JBL DD67000, DD65000 User Manual

Project Everest
DD65000 & DD67000
Product Commentaries and User Guide

Thank you for purchasing a
JBL Project Everest loudspeaker system.
Before using the system, please take the time to read through this user guide to understand this loudspeaker well and also to use it properly.

TC |
|
Table of |
|
||
|
Contents |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Preface: ........................................................................ |
6 |
Chapter 1: |
|
Legacy.............................................................................. |
8 |
Chapter 2: |
|
The Project Everest DD65000 and DD67000 |
|
Loudspeakers – a Triumph in Acoustics |
|
and Technology........................................................ |
14 |
Chapter 3: |
|
Unpacking the Project Everest System............ |
22 |
Chapter 4: |
|
Selecting Speaker Wire.......................................... |
26 |
Chapter 5: |
|
Amplifier Recommendations.................................. |
28 |
Chapter 6: |
|
Placement and Setup Considerations................ |
30 |
Chapter 7: |
|
Project Everest Adjustments.............................. |
32 |
Chapter 8: |
|
Project Everest Connections.............................. |
38 |
Chapter 9: |
|
Project Everest Care and Maintenance............ |
44 |
Troubleshooting and Service Guide: ................... |
44 |
Project Everest DD67000 System |
|
Specifications: .............................................................. |
46 |
Project Everest DD65000 System |
|
Specifications: .............................................................. |
47 |
5

Preface
Thank you for selecting a Project Everest DD65000 or DD67000 loudspeaker system. These loudspeakers represent the culmination of our research and developmental efforts in sound reproduction over the last half century. We have endeavored to create loudspeaker systems with no acoustical or electrical limitations whatsoever.
However, it is the level of your listening pleasure that ultimately determines how successful we are in this endeavor. To ensure a perfect listening experience, we ask you to carefully follow the setup and operation procedures outlined in this Project Everest User Guide.
This guide serves several purposes. It contains all necessary background information and detailed instructions for setting up your Project Everest loudspeaker system, including unpacking the loudspeaker, selecting the correct location, choosing speaker wire, wiring method and amplification, and connecting the speakers to their associated electronics. This information is found in Chapters 3 through 8. In addition, we have included a detailed description of your Project Everest loudspeakers in Chapter 2, so that you may become thoroughly acquainted with their unique design and technical features.
Despite the formidable nature of Project Everest, the setup procedure for these loudspeaker systems is relatively simple. Again, we strongly urge you to read this guide thoroughly before you begin, and then consult it frequently throughout the process. Certain considerations must be made in placing the speakers; their physical characteristics make it imperative that you become familiar with the entire setup process in advance.
Also, we believe that the historical and technical information included will add immeasurably to your complete enjoyment of your system. As a loudspeaker, the Project Everest DD65000 and
DD67000 are unparalleled in the field of sound reproduction. The story and principles behind them are an interesting, informative and fitting start to a lifetime of musical enjoyment.
7

1 |
Legacy |
|
|
|
the Historical Development of |
|
the JBL Project Loudspeakers |
|
|
Of those who have sought perfection in sound reproduction, only a few have actually come close. For one thing, it is a costly process. It is rare indeed when an individual or group is able to triumph over the constraints of economic and technological realities even once.
At JBL, this has happened nine times. In each case, our engineers were told to build the speaker system they had always wanted to build. Whatever resources were required would be made available. Thus began an ongoing search for new frontiers in sound reproduction, beginning in the mid-1950s and continuing to the present day.
The products that have resulted from this venture are now known as the JBL Project loudspeakers. Each represents the absolute peak of every technological, material and engineering innovation available at the time, combined into a single loudspeaker system. They are Hartsfield, Paragon, Everest DD55000, K2 S9500/7500, K2 S5500, K2 S9800, K2 S5800, Project Everest DD66000 and K2 S9900.
Although differing in performance details and physical attributes, all of the Project loudspeakers have shared a common objective
– to elevate sound reproduction to levels defined only by the limitations of existing materials and technology. The fact that all Project loudspeakers have many common features, despite their having been created over a span of nearly sixty years, is a testimony to the excellence of the technology and manufacturing techniques upon which JBL was built.
Defining the Project Concept
The Hartsfield began a tradition at JBL that continues today. First, engineer a product as close to perfection as possible. When it reaches that level, make it better.
In 1954, the Hartsfield was significant in that it represented not new technology, but rather a new level of technical manufacturing, in the spirit of the approach pioneered by James B. Lansing some twenty years before. Like its Project series successors, it was a highefficiency system incorporating compression driver technology and combining the qualities of high-output, low-distortion, exceptional stereo imaging and fatigue-free listening. Most important, it was the first loudspeaker system available to consumers to do all this.
JBL’s president in 1954, William Thomas, described the Hartsfield as the “speaker system we have always wanted to build [with] the finest components ever made available to serious listeners.”
9
JBL Hartsfield

JBL-Ranger Paragon
He went on to describe the process behind the creation of the
Hartsfield: “Most people who own and appreciate fine sound reproduction equipment look forward to the day when they will be able to assemble a system without limitation in just exactly the way they think it should be done. Periodically a manufacturer gets this same feeling. The science of acoustics has provided us with the basic principles available to all for achieving precision reproduction. It is only a matter of incorporating these methods into a system design, and then taking every bit of trouble necessary to build a system precisely to the design.”
He added, “It isn’t easy, but that’s the way it is done.”
The Ranger-Paragon, JBL’s second Project system, was the first serious attempt at a reflecting speaker system, and broke ground in what was at the time, the new concept of stereo imaging. Basically two independent full-range speaker systems installed in a handsome, curved cabinet nearly 9 feet (2.7 meters) wide, the Paragon’s enclosure was treated as an extension of its transducers.
In essence, the system had its own “built-in acoustics.” In many respects, the Paragon anticipated loudspeaker developments that would occur years and even decades later. This “built-in acoustics” concept was present in the Project Everest DD66000 and has now been further refined in the DD65000 and DD67000.
For nearly 30 years, the Paragon remained one of the world’s most highly-regarded home loudspeaker systems. Today, along with the Hartsfield, the Paragon is still the most sought-after speaker in the world.
In 1986, JBL introduced a new Project system that retained the Paragon’s overall sense of musicality while upgrading its character by incorporating three decades’ worth of continuous development in every facet of its design. Its name – Project Everest – reflected
the pinnacle of achievement it represented. This was the original Project Everest DD55000.
For the first time, the rest of the sound reproduction chain – and not the loudspeaker or its transducers – would impose limits on overall system performance. Like the Paragon and Hartsfield,
Project Everest was built around compression driver technology and addressed a more refined stereo image than was previously considered technically feasible.
Since the original Project Everest was introduced, sound recording and playback technology has undergone a revolution of its own. With the advent of the CD, extremely demanding recorded signals became the rule rather than the exception – the typical source material used by the average audio enthusiast became superior to the best demonstration material of even just a few years prior. In overall dynamics and transient response, transducers became once again a potentially weak link in the high-end audio reproduction chain.
It was in this environment that JBL set out to create its fourth and fifth Project loudspeakers, K2 S9500 and K2 S5500. As with Hartsfield, the simplicity of a two-way system was considered the most promising design track. Advances in transducer design and low-frequency alignment would make possible the construction of a two-way system of unprecedented physical and acoustical scale. Our engineers took the core components – the low-frequency and high-frequency transducers – and optimized them by redesigning their magnetic structures, diaphragms and framework for greater linearity, dynamic capability and transient response.
In the years following the introduction of the K2 S9500 and K2
S5500, sound reproduction technology underwent another series of revolutionary changes, with the introduction of DVD-Video,
Dolby® Digital, DTS®, DVD-Audio and Super Audio CD (SACD™). Frequency responses to 50kHz, as well as three-digit dynamic range and signal-to-noise ratio specifications have now become commonplace. To faithfully reproduce such robust sonic properties, the loudspeaker needed to undergo drastic improvements to its transducer, network and enclosure technologies.
The K2 S9800 employed a three-way design, incorporating an ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) compression driver and horn to reproduce high frequencies up to 50kHz. With the UHF driver handling the higher frequencies, the high-frequency (HF) transducer could then be upgraded to a new design using a 3-inch (75mm) diaphragm, which improved reproduction of lower frequencies and blended better with the woofer than the older generations’ 2-inch (50mm) diaphragm did. Both of these
new compression drivers utilized newly developed beryllium diaphragms to provide the lowest distortion and flattest frequency response possible.
To recreate the extremely high dynamic range provided by today’s audio sources, a brand-new low-frequency transducer was developed from the ground up, utilizing an Alnico magnet, a 4-inch (100mm) edge-wound voice coil, and a 15-inch (380mm) cone. Extensive computer-aided engineering and design effort was necessary to develop the optimized port tuning employed in Project K2 S9800, and resulted in a significant advance in the concept of state-of-the-art acoustic reproduction. As a result of these efforts, a loudspeaker system with higher sensitivity and a wider dynamic range became a reality without power compression or distortion, even at extremely high drive levels.
10 11
JBL Everest DD55000

JBL K2 S9500
The development of the Project Everest DD66000 loudspeaker system was undertaken as a celebration of JBL’s 60th anniversary and as a realization of the potential engendered by the breakthroughs discussed above. The stately character of the
Hartsfield, exceptional wood craftsmanship of the Paragon, the “built-in acoustics” which treat the enclosure as an extension of the transducers, and the state-of-the-art transducer technologies that were built up from two generations of the Project K2 developments were all poured into this new challenge to extend the acoustic and electrical possibilities in this Project Everest model.
12
JBL K2 S9800
Despite its 21st century power and sophistication, Project Everest
DD66000 was a synthesis of tradition and technology. It reflected the design, material, engineering and manufacturing expertise developed and refined through nearly six decades of experience that are the exclusive legacy of one loudspeaker builder – JBL. And now, with the introduction of the Project Everest DD65000 and DD67000 JBL presents additional refinements that enable these loudspeakers to outshine even the stellar performance standard set by the DD66000 system.
JBL Project Everest DD66000
2 |
Project Everest |
||
|
|||
|
a Triumph in Acoustics |
||
|
and Technology |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
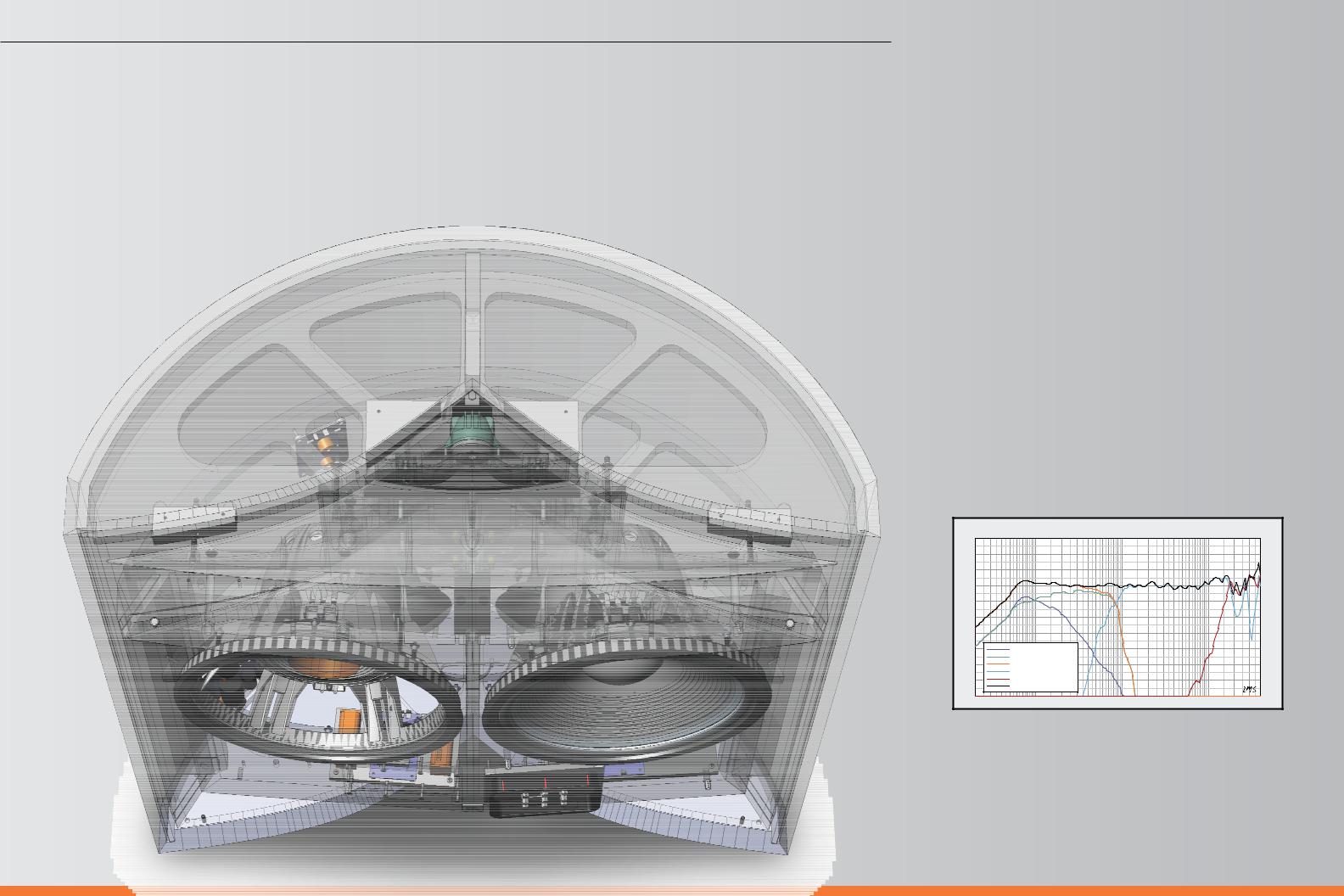
This chapter describes the primary features and components of the Project Everest
DD65000 and DD67000 loudspeaker systems.
The basic system configuration is what JBL historically has referred to as an “augmented two-way”. In the 1950s and 1960s, JBL primarily built two-way systems with a 12-inch or
15-inch (305mm or 380mm) woofer crossed over to a large-format compression driver/ horn combination. Some of the systems would be “augmented” by a UHF device, usually the 075 ring radiator which would operate above 8kHz. These systems would have only a single crossover point in the middle of the audio range, to minimize any sonic degradation caused by the dividing network.
The DD65000 and DD67000 both have a single midrange crossover point – the DD65000 at 750Hz and the DD67000 at 850Hz – blending one 1501 woofer to the 476 compression driver and horn combination. The 045 UHF driver is brought in at 20kHz to cover an octave and a half of ultrasonic frequencies. A second 1501 woofer operates in the bass frequency range from below 30Hz to around 150Hz, where it is rolled off at a gradual 6dB/octave. This first-order slope ensures proper amplitude and phase summing between the two woofers over their entire operating range. Both woofers operate below 150Hz, but only one of them extends up to the midrange crossover point. This is done to achieve proper directivity control throughout the entire woofer operating range, while delivering powerful and extended low-frequency performance. Above the midrange crossover point, the HF compression driver and horn combination operates unassisted, all the way to 20kHz (see graph, below).
SPL vs Freq
110 dBSPL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
105 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
|
DD67000 LF1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD67000 LF2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
DD67000 LF Combined |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD67000 HF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65 |
|
DD67000 UHF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD67000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6020Hz |
50 |
100 |
200 |
500 |
1k |
2k |
5k |
10k |
20k |
40k |
On-axis response of the DD67000 system and of each transducer through its crossover network (2.83V @ 1m)
15
 Loading...
Loading...