Emerson 133, 133HP Instruction Manual

Instruction Manual
Form 5007
June 2013
133 Series
133 Series Direct-Operated Regulators
Table of Contents |
|
Introduction................................................................... |
1 |
Specifi cations............................................................... |
2 |
Principle of Operation................................................... |
2 |
Installation..................................................................... |
3 |
Overpressure Protection.............................................. |
4 |
Startup.......................................................................... |
4 |
Adjustment.................................................................... |
5 |
Shutdown...................................................................... |
6 |
Maintenance................................................................. |
6 |
Parts Ordering............................................................. |
11 |
Parts List.................................................................... |
11 |
!WARNING
Failure to follow these instructions or to properly install and maintain this equipment could result in an explosion
and/or fi re causing property damage and personal injury or death.
Fisher® regulators must be installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with federal, state, and local codes, rules and regulations, and Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. (Regulator Technologies) instructions.
If the regulator vents gas or a leak develops in the system, service to the unit may be required. Failure to correct trouble could result in a hazardous condition.
Call a gas service person to service the unit. Only a qualifi ed person must install or service the regulator.
TYPES 133H, 133L, AND 133Z REGULATORS
W6803
TYPE 133HP REGULATOR
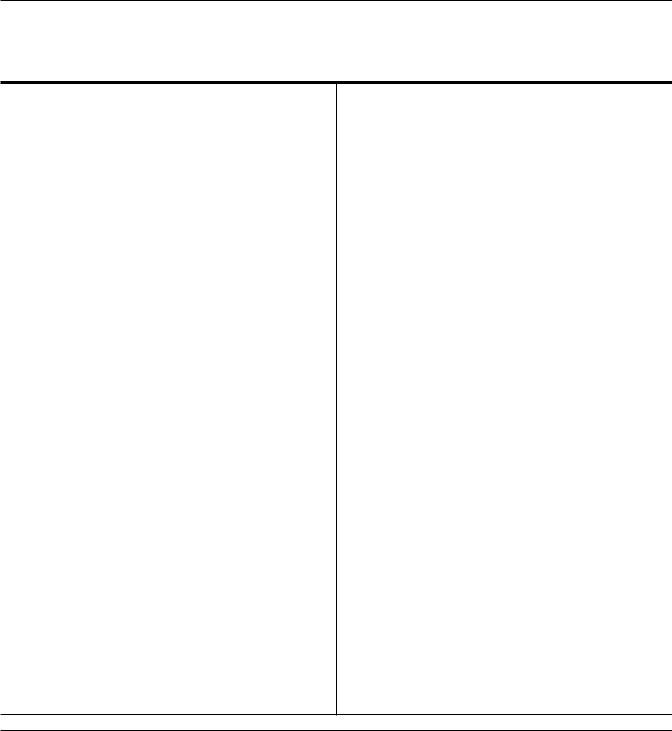
Figure 1. 133 Series Gas Regulators
Introduction
Scope of the Manual
This manual provides specifi cations, installation, adjustment and maintenance instructions, and parts ordering information for the 133 Series regulators.
Only personnel qualifi ed through training or experience should install, operate, and maintain this regulator. If there are any questions concerning these instructions, contact your local Sales Offi ce before proceeding.
Product Description
The 133 Series direct-operated gas regulators, shown in Figure 1 are primarily designed for industrial and commercial applications supplying gas to furnaces, burners, and other appliances. The 133 Series
D100270X012
www.fisherregulators.com
133 Series
Specifications
The Specifications section lists the specifications for the Type 133 Series direct-operated regulators. Factory specification is stamped on the nameplate fastened on the regulator at the factory.
Available Constructions
Type 133H:
High pressure construction for outlet pressure range of 1.5 to 10 psig / 0.10 to 0.69 bar. The
Type 133H can also use the 2 inches w.c. to 2 psig / 5 mbar to 0.14 bar springs of the Type 133L. The maximum operating inlet
pressure is 60 psig / 4.1 bar with a maximum emergency inlet pressure of 125 psig / 8.6 bar.
Type 133HP:
Extra high pressure construction for outlet pressure range of 2 to 60 psig / 0.14 to 4.1 bar. The maximum operating and emergency inlet pressure rating is 150 psig / 10.3 bar.
Type 133L:
Low pressure construction for outlet pressure range of 2 inches w.c. to 2 psig / 5 mbar to
0.14 bar. The maximum operating inlet pressure is 60 psig / 4.1 bar with a maximum emergency inlet pressure of 125 psig / 8.6 bar.
Type 133Z:
Zero governor construction for outlet pressure range of -1 to 4 inches w.c. / -2 to 10 mbar. The maximum operating inlet pressure is 20 psig / 1.4 bar with a maximum emergency inlet pressure of 125 psig / 8.6 bar.
Body Size and End Connection Styles
BODY SIZE |
BODY MATERIAL |
||
|
|
|
|
INCH |
DN |
Cast Iron Body |
WCC Steel Body |
|
|
|
|
2 |
50 |
NPT or CL125 FF Flanged |
NPT or CL150 RF Flanged |
|
|
|
|
Outlet Pressure Ranges
See Table 1
Maximum Inlet Pressures(1)
See Table 2
Maximum Outlet Pressures
See Table 2
Pressure Registration
External; downstream control line is required.
Temperature Capabilities(1)
-20 to 150°F / -29 to 66°C
Control Line Connection
Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z:
3/4 NPT (internal); connection will be positioned directly over body outlet (standard position)
or 90 degrees right or left of standard position if specified.
Type 133HP:
1/4 NPT (internal) connection positioned directly over body outlet.
Vent Connection
Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z:
1 NPT (internal) with screen; standard position is in line with control line connection directly over body outlet. Vent will always be positioned over the control line connection.
Type 133HP:
1/2 NPT (internal) connection positioned directly over body inlet with a Fisher® Type Y602-7 vent assembly.
Approximate Weight
Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z NPT End Connections: 35 pounds / 16 kg
Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z Flanged End Connections: 40 pounds / 18 kg
Type 133HP NPT End Connections:
56.5 pounds / 26 kg
Type 133HP Flanged End Connections:
62.5 pounds / 28 kg
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Instruction Manual or any applicable standard limitation should not be exceeded.
balancing system enables the regulator to provide accurate control gas pressure for maximum combustion efficiency despite varying inlet pressure conditions. The single port construction provides bubble-tight shutoff. An external downstream control line is required for
the operation of the regulator. A restriction collar is available to reduce the flow capacity of the regulator.
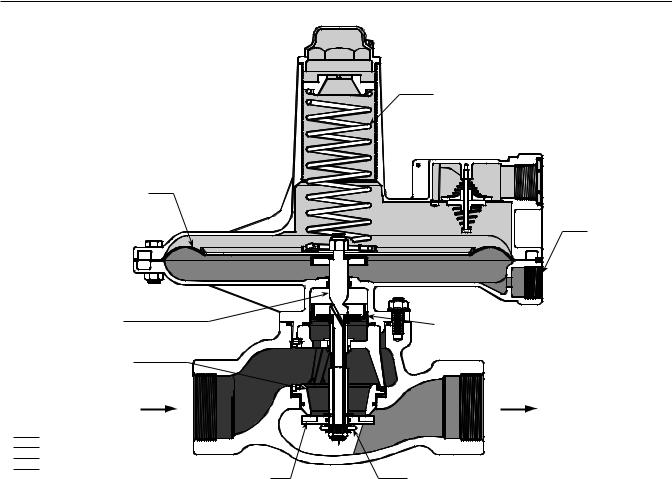
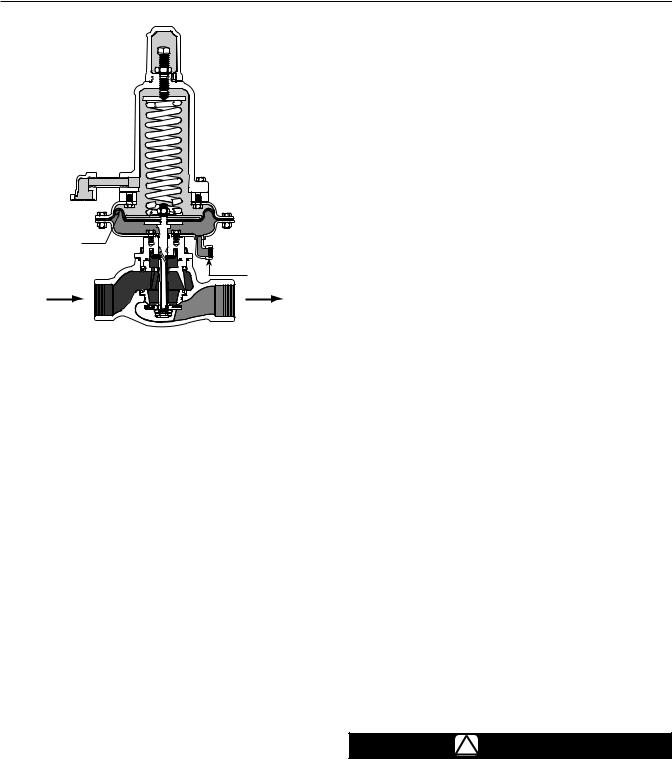
Principle of Operation
Refer to the operational schematics in Figures 2 and 3.
In the 133 Series, downstream pressure is registered under the diaphragm via the external control line and is used as the operating medium. Increased demand lowers the downstream pressure and allows the spring to move the diaphragm and stem assembly down, opening the valve disk, and supplying more gas to the
2
133 Series
CONTROL SPRING
DIAPHRAGM
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
STEM |
BALANCING |
|
DIAPHRAGM |
ORIFICE |
|
A6555

 INLET PRESSURE
INLET PRESSURE

 OUTLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE

 ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE

 BOOST PRESSURE
BOOST PRESSURE
VALVE DISK |
REGISTRATION DISK |
Figure 2. Operational Schematic of Type 133L Regulator (Also Typical of Type 133H)
downstream system. Decreased demand increases the downstream pressure and moves the diaphragm and stem assembly up, closing the valve disk, and decreasing the gas supply to the downstream system.
Boosting System
The 133 Series incorporates a balancing diaphragm and a boosting system. When the regulator is locked up, inlet pressure is registered on the top of the valve disk and on the bottom of the balancing diaphragm through registration holes in the top of the cage. Also, downstream pressure is registered on the bottom
of the valve disk and on the top of the balancing diaphragm through a passage formed by grooves in the registration disk and an annular space between the stem and stem sleeve.
When the valve disk is open, gas flows from the inlet over the edge of the valve disk to the outlet. Under the valve disk near the registration disk, there is little gas flow. The gas pressure near the registration disk is higher than it is in the flow path where gas velocity
tends to lower the pressure. The higher pressure near the disk is registered on the top of the balancing diaphragm through the registration disk and the annular space between the stem and stem sleeve.
This pressure registered on the top of the balancing diaphragm aids downward disk travel and compensates for spring and diaphragm effect. This improves regulator range ability and performance.
Installation
Before installing the 133 Series regulators, inspect it for shipping damage and be certain that the body and orifice are clean. Blow out the pipeline to remove pipe scale and other foreign material.
The regulator may be installed in any position as long as the flow through the body is the same as indicated by the flow direction arrow on the body and the vent opening is unobstructed and protected from the entrance of rain, ice, and other foreign material.
3
133 Series
VENT
ASSEMBLY
DIAPHRAGM
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
A6883

 INLET PRESSURE
INLET PRESSURE

 OUTLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE

 ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE

 BOOST PRESSURE
BOOST PRESSURE
Figure 3. Operational Schematic of Type 133HP
If the regulator has threaded end connections, coat external threads with pipe compound. For flanged end connections, tighten the flange bolts evenly.
Install a three valve bypass around the 133 Series if continuous operation is necessary.
The regulator must be protected from damage by vehicles and other outside sources.
Overpressure Protection
The 133 Series regulators have an outlet pressure rating that is lower than the inlet pressure rating. Some type of overpressure protection is needed if the actual inlet pressure exceeds the outlet pressure rating.
Maximum operating inlet pressure for the 133 Series regulators is given in Table 2. All models must
be protected against inlet pressure above their listed maximum.
Regulator operation below these emergency pressure limitations does not preclude the possibility of damage from external sources or from debris in the gas line.
The regulator should be inspected for damage after any overpressure condition.
Downstream Control Line
An external downstream control line must be installed before putting the 133 Series regulators in operation.
Without the control line, the regulator will remain wideopen. The downstream control line should be a pipe of at least 1/2 inch / 12.7 mm diameter; connect it to the downstream pipe line at least 5 to 10 pipe diameters from the regulator and in a straight section of pipe.
The external downstream control line connection on the Type 133HP is 1/4 NPT.
Vent
The 133 Series vent is screened to prevent insects or foreign material from entering. The Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z regulators have a 1 NPT (internal) connection and the Type 133HP has a 1/2 NPT internal connection. If a vent to the atmosphere is required for indoor installations, do the following:
• For Types 133H, 133L, and 133Z — remove the snap ring and screen (keys 8J and 8H, Figure 10, 11, or 12) and pipe the vent to the outside.
• For Type 133HP — remove the Type Y602-7 screened vent assembly and pipe nipple (keys 50 and 49, Figure 14) from the spring case (key 8) and pipe the vent to the outside.
The vent pipe should be as short as possible with minimum number of bends or elbows. The pipe should also have the largest practical diameter. Install a weather and bug resistant vent assembly on the outside end of the vent pipe.
For indoor installation that have been piped to the outside and for outdoor installations, the vent opening must be positioned so that water, ice, and other foreign material cannot enter the spring case. Use care not to place the vent opening below downspouts and eaves. The vent opening should be checked periodically to be sure that the opening has not been plugged with foreign material. On some installations it may be necessary to provide additional protection from the elements.
Startup
!WARNING
If the downstream system is already pressured by another regulator or by a manual bypass, then extra precautions must be taken when placing the 133 Series in service. The outlet of the regulator must never be subjected to pressure higher than the inlet pressure, or the balancing diaphragm may be damaged.
4

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
133 Series |
||
|
|
Table 1. 133 Series Outlet Pressure Ranges, Control Springs |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTLET PRESSURE RANGE |
|
CONTROL SPRINGS |
|
|
|
|
||||
TYPE |
Part Number |
Color Code |
Free Length |
|
Wire Diameter |
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
psig |
bar |
|
|
Inch |
|
mm |
|
Inch |
mm |
|
|
1.5 to 3 |
0.10 to |
0.21 |
1H975927032 |
Orange |
6.91 |
|
176 |
|
0.250 |
6.35 |
133H(1) |
2 to 5 |
0.14 to |
0.34 |
10A9440X012 |
Yellow |
6.47 |
|
164 |
|
0.283 |
7.19 |
|
5 to 10 |
0.34 to |
0.69 |
1J146927142 |
Blue |
6.19 |
|
157 |
|
0.375 |
9.52 |
|
2 to 5 |
0.14 to |
0.34 |
17B8632X012 |
Yellow |
8.50 |
|
216 |
|
0.282 |
7.16 |
|
4.5 to 10 |
0.31 to |
0.69 |
17B8633X012 |
Orange |
8.50 |
|
216 |
|
0.343 |
8.71 |
|
6 to 20 |
0.41 to 1.4 |
10C1238X012 |
Silver |
8.25 |
|
210 |
|
0.375 |
9.53 |
|
133HP(1) |
16 to 30 |
1.1 to |
2.1 |
10C1240X012 |
Red |
8.25 |
|
210 |
|
0.438 |
11.1 |
|
26 to 40 |
1.8 to |
2.8 |
10C1241X012 |
Blue |
8.25 |
|
210 |
|
0.500 |
12.7 |
|
36 to 50 |
2.5 to |
3.4 |
10C1242X012 |
Green |
8.25 |
|
210 |
|
0.500 |
12.7 |
|
45 to 60 |
3.1 to |
4.1 |
10C1243X012 |
White |
8.25 |
|
210 |
|
0.531 |
13.5 |
|
2 to 4 inches w.c. |
5 to 10 mbar |
1D892527022 |
Brown |
6.13 |
|
156 |
|
0.109 |
2.77 |
|
|
3.5 to 6 inches w.c. |
9 to 15 mbar |
1D892627022 |
Red |
7.53 |
|
191 |
|
0.112 |
2.85 |
|
133L(1) and 133H(2) |
5 to 9 inches w.c. |
12 to 22 mbar |
1D892727012 |
Black |
7.88 |
|
200 |
|
0.130 |
3.30 |
|
|
8.5 to 18 inches w.c. |
21 to 45 mbar |
1D893227032 |
White |
7.50 |
|
190 |
|
0.156 |
3.96 |
|
|
14 to 28 inches w.c. |
35 to 70 mbar |
1D893327032 |
Green |
7.25 |
|
184 |
|
0.182 |
4.62 |
|
|
0.75 to 2 |
0.05 to |
0.14 |
1H975827032 |
Blue |
7.09 |
|
180 |
|
0.225 |
5.72 |
|
-1 to 1 inch w.c. |
-3 to 3 mbar |
1K633427012 |
Unpainted |
2.00 |
|
50.8 |
|
0.075 |
1.91 |
|
|
(Extension Spring) |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
133Z(1) |
|
|
|
1K633427012 |
Unpainted |
2.00 |
|
50.8 |
|
0.075 |
1.91 |
|
|
|
(Extension Spring) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 to 4 inches w.c. |
0 to 10 mbar |
and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1D892527022 |
Brown |
6.13 |
|
156 |
|
0.109 |
2.77 |
|
|
|
|
(Compression Spring) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Pressure ranges shown are correct if the regulator is installed with the actuator portion above the body portion. If the regulator is installed with the actuator portion below the body, the pressure ranges will be lowered by approximately 2 inches w.c. / 5 mbar for the Type 133L and by approximately 3 inches w.c. / 7 mbar for the Types 133H and 133Z.
2. If the 2 inches w.c. / 5 mbar to 2 psig / 0.14 bar springs (all 6 ranges) are used in the Type 133H, the pressure ranges will increase by approximately 1 inch w.c. / 2 mbar due to the weight of the Type 133H parts (assuming that the actuator is installed above the body).
Table 2. Maximum Inlet and Outlet Pressures
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE NUMBER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PRESSURES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
133H |
|
133HP |
|
133L |
|
133Z |
|||||
|
psig |
|
bar |
psig |
|
bar |
psig |
|
bar |
psig |
|
bar |
Maximum Operating Inlet Pressure |
60 |
|
4.1 |
150 |
|
10.5 |
60 |
|
4.1 |
20 |
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Maximum Emergency Inlet Pressure |
125 |
|
8.6 |
|
125 |
|
8.6 |
125 |
|
8.6 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Operating Outlet Pressure(1) |
10 |
|
0.69 |
Setpoint |
Setpoint |
2 |
|
0.14 |
4 inches |
|
10 mbar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
w.c. |
|
|
|||
Maximum Outlet Pressure Over |
3 |
|
0.21 |
plus 40 |
|
plus 2.8 |
3 |
|
0.21 |
3 |
|
0.21 |
Outlet Pressure Setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Emergency Outlet |
15 |
|
1.0 |
150 |
|
10.5 |
15 |
|
1.0 |
15 |
|
1.0 |
(Casing) Pressure |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. With highest spring range available only. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Also, the control line pressure must never exceed the set point dictated by the spring setting by more than 3 psig / 0.21 bar, or the valve seat or diaphragm plates can be damaged. The procedure used in putting the regulator in service must be planned accordingly. Pressure gauges should always be used to monitor downstream and control line pressures during startup.
If the downstream system is not pressured by another regulator or by manual bypass, use the following procedure:
1.Check to see that all appliances are turned off.
2.Slowly open the upstream shutoff valve.
3.Slowly open the downstream shutoff valve.
4.Check all connections for leaks.
5.Make final control spring adjustments according to the adjustment procedures.
Adjustment
To increase the pressure setting, remove the closing cap (key 9, Figures 10, 11, 12, and 14) and turn the adjusting screw (key 11) clockwise; to lower the setting, turn the adjusting screw counterclockwise. A pressure gauge should always be used when
adjustments are being made. Do not adjust the spring to produce an outlet pressure setting above the limit
5
 Loading...
Loading...