Emerson Fisher 656 Installation Instructions
Instruction Manual |
656 Actuator |
D100304X012 |
August 2012 |
|
|
Fisherr 656 Diaphragm Actuator
Contents |
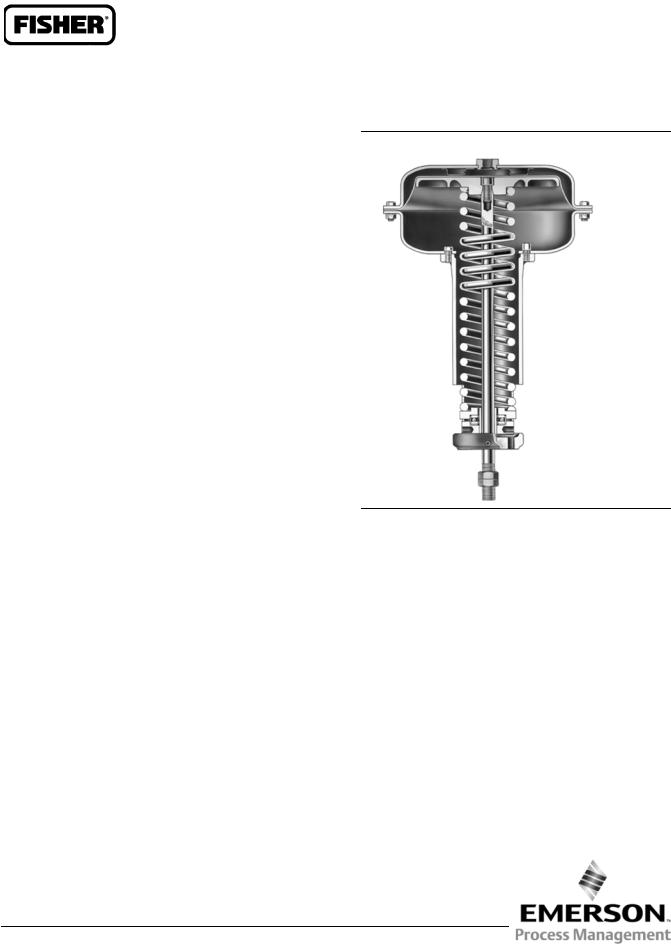
Figure 1. Fisher 656 Actuator |
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
Scope of Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
Principle of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
Maximum Pressure Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
Disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
Parts Ordering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
Handwheel Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
Casing-Mounted Adjustable Down |
|
Travel Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
11 |
W0454
Introduction
Scope of Manual
This instruction manual includes installation, maintenance, and parts information for Fisher 656 diaphragm actuators. Refer to separate manuals for instructions covering the valve, positioner, and accessories.
Description
Fisher 656 actuators are long stroke, spring opposed, direct-acting diaphragm actuators. They operate Vee-Ballt control valves, butterfly valves, built-in turbine valves, louvers, dampers and similar equipment. They are suitable for either push-down-to-close (PDTC) or push-down-to-open (PDTO) applications and are available in sizes 30, 40 and 60 to provide 54 mm (2.125 inch), 64 mm (3.5 inch) and 105 mm (4.125 inch) travel, respectively.
Do not install, operate, or maintain a 656 actuator without being fully trained and qualified in valve, actuator, and accessory installation, operation, and maintenance. To avoid personal injury or property damage, it is important to carefully read, understand, and follow all the contents of this manual, including all safety cautions and warnings. If you have any questions about these instructions, contact your Emerson Process Management sales office before proceeding.
www.Fisher.com

656 Actuator |
Instruction Manual |
August 2012 |
D100304X012 |
|
|
Table 1. Specifications
Maximum Recommended Casing Operating
Pressure(1)
2.4 bar (35 psig)
Maximum Allowable Casing Pressure(2)
|
Maximum |
Maximum |
Maximum |
|
|
Casing |
|
||
Actuator |
Excess |
Diaphragm |
|
|
Pressure for |
|
|||
Diaphragm |
Casing |
|
||
Size |
Actuator |
|
||
Pressure(1), |
Pressure(2,3), |
|
||
|
Sizing(2), |
|
||
|
Bar (Psig) |
Bar (Psig) |
|
|
|
Bar (Psig) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
8.6 (125) |
1.0 (15) |
9.7 (140) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
4.5 (65) |
0.69 (10) |
5.2 (75) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
2.8 (40) |
0.69 (10) |
3.4 (50) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.Additional pressure may be added when the actuator is at full travel. If the Maxi mum Excess Diaphragm Pressure is exceeded, damage to the diaphragm or dia phragm casing might result. See the Maximum Pressure Limitation section.
2.Maximum diaphragm casing pressure must not be exceeded and must not produce a force on the actuator stem greater than the maximum allowable actuator output thrust or the maximum allowable stem load. See the Maximum Pressure Limitation section.
3.This maximum casing pressure is not to be used for normal operating pressure. Its purpose is to allow for typical regulator supply settings and/or relief valve tolerances.
Operating Temperature Range(3)
J -40 to 82 C (-40 to 180 F) with Nitrile Elastomer
J -40 to 149 C (-40 to 300 F) with Silicone
Diaphragm
Casing Pressure Connection
1/4 NPT internal
Maximum Travel
|
MAXIMUM RATED |
|
|
|
STEM TRAVEL, |
|
|
ACTUATOR SIZE |
mm (INCHES) |
|
|
Standard |
Optional |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Travel |
Travel |
|
|
Stop |
Stop |
|
30 |
54 (2.125) |
Not available |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
89 (3.5) |
76 (3) |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
105 (4.125) |
97 (3.8125) |
|
|
|
|
|
Actuator Weight
Actuator Size |
Approximate |
Shipping Weight, |
|
|
kg (Pounds) |
30 |
23 (50) |
|
|
40 |
32 (70) |
|
|
60 |
73 (160) |
|
|
Options
J Top-mounted handwheel/adjustable travel stop J Casing-mounted adjustable down travel stop
1.Control and stability may be impaired if this pressure is exceeded.
2.Exceeding this pressure can cause damage to the diaphragm, diaphragm casing, or other parts.
3.The temperature limits in this manual and any applicable standard or code limitation for valve should not be exceeded.
Principle of Operation
In a direct acting diaphragm actuator, increasing loading pressure moves the actuator stem downward, compressing the spring. When the diaphragm pressure is decreased, the spring moves the actuator stem upward. In the event of failure of the loading pressure, the actuator stem moves to the extreme upward position.
Specifications
Refer to table 1 for Specifications of the 656 actuator. See the actuator nameplate for specific information for your actuator.

 WARNING
WARNING
To avoid personal injury or damage to equipment that may result in the malfunction of the control valve or loss of control of the process caused by excessive pressure, do not exceed the Maximum Pressures listed in table 1. Refer to the following Maximum Pressure Limitations section.
2

Instruction Manual |
656 Actuator |
D100304X012 |
August 2012 |
|
|
Maximum Pressure Limitations
The casing and diaphragm of 656 actuators are pressure operated. This air pressure provides energy to compress the spring, to stroke the actuator, and to seat the valve. The following explanations describe the maximum pressure limits for an actuator. Refer to the nameplate or table 1 for maximum values for your actuator.
DMaximum Casing Pressure for Actuator Sizing: This is the maximum pressure that can be applied at less than full travel of the actuator. If this stroking pressure is exceeded before the upper diaphragm plate contacts the travel stop, damage to the stem or other parts might result.
DMaximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure: Additional pressure may be added when the actuator is at full travel. If the Maximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure is exceeded, damage to the diaphragm or diaphragm casing might result.
Because the actuator has traveled its specified travel, and the diaphragm head is physically stopped from movement, the energy from any additional air pressure is transmitted to the diaphragm and diaphragm casings. The amount of air pressure that can be added once the actuator has traveled to the stops is limited by the resultant adverse effects that may occur. Exceeding this limiting factor could result in leakage or casing fatigue due to the deformation of the upper diaphragm casing.
DMaximum Diaphragm Casing Pressure: If the Maximum Diaphragm Casing Pressure is exceeded, damage to the diaphragm, diaphragm casing, or actuator might result.
Installation
When an actuator and valve are shipped together, the actuator is normally mounted on the valve. Follow the valve instructions when installing the valve and actuator in a pipeline. If the actuator is shipped separately, or if it is necessary to mount the actuator on the valve, four holes have been tapped into the yoke boss to anchor it to a mounting bracket.

 WARNING
WARNING
Always wear protective gloves, clothing, and eyewear when performing any maintenance operations to avoid personal injury.
To avoid personal injury or property damage caused by bursting of pressure retaining parts, be certain the diaphragm casing pressure does not exceed the limits listed in the Specifications table. Use pressure relieving or pressure limiting devices to prevent the diaphragm casing pressure from exceeding these limits.
If installing into an existing application, also refer to the WARNING at the beginning of the Maintenance section in this instruction manual.
To make the stem connection, follow the appropriate assembly step 10 in the Maintenance section. Standard actuator sizes 30 and 40 have mounting holes tapped 3/8 inch UNC, and the size 60 mounting holes are tapped 1/2 inch UNC.
A 1/4 NPT loading pressure connection is located in the top of the upper diaphragm case. Using either pipe or tubing, connect either the loading pressure connection or valve positioner input connection (if a valve positioner is furnished, the loading pressure connection to the actuator will be made at the factory) to the output pressure connection on the controller. Keep the length of the pipe or tubing as short as possible to avoid transmission lag in the control signal.
Adjustment
When the actuator is completely installed and connected to the controller, it should be checked for correct travel, freedom from friction and correct PDTC or PDTO action.
3

656 Actuator |
Instruction Manual |
August 2012 |
D100304X012 |
|
|
The actuator spring and diaphragm have been selected to meet the requirements of the application. It should be noted that the actuator spring has a constant rate of compression and that adjustment of the spring compression merely shifts the initial spring setpoint up or down to make the actuator travel within the initial spring setpoint and the maximum diaphragm pressure indicated on the nameplate.
In some instances, however, such as high friction butterfly and ball valves, the actuator will fully stroke with less diaphragm pressure than indicated on the nameplate. To increase the pressure required to initiate actuator stem movement, turn the lower bearing seat (key 14) up toward the spring case. To decrease the pressure at which movement begins, turn the lower bearing seat down, away from the spring case.
Maintenance

 WARNING
WARNING
Avoid personal injury or property damage from sudden release of process pressure or uncontrolled movement of parts. Before performing any maintenance operations:
D Do not remove the actuator from the valve while the valve is still pressurized.
DAlways wear protective gloves, clothing, and eyewear when performing any maintenance operations to avoid personal injury.
DDisconnect any operating lines providing air pressure, electric power, or a control signal to the actuator. Be sure the actuator cannot suddenly open or close the valve.
DUse bypass valves or completely shut off the process to isolate the valve from process pressure. Relieve process pressure from both sides of the valve. Drain the process media from both sides of the valve.
D Vent the power actuator loading pressure and relieve any actuator spring precompression.
D Use lock-out procedures to be sure that the above measures stay in effect while you are working on the equipment.
DThe valve packing box may contain process fluids that are pressurized, even when the valve has been removed from the pipeline. Process fluids may spray out under pressure when removing the packing hardware or packing rings, or when loosening the packing box pipe plug.
DCheck with your process or safety engineer for any additional measures that must be taken to protect against process media.
Disassembly
1.If the actuator is installed on a control valve, isolate or bypass the control valve.
2.Shut off the diaphragm loading pressure and remove the pipe or tubing from the loading pressure connection in the top of the diaphragm case.
3.Turn the lower bearing seat (key 14) down, away from the spring case to relieve all spring compression.
4.If the entire actuator is to be removed from its mounting, disconnect the actuator stem (key 10) from the stem connector, clevis, etc., and remove the jam nuts (key 23). Loosen the cap screws that hold the yoke (key 9) to its mounting plate or bracket, and lift the entire actuator from its mounting.
5.Remove the diaphragm case cap screws and nuts (keys 19 and 20) and lift the upper diaphragm case (key 1 ) off the actuator. Remove the diaphragm (key 2).
6.Lift out the diaphragm plate (key 4) and stem (key 10). They may be separated by removing the cap screw (key 3).
4
 Loading...
Loading...