Siemens Viva-E User manual

®

Preface
CE
This instrument conforms to the provisions of the EU Directive on In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices
(98/79/EC) of the European Parliament and the Council of 27 October 1998.
The contents of this manual with all figures, tables and graphics are intellectual property of ELITechGroup.
Unauthorized commercial or non-commercial excerption or copying of contents and use of this manual (in
total or in parts) are strictly forbidden unless the editor gives written permission for it.
This manual was written and produced with the utmost care. However, errors cannot be fully excluded.
ELITechGroup does not take any responsibilities and accepts no liabilities for incidents of any kind that may
occur because of errors in the manual.
All product names mentioned in this manual are registered trademarks.
®
The Viva-E
conformity. This declaration is supplied with each device in a separate file.
Please call Technical Support if you need advice or you have any questions.
has been conceptualized, manufactured and tested in accordance with the declaration of
®
Manufacturer:
ELITechGroup B.V.
also trading as ELITechGroup Clinical Systems
Van Rensselaerweg 4
6956 AV Spankeren
The Netherlands
Telephone: +31 313 430 500
Telefax: +31 313 427 807
e-mail: service.ecsnl@elitechgroup.com
Internet: www.elitechgroup.com
1
Until December 1, 2013 ELITechGroup B.V. was known as Vital Scientific B.V.
Any reference in this manual to Vital Scientific B.V. or Vital should be read as ELITechGroup B.V. or
ELITechGroup Clinical Systems.
1
,
Distributed by:
Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Products GmbH
European Headquarters
Ludwig-Erhard Str. 12
65760 Eschborn,
Germany
www.siemens.com/diagnostics
In the US:
Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.
P.O. Box 6101
Glasgow Business Community
Newark, Delaware 19714-6101
USA
1-800-227-8994
www.siemens.com/diagnostics
Viva-E, Syva and EMIT are trademarks of Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics (formerly Dade Behring). All
other trademarks are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Article No.: 6002-380-410 V05

®
Contents
1. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND POTENTIAL HAZARDS
1.1 General .......................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.1 Basic assumptions for risk analysis ...........................................................................................1-2
1.1.2 Operator qualification.................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.3 Service technician qualification ..................................................................................................1-3
1.2 Description of symbols ................................................................................................................................1-4
1.2.1 Symbols on the instrument.........................................................................................................1-4
1.2.2 Symbols in the manual...............................................................................................................1-4
1.3 Hazards.......................................................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.1 Electrical hazards.......................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.2 Mechanical hazards ...................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.3 Sample and reagent arms..........................................................................................................1-5
1.3.4 Lamp ..........................................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.5 Chemical hazards ......................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.6 Biohazard...................................................................................................................................1-6
1.3.7 Operational requirements...........................................................................................................1-6
1.3.8 Transport and storage requirement............................................................................................1-6
1.4 Installation ...................................................................................................................................................1-7
1.4.1 External connections..................................................................................................................1-7
1.4.2 Maintenance...............................................................................................................................1-7
1.4.3 Instrument unused for one month or longer ...............................................................................1-7
1.4.4 Coolant liquid .............................................................................................................................1-7
1.5 Use of materials with the analyzer ..............................................................................................................1-8
1.5.1 Specimens .................................................................................................................................1-8
1.5.2 Reagents and calibrators ...........................................................................................................1-8
1.5.3 Controls...................................................................................................................................... 1-8
1.5.4 Analytical results ........................................................................................................................1-8
2. INTRODUCTION
2.1 The system..................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.1 Intended use .............................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.2 System presentation ..................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 Computer control........................................................................................................................2-3
2.2 Modules.......................................................................................................................................................2-4
2.2.1 General ......................................................................................................................................2-4
2.2.2 Rotors.........................................................................................................................................2-5
2.2.3 Pipette system ..........................................................................................................................2-5
2.3 Cooling unit ................................................................................................................................................2-6
2.4 External barcode reader..............................................................................................................................2-7
2.5 Installation ...................................................................................................................................................2-8
2.5.1 Installation requirements ...........................................................................................................2-8
2.5.2 Move the analyzer .....................................................................................................................2-8
2.6 Performance and technical data ...............................................................................................................2-9
2.6.1 Performance ..............................................................................................................................2-9
2.6.2 Sample system ..........................................................................................................................2-9
2.6.3 Reagent system ......................................................................................................................2-10
2.6.4 Measurement station ..............................................................................................................2-10
2.6.5 Minimum PC requirements ......................................................................................................2-11
2.6.6 Cooling unit .............................................................................................................................2-11
2.6.7 External barcode reader ..........................................................................................................2-12
2.6.8 Accuracy and precision ..........................................................................................................2-12
2.7 Analyzer technical data (without washing unit or computer) ....................................................................2-13
2.7.1 Dimensions and weight ..........................................................................................................2-13
2.7.2 Power requirements ................................................................................................................2-13
2.7.3 Environmental requirements ................................................................................................... 2-13
2.7.4 Approvals ................................................................................................................................2-13
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. i

3. SYSTEM HANDLING BASICS
3.1 Work Preparation ........................................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Use of the manual......................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.2 Parts of the screen.....................................................................................................................3-3
3.1.3 Navigation keys..........................................................................................................................3-4
3.1.4 Emergency halt ..........................................................................................................................3-4
3.1.5 Messages ..................................................................................................................................3-4
3.2 Start the analyzer for the first time ..............................................................................................................3-5
3.2.1 Prepare the analyzer..................................................................................................................3-5
3.2.2 Start the analyzer....................................................................................................................... 3-5
3.2.3 Install the cooling unit ................................................................................................................3-6
3.2.4 Set the reagent rotor type .........................................................................................................3-7
3.2.5 Passwords .................................................................................................................................3-8
3.2.6 System liquid..............................................................................................................................3-9
3.2.7 System parameters .................................................................................................................3-10
3.3 Checklist....................................................................................................................................................3-12
3.3.1 Checklist for routine operation ...............................................................................................3-12
4. BASIC ROUTINE
4.1 Preparing tests ............................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.1 Methods to enter sample information and select tests...............................................................4-2
4.2 Enter sample data and test requests .......................................................................................................4-3
4.2.1 Request samples screen ...........................................................................................................4-3
4.2.2 Request samples parameters ...................................................................................................4-4
4.2.3 Request samples function keys .................................................................................................4-5
4.2.4 Request samples and assign tests with an external barcode reader ........................................ 4-6
4.2.5 Manually request samples and assign tests ............................................................................4-6
4.2.6 Request (multiple) samples efficiently .......................................................................................4-7
4.2.7 Requesting priority samples.......................................................................................................4-7
4.2.8 Request a test for a reagent blank.............................................................................................4-7
4.2.9 Request a control test ..............................................................................................................4-8
4.2.10 Request a test for calibration ...................................................................................................4-9
4.2.11 View, edit or delete sample requests ........................................................................................4-9
4.2.12 Print a worklist..........................................................................................................................4-10
4.3 Load the sample rotor and start the tests ...............................................................................................4-11
4.3.1 Preparation of samples, dead volume and over sampling ...................................................4-11
4.3.2 Loading pediatric sample cups.............................................................................................
4.3.3 Sample Handling screen ......................................................................................................... 4-12
4.3.4 Sample rotor positions and color codes ...................................................................................4-12
4.3.5 Worklist and color codes ..........................................................................................................4-14
4.3.6 Sample Handling function keys................................................................................................4-15
4.3.7 Load barcoded samples (with external barcode reader)..........................................................4-16
4.3.8 Load samples (without barcodes) ............................................................................................4-16
4.3.9 Load samples with mouse........................................................................................................4-17
4.3.10 Load samples during a sample run ..........................................................................................4-17
4.3.11 Load a reagent blank ...............................................................................................................4-17
4.3.12 Load a control ..........................................................................................................................4-18
4.3.13 Load a calibrator ......................................................................................................................4-18
4.4 Reagent info screen ..................................................................................................................................4-19
4.4.1 Reagent info parameters..........................................................................................................4-19
4.4.2 Reagent info function keys.......................................................................................................4-20
4.4.3 Check and refill reagents .........................................................................................................4-21
4.5 Start and stop the sample run ...................................................................................................................4-22
4.5.1 Start the analysis run ...............................................................................................................4-22
4.5.2 Unload samples .......................................................................................................................4-22
4.5.3 Error and warning messages ...................................................................................................4-23
4.6 Check and validate the results .................................................................................................................4-25
4.6.1 Evaluate results screen...................................................................................................
4.6.2 Sample list................................................................................................................................4-25
®
....4-11
.........4-25
ii VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
4.6.3 Sample details..........................................................................................................................4-26
4.6.4 Test results...............................................................................................................................4-26
4.6.5 Evaluate results function keys..................................................................................................4-27
4.6.6 Validation of a result.................................................................................................................4-28
4.6.7 Evaluate historic results ........................................................................................................... 4-28
4.6.8 Result details ...........................................................................................................................4-29
4.6.9 Result details function keys......................................................................................................4-31
4.6.10 Information screen for blank/calibration ...................................................................................4-32
4.6.11 Result details for a two reagent kinetic test..............................................................................4-33
4.6.12 Result details for an endpoint test with a reagent blank...........................................................4-35
4.6.13 Result details for a two point test .............................................................................................4-36
4.6.14 Result details for a measurement with a prozone check..........................................................4-38
4.6.15 Automatic results printout......................................................................................................... 4-39
5. EXTENDED ROUTINE
5.1 Program controls ......................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.2 Program control screen..............................................................................................................5-2
5.1.3 Program control parameters .....................................................................................................5-2
5.1.4 Program control function keys ...................................................................................................5-3
5.1.5 Enter a new control ....................................................................................................................5-3
5.1.6 Change a control (e.g. when the batch/lot number has changed) .............................................5-4
5.1.7 Program a control.......................................................................................................................5-5
5.1.8 Westgard rules .......................................................................................................................... 5-7
5.2 Calibrator programming ...........................................................................................................................5-8
5.2.1 Calibrators..................................................................................................................................5-8
5.2.2 Program a calibrator...................................................................................................................5-8
5.2.3 Program calibrator parameters ...............................................................................................5-10
5.2.4 Program calibrator function keys .............................................................................................5-10
5.3 Test programming ..................................................................................................................................5-11
5.3.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-11
5.3.2 Load the test parameters .........................................................................................................5-11
5.3.3 Program a new test or modify an existing test ........................................................................5-12
5.3.4 Test programming - Test parameters 1 .................................................................................5-14
5.3.5 Test programming - Test parameters 2 ...............................................................................5-18
5.3.6 Program test calibrator parameters ........................................................................................5-25
5.3.7 Program calibrator function keys .............................................................................................5-28
5.3.8 Calibration curves algorithms...................................................................................................5-29
5.3.9 Accept calibration curve parameters........................................................................................5-31
5.3.10 Absorbance check for calibrated tests .....................................................................................5-31
5.4 Quality control ..........................................................................................................................................5-32
5.4.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-32
5.4.2 Quality control screen ..............................................................................................................5-32
5.4.3 Quality control parameters .....................................................................................................5-32
5.4.4 Quality control function keys ....................................................................................................5-32
5.4.5 Graphic representation of quality control .................................................................................5-33
5.4.6 Fields visible in graphic and table modes (left hand side)........................................................5-33
5.4.7 Description of the graphic display ............................................................................................5-34
5.4.8 Description of the table mode ..................................................................................................5-35
5.5 Cuvette incompatibility ..............................................................................................................................5-36
5.5.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-36
5.5.2 Start needle and cuvette incompatibility...................................................................................5-36
5.5.3 Incompatibility parameters .......................................................................................................5-36
5.5.4 Incompatibility screen...............................................................................................................5-37
5.5.5 Define incompatible tests.........................................................................................................5-38
5.5.6 Define compatible tests............................................................................................................5-39
5.6 Profiles ...................................................................................................................................................... 5-40
5.6.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-40
5.6.2 Program profiles ......................................................................................................................5-40
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. iii

5.6.3 Program profile function keys...................................................................................................5-41
5.7 Reagent position .......................................................................................................................................5-42
5.7.1 Introduction to reagent position................................................................................................5-42
5.7.2 Program a reagent position......................................................................................................5-42
5.7.3 Reagent position function keys ................................................................................................5-43
5.8 Calculated results ....................................................................................................................................5-45
5.8.1 Introduction to calculated results..............................................................................................5-45
5.8.2 Calculated result programming screen ....................................................................................5-46
5.8.3 Calculated result programming parameters .............................................................................5-46
5.8.4 Calculated result programming function keys ..........................................................................5-48
5.9 Test messages and flags ..........................................................................................................................5-49
5.9.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-49
5.9.2 Test messages function keys...................................................................................................5-49
5.9.3 Test flags .................................................................................................................................5-50
5.9.4 Custom automatic evaluation and rerun ..................................................................................5-53
5.10 Set up a report ..........................................................................................................................................5-54
5.10.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................5-54
5.10.2 Report setup segments............................................................................................................ 5-54
5.10.3 Define a report set-up .............................................................................................................. 5-55
5.10.4 Report setup tabs and data fields ............................................................................................5-56
5.10.5 Report setup function keys.......................................................................................................5-59
®
6. MAINTENANCE
6.1 Maintenance procedures.............................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.1 User maintenance......................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.2 Replace cuvette rotor.................................................................................................................6-3
6.1.3 Manual cuvette rotor blank measurement..................................................................................6-3
6.1.4 Exclude a stained cuvette ..........................................................................................................6-4
6.1.5 Blank rotor function keys............................................................................................................6-5
6.1.6 Replace the photometer lamp....................................................................................................6-5
6.1.7 Replace syringes........................................................................................................................6-8
6.1.8 Washing/filling cuvette rotor .......................................................................................................6-9
6.1.9 Needle rinse.............................................................................................................................6-10
6.1.10 Replace the water filter ............................................................................................................6-10
6.1.11 Replace the drying block..........................................................................................................6-11
6.2 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................................6-12
6.2.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................6-12
6.2.2 Defective mixer belt..................................................................................................................6-12
6.2.3 Sample needle clogged............................................................................................................6-13
6.2.4 Removal of the rotor tray..........................................................................................................6-13
6.2.5 Error history..............................................................................................................................6-13
6.2.6 Error messages........................................................................................................................6-15
6.2.7 Hardware-error messages .......................................................................................................6-16
7. INSTALLATION
7.1 Hardware installation...................................................................................................................................7-2
7.2 Software installation....................................................................................................................................7-3
7.2.1 General ......................................................................................................................................7-3
7.2.2 Prepare PC ................................................................................................................................7-3
7.2.3 Install software ...........................................................................................................................7-6
7.2.4 Files............................................................................................................................................7-7
7.3 Configure software ......................................................................................................................................7-8
7.3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................7-8
7.3.2 Start communication selection ...................................................................................................7-9
7.3.3 Printer parameters ...................................................................................................................7-10
7.3.4 Host communication parameters .............................................................................................7-10
7.3.5 Communication function keys ..................................................................................................7-10
7.3.6 Configure analyzer communication handler.............................................................................7-11
7.3.7 Configure host port settings .....................................................................................................7-12
iv VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

7.3.8 Host - PC communication ........................................................................................................7-12
7.4 System backup procedure ........................................................................................................................7-13
7.4.1 Backup files..............................................................................................................................7-13
7.4.2 Start Restore point ...................................................................................................................7-13
7.4.3 Restore point parameters.........................................................................................................7-13
7.4.4 Restore point function keys......................................................................................................7-14
7.5 Data backup procedure.............................................................................................................................7-15
7.5.1 Setup........................................................................................................................................ 7-15
7.5.2 Data backup.............................................................................................................................7-15
7.6 Importing and exporting data ....................................................................................................................7-16
7.6.1 Exporting data..........................................................................................................................7-16
7.6.2 Importing data ..........................................................................................................................7-17
8. RESULTS EXPORT FILE
8.1 General .......................................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.2 Summary of new features ..........................................................................................................8-2
8.2 View or change system parameters (additions) ..........................................................................................8-3
8.3 Export results .............................................................................................................................................. 8-5
8.3.1 Select information and create export files..................................................................................8-5
8.3.2 Automatically create archive and export files.............................................................................8-7
8.4 Archive and search results ..........................................................................................................................8-8
8.4.1 Archive results............................................................................................................................8-8
8.4.2 Search results ............................................................................................................................8-8
8.5 Copy export files or archived results files to a USB drive ...........................................................................8-9
8.6 Networking ................................................................................................................................................8-10
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. v

®
vi VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
1SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND POTENTIAL HAZARDS
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 1-1

®
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
1.1 General
Before you start installing and working with the analyzer, you should read the safety precautions and
regulations shown in this chapter. Safety comes first!
The analyzer was designed and manufactured according to modern standards and with regard to
international safety regulations. All possible risks that were known at the time of manufacturing were
taken into account and either eliminated or reduced. Nevertheless, some sources of danger cannot
be eliminated. Please note the following guidelines.
When operating the analyzer all national or international guidelines and regulations must be
observed, as in the normal lab routine. Power supply accessories (cables/plugs) must be installed in
such a way that sources of danger (overheating of cables, short circuit due to incorrect fuse ratings,
loose cables etc.) are eliminated. The user should be aware, that if the analyzer is used in a manner
not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired. The
analyzer is supplied without anti-virus software. If you connect the analyzer to a network, make sure
that the network has the necessary protection.
1.1.1 Basic assumptions for risk analysis
Following assumptions are the basis for the risk analysis. It is assumed that:
• The Samples were adequately derived, prepared, handled, and labeled before being loaded
into the device.
• Reagents and calibrators were adequately stored, prepared, handled, and labeled before being
loaded into the device.
• Adequate quality control procedures are observed by laboratory personnel to check the
performance of the analyzing system by adequate use of control material.
• Laboratory personnel involved in operation and handling of the device are adequately trained.
• Laboratory personnel involved in operation and handling of the device are aware of the risks
involved in handling material of human origin (biological hazards) and that correct procedures
are followed to prevent infection.
• Service personnel involved in preventive and corrective maintenance of the device are
adequately trained.
• Service personnel who maintain the device know the risks of biological hazards and follow the
correct precautions.
• Preventive maintenance is performed in accordance with the instructions provided by the User
Manual and the Service Manual.
• Original replacement parts are used in maintenance of the device.
• Original disposables are used in operation of the device.
• Reagents and methods are validated before actual samples are measured.
• Service personnel must follow the instructions to install and check the device.
• Limit checks are correctly implemented and used in the test parameter settings. (absorbance,
reagent blank absorbance, control, calibrator, etc.).
• A rotor blank run is performed once every day before measurements are performed.
• Test results obtained from the instrument are carefully examined by an expert before any further
measures are taken based on the analytical results.
1.1.2 Operator qualification
The analyzer should only be used by qualified and trained personnel, who have taken part in a
special operator training course on the instrument.
For clinical tests, the instrument should be used under the management of a doctor or clinical
inspector.
1-2 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
1.1.3 Service technician qualification
To install, maintain and repair the instrument, a service technician has to be trained on the
instrument by the manufacturer or their representative. A service technician is also expected to be
familiar with the normal operation of the instrument as described in the operator manual and the
special operations as described in the Service manual.
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 1-3

®
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
1.2 Description of symbols
1.2.1 Symbols on the instrument
WARNING
Attention, consult instructions for use. This symbol appears on several parts of the analyzer. The
specific meaning that applies for those parts is described in 1.3 Hazards.
WARNING
Hot surface. This label is attached on or close to parts of the instrument that get hot when the
instrument is switched on. Make sure to keep fingers and other body parts clear of the hot surface.
WARNING
Pinch point. Fingers and other body parts can be pinched where this label shows. Make sure to
keep fingers and other body parts clear of the pinch point.
BIOHAZARD
The contents of the container marked with this symbol are a biological hazard and are potentially
infectious. This symbol is shown on waste bottles.
ATTENTION
This symbol means that at the end of life, the analyzer must be separately collected in accordance
to the European Directive 2002/96/EC.
1.2.2 Symbols in the manual
WARNING
Failure to follow information contained in warning messages could lead to serious personal injury
and/or damage to the analyzer.
ATTENTION
Failure to follow information contained in the attention messages could lead to damage to the
analyzer.
Note
Notes contain additional information corresponding to the text.
1-4 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
1.3 Hazards
1.3.1 Electrical hazards
WARNING
To prevent the risk of electrical shock and/or damage to the instrument, operators should not open
the covers of live parts (electrical) of the instrument. Only authorized personnel, e.g. service
technicians, may open the instrument to perform maintenance or repairs.
Touching the live parts when the power is on may cause severe injury or death.
1.3.2 Mechanical hazards
WARNING
DO NOT wear loose garments or jewelry that could catch in mechanisms.
DO NOT put your fingers/hands into the pathway of any part while the analyzer is in operation.
DO NOT attempt mechanical repair unless the instrument is not in operation or OFF.
1.3.3 Sample and reagent arms
WARNING
Do not touch movable parts of the system (rotors, arms, etc.) while they are in motion.
Particular attention and caution must be paid to sample and reagent needles. Although the greatest
possible safety precautions were taken, these parts still are potentially hazardous. However, the
system automatically interrupts the procedure if the needles are touched. Always keep rotors
covered with the supplied caps, except when loading or unloading. Covering protects sample
material and reagents from contamination.
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
1.3.4 Lamp
WARNING
During operation, the photometric lamp becomes extremely hot. DO NOT look directly into the light
path of the lamp when it is on.
DO NOT touch the lamp when it is on!
If the lamp needs to be changed, wait until the lamp has cooled down.
1.3.5 Chemical hazards
The operator is responsible for taking all necessary precautions against hazards associated with the
use of clinical laboratory chemicals. Specific recommendations for each reagent used with the
analyzer are normally found on the manufacturer's package inserts or on product information sheets
for each chemical. Wipe up any reagent spillage on the instrument immediately.
Additional precautions:
Consult the reagent manufacturer for information on the concentrations of heavy metals and other
toxic constituents in each reagent.
Avoid direct body-contact with reagents and cleaning solutions. Direct body-contact may result in
irritation or damage to your skin. Refer to the manufacturer's reagent kit box and package inserts, or
product information sheets for specific instructions.
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 1-5

®
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
1.3.6 Biohazard
BIOHAZARD
Patient samples, controls, calibrators and liquid waste are potentially infectious. The handling of
patient samples, control sera and liquid waste must be performed according to national and
international laboratory safety regulations.
Patient samples, controls, calibrators and liquid waste should be considered potentially infectious
and capable of transmitting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV) and other
blood borne pathogens. The handling of these substances must be performed in accordance with
established laboratory safety regulations in order to minimize risk to laboratory staff. This includes
wearing of gloves, splash protection, etc. Contact of skin and mucous membranes must be avoided.
This also applies to all components of the instrument that are exposed to these substances. If any
specimen is spilled on the instrument, wipe it up immediately and clean the contaminated surface
with a disinfectant.
In various countries there are regulations on the disposal of waste. Refer to local sources for
additional information on correct waste disposal.
1.3.7 Operational requirements
WARNING
Do not place the analyzer against a wall. There must be access at all times to the rear panels of the
analyzer. Make sure the power switch can be reached and there is free circulation of ventilation air.
ATTENTION
The cooling unit must be filled with liquid. The level should be visible and between a minimum and
a maximum level. Check liquid level every 3 months. For details on the liquid to be used, see
2.3 Cooling unit.
1.3.8 Transport and storage requirement
ATTENTION
Always store the analyzer in an environment with temperatures between -10 °C and +45 °C.
1-6 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

1.4 Installation
The analyzer, cooling unit and other devices, parts and accessories are shipped in transport boxes
and have to be unpacked and installed by a qualified service technician from the manufacturer or his
designated representative. If these instructions are not observed, The manufacturer does not
assume responsibility for occurring damage or improper operation of the analyzer. The customer is
responsible for providing the necessary facilities as described in detail in 2.6 Performance and
technical data.
1.4.1 External connections
ATTENTION
Only instruments that meet the relevant safety requirements may be connected to the analyzer.
Only use UL-listed power supply cable and power distribution blocks.
1.4.2 Maintenance
ATTENTION
For continued protection against risk of fire only use fuses of the specified type and current ratings.
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
For maintenance and repair procedures (e.g. replacement of cuvette rotor, photometer lamp) follow
the instructions given by service personnel or specified in the manual.
Do not use unsuitable tools for repairs (e.g. screwdrivers which are not insulated for work performed
at electrical components).
During operation and maintenance of the instrument, proceed according to the instructions and do
not touch any parts of the instrument other than those specified.
Avoid touching any mechanical parts while the instrument is operating. This may cause operation to
stop or damage the instrument.
Only original spare parts should be used in the maintenance of this analyzer.
Only original disposables and accessories should be used in the operation of this analyzer.
Make sure the front covers are closed while the instrument is in operation.
1.4.3 Instrument unused for one month or longer
If the instrument is not to be used for one month or longer, contact Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics
Technical Support for further information before you switch off the analyzer.
1.4.4 Coolant liquid
The cooling unit of the analyzer is filled with ethylene glycol. Any spills during maintenance should
be disposed of according to local regulations.
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 1-7

®
Safety Precautions and Potential Hazards
1.5 Use of materials with the analyzer
1.5.1 Specimens
This analyzer is designed for measurements of analytes in samples of serum, plasma and urine or
extract solutions from the Siemens immunosuppressant assays. Patient samples should be
prepared and handled in accordance with the instructions from the reagent manufacturer. Refer to
the reagent kit insert for detailed instructions.
ATTENTION
Make sure that the sample/reagent mixture does not contain any blood clots, dust or other insoluble
contaminants. If insoluble contaminants are contained in the sample, correct measuring values may
not be obtained.
1.5.2 Reagents and calibrators
The manufacturer recommends the use of Syva®/Siemens reagents and calibrators in combination
with this analyzer.
ATTENTION
Treat all reagents according the manufacturer's recommendations. Refer to the reagent kit box and
package inserts, and product information sheets for specific instructions.
WARNING
Vital Scientific B.V. assumes no responsibility for erroneous test results caused by reagent kits,
calibrators and test parameters that are not provided by Vital Scientific B.V.
WARNING
Siemens assumes no responsibility for erroneous test results caused by reagent kits, calibrators
and test parameters that are not provided by Siemens.
1.5.3 Controls
The manufacturer recommends the use of quality control solutions with known values for each test
in accordance with international regulations and guidelines. Results obtained should fall within the
limits defined by the day to day variability of the system as determined in the user laboratory. If the
results fall outside the laboratory’s established limits, refer to the troubleshooting information in this
manual or contact your agent.
1.5.4 Analytical results
The analytical results do not only depend upon correct operation of the analyzer but also on a
variety of external influences beyond the control of the manufacturer. Therefore the test results
obtained with this instrument must be carefully examined by a clinical inspector or doctor, before any
diagnostic or therapeutic measures are taken based on the analytical results.
WARNING
An incorrectly measured result may lead to an error in diagnosis, thereby posing a danger to the
patient.
1-8 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2INTRODUCTION
Introduction
Introduction
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-1

®
Introduction
2.1 The system
2.1.1 Intended use
The analyzer is an automatic chemistry analyzer, used in combination with certain reagents for in
vitro diagnostic measurement of analytes in samples of serum, plasma, urine and aqueous standard
solutions. Most clinical chemistry tests that require a photometric measurement can be adapted for
the system. The analyzer is intended for use in laboratories. The analyzer has to be operated by
trained operators.
2.1.2 System presentation
The analyzer is a universal system. The price-performance-relation is optimized for small and
medium workload; up to 180 tests per hour. It is easy to adapt the analyzer in any kind of laboratory.
In the main unit of the system, the actual analyzer, all liquid handling and measurements take place.
A separate computer controls the analyzer unit, collects the raw data and provides the user
interface. A cooling unit enables the system to ensure the precision of all ´on-board´ reagents.
Environmental compatibility and economic efficiency are guaranteed. Easy operation (menu and
message control by display), short training time as well as recording of sample and test data with
barcode scanner reduce personnel assignment and save a maximum of time.
2-2 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2.1.3 Computer control
ATTENTION
Only run the software in order to operate the analyzer. The use of other software might cause
failure in the communication between the analyzer and the computer.
An external computer and a monitor provide the user interface for the analyzer. The operating
system is Microsoft
test results are saved on the computer. The software provides a standard way of output on a printer,
but the operator can change the format of the result report. Test parameters, control results and
calibration results are also saved on the computer and are ready for access.
It is possible to connect the analyzer to a lab data processing system (central processor/host
computer). If this is the case, it is possible to enter test requests directly from the host computer.
Also, the test results can be transferred to the host computer.
®
Introduction
Windows®. A keyboard or a barcode reader is necessary to enter data. The
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-3
®
Introduction
2.2 Modules
2.2.1 General
Note
In the screen texts system liquid is replaced by water.
The analyzer is microprocessor controlled. All mechanical functions are directed and monitored by
dedicated processors. The operator has a constant view on the hardware status and performance of
the chemistries. When errors or flagged results occur for open channel assays, the analyzer offers
an automatic re-run facility. The re-run facility includes automatic pre-dilution by sample reduction
for high results. The results are printed as the analysis sequence is completed. The print is held
when a test is in evaluation or re-run. This prevents mixing-up the analysis sequence. The operator
can change the format of the result report. Prints of calibration curves, reaction curves, LeveyJennings plots, test methods, etc. are possible.
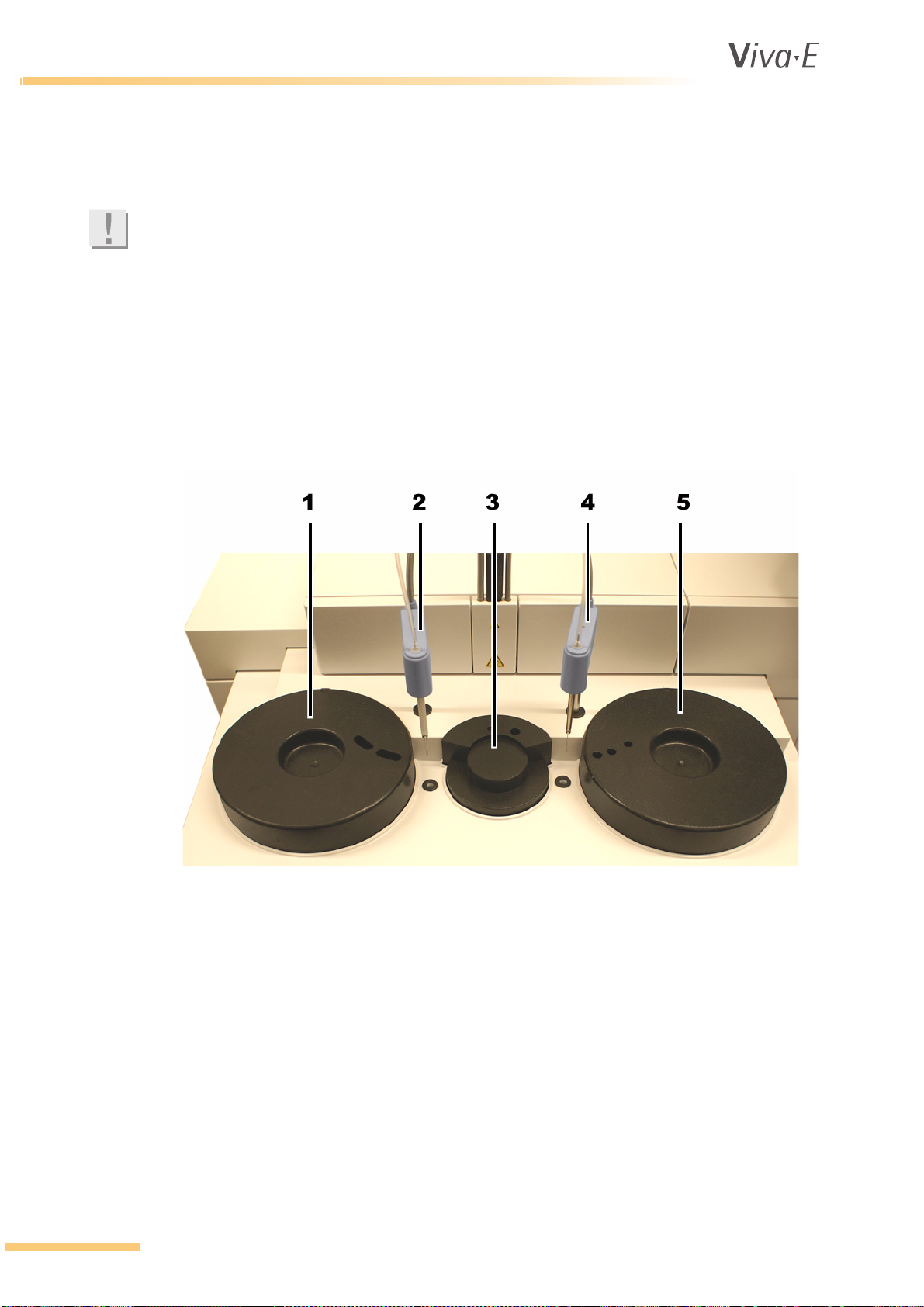
1 Reagent rotor
2 Reagent pipette
3 Cuvette rotor
4 Sample pipette
5 Sample rotor
2-4 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2.2.2 Rotors
Sample rotor
The sample rotor is designed to accept a variety of sample tubes and cups. The sample rotor is
covered. Emergency (STAT) samples and samples in pediatric cups can be tested without
interference of the routine workload.
Reagent rotor
The reagent rotor compartment is cooled to a maximum of 12°C below ambient temperature. The
rotor is covered to protect light sensitive reagents and to isolate from ambient temperature.
Cuvette rotor
Note
Replace the cuvette rotor when one of the eight wavelengths shows the message SD.ERR after the
rotor blank measurement. The quality and reliability is not guaranteed when the cuvette rotor is not
replaced.
The multi-use cuvette rotor contains 48 cuvettes and is incubated at 37°C. The cuvette rotor, made
for the manufacturer, is covered by a heated cover.
The maximum incubation time after sample addition is 11.5 minutes with a single reagent and 11.25
minutes with two or more reagents. After the last measurement, the rotor is washed and dried. To
avoid drying-in of the rotor, the reagent pipette automatically fills the rotor with water.
Introduction
Washing unit
The washing unit aspirates the reaction mixture after analysis and washes the cuvettes with 4 x 500
µl water. The waste is disposed in a waste container. The washing unit is equipped with liquid
sensors to avoid the flooding of the system with water.
2.2.3 Pipette system
Pipettes
Two syringes, a 1000 µl and a 100 µl, are used in combination with a valve block to pipette reagents
and samples. The pipette mechanisms are water-filled. Pipetting takes place by means of positive
water displacement with air bubble separation.
Sample pipette mechanism
The sample probe is equipped with a level detector and can aspirate volumes between 2µl and 30 µl
(in steps of 0.1 µl). The level detector in the sample probe detects if sufficient sample is present. The
probe dispenses the sample into the cuvette rotor and also mixes the reaction mixture. When a
sample is needed, the probe senses the liquid to take up an air bubble first before taking up the
sample. The probe is washed internally and externally afterwards.
Reagent pipette mechanism
The reagent probe is equipped with a level detector and can aspirate volumes between 10 µl and
399 µl (in steps of 1.0 µl). The level detector in the reagent probe detects if sufficient reagent is
present. A heating element in the probe pre-heats the cooled reagents. Reagents must be prepared
outside the analyzer. After the probe transfers the aspirated volume of reagent into the cuvette rotor,
the probe is washed internally and externally. After a 2nd or 3rd reagent is dispensed, the reagent
probe mixes the reaction mixture before it goes to the wash.
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-5

®
Introduction
2.3 Cooling unit
WARNING
The cooling unit with the analyzer is filled with ethylene glycol. Any spills during maintenance
should be disposed of according to local regulations.
The analyzer is equipped with an external cooling unit that guarantees cooling for loaded reagents.
The cooling unit operates as a sealed unit and needs little maintenance. The cooling unit is placed
behind the liquid waste and water bottles and provides a constant temperature for the reagents
located on the rotor, as required by the application protocol. When an acoustic signal sounds, the
cooling liquid must be refilled.
Note
Use a mixture of 1 part EUROL
The control display shows the temperature of the cooling liquid. The actual temperature of the
reagents will be slightly higher. The user cannot change the temperature setting of the cooling unit.
The unit and coolant are free from chlorofluorocarbons.
The installation is made by the service engineer and is not described in this manual.
®
to 1 part water.
2-6 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2.4 External barcode reader
ATTENTION
Switch off the computer before you install the external barcode reader.
You can shorten the operator time with an optional external barcode reader. This hand held barcode
reader can be connected to the keyboard of the PC. When requesting tests, you can enter sample
ID numbers from barcodes on the sample tubes. You can then assign tests with the use of the
barcode request menu card.
Most of the available barcodes can be read. The Codabar barcode is used for test requisitions. The
Codabar start character is used to differentiate between tests and profiles.
Introduction
The barcode reader can also be used to identify the samples when loading them or when viewing
the test results.
Note
The external barcode reader has a separate instruction manual. Please read the barcode reader
manual for information and user instruction.
Note
The manufacturer recommends that a fault safe barcode reader is used. Barcode readers that do
not use a checksum can give improper or false readings.
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-7

®
Introduction
2.5 Installation
2.5.1 Installation requirements
Only a qualified service technician may unpack the analyzer, cooling unit and other devices. The
manufacturer does not take responsibility for damage or improper operation of the analyzer, when
these instructions are not observed. The analyzer is inspected and ready for use when it is handed
over to the user.
Use the analyzer in closed rooms. It must be placed on a flat, horizontal surface that is not subject to
vibrations. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight.
The electrical connection has to be grounded according to common regulations to ensure proper
operation of the analyzer.
The analyzer is compliant with the requirements of the applicable EMC standards. Electronic
equipment that exceed the radiation limits defined in the EMC standards, like GSM and other
handheld mobile equipment, may affect proper operation of the equipment.
Note
This is a class A product. This product may cause interference in a domestic environment. In this
case the user may be required to take adequate arrangements.
2.5.2 Move the analyzer
Please follow the instructions below when the instrument needs to be moved.
1. Switch off the analyzer, the computer and the cooling unit.
2. Disconnect all cables and tubes.
3. Pull up the arm and place the arm protection tube over the shaft. This prevents the arm from
moving down.
4. Move the analyzer with at least 2 persons. Hold the instrument only by the metal frame on the
bottom.
ATTENTION
Do not lift the instrument by the door that covers the syringes. The door might come off the hinges,
causing the instrument to drop.
5. Connect all cables and tubes again when the analyzer is in place.
2-8 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2.6 Performance and technical data
2.6.1 Performance
Maximum throughput One reagent: 180 tests per hour
Two reagents: 133 tests per hour
Three reagents: 65 tests per hour
Accuracy Refer to 2.6.8 Accuracy and precision
Precision Refer to 2.6.8 Accuracy and precision
Programmable tests 5 per programmed reagent disc
Preprogrammed tests Up to 115
Quality control 1-3 per parameter, 120 controls programmable per reagent rotor
Sample processing Prioritized: STAT, Pediatric, Normal, in that order
Introduction
2.6.2 Sample system
Sample positions 51 patient samples
Emergency samples 3 positions
Calibrators 9 positions plus maximum 51 patient positions
Pediatric samples 6 positions, overflow goes to sample positions 1 - 51
Blank position 1
Controls 4 positions plus maximum 51 patient positions
Rinsing position 1
Sample tubes Primary/secondary tubes
Sample needle With level detector and integrated mixer
Pipetting capacity 2-30 µl (steps of 0.1 µl)
Syringe 100 µl
Diameter: 13 mm
Height: max. 78 mm
Adapter 6 (pediatric, sample rotor)
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-9

®
Introduction
2.6.3 Reagent system
Reagent rotor (Emit) 26 positions: 13 x 14 ml, 13 x 28 ml bottles
Volume/test Reagent 1: 110 – 399 µl, reagent 2: 0 – 180 µl,
Cooling Up to 12 °C below ambient temperature
Needle Pre-heated, with level detector
Pipetting capacity 400 µl (steps of 1 µl)
Syringe 1000 µl
Adaptors (Emit) 10 in total: 5 for 6 ml bottle, 5 for 3 ml bottle
2.6.4 Measurement station
Cuvette rotor Multi use disposable rotor with 48 cuvettes
reagent 3: 0 – 180 µl
Path length 6.8 mm
Minimum volume 220 µl
Maximum volume 400 µl
Wash station Fully automatic with overflow-level detector
Cuvette rinsing 4 × 500 µl system liquid
Light source Halogen lamp 12V 20W
Wavelength 340, 415, 505, 546, 570, 600, 660, and 700 nm
Wavelength uncertainty +/- 2 nm
Spectral half-width value 10 +/- 2 nm
Measuring range -0.1 to 3.0 Abs.
Temperature 37 °C ± 0.2 °C
Cycle time 27 sec. (DUAL MODE)
2-10 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
2.6.5 Minimum PC requirements
CPU Intel® Pentium® 800 MHz
RAM 128 MB
Monitor VGA monitor 1024 x 768 pixels
Hard Disk 2 GB
Additional drive CD-ROM drive
Operating system Windows
Serial ports 1 required for analyzer, 1 optional for host connection (a LAN
LAN connection Optional for host connection (a serial port can be used instead)
USB Ports One optional for printer
Parallel Ports Optional for printer
®
2000 or Windows® XP
connection can be used instead)
Introduction
2.6.6 Cooling unit
Weight (empty) 19.6 kg
Weight (filled) approx. 23 kg
Required space 84 cm²
Dimensions (cm) 24W × 37H × 35L
Coolant 3.5 liter, glycol-based
System Closed circulation
Connection Mains electrical connector
Power consumption 340 VA max.
At operating voltage 110 or 230 VAC (device-dependent)
Line frequency 50/60 Hz
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-11

®
Introduction
2.6.7 External barcode reader
Version Hand device
Technology CCD
Barcodes (standard) Codabar
Barcodes (optional) UPC-A +2, +5
UPC-E +2, +5
EAN-13 +2, +5
EAN-8 +2, +5
Code 39
Code 93
Code 128
Code 2 out of 5
2.6.8 Accuracy and precision
The chemical performance of clinical chemistry analyzers, in terms of accuracy and precision,
depend on the following: the characteristics of the instrument; the measurement techniques and the
materials used. Therefore, the chemical performance characteristics of a clinical chemistry analyzer
can only be established and postulated in terms of: the analyte; the specific reagent kit and
calibrator(s) used; the type and constitution of the specimens involved; etc.
The analyzers are designed as open systems. ´Open´ implies that most clinical chemistry tests and
techniques that require photometric measurement, can be adapted on the system. Only the test
parameters for a specific test need to be adjusted. The user needs to establish the required test
parameter settings to achieve satisfactory results, utilizing appropriate methods. The methods are
preferably based on international guidance documents, for example ECCLS or CLSI guidelines.
The manufacturer does not suggest or propose any particular reagents, calibrators and/or controls
on their analyzers from a specific manufacturer. Obtain information on the performance
characteristics from the selected reagent distributor and/or manufacturer. Various reagent
manufacturers have performed performance studies on these series of analyzers in combination
with their reagent kits. Therefore, they have application sheets available for various analytes. The
required information usually can be obtained from the reagent package inserts. Please contact your
local representative and/or reagent manufacturer for further information on the chemical
performance of their reagents on these analyzers.
Code 2 of 5 interleaved
MSI/Plessey
2-12 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.

®
Introduction
2.7 Analyzer technical data (without washing unit or computer)
2.7.1 Dimensions and weight
Width 115 cm
Height 49 cm
Depth 56 cm
Weight approx. 85 kg
2.7.2 Power requirements
Line Voltage 110/240 V nominal, tolerance 10%
Line Frequency 50/60 Hz
Power Consumption 1000VA
Installation category II (in accordance with IEC 664)
2.7.3 Environmental requirements
Ambient temperature 15 to 32 °C
Max. relative humidity 85% @ 32 °C
Pollution degree 2 (in accordance with IEC 664)
2.7.4 Approvals
CE
CB
UL
Note
The approvals listed here refer only to the instrument and operator console, not to additional
devices (cooling). For the approvals for these devices please refer to the corresponding manuals.
VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V. 2-13

®
Introduction
2-14 VITAL SCIENTIFIC B.V.
 Loading...
Loading...