MOTOROLA J112RLRA, J112RL1, J112 Datasheet
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document by J112/D
JFET Chopper |
Transistor |
|
|
|
|
||
N±Channel Ð Depletion |
|
|
|
|
|
1 DRAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GATE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
2 SOURCE |
|||
MAXIMUM RATINGS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rating |
Symbol |
Value |
|
|
|
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drain± Gate Voltage |
VDG |
± 35 |
|
|
|
Vdc |
|
Gate± Source Voltage |
VGS |
± 35 |
|
|
|
Vdc |
|
Gate Current |
IG |
50 |
|
|
|
mAdc |
|
Total Device Dissipation @ TA = 25°C |
PD |
350 |
|
|
|
mW |
|
Derate above 25°C |
|
2.8 |
|
|
|
mW/°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead Temperature |
TL |
300 |
|
|
|
°C |
|
Operating and Storage Junction |
TJ, Tstg |
± 65 to +150 |
|
|
|
°C |
|
Temperature Range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
J112
1
2 3
CASE 29±04, STYLE 5 TO±92 (TO±226AA)
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
OFF CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gate± Source Breakdown Voltage |
V(BR)GSS |
35 |
Ð |
Vdc |
(IG = ±1.0 μAdc) |
|
|
|
|
Gate Reverse Current |
IGSS |
Ð |
± 1.0 |
nAdc |
(VGS = ±15 Vdc) |
|
|
|
|
Gate Source Cutoff Voltage |
VGS(off) |
± 1.0 |
± 5.0 |
Vdc |
(VDS = 5.0 Vdc, ID = 1.0 μAdc) |
|
|
|
|
Drain±Cutoff Current |
ID(off) |
Ð |
1.0 |
nAdc |
(VDS = 5.0 Vdc, VGS = ±10 Vdc) |
|
|
|
|
ON CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zero±Gate±Voltage Drain Current(1) |
I |
5.0 |
Ð |
mAdc |
(VDS = 15 Vdc) |
DSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Static Drain±Source On Resistance |
rDS(on) |
Ð |
50 |
Ω |
(VDS = 0.1 Vdc) |
|
|
|
|
Drain Gate and Source Gate On±Capacitance |
Cdg(on) |
Ð |
28 |
pF |
(VDS = VGS = 0, f = 1.0 MHz) |
+ |
|
|
|
|
Csg(on) |
|
|
|
Drain Gate Off±Capacitance |
Cdg(off) |
Ð |
5.0 |
pF |
(VGS = ±10 Vdc, f = 1.0 MHz) |
|
|
|
|
Source Gate Off±Capacitance |
Csg(off) |
Ð |
5.0 |
pF |
(VGS = ±10 Vdc, f = 1.0 MHz) |
|
|
|
|
1. Pulse Width = 300 μs, Duty Cycle = 3.0%. |
|
|
|
|
(Replaces J111/D)
Motorola Small±Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Device Data |
1 |
Motorola, Inc. 1997 |
|
J112
TYPICAL SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(ns) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VGS(off) = 7.0 V |
|
|||
TIME |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
100 |
|
|
|
RK = RD′ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
DELAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, TURN±ON |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d(on) |
|
|
R |
|
= 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
t |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
|
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (mA) |
|
|
|
||||
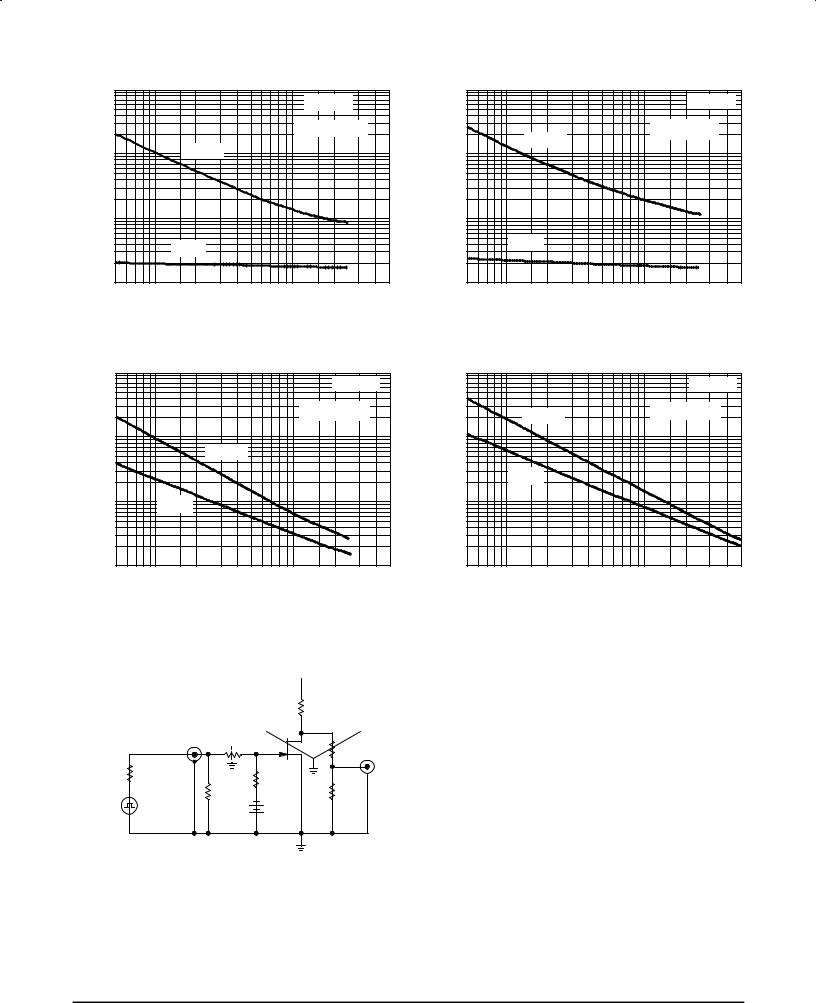
Figure 1. Turn±On Delay Time
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
|
(ns) |
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VGS(off) = 7.0 V |
|
||
TIME |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DELAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
RK = RD′ |
|
|
|
|
|
||
TURN±OFF |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
RK = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d(off) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.7 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
|
0.5 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (mA) |
|
|
|||||
Figure 3. Turn±Off Delay Time
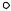 +VDD
+VDD
|
|
|
RD |
|
|
|
SET VDS(off) = 10 V |
|
|
|
INPUT |
RK |
|
RT |
|
|
|
||
RGEN |
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
50 |
Ω |
|
RGG |
|
|
|
50 Ω |
Ω |
|
|
|
50 |
||
VGEN |
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
GG |
|
INPUT PULSE |
RGG & RK |
|
|
|
|
|
tr ≤ 0.25 ns |
|
RD(RT ) 50) |
||||
tf ≤ 0.5 ns |
RD + |
|||||
PULSE WIDTH = 2.0 μs |
R |
R |
T ) |
50 |
|
|
DUTY CYCLE ≤ 2.0% |
|
D ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 5. Switching Time Test Circuit
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
RK |
= RD′ |
|
|
|
VGS(off) = 7.0 V |
|
||
(ns) |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TIME |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, RISE |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
|
RK = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.7 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
|
0.5 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (mA) |
|
|
|||||
Figure 2. Rise Time
|
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
RK = RD′ |
|
|
|
|
VGS(off) = 7.0 V |
|
|
(ns) |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TIME |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RK = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, FALL |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.7 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
5.0 |
7.0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
|
0.5 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (mA) |
|
|
|||||
Figure 4. Fall Time
NOTE 1
The switching characteristics shown above were measured using a test circuit similar to Figure 5. At the beginning of the switching interval, the gate voltage is at Gate Supply Voltage (±VGG). The
Drain±Source Voltage (VDS) is slightly lower than Drain Supply
Voltage (VDD) due to the voltage divider. Thus Reverse Transfer
Capacitance (Crss) or Gate±Drain Capacitance (Cgd) is charged to
VGG + VDS.
During the turn±on interval, Gate±Source Capacitance (Cgs) discharges through the series combination of RGen and RK. Cgd
must discharge to VDS(on) through RG and RK in series with the parallel combination of effective load impedance (R′D) and
Drain±Source Resistance (rds). During the turn±off, this charge flow is reversed.
Predicting turn±on time is somewhat difficult as the channel resistance rds is a function of the gate±source voltage. While Cgs discharges, VGS approaches zero and rds decreases. Since Cgd discharges through rds, turn±on time is non±linear. During turn±off, the situation is reversed with rds increasing as Cgd charges.
The above switching curves show two impedance conditions; 1) RK is equal to RD, which simulates the switching behavior of cascaded stages where the driving source impedance is normally the load impedance of the previous stage, and 2) RK = 0 (low impedance) the driving source impedance is that of the generator.
2 |
Motorola Small±Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Device Data |
 Loading...
Loading...