Page 1
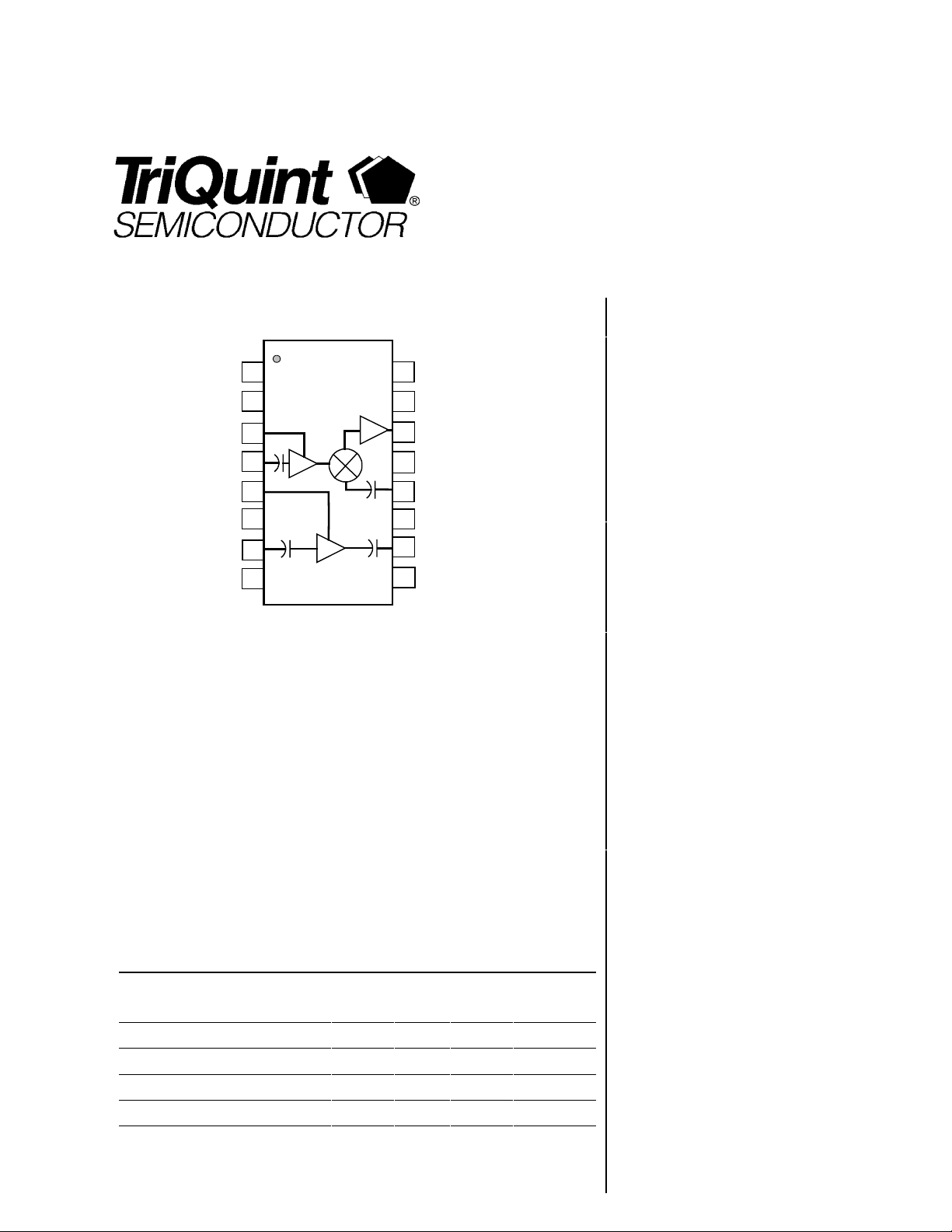
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS DIVISION
GND
1
GND
16
TQ5122
DATA SHEET
GND
Vdd MXR
MXR LO
VDD LNA
GND
RF IN
GND
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
15
GND
14
IF Output/Vdd
13
GND
MXR RF
12
GND
11
LNA
10
Out
9
Control
Input
Sleep
Product Description
The TQ5122 is a 3V, RF receiver IC designed specifically for Cellular band TDMA
applications. It’s RF performance meets the requirements for products designed to the
IS-136 TDMA and the AMPS standards. The TQ5122 includes a power–down mode
which allows current saving during standby and the non-operating portion of the TDMA
pulse. The TQ5122 contains LNA and Mixer circuits matched to the 800MHz cellular
band.
The mixer uses a high-side LO frequency. The IF has a usable frequency range of 85
to 150MHz. The LNA Output and Mixer Input ports are internally matched to simplify
the design and keep the number of external components to a minimum. The TQ5122
achieves excellent RF performance with low current consumption which yields long
standby times in portable applications. The small QSOP-16 package is ideally suited
for Cellular band mobile phones.
Electrical Specifications
1
3V Cellular TDMA/AMPS
Receiver IC With PowerDown
Features
Power-Down, “Sleep” Mode
Single 2.8V operation
Low-current operation
Small QSOP-16 plastic package
Few external components
Applications
IS-136 TDMA Mobile Phones
Dual Mode TDMA/AMPS Mobile Phones
AMPS Mobile Phones
Parameter Min Typ Max Units
Frequency 869 894 MHz
Gain 18.5 dB
Noise Figure 2.7 dB
Input 3rd Order Intercept -8.5 dBm
DC supply Current 12.0 mA
Note 1: Test Conditions: Vdd= 2.8VDC, Tc=25°C, Filter IL=2.5dB, RF=881MHz, LO=1016MHz,
IF=135MHz, LO input=-7dBm
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com 1
Page 2

TQ5122
Data Sheet
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Conditions Min. Typ/Nom Max. Units
RF Frequency 869 894 MHz
LO Frequency 954 1044 MHz
IF Frequency 85 150 MHz
LO input level -7 -4 0 dBm
Supply voltage 2.7 2.8 4.0 V
Gain 16.0 18.5 dB
Gain Variation vs. Temp. -40 to 85 °C +/-2.0 dB
Noise Figure 2.7 3.5 dB
Input 3rd Order Intercept -11.0 -8.5 dBm
Return Loss LNA input – with external match
Isolation LO to LNA RF in
IF Output Impedance Vdd = 2.8V; Sleep mode, Device On
Power Down, “sleep” Device On Voltage
Supply Current, Sleep mode, Device On Tc = + 25 °C 12 15 mA
Supply Current, Sleep mode, Device Off Enable voltage = 0, LO Drive off 100 1000
1,2
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
Ohm
Ohm
Ohm
VDC
µA
LNA output
Mixer RF input
Mixer LO input
LO to IF; after IF match
RF to IF; after IF match
Vdd = 2.8V; Sleep mode, Device Off
Vdd = 0V
Device Off Voltage 0
10
10
10
10
35
40
20
500
Approx. Open
<50
Vdd
0
Vdd VDC
Operating Temperature, case -40 25 +85 °C
Note 1: Test Conditions: Vdd=2.8VDC, Fil ter IL=2.5dB, RF=881MHz, LO=1016MHz, IF=135MHz, LO input=-7dBm, TC = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.
Note 2: Min./Max. limi ts are at +25
°
C case temperature unless otherwise spec ified.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Value Units
DC Power Supply 5.0 V
Power Dissipation 500 mW
Operating Temperature -55 to 100 °C
Storage Temperature -60 to 150 °C
Signal level on inputs/outputs +20 dBm
Voltage to any non supply pin -0.3 to Vdd + 0.3 V
2 For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Page 3
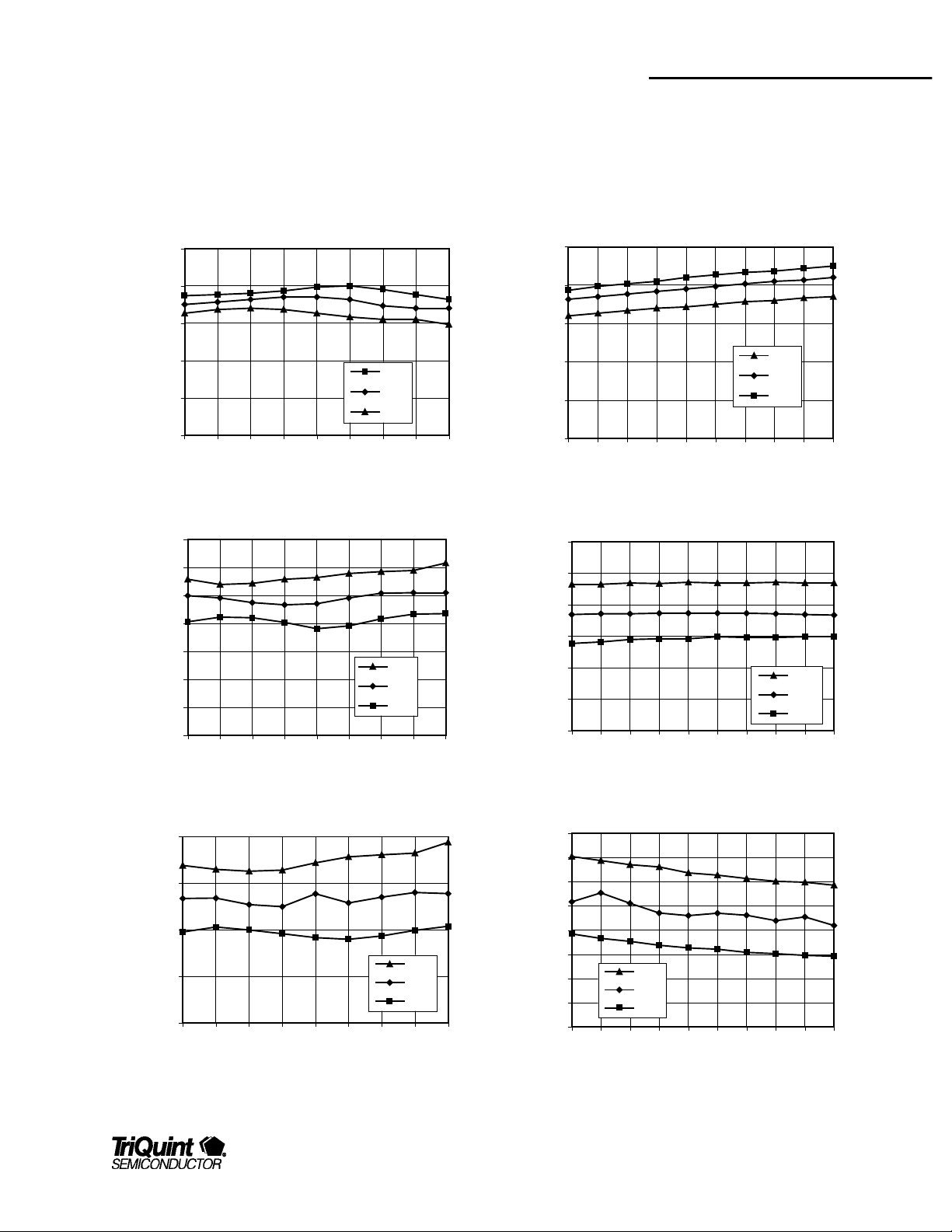
TQ5122
Data Sheet
Typical Performance
Test Conditions (Unl ess Otherwise Speci fied): Vdd=2.8VDC, Tc=25°C, filter IL=2.5dB, RF=881MHz, LO=1016MHz, IF= 135MHz, LO input=-7dBm
Gain vs. Frequency vs. Temperature
25
20
15
Gain (dB)
10
5
0
869 872 875 878 881 884 887 890 893
Frequency (MHz)
Input IP3 vs. Frequency vs. Temperature
-40C
+25C
+85C
-4
-6
-8
-10
-12
Input IP3 (dBm)
-14
-16
85C
25C
-40C
-18
869 872 875 878 881 884 887 890 893
Frequency (MHz)
25
20
15
Gain (dB)
10
5
0
2.7 2.8 2.9 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6
-4
-6
-8
-10
-12
Input IP3 (dBm)
-14
-16
2.7 2.8 2.9 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6
Gain vs. Vdd vs. Temperature
+85C
+25C
-40C
Vdd (volts)
Input IP3 vs. Vdd vs. Temperature
Vdd (volts)
+85C
+25C
-40C
NF vs. Frequency vs. Temperature
4
3
2
NF (dB)
1
0
869 872 875 878 881 884 887 890 893
Frequency (MHz)
+85C
+25C
-40C
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com 3
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
NF (dB)
1.5
1
0.5
0
2.7 2.8 2.9 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6
NF vs. Vdd vs. Temperature
+85C
+25C
-40C
Vdd (volts)
Page 4

TQ5122
Data Sheet
Application/Test Circuit
V MX
LO in
V LNA
LNA in
1
2
C3
3
L2
4
5
C2
6
L1
7
C1
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C5
L3
C4
Sleep Control
V IF
IF out
C6
F881
Bill of Material for TQ5122 Receiver Application/Test Circuit*
Component Reference Designator Part Number Value Size Manufacturer
Receiver IC U1 TQ5122 QSOP-16 TriQuint Semiconductor
Capacitor C1 2.7pF 0603
Capacitor C2, C3 22pF 0603
Capacitor C4 10pF 0603
Capacitor C5 1000pF 0603
Capacitor C6 8.2 pF 0603
Inductor L1 22nH 0603
Inductor L2 12nH 0603
Inductor L3 150nH 0805
Toyocom (select) F1 T726881A 627-881A Toyocom
* May vary due to printed circuit board layout and material.
4 For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Page 5

TQ5122
Data Sheet
TQ5122 Product Description
The TQ5122 3V RFIC Downconverter is designed specifically
for cellular band TDMA/AMPS applications. The TQ5122
contains LNA, Mixer and LO buffer circuits matched to the 800
MHz cellular frequency band. The IF frequency may be selected
between 85 and 150 MHz. Most RF ports are internally
matched to 50
Ω simplifying the design and minimizing the
number of external components. The TQ5122 also includes a
power–down mode switch which allows current saving during
standby and the non-operating portion of the TDMA pulse.
Operation
Please refer to the test circuit above.
Low Noise Amplifier (LNA)
The LNA section of the TQ5122 are cascaded common source
FET’s, see Figure 1. It is designed to operate on DC supply
voltages from 2.7V to 5V. The source terminal must be
grounded as close as possible to Pin 8 to avoid significant gain
reduction due to degeneration. The LNA requires an input
matching circuit to obtain best noise figure, gain and return loss.
The LNA output is close to 50
image reject filter.
LNA
in
BIAS
Figure 1. Simplified Schematic of LNA Section
LNA Input Match
Ω for direct connection to a 50 Ω
Vdd
LOAD
LNA
out
BIAS
presented to the input pin. Highest gain and lowest return loss
Γ
occur when
input impedance. A different source reflection coefficient,
is equal to the complex conjugate of the LNA
s
Γ
,
opt
which is experimentally determined, will provide the lowest noise
figure, F
The noise resistance, R
of the noise performance to changes in
min
.
, provides an indication of the sensitivity
n
Γ
as seen by the LNA
s
input.
2
opt S
ΓΓ
FF
LNA MIN
=+⋅
N
R
4
0
Z
+⋅−
11
−
22
opt
ΓΓ
s
()
Components such as filters and mixers placed after the LNA
degrade the overall system noise figure according to the
following equation:
F
FF
SYSTEM LNA
=+
F
and G
LNA
LNA and F
represent the linear noise factor and gain of the
LNA
is the noise factor of the next stage. The system
2
G
−2 1
LNA
noise figure is a compromise between the highest gain and
minimum noise figure of the LNA. See Table 1 for noise
parameters.
Table 1. TQ5122 Noise Parameters
Freq.
|Gopt| / Gopt
Fmin Rn
MHz
830 0.88 34.5 0.75 51.2
880 0.83 37.8 0.89 50.4
930 0.82 40.0 0.97 50.0
LNA Output Match
The output impedance of the LNA was designed for 50
internal 50
Ω match eliminates the need for external
Ω. The
components at this port. It also improves IP3 performance and
power gain.
The designer can make some Noise Figure and Gain trade off
by varying the off chip LNA input matching circuit values and
topology. This allows the TQ5122 to be optimized for specific
system requirements.
The LNA gain, noise figure and input return loss are a function
of the source impedance (Z
), or reflection coefficient (Γs),
s
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com 5
The output of the LNA is intended to be connected directly to an
image reject filter. Depending on the filter, additional
components may be needed to better match to the LNA output.
Some image reject filters may require a series inductor to
smooth the frequency response and improve overall
performance.
Page 6

TQ5122
Data Sheet
Mixer
The mixer of the TQ5122 uses a common source depletion
mode MESFET. The mixer is designed to operate on supply
voltages from 2.7V to 5V. A 50
Ω matched on-chip buffer
amplifier allows direct connection of the LO input to
commercially available VCO’s with output drive levels down to
-7dBm. The common-gate LO buffer provides good input match
and supplies the voltage gain needed to drive the mixer FET.
The mixer also has an "open-drain" IF output which provides
flexibility in matching to various IF frequencies and filter
impedances, see Figure 2.
Open Drain
IF Output
LO Input
LO Bias
and
Tuning
Mixer RF
Input
Figure 2, Mixer Section
degradation in conversion gain and system noise figure.
Sensitivity to the phenomena depends on the particular filter
model and the line length between the mixer input pin and the
filter. In some cases a small inductance can be added between
the filter and the mixer input to compensate. With some line
lengths and filter combinations, no inductor is necessary.
LO Buffer & Calculation of Nominal L2 Value
The node between the LO buffer amplifier and the mixer FET is
brought out to Pin 3 (V MX) and connected by an inductor to AC
ground. This inductor is selected to resonate with internal on
chip capacitance at the LO frequency in order to reduce out-ofband gain and improve noise performance.
The internal capacitance of the LO amplifier output plus the
stray capacitance on the board surrounding Pin 3 is
approximately 1.5 pF. The inductor is selected to resonate with
the total capacitance at the LO frequency using the following
equation:
L
1
=⋅=
Cf
Π
2
()
where C pF
,.
2
15
LO Input Port
The LO input port is matched to 50
Ω. This allows the TQ5122
to operate at low LO drivel levels. However, the values and
positions of L2 and C3 shown in the applications circuit effect
the gain of the LO buffer amplifier and are important to the
proper operation of the TQ5122. See “Calculation of nominal L2
Value” below
The common gate buffer amplifier provides the voltage gain
needed to drive the gate of the mixer FET while using very little
current (approximately 1.5mA).
Because of the 50
Ω input match of the buffer amplifier and the
internal DC blocking capacitor, the system VCO output can be
directly connected to the TQ5122 LO input via a 50
Ω
transmission line with no additional components.
Mixer Input
Although the mixer input port is matched to 50
Ω, TriQuint has
found that LO leakage through the Mixer RF input pin, can in
some cases, reflect off the SAW image reject filter and return
back to the mixer out of phase. This may cause some
The final values must be confirmed with measurements on a
board approximating the final layout. The final layout will affect
the value and position of L2 and its bypass capacitor, C3, see
Figure 5.
Network
Analyzer
Port 2
Port 1
3
Probe
-30
-32
-34
-36
-38
S21 (dB)
-40
-42
Frequency (MHz)
Figure 3. LO Buffer Frequency Response
4
TQ5122
1000
1100 1200900800700
6 For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Page 7

TQ5122
Data Sheet
Measuring the LO Frequency Response
The frequency response of the LO driver amplifier can be
measured using a semi-rigid probe, see Figure 3, and a network
analyzer.
Connect port 1 to the LO input (Pin 4) of the TQ5122 with the
source power set to deliver -7 dBm. Connect the coaxial probe
to Port 2 and place the probe tip approximately 0.1 inch away
from either Pin 3 or the inductor.
If the calculated shunt inductor (L2) is not a standard value, the
AC ground bypass capacitor C3 can be positioned along the
transmission line to adjust for the right inductance, see Figure 4.
Once this is completed, the peak of the response should be
centered at the center of the LO frequency band.
Placement of C3 will adjust between standard values of
GND
C3
Figure 4, Adjusting the AC Ground
inductors.
Pin 2
Pin 3
L2
topology must contain either an RF choke or shunt inductor. An
extra DC blocking capacitor is not necessary if the output will be
attached directly to a SAW or crystal bandpass filters.
Figure 5 illustrates a shunt L, series C, shunt C IF matching
network. It is one of the simplest matching networks and
requires the fewest components. DC current can be easily
injected through the shunt inductor and the series C provides a
DC block, if needed. The shunt C, is used to reduce the LO
leakage.
10 pF
Pin 14
150nH
Pin 13
1000pF
Figure 5, IF Output Match, 135 M Hz
IF out
8.2pF
V IF
Power down, “sleep” mode
The power down circuit is used to reduce average power
consumption in TDMA applications by toggling the receiver on
and off within the receive time slot when no signal is present.
Mixer IF Port
The Mixer IF output is an "open-drain" configuration, allowing for
flexibility in efficient matching to various filter types and at
various IF frequencies.
For evaluation of the LNA and mixer, it is usually necessary to
impedance match the IF port to the 50
Ω test systems. When
verifying or adjusting the matching circuit on the prototype circuit
board, the LO drive should be injected at pin 4 at the nominal
power level of -4 dBm, since the LO level does have an impact
on the IF port impedance.
There are several networks that can be used to properly match
the IF port to the SAW or crystal IF filter. The mixer supply
voltage is applied through the IF port, so the matching circuit
The power down circuitry operates through the incorporation of
enhancement-mode FET switches in all DC paths. Level
shifting circuitry is incorporated for the purpose of providing an
interface compatible with CMOS logic levels. The entire chip
nominally draws 100uA when the power-down pin is at 0V.
When the power-down pin is at 2.8V (Vdd), the chip draws
nominal specified current. The power-down pin itself, Pin 9,
draws approximately 40uA when 2.8V is applied. Less than 1uA
is sourced from the power-down pin when 0V is applied.
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com 7
Page 8

Package Pinout
TQ5122
Data Sheet
GND
GND
Vdd MXR
MXR LO
VDD LNA
GND
RF IN
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
GND
16
15
GND
14
IF Output/Vdd
13
GND
MXR RF
12
GND
11
LNA
10
Out
9
Control
Input
Sleep
Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Pin # Description and Usage
GND 1 Ground
GND 2 Ground
VDD_MXR 3 Mixer LO buffer supply voltage. Series inductor required for LO buffer tuning. Local external bypass capacitor required.
MXR LO IN 4
V
LNA 5 LNA DC supply voltage. Local external bypass capacitor required.
DD
GND 6 Ground
LNA IN 7
Mixer LO input. DC blocked, matched to 50Ω
LNA RF input. DC blocked. Requires external matching elements for noise match and match to 50Ω
GND, LNA 8 LNA first stage ground connection. Direct connection to ground required.
SLEEP 9 Power-Down mode control.
LNA OUT 10
LNA RF output. DC blocked. Matched to 50Ω.
GND 11 Ground
MXR_RF 12
Mixer RF input, DC blocked. Matched to 50Ω.
GND 13 Ground
IF OUT 14 IF output. Open drain output, connection to Vdd required. External matching is required.
GND 15 Ground
GND 16 Ground
For ground pins 1, 2, 6, 11, 13, 15, and 16, TriQuint recommends use of several via holes to the backside ground immediately adjacent to
the pin.
8 For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Page 9

Package Type: Power QSOP-16 Plastic Package
D
NOTE A
b
A
TQ5122
Data Sheet
E
E1
NOTE B
c
e
A1
θ
L
DESIGNATION DESCRIPTION ENGLISH METRIC NOTE
A OVERALL HEIGHT 0.064 +/-.005 in 1.63 +/-.13 mm C
A1 STANDOFF 0.007 +/-.003 in 0.18 +/-.08 mm C
b LEAD WIDTH 0.010 +/-.002 in 0.25 +/-.05 mm C
c LEAD THICKNESS 0.085 +/-.015 in 2.16 +/-.38 mm C
D PACKAGE LENGTH 0.193 +/-.004 in 4.90 +/-.10 mm A, C
e LEAD PITCH 0.025 BSC 0.635 BSC
E LEAD TIP SPAN 0.236 +/-.008 in 5.99 +/-.20 mm C
E1 PACKAGE WIDTH 0.154 +/-.003 in 3.91 +/-.08 mm B, C
L FOOT LENGTH 0.033 +/-.017 in 0.84 +/-.43 mm C
θ
FOOT ANGLE 4 +/-4 DEG 4 +/-4 DEG
NOTES:
A. The D dimension does not include mold flashing and mismatch. Mold flashing and mismatch shall not exceed .006 in (.15 mm) per
side.
B. The E1 dimension does not include mold flashing and mismatch. Mold flashing and mismatch shall not exceed .010 in (.25 mm)
per side.
C. Primary units are English inches. The metric equivalents are subject to rounding error.
Additional Information
For latest specifications, additional product information, worldwide sales and distribution locations, and information about TriQuint:
Web: www.triquint.com Tel: (503) 615-9000
Email: info_wireless@tqs.com Fax: (503) 615-8900
For technical questions and additional information on specific applications:
Email: info_wireless@tqs.com
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; TriQuint assumes no liability for inaccuracies or omissi ons. TriQuint as sumes no responsibility for the use of
this information, and all such information shall be entir ely at the user’s own risk. Pri ces and specifications are subject to change without notice. No patent rights or
licenses to any of the circuits described herein ar e implied or granted to any third party.
TriQuint does not authorize or warrant any TriQuint product for use in life-support devices and/or systems.
Copyright © 1999 TriQuint Semiconductor, Inc. All rights reserved.
Revision D, August 19, 1999
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com 9
 Loading...
Loading...