HP Pro 3500, Pro 3515, D8C44UTABA, Pro 3400 User Manual

Maintenance & Service Guide
HP Pro 3400 Microtower Business PC HP Pro 3405 Microtower Business PC HP Pro 3410 Microtower Business PC
HP Pro 3410 Small Form Factor Business PC HP Pro 3500 Microtower Business PC
HP Pro 3505 Microtower Business PC HP Pro 3515 Microtower Business PC
© Copyright 2011, 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Maintenance & Service Guide
Third Edition (November 2012)
First Edition (September 2011)
Document Part Number: 670580-003

About This Book
WARNING! Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or loss of life.
CAUTION: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or loss of information.
 NOTE: Text set off in this manner provides important supplemental information.
NOTE: Text set off in this manner provides important supplemental information.
iii
iv About This Book

Table of contents
1 Product Features ............................................................................................................................................ |
1 |
|
|
Feature Overview ................................................................................................................................. |
1 |
|
Microtower Components ...................................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
Small Form Factor Components .......................................................................................................... |
3 |
2 Activating and Customizing the Software .................................................................................................... |
4 |
|
|
Activating and customizing the software in Windows 7 ........................................................................ |
4 |
|
Activating the Windows operating system ........................................................................... |
4 |
|
Downloading Windows 7 updates ........................................................................................ |
5 |
|
Installing or upgrading device drivers .................................................................................. |
5 |
|
Customizing the monitor display .......................................................................................... |
5 |
|
Activating and customizing the software in Windows 8 ........................................................................ |
5 |
|
Activating the Windows Operating System .......................................................................... |
5 |
|
Downloading Windows 8 updates ........................................................................................ |
6 |
|
Customizing the monitor display .......................................................................................... |
6 |
3 |
Computer Setup (F10) Utility ......................................................................................................................... |
7 |
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities ............................................................................................................. |
7 |
|
Using Computer Setup (F10) Utilities .................................................................................. |
8 |
|
Computer Setup—File ......................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
Computer Setup—Storage ................................................................................................ |
10 |
|
Computer Setup—Security ................................................................................................ |
13 |
|
Computer Setup—Power ................................................................................................... |
17 |
|
Computer Setup—Advanced ............................................................................................. |
18 |
|
Recovering the Configuration Settings ............................................................................................... |
20 |
4 |
Illustrated parts catalog ............................................................................................................................... |
21 |
|
Microtower Chassis Spare Parts ........................................................................................................ |
21 |
|
Computer Major Components ............................................................................................ |
21 |
|
Cables ................................................................................................................................ |
25 |
|
Misc Parts .......................................................................................................................... |
26 |
v
Drives ................................................................................................................................. |
27 |
Misc Boards ....................................................................................................................... |
27 |
Sequential Part Number Listing ......................................................................................... |
28 |
Small Form Factor (SFF) Chassis Spare Parts .................................................................................. |
33 |
Computer major components ............................................................................................ |
33 |
Cables ................................................................................................................................ |
35 |
Misc Parts .......................................................................................................................... |
36 |
Drives ................................................................................................................................. |
37 |
Misc Boards ....................................................................................................................... |
37 |
Sequential Part Number Listing ......................................................................................... |
37 |
5 Serial ATA (SATA) Drive Guidelines and Features .................................................................................... |
40 |
SATA Hard Drives .............................................................................................................................. |
40 |
SATA Hard Drive Cables .................................................................................................................... |
40 |
SATA Data Cable .............................................................................................................. |
40 |
SMART ATA Drives ............................................................................................................................ |
41 |
6 Routine Care and Disassembly Preparation .............................................................................................. |
42 |
Electrostatic Discharge Information .................................................................................................... |
42 |
Generating Static ............................................................................................................... |
42 |
Preventing Electrostatic Damage to Equipment ................................................................ |
43 |
Personal Grounding Methods and Equipment ................................................................... |
43 |
Grounding the Work Area .................................................................................................. |
44 |
Recommended Materials and Equipment .......................................................................... |
44 |
Operating Guidelines .......................................................................................................................... |
45 |
Routine Care ...................................................................................................................................... |
45 |
General Cleaning Safety Precautions ................................................................................ |
45 |
Cleaning the Computer Case ............................................................................................ |
45 |
Cleaning the Keyboard ...................................................................................................... |
46 |
Cleaning the Monitor .......................................................................................................... |
46 |
Cleaning the Mouse ........................................................................................................... |
47 |
Service Considerations ...................................................................................................................... |
47 |
Power Supply Fan ............................................................................................................. |
47 |
Tools and Software Requirements .................................................................................... |
47 |
Screws ............................................................................................................................... |
47 |
Cables and Connectors ..................................................................................................... |
48 |
Hard Drives ........................................................................................................................ |
48 |
Lithium Coin Cell Battery ................................................................................................... |
48 |
vi
7 Removal and Replacement Procedures – Microtower Chassis ............................................................... |
49 |
Serviceability Features ....................................................................................................................... |
49 |
Preparation for Disassembly .............................................................................................................. |
49 |
Access Panel ...................................................................................................................................... |
50 |
Front Bezel ......................................................................................................................................... |
51 |
Memory .............................................................................................................................................. |
52 |
DDR3-SDRAM DIMMs ...................................................................................................... |
52 |
Populating DIMM Sockets ................................................................................................. |
53 |
Removing Memory Modules .............................................................................................. |
54 |
Expansion Cards ................................................................................................................................ |
56 |
Cable Management ............................................................................................................................ |
62 |
Cable Connections ............................................................................................................ |
63 |
Drives ................................................................................................................................................. |
64 |
Installing Additional Drives ................................................................................................. |
65 |
System Board Drive Connections ..................................................................... |
65 |
Removing an Optical Drive ............................................................................... |
70 |
Removing a Hard Drive ..................................................................................... |
70 |
Front I/O and USB Panel Housing Assembly ..................................................................................... |
72 |
Power Switch/LED Assembly ............................................................................................................. |
74 |
System Fan ........................................................................................................................................ |
76 |
Fan Sink Assembly ............................................................................................................................. |
78 |
Processor ........................................................................................................................................... |
79 |
Power Supply ..................................................................................................................................... |
82 |
System Board ..................................................................................................................................... |
83 |
Battery ................................................................................................................................................ |
85 |
8 Removal and Replacement Procedures – Small Form Factor (SFF) Chassis ......................................... |
87 |
Preparation for Disassembly .............................................................................................................. |
87 |
Access Panel ...................................................................................................................................... |
88 |
Front Bezel ......................................................................................................................................... |
90 |
Memory .............................................................................................................................................. |
91 |
DDR3-SDRAM DIMMs ...................................................................................................... |
91 |
Populating DIMM Sockets ................................................................................................. |
92 |
Removing DIMMs .............................................................................................................. |
93 |
Expansion Card .................................................................................................................................. |
96 |
Cable Management .......................................................................................................................... |
100 |
Cable Connections .......................................................................................................... |
101 |
Drives ............................................................................................................................................... |
102 |
Drive Positions ................................................................................................................. |
102 |
Removing Drives ............................................................................................................. |
103 |
Removing an Optical Drive ............................................................................. |
103 |
vii
Removing the Hard Drive ................................................................................ |
105 |
Power Switch .................................................................................................................................... |
109 |
Front USB Assembly ........................................................................................................................ |
111 |
Fan Assembly ................................................................................................................................... |
114 |
Fan Sink ........................................................................................................................................... |
116 |
Processor ......................................................................................................................................... |
118 |
Power Supply ................................................................................................................................... |
120 |
System Board ................................................................................................................................... |
122 |
Battery .............................................................................................................................................. |
124 |
Appendix A Power Cord Set Requirements ................................................................................................ |
126 |
General Requirements ..................................................................................................................... |
126 |
Japanese Power Cord Requirements .............................................................................................. |
126 |
Country-Specific Requirements ........................................................................................................ |
127 |
Appendix B POST Error Messages .............................................................................................................. |
128 |
POST Numeric Codes and Text Messages ..................................................................................... |
129 |
Interpreting POST Diagnostic Front Panel LEDs and Audible Codes .............................................. |
137 |
Appendix C Password Security and Resetting CMOS ............................................................................... |
141 |
Resetting the Password Jumper ...................................................................................................... |
142 |
Clearing and Resetting the CMOS ................................................................................................... |
142 |
Appendix D Troubleshooting Without Diagnostics .................................................................................... |
144 |
Safety and Comfort .......................................................................................................................... |
144 |
Before You Call for Technical Support ............................................................................................. |
144 |
Helpful Hints ..................................................................................................................................... |
145 |
Solving General Problems ................................................................................................................ |
147 |
Solving Power Problems .................................................................................................................. |
151 |
Solving Hard Drive Problems ........................................................................................................... |
153 |
Solving Media Card Reader Problems ............................................................................................. |
156 |
Solving Display Problems ................................................................................................................. |
158 |
Solving Audio Problems ................................................................................................................... |
163 |
Solving Printer Problems .................................................................................................................. |
165 |
Solving Keyboard and Mouse Problems .......................................................................................... |
167 |
Solving Hardware Installation Problems ........................................................................................... |
169 |
Solving Network Problems ............................................................................................................... |
171 |
Solving Memory Problems ............................................................................................................... |
174 |
Solving Processor Problems ............................................................................................................ |
176 |
Solving CD-ROM and DVD Problems .............................................................................................. |
176 |
viii
Solving USB Flash Drive Problems .................................................................................................. |
179 |
Solving Front Panel Component Problems ...................................................................................... |
180 |
Solving Internet Access Problems .................................................................................................... |
180 |
Solving Software Problems .............................................................................................................. |
182 |
Contacting Customer Support .......................................................................................................... |
184 |
Appendix E HP PC Hardware Diagnostics .................................................................................................. |
185 |
Why run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ............................................................................................ |
185 |
How to access and run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ..................................................................... |
186 |
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics to a USB device .......................................................... |
187 |
Appendix F Backup and Recovery ............................................................................................................... |
188 |
Restoring and recovering in Windows 7 ........................................................................................... |
188 |
System Restore ............................................................................................................... |
188 |
System Recovery ............................................................................................................. |
188 |
System Recovery when Windows is responding ............................................ |
189 |
System Recovery when Windows is not responding ...................................... |
190 |
System recovery using recovery media .......................................................... |
190 |
Creating recovery media ................................................................ |
191 |
Using recovery media ..................................................................... |
192 |
Backup and recovery in Windows 8 ................................................................................................. |
193 |
Backing up your information ............................................................................................ |
193 |
Performing a system recovery ......................................................................................... |
194 |
Using the Windows recovery tools .................................................................. |
194 |
Using f11 recovery tools .................................................................................. |
195 |
Using Windows 8 operating system media (purchased separately) ............... |
195 |
Appendix G Specifications ........................................................................................................................... |
196 |
MT Specifications ............................................................................................................................. |
196 |
SFF Specifications ........................................................................................................................... |
197 |
Index ................................................................................................................................................................. |
198 |
ix
x

1 Product Features
Feature Overview
The HP Pro 3400/3500 series includes the following features:
●Choice of Intel® (HP Pro 3500/3400/3410) or AMD processor (HP Pro 3515/3505/3405)
●Choice of integrated graphics or ATI or NVIDIA discrete graphics cards
●Up to 8 GB or 16 GB DDR3 SDRAM system memory available standard (depending on model)
●Hard drives (vary by model): 250 GB up to 2.0 TB
●Optical drives (vary by model): SuperMulti LightScribe drive SuperMulti DVD drive DVD-ROM drive
●Integrated Realtek Gigabit Ethernet Controllers
●10 USB 2.0 ports on HP Pro 3505, HP Pro 3500, and HP Pro 3400 (5 on board header (including 2 on Front I/O, 4 rear, 1 mini card)
●13 USB 2.0 ports on HP Pro 3405 (4 dual on board header (including 2 on Front I/O, 4 rear, 1 mini card)
●10 USB 2.0 ports on HP Pro 3410 (5 on board header (including 2 on Front I/O, 4 rear)
●4 USB 3.0 ports, 10 USB 2.0 ports on HP Pro 3515
●Video ports: DVI, VGA, HDMI (vary by model)
●HP Wireless NIC 802.11b/g/n Mini Card (1x1) (optional by model)
●5.1 channel audio (HP Pro 3500/3400/3410); 7.1 channel audio (HP Pro 3515/3505/3405)
●Windows 8, Windows 7, FreeDOS, or RedFlag Linux (varies by model)
Feature Overview |
1 |
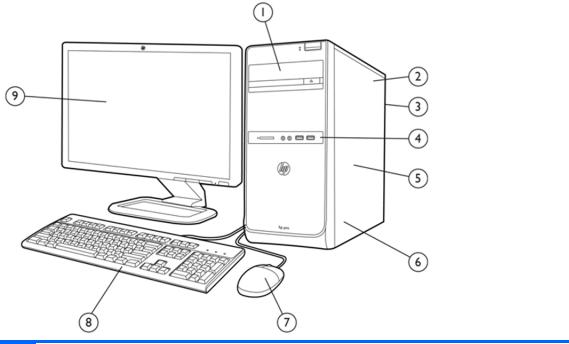
Microtower Components
1 |
(1) external 5.25” drive bay for optional optical |
6 |
(3) PCIe x1 slots, (1) PCIe x16 slot, (1) miniPCI |
|
drive |
|
slot*1 |
|
|
|
Model 3410: (1) PCIe x1 slot, (1) PCIe x16 slot, (2) |
|
|
|
PCI 2.2 slots |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Power Supply |
7 |
USB Scroll Mouse |
|
|
|
|
3 |
Rear I/O includes: (4) USB 2.0 ports, (2) USB 3.0 |
8 |
HP USB Standard Value Keyboard |
|
ports (3515), RJ-45 network interface, DVI, HDMI, |
|
|
|
or VGA video interfaces, microphone jack, audio |
|
|
|
in/out jacks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Front I/O includes: (2) USB 2.0 ports, dedicated |
9 |
Display (sold separately) |
|
headphone output, microphone jack |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
(1) internal 3.5” hard drive bay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
HP Pro 3410 has no mini PCI slot |
|
|
2 Chapter 1 Product Features
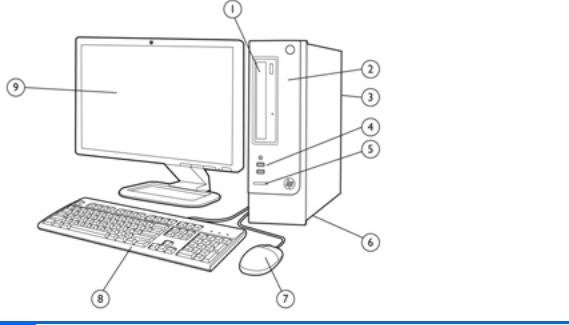
Small Form Factor Components
1 |
External 5.25” drive bay for optical drive |
6 |
Power Supply |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Internal 3.5” hard drive bay |
7 |
USB Scroll Mouse |
|
|
|
|
3 |
Rear I/O includes: (3) PCIe x1 slots, (1) PCIe x16 |
8 |
HP USB Standard Value Keyboard |
|
slot, (1) miniPCI slot, (4) USB 2.0 ports, RJ-45 |
|
|
|
network interface, DVI and VGA video interfaces, |
|
|
|
microphone jack, audio in/out jacks (5.1 channel |
|
|
|
audio out) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Front I/O includes: (2) USB 2.0 ports, dedicated |
9 |
Monitor (sold separately) |
|
headphone output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
HP 6-in-1 Media Card Reader (some models) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Small Form Factor Components |
3 |

2Activating and Customizing the Software
 NOTE: This chapter provides information for both Windows 7 and Windows 8.
NOTE: This chapter provides information for both Windows 7 and Windows 8.
Activating and customizing the software in Windows 7
If your computer was not shipped with a Windows® operating system, some portions of this documentation do not apply. Additional information is available in online help after you activate the operating system.
CAUTION: Do not add optional hardware or third-party devices to the computer until the operating system is successfully activated. Doing so may cause errors and prevent the operating system from installing properly.

 NOTE: Be sure there is a 10.2 cm (4 inch) clearance at the back of the unit and above the monitor to permit the required airflow.
NOTE: Be sure there is a 10.2 cm (4 inch) clearance at the back of the unit and above the monitor to permit the required airflow.
Activating the Windows operating system
The first time you turn on the computer, the operating system is set up and activated automatically. This process takes about 5 to 10 minutes. Carefully read and follow the instructions on the screen to complete the activation.
We recommend that you register your computer with HP during operating system setup so you can receive important software updates, facilitate support questions, and sign up for special offers.
CAUTION: After the activation process has begun, DO NOT TURN OFF THE COMPUTER UNTIL THE PROCESS IS COMPLETE. Turning off the computer during the activation process may damage the software that runs the computer or prevent its proper installation.

 NOTE: If the computer shipped with more than one operating system language on the hard drive, the activation process could take up to 60 minutes.
NOTE: If the computer shipped with more than one operating system language on the hard drive, the activation process could take up to 60 minutes.
4 |
Chapter 2 Activating and Customizing the Software |

Downloading Windows 7 updates
Microsoft may release updates to the operating system. To help keep the computer running optimally, HP recommends checking for the latest updates during the initial installation and periodically throughout the life of the computer.
1.To set up your Internet connection, click Start > Internet Explorer and follow the instructions on the screen.
2.After an Internet connection has been established, click the Start > All Programs > Windows Update.
3.Run Windows Update monthly thereafter.
Installing or upgrading device drivers
When installing optional hardware devices after the operating system installation is complete, you must also install the drivers for each of the devices.
In Windows 7, if prompted for the i386 directory, replace the path specification with C:\i386, or use the Browse button in the dialog box to locate the i386 folder. This action points the operating system to the appropriate drivers.
Obtain the latest support software, including support software for the operating system, from http://www.hp.com/support. Select your country and language, select Download drivers and software (and firmware), enter the model number of the computer, and press Enter.
Customizing the monitor display
If you wish, you can select or change the monitor refresh rates, screen resolution, color settings, font sizes, and power management settings.
For more information, refer to the online documentation provided with the graphics controller utility or the documentation that came with your monitor.
Right-click on the Windows desktop, then click Personalize to change display settings.
Activating and customizing the software in Windows 8
Additional information is available in online help after you activate the operating system.

 NOTE: Be sure there is a 10.2 cm (4 inch) clearance at the back of the unit and above the monitor to permit the required airflow.
NOTE: Be sure there is a 10.2 cm (4 inch) clearance at the back of the unit and above the monitor to permit the required airflow.
Activating the Windows Operating System
The first time you turn on the computer, the operating system is set up and activated automatically. This process takes about 5 to 10 minutes. Carefully read and follow the instructions on the screen to complete the activation.
We recommend that you register your computer with HP during operating system set up so you can receive important software updates, facilitate support questions, and sign up for special offers. You can also register your computer with HP using the Register with HP app on the Start screen.
Activating and customizing the software in Windows 8 |
5 |

CAUTION: After the activation process has begun, DO NOT TURN OFF THE COMPUTER UNTIL THE PROCESS IS COMPLETE. Turning off the computer during the activation process may damage the software that runs the computer or prevent its proper installation.
Downloading Windows 8 updates
Microsoft may release updates to the operating system. To help keep the computer running optimally, HP recommends checking for the latest updates during the initial installation and periodically throughout the life of the computer.
Run Windows Update as soon as possible after you set up your computer.
1.Point to the upper-right or lower-right corner of the Start screen to display the charms.
2.Click Settings > Change PC Settings > Windows Update.
3.Run Windows Update monthly thereafter.
Customizing the monitor display
You can customize display settings for Windows 8 separately for the Start screen and the Desktop.
To customize the Start screen:
1.Point to the upper-right or lower-right corner of the Start screen to display the charms.
2.Click Settings > Change PC Settings.
3.Click Personalize to change the display settings.
To customize the Desktop:
1.Click the Desktop app on the Start screen.
2.Right-click on the desktop, and then click Personalize to change display settings.
6 |
Chapter 2 Activating and Customizing the Software |

3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities
Use Computer Setup (F10) Utility to do the following:
●Change factory default settings.
●Set the system date and time.
●Set, view, change, or verify the system configuration, including settings for processor, graphics, memory, audio, storage, communications, and input devices.
●Modify the boot order of bootable devices such as hard drives, optical drives, or USB flash media devices.
●Enable Quick Boot, which is faster than Full Boot but does not run all of the diagnostic tests run during a Full Boot. You can set the system to:
always Quick Boot (default);
periodically Full Boot (from every 1 to 30 days); or
always Full Boot.
●Select Post Messages Enabled or Disabled to change the display status of Power-On Self-Test (POST) messages. Post Messages Disabled suppresses most POST messages, such as memory count, product name, and other non-error text messages. If a POST error occurs, the error is displayed regardless of the mode selected. To manually switch to Post Messages Enabled during POST, press any key (except F1 through F12).
●Establish an Ownership Tag, the text of which is displayed each time the system is turned on or restarted.
●Enter the Asset Tag or property identification number assigned by the company to this computer.
●Enable the power-on password prompt during system restarts (warm boots) as well as during power-on.
●Establish a setup password that controls access to the Computer Setup (F10) Utility and the settings described in this section.
●Secure integrated I/O functionality, including the serial, USB, or parallel ports, audio, or embedded NIC, so that they cannot be used until they are unsecured.
●Enable or disable removable media boot ability.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities |
7 |

●Solve system configuration errors detected but not automatically fixed during the Power-On SelfTest (POST).
●Replicate the system setup by saving system configuration information on a USB device and restoring it on one or more computers.
●Execute self-tests on a specified ATA hard drive (when supported by drive).
●Enable or disable DriveLock security (when supported by drive).
Using Computer Setup (F10) Utilities
Computer Setup can be accessed only by turning the computer on or restarting the system. To access the Computer Setup Utilities menu, complete the following steps:
1.Turn on or restart the computer.
2.Repeatedly press F10 when the monitor light turns green to access the utility.
You can also press Esc to a menu that allows you to access different options available at startup, including the Computer Setup utility.

 NOTE: If you do not press F10 at the appropriate time, you must restart the computer and again repeatedly press F10 when the monitor light turns green to access the utility.
NOTE: If you do not press F10 at the appropriate time, you must restart the computer and again repeatedly press F10 when the monitor light turns green to access the utility.
3.A choice of five headings appears in the Computer Setup Utilities menu: File, Storage, Security, Power, and Advanced.
4.Use the arrow (left and right) keys to select the appropriate heading. Use the arrow (up and down) keys to select the option you want, then press Enter. To return to the Computer Setup Utilities menu, press Esc.
5.To apply and save changes, select File > Save Changes and Exit.
●If you have made changes that you do not want applied, select Ignore Changes and Exit.
●To reset to factory settings or previously saved default settings (some models), select Apply Defaults and Exit. This option will restore the original factory system defaults.
 NOTE: Not all settings shown in the following sections are available for all models
NOTE: Not all settings shown in the following sections are available for all models
CAUTION: Do NOT turn the computer power OFF while the BIOS is saving the Computer Setup (F10) changes because the CMOS could become corrupted. It is safe to turn off the computer only after exiting the F10 Setup screen.
Table 3-1 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Heading |
Table |
|
|
File |
Computer Setup—File on page 9 |
|
|
Storage |
Computer Setup—Storage on page 10 |
|
|
Security |
Computer Setup—Security on page 13 |
|
|
Power |
Computer Setup—Power on page 17 |
|
|
Advanced |
Computer Setup—Advanced on page 18 |
|
|
8 |
Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility |

Computer Setup—File

 NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
Table 3-2 Computer Setup—File
Option |
Description |
|
|
|
|
System Information |
Lists: |
|
|
● |
Product name |
|
● |
SKU number |
|
● |
Processor type/speed/stepping |
|
● Cache size (L1/L2/L3) (dual core processors have this listed twice) |
|
|
● Installed memory size/speed, number of channels (single or dual) (if applicable) |
|
|
● Integrated MAC address for embedded, enabled NIC (if applicable) |
|
|
● System BIOS (includes family name and version) |
|
|
● |
Chassis serial number |
|
● |
Asset tracking number |
|
● |
ME firmware version |
|
● |
ME Management mode |
|
|
|
About |
Displays copyright notice. |
|
|
|
|
Set Time and Date |
Allows you to set system time and date. |
|
|
|
|
Flash System ROM |
Allows you to update the system ROM with a BIOS image file located on removable media. |
|
|
|
|
Replicated Setup |
Save to Removable Media |
|
|
Saves system configuration to a formatted USB flash media device. |
|
|
Restore from Removable Media |
|
|
Restores system configuration from a USB flash media device. |
|
|
|
|
Default Setup |
Save Current Settings as Default |
|
|
Saves the current system configuration settings as the default. |
|
|
Restore Factory Settings as Default |
|
|
Restores the factory system configuration settings as the default. |
|
|
|
|
Apply Defaults and |
Applies the currently selected default settings and clears any established passwords. |
|
Exit |
|
|
|
|
|
Ignore Changes |
Exits Computer Setup without applying or saving any changes. |
|
and Exit |
|
|
|
|
|
Save Changes and |
Saves changes to system configuration or default settings and exits Computer Setup. |
|
Exit |
|
|
|
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities |
9 |
Computer Setup—Storage

 NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
Table 3-3 Computer Setup—Storage
Option |
Description |
Device Configuration Lists all installed BIOS-controlled storage devices.
When a device is selected, detailed information and options are displayed. The following options may be presented:
●Hard Disk: Size, model, firmware version, serial number, connector color.
Translation mode (ATA disks only)
Lets you select the translation mode to be used for the device. This enables the BIOS to access disks partitioned and formatted on other systems and may be necessary for users of older versions of UNIX (e.g., SCO UNIX version 3.2). Options are Automatic, Bit-Shift,
LBA Assisted, User, and Off.
Available only when the drive translation mode is set to User, allows you to specify the parameters (logical cylinders, heads, and sectors per track) used by the BIOS to translate disk I/O requests (from the operating system or an application) into terms the hard drive can accept. Logical cylinders may not exceed 1024. The number of heads may not exceed 256. The number of sectors per track may not exceed 63.
CAUTION: Ordinarily, the translation mode selected automatically by the BIOS should not be changed. If the selected translation mode is not compatible with the translation mode that was active when the disk was partitioned and formatted, the data on the disk will be inaccessible.
●CD-ROM: Model, firmware version, serial number, connector color (not included for USB CDROM).
●SSD Life Used
NOTE: Displays for solid-state drives.
●SMART (ATA disks only)
●Diskette: Model and firmware version.
NOTE: Displays for USB diskette drives.
●Default Values (ATA disks only)
See Translation Mode above for details.
SATA Defaults
10 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility

Table 3-3 Computer Setup—Storage (continued)
Storage Options |
eSATA Port |
|
Allows you to set a SATA port as an eSATA port for use with an external drive. Default is enabled. |
|
This setting affects only the port with the black connector, labeled as eSATA on the system board. |
|
This port should have the eSATA back panel connector attached to use eSATA drives. For more |
|
information, see the eSATA white paper at www.hp.com. |
|
SATA Emulation |
|
Allows you to choose how the SATA controller and devices are accessed by the operating |
|
system. There are three supported options: IDE, RAID, and AHCI (default). |
|
CAUTION: SATA emulation changes may prevent access to existing hard drive data and |
|
degrade or corrupt established volumes. |
|
IDE - This is the most backwards-compatible setting of the three options. Operating systems |
|
usually do not require additional driver support in IDE mode. |
|
RAID - Allows DOS and boot access to RAID volumes. Use this mode with the RAID device driver |
|
loaded in the operating system to take advantage of RAID features. |
|
AHCI (default option) - Allows operating systems with AHCI device drivers loaded to take |
|
advantage of more advanced features of the SATA controller. |
|
NOTE: The RAID/AHCI device driver must be installed prior to attempting to boot from a RAID/ |
|
AHCI volume. If you attempt to boot from a RAID/AHCI volume without the required device driver |
|
installed, the system will crash (blue screen). RAID volumes may become corrupted if they are |
|
booted to after disabling RAID. |
|
Removable Media Boot |
|
Enables/disables ability to boot the system from removable media. Default is enabled. |
|
Max eSATA Speed |
|
Allows you to choose 1.5 Gbps or 3.0 Gpbs as the maximum eSATA speed. By default, the speed |
|
is limited to 1.5 Gbps for maximum reliability. |
|
CAUTION: Consult your eSATA drive and cable manufacturer before enabling 3.0 Gpbs speed. |
|
Some drive and cable combinations may not run reliably at 3.0 Gpbs. |
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 11

Table 3-3 Computer Setup—Storage (continued)
DPS Self-Test |
Allows you to execute self-tests on ATA hard drives capable of performing the Drive Protection |
|
System (DPS) self-tests. |
|
NOTE: This selection will only appear when at least one drive capable of performing the DPS |
|
self-tests is attached to the system. |
|
|
Boot Order |
Allows you to: |
|
● EFI Boot Sources: Specify the order in which EFI boot sources (such as a internal hard |
|
drive, USB hard drive, USB optical drive, or internal optical drive) are checked for a bootable |
|
operating system image. Each device on the list may be individually excluded from or |
|
included for consideration as a bootable operating system source. |
|
EFI boot sources always have precedence over legacy boot sources. |
|
● Legacy Boot Sources: Specify the order in which legacy boot sources (such as a network |
|
interface card, internal hard drive, USB optical drive, or internal optical drive) are checked for |
|
a bootable operating system image. Each device on the list may be individually excluded |
|
from or included for consideration as a bootable operating system source. |
|
Specify the order of attached hard drives. The first hard drive in the order will have priority in |
|
the boot sequence and will be recognized as drive C (if any devices are attached). |
|
NOTE: To drag a device to a preferred place, press Enter. To remove the device from |
|
consideration as a bootable device, press F5. |
|
You can use F5 to disable individual boot items, as well as disable EFI boot and/or legacy boot. |
|
NOTE: MS-DOS drive lettering assignments may not apply after a non-MS-DOS operating |
|
system has started. |
|
Shortcut to Temporarily Override Boot Order |
|
To boot one time from a device other than the default device specified in Boot Order, restart the |
|
computer and press Esc (to access the boot menu) and then F9 (Boot Order), or only F9 (skipping |
|
the boot menu) when the monitor light turns green. After POST is completed, a list of bootable |
|
devices is displayed. Use the arrow keys to select the preferred bootable device and press Enter. |
|
The computer then boots from the selected non-default device for this one time. |
|
|
12 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility

Computer Setup—Security

 NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
Table 3-4 Computer Setup—Security
Option |
Description |
|
|
Setup Password |
Allows you to set and enable a setup (administrator) password. |
|
NOTE: If the setup password is set, it is required to change Computer Setup options, flash the |
|
ROM, and make changes to certain plug and play settings under Windows. |
|
|
Power-On Password |
Allows you to set and enable a power-on password. The power-on password prompt appears |
|
after a power cycle or reboot. If the user does not enter the correct power-on password, the unit |
|
will not boot. |
Password Options
(This selection appears only if a power-on password or setup password is set.)
Allows you to enable/disable:
●Lock Legacy Resources (determines whether or not Windows Device Manager is allowed to change resource settings for serial and parallel ports).
●Setup Browse Mode (appears if a setup password is set) (allows viewing, but not changing, the F10 Setup Options without entering setup password). Default is enabled.
●Password prompt on F9 & F12 (requires setup password to use these boot functions). Default is enabled.
|
● Network Server Mode. Default is disabled. |
|
|
|
|
Smart Cover |
Allows you to: |
|
|
● Lock/unlock the Cover Lock. |
|
|
● Set the Cover Removal Sensor to Disable/Notify User/Setup Password. |
|
|
NOTE: Notify User alerts the user that the sensor has detected that the cover has been |
|
|
removed. Setup Password requires that the setup password be entered to boot the computer if |
|
|
the sensor detects that the cover has been removed. |
|
|
|
|
Device Security |
Allows you to set Device Available/Device Hidden (default is Device Available) for: |
|
|
● |
Embedded security device |
|
● |
System audio |
|
● USB controller (varies by model) |
|
|
● |
Network controller |
|
|
NOTE: You must disable AMT before trying to hide the network controller. |
|
● |
Serial port |
|
● |
Parallel port |
|
● SATA ports (varies by model) |
|
|
|
|
USB Security |
Allows you to set Enabled/Disabled (default is Enabled) for: |
|
|
● |
Front USB Ports |
|
● |
Rear USB Ports |
|
● |
Accessory USB Ports |
|
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 13

Table 3-4 Computer Setup—Security (continued)
Slot Security |
Allows you to disable any PCI or PCI Express slot. Default is enabled. |
|
|
Network Boot |
Enables/disables the computer’s ability to boot from an operating system installed on a network |
|
server. (Feature available on NIC models only; the network controller must be either a PCI |
|
expansion card or embedded on the system board.) Default is enabled. |
|
|
System IDs |
Allows you to set: |
|
● Asset tag (18-byte identifier), a property identification number assigned by the company to |
|
the computer. |
|
● Ownership tag (80-byte identifier) displayed during POST. |
|
● Universal Unique Identifier (UUID) number. The UUID can only be updated if the current |
|
chassis serial number is invalid. (These ID numbers are normally set in the factory and are |
|
used to uniquely identify the system.) |
|
● Keyboard locale setting for System ID entry. |
|
|
Master Boot Record |
Enables/disables Master Boot Record (MBR) security. |
Security |
The MBR contains information needed to successfully boot from a disk and to access the data |
|
|
|
stored on the disk. Master Boot Record Security may prevent unintentional or malicious changes |
|
to the MBR, such as those caused by some viruses or by the incorrect use of certain disk utilities. |
|
It also allows you to recover the "last known good" MBR, should changes to the MBR be detected |
|
when the system is restarted. |
|
When MBR Security is enabled, the BIOS prevents any changes being made to the MBR of the |
|
current bootable disk while in MS-DOS or Windows Safe Mode. |
|
NOTE: Most operating systems control access to the MBR of the current bootable disk; the |
|
BIOS cannot prevent changes that may occur while the operating system is running. |
|
Restores the backup Master Boot Record to the current bootable disk. Default is disabled. |
|
Only appears if all of the following conditions are true: |
|
● MBR security is enabled |
|
● A backup copy of the MBR has been previously saved |
|
● The current bootable disk is the same disk from which the backup copy was saved |
|
CAUTION: Restoring a previously saved MBR after a disk utility or operating system has |
|
modified the MBR, may cause the data on the disk to become inaccessible. Only restore a |
|
previously saved MBR if you are confident that the current bootable disk's MBR has been |
|
corrupted or infected with a virus. |
|
|
14 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility

Table 3-4 Computer Setup—Security (continued)
System Security |
Data Execution Prevention (enable/disable) - Helps prevent operating system security breaches. |
(these options are |
Default is enabled. |
hardware dependent) |
SVM CPU Virtualization (enable/disable). Controls the virtualization features of the processor. |
|
|
|
Changing this setting requires turning the computer off and then back on. Default is disabled. |
|
Virtualization Technology (VTx) (enable/disable) - Controls the virtualization features of the |
|
processor. Changing this setting requires turning the computer off and then back on. Default is |
|
disabled. |
|
Virtualization Technology Directed I/O (VTd) (enable/disable) - Controls virtualization DMA |
|
remapping features of the chipset. Changing this setting requires turning the computer off and |
|
then back on. Default is disabled. |
|
Trusted Execution Technology (enable/disable) - Controls the underlying processor and chipset |
|
features needed to support a virtual appliance. Changing this setting requires turning the |
|
computer off and then back on. Default is disabled. To enable this feature you must enable the |
|
following features: |
|
● Embedded Security Device Support |
|
● Virtualization Technology |
|
● Virtualization Technology Directed I/O |
|
Embedded Security Device (enable/disable) - Permits activation and deactivation of the |
|
Embedded Security Device. |
|
NOTE: To configure the Embedded Security Device, a Setup password must be set. |
|
● Reset to Factory Settings (Do not reset/Reset) - Resetting to factory defaults will erase all |
|
security keys and leave the device in a disabled state. Changing this setting requires that |
|
you restart the computer. Default is Do not reset. |
|
CAUTION: The embedded security device is a critical component of many security |
|
schemes. Erasing the security keys will prevent access to data protected by the Embedded |
|
Security Device. Choosing Reset to Factory Settings may result in significant data loss. |
|
● Measure boot variables/devices to PCR1 - Typically, the computer measures the boot path |
|
and saves collected metrics to PCR5 (a register in the Embedded Security Device). Bitlocker |
|
tracks changes to any of these metrics, and forces the user to re-authenticate if it detects |
|
any changes. Enabling this feature lets you set Bitlocker to ignore detected changes to boot |
|
path metrics, thereby avoiding re-authentication issues associated with USB keys inserted in |
|
a port. Default is enabled. |
|
|
System Security |
OS management of Embedded Security Device (enable/disable) - This option allows the user to |
(continued) |
limit OS control of the Embedded Security Device. Default is enabled. This option is automatically |
|
disabled if Trusted Execution Technology is enabled. |
|
● Reset of Embedded Security Device through OS (enable/disable) - This option allows the |
|
user to limit the operating system ability to request a Reset to Factory Settings of the |
|
Embedded Security Device. Default is disabled. |
|
NOTE: To enable this option, a Setup password must be set. |
|
● No PPI provisioning (Windows 8 only) - This option lets you set Windows 8 to bypass the PPI |
|
(Physical Presence Interface) requirement and directly enable and take ownership of the |
|
TPM on first boot. You cannot change this setting after TPM is owned/initialized, unless the |
|
TPM is reset. Default is disabled for non-Windows 8 systems, and enabled for Windows 8. |
|
● Allow PPI policy to be changed by OS. Enabling this option allows the operating system to |
|
execute TPM operations without Physical Presence Interface. Default is disabled. |
|
NOTE: To enable this option, a Setup password must be set. |
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 15

Table 3-4 Computer Setup—Security (continued)
DriveLock Security |
Allows you to assign or modify a master or user password for hard drives. When this feature is |
|
|
enabled, the user is prompted to provide one of the DriveLock passwords during POST. If neither |
|
|
is successfully entered, the hard drive will remain inaccessible until one of the passwords is |
|
|
successfully provided during a subsequent cold-boot sequence. |
|
|
NOTE: This selection will only appear when at least one drive that supports the DriveLock |
|
|
feature is attached to the system. |
|
|
|
|
Secure Boot |
This is a feature of Windows 8. |
|
Configuration |
● Legacy Support—Enable/Disable. Allows you to turn off all legacy support on the computer, |
|
|
||
|
including booting to DOS, running legacy graphics cards, booting to legacy devices, and so |
|
|
on. If set to disable, legacy boot options in Storage > Boot Order are not displayed. Default |
|
|
is enabled. |
|
|
● Secure Boot—Enable/Disable. Allows you to make sure an operating system is legitimate |
|
|
before booting to it, making Windows resistant to malicious modification from preboot to full |
|
|
OS booting, preventing firmware attacks. UEFI and Windows Secure Boot only allow code |
|
|
signed by pre-approved digital certificates to run during the firmware and OS boot process. |
|
|
Default is disabled, except for Windows 8 systems which have this setting enabled. Secure |
|
|
Boot enabled also sets Legacy Support to disabled. |
|
|
● Key Management—This option lets you manage the custom key settings. |
|
|
◦ |
Clear Secure Boot Keys—Don't Clear/Clear. Allows you to delete any previously loaded |
|
|
custom boot keys. Default is Don't Clear. |
|
◦ |
Key Ownership—HP Keys/Custom Keys. Selecting Custom Mode allows you to modify |
|
|
the contents of the secure boot signature databases and the platform key (PK) that |
verifies kernels during system start up, allowing you to use alternative operating systems. Selecting HP Keys causes the computer boot using the preloaded HP-specific boot keys. Default is HP Keys.
● Fast Boot—Enable/Disable. Fast boot disables the ability to interrupt boot, such as pressing f keys to access items before the operating system loads. Default is disabled.
NOTE: If Windows 8 detects a serious error, it will interrupt the boot process automatically and display advanced boot options.
From Windows 8, you can press Shift and select Restart to access the screen that lets you boot to a device or troubleshoot your computer.
16 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility

Computer Setup—Power

 NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
Table 3-5 Computer Setup—Power
Option |
Description |
|
|
|
|
OS Power |
● Idle Power Savings—Extended/Normal. Allows certain operating systems to decrease the |
|
Management |
processors power consumption when the processor is idle. Default is extended. |
|
|
● Runtime Power Management— Enable/Disable. Allows certain operating systems to reduce |
|
|
processor voltage and frequency when the current software load does not require the full |
|
|
capabilities of the processor. Default is enabled. |
|
|
● Unique Sleep State Blink Rates—Enable/Disable. This feature is designed to provide a |
|
|
visual indication of what sleep state the system is in. Each sleep state has a unique blink |
|
|
pattern. Default is disabled. |
|
|
NOTE: For Windows 8 systems with Fast Boot support, a normal shutdown goes to the S4 |
|
|
state, not the S5 state. |
|
|
◦ |
S0 (On) = Solid green LED. |
|
◦ |
S3 (Stand By)= 3 blinks at 1Hz (50% duty cycle) followed by a pause of 2 seconds |
|
|
(green LED) — repeated cycles of 3 blinks and a pause. |
|
◦ |
S4 (Hibernation)= 4 blinks at 1Hz (50% duty cycle) followed by a pause of 2 seconds |
|
|
(green LED) — repeated cycles of 4 blinks and a pause. |
|
◦ |
S5 (Soft Off) = LED is off. |
|
|
|
Hardware Power |
SATA Power Management – Enables or disables SATA bus and/or device power management. |
|
Management |
Default is enabled. |
|
|
S5 Maximum Power Savings – Turns off power to all nonessential hardware when system is off to |
|
|
meet EUP Lot 6 requirement of less than 0.5 Watt power usage. Default is disabled. |
|
|
PCI Express x16 Slot 1 – Sets Active State Power Management (ASPM) of the bus. ASPM lets |
|
|
you set lower power modes that activate when the bus is not being used. Options are Disabled, |
|
|
LOs, L1, LOs and L1. Default is ASPM Disabled. |
|
|
PCI Express x1 Slot 1 – Sets Active State Power Management (ASPM) of the bus. ASPM lets you |
|
|
set lower power modes that activate when the bus is not being used. Options are Disabled, LOs, |
|
|
L1, LOs and L1. Default is ASPM Disabled. |
|
|
Network Controller – Sets ASPM of the bus. ASPM lets you set lower power modes that activate |
|
|
when the bus is not being used. Options are Disabled, LOs, L1, LOs and L1. Default is ASPM |
|
|
Disabled. |
|
|
USB 3.0 Controller – Sets ASPM of the bus. ASPM lets you set lower power modes that activate |
|
|
when the bus is not being used. Options are Disabled, LOs, L1, LOs and L1. Default is ASPM |
|
|
Disabled. |
|
|
|
|
Thermal |
Fan idle mode—This bar graph controls the minimum permitted fan speed. |
|
|
NOTE: This setting only changes the minimum fan speed. The fans are still automatically |
|
|
controlled. |
|
|
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 17

Computer Setup—Advanced

 NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration.
Table 3-6 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users)
Option |
Heading |
|
|
|
|
Power-On Options |
Allows you to set: |
|
|
● POST mode (QuickBoot, Clear Memory, FullBoot, or FullBoot Every x Days). |
|
|
◦ |
QuickBoot (default) = Do not clear memory or perform a memory test. |
|
◦ |
FullBoot = Memory test (count) on cold boot. Clears memory on all boots. |
|
◦ |
Clear Memory = No memory count on cold boot. Clears memory on all boots. |
|
◦ |
FullBoot Every x Days = Memory count on 1st cold boot on or after the xth day. No |
|
|
more memory counts until 1st cold boot on or after x days. Clears memory on all boots. |
|
● POST messages (enable/disable). Enabling this feature will cause the system to display |
|
|
POST error messages, which are error messages displayed on the monitor during the Power |
|
|
On Self Test if the BIOS encounters some kind of problem while starting the PC. A POST |
|
|
error message will only display on screen if the computer is capable of booting this far. If the |
|
|
POST detects an error before this point, a beep code is generated instead. Default is |
|
|
disabled. |
|
|
● Press the ESC key for Startup Menu (Enable/Disable). This feature controls the display of |
|
|
the text “Press the ESC key for Startup Menu” during POST. This text does not display on |
|
|
Windows 8 systems with Fast Boot support. Other text also will not display (for example, |
|
|
Ownership Tag). Default is enabled. |
|
|
● Option ROM Prompt (enable/disable). Enabling this feature will cause the system to display |
|
|
a message before loading option ROMs. Default is enabled. |
|
|
● After Power Loss (off/on/previous state). Default is Power off. Setting this option to: |
|
|
◦ |
Power off—causes the computer to remain powered off when power is restored. |
|
◦ |
Power on—causes the computer to power on automatically as soon as power is |
|
|
restored. |
|
◦ |
Previous state—causes the computer to power on automatically as soon as power is |
|
|
restored, if it was on when power was lost. |
NOTE: If you turn off power to the computer using the switch on a power strip, you will not be able to use the suspend/sleep feature or the Remote Management features.
● POST Delay (in seconds). Enabling this feature will add a user-specified delay to the POST process. This delay is sometimes needed for hard disks on some PCI cards that spin up very slowly, so slowly that they are not ready to boot by the time POST is finished. The POST delay also gives you more time to select F10 to enter Computer (F10) Setup. Default is None.
● Remote Wakeup Boot Source (remote server/local hard drive). Default is Local hard drive.
● Factory Recovery Boot Support (Enable/Disable). Provides the ability for the BIOS to redirect the boot to the recovery partition on the user hard drive, if present. Some versions of the recovery software honor the F11 key press even when this feature is disabled by the BIOS. Default is disabled.
● Bypass F1 Prompt on Configuration Changes (Enable/Disable). Allows you to set the computer not to confirm when changes were made. Default is disabled.
18 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility

Table 3-6 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
BIOS Power-On |
Allows you to set the computer to turn on automatically at a time you specify. |
|
|
Onboard Devices |
Allows you to set resources for or disable Legacy devices. |
|
Select the Legacy device's IRQ, DMA, and I/O Range. The settings may not take effect for all |
|
operating systems. To hide a device from the operating system, see Security > Device Security. |
|
|
Bus Options |
Allows you to enable or disable: |
|
● PCI SERR# Generation. Default is enabled. |
|
● PCI VGA Palette Snooping, which sets the VGA palette snooping bit in PCI configuration |
|
space; only needed when more than one graphics controller is installed. Default is disabled. |
|
|
Device Options |
Allows you to set: |
|
● Printer mode (Bi-Directional, EPP + ECP, Output Only). ECP = Enhanced Capabilities Port, |
|
EPP = Enhanced Parallel Port. Default is EPP+ECP. |
|
● Num Lock State at Power-On (off/on). Default is off. |
|
● Integrated Video (enable/disable). Use this option to disable the integrated video controller |
|
when another video controller is present in the system. Default is enabled. |
|
● Integrated Graphics (Auto/Disable/Force) Use this option to manage integrated (UMA) |
|
graphics memory allocation. The value you choose is allocated permanently to graphics and |
|
is unavailable to the operating system. For example, if you set this value to 512M on a |
|
system with 2 GB of RAM, the system always allocates 512 MB for graphics and the other |
|
1.5 GB for use by the BIOS and operating system. Default is Auto which sets memory |
|
allocation to 512 MB. |
|
If you select Force, the UMA Frame Buffer Size option displays, which lets you set the UMA |
|
memory size allocation between 32 MB and 1 GB. |
|
● Internal Speaker (does not affect external speakers). Default is enabled. |
|
● NIC PXE Option ROM Download (PXE, iSCSI, disabled). The BIOS contains an embedded |
|
NIC option ROM to allow the unit to boot through the network to a PXE server. This is |
|
typically used to download a corporate image to a hard drive. The NIC option ROM takes up |
|
memory space below 1MB commonly referred to as DOS Compatibility Hole (DCH) space. |
|
This space is limited. This F10 option will allow users to disable the downloading of this |
|
embedded NIC option ROM thus giving more DCH space for additional PCI cards which may |
|
need option ROM space. The default will be to have the NIC option-ROM-enabled. Default is |
|
PXE. |
|
● SATA RAID Option ROM Download (enable/disable). The BIOS contains an embedded |
|
SATA RAID option ROM for RAID support. This can be temporarily disabled to save DCH |
|
space. Note that with the option ROM disabled, users will be unable to boot to hard drives in |
|
the system while running in RAID mode. Default is disabled. |
|
● Multi-Processor (enable/disable). Use this option to disable multi-processor support under |
|
the OS. Default is enabled. |
|
● Hyper threading (enable/disable). Use this option to disable processor hyper-threading. |
|
● Turbo Mode (enable/disable). Allows you to enable and disable the Intel Turbo Mode feature, |
|
which allows one core of the system to run at a higher than standard frequency and power if |
|
other cores are idle. Default is enabled. |
|
|
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 19

Table 3-6 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
VGA Configuration |
Displayed only if there is an add-in video card in the system. Allows you to specify which VGA |
|
controller will be the “boot” or primary VGA controller. |
|
|
AMT Configuration |
Allows you to set: |
|
● AMT (enable/disable). Allows you to enable or disable functions of the embedded |
|
Management Engine (ME) such as Active Management Technology (AMT). If set to disable, |
|
the Management Engine is set to a temporarily disabled state and will not provide functions |
|
beyond necessary system configuration. Default is enabled. |
|
● Unconfigure AMT/ME (enable/disable). Allows you to unconfigure any provisioned |
|
management settings for AMT. The AMT settings are restored to factory defaults. This |
|
feature should be used with caution as AMT will not be able to provide any set AMT |
|
management functions once unconfigured. Default is disabled. |
|
● Hide Unconfigure ME Confirmation Prompt (enable/disable). Allows you to set the system to |
|
not display the confirmation to unconfigure ME. |
|
● Watchdog Timer (enable/disable). Allows you to set amount of time for a operating system |
|
and BIOS watchdog alert to be sent if the timers are not deactivated. BIOS watchdog is |
|
deactivated by BIOS and would indicate that a halt occurred during execution if the alert is |
|
sent to the management console. An operating system alert is deactivated by the operating |
|
system image and would indicate that a hang occurred during its initialization. Default is |
|
enabled. |
|
|
Recovering the Configuration Settings
This method of recovery requires that you first perform the Save to Removable Media command with the Computer Setup (F10) Utility before Restore is needed. (See Computer Setup—File
on page 9 in the Computer Setup—File table.)

 NOTE: It is recommended that you save any modified computer configuration settings to a USB flash media device and save the device for possible future use.
NOTE: It is recommended that you save any modified computer configuration settings to a USB flash media device and save the device for possible future use.
To restore the configuration, insert the USB flash media device with the saved configuration and perform the Restore from Removable Media command with the Computer Setup (F10) Utility. (See Computer Setup—File on page 9 in the Computer Setup—File table.)
20 Chapter 3 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
 Loading...
Loading...