Page 1
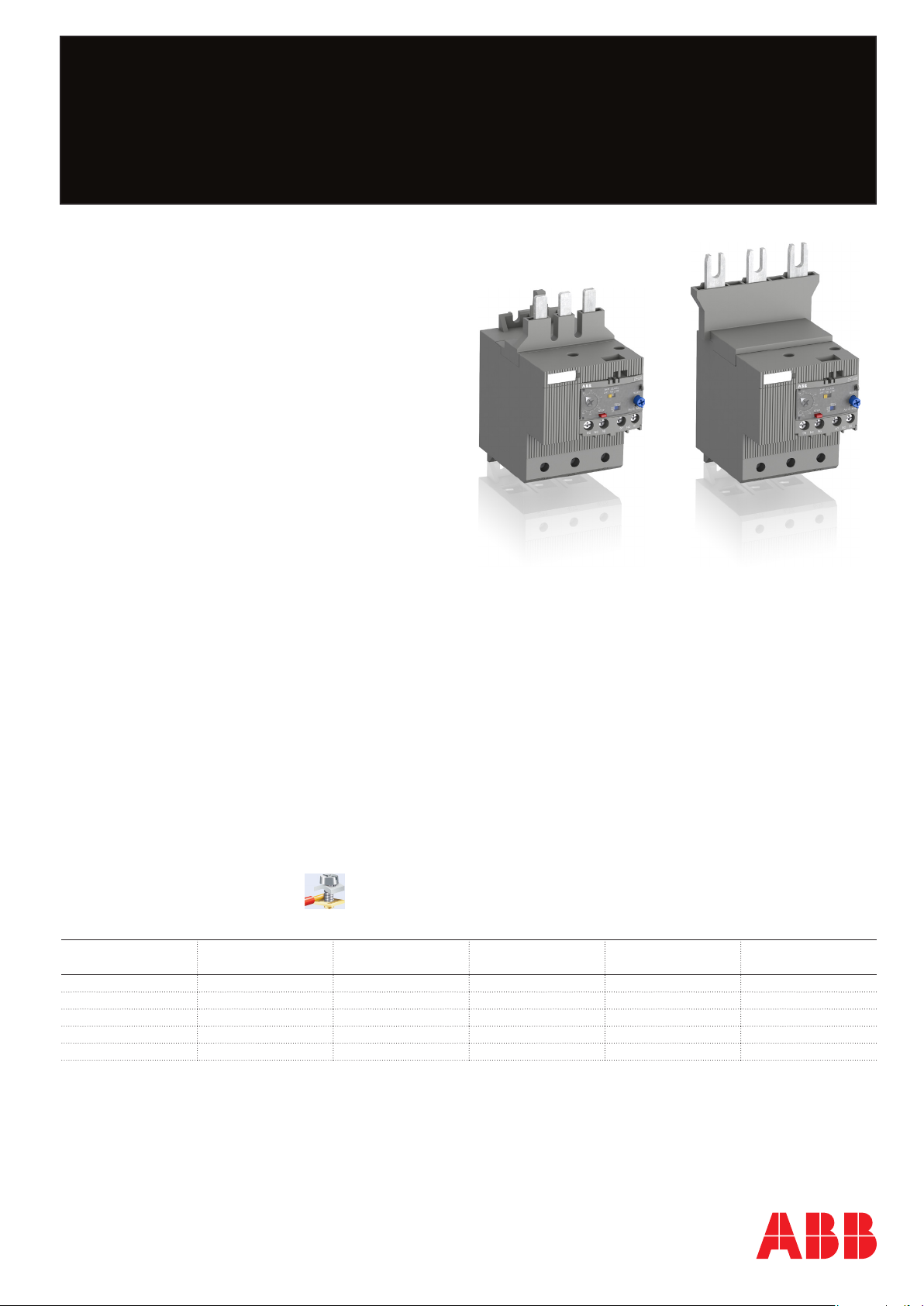
Data sheet
Electronic overload relay EF65, EF96 and EF146
Electronic overload relays offer reliable
protection in case of overload and
phase-failure. They are the alternative to
thermal overload relays. Motor starters
are combinations of overload relays and
contactors.
Description
– Overload protection – trip class 10E, 20E, 30E selectable
– Phase loss sensitivity
– Temperature compensation from -25 … +70 °C
– Adjustable current setting for overload protection
– Automatic or manual reset selectable
– Trip-free mechanism
– Status indication
– STOP and TEST function
– Direct mounting onto block contactors
– Sealable operating elements
– Self-supplied devices
Order data
EF65, EF96, EF146 screw terminal
For AF40 … AF146 block contactors
2CDC231001V0013
2CDC231003V0013
Setting range
A
20 ... 56 EF65-56 1SAX331001R1102 AF40, AF52, AF65 1 0.821
25 ... 70 EF65-70 1SAX331001R1101 AF40, AF52, AF65 1 0.821
20 ... 56 EF96-56 1SAX341001R1102 AF80, AF96 1 0.802
36 ... 100 EF96-100 1SAX341001R1101 AF80, AF96 1 0.802
54 ... 150 EF146-150 1SAX351001R1101 AF116, AF140, AF146 1 0.879
Suitable for mounting on:
AF40, AF52, AF65
AF80, AF96
AF116, AF140, AF146
Type Order code Suitable for Packing unit
pc
Weight per pc
kg
Page 2
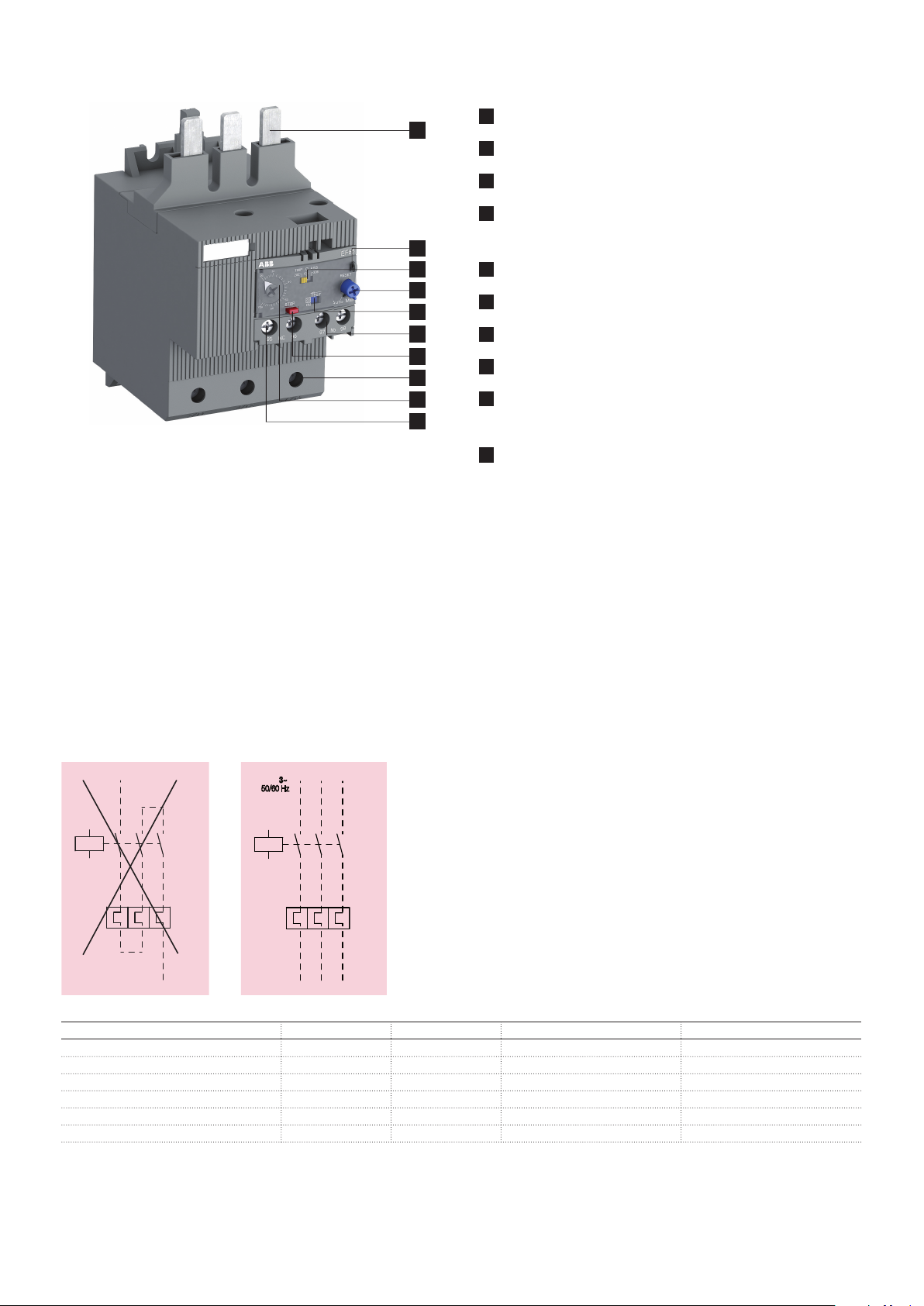
Functional description
1~
3~
1
Terminals (1L1, 3L2, 5L3)
1
2
Sealable operating elements
3
Trip class 10E, 20E, 30E selectable
4
RESET
Automatic or manual reset selectable
2
5
TEST - Status indication
6
Signaling contacts 97-98
7
STOP
8
Terminals 2T1, 4T2, 6T3
9
Current setting range / Self-test function ST
Adjustable current setting for overload protection
10
Tripping contacts 95-96
2CDC232017F0013
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Application / internal function
The self-supplied electronic overload relays are three pole electronic/mechanical devices. The motor current flows through
build-in current transformers and an evaluation circuit will recognize an overload (over current). This will lead to a release
of the relay and a change of the contacts switching position (95-96 / 97-98). The contact 95-96 is used to control the load
contactor. The electronic overload relay is self-supplied, which mean no extra external supply is needed.
The overload relays have a setting scale in Amperes, which allows the direct adjusting of the relay without any additional
calculation. In compliance with international and national standards, the setting current is the rated current of the motor and
not the tripping current (no tripping at 1.05 x I, tripping at 1.2 x I; I = setting current). The relays are constructed in a way
that they protect themselves in the event of an overload. The overload relay has to be protected against short-circuit. The
appropriate short-circuit protective devices are shown in the following tables.
To prevent thermal overloads in heavy duty applications, the correct cable sizes have to be selected.
Operation mode
50/60 Hz
2CDC232013F0012
Contact 95-96 Contact 97-98 Opto-mechanical slide Comment
Trip state open closed
RESET state closed open ON
TEST manual reset mode open closed
TEST auto reset mode open closed
STOP while device is in trip state open closed STOP button has no function
STOP while device is in RESET state open open while STOP button is pressed
2CDC232005F0013
2 - 2CDC107041D0201
Page 3
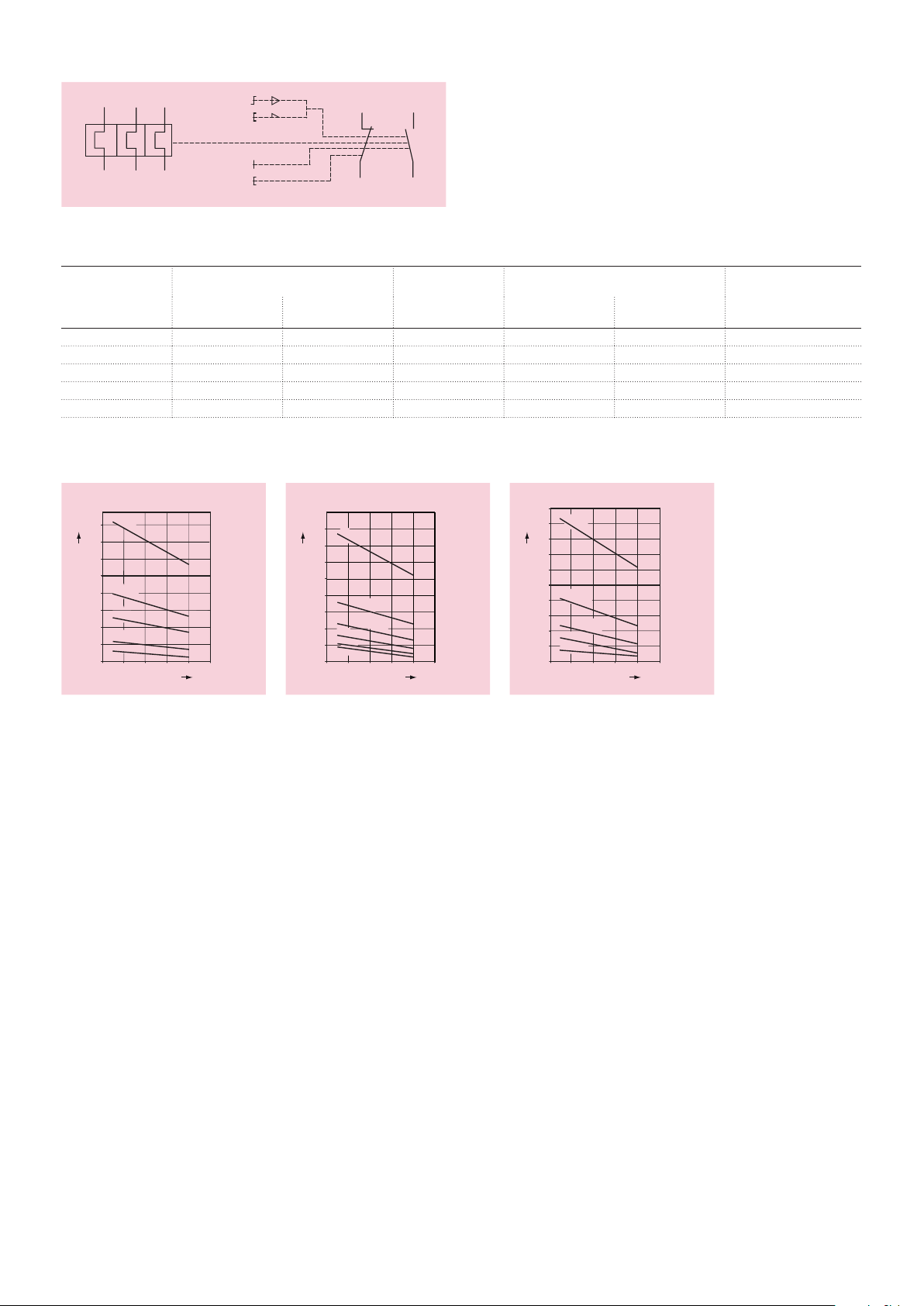
Wiring diagram
97
98
Auto
2CDC232001F0011
duty ratio
(Op/h)
switching frequency
Trip class 10E
)
duty ratio
(Op/h)
switching frequency
Trip class 20E
)
duty ratio
(Op/h)
switching frequency
Trip class 30E
)
RESET
Man
95
TEST
2T1 4T2 6T3
STOP
96
2CDC232001F0011
Resistance and power loss per pole and short-circuit protective devices
Type Setting range Resistance per
pole
EF65-56
EF65-70
EF96-56
EF96-100
EF146-150
lower value
A
20 56 0.09 0.04 0.28
25 70 0.09 0.06 0.45
20 56 0.09 0.04 0.28
36 100 0.09 0.12 0.90
54 150 0.07 0.21 1.58
upper value
A
mΩ
Power loss per pole Short-circuit protec-
at lower value Wat upper value Wcoordination type 2
Intermittent periodic duty
t = 0.5 s
a
160
140
120
100
t = 1 s
a
80
60
t = 1.5 s
a
40
t = 3 s
a
20
t = 5 s
a
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
80
t = 2 s
a
70
60
50
40
t = 4 s
a
30
20
10
(%
2CDC232001F0214
t = 6 s
a
t = 8 s
a
t = 10 s
a
t = 12 s
a
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
(%
2CDC232002F0214
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
t = 5 s
a
t = 10 s
a
t = 15 s
a
t = 20 s
a
t = 25 s
a
5
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
tive devices
Fuse 160 A, Type gG
Fuse 160 A, Type gG
Fuse 160 A, Type gG
Fuse 200 A, Type gG
Fuse 315 A, Type gG
(%
2CDC232003F0214
Trip class 10E Trip class 20E Trip class 30E
2CDC107041D0201 - 3
Page 4

Dimensions
120.2
55
4.73"
2.17"
43.7
121.7
1.72"
4.79"
89.05 3.51"
139.4 5.49"
4.14"
1.51"
3.35"
38.4
105.2
2.92"
85.2
74.2
56.6 3
8
34.65
1.36"
8
0.31"
1"
25.4
4.06"
103.2
0.63"
0.22"
16
5.5
1.46"
37
2.28"
58
2.76"
70
0.39"
10
0.43"
11
53.3 3
17.2
3
0.12"
2.1" 0.12"
0.68"
74
2.91"
101.4
3.99"
105.2
4.14"
4.14"
105.2
1.51"
38.4
3.35"
2.92"
85.2
74.2
0.31"
1"
25.4
4.06"
103.2
0.43" 0.39"
11 10
16
0.63"
5.5
0.22"
37
1.46"
58
2.28"
70
2.76"
17.2
3
0.12"
2.23" 0.12"
0.68"
74
2.91"
101.4
3.99"
105.2
4.14"
2CDC232001F0012
EF65-56 / EF65-70 EF96-56, EF96-100
60.1 2.37"
13 0.5"
6.6 0.26"
127 5"
119.25 4.69"
117.4 4.62"
38.4 1.51"
88.9 3.5"
85.2 3.35"
74.2 2.92"
16 0.63"
5.5 0.22"
37 1.46"
58 2.28"
70 2.76"
15.5 0.61"
103.7 4.08"
4 0.16"
11 0.43" 10 0.39"
3 0.12"
74 2.91"
101.4 3.99"
105.2 4.14"
2CDC232003F0012
EF146-150
2CDC232002F0012
4 - 2CDC107041D0201
Page 5

Technical data IEC/EN
Data at TA = 40 °C and at rated values, if nothing else indicated
Main circuit
EF65, EF96, EF146
Rated operational voltage U
e
Setting range - electronic overload protection see table on page 1
Rated operational current AC-3 I
e
Trip class 10E, 20E, 30E, selectable
Rated frequency 50/60 Hz
Number of poles 3
Resistance per pole see table on page 3
Power loss per pole see table on page 3
Short-circuit protective devices see table on page 3
Isolation data EF65, EF96, EF146
Rated impulse withstand voltage U
Rated insulation voltage U
imp
i
Pollution degree 3
Overvoltage category up to III
Electrical connection EF65 EF96 EF146
Connecting capacity rigid 1x2x4 ... 35 mm²
flexible with ferrule 1x2x4 ... 35 mm²
flexible with ferrule insulated 1x2x4 ... 35 mm²
flexible 1x2x4 ... 35 mm²
Stripping length 20 mm 20 mm 20 mm
Tightening torque 4 Nm 6 Nm 8 Nm
Recommended screw driver Pozidriv 2 Hexagon 4 Hexagon 4
1000 V AC
- V DC
see upper value of setting range, on page 3
8 kV
1000 V
4 ... 70 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 50 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 50 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 70 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
4 ... 35 mm²
10 ... 95 mm²
10 ... 35 mm²
10 ... 70 mm²
10 ... 35 mm²
10 ... 70 mm²
10 ... 35 mm²
10 ... 70 mm²
10 ... 35 mm²
2CDC107041D0201 - 5
Page 6

Auxiliary circuit
95-96, 97-98
Rated operational voltage U
Conventional free air thermal current I
e
th
Rated frequency DC, 50/60 Hz
Number of poles 1NC + 1NO
Rated operational current Ie
acc. to IEC/EN 60947-5-1 for utilization category
at AC-15 at 110-120 V NC, 95-96 3.00 A
NO, 97-98 3.00 A
at AC-15 at 220-230-240 V NC, 95-96 3.00 A
NO, 97-98 3.00 A
at AC-15 at 400 V NC, 95-96 1.10 A
NO, 97-98 1.10 A
at AC-15 at 480-500 V NC, 95-96 0.75 A
NO, 97-98 0.75 A
at DC-13 at 24 V NC, 95-96 1.50 A
NO, 97-98 1.50 A
at DC-13 at 60 V NC, 95-96 0.55 A
NO, 97-98 0.55 A
at DC-13 at 110-120-125 V NC, 95-96 0.55 A
NO, 97-98 0.55 A
at DC-13 at 250 V NC, 95-96 0.27 A
NO, 97-98 0.27 A
Minimum switching capacity 12 V / 3 mA
Short-circuit protective devices fuse 6 A, Type gG
600 V AC / DC
6 A
l = 10-7; Ukd = 3 V / 500.000 operating cycles
Isolation data 95-96, 97-98
Rated impulse withstand voltage U
Rated insulation voltage U
i
imp
6 kV
690 V
Pollution degree 3
Overvoltage category up to III
Electrical connection 95-96, 97-98
Connecting capacity rigid 1x2x1 ... 4 mm²
1 ... 4 mm²
flexible with ferrule 1x2x0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
flexible with ferrule insulated 1x2x0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
flexible 1x2x0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
0.75 ... 2.5 mm²
Stripping length 9 mm
Tightening torque 0.8 ... 1.2 Nm
Recommended screw driver Pozidriv 2
6 - 2CDC107041D0201
Page 7

General data
Duty time 100 %
Operating frequency without early tripping up to 15 operations/h or 60 operations/h with
40 % duty ratio, if the motor breaking current 6 x In
and the motor starting time does not exceed 1 s
Dimensions (W x H x D) see dimension drawing
Weight see ordering data
Mounting mount on the contactor and tighten the screws of
the main circuit terminals
Mounting position optional, position 1-6
Minimum distance to other units same type horizontal none
vertical not applicable
Minimum distance to electrical conductive board horizontal 1.5 mm
vertical 1.5 mm
Degree of protection housing IP20
main circuit terminals IP10
Maximum operating altitude 2000 m
Electromagnetic compatibility
Immunity acc. to IEC 60947-1 Environment A
Emission acc. to IEC 60947-1 Environment B
Environmental data
Ambient air temperature
Operation
Storage -50 ... +85 °C
Ambient air temperature compensation acc. to IEC/EN 60947-4-1
Resistance to vibrations acc. to IEC 60068-2-6 5g / 3 ... 150 Hz
Resistance to shock acc. to IEC 60068-2-27 15g / 11 ms
open - compensated
open
-25 ... +70 °C
-25 ... +70 °C
Standards / directives
Standards IEC/EN 60947-1
IEC/EN 60947-4-1
IEC/EN 60947-5-1
UL 60947-1
UL 60947-4-1
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
ATEX Directive 2014/34/EC
2CDC107041D0201 - 7
Page 8

Technical data UL/CSA
Full load amps and short-circuit protective devices
Type Full load amps
(FLA)
EF65-56
EF65-70
EF96-56
EF96-100
EF146-150
Short circuit protective devices
480 V AC 600 V AC 600 V AC
SCCR Fuse type SCCR Fuse type SCCR Fuse type
56 A 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 100 kA 175 A, Class J
70 A 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 100 kA 175 A, Class J
56 A 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 10 kA 150 A, K5/RK5 100 kA 175 A, Class J
100 A 10 kA 200 A, K5/RK5 10 kA 200 A, K5/RK5 100 kA 225 A, Class J
150 A 10 kA 250 A, K5/RK5 10 kA 250 A, K5/RK5 100 kA 350 A, Class J
Main circuit
Maximum operational voltage 600 V AC
Trip rating 125 % of FLA
Full load amps (FLA) see table above
Short-circuit rating RMS symmetrical see table above
Short-circuit protective devices see table above
Electrical connection EF65 EF96 EF146
Connecting capacity stranded 1x2xAWG 10 ... 2
AWG 10 ... 2
flexible 1x2xAWG 10 ... 2
AWG 10 ... 2
Stripping length 20 mm 20 mm 20 mm
Tightening torque 55 lb.in 70 lb.in 70 lb.in
Recommended screw driver Pozidriv 2 Hexagon 4 Hexagon 4
AWG 10 ... 2
AWG 10 ... 2
AWG 10 ... 2
AWG 10 ... 2
AWG 6 ... 0
AWG 6 ... 2
AWG 6 ... 0
AWG 6 ... 2
Auxiliary circuit
Conventional thermal current 6 A
Making and breaking capacity NC / NO B600, Q600
Electrical connection
Connecting capacity stranded 1x2xAWG 18 ... 10
AWG 18 ... 10
flexible 1x2xAWG 18 ... 10
AWG 18 ... 10
Stripping length 9 mm
Tightening torque 7 ... 11 lb.in
Recommended screw driver Pozidriv 2
8 - 2CDC107041D0201
 Loading...
Loading...