Page 1
PRELIMINARY
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TOLVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ICS
HiPerClockS™
will generate both 125MHz and 25MHz clocks with mixed
LVDS and LVCMOS/LVTTL output logic. The ICS8440258-46
uses IDT’s 3
and can achieve <1ps typical rms phase jitter, easily meeting
Ethernet jitter requirements. The ICS8440258-46 is packaged
in a small, 5mm x 5mm VFQFN package.
The ICS8440258-46 is an 8 output synthesizer
optimized to generate Ethernet clocks and a
member of the HiPerClockS™ family of high
performance clock solutions from IDT. Using a
25MHz, 18pF parallel resonant crystal, the device
rd
generations low phase noise VCO technology
FEATURES
• Four differential LVDS outputs at 125MHz
• Selectable crystal oscillator interface or LVCMOS/LVTTL
• VCO range: 490MHz - 680MHz
• RMS phase jitter @ 125MHz, using a 25MHz crystal
• Full 2.5V operating supply
• 0°C to 70°C ambient operating temperature
• Available in both standard (RoHS 5) and lead-free (RoHS6)
PIN ASSIGNMENT
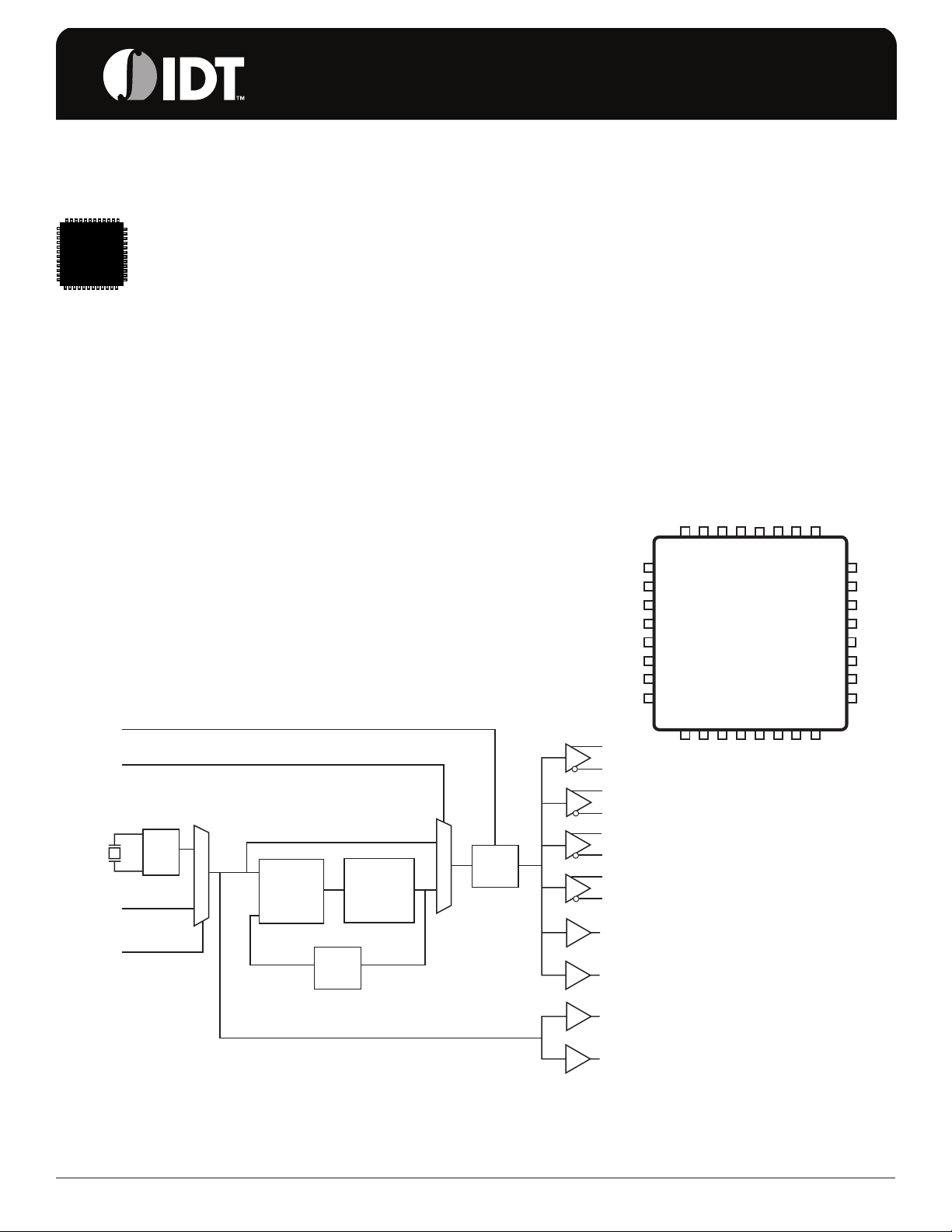
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Pulldown
MR
nPLL_SEL
XTAL_IN
XTAL_OUT
REF_CLK
nXTAL_SEL
Pulldown
25MHz
OSC
Pulldown
Pulldown
0
1
÷5
Phase
Detector
VCO
490-680MHz
0
1
÷25
ICS8440258-46
Two LVCMOS/LVTTL single-ended outputs at 125MHz
Two LVCMOS/LVTTL single-ended outputs at 25MHz
single-ended input
(1.875MHz - 20MHz): 0.34ps (typical)
packages
Q0
nQ0
Q1
nQ1
Q2
nQ2
Q3
nQ3
Q4
Q5
Q0
nQ0
GND
Q1
nQ1
V
Q2
nQ2
1
2
3
4
5
DD
6
7
8
nXTAL_SEL
XTAL_OUT
XTAL_IN
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
REF_CLK
MR
nPLL_SEL
V
DD
ICS8440258-46
32-Lead VFQFN
5mm x 5mm x 0.75mm
package body
K Package
Top View
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
DD
Q3
nQ3
Q4
V
GND
Q5
DDO1
V
VDDA
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
GND
nc
nc
nc
GND
Q7
V
DDO2
Q6
GND
Q6
Q7
The Preliminary Information presented herein represents a product in prototyping or pre-production. The noted characteristics are based on initial
product characterization. Integrated Circuit Systems, Incorporated (ICS) reserves the right to change any circuitry or specifications without notice.
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 1 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 2
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
TABLE 1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
rebmuNemaNepyTnoitpircseD
2,10Qn,0QtuptuO.slevelecafretniSDVL.stuptuokcolclaitnereffiD
,61,21,3
12,71
5,41Qn,1QtuptuO.slevelecafretniSDVL.stuptuokcolclaitnereffiD
72,11,6V
8,72Qn,2QtuptuO.slevelecafretniSDVL.stuptuokcolclaitnereffiD
01,93Qn,3QtuptuO.slevelecafretniSDVL.stuptuokcolclaitnereffiD
,51,31
02,81
41V
91V
42,32,22cndesunU.tcennocoN
52V
62LES_LLPntupnInwodlluP
82RMtupnInwodlluP
92KLC_FERtupnInwodlluP.tupnikcolcecnereferLTTVL/SOMCVLdedne-elgniS
03LES_LATXntupnInwodlluP
,13
23
:ETON
DNGrewoP.dnuorgylppusrewoP
DD
,5Q,4Q
7Q,6Q
1ODD
2ODD
ADD
,TUO_LATX
NI_LATX
rewoP.nipylppuseroC
tuptuO .slevelecafretniLTTVL/SOMCVL.stuptuokcolcdedne-elgniS
rewoP .stuptuoSOMCVL5Qdna4QrofnipylppustuptuorewoP
rewoP .stuptuoSOMCVL7Qdna6QrofnipylppustuptuorewoP
rewoP.nipylppusgolanA
tupnI
nwodlluP
.tuptuoOCVehtmorfnevirdsituptuoeht,WOLnehW.ssapyBLLP
=ycneuqerftuptuoehtdnadessapybsiLLPeht,HGIHnehW
.redividtuptuoN/ycneuqerfkcolcecnerefer
.slevelecafretniLTTVL/SOMCVL
erasredividlanretnieht,HGIHcigolnehW.teseRretsaMHGIHevitcA
lanretnieht,WOLcigolnehW.wologotstuptuoehtgnisuacteser
.slevelecafretniLTTVL/SOMCVL.delbaneerastuptuoehtdnasredivid
ecnereferLLPehtsastupniKLC_FERrolatsyrcehtneewtebstceleS
LATXstceles,WOLnehW.KLC_FERstceles,HGIHnehW.ecruos
.slevelecafretniLTTVL/SOMCVL.stupni
.tuptuoehtsiTUO_LATX.ecafretnirotallicsolatsyrC
.tupniehtsiNI_LATX
.seulavlacipytrof,scitsiretcarahCniP,2elbaTeeS.srotsisertupnilanretniotsrefer
TABLE 2. PIN CHARACTERISTICS
lobmySretemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
C
NI
C
DP
R
R
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 2 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
NWODLLUP
TUO
ecnaticapaCtupnI 4Fp
ecnaticapaCnoitapissiDrewoP 8Fp
rotsiseRnwodlluPtupnI 15kΩ
ecnadepmItuptuO 22
Ω
Page 3
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage, V
Inputs, V
Outputs, I
Outputs, I
I
(LVCMOS) -0.5V to V
O
(LVDS)
O
DD
4.6V
-0.5V to V
+ 0.5V
DD
+ 0.5V
DD
Continuous Current 10mA
Surge Current 15mA
Operating Temperature Range, TA -40°C to +85°C
NOTE: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum
Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These
ratings are stress specifications only. Functional operation of
product at these conditions or any conditions beyond those listed
DC Characteristics
in the
or
AC Characteristics
is not implied.
Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect product reliability.
Storage Temperature, T
STG
Package Thermal Impedance, θ
TABLE 3A. POWER SUPPLY DC CHARACTERISTICS, V
-65°C to 150°C
34.8°C/W (0 lfpm)
JA
DD
lobmySretemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
V
DD
V
ADD
V
ODD
I
I
I
I
,DD
,1ODD
2ODD
ADD
egatloVylppuSeroC573.25.2526.2V
egatloVylppuSgolanAV
egatloVylppuStuptuO573.25.2526.2V
tnerruCylppuSrewoP 071Am
tnerruCylppuSgolanA 31Am
TABLE 3B. LVCMOS/LVTTL DC CHARACTERISTICS, V
lobmySretemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
V
HI
V
LI
I
HI
I
LI
tupnI
tupnI
tuptuO
V
HO
1ETON
tuptuO
V
LO
1ETON
egatloVhgiHtupnI 7.1V
egatloVwoLtupnI 3.0-7.0V
,KLC_FER,RM
tnerruChgiH
LES_LATXn,LES_LLPn
,KLC_FER,RM
tnerruCwoL
;egatloVhgiH
;egatloVwoL
7Q:4Q
7Q:4Q
05htiwdetanimretstuptuO:1ETON Ω Vot
.margaidtiucriCtseTdaoLtuptuO
LES_LATXn,LES_LLPn
XODD
= V
V
V
DD
V
DDA
= V
VDDV=
DD
= V
DDA
V
,1ODD
V
,1ODD
= V
DDO1
= V
DDO1
NI
=V526.2%5±
1ODD
=V526.2%5±
1ODD
= 2.5V ± 5%,TA = 0°C TO 70°C
DDO2
31.0–5.2VDDV
DD
= V
= 2.5V ± 5%,TA = 0°C TO 70°C
DDO2
DD
V526.2=051Aµ
V,V526.2=
V0=5-Aµ
NI
8.1V
,noitamrofnItnemerusaeMretemaraPeeS.2/
3.0+V
5.0V
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 3 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 4
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
TABLE 3C. LVDS DC CHARACTERISTICS, V
lobmySretemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
V
∆ V
V
∆ V
DO
V
DO
SO
SO
DO
egatloVtesffO 52.1V
V
SO
egatloVtuptuOlaitnereffiD 093Vm
egnahCedutingaM 05Vm
egnahCedutingaM 05Vm
TABLE 4. CRYSTAL CHARACTERISTICS
retemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
noitallicsOfoedoM latnemadnuF
ycneuqerF 52zHM
)RSE(ecnatsiseRseireStnelaviuqE 05
ecnaticapaCtnuhS 7Fp
leveLevirD 1Wm
TABLE 5. AC CHARACTERISTICS, V
lobmySretemaraPsnoitidnoCtseTmuminiMlacipyTmumixaMstinU
f
TUO
t
)o(ks
t
)Ø(tij
t
Rt/F
cdoelcyCytuDtuptuO
tuptuO
VtaderusaeM
XODD
ycneuqerFtuptuO
;wekStuptuO
2,1ETON
rettiJesahPSMR
emiTllaF/esiR
.2/
= V
DD
DDA
5Q,4Q521zHM
7Q,6Q52zHM
7Q:4Q05sp
3ETON;)modnaR(
5Q,4Q)zHM02-zHM578.1(,zHM52173.0sp
7Q:4Q%08ot%024.1sn
7Q:4Q6445%
= V
DD
DDA
= V
DDO1
= V
= 2.5V ± 5%,TA = 0°C TO 70°C
DDO2
Ω
.latsyrctnanoserlellarapFp81nagnisudeziretcarahC:ETON
= V
= V
DDO1
= 2.5V ± 5%,TA = 0°C TO 70°C
DDO2
3:0Qn/3:0Q521zHM
3:0Qn/3:0Q05sp
3:0Qn/3:0Q)zHM02-zHM578.1(,zHM52143.0sp
3:0Qn/3:0Q%08ot%02084sp
3:0Qn/3:0Q05%
.snoitidnocdaollauqehtiwdnasegatlovylppusemasehttastuptuoneewtebwekssadenifeD:1ETON
.56dradnatSCEDEJhtiwecnadroccanidenifedsiretemarapsihT:2ETON
.tolPesioNesahPehtotreferesaelP:3ETON
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 4 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 5
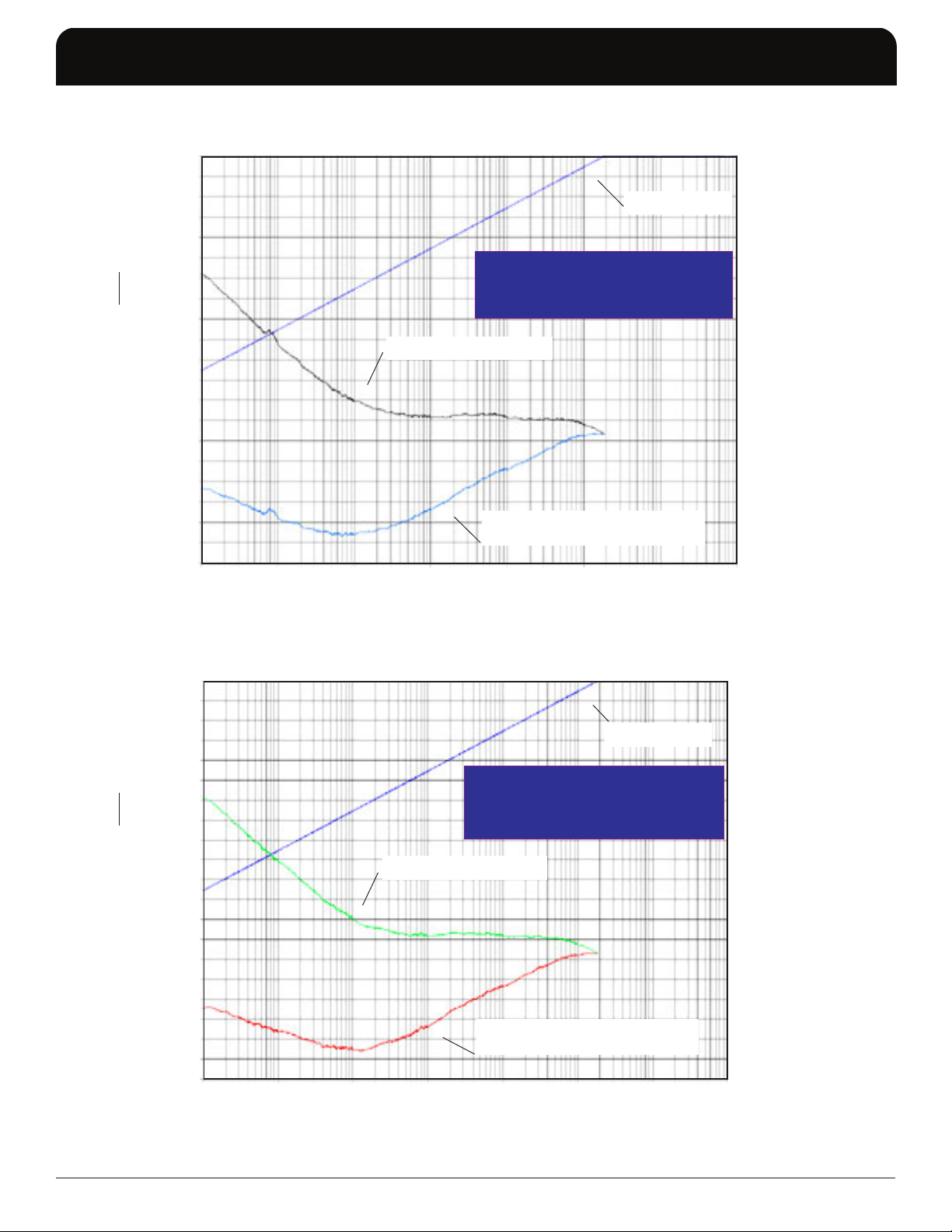
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
TYPICAL PHASE NOISE AT 125MHZ (LVCMOS)
0
➤
Ethernet Filter
125MHz
dBc
NOISE POWER
Hz
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
-150
-160
-170
-180
-190
-200
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
Raw Phase Noise Data
➤
1.875MHz to 20MHz = 0.37ps (typical)
➤
Phase Noise Result by adding
Ethernet Filter to raw data
RMS Phase Jitter (Random)
OFFSET FREQUENCY (HZ)
dBc
NOISE POWER
Hz
TYPICAL PHASE NOISE AT 125MHZ (LVDS)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
-150
-160
-170
-180
-190
-200
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
Raw Phase Noise Data
➤
1.875MHz to 20MHz = 0.34ps (typical)
➤
Phase Noise Result by adding
Ethernet Filter to raw data
RMS Phase Jitter (Random)
OFFSET FREQUENCY (HZ)
➤
Ethernet Filter
125MHz
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 5 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 6
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
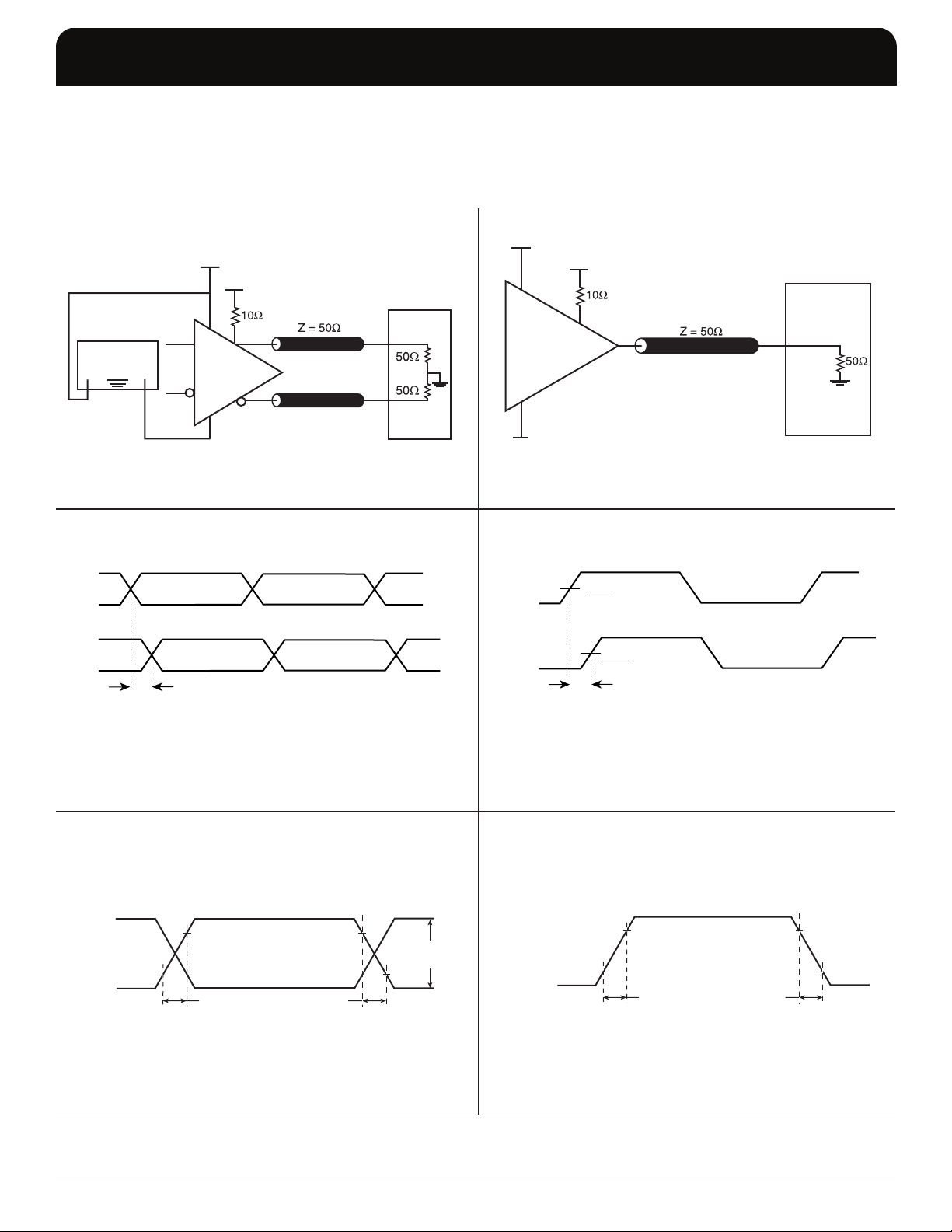
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
1.25V±5%
1.25V±5%
,
V
DD
V
DDO1,
V
DDO2
LVCMOS
GND
V
DDA
Qx
2.5V±5%
POWER SUPPLY
+–
Float GND
V
V
V
DD
DDO1,
DDO2
SCOPE
,
V
DDA
LVDS
Qx
nQx
-1.25V±5%
2.5V LVDS OUTPUT LOAD AC TEST CIRCUIT 2.5V LVCMOS OUTPUT LOAD AC TEST CIRCUIT
nQx
Qx
nQy
Qy
t
sk(o)
Qx
Qy
V
DDO
2
V
DDO
2
t
sk(o)
SCOPE
LVDS OUTPUT SKEW
80%
Clock
Outputs
20%
t
R
LVDS OUTPUT RISE/FALL TIME
80%
t
F
20%
V
OD
LVCMOS OUTPUT SKEW
80%
20%
Clock
Outputs
t
R
LVCMOS OUTPUT RISE/FALL TIME
80%
t
F
20%
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 6 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 7

ICS8440258-46
k
tPW
t
PERIOD
t
PW
t
PERIOD
odc = x 100%
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
Phase Noise Plot
nQ0:nQ3
Q0:Q3
Noise Power
Phase Noise Mas
Offset Frequency
f
1
RMS Jitter = Area Under the Masked Phase Noise Plot
f
2
RMS PHASE JITTER
V
DDO
t
PERIOD
t
PW
t
PERIOD
2
x 100%
Q4:Q7
t
PW
odc =
LVCMOS OUTPUT DUTY CYCLE/PULSE WIDTH/PERIOD
LVDS OUTPUT DUTY CYCLE/PULSE WIDTH/PERIOD
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 7 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 8

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
APPLICATION INFORMATION
POWER SUPPLY FILTERING T ECHNIQUES
As in any high speed analog circuitry, the power supply pins
are vulnerable to random noise. The ICS8440258-46 provides
separate power supplies to isolate any high switching noise
, V
, V
from the outputs to the internal PLL. V
should be individually connected to the power supply plane
DD
DDA
DDO1
and V
DDO2
through vias, and bypass capacitors should be used for each
pin. To achieve optimum jitter performance, power supply isolation is required.
Figure 1
illustrates how a 10Ω resistor along
with a 10µF and a .01µF bypass capacitor should be connected
to each V
DDA
.
V
DD
V
DDA
FIGURE 1. POWER SUPPLY FILTERING
.01µF
.01µF
2.5V
10Ω
10µF
CRYSTAL INPUT INTERFACE
The ICS8440258-46 has been characterized with 18pF parallel
resonant crystals. The capacitor values shown in
18pF Parallel Cry stal
Figure 2
X1
below
Figure 2. CRYSTAL INPUt INTERFACE
were determined using a 25MHz, 18pF parallel resonant crystal
and were chosen to minimize the ppm error.
XTAL_IN
C1
22p
XTAL_OUT
C2
22p
ICS84332
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 8 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 9

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
LVCMOS TO XTAL INTERFACE
The XTAL_IN input can accept a single-ended LVCMOS
signal through an AC couple capacitor. A general interface
diagram is shown in
Figure 3.
The XTAL_OUT pin can be left
floating. The input edge rate can be as slow as 10ns. For
LVCMOS inputs, it is recommended that the amplitude be
reduced from full swing to half swing in order to prevent signal
interference with the power rail and to reduce noise. This
configuration requires that the output impedance of the driver
(Ro) plus the series resistance (Rs) equals the transmission
line impedance. In addition, matched termination at the crystal
input will attenuate the signal in half. This can be done in one
of two ways. First, R1 and R2 in parallel should equal the
transmission line impedance. For most 50Ω applications, R1
and R2 can be 100Ω. This can also be accomplished by
removing R1 and making R2 50Ω.
VDD
Ro
Rs
Zo = 50
Zo = Ro + Rs
Figure 3. GENERAL DIAGRAM FOR LVCMOS DRIVER TO XTAL INPUT INTERFACE
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR UNUSED INPUT AND OUTPUT PINS
INPUTS:
VDD
R1
.1uf
XTA L _ I N
R2
XTA L _ OU T
OUTPUTS:
CRYSTAL INPUT:
For applications not requiring the use of the crystal oscillator input,
both XTAL_IN and XTAL_OUT can be left floating. Though not
required, but for additional protection, a 1kW resistor can be tied
from XTAL_IN to ground.
REF_CLK I
NPUT:
For applications not requiring the use of the reference clock, it
LVCMOS OUTPUT:
All unused LVCMOS output can be left floating. There should be
no trace attached.
LVDS O
UTPUT
All unused LVDS output pairs can be either left floating or
terminated with 100Ω across. If they are left floating, there should
be no trace attached.
can be left floating. Though not required, but for additional
protection, a 1kΩ resistor can be tied from the REF_CLK to
ground.
LVCMOS C
ONTROL PINS:
All control pins have internal pull-downs; additional resistance is
not required but can be added for additional protection. A 1kΩ
resistor can be used.
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 9 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 10

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
2.5V LVDS DRIVER T ERMINATION
Figure 4
shows a typical termination for LVDS driver in
characteristic impedance of 100Ω differential (50Ω single)
transmission line environment. For buffer with multiple LDVS driver,
it is recommended to terminate the unused outputs.
2.5V
LVDS_D river
100 Ohm Differential Transmiss ion Line
ΩΩ
100
Ω Differential Transmission Line
ΩΩ
FIGURE 4. TYPICAL LVDS DRIVER TERMINATION
THERMAL RELEASE PATH
The expose metal pad provides heat transfer from the device to
the P.C. board. The expose metal pad is ground pad connected
to ground plane through thermal via. The exposed pad on the
device to the exposed metal pad on the PCB is contacted through
2.5V
+
R1
100
solder as shown in
-
Figure 5.
For further information, please refer
to the Application Note on Surface Mount Assembly of Amkor’s
Thermally /Electrically Enhance Leadframe Base Package, Amkor
Technology.
SOLDER M ASK
SIGNAL
TRACE
GROUND PLANE
EXPOSED PAD
THERM AL VIA
SOLDER
Expose M etal Pad
(GROUND PAD)
SIGNAL
TRACE
FIGURE 5. P.C. BOARD FOR EXPOSED PAD THERMAL RELEASE PATH EXAMPLE
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 10 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 11

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
POWER CONSIDERATIONS
This section provides information on power dissipation and junction temperature for the ICS8440258-46.
Equations and example calculations are also provided.
1. Power Dissipation.
The total power dissipation for the ICS840258-46 is the sum of the core power plus the power dissipated in the load(s).
The following is the power dissipation for V
Core and LVDS Output Power Dissipation
= 2.5V + 5% = 2.625V, which gives worst case results.
DD
• Power (core, LVDS) = V
DD_MAX
* (IDD + I
LVCMOS Output Power Dissipation
• Output Impedance R
Output Current I
• Power Dissipation on the R
Power (R
OUT
) = R
Power Dissipation due to Loading 50Ω to V
OUT
= V
OUT
DDO_MAX
OUT
* (I
OUT
)2 = 12Ω * (21.2mA)2 = 5.4mW per output
OUT
• Total Power Dissipation on the R
Total Power (R
) = 5.4mW * 4 = 21.6mW
OUT
• Dynamic Power Dissipation at 125MHz
Power (125MHz) = C
Total Power (125MHz) = 6.9mW * 2 = 13.8mW
* Frequency * (V
PD
• Dynamic Power Dissipation at 25MHz
Power (25MHz) = C
Total Power (25MHz) = 1.4mW * 2 = 2.8mW
Total Power Dissipation
* frequency * (V
PD
• Total Power
= Power (core, LVDS) + Total Power (R
= 480.4mW + 21.6mW + 13.8mW + 2.8mW
= 518.6mW
+ I
DDO2
+ I
OUT
DDO1
/ [2 * (50Ω + R
per LVCMOS output
OUT
)2 = 8pF * 125MHz * (2.625V)2 = 6.9mW per output
DDO
)2 = 8pF * 25MHz * (2.625V)2 = 1.4 mW per output
DDO
) + Total Power (125MHz) + Total Power (25MHz)
OUT
) = 2.625V * (170mA + 13mA) = 480.4mW
DDA
/2
DDO
)] = 2.625V / [2 * (50Ω + 12Ω)] = 21.2mA
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 11 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 12

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
2. Junction Temperature.
Junction temperature, Tj, is the temperature at the junction of the bond wire and bond pad and directly affects the
TM
reliability of the device. The maximum recommended junction temperature for HiPerClockS
The equation for Tj is as follows: Tj = θ
* Pd_total + T
JA
A
devices is 125°C.
Tj = Junction Temperature
= Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance
θ
JA
Pd_total = Total Device Power Dissipation (example calculation is in section 1 above)
= Ambient Temperature
T
A
In order to calculate junction temperature, the appropriate junction-to-ambient thermal resistance θ
Assuming no air flow and a multi-layer board, the appropriate value is 34.8°C/W per Table 6.
must be used.
JA
Therefore, Tj for an ambient temperature of 70°C with all outputs switching is:
70°C + 0.519W * 34.8°C/W = 88°C. This is below the limit of 125°C.
This calculation is only an example. Tj will obviously vary depending on the number of loaded outputs, supply voltage, air
flow, and the type of board (single layer or multi-layer).
TABLE 6. THERMAL RESISTANCE
θθ
θJA FOR 32-LEAD VFQFN, FORCED CONVECTION
θθ
θθ
θJA vs. Air Flow (Linear Feet per Minute)
θθ
0
Multi-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards 34.8°C/W
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 12 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 13

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
RELIABILITY INFORMATION
TABLE 7. θ
VS. AIR FLOW TABLE FOR 32 LEAD VFQFN
JA
θθ
θ
vs. Air Flow (Linear Feet per Minute)
θθ
JA
Multi-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards 34.8°C/W
TRANSISTOR COUNT
The transistor count for ICS8440258-46 is: 2589
0
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 13 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 14

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
PACKAGE OUTLINE - K SUFFIX FOR 32 LEAD VFQFN
T
ABLE 8. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
NOITAIRAVCEDEJ
LOBMYS
N
A
1A
3A
b
N
D
N
E
D
2D
E
2E
e
L
Reference Document: JEDEC Publication 95, MO-220
MUMINIMLANIMONMUMIXAM
08.0--00.1
0--50.0
81.052.003.0
52.152.252.3
52.152.252.3
03.004.005.0
SRETEMILLIMNISNOISNEMIDLLA
2-DHHV
23
.feR52.0
8
8
CISAB00.5
CISAB00.5
CISAB05.0
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 14 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 15
ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
TABLE 9. ORDERING INFORMATION
rebmuNredrO/traPgnikraMegakcaPgnigakcaPgnippihSerutarepmeT
64-KA8520448SCI64A85204SCINFQFVdaeL23yarTC°07otC°0
T64-KA8520448SCI64A85204SCINFQFVdaeL23leeR&epaT0001C°07otC°0
FL64-KA8520448SCIDBTNFQFV"eerF-daeL"daeL23yarTC°07otC°0
TFL64-KA8520448SCIDBTNFQFV"eerF-daeL"daeL23leeR&epaT0001C°07otC°0
.tnailpmocSHoReradnanoitarugifnoceerF-bPehterarebmuntrapehtotxiffus"FL"nahtiwderedroeratahtstraP:ETON
While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Device Technology, Incorporated (IDT) assumes no responsibility for either its use or for
infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would result from its use. No other circuits, patents, or licenses are implied. This product is intended for use in normal commercial and
industrial applications. Any other applications such as those requiring high reliability or other extraordinary environmental requirements are not recommended without additional processing by IDT. IDT
reserves the right to change any circuitry or specifications without notice. IDT does not authorize or warrant any IDT product for use in life support devices or critical medical instruments.
IDT™ / ICS™ LVDS/LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER 15 ICS8440258-46 REV B AUGUST 24, 2006
Page 16

ICS8440258-46
FEMTOCLOCK™ CRYSTAL/LVCMOS-TO-LVDS/ LVCMOS FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PRELIMINARY
Innovate with IDT and accelerate your future networks. Contact:
www.IDT.com
For Sales
800-345-7015
408-284-8200
Fax: 408-284-2775
Corporate Headquarters
Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
6024 Silver Creek Valley Road
San Jose, CA 95138
United States
800 345 7015
+408 284 8200 (outside U.S.)
© 2006 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Product specifications subject to change without notice. IDT, the IDT logo, ICS and HiPerClockS are trademarks
of Integrated Device Technology, Inc. Accelerated Thinking is a service mark of Integrated Device Technology, Inc. All other brands, product names and marks are or may be
trademarks or registered trademarks used to identify products or services of their respective owners.
Printed in USA
For Tech Support
netcom@idt.com
480-763-2056
Asia Pacific and Japan
Integrated Device Technology
Singapore (1997) Pte. Ltd.
Reg. No. 199707558G
435 Orchard Road
#20-03 Wisma Atria
Singapore 238877
+65 6 887 5505
Europe
IDT Europe, Limited
321 Kingston Road
Leatherhead, Surrey
KT22 7TU
England
+44 (0) 1372 363 339
Fax: +44 (0) 1372 378851
Page 17

 Loading...
Loading...