Samsung DVD-V940K, DVD-V29000K, SV-DVD240, DVD-V645K, DVD-V25000K Training Manual
...
DVD-VCR COMBINATION
Chassis : Kaiser Karaoke
DVD-V940K/V645K/V642K
DVD-V29000K/V25000K
SV-DVD240
TRAINING
1. Precautions
2. Reference Information
3. Product Specification
4. Operating Instructions
5. Disassembly and Reassembly
6. Alignment and Adjustment
7. Circuit Operating Description
8. VCR Deck Operating Description
9. Troubleshooting
10. Block Diagram
11. Wiring Diagram
12. Schematic Diagrams
Manual
DVD-VCR COMBINATION CONTENTS
TRAINING MANUAL
DVD-V940K/V645K/V642K/V29000K/V25000K, SV-DVD240
ELECTRONICS
© Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. APR. 2004
Printed in Korea
AK82-00557A
This Service Manual is a property of Samsung Electronics Co .,Ltd.
Any unauthorized use of Manual can be punished under applicable
International and/or domestic law.
IMPORTANT SERVICE GUIDE
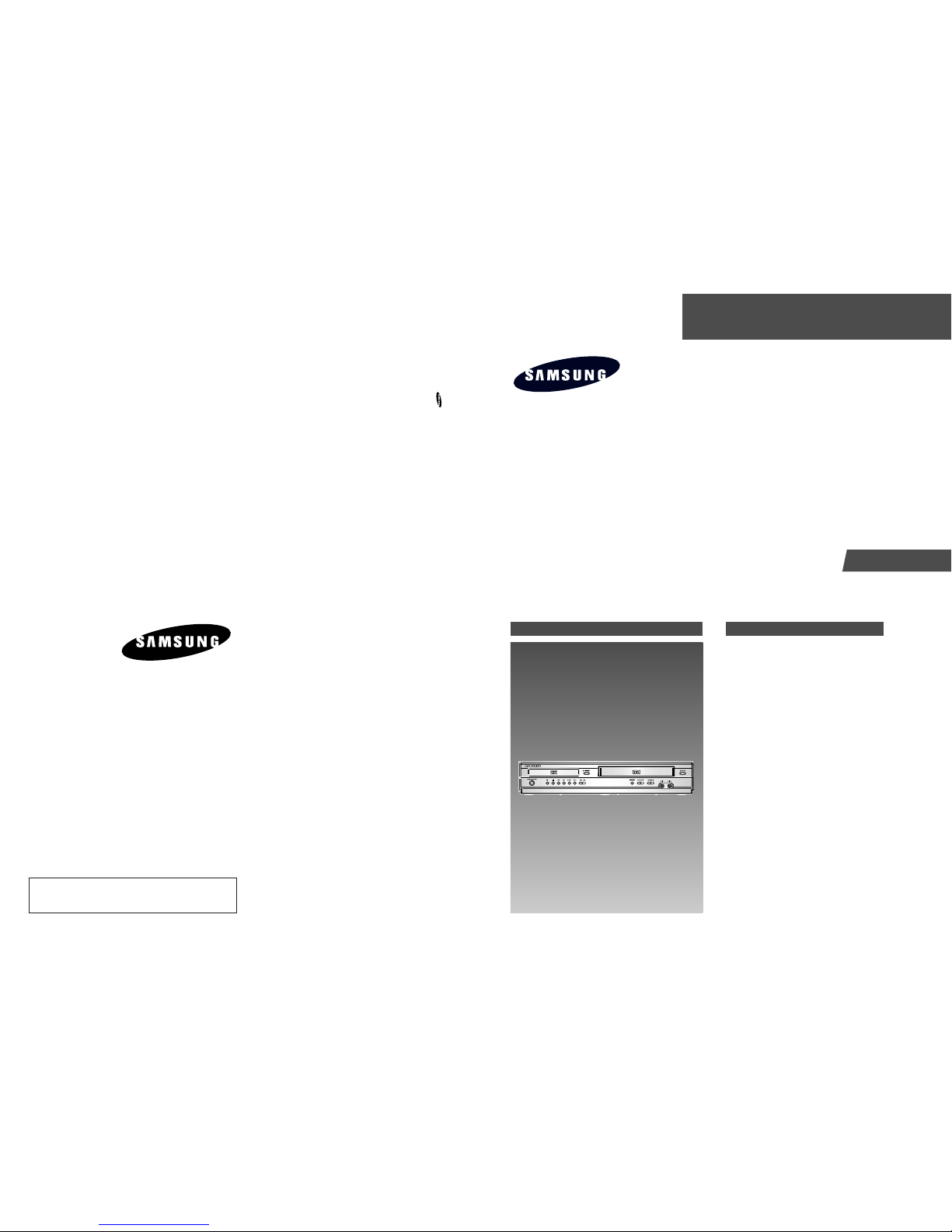
◆ MODE SWITCH (PROGRAM SWITCH) ASSEMBLY POINT
1) When installing the ass’y deck on the Main PCB, be sure to align the assembly point of mode switch.
VCR MAIN PCB
ASSEMBLY POINT
Fig. 1
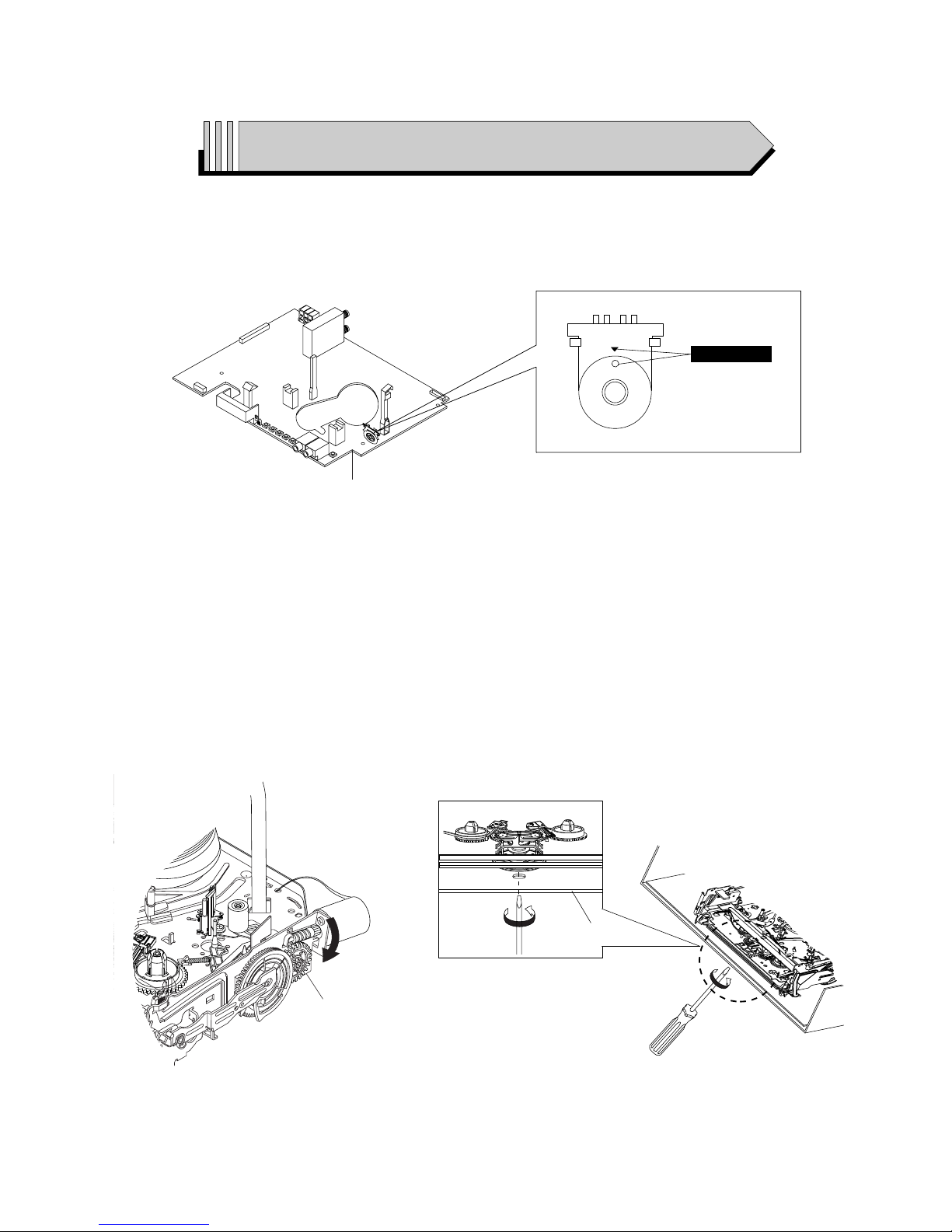
◆ HOW TO EJECT THE CASSETTE TAPE
(If the tape is stuck in the unit)
1) Turn the Gear Worm Πclockwise in the direction of arrow with a screwdriver. (See Fig. 2)
(Other method ; Remove the screw of Motor Load Ass’y, Separate the Motor Load Ass’y)
2) When Slider S, T approachs the unloading position, rotate holder Clutch counterclockwise after inserting screwdriver in the
frame’s bottom hole in order to wind the unwound tape. (Refer to Fig. 3)
(If you rotate Gear Worm Πcontinuously when tape is unwinding, you may cause tape contamination by grease and
tape damage. Be sure to wind the unwound tape with the unit in the horizontall position.)
3) Rotate Gear Worm Πclockwise using a screwdriver until the mecha is in the eject state. Remove the tape. (Refer to Fig. 2)
Fig. 2 Fig. 3
ΠGEAR WORM
FRAME
Samsung Electronics 1-1
1. Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
1) Before returning an instrument to the customer,
always make a safety check of the entire instrument,
including, but not limited to, the following items:
(1) Be sure that no built-in protective devices are
defective or have been defeated during servicing.
(1)Protective shields are provided to protect both
the technician and the customer. Correctly replace
all missing protective shields, including any
removed for servicing convenience.
(2)When reinstalling the chassis and/or other assembly in the cabinet, be sure to put back in place
all protective devices, including, but not limited to,
nonmetallic control knobs, insulating fish papers,
adjustment and compartment covers/shields, and
isolation resistor/capacitor networks. Do not operate this instrument or permit it to be operated without all protective devices correctly installed and
functioning.
(2) Be sure that there are no cabinet openings through
which adults or children might be able to insert
their fingers and contact a hazardous voltage. Such
openings include, but are not limited to, excessively wide cabinet ventilation slots, and an improperly fitted and/or incorrectly secured cabinet back
cover.
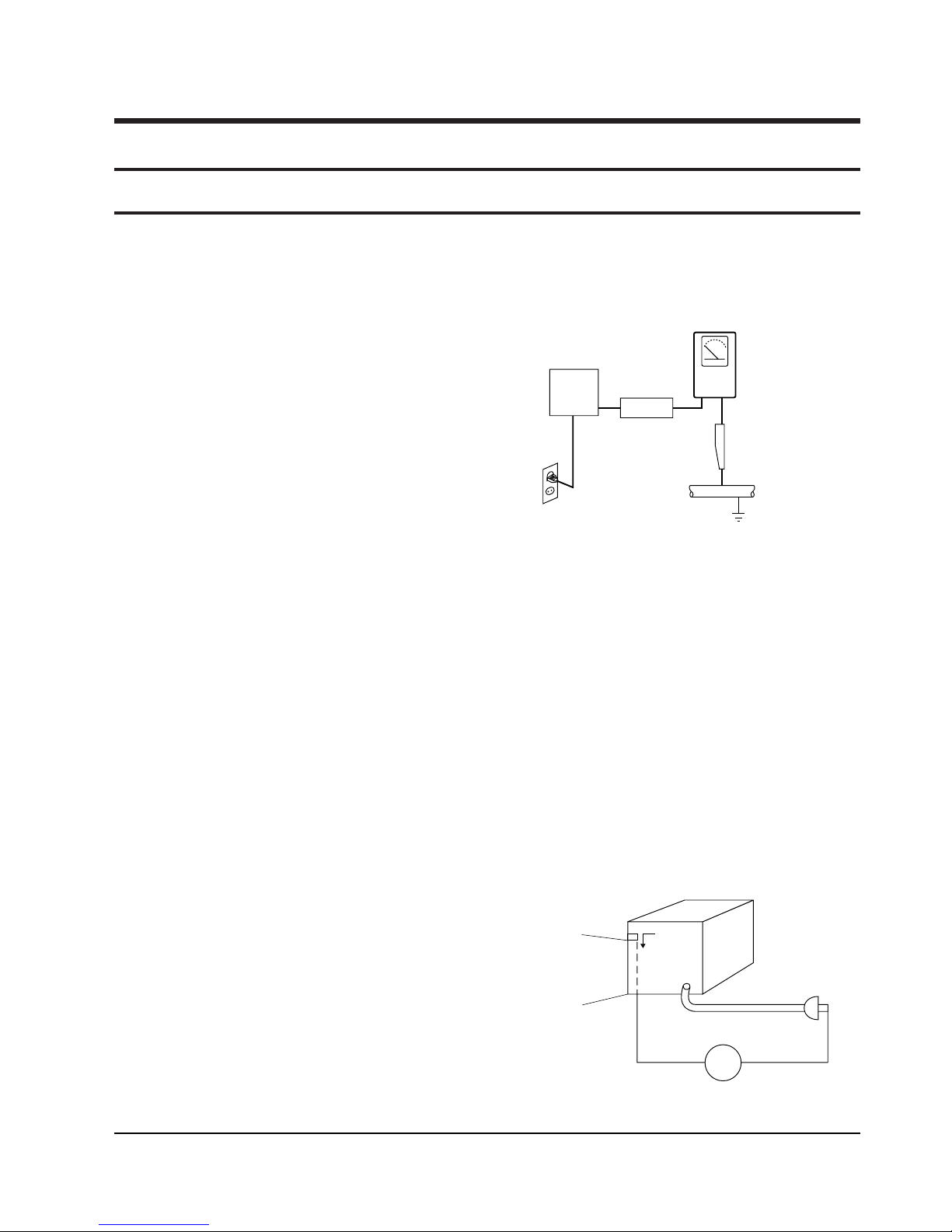
(3) Leakage Current Hot Check-With the instrument
completely reassembled, plug the AC line cord
directly into a 120V AC outlet. (Do not use an isolation transformer during this test.) Use a leakage
current tester or a metering system that complies
with American National Standards institute (ANSI)
C101.1 Leakage Current for Appliances and
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 1270 (40.7). With
the instrument’s AC switch first in the ON position
and then in the OFF position, measure from a
known earth ground (metal water pipe, conduit,
etc.) to all exposed metal parts of the instrument
(antennas, handle brackets, metal cabinets, screwheads, metallic overlays, control shafts, etc.), especially any exposed metal parts that offer an electrical return path to the chassis.
Any current measured must not exceed 0.5mA.
Reverse the instrument power cord plug in the outlet and repeat the test. See Fig. 1-1.
Any measurements not within the limits specified
herein indicate a potential shock hazard that must
be eliminated before returning the instrument to
the customer.
Fig. 1-1 AC Leakage Test
(4) Insulation Resistance Test Cold Check-(1) Unplug
the power supply cord and connect a jumper wire
between the two prongs of the plug. (2) Turn on the
power switch of the instrument. (3) Measure the
resistance with an ohmmeter between the
jumpered AC plug and all exposed metallic cabinet
parts on the instrument, such as screwheads,
antenna, control shafts, handle brackets, etc. When
an exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis, the reading should be between 1 and 5.2
megohm. When there is no return path to the chassis, the reading must be infinite. If the reading is
not within the limits specified, there is the possibility of a shock hazard, and the instrument must be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer. See Fig. 1-2.
Fig. 1-2 Insulation Resistance Test
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
(READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE
0.5mA)
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
EARTH
GROUND
TEST ALL
EXPOSED METER
SURFACES
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
2-WIRE CORD
Antenna
Terminal
Exposed
Metal Part
ohm
ohmmeter

Precautions
1-2 Samsung Electronics
2) Read and comply with all caution and safety related notes on or inside the cabinet, or on the chassis.
3) Design Alteration Warning-Do not alter or add to
the mechanical or electrical design of this instrument. Design alterations and additions, including
but not limited to, circuit modifications and the
addition of items such as auxiliary audio output
connections, might alter the safety characteristics of
this instrument and create a hazard to the user. Any
design alterations or additions will make you, the
servicer, responsible for personal injury or property
damage resulting therefrom.
4) Observe original lead dress. Take extra care to
assure correct lead dress in the following areas:
(1) near sharp edges, (2) near thermally hot parts (be
sure that leads and components do not touch thermally hot parts), (3) the AC supply, (4) high voltage,
and (5) antenna wiring. Always inspect in all areas
for pinched, out-of-place, or frayed wiring, Do not
change spacing between a component and the
printed-circuit board. Check the AC power cord for
damage.
5) Components, parts, and/or wiring that appear to
have overheated or that are otherwise damaged
should be replaced with components, parts and/ or
wiring that meet original specifications.
Additionally, determine the cause of overheating
and/or damage and, if necessary, take corrective
action to remove any potential safety hazard.
6) Product Safety Notice-Some electrical and mechanical parts have special safety-related characteristics
which are often not evident from visual inspection,
nor can the protection they give necessarily be
obtained by replacing them with components rated
for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Parts that have special safety characteristics are identified by shading,
an ( )or a ( )on schematics and parts lists. Use
of a substitute replacement that does not have the
same safety characteristics as the recommended
replacement part might create shock, fire and/or
other hazards. Product safety is under review continuously and new instructions are issued whenever appropriate.

Precautions
Samsung Electronics 1-3
1-2 Servicing Precautions
CAUTION : Before servicing units covered by this
service manual and its supplements, read and follow
the Safety Precautions section of this manual.
Note : If unforseen circumstances create conflict
between the following servicing precautions and any
of the safety precautions, always follow the safety precautions. Remember: Safety First.
1-2-1 General Servicing Precautions
(1) a. Always unplug the instrument’s AC power cord
from the AC power source before (1) re-moving
or reinstalling any component, circuit board,
module or any other instrument assembly, (2)
disconnecting any instrument electrical plug or
other electrical connection, (3) connecting a test
substitute in parallel with an electrolytic capacitor in the instrument.
b. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage inter-
locks with which instruments covered by this
service manual might be equipped.
c. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and
/or any of its electrical assemblies unless all
solid-state device heat sinks are correctly installed.
d. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead
to the instrument chassis ground before connecting the test instrument positive lead. Always
remove the test instrument ground lead last.
Note : Refer to the Safety Precautions section ground
lead last.
(2) The service precautions are indicated or printed on
the cabinet, chassis or components. When servicing, follow the printed or indicated service precautions and service materials.
(3) The components used in the unit have a specified
flame resistance and dielectric strength.
When replacing components, use components
which have the same ratings. Components identified by shading, by( ) or by ( ) in the circuit diagram are important for safety or for the characteristics of the unit. Always replace them with the exact
replacement components.
(4) An insulation tube or tape is sometimes used and
some components are raised above the printed
wiring board for safety. The internal wiring is
sometimes clamped to prevent contact with heating components. Install such elements as they
were.
(5) After servicing, always check that the removed
screws, components, and wiring have been installed correctly and that the portion around the
serviced part has not been damaged and so on.
Further, check the insulation between the blades of
the attachment plug and accessible conductive
parts.
1-2-2 Insulation Checking Procedure
Disconnect the attachment plug from the AC outlet
and turn the power ON. Connect the insulation resistance meter (500V) to the blades of the attachment
plug. The insulation resistance between each blade of
the attachment plug and accessible conductive
parts(see note) should be more than 1 Megohm.
Note : Accessible conductive parts include metal panels, input terminals, earphone jacks, etc.

Precautions
1-4 Samsung Electronics
1-3 ESD Precautions
Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD)
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity.
Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices(ESD). Examples of typical ESD
devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistors and semiconductor chip components. The
following techniques should be used to help reduce
the incidence of component damage caused by static
electricity.
(1) Immediately before handling any semiconductor
component or semiconductor-equipped assembly,
drain off any electrostatic charge on your body by
touching a known earth ground. Alternatively,
obtain and wear a commercially available discharging wrist strap device, which should be
removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
(2) After removing an electrical assembly equipped
with ESD devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
(3) Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or
unsolder ESD devices.
(4) Use only an anti-static solder removal devices.
Some solder removal devices not classified as
“anti-static” can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESD devices.
(5) Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESD devices.
(6) Do not remove a replacement ESD device from its
protective package until immediately before your
are ready to install it.(Most replacement ESD
devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or
comparable conductive materials).
(7) Immediately before removing the protective ma-
terials from the leads of a replacement ESD device,
touch the protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION : Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
(8) Minimize bodily motions when handling unpack-
aged replacement ESD devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the brushing together of your
clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity sufficient
to damage an ESD device).
Precautions
Samsung Electronics 1-5
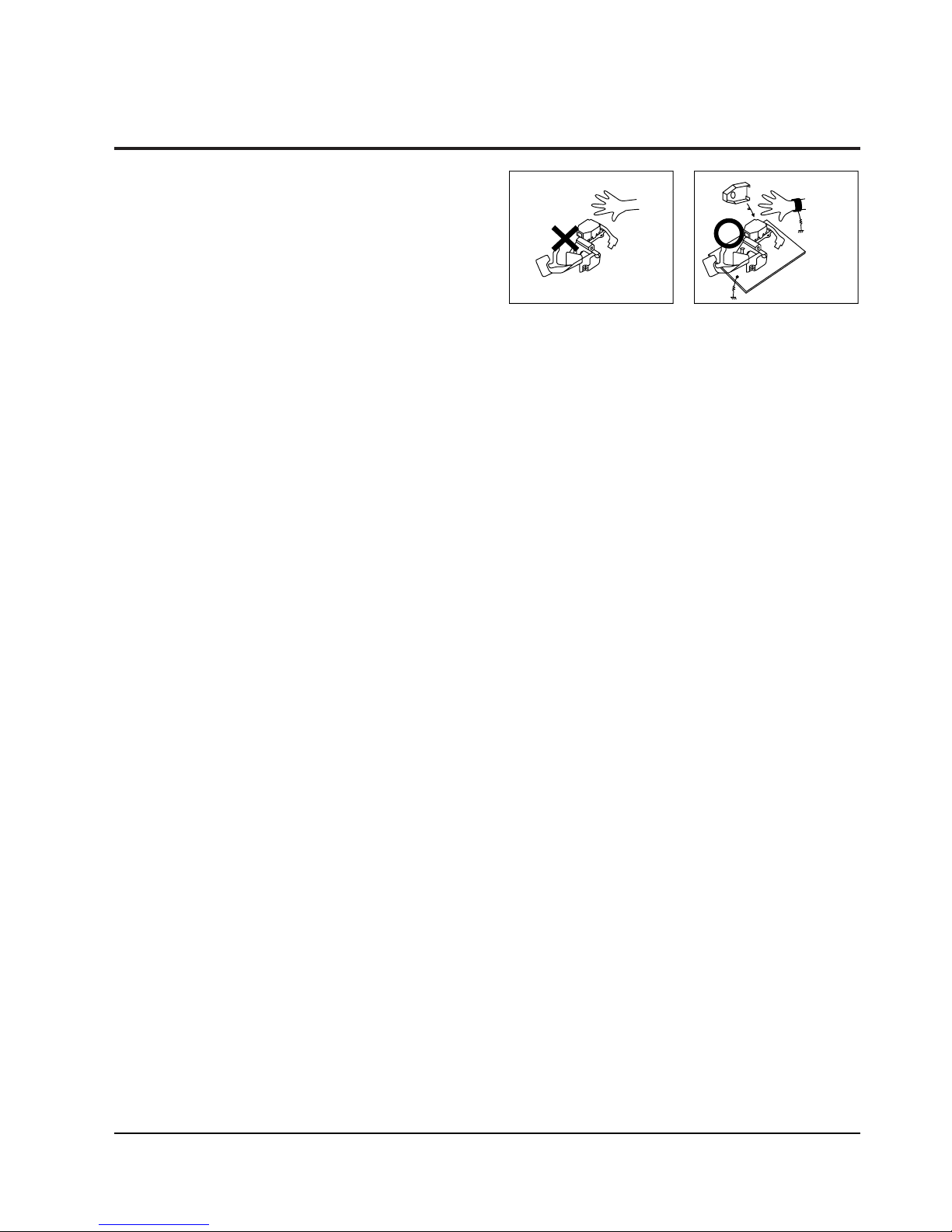
1-4 Handling the optical pick-up
The laser diode in the optical pick up may suffer electrostatic breakdown because of potential static electricity from clothing and your body.
The following method is recommended.
(1) Place a conductive sheet on the work bench (The
black sheet used for wrapping repair parts.)
(2) Place the set on the conductive sheet so that the
chassis is grounded to the sheet.
(3) Place your hands on the conductive sheet(This
gives them the same ground as the sheet.)
(4) Remove the optical pick up block
(5) Perform work on top of the conductive sheet. Be
careful not to let your clothes or any other static
sources to touch the unit.
◆ Be sure to put on a wrist strap grounded to the
sheet.
◆ Be sure to lay a conductive sheet made of copper
etc. Which is grounded to the table.
Fig.1-3
(6) Short the short terminal on the PCB, which is in-
side the Pick-Up ASS’Y, before replacing the PickUp. (The short terminal is shorted when the PickUp Ass’y is being lifted or moved.)
(7) After replacing the Pick-up, open the short termi-
nal on the PCB.
THE UNIT
WRIST-STRAP
FOR GROUNDING
1M
1M
CONDUCTIVE SHEET

Precautions
1-6 Samsung Electronics
1-5 Pick-up disassembly and reassembly
1-5-1 Disassembly
1) Remove the power cord.
2) Disassemble the Deck-Assy.
3) Make solder land 2 points short on Pick-up.
(See Fig. 1-4)
4) Disassemble the Pick-up.
1-5-2 Assembly
1) Replace the Pick-up.
2) Remove the soldering 2 points on Pick-up.
3) Reassemble the Deck-Assy.
PICK-UP ASS'Y
SOLDER LAND 2 POINTS SHORT
Note : If the assembly and disassembly are not done in correct sequence, the Pick-up may be damaged.
Fig. 1-4
Samsung Electronics 2-1
2. Reference Information
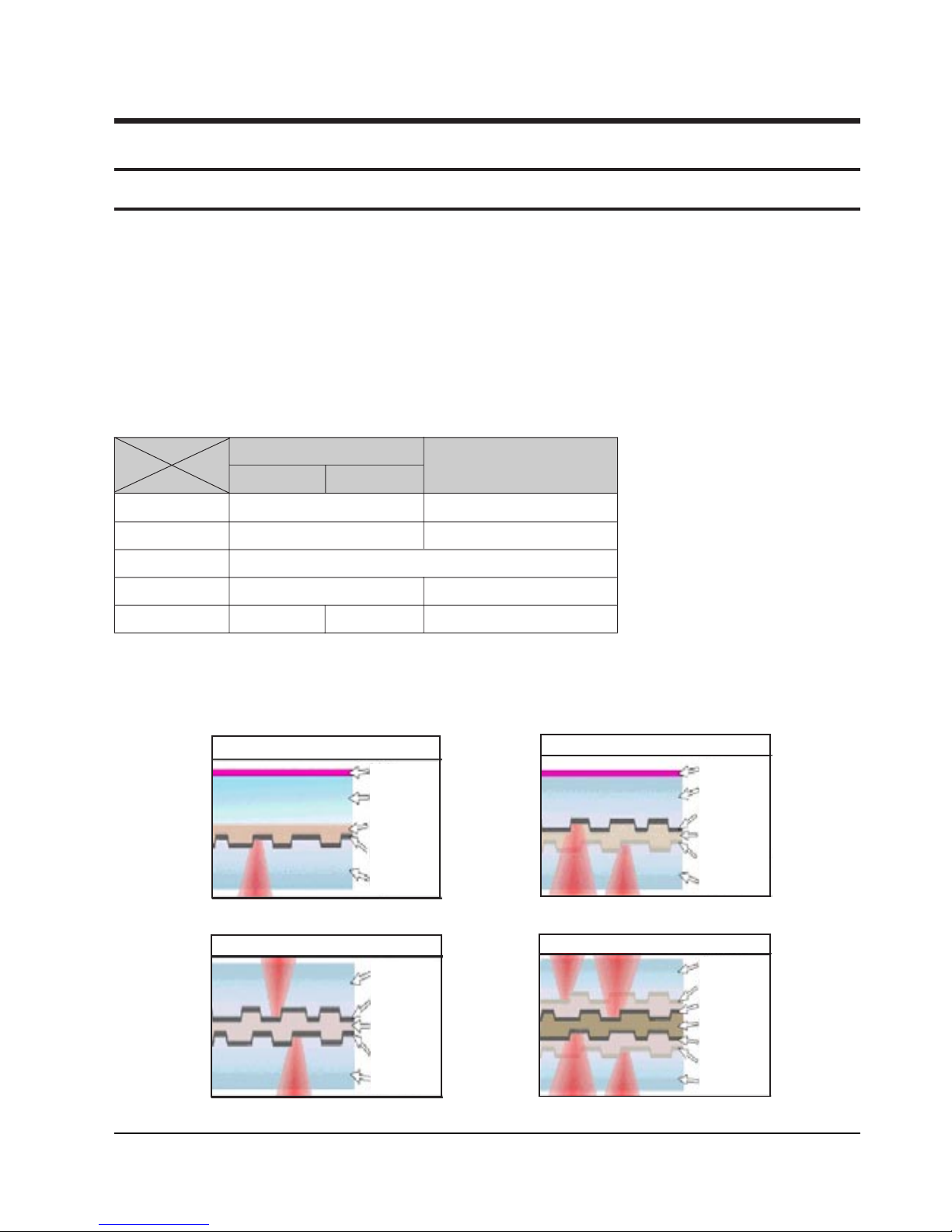
2-1 Introduction to DVD
2-1-1 The Definition of DVD
DVD is the next generation medium and is the acronym of the Digital Versatile Disc or the Digital Video Disc,
which maximizes the saving density of the disk surface using the MPEG-2 compression technology to enable the
storage of 17G bytes of data on the same size CD.
1) 7 times the storage capacity of the conventional CD
◆ Minimized the track pitch and pit size to 1/2 of conventional CD.
◆ Uses red laser with short-wavelenght of 650nm (635nm).
⌘ DVD Vs. CD-ROM
DVD
CD-ROM
Single-Layer Dual-Layer
Laser Wavelength 650nm (635nm) 780nm
Track Pitch 0.75um 1.6um
Disc Diameter 120mm
Disc Thickness 1.2 (0.6 x 2) mm 1.2mm
Linear Velocity 3.49m/s 3.84m/s 1.2 ~ 1.4m/s
2) Disc Formats
DVD consists of two 0.6mm discs attached together, enabling access to the upper and lower side of the disk,
and 4 sides could be used at maximum.
Single Layer : 4.7GByte
Polycarbonate
Label
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
Polycarbonate
Label
Polycarbonate
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
Semi-reflective layer
Polycarbonate
Dual Layer : 8.5GByte
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
Reflective layer
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
Dual Side Single Layer : 9.5GByte
Polycarbonate
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
Reflective layer
Semi-reflective layer
Semi-reflective layer
Polycarbonate
Dual Side Dual Layer : 17GByte
Reference Information
2-2 Samsung Electronics
2-1-2 DVD Types
FORMAT TYPE APPLICATIONS
DVD-Video Playback Only High quality image and sound for movies and other video media.
DVD-ROM Read Only Multi-functional, multi-midia software that requires large storage capacity.
DVD-Audio Playback Only High quality sound that exceeds the CD, multi-channel Audio.
DVD-R 1 Time Recording Storage media for the computer.
DVD-RAM Rewritable Data access/storage media for the computer.

Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-3
2-2 DVD-Video Fromat
2-2-1 Main Features
1) Able to store up to 160 minutes of Movie by utilizing the MPEG-2 compression technology. ( Aver. 133min.)
2) Enables more than 500 lines of horizontal resolution. (Class corresponding to the Master Tapes used in
broadcasting stations)
3) Provides Dolby Digital 5.1ch Surround 3D sound, which enables theater quality sound (NTSC area).
◆ For PALareas, 1 of either MPEG-2 Audio or Dolby Digital must be selected.
4) Multi-Language
◆ Able to store up to 8 languages of dubbing.
◆ Able to store up to 32 subtitle languages.
5) Milti-Aspect Ratio
3TV Mode alternatives ; 16:9 Wide Screen (DVD Basic)/4:3 Pan & Scan/Letter Box.
6) Multi-Story
Possible to implement Interactive Viewing which enables the user to select the scenario.
7) Multi-Angle
Able to view the camera angle you selected among the scenes recorded with multiple camera angles.
Note ; The above media features must have the DVD Title that contains the appropriate contents to function
properly.
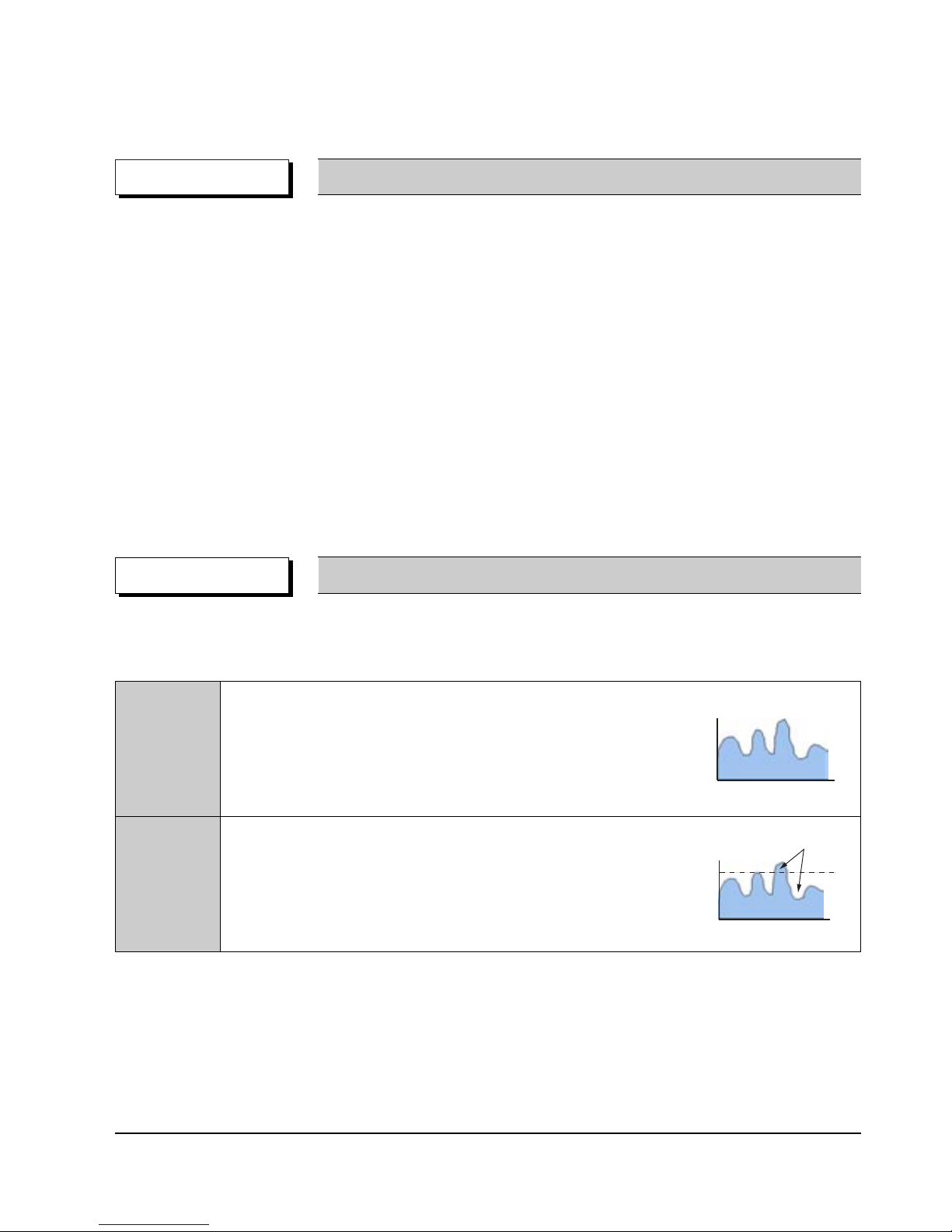
2-2-2 Audio & Video Specifications
Classification DVD-Video Video-CD LD
Compression MPEG-2 MPEG-1
Analog
Pixel 720 x 480 352 x 240
VIDEO
Horizontal resolution Max. 500 Lines Max. 250 Lines Max.420 Lines
Compression rate 1/40 1/140
Analog
Transmission speed Max. 9.8Mbps (variable) 1.15Mbps (fixed)
TV aspect 16:9 / 4:3 4:3 4:3
Audio Max. 8 streams 2CH stereo
Recording type Dolby Digital Linear PCM MPEG-1 Layer 2
AUDIO Transmission rate 448Kbps/stream 6.144Mbps/stream 224Kbps
or
Channel 5.1CH/stream 8CH/stream 2CH
Sampling frequency 48KHz 16, 20, 24Bit/48, 96KHz 16Bit/44.1KHz
2 Analog CH.
2 Digital CH.
(16Bit/44.1KHz)
1 Analog CH.
1 Stream of Dolby Digital
2 Digital CH.
(16Bit/44.1KHz)
Reference Information
2-4 Samsung Electronics
2-2-3 Detailed Feature
As the storage capacity increases, the DVD-Video separates the main data and the additional data such as the
Multi-Function into different data areas, enabling the control of time-data ratio to provide the format that enables
the flexible Software development
◆ 1 Movie (3.5Mbps)
+ Subtitle (1 Language)
+ Surround Audio (1 Language)
= 160min storage (4.673Gbytes)
◆ 1 Movie (3.5Mbps)
+ Subtitle (4 Language)
+ Surround Audio (4 Language)
= 160min storage (4.680Gbytes)
◆ 1 Music Video (4Mbps)
+ 2ch High quality Audio (96kHz/24bit)
= 72min storage (4.648Gbytes)
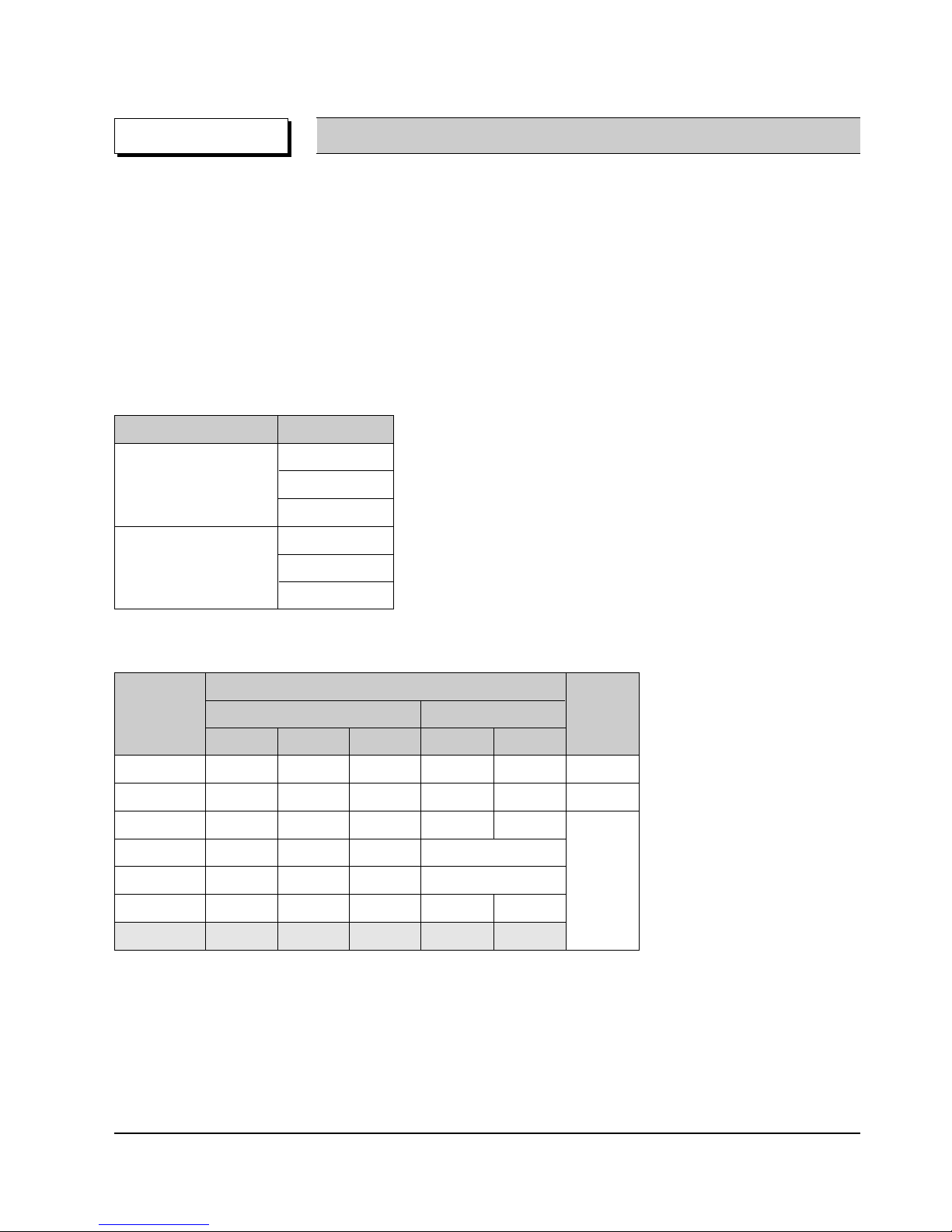
DVD-Video Feature 1 When Developing the DVD Software, various addition and modification is possible.
DVD-Video uses the variable compresion technology, the MPEG-2 to compress the moving image optimally, minimizing the Data loss to Provide a clear, natural screen while increasing the storage time.
DVD-Video Feature 2 Application of the MPEG-2 compression technology.
◆ MPEG-2 (Variable compression : Max. 1/40)
✓ Field unit compression.
DVD-Video
✓ Compression rate change according to the amount of Data.
✓ Differentiates the still image anf the moving image
compression rete, reducing Data loss and enables
efficient compression.
◆ MPEG-1 (Fixed compression : Max. 1/140)
✓ Frame unit compression.
Video-CD
✓ Compresses all data using the same ratio.
- Fast movements are jagged, and unnatural
Time
Amount of data
Time
Amount of data
Loss area
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-5
DVD-Video can store the audio using the 5.1ch Dolby Digital compression or the advanced Liner PCM method,
providing the better-than-CD quality and theater like audio quality.
◆ Dolby Digital (AC-3)
✓ Unlike the traditional Dolby pro-Logic method, the Dolby Digital method separates all 5 main channels
(Front L/R, Center, Surround (Rear) L/R)and the Sub woofer to provide live surround audio.
✓ Using the Down Mix method, the conventional Dolby Pro-Logic and Stereo are all compatible.
✓ Each separated channels are played back at CD quality sound. (Frequency band: 20Hz ~ 20KHz)
◆ Linear PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
✓ Provides the high quality Digital sound without the audio data compression.
✓ Various Digital Recordings are possible as shown in the table to the right.
DVD-Video Feature 3 High quality surround audio.
Sampling Frequency Bit Rate
16bit
48KHz 20bit
24bit
16bit
96KHz 20bit
24bit
◆ Dolby Digital compatible Audio Mode
Audio Coding
Channel Format
Mode
Front Surround (Rear) Remark
LCRLR
1/0 O Mono
2/0 OO Stereo
3/0 OOO
2/1 OOMono
3/1 OOO Mono Surround
2/2 OOOO
3/2 OOOOO
Reference Information
2-6 Samsung Electronics
◆ Audio Dubbing - Max. 8 Languages
◆ Subtitle - Max. 32 Languages. Capable of storing, and selectiong.
◆ Linear PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
DVD-Video Feature 4 Multi-Language
◆ Unlike the conventional VCD or LD, DVD-Video has the default of 16:9 Wide, and can be viewed using the
conventional 4:3 TV, enabling the expansion of viewer selection capabilities.
✓ 16 : 9 TV : Wide Mode (16:9 Wide Full Screen)
✓ 4 : 3 TV : Letter Box Mode, Pan & Scan Mode
DVD-Video Feature 5 Multi-Aspect
4:3 Pan & Scan
16:9 Wide
4:3 Letter Box
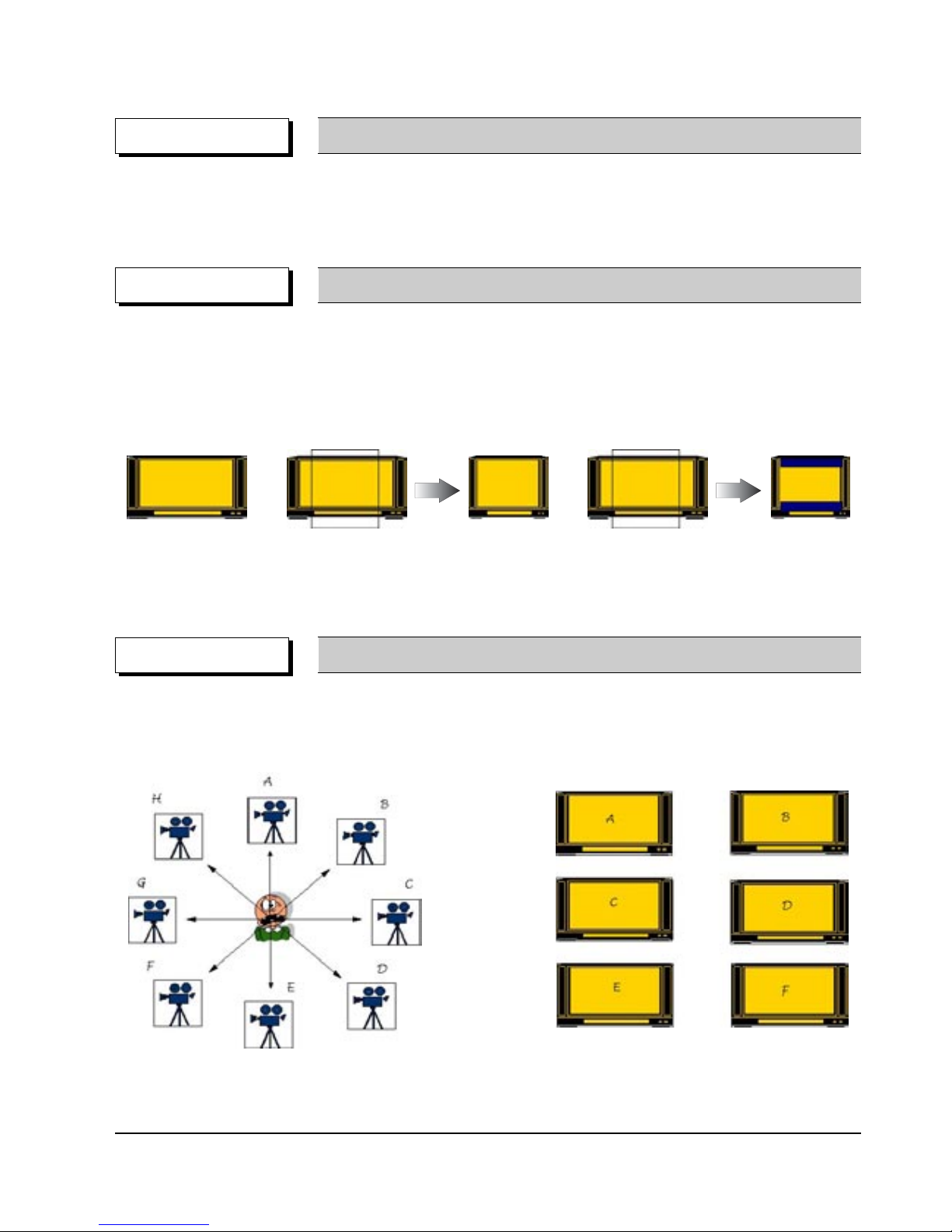
◆ Up to 9 angles of view may be stored, enabling the viewer to select a specific viewpoint at a given time.
--> Especially, for the Music Video and Sports Title, this provides a more lively image of the scene.
DVD-Video Feature 6 Multi-Angle
Note ; Only enable to be worked correctly by an appropriate data supported this function in Disc.
Note ; Only enable to be worked correctly by an appropriate data supported this function in Disc.
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-7
◆ DVD-Video provides the enviroment suitable for the bi-directional Software develoment, providing multiple
scenarios. This feature enables the Multi-Story function.
DVD-Video Feature 7
Multi-Story
◆ For the titles that are not suitable for children viewing, Parental Locks are set, requesting user defined
passwords for viewing
◆ Parential Locks may be set on specific frames of the Title, enabling the player to skip those frames during
playback.
OPTION Parental Lock
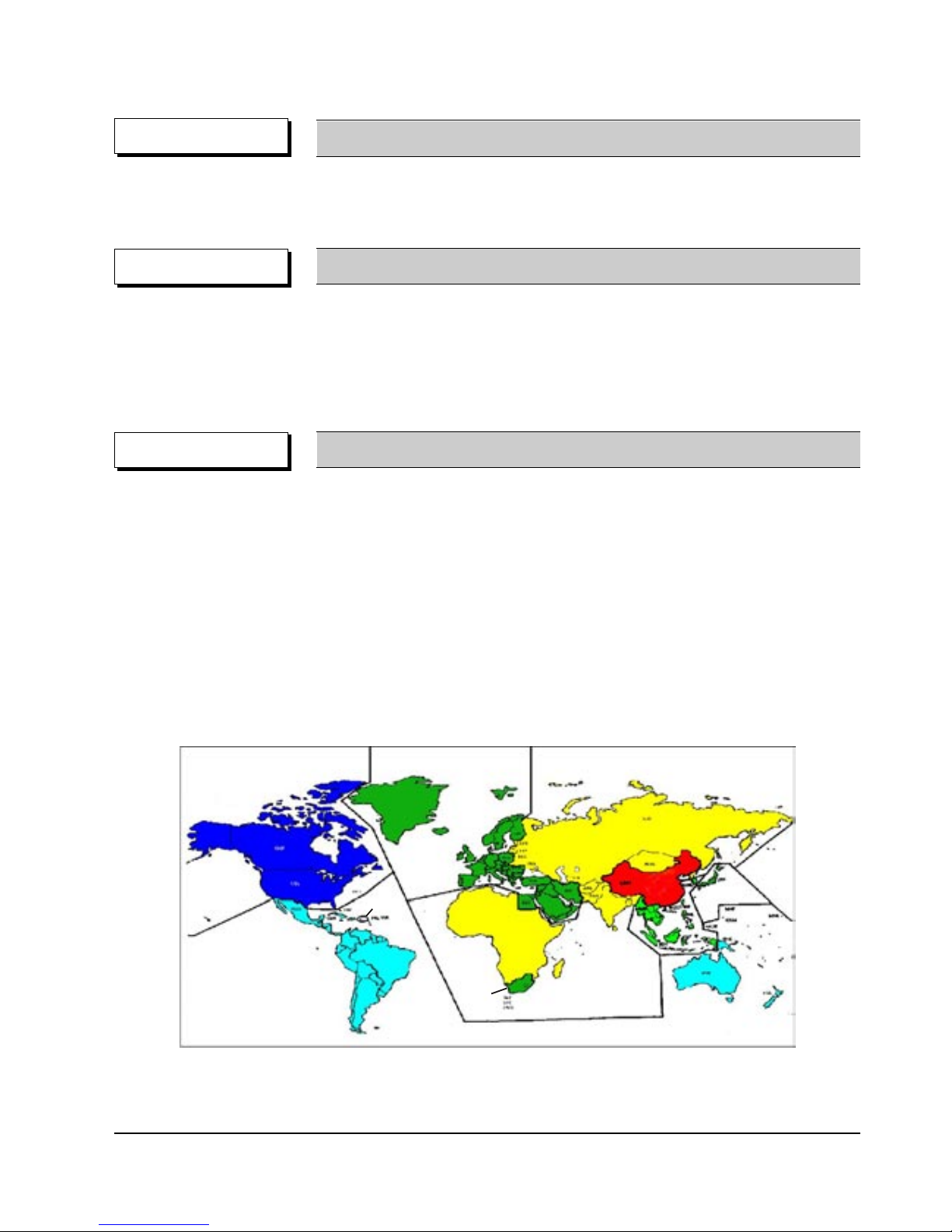
◆ Classify the world into 6 regions, and if the DVD Title and the Player’s “Reginal Code” do not agree, playback
is prohibited.
⌘ Regionnal Coding is optional for the Soft developers (Region 0 All Code), but the Hardware developers
must adopt the appropriate regionnal code for sale.
✓ Region 1 : The United States and its territories, Canada.
✓ Region 2 : Europe, Japan, Greenland, Egypt, South Africa, the Middle East.
✓ Region 3 : Taiwan, Hongkong, Korea, South East Asia.
✓ Region 4 : Mexico, South America, Australia, New Zealand.
✓ Region 5 : Russia, Eastern Europe, India, Africa.
✓ Region 6 : China.
✓ Region 0 : Worldwide (All Code)
COPYRIGHT Regional Code & Macrovision
◆ Adoptation of the Macrovision System disables the copying on to other media.
Œ
Œ
¨
¨
Œ
´
ˇ
ˆ
Ø
´
´
ˆ
Reference Information
2-8 Samsung Electronics
◆ The image quality of the DVD-Video may vary accoring to the quality of the Master and the Authoring Process
✓ The image quality of the DVD-Video varies according to the Digital Mastering Source such as the
conventional LD, VCD, or Original Film.
✓ Different Authoring Process are used accoring to the Software developers, and this may affect the
DVD image quality.
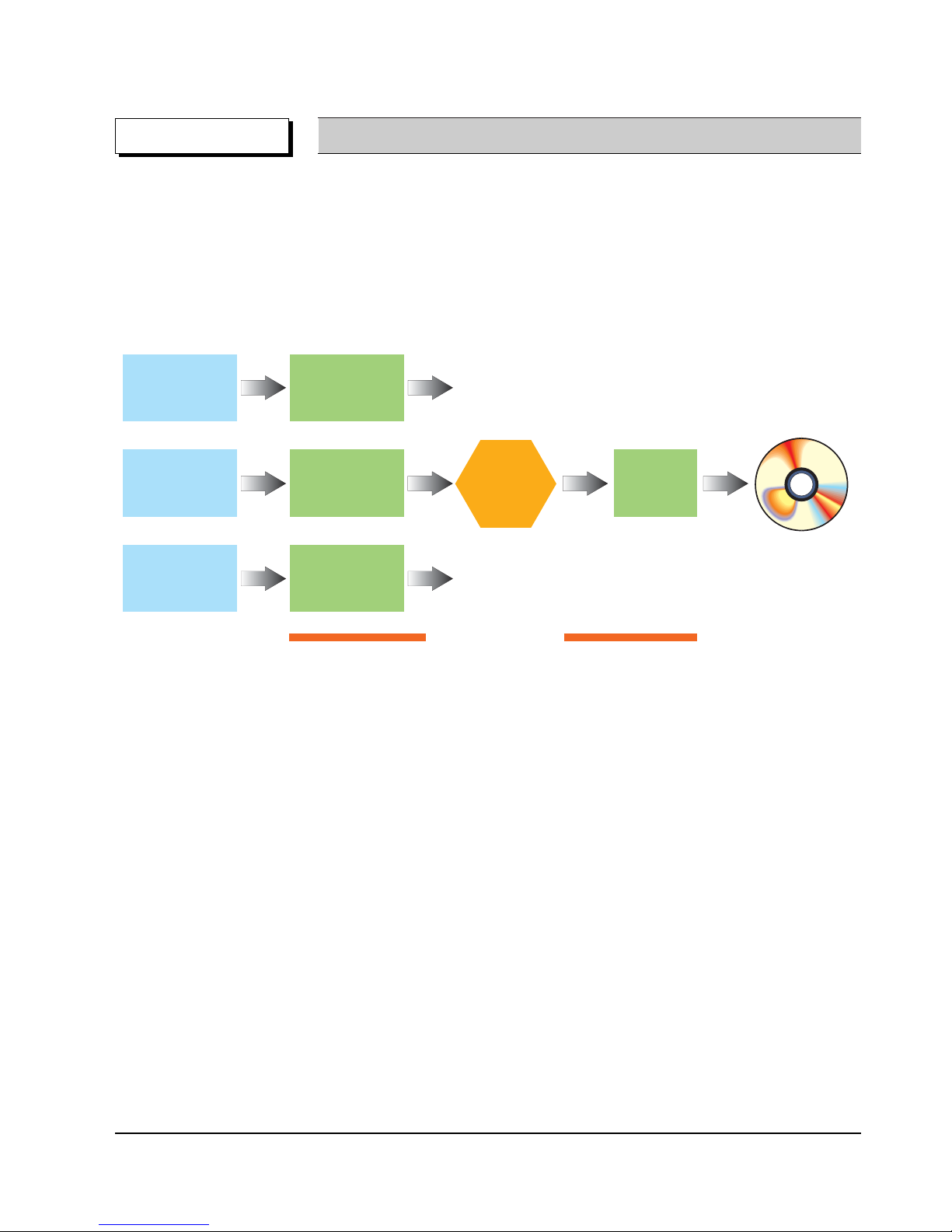
⌘ Authoring Process
Remark DVD-Video Authoring Process
Video/Audio
Master
Surround Audio
Master
Subtitle
Master
MPEG-2
Encoding
AC-3/MPEG Audio
Encoding
Cutting
Master
Disc
Production
Subtitle
Encoding
Authoring Process
Video/Audio
Subtitle
Multiplexing
bit stream
bit stream
bit stream
Samsung Electronics 3-1
3. Product Specification
Rated Voltage 220 - 240V, 50Hz
General Power Consumption 19 Watts
Weight 3.8Kg
Size 430mm x 282mm x 82mm
Operating ambient Temperature +5°C ~ +35°C
Installation Conditions Operation position : Horizontal, Relative humidity : Below 75%
Input
Video input (Rear) Euro Scart socket : 1.0Vp-p (unbalanced) 75ohm
Audio input (Rear) Euro Scart socket : -8dBm, 47Kohm unbalnced
RF out UHF 28-69 (lnitial CH36)
Audio (DVD, VCR) RCA jack
Output Audio (DVD only) Digital audio out (OPTICAL, COAXIAL, RCA jack)
Video (DVD, VCR) RCA jack
Video (DVD only) S-Video out, COMPONENT out : RCA jack
Tape format VHS type video tape, S-VHS type video tape (Playback only)
Color system PAL, NTSC4.43, MESECAM, NTSC playback on PAL TV
VCR Video S/N Above 43dB (standard recording)
Resolution Above 240 lines (standard recording)
Audio S/N Above 50dB (Hi-Fi), 39dB (Mono)
Audio frequency characteristics 20Hz - 20KHz (Hi-Fi)
Disc DVD, CD (12Cm), CD (8Cm),
DVD Audio S/N 95dB
Audio dynamic range 105dB
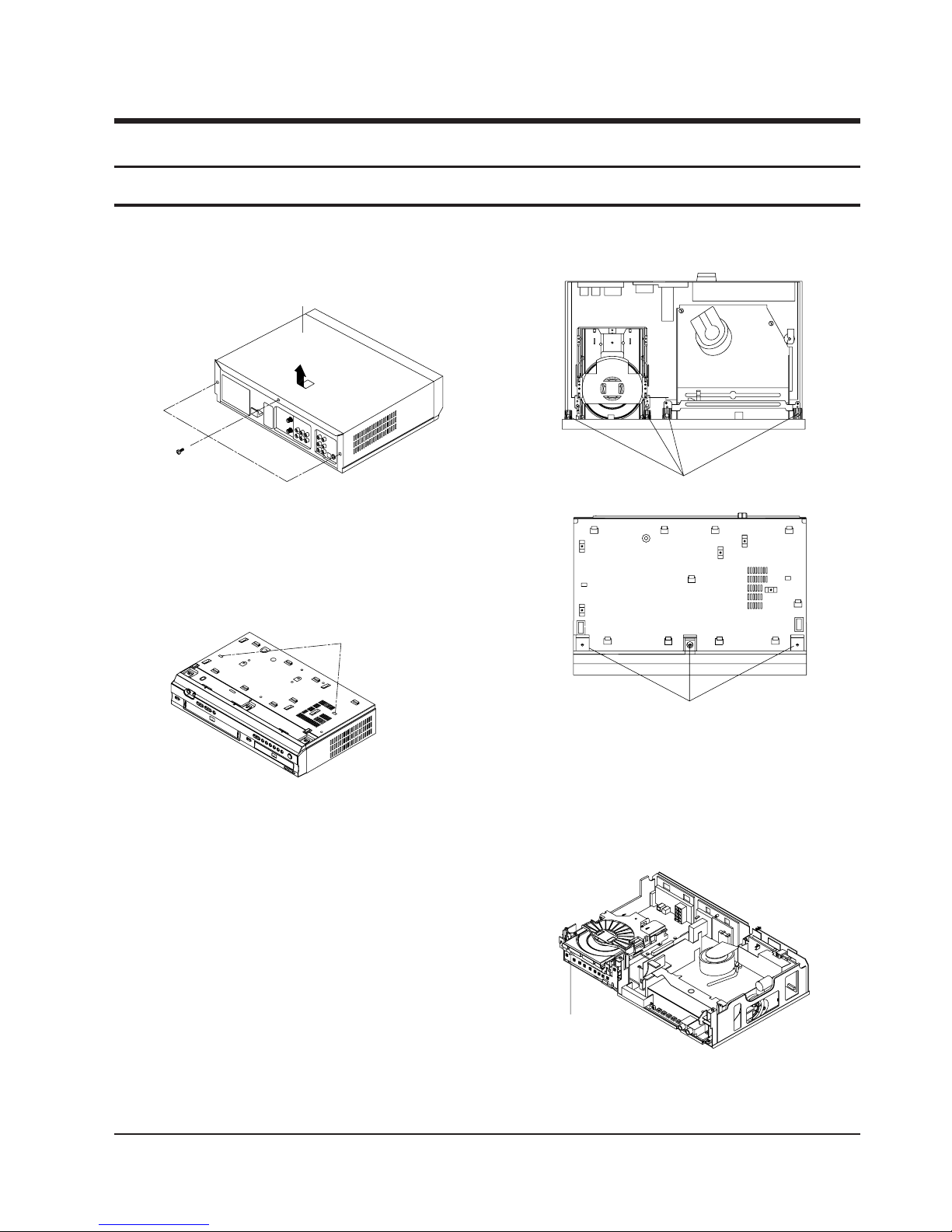
Samsung Electronics 5-1
5. Disassembly and Reassembly
5-1 Cabinet and PCB
5-1-1 Cabinet Top Removal
ΠREMOVE 3 SCREWS
´ Lift up the Cabinet Top in the direction of arrow.
Fig. 5-1 Cabinet Top Removal
5-1-2 Ass’y Bottom Cover Removal
ΠRELEASE 2 HOOKS
(Bottom View)
5-1-4 Function PCB Removal
ΠRELEASE 1 HOOK
Fig. 5-4 Function PCB Removal
Fig. 5-2 Ass’y Bottom Cover Removal
´ RELEASE 3 HOOKS
(Bottom View)
ΠRELEASE 4 HOOKS
(Top View)
Fig. 5-3 Ass’y Front Panel Removal
5-1-3 Ass’y Front Panel Removal
5-2
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
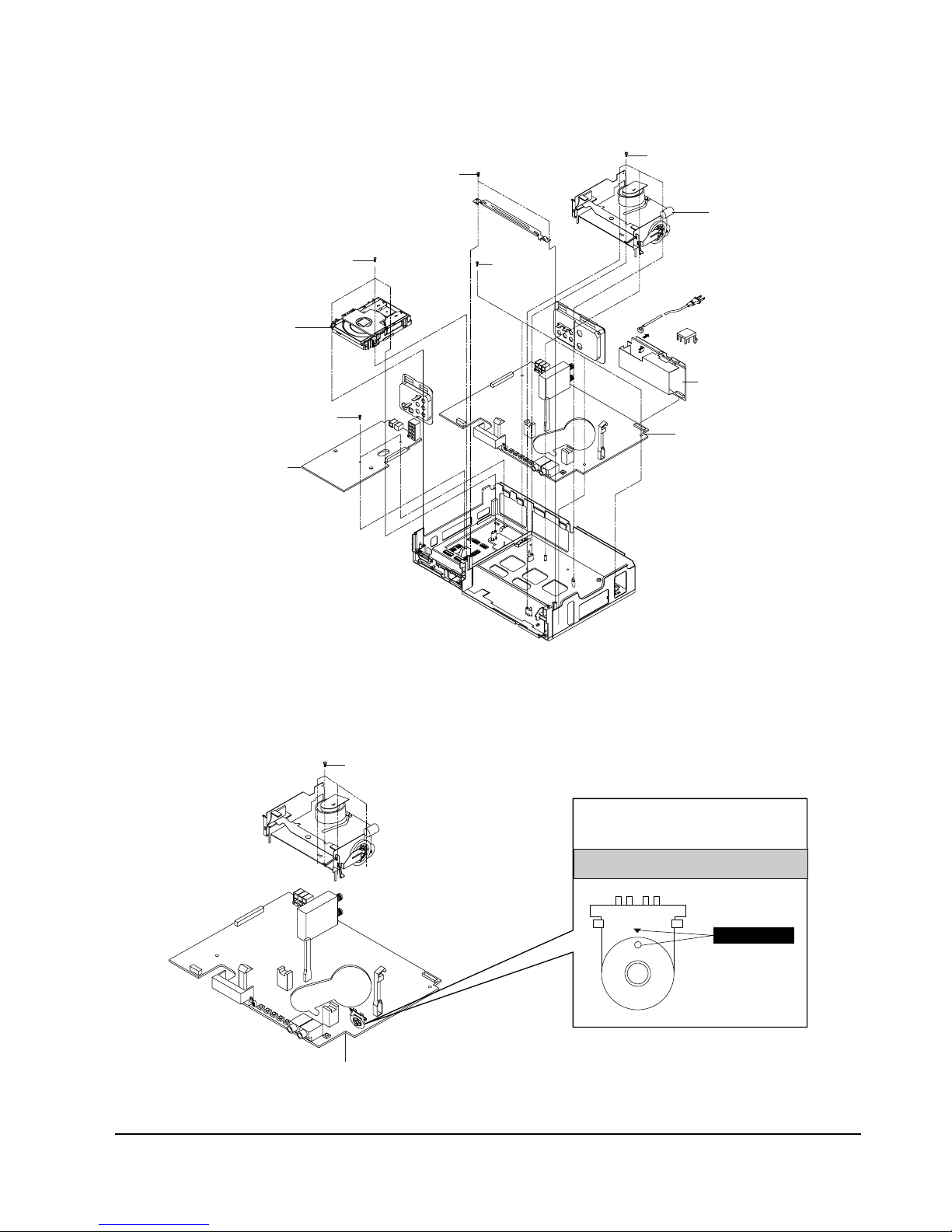
5-1-5 Chassis Removal
VCR MAIN PCB
S.M.P.S PCB
DVD DECK
VCR DECK
DVD MAIN PCB
ΠREMOVE 2 SCREWS
´ REMOVE 4 SCREWS
ˇ REMOVE 3 SCREWS
¨ REMOVE 2 SCREWS
ˆ REMOVE
3 SCREWS
Fig. 5-5 Chassis Removal
5-1-6 VCR Main PCB Removal
ΠREMOVE 4 SCREWS
VCR MAIN PCB
MODE SWITCH
When installing the ass'y full deck on the Main PCB,
be sure to align the assembly point of mode switch.
ASSEMBLY POINT
Fig. 5-6 VCR Main PCB Removal
Disassembly and Reassembly
5-3Samsung Electronics
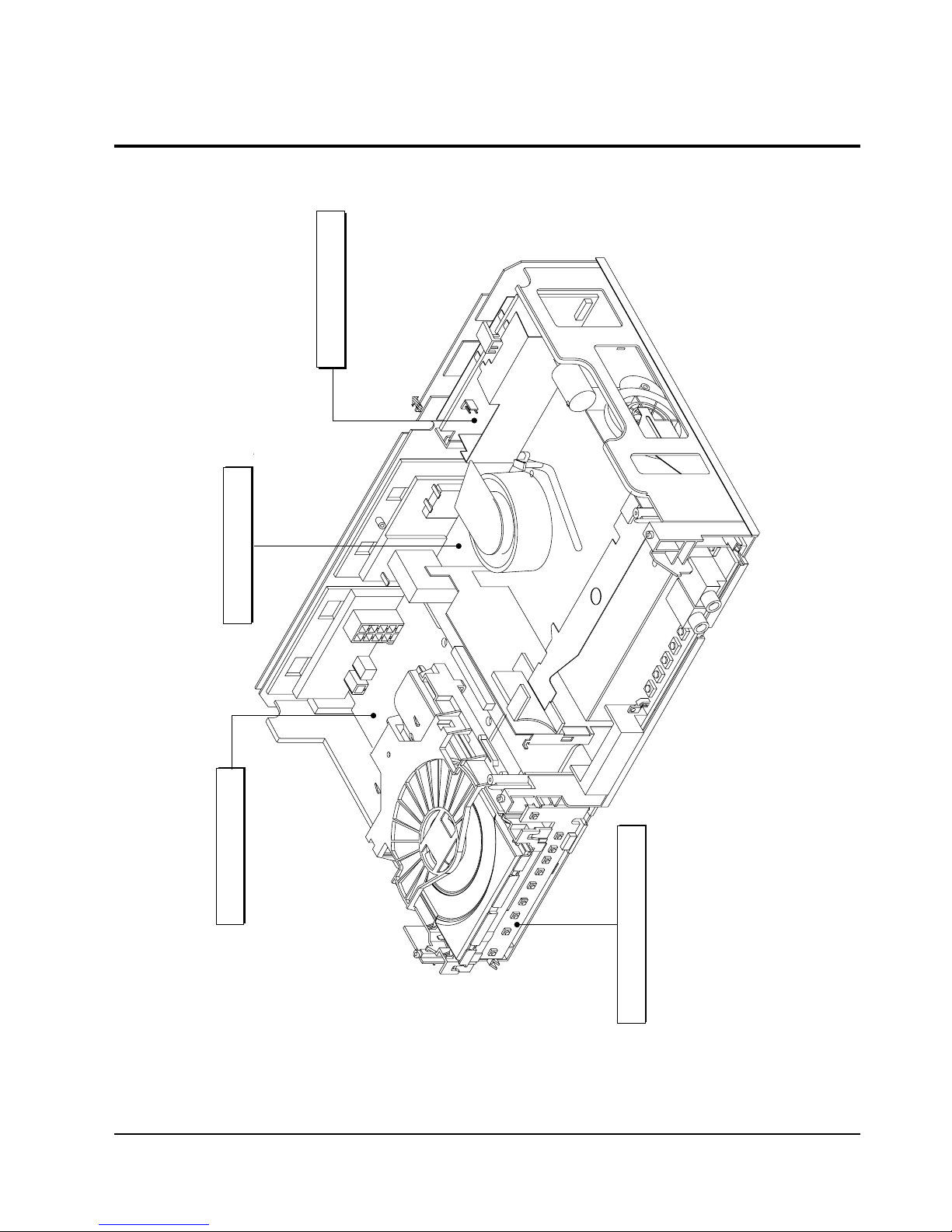
5-2 Circuit Board Locations
DVD MAIN PCB
FUNCTION PCB
VCR MAIN PCB
S.M.P.S PCB
Fig. 5-7 Circuit Board Locations
5-4
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
5-3 VCR Deck Parts Locations
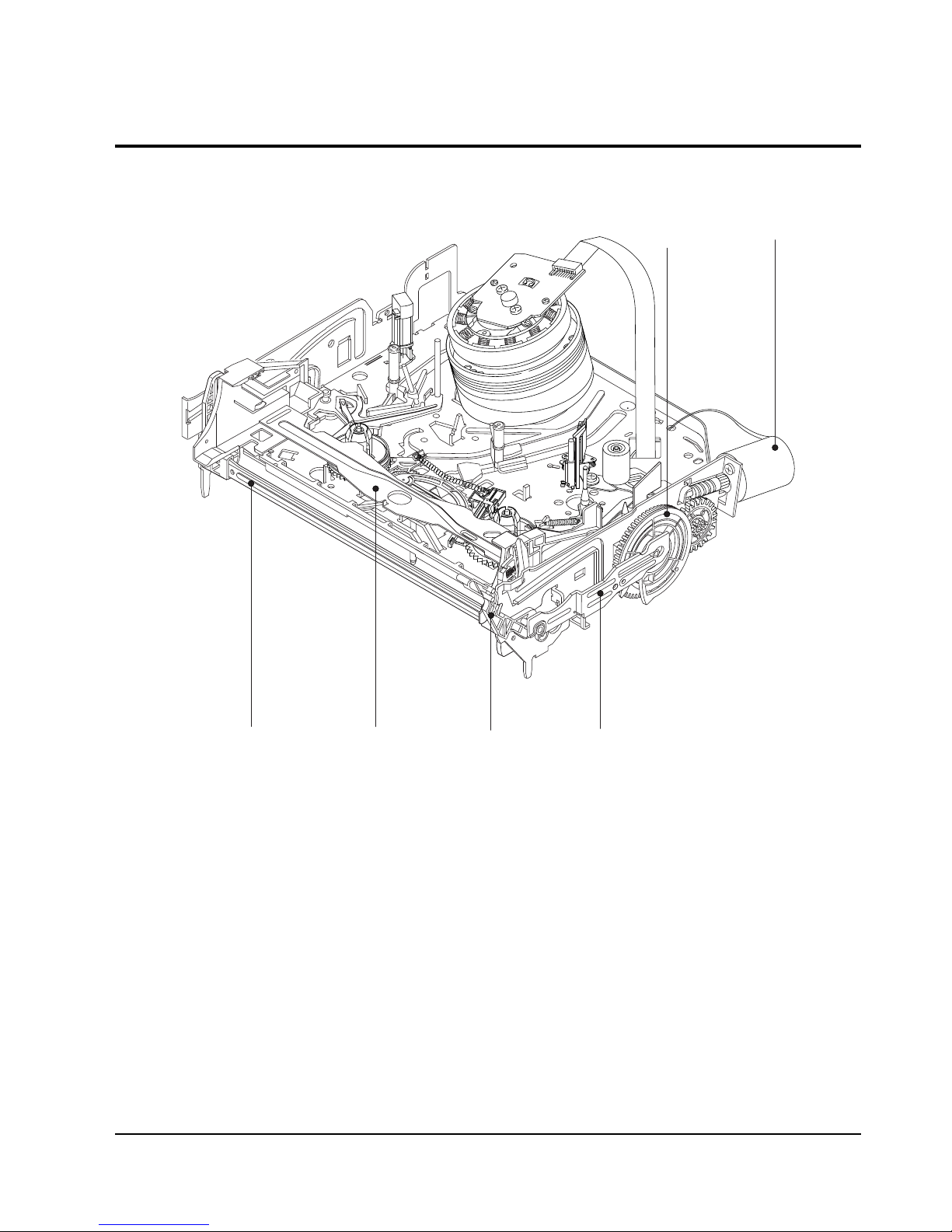
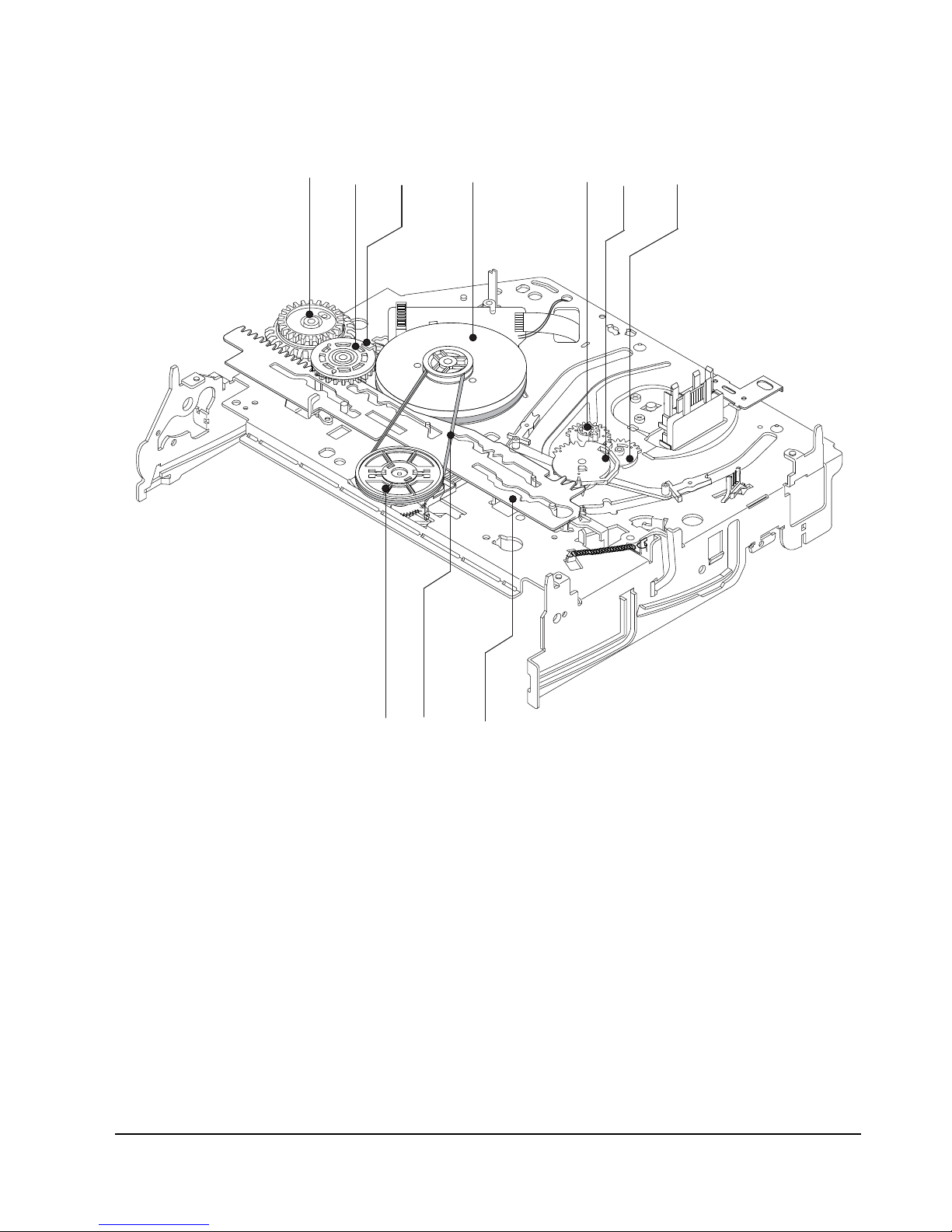
5-3-1 Top View
Œ
´
ˆ
Ø
ˇ
¨
Fig. 5-8 Top parts Location-1
ΠGEAR FL CAM
´ MOTOR LOADING ASS’Y
ˇ LEVER FL ARM ASS’Y
¨ HOLDER FL CASSETTE ASS’Y
ˆ LEVER FL DOOR
Ø SLIDER FL DRIVE

Disassembly and Reassembly
5-5Samsung Electronics
Œ
´
Ø
∏”’ Ô˝
Ò
˝
ˇ¨
ˆ
Fig. 5-9 Top Parts Location-2
ΠFE HEAD
´ CYLINDER ASS’Y
ˇ ACE HEAD ASS’Y
¨ LEVER UNIT PINCH ASS’Y
ˆ LEVER #9 GUIDE ASS’Y
Ø LEVER TENSION ASS’Y
∏ BAND BRAKE ASS’Y
” DISK S REEL
’ LEVER S BRAKE ASS’Y
˝ GEAR IDLE
Ô LEVER IDLE
LEVER T BRAKE ASS’Y
Ò DISK T REEL
5-6
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
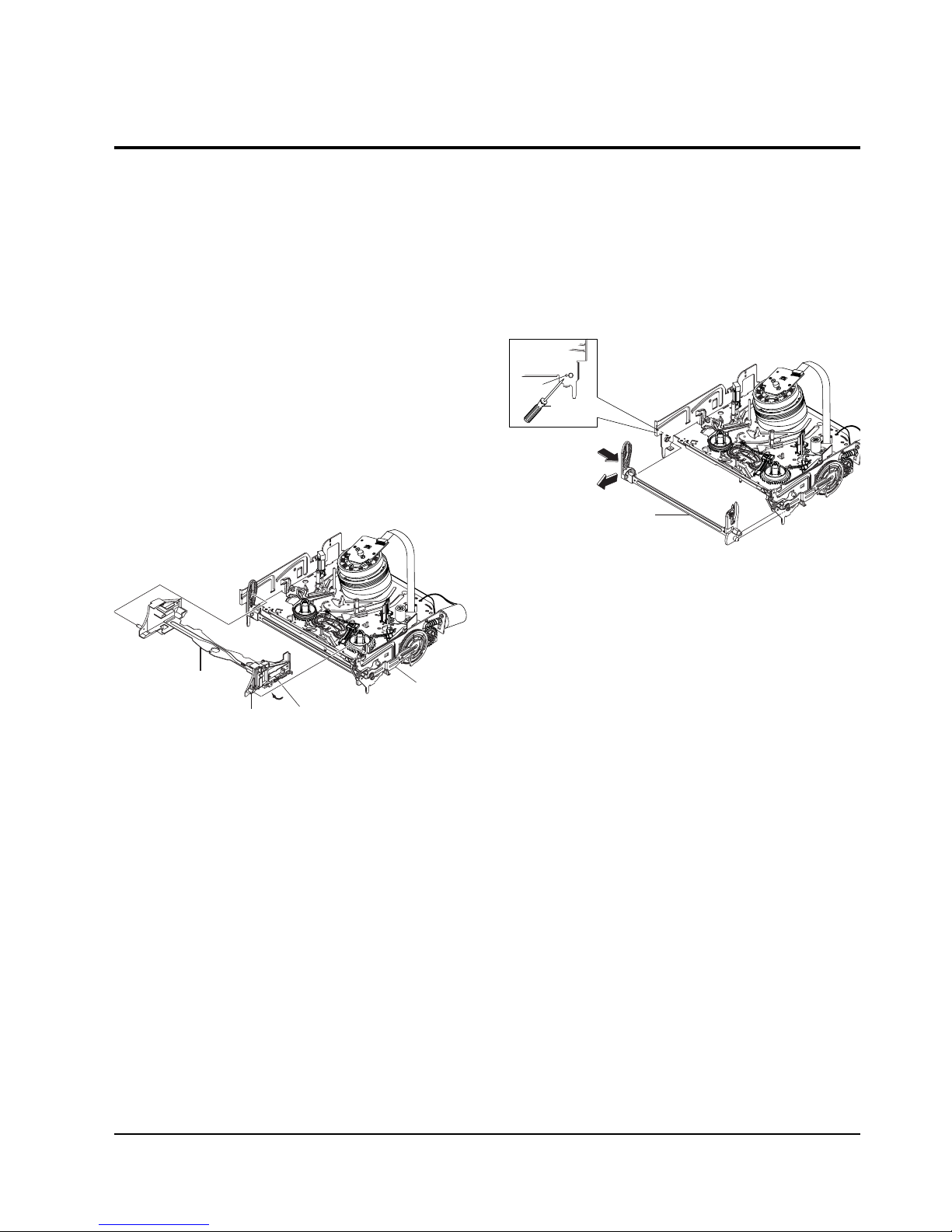
5-3-2 Bottom View
Œ
´ˇ
¨
ˆ
Ø
∏
”
’
˝
Fig. 5-10 Bottom Parts Location
ΠGEAR JOINT 1
´ GEAR JOINT 2
ˇ BRAKET GEAR
¨ MOTOR CAPSTAN ASS’Y
ˆ LEVER T LOAD ASS’Y
Ø GEAR LOADING DRIVE
∏ LEVER S LOAD ASS’Y
” HOLDER CLUTCH ASS’Y
’ BELT PULLEY
˝ SLIDER CAM
Disassembly and Reassembly
5-7Samsung Electronics
5-4 VCR Deck
ΠLEVER FL ARM ASS'Y
"C"
"B"
PIN
HOLE "A"
5-4-1 Holder FL Cassette Ass’y Removal
1) Pull the Holder FL Cassette Ass'y Πto the eject
position.
2) Pull the Holder FL Cassette Ass'y Πas grasping
the Holder FL Cassette Ass'y Πand Lever FL
Cassette-R ´ in the same time to release hooking
from Main Base until the Boss [A] of Holder FL
Cassette Ass'y Πis taken out from the Rail [B].
3) Lift the Holder FL Cassette Ass'y Œ, in this time,
you have to grasp the Lever FL Cassette-R ´
Continuously until the Holder FL Cassette Ass'y
Πis taken out completely.
Note : Be sure to insert Lever FL Cassette-R ´ in the
direction of “A” to prevent separation and breakage
of the Lever FL Cassette-R ´ at disassembling and
reassembling.
RAIL [B]
BOSS [A]
´ LEVER FL CASSETTEE -R
"A"
ΠHOLDER FL
CASSETTEE ASS'Y
Fig. 5-11 Holder FL Cassette Ass’y Removal
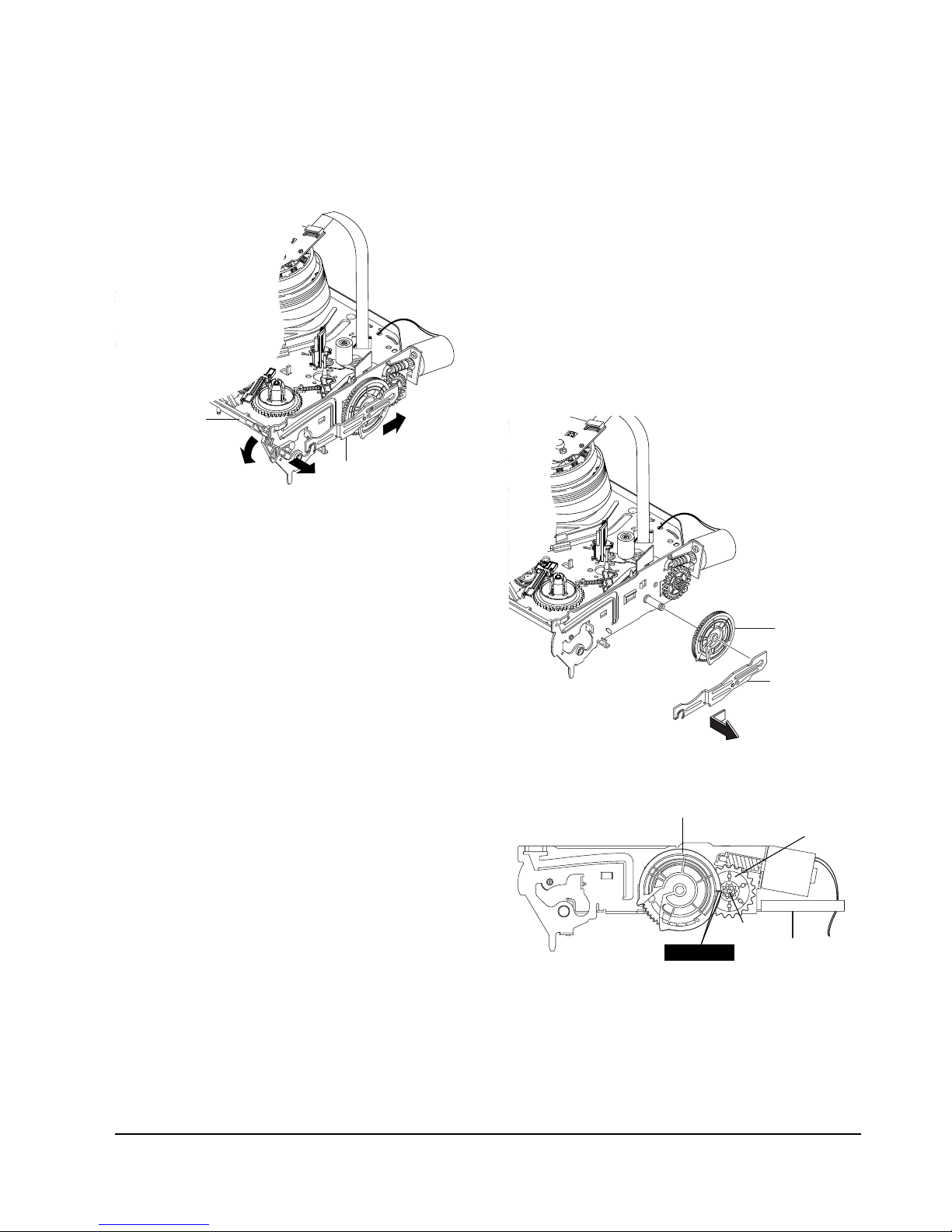
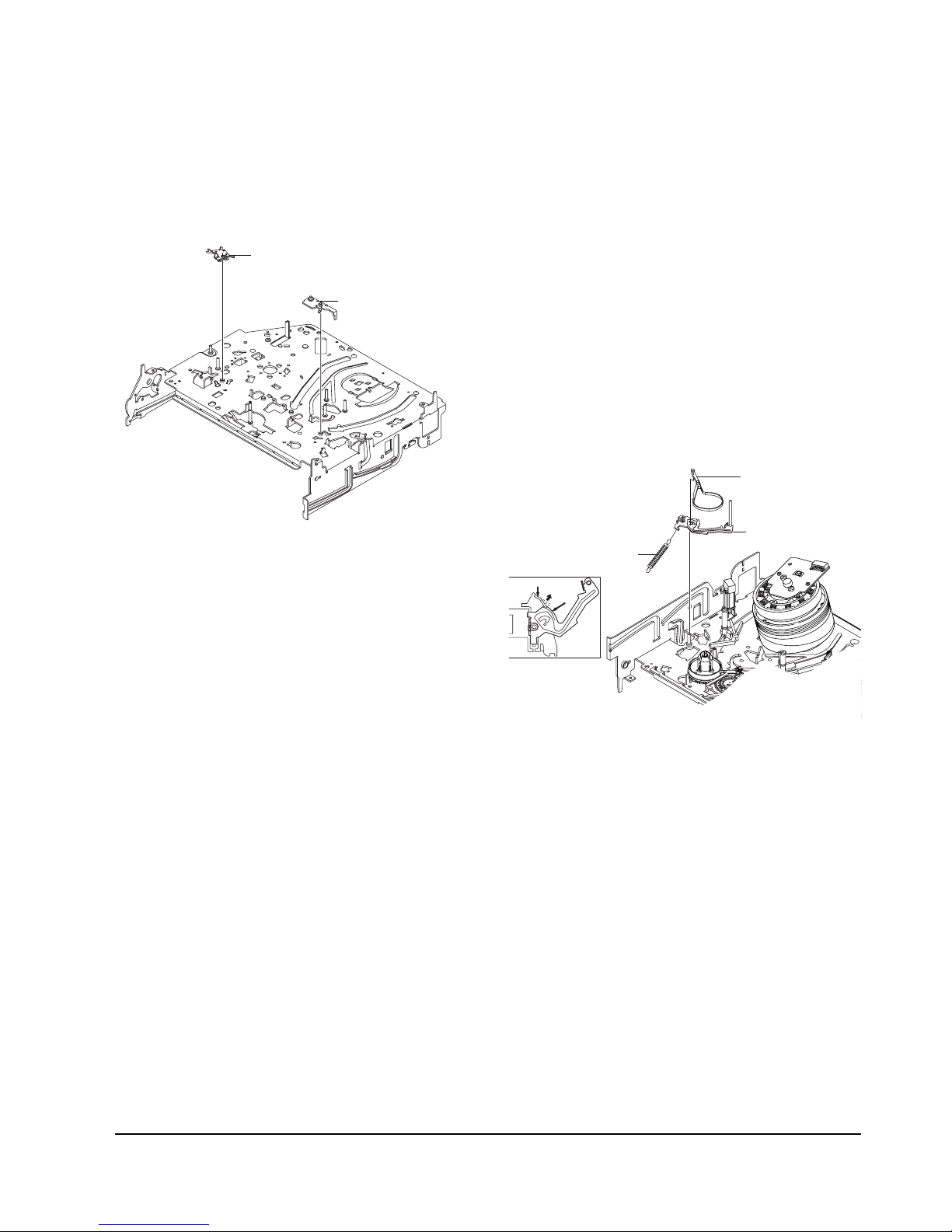
5-4-2 Lever FL Arm Ass’y Removal
1) Push the hole “A” in the direction of arrow “B”
use the pin.(about Dia. 2.5)
2) Pull out the Lever FL Arm Ass'y Πfrom the Boss
of Main Base.
3) Remove the Lever FL Arm Ass'y Πin the direction
of arrow “C”.
Fig. 5-12 Lever FL Arm Ass’y Removal
5-8
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
ΠGEAR FL CAM
GEAR WORM WHEEL
POST
TIMING POINT
Fig. 5-15 Gear FL Cam, Gear Worm
5-4-4 Slider FL Drive, Gear FL Cam Removal
1) Pull the Slider FL Drive Πto the front direction.
2) Remove the Slider FL Drive Πin the direction of
arrow. (Refer to Fig. 5-13)
3) Remove the Gear FL cam ´.
Note : When reinstalling be sure to reassemble Slider
FL drive Πafter you insert the Boss of Lever FL
ARM-R in Groove of Slider Fl drive Œ.
Assembly : Align the Gear FL Cam Πwith the Gear
worm wheel Post as shown drawing.
(Refer to Timing point)
ΠSLIDER FL DRIVE
´ GEAR FL CAM
Fig. 5-14 Slider FL Drive Removal
5-4-3 Lever FL Door Removal
1) Release the Hook ´ and Remove the Lever FL
Door Œ in the direction of arrow “A”.
Fig. 5-13 Lever FL Door Removal
"B"
"C"
"A"
´ LEVER FL DOOR
ΠSLIDER FL DRIVE

Disassembly and Reassembly
5-9Samsung Electronics
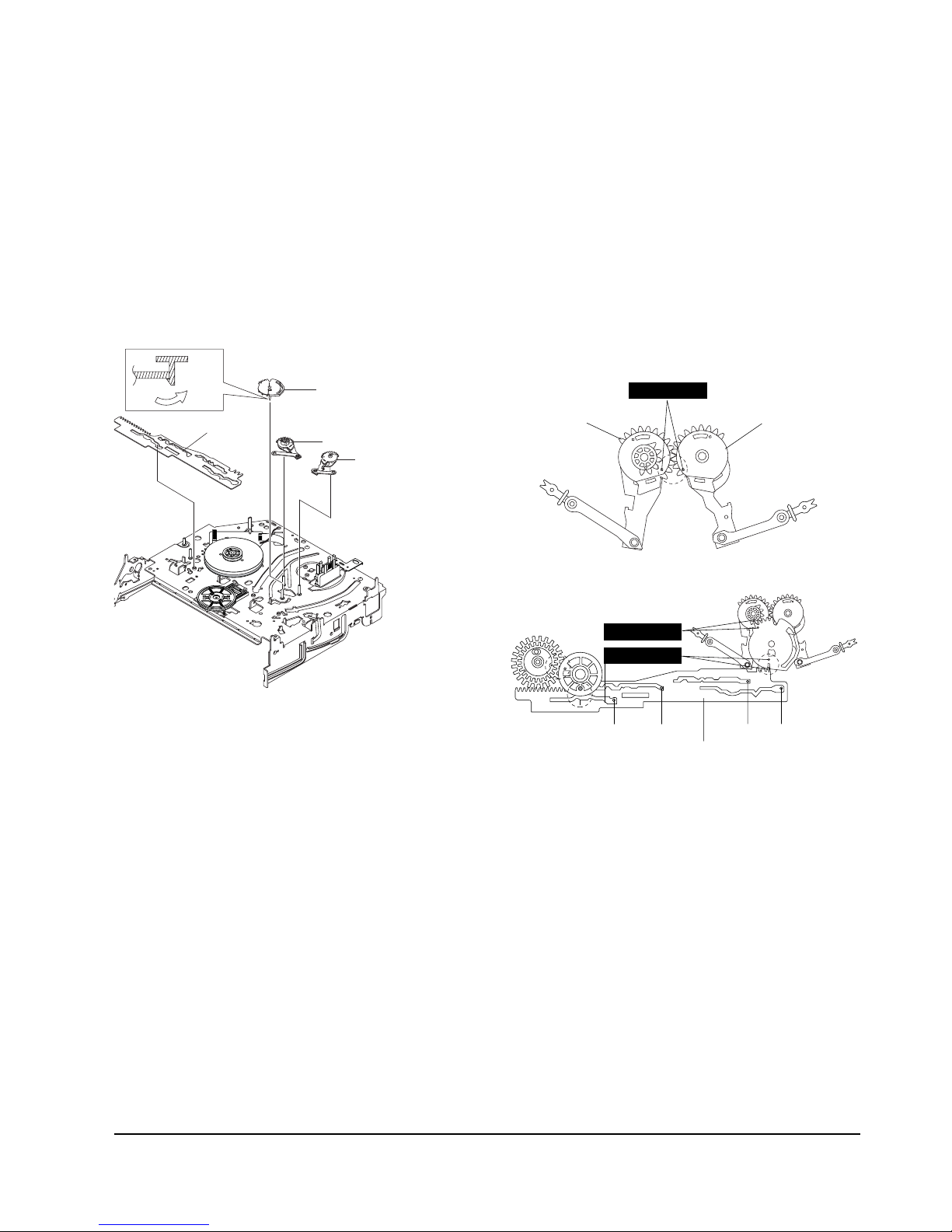
5-4-5 Gear Worm Wheel Removal
1) Remove the Gear Worm wheel Œ.
ΠGEAR WORM WHEEL
Fig. 5-16 Gear Worm Wheel Removal
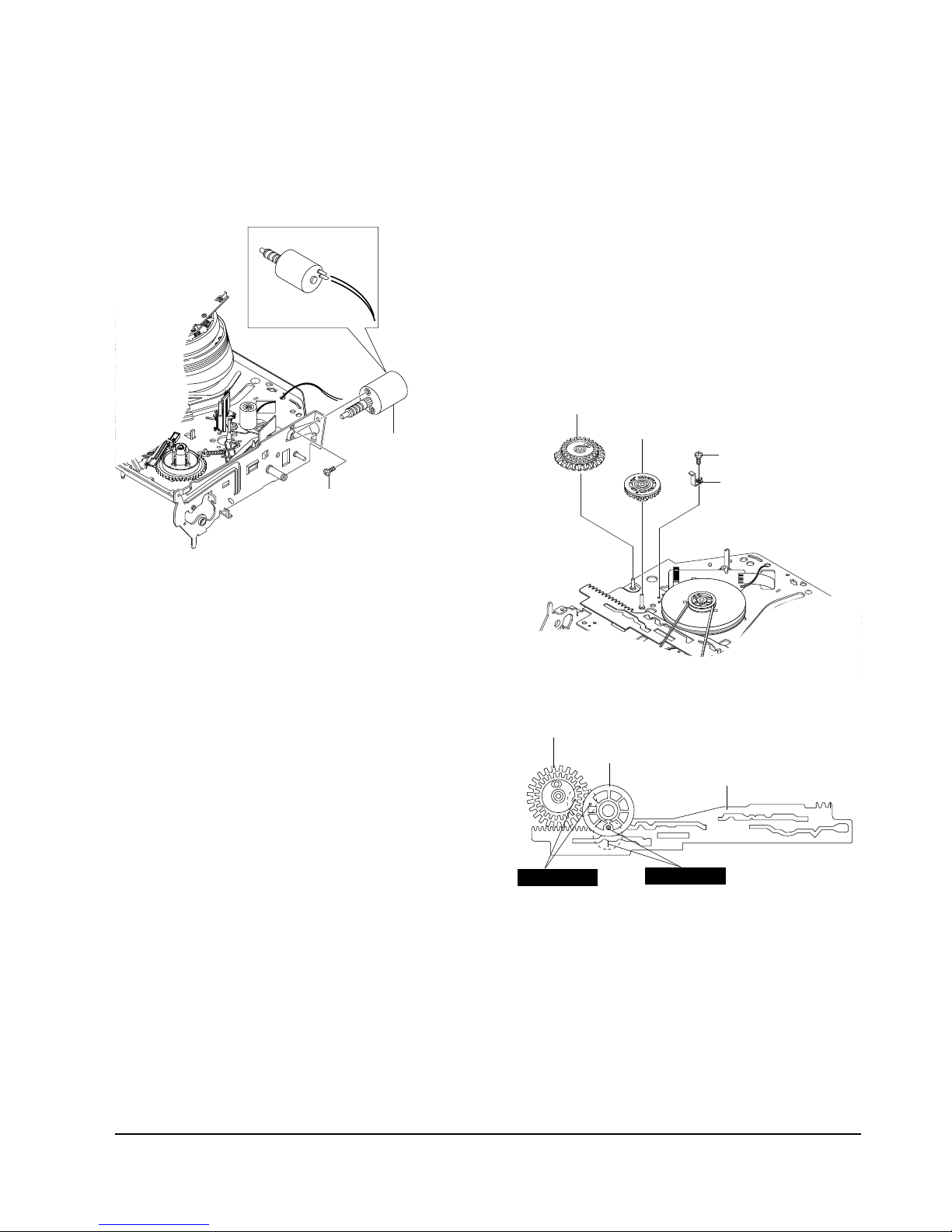
5-4-6 Cable Flat Removal
1) Remove the Drum connecting part of Cable Flat Œ
from Connector Waffer ´.
´ CONNECTOR WAFER
ΠCABLE FLAT
Fig. 5-17 Cable Flat Removal
5-10
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
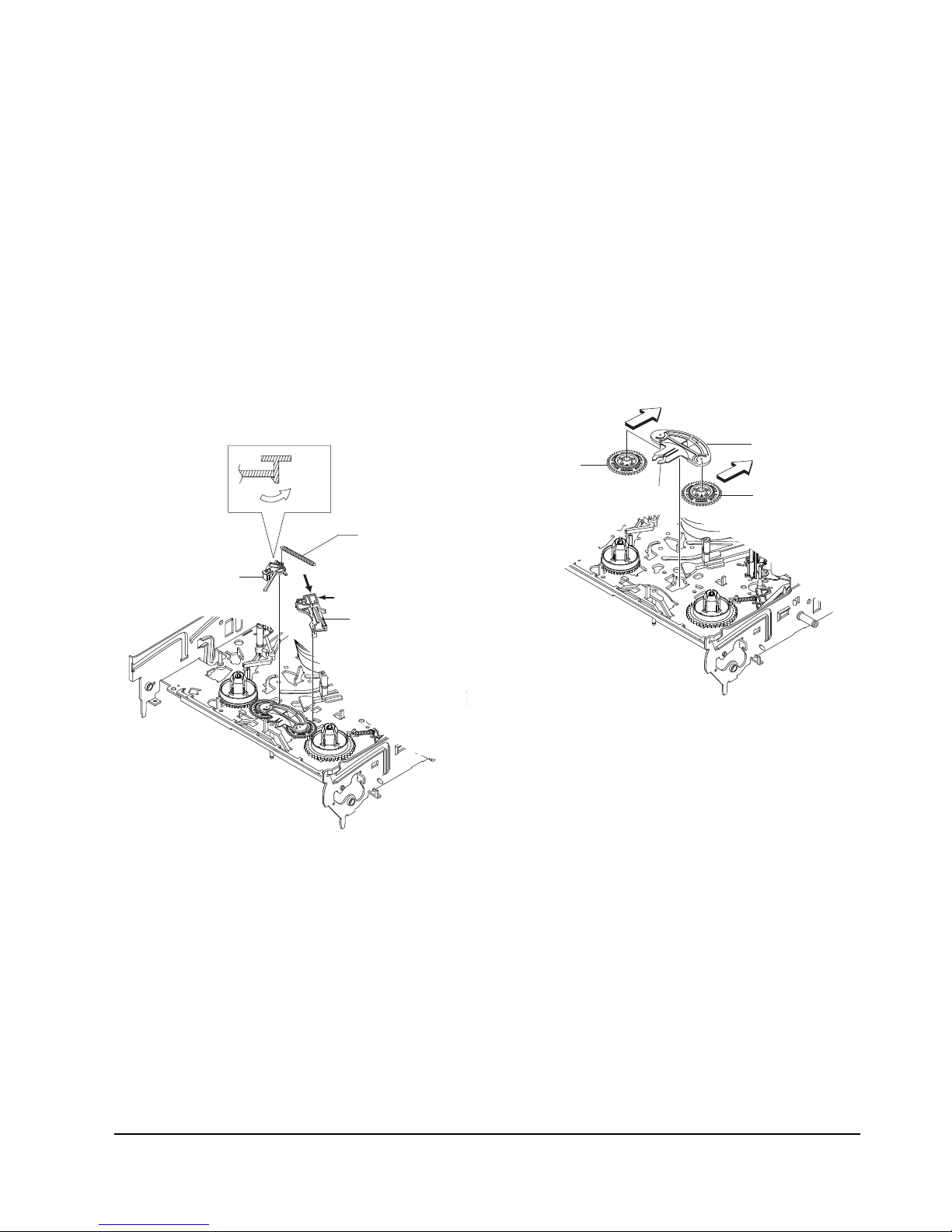
5-4-8 Bracket Gear, Gear Joint 2, 1 Removal
1) Remove the SCREW Œ.
2) Remove the Bracket Gear ´.
3) Remove the Gear Joint 2 ˇ.
4) Remove the Gear Joint 1 ¨.
Assembly :
1) Be sure to align dot mark of Gear Joint 1 Œwith
dot mark of Gear Joint 2 ´ as shown Fig 5-20.
(Refer to Timing point1)
2) Confirm the Timing Point 2 of the Gear Joint 2 ´
and Slider Cam ˇ.
ΠSCREW
´ BRAKET GEAR
¨ GEAR JOINT 1
ˇ GEAR JOINT 2
Fig. 5-19 Bracket Gear, Gear Joint 1,2 Removal
ΠGEAR JOINT1
´ GEAR JOINT2
ˇ SLIDER CAM
TIMING POINT 1
TIMING POINT 2
Fig. 5-20 Gear Joint 1,2 Assembly
5-4-7 Motor Loading Ass’y Removal
1) Remove the screw Œ.
2) Remove the Motor Loading Ass’y ´.
´ MOTOR LOADING ASS`Y
ΠSCREW
Fig.5-18 Motor Loading Ass’y Removal
Disassembly and Reassembly
5-11Samsung Electronics
5-4-10 Gear Loading Drive, Slider Cam,
Lever Load S, T Ass’y Assembly
1) When reinstalling, be sure to align dot of Lever
Load T Ass'y Œwith dot of Lever Load S Ass'y ´
as shown in drawing, (Refer to Timing Point 1).
2) Insert the Pin A,B,C,D into the Slider Cam ˇhole,
3) Be sure to align dot of Lever Load T Πand dot of
Gear Loading Drive ¨, (Refer to Timing Point 2).
4) Aline dot of Gear Loading drive ¨ with mark of
Slider Cam ˇ as shown in drawing(Refer to
Timing Point 3).
´ LEVER LOAD S
Œ
LEVER LOAD T
PIN A
PIN C
PIN B
PIN D
ˇ SLIDER CAM
TIMING POINT 2
TIMING POINT 1
TIMING POINT 3
Fig. 5-22 Gear Loading Drive, Slider Cam,
Lever Load S, T Ass’y Assembly
5-4-9 Gear Loading Drive, Slider Cam,
Lever Load S, T Ass’y Removal
1) Remove the Belt Pulley. (Refer to Fig. 5-38)
2) Remove the Gear Loading Drive Πafter releasing
Hook [A] in the direction arrow as shown in detail
drawing.
3) Remove the Slider Cam ´.
4) Remove the Lever Load S Ass’y ˇ & Lever Load T
Ass’y ¨.
ΠGEAR LOADING DRIVE
ˇ LEVER LOAD S ASS'Y
¨ LEVER LOAD T ASS'Y
´ SLIDE CAM
HOOK(A)
Fig. 5-21 Gear Loading Drive, Slider Cam,
Lever T, S Load Ass’y Removal
5-12
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics
5-4-12 Lever Tension Ass’y,
Band Brake Ass’y Removal
1) Remove the Lever Brake S Ass'y (Refer to Fig 5-25).
2) Remove the Spring Tension Lever Œ.
3) Rotate stopper of Main Base in the direction of
arrow “A”.
4) Lift the Lever Tension Ass'y ´ & Band brake
Ass'y ˇ.
Note :
1) When replacing the Lever Tension Ass'y ´, be sure
to apply Grease on the post,
2) Take care not to touch stain on the felt side, and not
to be folder and broken Band brake Ass'y
3) After Lever Tension Ass'y seated, Rotate stopper of
Main Base to the Mark[B].
ΠSPRING TENTION LEVER
´ LEVER TENTION ASS`Y
ˇ BAND BRAKE ASS`Y
STOPPER
MARK[B]
"A"
Fig. 5-24 Lever Tension Ass’y,
Band Brake Ass’y Removal
5-4-11 Lever Pinch Drive,
Lever Tension Drive Removal
1) Remove the Lever Pinch Drive Œ, Lever Tension
Drive ´.
ΠLEVER PINCH DRIVE
´ LEVER TENSION DRIVE
Fig. 5-23 Lever Pinch Drive,
Lever Tension Drive Removal
Disassembly and Reassembly
5-13Samsung Electronics
5-4-14 Gear Idle Ass’y Removal
1) Push the Lever Idle Πin the direction of arrow
“A”, “B”.
2) Lift the Lever Idle Œ.
Assembly :
1) Apply oil in two Bosses of Lever Idle Œ.
2) Assemble the Gear Idle ´ with the Lever Idle Œ.
Note : When replacing the Gear Idle ´, be sure to
add oil in the boss of Lever Idle Œ.
´ GEAR IDLE
"B"
ΠLEVER IDLE
´ GEAR IDLE
"A"
HOOK "C"
Fig. 5-26 Gear Idle Ass’y Removal
5-4
-13 Lever Brake S, T Ass’y
Removal
1) Release the Hook [A] and the Hook [B], [C] in the
direction of arrow as shown in Fig 5-25.
2) Lift the Lever S, T Brake Ass'y Œ, ´ with spring
brake ˇ.
Assembly :
1)Assembly the Lever S Brake Ass'y Πon the Main
Base.
2)Assembly the Lever T Brake Ass'y ´ with spring
brake ˇ.
Note : Take extreme care not to be folded and
transformed Spring Brake at removing or reinstalling.
HOOK(A)
´ LEVER T BRAKE ASS`Y
ΠLEVER S BRAKE ASS'Y
HOOK(B)
HOOK(C)
ˇ SPRING BRAKE
Fig. 5-25 Lever Brake S, T Ass’y Removal
 Loading...
Loading...