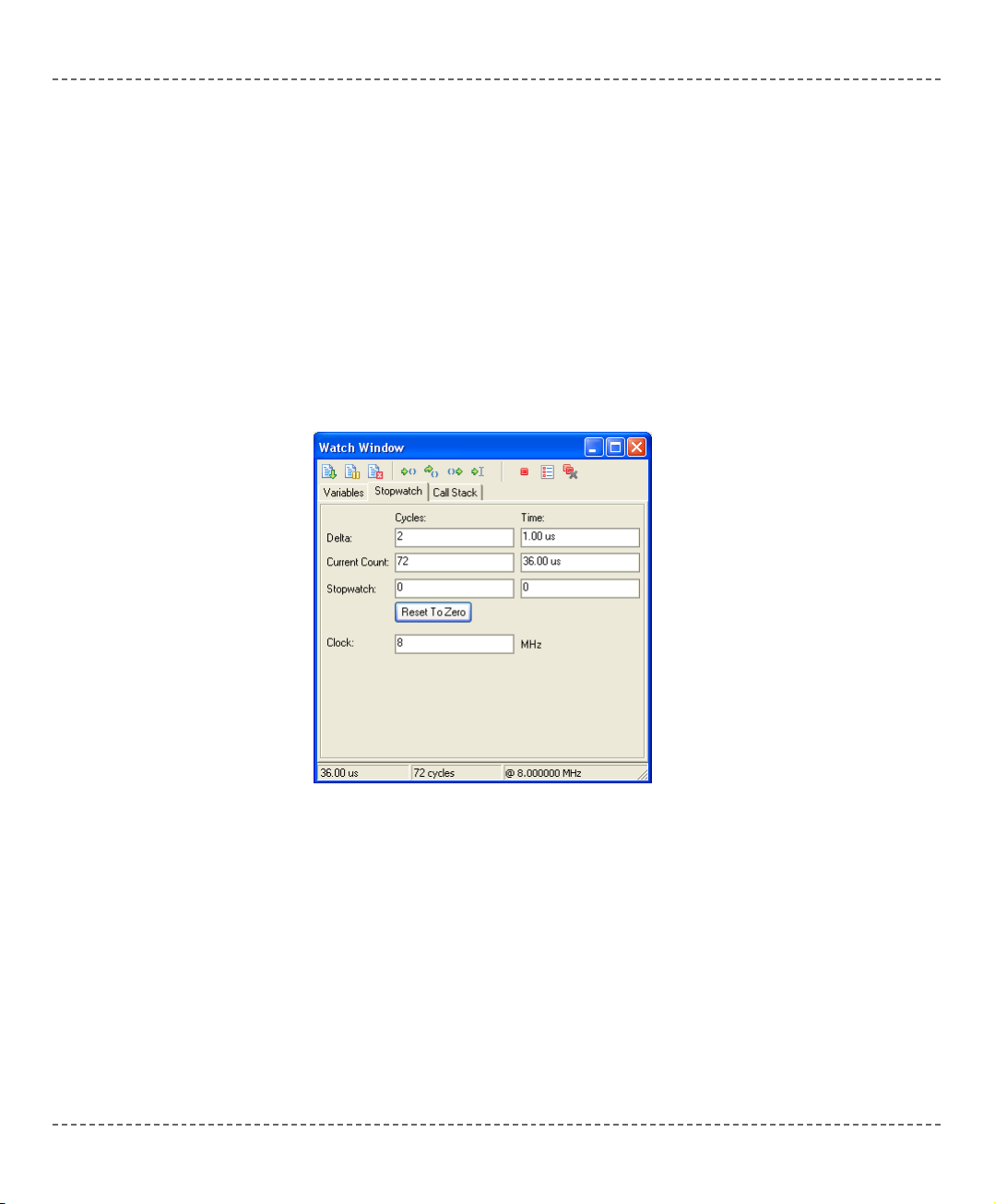
Stopwatch Window
The Stopwatch Window displays the current count of cycles/time since the last
Debugger action. Stopwatch measures the execution time (number of cycles) from
the moment the Debugger is started, and can be reset at any time. Delta represents
the number of cycles between the previous instruction line (line where the
Debugger action was performed) and the active instruction line (where the
Debugger action landed).
Note: You can change the clock in the Stopwatch Window; this will recalculate
values for the newly specified frequency. Changing the clock in the Stopwatch
Window does not affect the actual project settings – it only provides a simulation.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
9
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 18
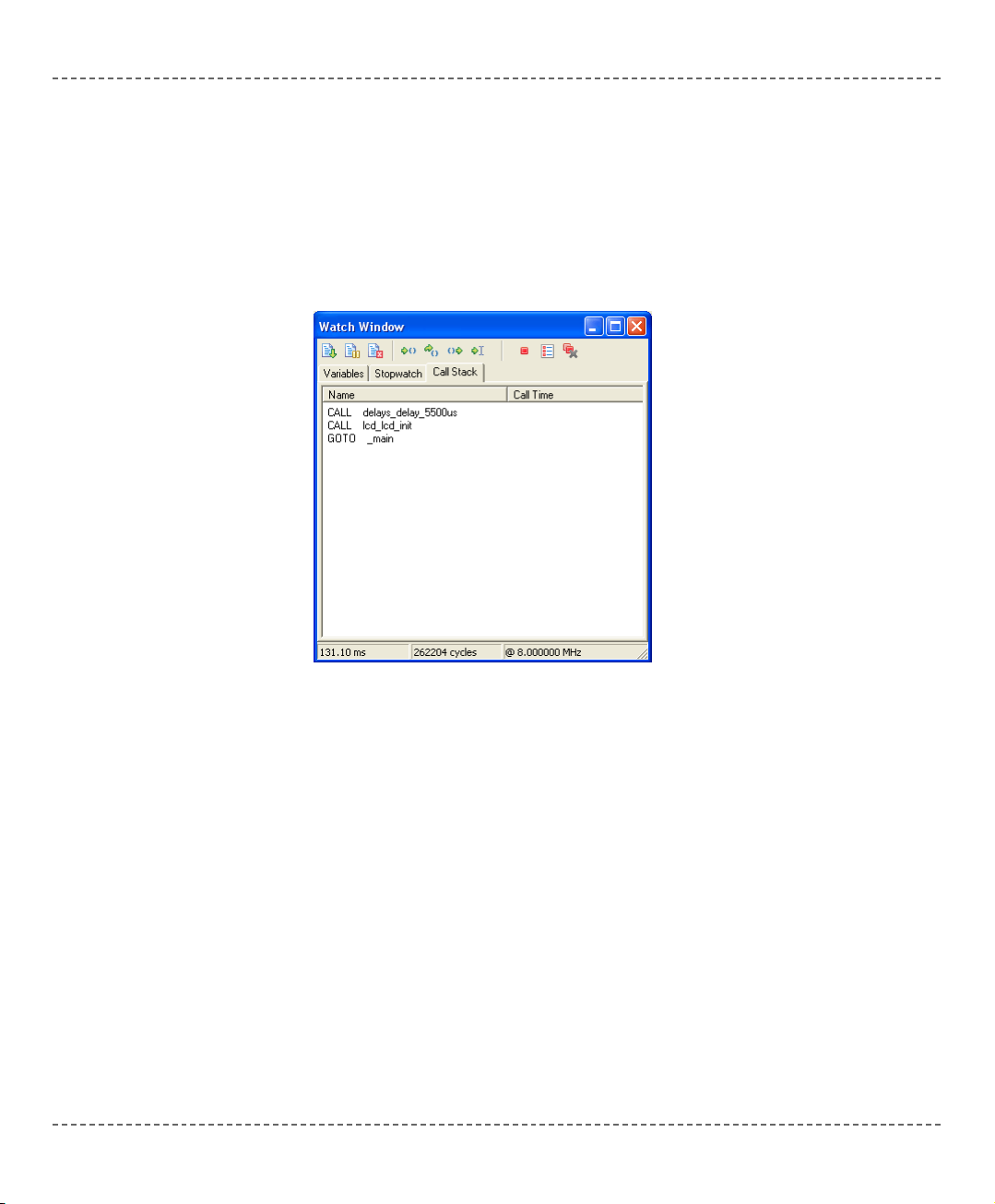
Call Stack Window
The Call Stack Window keeps track of depth and order of nested routine calls in
program simulation. Check the Nested Calls Limitations for more information.
Note: Real scenarios may differ from the simulation, depending on runtime
program parameters.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
10
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 19
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
11
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
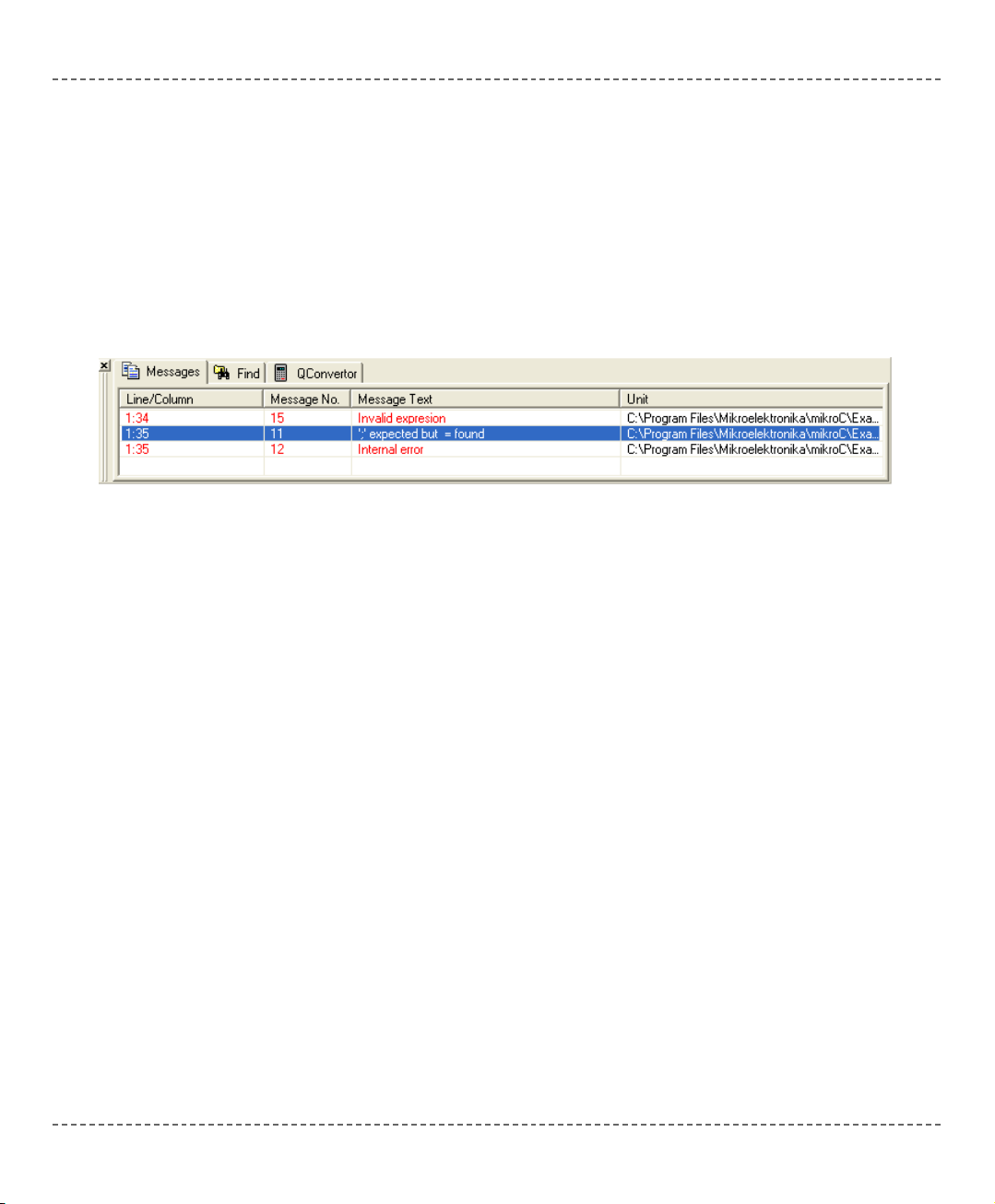
In case that errors were encountered during compiling, the compiler will report
them and won't generate a hex file. The Error Window will be prompted at the
bottom of the main window by default.
The Error Window is located under the message tab, and displays location and
type of errors compiler has encountered. The compiler also reports warnings, but
these do not affect the output; only errors can interefere with generation of hex.
Double click the message line in the Error Window to highlight the line where the
error was encountered.
Consult the Error Messages for more information about errors recognized by the
compiler.
ERROR WINDOW
Page 20
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
12
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
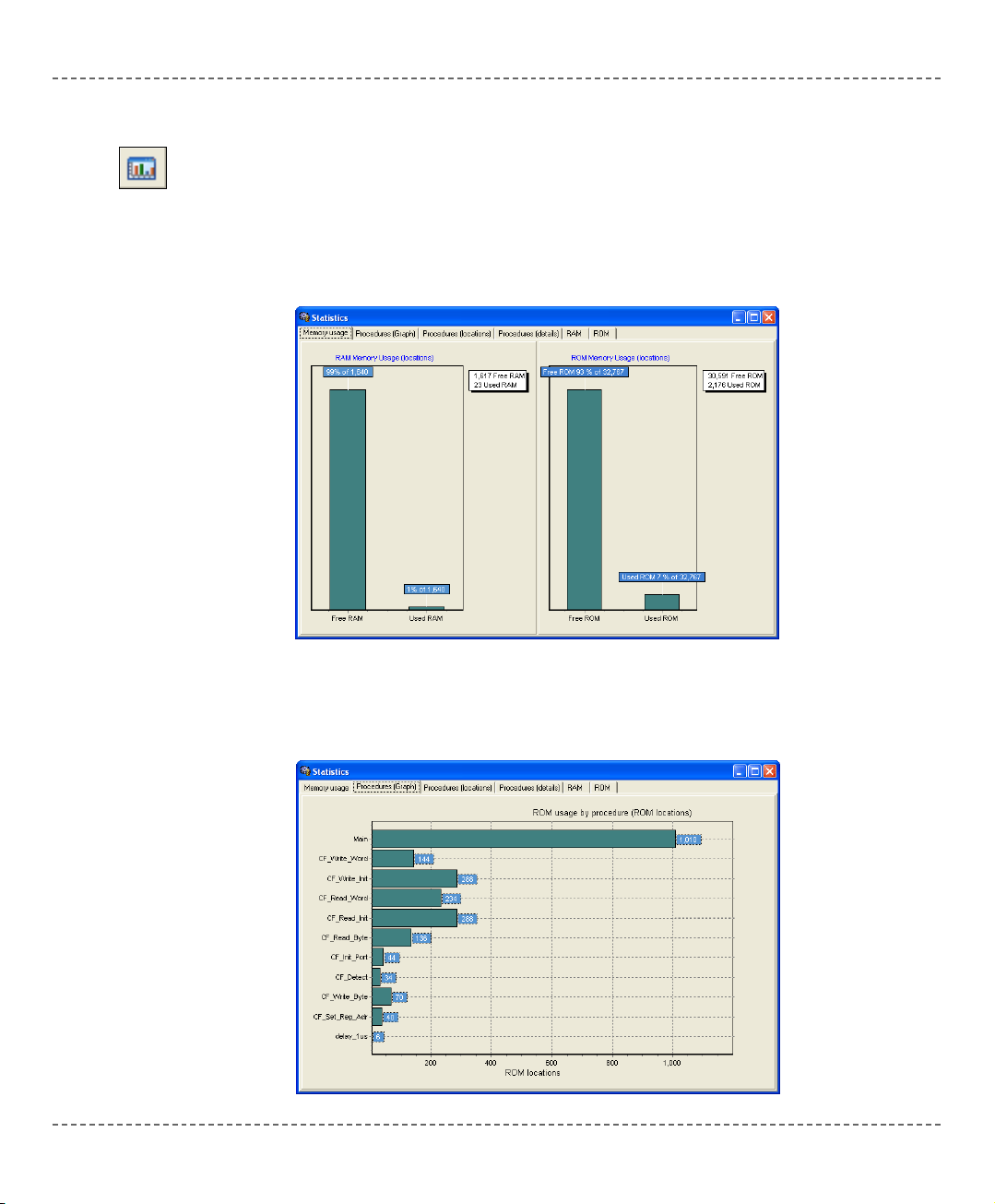
After successful compilation, you can review statistics of your code. Select Project
> View Statistics from the drop-down menu, or click the Statistics icon. There are
six tab windows:
Memory Usage Window
Provides overview of RAM and ROM memory usage in form of histogram.
Procedures (Graph) Window
Displays functions in form of histogram, according to their memory allotment.
STATISTICS
Statistics Icon.
Page 21
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
13
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
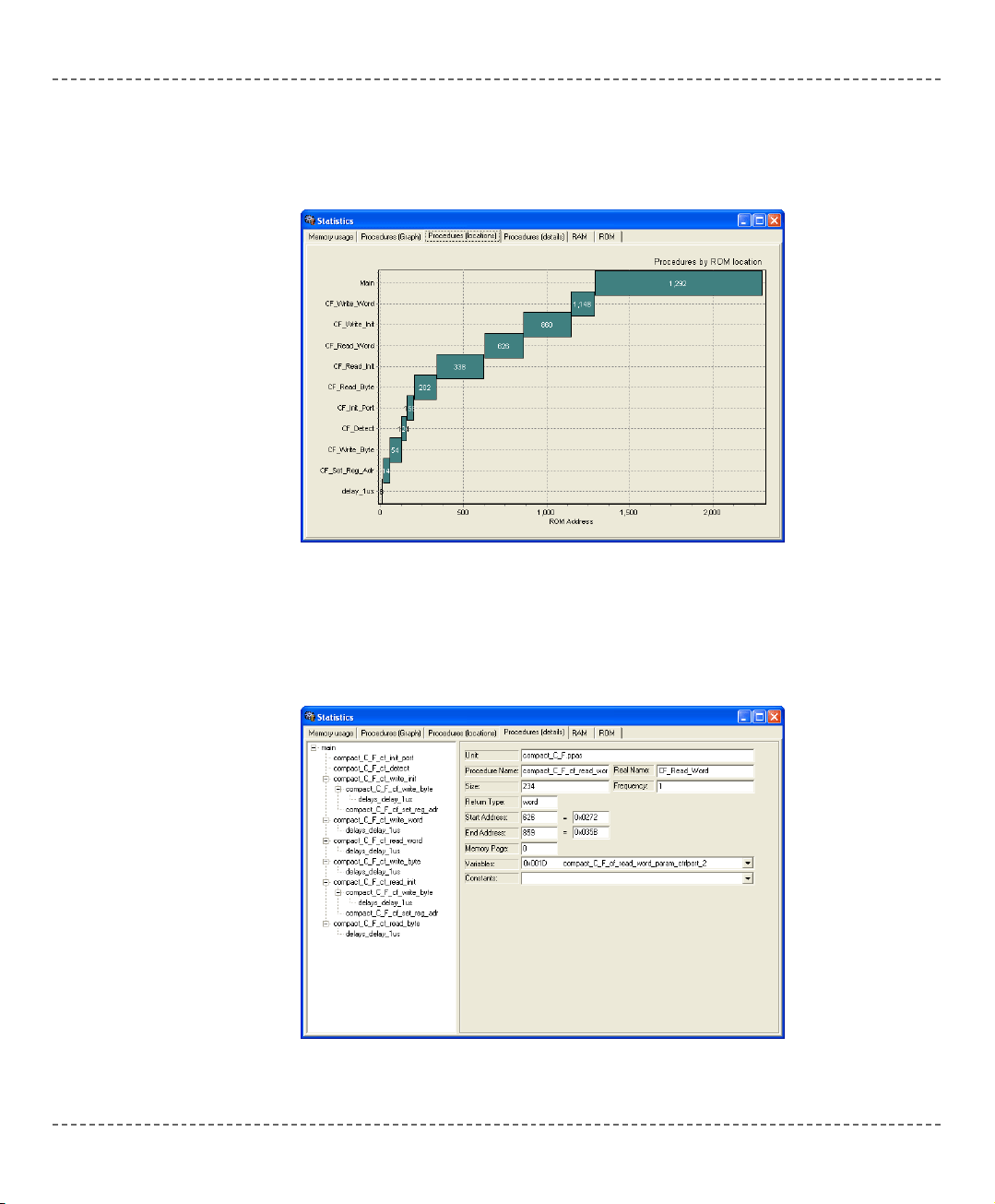
Procedures (Locations) Window
Displays how functions are distributed in microcontroller’s memory.
Procedures (Details) Window
Displays complete call tree, along with details for each function:
size, start and end address, calling frequency, return type, etc.
Page 22
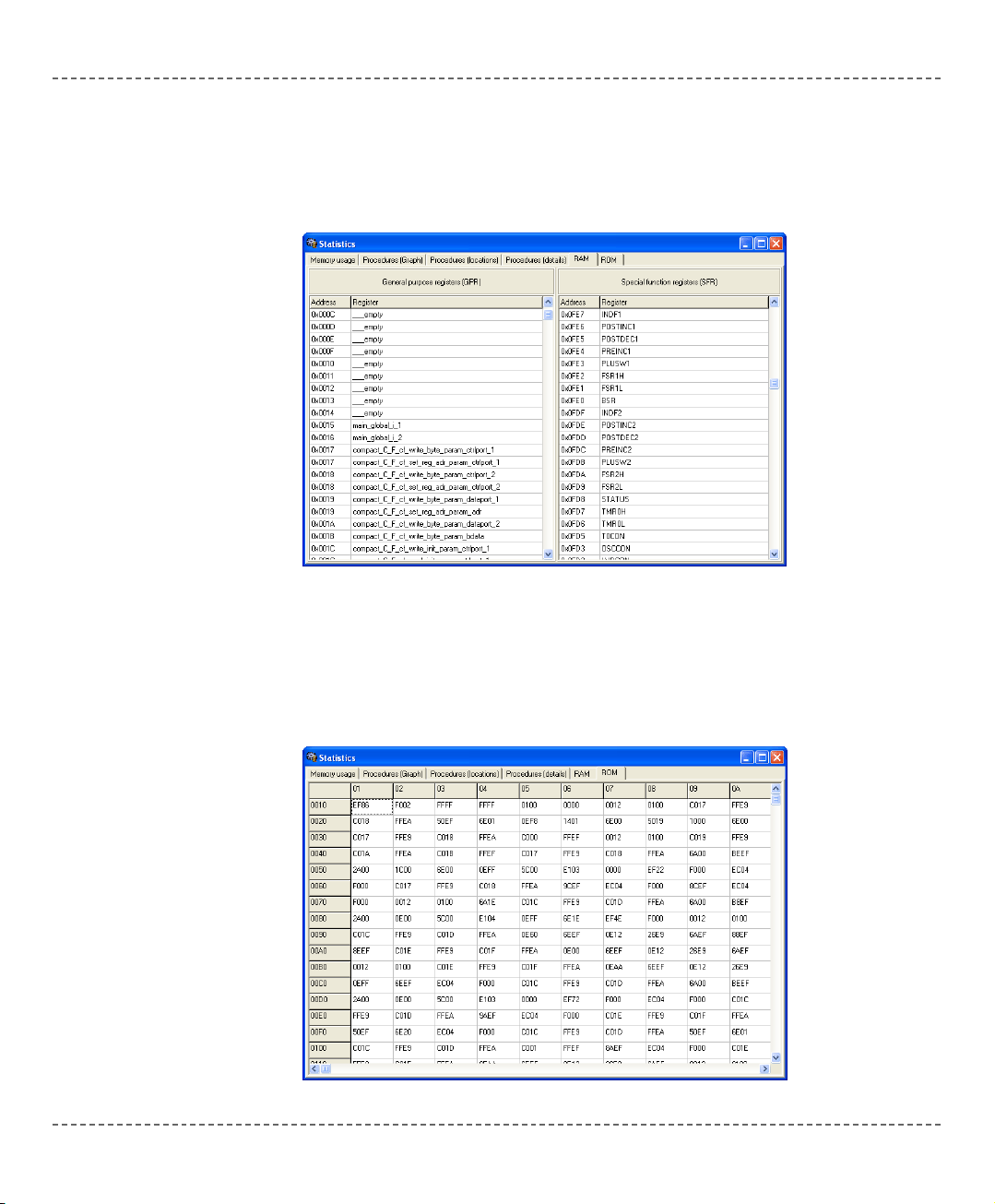
RAM Window
Summarizes all GPR and SFR registers and their addresses. Also displays symbolic names of variables and their addresses.
ROM Window
Lists op-codes and their addresses in form of a human readable hex code.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
14
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 23
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
15
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
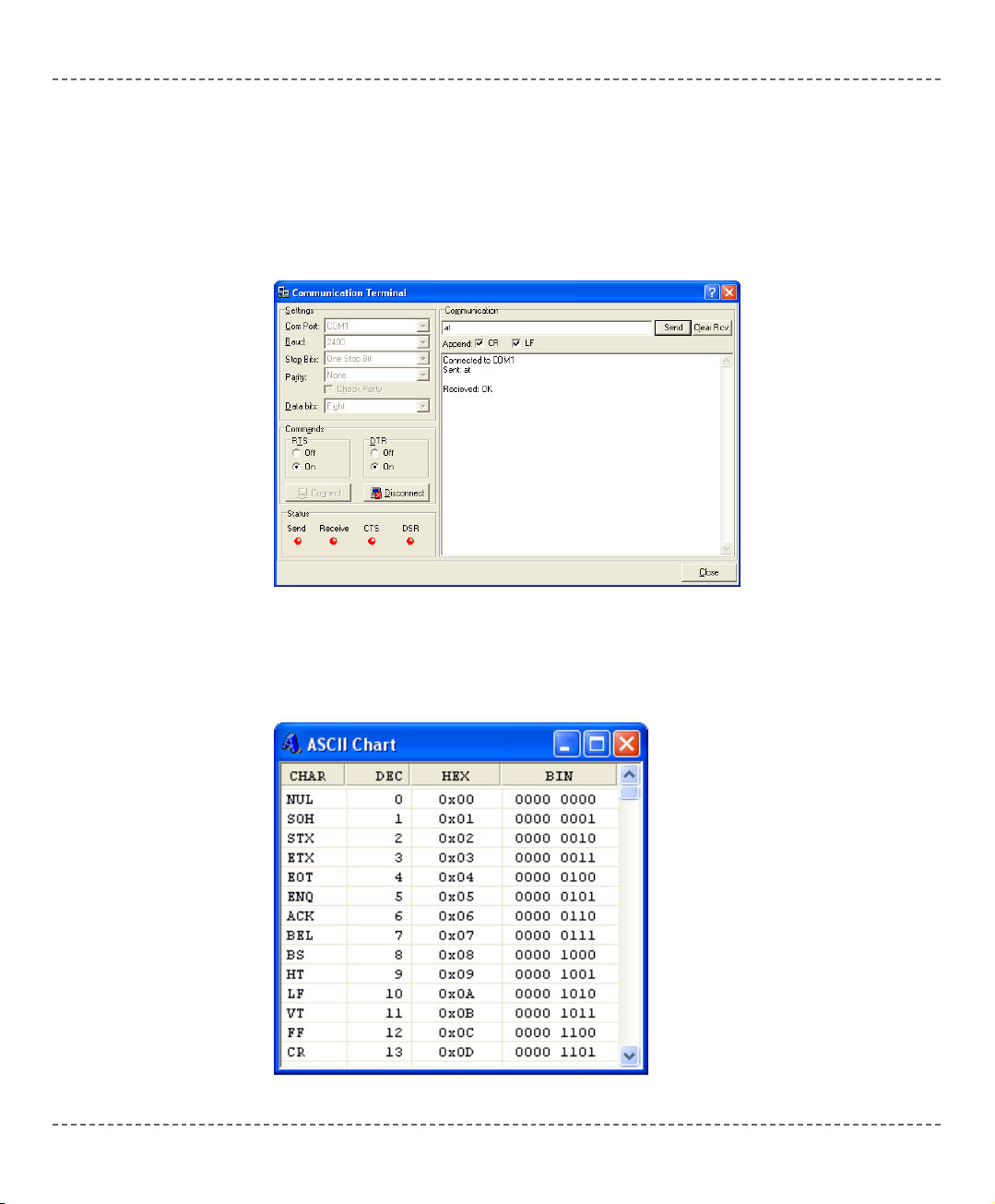
USART Terminal
mikroC includes the USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver
Transmitter) communication terminal for RS232 communication. You can launch
it from the drop-down menu Tools > Terminal or by clicking the Terminal icon.
ASCII Chart
The ASCII Chart is a handy tool, particularly useful when working with LCD display. You can launch it from the drop-down menu Tools > ASCII chart.
INTEGRATED TOOLS
Page 24
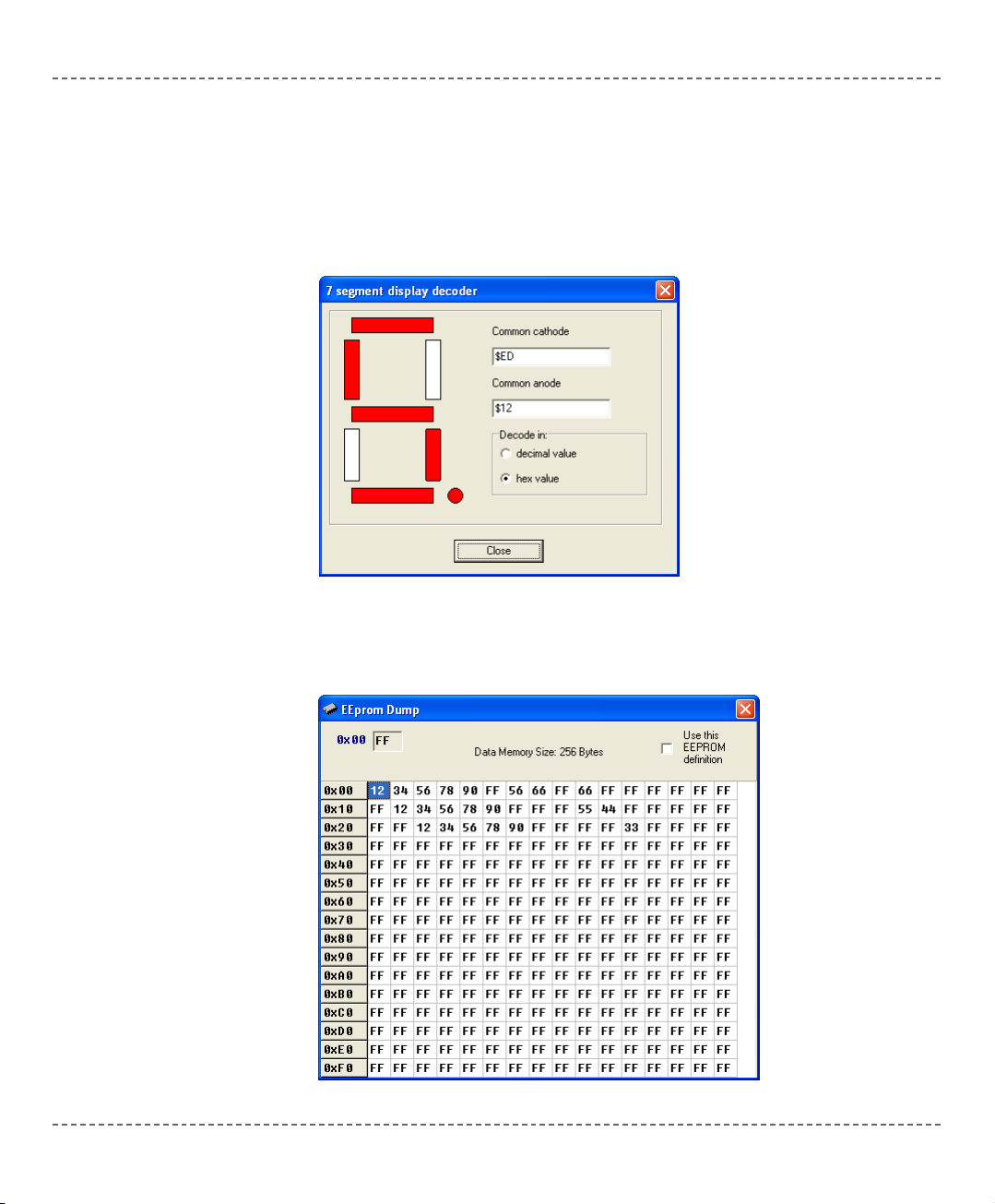
7 Segment Display Decoder
The 7seg Display Decoder is a convenient visual panel which returns decimal/hex
value for any viable combination you would like to display on 7seg. Click on the
parts of 7 segment image to get the desired value in the edit boxes. You can launch
it from the drop-down menu Tools > 7 Segment Display.
EEPROM Editor
EEPROM Editor allows you to easily manage EEPROM of PIC microcontroller.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
16
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 25

mikroBootloader
mikroBootloader can be used only with PICmicros that support flash write.
1. Load the PIC with the appropriate hex file using the conventional programming
techniques (e.g. for PIC16F877A use p16f877a.hex).
2. Start mikroBootloader from the drop-down menu Tools > Bootoader.
3. Click on Setup Port and select the COM port that will be used. Make sure that
BAUD is set to 9600 Kpbs.
4. Click on Open File and select the HEX file you would like to upload.
5. Since the bootcode in the PIC only gives the computer 4-5 sec to connect, you
should reset the PIC and then click on the Connect button within 4-5 seconds.
6. The last line in then history window should now read “Connected”.
7. To start the upload, just click on the Start Bootloader button.
8. Your program will written to the PIC flash. Bootloader will report an errors that
may occur.
9. Reset your PIC and start to execute.
The boot code gives the computer 5 seconds to get connected to it. If not, it starts
running the existing user code. If there is a new user code to be downloaded, the
boot code receives and writes the data into program memory.
The more common features a bootloader may have are listed below:
- Code at the Reset location.
- Code elsewhere in a small area of memory.
- Checks to see if the user wants new user code to be loaded.
- Starts execution of the user code if no new user code is to be loaded.
- Receives new user code via a communication channel if code is to be loaded.
- Programs the new user code into memory.
Integrating User Code and Boot Code
The boot code almost always uses the Reset location and some additional program
memory. It is a simple piece of code that does not need to use interrupts; therefore,
the user code can use the normal interrupt vector at 0x0004. The boot code must
avoid using the interrupt vector, so it should have a program branch in the address
range 0x0000 to 0x0003. The boot code must be programmed into memory using
conventional programming techniques, and the configuration bits must be programmed at this time. The boot code is unable to access the configuration bits,
since they are not mapped into the program memory space.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
17
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 26

mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
18
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Below is the complete list of keyboard shortcuts available in mikroC IDE. You can
also view keyboard shortcuts in Code Explorer window, tab Keyboard.
IDE Shortcuts
F1 Help
CTRL+N New Unit
CTRL+O Open
CTRL+F9 Compile
CTRL+F11 Code Explorer on/off
CTRL+SHIFT+F5 View breakpoints
Basic Editor shortcuts
F3 Find, Find Next
CTRL+A Select All
CTRL+C Copy
CTRL+F Find
CTRL+P Print
CTRL+R Replace
CTRL+S Save unit
CTRL+SHIFT+S Save As
CTRL+V Paste
CTRL+X Cut
CTRL+Y Redo
CTRL+Z Undo
Advanced Editor shortcuts
CTRL+SPACE Code Assistant
CTRL+SHIFT+SPACE Parameters Assistant
CTRL+D Find declaration
CTRL+G Goto line
CTRL+J Insert Code Template
CTRL+<number> Goto bookmark
CTRL+SHIFT+<number> Set bookmark
CTRL+SHIFT+I Indent selection
CTRL+SHIFT+U Unindent selection
CTRL+ALT+SELECT Select columns
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
Page 27

Debugger Shortcuts
F4 Run to Cursor
F5 Toggle breakpoint
F6 Run/Pause Debugger
F7 Step into
F8 Step over
F9 Debug
CTRL+F2 Reset
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
19
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 28

mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
20
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 29

CHAPTER
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
2
Building
Applications
Creating applications in mikroC is easy and intuitive. Project Wizard allows you to
set up your project in just few clicks: name your application, select chip, set flags,
and get going.
mikroC allows you to distribute your projects in as many files as you find appropriate. You can then share your mikroCompiled Libraries (
.mcl files) with other
developers without disclosing the source code. The best part is that you can use
.mcl bundles created by mikroPascal or mikroBasic!
Page 30

mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
22
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
mikroC organizes applications into projects, consisting of a single project file
(extension .ppc) and one or more source files (extension .c). You can compile
source files only if they are part of a project.
Project file carries the following information:
- project name and optional description,
- target device,
- device flags (config word) and device clock,
- list of project source files with paths.
New Project
The easiest way to create project is by means of New Project Wizard, drop-down
menu Project > New Project. Just fill the dialog with desired values (project name
and description, location, device, clock, config word) and mikroC will create the
appropriate project file. Also, an empty source file named after the project will be
created by default.
Editing Project
Later, you can change project settings from drop-down menu Project > Edit
Project. You can rename the project, modify its description, change chip, clock,
config word, etc. To delete a project, simply delete the folder in which the project
file is stored.
Add/Remove Files from Project
Project can contain any number of source files (extension .c). The list of relevant
source files is stored in the project file (extension .ppc). To add source file to
your project, select Project > Add to Project from drop-down menu. Each added
source file must be self-contained, i.e. it must have all the necessary definitions
after preprocessing. To remove file(s) from your project, select Project > Remove
from Project from drop-down menu.
Note: For inclusion of header files, use the preprocessor directive
#include.
PROJECTS
New Project.
Edit Project.
Add to Project.
Remove from
Project.
Page 31

Source files containing C code should have the extension .c. List of source files
relevant for the application is stored in project file with extension .ppc, along
with other project information. You can compile source files only if they are part
of a project.
Use the preprocessor directive
#include to include headers. Do not rely on pre-
processor to include other source files — see Projects for more information.
Search Paths
Paths for source files (
.c)
You can specify your own custom search paths. This can be configured by selecting Tools > Options from drop-down menu and then tab window Advanced.
In project settings, you can specify either absolute or relative path to the source
file. If you specify a relative path, mikroC will look for the file in following locations, in this particular order:
1. the project folder (folder which contains the project file
.ppc),
2. your custom search paths,
3. mikroC installation folder > “uses” folder.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
23
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
SOURCE FILES
Page 32

Paths for Header Files (.h)
Header files are included by means of preprocessor directive
#include. If you
place an explicit path to the header file in preprocessor directive, only that location
will be searched.
If
#include directive was used with the <header_name> version, the search is
made successively in each of the following locations, in this particular order:
1. mikroC installation folder > “include” folder,
2. your custom search paths.
The
"header_name" version specifies a user-supplied include file; mikroC will
look for the header file in following locations, in this particular order:
1. the project folder (folder which contains the project file
.ppc),
2. mikroC installation folder > “include” folder,
3. your custom search paths.
Managing Source Files
Creating a new source file
To create a new source file, do the following:
Select File > New from drop-down menu, or press CTRL+N, or click the New
File icon. A new tab will open, named “Untitled1”. This is your new source file.
Select File > Save As from drop-down menu to name it the way you want.
If you have used New Project Wizard, an empty source file, named after the project with extension
.c, is created automatically. mikroC does not require you to
have source file named same as the project, it’s just a matter of convenience.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
24
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
New File.
Page 33

Opening an Existing File
Select File > Open from drop-down menu, or press CTRL+O, or click the Open
File icon. The Select Input File dialog opens. In the dialog, browse to the location
of the file you want to open and select it. Click the Open button.
The selected file is displayed in its own tab. If the selected file is already open, its
current Editor tab will become active.
Printing an Open File
Make sure that window containing the file you want to print is the active window.
Select File > Print from drop-down menu, or press CTRL+P, or click the Print
icon. In the Print Preview Window, set the desired layout of the document and
click the OK button. The file will be printed on the selected printer.
Saving File
Make sure that window containing the file you want to save is the active window.
Select File > Save from drop-down menu, or press CTRL+S, or click the Save
icon. The file will be saved under the name on its window.
Saving File Under a Different Name
Make sure that window containing the file you want to save is the active window.
Select File > Save As from drop-down menu, or press SHIFT+CTRL+S. The New
File Name dialog will be displayed. In the dialog, browse to the folder where you
want to save the file. In the File Name field, modify the name of the file you want
to save. Click the Save button.
Closing a File
Make sure that tab containing the file you want to close is the active tab. Select
File > Close from drop-down menu, or right click the tab of the file you want to
close in Code Editor. If the file has been changed since it was last saved, you will
be prompted to save your changes.
Open File Icon.
Print File Icon.
Save File Icon.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
25
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Save File As.
Close File.
Page 34

When you have created the project and written the source code, you will want to
compile it. Select Project > Build from drop-down menu, or click Build Icon, or
simply hit CTRL+F9.
Progress bar will appear to inform you about the status of compiling. If there are
errors, you will be notified in the Error Window. If no errors are encountered,
mikroC will generate output files.
Output Files
Upon successful compilation, mikroC will generate output files in the project folder (folder which contains the project file
.ppc). Output files are summarized
below:
Intel HEX file (
.hex)
Intel style hex records. Use this file to program PIC MCU.
Binary mikro Compiled Library (
.mcl)
Binary distribution of application that can be included in other projects.
List File (
.lst)
Overview of PIC memory allotment: instruction addresses, registers, routines, etc.
Assembler File (
.asm)
Human readable assembly with symbolic names, extracted from the List File.
Assembly View
After compiling your program in mikroC, you can click View Assembly Icon or
select Project › View Assembly from drop-down menu to review generated assembly code (.asm file) in a new tab window. Assembly is human readable with symbolic names. All physical addresses and other information can be found in
Statistics or in list file (.lst).
If the program is not compiled and there is no assembly file, starting this option
will compile your code and then display assembly.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
26
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
View Assembly
Icon.
Compile Icon.
COMPILATION
Page 35

Error Messages
- Specifier needed
- Invalid declarator
- Expected '(' or identifier
- Integer const expected
- Array dimension must be greater then 0
- Local objects cannot be extern
- Declarator error
- Bad storage class
- Arguments cannot be of void type
- Specifer/qualifier list expected
- Address must be greater than 0
- Identifier redefined
- case out of switch
- default label out of switch
- switch exp. must evaluate to integral type
- continue outside of loop
- break outside of loop or switch
- void func cannot return values
- Unreachable code
- Illegal expression with void
- Left operand must be pointer
- Function required
- Too many chars
- Undefined struct
- Nonexistent field
- Aggregate init error
- Incompatible types
- Identifier redefined
- Function definition not found
- Signature does not match
- Cannot generate code for expression
- Too many initializers of subaggregate
- Nonexistent subaggregate
- Stack Overflow: func call in complex expression
- Syntax Error: expected %s but %s found
- Array element cannot be function
- Function cannot return array
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
27
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
ERROR MESSAGES
Page 36

- Inconsistent storage class
- Inconsistent type
- %s tag redefined
- Illegal typecast
- %s is not a valid identifier
- Invalid statement
- Constant expression required
- Internal error %s
- Too many arguments
- Not enough parameters
- Invalid expresion
- Identifier expected, but %s found
- Operator [%s] not applicable to this operands [%s]
- Assigning to non-lvalue [%s]
- Cannot cast [%s] to [%s]
- Cannot assign [%s] to [%s]
- lvalue required
- Pointer required
- Argument is out of range
- Undeclared identifier [%s] in expression
- Too many initializers
- Cannot establish this baud rate at %s MHz clock
Compiler Warning Messages
- Highly inefficent code: func call in complex expression
- Inefficent code: func call in complex expression
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
28
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 37

CHAPTER
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
3
mikroC Language
Reference
C offers unmatched power and flexibility in programming microcontrollers.
mikroC adds even more power with an array of libraries, specialized for PIC HW
modules and communications. This chapter should help you learn or recollect C
syntax, along with the specifics of programming PIC microcontrollers. If you are
experienced in C programming, you will probably want to consult mikroC
Specifics first.
Page 38

In order to get the most from your mikroC compiler, you should be familiar with
certain aspects of PIC MCU. This knowledge is not essential, but it can provide
you a better understanding of PICs’ capabilities and limitations, and their impact
on the code writing.
Types Efficiency
First of all, you should know that PIC’s ALU, which performs arithmetic operations, is optimized for working with bytes. Although mikroC is capable of handling very complex data types, PIC may choke on them, especially if you are
working on some of the older models. This can dramatically increase the time
needed for performing even simple operations. Universal advice is to use the
smallest possible type in every situation. It applies to all programming in general,
and doubly so with microcontrollers.
When it comes down to calculus, not all PICmicros are of equal performance. For
example, PIC16 family lacks hardware resources to multiply two bytes, so it is
compensated by a software algorithm. On the other hand, PIC18 family has HW
multiplier, and as a result, multiplication works considerably faster.
Nested Calls Limitations
Nested call represents a function call within function body, either to itself (recursive calls) or to another function. Recursive calls, as form of cross-calling, are
unsupported by mikroC due to the PIC’s stack and memory limitations.
mikroC limits the number of non-recursive nested calls to:
- 8 calls for PIC12 family,
- 8 calls for PIC16 family,
- 31 calls for PIC18 family.
The number of allowed nested calls decreases by one if you use any of the following operators in the code:
* / %. It further decreases by one if you use interrupt
in the program. If the allowed number of nested calls is exceeded, compiler will
report stack overflow error.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
30
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
PIC SPECIFICS
Page 39

PIC16 Specifics
Breaking Through Pages
In applications targeted at PIC16, no single routine should exceed one page (2,000
instructions). If routine does not fit within one page, linker will report an error.
When confront with this problem, maybe you should rethink the design of your
application – try breaking the particular routine into several chunks, etc.
Limits of Indirect Approach Through FSR
Pointers with PIC16 are “near”: they carry only the lower 8 bits of the address.
Compiler will automatically clear the 9th bit upon startup, so that pointers will
refer to banks 0 and 1. To access the objects in banks 3 or 4 via pointer, user
should manually set the IRP, and restore it to zero after the operation. The stated
rules apply to any indirect approach: arrays, structures and unions assignments,
etc.
Note: It is very important to take care of the IRP properly, if you plan to follow
this approach. If you find this method to be inappropriate with too many variables,
you might consider upgrading to PIC18.
Note: If you have many variables in the code, try rearranging them with linker
directive
absolute. Variables that are approached only directly should be moved
to banks 3 and 4 for increased efficiency.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
31
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 40

ANSI Standard Issues
Divergence from the ANSI C Standard
mikroC diverges from the ANSI C standard in few areas. Some of these modifications are improvements intenteded to facilitate PIC programming, while others are
result of PICmicro hardware limitations:
Function cross-calling and recursion are unsupported due to the PIC’s limitations
of no easily-usable stack and limited memory.
Pointers to variables and pointers to constants are not compatible, i.e. no assigning
or comparison is possible between the two.
Function calls from within interrupts are a special case. See Interrupts.
mikroC treats identifiers declared with const qualifier as “true constants” (C++
style). This allows using const objects in places where ANSI C would expect a
constant expression. If aiming at portability, use the traditional preprocessor
defined constants. See Type Qualifiers and Constants.
Tags scope is specific. Due to separate name space, tags are virtually removed
from normal scope rules: they have file scope, but override any block rules.
Ellipsis (
...) in formal argument lists is unsupported.
mikroC allows C++ style single–line comments using two adjacent slashes (
//).
Features under construction: pointers to functions, and anonymous structures.
Implementation-defined Behavior
Certain sections of the ANSI standard have implementation-defined behavior. This
means that the exact behavior of some C code can vary from compiler to compiler.
Throughout the help are sections describing how the mikroC compiler behaves in
such situations. The most notable specifics include: Floating-point Types, Storage
Classes, and Bit Fields.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
32
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
mikroC SPECIFICS
Page 41

Predefined Globals and Constants
To facilitate PIC programming, mikroC implements a number of predefined globals and constants.
All PIC SFR registers are implicitly declared as global variables of
volatile
unsigned short. These identifiers have external linkage, and are visible in the
entire project. When creating a project, mikroC will include an appropriate .def
file, containing declarations of available SFR and constants (such as
T0IE, INTF,
etc). Identifiers are all in uppercase, identical to nomenclature in Microchip
datasheets. For the complete set of predefined globals and constants, look for
“Defs” in your mikroC installation folder, or probe the Code Assistant for specific
letters (Ctrl+Space in Editor).
Device Clock Constants
There are two built-in constants related to device clock:
___FOSC and ___FCY.
Constant ___FOSC equals the frequency that is provided by an external oscillator,
while ___FCY is the operating frequency of PIC. Both constants can be used anywhere in the code, and are automatically updated as you change target PIC in your
project. Source files that use these constants are recompiled any time the clock is
changed in IDE.
Accessing Individual Bits
mikroC allows you to access individual bits of 8-bit variables, types char and
unsigned short. Simply use the direct member selector (.) with a variable,
followed by one of identifiers
F0, F1, … , F7. For example:
// If RB0 is set, set RC0:
if (PORTB.F0) PORTC.F0 = 1;
There is no need for any special declarations; this kind of selective access is an
intrinsic feature of mikroC and can be used anywhere in the code. Identifiers
F0–F7 are not case sensitive and have a specific namespace.
Provided you are familiar with the particular chip, you can access bits by their
name:
INTCON.TMR0F = 0;
// Clear TMR0F
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
33
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 42

Interrupts
Interrupts can be easily handled by means of reserved word interrupt. mikroC
implictly declares function interrupt which cannot be redeclared. Its prototype is:
void interrupt(void);
Write your own definition (function body) to handle interrupts in your application.
mikroC saves the following SFR on stack when entering interrupt and pops them
back upon return:
PIC12 and PIC16 family:
W, STATUS, FSR, PCLATH
PIC18 family: FSR (fast context is used to save WREG, STATUS, BSR)
Note: mikroC does not support low priority interrupts; for PIC18 family, interrupts
must be of high priority.
Function Calls from Interrupt
You cannot call functions from within interrupt routine, but you can make a
function call from embedded assembly in interrupt. For this to work, the called
function (
func1 in further text) must fulfill the following conditions:
1.
func1 does not use stack (or the stack is saved before call, and restored after),
2. func1 must use global variables only.
The stated rules also apply to all the functions called from within
func1.
Note: mikroC linker ignores calls to functions that occur only in interrupt assembler. For linker to recognize these functions, you need to make a call in C code,
outside of interrupt body.
Here is a simple example of handling the interrupts from TMR0 (if no other
interrupts are allowed):
void interrupt() {
counter++;
TMR0 = 96;
INTCON = $20;
}
//~
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
34
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 43

Linker Directives
mikroC uses internal algorithm to distribute objects within memory. If you need to
have variable or routine at specific predefined address, use linker directives
absolute and org.
Directive absolute
Directive absolute specifies the starting address in RAM for variable. If variable is
multi-byte, higher bytes are stored at consecutive locations. Directive absolute is
appended to the declaration of variable:
int foo absolute 0x23;
// Variable will occupy 2 bytes at addresses 0x23 and 0x24;
Be careful when using absolute directive, as you may overlap two variables by
mistake. For example:
char i absolute 0x33;
// Variable i will occupy 1 byte at address 0x33
long jjjj absolute 0x30;
// Variable will occupy 4 bytes at 0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33,
// so changing i changes jjjj highest byte at the same time
Directive org
Directive
org specifies the starting address of routine in ROM.
Directive org is appended to the function definition. Directives applied to nondefining declarations will be ignored, with an appropriate warning issued by linker. Directive
org cannot be applied to an interrupt routine.
Here is a simple example:
void func(char par) org 0x200 {
// Function will start at address 0x200
nop;
}
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
35
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 44

These topics provide a formal definition of the mikroC lexical elements. They
describe the different categories of word-like units (tokens) recognized by a language.
In the tokenizing phase of compilation, the source code file is parsed (that is, broken down) into tokens and whitespace. The tokens in mikroC are derived from a
series of operations performed on your programs by the compiler and its built-in
preprocessor.
A mikroC program starts as a sequence of ASCII characters representing the
source code, created by keystrokes using a suitable text editor (such as the mikroC
editor). The basic program unit in mikroC is the file. This usually corresponds to a
named file located in RAM or on disk and having the extension
.c.
Whitespace
Whitespace is the collective name given to spaces (blanks), horizontal and vertical
tabs, newline characters, and comments. Whitespace can serve to indicate where
tokens start and end, but beyond this function, any surplus whitespace is discarded. For example, the two sequences
int i; float f;
and
int i;
float f;
are lexically equivalent and parse identically to give the six tokens.
The ASCII characters representing whitespace can occur within literal strings, in
which case they are protected from the normal parsing process (they remain as
part of the string).
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
36
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
LEXICAL ELEMENTS
Page 45

Comments
Comments are pieces of text used to annotate a program, and are technically
another form of whitespace. Comments are for the programmer’s use only; they
are stripped from the source text before parsing. There are two ways to delineate
comments: the C method and the C++ method. Both are supported by mikroC.
C comments
C comment is any sequence of characters placed after the symbol pair
/*. The
comment terminates at the first occurrence of the pair
*/ following the initial /*.
The entire sequence, including the four comment-delimiter symbols, is replaced by
one space after macro expansion.
In mikroC,
int
/* type */i /* identifier */
;
parses as:
int i;
Note that mikroC does not support the nonportable token pasting strategy using
/**/. For more on token pasting, refer to Preprocessor topics.
C++ comments
mikroC allows single-line comments using two adjacent slashes (
//). The com-
ment can start in any position, and extends until the next new line. The following
code,
int i;
// this is a comment
int j;
parses as:
int i;
int j;
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
37
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 46

Token is the smallest element of a C program that is meaningful to the compiler.
The parser separates tokens from the input stream by creating the longest token
possible using the input characters in a left–to–right scan.
mikroC recognizes following kinds of tokens:
- keywords,
- identifiers,
- constants,
- operators,
- punctuators (also known as separators).
Token Extraction Example
Here is an example of token extraction. Let’s have the following code sequence:
inter = a+++b;
First, note that inter would be parsed as a single identifier, rather than as the
keyword
int followed by the identifier er.
The programmer who wrote the code might have intended to write
inter = a + (++b)
but it won’t work that way. The compiler would parse it as the following seven
tokens:
inter
// identifier
=
// assignment operator
a
// identifier
++
// postincrement operator
+
// addition operator
b
// identifier
;
// semicolon separator
Note that +++ parses as ++ (the longest token possible) followed by +.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
38
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
TOKENS
Page 47

Constants or literals are tokens representing fixed numeric or character values.
mikroC supports:
- integer constants,
- floating point constants,
- character constants,
- string constants (strings literals),
- enumeration constants.
The data type of a constant is deduced by the compiler using such clues as numeric value and the format used in the source code.
Integer Constants
Integer constants can be decimal (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16), binary (base
2), or octal (base 8). In the absence of any overriding suffixes, the data type of an
integer constant is derived from its value.
Long and Unsigned Suffixes
The suffix
L (or l) attached to any constant forces the constant to be represented
as a
long. Similarly, the suffix U (or u) forces the constant to be unsigned. You
can use both L and U suffixes on the same constant in any order or case: ul, Lu,
UL, etc.
In the absence of any suffix (
U, u, L, or l), constant is assigned the “smallest” of
the following types that can accommodate its value: short, unsigned short,
int, unsigned int, long int, unsigned long int.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
39
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
CONSTANTS
Page 48

Otherwise:
If the constant has a
U or u suffix, its data type will be the first of the following
that can accommodate its value: unsigned short, unsigned int, unsigned
long int.
If the constant has an
L or l suffix, its data type will be the first of the following
that can accommodate its value:
long int, unsigned long int.
If the constant has both U and L suffixes, (ul, lu, Ul, lU, uL, Lu, LU, or UL), its
data type will be
unsigned long int.
Decimal Constants
Decimal constants from -2147483648 to 4294967295 are allowed. Constants
exceeding these bounds will produce an “Out of range” error. Decimal constants
must not use an initial zero. An integer constant that has an initial zero is interpreted as an octal constant.
In the absence of any overriding suffixes, the data type of a decimal constant is
derived from its value, as shown below:
< -2147483648 Error: Out of range!
-2147483648 .. -32769 long
-32768 .. -129 int
-128 .. 127 short
128 .. 255 unsigned short
256 .. 32767 int
32768 .. 65535 unsigned int
65536 .. 2147483647 long
2147483648 .. 4294967295 unsigned long
> 4294967295 Error: Out of range!
Hexadecimal Constants
All constants starting with
0x (or 0X) are taken to be hexadecimal. In the absence
of any overriding suffixes, the data type of an hexadecimal constant is derived
from its value, according to the rules presented above. For example,
0xC367 will
be treated as
unsigned int.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
40
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 49

Binary Constants
All constants starting with
0b (or 0B) are taken to be binary. In the absence of any
overriding suffixes, the data type of an binary constant is derived from its value,
according to the rules presented above. For example, 0b11101 will be treated as
short.
Octal Constants
All constants with an initial zero are taken to be octal. If an octal constant contains
the illegal digits 8 or 9, an error is reported. In the absence of any overriding suffixes, the data type of an octal constant is derived from its value, according to the
rules presented above. For example,
0777 will be treated as int.
Floating Point Constants
A floating-point constant consists of:
- Decimal integer,
- Decimal point,
- Decimal fraction,
-
e or E and a signed integer exponent (optional),
- Type suffix: f or F or l or L (optional).
You can omit either the decimal integer or the decimal fraction (but not both). You
can omit either the decimal point or the letter
e (or E) and the signed integer expo-
nent (but not both). These rules allow for conventional and scientific (exponent)
notations.
Negative floating constants are taken as positive constants with the unary operator
minus (
-) prefixed.
mikroC limits floating-point constants to range
±1.17549435082E38 .. ±6.80564774407E38.
mikroC floating-point constants are of type
double. Note that mikroC’s imple-
mentation of ANSI Standard considers
float and double (together with the
long double variant) to be the same type.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
41
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 50

Character Constants
A character constant is one or more characters enclosed in single quotes, such as
'A', '+', or '\n'. In C, single-character constants have data type int. Multi-
character constants are referred to as string constants or string literals. For more
information refer to String Constants.
Escape Sequences
The backslash character (
\) is used to introduce an escape sequence, which allows
the visual representation of certain nongraphic characters. One of the most common escape constants is the newline character (
\n).
A backslash is used with octal or hexadecimal numbers to represent the ASCII
symbol or control code corresponding to that value; for example,
'\x3F' for the
question mark. You can use any string of up to three octal or any number of hexadecimal numbers in an escape sequence, provided that the value is within legal
range for data type char (0 to 0xFF for mikroC). Larger numbers will generate the
compiler error “Numeric constant too large”.
For example, the octal number
\777 is larger than the maximum value allowed
(\377) and will generate an error. The first nonoctal or nonhexadecimal character
encountered in an octal or hexadecimal escape sequence marks the end of the
sequence.
Note: You must use
\\ to represent an ASCII backslash, as used in operating sys-
tem paths.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
42
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 51

The following table shows the available escape sequences in mikroC:
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
43
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Sequence Value Char What it does
\a 0x07
BEL Audible bell
\b 0x08
BS Backspace
\f 0x0C
FF Formfeed
\n 0x0A
LF Newline (Linefeed)
\r 0x0D
CR Carriage Return
\t 0x09
HT Tab (horizontal)
\v 0x0B
VT Vertical Tab
\\ 0x5C
\ Backslash
\' 0x27
'
Single quote
(Apostrophe)
\" 0x22
" Double quote
\? 0x3F
? Question mark
\O
any
O = string of up to 3
octal digits
\xH
any
H = string of hex dig-
its
\XH
any
H = string of hex dig-
its
Page 52

String Constants
String constants, also known as string literals, are a special type of constants
which store fixed sequences of characters. A string literal is a sequence of any
number of characters surrounded by double quotes:
"This is a string."
The null string, or empty string, is written like "". A literal string is stored internally as the given sequence of characters plus a final null character. A null string is
stored as a single null character.
The characters inside the double quotes can include escape sequences, e.g.
"\t\"Name\"\\\tAddress\n\n"
Adjacent string literals separated only by whitespace are concatenated during the
parsing phase. For example:
"This is " "just"
" an example."
is an equivalent to
"This is just an example."
Line continuation with backslash
You can also use the backslash (
\) as a continuation character to extend a string
constant across line boundaries:
"This is really \
a one-line string."
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
44
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 53

Enumeration Constants
Enumeration constants are identifiers defined in enum type declarations. The identifiers are usually chosen as mnemonics to assist legibility. Enumeration constants
are of
int type. They can be used in any expression where integer constants are
valid.
For example:
enum weekdays {SUN = 0, MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT};
The identifiers (enumerators) used must be unique within the scope of the enum
declaration. Negative initializers are allowed. See Enumerations for details of
enum declarations.
Pointer Constants
A pointer or the pointed-at object can be declared with the const modifier.
Anything declared as a const cannot be have its value changed. It is also illegal
to create a pointer that might violate the nonassignability of a constant object.
Constant Expressions
A constant expression is an expression that always evaluates to a constant and
consists only of constants (literals) or symbolic constants. It is evaluated at compile-time and it must evaluate to a constant that is in the range of representable
values for its type. Constant expressions are evaluated just as regular expressions
are.
Constant expressions can consist only of the following: literals, enumeration constants, simple constants (no constant arrays or structures), sizeof operators.
Constant expressions cannot contain any of the following operators, unless the
operators are contained within the operand of a
sizeof operator: assignment,
comma, decrement, function call, increment.
You can use a constant expression anywhere that a constant is legal.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
45
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 54

Keywords are words reserved for special purposes and must not be used as normal
identifier names.
Beside standard C keywords, all relevant SFR are defined as global variables and
represent reserved words that cannot be redefined (for example:
TMR0, PCL, etc).
Probe the Code Assistant for specific letters (Ctrl+Space in Editor) or refer to
Predefined Globals and Constants.
Here is the alphabetical listing of keywords in C:
asm enum signed
auto extern sizeof
break float static
case for struct
char goto switch
const if typedef
continue int union
default long unsigned
do register void
double return volatile
else short while
Also, mikroC includes a number of predefined identifiers used in libraries. You
could replace these by your own definitions, if you plan to develop your own
libraries. For more information, see mikroC Libraries.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
46
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
KEYWORDS
Page 55

Identifiers are arbitrary names of any length given to functions, variables, symbolic constants, user-defined data types, and labels. All these program elements will
be referred to as objects throughout the help (not to be confused with the meaning
of object in object-oriented programming).
Identifiers can contain the letters
a to z and A to Z, the underscore character “_”,
and the digits 0 to 9. The only restriction is that the first character must be a letter
or an underscore.
Case Sensitivity
mikroC identifiers are not case sensitive at present, so that Sum, sum, and suM represent an equivalent identifier. However, future versions of mikroC will offer the
option of activating/suspending case sensitivity. The only exceptions at present are
the reserved words
main and interrupt which must be written in lowercase.
Uniqueness and Scope
Although identifier names are arbitrary (within the rules stated), errors result if the
same name is used for more than one identifier within the same scope and sharing
the same name space. Duplicate names are legal for different name spaces regardless of scope rules. For more information on scope, refer to Scope and Visibility.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
47
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
IDENTIFIERS
Page 56

The mikroC punctuators (also known as separators) include brackets, parentheses,
braces, comma, semicolon, colon, asterisk, equal sign, and pound sign. Most of
these punctuators also function as operators.
Brackets
Brackets [ ] indicate single and multidimensional array subscripts:
char ch, str[] = "mikro";
int mat[3][4];
/* 3 x 4 matrix */
ch = str[3];
/* 4th element */
Parentheses
Parentheses ( ) are used to group expressions, isolate conditional expressions,
and indicate function calls and function parameters:
d = c * (a + b);
/* override normal precedence */
if (d == z) ++x;
/* essential with conditional statement */
func();
/* function call, no args */
void func2(int n);
/* function declaration with parameters */
Parentheses are recommended in macro definitions to avoid potential precedence
problems during expansion:
#define CUBE(x) ((x)*(x)*(x))
For more information, refer to Expressions and Operators Precedence.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
48
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
PUNCTUATORS
Page 57

Braces
Braces { } indicate the start and end of a compound statement:
if (d == z) {
++x;
func();
}
The closing brace serves as a terminator for the compound statement, so a semicolon is not required after the }, except in structure declarations. Often, the semicolon is illegal, as in
if (statement)
{ ... }; /* illegal semicolon! */
else
{ ... };
For more information, refer to Compound Statements.
Comma
The comma (,) separates the elements of a function argument list:
void func(int n, float f, char ch);
The comma is also used as an operator in comma expressions. Mixing the two
uses of comma is legal, but you must use parentheses to distinguish them. Note
that (
exp1, exp2) evalutates both but is equal to the second:
/* call func with two args */
func(i, j);
/* also calls func with two args! */
func((exp1, exp2), (exp3, exp4, exp5));
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
49
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 58

Semicolon
The semicolon (;) is a statement terminator. Any legal C expression (including the
empty expression) followed by a semicolon is interpreted as a statement, known as
an expression statement. The expression is evaluated and its value is discarded. If
the expression statement has no side effects, mikroC might ignore it.
a + b;
/* evaluate a + b, but discard value */
++a;
/* side effect on a, but discard value of ++a */
;
/* empty expression or a null statement */
Semicolons are sometimes used to create an empty statement:
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) ;
For more information, see Statements.
Colon
Use the colon (:) to indicate a labeled statement. For example:
start: x = 0;
...
goto start;
Labels are discussed in Labeled Statements.
Asterisk (Pointer Declaration)
The asterisk (*) in a declaration denotes the creation of a pointer to a type:
char *char_ptr;
/* a pointer to char is declared */
You can also use the asterisk as an operator to either dereference a pointer or as
the multiplication operator:
i = *char_ptr;
For more information, see Pointers.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
50
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 59

Equal Sign
The equal sign (=) separates variable declarations from initialization lists:
int test[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int x = 5;
The equal sign is also used as the assignment operator in expressions:
int a, b, c;
a = b + c;
For more information, see Assignment Operators.
Pound Sign (Preprocessor Directive)
The pound sign (#) indicates a preprocessor directive when it occurs as the first
nonwhitespace character on a line. It signifies a compiler action, not necessarily
associated with code generation. See Preprocessor Directives for more information.
# and ## are also used as operators to perform token replacement and merging
during the preprocessor scanning phase. See Preprocessor Operators.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
51
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 60

Objects
An object is a specific region of memory that can hold a fixed or variable value
(or set of values). To prevent confusion, this use of the word object is different
from the more general term used in object-oriented languages. Our definiton of the
word would encompass functions, variables, symbolic constants, user-defined data
types, and labels.
Each value has an associated name and type (also known as a data type). The
name is used to access the object. This name can be a simple identifier, or it can
be a complex expression that uniquely references the object.
Objects and Declarations
Declarations establish the necessary mapping between identifiers and objects.
Each declaration associates an identifier with a data type.
Associating identifiers with objects requires each identifier to have at least two
attributes: storage class and type (sometimes referred to as data type). The mikroC
compiler deduces these attributes from implicit or explicit declarations in the
source code. Commonly, only the type is explicitly specified and the storage class
specifier assumes automatic value auto.
Generally speaking, an identifier cannot be legally used in a program before its
declaration point in the source code. Legal exceptions to this rule (known as forward references) are labels, calls to undeclared functions, and struct or union tags.
The range of objects that can be declared includes:
variables; functions; types; arrays of other types; structure, union, and enumeration
tags; structure members; union members; enumeration constants; statement labels;
preprocessor macros.
The recursive nature of the declarator syntax allows complex declarators. You’ll
probably want to use typedefs to improve legibility if constructing complex
objects.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
52
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
OBJECTS AND LVALUES
Page 61

Lvalues
An lvalue is an object locator: an expression that designates an object. An example
of an lvalue expression is *P, where P is any expression evaluating to a non-null
pointer. A modifiable lvalue is an identifier or expression that relates to an object
that can be accessed and legally changed in memory. A const pointer to a constant,
for example, is not a modifiable lvalue. A pointer to a constant can be changed
(but its dereferenced value cannot).
Historically, the l stood for “left”, meaning that an lvalue could legally stand on
the left (the receiving end) of an assignment statement. Now only modifiable lvalues can legally stand to the left of an assignment operator. For example, if a and b
are nonconstant integer identifiers with properly allocated memory storage, they
are both modifiable lvalues, and assignments such as
a = 1 and b = a + b are
legal.
Rvalues
The expression a + b is not an lvalue: a + b = a is illegal because the expression on the left is not related to an object. Such expressions are sometimes called
rvalues (short for right values).
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
53
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 62

Scope
The scope of identifier is the part of the program in which the identifier can be
used to access its object. There are different categories of scope: block (or local),
function, function prototype, and file. These depend on how and where identifiers
are declared.
Block Scope
The scope of an identifier with block (or local) scope starts at the declaration point
and ends at the end of the block containing the declaration (such a block is known
as the enclosing block). Parameter declarations with a function definition also
have block scope, limited to the scope of the function body.
File Scope
File scope identifiers, also known as globals, are declared outside of all blocks;
their scope is from the point of declaration to the end of the source file.
Function Scope
The only identifiers having function scope are statement labels. Label names can
be used with goto statements anywhere in the function in which the label is
declared. Labels are declared implicitly by writing label_name: followed by a
statement. Label names must be unique within a function.
Function Prototype Scope
Identifiers declared within the list of parameter declarations in a function prototype (not part of a function definition) have function prototype scope. This scope
ends at the end of the function prototype.
Tag Scope
Structure, union, and enumeration tags are somewhat specific in mikroC. Due to
separate name space, tags are virtually removed from normal scope rules: they
have file scope, but override any block rules. Thus, deeply nested declaration of
structure is identical to an equivalent global declaration. As a consequence, once
that you have defined a tag, you cannot redefine it in any block within file.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
54
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
SCOPE AND VISIBILITY
Page 63

Visibility
The visibility of an identifier is that region of the program source code from which
legal access can be made to the identifier’s associated object.
Scope and visibility usually coincide, though there are circumstances under which
an object becomes temporarily hidden by the appearance of a duplicate identifier:
the object still exists but the original identifier cannot be used to access it until the
scope of the duplicate identifier is ended.
Technically, visibility cannot exceed scope, but scope can exceed visibility. Take a
look at the following example:
void f (int i) {
int j;
// auto by default
j = 3;
// int i and j are in scope and visible
{
// nested block
double j;
// j is local name in the nested block
j = 0.1;
// i and double j are visible;
// int j = 3 in scope but hidden
}
// double j out of scope
j += 1;
// int j visible and = 4
}
// i and j are both out of scope
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
55
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 64

Name space is the scope within which an identifier must be unique. C uses four
distinct categories of identifiers:
Goto label names
These must be unique within the function in which they are declared.
Structure, union, and enumeration tags
These must be unique within the block in which they are defined. Tags declared
outside of any function must be unique.
Structure and union member names
These must be unique within the structure or union in which they are defined.
There is no restriction on the type or offset of members with the same member
name in different structures.
Variables, typedefs, functions, and enumeration members
These must be unique within the scope in which they are defined. Externally
declared identifiers must be unique among externally declared variables.
Duplicate names are legal for different name spaces regardless of scope rules.
For example:
int blue = 73;
{
// open a block
enum colors { black, red, green, blue, violet, white } c;
/* enumerator blue hides outer declaration of int blue */
struct colors { int i, j; };
// ILLEGAL: colors duplicate tag
double red = 2;
// ILLEGAL: redefinition of red
}
blue = 37;
// back in int blue scope
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
56
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
NAME SPACES
Page 65

Duration, closely related to storage class, defines the period during which the
declared identifiers have real, physical objects allocated in memory. We also distinguish between compile-time and run-time objects. Variables, for instance, unlike
typedefs and types, have real memory allocated during run time. There are two
kinds of duration: static and local.
Static Duration
Memory is allocated to objects with static duration as soon as execution is underway; this storage allocation lasts until the program terminates. Static duration
objects usually reside in fixed data segments allocated according to the memory
model in force. All globals have static duration. All functions, wherever defined,
are objects with static duration. Other variables can be given static duration by
using the explicit
static or extern storage class specifiers.
In mikroC, static duration objects are not initialized to zero (or null) in the absence
of any explicit initializer.
An object can have static duration and local scope – see the example on the following page.
Local Duration
Local duration objects are also known as automatic objects. They are created on
the stack (or in a register) when the enclosing block or function is entered. They
are deallocated when the program exits that block or function. Local duration
objects must be explicitly initialized; otherwise, their contents are unpredictable.
The storage class specifier
auto can be used when declaring local duration vari-
ables, but is usually redundant, because auto is the default for variables declared
within a block.
An object with local duration also has local scope, because it does not exist outside of its enclosing block. The converse is not true: a local scope object can have
static duration.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
57
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
DURATION
Page 66

Here is an example of two objects with local scope, but with different duration:
void f() {
/* local duration var; init a upon every call to f */
int a = 1;
/* static duration var; init b only upon 1st call to f */
static int b = 1;
/* checkpoint! */
a++;
b++;
}
void main() {
/* At checkpoint, we will have: */
f();
// a=1, b=1, after first call,
f();
// a=1, b=2, after second call,
f();
// a=1, b=3, after third call,
// etc.
}
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
58
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 67

C is strictly typed language, which means that every object, function, and expression need to have a strictly defined type, known in the time of compilation. Note
that C works exclusively with numeric types.
The type serves:
- to determine the correct memory allocation required initially,
- to interpret the bit patterns found in the object during subsequent accesses,
- in many type-checking situations, to ensure that illegal assignments are trapped.
mikroC supports many standard (predefined) and user-defined data types, including signed and unsigned integers in various sizes, floating-point numbers in various precisions, arrays, structures, and unions. In addition, pointers to most of these
objects can be established and manipulated in memory.
The type determines how much memory is allocated to an object and how the program will interpret the bit patterns found in the object’s storage allocation. A given
data type can be viewed as a set of values (often implementation-dependent) that
identifiers of that type can assume, together with a set of operations allowed on
those values. The compile-time operator,
sizeof, lets you determine the size in
bytes of any standard or user-defined type.
The mikroC standard libraries and your own program and header files must provide unambiguous identifiers (or expressions derived from them) and types so that
mikroC can consistently access, interpret, and (possibly) change the bit patterns in
memory corresponding to each active object in your program.
Type Categories
The fudamental types represent types that cannot be separated into smaller parts.
They are sometimes referred to as unstructured types. The fundamental types are
void, char, int, float, and double, together with short, long, signed, and
unsigned variants of some of these.
The derived types are also known as structured types. The derived types include
pointers to other types, arrays of other types, function types, structures, and
unions.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
59
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
TYPES
Page 68

Arithmetic Types
The arithmetic type specifiers are built from the following keywords: void, char,
int, float, and double, together with prefixes short, long, signed, and
unsigned. From these keywords you can build the integral and floating-point
types. Overview of types is given on the following page.
Integral Types
Types
char and int, together with their variants, are considered integral data
types. Variants are created by using one of the prefix modifiers short, long,
signed, and unsigned.
The table below is the overview of the integral types – keywords in parentheses
can be (and often are) omitted.
The modifiers signed and unsigned can be applied to both char and int. In
the absence of unsigned prefix, signed is automatically assumed for integral types.
The only exception is the char, which is unsigned by default. The keywords
signed and unsigned, when used on their own, mean signed int and
unsigned int, respectively.
The modifiers short and long can be applied only to the int. The keywords
short and long used on their own mean short int and long int, respective-
ly.
Floating-point Types
Types
float and double, together with the long double variant, are consid-
ered floating-point types. mikroC’s implementation of ANSI Standard considers all
three to be the same type.
Floating point in mikroC is implemented using the Microchip AN575 32-bit format (IEEE 754 compliant).
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
60
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
FUNDAMENTAL TYPES
Page 69

Below is the overview of arithmetic types:
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
61
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Type Size Range
(unsigned) char
8-bit 0 .. 255
signed char
8-bit - 128 .. 127
(signed) short (int)
8-bit - 128 .. 127
unsigned short (int)
8-bit 0 .. 255
(signed) int
16-bit -32768 .. 32767
unsigned (int)
16-bit 0 .. 65535
(signed) long (int)
32-bit -2147483648 .. 2147483647
unsigned long (int)
32-bit 0 .. 4294967295
float
32-bit
±1.17549435082E-38 ..
±6.80564774407E38
double
32-bit
±1.17549435082E-38 ..
±6.80564774407E38
long double
32-bit
±1.17549435082E-38 ..
±6.80564774407E38
Page 70

Enumerations
An enumeration data type is used for representing an abstract, discreet set of values with appropriate symbolic names.
Enumeration Declaration
Enumeration is declared like this:
enum
tag{enumeration-list
};
Here,
tag
is an optional name of the enumeration;
enumeration-list
is a list
of discreet values, enumerators. The enumerators listed inside the braces are also
known as enumeration constants. Each is assigned a fixed integral value. In the
absence of explicit initializers, the first enumerator is set to zero, and each succeeding enumerator is set to one more than its predecessor.
Variables of
enum type are declared same as variables of any other type. For
example, the following declaration
enum colors {black, red, green, blue, violet, white} c;
establishes a unique integral type, colors, a variable c of this type, and a set of
enumerators with constant integer values (black = 0, red = 1, ...). In C, a
variable of an enumerated type can be assigned any value of type int – no type
checking beyond that is enforced. That is:
c = red;
// OK
c = 1;
// Also OK, means the same
With explicit integral initializers, you can set one or more enumerators to specific
values. The initializer can be any expression yielding a positive or negative integer
value (after possible integer promotions). Any subsequent names without initializers will then increase by one. These values are usually unique, but duplicates are
legal.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
62
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 71

The order of constants can be explicitly re-arranged. For example:
enum colors { black,
// value 0
red,
// value 1
green,
// value 2
blue=6,
// value 6
violet,
// value 7
white=4 };
// value 4
Initializer expression can include previously declared enumerators. For example,
in the following declaration:
enum memory_sizes { bit = 1, nibble = 4 * bit,
byte = 2 * nibble, kilobyte = 1024 * byte };
nibble would acquire the value 4, byte the value 8, and kilobyte the value
8192.
Anonymous Enum Type
In our previous declaration, the identifier
colors is the optional enumeration tag
that can be used in subsequent declarations of enumeration variables of type
colors:
enum colors bg, border;
// declare variables bg and border
As with struct and union declarations, you can omit the tag if no further variables
of this enum type are required:
/* Anonymous enum type: */
enum {black, red, green, blue, violet, white} color;
Enumeration Scope
Enumeration tags share the same name space as structure and union tags.
Enumerators share the same name space as ordinary variable identifiers. For more
information, consult Name Spaces.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
63
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 72

Void Type
void is a special type indicating the absence of any value. There are no objects of
void; instead, void is used for deriving more complex types.
Void Functions
Use the
void keyword as a function return type if the function does not return a
value. For example:
void print_temp(char temp) {
Lcd_Out_Cp("Temperature:");
Lcd_Out_Cp(temp);
Lcd_Chr_Cp(223);
// degree character
Lcd_Chr_Cp('C');
}
Use void as a function heading if the function does not take any parameters.
Alternatively, you can just write empty parentheses:
main(void) {
// same as main()
...
}
Generic Pointers
Pointers can be declared as
void, meaning that they can point to any type. These
pointers are sometimes called generic.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
64
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 73

The derived types are also known as structured types. These types are used as elements in creating more complex user-defined types.
Arrays
Array is the simplest and most commonly used structured type. Variable of array
type is actually an array of objects of the same type. These objects represent elements of an array and are identified by their position in array. An array consists of
a contiguous region of storage exactly large enough to hold all of its elements.
Array Declaration
Array declaration is similar to variable declaration, with the brackets added after
identifer:
type array_name[constant-expression
]
This declares an array named as
array_name
composed of elements of
type
.
The
type
can be scalar type (except void), user-defined type, pointer, enumera-
tion, or another array. Result of the
constant-expression
within the brackets
determines the number of elements in array. If an expression is given in an array
declarator, it must evaluate to a positive constant integer. The value is the number
of elements in the array.
Each of the elements of an array is numbered from 0 through the number of elements minus one. If the number is
n, elements of array can be approached as
variables
array_name
[0] ..
array_name
[n-1] of
type
.
Here are a few examples of array declaration:
#define MAX = 50
int vector_one[10];
/* an array of 10 integers */
float vector_two[MAX];
/* an array of 50 floats */
float vector_three[MAX - 20];
/* an array of 30 floats */
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
65
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
DERIVED TYPES
Page 74

Array Initialization
Array can be initialized in declaration by assigning it a comma-delimited sequence
of values within braces. When initializing an array in declaration, you can omit the
number of elements – it will be automatically determined acording to the number
of elements assigned. For example:
/* An array which holds number of days in each month: */
int days[12] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
/* This declaration is identical to the previous one */
int days[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
If you specify both the length and starting values, the number of starting values
must not exceed the specified length. Vice versa is possible, when the trailing
“excess” elements will be assigned some encountered runtime values from memory.
In case of array of
char, you can use a shorter string literal notation. For example:
/* The two declarations are identical: */
const char msg1[] = {'T', 'e', 's', 't', '\0'};
const char msg2[] = "Test";
For more information on string literals, refer to String Constants.
Arrays in Expressions
When name of the array comes up in expression evaluation (except with operators
& and sizeof ), it is implicitly converted to the pointer pointing to array’s first
element. See Arrays and Pointers for more information.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
66
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 75

Multi-dimensional Arrays
An array is one-dimensional if it is of scalar type. One-dimensional arrays are
sometimes referred to as vectors.
Multidimensional arrays are constructed by declaring arrays of array type. These
arrays are stored in memory in such way that the right most subscript changes
fastest, i.e. arrays are stored “in rows”. Here is a sample 2-dimensional array:
float m[50][20];
/* 2-dimensional array of size 50x20 */
Variable m is an array of 50 elements, which in turn are arrays of 20 floats each.
Thus, we have a matrix of 50x20 elements: the first element is m[0][0], the last
one is
m[49][19]. First element of the 5th row would be m[0][5].
If you are not initializing the array in the declaration, you can omit the first dimension of multi-dimensional array. In that case, array is located elsewhere, e.g. in
another file. This is a commonly used technique when passing arrays as function
parameters:
int a[3][2][4];
/* 3-dimensional array of size 3x2x4 */
void func(int n[][2][4]) {
/* we can omit first dimension */
//...
n[2][1][3]++;
/* increment the last element*/
}//~
void main() {
//...
func(a);
}//~!
You can initialize a multi-dimensional array with an appropriate set of values
within braces. For example:
int a[3][2] = {{1,2}, {2,6}, {3,7}};
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
67
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 76

Pointers
Pointers are special objects for holding (or “pointing to”) memory addresses. In C,
address of an object in memory can be obtained by means of unary operator &. To
reach the pointed object, we use indirection operator (
*) on a pointer.
A pointer of type “pointer to object of type” holds the address of (that is, points to)
an object of type. Since pointers are objects, you can have a pointer pointing to a
pointer (and so on). Other objects commonly pointed at include arrays, structures,
and unions.
A pointer to a function is best thought of as an address, usually in a code segment,
where that function’s executable code is stored; that is, the address to which control is transferred when that function is called.
Although pointers contain numbers with most of the characteristics of unsigned
integers, they have their own rules and restrictions for declarations, assignments,
conversions, and arithmetic. The examples in the next few sections illustrate these
rules and restrictions.
Note: Currently, mikroC does not support pointers to functions, but this feature
will be implemented in future versions.
Pointer Declarations
Pointers are declared same as any other variable, but with
* ahead of identifier.
Type at the beginning of declaration specifies the type of a pointed object. A pointer must be declared as pointing to some particular type, even if that type is void,
which really means a pointer to anything. Pointers to
void are often called gener-
ic pointers, and are treated as pointers to char in mikroC.
If type is any predefined or user-defined type, including void, the declaration
type
*p;
/* Uninitialized pointer */
declares p to be of type “pointer to
type
”. All the scoping, duration, and visibility
rules apply to the p object just declared. You can view the declaration in this way:
if
*p is an object of
type
, then p has to be a pointer to such objects.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
68
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 77

Note: You must initialize pointers before using them! Our previously declared
pointer
*p is not initialized (i.e. assigned a value), so it cannot be used yet.
Note: In case of multiple pointer declarations, each identifier requires an indirect
operator. For example:
int *pa, *pb, *pc;
/* is same as: */
int *pa;
int *pb;
int *pc;
Once declared, though, a pointer can usually be reassigned so that it points to an
object of another type. mikroC lets you reassign pointers without typecasting, but
the compiler will warn you unless the pointer was originally declared to be pointing to
void. You can assign a void pointer to a non-void pointer – refer to Void
Type for details.
Null Pointers
A null pointer value is an address that is guaranteed to be different from any valid
pointer in use in a program. Assigning the integer constant 0 to a pointer assigns a
null pointer value to it. Instead of zero, the mnemonic
NULL (defined in the stan-
dard library header files, such as stdio.h) can be used for legibility. All pointers
can be successfully tested for equality or inequality to
NULL.
For example:
int *pn = 0; /* Here's one null pointer */
int *pn = NULL; /* This is an equivalent declaration */
/* We can test the pointer like this: */
if ( pn == 0 ) { ... }
/* .. or like this: */
if ( pn == NULL ) { ... }
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
69
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 78

Pointer Arithmetic
Pointer arithmetic in C is limited to:
- assigning one pointer to another,
- comparing two pointers,
- comparing pointer to zero (
NULL),
- adding/subtracting pointer and an integer value,
- subtracting two pointers.
The internal arithmetic performed on pointers depends on the memory model in
force and the presence of any overriding pointer modifiers. When performing
arithmetic with pointers, it is assumed that the pointer points to an array of
objects.
Arrays and Pointers
Arrays and pointers are not completely independent types in C. When name of the
array comes up in expression evaluation (except with operators
& and sizeof ), it
is implicitly converted to the pointer pointing to array’s first element. Due to this
fact, arrays are not modifiable lvalues.
Brackets
[ ] indicate array subscripts. The expression
id[exp
]
is defined as
*((id) + (
exp
))
where either:
id
is a pointer and
exp
is an integer, or
id
is an integer and
exp
is a pointer.
The following is true:
&a[i] = a + i
a[i] = *(a + i)
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
70
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 79

According to these guidelines, we can write:
pa = &a[4];
// pa points to a[4]
x = *(pa + 3);
// x = a[7]
y = *pa + 3;
// y = a[4] + 3
Also, you need to be careful with operator precedence:
*pa++;
// is equal to *(pa++), increments the pointer!
(*pa)++;
// increments the pointed object!
Following examples are also valid, but better avoid this syntax as it can make the
code really illegible:
(a + 1)[i] = 3;
// same as: *((a + 1) + i) = 3, i.e. a[i + 1] = 3
(i + 2)[a] = 0;
// same as: *((i + 2) + a) = 0, i.e. a[i + 2] = 0
Assignment and Comparison
You can use a simple assignment operator (=) to assign value of one pointer to
another if they are of the same type. If they are of different types, you must use a
typecast operator. Explicit type conversion is not necessary if one of the pointers is
generic (of
void type).
Assigning the integer constant 0 to a pointer assigns a null pointer value to it. The
mnemonic
NULL (defined in the standard library header files, such as stdio.h)
can be used for legibility.
Two pointers pointing into the same array may be compared by using relational
operators
==, !=, <, <=, >, and >=. Results of these operations are same as if they
were used on subscript values of array elements in question:
int *pa = &a[4], *pb = &a[2];
if (pa > pb) { ...
// this will be executed as 4 is greater than 2
}
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
71
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 80

You can also compare pointers to zero value – this tests if pointer actually points
to anything. All pointers can be successfully tested for equality or inequality to
NULL:
if (pa == NULL) { ... }
if (pb != NULL) { ... }
Note: Comparing pointers pointing to different objects/arrays can be performed at
programmer’s responsibility — precise overview of data’s physical storage is
required.
Pointer Addition
You can use operators
+, ++, and += to add an integral value to a pointer. The
result of addition is defined only if pointer points to an element of an array and if
the result is a pointer pointing into the same array (or one element beyond it).
If a pointer is declared to point to
type
, adding an integral value to the pointer
advances the pointer by that number of objects of type. Informally, you can think
of
P+n as advancing the pointer P by (n*sizeof(
type
)) bytes, as long as the
pointer remains within the legal range (first element to one beyond the last element). If
type
has size of 10 bytes, then adding 5 to a pointer to
type
advances
the pointer 50 bytes in memory. In case of void type, size of the step is one byte.
For example:
int a[10];
// array a containing 10 elements of int
int *pa = &a[0];
// pa is pointer to int, pointing to a[0]
*(pa + 3) = 6;
// pa+3 is a pointer pointing to a[3],
// so a[3] now equals 6
pa++;
// pa now points to the next element of array, a[1]
There is no such element as “one past the last element”, of course, but a pointer is
allowed to assume such a value. C “guarantees” that the result of addition is
defined even when pointing to one element past array. If
P points to the last array
element, P+1 is legal, but P+2 is undefined.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
72
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 81

This allows you to write loops which access the array elements in a sequence by
means of incrementing pointer — in the last iteration you will have a pointer
pointing to one element past an array, which is legal. However, applying the indirection operator (
*) to a “pointer to one past the last element” leads to undefined
behavior.
For example:
void f (some_type a[], int n) {
/* function f handles elements of array a; */
/* array a has n elements of some_type */
int i;
some_type *p = &a[0];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
/* .. here we do something with *p .. */
p++;
/* .. and with the last iteration p exceeds
the last element of array a */
}
/* at this point, *p is undefined! */
}
Pointer Subtraction
Similar to addition, you can use operators
-, --, and -= to subtract an integral
value from a pointer.
Also, you may subtract two pointers. Difference will equal the distance between
the two pointed addresses, in bytes.
For example:
int a[10];
int *pi1 = &a[0], *pi2 = &[4];
i = pi2 - pi1;
// i equals 8
pi2 -= (i >> 1);
// pi2 = pi2 - 4: pi2 now points to a[0]
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
73
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 82

Structures
A structure is a derived type usually representing a user-defined collection of
named members (or components). The members can be of any type, either fundamental or derived (with some restrictions to be noted later), in any sequence. In
addition, a structure member can be a bit field type not allowed elsewhere.
Unlike arrays, structures are considered single objects. The mikroC structure type
lets you handle complex data structures almost as easily as single variables.
Note: mikroC does not support anonymous structures (ANSI divergence).
Structure Declaration and Initialization
Structures are declared using the keyword
struct:
struct
tag{ member-declarator-list
};
Here,
tag
is the name of the structure;
member-declarator-list
is a list of
structure members, actually a list of variable declarations. Variables of structured
type are declared same as variables of any other type.
The member type cannot be the same as the struct type being currently declared.
However, a member can be a pointer to the structure being declared, as in the following example:
struct mystruct { mystruct s;};
/* illegal! */
struct mystruct { mystruct *ps;};
/* OK */
Also, a structure can contain previously defined structure types when declaring an
instance of a declared structure. Here is an example:
/* Structure defining a dot: */
struct Dot {float x, y;};
/* Structure defining a circle: */
struct Circle {
double r;
struct Dot center;
} o1, o2;
/* declare variables o1 and o2 of circle type */
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
74
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 83

Note that you can omit structure tag, but then you cannot declare additional
objects of this type elsewhere. For more information, see the “Untagged
Structures” below.
Structure is initialized by assigning it a comma-delimited sequence of values within braces, similar to array. Referring to declarations from the previous example:
/* Declare and initialize dots p and q: */
struct Dot p = {1., 1.}, q = {3.7, -0.5};
/* Initialize already declared circles o1 and o2: */
o1 = {1, {0, 0}};
// r is 1, center is at (0, 0)
o2 = {4, { 1.2, -3 }};
// r is 4, center is at (1.2, -3)
Incomplete Declarations
Incomplete declarations are also known as forward declarations. A pointer to a
structure type
A can legally appear in the declaration of another structure B before
A has been declared:
struct A;
// incomplete
struct B {struct A *pa;};
struct A {struct B *pb;};
The first appearance of A is called incomplete because there is no definition for it
at that point. An incomplete declaration is allowed here, because the definition of
B doesn’t need the size of A.
Untagged Structures and Typedefs
If you omit the structure tag, you get an untagged structure. You can use untagged
structures to declare the identifiers in the comma-delimited
struct-id-list to
be of the given structure type (or derived from it), but you cannot declare additional objects of this type elsewhere.
It is possible to create a typedef while declaring a structure, with or without a tag:
typedef struct { ... } Mystruct;
Mystruct s, *ps, arrs[10];
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
75
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 84

Structure Assignment
Variables of same structured type may be assigned one to another by means of
simple assignment operator (
=). This will copy the entire contents of the variable
to destination, regardless of the inner complexitiy of a given structure.
Note that two variables are of same structured type only if they were both defined
by the same instruction or were defined using the same type identifier. For example:
/* a and b are of the same type: */
struct {int m1, m2;} a, b;
/* But c and d are _not_ of the same type although
their structure descriptions are identical: */
struct {int m1, m2;} c;
struct {int m1, m2;} d;
Size of Structure
You can get size of the structure in memory by means of operator
sizeof. Size of
the structure does not necessarily need to be equal to the sum of its members’
sizes. It is often greater due to certain limitations of memory storage.
Structures and Functions
A function can return a structure type or a pointer to a structure type:
mystruct func1();
// func1() returns a structure
mystruct *func2();
// func2() returns pointer to structure
A structure can be passed as an argument to a function in the following ways:
void func1(mystruct s);
// directly
void func2(mystruct *sptr);
// via pointer
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
76
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 85

Structure Member Access
Structure and union members are accessed using the following two selection operators:
. (period)
-> (right arrow)
The operator
. is called the direct member selector and it is used to directly access
one of the structure’s members. Suppose that the object s is of struct type S. Then
if
m is a member identifier of type M declared in s, the expression
s.m
// direct access to member m
is of type M, and represents the member object m in s.
The operator
-> is called the indirect (or pointer) member selector. Suppose that
ps is a pointer to s. Then if m is a member identifier of type M declared in s, the
expression
ps->m
// indirect access to member m;
// identical to (*ps).m
is of type M, and represents the member object m in s. The expression ps->m is a
convenient shorthand for (*ps).m.
For example:
struct mystruct {
int i; char str[10]; double d;
} s, *sptr = &s;
.
.
.
s.i = 3;
// assign to the i member of mystruct s
sptr -> d = 1.23;
// assign to the d member of mystruct s
The expression s.m is an lvalue, provided that s is an lvalue and m is not an array
type. The expression sptr->m is an lvalue unless m is an array type.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
77
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 86

Accessing Nested Structures
If structure
B contains a field whose type is structure A, the members of A can be
accessed by two applications of the member selectors:
struct A {
int j; double x;
};
struct B {
int i; struct A a; double d;
} s, *sptr;
//...
s.i = 3;
// assign 3 to the i member of B
s.a.j = 2;
// assign 2 to the j member of A
sptr->d = 1.23;
// assign 1.23 to the d member of B
sptr->a.x = 3.14;
// assign 3.14 to x member of A
Structure Uniqueness
Each structure declaration introduces a unique structure type, so that in
struct A {
int i,j; double d;
} aa, aaa;
struct B {
int i,j; double d;
} bb;
the objects aa and aaa are both of type struct A, but the objects aa and bb are of
different structure types. Structures can be assigned only if the source and destination have the same type:
aa = aaa;
/* OK: same type, member by member assignment */
aa = bb;
/* ILLEGAL: different types */
/* but you can assign member by member: */
aa.i = bb.i;
aa.j = bb.j;
aa.d = bb.d;
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
78
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 87

Unions
Union types are derived types sharing many of the syntactic and functional features of structure types. The key difference is that a union allows only one of its
members to be “active” at any given time, the most recently changed member.
Note: mikroC does not support anonymous unions (ANSI divergence).
Union Declaration
Unions are declared same as structures, with the keyword
union used instead of
struct:
union
tag{ member-declarator-list
};
Unlike structures’ members, the value of only one of union’s members can be
stored at any time. Let’s have a simple example:
union myunion {
// union tag is 'myunion'
int i;
double d;
char ch;
} mu, *pm = μ
The identifier mu, of type union myunion, can be used to hold a 2-byte int, a
4-byte double, or a single-byte char, but only one of these at any given time.
Size of Union
The size of a union is the size of its largest member. In our previous example, both
sizeof(union myunion) and sizeof(mu) return 4, but 2 bytes are unused
(padded) when
mu holds an int object, and 3 bytes are unused when mu holds a
char.
Union Member Access
Union members can be accessed with the structure member selectors (
. and ->),
but care is needed. Check the example on the following page.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
79
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 88

Referring to declarations from the previous example:
mu.d = 4.016;
Lcd_Out_Cp(FloatToStr(mu.d));
// OK: displays mu.d = 4.016
Lcd_Out_Cp(IntToStr(mu.i));
// peculiar result
pm->i = 3;
Lcd_Out_Cp(IntToStr(mu.i));
// OK: displays mu.i = 3
The second Lcd_Out_Cp is legal, since mu.i is an integral type. However, the bit
pattern in mu.i corresponds to parts of the previously assigned double. As such,
it probably does not provide a useful integer interpretation.
When properly converted, a pointer to a union points to each of its members, and
vice versa.
Bit Fields
Bit fields are specified numbers of bits that may or may not have an associated
identifier. Bit fields offer a way of subdividing structures into named parts of userdefined sizes.
mikroC implementation of bit fields requires you to set aside a structure for the
purpose, i.e. you cannot have a structure containing bit fields and other objects.
Bit fields structure can contain up to 8 bits.
You cannot take the address of a bit field.
Note: If you need to handle specific bits of 8-bit variables (char and unsigned
short) or registers, you don’t need to declare bit fields. Much more elegant solution is to use mikroC’s intrinsic ability for individual bit access — see Accessing
Individual Bits for more information.
Bit Fields Declaration
Bit fields can be declared only in structures. Declare a structure normally, and
assign individual fields like this (fields need to be unsigned):
struct
tag
{ unsigned
bitfield-declarator-list
; }
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
80
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 89

Here,
tag
is an optional name of the structure;
bitfield-declarator-list
is
a list of bit fields. Each component identifer requires a colon and its width in bits
to be explicitly specified. Total width of all components cannot exceed one byte (8
bits).
As an object, bit fields structure takes one byte. Individual fields are packed within byte from right to left. In
bitfield-declarator-list
, you can omit identi-
fier(s) to create artificial “padding”, thus skipping irrelevant bits.
For example, if we need to manipulate only bits 2–4 of a register as one block, we
could create a structure:
struct {
unsigned : 2,
// Skip bits 0 and 1, no identifier here
mybits : 3;
// Relevant bits 2, 3, and 4
// Bits 5, 6, and 7 are implicitly left out
} myreg;
Here is an example:
typedef struct {
prescaler : 2; timeronoff : 1; postscaler : 4;} mybitfield;
which declares structured type mybitfield containing three components:
prescaler (bits 0 and 1), timeronoff (bit 2), and postscaler (bits 3, 4, 5,
and 6).
Bit Fields Access
Bit fields can be accessed in same way as the structure members. Use direct and
indirect member selector (
. and ->). For example, we could work with our
previously declared mybitfield like this:
// Declare a bit field TimerControl:
mybitfield TimerControl;
void main() {
TimerControl.prescaler = 0;
TimerControl.timeronoff = 1;
TimerControl.postscaler = 3;
T2CON = TimerControl;
}
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
81
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 90

C is strictly typed language, with each operator, statement and function demanding
appropriately typed operands/arguments. However, we often have to use objects of
“mismatching” types in expressions. In that case, type conversion is needed.
Conversion of object of one type is changing it to the same object of another type
(i.e. applying another type to a given object). C defines a set of standard conversions for built-in types, provided by compiler when necessary.
Conversion is required in following situations:
- if statement requires an expression of particular type (according to language
definition), and we use an expression of different type,
- if operator requires an operand of particular type, and we use an operand of
different type,
- if a function requires a formal parameter of particular type, and we pass it an
object of different type,
- if an expression following the keyword return does not match the declared
function return type,
- if intializing an object (in declaration) with an object of different type.
In these situations, compiler will provide an automatic implicit conversion of
types, without any user interference. Also, user can demand conversion explicitly
by means of typecast operator. For more information, refer to Explicit
Typecasting.
Standard Conversions
Standard conversions are built in C. These conversions are performed automatically, whenever required in the program. They can be also explicitly required by
means of typecast operator (refer to Explicit Typecasting).
The basic rule of automatic (implicit) conversion is that the operand of simpler
type is converted (promoted) to the type of more complex operand. Then, type of
the result is that of more complex operand.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
82
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
TYPES CONVERSIONS
Page 91

Arithmetic Conversions
When you use an arithmetic expression, such as
a+b, where a and b are of differ-
ent arithmetic types, mikroC performs implicit type conversions before the expression is evaluated. These standard conversions include promotions of “lower” types
to “higher” types in the interests of accuracy and consistency.
Assigning a signed character object (such as a variable) to an integral object
results in automatic sign extension. Objects of type
signed char always use
sign extension; objects of type unsigned char always set the high byte to zero
when converted to
int.
Converting a longer integral type to a shorter type truncates the higher order bits
and leaves low-order bits unchanged. Converting a shorter integral type to a longer
type either sign-extends or zero-fills the extra bits of the new value, depending on
whether the shorter type is signed or unsigned, respectively.
Note: Conversion of floating point data into integral value (in assignments or via
explicit typecast) produces correct results only if the
float value does not exceed
the scope of destination integral type.
First, any small integral types are converted according to the following rules:
1.
char converts to int
2. signed char converts to int, with the same value
3.
short converts to int, with the same value, sign-extended
4. unsigned short converts to unsigned int, with the same value, zero-filled
5. enum converts to int, with the same value
After this, any two values associated with an operator are either
int (including
the long and unsigned modifiers), or they are float (equivalent with double
and long double in mikroC).
1. If either operand is float, the other operand is converted to float
2. Otherwise, if either operand is unsigned long, the other operand is converted
to
unsigned long
3. Otherwise, if either operand is long, the other operand is converted to long
4. Otherwise, if either operand is unsigned, the other operand is converted to
unsigned
5. Otherwise, both operands are int
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
83
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 92

The result of the expression is the same type as that of the two operands.
Here are several examples of implicit conversion:
2+3.1
// = 2. + 3.1 = 5.1
5/4*3.
// = (5/4)*3. = 1*3. = 1.*3. = 3.0
3.*5/4
// = (3.*5)/4 = (3.*5.)/4 = 15./4 = 15./4. = 3.75
Pointer Conversions
Pointer types can be converted to other pointer types using the typecasting mechanism:
char *str;
int *ip;
str = (char *)ip;
More generally, the cast (
type
*) will convert a pointer to type “pointer to
type
”.
Explicit Types Conversions (Typecasting)
In most situations, compiler will provide an automatic implicit conversion of types
where needed, without any user interference. Also, you can explicitly convert an
operand to another type using the prefix unary typecast operator:
(
type) object
For example:
char a, b;
/* Following line will coerce a to unsigned int: */
(unsigned int) a;
/* Following line will coerce a to double,
then coerce b to double automatically,
resulting in double type value: */
(double) a + b;
// equivalent to ((double) a) + b;
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
84
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 93

Introduction to Declarations
Declaration introduces one or several names to a program – it informs the compiler what the name represents, what is its type, what are allowed operations with it,
etc. This section reviews concepts related to declarations: declarations, definitions,
declaration specifiers, and initialization.
The range of objects that can be declared includes:
- Variables
- Constants
- Functions
- Types
- Structure, union, and enumeration tags
- Structure members
- Union members
- Arrays of other types
- Statement labels
- Preprocessor macros
Declarations and Definitions
Defining declarations, also known as definitions, beside introducing the name of
an object, also establish the creation (where and when) of the object; that is, the
allocation of physical memory and its possible initialization. Referencing declarations, or just declarations, simply make their identifiers and types known to the
compiler.
Here is an overview. Declaration is also a definition, except if:
- it declares a function without specifying its body,
- it has an extern specifier, and has no initializator or body (in case of func.),
- it is a typedef declaration.
There can be many referencing declarations for the same identifier, especially in a
multifile program, but only one defining declaration for that identifier is allowed.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
85
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
DECLARATIONS
Page 94

Let’s have an example:
/* Here is a nondefining declaration of function max; */
/* it merely informs compiler that max is a function */
int max();
/* Here is a definition of function max: */
int max(int x, int y) {
return (x>=y) ? x : y;
}
int i;
/* Definition of variable i */
int i;
/* Error: i is already defined! */
Declarations and Declarators
A declaration is a list of names. The names are sometimes referred to as declarators or identifiers. The declaration begins with optional storage class specifiers,
type specifiers, and other modifiers. The identifiers are separated by commas and
the list is terminated by a semicolon.
Declarations of variable identifiers have the following pattern:
storage-class[type-qualifier] type var1[=init1
],
var2[=init2
],
...;
where var1, var2,... are any sequence of distinct identifiers with optional initializers. Each of the variables is declared to be of
type
; if omitted,
type
defaults to
int. Specifier
storage-class
can take values extern, static, register, or
the default
auto. Optional
type-qualifier
can take values const or
volatile. For more details, refer to Storage Classes and Type Qualifiers.
Here is an example of variable declaration:
/* Create 3 integer variables called x, y, and z and
initialize x and y to the values 1 and 2, respectively: */
int x = 1, y = 2, z;
// z remains uninitialized
These are all defining declarations; storage is allocated and any optional initializers are applied.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
86
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 95

Linkage
An executable program is usually created by compiling several independent translation units, then linking the resulting object files with preexisting libraries. The
term translation unit refers to a source code file together with any included files,
but less any source lines omitted by conditional preprocessor directives. A problem
arises when the same identifier is declared in different scopes (for example, in different files), or declared more than once in the same scope.
Linkage is the process that allows each instance of an identifier to be associated
correctly with one particular object or function. All identifiers have one of two
linkage attributes, closely related to their scope: external linkage or internal linkage. These attributes are determined by the placement and format of your declarations, together with the explicit (or implicit by default) use of the storage class
specifier
static or extern.
Each instance of a particular identifier with external linkage represents the same
object or function throughout the entire set of files and libraries making up the
program. Each instance of a particular identifier with internal linkage represents
the same object or function within one file only.
Linkage Rules
Local names have internal linkage; same identifier can be used in different files to
signify different objects. Global names have external linkage; identifier signifies
the same object throughout all program files.
If the same identifier appears with both internal and external linkage within the
same file, the identifier will have internal linkage.
Internal Linkage Rules:
1. names having file scope, explicitly declared as
static, have internal linkage,
2. names having file scope, explicitly declared as const and not explicitly,
declared as extern, have internal linkage,
3.
typedef names have internal linkage,
4. enumeration constants have internal linkage .
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
87
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 96

External Linkage Rule:
1. names having file scope, that do not comply to any of previously stated internal
linkage rules, have external linkage.
The storage class specifiers
auto and register cannot appear in an external
declaration. For each identifier in a translation unit declared with internal linkage,
no more than one external definition can be given. An external definition is an
external declaration that also defines an object or function; that is, it also allocates
storage. If an identifier declared with external linkage is used in an expression
(other than as part of the operand of
sizeof), then exactly one external definition
of that identifier must be somewhere in the entire program.
mikroC allows later declarations of external names, such as arrays, structures, and
unions, to add information to earlier declarations. Here's an example:
int a[];
// No size
struct mystruct;
// Tag only, no member declarators
.
.
.
int a[3] = {1, 2, 3};
// Supply size and initialize
struct mystruct {
int i, j;
};
// Add member declarators
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
88
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 97

Storage Classes
Associating identifiers with objects requires each identifier to have at least two
attributes: storage class and type (sometimes referred to as data type). The mikroC
compiler deduces these attributes from implicit or explicit declarations in the
source code.
Storage class dictates the location (data segment, register, heap, or stack) of the
object and its duration or lifetime (the entire running time of the program, or during execution of some blocks of code). Storage class can be established by the
syntax of the declaration, by its placement in the source code, or by both of these
factors:
storage-class type identifier
The storage class specifiers in mikroC are:
auto
register
static
extern
Auto
Use the
auto modifer to define a local variable as having a local duration. This is
the default for local variables and is rarely used. You cannot use auto with globals. See also Functions.
Register
By default, mikroC stores variables within internal microcontroller memory. Thus,
modifier
register technically has no special meaning. mikroC compiler simply
ignores requests for register allocation.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
89
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 98

Static
Global name declared with
static specifier has internal linkage, meaning that it
is local for a given file. See Linkage for more information.
Local name declared with
static specifier has static duration. Use static with
a local variable to preserve the last value between successive calls to that function.
See Duration for more information.
Extern
Name declared with
extern specifier has external linkage, unless it has been pre-
viously declared as having internal linkage. Declaration is not a definition if it has
extern specifier and is not initialized. The keyword extern is optional for a
function prototype.
Use the
extern modifier to indicate that the actual storage and initial value of a
variable, or body of a function, is defined in a separate source code module.
Functions declared with extern are visible throughout all source files in a program, unless you redefine the function as
static.
See Linkage for more information.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
90
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
Page 99

Type Qualifiers
Type qualifiers const and volatile are optional in declarations and do not actually affect the type of declared object.
Qualifier const
Qualifier
const implies that the declared object will not change its value during
runtime. In declarations with const qualifier, you need to initialize all the objects
in the declaration.
Effectively, mikroC treats objects declared with
const qualifier same as literals or
preprocessor constants. Compiler will report an error if trying to change an object
declared with
const qualifier.
For example:
const double PI = 3.14159;
Qualifier volatile
Qualifier
volatile implies that variable may change its value during runtime
indepent from the program. Use the volatile modifier to indicate that a variable
can be changed by a background routine, an interrupt routine, or an I/O port.
Declaring an object to be volatile warns the compiler not to make assumptions
concerning the value of the object while evaluating expressions in which it occurs
because the value could change at any moment.
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
91
page
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
Page 100

Typedef Specifier
Specifier typedef introduces a synonym for a specified type. You can use type-
def declarations to construct shorter or more meaningful names for types already
defined by the language or for types that you have declared. You cannot use the
typedef specifier inside a function definition.
The specifier
typedef stands first in the declaration:
typedef <type-definition> synonym
;
The typedef keyword assigns the
synonym
to the
<type-definition>
. The
synonym
needs to be a valid identifier.
Declaration starting with the
typedef specifier does not introduce an object or
function of a given type, but rather a new name for a given type. That is, the
typedef declaration is identical to “normal” declaration, but instead of objects, it
declares types. It is a common practice to name custom type identifiers with starting capital letter — this is not required by C.
For example:
// Let's declare a synonym for "unsigned long int":
typedef unsigned long int Distance;
// Now, synonym "Distance" can be used as type identifier:
Distance i;
// declare variable i of unsigned long int
In typedef declaration, as in any declaration, you can declare several types at once.
For example:
typedef int *Pti, Array[10];
Here, Pti is synonym for type “pointer to int”, and Array is synonym for type
“array of 10
int elements”.
mikroC
- C Compiler for Microchip PIC microcontrollers
mikroC
making it simple...
92
MikroElektronika: Development tools - Books - Compilers
page
 Loading...
Loading...