Page 1

®
ICM7555, ICM7556
Data Sheet August 24, 2006
General Purpose Timers
The ICM7555 and ICM7556 are CMOS RC timers providing
significantly improved performance over the standard
SE/NE 555/6 and 355 timers, while at the same time being
direct replacements for those devices in most applications.
Improved parameters include low supply current, wide
operating supply voltage range, low THRESHOLD,
TRIGGER
supply current during output transitions, higher frequency
performance and no requirement to decouple CONTROL
VOLTAGE for stable operation.
Specifically, the ICM7555 and ICM7556 are stable
controllers capable of producing accurate time delays or
frequencies. The ICM7556 is a dual ICM7555, with the two
timers operating independently of each other, sharing only
V+ and GND. In the one shot mode, the pulse width of each
circuit is precisely controlled by one external resistor and
capacitor. For astable operation as an oscillator, the free
running frequency and the duty cycle are both accurately
controlled by two external resistors and one capacitor. Unlike
the regular bipolar SE/NE 555/6 devices, the CONTROL
VOLTAGE terminal ne ed not be decouple d with a cap acitor.
The circuits are triggered and rese t on fa lling (negative)
waveforms, and the output inverter can source or sink
currents large enough to drive TTL loads, or provide minimal
offsets to drive CMOS loads.
and RESET currents, no crowbarring of the
FN2867.9
Features
• Exact Equivalent in Most Cases for SE/NE555/556 or
TLC555/556
• Low Supply Current
- ICM7555. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60μA
- ICM7556. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120μA
• Extremely Low Input Currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20pA
• High Speed Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1MHz
• Guaranteed Supply Voltage Range . . . . . . . . . 2V to 18V
• Temperature Stability . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.005%/°C at +25°C
• Normal Reset Function - No Crowbarring of Supply During
Output Transition
• Can be Used with Higher Impedance Timing Elements
than Regular 555/6 for Longer RC Time Constants
• Timing from Microseconds through Hours
• Operates in Both Astable and Monostable Modes
• Adjustable Duty Cycle
• High Output Source/Sink Driver can Drive TTL/CMOS
• Outputs have Very Low Offsets, HI and LO
• Pb-Free Plus Anneal Available (RoHS Compliant)
Applications
• Precision Timing
• Pulse Generation
• Sequential Timing
Pinouts
ICM7555 (8 LD PDIP, SOIC)
TOP VIEW
1
GND
RESET
2
3
4
TRIGGER
OUTPUT
1
8
V
DD
7
DISCHARGE
6
THRESHOLD
CONTROL
5
VOLTAGE
• Time Delay Generation
• Pulse Width Modulation
• Pulse Position Modulation
• Missing Pulse Detector
ICM7556 (14 LD PDIP, CERDIP)
TOP VIEW
DISCHARGE
THRESH-
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT
TRIGGER
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
Copyright © Intersil Americas Inc. 2002, 2004, 2005, 2006. All Rights Reserved
1
2
OLD
3
RESET
4
5
6
GND
7
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
14
V
DD
DISCHARGE
13
12
THRESHOLD
CONTROL
11
VOLTAGE
RESET
10
OUTPUT
9
TRIGGER
8
Page 2
ICM7555, ICM7556
Ordering Information
TEMP. RANGE
PART NUMBER PART MARKING
ICM7555CBA 7555 CBA 0 to +70 8 Ld SOIC M8.15
ICM7555CBA-T 7555 CBA 0 to +70 8 Ld SOIC Tape and Reel M8.15
ICM7555CBAZ (Note) 7555 CBAZ 0 to +70 8 Ld SOIC (Pb-free) M8.15
ICM7555CBAZ-T (Note) 7555 CBAZ 0 to +70 8 Ld SOIC (Pb-free)
ICM7555IBA 7555 IBA -25 to +85 8 Ld SOIC M8.15
ICM7555IBAT 7555 IBA -25 to +85 8 Ld SOIC Tape and Reel M8.15
ICM7555IBAZ (Note) 7555 IBAZ -25 to +85 8 Ld SOIC (Pb-free) M8.15
ICM7555IBAZ-T (Note) 7555 IBAZ -25 to +85 8 Ld SOIC (Pb-free)
ICM7555IPA 7555 IPA -25 to +85 8 Ld PDIP E8.3
ICM7555IPAZ (Note) 7555 IPAZ -25 to +85 8 Ld PDIP** (Pb-free) E8.3
ICM7556IPD ICM7556IPD -25 to +85 14 Ld PDIP E14.3
ICM7556IPDZ (Note) ICM7556IPDZ -25 to +85 14 Ld PDIP** (Pb-free) E14.3
ICM7556MJD ICM7556MJD -55 to +125 14 Ld Cerdip F14.3
**Pb-free PDIPs can be used for through hole wave solder processing only. They are not intended for use in Reflow solder processing
applications.
(°C) PACKAGE PKG. DWG. #
M8.15
Tape and Reel
M8.15
Tape and Reel
NOTE: Intersil Pb-free products employ special Pb-free material sets; molding compounds/die attach materials and 100% matte tin plate
termination finish, which are RoHS compliant and compatible with both SnPb and Pb-free soldering operations. Intersil Pb-free products are
MSL classified at Pb-free peak reflow te mperatures that meet or exceed the Pb-free re q uire men ts of IPC/JEDEC J STD-020.
2
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 3

ICM7555, ICM7556
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
Supply Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+18V
Input Voltage
Trigger
, Control Voltage, Threshold,
Reset
(Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V+ +0.3V to GND -0.3V
Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100mA
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range
ICM7555C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
ICM7555I, ICM7556I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -25°C to +85°C
ICM7556M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55°C to +125°C
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTES:
1. Due to the SCR structure inherent in the CMOS process used to fabricate these devices, connecting any terminal to a voltage greater than
V+ +0.3V or less than V- -0.3V may cause destructive latchup. For this reason it is recommended that no inputs from external sources not
operating from the same power supply be applied to the device before its power supply is established. In multiple supply systems, the supply
of the ICM7555 and ICM7556 must be turned on first.
2. θ
is measured with the component mounted on a low effective thermal conductivity test board in free air. See Tech Brief 379 for details.
JA
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 2) θ
14 Lead CERDIP Package. . . . . . . . . . 80 24
(°C/W) θJC (°C/W)
JA
14 Lead PDIP Package* . . . . . . . . . . . 115 N/A
8 Lead PDIP Package* . . . . . . . . . . . . 130 N/A
8 Lead SOIC Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170 N/A
Maximum Junction Temperature (Hermetic Package) . . . . . . . +175°C
Maximum Junction Temperature (Plastic Package) . . . . . . .+150°C
Maximum Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . -65°C to +150°C
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s) . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
(SOIC - Lead Tips Only)
* Pb-free PDIPs can be used for through hole wave solder
processing only. They are not intended for use in Reflow solder
processing applications.
Electrical Specifications Applies to ICM7555 and ICM7556, unless otherwise specified
T
A
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS
Static Supply Current I
Monostable Timing Accuracy R
Drift with Temperature
(Note 3)
Drift with Supply (Note 3) V
Astable Timing Accuracy R
Drift with Temperature
(Note 3)
Drift with Supply (Note 3) V
Threshold Voltage V
Trigger Voltage V
Trigger Current I
TRIGVDD
TRIG
Threshold Current I
Control Voltage V
ICM7555 VDD = 5V 40 200 300 μA
DD
V
= 15V 60 300 300 μA
DD
ICM7556 VDD = 5V 80 400 600 μA
V
= 15V 120 600 600 μA
DD
= 10K, C = 0.1μF, VDD = 5V 2 %
A
V
= 5V 150 ppm/°C
DD
V
= 10V 200 ppm/°C
DD
= 15V 250 ppm/°C
V
DD
= 5V to 15V 0.5 0.5 %/V
DD
= RB = 10K, C = 0.1μF, VDD = 5V 2 %
A
V
= 5V 150 ppm/°C
DD
V
= 10V 200 ppm/°C
DD
= 15V 250 ppm/°C
V
DD
= 5V to 15V 0.5 0.5 %/V
DD
VDD = 15V 62677161 72% V
TH
= 15V 28323627 37% V
VDD = 15V 10 50 nA
VDD = 15V 10 50 nA
TH
VDD = 15V 62677161 72% V
CV
= +25°C
(NOTE 4)
-55°C TO +125°C
UNITSMIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
858 1161 μs
1717 2323 μs
DD
DD
DD
3
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 4

ICM7555, ICM7556
Electrical Specifications Applies to ICM7555 and ICM7556, unless otherwise specified (Continued)
= +25°C
T
A
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS
Reset Voltage V
Reset Current I
RST
Discharge Leakage I
Output Voltage V
V
Discharge Output Voltage V
Supply Voltage (Note 3) V
Output Rise Time (Note 3) t
Output Fall Time (Note 3) t
Oscillator Frequency
(Note 3)
f
MAX
NOTES:
3. These parameters are based upon characterization data and are not tested.
4. Applies only to military temperature range product (M suffix).
VDD = 2V to 15V 0.4 1.0 0.2 1.2 V
RST
VDD = 15V 10 50 nA
VDD = 15V 10 50 nA
DIS
VDD = 15V, I
OL
V
= 5V, I
DD
VDD = 15V, I
OH
VDD = 5V, I
VDD = 5V, I
DIS
V
= 15V, I
DD
Functional Operation 2.0 18.0 3.0 16.0 V
DD
RL = 10M, CL = 10pF, VDD = 5V 75 ns
R
RL = 10M, CL = 10pF, VDD = 5V 75 ns
F
VDD = 5V, RA = 470Ω, RB = 270Ω,
= 20mA 0.4 1.0 1.25 V
SINK
= 3.2mA 0.2 0.4 0.5 V
SINK
SOURCE
SOURCE
SINK
SINK
= 0.8mA 14.3 14.6 14.2 V
= 0.8mA 4.0 4.3 3.8 V
= 15mA 0.2 0.4 0.6 V
= 15mA 0.4 V
1MHz
C = 200pF
(NOTE 4)
-55°C TO +125°C
UNITSMIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
Functional Diagram
V
DD
8
R
COMPARATOR
THRESHOLD
6
5
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
TRIGGER
2
R
R
GND
A
+
-
+
-
COMPARATOR
B
1
NOTE: This functional diagram reduces the circuitry down to its simplest equivalent components. Tie down unused inputs.
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE TRIGGER
VOLTAGE RESET OUTPUT DISCHARGE SWITCH
Don’t Care Don’t Care Low Low On
2
>
/3(V+) >1/3(V+) High Low On
2
<
/3(V+) >1/3(V+) High Stable Stable
Don’t Care <
1
/3(V+) High High Off
FLIP-FLOP
4
RESET
TRUTH TABLE
OUTPUT
DRIVERS
3
7
DISCHARGE
n
1
OUTPUT
NOTE: RESET
will dominate all other inputs: TRIGGER will dominate over THRESHOLD.
4
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 5

Schematic Diagram
ICM7555, ICM7556
PP P
R
V
P
DD
THRESHOLD
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
TRIGGER
R = 100kΩ ±20% (TYP)
NN
R
PP
R
Application Information
General
The ICM7555 and ICM7556 devices are, in most instances,
direct replacements for the NE/SE 555/6 devices. However,
it is possible to effect economies in the external component
count using the ICM7555 and ICM7556. Because the bipolar
NE/SE 555/6 devices produce large crowbar currents in the
output driver, it is necessary to decouple the power supply
lines with a good capacitor close to the device. The ICM7555
and ICM7556 devices produce no such transients. See
Figure 1.
500
400
300
200
100
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
FIGURE 1. SUPPLY CURRENT TRANSIENT COMPARED WITH
TA = 25°C
SE/NE555
0
ICM7555/56
400 8006002000
TIME (ns)
A STANDARD BIPOLAR 555 DURING AN OUTPUT
TRANSITION
NPN
NNNNN
RESET DISCHARGE
NN
The ICM7555 and ICM7556 produce supply current spikes
of only 2mA - 3mA instead of 300mA - 400mA and supply
decoupling is normally not necessary. Also, in most
instances, the CONTROL VOLTAGE decoupling capacitors
are not required since the input impedance of the CMOS
comparators on chip are very high. Thus, for many
applications, two capacitors can be saved using an ICM7555
and three capacitors with an ICM7556.
POWER SUPPLY CONSIDERATIONS
Although the supply current consumed by the ICM7555 and
ICM7556 devices is very low, the total system supply current
can be high unless the timing components are high
impedance. Therefore, use high values for R and low values
for C in Figures 2A, 2B, and 3.
GND
TRIGGER
OUTPUT
R
1
2
3
V
DD
4
RESET
FIGURE 2A. ASTABLE OPERATION
V
DD
8
DISCHARGE
7
THRESHOLD
6
5
C
OUTPUT
GND
V
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
OPTIONAL
CAPACITOR
DD
10K
ALTERNATE OUTPUT
5
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 6

ICM7555, ICM7556
V
DD
R
A
1
2
OUTPUT
V
DD
FIGURE 2B. ALTERNATE ASTABLE CONFIGURATION
3
4
C
8
7
6
R
5
B
OPTIONAL
CAPACITOR
OUTPUT DRIVE CAPABILITY
The output driver consists of a CMOS inverter capable of
driving most logic families including CMOS and TTL. As
such, if driving CMOS, the output swing at all supply
voltages will equal the supply voltage. At a supply voltage of
4.5V or more, the ICM7555 and ICM7556 will drive at least
two standard TTL loads.
ASTABLE OPERATION
The circuit can be connected to trigger itself and free run as
a multivibrator, see Figure 2A. The output swings from rail to
rail, and is a true 50% duty cycle square wave. (Trip points
and output swings are symmetrical.) Less than a 1%
frequency variation is observed over a voltage range of +5V
to +15V.
1
------------------
f
=
1.4 RC
(EQ. 1)
The timer can also be connected as shown in Figure 2B. In this
circuit, the frequency is:
f1.44RA2RB+()⁄ C=
The duty cycle is controlled by the values of R
and RB, by the
A
(EQ. 2)
equation:
DRARB+()RA2RB+()⁄=
(EQ. 3)
= -ln
(1/3) R
1
2
3
4
C = 1.1RAC
A
ICM7555
OPTIONAL
CAPACITOR
V
DD
8
DISCHARGE
7
THRESHOLD
6
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
5
R
A
C
t
OUTPUT
TRIGGER
OUTPUT
RESET
≤18V
V
DD
FIGURE 3. MONOSTABLE OPERATION
CONTROL VOLT AGE
The CONTROL VOLTAGE terminal permits the two trip
voltages for the THRESHOLD and TRIGGER
internal
comparators to be controlled. This provides the possibility of
oscillation frequency modulation in the astable mode or even
inhibition of oscillation, depending on the applied voltage. In
the monostable mode, delay times can be changed by
varying the applied voltage to the CONTROL VOLTAGE pin.
RESET
The RESET terminal is designed to have essentially the
same trip voltage as the standard bipolar 555/6, i.e., 0.6V to
0.7V. At all supply voltages it represents an extremely high
input impedance. The mode of operation of the RESET
function is, however, much improved over the standard
bipolar NE/SE 555/6 in that it controls only the internal flipflop, which in turn controls simultaneously the state of the
OUTPUT and DISCHARGE pins. This avoids the multiple
threshold problems sometimes encountered with slow falling
edges in the bipolar devices.
MONOSTABLE OPERATION
In this mode of operation, the timer functions as a one-shot.
See Figure 3. Initially the external capacitor (C) is held
discharged by a transistor inside the timer. Upon application of
a negative TRIGGER
pulse to pin 2, the internal flip-flop is set
which releases the short circuit across the external capacitor
and drives the OUTPUT high. The voltage across the capacitor
now increases exponentially with a time constant t = R
When the voltage across the capacitor equals
2
/3 V+, the
C.
A
comparator resets the flip-flop, which in turn discharges the
capacitor rapidly and also drives the OUTPUT to its low state.
TRIGGER
must return to a high state before the OUTPUT can
return to a low state.
6
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 7
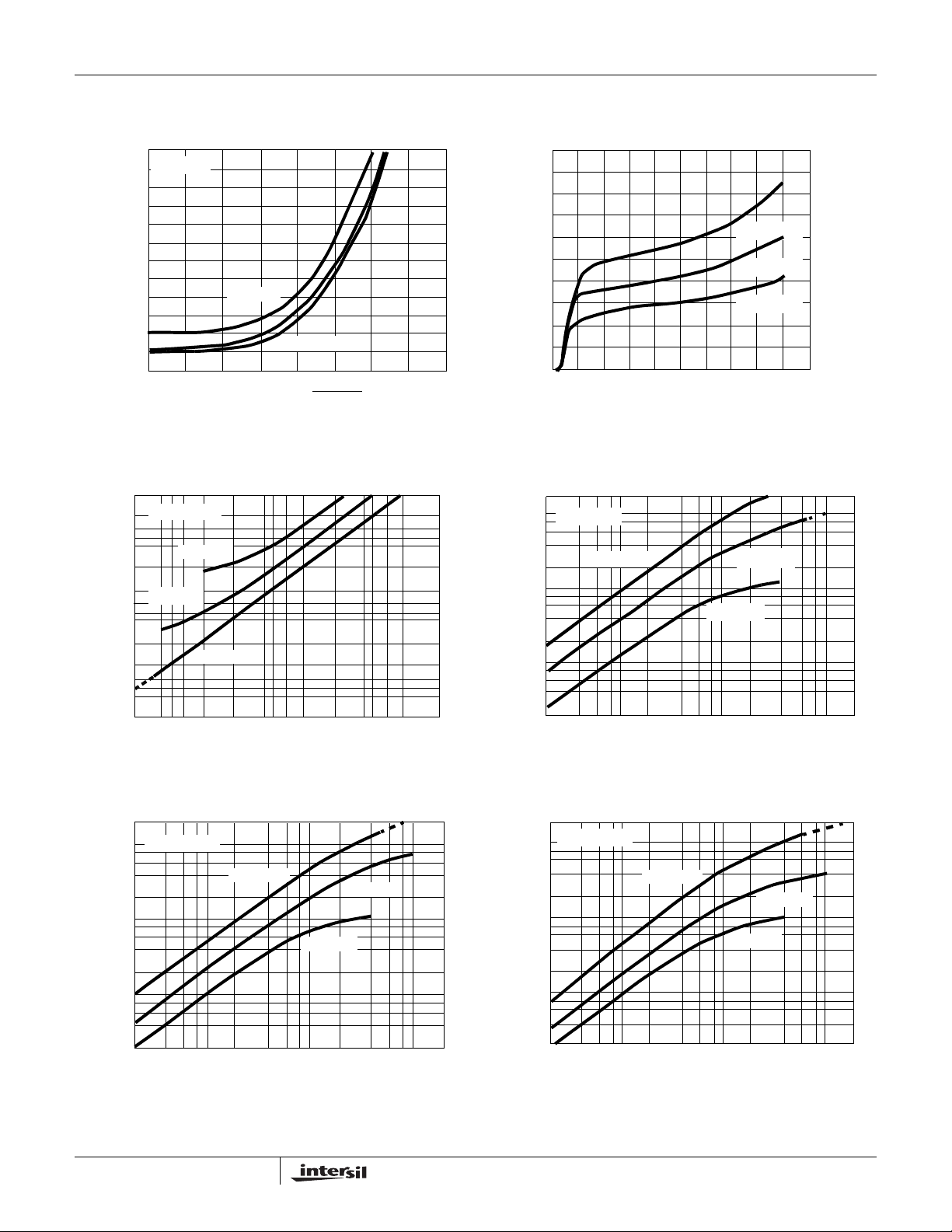
Typical Performance Curves
ICM7555, ICM7556
1200
TA = 25°C
1100
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
MINIMUM PULSE WIDTH (ns)
200
VDD = 5V
100
0
010203040
LOWEST VOLTAGE LEVEL OF TRIGGER
VDD = 2V
VDD = 18V
PULSE (%VDD)
FIGURE 4. MINIMUM PULSE WIDTH REQUIRED FOR
TRIGGERING
-0.1
TA = 25°C
-1.0
VDD = 2V
VDD = 5V
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
SUPPLY CURRENT (ICM7555) (μA)
20
0
0 2 4 6 8 10121416 18 20
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
TA = -20°C
TA = 25°C
TA = 70°C
FIGURE 5. SUPPLY CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
100
TA = -20°C
10.0
VDD = 18V
VDD = 5V
VDD = 2V
400
360
320
280
240
200
160
120
80
40
0
SUPPLY CURRENT (ICM7556) (μA)
1.0
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT (mA)
0.1
0.01 0.1 1.0 10.0
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE (V)
OUTPUT SOURCE CURRENT (mA)
-10.0
-100
VDD = 18V
OUTPUT VOLTAGE REFERENCED TO V
DD
-0.01-0.1-1.0-10
(V)
FIGURE 6. OUTPUT SOURCE CURRENT vs OUTPUT VOLTAGE FIGURE 7. OUTPUT SINK CURRENT vs OUTPUT VOLTAGE
100
TA = 25°C
VDD = 18V
10.0
1.0
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT (mA)
0.1
0.01 0.1 1.0 10.0
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE (V)
VDD = 5V
VDD = 2V
100
TA = 70°C
VDD = 18V
10.0
1.0
OUTPUT SINK CURRENT (mA)
0.1
0.01 0.1 1.0 10.0
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE (V)
VDD = 5V
VDD = 2V
FIGURE 8. OUTPUT SINK CURRENT vs OUTPUT VOLTAGE FIGURE 9. OUTPUT SINK CURRENT vs OUTPUT VOLTAGE
7
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 8

Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
8
TA = 25°C
6
4
2
0
RA = RB = 10MΩ
C = 100pF
ICM7555, ICM7556
100
10.0
TA = 25°C
VDD = 18V
VDD = 5V
VDD = 2V
2
4
6
NORMALIZED FREQUENCY DEVIATION (%)
8
0.1 1.0 10.0 100.0
RA = RB = 10kΩ
C = 0.1μF
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
FIGURE 10. NORMALIZED FREQUENCY STABILITY IN THE
ASTABLE MODE vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
600
VDD = 5V
500
400
300
200
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
100
0
TA = 70°C
TA = 25°C
TA = -20°C
010203040
LOWEST VOLTAGE LEVEL OF TRIGGER
PULSE (%VDD)
FIGURE 12. PROPAGATION DELAY vs VOLTAGE LEVEL OF
TRIGGER PULSE
1.0
DISCHARGE SINK CURRENT (mA)
0.1
0.01 0.1 1.0 10.0
DISCHARGE LOW VOLTAGE (V)
FIGURE 11. DISCHARGE OUTPUT CURRENT vs DISCHARGE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
+1.0
+0.9
+0.8
+0.7
+0.6
+0.5
+0.4
+0.3
+0.2
+0.1
NORMALIZED FREQUENCY DEVIATION (%)
-0.1
RA = RB = 10kΩ
C = 0.1μF
VDD = 2V
0
VDD = 5V
VDD = 18V
VDD = 2V
06080
TEMPERATURE (°C)
4020-20
FIGURE 13. NORMALIZED FREQUENCY STABILITY IN THE
ASTABLE MODE vs TEM PER ATURE
1.0
TA = 25°C
(RA + 2RB)
100.1 1 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
CAPACITANCE (F)
100m
10m
1m
100μ
10μ
1μ
100n
10n
1n
100p
10p
1p
FIGURE 14. FREE RUNNING FREQUENCY vs R
8
1kΩ
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
, RB AND C
A
1.0
1m
1μ
1n
1p
TA = 25°C
1kΩ
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
10μ100n 1μ 100μ 1m 10m 100m 1 10
TIME DELAY (s)
R
A
CAPACITANCE (F)
100m
10m
100μ
10μ
100n
10n
100p
10p
FIGURE 15. TIME DELAY IN THE MONOSTABLE MODE vs
AND C
R
A
August 24, 2006
FN2867.9
Page 9
ICM7555, ICM7556
Small Outline Plastic Packages (SOIC)
N
INDEX
AREA
123
-A-
E
-B-
SEATING PLANE
D
A
-C-
0.25(0.010) BM M
H
L
h x 45°
α
e
B
0.25(0.010) C AM BS
M
NOTES:
1. Symbols are defined in the “MO Series Symbol List” in Section 2.2 of
Publication Number 95.
2. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
3. Dimension “D” does not include mold flash, protrusions or gate burrs.
Mold flash, protrusion and gate burrs shall not exceed 0.15mm (0.006
inch) per side.
4. Dimension “E” does not include interlead flash or protrusions. Interlead flash and protrusions shall not exceed 0.25mm (0.010 inch) per
side.
5. The chamfer on the body is optional. If it is not present, a visual index
feature must be located within the crosshatched area.
6. “L” is the length of terminal for soldering to a substrate.
7. “N” is the number of terminal positions.
8. Terminal numbers are shown for reference only.
9. The lead width “B”, as measured 0.36mm (0.014 inch) or greater
above the seating plane, shall not exceed a maximum value of
0.61mm (0.024 inch).
10. Controlling dimension: MILLIMETER. Converted inch dimensions
are not necessarily exact.
A1
C
0.10(0.004)
M8.15 (JEDEC MS-012-AA ISSUE C)
8 LEAD NARROW BODY SMALL OUTLINE PLASTIC PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A 0.0532 0.0688 1.35 1.75 -
A1 0.0040 0.0098 0.10 0.25 -
B 0.013 0.020 0.33 0.51 9
C 0.0075 0.0098 0.19 0.25 -
D 0.1890 0.1968 4.80 5.00 3
E 0.1497 0.1574 3.80 4.00 4
e 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC -
H 0.2284 0.2440 5.80 6.20 -
h 0.0099 0.0196 0.25 0.50 5
L 0.016 0.050 0.40 1.27 6
N8 87
α
0° 8° 0° 8° -
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 1 6/05
9
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 10

Dual-In-Line Plastic Packages (PDIP)
ICM7555, ICM7556
N
D1
-C-
E1
-B-
A2
A
L
A
1
e
C
e
e
INDEX
AREA
BASE
PLANE
SEATING
PLANE
D1
B1
12 3 N/2
-AD
e
B
0.010 (0.25) C AM BS
NOTES:
1. Controlling Dimensions: INCH. In case of conflict between
English and Metric dimensions, the inch dimensions control.
2. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
3. Symbols are defined in the “MO Series Symbol List” in Section
2.2 of Publication No. 95.
4. Dimensions A, A1 and L are measured with the package seated
in JEDEC seating plane gauge GS-3.
5. D, D1, and E1 dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.010 inch
(0.25mm).
6. E and are measured with the leads constrained to be per-
7. e
e
pendicular to datum .
A
and eC are measured at the lead tips with the leads uncon-
B
strained. e
must be zero or greater.
C
-C-
8. B1 maximum dimensions do not include dambar protrusions.
Dambar protrusions shall not exceed 0.010 inch (0.25mm).
9. N is the maximum number of terminal positions.
10. Corner leads (1, N, N/2 and N/2 + 1) for E8.3, E16.3, E18.3,
E28.3, E42.6 will have a B1 dimension of 0.030 - 0.045 inch
(0.76 - 1.14mm).
E8.3 (JEDEC MS-001-BA ISSUE D)
8 LEAD DUAL-IN-LINE PLASTIC PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A-0.210 - 5.33 4
E
A1 0.015 - 0.39 -4
A2 0.115 0.195 2.93 4.95 -
B 0.014 0.022 0.356 0.558 -
C
L
A
C
B
B1 0.045 0.070 1.15 1.77 8, 10
C 0.008 0.014 0.204 0.355 D 0.355 0.400 9.01 10.16 5
D1 0.005 - 0.13 -5
E 0.300 0.325 7.62 8.25 6
E1 0.240 0.280 6.10 7.11 5
e 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC -
e
A
e
B
0.300 BSC 7.62 BSC 6
- 0.430 - 10.92 7
L 0.115 0.150 2.93 3.81 4
N8 89
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 0 12/93
10
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 11

Dual-In-Line Plastic Packages (PDIP)
ICM7555, ICM7556
N
D1
-C-
E1
-B-
A1
A2
E
A
L
e
C
C
L
e
A
C
e
B
INDEX
AREA
BASE
PLANE
SEATING
PLANE
D1
B1
12 3 N/2
-AD
e
B
0.010 (0.25) C AM BS
NOTES:
1. Controlling Dimensions: INCH. In case of conflict between English
and Metric dimensions, the inch dimensions control.
2. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
3. Symbols are defined in the “MO Series Symbol List” in Section 2.2 of
Publication No. 95.
4. Dimensions A, A1 and L are measured with the package seated in
JEDEC seating plane gauge GS-3.
5. D, D1, and E1 dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusions.
Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.010 inch (0.25mm).
6. E and are measured with the leads constrained to be perpen-
7. e
e
dicular to datum .
A
and eC are measured at the lead tips with the leads uncon-
B
strained. e
-C-
must be zero or greater.
C
8. B1 maximum dimensions do not include dambar protrusions. Dambar
protrusions shall not exceed 0.010 inch (0.25mm).
9. N is the maximum number of terminal positions.
10. Corner leads (1, N, N/2 and N/2 + 1) for E8.3, E16.3, E18.3, E28.3,
E42.6 will have a B1 dimension of 0.030 - 0.045 inch (0.76 -
1.14mm).
E14.3 (JEDEC MS-001-AA ISSUE D)
14 LEAD DUAL-IN-LINE PLASTIC PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A-0.210 - 5.33 4
A1 0.015 - 0.39 -4
A2 0.115 0.195 2.93 4.95 -
B 0.014 0.022 0.356 0.558 B1 0.045 0.070 1.15 1.77 8
C 0.008 0.014 0.204 0.355 -
D 0.735 0.775 18.66 19.68 5
D1 0.005 - 0.13 -5
E 0.300 0.325 7.62 8.25 6
E1 0.240 0.280 6.10 7.11 5
e 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC -
e
A
e
B
0.300 BSC 7.62 BSC 6
- 0.430 - 10.92 7
L 0.115 0.150 2.93 3.81 4
N14 149
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 0 12/93
11
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
Page 12
ICM7555, ICM7556
Ceramic Dual-In-Line Frit Seal Packages (CERDIP)
LEAD FINISH
c1
-A-
-B-
bbb C A - B
S
BASE
PLANE
SEATING
PLANE
S1
b2
b
ccc C A - BMD
D
A
A
e
S
S
NOTES:
1. Index area: A notch or a pin one identification mark shall be located adjacent to pin one and shall be located within the shaded
area shown. The manufacturer’s identification shall not be used
as a pin one identification mark.
2. The maximum limits of lead dimensions b and c or M shall be
measured at the centroid of the finished lead surfaces, when
solder dip or tin plate lead finish is applied.
3. Dimensions b1 and c1 apply to lead base metal only. Dimension
M applies to lead plating and finish thickness.
4. Corner leads (1, N, N/2, and N/2+1) may be configured with a
partial lead paddle. For this configuration dimension b3 replaces
dimension b2.
5. This dimension allows for off-center lid, meniscus, and glass
overrun.
6. Dimension Q shall be measured from the seating plane to the
base plane.
7. Measure dimension S1 at all four corners.
8. N is the maximum number of terminal positions.
9. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M - 1982.
10. Controlling dimension: INCH.
-DBASE
E
D
S
S
Q
A
-CL
METAL
b1
M
(b)
SECTION A-A
α
(c)
M
eA
eA/2
aaa CA - B
M
c
D
S
S
F14.3 MIL-STD-1835 GDIP1-T14 (D-1, CONFIGURATION A)
14 LEAD CERAMIC DUAL-IN-LINE FRIT SEAL PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A-0.200 - 5.08 -
b 0.014 0.026 0.36 0.66 2
b1 0.014 0.023 0.36 0.58 3
b2 0.045 0.065 1.14 1.65 b3 0.023 0.045 0.58 1.14 4
c 0.008 0.018 0.20 0.46 2
c1 0.008 0.015 0.20 0.38 3
D-0.785 - 19.94 5
E 0.220 0.310 5.59 7.87 5
e 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC eA 0.300 BSC 7.62 BSC -
eA/2 0.150 BSC 3.81 BSC -
L 0.125 0.200 3.18 5.08 -
Q 0.015 0.060 0.38 1.52 6
S1 0.005 - 0.13 -7
α
90° 105° 90° 105° aaa - 0.015 - 0.38 bbb - 0.030 - 0.76 ccc - 0.010 - 0.25 -
M-0.0015 - 0.038 2, 3
N14 148
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 0 4/94
All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems.
Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality
Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design, software and/or specifications at any time without
notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implicat ion or oth erwise u nde r any p a tent or p at ent r ights of Intersil or its subsidiari es.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see www.intersil.com
12
FN2867.9
August 24, 2006
 Loading...
Loading...