Grass Valley DHP User Manual

DHP
Dynamic Hybrid Path nding Service
Reference Manual
UG0060-01
25 Nov 2014

Copyright & Trademark Notice
Copyright © 2014 Grass Valley. All rights reserved.
Belden, Belden Sending All The Right Signals, and the Belden logo are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Belden Inc. or its affiliated companies in the United States and
other jurisdictions. Grass Valley, NVISION, NV9000, NV9000-SE Utilities, and DHP are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Grass Valley. Belden Inc., Grass Valley, and other
parties may also have trademark rights in other terms used herein.
Terms and Conditions
Please read the following terms and conditions carefully. By using DHP documentation, you
agree to the following terms and conditions.
Grass Valley hereby grants permission and license to owners of DHP routers to use their
product manuals for their own internal business use. Manuals for Grass Valley products may
not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
including photocopying and recording, for any purpose unless specifically authorized in
writing by Grass Valley.
A Grass Valley manual may have been revised to reflect changes made to the product during
its manufacturing life. Thus, different versions of a manual may exist for any given product.
Care should be taken to ensure that one obtains the proper manual version for a specific
product serial number.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of Grass Valley.
Warranty information is available in the support section of the Grass Valley web site
(www.grassvalley.com).
Title DHP Reference Manual
Part Number UG0060-01
Revision 1.1 (25 Nov 14)
ii
Change History
Rev. Date ECO Description Approved
1.0 21 Apr 09 18826 Initial release. D.Cox
1.1 25 Nov 14 19357 DHP activation file is SV1062-01. New format. Added
Safety Compliance
Korean Compliance (KCC) Statement
이 기기는 업무용 (A 급 ) 전자파적합기기로서 판
매자
또는 사용자는 이 점을 주의하시기 바라
며
, 가정외의 지역에서 사용하는 것을 목적으로
합니다
Please note this is a Class A device. Sellers or users need to take note of this and should not
use this equipment in a domestic environment.
.
Korean compliance statement. Client assignments (in
server mode) preserved over power cycles.
KCC-REM-XEI-NV8500
급 기기
A
( 업무용 방송통신 기자재 )
Class A Equipment
(Commercial Broadcasting & Communication Equipment)
DHP
Reference Manual
D.Cox
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
Declaration of Conformance (CE)
All of the equipment described in this manual has been designed to conform with the
required safety and emissions standards of the European Community. Products tested and
verified to meet these standards are marked as required by law with the CE mark.
When shipped into member countries of the European Community, this equipment is
accompanied by authentic copies of original Declarations of Conformance on file in the
Grass Valley offices in Grass Valley, California USA.
Software License Agreement and Warranty Information
Contact Grass Valley for details on the software license agreement and product warranty.
iii

Important Safeguards and Notices
This section provides important safety guidelines for operators and service personnel.
Specific warnings and cautions appear throughout the manual where they apply. Please
read and follow this important information, especially those instructions related to the risk
of electric shock or injury to persons.
WAR NIN G
Any instructions in this manual that require opening the equipment cover or enclosure are
for use by qualified service personnel only. To reduce the risk of electric shock, do not
perform any service other than that contained in the operating instructions unless you are
qualified to do so.
Restriction on Hazardous Substances (RoHs)
Grass Valley is in compliance with EU Directive RoHS 2002/95/EC governing the restricted
use of certain hazardous substances and materials in products and in our manufacturing
processes.
Grass Valley has a substantial program in place for RoHS compliance that includes significant
investment in our manufacturing process, and a migration of Grass Valley product electronic
components and structural materials to RoHS compliance.
It is our objective at Miranda GVD to maintain compliance with all relevant environmental
and product regulatory requirements. Detailed information on specific products or on the
RoHS program at Grass Valley is available from Grass Valley Customer Support at
1-800-719-1900 (toll-free) or
1-530-265-1000 (outside the U.S.).
iv
Symbols and Their Meanings
The lightning flash with arrowhead symbol within an equilateral triangle alerts the
user to the presence of dangerous voltages within the product’s enclosure that
may be of sufficient magnitude to constitute a risk of electric shock to persons.
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle alerts the user to the presence
of important operating and maintenance/service instructions.
The Ground symbol represents a protective grounding terminal. Such a terminal
must be connected to earth ground prior to making any other connections to the
equipment.
The fuse symbol indicates that the fuse referenced in the text must be replaced
with one having the ratings indicated.
DHP
Reference Manual
The presence of this symbol in or on Grass Valley equipment means that it has been
designed, tested and certified as complying with applicable Underwriter’s
Laboratory (USA) regulations and recommendations.
The presence of this symbol in or on Grass Valley equipment means that it has been
designed, tested and certified as essentially complying with all applicable
European Union (CE) regulations and recommendations.
General Warnings
A warning indicates a possible hazard to personnel which may cause injury or death.
Observe the following general warnings when using or working on this equipment:
• Heed all warnings on the unit and in the operating instructions.
• Do not use this equipment in or near water.
• This equipment is grounded through the grounding conductor of the power cord. To
avoid electrical shock, plug the power cord into a properly wired receptacle before connecting the equipment inputs or outputs.
• Route power cords and other cables so they are not likely to be damaged.
• Disconnect power before cleaning the equipment. Do not use liquid or aerosol cleaners; use only a damp cloth.
• Dangerous voltages may exist at several points in this equipment. To avoid injury, do
not touch exposed connections and components while power is on.
• Do not wear rings or wristwatches when troubleshooting high current circuits such as
the power supplies.
v

• To avoid fire hazard, use only the specified fuse(s) with the correct type number, voltage
and current ratings as referenced in the appropriate locations in the service instructions or on the equipment. Always refer fuse replacements to qualified service personnel.
• To avoid explosion, do not operate this equipment in an explosive atmosphere.
• Have qualified service personnel perform safety checks after any service.
General Cautions
A caution indicates a possible hazard to equipment that could result in equipment damage.
Observe the following cautions when operating or working on this equipment:
• When installing this equipment, do not attach the power cord to building surfaces.
• To prevent damage to equipment when replacing fuses, locate and correct the problem
that caused the fuse to blow before re-applying power.
• Use only the specified replacement parts.
• Follow static precautions at all times when handling this equipment.
• This product should only be powered as described in the manual. To prevent equipment damage, select the proper line voltage on the power supply(ies) as described in
the installation documentation.
• To prevent damage to the equipment, read the instructions in the equipment manual
for proper input voltage range selection.
• Some products include a backup battery. There is a risk of explosion if the battery is
replaced by a battery of an incorrect type. Dispose of batteries according to instructions.
• Products that have (1) no on/off switch and (2) use an external power supply must be
installed in proximity to a main power outlet that is easily accessible.
• To reduce the risk of electrical shock, plug each power supply cord into a separate
branch circuit having a separate service ground.
vi

Table of Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
NV8500 Review . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
I/O Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Standard Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Disembedder and Embedder Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
MADI Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Expansion Cabling for the NV8576-Plus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
DHP Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Preliminary DHP Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Other DHP Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 DHP Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Activation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Configuration Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
DHP Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Router Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
NV9000-SE Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
DHP Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Initialization—the Configuration Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
‘HybridCards’ Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
‘HybridPorts’ Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Software Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
More in NV9000-SE Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Audio for Standard Inputs and Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
MADI Port Numbering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Requirements for Adding DHP to a Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Clear the Crosspoint Matrices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
NV9000 Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Start the System with DHP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Setting the Service to Automatic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Starting the Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Verify . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
DHP Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Takes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Standard or Embedder Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
MADI Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Standard to Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Standard to Embedder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Standard to MADI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Standard to (Standard + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Standard to (Embedder + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
vii

Table of Contents
Disembedder to Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Disembedder to Embedder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Disembedder to MADI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Disembedder to (Standard + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Disembedder to (Embedder + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MADI to Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MADI to Embedder. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MADI to MADI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MADI to (Standard + MADI). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
MADI to (Embedder + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Mixed to Standard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Mixed to Embedder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Mixed to MADI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Mixed to (Standard + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Mixed to (Embedder + MADI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Embedders and Disembedders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Product Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Architectural Defects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3 NV9000 Web Suite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
DHP Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
DHP Disembedder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
DHP Embedder. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
DHP Re-Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
DHP Drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Signal Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Sample NV9000 Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Non-Core Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
DHP Core Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Re-embedders tied to Standard Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Disembedders tied to Standard Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
4 Misc. Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
I/O Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
I/O Backplane Connector Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Slot Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
NV8144, NV8140, or NV8280. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
NV8576 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
NV8576-Plus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Contact Us . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
viii

Chapter 1 provides a brief introduction to DHP and the NV8500.
Topics
NV8500 Review . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
DHP Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
NV8500 Review
You may safely skip this section if you are familiar with the NV8500 routers.
The NV8500 family of routers comprises 4 routers:
• NV8144 — 8RU, 144×144 video matrix
• NV8140 — 8RU, 144×288 video matrix
• NV8280 — 16RU, 288×576 video matrix
• NV8576 — 32RU, 576×1152 video matrix
• Stand-alone NV8576-Plus — 32RU, 576×576 video matrix
• Expanded NV8576-Plus — Two 32RU frames, interconnected, 1152×1152 video matrix
The routers in the NV8500 family switch both video (SD, HD, 3Gig), and audio (AES sync and
async). The routers support two classes of input and output cards:
1Standard
(The NV8140 does not support AES async at this time.)
2Hybrid
There are disembedder cards (that extract audio from video input).
There are embedder cards (that insert audio into video output).
There are MADI
MADI input. MADI output cards have 16 video outputs and two MADI outputs. For the
NV8576-Plus, there are expansion output cards that have 8 video outputs and one MADI outputs.
If any hybrid I/O cards are present, the router is considered a hybrid router. All its control cards
and all its crosspoint cards must be hybrid cards. Otherwise, you can consider the router a standard router and all its control cards and crosspoint cards can be standard cards.
You can have a combination of the card types in your router. Standard input cards do not
disembed audio; standard output cards do not re-embed audio. With the hybrid cards, the
Introduction
— video (SD, HD, 3Gig rates automatically detected), or AES (async).
— combining audio with video (SD, HD, 3Gig).
1
input and output cards. MADI input cards have 8 video inputs and one
1. MADI (multi-channel audio digital interface) is time-multiplexed AES. The NV8500 supports 64-channel
and 56-channel MADI. A DIP switch configures a MADI output card for 56-channel mode. MADI input
cards accept any number of channels (up to 64).
1

Introduction
WECO Coax
Coax*
WECO Coax SFP WECO Coax SFP
Input
Output Expansion Output
SFP
NV8500 Review
routers can disembed audio, recombine the audio, and re-embed the recombined audio at
output.
With DHP (dynamic hybrid pathfinding), the routers can route standard input through an
internal pool of hybrid disembedder cards and embedder cards after which the audio from the
standard input can be recombined and re-embedded on output. The point of DHP is that it
allows you to populate the router with many relatively inexpensive standard I/O cards and a few
hybrid cards and still have the benefits of hybrid routing (the ability to breakaway audio entirely
within the router).
I/O Cards
Each router has a certain number of input card slots and a certain number of output card slots:
Router Input Slots Output Slots Nominal Video Matrix Size
NV8144 16 8 144×144
NV8140 8 16 144×288
NV8280 32 32 288×576
NV8576 64 64 576×1152
NV8576-Plus
(stand-alone)
NV8576-Plus
(expanded)
128 128 576×576
128 128 1152×1152
You may populate the slots with any type of input or output card your system requires.
Input cards are coupled with input backplane connector modules (or backplanes, for brevity).
Output cards are coupled with output backplanes. Backplanes typically have coax (DIN 1.0/2.3)
connectors or fiber optic (SFP) connectors. (Balanced AES modules use WECO quick-release
connectors.):
2

DHP
Reference Manual
For routers other than the NV8140, Input backplane modules each have 9 connectors. Output
backplane modules each have 18 connectors. Expansion output backplane modules (only for
the NV8576-Plus) have 9 connectors and two 28-pin expansion ports.
For the NV8140, input backplanes for the NV8140 have 18 connectors.
Standard Cards
Standard input cards use all 9 connectors of the backplane modules. Standard output cards use
all 18 connectors of the backplane modules.
Disembedder and Embedder Cards
For routers other than the NV8140, hybrid disembedder (input) cards use 8 of the 9 connectors.
The 9th connector is not used. Hybrid embedder (output) cards use 16 of the 18 connectors. The
9th and 18th connectors are not used.
For the NV8140, hybrid disembedder (input) cards use 16 of their 18 connectors. The 9th and
18th connectors are not used.
Hybrid expansion embedder (output) cards use 8 of the 9 connectors.
There are no video ports or audio ports associated with the unused connectors.
MADI Cards
(MADI cards are also known as 3Gig/TDM cards.)
For routers other than the NV8140, hybrid MADI input cards use the first 8 connectors for video
input and use the 9th connector for MADI input (up to 64 channels). Hybrid MADI output cards
use connectors 1–8 and 10–17 for video output and use the 9th and 18th connectors for MADI
output (56 or 64 channels each).
These MADI input cards have 64 audio ports. The remaining 80 ports of the card’s port space are
unused.
For the NV8140, hybrid MADI input cards use connectors 1–8 and 10–17 for video input and use
the 9th and 18th connectors for MADI input (up to 64 channels each).
These MADI input cards have 128 audio ports. The remaining 160 ports of the card’s port space are
unused.
Hybrid MADI output cards use connectors 1–8 and 10–17 for video output and use the 9th and
18th connectors for MADI output (56 or 64 channels each).
Hybrid expansion MADI output cards use the first 8 connectors for video output and use the 9th
connector for MADI output (56 or 64 channels).
MADI output cards have 128 audio ports. The remaining 160 ports of the card’s port space are
unused.
Expansion Cabling for the NV8576-Plus
The expanded NV8576-Plus router comprises two interconnected router frames. The frames use
expansion cards and expansion backplane modules. Expansion output backplanes have 9 connectors and two 28-pin expansion connectors. Cables connect the 2 router frames on the expansion
connectors.
3
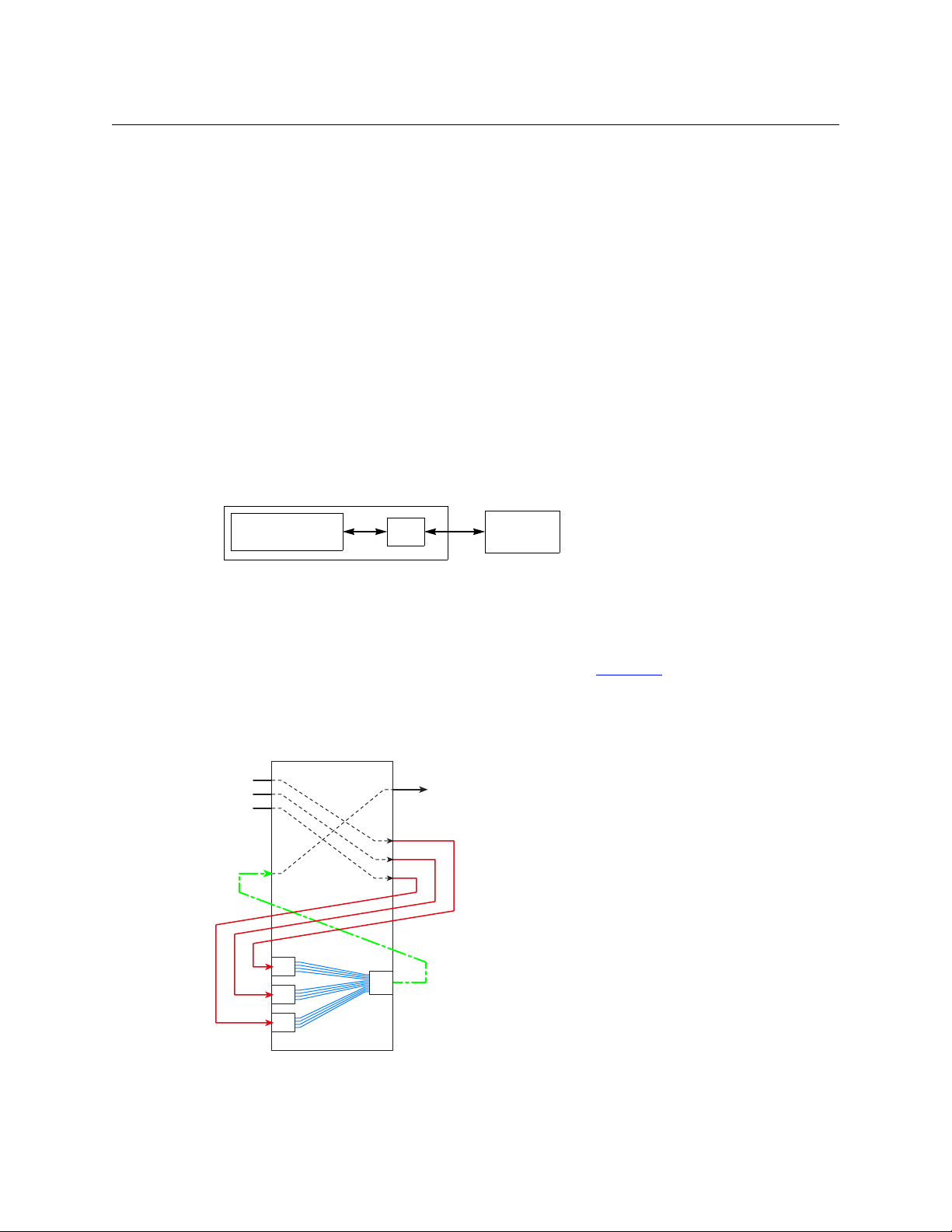
Introduction
Control System
Software
DHP
Hybrid
Router
NV9000
Std In
Std Out
Std In
Std Out
Std Out
Std In
DIS
DIS
DIS
Std In
EMB
Std Out
This scenario combines audio from 3 separate standard
inputs and routes the video from one of the inputs with
the combined audio on a standard output.
A disembedder port is required for each standard input
port from which audio is to be extracted. An embedder
port is required for the output that is to receive the
recombined audio.
Further, an additional standard output port is required
for each standard input port from which audio is to be
extracted. An additional standard input port is also
required for the output that is to receive the recombined
audio.
The DHP service routes the signals through a pool of
available hybrid cards internally. External cabling is
required for every DHP path.
DHP Summary
Expansion output cards provide 9 outputs. Expansion output backplanes have 9 connectors and
two 28-pin expansion connectors. Expansion filler cards provide no outputs, but support the
expansion connections. Cables connect the 2 router frames on the expansion connectors.
DHP Summary
DHP (dynamic hybrid pathfinding) allows the NV8500 router to perform hybrid routing with
relatively few hybrid cards. With DHP, the router passes standard inputs through an internal pool
of hybrid disembedder cards and embedder cards after which the audio from the standard
inputs can be recombined and re-embedded on output.
The point of DHP is that it allows you to populate the router with many relatively inexpensive
standard I/O cards and a few hybrid cards and still have the benefits of hybrid routing (that is, to
allow audio from standard inputs to be disembedded and re-embedded for standard outputs,
all within the router).
DHP is a service that resides in the NV9000. The NV9000 control software treats the DHP service
as if it were a hybrid router.
4
The DHP service then communicates with the router directly. All takes to a hybrid router go
through the DHP service, transparently. All status from the router also goes through the DHP
service.
DHP is licensed software (EC9540) that ships with the NV9000. The purchase of the license
allows you to activate the DHP service in the NV9000. See Activation
If you have an older version of the NV9000 software that does not include DHP, you will need
on page 7.
to obtain an updated version of the NV9000 software.
Figure 1-1 shows a fairly typical route using DHP:
Fig. 1-1: DHP Scenario — Recombining Audio from Standard Input
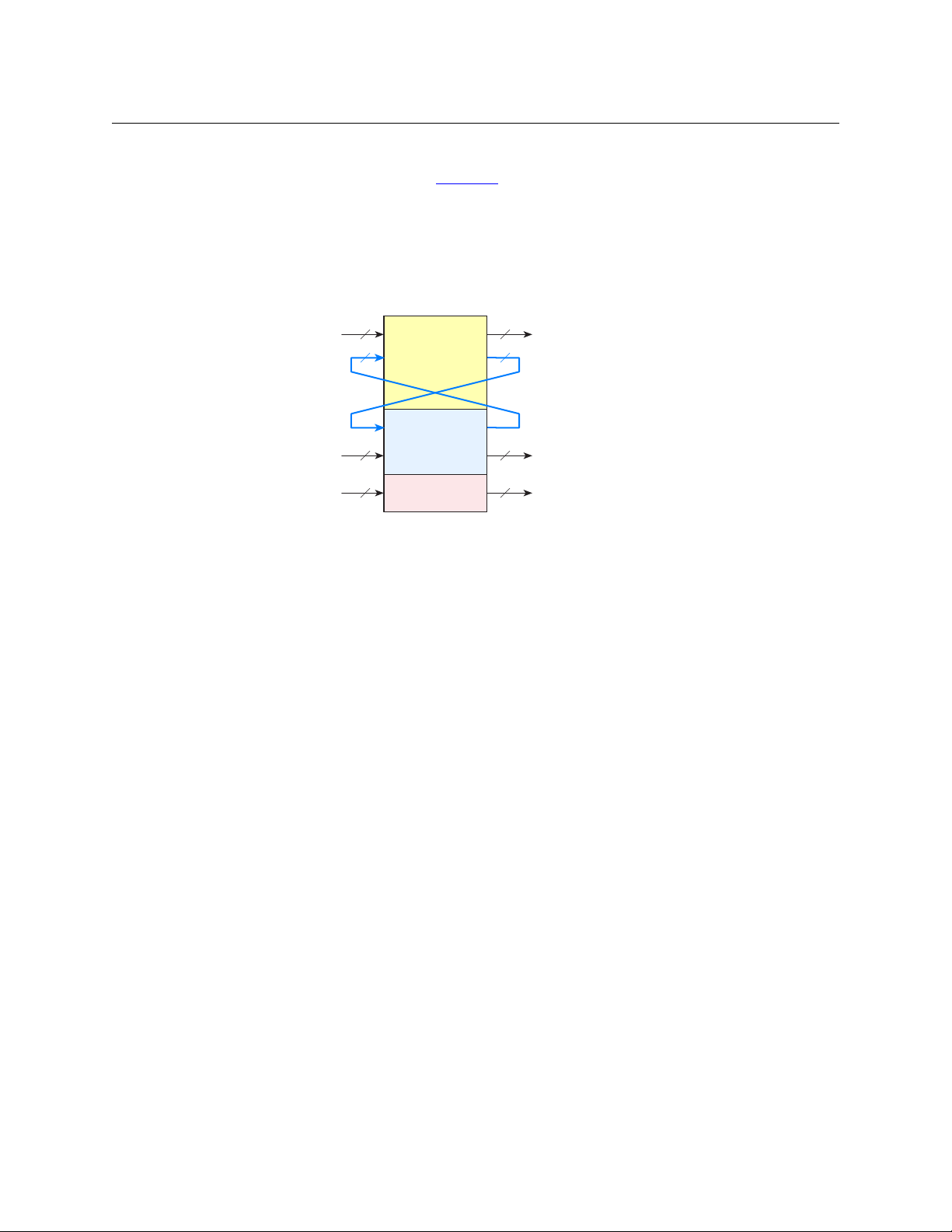
DHP
NV8500 Router
Standard Video
(with or without
embedded audio)
AES
Hybrid
Standard Video In Standard Video Out
AES In AES Out
Hybrid In Hybrid Out
DHP Links DHP Links
External cabling is required
for every DHP path.
Reference Manual
This is only one of a few dozen DHP scenarios. Other scenarios involve MADI inputs and outputs
and AES inputs and outputs. See Examples
on page 24 for a discussion of DHP scenarios.
Preliminary DHP Analysis
In the analysis of your system, you should determine the number of inputs and outputs of each
type:
Fig. 1-2: DHP Links
This evaluation includes the number of standard inputs and standard outputs, the number of
hybrid inputs and outputs, and the number of AES inputs and outputs.
If your router is to perform DHP, you will also need the size of the DHP pool (or DHP “core”), i.e,
the number of DHP links required by your router. This number might be difficult to determine.
Keep in mind that the DHP links are dedicated disembedders and re-embedders and are not to
be considered inputs and outputs. There are several factors to consider.
These are two of the factors:
1 The number of DHP paths that can be in use simultaneously.
2 The number of ports required for each path.
As stated earlier, and illustrated in Figure 1-1, a certain number of hybrid ports and a certain
number of additional standard ports are required for each DHP path.
Potentially, 16 sources could each provide a single audio channel to an output. This would be
considered an extreme and unusual case. If all 16 audio channels come from a single source,
DHP is not used for that route. Thus, the minimum number of sources for DHP is 2 and the
maximum is 16. The number of destinations for DHP is always 1.
You need to determine the average number of ports among all the DHP paths in use simultaneously. The average is, of course, somewhere between 2 and 16, probably very close to 2.
Thus, letting ‘A’ be the average number of sources, and ‘N’ be the number of simultaneous DHP
paths,
Disembedder ports = A × N
Embedder ports = N
Additional standard input ports = N
Additional standard output ports = A × N
Note that DHP is used for disembedding and re-embedding audio. Therefore the hybrid cards
that constitute the DHP core must be one of these:
5

Introduction
DHP Summary
8500H-IP-3G-DEM-CX (disembedding, input)
8500H-OP-3G-EMB-CX (embedding, output)
8500H-OPX-3G-EMB-CX (embedding, expansion output)
[There are no fiber-optic hybrid cards at this time.]
Note: ports belonging to the DHP core cannot be used as routable inputs or outputs. Panel
operators cannot route to them or from them directly.
Other DHP Considerations
Tielines
The NV8500 router that DHP is servicing might involve some tielines. You must identify the
inputs and outputs of all tielines in a DHP configuration (initialization) file.
Force Embedder Off
The DHP configuration allows you to specify, for some inputs, that when they are routed to
embedder outputs, the embedder is forced off (i.e, the embedder is bypassed). In such a case,
the audio from the input is kept intact and passed through the output without change. This
option is controlled by “EO” commands in DHP’s port configuration files.
It might be a point of confusion that, in MRC, there is just the opposite function: some inputs in
the router are configured to force any embedding output to use its embedder, rather then let
the router follow switching rules to determine the embedder state.
If your router uses DHP, it is imperative that you do not ever use the “force embedder ON” function in MRC.
ASI Signals
You must identify ASI inputs and ASI outputs in a DHP initialization file.
See ‘HybridPorts’ Files
on page 16 for detail.
6

Activation
DHP Service
Chapter 2 provides detailed information about DHP.
Topics
Activation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Configuration Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
DHP Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
DHP is licensed software (EC9540) that ships with the NV9000. The purchase of the license
allows you to activate the DHP service in the NV9000.
Follow these steps to activate the DHP service:
1 Obtain the NV9000 Control System CD from Miranda (GVD). This CD contains one or more
activation programs depending on which licenses you have purchased.
2 Copy the DHP activation file (presently SV1062-01.exe) from the CD to a USB drive.
3 Connect a keyboard, mouse, and monitor to the NV9000 frame.
4 Login to the NV9000. The default username is
ware
.
5 Insert the USB drive into a free USB slot of the NV9000.
6 When the USB drive window appears, double-click the DHP activation file. The activation
program takes no more than a second to finish.
7 Remove the USB drive from the NV9000.
It might be convenient to activate all the services you have purchased at this time, if you
have purchased more than one. Just copy all your service activation programs to the USB
drive and run each one individually on the NV9000.
If you have an older version of the NV9000 software that does not include DHP, you will
need to obtain an updated version of the NV9000 software.
Repeat the activation process for each NV9000 that is to use DHP.
(You will have to log in again later to install the DHP configuration files. See Initialization—the
Configuration Files on page 13)
envyadmin and the default password is soft-
7

DHP Service
Definitions
Definitions
Standard card Standard input or output card. Standard input or output is video
(3Gig, HD, or SD) with or without embedded audio. No disembedding or embedding occurs. Using standard cards only, the signal
passes unchanged. through the router.
Standard input card 8500-3GIG-IN-COAX
8500-HD-IN-COAX
8144-3GIG-IN-COAX
8144-HD-IN-COAX
8500-3GIG-IN-FIBER
Standard output card 8500-3GIG-OUT-COAX
8500-3GIG-OUT-COAX-EXP (for expanded routers)
8500-HD-OUT-COAX
8500-HD-OUT-COAX-EXP (for expanded routers)
8144-3GIG-OUT-COAX
8144-HD-OUT-COAX
8500-3GIG-IN-FIBER
8500-3GIG-OUT-FIBER
8500-3GIG-OUT-FIBER-EXP (for expanded routers)
Hybrid cards Hybrid cards are those that receive or transmit both video and
audio signals.
MADI card
MADI input card 8500H-IP-TDM-CX
MADI output card 8500H-OP-3G-TDM-CX
Disembedder card 8500H-IP-3G-DEM-CX
Embedder card 8500H-OP-3G-EMB-CX
Well-known ports A list of Ethernet port numbers that are used globally and are
Audio shuffling The concept of recombining audio from several inputs and
Force embedder off Under normal circumstances, the embedder of a router output is
1
MADI input or output card. The MADI ports support 64 TDM audio
channels at 48.000 kHz. (The input cards and the expansion output
card have 8 ports of standard video and one MADI input port). The
MADI output card has 16 video ports and 2 MADI ports.
8500H-OPX-3G-TDM-CX (for expanded routers)
8500H-OPX-3G-EMB-CX (for expanded routers)
registered with the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)
http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
embedding it in one (or more) outputs.
enabled or disabled automatically according to internal switching
rules. It is possible in DHP for router inputs to be configured so that
they force the embedder to be bypassed.
1. MADI input rates (and number of channels) are determined by the actual MADI input stream. The MADI
output rate is exactly 48.0 kHz (samples per second). MADI output supports either 56 or 64 channels, according to a DIP switch setting.
8

Tieline A connection between the output of one router and the input of
Configuration
As a service, DHP interprets take commands from the NV9000 and calculates routes that require
disembedded and re-embedded audio, and relays appropriate commands to the router. DHP
manages a pool of DHP ports that we call the DHP core. DHP also determines whether the route
requires use of the DHP core. A case where it does not require the core is a take from a standard
input to a standard output.
There are several steps in configuring DHP. These involve MRC, NV9000-SE Utilities (and your
NV9000 configuration) and DHP configuration files.
The order in which you perform the configuration steps is not critical as long as you perform all
the configuration tasks and have valid DHP configuration files installed before you restart your
NV9000 with DHP active.
There is no feedback that can tell you whether DHP is active and running properly, except that
DHP will not work if you have, for example, an improper DHP configuration file.
If you are using the NV9000 Web Suite to monitor DHP, and DHP is not operating, the DHP pages
will “freeze” and display stale data. The web suite has no failure report.
DHP
Reference Manual
another router (or possibly of the same router). A multi-hop tieline
is one that involves connections among more than two routers.
Warnings
If you are adding DHP to an existing router, save your existing configuration before doing so. If
you ever decide to stop using DHP, your router will need a non-DHP configuration to operate.
Do not restart your NV9000 without correct DHP configuration files. DHP might fail to start if it
detects errors in its configuration files.
Assumptions made here: your NV9000 is configured and is communicating with the router that
is to use DHP. This document does not address NV9000 configuration apart from the requirements for DHP.
Summary
This is a summary of the DHP configuration steps. Details follow.
1 Following your DHP analysis, populate the router with cards belonging to the DHP core.
Make notes about what you have done.
2 In MRC, define or redefine router partitions for the router.
3 In MRC, specify or re-specify the card types for all slots of the router.
4In MRC, ensure that no router input has its “force embedder on” attribute set true.
5 In NV9000-SE Utilities
a Make the NV9000 communicate with DHP (instead of the router)
b Make DHP communicate with the router’s control card(s).
6 In NotePad or a similar tool, write the DHP configuration files. Verify that they are correct and
save them in the folder
C:\nvision of the NV9000 system controller(s).
9
DHP Service
Configuration Process
7 In NV9000-SE Utilities
a Ensure that a level set exists that includes all audio levels in use.
b Explicitly define all audio levels for standard inputs and outputs that can be switched
using DHP. [For standard I/O that will never be switched by DHP, this is not necessary.]
8 In NV9000-SE Utilities, if your router has MADI ports
a Add 40,000 to any and all MADI port numbers. (DHP requires this.)
b Add 40,000 to the audio matrix size.
9 In NV9000-SE Utilities, clear the DHP portion of the router’s crosspoint matrix.
10 Remove any previously defined sources and destinations from the DHP core portion of the
NV9000 configuration.
11 Finally, write the new configuration to the NV9000 and restart the NV9000. Then set the DHP
service to “automatic” and start the DHP service.
Configuration Process
[1] DHP Core
In your analysis of the DHP requirements of your router, you will have determined the number
and type of hybrid cards to include in the DHP core.
If you are adding DHP to an existing router, place the disembedder (input) cards and embedder
(output) cards that form the DHP core in the router. Also place the cards’ matching backplane
connector modules. The cards in the DHP core do not have to be contiguous.
If you are starting with a new unconfigured router, it is probable that the cards belonging to
your DHP core have been installed at the factory.
In either case, make sure that the cards and backplane modules are installed properly and make
careful written notes about which slots you have used for the DHP core. The port numbers for
the cards in those slots are critical to the configuration process.
10
[2]
Router Levels
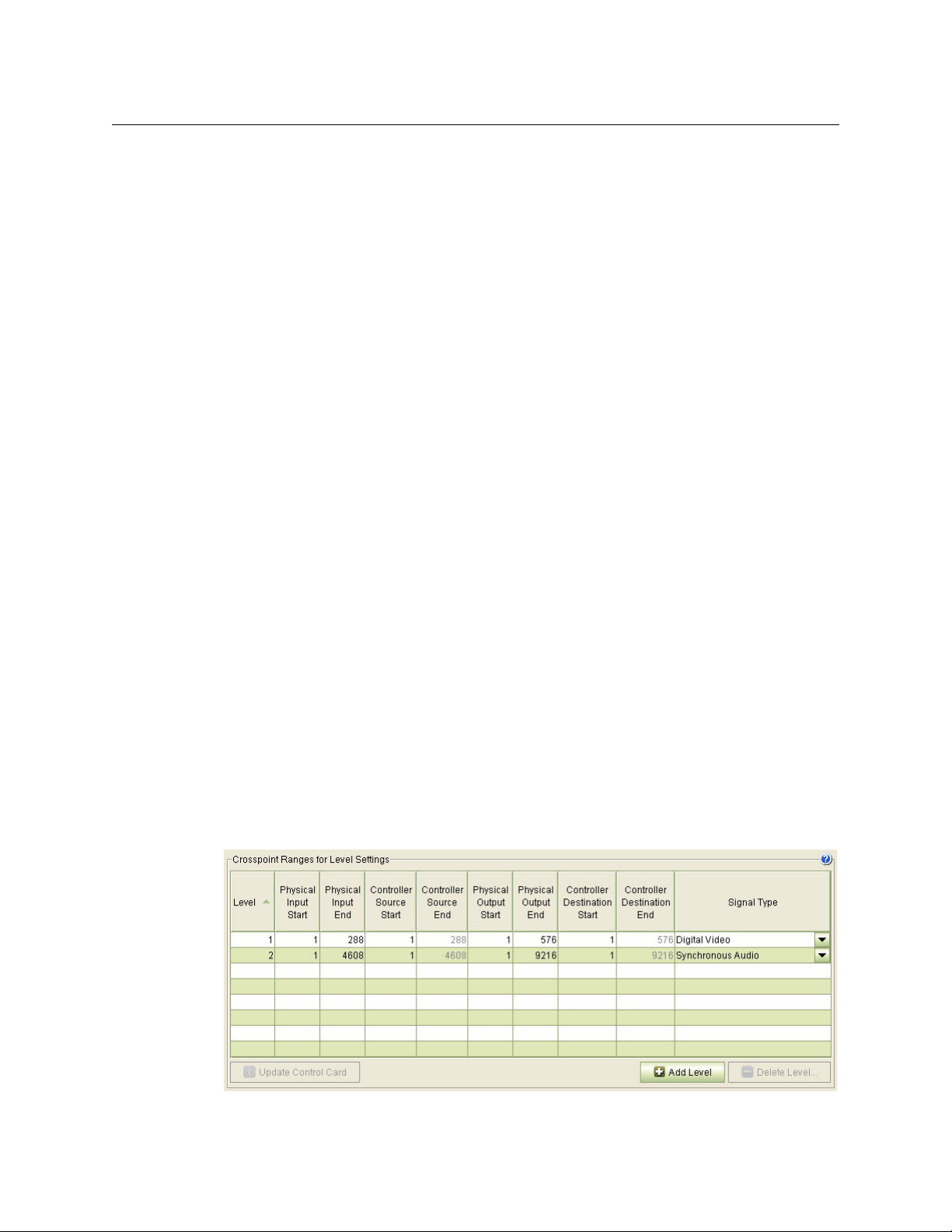
DHP requires that your router have exactly one ‘Digital Video’ partition and one ‘Synchronous
Audio’ partition. Partitions of other types are acceptable, such as a monitor partition. Use the
‘Router Levels’ page in MRC to define the partitions. This example is typical for an NV8280:
Fig. 2-1: Router Partitions for an NV8280 Using DHP
Reference Manual
[3] NV9000-SE Configuration
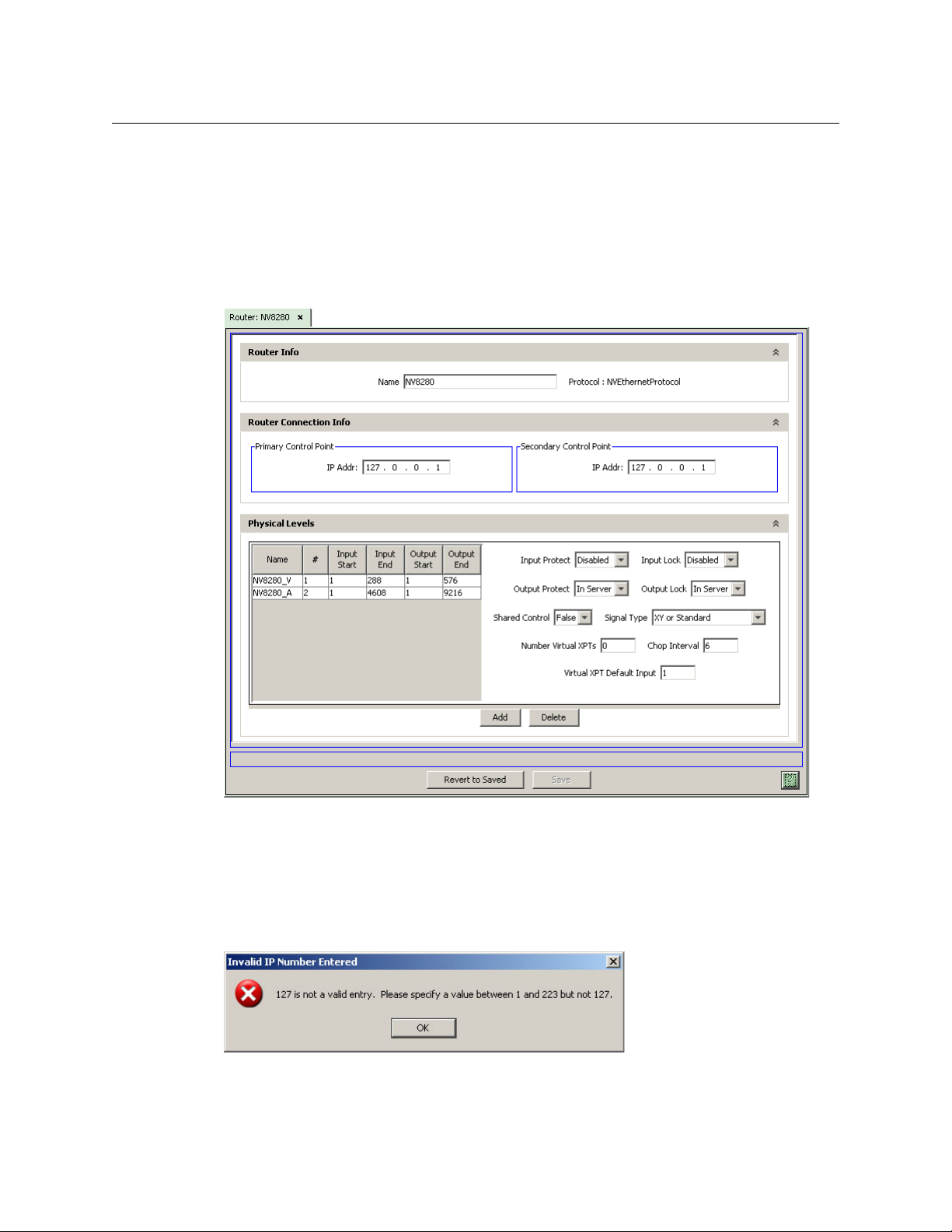
If you are adding DHP to a router, you will have to change your NV9000-SE Utilities settings to
conform to what is discussed here.
DHP stands between the NV9000 control process and the router. The control process communicates with DHP as if it were the router. Therefore, in NV9000-SE Utilities, you must specify the IP
address of the router as 127.0.0.1 (which is, in a sense, the address of DHP). If you are creating a
new router definition, you will see a page similar to this:
DHP
Fig. 2-2: Router Details (NV8280 Shown)
Note: if your router has MADI cards, add 40,000 to the audio level size (i.e., to the ‘Input End’ field
and the ‘Output End’ field).
(This IP address is called a “loopback address.”)
Note that NV9000-SE Utilities will give you a warning message, because, under normal circumstances, 127.0.0.1 is an unusable address:
You can ignore this message, because the use of DHP is an exceptional circumstance.
11
DHP Service
Configuration Process
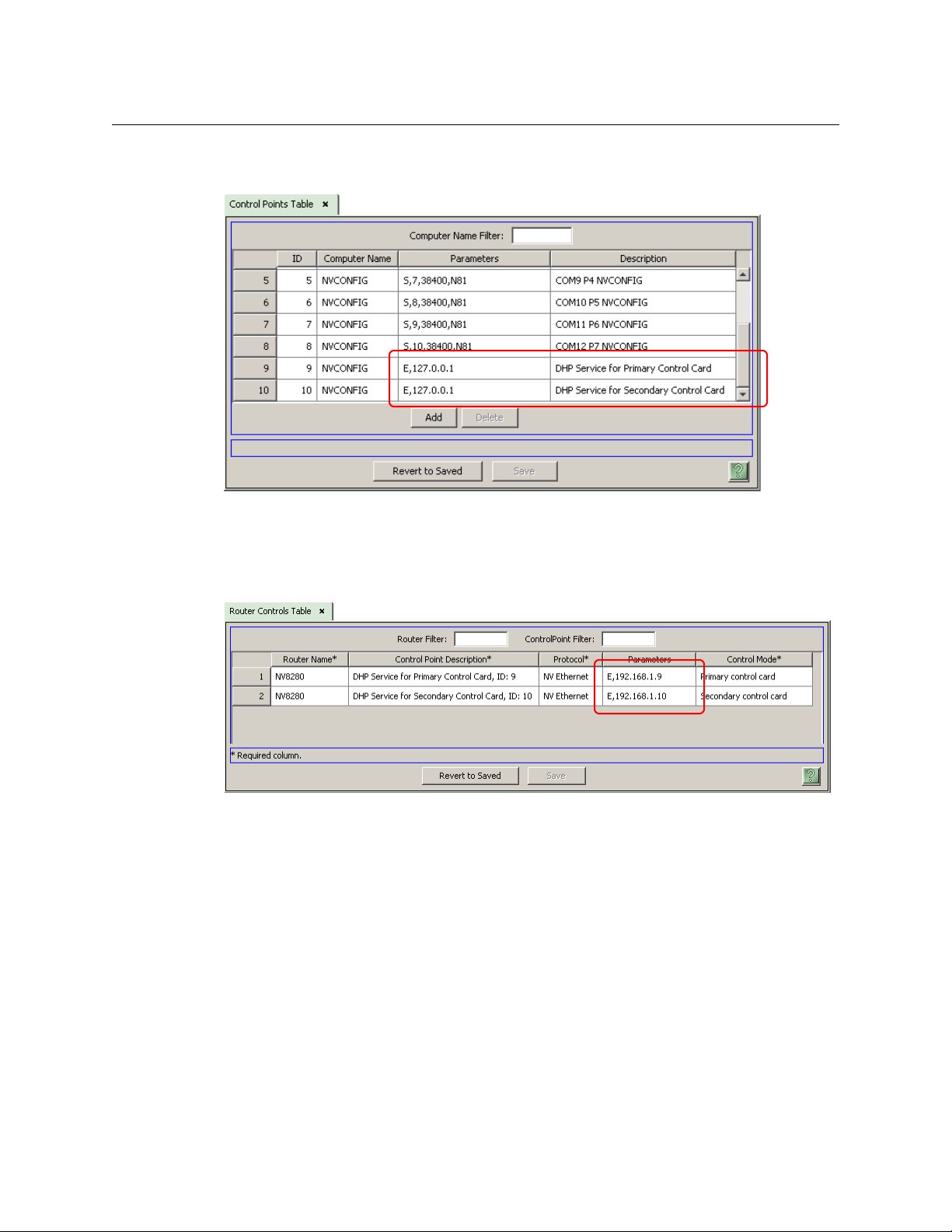
Then, in the ‘Control Points’ table (under the ‘Views’ navigation pane), change the description
field for the DHP proxy of the router: This is a sample control point table (for an NV8280):
Changing the description is not actually necessary, but very helpful.
If you are modifying an existing router definition, it is here that you would change its IP address
to 127.0.0.1.
Then, update the parameters fields in the ‘Router Controls’ table:
12
Define the parameters field as “E”, comma, and the IP address of the router control card. Doing
that lets the DHP service know the IP address of the router control card with which it is to
communicate.
(If you are modifying an existing router definition, the values you enter in the parameters field
here are what were in the parameters field of the control points table. These IP addresses will
have been initially defined in MRC.)
When there are two control cards, one primary and one secondary, only one of those control
cards is actively running. The other control card is in stand-by mode.
Similarly, when there are two control cards, the NV9000 will launch two DHP services at startup.
One of the DHP services is active and the other is stand-by (running, but idle).
At this stage, the ‘Control Points’ table is not quite finished
— you must specify the DHP ports.
 Loading...
Loading...