Sony SLD1132VS Datasheet
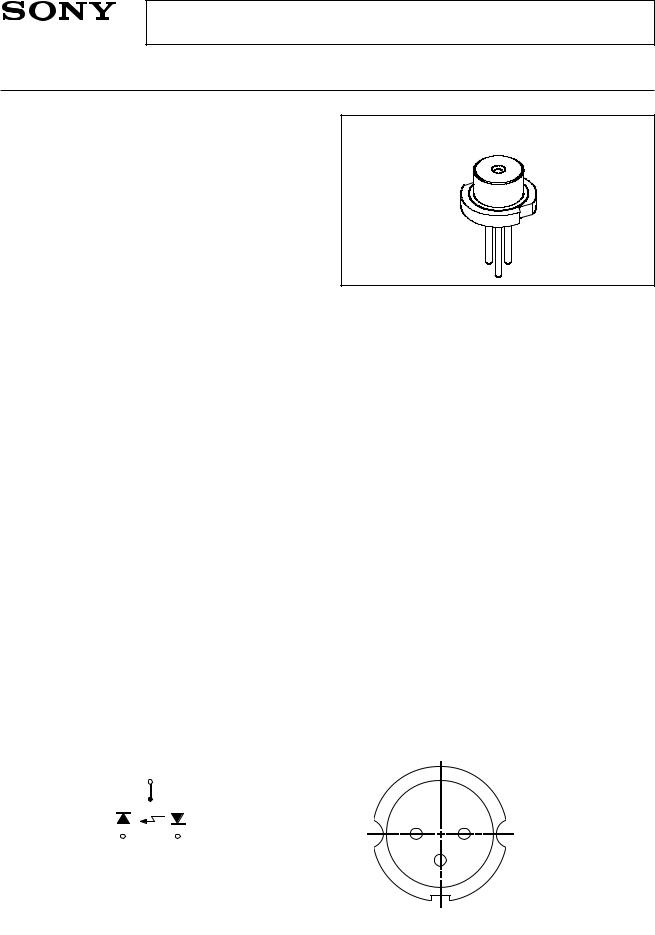
SLD1132VS
635nm Red Laser Diode
Description |
|
The SLD1132VS is a red laser diode designed for |
M-274 |
|
|
laser pointers. Its wavelength (635nm typ.) is |
|
shortened by 35nm and visibility is increased by |
|
approximately 7 times, compared to the conven- |
|
tional visible laser diode (670nm typ.). |
|
Features
• Short wavelength (635nm typ.)
•Small package (φ5.6)
•Fundamental traverse/single longitudinal mode
Applications
Laser pointers
Structure
•AlGaInP quantum well structure laser diode
•PIN photo diode for optical power output monitor
Recommended Optical Power Output
3mW
Absolute Maximum Ratings |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
• Optical power output |
Po |
5 |
mW |
|
|||||
• Reverse voltage |
VR LD |
2 |
|
V |
|
||||
|
|
|
PD |
15 |
|
V |
|
||
• Operating temperature |
Topr |
–10 to +40 |
°C |
|
|||||
• Storage temperature |
Tstg |
–40 to +85 |
°C |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Connection Diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
Pin Configuration |
|
||
3 |
COMMON |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
LD |
|
|
|
|
|
||
PD |
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1. LD cathode
2. PD anode
3. COMMON
Bottom View
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
– 1 –
E94Y01C98-PS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLD1132VS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical and Optical Characteristics (Tc = 25°C) |
|
|
Tc: Case temperature |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
|
Symbol |
Conditions |
Min. |
Typ. |
|
Max. |
Unit |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threshold current |
Ith |
|
|
50 |
|
70 |
mA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating current |
Iop |
Po = 3mW |
|
60 |
|
80 |
mA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating voltage |
Vop |
Po = 3mW |
|
2.4 |
|
3.0 |
V |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wavelength |
|
|
λ |
Po = 3mW |
625 |
635 |
|
645 |
nm |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Radiation |
|
Perpendicular |
θ |
Po = 3mW |
24 |
32 |
|
40 |
degree |
|||
angle |
|
Parallel |
θ// |
5 |
7 |
|
12 |
degree |
||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Position |
X, Y, Z |
|
|
|
|
±80 |
µm |
|||
Positional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Δφ |
Po = 3mW |
|
|
|
±3 |
degree |
||||
accuracy |
|
Angle |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Δφ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±4 |
degree |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential efficiency |
ηD |
Po = 3mW |
0.15 |
0.35 |
|
0.8 |
mW/mA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Astigmatism |
|
|
As |
| Z // – Z | |
|
|
|
20 |
µm |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Monitor current |
Imon |
Po = 3mW, Vr = 5V |
0.05 |
0.10 |
|
0.30 |
mA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Handling Precautions
(1) Eye protection against laser beams
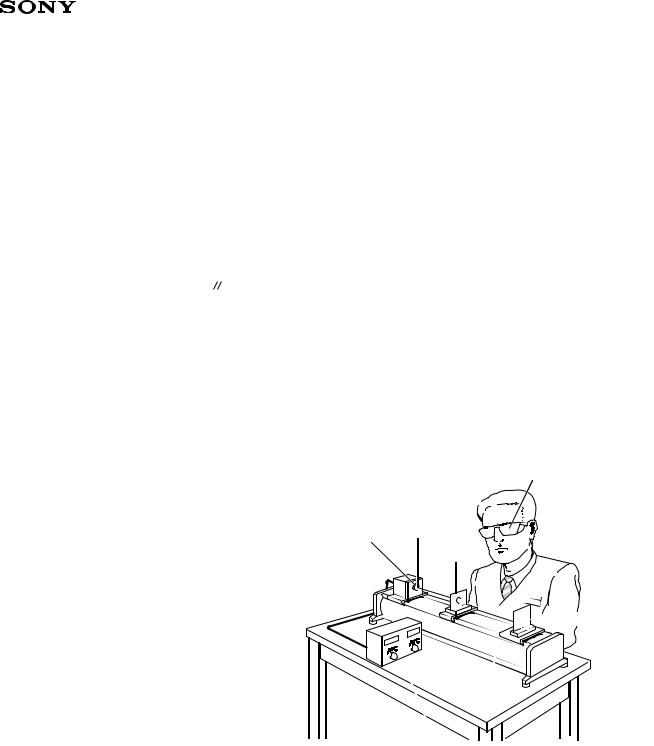
The optical output of laser diodes ranges from several mW to 3W. However the optical power density of the laser beam at the diode chip reaches 1MW/cm2. Unlike gas lasers, since laser diode beams are divergent, uncollimated laser diode beams are fairly safe at a laser diode. For observing laser beams, ALWAYS use safety goggles that block infrared rays. Usage of IR scopes, IR cameras and fluorescent plates is also recommended for monitoring laser beams safely.
Safety goggles for protection from laser beam
Laser diode |
Lens |
Optical material
 IR fluorescent plate
IR fluorescent plate
Optical board
Optical power output control device
Temperature control device
(2) Prevention of surge current and electrostatic discharge
Laser diode is most sensitive to electrostatic discharge among semiconductors. When a large current is passed through the laser diode even for an extremely short time (in the order of nanosecond), the strong light emitted from the laser diode promotes deterioration and then laser diodes are destroyed. Therefore, note that the surge current should not flow the laser diode driving circuit from switches and others. Also, if the laser diode is handled carelessly, it may be destructed instantly because electrostatic discharge is easily applied by a human body. Be great careful about excess current and electrostatic discharge.
– 2 –
 Loading...
Loading...