Linksys BEFSR41 User Manual

Instant Broadband™ Series
EtherFast®
Cable/DSL Routers
Use this User Guide to install the following Linksys product(s):
BEFSRU31 EtherFast Cable/DSL Router with USB Port and 10/100 3-Port Switch BEFSR41 v2 EtherFast Cable/DSL Router with 10/100 4-Port Switch BEFSR11 EtherFast 1-Port Cable/DSL Router
User Guide
COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Copyright © 2001 Linksys, All Rights Reserved. Instant Broadband is a registered trademark of Linksys. Microsoft, Windows, and the Windows logo are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks and brand names are the property of their respective proprietors.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys guarantees that every Instant Broadband EtherFast Cable/DSL Router will be free from physical defects in material and workmanship for one year from the date of purchase, when used within the limits set forth in the Specification section of this User Guide. If the product proves defective during this warranty period, call Linksys Customer Support in order to obtain a Return Authorization number. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING. When returning a product, mark the Return Authorization number clearly on the outside of the package and include your original proof of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. All customers located outside of the United States of America and Canada shall be held responsible for shipping and handling charges.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS OFFERS NO REFUNDS FOR ITS PRODUCTS. Linksys makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Linksys reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity. Please direct all inquiries to:
Linksys P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
FCC STATEMENT
The Instant Broadband EtherFast Cable/DSL Router has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
•Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
•Increase the separation between the equipment or device
•Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
•Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
UG-BEFSR11/41/U31-010521A-AC

Instant Broadband Series |
|
Table of Contents |
|
Introduction |
1 |
The Linksys EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
1 |
Features |
1 |
Package Contents for the 1-Port Router (BEFSR11) |
2 |
Network Requirements |
2 |
Package Contents for the 3-Port Router (BEFSRU31) |
3 |
Network Requirements |
3 |
Package Contents for the 4-Port Router (BEFSR41) |
4 |
Network Requirements |
4 |
Getting to Know the 4-Port |
|
EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
5 |
The 4-Port Router’s Rear Panel |
5 |
The 4-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs |
6 |
Getting to Know the 1-Port |
|
EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
8 |
The 1-Port Router’s Rear Panel |
8 |
The 1-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs |
9 |
Getting to Know the 3-Port |
|
EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
11 |
The 3-Port Router’s Rear Panel |
11 |
The 3-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs |
13 |
Connecting the Cable/DSL Router |
|
to Your Network |
15 |
Overview |
15 |
LANs and WANs |
15 |
IP Addresses: A Quick Lesson |
16 |
Connecting Your Hardware Together & Booting Up |
18 |
Uplinking: Connecting More Devices to Your Router |
20 |
Configuring the BEFSRU31’s USB Port |
21 |
Windows 98 Configuration |
21 |
Windows 2000 Configuration |
25 |
Windows Millennium Configuration |
29 |
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Configuring Your Network with the |
|
Cable/DSL Router |
31 |
Configuring PCs to Connect to the Cable/DSL Router |
31 |
Configuring the Cable/DSL Router |
33 |
The Cable/DSL Router’s Web-based Utility |
36 |
Quick and Easy Router Administration |
36 |
Setup |
37 |
Password |
39 |
Status |
40 |
DHCP |
41 |
Logging |
42 |
Help |
43 |
IP Filtering |
45 |
IP Forwarding |
47 |
Dynamic Routing |
49 |
Static Routing |
50 |
DMZ Hosting |
52 |
MAC Address Cloning |
53 |
Troubleshooting |
54 |
Common Problems |
54 |
Frequently Asked Questions |
56 |
Glossary |
60 |
Appendix |
73 |
How to Ping Your ISP’s E-mail & Web Addresses |
73 |
Installing the TCP/IP Protocol |
76 |
Twisted-Pair Cabling |
78 |
Crimping Your Own Network Cables |
79 |
4-Port Router Specifications |
80 |
4-Port Environmental Specifications |
80 |
1-Port Router Specifications |
81 |
1-Port Environmental Specifications |
81 |
3-Port Router Specifications |
82 |
3-Port Environmental Specifications |
82 |
Customer Support |
83 |

Instant Broadband Series
Introduction
The Linksys EtherFast Cable/DSL Router
Congratulations on the purchase of the EtherFast Cable/DSL Router from Linksys! The EtherFast Cable/DSL Router is the perfect solution for connecting a network of PCs to a high-speed broadband Internet connection and to an Ethernet network backbone. Configurable as a DHCP server, the EtherFast Cable/DSL Router is the only visible network device on the Internet. The Router also serves as your Internet NAT firewall, protecting your network’s PCs from being accessed by external users. All incoming data packets are monitored and filtered. The Router can also be configured to block internal users' access to the Internet with IP Filtering, as well as to play Internet games, videoconference, and much more.
Now all of your PCs can enjoy lightning-fast broadband Internet connections and share internal network data. Link them all together and network faster than you ever thought possible.
Features
•Connect a Broadband Modem to an Ethernet Network Backbone
•Equipped With a 3 or 4-Port 10/100 Switch (BEFSRU31 & BEFSR41 v2 only)
•Connects Up to 254 PCs to the Internet with Just One IP Address
•NAT Firewall Protects Your PCs From Outside Intruders on the Internet
•Configurable Through a PC’s Web Browser Using Netscape Navigator 4.0 or Internet Explorer 4.0 or Higher
•Supports IPSec Pass-Through for Virtual Private Networking (VPNs)*
•Administer Your Router Remotely Over the Internet
•10/100 Switch Speeds Up Your Gaming and Multimedia Connections (BEFSRU31 & BEFSR41 v2 only)
•Configurable as a DHCP Server on Your Network
•Compatible with Virtually All Standard Internet Applications
•Administrators Can Block Specific Internal Users' Internet Access
•DMZ Hosting Feature Enables Internet Multimedia Applications Such as Video-Conferencing and Internet Gaming
*Limited IPSec Support
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Package Contents for the 1-Port Router (BEFSR11)
•One EtherFast 10/100 1-Port Cable/DSL Router
•One Power Adapter
•One User Guide and Registration Card
•One Tech Helper CD-ROM
Network Requirements
•One RJ-45 broadband Internet connection through a cable or DSL modem
•One PC with a 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card or adapter installed
•TCP/IP network protocol installed on each PC
•UTP CAT 5 network cables with RJ-45 connectors
•Internet Explorer 4.0 and higher or Netscape Navigator 4.0 and higher (Version 5.5 for Internet Explorer and Version 4.7 for Netscape Navigator highly recommended for optimal results)
1 |
2 |

Instant Broadband Series
Package Contents for the 3-Port Router (BEFSRU31)
•One EtherFast Cable/DSL Router with USB Port & 10/100 3-Port Switch
•One USB Cable
•One 3.5” Floppy Disk for USB Setup
•One Power Adapter
•One User Guide and Registration Card
•One Tech Helper CD-ROM
Network Requirements
•One RJ-45 broadband Internet connection through a cable or DSL modem
•One PC with a 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card or adapter installed, or a PC with a USB port
•TCP/IP network protocol installed on each PC
•UTP CAT 5 network cables with RJ-45 connectors
•Internet Explorer 4.0 and higher or Netscape Navigator 4.0 and higher (Version 5.5 for Internet Explorer and Version 4.7 for Netscape Navigator highly recommended for optimal results)
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Package Contents for the 4-Port Router (BEFSR41)
•One EtherFast Cable/DSL Router with 10/100 4-Port Switch
•One Power Adapter
•One User Guide and Registration Card
•One Tech Helper CD-ROM
Network Requirements
•One RJ-45 broadband Internet connection through a cable or DSL modem
•One PC with a 10Mbps or 10/100 Mbps Ethernet card or adapter installed
•TCP/IP network protocol installed on each PC
•UTP CAT 5 network cables with RJ-45 connectors
•Internet Explorer 4.0 and higher or Netscape Navigator 4.0 and higher (Version 5.5 for Internet Explorer and Version 4.7 for Netscape Navigator highly recommended for optimal results)
3 |
4 |

Instant Broadband Series
Getting to Know the 4-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router
The 4-Port Router’s Rear Panel
Your Router’s ports, where network cables are connected, are located on the rear panel of your Router.
The 4-Port Router’s Ports |
|
WAN |
The WAN (Wide Area Network) port is where you |
|
connect your cable or DSL modem. |
Ports 1-4 |
These four LAN (Local Area Network) ports con- |
|
nect to network devices, such as PCs, print servers, |
|
and remote hard drives. If port 1 is being used, the |
|
Uplink port will not work because these two shared |
|
ports have internally shared wiring. |
Uplink |
The Uplink port is used to expand your network by |
|
connecting to another switch or hub. Uplinking to a |
|
switch or a hub is done by simply running a cable |
|
from the Uplink port to the other device. See the |
|
Uplinking: Connecting More Devices to the |
|
Router section for more on uplinking. |
|
If the Uplink port is being used, Port 1 will not |
|
work. |
Power |
The Power port is where you will connect the |
|
power adapter. |
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
4-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs
The LAN Indicators
Power |
Green. The Power LED lights up when the Router is powered |
|
on. |
Link/Act |
Green. The Link/Act LED serves two purposes. If the LED |
|
is continuously lit up, the Router is successfully connected to |
|
a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3 or 4). If the |
|
LED is flickering, the Router is actively sending or receiving |
|
data over that port. |
Full/Col |
Green. The Full/Col LED also serves two purposes. If this |
|
LED is lit up continuously, the connection made through the |
|
corresponding port is running in Full Duplex mode. If the |
|
LED flickers, the connection is experiencing collisions. |
|
Infrequent collisions are normal. |
|
If this LED flickers too often, there may be a problem with |
|
your connection. See the Troubleshooting section if you |
|
encounter this problem. |
100Orange. The 100 LED lights up when a successful 100Mbps connection is made through the corresponding port.
If this LED does not light up, then your connection speed is 10 Mbps.
5 |
6 |

|
Instant Broadband Series |
The WAN Indicators |
|
Link |
Green. The Link LED lights up when a successful connec- |
|
tion is made between the Router and your broadband device |
|
or network. |
Act |
Green. The Act LED flickers when the Router is sending or |
|
receiving data over the broadband WAN port (to the |
|
Internet). |
Diag |
Red. The Diag LED lights up when the Router goes through |
|
its self-diagnosis mode during every boot-up. It will turn off |
|
upon successful completion of the diagnosis. |
If this LED stays on for an abnormally long period of time, see the Troubleshooting section.
The Reset Button* The Reset button can be used in one of two ways.
1.If your Router is having problems connecting to the Internet, press the Reset button for just a moment with a paper clip or a pencil tip. This clears up any jammed connections, and is similar to pressing the Reset button on your PC to reboot it.
2.If you are experiencing extreme problems with your Router and have tried all other troubleshooting measures, press the Reset Button and hold it down until the red Diag LED on the front panel turns on and off completely.
This will restore factory defaults and clear all of the Router’s settings, including the IP addresses you entered.
*The Reset Button is located on the front panel of the 4-Port Router, and the rear panel of the 3- Port Router and the 1-Port Router.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Getting to Know the 1-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router
The One-Port Router’s Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Router is where all of the Router’s cabling connections are made, and where you can reset or configure the Router’s LAN port.
The One-Port Router’s Ports
WAN |
The WAN (Wide Area Network) port is where you |
|
connect your cable or DSL modem. |
LAN |
The LAN (Local Area Network) port is where you |
|
connect your Router to a PC, hub, or switch. If you |
|
have more than one PC, connect an Ethernet hub or |
|
switch to your Router, then connect your PCs to that |
|
hub or switch. |
Power |
The Power port is where you will connect the |
|
power adapter. |
7 |
8 |

|
Instant Broadband Series |
Buttons & Switches |
|
The Reset Button |
Details on the Reset button are found in the Getting |
|
to Know the 4-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
|
section. |
The Crossover Switch
When“uplinking,” or connecting two pieces of network hardware together, such as a hub and a switch, a general rule of thumb is to plug one end of a network cable into a straight-through port, and the other end into a crossover port. Standard ports are straight-through ports, and uplink ports are crossover ports.
T h e 1 - Port
Note: The diagram above is for reference purposes only. Every network is different. If you do not make a connection to a hub or switch by using the settings above, change the position of the Crossover Switch.
The 1-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs
The LAN Indicators
Power |
Green. The Power LED lights up green when the Router is |
|
powered on. |
Link/Act |
Green. The Link/Act LED serves two purposes. If the LED |
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
is continuously lit up, the Router is successfully connected to a device through the LAN port. If the LED is flickering, the Router is actively sending or receiving data through the LAN port.
Full/Col Green. The Full/Col LED also serves two purposes. If this LED remains lit, a LAN port connection is being successfully maintained. If the LED flickers, the connection is experiencing collisions. Infrequent collisions are normal.
If this LED flickers too often, there may be a problem with your connection. See the Troubleshooting section if you encounter this problem.
10/100 Orange. The 10/100 LED lights up when a successful 100Mbps connection is made through the corresponding port.
If a connection is running at 10Mbps, the 10/100 LED will not light up.
The WAN Indicators
Link |
Green. The Link LED lights up when a successful connec- |
|
tion is made between the Router and your broadband device |
|
or network. |
Act |
Green. The Act LED flickers when the Router is sending or |
|
receiving data over the broadband WAN port. |
Diag |
Red. The Diag LED lights up when the Router goes through |
|
its self-diagnostic mode. It will turn off upon successful |
|
completion of the diagnosis. |
|
If this LED stays on for an abnormally long period of time, |
|
see the Troubleshooting section. |
9 |
10 |

Instant Broadband Series
Getting to Know the 3-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router
The 3-Port Router’s Rear Panel Ports
The 3-Port Router’s Ports |
|
Ports 1-3 |
These three LAN ports connect to your PCs, hubs, |
|
switches, print servers, or any other device with an |
|
Ethernet port. |
Uplink |
The Uplink port connects to another hub or switch |
|
for port expansion when you run out of open ports |
|
for your network devices. Since the Uplink port |
|
and the standard port right next to it share internal |
|
wiring, you can only use one of the two ports at a |
|
time. |
WAN |
This WAN port connects to your cable or DSL |
|
modem. Your modem connection will not work |
|
from any other port. |
Power |
The Power port is where you will connect the power |
|
adapter. |
USB |
The USB port (Type B - slave) can connect to a |
|
USB-ready PC or a USB hub. This allows you to |
|
enjoy an immediate, plug-and-play connection |
|
without even installing a network adapter for your |
|
PC. To work with USB ports, your PC must be run- |
|
ning Windows 98, 2000, or Millennium. |
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
USB ports do not work on PCs running
Windows 95 or Windows NT.
USB Compatibility with Your PC
To use the USB port on the 3-Port Router, you must have Windows 98, 2000, or Millennium installed on your PC. USB cannot run in a Windows 95 or NT environment.
Also, your PC must have a USB port installed and enabled. Some PCs may have a disabled USB port. If your port doesn’t seem to be working, there may be jumpers on the motherboard or a menu option in the BIOS to enable a PC’s USB port.
Other motherboards have USB interfaces, but no ports. You can install your own USB port and attach it to your PC’s motherboard using hardware purchased at retail computer stores. See your PC’s User Guide for instructions.
This USB icon denotes the presence of a USB port or connector.
Your 3-Port Router comes with a USB cable that has two different types of connectors. Type A, the master connector, is shaped like a rectangle and plugs into your PC’s USB port. Type B, the slave connector, resembles a square and connects to the USB port on the rear panel of your Router.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB Type A |
|
USB Type B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
12 |

|
Instant Broadband Series |
Buttons |
|
The Reset Button |
Details on the Reset button are found in the Getting |
|
to Know the 4-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router |
|
section. |
The 3-Port Router’s Front Panel LEDs
The LAN Indicators
Power |
Green. The Power LED lights up green when the Router is |
|
powered on. |
Link/Act |
Green. The Link/Act LED serves two purposes. If the LED |
|
is continuously lit up, the Router is successfully connected to |
|
a device through the corresponding RJ-45 port (1, 2, or 3). If |
|
the LED flickers, then that port is sending or receiving data |
|
to and from the network. |
Full/Col |
Green. The Full/Col LED also serves two purposes. If this |
|
LED is continuously lit up, the connection made through the |
|
corresponding port is successfully running in Full Duplex |
|
mode. If the LED is flickering, the connection is experien- |
|
ing collisions. Infrequent collisions are normal. |
|
If this LED flickers too often, there may be a problem with |
|
your connection. See the Troubleshooting section if you have |
|
problems. |
100Orange. The 100 LED lights up when a successful 100Mbps connection is made through the corresponding port. If this LED does not light up, then your connection speed is 10 Mbps.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
USB |
The USB LED lights up when the USB port is successfully |
|
connected to a PC, USB hub, or other USB device. |
The WAN Indicators |
|
Link |
Green. The Link LED lights up when a successful connec- |
|
tion is made between the Router and your broadband device |
|
or network. |
Act |
Green. The Act LED flickers when the Router is sending or |
|
receiving data over the broadband WAN port. |
Diag |
Red. The Diag LED lights up when the Router goes through |
|
its self-diagnostic mode. It will turn off upon successful |
|
completion of the diagnosis. |
If this LED stays on for an abnormally long period of time, see the Troubleshooting section.
13 |
14 |

Instant Broadband Series
Connecting the Cable/DSL Router to Your Network
Overview
Unlike a hub or a switch, the Cable/DSL Router’s setup consists of more than simply plugging hardware together. Since the Router acts as a DHCP server, you will have to set some values for the Router and also configure your networked PCs to accept the IP addresses that the Router assigns them.
You will need the following data from your ISP (Internet Service Provider) to install the Cable/DSL Router:
• Your broadband-configured PCs’ Computer Name and Workgroup Name
• Your broadband-configured PCs’ fixed Internet IP Address
• Your Subnet Mask |
} |
Only if applicable |
• Your Default Gateway |
|
|
• Your Primary DNS Server IP address(es) |
|
The installation technician from your ISP should have left this information with you after installating your broadband connection. If not, you can call your ISP to request the data.
Once you have the above values, you can begin the Installation and Setup of your EtherFast Cable/DSL Router.
LANs and WANs
Simply put, a router is a network device that connects two networks together.
In this instance, your EtherFast Cable/DSL Router connects your Local Area Network (LAN), or the group of PCs in your home or office, to the Wide Area Network (WAN), that is, the Internet. Your Router processes and regulates the data that travels between these two networks.
Think of your Router as a network device with two sides: the first side is made up of your private Local Area Network (LAN) of PCs, which this User Guide sometimes calls the “internal LAN.” The other, public side is the Internet, or the Wide Area Network (WAN), outside of your home or office.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Your Router’s firewall (NAT) protects your network of PCs with security so users on the public, Internet side cannot “see” your PCs. This is how your internal LAN, or network, remains private.
Remember that your Router’s ports connect to two sides: your 10/100 LAN port(s) and the Internet WAN port. The LAN port(s) transmit data at 10Mbps or 100 Mbps, whereas the broadband port, or WAN port, transmits data at 10 Mbps, because 10Mbps is currently the maximum speed for cable and DSL service.
IP Addressing: A Quick Lesson |
|
|
|
What’s an IP Address? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Since your Router is a device that con- |
||
|
|
nects two networks, it needs two IP |
|
IP stands for Internet Protocol. Every |
|
addresses - one for the LAN side, and |
|
device on an IP-based network, including |
|
one for the WAN side. In this User |
|
PCs, print servers, and routers, requires an |
|
Guide, you’ll see references to the |
|
IP address to identify its “location,” or |
|
“WAN IP address” and the “LAN IP |
|
address, on the network. Since the Internet |
|
address.” |
|
is simply one huge global network, every |
|
Since the Router has firewall security |
|
PC that logs on to the Internet also requires |
|
||
an IP address. |
|
(NAT), the only IP address that can be |
|
|
|
seen from the Internet for your net- |
|
There are two ways of assigning an IP |
|
work is the Router’s WAN IP address. |
|
address to your network devices. |
|
However, even this WAN IP address |
|
|
|
||
Static IP Addresses |
|
for the Router can be blocked, so that |
|
|
|
your Router and network seem invisi- |
|
A static IP address is a fixed IP address |
|
ble to the Internet - see the Blocking |
|
that you assign manually to a PC or other |
|
WAN Requests description under IP |
|
device on the network. Since a static IP |
|
Filtering. |
|
address remains valid until you disable it, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
static IP addressing insures that the device assigned it will always have that same IP address. Static IP addresses are commonly used with network devices such as server PCs or print servers.
If you use your Router to share your cable or DSL Internet connection, contact your ISP to find out if they have assigned a static IP address to your account. If so, you will need that static IP address when configuring your Router.
15 |
16 |
Instant Broadband Series
Dynamic IP Addresses
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network, such as PCs and print servers. These IP addresses are called “dynamic” because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or device. After a certain time period, they expire and may change.
If a PC logs on to the network (or the Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the DHCP server will assign it a new dynamic IP address.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Servers
PCs and other network devices using dynamic IP addressing are assigned a new IP address by a DHCP server. DHCP frees you from having to assign IP addresses manually every time a new user is added to your network.
DHCP servers can either be a designated PC on the network or another network device, such as the Cable/DSL Router.
By factory default, a DHCP server (LAN side) is enabled on your Router. If you already have a DHCP server running on your network, you must disable one of the two DHCP servers. If you run more than one DHCP server on your network,you will experience network errors, such as conflicting IP addresses. To disable DHCP on your Router, see the section on DHCP in The Cable/DSL Router’s Web-based Utility.
Even if you assign a static IP address to a PC, other PCs can still use DHCP’s dynamic IP addressing, as long as the static IP is not within DHCP range of the LAN IP Address.
If the dynamic IP addressing fails to provide a dynamic IP address for any reason, please refer to the Troubleshooting Section.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Connecting Your Hardware Together and Booting Up
1.Before you begin, make sure that all of your hardware is powered off, including your Router, PCs, hubs, switches, and the cable or DSL modem.
2.A. If you have the 4-Port Cable/DSL Router, connect one end of a network cable to one of the LAN ports (labeled 1, 2, 3, or 4) on the back of the Router, and the other end into a standard port on a network device, e.g., a PC, print server, hub, or switch. See the Twisted-Pair Cabling section for details on network cabling.
A standard port is any port other than the WAN port and the Uplink port. It’s a straight-through port.
Repeat the above step to connect more PCs or network devices to the Router.
2.B. If you are connecting the 1-Port Router to just one PC, plug one end of a network cable into the Router’s LAN port and the other end into the PC’s network adapter port. Set the Crossover Switch to crossover mode (X). If the crossover mode does not light up a Link LED, see the chart in the
Getting to Know the 1-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router section.
If you are connecting the 1-Port Router to a hub or switch, plug one end of a network cable into the Router’s LAN port, and the other end into to a standard port on your network’s hub or switch. Set the LAN port’s Crossover Switch to its straight-through (II) mode. Please refer to the chart in the
Getting to Know the 1-Port EtherFast Cable/DSL Router section.
If your hub or switch has no more standard ports available, connect the Router using its LAN port to the Uplink port on the hub or switch. Set the Crossover Switch to straight-through mode (II) for this set-up.
2.C. If you have the 3-Port Cable/DSL Router, connect one end of a network cable from the one of the Router’s LAN ports (labeled 1, 2, or 3) to a port on a PC, hub, switch, or other network device.
The 3-Port Router features one USB plug-and-play port that connects instantly to any USB-ready PC or hub. This allows you to connect to and access your Router without even installing any network cards.
17 |
18 |

Instant Broadband Series
3.Connect the network cable from your cable or DSL modem to the WAN port on your Router’s rear panel. This is the only port that will work for your modem connection.
4.Connect the power adapter to the Power port on the rear panel of the Router, then plug the power adapter into a power outlet.
 Note: It is highly recommended that you plug your Router into a power strip with surge protection.
Note: It is highly recommended that you plug your Router into a power strip with surge protection.
•The Power LED on the front panel will light up green as soon as the power adapter is connected properly.
•The Diag LED will light up red for a few seconds when the Router goes through its self-diagnostic test. This LED will turn off when the self-test is complete.
5.Power on the cable or DSL modem.
6.Press the Reset button on the Router’s front panel with a paper clip or a pencil. Hold the button in until the Diag LED lights up and then turns off. This will restore the Router’s factory default settings.
Technical Checkpoint:
Did you remember to check for Link LEDs for all your connections?
If all of your Link LEDs are not lighting up, make sure that all your cables are securely plugged in, and that all of your hardware is powered on properly.
The Router’s hardware installation is now complete!
Continue with the next section to configure the Router with your PCs.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
Uplinking: Connecting More Devices to Your Router
If your Router’s LAN ports are all full and you still have PCs and/or devices to connect, connect a hub or a switch to your Router.
To do so, use the Router’s Uplink port to connect to a standard port on a hub or switch. If you have a PC/device connected to the port right next to the Uplink port (on the 3- and 4-Port Routers), disconnect that PC/device and plug it into an open port on the new hub or switch.
Since the Uplink port shares internal wiring with the port right next to it, you can only use only one of these two ports at a time: these ports are called shared ports.
If your new hub or switch also has an Uplink port, it too can be uplinked when you next run out of ports, and so on.
Use the Router’s Uplink port to connect to a standard port on a hub or switch. This leaves you with new, open ports on the hub or switch, to which you can add more PCs and/or network devices.
See your nearest Linksys retailer or visit www.linksys.com for complete product lines of 10/100 Mbps hubs and switches.
19 |
20 |
Instant Broadband Series
Configuring the BEFSRU31’s
USB Port
Use the enclosed USB cable to connect your PC to the Router: the Type A end connects to your PC’s USB port, while Type B connects to the Router’s USB port. Now that all of your Router’s hardware is connected together, you must enable the PC that will connect to the Router through its USB port.
Since your USB connection acts as a network adapter for your PC, there’s no need for you to install a network adapter for that PC. Just follow the directions below to enable your PC’s USB connection to the Router:
•If you are running Windows 98, continue on this page, below.
•For other Windows operating systems, please refer to the apropriate section as listed in the Table of Contents.
After you finish this configuration, make sure that TCP/IP is installed on your PC(s). For instructions on installing TCP/IP, see the Installing the TCP/IP Protocol section in the Appendix.
You can also connect your Router’s USB port to other USB devices besides USB-ready PCs, such as USB hubs.
USB Configuration for Windows 98
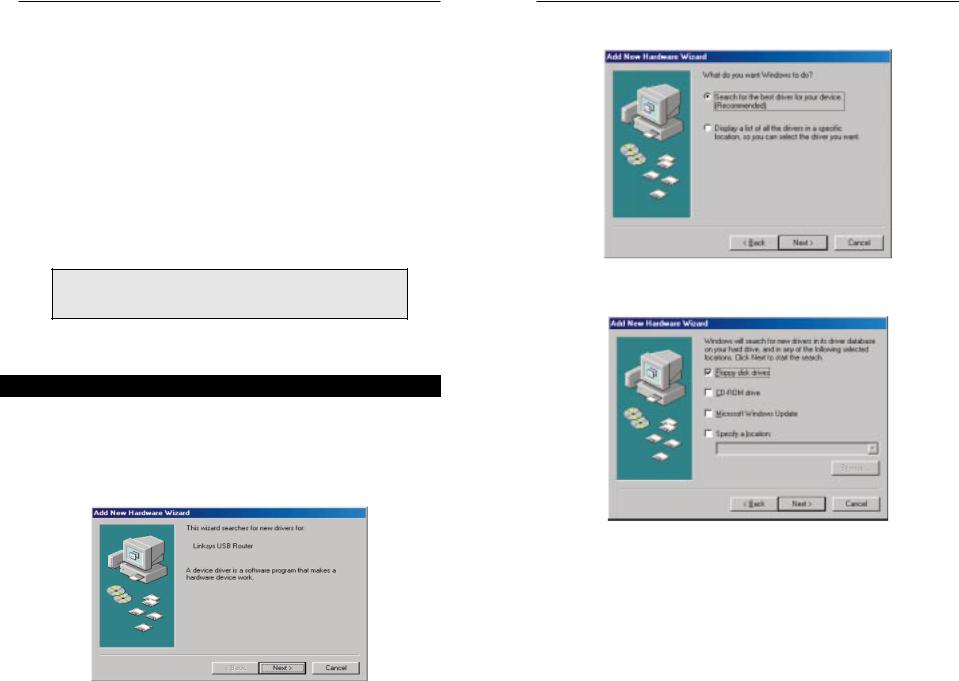
1.With the router connected to your PC’s USB port, start up your PC in Windows 98 and insert the driver diskette.
2.Windows will display a message saying that it has detected new hardware. Click the Next button.
EtherFast Cable/DSL Routers
3. Select “Search for the best driver for your device (Recommended).” Click the Next button.
4. Select “Floppy disk drives” and click the Next button to start the search for your driver.
21 |
22 |
 Loading...
Loading...