Lowrance electronic GlobalMap 5300C iGPS User Manual

Pub. 988-0152-191
www.lowrance.com
GlobalMap® 5300c iGPS
Mapping GPS Receiver
Operation Instructions

Copyright © 2006 Lowrance Electronics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be copied, reproduced, republished, transmitted or distributed for any purpose, without prior written consent of Lowrance. Any unauthorized commercial distribution of this manual is strictly prohibited.
Lowrance® is a registered trademark of Lowrance Electronics, Inc. MapCreate™, FreedomMaps™ and NauticPath™ are trademarks of LEI. Fishing Hot Spots® is a registered trademark of Fishing Hot Spots Inc. LakeMaster® and Pro Maps are trademarks or registered trademarks of WayPoint Technologies, Inc. Navionics® is a registered trademark of Navionics, Inc. DURACELL® is a registered trademark of Duracell, Inc. RAYOVAC® is a registered trademark of Rayovac Corporation. Energizer® and e2® are registered trademarks of Energizer Holdings, Inc.
Points of Interest Data in this unit are by infoUSA, copyright © 2001-2006, All Rights Reserved. infoUSA is a trademark of infoUSA, Inc.
Lowrance Electronics may find it necessary to change or end our policies, regulations and special offers at any time. We reserve the right to do so without notice. All features and specifications subject to change without notice. On the cover: GlobalMap 5300c iGPS. All screens in this manual are simulated.
For free owner's manuals and the most current information on this product, its operation and accessories,
visit our web site: www.lowrance.com
Lowrance Electronics Inc.
12000 E. Skelly Dr.
Tulsa, OK USA 74128-2486
Printed in USA.
Table of Contents |
|
Section 1: Read Me First! ......................................................... |
1 |
Specifications: GlobalMap® 5300c iGPS ...................................... |
2 |
How to use this manual: typographical conventions .................. |
8 |
Section 2: Installation............................................................. |
11 |
Preparations ................................................................................ |
11 |
Power Connections...................................................................... |
11 |
Powering Your Display Unit ...................................................... |
12 |
Power Diagram A ........................................................................ |
14 |
Power Diagram B ........................................................................ |
15 |
Powering a NMEA 2000 Network Bus ...................................... |
15 |
Connecting to a NMEA 2000 Network ...................................... |
16 |
NMEA 0183 Cable Connections ................................................. |
16 |
NMEA 0183 Wiring................................................................. |
16 |
Mounting the Unit: Bracket or Portable ................................... |
18 |
MMC or SD Card Memory Card Installation............................ |
22 |
Other Accessories ........................................................................ |
23 |
Cleaning Towel........................................................................ |
23 |
Face Cover ................................................................................... |
24 |
Section 3: Basic GPS Operation ........................................... |
25 |
Keyboard...................................................................................... |
25 |
Power/lights on and off ............................................................... |
26 |
Main Menu................................................................................... |
26 |
Pages ............................................................................................ |
28 |
Satellite Status Page............................................................... |
28 |
Navigation Page ...................................................................... |
30 |
Map Page ................................................................................. |
33 |
Background map vs. MapCreate map content ...................... |
34 |
Map with Custom Gauges....................................................... |
37 |
Radar............................................................................................ |
38 |
Basic GPS Quick Reference........................................................ |
40 |
Find Your Current Position........................................................ |
41 |
Moving Around the Map: Zoom & Cursor Arrow Keys............. |
41 |
Selecting Any Map Item With the Cursor ................................. |
42 |
Searching ..................................................................................... |
42 |
Set a Waypoint ............................................................................ |
44 |
Navigate To a Waypoint ............................................................. |
46 |
Set Man Overboard (MOB) Waypoint........................................ |
47 |
Navigate Back to MOB Waypoint .............................................. |
47 |
Navigate to Cursor Position on Map.......................................... |
48 |
Navigate to a Point of Interest ................................................... |
49 |
Creating and Saving a Trail ....................................................... |
50 |
i |
|
Displaying a Saved Trail ............................................................ |
51 |
Navigating Trails ........................................................................ |
52 |
Transfer Custom Maps and GPS Data Files............................. |
56 |
Cancel Navigation....................................................................... |
58 |
Section 4: Advanced Operations .......................................... |
59 |
Find Distance from different Locations..................................... |
59 |
Find Distance from Point to Point ............................................. |
59 |
Icons ............................................................................................. |
59 |
Create Icon on Map ................................................................. |
60 |
Create Icon at Current Position ............................................. |
60 |
Delete an Icon.......................................................................... |
60 |
Navigate to an Icon ................................................................. |
61 |
Routes .......................................................................................... |
61 |
Create and Save a Route ........................................................ |
62 |
Delete a Route ......................................................................... |
64 |
Edit a Route Name.................................................................. |
64 |
Edit Route Waypoints ............................................................. |
65 |
Navigate a Route..................................................................... |
66 |
Navigate a Route in Reverse .................................................. |
66 |
Trails ............................................................................................ |
67 |
Delete a Trail........................................................................... |
67 |
Edit a Trail Name ................................................................... |
68 |
Edit a Trail Color .................................................................... |
68 |
Edit a Trail Pattern................................................................. |
68 |
Utilities ........................................................................................ |
69 |
Alarm Clock ............................................................................. |
69 |
Sun/Moon Rise & Set Calculator............................................ |
69 |
Trip Calculator ........................................................................ |
69 |
Trip Down Timer ..................................................................... |
69 |
Trip Up Timer.......................................................................... |
69 |
Waypoints .................................................................................... |
69 |
Delete a Waypoint ................................................................... |
69 |
Edit a Waypoint....................................................................... |
70 |
Selecting a Waypoint .............................................................. |
70 |
Set a Waypoint by Average Position...................................... |
71 |
Set a Waypoint by Projecting a Position................................ |
72 |
Section 5: System & GPS Setup............................................ |
73 |
Alarms.......................................................................................... |
73 |
Auto Satellite Search .................................................................. |
74 |
Check MMC Files and Storage Space........................................ |
75 |
Communications Port Configuration......................................... |
75 |
Configure NMEA......................................................................... |
76 |
Coordinate System Selection...................................................... |
76 |
ii |
|
Map Fix ........................................................................................ |
78 |
Customize Page Displays............................................................ |
79 |
GPS Simulator............................................................................. |
80 |
Initialize GPS .............................................................................. |
82 |
Map Auto Zoom ........................................................................... |
83 |
Map Data ..................................................................................... |
83 |
Map Datum Selection.................................................................. |
85 |
Map Detail Category Selection................................................... |
86 |
Map Orientation.......................................................................... |
86 |
NauticPath™ USA Marine Charts............................................. |
87 |
Nautical Chart Notes .............................................................. |
88 |
Port Information...................................................................... |
88 |
Tidal Current Information...................................................... |
89 |
Tide Information ..................................................................... |
91 |
Navionics® Charts ....................................................................... |
92 |
Overlay Data ............................................................................... |
93 |
Pop-up Help ................................................................................. |
97 |
Reset Options............................................................................... |
98 |
Screen Contrast and Brightness ................................................ |
99 |
Set Language............................................................................. |
100 |
Set Local Time........................................................................... |
100 |
Show WAAS Alarm ................................................................... |
101 |
Software Version Information.................................................. |
102 |
Sounds and Alarm Sound Styles.............................................. |
102 |
Track Smoothing ....................................................................... |
104 |
Trail Options.............................................................................. |
104 |
Transparency............................................................................. |
107 |
Units of Measure ....................................................................... |
108 |
Section 6: Searching.............................................................. |
111 |
Find Streets ............................................................................... |
111 |
Find Any Item Selected by Map Cursor .................................. |
113 |
Find Interstate Highway Exits ................................................ |
113 |
Find Map Places or Points of Interest (POI) ........................... |
116 |
Find Streets or Intersections.................................................... |
118 |
Find Waypoints ......................................................................... |
121 |
Section 7: NMEA 2000 ........................................................... |
125 |
NMEA 2000 Menu..................................................................... |
125 |
Internal GPS Receiver .............................................................. |
125 |
Bus Setup................................................................................... |
126 |
Engine & Tank Configuration.................................................. |
127 |
Tank Select ........................................................................ |
127 |
Tank Size ........................................................................... |
128 |
Set Configuration button .................................................. |
128 |
iii |
|
Device Configuration Menu.................................................. |
129 |
Device Information and Device Data ................................... |
129 |
Fuel Management Menu........................................................... |
130 |
Tank Location.................................................................... |
130 |
Fuel Added......................................................................... |
130 |
Add Fuel............................................................................. |
130 |
Fill Tank............................................................................. |
131 |
Adding Fuel to Tank ............................................................. |
131 |
Engine Operations................................................................. |
131 |
Engine Select ..................................................................... |
131 |
NMEA 2000 Alarms .................................................................. |
132 |
Waypoint Sharing ..................................................................... |
133 |
Backlight Synchronization ....................................................... |
133 |
Configuring EP Sensors............................................................ |
133 |
EP-35 Temperature Configuration ...................................... |
134 |
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... |
134 |
Instance.............................................................................. |
134 |
Restore Defaults ................................................................ |
135 |
EP-10 Fuel Flow Configuration............................................ |
135 |
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... |
136 |
Instance.............................................................................. |
136 |
Restore Defaults ................................................................ |
136 |
EP-15 Fluid Level Configuration ......................................... |
137 |
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... |
138 |
Instance.............................................................................. |
138 |
Restore Defaults ................................................................ |
139 |
Suzuki Engine Interface Configuration............................... |
139 |
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... |
140 |
Instance.............................................................................. |
140 |
Restore Defaults ................................................................ |
141 |
Calibrating EP Sensors............................................................. |
141 |
EP-10 Fuel Flow Calibration................................................ |
141 |
EP-15 Fluid Level Calibration ............................................. |
143 |
2-Point Calibration............................................................ |
143 |
3-Point Calibration............................................................ |
144 |
5-Point Calibration............................................................ |
145 |
Fuel Flow Calibration in a Suzuki Engine Interface.......... |
146 |
Engine Trim Calibration....................................................... |
147 |
Reset Trim Calibration ......................................................... |
148 |
Bennett Trim Tabs Calibration............................................ |
148 |
Section 8: Supplemental Material ..................................... |
151 |
iv
NOTICE!
The storage and operation temperature range for your unit is from -20 degrees to +167 degrees Fahrenheit (-28 degrees to +75 degrees Celsius). Extended storage or operation in temperatures higher or lower than specified will damage the liquid crystal display in your unit. This type of damage is not covered by the warranty. For more information, contact the factory's Customer Service Department; phone numbers are listed on the last page of the manual.
WARNING!
A CAREFUL NAVIGATOR NEVER RELIES ON ONLY ONE METHOD TO OBTAIN POSITION INFORMATION.
CAUTION
When showing navigation data to a position (waypoint), a GPS unit will show the shortest, most direct path to the waypoint. It provides navigation data to the waypoint regardless of obstructions. Therefore, the prudent navigator will not only take advantage of all available navigation tools when traveling to a waypoint, but will also visually check to make sure a clear, safe path to the waypoint is always available.
WARNING!
When a GPS unit is used in a vehicle, the vehicle operator is solely responsible for operating the vehicle in a safe manner. Vehicle operators must maintain full surveillance of all pertinent driving, boating or flying conditions at all times. An accident or collision resulting in damage to property, personal injury or death could occur if the operator of a GPSequipped vehicle fails to pay full attention to travel conditions and vehicle operation while the vehicle is in motion.
v
Notes
vi
Section 1: Read Me First!
How this manual can get you out on the road, fast!
Welcome to the exciting world of digital GPS! We know you're anxious to begin navigating, but we have a favor to ask. Before you grab the GlobalMap® 5300c iGPS and begin installing it, please give us a moment or two to explain how our manual can help you get the best performance from your compact, wide-screen, mapping GPS receiver.
First, we want to thank you for buying a Lowrance GPS unit. Whether you're a first time user or a professional fisherman, you'll discover that your GlobalMap 5300c is easy to use, yet capable of handling demanding navigation tasks. When you team your unit with our custom mapping software MapCreate™, you have an incredible combination. You won't find another GPS unit with this much power and this many features for this price!
Our goal for this book is to get you on the road fast, with a minimum of fuss. Like you, we'd rather spend more time navigating and less time reading the manual!
So, we designed our book so that you don't have to read the whole thing from front to back for the information you want. At the start (or end) of each segment, we'll tell you what content is coming up next. If it's a concept you're already familiar with, we'll show you how and where to skip ahead for the next important topic. We've also made it easy to look up any tips you may need from time to time. Here's how:
The manual is organized into 7 sections. This first section is an introduction to Lowrance GPS. It tells you the basics you need to know before you can make the unit look around and tell you where you are.
Section 2 will help you install your unit. We'll show you how to get the MultiMedia Card (MMC) correctly installed inside the unit. We'll also tell you about some of the available accessories.
Section 3 covers Basic GPS Operation. It will show you how easy it is to run the GlobalMap 5300c, right out of the box. This section features a one-page GPS Quick Reference. (If you've already jumped ahead and figured out how to install the unit yourself, and you just can't wait any longer, turn to the Quick Reference on page 40 and head for the road with your GPS unit!)
Section 3 contains short, easy-to-scan GPS lessons that follow one another in chronological order. They're all you'll need to know to find your way on the water or in the wilderness quickly.
1
After you've learned the basics (or if you already have some GPS experience), you may want to try out some of the GlobalMap 5300c's many advanced navigation features. That brings us to Section 4, Advanced GPS Operations.
When you come to a GPS menu command on the GlobalMap 5300c's screen, you can look it up in the manual by skimming over the table of contents, just flipping through Section 3 or scanning through the command portion of Section 4.
This unit is ready to use right out of the box, but you can fine tune and customize its operation with dozens of options. We describe how to use general system options along with GPS options in Section 5, System Setup and GPS Setup Options.
In Section 6, we go into more detail on one of the GlobalMap 5300c's most remarkable capabilities — Searching. We'll introduce a search example in the Basic GPS Operation section, but there are so many map items you can search for, we had to give this function its own section in the manual! For example, did you know this unit can look up business phone numbers, functioning as a virtual Yellow Pages? We’ll show you how in Section 6.
Finally, in Section 7, we offer Supplemental Material, including a list of the GPS datums used, warranties and customer service information.
Now, if you're into the fine details, glance over the next segment on specifications to see just how much GPS power your GlobalMap 5300c contains.
Specifications: GlobalMap® 5300c iGPS
|
General |
Display: ............................ |
Color 5.0" (12.7 cm) diagonal; SolarMax™ |
|
TFT display programmable to viewing pref- |
|
erence. |
Resolution: ...................... |
480 pixel x 480 pixel resolution; 230,400 to- |
|
tal pixels. |
Backlighting: ................... |
Fluorescent cold cathode backlit screen with |
|
multiple lighting levels; backlit keypad. |
Input power: ................... |
10 to 15 volts DC. |
Case size: ......................... |
5.4" H x 6.9" W x 3.4" D (13.8 x 17.6 x 8.6 |
|
cm); sealed and waterproof; suitable for salt- |
|
water use. |
MMC slots:....................... |
One with waterproof door (SD card compati- |
|
ble). |
2
Recording:........................ |
MMC & SD memory cards for recording GPS |
|
trip details and displaying charts or maps. |
Back-up memory:........... |
Built-in memory stores GPS data for dec- |
|
ades. User settings are stored when unit is |
|
turned off. |
Languages: ...................... |
10; menu languages selectable by user. |
|
GPS |
Receiver/antenna: ......... |
Internal; Built-in 12 parallel channel |
|
GPS/WAAS . |
Background map: .......... |
Built-in custom, detailed Lowrance map. |
|
Contains: enhanced detail of continental U.S. |
|
and Hawaii. Includes more than 60,000 nav |
|
aids and 10,000 wrecks/obstructions in |
|
coastal and Great Lakes waters. Metro ar- |
|
eas, selected major streets/highways and in- |
|
terstate exit services details included. |
Custom mapping:........... |
MapCreate™ software optional; optional |
|
plug and play LEI FreedomMaps™ offer the |
|
same high detail without the computer work |
|
of MapCreate. Other plug and play mapping |
|
options include Fishing Hot Spots® Elite, LEI |
|
NauticPath™, LakeMaster® ProMaps and |
|
Navionics® charts. |
Mapping memory: ......... |
Up to 2 gigabytes on one MMC (or SD) card. |
Position updates:........... |
Every second. |
Position points:.............. |
1,000 waypoints; 1,000 event marker icons. |
Audible alarms:.............. |
Arrival/off-course/anchor. |
Graphic symbols for |
|
waypoints or event |
63. |
marker icons:.................. |
|
Routes: ............................. |
100; up to 100 waypoints per route. |
Plot Trails:....................... |
10 savable; up to 9,999 points per trail. |
Zoom range: .................... |
39 ranges; 0.02 to 4,000 miles. |
NOTE:
The above memory capacities refer only to the GlobalMap 5300c's onboard memory. The amount of GPS data you can record and save for recall later is limited only by the number of MMC cards you have.
3
How Lowrance GPS Works
You'll navigate faster and easier if you understand how the GlobalMap 5300c scans the sky to tell you where you are on the earth — and, where you're going. (But if you already have a working understanding of GPS receivers and the GPS navigation system, skip on ahead to Section 2, Installation & Accessories on page 11. If you're new to GPS, read on, and you can later impress your friends with your new-found knowledge.)
First, think of your unit as a small but powerful computer. (But don't worry — we made it easy to use, so you don't need to be a computer expert to find your way!) The GlobalMap 5300c includes a keypad and a screen with menus so you can tell it what to do. The screen also lets the unit show your location on a moving map, as well as point the way to your destination.
This gimbal-mounted GlobalMap 5300c uses an internal antenna/receiver module, which makes the whole system work something like your car radio. But instead of your favorite dance tunes, this receiver tunes in to a couple of dozen GPS satellites circling the earth. (It will also listen in to the WAAS satellites in orbit, but more about that in the upcoming segment introducing you to GPS and WAAS.)
Your unit listens to signals from as many satellites as it can see above the horizon, eliminates the weakest signals, then computes its location in relation to those satellites. Once the GlobalMap 5300c figures its latitude and longitude, it plots that position on the moving map shown on the screen. The whole process takes place several times a second!
The performance doesn't stop there. Stored in the permanent memory of each unit is a basic background map of the entire world. We lock it in here at the factory — you can't change or erase this map.
The background map is suitable for many navigation chores, but for maximum accuracy and much more detail, you need our optional mapmaking software, MapCreate™. Some unit features — such as searching for businesses and addresses — won't work without a custom MapCreate map. There is so much detail in our background map (and even more in MapCreate) that we'll describe their contents and differences in Section 3, Basic GPS Operations, on page 34.
Another portion of the GlobalMap 5300c's onboard memory is devoted to recording GPS navigation information, which includes waypoints, event marker icons, trails and routes. This lets you look back the way you came. Think of this data storage like the hard drive memory in a computer or a tape in a cassette tape recorder. You can save several different GPS data
4
files, erase 'em and record new ones, over and over again. Like any computer file, these GPS Data Files (file format *.usr) can be shared between Lowrance GPS or sonar/GPS units or even personal computers.
This GlobalMap 5300c has one more thing in common with a personal computer. Just as computers have a floppy disk drive for storing and exchanging files, the unit has a slot for an MMC (MultiMedia Card) or SD (Secure Digital card) flash memory card. These solid-state memory devices are about the size of a postage stamp, but can hold data ranging from 8 MB to 2 GB in size. (Compare that to a floppy disk's 1.44 MB capacity!) This unit uses all that MMC space for two key GPS purposes.
First, you can backup your onboard GPS Data Files by copying them to the MMC. Since the MMC is removable (like a floppy disk or a cassette tape), you can store these GPS Data Files on a personal computer equipped with an MMC card reader. (Or store them on a pocketful of MMCs, if you don't have a computer.) Our MapCreate mapping software can save, edit or create its own GPS Data Files, which can be copied to the MMC and then loaded from the MMC into the unit's memory. (NOTE: No matter where they come from, GPS Data Files must be loaded from the MMC into memory before the GlobalMap 5300c can use them.)
The other key GPS use for MMCs is storage of special high-detail, custom maps, which you can produce on your computer with our MapCreate software. These MapCreate custom maps contain much greater detail than the basic background map. These Custom Map Files (file format *.lcm) can also be shared between Lowrance GPS or sonar/GPS units and personal computers.
This unit automatically reads Custom Map Files directly from the MMC or SD card. To use a custom map, all you need to do is slide an MMC containing a map into the GlobalMap 5300c.
Introduction to GPS and WAAS
Well, now you know the basics of how the unit does its work. You might be ready to jump ahead to Section 2, Installation & Accessories, on page 11, so you can mount your GlobalMap 5300c and plug in the power. Or you might want to see how our text formatting makes the manual tutorials easy to skim. If that's the case, move on to "How to Use This Manual" on page 8. But, if you want to understand the current state of satellite navigation, look over this segment describing how GPS and its new companion WAAS work together to get you where you're going.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) was launched July 17, 1995 by the United States Department of Defense. It was designed as a 24-hour-a- day, 365-days-a-year, all weather global navigation system for the armed
5
forces of the U.S. and its allies. Civilian use was also available at first, but it was less accurate because the military scrambled the signal somewhat, using a process called Selective Availability (SA).
GPS proved so useful for civilian navigation that the federal government discontinued SA on May 2, 2000, after the military developed other methods to deny GPS service to enemy forces. Reliable accuracy for civilian users jumped from 100 meters (330 feet) under SA to the present level of 10 to 20 meters (about 30 to 60 feet.)
Twenty-four satellites orbit 10,900 nautical miles above the Earth, passing overhead twice daily. A series of ground stations (with precisely surveyed locations) controls the satellites and monitors their exact locations in the sky. Each satellite broadcasts a low-power signal that identifies the satellite and its position above the earth. Three of these satellites are spares, unused until needed. The rest virtually guarantee that at least four satellites are in view nearly anywhere on Earth at all times.
A minimum of three satellites are required to determine a 2D fix.
The system requires signal reception from three satellites in order to determine a position. This is called a 2D fix. It takes four satellites to determine both position and elevation (your height above sea level — also called altitude). This is called a 3D fix.
Remember, the unit must have a clear view of the satellites in order to receive their signals. Unlike radio or television signals, GPS works at very high frequencies. These signals can be easily blocked by trees, buildings, an automobile roof, even your body.
Like most GPS receivers, this unit doesn’t have a compass or any other navigation aid built inside. It relies solely on the signals from the satellites to calculate a position. Speed, direction of travel, and distance are all calculated from position information. Therefore, in order for the GlobalMap 5300c to determine direction of travel, you must be moving and the faster, the better.
6
This is not to say that it won’t work at walking or trolling speeds — it will. There will simply be more "wandering" of the data shown on the display.
GPS alone is accurate for route navigation, but the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration has special aircraft navigation needs that go beyond basic GPS. So, the FAA has developed a program to boost GPS performance with its Wide Area Augmentation System, or WAAS. The FAA commissioned the system on July 11, 2003.
WAAS is designed to increase GPS accuracy to within 7.6 meters vertically and horizontally, but it consistently delivers accuracies within 1-2 meters horizontal and 2-3 meters vertical, according to the FAA. It does this by broadcasting correction signals on GPS frequencies. Your unit automatically receives both GPS and WAAS signals.
There, however, are some fringe areas of the U.S., including parts of Alaska that do not yet receive robust WAAS coverage. Continued WAAS development is planned to extend WAAS coverage in the years to come.
WAAS boosts the accuracy of land GPS navigation, but the system is designed for aircraft. The satellites are in a fixed orbit around the Equator, so they appear very low in the sky to someone on the ground in North America. Aircraft and vessels on open water can get consistently good WAAS reception, but terrain, foliage or even large manmade structures can sometimes block the WAAS signal from ground receivers.
You'll find that using your GPS receiver is both easy and amazingly accurate. It’s easily the most accurate method of electronic navigation available to the general public today. Remember that this receiver is only a tool. Always have another method of navigation available, such as a map or chart and a compass.
Also remember that this unit will always show navigation information in the shortest line from your present position to a waypoint, regardless of terrain! It only calculates position, it can’t know what’s between you and your destination, for example. It’s up to you to safely navigate around obstacles, no matter how you’re using this product.
Free Training Aids Available
Now that you know something about the technology that makes this unit possible, you are ready to start learning how to use that technology. This manual will guide you through the process of setting up and running your unit, but that is only one of many resources available.
7
If you or a friend has Internet access, visit our web site. Find us at WWW.LOWRANCE.COM. The site is packed with additional information on using our products.
Emulator
For the ultimate training aid, be sure to download the free emulator software for your unit. This program can help you learn both basic and advanced operations without burning fuel!
This PC application simulates the actual GPS unit on your computer. You can run it from your computer keyboard or use your mouse to press the virtual keys. Easy download and installation instructions are available on our web site.
The emulator works exactly like your real GPS unit. When using the GPS Simulators you can run GPS routes and trails, even create real waypoints you can use in the field.
And that is just some of the material available on our web site. To find out what we have available, log on and look around. For now, we'll get back to how to use this particular unit.
How to use this manual: typographical conventions
Many instructions are listed as numbered steps. The keypad and arrow "keystrokes" appear as boldface type. So, if you're in a real hurry (or just need a reminder), you can skim the instructions and pick out what menu command to use by finding the boldface command text. The following paragraphs explain how to interpret the text formatting for those commands and other instructions:
Arrow Keys
The arrow keys control the movement of dotted cross-hair lines on your mapping screen called the cursor. The arrow keys help you move around the menus so you can execute different commands. They are represented by symbols like these, which denote the down arrow key, the up arrow, the left arrow and the right arrow: ↓ ↑, ← →.
Keyboard
The other keys perform a variety of functions. When the text refers to a key to press, the key is shown in bold, sans serif type. For example, the "Enter/Icons" key is shown as ENT and the "Menu" key is shown as
MENU.
Menu Commands
A menu command or a menu option will appear in small capital letters, in a bold sans serif type like this: ROUTE PLANNING. These indicate that you are to select this command or option from a menu or take an action
8
of some kind with the menu item. Text that you may need to enter or file names you need to select are show in italic type, such as trail name.
Instructions = Menu Sequences
Most functions you perform with this unit are described as a sequence of key strokes and selecting menu commands. We've written them in a condensed manner for quick and easy reading.
For example, instructions for navigating a trail would look like this:
1.From the Map Page, press MENU|MENU|↓ to MY TRAILS|ENT.
2.Press ↓ to Trail 1|ENT|→|↓ to NAVIGATE|ENT.
3.You are asked to wait while it converts the trail into a route.
4.The wait message disappears and the GlobalMap 5300c begins showing navigation information along the trail. Now, begin moving and follow your GlobalMap 5300c.
Translated into complete English, step 1 above would mean: "Start on the Map Page. Press the Menu key twice. Next, repeatedly press (or press and hold) the down arrow key to scroll down the menu and select (highlight) the My Trails menu command. Finally, press the Enter key."
Step 2 would mean: "Press the down arrow key repeatedly to scroll to the trail named Trail 1, and press Enter. Next, press the right arrow key and then the down arrow key to highlight the Navigate command, then press Enter."
9
Notes
10
Section 2: Installation
Preparations
You can install the GPS system in some other order if you prefer, but we recommend this installation sequence:
Caution:
You should read over this entire installation section before drilling any holes in your vehicle or vessel!
1. Determine the approximate location for the GPS unit, so you can plan how and where to route the power cable. This will help you make sure you have enough cable length for the desired configuration.
NOTE:
The GPS antenna is inside the unit, so you must mount the unit in a location with an unobstructed view of the sky.
2.Determine the location of your battery or other power connection, along with the power cable route.
3.Install the power cable and route it to the GPS unit.
4.Mount the GPS unit.
Power Connections
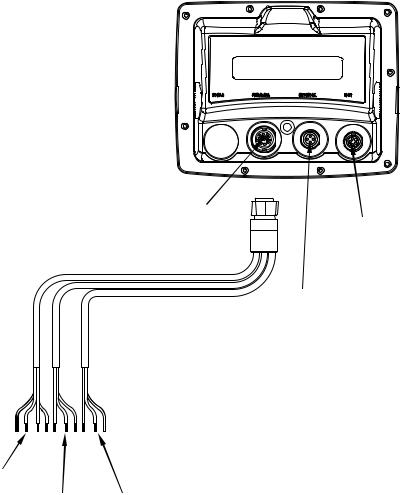
Your unit comes with a power/data cable that splits into three branches, each with several exposed wires.
The thicker three-wire cable (white, red and black) is the power supply for your display unit. This cable has no label.
The thinner branch with three wires (red, black and shield) is the power cable for a NMEA 2000 network. It is labeled "NMEA 2000 POWER."
The branch with four wires (blue, yellow, orange, and shield) is a data cable, labeled "RS-232 COMM." It supports a serial communication port. This allows your unit to exchange NMEA 0183 data with another device, such as an autopilot, DSC marine radio or computer.
11
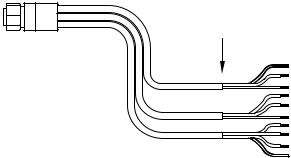
Display unit power wires: white, red and black
To unit
NMEA 2000 power wires:
 red, black and shield
red, black and shield
Data cable wires:  blue, yellow, orange,
blue, yellow, orange,
and shield
The Power/Data cable for this unit.
NOTE:
There are two basic power connection options, which are shown in the following two diagrams. Read the following instructions carefully to determine which power connection applies to your unit. Depending on your configuration, you may not use all of these wires.
Caution:
All of the wires in the power/data cable have bare ends for easier installation. The bare ends on any unused wires could cause an electrical short if left exposed. To prevent this, you should cover the individual wire ends – either by capping them with wire nuts, wrapping them with electrical tape or both. (You should cut off the bare wire before taping off the ends.)
Powering Your Display Unit
The display unit works from a 12-volt DC battery system. Attach the display power cable (with provided 3-amp fuse) to an accessory switch or power bus. If this results in electrical interference, connect direct to a battery but install an in-line switch on the cable.
Caution:
We strongly recommend that you shut off the power supply to the power cable when the unit is not in use, especially in saltwater environments. When the unit is turned off but still connected to a power supply, electrolysis can occur in the power cable plug. This may result in corrosion of the plug body along with the electrical contacts in the cable and the unit's power socket. Risk of electrolysis corrosion is even greater when the cable is unplugged from the unit, but still connected to a power source.
We recommend you connect the power cable to the auxiliary power switch included in most boat designs. If that results in electrical
12
interference, or if such a switch is not available, we recommend connecting direct to the battery and installing an in-line switch. This will let you shut off power to the power cable when the unit is not in use. When you are not using the unit, you should always shut off power to the power cable, especially when the power cable is disconnected from the unit.
WARNING:
This product must be independently fused with the enclosed 3-amp fuse (or equivalent), even if you connect to a fused accessory or power bus.
If a malfunction happens inside the unit, extensive damage can occur if the enclosed fuse is not used. As with all electrical devices, this unit could be damaged to a point that it is unrepairable and could even cause harm to the user when not properly fused.
Failure to use a 3-amp fuse will void your warranty.
If possible, keep the power cable away from other boat wiring, especially the engine's wires. This will provide the best isolation from electrical noise. If the cable is not long enough, splice #18 gauge wire onto it.
The display power cable has three wires, white, red and black. Red is the positive (+) lead, black is negative (–) or ground. The white wire is unused by your unit and should be capped. Make sure to attach the in-line fuse holder to the red lead as close to the power source as possible.
For example, if you have to extend the power cable to the power bus or battery, attach one end of the fuse holder directly to the power bus or battery. This will protect both the unit and the power cable in the event of a short.
This unit has reverse polarity protection. No damage will occur if the power wires are reversed. However, the unit will not work until the wires are attached correctly.
13
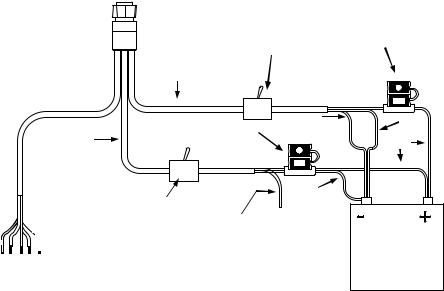
|
Power Diagram A |
|
|
To unit |
|
Mandatory |
|
|
|
network |
|
|
|
power-off |
3-amp fuse |
|
|
switch |
|
|
NMEA 2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Cable |
|
|
|
|
Shield |
Black |
Display Unit |
3-amp fuse |
Red |
|
Power Cable |
|
|
|
|
Recommended |
Black |
|
|
|
|
|
|
display unit |
White |
|
|
power-off switch |
12 volt DC |
|
|
(unused) |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
power source |
Data Cable
Use this method if you are powering the display unit and a GPS module or the display unit and a NMEA 2000 network. (Fuses may be different from those shown.).
The network and any NMEA 2000 devices, including the GPS module, will not operate unless the NMEA 2000 Power Cable is connected to power. The NMEA 2000 power cable must be connected to power even if your only NMEA 2000 device is the GPS module and it is connected to the display unit's Network socket. (However, never connect multiple power sources to a NMEA 2000 network. If you have a network that is already powered, see diagram B on page 15.)
14
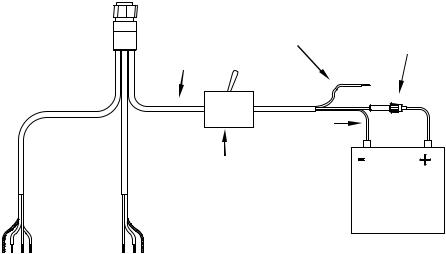
Power Diagram B
To unit |
|
|
Red wire with |
||
|
|
|
White wire |
||
|
|
Display Unit |
(unused) |
3-amp fuse |
|
|
|
Power Cable |
|
|
|
All unused Data |
|
Black wire |
|
||
or NMEA 2000 |
|
|
|
||
power wires |
Recommended |
|
|||
should be |
|
12 volt DC |
|||
|
power off switch |
||||
capped with |
|||||
|
|
power source |
|||
wire nuts and |
|
|
|||
electrical tape |
|
|
|
||
to prevent |
|
|
|
|
|
shorts. |
|
|
|
|
|
Data Cable |
NMEA 2000 Power Cable |
|
|
||
Use this method if you are only powering your display unit and are not powering a NMEA 2000 network or any NMEA 2000 accessory device, including a GPS module. (Fuse may be different from that shown.)
The method in diagram B is also used when your display unit is connected to a NMEA 2000 network that is already connected to power.
(Never connect multiple power sources to a NMEA 2000 network.)
Powering a NMEA 2000 Network Bus
A NMEA 2000 bus must be connected to a power source to operate. NMEA 2000 devices, including GPS modules, draw their power from the network bus.
If you have a pre-existing NMEA 2000 network installation, it may already be connected to another power source. If you are not sure about a network's power status, consult the boat manufacturer or dealer. If your NMEA 2000 bus is already powered, you can ignore the NMEA 2000 Power cable and use the method shown in Power Diagram B above.
Never attach two power sources to a single NMEA 2000 bus.
If you do need to power your NMEA 2000 bus, attach the NMEA 2000 Power cable to an accessory switch as indicated in power diagram A on page 14. The NMEA 2000 Power cable's red wire should be attached (with provided 3-amp fuse) to the positive (+) terminal. The NMEA 2000 Power cable's black and shield wires should both be attached to the negative (–) terminal.
15
WARNING:
The NMEA 2000 network bus is always on and constantly drawing power. You must connect NMEA power to a switched power source so you can turn off the network when not in use. Failure to connect to and use a power switch will drain your boat battery, which could stop your boat's operation.
Connecting to a NMEA 2000 Network
Your unit can be connected to a NMEA 2000 bus, receiving sensor information from units and devices attached to the network. Contact LEI Extras (look inside back cover for accessory ordering information) for NMEA 2000 accessories.
NOTE:
GPS data from your internal GPS receiver can not be transmitted across a NMEA 2000 network. The only way to transmit GPS data across the network is to add a LGC module to the network. For more information see page 125.
NMEA 0183 Cable Connections
NMEA 0183 is a standard communications format for marine electronic equipment. For example, an autopilot can connect to the NMEA interface on the GlobalMap 5300c and receive positioning information. The GlobalMap 5300c can exchange information with any device that transmits or receives NMEA 0183 data.
See the following diagram for general wiring connections. Read your other product’s owner’s manual for more wiring information.
NMEA 0183 Wiring
(Data cable)
To exchange NMEA 0183 data, the GlobalMap 5300c has one NMEA 0183 version 2.0 communication port. Com port one (Com-1) can be used to receive NMEA format GPS data. The com port can also transmit NMEA format GPS data to another device.
The four wires for the com port are combined with the Power Supply cable and NMEA 2000 Power cable to form the power/data cable (shown earlier). Com-1 uses the yellow wire to transmit, the orange wire to receive and the shield wire for signal ground. Your unit does not use the blue wire.
16
|
Orange (Receive) |
|
NMEA Transmit |
To Other |
|
Com-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
To GlobalMap |
|
|
|
|
GPS Receiver |
Shield (Ground) |
|
|
Ground |
||
5300c |
|
|
|
|
|
Com-1 wiring to receive NMEA position information from some other GPS receiver
Com-1 |
Yellow (Transmit) |
|
NMEA Receive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
To Other |
|
|
|
|
|
||
To GlobalMap |
Shield (Ground) |
|
|
Ground |
Device |
5300c |
|
|
|
|
|
Com-1 wiring to transmit NMEA position information to another NMEA-compatible device.
17
Power/Data
socket Ethernet (future enhancement
Network
Port
Data |
|
|
Cable |
NMEA 2000 |
Power Supply |
|
||
|
Power cable |
cable |
GlobalMap 5300c iGPS Cable Connections.
Mounting the Unit: Bracket or Portable
You can install the GlobalMap 5300c on the top of a dash with the supplied gimbal bracket. It can also be mounted on a portable power supply.
If you use the supplied bracket, you may be interested in the optional R-A-M® bracket mounting system. This converts the unit's gimbal bracket to a swivel mount, which can be used on the dash or overhead mounting positions. R-A-M offers permanent mounts and temporary mounts suitable for many vehicle types. See your Lowrance dealer or
18

visit the LEI web site (www.lei-extras.com) for the latest options; accessory ordering information is on the inside back cover of this manual. For a complete look at the many mounting options, visit the RAM web site at www.ram-mount.com.
Optional R-A-M mounting system.
Bracket Installation
Mount the GlobalMap 5300c in any convenient location, provided there is clearance behind the unit when it's tilted for the best viewing angle.
Caution:
The unit must be installed in a location with a clear view of the sky, so the internal GPS antenna can lock-on to satellite signals. The antenna is located near the back of the case, so that tilting the unit at an extreme angle will obstruct the internal antenna's view of the sky and can block or degrade satellite signal reception. For example: If the unit is installed on the deck of a boat and you are fishing in a standing position or in a chair, tilting the unit horizontal may provide the best view of the display. However, a horizontal position usually hampers antenna operation in this type of unit.
You can still mount the unit on a deck and maintain good reception. Just switch to the Satellite Page, then slowly tilt the unit back. As the angle increases, watch for signal degradation or loss of lock. This step allows you to tilt the unit as much as possible while maintaining satellite lock. After you've determined the best combination of unit visibility and signal strength, you can switch back to the Sonar or Map page for normal operation
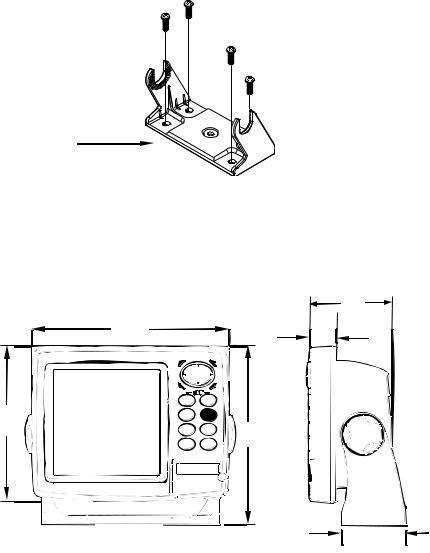
Make sure there is enough room behind the GlobalMap 5300c to attach the power cable. (A drawing on the next page shows the dimensions of a gim- bal-mounted GlobalMap 5300c.)
19
Holes in the bracket's base allow wood screw or through-bolt mounting. You may need to place a piece of plywood on the back side of thin fiberglass panels to reinforce the panel and secure the mounting hardware.
Front
Install the gimbal bracket. Orient the bracket so the arms slope toward the front of your unit.
Drill a 1-inch (25.4 mm) hole in the dash for the power cable. The best location for this hole is immediately under the gimbal bracket location. This way, the bracket can be installed so that it covers the hole, holds the cables in position and results in a neat installation. Some customers, however, prefer to mount the bracket to the side of the cable hole
— it's a matter of personal preference. 72.9
[2.87]
173.9 [6.85] 23.4
[0.92]
137.9  [5.43] 157.9
[5.43] 157.9
[6.22]
Millimeter |
56.9 |
[Inch] |
[2.24] |
Front view (left) and side view (right) showing dimensions of the GlobalMap 5300c when mounted on gimbal bracket.
After drilling the hole, pass the power cable's bare-wire end down though the hole from the top.
20
If you wish, you can fill in the hole around the cables with a good marine sealant compound. (Some marine dealers stock cable hole covers to conceal the opening.) No matter what type of installation you prefer, be sure to leave enough slack in the cables to allow tilting or swiveling the GlobalMap 5300c. If you choose to fill in the hole, be sure to position the cables against the rear edge of the hole as you apply the fill material.
Before positioning the bracket, be sure to hold the cables against the rear edge of the hole. Then, slide the bracket over the hole and butt the rear of the bracket base firmly against the cables, thus pinning them in place against the side of the hole. Finally, fasten the bracket to the dash. Attach the unit to the gimbal bracket using the supplied gimbal knobs and washers.
Portable Installation
Like many Lowrance products, the GlobalMap 5300c is capable of portable operation by using an optional portable power pack. The power pack expands the uses for your GPS unit. The portable power pack makes it easy to transfer your unit from a boat to a car, recreational vehicle, airplane or other vehicle without drilling and mounting a second bracket. You can use your unit in your own car or boat, then take it along when riding in a friend's vehicle that's not equipped with GPS.
Most LEI portable power packs can be used with eight "D" cell alkaline batteries. Some use an optional sealed, rechargeable battery. For information on the PPP for your unit, see the accessory ordering information inside the back cover of this manual.
"D" cell battery
Installing batteries in a typical portal power pack.
21

MMC or SD Card Memory Card Installation
Your GlobalMap 5300c uses a MultiMedia Card to store information, such as custom maps, waypoints, trails and other GPS data. The unit can also use Secure Digital Cards (SD card) to store data.
NOTE:
Throughout this manual, we will use the term MMC, but just remember that your unit can use an MMC or SD card to store data.
Both of these solid-state flash memory devices are about the size of a postage stamp. An SD card is slightly thicker than an MMC. As this manual went to press, MMCs and SD cards were available in various storage capacities up to 2 gigabytes.
Additional MMC cards are available from LEI Extras; see ordering information inside the back cover of this manual. MMCs and SD cards are also available at many camera and consumer electronics stores.
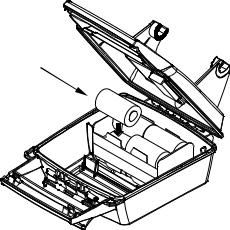
The MMC slot is located in a compartment on the front of the case. The compartment door is located at the lower right corner. The following figure shows a close-up with the door opened.
Thumb
screw
Insert card face up, this way
Memory card compartment with a 16 MB MMC card installed.
To remove an MMC
1.Open the card compartment door by unscrewing the thumb screw. The screw should only be finger tight. If it was over-tightened, use a thumbnail, a coin or a screwdriver to open the door.
2.Just press a finger against the label of the MMC and drag it from the slot.
3.Close the compartment door and fasten the thumbnail screw finger tight.
22
 Loading...
Loading...