Husqvarna 340, CARB 340, 345, 346XP, 350 User Manual
...
Workshop manual
340 345 346XP
350 351 353
English

Workshop manual Husqvarna 340/345/346XP/350/351/353
Contents |
|
Introduction ........................................................... |
2 |
Safety regulations ................................................. |
3 |
General instructions ........................................... |
3 |
Special instructions ............................................ |
3 |
Special tools .......................................................... |
4 |
Technical data ....................................................... |
6 |
Construction and function ................................... |
8 |
Carburettor ......................................................... |
8 |
Troubleshooting .................................................. |
10 |
Repair instructions ............................................. |
12 |
Chain brake ...................................................... |
12 |
Silencer ............................................................ |
14 |
Chain catcher ................................................... |
14 |
Stop switch ....................................................... |
15 |
Stop switch – resistance measurement ........... |
15 |
Choke control ................................................... |
16 |
Throttle trigger .................................................. |
17 |
Hand grip heater .............................................. |
18 |
Starter assembly .............................................. |
21 |
Starter cord ...................................................... |
21 |
Recoil spring .................................................... |
22 |
Ignition module – testing .................................. |
23 |
Ignition module and flywheel ............................ |
23 |
Generator ......................................................... |
24 |
Centrifugal clutch ............................................. |
26 |
Oil pump ........................................................... |
27 |
Carburettor ....................................................... |
30 |
Carburettor – pressure testing ......................... |
33 |
Carburettor heater ............................................ |
34 |
Air intake system .............................................. |
35 |
Carburettor – adjustment ................................. |
37 |
Fuel tank .......................................................... |
38 |
Fuel filter .......................................................... |
39 |
Fuel hose ......................................................... |
39 |
Piston and cylinder ........................................... |
41 |
Decompression valve – pressure testing ......... |
42 |
Cylinder – pressure testing .............................. |
44 |
Crankcase and crankshaft ............................... |
45 |
Crankshaft bearings ......................................... |
46 |
Repairing damaged threads ............................. |
49 |
Thread insert .................................................... |
49 |
Guide bar bolts ................................................. |
49 |
Appendix A, Carburettor – EPA models ........... |
50 |
English – 1

Introduction
Arrangement of the manual
This workshop manual can be used in two different ways.
•To repair a specific sub-assembly on a chainsaw.
•To dismantle and reassemble a complete chainsaw.
Repairing a specific sub-assembly
If a specific sub-assembly on the chainsaw needs to be repaired:
1.Look up the page referring to the relevant subassembly.
2.Follow the instructions under the headings: Removal/Dismantling
Cleaning and inspection Refitting/Reassembly
Dismantling and reassembling the entire chainsaw
If the entire chainsaw is to be dismantled, follow the instructions under the heading “Removal/ Dismantling”.
Work through the manual and follow the instructions given in each section under the heading “Removal/Dismantling”.
Then follow all the “Cleaning and inspection” instructions in each section.
Working from the back of the manual, follow all the instructions under the headings “Refitting/ Reassembly” in reverse order.
Each of the sections covering removal/dismantling and refitting/reassembly include the relevant lubrication instructions and bolt torques for each stage of repair.
Construction and function
This chapter gives a simple description of the chainsaw carburettor and its various parts.
Troubleshooting
These pages describe the most common faults that affect a chainsaw. They are divided into four different groups with the most likely faults described first.
Repair instructions
The section that describes how to repair the chainsaw consists of detailed, step-by-step instructions. It explains in detail the special tools, lubricants and bolt torques that are needed when working on each component.
This workshop manual covers the following chainsaw models:
340
345
346XP
350
351
353
2 – English

Safety regulations
General instructions
This workshop manual gives detailed instructions on how to troubleshoot, repair and test a chainsaw. This section also describes the various safety precautions that should be taken when carrying out repairs.
The workshop manual has been written for personnel who are assumed to have general experience of repairing and servicing chainsaws.
Workshops where chainsaws are repaired must be equipped with safety equipment that meets local regulations.
No-one should carry out repairs on a chainsaw until they have read and understood the contents of this workshop manual.
Chainsaws are type-approved to meet the relevant safety legislation, but this only applies when the saw is fitted with the cutting equipment specified in the user’s manual. The fitting of any other equipment, or of accessories or parts that are not approved by Jonsered, could mean that the saw no longer meets these safety requirements and the person who carried out the work may be held responsible for its non-conformance.
In this workshop manual the following boxes indicate where caution should be taken.
WARNING!
The warning text warns of the risk of personal injury if the instructions are not followed.
Special instructions
The fuel that is used in a chainsaw poses the following hazards:
•The fuel and its fumes are toxic.
•May cause irritation to skin or eyes.
•May cause breathing difficulties.
•Highly flammable.
When using compressed air the air jet should never be pointed at the body. Air can be forced into the bloodstream and cause fatal injury.
Wear ear protection when testing saws.
After testing a saw do not touch the silencer until it has cooled down. The silencer gets very hot and you may burn yourself. Wear protective gloves when working on the silencer.
The guide bar, chain and clutch cover (chain brake) must be fitted before the saw is started. If not, the clutch may come loose and cause injury.
Poor chain lubrication can result in failure of the chain, which could cause serious or fatal injury.
Take care to ensure that the spring inside the starter assembly does not fly out and cause injury. Wear eye protection. If the spring is under compression when the pulley is removed it could fly out and cause injury.
Before removing the tensioning spring from the chain brake, ensure that the brake is in the on position, otherwise the spring may fly out and cause injury.
NOTE!
The warning text warns of the risk of material damage if the instructions are not followed.
After completing the repair the chain brake must be tested, see “Chain brake – reassembly \ Operating test”.
Always consider the fire risk. A chainsaw can produce sparks that could start a fire.
Inspect the chain catcher and replace it if it is damaged.
English – 3
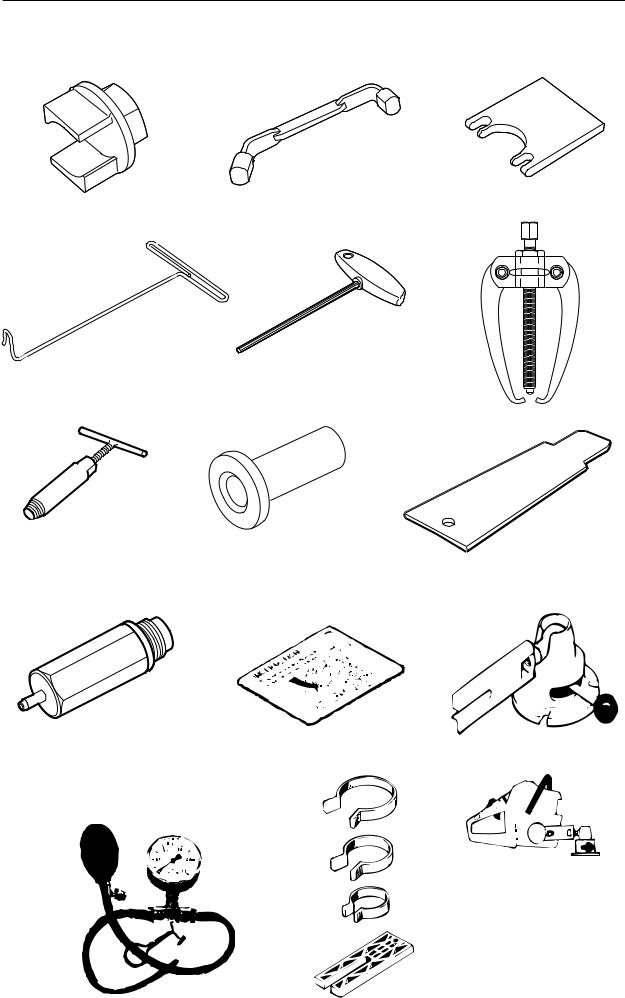
Special tools
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
4 – English
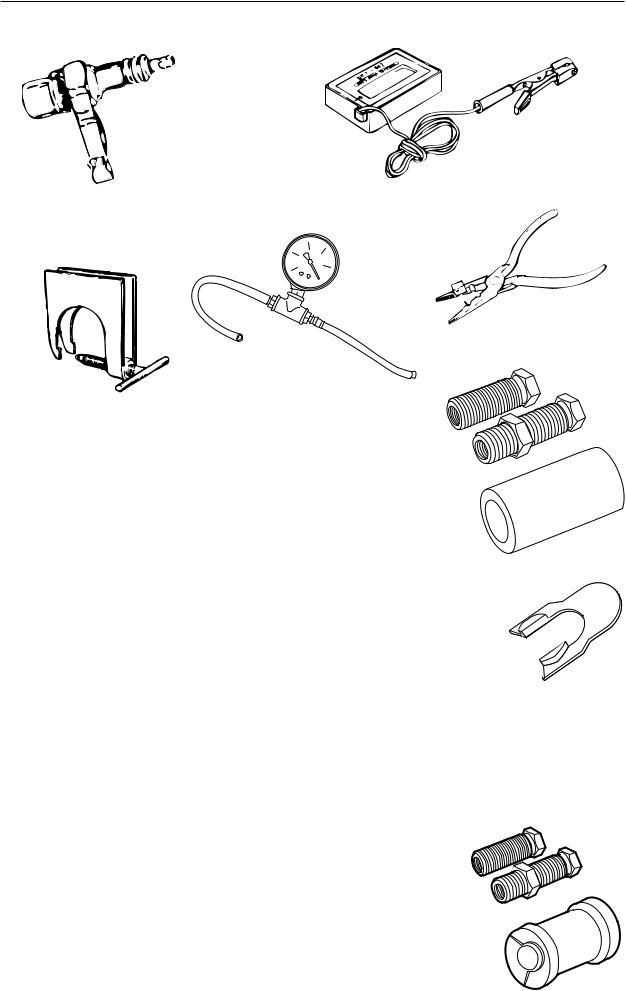
Special tools
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 b
20 c
Item |
Description |
Used for |
Order no. |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Clutch tool |
Centrifugal clutch |
502 54 16-01 |
2 |
Piston stop |
Locking crankshaft |
502 54 15-01 |
3 |
Stop plate |
Locating intake gaiter |
502 54 17-01 |
4 |
Fuel filter hook |
Withdrawing the fuel filter |
502 50 83-01 |
5 |
Allen key |
For M5 bolts |
502 50 18-01 |
6 |
Puller |
Frame bearing |
504 90 90-02 |
7 |
Removal tool |
Remove seal from clutch side |
502 50 55-01 |
8 |
Mandrel, sealing ring |
Removing crankshaft |
502 54 21-01 |
9 |
Cover plate |
Sealing during pressure testing |
502 54 11-02 |
10 |
Pressure tester |
Connection to cylinder |
503 84 40-02 |
11 |
Feeler gauge |
Adjusting ignition module |
502 51 34-02 |
12 |
Clamp stand |
Clamping the saw |
502 51 02-01 |
13 |
Pressure gauge |
Pressurisation during testing |
502 50 38-01 |
14 |
Piston fitting kit |
Fitting piston |
502 50 70-01 |
15 |
Test plug |
Checking ignition module |
502 71 13-01 |
16 |
Rev counter |
Adjusting carburettor |
502 71 14-01 |
17 |
Removal tool |
Removing crankshaft |
502 51 61-01 |
18 |
Vacuum gauge |
Vacuum test |
502 50 37-01 |
19 |
Assembly pliers |
Fitting spark plug guard |
502 50 06-01 |
20a |
Sleeve |
Fitting crankshaft |
502 50 30-18 |
20b |
Shaft extension |
Flywheel side |
502 50 30-18 |
20c |
Shaft extension |
Clutch side |
502 50 30-18 |
21 |
Stop plate |
Removing crankshaft |
502 54 18-01 |
22 |
Assembly tool |
Assembling spring, chain brake |
502 50 67-01 |
23 |
Crankshaft tool |
Fitting crankshaft seal |
502 50 30-16 |
|
|
|
|
20 a
21
23
English – 5

Technical data
|
Displacement |
Cylinder bore |
Stroke |
Max power/speed |
|
cm3/cubic inches |
Ø mm/Ø inches |
mm/inches |
kW/hp/rpm |
340: |
40,8 / 2,44 |
40 / 1,57" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,0 / 2,7 / 9 000 |
345: |
45,0 / 2,75 |
42 / 1,65" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,2 / 3,0 / 9 000 |
346XP/G: |
45,0 / 2,75 |
42 / 1,65" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,5 / 3,4 / 9 600 |
350: |
49,4 / 3,01 |
44 / 1,73" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,3 / 3,1 / 9 000 |
350 EPA: |
51,7 / 3,15 |
45 / 1,77" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,3 / 3,1 / 9 000 |
351/G: |
49,4 / 3,01 |
44 / 1,73" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,3 / 3,1 / 9 000 |
353/G: |
51,7 / 3,15 |
45 / 1,77" |
32 / 1,28" |
2,4 / 3,3 / 9 000 |
|
Spark plug gap |
Ignition system |
Air gap |
Carburettor type |
||
|
mm/inches |
|
mm/inches |
|
||
340: |
0,5 |
/ 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 |
/ 0,012" |
Walbro HDA 195 |
345: |
0,5 |
/ 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 |
/ 0,012" |
Walbro HDA 195 |
346XP/G: |
0,5 / 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 / 0,012" |
Zama C3-EL17 |
||
350: |
0,5 / 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 / 0,012" |
Walbro HDA 195 |
||
350 EPA: |
0,5 / 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 / 0,012" |
Zama C3-EL18 |
||
351/G: |
0,5 / 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 / 0,012" |
Zama C3-EL17 |
||
353/G: |
0,5 / 0,02" |
SEM CD |
0,3 / 0,012" |
Zama C3-EL17 |
||
Effective cutting length |
Chain speed at |
Chain pitch |
Drive link |
|
|
cm/inches |
max power – revs |
mm/inches |
mm/inches |
|
|
m/s – rpm |
|
|
340: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
345: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
346XP/G: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
18,5 / 9 600 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
350: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
350 EPA: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
351/G: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
353/G: |
30-48 / 12"-19" |
17,3 / 9 000 |
8,25 / 0,325" |
1,3 / 0,050" - 1,5 / 0,058" |
6 – English
Technical data
rpm
|
Idling speed |
Engagement speed |
Max. speed |
Spark plug |
||
|
rpm |
rpm |
rpm |
|
||
340: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
12 500 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
345: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
12 500 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
346XP/G: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
14 200 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
350: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
13 000 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
350 EPA: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
13 000 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
351/G: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
13 000 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
353/G: |
2 700 |
3 800 |
13 000 |
NGK BPMR 7A, Champion RCJ 7Y |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAS |
|
OIL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel tank capacity |
Oil pump capacity at |
Oil tank capacity |
Automatic oil pump |
|
Litres/US pints |
8,500 rpm, |
Litres/US pints |
|
|
|
ml/min |
|
|
340: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
9 |
0,25 / 0,53 |
Yes |
345: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
9 |
0,25 / 0,53 |
Yes |
346XP/G: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
5 - 12 |
0,28 / 0,59 |
Yes |
350: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
5 - 12 |
0,26 / 0,55 |
Yes |
350 EPA: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
5 - 12 |
0,26 / 0,55 |
Yes |
351/G: |
0,5 / 1,05 |
5 - 12 |
0,28 / 0,59 |
Yes |
353/G: |
0,5 / 1,06 |
5 - 12 |
0,28 / 0,59 |
Yes |
|
Weight without bar and chain |
Weight with bar and chain |
Heated hand grips |
|
kg / lbs |
kg / lbs |
|
340: |
4,7 / 10,3 |
5,5 / 12,1 |
- |
345: |
4,7 / 10,3 |
5,5 / 12,1 |
- |
346XP: |
4,8 / 10,6 |
5,6 / 12,2 |
- |
346XPG: |
4,9 / 10,8 |
5,7 / 12,4 |
Yes |
350: |
4,8 / 10,6 |
5,6 / 12,2 |
- |
350 EPA: |
4,8 / 10,6 |
5,6 / 12,2 |
- |
351: |
4,8 / 10,6 |
5,6 / 12,2 |
- |
351G: |
4,9 / 10,8 |
5,7 / 12,4 |
Yes |
353: |
5,0 / 11,0 |
5,8 / 12,6 |
- |
353G: |
5,1 / 11,2 |
5,9 / 13,0 |
Yes |
English – 7
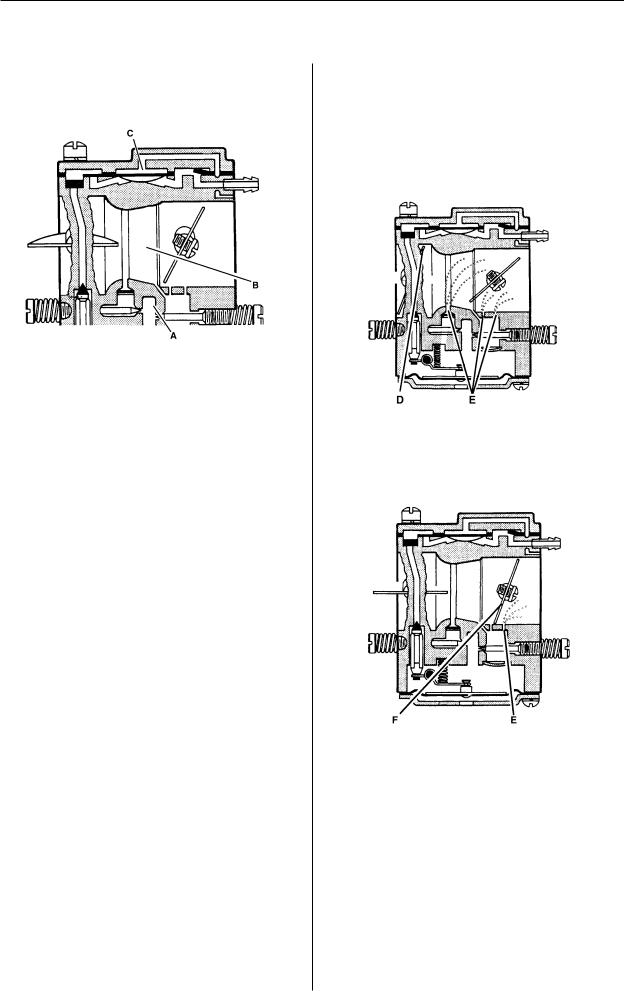
Construction and function
Carburettor
The carburettor consists of three sub-systems:
•The metering unit (A) which contains the jets and the fuel control mechanism. This measures out the right amount of fuel to suit the speed of the saw and the power demand.
•The mixing unit (B) consists of the choke, diffuser jets and throttle valve. This is where the air and fuel are mixed to create a flammable mixture.
•The pump unit (C) pumps fuel from the tank to the metering system inside the carburettor. One side of the pump diaphragm is connected to the crankcase and pulses as a result of pressure changes in the crankcase. The other side of the diaphragm sucks in the fuel.
The carburettor works in different ways depending on the setting:
•Cold start mode
•Idling mode
•Part throttle mode
•Full throttle mode
In the cold start mode the choke valve (D) is completely closed. This increases the vacuum in the carburettor so that fuel is sucked through the diffuser jets faster (E).
In idling mode the throttle valve (F) is closed. Air is sucked through an aperture in the throttle valve and a small amount of fuel is supplied through the diffuser jet (E).
8 – English
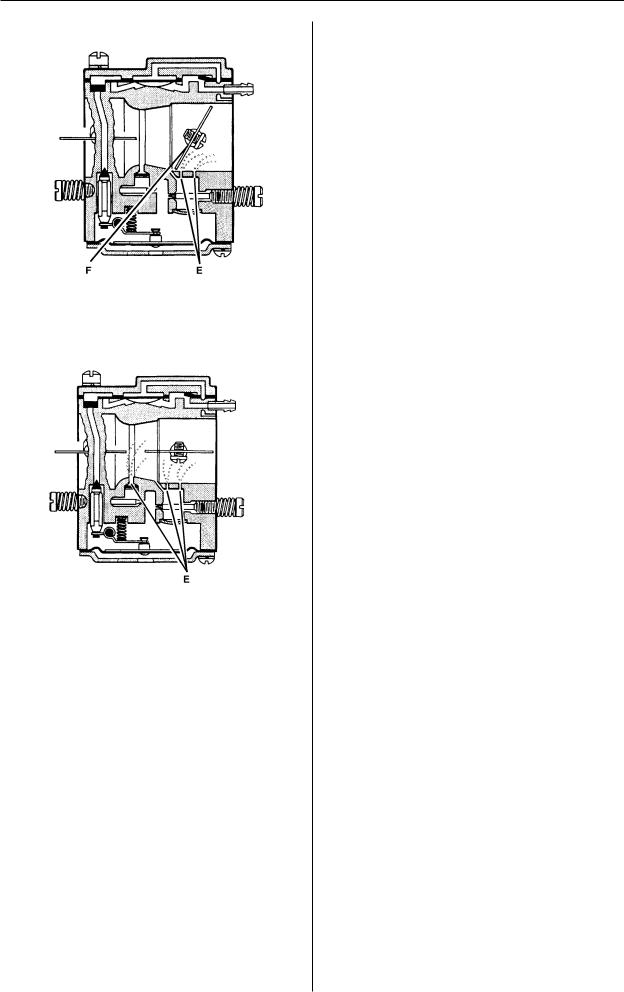
Construction and function
In part throttle mode the throttle valve (F) is partially open. Fuel is supplied through the diffuser jets
(E).
In full throttle mode both valves are open and fuel is supplied through all the diffuser jets (E).
English – 9

Troubleshooting
The various faults that can affect a chainsaw are divided into four groups. In each group the likely symptoms are given on the left and possible causes are listed on the right. The most likely faults are given first, and so on.
Starting
Difficulty starting |
Adjust L screw |
|
Air filter blocked |
|
Choke not working |
|
Worn choke pivot |
|
Worn choke valve |
|
Fuel filter blocked |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Piston ring seized |
|
Blocked impulse channel |
|
|
Carburettor |
Loose or faulty fuel pipe |
leaking fuel |
Hole in diaphragm |
|
Worn needle valve |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Needle valve set too high |
|
Leak in metering system (air |
|
or fuel) |
|
Loose cover on carburettor |
|
pump side |
|
|
Flooding when |
Worn needle valve |
engine not |
Needle valve set too high |
running |
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
|
Idling (low rpm) |
|
|
|
Will not idle |
Adjust L screw |
|
Leaking air intake hose |
|
(rubber) |
|
Loose carburettor mounting |
|
bolts |
|
Loose or faulty fuel hose |
|
Fuel filter blocked |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Fuel tank vent blocked |
|
Throttle valve pivot stiff |
|
Throttle pushrod sticking |
|
Defective throttle return spring |
|
Bent throttle stop |
|
Faulty diffuser jet |
|
|
Idling too rich |
Adjust L screw |
|
Worn needle valve |
|
Needle valve set too high |
|
Worn needle valve lever |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/ |
|
cover plate |
|
Needle valve assembly |
|
sticking |
|
|
Idling (low rpm) (cont.)
Idles when L |
Worn needle valve |
screw closed |
Leaking control diaphragm/ |
|
cover plate |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Worn needle valve lever |
|
Faulty diffuser jet |
|
|
Idling uneven |
Fuel filter blocked |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Leaking air intake hose (rubber) |
|
Loose carburettor mounting |
|
bolts |
|
Worn throttle valve pivot |
|
Loose throttle valve screw |
|
Worn throttle valve |
|
Needle valve assembly |
|
sticking |
|
Leak in metering system (air |
|
or fuel) |
|
Metering system centre knob |
|
is worn |
|
Hole in diaphragm |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/ |
|
cover plate |
|
Crankcase leaking |
|
|
L screw requires |
Fuel line blocked |
constant |
Needle valve set too high |
adjustment |
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Leak in metering system (air |
|
or fuel) |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/ |
|
cover plate |
|
Faulty diffuser jets |
|
Crankcase leaking |
|
|
Too much fuel at |
Needle valve set too high |
idling |
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Metering system damaged |
|
Worn needle valve |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/ |
|
cover plate |
|
Metering system incorrectly |
|
assembled |
|
|
10 – English

Troubleshooting
High rpm
Will not run at |
Adjust H screw |
full throttle |
Blocked air filter |
|
Blocked fuel tank vent |
|
Blocked fuel filter |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Loose or damaged fuel hose |
|
Impulse channel leaking |
|
Impulse channel blocked |
|
Loose cover on carburettor pump |
|
side |
|
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Leaking air intake hose (rubber) |
|
Loose carburettor mounting bolts |
|
Needle valve set too low |
|
Metering system damaged |
|
Metering system incorrectly |
|
assembled |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/cover |
|
plate |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Blocked silencer |
|
|
Low power |
Adjust H screw |
|
Blocked fuel tank vent |
|
Blocked fuel filter |
|
Impulse channel leaking |
|
Impulse channel blocked |
|
Loose cover on carburettor pump |
|
side |
|
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Blocked air filter |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Leak in metering system (air or fuel) |
|
Metering system incorrectly |
|
assembled |
|
Loose diaphragm rivet |
|
Hole in diaphragm |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/cover |
|
plate |
|
|
Will not “four- |
Blocked fuel tank vent |
stroke” |
Blocked fuel filter |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Loose or damaged fuel hose |
|
Impulse channel leaking |
|
Impulse channel blocked |
|
Loose cover on carburettor pump |
|
side |
|
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Leaking air intake hose (rubber) |
|
Loose carburettor mounting bolts |
|
Needle valve set too low |
|
Leak in metering system (air or fuel) |
|
Metering unit incorrectly assembled |
|
Loose diaphragm rivet |
|
Hole in diaphragm |
|
Leaking control diaphragm/cover |
|
plate |
|
|
Acceleration and retardation
Does not |
Adjust L screw |
accelerate |
Adjust H screw |
|
Blocked air filter |
|
Blocked fuel tank vent |
|
Blocked fuel filter |
|
Fuel line blocked |
|
Loose or damaged fuel hose |
|
Impulse channel blocked |
|
Loose cover on carburettor pump |
|
side |
|
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Leaking air intake hose (rubber) |
|
Loose carburettor mounting bolts |
|
Needle valve set too low |
|
Metering system incorrectly |
|
assembled |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Faulty diffuser jets |
|
Blocked silencer |
|
|
Engine stalls |
Adjust L screw |
when throttle |
Adjust H screw |
released |
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Needle valve set too high |
|
Needle valve assembly sticking |
|
Faulty diffuser jets |
|
|
Over rich |
Adjust L screw |
acceleration |
Adjust H screw |
|
Blocked air filter |
|
Faulty pump diaphragm |
|
Faulty diffuser jets |
|
|
Troubleshooting methods
In addition to the faults described in the above table, trouble shooting can be carried out on specific components or sub-systems of the chainsaw. The various procedures are described in the relevant chapters, see the contents page, as follows:
•Checking the operation of the chain brake
•Measuring the resistance of the stop plate
•Pressure testing the carburettor
•Pressure testing the decompression valve
•Pressure testing the cylinder
English – 11
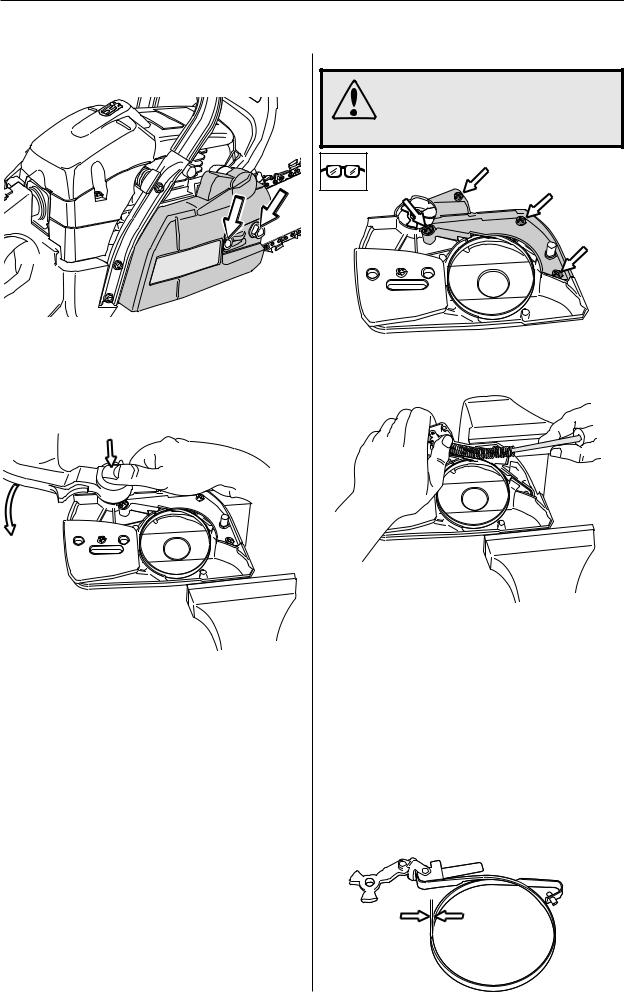
Repair instructions
Chain brake – dismantling
1
Disengage the brake by pushing the kickback guard backwards. Unscrew the guide bar bolts and remove the clutch cover, chain and guide bar.
2
Grip the clutch cover carefully in a vice. Release the brake spring by using the kickback guard from the saw as a tool. Engage it with the brake mechanism and turn anticlockwise to activate the brake.
3
WARNING!
Make sure the spring does not fly out and cause injury. Wear eye protection.
Remove the screws and carefully remove the cover from the chain brake spring.
4
Place one hand over the spring and insert a small screwdriver between the bottom end of the spring and the clutch cover. Carefully prise the spring upwards so that it slides onto the screwdriver shaft.
Cleaning and inspection
•Clean and inspect all parts carefully. If there are any cracks or other defects replace the damaged parts with new ones. Always use original parts.
•Measure the thickness of the chain brake band. It must be no less than 0.6 mm at any point.
•Lubricate the elbow joint with grease.
min 0,6 mm
12 – English
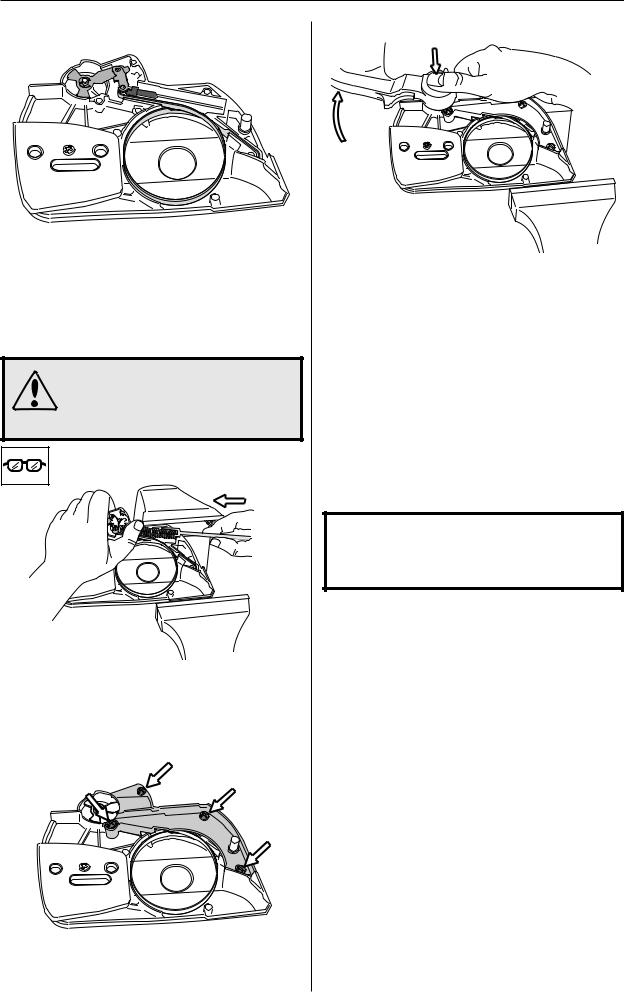
Repair instructions
Chain brake – reassembly
1
Bolt the elbow joint to the brake band and tighten to a torque of 1–1.5 Nm.
Locate the elbow joint and connected brake band in their recesses in the clutch cover. Lubricate the recess for the spring with grease.
2
WARNING!
Make sure the spring does not fly out and cause injury. Wear eye protection.
Grip the clutch cover in a vice. Compress the spring with special tool 502 50 67-01 and push it down with your thumb.
3
Fit the cover over the chain brake spring, tightening the screws to a torque of 1–1.5 Nm.
4
Tension the brake spring by using the kickback guard from the saw as a tool. Engage it with the brake mechanism and turn clockwise to release the brake.
5
Turn the chain tensioner anticlockwise as far as it will go.
Refit:
•guide bar
•chain
•clutch cover
NOTE!
After completing the repair the chain brake must be tested as described below.
Operating test:
The engine must not be running during the test.
Guide bar length |
Height |
|
|
38cm/15" |
50 cm/20" |
|
|
•Hold the chainsaw over a firm surface. The height of the guide bar above the surface is given in the table above.
•Let go of the front handle and let the chainsaw fall towards the surface.
•When the guide bar hits the surface the chain brake must engage.
English – 13
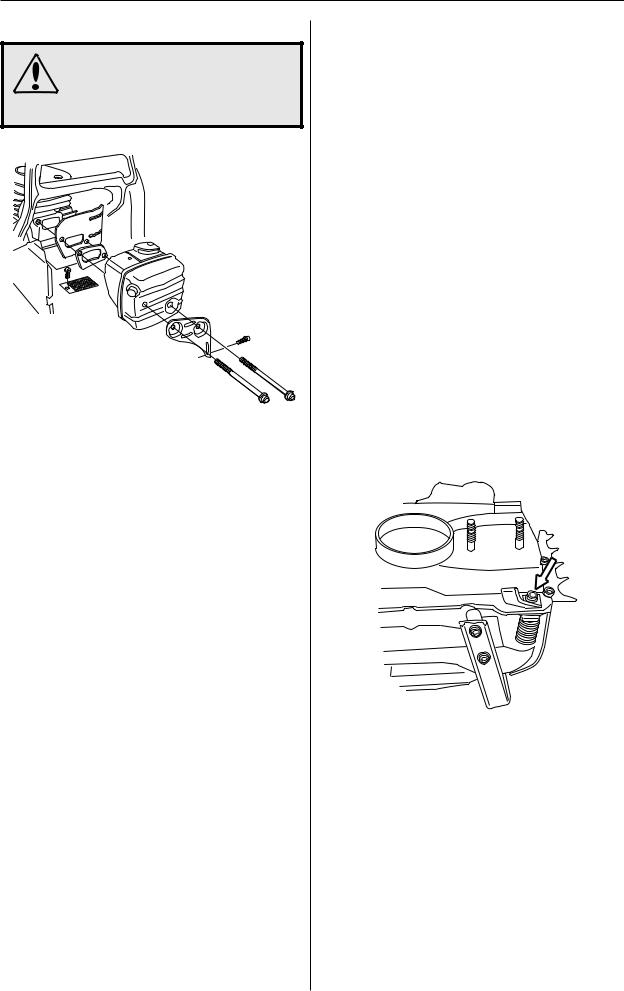
Repair instructions
Silencer – removal
WARNING!
Do not touch the silencer until it has cooled down, otherwise you may burn yourself.
1
Remove the cylinder cover, silencer support, silencer, gasket and cooling plate.
2
If the saw is fitted with a spark arrestor mesh this must also be removed.
Cleaning and inspection
Clean and inspect all parts carefully. If there are any cracks or other defects replace the damaged parts with new ones.
The spark arrestor mesh is best cleaned with a wire brush. If the mesh is damaged it must be replaced.
If the mesh is blocked the saw will overheat and this will cause damage to cylinder and piston. Never use the saw with a silencer that is in poor condition. Always use original parts.
Silencer – refitting
1
If the saw is equipped with a spark arrestor mesh this should be fitted first.
2
Refit
•cooling plate
•gasket
•silencer, tighten bolts to a torque of 8–10 Nm.
•silencer support
•cylinder cover
3
Run the saw for at least 1 minute, then retighten the silencer bolts to 8–10 Nm.
Chain catcher – replacement
If the chain catcher is worn it must be replaced with a new one.
1
Release the brake by pushing the kickback guard backwards. Undo the guide bar bolts and remove the clutch cover, chain and guide bar.
2
Remove the chain catcher and replace it with a new one. Check that the vibration damping spring locates correctly against the crankcase when you bolt the new chain catcher in position.
A worn (damaged) chain catcher on 340, 345 or 350 can be replaced with the same chain catcher as 346XP, 351 and 353 (see figure above).
3
Turn the chain tensioner anticlockwise as far as it will go.
Refit:
•guide bar
•chain
•clutch cover
14 – English
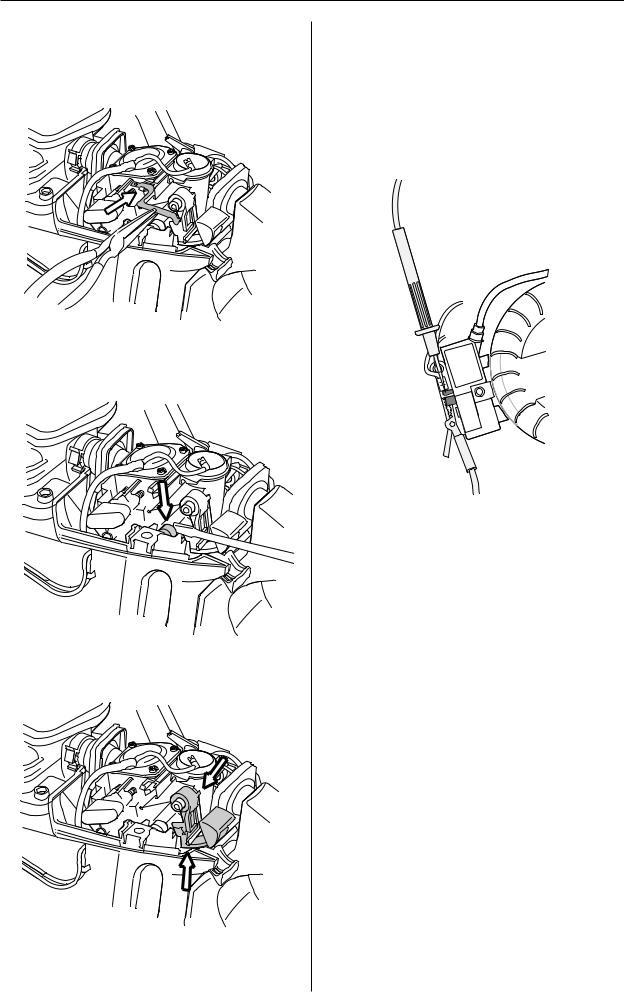
Repair instructions
Stop switch – removal
1
Remove the cylinder cover and air filter.
2
Disconnect both leads from the stop plate and stop switch. Remove the stop plate by carefully sliding it over the lug on the front mounting.
3
Carefully prise the carburettor assembly off the lefthand rubber mounting using a small screwdriver.
4
Carefully prise the stop switch’s upper mounting off the air filter holder while lifting the switch to release it from the lower mounting.
Cleaning and inspection
Clean and inspect all parts carefully. If there are any cracks or other defects replace the damaged parts with new ones. Always use original parts.
Stop switch – resistance measurement
Clean the mating surfaces and check the resistance as follows:
Measure the resistance by connecting a multimeter to the ignition coil. NOTE! The switch must be in the “on” position to give the correct reading.
The resistance must not be higher than 0.2 ohm when the switch is in the on position.
English – 15
 Loading...
Loading...