NEC IS010-12E User Manual

NEC Storage Manager
Messages Handbook
IS010-12E

© NEC Corporation 2001-2004
No part of the contents of this book may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form without permission of NEC Corporation.
The contents of this book may be modified without notice in the future.

Preface
This manual explains messages handled by NEC Storage Manager. The messages are listed in the order of message
IDs. Refer to the “NEC Storage Manager Manual Guide” (IS901) for the overview of the NEC Storage and the
related manuals.
Remarks 1. This manual explains functions implemented by the following program products:
• NEC Storage Manager and NEC Storage BaseProduct
• NEC Storage AccessControl
• NEC Storage PerformanceMonitor
• NEC Storage PerformanceOptimizer
• NEC Storage ReallocationControl
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl/DisasterRecovery
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl SQL Option
2. This manual is applicable to the program products of the following versions:
• NEC Storage Manager Ver3.3
• NEC Storage BaseProduct Ver3.3
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl Ver3.3
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl/DisasterRecovery Ver3.3
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl SQL Option Ver3.2
• NEC Storage SnapControl Ver3.3
3. The NEC Storage Manager is referred to as iSM or Storage Manager in the text of this manual. Also,
the NEC Storage series disk array subsystem is referred to as a disk array.
4. The following descriptions in the text of this manual refer to the corresponding products.
Description Corresponding Product
Storage Manager NEC Storage Manager
BaseProduct NEC Storage BaseProduct
ReplicationControl SQL
Option
NEC Storage ReplicationControl SQL Option
AccessControl NEC Storage AccessControl
DynamicDataReplication NEC Storage DynamicDataReplication
PerformanceMonitor NEC Storage PerformanceMonitor
RemoteDataReplication NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication
NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication/DisasterRecovery
ReplicationControl NEC Storage ReplicationControl
NEC Storage ReplicationControl/DisasterRecovery
SnapControl NEC Storage SnapControl
5. The following descriptions in the text of this manual refer to the corresponding manuals.
Description Corresponding Manual
User's Manual (UNIX) NEC Storage Manager User's Manual (UNIX) (IS001)
User's Manual NEC Storage Manager User's Manual (IS004)
Data Replication User's Manual
(Function Guide)
NEC Storage Data Replication User's Manual
(Function Guide) (IS015)
Data Replication User's Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows) (IS016)
NEC Storage Data Replication User's Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows) (IS016)
Data Replication Command Reference NEC Storage Data Replication Command Reference (IS021)
6. The term “Microsoft SQL Server 2000” in this text refers to as either Microsoft SQL Server 2000
Enterprise Edition or the Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition.
7. Trademarks and registered trademarks
• HP-UX is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Co. in the United States.
• UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
• Microsoft® and Windows® are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
• Solaris is a trademark or a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and
other countries.
• Linux is a trademark or registered trademark of Mr. Linus Torvalds in the United States and other
countries.
Other product names and company names, etc. are registered trademarks or trademarks of the
associated companies.
The First Edition in May 2002
The Twelfth Edition in November 2004

i
Contents
Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations ..................................................................................................................1
1.1 Message Classification ................................................................................................................................................3
1.2 Message Output Destinations ...................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3 Message Output Format ..............................................................................................................................................6
Chapter 2 Message List ....................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.1 Interpretation of Message List.....................................................................................................................................8
2.2 Message List................................................................................................................................................................9
Appendix A Message Output Destination List .................................................................................................................634
Appendix B Changed Message List...................................................................................................................................673

ii
This page is intentionally left blank.

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
1
Chapter 1 Messages and Output
Destinations
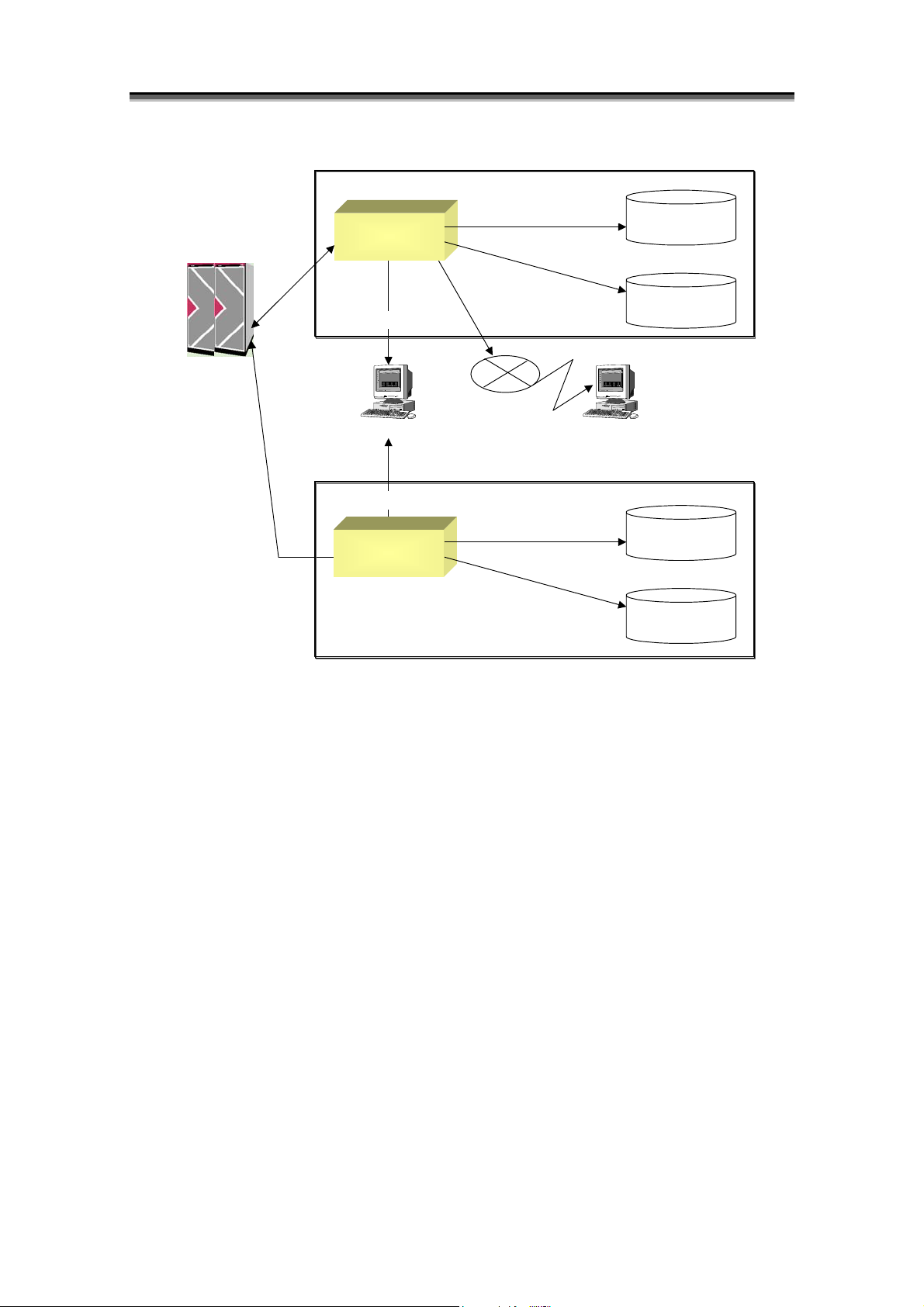
The Storage Manager outputs the information, which is required for maintenance and operation of a disk array and
the Storage Manager, to log files of the console/terminal and the management server. The log files to which a
message is output are syslog, event log, and operation log. The message describes information that indicates
events to be reported to an administrator, such as system state transition, fault and error detection, and command
input results.
The ReplicationControl outputs the operation information of data replication in a message format, to the log files
of the console/terminal and the business server. The message is output to syslog, event log, and operation log.
The message describes the information for checking operating conditions, such as command execution results, and
fault and error detection information, etc.
If ESMPRO Agent has been installed in the management server on which the Storage Manager has started,
messages are output to ESMPRO Manager.
Figure 1-1 shows an overview of message output.
Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
2
Business
server
Management server
Storage Manager
Console/Terminal
Disk array
Output to syslog (UNIX) or event log
(Windows)
Output to console/terminal
Syslog or
event log
Operation log
Output to syslog (UNIX) or even
t
log (Windows)
Output to console/terminal
ReplicationControl
Syslog or
event log
Operation log
Output to ESMPRO Manager when ESMPRO
Agent installed (only for Windows)
Figure 1-1 Overview of Message Output

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
3
1
1
1
.
.
.
1
1
1
M
M
M
e
e
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
a
a
a
g
g
g
e
e
e
C
C
C
l
l
l
a
a
a
s
s
s
s
s
s
i
i
i
f
f
f
i
i
i
c
c
c
a
a
a
t
t
t
i
i
i
o
o
o
n
n
n
A message classification is assigned to a message, according to its level of urgency. Messages are
classified into the following four classifications, in the order of urgency: “ERROR”, “WARNING”,
“NOTICE”, and “INFO”. A message classification is also referred to as a message level.
Meanings of the messages are as follows:
y ERROR: Error message
This message indicates an error that has a critical effect to the functions, and prompt recovery by an
administrator is required. An administrator must troubleshoot and recover the system promptly.
y WARNING: Warning message
This message indicates an event that requires attention regarding the system operations, though the
event does not necessarily lead to the system down immediately. An administrator must remove the
cause of the event and take measures to operate the system normally.
y NOTICE: Notifying message
This message notifies the state of internal processes. Although the event notified by the message
does not have any effect on the main functions of disk arrays, an administrator must take appropriate
measures as necessary.
y INFO: Information message
This message indicates operating information. No measures are required.

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
4
1
1
1
.
.
.
2
2
2
M
M
M
e
e
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
a
a
a
g
g
g
e
e
e
O
O
O
u
u
u
t
t
t
p
p
p
u
u
u
t
t
t
D
D
D
e
e
e
s
s
s
t
t
t
i
i
i
n
n
n
a
a
a
t
t
t
i
i
i
o
o
o
n
n
n
s
s
s
The output destinations of messages depend on functions and OS to be used. Output destinations are
the console/terminal, operation log, syslog, event log, and ESMPRO Manager. Message output
destinations are described as follows:
y Console/Terminal
A console is a monitoring terminal that is directly connected to the monitoring server of the iSM.
On the other hand, a terminal is a client terminal that is connected to the monitoring server via telnet,
etc. When a command is issued from the iSM or the ReplicationControl, a message indicating
execution result is displayed on the console or the terminal where the command is executed.
y Operation log
Operation log, which is output on UNIX and Windows, records the messages output from the iSM or
the ReplicationControl only. During the operation of iSM client, the information output to the
operation log is also displayed on the message display area of the state monitor screen. Operation
logs are output as the following directory/file names by default.
(1) Storage Manager operation log
UNIX system:
/opt/iSMsvr/etc/log/iSM_Log.log
Windows system:
<Installation directory>\iSMsvr\etc\log\iSM_Log.log
(2) ReplicationControl operation log
HP-UX system:
/opt/iSMrpl/etc/*.log
/opt/iSMvol/etc/*.log
Solaris system:
/opt/NECiSMrpl/etc/*.log
/opt/NECiSMvol/etc/*.log
Windows system:
<Installation directory>\iSMrpl\etc\trace\*.log
<Installation directory>\iSMvol\etc\trace\*.log

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
5
y syslog
This is output on UNIX system. Together with the messages output by UNIX, the messages output
from iSM and ReplicationControl are recorded. The output format depends on the OS (HP-UX or
Solaris). Output/no output or output destinations of messages, which is output to syslog, can be
specified by modifying descriptions for type (level) and function (facility) in OS settings file
(/etc/syslog.conf).
Note 1: On Solaris system, a message, of which function is “daemon” and classification is “INFO”,
is not output as the default value. Also, a message, of which function is “user” and
classification is “WARNING”, “NOTICE”, or “INFO” is not output as the default value.
To output these kinds of messages, modify the OS settings file.
Note 2: The function of messages output from the iSM to syslog is “Daemon”. However, the
function of the messages output by the ReplicationControl command is “user”.
Messages are output being affixed the following directory/file name as the default value:
HP-UX system:
/var/adm/syslog/syslog.log
Solaris system:
/var/adm/messages
y Event log
This is output on Windows system. Together with the messages output by windows, the messages
output from the iSM and the ReplicationControl are recorded. The messages are output to
application log in the event log. The event log has the functions similar to those of UNIX syslog,
however, the content of the log are different. The event log can be viewed using the [Event Viewer]
in the Management Tool. A message classification and an event log type correspond as follows.
ERROR: Error
WARNING: Warning
NOTICE/ INFO: Information
y ESMPRO Manager
Messages are output to ESMPRO Manager in the Windows environment. If ESMPRO Agent has
been installed in the management server on which the Storage Manager has started, messages to be
notified to the ESMPRO manager of all the messages that the Storage Manager server outputs to an
event log are automatically set to display on the ESMPRO Manager alert viewer. To change the
setting, ESMPRO Agent notification setting must be changed. The notification function provided by
ESMPRO is also available.

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
6
1
1
1
.
.
.
3
3
3
M
M
M
e
e
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
a
a
a
g
g
g
e
e
e
O
O
O
u
u
u
t
t
t
p
p
p
u
u
u
t
t
t
F
F
F
o
o
o
r
r
r
m
m
m
a
a
a
t
t
t
This section describes the message output format and the errno output rule. For details on the message
text, refer to Chapter 2 “Message List”.
The following shows the output format of a message:
Mon Date hh:mm:ss hhhhhh ffffffff :mmmmmm cccccccc : iSMyyyyy : Message body
Mon Date : Month and date
hh:mm:ss : Time
hhhhhh : Host name
ffffffff : Function identifier
mmmmmm : Message classification
cccccccc : Command name and function name
yyyyy : Message number
The message, which is output to application log in the event log, includes the following values specified
for each item:
y Classification
ERROR : Error
WARNING : Warning
NOTICE : Information
INFO : Information
y Source
Storage Manager : (fixed)
y Classification
None (fixed)
y Event ID
Number part in the message ID output to the operation log.
The following describes output rules for errno:
y Windows system
1. Routine in C Runtime library: errno value is defined by the library.
2. WIN32 API: The value returned by GetLastError with 20000 added is output.
3. Socket API: The value returned by WSGetLastError with 20000 added is output.

Chapter 1 Messages and Output Destinations
7
y UNIX system
1. A defined value is output as is.

Chapter 2 Message List
8
Chapter 2 Message List
2
2
2
.
.
.
1
1
1
I
I
I
n
n
n
t
t
t
e
e
e
r
r
r
p
p
p
r
r
r
e
e
e
t
t
t
a
a
a
t
t
t
i
i
i
o
o
o
n
n
n
o
o
o
f
f
f
M
M
M
e
e
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
a
a
a
g
g
g
e
e
e
L
L
L
i
i
i
s
s
s
t
t
t
2.2 “Message List” describes the messages in the order of message IDs. The message are described in
the following format:
iSMxxxxx: AAAAA<aaa>,<bbb...b>
Message ID (iSMxxxxx) and message body (AAAAA<aaa>,<bbb...b>) are described.
Descriptions using parentheses such as <aaa> and <bbb...b> indicate that parameter values are not fixed.
(The parentheses “<” and “>” are not displayed in the actual message.)
For details of parameter values, refer to [Explanation].
Messages subject to ALIVE report (including ALIVE report from a disk array) are followed by the
keyword [_ALERT_] and output to each destination. For messages subject to ALIVE report
excluding ALIVE report from a disk array, refer to Appendix A “Message Output Destination List”.
[Classification] Message classification (ERROR, WARNING, NOTICE, or INFO) is described.
A message that is not output to syslog, event log, or operation log is output
without a message classification. This field is blank for such a message that is
output without a message classification.
[Explanation] This field describes the causes of the message output, etc. Parameters in the
message are also described in this field.
If a message is output on a specific OS (UNIX or Windows), applicable OS names
are described in this field. Unless otherwise noted, the message is a common
message that is independent of OS.
[Measure] This field describes measures to be taken by an administrator. An administrator
must follow the instructions to take measures.
Note: For output destination of a message, refer to Appendix A “Message Output Destination List”.

Chapter 2 Message List
9
2
2
2
.
.
.
2
2
2
M
M
M
e
e
e
s
s
s
s
s
s
a
a
a
g
g
g
e
e
e
L
L
L
i
i
i
s
s
s
t
t
t
iSM01000 ∼
iSM01001: Storage Manager has started
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that iSM server has started.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01002: Storage Manager is ready
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that iSM server has become capable of operation.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01003: Storage Manager has terminated
normally
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that iSM server has normally terminated.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
[Measures] Unnecessary

Chapter 2 Message List
10
iSM01004: Storage Manager has terminated
emergency
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] Emergency shutdown of iSM server.
This message is output in the iSM server abort processing when iSMsvr stop -e is
executed or the system is shut down.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01005: Command is entered.command=
<aaa…a>
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that a command is entered.
This message is output on UNIX system.
aaa...a: command that is entered
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01006: Termination of Storage Manager is
started
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] It shows that abort processing of iSM server is started.
[Measures] Unnecessary

Chapter 2 Message List
11
iSM01010: Storage Manager has restarted
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that the iSM server is restarted.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01011: <aaa...a> has restarted
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that a process indicated with aaa...a is restarted.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
aaa...a : Process name
[Measures] Unnecessary

Chapter 2 Message List
12
iSM01101: The function is not available.
function=<aaa...a>
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] The function indicated with aaa...a has become unavailable. iSM server will
block the function.
aaa...a : Unavailable function
PerformanceMonitor : Performance monitoring function
ReplicationControl : Replication control function
msgdrv : Event link function
config GUI : Configuration setting GUI function
ALIVEmail : ALIVEmail function
PerformanceOptimizer : Performance optimization function
iSMcmd : Configuration setting GUI function
FileTransfer : File transfer function
SnapShot : Snapshot function
[Measures] Examine the cause by studying iSM server’s syslog or iSM operation log.
To use a function indicated with aaa...a, the iSM server must be restarted.
iSM01102: Command failed
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that iSMsvr stop/update/prf_start/prf_stop/prf_update command
execution is failed. The entered command is ignored.
A message indicating the error cause is displayed before this message is output.
This error may occur when the linkage function or performance monitoring
function is terminated.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Investigate and remove the cause of error by referencing the message that is
displayed before this message. Restart the iSM server if necessary.

Chapter 2 Message List
13
iSM01103: Socket access failed. process=
<aaa...a> func=<bbb...b>
[errno=<ccc>|error=<ddd...d>]
detail=<ee-fff>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] Error has occurred in the socket communication between the processes indicated
with aaa...a and the main process. This error occurs when the process has stopped
or the file environment of iSM Server’s socket path (/opt/iSMsvr/etc/sock) is in
an incorrect status.
aaa...a : Process name
bbb...b : Socket system function name
ccc : Error number
ddd...d : Error contents
timeout : Time out
socket close : Socket is closed
ee-fff : Detail code (This code is not disorder reason but a value for
maintenance.)
[Measures] If an error number is output, check the function name and the error number to
take measures, and restart the iSM server if necessary. When an error contents
is output, examine the cause through the previous message output before this
message and restart the iSM server if necessary.

Chapter 2 Message List
14
iSM01105: File access failed. file=<aaa...a>
func=<bbb...b> errno=<ccc>
detail=<dd-eee>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that an error has occurred in accessing the file indicated with aaa...a.
In this message case, the environment of environment definition file
(/etc/iSMsvr/iSMsvr.conf) or control file (files under /opt/iSMsvr/etc.) may be in
an incorrect status.
aaa...a : File path name
bbb...b : File system function name
ccc : Error number
dd-eee : Detail code (This code is not disorder reason but a value for
maintenance.)
[Measures] Resolve the problem by checking the file path name, function name and error
number, and restart the iSM server.
iSM01106: System call error occurred.
process=<aaa...a> func=<bbb...b>
errno=<ccc> detail=<dd-eee>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that an error has occurred in the system function except the access of
socket/file.
The following hindrance is likely as an example.
y In case of syslog:
The shared memory has been deleted incorrectly with the ipcrm command.
(Access error of shared memory)
y In case of operation log:
System overloading occurred by requests of iSM server. Some resources
have been lost.
aaa...a : Process name
bbb...b : System function name
ccc : Error number
dd-eee : Detail code (This code is not disorder reason but a value for
maintenance.)
[Measures] Check the function name and error number to take measures, and restart the iSM
server if necessary.

Chapter 2 Message List
15
iSM01107: <aaa...a> process has terminated
abnormally
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] It shows that the process indicated with aaa...a has been abnormally terminated.
A message of the cause has been reported from the abnormally terminated
process right before this message.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
aaa...a : Process name
[Measures] Resolve the problem through the previous message output before this message,
and restart the iSM server if necessary.
iSM01108: Storage Manager has already started
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that the iSM server has already started.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01109: Internal error occurred.
detail=<aa-bbb>
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] It shows that an internal error has occurred in the main process of iSM server.
iSM server will be terminated.
aa-bbb : Detail code (This code is not disorder reason but a value for
maintenance.)
[Measures] Acquire the information and restart the iSM server if necessary. For the
acquiring method of the information, refer to 6.1.9 “Information Gathering
Method when Server Fault with Unknown Cause” of the “User’s Manual”.
Chapter 2 Message List
16
iSM01110: Illegal configuration. file=<aaa...a>
line=<bbb...b> [section=<ccc...c>]
[keyword=<ddd...d>]
[value=<eee...e>] [token=<fff...f>]
[detail=<ggg...g>]
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that an illegal configuration is detected in the environment definition
file. iSM Server will be abnormally terminated.
aaa...a : Environment definition file name
bbb...b : Line number with illegal configuration
ccc...c : Section name or words wherein illegal configuration was found
ddd...d : Parameter name or words wherein illegal configuration was
found
eee...e : Parameter value or words wherein illegal configuration was
found
fff...f : Words wherein illegal configuration was found
ggg...g : Detailed information
[Measures] Find out incorrect description in the file through the output message, correct it
and then restart the iSM server.
Probable causes of detail information output are as follows:
Detail Information Content
Duplicate section The same section name has been specified more than
once.
Duplicate keyword The same keyword has been specified more than once.
Too many diskarray The number of disk arrays exceeds the limitation.
Too many diskarray
number
The disk array number exceeds the value n of
diskarray[n].
Too many ip The number of IP addresses exceeds the limitation.
Too many special
file
The number of specified special files exceeds the
limitation.
Too many disk The specified disk number exceeds the limitation.
Too may login The number of user information items exceeds the
limitation.
Too many login
number
The user number exceeds the value n of login[n].

Chapter 2 Message List
17
iSM01111: User definition does not exist, Client
cannot be connected. file=<aaa...a>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that there is no specification of the indispensable parameter of the
environment definition file. The indispensable parameter is a login parameter in
the client section.
aaa...a : Environment definition file name
[Measures] Specify the login parameter of the client section in the environment definition
file and restart the iSM server.
iSM01113: iSMadm cannot use UDP port 162.
file=<aaa...a> line=<bbb...b>
[section=<ccc...c>]
[keyword=<ddd...d>]
[value=<eee...e>]
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that the port 162 specified by iSMadm user cannot be used. iSM
Server will be abnormally terminated.
This message is output on UNIX system.
aaa...a : Environment definition file name
bbb...b : Line number with illegal configuration
ccc...c : Section name or words wherein illegal configuration was found
ddd...d : Parameter name or words wherein illegal configuration was
found
eee...e : Parameter value or words wherein illegal configuration was
found
[Measures] Restart the iSM server with Super User to receive SNMP trap while the iSM
server uses the port 162. If the iSM server does not use the port 162 for
receiving SNMP trap, restart the iSM server after deleting the parameter for
snmp_port.

Chapter 2 Message List
18
iSM01230: Storage Manager has terminated
abnormally
[Classification] WARNING
[Explanation] It shows that iSM server has terminated abnormally. The message of the cause
has displayed before this message.
For Windows, this message is target of ESMPRO Manager Report.
[Measures] Examine the cause through the previous message output before this message and
restart the iSM server if necessary.
iSM01232: Storage Manager has terminated
abnormally by signal.signo=<aaa>
[Classification] ERROR
[Explanation] It shows that iSM server has terminated abnormally due to the signal. The user
may send the kill signal.
This message is output on UNIX system.
aa…a: Signal number
[Measures] Restart the iSM server.
iSM01400: This function is not supported
[Explanation] It indicates that functions other than start, stop, update, or prf_update has been
specified by iSMsvr command.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Check command format and retry.

Chapter 2 Message List
19
iSM01401: Usage: iSMsvr start
[Explanation] It indicates that description of iSMsvr start command is incorrect. A specifiable
format is shown in the message. Execute the command in valid format.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Check command format and retry.
iSM01402: Usage: iSMsvr stop [-e]
[Explanation] It indicates that description of iSMsvr stop command is incorrect. A specifiable
format is shown in the message. Execute the command in valid format.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Check command format and retry.
iSM01403: Usage: iSMsvr update {-m | -s name |
-r name}
[Explanation] It indicates that description of iSMsvr update command is incorrect. A
specifiable format is shown in the message. Execute the command in valid
format.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Check command format and retry.
iSM01407: Rejected: Storage Manager is not
ready
[Explanation] It indicates that a command was not accepted because the iSM is not operative.
[Measures] Retry command execution when the iSM becomes operative.

Chapter 2 Message List
20
iSM01408: Rejected: System function error
(<aaa...a>) <bbb...b>
[Explanation] It indicates that an error occurred in a system function indicated by “aaa...”.
aaa...a : System function name
bbb...b : Error description
errno= zzzz : Error number
socket close : Socket with iSM closed
timeout : Time-out occurred in socket communication
with the iSM.
[Measures] Check error description and retry command execution.
If this message is output on a HP-UX system, the following reason is assumed:
iSM01408: Rejected: System function error (execl) errno=13
When the iSM server is operated by the administrator for iSM, the setting of the
administrator for iSM may not be deleted before uninstallation of the iSM server.
In this case, register the administrator for iSM again (delete and set) using the
iSM setting command (iSMmkadm). For details on the administrator for iSM
setting command, refer to the “User's Manual (UNIX)”.
iSM01409: Rejected: msgdrv is not available
[Explanation] It indicates that the event link function is not available.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Restarting the iSM is required to use the event link function.
iSM01410: This request is accepted
[Explanation] It indicates that a device monitoring stop/restart command request has been
received. For actual stop/restart operations, refer to syslog.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Unnecessary

Chapter 2 Message List
21
iSM01411: Rejected: PerformanceMonitor is not
available
[Explanation] It indicates that the performance monitor function is not available.
[Measures] Unnecessary
iSM01412: Internal error. detail=<aaaa>
[Explanation] It indicates that an internal error has occurred.
aaaa : Internal code
[Measures] Obtain information and restart the iSM.
iSM01413: Usage: iSMsvr prf_update -t value
[Explanation] It indicates that description of iSMsvr prf_update command is incorrect. A
specifiable format is shown in the message. Execute the command in valid
format.
This message is output on UNIX system.
[Measures] Check command format and retry.
iSM01901: Function error has occurred.
Function name=<aaa...a> Error
code=<bbb> Error Message=<ccc...c>
[Classification] ERROR
[Explanation] It is an internal error of iSMmainNT. This seems to be a problem depending on
Windows system.
This message is output on Windows system.
aaa...a : Function name
bbb : Error number
ccc...c : Error message
[Measures] Resolve the problem by checking the function name and the error number, and
restart the iSM server.

Chapter 2 Message List
22
iSM02000 ∼
iSM02010: In initialization, port setting failed
errno=<aaaaa>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that port number setting has failed in the initializing process.
aaaaa : Error number
[Measures] Take the measures below.
For UNIX : Check the port number setting in the [client] section of the
environment definition file in order to see if the iSM port number
which is specified in the iSMsvr_port parameter or the port
number of 8020 at the time of an abbreviation is being used in
other service, or if the specified port number is correct. To
check the port number being used, use netstat command.
For Windows: Check the server operation environment and review the port
number settings.
iSM02011: In initialization, shared memory
allocation failed errno=<aaaaa>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that the acquisition of shared memory has failed in the initializing
process.
aaaaa : Error number
[Measures] Take the measures below.
For UNIX : Check the shared memory status by using ipcs command since
there is a shortage of usable memory in the system.
For Windows: Check the server operating status including memory usage status.

Chapter 2 Message List
23
iSM02020: Function Error has occurred
name=<aaa...a> code=<bbbbb>
errno=<ccccc>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that a function error has occurred.
This message is output on UNIX system.
aaa...a : Function name
bbbbb : Internal code
ccccc : Error number
[Measures] Check the settings relevant to the applicable function.
Example: iSMclcomm iSM02020:Function Error has occurred name=recv
code=417 errno=232
In this case, recv function has error-returned in the
errno=232(ECONNRESET:Connection reset by peer) and it is
thought that the socket has been disconnected from a client.
iSM02021: Internal Error has occurred
code=<aaaaa> errno=<bbbbb>
[Classification] NOTICE
[Explanation] It shows that an internal error has occurred.
This message is output on UNIX system.
aaaaa : Internal code
bbbbb : Error number
[Measures] Check the connection status of iSM client, the environment of server operation
and various settings. This message is usually output together with iSM02020.
For the specific cause, refer to iSM02020.
Example: iSMclcomm iSM02020:Function Error has occurred name=recv
code=417 errno=232
iSMclmaind iSM02021:Internal Error has occurred code=1366
errno=*
This case shows that the socket has been disconnected from a client in
iSM02020 and the communication process for the client has ended.

Chapter 2 Message List
24
iSM02040: iSM/Client connected user=<aaa...a>
client=<bbbbbbbb> ip=<ccc...c>
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that an iSM client is connected.
aaa...a : User name
bbbbbbbb : iSM client name
ccc...c : iSM client’s IP address
[Measures] Unnecessary (This message indicates that the operation is completed as
required.)
iSM02041: iSM/Client terminated user=<aaa...a>
client=<bbbbbbbb> ip=<ccc...c>
[Classification] INFO
[Explanation] It shows that an iSM client has exited.
aaa...a : User name
bbbbbbbb : iSM client name
ccc...c : iSM client’s IP address
[Measures] Unnecessary (This message indicates that the operation is completed as
required.)
 Loading...
Loading...