Texas Instruments OPA2373AIDGS, OPA2373AIDRC, OPA2374AIDCN, OPA373AIDBV, OPA374AIDBV Schematic [ru]
...
OPA373, OPA2373
OPA374
OPA2374, OPA4374
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008
6.5MHz, 585 A, Rail-to-Rail I/O
CMOS Operational Amplifier
FEATURES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
D |
LOW OFFSET: 5mV (max) |
|
|
|
|
The OPA373 and OPA374 families of operational |
||||||||||||||
D |
LOW IB: 10pA (max) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
amplifiers are low |
power |
and |
low cost with |
excellent |
|||||||||||
D |
HIGH BANDWIDTH: 6.5MHz |
|
|
|
bandwidth (6.5MHz) and slew rate (5V/ s). The input |
|||||||||||||||
D RAIL-TO-RAIL INPUT AND OUTPUT |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
range extends 200mV beyond the rails and the output |
||||||||||||||||||
|
SINGLE SUPPLY: +2.3V to +5.5V |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
D |
|
|
range is within 25mV of the rails. The speed/power ratio |
|||||||||||||||||
D |
SHUTDOWN: OPAx373 |
|
|
|
|
|
and small size make them ideal for portable and |
|||||||||||||
D SPECIFIED UP TO +125°C |
|
|
|
battery-powered applications. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
D MicroSIZE PACKAGES: SOT23-5, SOT23-6, |
|
The OPA373 family includes a shutdown mode. Under |
||||||||||||||||||
|
SOT23-8 and DFN-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
logic control, the amplifiers can be switched from normal |
||||||||||||||
APPLICATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
operation to a standby current that is less than 1 A. |
|||||||||||||||
D |
PORTABLE EQUIPMENT |
|
|
|
|
The OPA373 and OPA374 families of operational |
||||||||||||||
D |
BATTERY-POWERED DEVICES |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
amplifiers are specified for single or dual power supplies |
|||||||||||||||||
D |
ACTIVE FILTERS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
of +2.7V to +5.5V, with operation from +2.3V to +5.5V. All |
||||||||||||
D |
DRIVING A/D CONVERTERS |
|
|
|
models are specified for −40 °C to +125°C. |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
OPA373 |
|
|
|
|
|
OPA374 |
|
|
|
OPA2373 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Out |
1 |
A75 |
6 |
V+ |
Out |
1 |
|
5 |
V+ |
OUT A |
1 |
|
10 |
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
V− |
2 |
5 |
Enable |
V− |
2 |
|
|
|
−IN A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
9 |
OUT B |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
− IN |
|
|
|
|
|
−IN |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+IN |
3 |
|
4 |
+IN |
3 |
|
4 |
+IN A |
3 |
B |
8 |
− IN B |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOT23−6(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
SOT23−5 |
|
|
4 |
|
7 |
+IN B |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
OPA373 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable A |
5 |
|
6 |
Enable B |
OPA2373 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSOP−10 |
OUT A |
|
|
|
|
V+ |
||
NC(2) |
1 |
|
8 |
Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exposed |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA4374 |
|
|
−IN A |
|
|
|
OUT B |
|||
− IN |
2 |
|
7 |
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
thermal |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
die pad on |
|
−IN B |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+IN A |
|
|
|
|||
+IN |
3 |
|
6 |
OUT |
|
OUT A |
1 |
|
|
|
14 |
OUT D |
|
|
underside |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
V− |
|
|
(Must be |
|
+IN B |
|||||||||
V− |
|
|
|
NC(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
connected to V−) |
|
|||
4 |
|
5 |
|
− IN A |
2 |
|
|
|
13 |
− IN D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
A |
|
D |
Enable A |
|
|
|
|
Enable B |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
SO−8 |
|
|
|
|
+IN A |
3 |
|
|
|
12 |
+IN D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DFN−10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+ |
4 |
|
|
|
11 |
V− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA374 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA2374 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+IN B |
5 |
|
|
|
10 |
+IN C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC(2) |
1 |
|
8 |
NC(2) |
|
− IN B |
6 |
B |
|
C |
9 |
− IN C |
OUT A |
1 |
|
|
8 |
V+ |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
||||
|
−IN |
2 |
|
7 |
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−IN A |
2 |
|
7 |
OUT B |
||
|
|
|
OUT B |
7 |
|
|
|
8 |
OUT C |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
||||
|
+IN |
3 |
|
6 |
OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+IN A |
3 |
|
6 |
−IN B |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
V− |
4 |
|
5 |
NC(2) |
|
|
|
SO−14, TSSOP−14 |
|
|
|
V− |
4 |
|
|
5 |
+IN B |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
SO−8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SO−8, SOT23−8 |
|
|
(1)Pin 1 of the SOT23-6 is determined by orienting the package marking as shown.
(2)NC indicates no internal connection.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products |
Copyright 2003-2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated |
conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. |
|
Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters. |
|
www.ti.com

OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
OPA374 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
|
|
|
www.ti.com |
||
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
|
|
|
|||
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION(1) |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
PACKAGE |
SPECIFIED |
PACKAGE |
ORDERING |
TRANSPORT |
|
PRODUCT |
PACKAGE-LEAD |
TEMPERATURE |
|||||
DESIGNATOR |
MARKING |
NUMBER |
MEDIA, QUANTITY |
||||
|
|
RANGE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA373 |
SOT23-6 |
DBV |
−40 °C to +125°C |
A75 |
OPA373AIDBVT |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA373AIDBVR |
Tape and Reel, 3000 |
|
OPA373 |
SO-8 |
D |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OPA373A |
OPA373AID |
Rails, 100 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA373AIDR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
OPA2373 |
MSOP-10 |
DGS |
−40 °C to +125°C |
AYO |
OPA2373AIDGST |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA2373AIDGSR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
OPA2373 |
DFN-10 |
DRC |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OCEQ |
OPA2373AIDRCT |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA2373AIDRCR |
Tape and Reel, 3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA374 |
SOT23-5 |
DBV |
−40 °C to +125°C |
A76 |
OPA374AIDBVT |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA374AIDBVR |
Tape and Reel, 3000 |
|
OPA374 |
SO-8 |
D |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OPA274A |
OPA374AID |
Rails, 100 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA374AIDR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
OPA2374 |
SOT23-8 |
DCN |
−40 °C to +125°C |
ATP |
OPA2374AIDCNT |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA2374AIDCNR |
Tape and Reel, 3000 |
|
OPA2374 |
SO-8 |
D |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OPA2374A |
OPA2374AID |
Rails, 100 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA2374AIDR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
OPA4374 |
SO-14 |
D |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OPA4374A |
OPA4374AID |
Rails, 58 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA4374AIDR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
OPA4374 |
TSSOP-14 |
PW |
−40 °C to +125°C |
OPA4374A |
OPA4374AIPWT |
Tape and Reel, 250 |
|
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
″ |
OPA4374AIPWR |
Tape and Reel, 2500 |
|
(1) For the most current package and ordering information, see the Package Option Addendum located at the end of this datasheet.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Supply Voltage |
. . . . . . . . . . . . +7.0V |
Signal Input Terminals, Voltage(2) . . . . . . . . . |
−0.5V to (V+) + 0.5V |
Current(2) . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . ±10mA |
Output Short-Circuit(3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . Continuous |
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . −55 °C to +150°C |
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . −65 °C to +150°C |
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . +150°C |
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . +300°C |
(1)Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage.
Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied.
(2)Input terminals are diode-clamped to the power-supply rails.
Input signals that can swing more than 0.5V beyond the supply rails should be current-limited to 10mA or less.
(3)Short-circuit to ground, one amplifier per package.
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe
proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
2

|
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
www.ti.com |
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: VS = +2.7V to +5.5V
Boldface limits apply over the specified temperature range, TA = −40 °C to +125°C.
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted.
|
|
|
|
|
OPA373, OPA2373, OPA374, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PARAMETER |
|
CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OFFSET VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input Offset Voltage |
VOS |
VS = 5V |
|
|
1 |
5 |
mV |
|||||
over Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.5 |
mV |
||||
Drift |
dVOS/dT |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
µV/°C |
||||
vs Power Supply |
PSRR |
VS = 2.7V to 5.5V, VCM < (V+) − 2V |
|
25 |
100 |
µV/V |
||||||
over Temperature |
|
VS = 2.7V to 5.5V, VCM < (V+) − 2V |
|
|
150 |
µV/V |
||||||
Channel Separation, DC |
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
µV/V |
||||
f = 1kHz |
|
|
|
|
|
128 |
|
dB |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common-Mode Voltage Range |
VCM |
|
|
|
(V−) − 0.2 |
|
(V+) + 0.2 |
V |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio |
CMRR |
(V−) − 0.2V < V |
CM < (V+) − 2V |
80 |
90 |
|
dB |
|||||
over Temperature |
|
(V−) − 0.2V < V |
CM < (V+) − 2V |
70 |
|
|
dB |
|||||
|
|
VS = 5.5V, (V−) − 0.2V < V |
CM < (V+) + 0.2V |
66 |
|
|
dB |
|||||
over Temperature |
|
VS = 5.5V, (V−) − 0.2V < V |
CM < (V+) + 0.2V |
60 |
|
|
dB |
|||||
INPUT BIAS CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input Bias Current |
IB |
|
|
|
|
±0.5 |
±10 |
pA |
||||
Input Offset Current |
IOS |
|
|
|
|
±0.5 |
±10 |
pA |
||||
INPUT IMPEDANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential |
|
|
|
|
|
1013 3 |
|
Ω pF |
||||
Common-Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
1013 6 |
|
Ω pF |
||||
NOISE |
|
VCM < (V+) − 2V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Input Voltage Noise, f = 0.1Hz to 10Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
µVPP |
||||
Input Voltage Noise Density, f = 10kHz |
en |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
nV/√ |
Hz |
|
||
Input Current Noise Density, f = 10kHz |
in |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
fA/√ |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Hz |
|||||||
OPEN-LOOP GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Open-Loop Voltage Gain |
AOL |
VS = 5V, RL = 100kΩ, 0.025V < VO < 4.975V |
94 |
110 |
|
dB |
||||||
over Temperature |
|
VS = 5V, RL = 100kΩ, 0.025V < VO < 4.975V |
80 |
|
|
dB |
||||||
|
|
VS = 5V, RL = 5kΩ, 0.125V < VO < 4.875V |
94 |
106 |
|
dB |
||||||
over Temperature |
|
VS = 5V, RL = 5kΩ, 0.125V < VO < 4.875V |
80 |
|
|
dB |
||||||
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage Output Swing from Rail |
|
RL = 100kΩ |
|
18 |
25 |
mV |
||||||
over Temperature |
|
RL = 100kΩ |
|
|
25 |
mV |
||||||
|
|
RL = 5kΩ |
|
|
100 |
125 |
mV |
|||||
over Temperature |
|
RL = 5kΩ |
|
|
|
125 |
mV |
|||||
Short-Circuit Current |
ISC |
|
|
|
See Typical Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Capacitive Load Drive |
CLOAD |
|
|
|
See Typical Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Open-Loop Output Impedance |
|
f = 1MHz, IO = 0 |
|
220 |
|
Ω |
||||||
FREQUENCY RESPONSE |
|
CL = 100pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gain-Bandwidth Product |
GBW |
|
|
|
|
6.5 |
|
MHz |
||||
Slew Rate |
SR |
G = +1 |
|
|
5 |
|
V/µs |
|||||
Settling Time, 0.1% |
tS |
VS = 5V, 2V Step, G = +1 |
|
1 |
|
µs |
||||||
0.01% |
|
VS = 5V, 2V Step, G = +1 |
|
1.5 |
|
µs |
||||||
Overload Recovery Time |
|
VIN • Gain > VS |
|
0.3 |
|
µs |
||||||
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise |
THD+N |
VS = 5V, VO = 3VPP, G = +1, f = 1kHz |
|
0.0013 |
|
% |
|
|
||||
ENABLE/SHUTDOWN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tOFF |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
µs |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
tON |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
µs |
||||
VL (shutdown) |
|
|
|
|
V− |
|
(V−) + 0.8 |
V |
||||
VH (amplifier is active) |
|
|
|
|
(V−) + 2 |
|
V+ |
V |
||||
Input Bias Current of Enable Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
µA |
||||
IQSD (per amplifier) |
|
|
|
|
|
< 0.5 |
1 |
µA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
3

OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA374 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
|
|
|
www.ti.com |
|
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: VS = +2.7V to +5.5V (continued) |
|
|
|
|||
Boldface limits apply over the specified temperature range, TA = −40 °C to +125°C. |
|
|
|
|||
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
OPA373, OPA2373, OPA374, |
|
||
|
|
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARAMETER |
|
CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POWER SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specified Voltage Range |
VS |
|
2.7 |
|
5.5 |
V |
Operating Voltage Range |
|
|
|
2.3 to 5.5 |
|
V |
Quiescent Current (per amplifier) |
IQ |
IO = 0 |
|
585 |
750 |
A |
over Temperature |
|
|
|
|
800 |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TEMPERATURE RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specified Range |
|
|
−40 |
|
+125 |
°C |
|
|
|
||||
Operating Range |
|
|
−55 |
|
+150 |
°C |
|
|
|
||||
Storage Range |
|
|
−65 |
|
+150 |
°C |
|
|
|
||||
Thermal Resistance |
qJA |
|
|
|
|
°C/W |
|
|
|
|
|||
SOT23-5, SOT23-6, SOT23-8 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
°C/W |
MSOP-10, SO-8 |
|
|
|
150 |
|
°C/W |
|
|
|
|
|||
SO-14, TSSOP-14 |
|
|
|
100 |
|
°C/W |
|
|
|
|
|||
DFN-10 |
|
JEDEC High-K Board |
|
56 |
|
°C/W |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
|
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
www.ti.com |
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
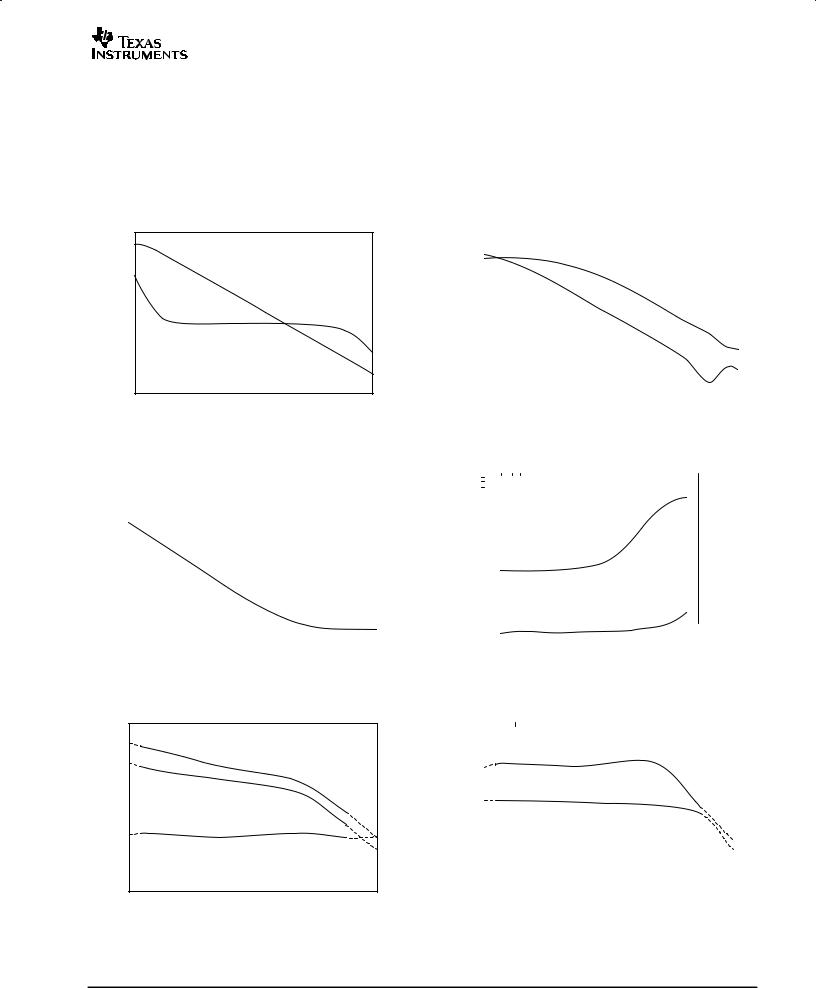
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted.
|
|
|
|
120 |
|
|
OPEN−LOOP GAIN AND PHASE vs FREQUENCY |
|
|
|
30 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
(dB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−30 |
|
|||
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
)( |
||
|
|
|
GainOpen−Loop |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MarginPhase |
||
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−60 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
−20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−180 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
10 |
100 |
|
|
1k |
10k |
|
100k |
1M |
|
10M |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPECTRAL DENSITY vs FREQUENCY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
(nV/√Hz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NoiseVoltage |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100k |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPEN−LOOP GAIN AND POWER−SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
130 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
REJECTION RATIO vs TEMPERATURE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 100kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
(dB) |
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSRR, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL |
= 5kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
OL |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−50 |
− 25 |
0 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
75 100 |
125 |
|
150 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Temperature (_C)
POWER−SUPPLY AND COMMON−MODE
REJECTION RATIO vs FREQUENCY
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(dB) |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
CMRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSRR |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
|
|
10k |
100k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1M |
|
|
10M |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION+NOISE |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
0.100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vs FREQUENCY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(%) |
|
|
|
RL = 5kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HarmonicTotalDistortion+Noise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G = 1V/V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G = 10V/V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
0.010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10k |
100k |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
120 |
|
|
COMMON−MODE REJECTION RATIO vs TEMPERATURE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
110 |
|
|
VS = 5.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCM = − 0.2V to 3.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
(dB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCM = − 0.2V to 5.7V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−50 −25 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
50 |
|
|
75 |
|
100 125 |
|
150 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Temperature (_C)
5
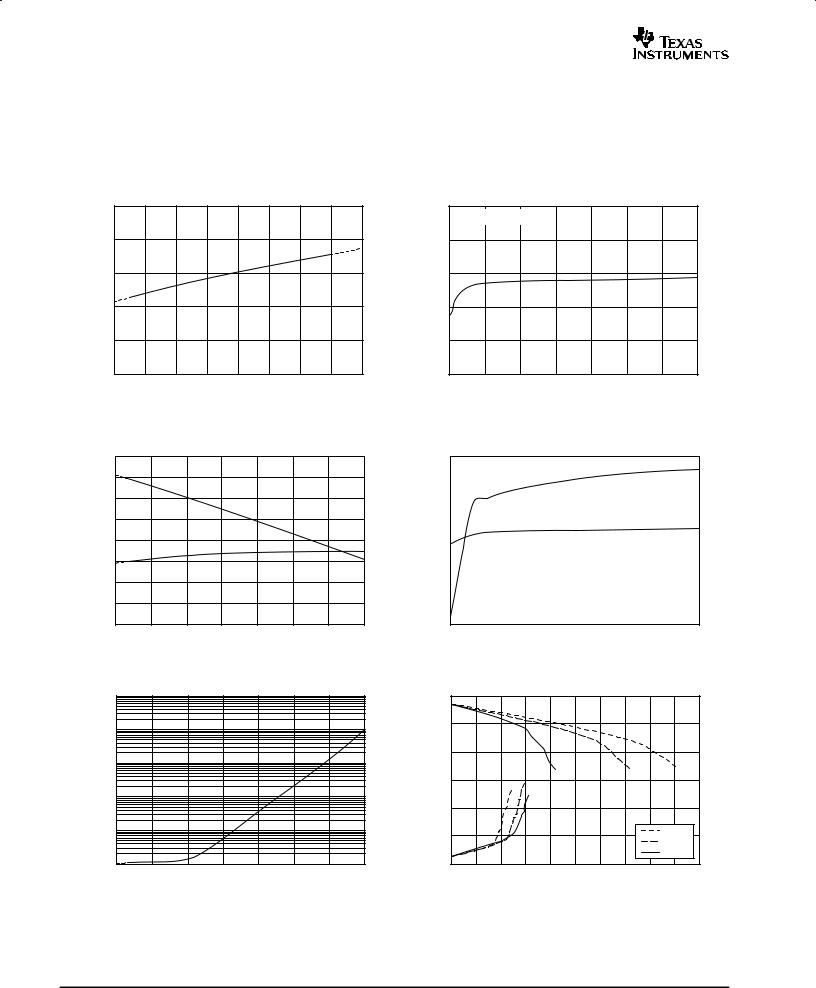
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
www.ti.com |
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted.
|
800 |
( A) |
700 |
|
|
Current |
600 |
Quiescent |
500 |
|
|
|
400 |
|
300 |
−50
|
16 |
|
(mA) |
14 |
|
12 |
||
Current |
||
10 |
||
|
||
Short−Circuit |
8 |
|
6 |
||
|
||
|
4 |
2
0
−50
QUIESCENT CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
Quiescent Current ( A)
−25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
|
|
Temperature (_C) |
|
|
|
||
SHORT−CIRCUIT CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
+ISC
−ISC
− 25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
|
|
Temperature (_C) |
|
|
|
|
QUIESCENT CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
800
VOUT = 1/2[(V+) − (V−)]
700
600
500
400
300
|
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply Voltage (V) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
CONTINUOUS SHORT−CIRCUIT CURRENT vs |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
POWER−SUPPLY VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ISC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−ISC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short−Circuit |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Power−Supply Voltage (V) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Input Bias Current (pA)
INPUT BIAS CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE |
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING vs OUTPUT CURRENT |
10k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(V) |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 55_C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25_C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150_C |
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 50 |
−25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
|
0 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
18 |
20 |
|
|
|
Temperature (_C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Current (mA) |
|
|
|
|
|||
6
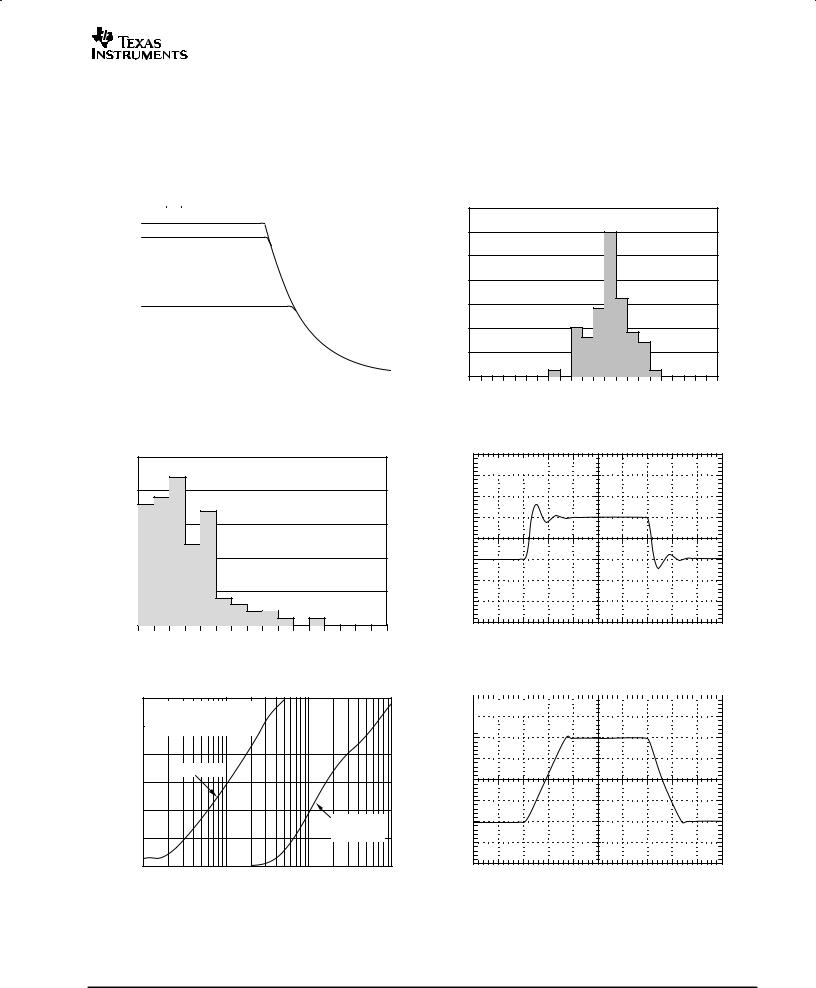
|
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
www.ti.com |
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted.
|
6 |
MAXIMUM OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs FREQUENCY |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 5.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
VS = 5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(V |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Voltage |
3 |
VS = |
2.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10k |
100k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1M |
10M |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT MAGNITUDE
PRODUCTION DISTRIBUTION
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Typical production distribution |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of packaged units. |
|
Population |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 11 12 |
13 14 15 16 |
|
|
|
|
Offset Voltage Drift (µV/_C) |
|
|||||
OFFSET VOLTAGE PRODUCTION DISTRIBUTION
Population |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 5 |
− 4 |
−3 |
− 2 |
− 1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
5.5 |
|
|
|
|
Offset Voltage (mV) |
|
|
|
|
|||
SMALL−SIGNAL STEP RESPONSE
CL = 100pF
50mV/div
200ns/div
Small−Signal Overshoot (%)
|
SMALL−SIGNAL OVERSHOOT vs LOAD CAPACITANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LARGE −SIGNAL STEP RESPONSE |
|||||||||||||||||||
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refer to the Capacitive Load |
|
|
|
|
|
CL = 100pF |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
50 |
and Stability section for tips |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
on improving performance. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
1V/div |
30 |
G = +1V/V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G = ±10V/V |
|
10 |
|
|
RFB = 10kΩ |
|
0 |
|
|
|
400ns/div |
10 |
100 |
1k |
10k |
|
|
Load Capacitance (pF) |
|
|
|
7
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
www.ti.com |
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
At TA = +25°C, RL = 10kΩ connected to VS/2, and VOUT = VS/2, unless otherwise noted.
Settling Time ( s)
100
10
1
0.1
1
SETTLING TIME vs CLOSED−LOOP GAIN
0.01%
0.1%
10 100
Closed−Loop Gain (V/V)
Channel Separation (dB)
CHANNEL SEPARATION vs FREQUENCY
140 












 G = +1V/V, All Channels
G = +1V/V, All Channels
120 RL = 5kΩ
100
80
60
40
20
0
10 |
100 |
1K |
10K |
100K |
1M |
10M |
100M |
Frequency (Hz)
8
www.ti.com
APPLICATIONS
The OPA373 and OPA374 series op amps are unity-gain stable and suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications. Rail-to-rail input and output make them ideal for driving sampling Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs). Excellent ac performance makes them well-suited for audio applications. The class AB output stage is capable of driving 100kΩ loads connected to any point between V+ and ground.
The input common-mode voltage range includes both rails, allowing the OPA373 and OPA374 series op amps to be used in virtually any single-supply application up to a supply voltage of +5.5V.
Rail-to-rail input and output swing significantly increases dynamic range, especially in low-supply applications.
Power-supply pins should be bypassed with 0.01µF ceramic capacitors.
OPERATING VOLTAGE
The OPA373 and OPA374 op amps are specified and tested over a power-supply range of +2.7V to +5.5V (±1.35V to ±2.75V). However, the supply voltage may range from +2.3V to +5.5V (±1.15V to ±2.75V). Supply voltages higher than 7.0V (absolute maximum) can permanently damage the amplifier. Parameters that vary over supply voltage or temperature are shown in the Typical Characteristics section of this data sheet.
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE RANGE
The input common-mode voltage range of the OPA373 and OPA374 series extends 200mV beyond the supply rails. This is achieved with a complementary input stage—an N-channel input dif ferential pair in parallel with a P-channel differential pair. The N-channel pair is active for input voltages close to the positive rail, typically (V+) − 1.65V to 200mV above the positive supply, while the P-channel pair is on for inputs from 200mV below the negative supply to approximately (V+) − 1.65V . There is a 500mV transition region, typically (V+) − 1.9V to (V+) − 1.4V, in which both pairs are on. This 500mV transition region, shown in Figure 1, can vary ±300mV with process variation. Thus, the transition region (both stages on) can range from (V+) − 2.2V to (V+) − 1.7V on the low end, up to (V+) − 1.6V to (V+) − 1.1V on the high end. Within the 500mV transition region PSRR, CMRR, offset voltage, offset drift, and THD may be degraded compared to operation outside this region.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA373, OPA2373 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA374 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
||||||
|
|
|
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|||||||||||
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mV) |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Offset |
− 0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 1.5 |
|
V− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 0.5 |
0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Common−Mode Voltage (V) |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Figure 1. Behavior of Typical Transition Region at
Room Temperature
RAIL-TO-RAIL INPUT
The input common-mode range extends from (V−) − 0.2V to (V+) + 0.2V. For normal operation, inputs should be limited to this range. The absolute maximum input voltage is 500mV beyond the supplies. Inputs greater than the input common-mode range but less than the maximum input voltage, while not valid, will not cause any damage to the op amp. Unlike some other op amps, if input current is limited, the inputs may go beyond the supplies without phase inversion, as shown in Figure 2.
G = +1V/V, VS = 5V
VIN
5V
VOUT
1V/div
0V
1µs/div
Figure 2. OPA373: No Phase Inversion with Inputs Greater Than the Power-Supply Voltage
Normally, input bias current is approximately 500fA; however, input voltages exceeding the power supplies by more than 500mV can cause excessive current to flow in or out of the input pins. Momentary voltages greater than 500mV beyond the power supply can be tolerated if the current on the input pins is limited to 10mA. This is easily accomplished with an input resistor; see Figure 3. (Many input signals are inherently current-limited to less than 10mA, therefore, a limiting resistor is not required.)
9
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
www.ti.com |
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
V+
IOVERLOAD
10mA max
R |
OPA373 |
VOUT |
VIN
Figure 3. Input Current Protection for Voltages Exceeding the Supply Voltage
RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT
A class AB output stage with common-source transistors is used to achieve rail-to-rail output. For light resistive loads ( > 100kΩ), the output voltage can typically swing to within 18mV from the supply rails. With moderate resistive loads (5kΩ to 50kΩ), the output can typically swing to within 100mV from the supply rails and maintain high open-loop gain. See the Typical Characteristic curve,
Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current, for more information.
CAPACITIVE LOAD AND STABILITY
OPA373 series op amps can drive a wide range of capacitive loads. However, under certain conditions, all op amps may become unstable. Op amp configuration, gain, and load value are just a few of the factors to consider when determining stability. An op amp in unity-gain configuration is the most susceptible to the effects of capacitive load. The capacitive load reacts with the op amp output resistance, along with any additional load resistance, to create a pole in the small-signal response that degrades the phase margin. The OPA373 series op amps perform well in unity-gain configuration, with a pure capacitive load up to approximately 250pF. Increased gains allow the amplifier to drive more capacitance. See the Typical Characteristics curve, Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load, for further details.
One method of improving capacitive load drive in the unity-gain configuration is to insert a small (10Ω to 20Ω) resistor, RS, in series with the output, as shown in Figure 4. This significantly reduces ringing while maintaining dc performance for purely capacitive loads. When there is a resistive load in parallel with the capacitive load, RS must be placed within the feedback loop as shown to allow the feedback loop to compensate for the voltage divider created by RS and RL.
In unity-gain inverter configuration, phase margin can be reduced by the reaction between the capacitance at the op amp input and the gain setting resistors, thus degrading capacitive load drive. Best performance is achieved by using small valued resistors. However, when large valued resistors cannot be avoided, a small (4pF to 6pF)
capacitor, CFB, can be inserted in the feedback, as shown in Figure 5. This significantly reduces overshoot by compensating the effect of capacitance, CIN, which includes the amplifier input capacitance and printed circuit board (PCP) parasitic capacitance.
V+
RS 10Ω to 20Ω
OPA373 |
VOUT |
VIN
RL CL
Figure 4. Series Resistor in Unity-Gain Configuration Improves Capacitive Load Drive
CFB |
|
RF |
|
V+ |
|
RI |
|
VIN |
|
OPA373 |
VOUT |
CIN |
CL |
|
Figure 5. Improving Capacitive Load Drive
For example, when driving a 100pF load in unity-gain inverter configuration, adding a 6pF capacitor in parallel with the 10kΩ feedback resistor decreases overshoot from 57% to 12%, as shown in Figure 6.
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
G = − 1V/V |
|
|
|
50 |
RFB = 10kΩ |
|
|
(%) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overshoot |
30 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CFB = 6pF |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
100 |
1k |
10k |
Load Capacitance (pF)
Figure 6. Improving Capacitive Load Drive
10
|
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
www.ti.com |
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
|
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
DRIVING ADCs
The OPA373 and OPA374 series op amps are optimized for driving medium-speed sampling ADCs. The OPA373 and OPA374 op amps buffer the ADC input capacitance and resulting charge injection, while providing signal gain.
The OPA373 is shown driving the ADS7816 in a basic noninverting configuration, as shown in Figure 7. The ADS7816 is a 12-bit, MicroPower sampling converter in the MSOP-8 package. When used with the low-power, miniature packages of the OPA373, the combination is ideal for space-limited, low-power applications. In this configuration, an RC network at the ADC input can be used to provide anti-aliasing filtering.
Figure 8 shows the OPA373 driving the ADS7816 in a speech band-pass filtered data acquisition system. This small, low-cost solution provides the necessary amplification and signal conditioning to interface directly with an electret microphone. This circuit will operate with VS = 2.7V to 5V.
The OPA373 is shown in the inverting configuration described in Figure 9. In this configuration, filtering may be accomplished with the capacitor across the feedback resistor.
ENABLE/SHUTDOWN
OPA373 and OPA374 series op amps typically require 585 A quiescent current. The enable/shutdown feature of the OPA373 allows the op amp to be shut off in order to reduce this current to less than 1 A.
VIN 
VIN = 0V to 5V for 0V to 5V output.
|
|
+5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1µF |
|
0.1µF |
|
|
|
8 |
V+ |
1 |
VREF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
500Ω |
+In |
|
|
DCLOCK |
|
|
|
ADS7816 |
|
6 |
Serial |
||
OPA373 |
|
|
||||
2 |
12−Bit ADC |
|
DOUT |
Interface |
||
|
|
5 |
||||
|
|
− In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS/SHDN |
|
||
|
3300pF |
|
|
|
3 |
GND |
|
4 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fSAMPLE = 100kHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC network filters high frequency noise. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: ADC Input = 0 to VREF |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 7. The OPA373 in Noninverting Configuration Driving the ADS7816
|
|
V+ = +2.7V to +5V |
|
|
Passband 300Hz to 3kHz |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
R9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
510kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
R2 |
R4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5kΩ |
1MΩ |
20kΩ |
|
C3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1000pF |
|
R7 |
R8 |
|
|
VREF |
1 |
8 |
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
51kΩ |
150kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
DCLOCK |
|
|
|
OPA2373 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Electret |
R3 |
|
1/2 |
+IN |
|
ADS7816 |
6 |
DOUT |
|
|||
|
|
|
Serial |
|||||||||
Microphone(1) |
1MΩ |
R |
C2 |
OPA2373 |
2 |
12−Bit ADC |
5 |
CS/SHDN |
Interface |
|||
|
|
6 |
1000pF |
|
− IN |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
100kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
GND |
|
|
|
NOTE: (1) Electret microphone |
G = 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
powered by R1. |
|
R5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 8. The OPA2373 as a Speech Bypass Filtered Data Acquisition System
11
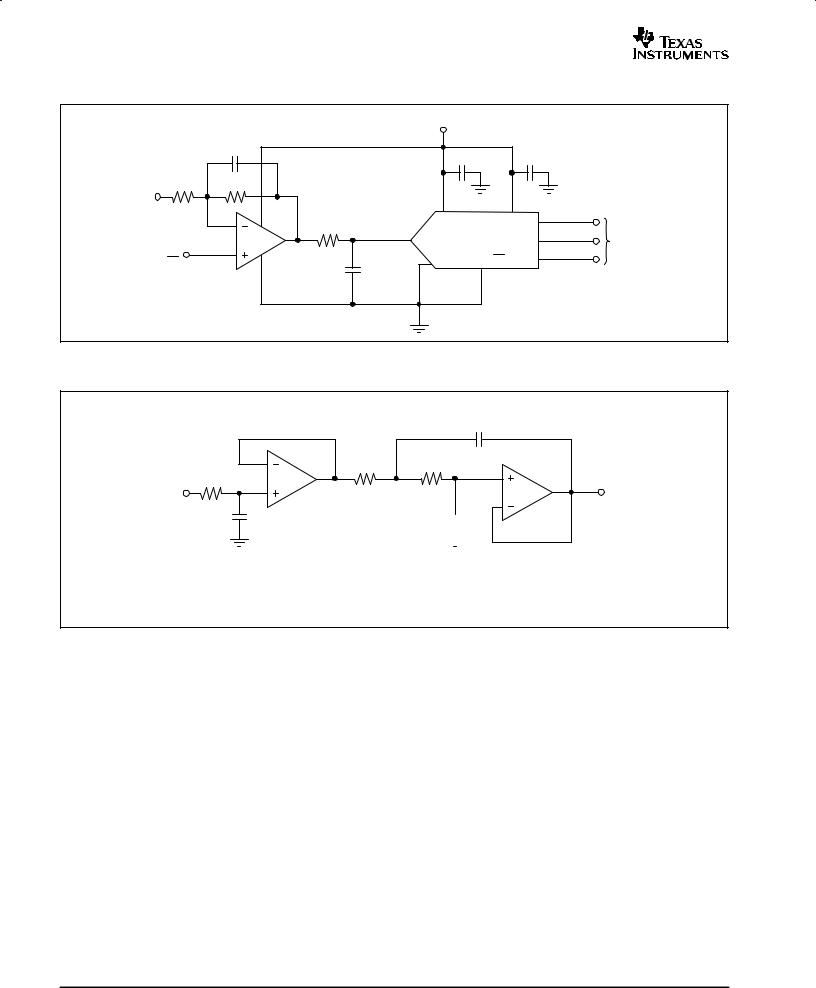
OPA373, OPA2373 |
|
OPA374 |
|
OPA2374, OPA4374 |
www.ti.com |
SBOS279E − SEPTEMBER 2003 − REVISED MAY 2008 |
|
|
|
+5V |
|
|
|
|
|
330pF |
|
0.1µF |
|
0.1µF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
5kΩ |
5kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
VIN |
|
8 |
V+ |
1 |
VREF |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
500kΩ |
+IN |
|
DCLOCK |
|
|
|
ADS7816 |
|
6 |
Serial |
||
|
|
|
||||
OPA373 |
2 |
|
12−Bit ADC |
DOUT |
Interface |
VS |
−IN |
|
CS/SHDN |
5 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
||
3300pF |
|
3 |
GND |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
NOTE: ADC Input = 0 to VREF |
|
Figure 9. The OPA373 in Inverting Configuration Driving the ADS7816
|
|
|
C3 |
|
|
|
330pF |
|
|
R2 |
R3 |
R1 |
1/2 |
2.72kΩ |
21.4kΩ |
11.7kΩ |
OPA373 |
|
1/2 |
|
|
|
OPA373 |
C1 |
|
|
|
|
|
C2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
680pF |
|
|
|
|
|
330pF |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: FilterPro is a low-pass filter design program available for download at no cost from TI’s web site (www.ti.com). The program can be used to determine component values for other cutoff frequencies or filter types.
Figure 10. Three-Pole Sallen-Key Butterworth Low-Pass Filter
12
 Loading...
Loading...