Page 1

LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
1.2MHz
, 32V
Step
-Up
LED Driver with 320mA Current Limit
General Description
LA8304 is a current mode, step-up DC-DC
converter that is designed driving up to 6 series
LEDs from a single cell Li-Ion battery. It utilizes
PWM control scheme that switches with 1.2MHz
fixed frequency and 320mA current limit.
The input voltage range is from 2.5V to 10V,
and available in adjustable output up to 32V. It
provides 104mV low feedback voltage to reduce
power loss and improve efficiency. In portable
applications, the LA8304 provides 0.1uA low
shutdown current to extend battery life. The
fast switching frequency of 1.2MHz allows using
small size, low cost and low height capacitors
and inductors.
The under voltage lockout function prevents low
input voltage start up until the input voltage
reaches the UVLO threshold voltage. Other
features of dimming control, over voltage
protection, and thermal shutdown protection
are also included. The package is available in
standard SOT-23-6.
LA8304
Features
Adjustable Output Voltage up to 32V
ll
Driving up to 6 Series LEDs
ll
2.5V to 10V Input Voltage Range
ll
320mA Switching Current Limit
ll
1.2MHz Oscillation Frequency
ll
104mV Reference Voltage
ll
Low Shutdown Current: 0.1uA
ll
Current Mode for Excellent Response
ll
PWM / Analog Dimming Control
ll
Under Voltage Lockout
ll
Optional 29V Over Voltage Protection
ll
Thermal shutdown Protection
ll
Standard SOT-23-6 Package
ll
Meet RoHS Standard
ll
Applications
Digital Still and Video Cameras
ll
Mobile Phone
ll
PDA, Handheld Computer
ll
PMP, MP3 Player
ll
GPS
ll
Ordering Information
LA8304 1 2 3 4
1 (Package Type) => C: SOT-23
2 (Number of Pins) => E: 6 pin
3 (Output Voltage) => Blank: Adjustable
4 (Special Feature) => Blank: N/A
Available Part Number
LA8304CE
Marking Information
1 2 3 4
1 2 (Product Code)
LA8304CE : LB
3 4 (Date Code)
For date code rule, please contact our
sales representative directly.
- 1 -
Page 2

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Typical Application
Li-Ion Battery Application - For 6 Series LEDs with PWM Dimming
ll
Li-Ion Battery
2.7V~4.2V
1uF
PWM Dimming
Control
22uH
1
IN
6
EN FB
4
SW
LA8304
GND
2
SBD
OV
5
I
LED_MAX=
3
20mA
Li-Ion Battery Application - For 6 Series LEDs with Analog Dimming
ll
Li-Ion Battery
2.7V~4.2V
22uH
SBD
1uF
IN
6
EN FB
4
1
SW
LA8304
GND
2
OV
5
3
0V~2V
Analog Dimming
I
LED_MAX
96K Ohm
=20mA
5K Ohm
0.22uF
5.2 Ohm
0.22uF
5.2 Ohm
- 2 -
Page 3

LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Efficiency Curve
Driving 3 Series LEDs Driving 4 Series LEDs
LA8304
Vin = 2.7V Vin = 3.6V
Vin = 4.2V Vin = 5V
90%
80%
70%
60%
Efficiency (%)
50%
40%
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output Current (mA)
Driving 6 Series LEDs
Vin = 2.7V Vin = 3.6V
Vin = 4.2V Vin = 5V
90%
Vin = 2.7V Vin = 3.6V
Vin = 4.2V Vin = 5V
90%
80%
70%
60%
Efficiency (%)
50%
40%
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output Current (mA)
80%
70%
60%
Efficiency (%)
50%
40%
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output Current (mA)
- 3 -
Page 4

LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Quick Design Table
For Li-Ion Battery Application, V
LA8304
= 2.7V~4.2V, continuous current mode operation.
IN
C1: Recommended Input Capacitor
C2: Minimum Output Capacitor
L1: Recommended Inductor
R1: Current Setting Resistor
I
LEDs
2 Series
3 Series
LED
5mA
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 1uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 20.8Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 1uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 20.8Ohm
2.7V~4.2V
C1
L1
IN
6
LA8304
EN
4
SW
GND
SBD
1
OV
5
FB
3
2
10mA 15mA 20mA
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 2.2uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 10.4Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 1uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 10.4Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 4.7uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 6.93Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 2.2uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 6.93Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 4.7uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 5.2Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 2.2uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 5.2Ohm
C2
R1
4 Series
6 Series
5 Series
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.68uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 20.8Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.22uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 20.8Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.22uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 20.8Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 1uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 10.4Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.47uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 10.4Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.22uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 10.4Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 2.2uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 6.93Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.68uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 6.93Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.22uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 6.93Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 2.2uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 5.2Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.68uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 5.2Ohm
C1 : 1uF
C2 : 0.22uF
L1 : 22uH
R1 : 5.2Ohm
- 4 -
Page 5
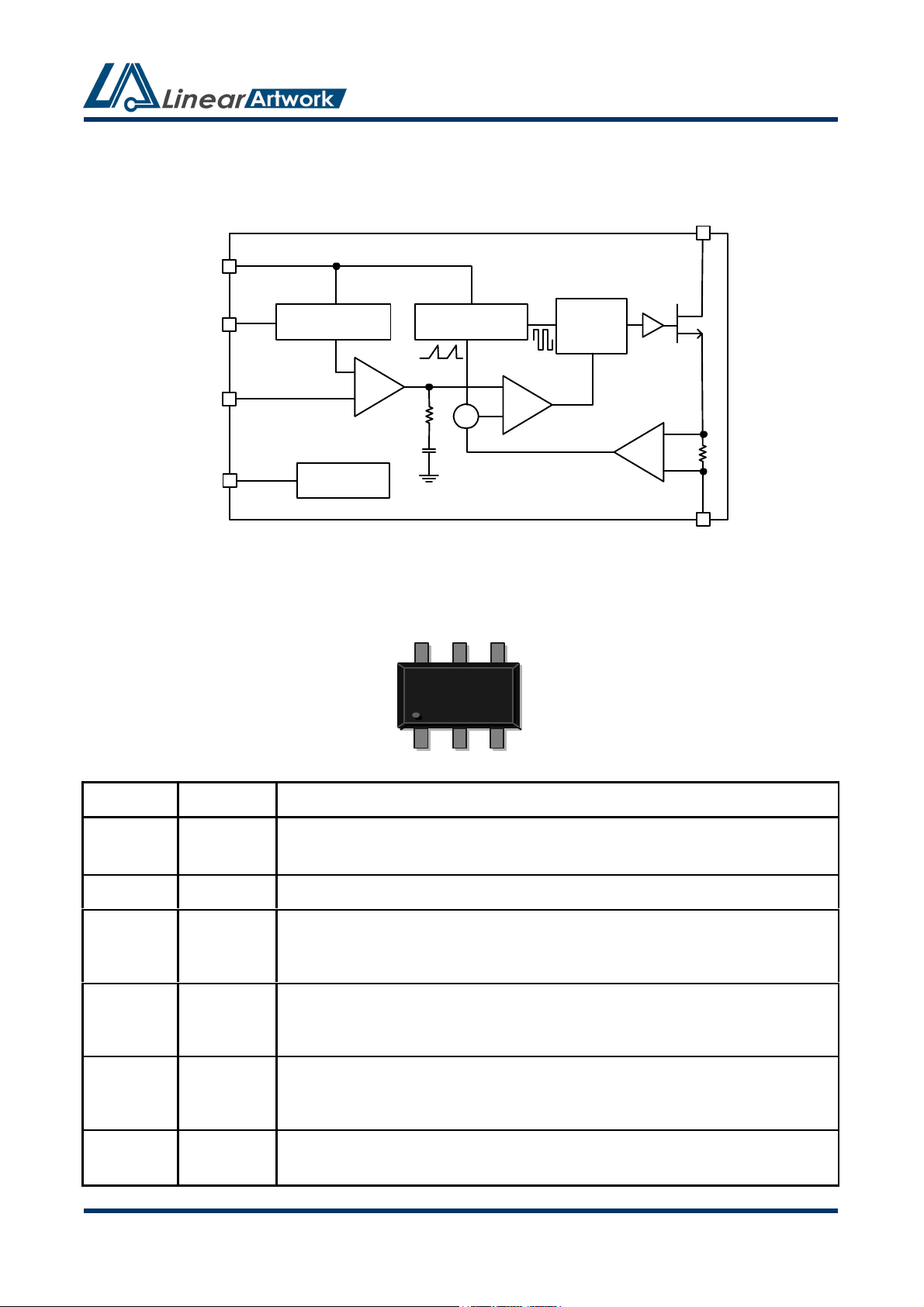
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Functional Block Diagram
LA8304
IN
EN
FB
OV
Pin Configurations
104mV Reference
Voltage
+
-
Error Amplifier
Over Voltage
Protection
1.2MHz OSC &
Ramp Generator
+
OV
IN
EN
-
+
F/F
S
Error Comparator
Q
R
Current Sensing
+
-
Amplifier
SW
GND
Pin No. Name Description
1 SW
This switching pin of the converter. Connect this pin to the node between the
inductor and the rectifier diode.
2 GND
The ground pin of the converter. Connect this pin to the circuit ground.
3 FB
4 EN
5 OV
This pin senses the feedback voltage to regulate the output voltage. Connect
a voltage divider to set the output voltage. For LED applications, connect a
resistor (RFB) to set LED current by the following formula: I
This pin allows an external logic control signal to turn-on/off this device. Drive
this pin to low level to turn-off this device, drive it to high level to turn-on this
device. Do not leave EN floating.
The over voltage input pin. Connect this pin to output to trigger the over
voltage protection and prevent the output over 29V. Leave OV floating to
disable this function.
6 IN
The input pin of the converter. Connect a capacitor from this pin to ground to
bypass noise on the input of this device.
SOT-23-6
SW
GND
FB
=104mV/RFB
LED
- 5 -
Page 6

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Rating
Input Voltage
SW, OV Pin Voltage Range
10V
-0.3V ~ 34V
FB Pin Voltage Range
-0.3V ~ 10V
EN Pin Voltage Range
Storage Temperature Range
-0.3V ~ 10V
-65oC ~ 150oC
Junction Temperature
Lead Soldering Temperature (10 sec)
150 oC
300 oC
These are stress ratings only and functional operation is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for
prolonged time periods may affect device reliability. All voltages are with respect to ground.
Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Rating
Input Voltage Range
Ambient Temperature Range
2.5V ~ 10V
-40oC ~ 85oC
Junction Temperature Range
These are conditions under which the device functions but the specifications might not be guaranteed. For
guaranteed specifications and test conditions, please see the Electrical Specifications.
-40oC ~ 125oC
Package Information
Parameter Package Symbol Rating
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Case)
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Ambient)
SOT-23-6
θ
110
JC
θ
220
JA
o
C/W
o
C/W
- 6 -
Page 7

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Electrical Specifications
VIN= VEN=3.6V, TA=25ºC, unless otherwise noted.
Parameter Symbol Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Units
Feedback Voltage VFB
Efficiency η
Oscillation Frequency F
Maximum Duty Cycle DC
Switch Saturation
Voltage
Current Limit I
Supply Current IIN
V
LIM
Shutdown Current IS
EN Pin Input Threshold
Voltage
VEN
EN Pin Bias Current IEN
Switch Leakage
Current
ISL
FB Pin Bias Current IFB
Under Voltage Lockout UVLO
OSC
SAT
MAX
94 104 114 mV
Drive 3 series LEDs, I
0.9 1.2 1.5 MHz
VFB=0V 85 90 %
ISW=250mA 350 mV
Duty Cycle = 60%
VFB=0.15V 2 2.6 mA
VEN=0V 0.1 1 uA
Regulator OFF 0.5
Regulator ON 1
Regulator OFF 1
Regulator ON 100
VSW=5V, VEN=0V 0.01 5 uA
0.01 0.045 1 uA
VIN Rising 2.1 V
=20mA 82 %
LED
320 mA
0.7
V
uA
Under Voltage Lockout
Hysteresis
Over Voltage
Protection Threshold
Line Regulation
Load Regulation
Over Temperature
Shutdown
Over Temperature
Shutdown Hysteresis
UVLO
VOV
△V
LINE
△V
LOAD
TSD
T
HYS
HYS
20 mV
VOV Rising 29 V
VIN=2.7V~4.2V
Drive 3 series LEDs, I
Drive 3 series LEDs
I
= 1mA~20mA
LED
145
10
- 7 -
=20mA
LED
1 %/V
0.1 %/mA
o
C
o
C
Page 8

LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Typical Performance Characteristics
VIN=3.6V, T
=25ºC, unless otherwise noted.
A
Frequency vs. Input Voltage Frequency vs. Temperature
LA8304
1.6
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
Frequency (MHz)
1.1
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Input Voltage (V)
1.6
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
Frequency (MHz)
1.1
1
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
Feedback Voltage vs. Input Voltage Feedback Voltage vs. Temperature
120
110
100
90
120
110
100
90
80
Feedback Voltage (mV)
70
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Input Voltage (V)
80
Feedback Voltage (mV)
70
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
Line Regulation Load Regulation
6
5.5
5
4.5
LED Current (mA)
4
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Input Voltage (V)
120
110
100
90
80
Feedback Voltage (mV)
70
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output Current (mA)
- 8 -
Page 9

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Typical Performance Characteristics (Contd.)
Shutdown Current vs. Input Voltage Supply Current vs. Input Voltage
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
Shutdown Current (uA)
0.01
0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Input Voltage (V)
3.5
3
2.5
2
Supply Current (mA)
1.5
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Input Voltage (V)
EN Bias Current vs. Temperature FB Bias Current vs. Temperature
220
180
140
100
60
EN Pin Bias Current (uA)
20
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
FB Pin Bias Current (uA)
0
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
SW Leakage Current vs. Temperature Current Limit vs. Duty Cycle
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
SW Leakage Current (uA)
0
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
500
400
300
200
Current Limit (mA)
100
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Duty Cycle(%)
- 9 -
Page 10

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Application Information
LED Current Setting
This device is a constant current boost regulator that develops 104mV reference voltage between
FB and GND. Use 1% chip resistor to set the LED current and attain the better current accuracy.
The LED current can be calculated by the following formula:
V
OUT
GND
SW
FB
VFB
ILED
RFB
I
LED
= V
/ RFB ; where VFB = 104mV
FB
Under Voltage Lockout
The under voltage lockout prevents this device from turning on the internal power switch at lower
input voltage. It avoids wrong operation under undefined conditions. The under voltage lockout
threshold is approximately 2.1V. When the input voltage drop under the threshold voltage, this
device will be disabled and auto recovery once the input voltage rise above it.
Dimming Control
- PWM Dimming
Connect an external PWM signal at EN pin to turn on or off this device. It is a simple method of
brightness control for LED. A 0% duty cycle will turn off this device and corresponds to zero the
LED current. A 100% duty cycle corresponds to full current. The variation of the average LED
current is proportionally with the PWM duty cycle.
The minimum PWM frequency must higher than 100Hz, and the typical value is 1KHz. The
following circuit is PWM dimming control from EN pin.
V
IN
IN
EN GNDPWM
- Analog Dimming
The analog dimming control using a DC voltage (V
increases, the voltage drop on R2 increases. Thus the LED current decreases. The R1 and R2 must
- 10 -
) is shown in the following circuit. As the V
DIM
DIM
Page 11

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
2R×V)2R+1R(×V
2R×)VV(
I1R2
R
1
R
make the DC source current much larger than the FB bias current and much smaller than the LED
current. The LED current can be calculated by the following formula:
DIMFB
R1
R2
-
FB
R×1R
RFB
LED
=I
GND
VDIM
FB
If the V
is taken below the VFB, the inverse will happen and the brightness will increase.
DIM
The analog dimming circuit can be tailored for different resistor value using the following formula:
FBMAX_DIM
=1R
1(×V
FB
-
I
-
I
UNDIMMED_LED
MIN_DIMMED_LED
)
Example:
V
I
I
DIM_MAX
LED_DIMMED_MIN
LED_UNDIMMED
= 2V
= 1mA ; V
= 20mA ; V
=2V
DIM
DIM=VFB
=0.104V
R2 = 5KOhm → R1 = 96KOhm
The analog dimming circuit can be tailored for different dimming voltage range using the following
formula:
MIN_DIMMED_LED
×V=V
FBDIM -
+1(×
2R
I
UNDIMMED_LED
)
- Filtered PWM Dimming from FB
Filtered PWM circuit can be used to replace the DC voltage source in dimming control. The circuit
is shown in the following figure that is suitable for the soft-start function is used, and the PWM
frequency of the brightness control is too high to result in the device without fully turns on or off.
10K
PWM
0.1u
R1
GND
FB
R2
RFB
Delay Start-up
The following circuit uses the EN pin to provide a time delay between the input voltage is applied
- 11 -
Page 12

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
and the output voltage comes up. As the instant of the input voltage rises, the charging of
capacitor C
pulls the EN pin low, keeping the device off. Once the capacitor voltage rises above
DELAY
the EN pin threshold voltage, the device will start to operate.
V
IN
RDELAY
CDELAY
VEN
IN
EN
GND
VIN x (1 – e
Where T is the start-up delay time, R is R
DELAY
This feature is useful in situations where the input power source is limited in the amount of current
it can deliver. It allows the input voltage to rise to a higher voltage before the device starts
operating.
-T/(RxC)
, C is C
) > VEN
, and the typical VEN is 0.7V.
DELAY
Soft-Start
In some application, the large start-up current or overshooting voltage maybe causes problems.
The major problem occurs when the input power source to the regulator is current-limited or has
poor load regulation. Both of which will cause input voltage to drop during start-up.
The following circuits are the recommended soft-start circuits those are formed by RSS, CSS and D
SS
(or QSS). They prevent excessive input inrush current and output overshooting voltage during
start-up. If both dimming control and soft-start are used, use a lower frequency PWM signal or
implement dimming through the FB pin are recommended.
GND
SW
FB
DSS
CSS
RSS
V
OUT
SW
FB
GND
QSS
V
OUT
CSS
RSS
Layout Considerations
PC board layout is very important, especially for higher frequency switching regulators. A good
layout minimizes EMI on the feedback path and provides best efficiency.
The following layout guides should be used to ensure proper operation of this device.
(1) Minimize the copper area and length of all trace connected to SW.
(2) The feedback path should be close to FB and keep noisy traces away; also keep them separate
using grounded copper.
- 12 -
Page 13

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
(3) The ground of the feedback resistor should be connect to GND directly to ensure a clean
connection
(4) The (-) plate of the output capacitor should be close to GND.
(5) Keep the (-) plates of input and output capacitors as close as possible.
- 13 -
Page 14

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Component Selection
Inductor Selection
The 1.2MHz high switching frequency minimizes the inductance. Use a low DCR surface mount
inductor to reduce the board size and improve the efficiency. A 22uH inductor is recommended for
most applications.
Capacitors Selection
The small size, low ESR multi layer ceramic capacitors are ideal for most applications. X7R and X5R
types are recommended because the stable capacitance and temperature coefficient.
The input capacitor is required to supply current to the regulator and maintain the DC input
voltage. A 1uF low ESR capacitor is preferred to provide the better performance and the less ripple
voltage. The suitable value of output capacitor is 0.22uF~4.7uF or more.
Rectifier Diode Selection
The rectifier diode provides a current path for the inductor current when the internal power switch
turns off. The best solution is Schottky diode because its low forward voltage will reduce the
conduction loss, and the fast recovery time (or low diode capacitance) will reduce the switch loss.
Choose a Schottky diode with 100mA ~ 200mA current rating is sufficient for most application.
- 14 -
Page 15

Evaluation Board Layout
Evaluation Board Schematic
LA8304
J1
VIN
J5
SW
GND
D1
1
TP1
5
OV
R3
C3
C5
D7
D2
D3
D4R2
D5
D6
1
C1
1
2
3
L1
C2
U1
6
R1
4 3
C6
1
IN
EN FB
2
J3
1
C4
VOUT
J2
1
GND
J4
1
GND
Bill of Materials
VIN=2.7~4.2V, for 6 series LEDs application, I
Designation Descriptions Manufacturer Part # Manufacturer Manufacturer Website
U1
L1
D1
C1
C3
C2,C4
R1,R2,C5,C6
R3
D2~D7
J5
J1,J2,J3,J4
TP1
1.2M, 32V Step-Up LED Driver, SOT-23-6 Package LA8304CE
Surface Mount Inductor 22uH, 420mA, 84mOhm,
3.0*3.0*1.2mm
Schottky Diode 30V, 0.5A, 0.47VF, SOD-323 RB551V-30
MLCC 1uF, 0805, X7R, 25V TMK212BJ105KD-T Taiyo Yuden www.yuden.co.jp
MLCC 0.22uF, 0805, X7R, 50V UMK212BJ224KG-T Taiyo Yuden www.yuden.co.jp
MLCC 0.1uF, 0603, B, 50V C1608JB1H104K TDK www.tdk.com
Chip Resistor, 5.2Ohm, 0805, ±1%
Male Header 180° 3*1P 2.54mm
Terminal Binding Post 1.6mm
Male Header 180° 1P 2.54mm
=20mA
LED
NR3012T220M Taiyo Yuden www.yuden.co.jp
No Connection
RC0805FR-075R2L Yageo www.yageo.com
0603 Package Chip LED
Linear Artwork www.linear-artwork.com
Tiptek www.tip-tek.com.tw
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27, 2009
- 15 -
Page 16

LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
Package Outline
SOT-23-6
E1
E
LA8304
D
e1
A
(MAX.)
e
A2
A1
REF. REF.
A L
A1 0 0.10 L1
A2 1.10 1.30
c b 0.30 0.50
D 2.70 3.10 e
E 2.60 3.00 e1
E1 1.40 1.80
Millimeter Millimter
Min. Max . Min. Max .
1.45 MAX . 0.37 REF.
0.12 REF.
(TYP.)
b
0.20
DIMENSIONS
Y
Θ
L
0
°
(REF.)
0.60 REF.
0.95 REF.
1.90 REF.
10
c(REF.)
Y
(REF.)
L1
°
- 16 -
Page 17

LA8304
LA8304-A01 Aug. 27
, 2009
NOTICE
The specifications and product information of Linear Artwork, Inc. are subject to change without any prior notice,
and customer should contact Linear Artwork, Inc. to obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and
verify that such information is current and complete.
The information provided here is believed to be reliable and accurate; however Linear Artwork, Inc. makes no
guarantee for any errors that appear in this document.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
Linear Artwork products are not designed or authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or
systems without the express written approval of the president of Linear Artwork, Inc. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body,
or (b) support or sustain life, and (c) whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions
for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury of the user.
2. A critical component in any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be
reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
Linear Artwork, Inc.
Headquarter
7F, No.207-1, Sec.3, Beisin Rd., Sindian City, Taipei County, Taiwan 231, R.O.C.
TEL : +886-2-8913-1898 FAX : +886-2-8913-1980
Branch Office
Room 222, 2F, Dongfang Plaza, No.1072, Jianshe Rd., Luohu District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China.
TEL / FAX : +86-755-8218-0700
Website : www.linear-artwork.com E-mail : sales@linear-artwork.com
- 17 -
Page 18

 Loading...
Loading...