LINKSYS E2500 User Manual

User Guide
Linksys E2500
Advanced Dual-Band N Router

Linksys E2500 Table of Contents
Contents
Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration 13
How to Access the Browser-Based Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Setup > Basic Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Setup > DDNS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Setup > MAC Address Clone. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Setup > Advanced Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Wireless > Wireless Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Wireless > Wireless MAC Filter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Wireless > Advanced Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Security > Firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Security > VPN Passthrough. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Access Restrictions > Internet Access Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Applications and Gaming > Single Port Forwarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Applications and Gaming > Port Range Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Applications & Gaming > Port Range Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Applications and Gaming > DMZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Applications and Gaming > QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Administration > Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Administration > Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Administration > Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Administration > Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Administration > Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Status > Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Status > Local Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Status > Wireless Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 44
Appendix B: Specifications 58
i

Linksys E2500 Table of Contents
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
ii
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
After setting up the Router with the setup software
(located on the CD-ROM), the Router will be ready for use.
If you would like to change its advanced settings, use the
Router’s browser-based utility. This chapter describes each
web page of the utility and each page’s key functions. You
can access the utility via a web browser on a computer
connected to the Router.
The browser-based utility has these main tabs: Setup,
Wireless, Security, Storage, Access Restrictions, Applications
& Gaming, Administration, and Status. Additional tabs will
be available after you click one of the main tabs.
How to Access the Browser-Based Utility
To access the browser-based utility, launch the web
browser on your computer, and enter the Router’s default
IP address, 192.168.1.1 in the Address field. Then press
Enter.
NOTE: You can also access the browser-based
utility on Windows computers by entering the
device name in the Address field. Refer to Device
Name under “Router Address” on page 4.
Setup > Basic Setup
The first screen that appears is the Basic Setup screen. This
allows you to change the Router’s general settings.
A login screen will appear. (Non-Windows 7 users will see
a similar screen.) In the User name field, enter admin. Then
enter the password created during the setup software.
(If you did not run the setup software, then use the
default password, admin. You can set a new password
on the Administration > Management screen. Refer to
“Administration > Management” on page 21.) Click OK
to continue.
Windows 7 Login Screen
NOTE: You can also access the browser-based
utility through the Cisco Connect software. For
more information, refer to “Router Settings” on
page 10.
Setup > Basic Setup
Language
Select your language
one from the drop-down menu. The language of the
browser-based utility will change five seconds after you
select another language.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
To use a different language, select
Internet Setup
The Internet Setup section configures the Router to your
Internet connection. Most of this information can be
obtained through your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Internet Connection Type
Select the type of Internet connection your ISP provides
from the drop-down menu. The available types are:
• Automatic Configuration - DHCP
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
• Static IP
• PPPoE
• PPTP
• L2TP
• Telstra Cable
1
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
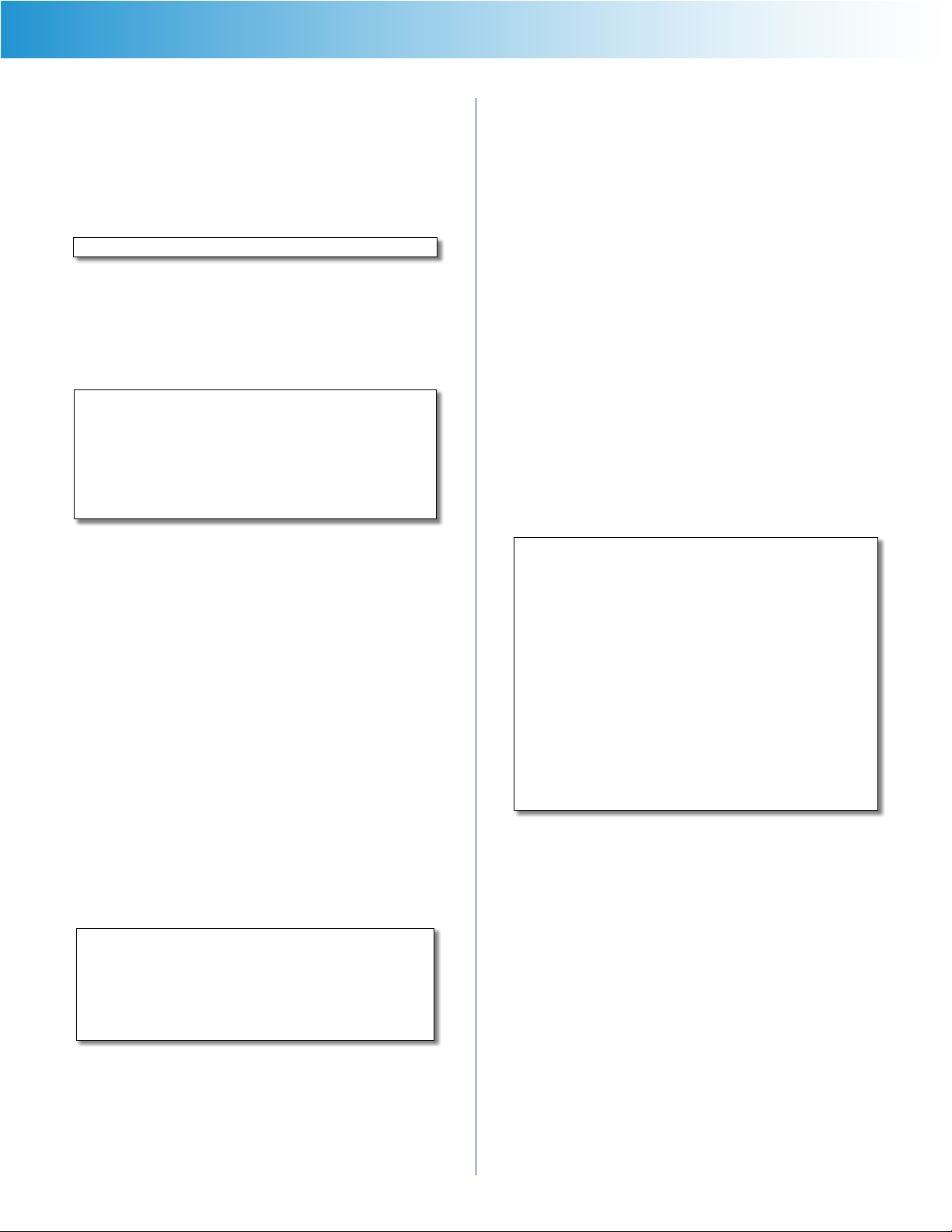
Automatic Configuration - DHCP
The default Internet Connection Type is set to Automatic
Configuration - DHCP. Keep the default only if your ISP
supports DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) or
if you connect using a dynamic IP Address. (This option
usually applies to cable connections.)
Internet Connection Type > Automatic Configuration - DHCP
Static IP
If you are required to use a permanent IP address to
connect to the Internet, select Static IP.
Internet Connection Type > Static IP
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time You can configure
the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle
Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router
to automatically re-establish your connection as soon
as you attempt to access the Internet again. To use this
option, select Connect on Demand. In the Max Idle Time
field, enter the number of minutes you want to elapse
before your Internet connection terminates. The default is
5 minutes.
Keep Alive: Redial Period If you select this option, the
Router will periodically check your Internet connection. If
you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically
re-establish your connection. To use this option, select
Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, specify how often
the Router should check the Internet connection. The
default is 30 seconds.
PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a service that
applies to connections in Europe only.
IP Address This is the Router’s IP address, when seen
from the Internet. Your ISP will provide you with the IP
address you need to enter here.
Subnet Mask This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as seen
by users on the Internet (including your ISP). Your ISP will
provide you with the Subnet Mask.
Default Gateway Your ISP will provide you with the
Gateway address, which is the ISP server’s IP address.
DNS Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS
(Domain Name System) server IP address.
PPPoE
Some DSL-based ISPs use PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol
over Ethernet) to establish Internet connections. If you are
connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with
your ISP to see if they use PPPoE. If they do, you will have
to enable PPPoE.
Internet Connection Type > PPTP
If your ISP supports DHCP or you are connecting through
a dynamic IP address, then select Obtain an IP Address
Automatically. If you are required to use a permanent IP
address to connect to the Internet, then select Specify an
IP Address. Then configure the following:
Internet IP Address This is the Router’s IP address, as
seen from the Internet. Your ISP will provide you with the
IP Address you need to specify here.
Internet Connection Type > PPPoE
User Name and Password Enter the User Name and
Password provided by your ISP.
Service Name (optional) If provided by your ISP, enter
the Service Name.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
Subnet Mask This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as seen
by users on the Internet (including your ISP). Your ISP will
provide you with the Subnet Mask.
Default Gateway Your ISP will provide you with the
Gateway address, which is the ISP server’s IP address.
DNS Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS
(Domain Name System) Server IP address.
2

Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
Server IP Address Your ISP will provide you with the
Server IP Address.
User Name and Password Enter the User Name and
Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time You can configure
the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle
Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router
to automatically re-establish your connection as soon
as you attempt to access the Internet again. To use this
option, select Connect on Demand. In the Max Idle Time
field, enter the number of minutes you want to elapse
before your Internet connection terminates. The default is
5 minutes.
Keep Alive: Redial Period If you select this option, the
Router will periodically check your Internet connection. If
you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically
re-establish your connection. To use this option, select
Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, specify how often
the Router should check the Internet connection. The
default is 30 seconds.
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a service that applies
to connections in Israel only.
Keep Alive: Redial Period If you select this option, the
Router will periodically check your Internet connection. If
you are disconnected, then the Router will automatically
re-establish your connection. To use this option, select
Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field, specify how often
the Router should check the Internet connection. The
default is 30 seconds.
Telstra Cable
Telstra Cable is a service that applies to connections in
Australia only.
Internet Connection Type > Telstra Cable
Server IP Address This is the IP address of the Telstra
Cable. Your ISP will provide you with the IP Address you
need to specify here.
User Name and Password Enter the User Name and
Password provided by your ISP.
Optional Settings
Some of these settings may be required by your ISP. Verify
with your ISP before making any changes.
Internet Connection Type > L2TP
Server IP Address This is the IP address of the L2TP
Server. Your ISP will provide you with the IP Address you
need to specify here.
User Name and Password Enter the User Name and
Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time You can configure
the Router to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle
Time). If your Internet connection has been terminated
due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router
to automatically re-establish your connection as soon
as you attempt to access the Internet again. To use this
option, select Connect on Demand. In the Max Idle Time
field, enter the number of minutes you want to elapse
before your Internet connection terminates. The default is
5 minutes.
Optional Settings
Host Name/Domain Name These fields allow you to
supply a host and domain name for the Router. Some ISPs,
usually cable ISPs, require these names as identification.
You may have to check with your ISP to see if your
broadband Internet service has been configured with a
host and domain name. In most cases, leaving these fields
blank will work.
MTU MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies
the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission.
Select Manual if you want to manually enter the largest
packet size that is transmitted. To have the Router select
the best MTU for your Internet connection, keep the
default setting, Auto.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
3

Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
Size When Manual is selected in the MTU field, this option
is enabled. Leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. The
default size depends on the Internet Connection Type:
• DHCP, Static IP, or Telstra: 1500
• PPPoE: 1492
• PPTP or L2TP: 1460
Network Setup
The Network Setup section configures the IP settings for
your local network.
Router Address
This presents the Router’s IP Address, the Subnet Mask,
and the Device Name as seen by your network.
Router IP Address
IP Address This is the IP address of the router and is used
as the base for all of your local network settings.
Subnet Mask This is the subnet mask address for your
router. It offers a selection of addresses from a drop-down
menu. Most users will not need to change this setting.
DHCP Server DHCP is enabled by factory default. If you
already have a DHCP server on your network, or you do
not want a DHCP server, then select Disabled (no other
DHCP features will be available).
DHCP Reservation Click DHCP Reservation if you want
to assign a fixed local IP address to a specific device on
your network. This is helpful if you have a device you need
to access at the same address all the time such as a media
server or print server. You can reserve the IP address for
the specific device by selecting it from the list of devices
or by manually entering the MAC address of the device.
DHCP Reservation
You will see a list of DHCP clients with the following
information: Client Name, Interface, IP Address, and
MAC Address.
Device Name The default device name is Ciscoxxxxx.
xxxxx represents the last 5 digits of your serial number.
This can be found on the bottom of the router. (The Device
name is also the Router’s NetBIOS name.)
NOTE: If you used the setup software
for installation, then the device name is
synchronized with the name of your wireless
network (up to 15 characters).
DHCP Server Settings
The settings allow you to configure the Router’s DHCP
server function. The Router can be used as a DHCP server
for your network. A DHCP server automatically assigns an
IP address to each computer or device on your network.
NOTE: If you choose to enable the DHCP server
option, make sure there is no other DHCP server
on your network.
DHCP Reservation
• Select Clients from DHCP Table Click the Select
check box to reserve a client’s IP address. Then click
Add Clients.
• Manually Add Client To manually assign an IP
address, enter the client’s name in the Enter Client
Name field. Enter the IP address you want it to have
in the Assign IP Address field. Enter its MAC address in
the To This MAC Address field. Then click Add and click
Save Settings.
Clients Already Reserved
A list of DHCP clients and their fixed local IP addresses
are displayed at the bottom of the screen. If you want
to remove a client from this list, click Remove.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click
Cancel Changes to clear your changes. To update
the on-screen information, click Refresh. To exit this
screen, click Close.
Start IP Address The Start IP Address specifies the
starting IP address for the range of addresses assigned
by your Router when it functions as a DHCP server. (The
first IP address assigned by the Router will be randomly
selected within the range you specify.)
DHCP Server Setting
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
Because the Router’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1,
the Start IP Address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater, but
4
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
smaller than 192.168.1.254. The default Start IP Address is
192.168.1.100.
Maximum Number of Users Enter the maximum
number of computers that you want the DHCP server to
assign IP addresses to. This number cannot be greater
than 253. The default is 50.
IP Address Range The range of available IP addresses is
displayed.
Client Lease Time The Client Lease Time is the amount
of time a network user will be allowed connection to the
Router with their current dynamic IP address. Enter the
amount of time, in minutes, that the user will be “leased”
this dynamic IP address. After the time is up, the user will
be automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address, or
the lease will be renewed. The default is 0 minutes, which
means one day.
Static DNS (1-3)
the Internet translates domain or website names into
Internet addresses or URLs. Your ISP will provide you with at
least one DNS Server IP Address. If you wish to use another,
enter that IP Address in one of these fields. You can enter up
to three DNS Server IP Addresses here. The Router will use
these for quicker access to functioning DNS servers
The Domain Name System (DNS) is how
.
Setup > DDNS
The Router offers a Dynamic Domain Name System
(DDNS) feature. DDNS lets you assign a fixed host and
domain name to a dynamic Internet IP address. It is useful
when you are hosting your own website, FTP (File Transfer
Protocol) server, or other server behind the Router.
Before you can use this feature, you need to sign
up for DDNS service with a DDNS service provider,
www.dyndns.org or www.tzo.com. If you do not want to
use this feature, keep the default, Disabled.
DDNS
DDNS Service
If your DDNS service is provided by DynDNS.org, then
select DynDNS.org from the drop-down menu. If your
DDNS service is provided by TZO, then select TZO.com.
The features available on the DDNS screen will vary,
depending on which DDNS service provider you use.
DynDNS.org
WINS The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS)
manages each computer’s interaction with the Internet. If
you use a WINS server, enter that server’s IP address here.
Otherwise, leave this blank.
Time Settings
Time Setting
Time Zone Select the time zone in which your network
functions from this drop-down menu.
Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving
changes Select this option to have the Router
automatically adjust for daylight saving time.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
Reboot
Reboot
Reboot Use this option to reboot your Router.
Setup > DDNS > DynDNS
Username Enter the Username for your DDNS account.
Password Enter the Password for your DDNS account.
Host Name The DDNS URL assigned by the DDNS service
is displayed.
System Select the DynDNS service you use: Dynamic,
Static, or Custom. The default selection is Dynamic.
Mail Exchange (Optional) Enter the address of your mail
exchange server, so e-mails to your DynDNS address go to
your mail server.
Backup MX This feature allows the Mail eXchange (MX)
server to be a backup. To disable this feature, keep the
default, Disabled. To enable the feature, select Enabled. If
you are not sure which setting to select, keep the default,
Disabled.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
5
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
Wildcard This setting enables or disables wildcards
for your host. For example, if your DDNS address is
myplace.dyndns.org and you enable wildcards, then
x.myplace.dyndns.org will work as well (x is the wildcard).
To disable wildcards, keep the default, Disabled. To
enable wildcards, select Enabled. If you are not sure
which setting to select, keep the default, Disabled.
Internet IP Address The Router’s Internet IP address is
displayed here. Because it is dynamic, it will change.
Status The status of the DDNS service connection is
displayed.
Update To manually trigger an update, click Update.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
TZO.com
MAC Address Clone
Enabled/Disabled To have the MAC address cloned,
select Enabled.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address registered with
your ISP here.
Clone My PC’s MAC Click this button to clone the MAC
address of the computer you are using.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
Setup > MAC Address Clone
Setup > DDNS > TZO
E-mail Address, TZO Password, and Domain
Name Enter the settings of the account you set up with
TZO.
Internet IP Address The Router’s Internet IP address is
displayed here. Because it is dynamic, it will change.
Status The status of the DDNS service connection is
displayed.
Update To manually trigger an update, click Update.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
Setup > MAC Address Clone
A MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a unique
piece of hardware for identification. Some ISPs require you
to register a MAC address in order to access the Internet. If
you do not wish to re-register the MAC address with your
ISP, you can use the MAC Address Clone feature to assign
the currently registered MAC address to the Router.
Setup > Advanced Routing
This screen is used to set up the Router’s advanced
functions. Operating Mode allows you to select the
type(s) of advanced functions you use. Dynamic Routing
automatically adjusts how packets travel on your network.
Static Routing sets up a fixed route to another network
destination.
Setup > Advanced Routing
Advanced Routing
NAT
Enabled/Disabled If this Router is hosting your network’s
connection to the Internet, keep the default, Enabled. If
another router exists on your network, select Disabled.
When the NAT setting is disabled, dynamic routing will be
available.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
6

Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
Dynamic Routing (RIP)
Dynamic routing uses the Routing Information Protocol
(RIP). This option enables the Router to automatically
adjust to physical changes in the network’s layout and
exchange routing tables with other router(s). The Router
determines the network packets’ route based on the
fewest number of hops between the source and the
destination.
Enabled/Disabled When the NAT setting is enabled, the
Dynamic Routing option is automatically disabled. When
the NAT setting is disabled, this option is available. Select
Enabled to use the Dynamic Routing option.
Static Routing
A static route is a pre-determined pathway that network
information must travel to reach a specific host or
network. Enter the information described below to set up
a new static route.
Route Entries To set up a static route between the Router
and another network, select a number from the dropdown list. Click Delete This Entry to delete a static route.
Enter Route Name Enter a name for the Route here,
using a maximum of 25 alphanumeric characters.
Destination LAN IP The Destination LAN IP is the address
of the remote network or host to which you want to assign
a static route.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask determines which
portion of a Destination LAN IP address is the network
portion, and which portion is the host portion.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway device that
allows for contact between the Router and the remote
network or host.
Interface This interface tells you whether the Destination
IP Address is on the LAN & Wireless (Ethernet and wireless
networks) or the Internet (WAN).
Click Show Routing Table to view the static routes you
have already set up.
Routing Table
For each route, the Destination LAN IP address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway, and Interface are displayed. Click
Refresh to update the information. Click Close to exit
this screen.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings
The basic settings for wireless networking are set on this
screen.
There are two ways to configure the Router’s wireless
network(s), manual and Wi-Fi Protected Setup.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup is a feature that makes it easy to set
up your wireless network. If you have client devices, such
as wireless adapters, that support Wi-Fi Protected Setup,
then you can use Wi-Fi Protected Setup.
Simultaneous Networks
For more wireless bandwidth, the Router can create two
simultaneous yet separate Wireless-N networks, one using
the Wireless-N 5 GHz band and one using the Wireless-N
2.4 GHz band. You can use Wi-Fi Protected Setup to
easily configure and connect to both networks (refer to
“Wi-Fi Protected Setup” on page 9), or you can manually
configure the Router.
If you use manual configuration, then set up each network
with the following:
• Unique Network Name (SSID)
• Wireless security settings (refer to
“5 GHz or 2.4 GHz Wireless Security” on page 10)
Decide which computers and other wireless devices
should join which network. Wireless-N devices support
both the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz bands, so they can join either
the 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz network. Wireless-G and Wireless-B
devices support only the 2.4 GHz band, so they should
join the 2.4 GHz network. Wireless-A devices support only
the 5 GHz band, so they should join the 5 GHz network.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
For the 5 GHz network, configure all computers and other
wireless devices with the same 5 GHz Network Name
(SSID) and wireless security settings. For the 2.4 GHz
network, configure all computers and other wireless
devices with the same 2.4 GHz Network Name (SSID) and
wireless security settings.
Routing Table
NOTE: Make sure each network uses a unique
Network Name (SSID).
7
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
5 GHz Wireless Settings
Network Mode Select the wireless standards running on
your 5 GHz network.
• Mixed If you have both Wireless-A and Wireless-N
(5 GHz) devices in your network, keep the default,
Mixed.
• Wireless-A Only If you have only Wireless-A devices,
select Wireless-A Only.
• Wireless-N Only If you have only Wireless-N (5 GHz)
devices, select Wireless-N Only.
• Disabled If you do not have any Wireless-A and
Wireless-N (5GHz) devices in your network, select
Disabled.
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings
Configuration View To manually configure your
wireless networks, select Manual. Proceed to the Wireless
Configuration (Manual) section. To use Wi-Fi Protected
Setup, select Wi-Fi Protected Setup. Proceed to
“Wi-Fi Protected Setup” on page 9.
Wireless Configuration (Manual)
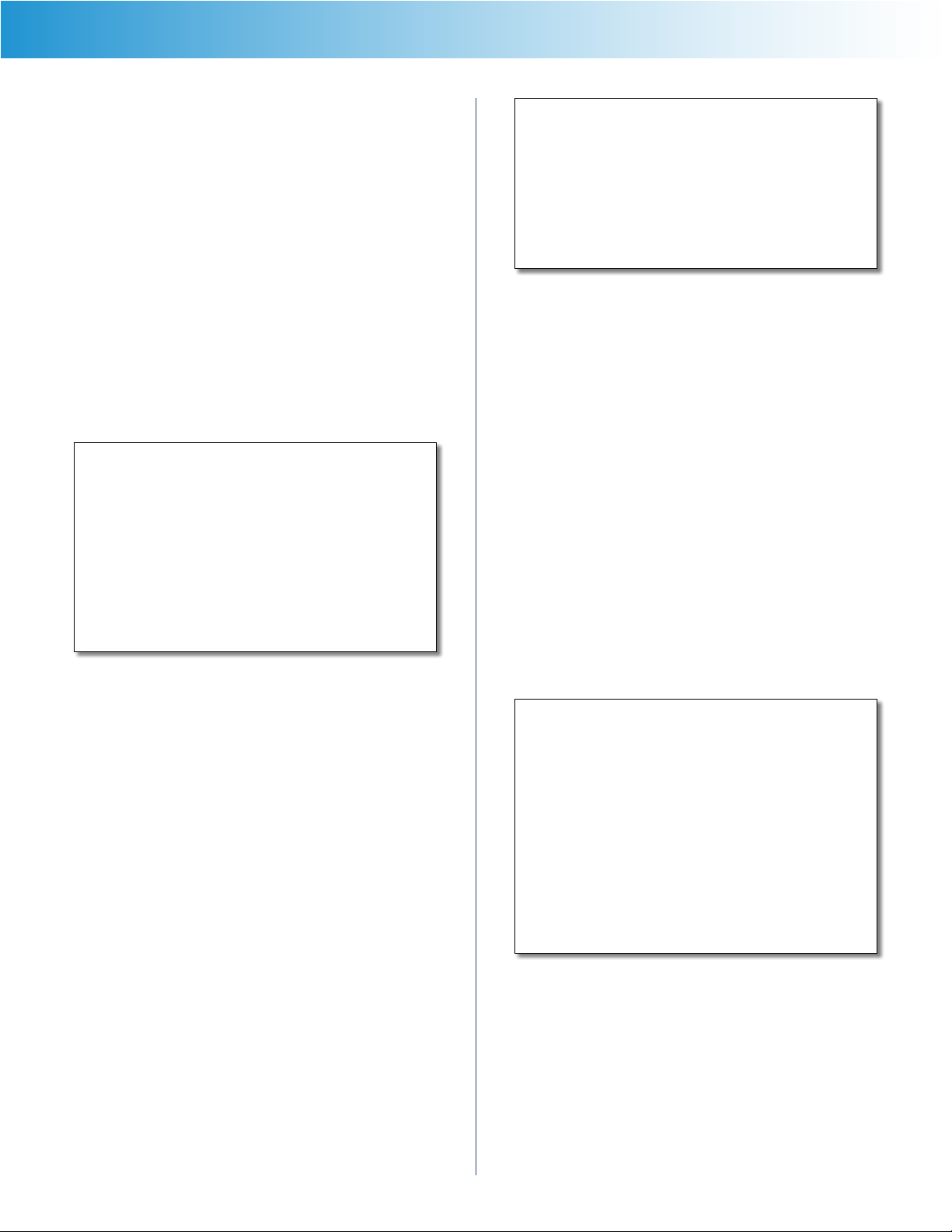
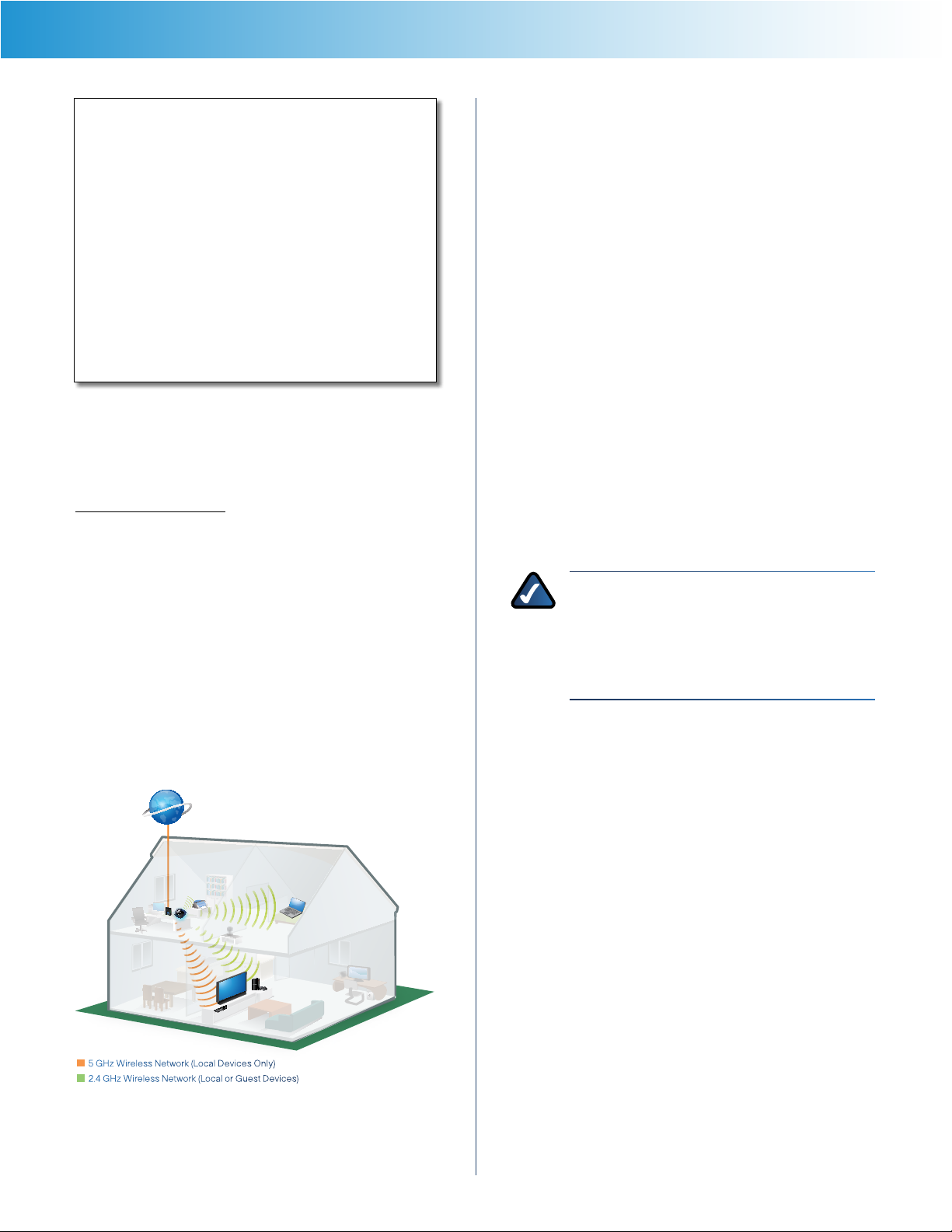
Your Linksys E2500 can run two networks at the same
time, one network using the 5 GHz radio frequency band
and the other network using the 2.4 GHz radio frequency
band. This allows you to isolate higher-priority traffic, such
as video and voice applications, on the 5 GHz network,
which is less prone to interference.
The computers and devices running your video and voice
applications can use the 5 GHz network, while your guest
access and computers that are only browsing the web can
use the 2.4 GHz network.
Internet
Printer
Modem
Router
Blu-ray Player
5 GHz Wireless Network (Local Devices Only)
2.4 GHz Wireless Network (Local or Guest Devices)
If you set the Configuration View to Manual, the Basic
Wireless Settings screen displays the following fields.
Family Notebook
Gaming Console
1
2
1
2
Network Name (SSID) The Service Set Identifier (SSID)
is the network name shared by all devices in a wireless
network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32
keyboard characters. The default is Ciscoxxxxx (xxxxx are
the last five digits of the Router’s serial number, found on
the product label on the left side of the Router’s bottom
panel). The setup software that you use to install your
Router and set up your wireless network changes the
default Network Name to an easy-to-remember name.
NOTE: If you restore the Router’s factory default
settings (by pressing the Reset button or using
the Administration > Factory Defaults screen),
the Network Name will return to its default
value, and all devices on your wireless network
will need to be reconnected..
Channel Width For best performance in a network
using Wireless-A and Wireless-N (5 GHz) devices, keep the
default, Auto (20MHz or 40MHz). For a channel width
of 40 MHz, select 40MHz only. For a channel width of 20
MHz, select 20MHz only.
Channel Select the channel from the drop-down list for
Wireless-A and Wireless-N (5GHz) networking. If you are
not sure which channel to select, keep the default, Auto.
SSID Broadcast When wireless clients survey the local
area for wireless networks to associate with, they will
detect the SSID broadcast by the Router. To broadcast the
Router’s SSID, keep the default, Enabled. If you do not
want to broadcast the Router’s SSID, then select Disabled.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
2.4 GHz Wireless Settings
Network Mode Select the wireless standards running on
your 2.4 GHz network.
• Mixed If you have both Wireless-B, Wireless-G and
Wireless-N (2.4 GHz) devices in your network, keep the
default, Mixed.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
8
Linksys E2500 Chapter 1: Advanced Configuration
• Wireless-B/G Only If you have both Wireless-B and
Wireless-G (2.4 GHz) devices in your network, select
Wireless-B/G Only.
• Wireless-B Only If you have only Wireless-B devices,
select Wireless-B Only.
• Wireless-G Only If you have only Wireless-G devices,
select Wireless-G Only.
• Wireless-N Only If you have only Wireless-N (2.4 GHz)
devices, select Wireless-N Only.
• Disabled If you do not have any Wireless-B, Wireless-G
and Wireless-N (2.4 GHz) devices in your network,
select Disabled.
Network Name (SSID) The Service Set Identifier (SSID)
is the network name shared by all devices in a wireless
network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32
keyboard characters. The default is Ciscoxxxxx (xxxxx are
the last five digits of the Router’s serial number, found on
the product label on the left side of the Router’s bottom
panel). The setup software that you use to install your
Router and set up your wireless network changes the
default Network Name to an easy-to-remember name.
NOTE: If you restore the Router’s factory default
settings (by pressing the Reset button or using
the Administration > Factory Defaults screen),
the Network Name will return to its default
value, and all devices on your wireless network
will need to be reconnected..
Channel Width For best performance in a network using
Wireless-B, Wireless-G and Wireless-N (2.4 GHz) devices,
select Auto (20MHz or 40MHz). For a channel width of 20
MHz, keep the default, 20MHz only.
Channel Select the channel from the drop-down list
for Wireless-B, Wireless-G, and Wireless-N (2.4 GHz)
networking. If you are not sure which channel to select,
keep the default, Auto.
SSID Broadcast When wireless clients survey the local
area for wireless networks to associate with, they will
detect the SSID broadcast by the Router. To broadcast the
Router’s SSID, keep the default, Enabled. If you do not
want to broadcast the Router’s SSID, then select Disabled.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to clear your changes.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup
There are three methods available. Use the method that
applies to the client device you are configuring.
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
NOTE: Wi-Fi Protected Setup configures one
client device at a time. Repeat the instructions
for each client device that supports Wi-Fi
Protected Setup.
1. Use the Wi-Fi Protected Setup Button Use this
method if your client device has a Wi-Fi Protected
Setup button.
a. Click or press the Wi-Fi Protected Setup button on
the client device.
b. Click the Wi-Fi Protected Setup button on the
Router’s Wi-Fi Protected Setup screen.
The Wi-Fi Protected Setup LED flashes blue for two
minutes during the Wi-Fi Protected Setup process
and lights up blue when the Wi-Fi Protected Setup
process is successful.
The LED lights up amber if there is an error during
the Wi-Fi Protected Setup process. Make sure the
client device supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup. Wait
until the LED is off, and then try again.
The LED flashes when a Wi-Fi Protected Setup
session is active. The Router supports one session
at a time. Wait until the LED is solidly lit, or off before
starting the next Wi-Fi Protected Setup session.
c. After the client device has been configured,
click OK on the Router’s Wi-Fi Protected Setup
screen. Then refer back to your client device or its
documentation for further instructions.
2. Enter the client device’s PIN on the Router Use
this method if your client device has a Wi-Fi Protected
Setup PIN number.
Advanced Dual-Band N Router
a. Enter the PIN number from the client device in the
field on the Router’s Wi-Fi Protected Setup screen.
9
 Loading...
Loading...